

Class 12 Chemistry Case Study Questions Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: Class 12 / 12 board
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Download of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Case Study Questions Haloalkanes and Haloarenes to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: A chlorocompound (A) on reduction with Zn-Cu and ethanol gives the hydrocarbon (B) with five carbon atoms. When (A) is dissolved in dry ether and treated with sodium metal it gave 2,2,5,5 tetramethylhexane. The treatment of (A) with alcoholic KCN gives compound (C).
(i) The compound (A) is
| (a) 1-chloro- 2, 2-dimethylpropane | (b) 1-chloro- 2, 2-dimethyl butane |
| (c) 1-chloro-2-methyl butane | (d) 2-chloro-2-methyl butane. |
Answer: (a) 1-chloro- 2, 2-dimethylpropane.
(ii) The reaction of (C) with Na, C 2 H 5 OH gives
| (a) (CH ) C CH CONH | (b) (CH ) C NH |
| (c) (CH) C CH CH NH | (d) (CH ) CHCH NH |
Answer: (c) (CH)3C CH2CH2NH2
(iii) The reaction of (C) with Na, C 2 H 5 OH is called
| (a) Gilman reaction | (b) Mendius reaction |
| (c) Grooves process | (d) Swart’s reaction. |
Answer: (b) Mendius reaction
(iv) Compound (B) is
| (a) n-pentane | (b) 2, 2-dimethylpropane |
| (c) 2-methylbutane | (d) none of these. |
Answer: (b) 2, 2-dimethylpropane
Case Study 2: Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of two types; substitution nucleophilic bimolecular (SN2) and substitution nucleophilic unimolecular (SN1) depending on molecules taking part in determining the rate of reaction. The reactivity of alkyl halide towards SN1 and SN2 reactions depends on various factors such as steric hindrance, stability of intermediate or transition state and polarity of solvent. SN2 reaction mechanism is favored mostly by primary alkyl halide or transition state and polarity of the solvent, SN2 reaction mechanism is favored mostly by primary alkyl halide then secondary and then tertiary. This order is reversed in the case of SN1 reactions.
(i) Which of the following is most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? (a) C 6 H 5 Cl (b) CH 2 =CHCl (c) ClCH 2 CH=CH 2 (d) CH 3 CH=CHCl
Answer: (c) ClCH2CH=CH2
(ii) Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by (a) S N 1 mechanism (b) S N 2 mechanism (c) S N 1 and S N 2 mechanism (d) neither S N 1 nor S N 2 mechanism
Answer: (c) SN1 and SN2 mechanism
(iii) The most reactive nucleophile among the following is (a) CH 3 O- (b) C 6 H 5 O- (c) (CH 3 ) 2 CHO- (d) (CH 3 ) 3 CO-
Answer: (a) CH3O-
Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing S N 2 reactivity? (a) RCH 2 X > R 2 CHX > R 3 CX (b) R 3 CX > R 2 CHX >RCH 2 X (c) R 2 CHX >R 3 CX > RCH 2 X (d) RCH 2 X >R 3 CX >R 2 CHX
Answer: (a) RCH2X > R2CHX > R3CX
Case Study 3: A primary alkyl halide (A) C 4 H 9 Br reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (B). Compound (B) is reacted with HBr to give compound (C) which is an isomer of (A). When (A) reacted with sodium metal, it gave a compound (D) C 8 H 18 that is different than the compound obtained when n-butyl bromide reacted with sodium metal
(i) Which type of isomerism is present in compounds (A) and (C)?
Answer: (c) Chain
(ii) IUPAC name of compound (D) is
Answer: (c) 2-methyl heptane
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
Class 12 maths: case study of chapter 11 three dimensional geometry pdf download, class 12 chemistry case study questions chapter 7 the p-block elements, cbse class 12 physics term 1 mcq questions with explanations pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Case Study Questions Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry
Case Study Questions Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry
1. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Nucleophilic substitution reactions are of two types; substitution nucleophilic bimolecular (S N 2) and substitution nucleophilic unimolecular (S N 1) depending on molecules taking part in determining the rate of reaction. The reactivity of alkyl halide towards S N 1 and S N 2 reactions depends on various factors such as steric hindrance, stability of intermediate or transition state, and polarity of the solvent. S N 2 reaction mechanism is favoured mostly by primary alkyl halide or transition state and polarity of the solvent, S N 2 reaction mechanism is favoured mostly by primary alkyl halide then secondary and then tertiary. This order is reversed in the case of S N 1 reactions. (i) Which of the following is most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction? (a) C 6 H 5 Cl (b) CH 2 = CHCl (c) ClCH 2 CH = CH 2 (d) CH 3 CH = CHCl
(ii) Isopropyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis by (a) S N 1 mechanism (b) S N 2 mechanism (c) S N 1 and S N 2 mechanism (d) Neither S N 1 nor S N 2 mechanism
(iii) Tertiary alkyl halides are practically inert to substitution by S N 2 mechanism because of (a) Insolubility (b) Instability (c) Inductive effect (d) Steric Hindrance
(iv) Which of the following is the correct order of decreasing S N 2 reactivity? (a) RCH 2 X > R 2 CHX > R 3 CX (b) R 3 CX > R 2 CHX >RCH 2 X (c) R 2 CHX > R 3 CX > RCH 2 X (d) RCH 2 X > R 3 CX > R 2 CHX
(v) An organic molecule necessarily shows optical activity if it- a) Contains asymmetric carbon atoms b) Is non-polar c) Is non-superimposable on its mirror image d) Is superimposable on its mirror image.
2. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: The replacement of hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon, aliphatic or aromatic results in the formation of haloalkanes and haloarenes respectively. Haloalkanes contain a halogen atom attached to sp 3 hybridized carbon atom of an alkyl group whereas haloarenes contain a halogen atom attached to sp 2 hybridized carbon atom of an aryl group. Haloalkanes and haloarenes may be classified on the basis of the number of halogen atoms in their structures as mono, di, or poly halogen compounds and also on the basis of the state of hybridization of the carbon atom to which the halogen atom is bonded. (i) Which of the following halide is 2°? (a) Isopropyl chloride (b) Isobutyl chloride (c) n-propyl chloride (d) n-butyl chloride
(ii) Which of the following is a Gem-dibromide is: (a) CH 3 CH(Br)CH 2 (Br) (b) CH 3 CBr 2 CH 3 (c) CH 2 (Br)CH 2 CH 2 (d) CH 2 BrCH 2 Br
(iii) IUPAC name of (CH 3 ) 3 CCl is: (a) 3-Chlorobutane (b) 2-Chloro-2-methylpropane (c) t-butyl chloride (d) n-butyl chloride
(iv) Which of the following is a primary halide? (a) Isopropyl iodide (b) Secondary butyl iodide (c) Tertiarybutyl bromide (d) Neohexyl chloride
(v) Which one of the following is not an allylic halide? (a) 4-Bromopent-2-ene (b) 3-Bromo-2-methylbut-1-ene (c) 1-Bromobut-2-ene (d) 4-Bromobut-1-ene
3. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Alkyl halides are prepared by the free radical halogenation of alkanes, addition of halogen acids to alkenes, replacement of -OH group of alcohols with halogens using phosphorus halides, thionyl chloride, or halogen acids. Aryl halides are prepared by electrophilic substitution to arene. Fluorine and iodides are best prepared by the halogen exchange method. These compounds find wide applications in industry as well as in day-to-day life. These compounds are generally used as solvents and as starting materials for the synthesis of a large number of organic compounds. (i) The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into an alkyl chloride is by treating the alcohol with (a) PCl 5 (b) Dry HCl in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl 2 (c) SOCl 2 in presence of pyridine (d) None of these
(ii) The catalyst used in the preparation of an alkyl chloride by the action of dry HCl on alcohol is (a) anhydrous AlCl 3 (b) FeCl 3 (c) anhydrous ZnCl 2 (d) Cu
(iii) An alkyl halide reacts with metallic sodium in dry ether. The reaction is known as: (a) Frankland’s reaction (b) Sandmeyer’s reaction (c) Wurtz reaction (d) Kolbe’s reaction
(iv) Fluorobenzene (C 6 H 5 F) can be synthesized in the laboratory (a) By direct fluorination of benzene with F 2 gas (b) By reacting bromobenzene with NaF solution (c) By heating phenol with HF and KF (d) From aniline by diazotization followed by heating the diazonium salt with HBF 4
Related Posts

Solid State Chemistry Class 12 Notes PDF Download

CBSE Sample Paper Session 2022-23 (Chemistry) PDF

Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 – Questions & Answers
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Type above and press Enter to search. Press Esc to cancel.
Not Able To Find Desired Paper or Worksheet SEARCH
Find papers & worksheets search, case study questions for class 12 chemistry chapter 10 haloalkanes and haloarenes.

- (0) Comments
- 9 Downloads
Related Papers
Click to view more related papers, display_name = "class 11" && $paper->display_name = "class 12") { // echo $paper->display_name." questions papers and worksheets"; } //else { // echo $paper->display_name." sample papers and previous year papers"; //} //>, important questions, mcq's, ncert solutions - class 12 chemistry.
Get here all the Important questions for Class 12 Chemistry chapter wise as free PDF download. Here you will get Extra Important Questions with answers, Numericals and Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ's) chapter wise in Printable format. Solving Chapter wise questions is one of the best ways to prepare for the examination. Students are advised to understand the concepts and theories of Chemistry properly before the exam. You can easily find 1 Mark, 2 marks, 3 marks, and 5 marks questions from each chapter of Class 12 Chemistry and prepare for exam more effectively. These preparation material for Class 12 Chemistry , shared by teachers, parents and students, are as per latest NCERT and CBSE Pattern syllabus and assure great success in achieving high score in Final CBSE Board Examinations.
Latest MCQ's and Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry
class 12 chemistry chapter 1 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 2 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 3 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 4 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 5 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 6 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 7 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 8 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 9 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 10 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 11 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 12 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 13 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 14 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 15 important questions with answers class 12 chemistry chapter 16 important questions with answers mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 1 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 2 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 3 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 4 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 5 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 6 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 7 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 8 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 9 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 10 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 11 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 12 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 13 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 14 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 15 mcqs of chemistry class 12 chapter 16 The Solid State Class 12 Case Study Questions Solutions Class 12 Case Study Questions Notes Electrochemistry Class 12 Case Study Questions Chemical Kinetics Class 12 Case Study Questions Surface Notes Class 12 Case Study Questions General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements Class 12 Case Study Questions The p-Block Elements Class 12 Case Study Questions The d and f Block Elements Class 12 Case Study Questions Coordination Compounds Class 12 Case Study Questions Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Case Study Questions Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Class 12 Case Study Questions Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids Class 12 Case Study Questions Amines Class 12 Case Study Questions Biomolecules Class 12 Case Study Questions Polymers Class 12 Case Study Questions Chemistry in Everyday Life Class 12 Case Study Questions
Total Papers :
| Class 12 Chemistry Marks Distribution | |
|---|---|
| Units | Marks |
| Solid State | 23 |
| Solutions | |
| Electrochemistry | |
| Chemical Kinetics | |
| Surface Chemistry | |
| General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements | 19 |
| p- Block Elements | |
| d - and f- Block Elements | |
| Coordination Compounds | |
| Haloalkanes and Haloarenes | 28 |
| Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers | |
| Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids | |
| Organic Compounds containing Nitrogen | |
| Biomolecules | |
| Polymers | |
| Chemistry in Everyday Life | |
| Total | 70 |
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Syllabus
- Solid State
- Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- p-Block Elements
- d- and f-Block Elements
- Coordination Compounds
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes.
- Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Organic compounds containing Nitrogen
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday life
Unit II: Solutions 15 Periods
Types of solutions, expression of concentration of solutions of solids in liquids, solubility of gases in liquids, solid solutions, Raoult's law, colligative properties - relative lowering of vapour pressure, elevation of boiling point, depression of freezing point, osmotic pressure, determination of molecular masses using colligative properties, abnormal molecular mass, Van't Hoff factor.
Unit III: Electrochemistry 18 Periods
Redox reactions, EMF of a cell, standard electrode potential, Nernst equation and its application to chemical cells, Relation between Gibbs energy change and EMF of a cell, conductance in electrolytic solutions, specific and molar conductivity, variations of conductivity with concentration, Kohlrausch's Law, electrolysis and law of electrolysis (elementary idea), dry cell-electrolytic cells and Galvanic cells, lead accumulator, fuel cells, corrosion.
Unit IV: Chemical Kinetics 15 Periods
Rate of a reaction (Average and instantaneous), factors affecting rate of reaction: concentration, temperature, catalyst; order and molecularity of a reaction, rate law and specific rate constant, integrated rate equations and half-life (only for zero and first order reactions), concept of collision theory (elementary idea, no mathematical treatment), activation energy, Arrhenius equation.
Unit VIII: d and f Block Elements 18 Periods
General introduction, electronic configuration, occurrence and characteristics of transition metals, general trends in properties of the first-row transition metals – metallic character, ionization enthalpy, oxidation states, ionic radii, colour, catalytic property, magnetic properties, interstitial compounds, alloy formation, preparation and properties of K2Cr2O7 and KMnO4.
Lanthanoids – Electronic configuration, oxidation states, chemical reactivity and lanthanoid contraction and its consequences.
Actinoids - Electronic configuration, oxidation states and comparison with lanthanoids.
Unit IX: Coordination Compounds 18 Periods
Coordination compounds - Introduction, ligands, coordination number, colour, magnetic properties and shapes, IUPAC nomenclature of mononuclear coordination compounds. Bonding, Werner's theory, VBT, and CFT; structure and stereoisomerism, the importance of coordination compounds (in qualitative analysis, extraction of metals and biological system).
Unit X: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. 15 Periods Haloalkanes: Nomenclature, nature of C–X bond, physical and chemical properties, optical rotation mechanism of substitution reactions.
Haloarenes: Nature of C–X bond, substitution reactions (Directive influence of halogen in monosubstituted compounds only). Uses and environmental effects of - dichloromethane, trichloromethane, tetrachloromethane, iodoform, freons, DDT.
Unit XI: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers 14 Periods
Alcohols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties (of primary alcohols only), identification of primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols, mechanism of dehydration, uses with special reference to methanol and ethanol.
Phenols: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, acidic nature of phenol, electrophilic substitution reactions, uses of phenols.
Ethers: Nomenclature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses.
Unit XII: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids 15 Periods
Aldehydes and Ketones: Nomenclature, nature of carbonyl group, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, mechanism of nucleophilic addition, reactivity of alpha hydrogen in aldehydes, uses.
Carboxylic Acids: Nomenclature, acidic nature, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties; uses.
Unit XIII: Amines 14 Periods
Amines: Nomenclature, classification, structure, methods of preparation, physical and chemical properties, uses, identification of primary, secondary and tertiary amines.
Diazonium salts: Preparation, chemical reactions and importance in synthetic organic chemistry.
Unit XIV: Biomolecules 18 Periods
Carbohydrates - Classification (aldoses and ketoses), monosaccharides (glucose and fructose), D-L configuration oligosaccharides (sucrose, lactose, maltose), polysaccharides (starch, cellulose, glycogen); Importance of carbohydrates.
Proteins - Elementary idea of - amino acids, peptide bond, polypeptides, proteins, structure of proteins - primary, secondary, tertiary structure and quaternary structures (qualitative idea only), denaturation of proteins; enzymes. Hormones - Elementary idea excluding structure.
Vitamins - Classification and functions. Nucleic Acids: DNA and RNA.
Structure of CBSE Chemistry Sample Paper for Class 12 Science is
| Type of Question | Marks per Question | Total No. of Questions | Total Marks |
|---|---|---|---|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions | 1 | 5 | 5 |
| Short Answer Type Questions - 1 | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| Short Answer Type Questions - 2 | 3 | 12 | 36 |
| Value Based Type Questions | 4 | - | 4 |
| Long Answer Type Questions | 3 | 5 | 15 |
| Total | 26 | 70 | |
For Preparation of exams students can also check out other resource material
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Sample Papers
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Worksheets
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Question Papers
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Test Papers
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Revision Notes
Question Bank of Other Subjects of Class 12
Importance of Question Bank for Exam Preparation?
There are many ways to ascertain whether a student has understood the important points and topics of a particular chapter and is he or she well prepared for exams and tests of that particular chapter. Apart from reference books and notes, Question Banks are very effective study materials for exam preparation. When a student tries to attempt and solve all the important questions of any particular subject , it becomes very easy to gauge how much well the topics have been understood and what kind of questions are asked in exams related to that chapter.. Some of the other advantaging factors of Question Banks are as follows
- Since Important questions included in question bank are collections of questions that were asked in previous exams and tests thus when a student tries to attempt them they get a complete idea about what type of questions are usually asked and whether they have learned the topics well enough. This gives them an edge to prepare well for the exam.Students get the clear idea whether the questions framed from any particular chapter are mostly either short or long answer type questions or multiple choice based and also marks weightage of any particular chapter in final exams.
- CBSE Question Banks are great tools to help in analysis for Exams. As it has a collection of important questions that were asked previously in exams thereby it covers every question from most of the important topics. Thus solving questions from the question bank helps students in analysing their preparation levels for the exam. However the practice should be done in a way that first the set of questions on any particular chapter are solved and then solutions should be consulted to get an analysis of their strong and weak points. This ensures that they are more clear about what to answer and what can be avoided on the day of the exam.
- Solving a lot of different types of important questions gives students a clear idea of what are the main important topics of any particular chapter that needs to focussed on from examination perspective and should be emphasised on for revision before attempting the final paper. So attempting most frequently asked questions and important questions helps students to prepare well for almost everything in that subject.
- Although students cover up all the chapters included in the course syllabus by the end of the session, sometimes revision becomes a time consuming and difficult process. Thus, practicing important questions from Question Bank allows students to check the preparation status of each and every small topic in a chapter. Doing that ensures quick and easy insight into all the important questions and topics in each and every individual. Solving the important questions also acts as the revision process.
Question Bank of Other Classes
To Prepare better for CBSE paperclass; ?> " title="Download Free CBSE Papers">Ribblu.com brings to you all the previous years papers & worksheets of subject; ?//> for CBSE paperclass; ?>. This CBSE paper and worksheet can be instrumental in students achieving maximum marks in their exams. These Papers and worksheets help students gain confidence and make them ready to face their school examinations. These Papers and worksheets school wise, covers important concepts from an examination perspective. Students and parents can download all the available papers & worksheets directly in the form of PDF. One can use these papers and worksheets to get extensive practice and familiarise themselves with the format of the question paper.
You can help other users
Be the first to write comment .
Upload papers and the more your paper get downloaded the more you earn the points
You may send papers on email [email protected] along with userid
- Downloaded by: Priyanka Sharma
- Downloaded by: Minakshi Hase
- Downloaded by: Rayasha
Rules and regulations for uploads
| 1. | The uploaded material should be original and not duplicated. |
| 2. | It should be clear, legible and genuine. The file type should be pdf for multiple pages and jpg is allowed only for single page document. Use apps like “cam scanner” for mobile capture, crop and edit photos and save it as pdf. One file should be complete in all aspects like one full question paper, Notes of a complete topic. File name should be self explanatory (eg. CBSE 10th 2012 hindi question paper by – ‘Name of the uploader’) |
| 3. | No copyright violations allowed. |
| 4. | Points and coupons will be given at the sole discretion of Ribblu. |
| 5. | Ribblu admin has the power to reject, remove, alter, approve, accept any material that is uploaded by the user without consent of owner. |
Write your comment
Report this paper, how to earn points.
Upload Papers / Worksheets and Earn 50 Points.
The uploaded material should be original paper or worksheet of any school. Check out some videos on how to upload papers on ribblu
Rate & Review your school and Earn 25 Points.
Review any school that you may be knowing and once your review is approved, you will be credited with 25 points.
Answer on question posted on JustAsk and earn 15 points.
JustAsk is a platform where you can help others to find answers of any question. Share your Knowledge. Answer questions and once approved you will earn 15 points
Complete your profile and earn upto 25 Points.
Edit and complete your user profile and earn points. The more details you submit, the more points you will earn.
Download Ribblu Mobile App and you will (Earn 20 Points) (one time only)
CBSE Schools
- CBSE Schools In Delhi
- CBSE Schools In Noida
- CBSE Schools In Greater Noida
- CBSE Schools In Faridabad
- CBSE Schools In Ghaziabad
- CBSE Schools In Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools In Mumbai
- CBSE Schools In Pune
- CBSE Schools In Bangalore
- CBSE Schools In Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools In Kolkata
- CBSE Schools In Chennai
- CBSE Schools In Patna
- CBSE Schools In Meerut
- CBSE Schools In Kanpur
- CBSE Schools In Indore
- CBSE Schools In Ludhiana
- CBSE Schools In Dehradun
Top Schools
- Schools In Delhi
- Schools In Noida
- Schools In Greater Noida
- Schools In Faridabad
- Schools In Ghaziabad
- Schools In Gurgaon
- Schools In Mumbai
- Schools In Pune
- Schools In Bangalore
- Schools In Hyderabad
- Schools In Kolkata
- Schools In Chennai
- Schools In Patna
- Schools In Meerut
- Schools In Kanpur
- Schools In Indore
- Schools In Ludhiana
- Schools In Dehradun
Other Schools
- Pre Nursery Schools In Noida
- Day Boarding Schools In Noida
- Pre Nursery Schools In Gurgaon
- Pre Nursery Schools In Delhi
- Play Schools In Delhi
- Day Boarding Schools In Delhi
CBSE Papers
- CBSE Class 1 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 2 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 3 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 4 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 5 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 6 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 7 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 8 Sample Papers
Paper Categories
- Question Bank
- Question Papers
- Revision Notes
- Sample Papers
- Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers

NCERT Solutions for Class 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11 and 12
NCERT Solutions For Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Read also Haloalkanes and Haloarenes NCERT Solutions
Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes :
| 10 | Haloalkanes and Haloarenes |
| 10.1 | Classification |
| 10.2 | Nomenclature |
| 10.3 | Nature of C–X Bond |
| 10.4 | Methods of Preparation of Haloalkanes |
| 10.5 | Preparation of Haloarenes |
| 10.6 | Physical Properties |
| 10.7 | Chemical Reactions |
NCERT Solutions CBSE Sample Papers Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry
NCERT IN TEXT QUESTIONS
10.6. Arrange each set of compounds in order of increasing boiling points : (i) Bromomethane, bromoform, chloromethane, dibromomethane (ii) 1- Chloropropane, isopropylchloride, 1- chlorobutane. Ans: (i) The boiling points of organic compounds are linked with the van der Waals’ forces of attraction which depend upon the molecular size. In the present case, all the compounds contain only one carbon atom. The molecular size depends upon size of the halogen atom and also upon the number of halogen atoms present in different molecules. The increasing order of boiling points is : CH 3 Cl(chloromethane) < CH 3 Br (bromomethane) < CH 2 Br 2 (dibromomethane) < CHBr 3 (bromoform)
(ii) The same criteria is followed in this case. We all know that the branching of the carbon atom chain decreases the size of the isomer and this decreases its boiling point as compared to straight chain isomer. The increasing order of boiling point is : (CH 3 ) 2 CHCl (isopropylchloride or 2-chloropropane) < ClCH 2 CH 2 CH 3 (1-chloropropane) < ClCH 2 CH 2 CH 2 CH 3 (1-chlorobutane)
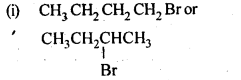
NCERT EXERCISES
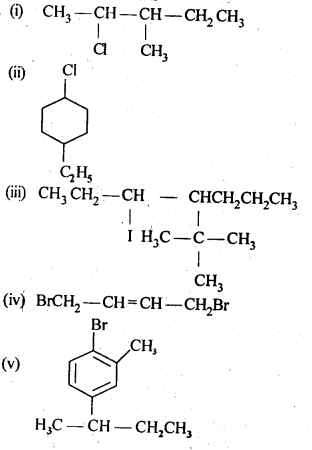
10.1. Name the following halides according to the IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl (primary, secondary, tertiary), vinyl, or aryl halides: (i)(CH 3 )2CHCH(Cl)CH 3 (ii) CH 3 CH 2 CH(CH 3 )CH(C 2 H 5 )CI (iii) CH 3 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 2 CH 2 I (iv)(CH 3 )3CCH 2 CH(Br)C6H 5 (v)CH 3 CH(CH 3 )CH(Br)CH 3 (vi)CH 3 C(C2H 5 ) 2 CH2Br (vii)CH 3 C(Cl)(C 2 H 5 )CH 2 CH 3 (viii)CH 3 CH=C(CI)CH 2 CH(CH 3 ) 2 (ix)CH 3 CH=CHC(Br)(CH 3 ) 2 (x)P-CIC 6 H 4 CH 2 CH(CH 3 ) 2 (xi)m-ClCH 2 C 6 H 4 CH 2 C(CH 3 ) 3 (xii)o-Br -C 6 H 4 CH (CH 3 )CH 2 CH 3 Ans: (i) 2-Chloro-3methylbutane, 2° alkyl halide (ii) 3-Chloro-4methyl hexane, 2° alkyl halide (iii) 1 -Iodo-2,2-dimethylbutane, 1 ° alkyl halide (iv) l-Bromo-3, 3-dimethyl -1-phenylbutane, 2° benzylic halide (v) 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane, 2° alkyl halide (vi) 1-Bromo-2-ethyI-2-methylbutane, 1° alkyl halide (vii)3-Chloro-3-methylpentane, 3° alkyl halide (viii) 3-Chloro-5-methylhex-2-ene, vinylic halide (ix)4-Bromo-4-methylpent-2-ene, allylic halide (x)1-Chloro-4-(2-methylpropyl) benzene, aryl halide (xi)1-Chloromethyl-3- (2,2-dimethylpropyl) benzene, 1 ° benzylic halide. (xii)1-Bromo-2-(l-methylpropyl) benzene,aryl halide.
10.2. Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds: (i) CH 3 CH(CI)CH (Br)CH 3 (ii) CHF 2 CBrCIF (iii) CICH 2 C=CCH 2 Br (iv) (CCl 3 ) 3 CCl (v)CH 3 C(p-ClC 6 H 4 ) 2 CH(Br)CH 3 (vi)(CH 3 ) 3 CCH=C(CI)C 6 H 4 I -p Ans: (i) 2-Bromo-3-chlorobutane (ii) 1 JBromo-1 -chloro-1,2,2-trifluoroethane (iii) l-Bromo-4-chlorobut-2-yne (iv)2-(Trichloromethyl)-l, 1,1,2,3,3,3- heptachloropropane (v)2-Bromo-3,3-bis-(4-chlorophenyl) butane (vi)l-Chloro-l-(4-iodophenyl)-3,3- dimethylbut-l-ene.
10.9. Which compound in each of the following-pairs . will react faster in SN2 reaction with -OH? (i)CH 3 Br or CH 3 I (ii)(CH 3 ) 3 CCl or CH 3 Cl Ans: (i)Since I – ion is a better leaving group than Br- ion, therefore, CH 3 I reacts faster CH 3 Br in S N 2 reaction with OH – ion. (ii)On steric grounds, 1° alkyl halides are more reactive than tert-alkyl halides in S N 2 reactions. Therefore, CH 3 CI will react at a faster rate than (CH 3 ) 3 CCl in a S N 2 reaction with OH – ion.
10.12. Explain why (i) the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride? (ii) alkyl halides, though polar, are immiscible with water? (iii) Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions? Ans: (i) sp 2 -hybrid carbon in chlorobenzene is more electronegative than a sp 3 -hybrid carbon in cyclohexylchloride, due to greater s-character. Thus, C atom of chlorobenzene has less tendency to release electrons to Cl than carbon atom of cyclohexylchloride. As a result, C – Cl bond in chlorobenzene is less polar than in cyclohexylchloride. Further, due to delocalization of lone pairs of electrons of the Cl atom over the benzene ring, C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene acquires some double bond character while the C – Cl in cyclohexy! chloride is a pure single bond. In other words, C-Cl bond in chlorobenzene is shorter than in cyclohexyl chloride. Since dipole moment is a product of charge and distance, therefore, chlorobenzene has lower dipole moment than cyclohexylchloride due to lower magnitude of negative charge on the Cl atom and shorter C-Cl distance.
(ii) Alkyl halides are polar molecules, therefore, their molecules are held together by dipole-dipole attraction. The molecules of H 2 O are hold together by H-bonds. Since the new forces of attraction between water and alkyl halide molecules are weaker than the forces of attraction already existing between alkyl halide – alkyl halide molecules and water-water molecules, thefefore, alkyl halides are immiscible (not soluble) in water. Alkyl halide are neither able to form H- bonds with water nor are able to break the H-bounding network of water.
10.13. Give the uses of freon 12, DDT, carbon tetrachloride, and iodoform. Ans: Iodoform: It was earlier used as an antiseptic but the antiseptic properties are due to the liberation of free iodine and not due to iodoform itself. Due to its objectionable smell, it has been replaced by other formulations containing iodine. Carbon tetrachloride: Uses: (i)As an industrial solvent for oil, fats, resins etc.and also in dry cleaning. (ii)CCl 4 vapours are highly non-inflammable, thus CCl 4 is used as a fire extinguisher under the name pyrene. (iii)Used in the manufacture of refrigerants and propellants for aerosol cans. Freons: Freon-12 (CCl 2 F 2 ) is most common freons in industrial use. Uses: For aerosol propellants, refrigeration, and air conditioning purposes. DDT (p -p’ – Dichloro diphenyl – trichloro ethane): (i)The use of DDT increased enormously on a worldwide basis after World War II, primarily because of its effectiveness against the mosquitoes that spreads malaria and other insects which damages crops.
(ii) However, problems related to extensive use of DDT began to appear in the late 1940 s. Many species of insects developed resistance to DDT, it was also discovered to have a high toxicity towards fishes. DDT is not metabolised very rapidly by animals, instead, it is deposited and stored in the fatty tissues. If the ingestion continues at a steady rate, DDT builds up within the animal’s overtime.
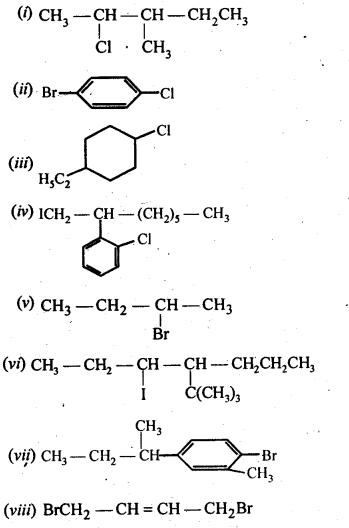
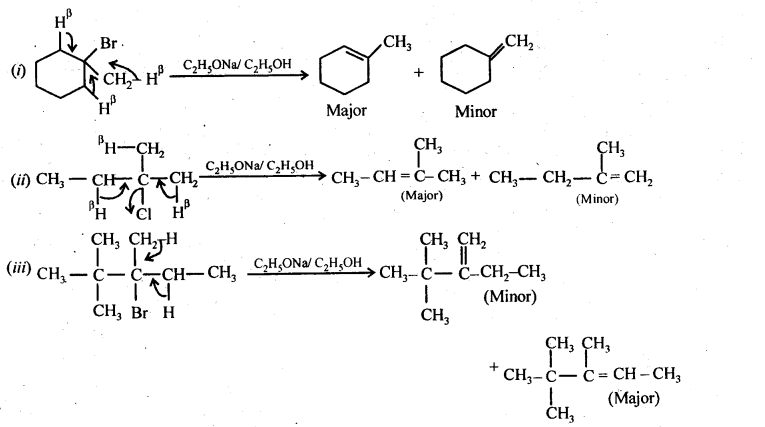
10.20. The treatment of alkyl chlorides with aqueous KOH leads to the formation of alcohols but in presence of alcoholic KOH, alkenes are major products. Explain. (Pb. Board 2009, Haryana Board 2013) Answer: In aqueous medium i.e., water, KOH will be completely dissociated to give OH – ions. They being a strong nucleophile, will bring about the substitution of alkyl halides to form alcohols. At the same time, the OH” ions will be highly hydrated also. They will not be able to abstract a proton (H + ) from the p-carbon atom to form alkenes. In other words, in aqueous medium, OH – ions will behave as weak base and elimination leading to alkenes will not be feasible. In alcoholic KOH, the solution will also contain ethoxide ions (C 2 H 5 O – ) in addition to OH – ions. They being a stronger base than OH – ions, will abstract a H + ion from the β-carbon atom giving alkene as the product as a result of dehydrohalogenation.
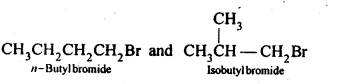
More Resources for CBSE Class 12:
- CBSE Class 12 Maths
- RD Sharma class 12 Solutions
- CBSE Class 12th English Flamingo
- CBSE Class 12th English Vistas
- CBSE Class 12 Accountancy
- CBSE Sample Papers For Class 12
NCERT Solutions Maths Physics Chemistry Biology Science
Free Resources
NCERT Solutions
Quick Resources
- Class 12 Chemistry Mcqs
- Class 12 Chemistry Mcqs Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs
Class 12 chemistry MCQs with answers are provided here for chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. These MCQs are based on the CBSE board curriculum and correspond to the most recent Class 12 chemistry syllabus. By practising these Class 12 Multiple choice questions, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Annual examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE.
Download Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs PDF by clicking on the button below. Download PDF
Class 12 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs
1. What is the class of the substitution product of LiAlH 4 and an alkyl halide reaction?
a) Haloalkane
b) Alkyl nitrite
c) Nitroalkane
d) Hydrocarbon
Explanation : The H atom in LiAlH 4 acts as a nucleophile, attacking and substituting the halogen in the alkyl halide to generate the basic hydrocarbon.
2. Which of the following statements about SN 2 mechanisms is incorrect?
a) The transition state is stable
b) The complete mechanism takes place in a single step
c) The rate of the reaction depends on the concentration of both reactants
d) There is an inversion of configuration
Explanation : The carbon atoms are concurrently attached to the entering nucleophile and the existing group in the transition state of SN 2 processes, and are thus connected to five atoms at the same time. It is impossible to isolate such a geometry since it is unstable.
3. A mono haloarene is an example of __________
a) aliphatic halogen compound
b) side-chain substituted aryl halide
c) alkyl halide
d) aromatic halogen compound
Explanation : A mono haloarene is a halogenated benzene ring with the halogen linked straight to it. Aromatic halogen compounds with the halogen not directly linked to the benzene ring are side chain substituted aryl halides.
4. What is 3-Bromopropene’s common name?
a) Allyl bromide
b) Vinyl bromide
c) Tert-Butyl bromide
d) Propylidene bromide
Explanation : The parent chain of 3-Bromopropene has three C atoms, with a double bond at C-1 and Br at C-3. As a result, it is an allylic halide because Br is connected to the C adjacent to the C-C double bond.
5. Which of the following is the right name for the compound H 3 C-CHCl 2 ?
a) 1,2-Dichloroethane
b) Ethylene dichloride
c) Ethylidene chloride
d) Vic-dichloride
Explanation : Both halogens are on the same carbon atom in the given molecule, making it a dihaloalkane. These are also known as alkylidene halides or gem-dihalides.
6. What is the catalyst in the chloroalkane reaction of a primary alcohol with HCl?
a) red phosphorous
b) concentrated H 2 SO 4
c) anhydrous ZnCl 2
d) pyridine
Explanation : The presence of anhydrous ZnCl 2 in alcohols is supposed to disrupt the C-O bond. ZnCl 2 is a Lewis acid that reacts with the alcohol group’s oxygen.
7. When ethanol combines with PCl 5 , it produces three products: chloroethane, hydrochloric acid, and ______. What is the third item on the list?
a) Phosphorus acid
b) Phosphoryl chloride
c) Phosphorus trichloride
d) Phosphoric acid
Explanation : CH 3 CH 2 OH reacts with PCl 5 to produce CH 3 CH 2 Cl, POCl 3 (phosphoryl acid), and HCl. This is a procedure for making chloroalkanes from alcohols.
8. Which of the following substances has the highest melting point?
a) Chloromethane
b) Tetrachloromethane
c) Trichloromethane
d) Dichloromethane
Explanation : As the molecule masses and the number of halogen atoms grows, the boiling points and intermolecular forces of attraction increase as well.
9. Which sequence should isomeric dichlorobenzenes be boiled in?
a) para>ortho>meta
b) meta>ortho>para
c) ortho>meta>para
d) para>meta>ortho
Explanation : In comparison to meta and ortho isomers, para isomers have the highest melting temperatures due to their symmetry and ease of fitting into a crystal lattice.
10. Which of the following statements about the interaction between C 2 H 4 and Cl 2 in CCl 4 is incorrect?
a) It results in the formation of a vicinal dihalide
b) It results in the discharge of a reddish-brown colour
c) It results in the formation of a colourless compound
d) It results in the breaking of the C-C double bond
Explanation : When Br 2 interacts with an alkene to generate a vic-dihalide, it gives off a reddish-brown colour. As a result, it’s a crucial test for detecting a double bond.
| CHEMISTRY Related Links | |

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- School Solutions
- Star Program
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Economics
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 12 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Physics
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Chemistry
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Biology
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Commerce
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Accountancy
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 11 Statistics
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 10 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 9 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 8 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 6 Social Science
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 5 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 4 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 EVS
- NCERT Solutions Class 3 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 2 Hindi
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Maths
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 English
- NCERT Solutions Class 1 Hindi
- NCERT Books Class 12
- NCERT Books Class 11
- NCERT Books Class 10
- NCERT Books Class 9
- NCERT Books Class 8
- NCERT Books Class 7
- NCERT Books Class 6
- NCERT Books Class 5
- NCERT Books Class 4
- NCERT Books Class 3
- NCERT Books Class 2
- NCERT Books Class 1
- Important Questions Class 12
- Important Questions Class 11
- Important Questions Class 10
- Important Questions Class 9
- Important Questions Class 8
- Important Questions Class 7
- important questions class 6
- CBSE Class 12 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 11 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 8 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 7 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 6 Revision Notes
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 11 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 10 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 9 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 8 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 7 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 6 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 5 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 4 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 3 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 2 Syllabus
- CBSE Class 1 Syllabus
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 5
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 4
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 3
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 2
- CBSE Sample Question Papers For Class 1
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 12
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers Class 10
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 8 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 9 Science
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Maths
- Extra Questions For Class 10 Science
- NEET 2021 Question Paper
- NEET 2020 Question Paper
- NEET 2019 Question Paper
- NEET 2018 Question Paper
- NEET 2017 Question Paper
- NEET 2016 Question Paper
- NEET 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Physics Questions
- NEET Chemistry Questions
- NEET Biology Questions
- NEET Sample Papers
- NEET Physics Syllabus
- NEET Chemistry Syllabus
- NEET Biology Syllabus
- NEET Mock Test
- NEET Eligibility Criteria
- JEE Main 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Main 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Main Sample Papers
- JEE Main Physics Syllabus
- JEE Main Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Main Maths Syllabus
- JEE Main Physics Questions
- JEE Main Chemistry Questions
- JEE Main Maths Questions
- JEE main revision notes
- JEE Main Mock Test
- JEE Advanced Physics Questions
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Questions
- JEE Advanced Maths Questions
- JEE Advanced 2021 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2020 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2019 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2018 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2017 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2016 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced 2015 Question Paper
- JEE Advanced Physics Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Chemistry Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Maths Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Mock Test
- ISC Class 12 Syllabus
- ISC Class 11 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 10 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 9 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 8 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 7 Syllabus
- ICSE Class 6 Syllabus
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers for Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers for Class 6
- ICSE Class 10 Revision Notes
- ICSE Class 9 Revision Notes
- ISC Important Questions for Class 12
- ISC Important Questions for Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions for Class 6
- ISC Class 12 Question Paper
- ICSE Class 10 Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Syllabus
- Maharashtra Board Sample Question Paper
- Maharashtra Board Previous Year Question Paper
- AP Board Syllabus
- AP Board Sample Question Paper
- AP Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Board Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Telangana Board Syllabus
- Telangana Board Sample Question Paper
- Telangana Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Syllabus
- Karnataka Board Sample Question Paper
- Karnataka Board Previous Year Question Paper
- Examination Full Forms
- Physics Full Forms
- Chemistry Full Forms
- Biology Full Forms
- Educational Full Form
- CUET Eligibility Criteria
- CUET Exam Pattern
- CUET Cutoff
- CUET Syllabus
- CUET Admit Card
- CUET Counselling
- CUET Previous Year Question Papers
- CUET Application Form
- CUET Sample Papers
- CUET Exam Centers
- CUET Exam Dates
- CUET Results
- Physics Formulas
- Chemistry Formulas
- Math Formulas
- Algebra Formulas
- Geometry Formulas
- Trigonometry Formulas
- Subscription
Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10
Home » CBSE » Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10

- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions Class 6
- CBSE Previous Year Question Papers
- CBSE Revision Notes
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE Extra Questions
- CBSE Sample Papers
- ISC & ICSE Syllabus
- ICSE Syllabus Class 9
- ICSE Syllabus Class 8
- ICSE Syllabus Class 7
- ICSE Syllabus Class 6
- ICSE Syllabus Class 10
- ICSE Question Paper
- ICSE Sample Question Papers
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 12
- ISC Sample Question Papers For Class 11
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 10
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 9
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 8
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 7
- ICSE Sample Question Papers For Class 6
- ICSE Revision Notes
- ICSE Important Questions
- ISC Important Questions For Class 12
- ISC Important Questions For Class 11
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 10
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 9
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 8
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 7
- ICSE Important Questions For Class 6
- Maharashtra board
- Rajasthan-Board
- Andhrapradesh Board
- AP Board syllabus
- Telangana Board
- Tamilnadu Board
- Tamilnadu Sample Question Paper
- Tamilnadu Syllabus
- Tamilnadu Previous Year Question Paper
- NCERT Solutions Class 12
- NCERT Solutions Class 10
- NCERT Solutions Class 11
- NCERT Solutions Class 9
- NCERT Solutions Class 8
- NCERT Solutions Class 7
- NCERT Solutions Class 6
- NCERT Solutions Class 5
- NCERT Solutions Class 4
- NCERT Solutions Class 3
- NCERT Solutions Class 2
- NCERT Solutions Class 1
- JEE Main Question Papers
- JEE Main Syllabus
- JEE Main Questions
- JEE Main Revision Notes
- JEE Advanced Question Papers
- JEE Advanced Syllabus
- JEE Advanced Questions
- JEE Advanced Sample Papers
- NEET Question Papers
- Neet 2021 Question Paper
- Neet 2020 Question Paper
- Neet 2019 Question Paper
- Neet 2018 Question Paper
- Neet 2017 Question Paper
- Neet 2016 Question Paper
- Neet 2015 Question Paper
- NEET Syllabus

Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 – Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Important Questions Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 prepared by Extramarks help students prepare for board exams effectively. This set contains the marks distribution of Important Questions , numerical, terminologies and concepts related to Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. C hapter 10 Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions prepared by Extramarks subject matter experts will help students gain in-depth understanding of the above mentioned topics.
These questions are curated by subject matter experts in accordance with the CBSE Syllabus . Chemistry Class 12 Chapter 10 Important Questions are presented with step-by-step solutions. Students can refer to this set of important questions from the Extramarks website.
CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapter-10 Important Questions
Important questions for class 12 chemistry chapter 10.
Q1.] Arrange the following in the increasing order of properly indicated:
i.] bromomethane, chloromethane, dichloromethane. (Increasing order of boiling points).
Ans. All the above-mentioned compounds are haloalkanes. The order will be:
Chloromethane < Bromomethane < Dichloromethane
The reason behind this is that as the halogen size increases the boiling point will increase. Similarly, the boiling point will increase as the number of halogen atoms rises in the similar chain.
ii.] 1-chloropropane, isopropyl chloride, 1-chlorobutane (Increasing order of boiling point)
Ans. A chlorine atom is existent in the compounds and there are distinct sizes of the alkyl chain. The order will be:
Isopropyl chloride < 1- Chloropropane < 1 – Chlorobutane
This happens as the branching of the chain expands the boiling point will fall and as the chain’s size increases the boiling point will inflate.
iii.] o,m,p-dichlorobenzenes (Increasing order of melting points)
Ans. p-dichlorobenzene has the highest melting point due to its symmetry and structure. The melting point of a compound is connected to its symmetry. Similarly, the symmetry of the compound goes after the same pattern as the melting point. The order is given below:
m-Dichlorobenzene < o-Dichlorobenzene < p-Dichlorobenzene
Q2] How do the below-stated conversions occur?
- Ethanol to but-1-yne
Ans. Chloroethane Is formed when ethanol reacts with SOC l 2 and pyridine. Acetylene reacts with NaN H 2 which forms sodium acetylide. But-1-yne is formed when Chloroethane and Sodium acetylide react. The reactions are :
SOC l 2 / Pyridine
C H 3 C H 2 OH ⟶ C H 3 C H 2 – Cl
Liq. N H 3 ,196K
CH CH+NaN H 2 ⟶ HC C – N a +
C H 3 C H 2 Cl+HC C – N a + ⟶ C H 3 C H 2 – C ≡ CH + NaCl
- 1-bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
Ans. Propene is formed when 1-Bromopropane reacts with alcoholic KOH. HBr reacts with Propene which produces 2-Bromopropane. The reaction is as follows:
Alc. KOH HBr
C H 3 C H 2 C H 2 Br ⟶ C H 3 CH=C H 2 ⟶ C H 3 – CH Br -C H 3
iii. Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid
Ans. KCN reacts with ethyl chloride to give propanenitrile. Propanoic acid is produced when propanenitrile goes through hydrolysis. The reaction is as follows:
KCN H + / H 2 O
C H 3 C H 2 Cl ⟶ C H 3 C H 2 CN ⟶ C H 3 C H 2 COOH
- But-1-ene to n-butyl iodide
Ans: When but-1-ene reacts with HBr in the existence of peroxide, 1-Bromobutane is produced. NaI reacts with 1-Bromobutane in the presence of Acetone to form n-butyl iodide. The reaction is as follows:
HBr
C H 3 C H 2 CH=C H 2 ⟶ C H 3 C H 2 C H 2 C H 2 Br
peroxide
NaI
C H 3 C H 2 C H 2 C H 2 Br ⟶ C H 3 C H 2 C H 2 C H 2 I
Acetone
Q3.] What is the difference between following
- i) Electrophilic and Nucleophilic substitution reactions.
| 1. A chemical reaction where the functional group is connected to a compound is exchanged by an electrophile is called an electrophilic substitution reaction. 2. The two primary types of electrophilic substitution reaction are electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions and electrophilic aliphatic substitution reactions. | 1. When a nucleophile strikes a haloalkane with a partial positive charge atom or group, a Nucleophilic substitution reaction takes place. 2. The two types of nucleophilic substitution reactions are substitution nucleophilic unimolecular and Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular.
|
- ii) Retention and Inversion of configuration.
Ans.
| 1. The conservation of integrity of the spatial adjustment of bonds to an asymmetric centre during a chemical reaction or transformation is called Retention of configuration. 2. The retention in configuration transforms the R-configuration of the compound into R and S-configuration of the compound converts into S. | 1. A process in which the absolute and relative configurations of atoms or molecules are not changed are called Inversion of configuration. 2. The inversion in configuration converts the R-configuration of the compound into S and S-configuration of the compound converts into R. |
Q4.) Identify which compound in the pairs will react faster in S n 2 reaction with O H – ?
- a) C H 3 Br or C H 3 I
Ans. The iodide ion is a bigger atom than bromide ion still both compounds are considered to be alkyl halide. So, I – ion is better leaving group than B r – ion. Thus, C H 3 I will react quicker than C H 3 Br with regards S n 2 reaction in the presence of hydroxyl ion.
- b) C H 3 3 CCl or C H 3 Cl
Ans. The steric obstacles should be reduced in S n 2 reaction . C H 3 3 CCl has extreme steric hindrance and C H 3 Cl has limited steric hindrance. Therefore, C H 3 Cl will react rapidly to the S n 2 reaction in the presence of hydroxyl ion.
Q5.) In the following pairs of halogen compounds, which compound undergoes faster S N 1 reaction?
- i) C H 3 3 C-Cl and C 6 H 5 C H 2 Cl
- ii) C H 2 =CH-Cl and C H 2 =CH-C H 2 Cl
iii) C 6 H 5 C H 2 Cl and C 6 H 5 C Cl C 6 H 5
Ans. For the S N 1 reaction the order of reactivity is 3°>2°>1° ,
- i) The former compound is a tertiary compound and the latter compound is primary compound. Therefore, the former compound will go through a quicker S N 1
- ii) The former compound is the vinylic primary compound whereas the second compound is the primary compound. Therefore, the second compound will go through rapid S N 1 reaction as there will be resonance in the former compound.
iii) The former compound is the primary compound and the latter compound is the secondary compound. Hence, the second compound will go through quicker S N 1 reaction in comparison to the first compound.
Q6.) Give one use of each of the following:
(i) Freon-12
Ans: Freon-12 CC l 2 F 2 , is used by the industry which is the most prevalent form of the refrigerant or air-conditioning components, aerosol propellants.
(ii) Iodoform
Ans: The Iodoform was used earlier as an antiseptic due to the liberation of free iodine from it, and not due to the substance itself. As it leaves an peculiar odour it has been replaced by other iodine-containing formulations.
Ans: DDT was first discovered to be used as chlorinated organic insecticides in 1939 . After World War II, DDT was used as it due to its effectiveness against mosquitoes that led to disease like malaria and insects harming the crops leading to rise in its demand.
Q7.) An organic compound (A) having molecular formula C 3 H 7 Cl reaction with alcoholic solution of KCN gives compound B. The compound B on hydrolysis with dilute HCl gives compound C. C on reduction with H 2 /Ni gives 1-aminobutane. Identify A, B and C.
Ans. The formula C 3 H 7 Cl depicts that compound (A) is an alkyl halide. Compound (B) is formed when there is a reaction with KCN. When compound (C) is reduced with hydrogen and nickel it produces 1-aminobutane that concludes that all the compounds mentioned above in the question are straight-chain compounds. Therefore, compound (A) is a 1-Chloropropane, compound (B) is a Propionitrile, and compound (C) is a Butanamide. The reactions are mentioned below:
C H 3 -C H 2 -C H 2 -Cl+KCN ⟶ C H 3 -C H 2 -C H 2 -CN+KCl
H 2 O/HCl
C H 3 -C H 2 -C H 2 -CN ⟶ C H 3 -C H 2 -C H 2 -CON H 2
H 2 /Ni
C H 3 -C H 2 -C H 2 -CON H 2 ⟶ C H 3 C H 2 C H 2 C H 2 N H 2
Q8. Elimination reactions (especially B-elimination) are as common as the nucleophilic substitution reaction in case of alkyl halides. State the reagents applied for use in both the cases.
Ans. The reactions like nucleophilic substitution and elimination (beta-elimination) reactions are more likely to be possible with alkyl halides. The elimination reaction is well-suited to strong, huge bases and high temperatures. Whereas, the substitution reaction works well at lower temperatures for smaller and weaker bases.
Q9. Diphenyls are a potential threat to the environment. How are aryl halides used to form these?
Ans. When coal and mineral oil are not burned entirely, the diphenyl is produced in the environment. These are usually present in car exhaust gases, exhaust air of home and industrial heating systems. Several case studies have shown that ingestion of diphenyl has led to several health problems in humans as well as animals such as well as harmful effects on the liver, kidneys, eye and skin irritation, as well as damage to the central/peripheral nervous system. In the presence of dry ether, when aryl halides are in contact with sodium, diphenyl is produced. This reaction is termed a fitting reaction.
Q10. Describe the reactions mentioned below and give a example:
(A) Swarts reaction.
(B) Finkelstein reaction.
(C) Wurtz reaction.
Ans. (A) Swarts reaction.
Alkyl fluorides from alkyl chlorides or alkyl bromides are formed by using the Swarts reaction. This can be achieved by heating the alkyl chloride/ bromide in the existence of fluoride in specific heavy metals. The reaction is as follows:
C H 3 – Br+AgF → C H 3 F+AgBr
When an alkyl bromide or alkyl chloride is changed into an alkyl iodide, which is further treated with a sodium iodide solution present in an acetone. The reaction is as follows:
C H 3 C H 2 Br+NaI → C H 3 C H 2 I+NaBr
When alkyl halides come in contact with sodium metal in a dry ethereal (moisture-free) solution form higher alkanes. It can also be applied to produce higher alkanes with an equal number of carbon atoms. The reaction is as follows:
2RX+2Na ⟶RR+2NaX
Q11. Why is it mandatory to eliminate water, alcohols, and amines while using a Grignard reagent?
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. why should students of class 12 refer to extra questions for class 12 chemistry chapter 10 solutions.
Class 12 is an important academic year for every student. Therefore, students should extensively practise the papers of past years as well as extra questions for their board exams. Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Important Question s will be beneficial for CBSE Class 12 students to score excellent marks in their Class 12 board exams. These notes consist of the important topics from Chapter 10 of Chemistry which will aid the students to get a thorough understanding of the chapter and help them clear their doubts. Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Important Questions are made in accordance with the CBSE Syllabus .
2. What are organo-metallic compounds?
Compounds consisting of carbon-metal bonds are derived when some specific metals react with organic chlorides, bromides, and iodides. These compounds are called organo-metallic compounds.
CBSE Related Links


CBSE 12th Standard Chemistry Subject Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Chapter Case Study Questions 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 , and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
Cbse 12th standard chemistry subject haloalkanes and haloarenes case study questions 2021.
12th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes. The low reactivity of haloarenes can be attributed to (i) resonance effect (ii) Sp 2 hybridisation of C - X bond (iii) polarity of C - X bond (iv) instability of phenyl cation (formed by self-ionisation ofhaloarene) (v) repulsion between the electron rich attacking nucleophiles and electron rich arenes. Reactivity of haloarenes can be increased or decreased by the presence of certain groups at certain positions for example, nitro (-NO 2 ) group at olp positions increases the reactivity of haloarenes towards nucleophilc substitution reactions. The following questions are multiple choice questions. Choose the most appropriate answer: (i) Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reaction as compared to alkyl halides due to
(ii) Which of the following aryl halides is the most reactive towards nucleophilic substitution?
(iii) Which one of the following will react fastest with aqueous NaOH?
The reactivity of the compounds (i) MeBr, (ii) PhCH 2 Br, (iii) MeCI, (iv) p- MeOC 6 H 4 Br decreases as
| ) | ||||
| 1. | NaOH or KOH or moist Ag O | OH | ROH | Alcohol |
| 2. | H O | H O | ROH | Alcohol |
| 3. | NaI | I | R-I | Alkyl iodide |
| 4. | R'NH | \(R^{\prime} \ddot{\mathrm{N}} \mathrm{H}_{2}\) | RNHR' | Sec. amine |
| 5. | KCN | \(\overline{\mathrm{C}} \equiv \mathrm{N}:\) | RCN | Nitrile (cyanide) |
| 6. | KNO | O=N-O | R-O-N=O | Alkyl nitrite |
In these questions (i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices. (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion. (b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion. (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason' is wrong statement. (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement. (i) Assertion: Alkyl halides are hydrolysed to alcohols by moist silver oxide. Reason: RCI is hydrolysed to ROH easily but reactions slow down on addition of KI. (ii) Assertion : Alkyl halides form alkenes when heated above 300°C. Reason: CH 3 CH 2 I reacts slowly with strong base as compared to CD 3 CH 2 I. (iii) Assertion : RBr reacts with AgNO 2 to give nitro alkane. Reason: Silver nitrite (AgNO 2 ) is an ionic compound, therefore the negative charge on nitrogen is the attacking site. (iv) Assertion: The nucleophilic substitution of vinyl chloride is difficult than ethyl chloride. Reason: Vinyl group is electron donating group.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: The order of reactivity towards S N 1 reaction depends upon the stability of carbocation in the first step. Greater the stability of the carbocation, greater will be its ease of formation from alkyl halide and hence faster will be the rate of the reaction. As we know, 3° carbocation is most stable, therefore, the tert-alkyl that halides will undergo S N 1 reaction very fast. For example, it has been observed that the reaction (CH 3 ) 3 CBr with OH - ion to give 2-methyl-2-propanol is about 1 million times as fast as the corresponding reaction of the methyl bromide to give methanol. The primary alkyl halides always react predominantly by S N 2 mechanism. On the other hand, the tertiary alkyl halides react predominantly by S N 1 mechanism. Secondary alkyl halides may react by either mechanism or by both the mechanisms without much preference depending upon the nature of the nucleophile and solvent. In these questions ( i-iv), a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices. (a) Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion. (b) Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion. (c) Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement. (d) Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement. (i) Assertion: Low concentration of nucleophile favours S N 1mechanism. Reason: 2° alkyl halides are less reactive than 1° towards S N 1 reactions. (ii) Assertion: Polar solvent slows down S N 2reactions. Reason: CH 3 -Br is less reactive than CH 3 Cl. (iii) Assertion: Benzyl bromide when kept in acetone- water it produces benzyl alcohol. Reason: The reaction follows S N 2 mechanism. (iv) Assertion: Rate of hydrolysis of methyl chloride to methanol is higher in DMF than in water. Reason: Hydrolysis of methyl chloride follows second order kinetics.
*****************************************
Related 12th standard cbse chemistry materials, other 12th standard cbse materials.

CBSE 12th Physics Wave Optics Chapter Case Study Question with Answers
Cbse 12th physics ray optics and optical instruments chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics nuclei chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics moving charges and magnetism chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics electromagnetic induction chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics atoms chapter case study question with answers, 12th physics alternating current chapter case study question with answers cbse.

12th Maths Vector Algebra Chapter Case Study Question with Answers CBSE
12th maths three dimensional geometry chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths probability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths linear programming chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths differential equations chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths continuity and differentiability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths application of integrals chapter case study question with answers cbse.

Class 12th Economics - Non-Competitive Markets Case Study Questions and Answers 2022 - 2023
Tamilnadu stateboard 12th standard cbse study materials.

Tamilnadu Stateboard 12th Standard CBSE Subjects


Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - NCERT Solutions
From this chapter, you will be able to name haloalkanes and haloarenes according to the IUPAC system of nomenclature from their given structures. Description of the reactions involved in the preparation of haloalkanes, haloarenes and understand various reactions that they go through. Correlation of the structures of haloalkanes and haloarenes with various types of reactions is also given. Use of stereochemistry as a tool for understanding the reaction mechanism. Highlighting the environmental effects of polyhalogen compounds.
Download pdf of NCERT Solutions for Class Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Download pdf of NCERT Examplar with Solutions for Class Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Exercise 1 ( Page No. : 307 )
| Q1 | |
| Ans: |
|
| Q2 | |
| Ans: | SO ), KI produces HI 2KI + H SO → 2KHSO + 2HI Since H SO is an oxidizing agent, it oxidizes HI (produced in the reaction to I ). 2HI + H SO → I + SO + H O As a result, the reaction between alcohol and HI to produce alkyl iodide cannot occur. Therefore, sulphuric acid is not used during the reaction of alcohols with KI. Instead, a non-oxidizing acid such as H PO is used. |
| Q3 | |
| Ans: |
|
| Q4 | |
| Ans: | H . This is because, replacement of any H-atom leads to the formation of the same product. The isomer is neopentane.
Neopentane
(ii) To have three isomeric monochlorides, the isomer of the alkane of the molecular formula C H should contain three different types of H-atoms. Therefore, the isomer is n-pentane. It can be observed that there are three types of H atoms labelled as a, b and c in n-pentane.
(iii) To have four isomeric monochlorides, the isomer of the alkane of the molecular formula C5H12 should contain four different types of H-atoms. Therefore, the isomer is 2-methylbutane. It can be observed that there are four types of H-atoms labelled as a, b, c, and d in 2-methylbutane.
|
| Q6 | |
| Ans: |
For alkyl halides containing the same alkyl group, the boiling point increases with an increase in the atomic mass of the halogen atom. Since the atomic mass of Br is greater than that of Cl, the boiling point of bromomethane is higher than that of chloromethane. Further, for alkyl halides containing the same alkyl group, the boiling point increases with an increase in the number of halides. Therefore, the boiling point of Dibromomethane is higher than that of chloromethane and bromomethane, but lower than that of bromoform. Hence, the given set of compounds can be arranged in the order of their increasing boiling points as: Chloromethane < Bromomethane < Dibromomethane < Bromoform.
(ii)
For alkyl halides containing the same halide, the boiling point increases with an increase in the size of the alkyl group. Thus, the boiling point of 1-chlorobutane is higher than that of isopropyl chloride and 1-chloropropane. Further, the boiling point decreases with an increase in branching in the chain. Thus, the boiling point of isopropyl alcohol is lower than that of 1-chloropropane. Hence, the given set of compounds can be arranged in the increasing order of their boiling points as: Isopropyl chloride < 1-Chloropropane < 1-Chlorobutane |
| Q7 | |
| Ans: |
2-bromobutane is a 2° alkylhalide whereas 1-bromobutane is a 1° alkyl halide. The approaching of nucleophile is more hindered in 2-bromobutane than in 1-bromobutane. Therefore, 1-bromobutane reacts more rapidly than 2-bromobutane by an S 2 mechanism.
(ii)
2-Bromobutane is 2° alkylhalide whereas 2-bromo-2-methylpropane is 3° alkyl halide. Therefore, greater numbers of substituents are present in 3° alkyl halide than in 2° alkyl halide to hinder the approaching nucleophile. Hence, 2-bromobutane reacts more rapidly than 2-bromo-2-methylpropane by an S 2 mechanism.
(iii)
Both the alkyl halides are primary. However, the substituent -CH is at a greater distance to the carbon atom linked to Br in 1-bromo-3-methylbutane than in 1-bromo-2-methylbutane. Therefore, the approaching nucleophile is less hindered in case of the former than in case of the latter. Hence, the former reacts faster than the latter by S 2 mechanism. |
| Q8 | |
| Ans: |
S 1 reaction proceeds via the formation of carbocation. The alkyl halide (I) is 3° while (II) is 2°. Therefore, (I) forms 3° carbocation while (II) forms 2° carbocation. Greater the stability of the carbocation, faster is the rate of S 1 reaction. Since 3° carbocation is more stable than 2° carbocation. (I), i.e. 2-chloro-2-methylpropane, undergoes faster S 1 reaction than (II) i.e., 3-chloropentane.
(ii)
The alkyl halide (I) is 2° while (II) is 1°. 2° carbocation is more stable than 1° carbocation. Therefore, (I), 2-chloroheptane, undergoes faster S 1 reaction than (II), 1-chlorohexane. |
Exercise 2 ( Page No. : 312 )
| Q1 | |
| Ans: |
|
| Q2 | |
| Ans: |
|
| Q3 | |
| Ans: |
|
| Q4 | |
| Ans: |
CCl is a symmetrical molecule. Therefore, the dipole moments of all four C-Cl bonds cancel each other. Hence, its resultant dipole moment is zero. As shown in the above figure, in CHCl , the resultant of dipole moments of two C-Cl bonds is opposed by the resultant of dipole moments of one C-H bond and one C-Cl bond. Since the resultant of one C-H bond and one C-Cl bond dipole moments is smaller than two C-Cl bonds, the opposition is to a small extent. As a result, CHCl has a small dipole moment of 1.08 D. On the other hand, in case of CH Cl , the resultant of the dipole moments of two C-Cl bonds is strengthened by the resultant of the dipole moments of two C-H bonds. As a result, CH Cl has a higher dipole moment of 1.60 D than CHCl i.e., CH Cl has the highest dipole moment. Hence, the given compounds can be arranged in the increasing order of their dipole moments as: CCl < CHCl < CH Cl |
| Q5 | |
| Ans: | H belongs to the group with a general molecular formula CnH n. Therefore, it may either be an alkene or a cycloalkane. Since hydrocarbon does not react with chlorine in the dark, it cannot be an alkene. Thus, it should be a cycloalkane. Further, the hydrocarbon gives a single monochloro compound, C H Cl by reacting with chlorine in bright sunlight. Since a single monochloro compound is formed, the hydrocarbon must contain H-atoms that are all equivalent. Also, as all H-atoms of a cycloalkane are equivalent, the hydrocarbon must be a cycloalkane. Hence, the said compound is cyclopentane.
|
| Q6 | |
| Ans: | H Br. These isomers are given below.
|
| Q7 | |
| Ans: | |
| Q8 | |
| Ans: | For example, nitrite ion is an ambident nucleophile.
Nitrite ion can attack through oxygen resulting in the formation of alkyl nitrites. Also, it can attack through nitrogen resulting in the formation of nitroalkanes.
|
| Q9 | |
| Ans: | 2 mechanism, the reactivity of halides for the same alkyl group increases in the order. This happens because as the size increases, the halide ion becomes a better leaving group. R-F << R-Cl < R-Br < R-I Therefore, CH I will react faster than CH Br in S 2 reactions with OH .
(ii)
The S 2 mechanism involves the attack of the nucleophile at the atom bearing the leaving group. But, in case of (CH ) CCl, the attack of the nucleophile at the carbon atom is hindered because of the presence of bulky substituents on that carbon atom bearing the leaving group. On the other hand, there are no bulky substituents on the carbon atom bearing the leaving group in CH Cl. Hence, CH Cl reacts faster than (CH ) CCl in S 2 reaction with OH-. |
| Q10 | |
| Ans: |
Saytzeff's rule implies that in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to a doubly bonded carbon atoms is preferably produced. Therefore, alkene (I) i.e., 2-methylbut-2-ene is the major product in this reaction. (iii)
2,2,3-Trimethyl-3-bromopentane In the given compound, there are two different sets of equivalent β-hydrogen atoms labelled as a and b. Thus, dehydrohalogenation of the compound yields two alkenes.
According to Saytzeff's rule, in dehydrohalogenation reactions, the alkene having a greater number of alkyl groups attached to the doubly bonded carbon atom is preferably formed. Hence, alkene (I) i.e., 3,4,4-trimethylpent-2-ene is the major product in this reaction. |
| Q11 | |
| Ans: |
|
| Q12 | |
| Ans: |
In chlorobenzene, the Cl-atom is linked to a sp hybridized carbon atom. In cyclohexyl chloride, the Cl-atom is linked to a sp hybridized carbon atom. Now, sp hybridized carbon has more s-character than sp hybridized carbon atom. Therefore, the former is more electronegative than the latter. Therefore, the density of electrons of C - Cl bond near the Cl-atom is less in chlorobenzene than in cydohexyl chloride. Moreover, the - R effect of the benzene ring of chlorobenzene decreases the electron density of the C - Cl bond near the Cl-atom. As a result, the polarity of the C - Cl bond in chlorobenzene decreases. Hence, the dipole moment of chlorobenzene is lower than that of cyclohexyl chloride.
(ii) To be miscible with water, the solute-water force of attraction must be stronger than the solute-solute and water-water forces of attraction. Alkyl halides are polar molecules and so held together by dipole-dipole interactions. Similarly, strong H-bonds exist between the water molecules. The new force of attraction between the alkyl halides and water molecules is weaker than the alkyl halide-alkyl halide and water-water forces of attraction. Hence, alkyl halides (though polar) are immiscible with water.
(iii) Grignard reagents are very reactive. In the presence of moisture, they react to give alkanes.
Therefore, Grignard reagents should be prepared under anhydrous conditions. |
| Q13 | |
| Ans: | Freon-12 (dichlorodifluoromethane, CF2Cl2) is commonly known as CFC. It is used as a refrigerant in refrigerators and air conditioners. It is also used in aerosol spray propellants such as body sprays, hair sprays, etc. However, it damages the ozone layer. Hence, its manufacture was banned in the United States and many other countries in 1994.
Uses of DDT DDT (p, p-dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) is one of the best known insecticides. It is very effective against mosquitoes and lice. But due its harmful effects, it was banned in the United States in 1973.
Uses of carbontetrachloride (CCl ) (i) It is used for manufacturing refrigerants and propellants for aerosol cans. (ii) It is used as feedstock in the synthesis of chlorofluorocarbons and other chemicals. (iii) It is used as a solvent in the manufacture of pharmaceutical products. (iv) Until the mid 1960's, carbon tetrachloride was widely used as a cleaning fluid, a degreasing agent in industries, a spot reamer in homes, and a fire extinguisher.
Uses of iodoform (CHI ) Iodoform was used earlier as an antiseptic, but now it has been replaced by other formulations-containing iodine-due to its objectionable smell. The antiseptic property of iodoform is only due to the liberation of free iodine when it comes in contact with the skin. |
| Q14 | |
| Ans: | |
| Q15 | |
| Ans: |
The given reaction is an S 2 reaction. In this reaction, CN acts as the nucleophile and attacks the carbon atom to which Br is attached. CN ion is an ambident nucleophile and can attack through both C and N. In this case, it attacks through the C-atom.
|
| Q16 | |
| Ans: |
An S 2 reaction involves the approaching of the nucleophile to the carbon atom to which the leaving group is attached. When the nucleophile is sterically hindered, then the reactivity towards S 2 displacement decreases. Due to the presence of substituents, hindrance to the approaching nucleophile increases in the following order. 1-Bromopentane < 2-bromopentane < 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane Hence, the increasing order of reactivity towards S 2 displacement is: 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 2-Bromopentane < 1-Bromopentane
(ii)
Since steric hindrance in alkyl halides increases in the order of 1° < 2° < 3°, the increasing order of reactivity towards S 2 displacement is 3° < 2° < 1°. Hence, the given set of compounds can be arranged in the increasing order of their reactivity towards S 2 displacement as: 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 2-Bromo-3-methylbutane < 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane [2-Bromo-3-methylbutane is incorrectly given in NCERT]
(iii)
The steric hindrance to the nucleophile in the S 2 mechanism increases with a decrease in the distance of the substituents from the atom containing the leaving group. Further, the steric hindrance increases with an increase in the number of substituents. Therefore, the increasing order of steric hindrances in the given compounds is as below: 1-Bromobutane < 1-Bromo-3-methylbutane < 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane Hence, the increasing order of reactivity of the given compounds towards S 2 displacement is: 1-Bromo-2, 2-dimethylpropane < 1-Bromo-2-methylbutane < 1-Bromo-3- methylbutane < 1-Bromobutane |
| Q17 | |
| Ans: | |
| Q18 | |
| Ans: | -Dichlorobenzene is more symmetrical than -and -isomers. For this reason, it fits more closely than o-and m-isomers in the crystal lattice. Therefore, more energy is required to break the crystal lattice of -dichlorobenzene. As a result, p-dichlorobenzene has a higher melting point and lower solubility than -and -isomers. |
| Q19 | |
| Ans: |
|
| Q20 | |
| Ans: | ions. OH ion is a strong nucleophile, which leads the alkyl chloride to undergo a substitution reaction to form alcohol.
On the other hand, an alcoholic solution of KOH contains alkoxide (RO ) ion, which is a strong base. Thus, it can abstract a hydrogen from the β-carbon of the alkyl chloride and form an alkene by eliminating a molecule of HCl.
OH ion is a much weaker base than RO ion. Also, OH ion is highly solvated in an aqueous solution and as a result, the basic character of OH ion decreases. Therefore, it cannot abstract a hydrogen from the β-carbon. |
| Q21 | |
| Ans: | H Br. They are - bulyl bromide and isobutyl bromide.
Therefore, compound (a) is either n-butyl bromide or isobutyl bromide. Now, compound (a) reacts with Na metal to give compound (b) of molecular formula, C H , which is different from the compound formed when -butyl bromide reacts with Na metal. Hence, compound (a) must be isobutyl bromide.
Thus, compound (d) is 2, 5-dimethylhexane. It is given that compound (a) reacts with alcoholic KOH to give compound (b). Hence, compound (b) is 2-methylpropene.
Also, compound (b) reacts with HBr to give compound (c) which is an isomer of (a). Hence, compound (c) is 2-bromo-2-methylpropane.
|
| Q22 | |
| Ans: |
(ii) When bromobenzene is treated with Mg in the presence of dry ether, phenylmagnesium bromide is formed.
(iii) Chlorobenzene does not undergo hydrolysis under normal conditions. However, it undergoes hydrolysis when heated in an aqueous sodium hydroxide solution at a temperature of 623 K and a pressure of 300 atm to form phenol.
(iv) When ethyl chloride is treated with aqueous KOH, it undergoes hydrolysis to form ethanol.
(v) When methyl bromide is treated with sodium in the presence of dry ether, ethane is formed. This reaction is known as the Wurtz reaction.
(vi) When methyl chloride is treated with KCN, it undergoes a substitution reaction to give methyl cyanide.
|
Key Features of NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 'Haloalkanes and Haloarenes' question answers :
- All chapter question answers with detailed explanations.
- Simple language for easy comprehension.
- Aligned with the latest NCERT guidelines.
- Perfect for exam preparation and revision.
Popular Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
Give simple chemical tests to distinguish between the following pairs of compounds.
(i) Propanal and Propanone
(ii) Acetophenone and Benzophenone
(iii) Phenol and Benzoic acid
(iv) Benzoic acid and Ethyl benzoate
(v) Pentan-2-one and Pentan-3-one
(vi) Benzaldehyde and Acetophenone
(vii) Ethanal and Propanal
How the following conversions can be carried out?
(i) Propene to propan-1-ol
(ii) Ethanol to but-1-yne
(iii) 1-Bromopropane to 2-bromopropane
(iv) Toluene to benzyl alcohol
(v) Benzene to 4-bromonitrobenzene
(vi) Benzyl alcohol to 2-phenylethanoic acid
(vii) Ethanol to propanenitrile
(viii) Aniline to chlorobenzene
(ix) 2-Chlorobutane to 3, 4-dimethylhexane
(x) 2-Methyl-1-propene to 2-chloro-2-methylpropane
(xi) Ethyl chloride to propanoic acid
(xii) But-1-ene to n-butyliodide
(xiii) 2-Chloropropane to 1-propanol
(xiv) Isopropyl alcohol to iodoform
(xv) Chlorobenzene to p-nitrophenol
(xvi) 2-Bromopropane to 1-bromopropane
(xvii) Chloroethane to butane
(xviii) Benzene to diphenyl
(xix) tert-Butyl bromide to isobutyl bromide
(xx) Aniline to phenylisocyanide
A 5% solution (by mass) of cane sugar in water has freezing point of 271 K. Calculate the freezing point of 5% glucose in water if freezing point of pure water is 273.15 K.
A solution of glucose in water is labelled as 10% w/w, what would be the molality and mole fraction of each component in the solution? If the density of solution is 1.2 g mL -1 , then what shall be the molarity of the solution?
Henry's law constant for CO 2 in water is 1.67 x 10 8 Pa at 298 K. Calculate the quantity of CO 2 in 500 mL of soda water when packed under 2.5 atm CO 2 pressure at 298 K.
Calculate the mass of a non-volatile solute (molar mass 40 g mol -1 ) which should be dissolved in 114 g octane to reduce its vapour pressure to 80%.
The vapour pressure of pure liquids A and B are 450 and 700 mm Hg respectively, at 350 K. Find out the composition of the liquid mixture if total vapour pressure is 600 mm Hg. Also find the composition of the vapour phase.
Calculate the mole fraction of benzene in solution containing 30% by mass in carbon tetrachloride.
How many mL of 0.1 M HCl are required to react completely with 1 g mixture of Na 2 CO 3 and NaHCO 3 containing equimolar amounts of both?
If NaCl is doped with 10 -3 mol % of SrCl 2 , what is the concentration of cation vacancies?
Recently Viewed Questions of Class 12 Chemistry
A group 14 element is to be converted into n-type semiconductor by doping it with a suitable impurity. To which group should this impurity belong?
Concentrated nitric acid used in laboratory work is 68% nitric acid by mass in aqueous solution. What should be the molarity of such a sample of the acid if the density of the solution is 1.504 g mL -1 ?
Ionic solids conduct electricity in molten state but not in solid state. Explain.
For the reaction:
2A + B → A 2 B
the rate = k [A][B] 2 with k = 2.0 x 10 -6 mol -2 L 2 s -1 . Calculate the initial rate of the reaction when [A] = 0.1 mol L -1 , [B] = 0.2 mol L -1 . Calculate the rate of reaction after [A] is reduced to 0.06 mol L -1 .
Why are halogens strong oxidising agents?
Suggest two materials other than hydrogen that can be used as fuels in fuel cells.
Boiling point of water at 750 mm Hg is 99.63°C. How much sucrose is to be added to 500 g of water such that it boils at 100°C.Molal elevation constant for water is 0.52 K kg mol -1 .
Amongst the following ions which one has the highest magnetic moment value?
(i) [Cr(H 2 O) 6 ] 3+
(ii) [Fe(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+
(iii) [Zn(H 2 O) 6 ] 2+
Write the conditions to maximize the yield of H 2 SO 4 by Contact process.
Discuss the nature of bonding in the following coordination entities on the basis of valence bond theory:
(i) [Fe(CN) 6 ] 4-
(ii) [FeF 6 ] 3-
(iii) [Co(C 2 O 4 )3] 3-
(iv) [CoF 6 ] 3-
- The Solid State
- Electrochemistry
- Chemical Kinetics
- Surface Chemistry
- General Principles and Processes of Isolation of Elements
- The p-Block Elements
- The d-and f-Block Elements
- Coordination Compounds
- Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Alcohols Phenols and Ethers
- Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
- Biomolecules
- Chemistry in Everyday Life
NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Solutions for Class 12
- NCERT Solutions for Class 11
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9
- NCERT Solutions for Class 8
- NCERT Solutions for Class 7
- NCERT Solutions for Class 6
Quick Links
- NCERT Sample Papers
- NCERT Books
- CBSE Syllabus
- Scholarship for Students
- NCERT Exemplar
- CBSE Topper Answer Sheets
- CBSE Board Paper
- Multiplication Tables 2 to 30
- Latest Blog
- © 2024 SaralStudy
- Privacy Policy

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Important Question
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- Question Bank
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- Toppers Notes
- Most Repeated Question
- Diagram Based Question
- Study Planner
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Sample Papers
- Important Info
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- AP EAMCET Mock Test
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Mock Test
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Mock Test
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Mock Test
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Mock Test
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Mock Test
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Mock Test
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Mock Test
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- AMU Mock Test
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Mock Test
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Mock Test
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Mock Test
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- BCECE Previous Year Paper
- JCECE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- Verbal Ability & Reading Comprehension
- Logical Reasoning & Data Interpretation
- CAT Mock Test
- CAT Important Question
- CAT Vocabulary
- CAT English Grammar
- MBA General Knowledge
- CAT Mind Map
- CAT Study Planner
- CMAT Mock Test
- SRCC GBO Mock Test
- SRCC GBO PYQs
- XAT Mock Test
- SNAP Mock Test
- IIFT Mock Test
- MAT Mock Test
- CUET PG Mock Test
- CUET PG PYQs
- MAH CET Mock Test
- MAH CET PYQs
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- Solid State 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- Solutions 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- Electrochemistry 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- Chemical Kinetics 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- Surface Chemistry 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- p-Block Elements 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- d- and f-Block Elements 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- Coordination Compounds 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm
- Haloalkanes And Haloarenes 14 April, 2021, 6:33 pm

Solid State

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Chemistry MCQs for Class 12 with Answers Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 12 Minutes
MCQs Based On Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry are prepared by the subjects experts according to the latest pattern. These MCQs are very important for students who wants to score well in CBSE Board Exam. These MCQs on chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes will also help students in understanding the concepts very well.
Q.1. Gem-dibromide is (a) CH 3 CH(Br)CH 2 (Br) (b) CH 3 CBr 2 CH 3 (c) CH 2 (Br)CH 2 CH 2 (d) CH 2 BrCH 2 Br
Q.2. IUPAC name of (CH 3 ) 3 CCl (a) 3-Chlorobutane (b) 2-Chloro-2-methylpropane (c) t-butyl chloride (d) n-butyl chloride
Q.3. Which of the following is a primary halide? (a) Isopropyl iodide (b) Secondary butyl iodide (c) Tertiary butyl bromide (d) Neohexyl chloride
Q.4. When two halogen atoms are attached to same carbon atom then it is : (a) vic-dihalide (b) gem-dihalide (c) α, ω -halide (d) α, β -halide
Q.5. How many structural isomers are possible for a compound with molecular formula C 3 H 7 Cl ? (a) 2 (b) 5 (c) 7 (d) 9
Q.6. The compound which contains all the four 1°, 2°, 3° and 4° carbon atoms is (a) 2, 3-dimethyl pentane (b) 3-chloro-2, 3-dimethylpentane (c) 2, 3, 4-trimethylpentane (d) 3, 3-dimethylpentane
Q.7. IUPAC name of CH 3 CH 2 C(Br) = CH—Cl is (a) 2-bromo-1-chloro butene (b) 1-chloro-2-bromo butene (c) 3-chloro-2-bromo butene (d) None of the above
Q.8. Benzene hexachloride is (a) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 – hexachlorocyclohexane (b) 1, 1, 1, 6, 6, 6 – hexachlorocyclohexane (c) 1, 6 – phenyl – 1, 6 – chlorohexane (d) 1, 1 – phenyl – 6, 6 -chlorohexane
Q.9. The IUPAC name of CH 2 = CH—CH 2 Cl is (a) Allyl chloride (b) 1-chloro-3-propene (c) Vinyl chloride (d) 3-chloro-1-propene
Q.10. Which of the following halide is 2° ? (a) Isopropyl chloride (b) Isobutyl chloride (c) n-propyl chloride (d) n-butyl chloride
Q.11. Halogenation of alkanes is (a) a reductive process (b) an oxidative process (c) an isothermal process (d) an endothermal process
Q.12. C – X bond is strongest in (a) CH 3 Cl (b) CH 3 Br (c) CH 3 F (d) CH 3 I
Q.13. Which of the following will have the maximum dipole moment? (a) CH 3 F (b) CH 3 Cl (c) CH 3 Br (d) CH 3 I
Q.14. Phosgene is a common name for (a) phosphoryl chloride (b) thionyl chloride (c) carbon dioxide and phosphine (d) carbonyl chloride
Q.15. In the preparation of chlorobenzene from aniline, the most suitable reagent is (a) Chlorine in the presence of ultraviolet light (b) Chlorine in the presence of AlCl 3 (c) Nitrous acid followed by heating with Cu 2 Cl 2 (d) HCl and Cu 2 Cl 2
Q.16. Ethylene dichloride can be prepared by adding HCl to (a) Ethane (b) Ethylene (c) Acetylene (d) Ethylene glycol
Q.17. In which of the following conversions, phosphorus pentachloride is used as the reagent? (a) H 2 C = CH 2 → CH 3 CH 2 Cl (b) CH 3 CH 2 OH → CH 3 CH 2 Cl (c) H 3 C-O-CH3 → CH 3 Cl (d) CH ≡ CH → CH 2 = CHCl
Q.18. The decreasing order of boiling points of alkyl halides is (a) RF > RCl > RBr > RI (b) RBr > RCl > RI > RF (c) RI > RBr > RCl > RF (d) RCl > RF > RI > RBr
Q.19. The best method for the conversion of an alcohol into an alkyl chloride is by treating the alcohol with (a) PCl 5 (b) dry HCl in the presence of anhydrous ZnCl 2 (c) SOCl 2 in presence of pyridine (d) None of these
Q.20. Which of the following is liquid at room temperature (b.p. is shown against it)? (a) CH 3 I 42ºC (b) CH 3 Br 3ºC (c) C 2 H 5 Cl 12ºC (d) CH 3 F –78ºC
Q.21. The catalyst used in the preparation of an alkyl chloride by the action of dry HCl on an alcohol is (a) anhydrous AlCl 3 (b) FeCl 3 (c) anhydrous ZnCl 2 (d) Cu
Q.22. Chlorobenzene is prepared commercially by (a) Raschig process (b) Wurtz Fittig reaction (c) Friedel-Craft’s reaction (d) Grignard reaction
Q.23. Conant Finkelstein reaction for the preparation of alkyl iodide is based upon the fact that (a) Sodium iodide is soluble in methanol, while sodium chloride is insoluble in methanol (b) Sodium iodide is soluble in methanol, while NaCl and NaBr are insoluble in methanol (c) Sodium iodide is insoluble in methanol, while NaCl and NaBr are soluble (d) The three halogens differ considerably in their electronegativity
Q.24. Which of the following possesses highest melting point? (a) Chlorobenzene (b) m-dichlorobenzene (c) o-dichlorobenzene (d) p-dichlorobenzene
You may also like:
MCQ Questions Based On Class 12 Chemistry Term 1 Syllabus
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 1 Solid State
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 2 Solutions
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 7 The p-Block Elements
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
- MCQ Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 14 Biomolecules
Download Books – Exam Special
Sample Papers for CBSE 2025 Exams
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 8 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 9 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 10 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 All Subjects (for 2025 Exams)
CBSE Class 10 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Numerical Problems Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
CBSE Class 12 Most Downloaded Books
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Important Questions
CBSE Class 8 Most Downloaded Books
- Worksheets for CBSE Class 8 Maths – Chapterwise
ICSE Class 10
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Geography BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams
- ICSE Revision Notes for Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams
ICSE Class 9
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Important Numerical Problems for Class 9 Physics Exams
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 9 Geography BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
CBSE Chapter-Wise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Social Science Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapterwise Test Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Chapterwise Test papers
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
1 thought on “ Chemistry MCQs for Class 12 with Answers Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes ”
it was a great experience
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1: A chlorocompound (A) on reduction with Zn-Cu and ethanol gives the hydrocarbon (B) with five carbon atoms. When (A) is dissolved in dry ether and treated with sodium metal it ...
d) Is superimposable on its mirror image. Case Study Questions Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry. 2. Read the passage given below and answer the following questions: The replacement of hydrogen atom in a hydrocarbon, aliphatic or aromatic results in the formation of haloalkanes and haloarenes respectively.
CBSE 12th Standard Chemistry Subject Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Case Study Questions With Solution 2021. A primary alkyl halide (A) C 4 H 9 Br reacted with alcoholic KOH to give compound (B). Compound (B) is reacted with HBr to give compound (C) which is an isomer of (A). When (A) reacted with sodium metal, it gave a compound (D) C 8 H 18 that ...
There is Case Study Questions in class 12 Chemistry in session 2020-21. For the first time, the board has introduced the case study questions in the board exam. The first two questions in the board exam question paper will be based on Case Study and Assertion & Reason. The first question will have 5 MCQs … Continue reading Case Study Questions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes ...
The below-given steps are helpful for students wanting to download Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Case Study for Class 12 Chemistry with Solutions in a PDF file. Search Selfstudys.com using the internet browser. After loading the website, click on the navigation button. Click on CBSE from the list of categories. Find and Click on Case Study.
QB365 provides a detailed and simple solution for every Possible Case Study Questions in Class 12 Chemsitry Subject - Haloalkanes and Haloarenes, CBSE. It will help Students to get more practice questions, Students can Practice these question papers in addition to score best marks.
Important Questions, MCQ's, NCERT Solutions - Class 12 Chemistry . Get here all the Important questions for Class 12 Chemistry chapter wise as free PDF download. Here you will get Extra Important Questions with answers, Numericals and Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ's) chapter wise in Printable format. Solving Chapter wise questions is one of the best ways to prepare for the examination.
Class 12 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Important Questions with Answers Short Answer Type Questions. Q1. Aryl chlorides and bromides can be easily prepared by electrophilic substitution of arenes with chlorine and bromine respectively in the presence of Lewis acid catalysts.
Class 12 Chemistry NCERT Solutions Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes - Important Questions. Question 10.1: Name the following halides according to IUPAC system and classify them as alkyl, allyl, benzyl ( primary, secondary, tertiary ), vinyl or aryl halides : (i) (CH3)2CHCH (Cl)CH3. (ii) CH3CH2CH (CH3)CH (C2H5)Cl.
Topics and Subtopics in NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: NCERT Solutions CBSE Sample Papers Chemistry Class 12 Chemistry. NCERT IN TEXT QUESTIONS. (iii) 4-tert. Butyl-3-iodoheptane. (v) 1-Bromo-4-sec. butyl-2-methylbenzene.
Answer: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Previous Year Question 10: Give reasons for the following: (i) Benzyl chloride is highly reactive towards the SN1 reaction. (ii) 2-bromobutane is optically active but 1-bromobutane is optically inactive. (iii) Electrophilic reactions in haloarenes occur slowly. Answer:
By practising these Class 12 Multiple choice questions, students will be able to quickly review all of the ideas covered in the chapter and prepare for the Class 12 Annual examinations as well as other entrance exams such as NEET and JEE. Download Chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes MCQs PDF by clicking on the button below. Download PDF
This set contains the marks distribution of Important Questions, numerical, terminologies and concepts related to Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. Chapter 10 Class 12 Chemistry Important Questions prepared by Extramarks subject matter experts will help students gain in-depth understanding of the above mentioned topics. These questions are curated by ...
Also, solving the Class 12 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes important questions during board exam preparation helps students refresh their answering methods for a variety of questions that can be asked from the chapter Haloalkanes and Haloarenes. While Solving Chapter-End Questions: One of the best times to use the PDF file of CBSE Class 12 Chemistry ...
CBSE 12th Standard Chemistry Subject Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Case Study Questions 2021. Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes. The low reactivity of haloarenes can be attributed to. (v) repulsion between the electron rich attacking nucleophiles and electron rich arenes. Reactivity of haloarenes can be increased or decreased by the ...
CBSE 12th Standard Chemistry Subject Haloalkanes and Haloarenes Case Study Questions 2021. Haloarenes are less reactive than haloalkanes. The low reactivity of haloarenes can be attributed to. (v) repulsion between the electron rich attacking nucleophiles and electron rich arenes. Reactivity of haloarenes can be increased or decreased by the ...
Key Features of NCERT Class 12 Chemistry Chapter 'Haloalkanes and Haloarenes' question answers : All chapter question answers with detailed explanations. Simple language for easy comprehension. Aligned with the latest NCERT guidelines. Perfect for exam preparation and revision.
Directions : (Q. 16 to 20) Case IV: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions. In haloalkanes, when a nucleophile stronger than the halide ion approaches the positively charged carbon atom of an alkyl halide, the halogen atom along with its bonding electron pair gets displaced and a new bond with the carbon and the nucleophile is formed. These reactions are called ...
Case Study on Haloalkanes And Haloarenes Class 12 Chemistry: Here, you will get Case Study Questions on Class 12 Haloalkanes And Haloarenes PDF at free of cost. ... Along with you can also download Haloalkanes And Haloarenes case study questions for Class 12 exercise wise for getting higher marks in boa. Sharda University Admission - 100% ...
Some haloalkanes and haloarenes have adverse effects on the environment and are labeled as pollutants. One such example is chlorofluorocarbons (or CFCs), which lead to the depletion of the ozone layer which protects the Earth from the harmful radiation coming from the sun. ... Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our ...
These MCQs on chapter 10 Haloalkanes and Haloarenes will also help students in understanding the concepts very well. Q.1. Gem-dibromide is (a) CH 3 CH(Br)CH 2 (Br) (b) CH 3 CBr 2 CH 3 (c) CH 2 (Br)CH 2 CH 2 ... Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings;