
Python's Assignment Operator: Write Robust Assignments
Table of Contents
The Assignment Statement Syntax
The assignment operator, assignments and variables, other assignment syntax, initializing and updating variables, making multiple variables refer to the same object, updating lists through indices and slices, adding and updating dictionary keys, doing parallel assignments, unpacking iterables, providing default argument values, augmented mathematical assignment operators, augmented assignments for concatenation and repetition, augmented bitwise assignment operators, annotated assignment statements, assignment expressions with the walrus operator, managed attribute assignments, define or call a function, work with classes, import modules and objects, use a decorator, access the control variable in a for loop or a comprehension, use the as keyword, access the _ special variable in an interactive session, built-in objects, named constants.
Python’s assignment operators allow you to define assignment statements . This type of statement lets you create, initialize, and update variables throughout your code. Variables are a fundamental cornerstone in every piece of code, and assignment statements give you complete control over variable creation and mutation.
Learning about the Python assignment operator and its use for writing assignment statements will arm you with powerful tools for writing better and more robust Python code.
In this tutorial, you’ll:
- Use Python’s assignment operator to write assignment statements
- Take advantage of augmented assignments in Python
- Explore assignment variants, like assignment expressions and managed attributes
- Become aware of illegal and dangerous assignments in Python
You’ll dive deep into Python’s assignment statements. To get the most out of this tutorial, you should be comfortable with several basic topics, including variables , built-in data types , comprehensions , functions , and Python keywords . Before diving into some of the later sections, you should also be familiar with intermediate topics, such as object-oriented programming , constants , imports , type hints , properties , descriptors , and decorators .
Free Source Code: Click here to download the free assignment operator source code that you’ll use to write assignment statements that allow you to create, initialize, and update variables in your code.
Assignment Statements and the Assignment Operator
One of the most powerful programming language features is the ability to create, access, and mutate variables . In Python, a variable is a name that refers to a concrete value or object, allowing you to reuse that value or object throughout your code.
To create a new variable or to update the value of an existing one in Python, you’ll use an assignment statement . This statement has the following three components:
- A left operand, which must be a variable
- The assignment operator ( = )
- A right operand, which can be a concrete value , an object , or an expression
Here’s how an assignment statement will generally look in Python:
Here, variable represents a generic Python variable, while expression represents any Python object that you can provide as a concrete value—also known as a literal —or an expression that evaluates to a value.
To execute an assignment statement like the above, Python runs the following steps:
- Evaluate the right-hand expression to produce a concrete value or object . This value will live at a specific memory address in your computer.
- Store the object’s memory address in the left-hand variable . This step creates a new variable if the current one doesn’t already exist or updates the value of an existing variable.
The second step shows that variables work differently in Python than in other programming languages. In Python, variables aren’t containers for objects. Python variables point to a value or object through its memory address. They store memory addresses rather than objects.
This behavior difference directly impacts how data moves around in Python, which is always by reference . In most cases, this difference is irrelevant in your day-to-day coding, but it’s still good to know.
The central component of an assignment statement is the assignment operator . This operator is represented by the = symbol, which separates two operands:
- A value or an expression that evaluates to a concrete value
Operators are special symbols that perform mathematical , logical , and bitwise operations in a programming language. The objects (or object) on which an operator operates are called operands .
Unary operators, like the not Boolean operator, operate on a single object or operand, while binary operators act on two. That means the assignment operator is a binary operator.
Note: Like C , Python uses == for equality comparisons and = for assignments. Unlike C, Python doesn’t allow you to accidentally use the assignment operator ( = ) in an equality comparison.
Equality is a symmetrical relationship, and assignment is not. For example, the expression a == 42 is equivalent to 42 == a . In contrast, the statement a = 42 is correct and legal, while 42 = a isn’t allowed. You’ll learn more about illegal assignments later on.
The right-hand operand in an assignment statement can be any Python object, such as a number , list , string , dictionary , or even a user-defined object. It can also be an expression. In the end, expressions always evaluate to concrete objects, which is their return value.
Here are a few examples of assignments in Python:
The first two sample assignments in this code snippet use concrete values, also known as literals , to create and initialize number and greeting . The third example assigns the result of a math expression to the total variable, while the last example uses a Boolean expression.
Note: You can use the built-in id() function to inspect the memory address stored in a given variable.
Here’s a short example of how this function works:
The number in your output represents the memory address stored in number . Through this address, Python can access the content of number , which is the integer 42 in this example.
If you run this code on your computer, then you’ll get a different memory address because this value varies from execution to execution and computer to computer.
Unlike expressions, assignment statements don’t have a return value because their purpose is to make the association between the variable and its value. That’s why the Python interpreter doesn’t issue any output in the above examples.
Now that you know the basics of how to write an assignment statement, it’s time to tackle why you would want to use one.
The assignment statement is the explicit way for you to associate a name with an object in Python. You can use this statement for two main purposes:
- Creating and initializing new variables
- Updating the values of existing variables
When you use a variable name as the left operand in an assignment statement for the first time, you’re creating a new variable. At the same time, you’re initializing the variable to point to the value of the right operand.
On the other hand, when you use an existing variable in a new assignment, you’re updating or mutating the variable’s value. Strictly speaking, every new assignment will make the variable refer to a new value and stop referring to the old one. Python will garbage-collect all the values that are no longer referenced by any existing variable.
Assignment statements not only assign a value to a variable but also determine the data type of the variable at hand. This additional behavior is another important detail to consider in this kind of statement.
Because Python is a dynamically typed language, successive assignments to a given variable can change the variable’s data type. Changing the data type of a variable during a program’s execution is considered bad practice and highly discouraged. It can lead to subtle bugs that can be difficult to track down.
Unlike in math equations, in Python assignments, the left operand must be a variable rather than an expression or a value. For example, the following construct is illegal, and Python flags it as invalid syntax:
In this example, you have expressions on both sides of the = sign, and this isn’t allowed in Python code. The error message suggests that you may be confusing the equality operator with the assignment one, but that’s not the case. You’re really running an invalid assignment.
To correct this construct and convert it into a valid assignment, you’ll have to do something like the following:
In this code snippet, you first import the sqrt() function from the math module. Then you isolate the hypotenuse variable in the original equation by using the sqrt() function. Now your code works correctly.
Now you know what kind of syntax is invalid. But don’t get the idea that assignment statements are rigid and inflexible. In fact, they offer lots of room for customization, as you’ll learn next.
Python’s assignment statements are pretty flexible and versatile. You can write them in several ways, depending on your specific needs and preferences. Here’s a quick summary of the main ways to write assignments in Python:
Up to this point, you’ve mostly learned about the base assignment syntax in the above code snippet. In the following sections, you’ll learn about multiple, parallel, and augmented assignments. You’ll also learn about assignments with iterable unpacking.
Read on to see the assignment statements in action!
Assignment Statements in Action
You’ll find and use assignment statements everywhere in your Python code. They’re a fundamental part of the language, providing an explicit way to create, initialize, and mutate variables.
You can use assignment statements with plain names, like number or counter . You can also use assignments in more complicated scenarios, such as with:
- Qualified attribute names , like user.name
- Indices and slices of mutable sequences, like a_list[i] and a_list[i:j]
- Dictionary keys , like a_dict[key]
This list isn’t exhaustive. However, it gives you some idea of how flexible these statements are. You can even assign multiple values to an equal number of variables in a single line, commonly known as parallel assignment . Additionally, you can simultaneously assign the values in an iterable to a comma-separated group of variables in what’s known as an iterable unpacking operation.
In the following sections, you’ll dive deeper into all these topics and a few other exciting things that you can do with assignment statements in Python.
The most elementary use case of an assignment statement is to create a new variable and initialize it using a particular value or expression:
All these statements create new variables, assigning them initial values or expressions. For an initial value, you should always use the most sensible and least surprising value that you can think of. For example, initializing a counter to something different from 0 may be confusing and unexpected because counters almost always start having counted no objects.
Updating a variable’s current value or state is another common use case of assignment statements. In Python, assigning a new value to an existing variable doesn’t modify the variable’s current value. Instead, it causes the variable to refer to a different value. The previous value will be garbage-collected if no other variable refers to it.
Consider the following examples:
These examples run two consecutive assignments on the same variable. The first one assigns the string "Hello, World!" to a new variable named greeting .
The second assignment updates the value of greeting by reassigning it the "Hi, Pythonistas!" string. In this example, the original value of greeting —the "Hello, World!" string— is lost and garbage-collected. From this point on, you can’t access the old "Hello, World!" string.
Even though running multiple assignments on the same variable during a program’s execution is common practice, you should use this feature with caution. Changing the value of a variable can make your code difficult to read, understand, and debug. To comprehend the code fully, you’ll have to remember all the places where the variable was changed and the sequential order of those changes.
Because assignments also define the data type of their target variables, it’s also possible for your code to accidentally change the type of a given variable at runtime. A change like this can lead to breaking errors, like AttributeError exceptions. Remember that strings don’t have the same methods and attributes as lists or dictionaries, for example.
In Python, you can make several variables reference the same object in a multiple-assignment line. This can be useful when you want to initialize several similar variables using the same initial value:
In this example, you chain two assignment operators in a single line. This way, your two variables refer to the same initial value of 0 . Note how both variables hold the same memory address, so they point to the same instance of 0 .
When it comes to integer variables, Python exhibits a curious behavior. It provides a numeric interval where multiple assignments behave the same as independent assignments. Consider the following examples:
To create n and m , you use independent assignments. Therefore, they should point to different instances of the number 42 . However, both variables hold the same object, which you confirm by comparing their corresponding memory addresses.
Now check what happens when you use a greater initial value:
Now n and m hold different memory addresses, which means they point to different instances of the integer number 300 . In contrast, when you use multiple assignments, both variables refer to the same object. This tiny difference can save you small bits of memory if you frequently initialize integer variables in your code.
The implicit behavior of making independent assignments point to the same integer number is actually an optimization called interning . It consists of globally caching the most commonly used integer values in day-to-day programming.
Under the hood, Python defines a numeric interval in which interning takes place. That’s the interning interval for integer numbers. You can determine this interval using a small script like the following:
This script helps you determine the interning interval by comparing integer numbers from -10 to 500 . If you run the script from your command line, then you’ll get an output like the following:
This output means that if you use a single number between -5 and 256 to initialize several variables in independent statements, then all these variables will point to the same object, which will help you save small bits of memory in your code.
In contrast, if you use a number that falls outside of the interning interval, then your variables will point to different objects instead. Each of these objects will occupy a different memory spot.
You can use the assignment operator to mutate the value stored at a given index in a Python list. The operator also works with list slices . The syntax to write these types of assignment statements is the following:
In the first construct, expression can return any Python object, including another list. In the second construct, expression must return a series of values as a list, tuple, or any other sequence. You’ll get a TypeError if expression returns a single value.
Note: When creating slice objects, you can use up to three arguments. These arguments are start , stop , and step . They define the number that starts the slice, the number at which the slicing must stop retrieving values, and the step between values.
Here’s an example of updating an individual value in a list:
In this example, you update the value at index 2 using an assignment statement. The original number at that index was 7 , and after the assignment, the number is 3 .
Note: Using indices and the assignment operator to update a value in a tuple or a character in a string isn’t possible because tuples and strings are immutable data types in Python.
Their immutability means that you can’t change their items in place :
You can’t use the assignment operator to change individual items in tuples or strings. These data types are immutable and don’t support item assignments.
It’s important to note that you can’t add new values to a list by using indices that don’t exist in the target list:
In this example, you try to add a new value to the end of numbers by using an index that doesn’t exist. This assignment isn’t allowed because there’s no way to guarantee that new indices will be consecutive. If you ever want to add a single value to the end of a list, then use the .append() method.
If you want to update several consecutive values in a list, then you can use slicing and an assignment statement:
In the first example, you update the letters between indices 1 and 3 without including the letter at 3 . The second example updates the letters from index 3 until the end of the list. Note that this slicing appends a new value to the list because the target slice is shorter than the assigned values.
Also note that the new values were provided through a tuple, which means that this type of assignment allows you to use other types of sequences to update your target list.
The third example updates a single value using a slice where both indices are equal. In this example, the assignment inserts a new item into your target list.
In the final example, you use a step of 2 to replace alternating letters with their lowercase counterparts. This slicing starts at index 1 and runs through the whole list, stepping by two items each time.
Updating the value of an existing key or adding new key-value pairs to a dictionary is another common use case of assignment statements. To do these operations, you can use the following syntax:
The first construct helps you update the current value of an existing key, while the second construct allows you to add a new key-value pair to the dictionary.
For example, to update an existing key, you can do something like this:
In this example, you update the current inventory of oranges in your store using an assignment. The left operand is the existing dictionary key, and the right operand is the desired new value.
While you can’t add new values to a list by assignment, dictionaries do allow you to add new key-value pairs using the assignment operator. In the example below, you add a lemon key to inventory :
In this example, you successfully add a new key-value pair to your inventory with 100 units. This addition is possible because dictionaries don’t have consecutive indices but unique keys, which are safe to add by assignment.
The assignment statement does more than assign the result of a single expression to a single variable. It can also cope nicely with assigning multiple values to multiple variables simultaneously in what’s known as a parallel assignment .
Here’s the general syntax for parallel assignments in Python:
Note that the left side of the statement can be either a tuple or a list of variables. Remember that to create a tuple, you just need a series of comma-separated elements. In this case, these elements must be variables.
The right side of the statement must be a sequence or iterable of values or expressions. In any case, the number of elements in the right operand must match the number of variables on the left. Otherwise, you’ll get a ValueError exception.
In the following example, you compute the two solutions of a quadratic equation using a parallel assignment:
In this example, you first import sqrt() from the math module. Then you initialize the equation’s coefficients in a parallel assignment.
The equation’s solution is computed in another parallel assignment. The left operand contains a tuple of two variables, x1 and x2 . The right operand consists of a tuple of expressions that compute the solutions for the equation. Note how each result is assigned to each variable by position.
A classical use case of parallel assignment is to swap values between variables:
The highlighted line does the magic and swaps the values of previous_value and next_value at the same time. Note that in a programming language that doesn’t support this kind of assignment, you’d have to use a temporary variable to produce the same effect:
In this example, instead of using parallel assignment to swap values between variables, you use a new variable to temporarily store the value of previous_value to avoid losing its reference.
For a concrete example of when you’d need to swap values between variables, say you’re learning how to implement the bubble sort algorithm , and you come up with the following function:
In the highlighted line, you use a parallel assignment to swap values in place if the current value is less than the next value in the input list. To dive deeper into the bubble sort algorithm and into sorting algorithms in general, check out Sorting Algorithms in Python .
You can use assignment statements for iterable unpacking in Python. Unpacking an iterable means assigning its values to a series of variables one by one. The iterable must be the right operand in the assignment, while the variables must be the left operand.
Like in parallel assignments, the variables must come as a tuple or list. The number of variables must match the number of values in the iterable. Alternatively, you can use the unpacking operator ( * ) to grab several values in a variable if the number of variables doesn’t match the iterable length.
Here’s the general syntax for iterable unpacking in Python:
Iterable unpacking is a powerful feature that you can use all around your code. It can help you write more readable and concise code. For example, you may find yourself doing something like this:
Whenever you do something like this in your code, go ahead and replace it with a more readable iterable unpacking using a single and elegant assignment, like in the following code snippet:
The numbers list on the right side contains four values. The assignment operator unpacks these values into the four variables on the left side of the statement. The values in numbers get assigned to variables in the same order that they appear in the iterable. The assignment is done by position.
Note: Because Python sets are also iterables, you can use them in an iterable unpacking operation. However, it won’t be clear which value goes to which variable because sets are unordered data structures.
The above example shows the most common form of iterable unpacking in Python. The main condition for the example to work is that the number of variables matches the number of values in the iterable.
What if you don’t know the iterable length upfront? Will the unpacking work? It’ll work if you use the * operator to pack several values into one of your target variables.
For example, say that you want to unpack the first and second values in numbers into two different variables. Additionally, you would like to pack the rest of the values in a single variable conveniently called rest . In this case, you can use the unpacking operator like in the following code:
In this example, first and second hold the first and second values in numbers , respectively. These values are assigned by position. The * operator packs all the remaining values in the input iterable into rest .
The unpacking operator ( * ) can appear at any position in your series of target variables. However, you can only use one instance of the operator:
The iterable unpacking operator works in any position in your list of variables. Note that you can only use one unpacking operator per assignment. Using more than one unpacking operator isn’t allowed and raises a SyntaxError .
Dropping away unwanted values from the iterable is a common use case for the iterable unpacking operator. Consider the following example:
In Python, if you want to signal that a variable won’t be used, then you use an underscore ( _ ) as the variable’s name. In this example, useful holds the only value that you need to use from the input iterable. The _ variable is a placeholder that guarantees that the unpacking works correctly. You won’t use the values that end up in this disposable variable.
Note: In the example above, if your target iterable is a sequence data type, such as a list or tuple, then it’s best to access its last item directly.
To do this, you can use the -1 index:
Using -1 gives you access to the last item of any sequence data type. In contrast, if you’re dealing with iterators , then you won’t be able to use indices. That’s when the *_ syntax comes to your rescue.
The pattern used in the above example comes in handy when you have a function that returns multiple values, and you only need a few of these values in your code. The os.walk() function may provide a good example of this situation.
This function allows you to iterate over the content of a directory recursively. The function returns a generator object that yields three-item tuples. Each tuple contains the following items:
- The path to the current directory as a string
- The names of all the immediate subdirectories as a list of strings
- The names of all the files in the current directory as a list of strings
Now say that you want to iterate over your home directory and list only the files. You can do something like this:
This code will issue a long output depending on the current content of your home directory. Note that you need to provide a string with the path to your user folder for the example to work. The _ placeholder variable will hold the unwanted data.
In contrast, the filenames variable will hold the list of files in the current directory, which is the data that you need. The code will print the list of filenames. Go ahead and give it a try!
The assignment operator also comes in handy when you need to provide default argument values in your functions and methods. Default argument values allow you to define functions that take arguments with sensible defaults. These defaults allow you to call the function with specific values or to simply rely on the defaults.
As an example, consider the following function:
This function takes one argument, called name . This argument has a sensible default value that’ll be used when you call the function without arguments. To provide this sensible default value, you use an assignment.
Note: According to PEP 8 , the style guide for Python code, you shouldn’t use spaces around the assignment operator when providing default argument values in function definitions.
Here’s how the function works:
If you don’t provide a name during the call to greet() , then the function uses the default value provided in the definition. If you provide a name, then the function uses it instead of the default one.
Up to this point, you’ve learned a lot about the Python assignment operator and how to use it for writing different types of assignment statements. In the following sections, you’ll dive into a great feature of assignment statements in Python. You’ll learn about augmented assignments .
Augmented Assignment Operators in Python
Python supports what are known as augmented assignments . An augmented assignment combines the assignment operator with another operator to make the statement more concise. Most Python math and bitwise operators have an augmented assignment variation that looks something like this:
Note that $ isn’t a valid Python operator. In this example, it’s a placeholder for a generic operator. This statement works as follows:
- Evaluate expression to produce a value.
- Run the operation defined by the operator that prefixes the = sign, using the previous value of variable and the return value of expression as operands.
- Assign the resulting value back to variable .
In practice, an augmented assignment like the above is equivalent to the following statement:
As you can conclude, augmented assignments are syntactic sugar . They provide a shorthand notation for a specific and popular kind of assignment.
For example, say that you need to define a counter variable to count some stuff in your code. You can use the += operator to increment counter by 1 using the following code:
In this example, the += operator, known as augmented addition , adds 1 to the previous value in counter each time you run the statement counter += 1 .
It’s important to note that unlike regular assignments, augmented assignments don’t create new variables. They only allow you to update existing variables. If you use an augmented assignment with an undefined variable, then you get a NameError :
Python evaluates the right side of the statement before assigning the resulting value back to the target variable. In this specific example, when Python tries to compute x + 1 , it finds that x isn’t defined.
Great! You now know that an augmented assignment consists of combining the assignment operator with another operator, like a math or bitwise operator. To continue this discussion, you’ll learn which math operators have an augmented variation in Python.
An equation like x = x + b doesn’t make sense in math. But in programming, a statement like x = x + b is perfectly valid and can be extremely useful. It adds b to x and reassigns the result back to x .
As you already learned, Python provides an operator to shorten x = x + b . Yes, the += operator allows you to write x += b instead. Python also offers augmented assignment operators for most math operators. Here’s a summary:
| Operator | Description | Example | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adds the right operand to the left operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Subtracts the right operand from the left operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Multiplies the right operand with the left operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Divides the left operand by the right operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Performs of the left operand by the right operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Finds the remainder of dividing the left operand by the right operand and stores the result in the left operand | |||
| Raises the left operand to the power of the right operand and stores the result in the left operand |
The Example column provides generic examples of how to use the operators in actual code. Note that x must be previously defined for the operators to work correctly. On the other hand, y can be either a concrete value or an expression that returns a value.
Note: The matrix multiplication operator ( @ ) doesn’t support augmented assignments yet.
Consider the following example of matrix multiplication using NumPy arrays:
Note that the exception traceback indicates that the operation isn’t supported yet.
To illustrate how augmented assignment operators work, say that you need to create a function that takes an iterable of numeric values and returns their sum. You can write this function like in the code below:
In this function, you first initialize total to 0 . In each iteration, the loop adds a new number to total using the augmented addition operator ( += ). When the loop terminates, total holds the sum of all the input numbers. Variables like total are known as accumulators . The += operator is typically used to update accumulators.
Note: Computing the sum of a series of numeric values is a common operation in programming. Python provides the built-in sum() function for this specific computation.
Another interesting example of using an augmented assignment is when you need to implement a countdown while loop to reverse an iterable. In this case, you can use the -= operator:
In this example, custom_reversed() is a generator function because it uses yield . Calling the function creates an iterator that yields items from the input iterable in reverse order. To decrement the control variable, index , you use an augmented subtraction statement that subtracts 1 from the variable in every iteration.
Note: Similar to summing the values in an iterable, reversing an iterable is also a common requirement. Python provides the built-in reversed() function for this specific computation, so you don’t have to implement your own. The above example only intends to show the -= operator in action.
Finally, counters are a special type of accumulators that allow you to count objects. Here’s an example of a letter counter:
To create this counter, you use a Python dictionary. The keys store the letters. The values store the counts. Again, to increment the counter, you use an augmented addition.
Counters are so common in programming that Python provides a tool specially designed to facilitate the task of counting. Check out Python’s Counter: The Pythonic Way to Count Objects for a complete guide on how to use this tool.
The += and *= augmented assignment operators also work with sequences , such as lists, tuples, and strings. The += operator performs augmented concatenations , while the *= operator performs augmented repetition .
These operators behave differently with mutable and immutable data types:
| Operator | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Runs an augmented concatenation operation on the target sequence. Mutable sequences are updated in place. If the sequence is immutable, then a new sequence is created and assigned back to the target name. | ||
| Adds to itself times. Mutable sequences are updated in place. If the sequence is immutable, then a new sequence is created and assigned back to the target name. |
Note that the augmented concatenation operator operates on two sequences, while the augmented repetition operator works on a sequence and an integer number.
Consider the following examples and pay attention to the result of calling the id() function:
Mutable sequences like lists support the += augmented assignment operator through the .__iadd__() method, which performs an in-place addition. This method mutates the underlying list, appending new values to its end.
Note: If the left operand is mutable, then x += y may not be completely equivalent to x = x + y . For example, if you do list_1 = list_1 + list_2 instead of list_1 += list_2 above, then you’ll create a new list instead of mutating the existing one. This may be important if other variables refer to the same list.
Immutable sequences, such as tuples and strings, don’t provide an .__iadd__() method. Therefore, augmented concatenations fall back to the .__add__() method, which doesn’t modify the sequence in place but returns a new sequence.
There’s another difference between mutable and immutable sequences when you use them in an augmented concatenation. Consider the following examples:
With mutable sequences, the data to be concatenated can come as a list, tuple, string, or any other iterable. In contrast, with immutable sequences, the data can only come as objects of the same type. You can concatenate tuples to tuples and strings to strings, for example.
Again, the augmented repetition operator works with a sequence on the left side of the operator and an integer on the right side. This integer value represents the number of repetitions to get in the resulting sequence:
When the *= operator operates on a mutable sequence, it falls back to the .__imul__() method, which performs the operation in place, modifying the underlying sequence. In contrast, if *= operates on an immutable sequence, then .__mul__() is called, returning a new sequence of the same type.
Note: Values of n less than 0 are treated as 0 , which returns an empty sequence of the same data type as the target sequence on the left side of the *= operand.
Note that a_list[0] is a_list[3] returns True . This is because the *= operator doesn’t make a copy of the repeated data. It only reflects the data. This behavior can be a source of issues when you use the operator with mutable values.
For example, say that you want to create a list of lists to represent a matrix, and you need to initialize the list with n empty lists, like in the following code:
In this example, you use the *= operator to populate matrix with three empty lists. Now check out what happens when you try to populate the first sublist in matrix :
The appended values are reflected in the three sublists. This happens because the *= operator doesn’t make copies of the data that you want to repeat. It only reflects the data. Therefore, every sublist in matrix points to the same object and memory address.
If you ever need to initialize a list with a bunch of empty sublists, then use a list comprehension :
This time, when you populate the first sublist of matrix , your changes aren’t propagated to the other sublists. This is because all the sublists are different objects that live in different memory addresses.
Bitwise operators also have their augmented versions. The logic behind them is similar to that of the math operators. The following table summarizes the augmented bitwise operators that Python provides:
| Operator | Operation | Example | Equivalent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Augmented bitwise AND ( ) | |||
| Augmented bitwise OR ( ) | |||
| Augmented bitwise XOR ( ) | |||
| Augmented bitwise right shift | |||
| Augmented bitwise left shift |
The augmented bitwise assignment operators perform the intended operation by taking the current value of the left operand as a starting point for the computation. Consider the following example, which uses the & and &= operators:
Programmers who work with high-level languages like Python rarely use bitwise operations in day-to-day coding. However, these types of operations can be useful in some situations.
For example, say that you’re implementing a Unix-style permission system for your users to access a given resource. In this case, you can use the characters "r" for reading, "w" for writing, and "x" for execution permissions, respectively. However, using bit-based permissions could be more memory efficient:
You can assign permissions to your users with the OR bitwise operator or the augmented OR bitwise operator. Finally, you can use the bitwise AND operator to check if a user has a certain permission, as you did in the final two examples.
You’ve learned a lot about augmented assignment operators and statements in this and the previous sections. These operators apply to math, concatenation, repetition, and bitwise operations. Now you’re ready to look at other assignment variants that you can use in your code or find in other developers’ code.
Other Assignment Variants
So far, you’ve learned that Python’s assignment statements and the assignment operator are present in many different scenarios and use cases. Those use cases include variable creation and initialization, parallel assignments, iterable unpacking, augmented assignments, and more.
In the following sections, you’ll learn about a few variants of assignment statements that can be useful in your future coding. You can also find these assignment variants in other developers’ code. So, you should be aware of them and know how they work in practice.
In short, you’ll learn about:
- Annotated assignment statements with type hints
- Assignment expressions with the walrus operator
- Managed attribute assignments with properties and descriptors
- Implicit assignments in Python
These topics will take you through several interesting and useful examples that showcase the power of Python’s assignment statements.
PEP 526 introduced a dedicated syntax for variable annotation back in Python 3.6 . The syntax consists of the variable name followed by a colon ( : ) and the variable type:
Even though these statements declare three variables with their corresponding data types, the variables aren’t actually created or initialized. So, for example, you can’t use any of these variables in an augmented assignment statement:
If you try to use one of the previously declared variables in an augmented assignment, then you get a NameError because the annotation syntax doesn’t define the variable. To actually define it, you need to use an assignment.
The good news is that you can use the variable annotation syntax in an assignment statement with the = operator:
The first statement in this example is what you can call an annotated assignment statement in Python. You may ask yourself why you should use type annotations in this type of assignment if everybody can see that counter holds an integer number. You’re right. In this example, the variable type is unambiguous.
However, imagine what would happen if you found a variable initialization like the following:
What would be the data type of each user in users ? If the initialization of users is far away from the definition of the User class, then there’s no quick way to answer this question. To clarify this ambiguity, you can provide the appropriate type hint for users :
Now you’re clearly communicating that users will hold a list of User instances. Using type hints in assignment statements that initialize variables to empty collection data types—such as lists, tuples, or dictionaries—allows you to provide more context about how your code works. This practice will make your code more explicit and less error-prone.
Up to this point, you’ve learned that regular assignment statements with the = operator don’t have a return value. They just create or update variables. Therefore, you can’t use a regular assignment to assign a value to a variable within the context of an expression.
Python 3.8 changed this by introducing a new type of assignment statement through PEP 572 . This new statement is known as an assignment expression or named expression .
Note: Expressions are a special type of statement in Python. Their distinguishing characteristic is that expressions always have a return value, which isn’t the case with all types of statements.
Unlike regular assignments, assignment expressions have a return value, which is why they’re called expressions in the first place. This return value is automatically assigned to a variable. To write an assignment expression, you must use the walrus operator ( := ), which was named for its resemblance to the eyes and tusks of a walrus lying on its side.
The general syntax of an assignment statement is as follows:
This expression looks like a regular assignment. However, instead of using the assignment operator ( = ), it uses the walrus operator ( := ). For the expression to work correctly, the enclosing parentheses are required in most use cases. However, there are certain situations in which these parentheses are superfluous. Either way, they won’t hurt you.
Assignment expressions come in handy when you want to reuse the result of an expression or part of an expression without using a dedicated assignment to grab this value beforehand.
Note: Assignment expressions with the walrus operator have several practical use cases. They also have a few restrictions. For example, they’re illegal in certain contexts, such as lambda functions, parallel assignments, and augmented assignments.
For a deep dive into this special type of assignment, check out The Walrus Operator: Python’s Assignment Expressions .
A particularly handy use case for assignment expressions is when you need to grab the result of an expression used in the context of a conditional statement. For example, say that you need to write a function to compute the mean of a sample of numeric values. Without the walrus operator, you could do something like this:
In this example, the sample size ( n ) is a value that you need to reuse in two different computations. First, you need to check whether the sample has data points or not. Then you need to use the sample size to compute the mean. To be able to reuse n , you wrote a dedicated assignment statement at the beginning of your function to grab the sample size.
You can avoid this extra step by combining it with the first use of the target value, len(sample) , using an assignment expression like the following:
The assignment expression introduced in the conditional computes the sample size and assigns it to n . This way, you guarantee that you have a reference to the sample size to use in further computations.
Because the assignment expression returns the sample size anyway, the conditional can check whether that size equals 0 or not and then take a certain course of action depending on the result of this check. The return statement computes the sample’s mean and sends the result back to the function caller.
Python provides a few tools that allow you to fine-tune the operations behind the assignment of attributes. The attributes that run implicit operations on assignments are commonly referred to as managed attributes .
Properties are the most commonly used tool for providing managed attributes in your classes. However, you can also use descriptors and, in some cases, the .__setitem__() special method.
To understand what fine-tuning the operation behind an assignment means, say that you need a Point class that only allows numeric values for its coordinates, x and y . To write this class, you must set up a validation mechanism to reject non-numeric values. You can use properties to attach the validation functionality on top of x and y .
Here’s how you can write your class:
In Point , you use properties for the .x and .y coordinates. Each property has a getter and a setter method . The getter method returns the attribute at hand. The setter method runs the input validation using a try … except block and the built-in float() function. Then the method assigns the result to the actual attribute.
Here’s how your class works in practice:
When you use a property-based attribute as the left operand in an assignment statement, Python automatically calls the property’s setter method, running any computation from it.
Because both .x and .y are properties, the input validation runs whenever you assign a value to either attribute. In the first example, the input values are valid numbers and the validation passes. In the final example, "one" isn’t a valid numeric value, so the validation fails.
If you look at your Point class, you’ll note that it follows a repetitive pattern, with the getter and setter methods looking quite similar. To avoid this repetition, you can use a descriptor instead of a property.
A descriptor is a class that implements the descriptor protocol , which consists of four special methods :
- .__get__() runs when you access the attribute represented by the descriptor.
- .__set__() runs when you use the attribute in an assignment statement.
- .__delete__() runs when you use the attribute in a del statement.
- .__set_name__() sets the attribute’s name, creating a name-aware attribute.
Here’s how your code may look if you use a descriptor to represent the coordinates of your Point class:
You’ve removed repetitive code by defining Coordinate as a descriptor that manages the input validation in a single place. Go ahead and run the following code to try out the new implementation of Point :
Great! The class works as expected. Thanks to the Coordinate descriptor, you now have a more concise and non-repetitive version of your original code.
Another way to fine-tune the operations behind an assignment statement is to provide a custom implementation of .__setitem__() in your class. You’ll use this method in classes representing mutable data collections, such as custom list-like or dictionary-like classes.
As an example, say that you need to create a dictionary-like class that stores its keys in lowercase letters:
In this example, you create a dictionary-like class by subclassing UserDict from collections . Your class implements a .__setitem__() method, which takes key and value as arguments. The method uses str.lower() to convert key into lowercase letters before storing it in the underlying dictionary.
Python implicitly calls .__setitem__() every time you use a key as the left operand in an assignment statement. This behavior allows you to tweak how you process the assignment of keys in your custom dictionary.
Implicit Assignments in Python
Python implicitly runs assignments in many different contexts. In most cases, these implicit assignments are part of the language syntax. In other cases, they support specific behaviors.
Whenever you complete an action in the following list, Python runs an implicit assignment for you:
- Define or call a function
- Define or instantiate a class
- Use the current instance , self
- Import modules and objects
- Use a decorator
- Use the control variable in a for loop or a comprehension
- Use the as qualifier in with statements , imports, and try … except blocks
- Access the _ special variable in an interactive session
Behind the scenes, Python performs an assignment in every one of the above situations. In the following subsections, you’ll take a tour of all these situations.
When you define a function, the def keyword implicitly assigns a function object to your function’s name. Here’s an example:
From this point on, the name greet refers to a function object that lives at a given memory address in your computer. You can call the function using its name and a pair of parentheses with appropriate arguments. This way, you can reuse greet() wherever you need it.
If you call your greet() function with fellow as an argument, then Python implicitly assigns the input argument value to the name parameter on the function’s definition. The parameter will hold a reference to the input arguments.
When you define a class with the class keyword, you’re assigning a specific name to a class object . You can later use this name to create instances of that class. Consider the following example:
In this example, the name User holds a reference to a class object, which was defined in __main__.User . Like with a function, when you call the class’s constructor with the appropriate arguments to create an instance, Python assigns the arguments to the parameters defined in the class initializer .
Another example of implicit assignments is the current instance of a class, which in Python is called self by convention. This name implicitly gets a reference to the current object whenever you instantiate a class. Thanks to this implicit assignment, you can access .name and .job from within the class without getting a NameError in your code.
Import statements are another variant of implicit assignments in Python. Through an import statement, you assign a name to a module object, class, function, or any other imported object. This name is then created in your current namespace so that you can access it later in your code:
In this example, you import the sys module object from the standard library and assign it to the sys name, which is now available in your namespace, as you can conclude from the second call to the built-in dir() function.
You also run an implicit assignment when you use a decorator in your code. The decorator syntax is just a shortcut for a formal assignment like the following:
Here, you call decorator() with a function object as an argument. This call will typically add functionality on top of the existing function, func() , and return a function object, which is then reassigned to the func name.
The decorator syntax is syntactic sugar for replacing the previous assignment, which you can now write as follows:
Even though this new code looks pretty different from the above assignment, the code implicitly runs the same steps.
Another situation in which Python automatically runs an implicit assignment is when you use a for loop or a comprehension. In both cases, you can have one or more control variables that you then use in the loop or comprehension body:
The memory address of control_variable changes on each iteration of the loop. This is because Python internally reassigns a new value from the loop iterable to the loop control variable on each cycle.
The same behavior appears in comprehensions:
In the end, comprehensions work like for loops but use a more concise syntax. This comprehension creates a new list of strings that mimic the output from the previous example.
The as keyword in with statements, except clauses, and import statements is another example of an implicit assignment in Python. This time, the assignment isn’t completely implicit because the as keyword provides an explicit way to define the target variable.
In a with statement, the target variable that follows the as keyword will hold a reference to the context manager that you’re working with. As an example, say that you have a hello.txt file with the following content:
You want to open this file and print each of its lines on your screen. In this case, you can use the with statement to open the file using the built-in open() function.
In the example below, you accomplish this. You also add some calls to print() that display information about the target variable defined by the as keyword:
This with statement uses the open() function to open hello.txt . The open() function is a context manager that returns a text file object represented by an io.TextIOWrapper instance.
Since you’ve defined a hello target variable with the as keyword, now that variable holds a reference to the file object itself. You confirm this by printing the object and its memory address. Finally, the for loop iterates over the lines and prints this content to the screen.
When it comes to using the as keyword in the context of an except clause, the target variable will contain an exception object if any exception occurs:
In this example, you run a division that raises a ZeroDivisionError . The as keyword assigns the raised exception to error . Note that when you print the exception object, you get only the message because exceptions have a custom .__str__() method that supports this behavior.
There’s a final detail to remember when using the as specifier in a try … except block like the one in the above example. Once you leave the except block, the target variable goes out of scope , and you can’t use it anymore.
Finally, Python’s import statements also support the as keyword. In this context, you can use as to import objects with a different name:
In these examples, you use the as keyword to import the numpy package with the np name and pandas with the name pd . If you call dir() , then you’ll realize that np and pd are now in your namespace. However, the numpy and pandas names are not.
Using the as keyword in your imports comes in handy when you want to use shorter names for your objects or when you need to use different objects that originally had the same name in your code. It’s also useful when you want to make your imported names non-public using a leading underscore, like in import sys as _sys .
The final implicit assignment that you’ll learn about in this tutorial only occurs when you’re using Python in an interactive session. Every time you run a statement that returns a value, the interpreter stores the result in a special variable denoted by a single underscore character ( _ ).
You can access this special variable as you’d access any other variable:
These examples cover several situations in which Python internally uses the _ variable. The first two examples evaluate expressions. Expressions always have a return value, which is automatically assigned to the _ variable every time.
When it comes to function calls, note that if your function returns a fruitful value, then _ will hold it. In contrast, if your function returns None , then the _ variable will remain untouched.
The next example consists of a regular assignment statement. As you already know, regular assignments don’t return any value, so the _ variable isn’t updated after these statements run. Finally, note that accessing a variable in an interactive session returns the value stored in the target variable. This value is then assigned to the _ variable.
Note that since _ is a regular variable, you can use it in other expressions:
In this example, you first create a list of values. Then you call len() to get the number of values in the list. Python automatically stores this value in the _ variable. Finally, you use _ to compute the mean of your list of values.
Now that you’ve learned about some of the implicit assignments that Python runs under the hood, it’s time to dig into a final assignment-related topic. In the following few sections, you’ll learn about some illegal and dangerous assignments that you should be aware of and avoid in your code.
Illegal and Dangerous Assignments in Python
In Python, you’ll find a few situations in which using assignments is either forbidden or dangerous. You must be aware of these special situations and try to avoid them in your code.
In the following sections, you’ll learn when using assignment statements isn’t allowed in Python. You’ll also learn about some situations in which using assignments should be avoided if you want to keep your code consistent and robust.
You can’t use Python keywords as variable names in assignment statements. This kind of assignment is explicitly forbidden. If you try to use a keyword as a variable name in an assignment, then you get a SyntaxError :
Whenever you try to use a keyword as the left operand in an assignment statement, you get a SyntaxError . Keywords are an intrinsic part of the language and can’t be overridden.
If you ever feel the need to name one of your variables using a Python keyword, then you can append an underscore to the name of your variable:
In this example, you’re using the desired name for your variables. Because you added a final underscore to the names, Python doesn’t recognize them as keywords, so it doesn’t raise an error.
Note: Even though adding an underscore at the end of a name is an officially recommended practice , it can be confusing sometimes. Therefore, try to find an alternative name or use a synonym whenever you find yourself using this convention.
For example, you can write something like this:
In this example, using the name booking_class for your variable is way clearer and more descriptive than using class_ .
You’ll also find that you can use only a few keywords as part of the right operand in an assignment statement. Those keywords will generally define simple statements that return a value or object. These include lambda , and , or , not , True , False , None , in , and is . You can also use the for keyword when it’s part of a comprehension and the if keyword when it’s used as part of a ternary operator .
In an assignment, you can never use a compound statement as the right operand. Compound statements are those that require an indented block, such as for and while loops, conditionals, with statements, try … except blocks, and class or function definitions.
Sometimes, you need to name variables, but the desired or ideal name is already taken and used as a built-in name. If this is your case, think harder and find another name. Don’t shadow the built-in.
Shadowing built-in names can cause hard-to-identify problems in your code. A common example of this issue is using list or dict to name user-defined variables. In this case, you override the corresponding built-in names, which won’t work as expected if you use them later in your code.
Consider the following example:
The exception in this example may sound surprising. How come you can’t use list() to build a list from a call to map() that returns a generator of square numbers?
By using the name list to identify your list of numbers, you shadowed the built-in list name. Now that name points to a list object rather than the built-in class. List objects aren’t callable, so your code no longer works.
In Python, you’ll have nothing that warns against using built-in, standard-library, or even relevant third-party names to identify your own variables. Therefore, you should keep an eye out for this practice. It can be a source of hard-to-debug errors.
In programming, a constant refers to a name associated with a value that never changes during a program’s execution. Unlike other programming languages, Python doesn’t have a dedicated syntax for defining constants. This fact implies that Python doesn’t have constants in the strict sense of the word.
Python only has variables. If you need a constant in Python, then you’ll have to define a variable and guarantee that it won’t change during your code’s execution. To do that, you must avoid using that variable as the left operand in an assignment statement.
To tell other Python programmers that a given variable should be treated as a constant, you must write your variable’s name in capital letters with underscores separating the words. This naming convention has been adopted by the Python community and is a recommendation that you’ll find in the Constants section of PEP 8 .
In the following examples, you define some constants in Python:
The problem with these constants is that they’re actually variables. Nothing prevents you from changing their value during your code’s execution. So, at any time, you can do something like the following:
These assignments modify the value of two of your original constants. Python doesn’t complain about these changes, which can cause issues later in your code. As a Python developer, you must guarantee that named constants in your code remain constant.
The only way to do that is never to use named constants in an assignment statement other than the constant definition.
You’ve learned a lot about Python’s assignment operators and how to use them for writing assignment statements . With this type of statement, you can create, initialize, and update variables according to your needs. Now you have the required skills to fully manage the creation and mutation of variables in your Python code.
In this tutorial, you’ve learned how to:
- Write assignment statements using Python’s assignment operators
- Work with augmented assignments in Python
- Explore assignment variants, like assignment expression and managed attributes
- Identify illegal and dangerous assignments in Python
Learning about the Python assignment operator and how to use it in assignment statements is a fundamental skill in Python. It empowers you to write reliable and effective Python code.
🐍 Python Tricks 💌
Get a short & sweet Python Trick delivered to your inbox every couple of days. No spam ever. Unsubscribe any time. Curated by the Real Python team.

About Leodanis Pozo Ramos

Leodanis is an industrial engineer who loves Python and software development. He's a self-taught Python developer with 6+ years of experience. He's an avid technical writer with a growing number of articles published on Real Python and other sites.
Each tutorial at Real Python is created by a team of developers so that it meets our high quality standards. The team members who worked on this tutorial are:

Master Real-World Python Skills With Unlimited Access to Real Python
Join us and get access to thousands of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
Join us and get access to thousands of tutorials, hands-on video courses, and a community of expert Pythonistas:
What Do You Think?
What’s your #1 takeaway or favorite thing you learned? How are you going to put your newfound skills to use? Leave a comment below and let us know.
Commenting Tips: The most useful comments are those written with the goal of learning from or helping out other students. Get tips for asking good questions and get answers to common questions in our support portal . Looking for a real-time conversation? Visit the Real Python Community Chat or join the next “Office Hours” Live Q&A Session . Happy Pythoning!
Keep Learning
Related Topics: intermediate best-practices python
Keep reading Real Python by creating a free account or signing in:
Already have an account? Sign-In
Almost there! Complete this form and click the button below to gain instant access:
Python's Assignment Operator: Write Robust Assignments (Source Code)
🔒 No spam. We take your privacy seriously.

Python Conditional Assignment
When you want to assign a value to a variable based on some condition, like if the condition is true then assign a value to the variable, else assign some other value to the variable, then you can use the conditional assignment operator.
In this tutorial, we will look at different ways to assign values to a variable based on some condition.
1. Using Ternary Operator
The ternary operator is very special operator in Python, it is used to assign a value to a variable based on some condition.
It goes like this:
Here, the value of variable will be value_if_true if the condition is true, else it will be value_if_false .
Let's see a code snippet to understand it better.
You can see we have conditionally assigned a value to variable c based on the condition a > b .
2. Using if-else statement
if-else statements are the core part of any programming language, they are used to execute a block of code based on some condition.
Using an if-else statement, we can assign a value to a variable based on the condition we provide.
Here is an example of replacing the above code snippet with the if-else statement.
3. Using Logical Short Circuit Evaluation
Logical short circuit evaluation is another way using which you can assign a value to a variable conditionally.
The format of logical short circuit evaluation is:
It looks similar to ternary operator, but it is not. Here the condition and value_if_true performs logical AND operation, if both are true then the value of variable will be value_if_true , or else it will be value_if_false .
Let's see an example:
But if we make condition True but value_if_true False (or 0 or None), then the value of variable will be value_if_false .
So, you can see that the value of c is 20 even though the condition a < b is True .
So, you should be careful while using logical short circuit evaluation.
While working with lists , we often need to check if a list is empty or not, and if it is empty then we need to assign some default value to it.
Let's see how we can do it using conditional assignment.
Here, we have assigned a default value to my_list if it is empty.
Assign a value to a variable conditionally based on the presence of an element in a list.
Now you know 3 different ways to assign a value to a variable conditionally. Any of these methods can be used to assign a value when there is a condition.
The cleanest and fastest way to conditional value assignment is the ternary operator .
if-else statement is recommended to use when you have to execute a block of code based on some condition.
Happy coding! 😊
previous episode
Python for absolute beginners, next episode, variables and assignment.
Overview Teaching: 15 min Exercises: 15 min Questions How can I store data in programs? Objectives Write scripts that assign values to variables and perform calculations with those values. Correctly trace value changes in scripts that use assignment.
Use variables to store values
Variables are one of the fundamental building blocks of Python. A variable is like a tiny container where you store values and data, such as filenames, words, numbers, collections of words and numbers, and more.
The variable name will point to a value that you “assign” it. You might think about variable assignment like putting a value “into” the variable, as if the variable is a little box 🎁
(In fact, a variable is not a container as such but more like an adress label that points to a container with a given value. This difference will become relevant once we start talking about lists and mutable data types.)
You assign variables with an equals sign ( = ). In Python, a single equals sign = is the “assignment operator.” (A double equals sign == is the “real” equals sign.)
- Variables are names for values.
- In Python the = symbol assigns the value on the right to the name on the left.
- The variable is created when a value is assigned to it.
- Here, Python assigns an age to a variable age and a name in quotation marks to a variable first_name :
Variable names
Variable names can be as long or as short as you want, but there are certain rules you must follow.
- Cannot start with a digit.
- Cannot contain spaces, quotation marks, or other punctuation.
- May contain an underscore (typically used to separate words in long variable names).
- Having an underscore at the beginning of a variable name like _alistairs_real_age has a special meaning. So we won’t do that until we understand the convention.
- The standard naming convention for variable names in Python is the so-called “snake case”, where each word is separated by an underscore. For example my_first_variable . You can read more about naming conventions in Python here .
Use meaningful variable names
Python doesn’t care what you call variables as long as they obey the rules (alphanumeric characters and the underscore). As you start to code, you will almost certainly be tempted to use extremely short variables names like f . Your fingers will get tired. Your coffee will wear off. You will see other people using variables like f . You’ll promise yourself that you’ll definitely remember what f means. But you probably won’t.
So, resist the temptation of bad variable names! Clear and precisely-named variables will:
- Make your code more readable (both to yourself and others).
- Reinforce your understanding of Python and what’s happening in the code.
- Clarify and strengthen your thinking.
Use meaningful variable names to help other people understand what the program does. The most important “other person” is your future self!
Python is case-sensitive
Python thinks that upper- and lower-case letters are different, so Name and name are different variables. There are conventions for using upper-case letters at the start of variable names so we will use lower-case letters for now.
Off-Limits Names
The only variable names that are off-limits are names that are reserved by, or built into, the Python programming language itself — such as print , True , and list . Some of these you can overwrite into variable names (not ideal!), but Jupyter Lab (and many other environments and editors) will catch this by colour coding your variable. If your would-be variable is colour-coded green, rethink your name choice. This is not something to worry too much about. You can get the object back by resetting your kernel.
Use print() to display values
We can check to see what’s “inside” variables by running a cell with the variable’s name. This is one of the handiest features of a Jupyter notebook. Outside the Jupyter environment, you would need to use the print() function to display the variable.
You can run the print() function inside the Jupyter environment, too. This is sometimes useful because Jupyter will only display the last variable in a cell, while print() can display multiple variables. Additionally, Jupyter will display text with \n characters (which means “new line”), while print() will display the text appropriately formatted with new lines.
- Python has a built-in function called print() that prints things as text.
- Provide values to the function (i.e., the things to print) in parentheses.
- To add a string to the printout, wrap the string in single or double quotations.
- The values passed to the function are called ‘arguments’ and are separated by commas.
- When using the print() function, we can also separate with a ‘+’ sign. However, when using ‘+’ we have to add spaces in between manually.
- print() automatically puts a single space between items to separate them.
- And wraps around to a new line at the end.
Variables must be created before they are used
If a variable doesn’t exist yet, or if the name has been misspelled, Python reports an error (unlike some languages, which “guess” a default value).
The last line of an error message is usually the most informative. This message lets us know that there is no variable called eye_color in the script.
Variables Persist Between Cells Variables defined in one cell exist in all other cells once executed, so the relative location of cells in the notebook do not matter (i.e., cells lower down can still affect those above). Notice the number in the square brackets [ ] to the left of the cell. These numbers indicate the order, in which the cells have been executed. Cells with lower numbers will affect cells with higher numbers as Python runs the cells chronologically. As a best practice, we recommend you keep your notebook in chronological order so that it is easier for the human eye to read and make sense of, as well as to avoid any errors if you close and reopen your project, and then rerun what you have done. Remember: Notebook cells are just a way to organize a program! As far as Python is concerned, all of the source code is one long set of instructions.
Variables can be used in calculations
- We can use variables in calculations just as if they were values. Remember, we assigned 42 to age a few lines ago.
This code works in the following way. We are reassigning the value of the variable age by taking its previous value (42) and adding 3, thus getting our new value of 45.
Use an index to get a single character from a string
- The characters (individual letters, numbers, and so on) in a string are ordered. For example, the string ‘AB’ is not the same as ‘BA’. Because of this ordering, we can treat the string as a list of characters.
- Each position in the string (first, second, etc.) is given a number. This number is called an index or sometimes a subscript.
- Indices are numbered from 0 rather than 1.
- Use the position’s index in square brackets to get the character at that position.
Use a slice to get a substring
A part of a string is called a substring. A substring can be as short as a single character. A slice is a part of a string (or, more generally, any list-like thing). We take a slice by using [start:stop] , where start is replaced with the index of the first element we want and stop is replaced with the index of the element just after the last element we want. Mathematically, you might say that a slice selects [start:stop] . The difference between stop and start is the slice’s length. Taking a slice does not change the contents of the original string. Instead, the slice is a copy of part of the original string.
Use the built-in function len() to find the length of a string
The built-in function len() is used to find the length of a string (and later, of other data types, too).
Note that the result is 6 and not 7. This is because it is the length of the value of the variable (i.e. 'helium' ) that is being counted and not the name of the variable (i.e. element )
Also note that nested functions are evaluated from the inside out, just like in mathematics. Thus, Python first reads the len() function, then the print() function.
Choosing a Name Which is a better variable name, m , min , or minutes ? Why? Hint: think about which code you would rather inherit from someone who is leaving the library: ts = m * 60 + s tot_sec = min * 60 + sec total_seconds = minutes * 60 + seconds Solution minutes is better because min might mean something like “minimum” (and actually does in Python, but we haven’t seen that yet).
Swapping Values Draw a table showing the values of the variables in this program after each statement is executed. In simple terms, what do the last three lines of this program do? x = 1.0 y = 3.0 swap = x x = y y = swap Solution swap = x # x->1.0 y->3.0 swap->1.0 x = y # x->3.0 y->3.0 swap->1.0 y = swap # x->3.0 y->1.0 swap->1.0 These three lines exchange the values in x and y using the swap variable for temporary storage. This is a fairly common programming idiom.
Predicting Values What is the final value of position in the program below? (Try to predict the value without running the program, then check your prediction.) initial = "left" position = initial initial = "right" Solution initial = "left" # Initial is assigned the string "left" position = initial # Position is assigned the variable initial, currently "left" initial = "right" # Initial is assigned the string "right" print(position) left The last assignment to position was “left”
Can you slice integers? If you assign a = 123 , what happens if you try to get the second digit of a ? Solution Numbers are not stored in the written representation, so they can’t be treated like strings. a = 123 print(a[1]) TypeError: 'int' object is not subscriptable
Slicing What does the following program print? library_name = 'social sciences' print('library_name[1:3] is:', library_name[1:3]) If thing is a variable name, low is a low number, and high is a high number: What does thing[low:high] do? What does thing[low:] (without a value after the colon) do? What does thing[:high] (without a value before the colon) do? What does thing[:] (just a colon) do? What does thing[number:negative-number] do? Solution library_name[1:3] is: oc It will slice the string, starting at the low index and ending an element before the high index It will slice the string, starting at the low index and stopping at the end of the string It will slice the string, starting at the beginning on the string, and ending an element before the high index It will print the entire string It will slice the string, starting the number index, and ending a distance of the absolute value of negative-number elements from the end of the string
Key Points Use variables to store values. Use meaningful variable names. Python is case-sensitive. Use print() to display values. Variables must be created before they are used. Variables persist between cells. Variables can be used in calculations. Use an index to get a single character from a string. Use a slice to get a substring. Use the built-in function len to find the length of a string.

Learning Python by doing
- suggest edit
Variables, Expressions, and Assignments
Variables, expressions, and assignments 1 #, introduction #.
In this chapter, we introduce some of the main building blocks needed to create programs–that is, variables, expressions, and assignments. Programming related variables can be intepret in the same way that we interpret mathematical variables, as elements that store values that can later be changed. Usually, variables and values are used within the so-called expressions. Once again, just as in mathematics, an expression is a construct of values and variables connected with operators that result in a new value. Lastly, an assignment is a language construct know as an statement that assign a value (either as a constant or expression) to a variable. The rest of this notebook will dive into the main concepts that we need to fully understand these three language constructs.
Values and Types #
A value is the basic unit used in a program. It may be, for instance, a number respresenting temperature. It may be a string representing a word. Some values are 42, 42.0, and ‘Hello, Data Scientists!’.
Each value has its own type : 42 is an integer ( int in Python), 42.0 is a floating-point number ( float in Python), and ‘Hello, Data Scientists!’ is a string ( str in Python).
The Python interpreter can tell you the type of a value: the function type takes a value as argument and returns its corresponding type.
Observe the difference between type(42) and type('42') !
Expressions and Statements #
On the one hand, an expression is a combination of values, variables, and operators.
A value all by itself is considered an expression, and so is a variable.
When you type an expression at the prompt, the interpreter evaluates it, which means that it calculates the value of the expression and displays it.
In boxes above, m has the value 27 and m + 25 has the value 52 . m + 25 is said to be an expression.
On the other hand, a statement is an instruction that has an effect, like creating a variable or displaying a value.
The first statement initializes the variable n with the value 17 , this is a so-called assignment statement .
The second statement is a print statement that prints the value of the variable n .
The effect is not always visible. Assigning a value to a variable is not visible, but printing the value of a variable is.
Assignment Statements #
We have already seen that Python allows you to evaluate expressions, for instance 40 + 2 . It is very convenient if we are able to store the calculated value in some variable for future use. The latter can be done via an assignment statement. An assignment statement creates a new variable with a given name and assigns it a value.
The example in the previous code contains three assignments. The first one assigns the value of the expression 40 + 2 to a new variable called magicnumber ; the second one assigns the value of π to the variable pi , and; the last assignment assigns the string value 'Data is eatig the world' to the variable message .
Programmers generally choose names for their variables that are meaningful. In this way, they document what the variable is used for.
Do It Yourself!
Let’s compute the volume of a cube with side \(s = 5\) . Remember that the volume of a cube is defined as \(v = s^3\) . Assign the value to a variable called volume .
Well done! Now, why don’t you print the result in a message? It can say something like “The volume of the cube with side 5 is \(volume\) ”.
Beware that there is no checking of types ( type checking ) in Python, so a variable to which you have assigned an integer may be re-used as a float, even if we provide type-hints .
Names and Keywords #
Names of variable and other language constructs such as functions (we will cover this topic later), should be meaningful and reflect the purpose of the construct.
In general, Python names should adhere to the following rules:
It should start with a letter or underscore.
It cannot start with a number.
It must only contain alpha-numeric (i.e., letters a-z A-Z and digits 0-9) characters and underscores.
They cannot share the name of a Python keyword.
If you use illegal variable names you will get a syntax error.
By choosing the right variables names you make the code self-documenting, what is better the variable v or velocity ?
The following are examples of invalid variable names.
These basic development principles are sometimes called architectural rules . By defining and agreeing upon architectural rules you make it easier for you and your fellow developers to understand and modify your code.
If you want to read more on this, please have a look at Code complete a book by Steven McConnell [ McC04 ] .
Every programming language has a collection of reserved keywords . They are used in predefined language constructs, such as loops and conditionals . These language concepts and their usage will be explained later.
The interpreter uses keywords to recognize these language constructs in a program. Python 3 has the following keywords:
False class finally is return
None continue for lambda try
True def from nonlocal while
and del global not with
as elif if or yield
assert else import pass break
except in raise
Reassignments #
It is allowed to assign a new value to an existing variable. This process is called reassignment . As soon as you assign a value to a variable, the old value is lost.
The assignment of a variable to another variable, for instance b = a does not imply that if a is reassigned then b changes as well.
You have a variable salary that shows the weekly salary of an employee. However, you want to compute the monthly salary. Can you reassign the value to the salary variable according to the instruction?
Updating Variables #
A frequently used reassignment is for updating puposes: the value of a variable depends on the previous value of the variable.
This statement expresses “get the current value of x , add one, and then update x with the new value.”
Beware, that the variable should be initialized first, usually with a simple assignment.
Do you remember the salary excercise of the previous section (cf. 13. Reassignments)? Well, if you have not done it yet, update the salary variable by using its previous value.
Updating a variable by adding 1 is called an increment ; subtracting 1 is called a decrement . A shorthand way of doing is using += and -= , which stands for x = x + ... and x = x - ... respectively.
Order of Operations #
Expressions may contain multiple operators. The order of evaluation depends on the priorities of the operators also known as rules of precedence .
For mathematical operators, Python follows mathematical convention. The acronym PEMDAS is a useful way to remember the rules:
Parentheses have the highest precedence and can be used to force an expression to evaluate in the order you want. Since expressions in parentheses are evaluated first, 2 * (3 - 1) is 4 , and (1 + 1)**(5 - 2) is 8 . You can also use parentheses to make an expression easier to read, even if it does not change the result.
Exponentiation has the next highest precedence, so 1 + 2**3 is 9 , not 27 , and 2 * 3**2 is 18 , not 36 .
Multiplication and division have higher precedence than addition and subtraction . So 2 * 3 - 1 is 5 , not 4 , and 6 + 4 / 2 is 8 , not 5 .
Operators with the same precedence are evaluated from left to right (except exponentiation). So in the expression degrees / 2 * pi , the division happens first and the result is multiplied by pi . To divide by 2π, you can use parentheses or write: degrees / 2 / pi .
In case of doubt, use parentheses!
Let’s see what happens when we evaluate the following expressions. Just run the cell to check the resulting value.
Floor Division and Modulus Operators #
The floor division operator // divides two numbers and rounds down to an integer.
For example, suppose that driving to the south of France takes 555 minutes. You might want to know how long that is in hours.
Conventional division returns a floating-point number.
Hours are normally not represented with decimal points. Floor division returns the integer number of hours, dropping the fraction part.
You spend around 225 minutes every week on programming activities. You want to know around how many hours you invest to this activity during a month. Use the \(//\) operator to give the answer.
The modulus operator % works on integer values. It computes the remainder when dividing the first integer by the second one.
The modulus operator is more useful than it seems.
For example, you can check whether one number is divisible by another—if x % y is zero, then x is divisible by y .
String Operations #
In general, you cannot perform mathematical operations on strings, even if the strings look like numbers, so the following operations are illegal: '2'-'1' 'eggs'/'easy' 'third'*'a charm'
But there are two exceptions, + and * .
The + operator performs string concatenation, which means it joins the strings by linking them end-to-end.
The * operator also works on strings; it performs repetition.
Speedy Gonzales is a cartoon known to be the fastest mouse in all Mexico . He is also famous for saying “Arriba Arriba Andale Arriba Arriba Yepa”. Can you use the following variables, namely arriba , andale and yepa to print the mentioned expression? Don’t forget to use the string operators.
Asking the User for Input #
The programs we have written so far accept no input from the user.
To get data from the user through the Python prompt, we can use the built-in function input .
When input is called your whole program stops and waits for the user to enter the required data. Once the user types the value and presses Return or Enter , the function returns the input value as a string and the program continues with its execution.
Try it out!
You can also print a message to clarify the purpose of the required input as follows.
The resulting string can later be translated to a different type, like an integer or a float. To do so, you use the functions int and float , respectively. But be careful, the user might introduce a value that cannot be converted to the type you required.
We want to know the name of a user so we can display a welcome message in our program. The message should say something like “Hello \(name\) , welcome to our hello world program!”.
Script Mode #
So far we have run Python in interactive mode in these Jupyter notebooks, which means that you interact directly with the interpreter in the code cells . The interactive mode is a good way to get started, but if you are working with more than a few lines of code, it can be clumsy. The alternative is to save code in a file called a script and then run the interpreter in script mode to execute the script. By convention, Python scripts have names that end with .py .
Use the PyCharm icon in Anaconda Navigator to create and execute stand-alone Python scripts. Later in the course, you will have to work with Python projects for the assignments, in order to get acquainted with another way of interacing with Python code.
This Jupyter Notebook is based on Chapter 2 of the books Python for Everybody [ Sev16 ] and Think Python (Sections 5.1, 7.1, 7.2, and 5.12) [ Dow15 ] .
- Table of Contents
- Course Home
- Assignments
- Peer Instruction (Instructor)
- Peer Instruction (Student)
- Change Course
- Instructor's Page
- Progress Page
- Edit Profile
- Change Password
- Scratch ActiveCode
- Scratch Activecode
- Instructors Guide
- About Runestone
- Report A Problem
- 1.1 Preface
- 1.2 Why Programming? Why Java?
- 1.3 Variables and Data Types
- 1.4 Expressions and Assignment Statements
- 1.5 Compound Assignment Operators
- 1.6 Casting and Ranges of Variables
- 1.7 Java Development Environments (optional)
- 1.8 Unit 1 Summary
- 1.9 Unit 1 Mixed Up Code Practice
- 1.10 Unit 1 Coding Practice
- 1.11 Multiple Choice Exercises
- 1.12 Lesson Workspace
- 1.3. Variables and Data Types" data-toggle="tooltip">
- 1.5. Compound Assignment Operators' data-toggle="tooltip" >
1.4. Expressions and Assignment Statements ¶
In this lesson, you will learn about assignment statements and expressions that contain math operators and variables.
1.4.1. Assignment Statements ¶
Remember that a variable holds a value that can change or vary. Assignment statements initialize or change the value stored in a variable using the assignment operator = . An assignment statement always has a single variable on the left hand side of the = sign. The value of the expression on the right hand side of the = sign (which can contain math operators and other variables) is copied into the memory location of the variable on the left hand side.
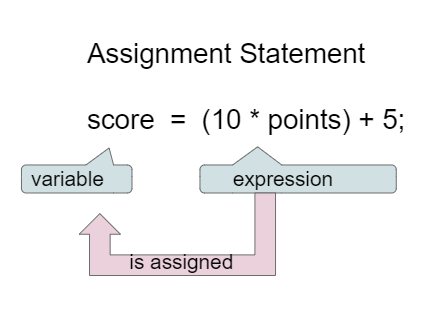
Figure 1: Assignment Statement (variable = expression) ¶
Instead of saying equals for the = operator in an assignment statement, say “gets” or “is assigned” to remember that the variable on the left hand side gets or is assigned the value on the right. In the figure above, score is assigned the value of 10 times points (which is another variable) plus 5.
The following video by Dr. Colleen Lewis shows how variables can change values in memory using assignment statements.
As we saw in the video, we can set one variable to a copy of the value of another variable like y = x;. This won’t change the value of the variable that you are copying from.

Click on the Show CodeLens button to step through the code and see how the values of the variables change.
The program is supposed to figure out the total money value given the number of dimes, quarters and nickels. There is an error in the calculation of the total. Fix the error to compute the correct amount.
Calculate and print the total pay given the weekly salary and the number of weeks worked. Use string concatenation with the totalPay variable to produce the output Total Pay = $3000 . Don’t hardcode the number 3000 in your print statement.

Assume you have a package with a given height 3 inches and width 5 inches. If the package is rotated 90 degrees, you should swap the values for the height and width. The code below makes an attempt to swap the values stored in two variables h and w, which represent height and width. Variable h should end up with w’s initial value of 5 and w should get h’s initial value of 3. Unfortunately this code has an error and does not work. Use the CodeLens to step through the code to understand why it fails to swap the values in h and w.
1-4-7: Explain in your own words why the ErrorSwap program code does not swap the values stored in h and w.
Swapping two variables requires a third variable. Before assigning h = w , you need to store the original value of h in the temporary variable. In the mixed up programs below, drag the blocks to the right to put them in the right order.
The following has the correct code that uses a third variable named “temp” to swap the values in h and w.
The code is mixed up and contains one extra block which is not needed in a correct solution. Drag the needed blocks from the left into the correct order on the right, then check your solution. You will be told if any of the blocks are in the wrong order or if you need to remove one or more blocks.
After three incorrect attempts you will be able to use the Help Me button to make the problem easier.
Fix the code below to perform a correct swap of h and w. You need to add a new variable named temp to use for the swap.
1.4.2. Incrementing the value of a variable ¶
If you use a variable to keep score you would probably increment it (add one to the current value) whenever score should go up. You can do this by setting the variable to the current value of the variable plus one (score = score + 1) as shown below. The formula looks a little crazy in math class, but it makes sense in coding because the variable on the left is set to the value of the arithmetic expression on the right. So, the score variable is set to the previous value of score + 1.
Click on the Show CodeLens button to step through the code and see how the score value changes.
1-4-11: What is the value of b after the following code executes?
- It sets the value for the variable on the left to the value from evaluating the right side. What is 5 * 2?
- Correct. 5 * 2 is 10.
1-4-12: What are the values of x, y, and z after the following code executes?
- x = 0, y = 1, z = 2
- These are the initial values in the variable, but the values are changed.
- x = 1, y = 2, z = 3
- x changes to y's initial value, y's value is doubled, and z is set to 3
- x = 2, y = 2, z = 3
- Remember that the equal sign doesn't mean that the two sides are equal. It sets the value for the variable on the left to the value from evaluating the right side.
- x = 1, y = 0, z = 3
1.4.3. Operators ¶
Java uses the standard mathematical operators for addition ( + ), subtraction ( - ), multiplication ( * ), and division ( / ). Arithmetic expressions can be of type int or double. An arithmetic operation that uses two int values will evaluate to an int value. An arithmetic operation that uses at least one double value will evaluate to a double value. (You may have noticed that + was also used to put text together in the input program above – more on this when we talk about strings.)
Java uses the operator == to test if the value on the left is equal to the value on the right and != to test if two items are not equal. Don’t get one equal sign = confused with two equal signs == ! They mean different things in Java. One equal sign is used to assign a value to a variable. Two equal signs are used to test a variable to see if it is a certain value and that returns true or false as you’ll see below. Use == and != only with int values and not doubles because double values are an approximation and 3.3333 will not equal 3.3334 even though they are very close.
Run the code below to see all the operators in action. Do all of those operators do what you expected? What about 2 / 3 ? Isn’t surprising that it prints 0 ? See the note below.
When Java sees you doing integer division (or any operation with integers) it assumes you want an integer result so it throws away anything after the decimal point in the answer, essentially rounding down the answer to a whole number. If you need a double answer, you should make at least one of the values in the expression a double like 2.0.
With division, another thing to watch out for is dividing by 0. An attempt to divide an integer by zero will result in an ArithmeticException error message. Try it in one of the active code windows above.
Operators can be used to create compound expressions with more than one operator. You can either use a literal value which is a fixed value like 2, or variables in them. When compound expressions are evaluated, operator precedence rules are used, so that *, /, and % are done before + and -. However, anything in parentheses is done first. It doesn’t hurt to put in extra parentheses if you are unsure as to what will be done first.
In the example below, try to guess what it will print out and then run it to see if you are right. Remember to consider operator precedence .
1-4-15: Consider the following code segment. Be careful about integer division.
What is printed when the code segment is executed?
- 0.666666666666667
- Don't forget that division and multiplication will be done first due to operator precedence.
- Yes, this is equivalent to (5 + ((a/b)*c) - 1).
- Don't forget that division and multiplication will be done first due to operator precedence, and that an int/int gives an int result where it is rounded down to the nearest int.
1-4-16: Consider the following code segment.
What is the value of the expression?
- Dividing an integer by an integer results in an integer
- Correct. Dividing an integer by an integer results in an integer
- The value 5.5 will be rounded down to 5
1-4-17: Consider the following code segment.
- Correct. Dividing a double by an integer results in a double
- Dividing a double by an integer results in a double
1-4-18: Consider the following code segment.
- Correct. Dividing an integer by an double results in a double
- Dividing an integer by an double results in a double
1.4.4. The Modulo Operator ¶
The percent sign operator ( % ) is the mod (modulo) or remainder operator. The mod operator ( x % y ) returns the remainder after you divide x (first number) by y (second number) so 5 % 2 will return 1 since 2 goes into 5 two times with a remainder of 1. Remember long division when you had to specify how many times one number went into another evenly and the remainder? That remainder is what is returned by the modulo operator.

Figure 2: Long division showing the whole number result and the remainder ¶
In the example below, try to guess what it will print out and then run it to see if you are right.
The result of x % y when x is smaller than y is always x . The value y can’t go into x at all (goes in 0 times), since x is smaller than y , so the result is just x . So if you see 2 % 3 the result is 2 .
1-4-21: What is the result of 158 % 10?
- This would be the result of 158 divided by 10. modulo gives you the remainder.
- modulo gives you the remainder after the division.
- When you divide 158 by 10 you get a remainder of 8.
1-4-22: What is the result of 3 % 8?
- 8 goes into 3 no times so the remainder is 3. The remainder of a smaller number divided by a larger number is always the smaller number!
- This would be the remainder if the question was 8 % 3 but here we are asking for the reminder after we divide 3 by 8.
- What is the remainder after you divide 3 by 8?
1.4.5. FlowCharting ¶
Assume you have 16 pieces of pizza and 5 people. If everyone gets the same number of slices, how many slices does each person get? Are there any leftover pieces?
In industry, a flowchart is used to describe a process through symbols and text. A flowchart usually does not show variable declarations, but it can show assignment statements (drawn as rectangle) and output statements (drawn as rhomboid).
The flowchart in figure 3 shows a process to compute the fair distribution of pizza slices among a number of people. The process relies on integer division to determine slices per person, and the mod operator to determine remaining slices.
Figure 3: Example Flow Chart ¶
A flowchart shows pseudo-code, which is like Java but not exactly the same. Syntactic details like semi-colons are omitted, and input and output is described in abstract terms.
Complete the program based on the process shown in the Figure 3 flowchart. Note the first line of code declares all 4 variables as type int. Add assignment statements and print statements to compute and print the slices per person and leftover slices. Use System.out.println for output.

1.4.6. Storing User Input in Variables ¶
Variables are a powerful abstraction in programming because the same algorithm can be used with different input values saved in variables.

Figure 4: Program input and output ¶
A Java program can ask the user to type in one or more values. The Java class Scanner is used to read from the keyboard input stream, which is referenced by System.in . Normally the keyboard input is typed into a console window, but since this is running in a browser you will type in a small textbox window displayed below the code. The code below shows an example of prompting the user to enter a name and then printing a greeting. The code String name = scan.nextLine() gets the string value you enter as program input and then stores the value in a variable.
Run the program a few times, typing in a different name. The code works for any name: behold, the power of variables!
Run this program to read in a name from the input stream. You can type a different name in the input window shown below the code.
Try stepping through the code with the CodeLens tool to see how the name variable is assigned to the value read by the scanner. You will have to click “Hide CodeLens” and then “Show in CodeLens” to enter a different name for input.
The Scanner class has several useful methods for reading user input. A token is a sequence of characters separated by white space.
Method | Description |
|---|---|
nextLine() | Scans all input up to the line break as a String |
next() | Scans the next token of the input as a String |
nextInt() | Scans the next token of the input as an int |
nextDouble() | Scans the next token of the input as a double |
nextBoolean() | Scans the next token of the input as a boolean |
Run this program to read in an integer from the input stream. You can type a different integer value in the input window shown below the code.
A rhomboid (slanted rectangle) is used in a flowchart to depict data flowing into and out of a program. The previous flowchart in Figure 3 used a rhomboid to indicate program output. A rhomboid is also used to denote reading a value from the input stream.

Figure 5: Flow Chart Reading User Input ¶
Figure 5 contains an updated version of the pizza calculator process. The first two steps have been altered to initialize the pizzaSlices and numPeople variables by reading two values from the input stream. In Java this will be done using a Scanner object and reading from System.in.
Complete the program based on the process shown in the Figure 5 flowchart. The program should scan two integer values to initialize pizzaSlices and numPeople. Run the program a few times to experiment with different values for input. What happens if you enter 0 for the number of people? The program will bomb due to division by zero! We will see how to prevent this in a later lesson.
The program below reads two integer values from the input stream and attempts to print the sum. Unfortunately there is a problem with the last line of code that prints the sum.
Run the program and look at the result. When the input is 5 and 7 , the output is Sum is 57 . Both of the + operators in the print statement are performing string concatenation. While the first + operator should perform string concatenation, the second + operator should perform addition. You can force the second + operator to perform addition by putting the arithmetic expression in parentheses ( num1 + num2 ) .
More information on using the Scanner class can be found here https://www.w3schools.com/java/java_user_input.asp
1.4.7. Programming Challenge : Dog Years ¶
In this programming challenge, you will calculate your age, and your pet’s age from your birthdates, and your pet’s age in dog years. In the code below, type in the current year, the year you were born, the year your dog or cat was born (if you don’t have one, make one up!) in the variables below. Then write formulas in assignment statements to calculate how old you are, how old your dog or cat is, and how old they are in dog years which is 7 times a human year. Finally, print it all out.
Calculate your age and your pet’s age from the birthdates, and then your pet’s age in dog years. If you want an extra challenge, try reading the values using a Scanner.
1.4.8. Summary ¶
Arithmetic expressions include expressions of type int and double.
The arithmetic operators consist of +, -, * , /, and % (modulo for the remainder in division).
An arithmetic operation that uses two int values will evaluate to an int value. With integer division, any decimal part in the result will be thrown away, essentially rounding down the answer to a whole number.
An arithmetic operation that uses at least one double value will evaluate to a double value.
Operators can be used to construct compound expressions.
During evaluation, operands are associated with operators according to operator precedence to determine how they are grouped. (*, /, % have precedence over + and -, unless parentheses are used to group those.)
An attempt to divide an integer by zero will result in an ArithmeticException to occur.
The assignment operator (=) allows a program to initialize or change the value stored in a variable. The value of the expression on the right is stored in the variable on the left.
During execution, expressions are evaluated to produce a single value.
The value of an expression has a type based on the evaluation of the expression.
- Assignment Statement
An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program .
Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted by a variable name.

The symbol used in an assignment statement is called as an operator . The symbol is ‘=’ .
Note: The Assignment Operator should never be used for Equality purpose which is double equal sign ‘==’.
The Basic Syntax of Assignment Statement in a programming language is :
variable = expression ;
variable = variable name
expression = it could be either a direct value or a math expression/formula or a function call
Few programming languages such as Java, C, C++ require data type to be specified for the variable, so that it is easy to allocate memory space and store those values during program execution.
data_type variable_name = value ;
In the above-given examples, Variable ‘a’ is assigned a value in the same statement as per its defined data type. A data type is only declared for Variable ‘b’. In the 3 rd line of code, Variable ‘a’ is reassigned the value 25. The 4 th line of code assigns the value for Variable ‘b’.
Assignment Statement Forms
This is one of the most common forms of Assignment Statements. Here the Variable name is defined, initialized, and assigned a value in the same statement. This form is generally used when we want to use the Variable quite a few times and we do not want to change its value very frequently.
Tuple Assignment
Generally, we use this form when we want to define and assign values for more than 1 variable at the same time. This saves time and is an easy method. Note that here every individual variable has a different value assigned to it.
(Code In Python)
Sequence Assignment
(Code in Python)
Multiple-target Assignment or Chain Assignment
In this format, a single value is assigned to two or more variables.
Augmented Assignment
In this format, we use the combination of mathematical expressions and values for the Variable. Other augmented Assignment forms are: &=, -=, **=, etc.
Browse more Topics Under Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Concept of Data types
- Built-in Data Types
- Constants in Programing Language
- Access Modifier
- Variables of Built-in-Datatypes
- Declaration/Initialization of Variables
- Type Modifier
Few Rules for Assignment Statement
Few Rules to be followed while writing the Assignment Statements are:
- Variable names must begin with a letter, underscore, non-number character. Each language has its own conventions.
- The Data type defined and the variable value must match.
- A variable name once defined can only be used once in the program. You cannot define it again to store other types of value.
- If you assign a new value to an existing variable, it will overwrite the previous value and assign the new value.
FAQs on Assignment Statement
Q1. Which of the following shows the syntax of an assignment statement ?
- variablename = expression ;
- expression = variable ;
- datatype = variablename ;
- expression = datatype variable ;
Answer – Option A.
Q2. What is an expression ?
- Same as statement
- List of statements that make up a program
- Combination of literals, operators, variables, math formulas used to calculate a value
- Numbers expressed in digits
Answer – Option C.
Q3. What are the two steps that take place when an assignment statement is executed?
- Evaluate the expression, store the value in the variable
- Reserve memory, fill it with value
- Evaluate variable, store the result
- Store the value in the variable, evaluate the expression.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Data Types, Variables and Constants
- Variables in Programming Language
- Concept of Data Types
- Declaration of Variables
- Type Modifiers
- Access Modifiers
- Constants in Programming Language
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


1.7 Java | Assignment Statements & Expressions
An assignment statement designates a value for a variable. An assignment statement can be used as an expression in Java.
After a variable is declared, you can assign a value to it by using an assignment statement . In Java, the equal sign = is used as the assignment operator . The syntax for assignment statements is as follows:
An expression represents a computation involving values, variables, and operators that, when taking them together, evaluates to a value. For example, consider the following code:
You can use a variable in an expression. A variable can also be used on both sides of the = operator. For example:
In the above assignment statement, the result of x + 1 is assigned to the variable x . Let’s say that x is 1 before the statement is executed, and so becomes 2 after the statement execution.
To assign a value to a variable, you must place the variable name to the left of the assignment operator. Thus the following statement is wrong:
Note that the math equation x = 2 * x + 1 ≠ the Java expression x = 2 * x + 1

Which is equivalent to:
And this statement
is equivalent to:
Note: The data type of a variable on the left must be compatible with the data type of a value on the right. For example, int x = 1.0 would be illegal, because the data type of x is int (integer) and does not accept the double value 1.0 without Type Casting .
◄◄◄BACK | NEXT►►►
What's Your Opinion? Cancel reply
Enhance your Brain
Subscribe to Receive Free Bio Hacking, Nootropic, and Health Information
HTML for Simple Website Customization My Personal Web Customization Personal Insights
DISCLAIMER | Sitemap | ◘

HTML for Simple Website Customization My Personal Web Customization Personal Insights SEO Checklist Publishing Checklist My Tools
Top Posts & Pages
Variable Assignment
To "assign" a variable means to symbolically associate a specific piece of information with a name. Any operations that are applied to this "name" (or variable) must hold true for any possible values. The assignment operator is the equals sign which SHOULD NEVER be used for equality, which is the double equals sign.
The '=' symbol is the assignment operator. Warning, while the assignment operator looks like the traditional mathematical equals sign, this is NOT the case. The equals operator is '=='
Design Pattern
To evaluate an assignment statement:
- Evaluate the "right side" of the expression (to the right of the equal sign).
- Once everything is figured out, place the computed value into the variables bucket.
We've already seen many examples of assignment. Assignment means: "storing a value (of a particular type) under a variable name" . Think of each assignment as copying the value of the righthand side of the expression into a "bucket" associated with the left hand side name!
Read this as, the variable called "name" is "assigned" the value computed by the expression to the right of the assignment operator ('=');
Now that you have seen some variables being assigned, tell me what the following code means?
The answer to above questions: the assignment means that lkjasdlfjlskdfjlksjdflkj is a variable (a really badly named one), but a variable none-the-less. jlkajdsf and lkjsdflkjsdf must also be variables. The sum of the two numbers held in jlkajdsf and lkjsdflkjsdf is stored in the variable lkjasdlfjlskdfjlksjdflkj.
Examples of builtin Data and Variables (and Constants)
For more info, use the "help" command: (e.g., help realmin);
Examples of using Data and Variable
Pattern to memorize, assignment pattern.
The assignment pattern creates a new variable, if this is the first time we have seen the "name", or, updates the variable to a new value!
Read the following code in English as: First, compute the value of the thing to the right of the assignment operator (the =). then store the computed value under the given name, destroying anything that was there before.
Or more concisely: assign the variable "name" the value computed by "right_hand_expression"
- Stack Overflow for Teams Where developers & technologists share private knowledge with coworkers
- Advertising & Talent Reach devs & technologists worldwide about your product, service or employer brand
- OverflowAI GenAI features for Teams
- OverflowAPI Train & fine-tune LLMs
- Labs The future of collective knowledge sharing
- About the company Visit the blog
Collectives™ on Stack Overflow
Find centralized, trusted content and collaborate around the technologies you use most.
Q&A for work
Connect and share knowledge within a single location that is structured and easy to search.
Get early access and see previews of new features.
Best way to do conditional assignment in python
I tend to use this a lot, but it's ugly:
So I wrote this function:
So you can do:
Is there a built-in function for this (similar to ISNULL in T-SQL)?
6 Answers 6
The or operator does what you want:
In fact, it's chainable, like COALESCE (and unlike ISNULL ). The following expression evaluates to the left-most argument that converts to True.
- Thanks. Ha, I was actually trying that but dismissed it when trying 'a = 0 or None' and the console printed nothing. But trying 'a is None' after that gives 'True', plus I want 'None or 0' functionality anyway (getting late) :) By the way, thanks for the quick answer. – crizCraig Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 9:06
- 3 Just for the record, if you're to chain and operator, it will evaluate to right-most argument that converts to True if all arguments or the left-most argument that converts to False if any converts to False. – Michał Bentkowski Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 9:41
- 1 "a = 0 or None" Well of course the console won't print anything, you're assigning the result of 0 or None to a , and variables with None assigned to them don't automatically display None when shown in the console. You have to specifically use repr , str , or print . Or something like that. – JAB Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 14:15
You may use:
If get_something is True in boolean context, its value will be assigned to a . Otherwise - y will be assigned to a .
For more conditional code:
For your code:
With that you can do complex conditions like this:
- 6 Except this calls get_something twice. – Cat Plus Plus Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 9:14
- 1 can put get_somthing into a variable . Just only with OR you cant put conditions to work. – Phyo Arkar Lwin Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 9:17
- 1 Because the builtin or operator is simpler, and doesn't compute the expression twice. The OP is aware of the ternary conditional, buy looked for something simpler. – Beni Cherniavsky-Paskin Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 10:39
You can use a simple or , like so:
I have provided an answer to this question to another user. Check it out here:
Answer to similar question
To respond quickly here, do:
I'm also using the (a,b)[condition based on the value of a] form, saving the result of the get_something() call into a , in the rare cases that are best presented here: http://mail.python.org/pipermail/python-list/2002-September/785515.html
- I see. This would be if you wanted to check a for a more specific condition. But you need two lines so I would go with a = x if condition else y which is more readable. Interesting syntax though. Never seen anything like it :) – crizCraig Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 21:17
- @crizCraig: added a short example – alexandrul Commented Jul 15, 2011 at 21:30
Your Answer
Reminder: Answers generated by artificial intelligence tools are not allowed on Stack Overflow. Learn more
Sign up or log in
Post as a guest.
Required, but never shown
By clicking “Post Your Answer”, you agree to our terms of service and acknowledge you have read our privacy policy .
Not the answer you're looking for? Browse other questions tagged python or ask your own question .
- The Overflow Blog
- Where does Postgres fit in a world of GenAI and vector databases?
- Featured on Meta
- We've made changes to our Terms of Service & Privacy Policy - July 2024
- Bringing clarity to status tag usage on meta sites
- Feedback requested: How do you use tag hover descriptions for curating and do...
- What does a new user need in a homepage experience on Stack Overflow?
- Staging Ground Reviewer Motivation
Hot Network Questions
- How to attach a 4x8 plywood to a air hockey table
- Historical U.S. political party "realignments"?
- My enemy sent me this puzzle!
- How can you trust a forensic scientist to have maintained the chain of custody?
- How bad would near constant dreary/gloomy/stormy weather on our or an Earthlike world be for us and the environment?
- Submitting a paper as a nonacademic practitioner in a field
- How can I draw water level in a cylinder like this?
- Why is Emacs recompiling some packages on every startup?
- Completely introduce your friends
- Can I share a Live Motion Photo as a video?
- Stealth Mosquitoes?
- Iteration Limit for expression involving Gamma functions
- High CPU usage by process with obfuscated name on Linux server – Potential attack?
- What I have to do more to improve my regression model in r
- Is there a one-liner command or tool to create a virtual input device from default output on pipewire?
- What is this strengthening dent called in a sheet metal part?
- How would increasing atomic bond strength affect nuclear physics?
- Why does my PC take a long time to start, then when it's at the login screen it jumps to the desktop instantly?
- Is the theory of ordinals in Cantor normal form with just addition decidable?
- How to justify our beliefs so that it is not circular?
- My colleagues and I are travelling to UK as delegates in an event and the company is paying for all our travel expenses. what documents are required
- How do I safely remove a mystery cast iron pipe in my basement?
- Can a 2-sphere be squashed flat?
- Is it advisable to contact faculty members at U.S. universities prior to submitting a PhD application?
This browser is no longer supported.
Upgrade to Microsoft Edge to take advantage of the latest features, security updates, and technical support.
Writing assignment statements
- 8 contributors
Assignment statements assign a value or expression to a variable or constant . Assignment statements always include an equal sign ( = ).
The following example assigns the return value of the InputBox function to the variable.
The Let statement is optional and is usually omitted. For example, the preceding assignment statement can be written.
The Set statement is used to assign an object to a variable that has been declared as an object. The Set keyword is required. In the following example, the Set statement assigns a range on Sheet1 to the object variable myCell .
Statements that set property values are also assignment statements. The following example sets the Bold property of the Font object for the active cell.
- Visual Basic conceptual topics
Support and feedback
Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation? Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
Was this page helpful?
Additional resources
- Java Course
- Java Arrays
- Java Strings
- Java Collection
- Java 8 Tutorial
- Java Multithreading
- Java Exception Handling
- Java Programs
- Java Project
- Java Collections Interview
- Java Interview Questions
- Spring Boot
Java Assignment Operators with Examples
Operators constitute the basic building block of any programming language. Java too provides many types of operators which can be used according to the need to perform various calculations and functions, be it logical, arithmetic, relational, etc. They are classified based on the functionality they provide.
Types of Operators:
- Arithmetic Operators
- Unary Operators
- Assignment Operator
- Relational Operators
- Logical Operators
- Ternary Operator
- Bitwise Operators
- Shift Operators
This article explains all that one needs to know regarding Assignment Operators.
Assignment Operators
These operators are used to assign values to a variable. The left side operand of the assignment operator is a variable, and the right side operand of the assignment operator is a value. The value on the right side must be of the same data type of the operand on the left side. Otherwise, the compiler will raise an error. This means that the assignment operators have right to left associativity, i.e., the value given on the right-hand side of the operator is assigned to the variable on the left. Therefore, the right-hand side value must be declared before using it or should be a constant. The general format of the assignment operator is,
Types of Assignment Operators in Java
The Assignment Operator is generally of two types. They are:
1. Simple Assignment Operator: The Simple Assignment Operator is used with the “=” sign where the left side consists of the operand and the right side consists of a value. The value of the right side must be of the same data type that has been defined on the left side.
2. Compound Assignment Operator: The Compound Operator is used where +,-,*, and / is used along with the = operator.
Let’s look at each of the assignment operators and how they operate:
1. (=) operator:
This is the most straightforward assignment operator, which is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. This is the basic definition of an assignment operator and how it functions.
Syntax:
Example:
2. (+=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘+’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by adding the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right and then assigning the result to the operand on the left.
Note: The compound assignment operator in Java performs implicit type casting. Let’s consider a scenario where x is an int variable with a value of 5. int x = 5; If you want to add the double value 4.5 to the integer variable x and print its value, there are two methods to achieve this: Method 1: x = x + 4.5 Method 2: x += 4.5 As per the previous example, you might think both of them are equal. But in reality, Method 1 will throw a runtime error stating the “i ncompatible types: possible lossy conversion from double to int “, Method 2 will run without any error and prints 9 as output.
Reason for the Above Calculation
Method 1 will result in a runtime error stating “incompatible types: possible lossy conversion from double to int.” The reason is that the addition of an int and a double results in a double value. Assigning this double value back to the int variable x requires an explicit type casting because it may result in a loss of precision. Without the explicit cast, the compiler throws an error. Method 2 will run without any error and print the value 9 as output. The compound assignment operator += performs an implicit type conversion, also known as an automatic narrowing primitive conversion from double to int . It is equivalent to x = (int) (x + 4.5) , where the result of the addition is explicitly cast to an int . The fractional part of the double value is truncated, and the resulting int value is assigned back to x . It is advisable to use Method 2 ( x += 4.5 ) to avoid runtime errors and to obtain the desired output.
Same automatic narrowing primitive conversion is applicable for other compound assignment operators as well, including -= , *= , /= , and %= .
3. (-=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘-‘ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by subtracting the variable’s value on the right from the current value of the variable on the left and then assigning the result to the operand on the left.
4. (*=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘*’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by multiplying the current value of the variable on the left to the value on the right and then assigning the result to the operand on the left.
5. (/=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘/’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by dividing the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigning the quotient to the operand on the left.
6. (%=) operator:
This operator is a compound of ‘%’ and ‘=’ operators. It operates by dividing the current value of the variable on the left by the value on the right and then assigning the remainder to the operand on the left.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Java-Operators
- How to Get a Free SSL Certificate
- Best SSL Certificates Provider in India
- Elon Musk's xAI releases Grok-2 AI assistant
- What is OpenAI SearchGPT? How it works and How to Get it?
- Content Improvement League 2024: From Good To A Great Article
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

IMAGES
COMMENTS
In this tutorial, you'll learn how to use Python's assignment operators to write assignment statements that allow you to create, initialize, and update variables in your code.
We use Python assignment statements to assign objects to names. The target of an assignment statement is written on the left side of the equal sign (=), and the object on the right can be an arbitrary expression that computes an object.
The assignment operator, denoted by the "=" symbol, is the operator that is used to assign values to variables in Python. The line x=1 takes the known value, 1, and assigns that value to the variable with name "x". After executing this line, this number will be stored into this variable. Until the value is changed or the variable ...
In this tutorial, you used assignment expressions to make compact sections of Python code that assign values to variables inside of if statements, while loops, and list comprehensions.
Conditionally assigning a value in Python is a basic programming task. In this tutorial, we will look at 3 different ways to assign values conditionally in Python.
Write scripts that assign values to variables and perform calculations with those values. Correctly trace value changes in scripts that use assignment.
Once again, just as in mathematics, an expression is a construct of values and variables connected with operators that result in a new value. Lastly, an assignment is a language construct know as an statement that assign a value (either as a constant or expression) to a variable.
Assignment Operators are used to assign values to variables. This operator is used to assign the value of the right side of the expression to the left side operand. Python. # Assigning values using # Assignment Operator a = 3 b = 5 c = a + b # Output print(c) Output.
One should not use this approach if looping through large data sets since it introduces an unnecessary assignment in case we end up in the else-statement.
1.4.1. Assignment Statements ¶. Assignment statements initialize or change the value stored in a variable using the assignment operator =. An assignment statement always has a single variable on the left hand side. The value of the expression (which can contain math operators and other variables) on the right of the = sign is stored in the ...
Assignment (computer science) In computer programming, an assignment statement sets and/or re-sets the value stored in the storage location (s) denoted by a variable name; in other words, it copies a value into the variable. In most imperative programming languages, the assignment statement (or expression) is a fundamental construct.
What are Assignment Operators? Assignment operators are used in programming to assign values to variables. We use an assignment operator to store and update data within a program. They enable programmers to store data in variables and manipulate that data. The most common assignment operator is the equals sign (=), which assigns the value on the right side of the operator to the variable on ...
An assignment statement creates a new variable and gives it a value: This example makes three assignments. The first assigns a string to a new variable named message; the second gives the integer 17 to n; the third assigns the (approximate) value of π π to pi. A common way to represent variables on paper is to write the name with an arrow ...
In this lesson, you will learn about assignment statements and expressions that contain math operators and variables. 1.4.1. Assignment Statements ¶. Remember that a variable holds a value that can change or vary. Assignment statements initialize or change the value stored in a variable using the assignment operator =.
An Assignment statement is a statement that is used to set a value to the variable name in a program. Assignment statement allows a variable to hold different types of values during its program lifespan. Another way of understanding an assignment statement is, it stores a value in the memory location which is denoted.
An assignment statement designates a value for a variable. An assignment statement can be used as an expression in Java. After a variable is declared, you can assign a value to it by using an assignment statement. In Java, the equal sign = is used as the assignment operator. The syntax for assignment statements is as follows: variable ...
To "assign" a variable means to symbolically associate a specific piece of information with a name. Any operations that are applied to this "name" (or variable) must hold true for any possible values. The assignment operator is the equals sign which SHOULD NEVER be used for equality, which is the double equals sign.
Best way to do conditional assignment in python Asked 13 years, 1 month ago Modified 2 years, 7 months ago Viewed 24k times
Assignment statements assign a value or expression to a variable or constant. Assignment statements always include an equal sign ( = ). The following example assigns the return value of the InputBox function to the variable.
This is the most straightforward assignment operator, which is used to assign the value on the right to the variable on the left. This is the basic definition of an assignment operator and how it functions. Syntax:
Assignment statement in C/C++: The assignment statement is used to assign a value (computed from an expression) to a variable Syntax: Variable = Expression ; Notice The expression (value) has a type , and The variable has a type , and The variable can have a different type than the value assigned !!!