Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Starting the research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates

How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on October 12, 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on November 21, 2023.

A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organized and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research proposals.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: “A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management”
- Example research proposal #2: “Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use”
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesize prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasize again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
Methodology
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/research-process/research-proposal/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a problem statement | guide & examples, writing strong research questions | criteria & examples, how to write a literature review | guide, examples, & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
11.2 Steps in Developing a Research Proposal
Learning objectives.
- Identify the steps in developing a research proposal.
- Choose a topic and formulate a research question and working thesis.
- Develop a research proposal.
Writing a good research paper takes time, thought, and effort. Although this assignment is challenging, it is manageable. Focusing on one step at a time will help you develop a thoughtful, informative, well-supported research paper.
Your first step is to choose a topic and then to develop research questions, a working thesis, and a written research proposal. Set aside adequate time for this part of the process. Fully exploring ideas will help you build a solid foundation for your paper.
Choosing a Topic
When you choose a topic for a research paper, you are making a major commitment. Your choice will help determine whether you enjoy the lengthy process of research and writing—and whether your final paper fulfills the assignment requirements. If you choose your topic hastily, you may later find it difficult to work with your topic. By taking your time and choosing carefully, you can ensure that this assignment is not only challenging but also rewarding.
Writers understand the importance of choosing a topic that fulfills the assignment requirements and fits the assignment’s purpose and audience. (For more information about purpose and audience, see Chapter 6 “Writing Paragraphs: Separating Ideas and Shaping Content” .) Choosing a topic that interests you is also crucial. You instructor may provide a list of suggested topics or ask that you develop a topic on your own. In either case, try to identify topics that genuinely interest you.
After identifying potential topic ideas, you will need to evaluate your ideas and choose one topic to pursue. Will you be able to find enough information about the topic? Can you develop a paper about this topic that presents and supports your original ideas? Is the topic too broad or too narrow for the scope of the assignment? If so, can you modify it so it is more manageable? You will ask these questions during this preliminary phase of the research process.
Identifying Potential Topics
Sometimes, your instructor may provide a list of suggested topics. If so, you may benefit from identifying several possibilities before committing to one idea. It is important to know how to narrow down your ideas into a concise, manageable thesis. You may also use the list as a starting point to help you identify additional, related topics. Discussing your ideas with your instructor will help ensure that you choose a manageable topic that fits the requirements of the assignment.
In this chapter, you will follow a writer named Jorge, who is studying health care administration, as he prepares a research paper. You will also plan, research, and draft your own research paper.
Jorge was assigned to write a research paper on health and the media for an introductory course in health care. Although a general topic was selected for the students, Jorge had to decide which specific issues interested him. He brainstormed a list of possibilities.
If you are writing a research paper for a specialized course, look back through your notes and course activities. Identify reading assignments and class discussions that especially engaged you. Doing so can help you identify topics to pursue.
- Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs) in the news
- Sexual education programs
- Hollywood and eating disorders
- Americans’ access to public health information
- Media portrayal of health care reform bill
- Depictions of drugs on television
- The effect of the Internet on mental health
- Popularized diets (such as low-carbohydrate diets)
- Fear of pandemics (bird flu, HINI, SARS)
- Electronic entertainment and obesity
- Advertisements for prescription drugs
- Public education and disease prevention
Set a timer for five minutes. Use brainstorming or idea mapping to create a list of topics you would be interested in researching for a paper about the influence of the Internet on social networking. Do you closely follow the media coverage of a particular website, such as Twitter? Would you like to learn more about a certain industry, such as online dating? Which social networking sites do you and your friends use? List as many ideas related to this topic as you can.
Narrowing Your Topic
Once you have a list of potential topics, you will need to choose one as the focus of your essay. You will also need to narrow your topic. Most writers find that the topics they listed during brainstorming or idea mapping are broad—too broad for the scope of the assignment. Working with an overly broad topic, such as sexual education programs or popularized diets, can be frustrating and overwhelming. Each topic has so many facets that it would be impossible to cover them all in a college research paper. However, more specific choices, such as the pros and cons of sexual education in kids’ television programs or the physical effects of the South Beach diet, are specific enough to write about without being too narrow to sustain an entire research paper.
A good research paper provides focused, in-depth information and analysis. If your topic is too broad, you will find it difficult to do more than skim the surface when you research it and write about it. Narrowing your focus is essential to making your topic manageable. To narrow your focus, explore your topic in writing, conduct preliminary research, and discuss both the topic and the research with others.
Exploring Your Topic in Writing
“How am I supposed to narrow my topic when I haven’t even begun researching yet?” In fact, you may already know more than you realize. Review your list and identify your top two or three topics. Set aside some time to explore each one through freewriting. (For more information about freewriting, see Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” .) Simply taking the time to focus on your topic may yield fresh angles.
Jorge knew that he was especially interested in the topic of diet fads, but he also knew that it was much too broad for his assignment. He used freewriting to explore his thoughts so he could narrow his topic. Read Jorge’s ideas.
Conducting Preliminary Research
Another way writers may focus a topic is to conduct preliminary research . Like freewriting, exploratory reading can help you identify interesting angles. Surfing the web and browsing through newspaper and magazine articles are good ways to start. Find out what people are saying about your topic on blogs and online discussion groups. Discussing your topic with others can also inspire you. Talk about your ideas with your classmates, your friends, or your instructor.
Jorge’s freewriting exercise helped him realize that the assigned topic of health and the media intersected with a few of his interests—diet, nutrition, and obesity. Preliminary online research and discussions with his classmates strengthened his impression that many people are confused or misled by media coverage of these subjects.
Jorge decided to focus his paper on a topic that had garnered a great deal of media attention—low-carbohydrate diets. He wanted to find out whether low-carbohydrate diets were as effective as their proponents claimed.
Writing at Work
At work, you may need to research a topic quickly to find general information. This information can be useful in understanding trends in a given industry or generating competition. For example, a company may research a competitor’s prices and use the information when pricing their own product. You may find it useful to skim a variety of reliable sources and take notes on your findings.
The reliability of online sources varies greatly. In this exploratory phase of your research, you do not need to evaluate sources as closely as you will later. However, use common sense as you refine your paper topic. If you read a fascinating blog comment that gives you a new idea for your paper, be sure to check out other, more reliable sources as well to make sure the idea is worth pursuing.
Review the list of topics you created in Note 11.18 “Exercise 1” and identify two or three topics you would like to explore further. For each of these topics, spend five to ten minutes writing about the topic without stopping. Then review your writing to identify possible areas of focus.
Set aside time to conduct preliminary research about your potential topics. Then choose a topic to pursue for your research paper.
Collaboration
Please share your topic list with a classmate. Select one or two topics on his or her list that you would like to learn more about and return it to him or her. Discuss why you found the topics interesting, and learn which of your topics your classmate selected and why.
A Plan for Research
Your freewriting and preliminary research have helped you choose a focused, manageable topic for your research paper. To work with your topic successfully, you will need to determine what exactly you want to learn about it—and later, what you want to say about it. Before you begin conducting in-depth research, you will further define your focus by developing a research question , a working thesis, and a research proposal.
Formulating a Research Question
In forming a research question, you are setting a goal for your research. Your main research question should be substantial enough to form the guiding principle of your paper—but focused enough to guide your research. A strong research question requires you not only to find information but also to put together different pieces of information, interpret and analyze them, and figure out what you think. As you consider potential research questions, ask yourself whether they would be too hard or too easy to answer.
To determine your research question, review the freewriting you completed earlier. Skim through books, articles, and websites and list the questions you have. (You may wish to use the 5WH strategy to help you formulate questions. See Chapter 8 “The Writing Process: How Do I Begin?” for more information about 5WH questions.) Include simple, factual questions and more complex questions that would require analysis and interpretation. Determine your main question—the primary focus of your paper—and several subquestions that you will need to research to answer your main question.
Here are the research questions Jorge will use to focus his research. Notice that his main research question has no obvious, straightforward answer. Jorge will need to research his subquestions, which address narrower topics, to answer his main question.
Using the topic you selected in Note 11.24 “Exercise 2” , write your main research question and at least four to five subquestions. Check that your main research question is appropriately complex for your assignment.
Constructing a Working ThesIs
A working thesis concisely states a writer’s initial answer to the main research question. It does not merely state a fact or present a subjective opinion. Instead, it expresses a debatable idea or claim that you hope to prove through additional research. Your working thesis is called a working thesis for a reason—it is subject to change. As you learn more about your topic, you may change your thinking in light of your research findings. Let your working thesis serve as a guide to your research, but do not be afraid to modify it based on what you learn.
Jorge began his research with a strong point of view based on his preliminary writing and research. Read his working thesis statement, which presents the point he will argue. Notice how it states Jorge’s tentative answer to his research question.
One way to determine your working thesis is to consider how you would complete sentences such as I believe or My opinion is . However, keep in mind that academic writing generally does not use first-person pronouns. These statements are useful starting points, but formal research papers use an objective voice.
Write a working thesis statement that presents your preliminary answer to the research question you wrote in Note 11.27 “Exercise 3” . Check that your working thesis statement presents an idea or claim that could be supported or refuted by evidence from research.
Creating a Research Proposal
A research proposal is a brief document—no more than one typed page—that summarizes the preliminary work you have completed. Your purpose in writing it is to formalize your plan for research and present it to your instructor for feedback. In your research proposal, you will present your main research question, related subquestions, and working thesis. You will also briefly discuss the value of researching this topic and indicate how you plan to gather information.
When Jorge began drafting his research proposal, he realized that he had already created most of the pieces he needed. However, he knew he also had to explain how his research would be relevant to other future health care professionals. In addition, he wanted to form a general plan for doing the research and identifying potentially useful sources. Read Jorge’s research proposal.

Before you begin a new project at work, you may have to develop a project summary document that states the purpose of the project, explains why it would be a wise use of company resources, and briefly outlines the steps involved in completing the project. This type of document is similar to a research proposal. Both documents define and limit a project, explain its value, discuss how to proceed, and identify what resources you will use.
Writing Your Own Research Proposal
Now you may write your own research proposal, if you have not done so already. Follow the guidelines provided in this lesson.
Key Takeaways
- Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis.
- A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the assignment.
- Defining and narrowing a topic helps writers conduct focused, in-depth research.
- Writers conduct preliminary research to identify possible topics and research questions and to develop a working thesis.
- A good research question interests readers, is neither too broad nor too narrow, and has no obvious answer.
- A good working thesis expresses a debatable idea or claim that can be supported with evidence from research.
- Writers create a research proposal to present their topic, main research question, subquestions, and working thesis to an instructor for approval or feedback.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

How to Write a Research Proposal: (with Examples & Templates)

Table of Contents
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers’ plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed research that you intend to undertake. It provides readers with a snapshot of your project by describing what you will investigate, why it is needed, and how you will conduct the research.
Your research proposal should aim to explain to the readers why your research is relevant and original, that you understand the context and current scenario in the field, have the appropriate resources to conduct the research, and that the research is feasible given the usual constraints.
This article will describe in detail the purpose and typical structure of a research proposal , along with examples and templates to help you ace this step in your research journey.
What is a Research Proposal ?
A research proposal¹ ,² can be defined as a formal report that describes your proposed research, its objectives, methodology, implications, and other important details. Research proposals are the framework of your research and are used to obtain approvals or grants to conduct the study from various committees or organizations. Consequently, research proposals should convince readers of your study’s credibility, accuracy, achievability, practicality, and reproducibility.
With research proposals , researchers usually aim to persuade the readers, funding agencies, educational institutions, and supervisors to approve the proposal. To achieve this, the report should be well structured with the objectives written in clear, understandable language devoid of jargon. A well-organized research proposal conveys to the readers or evaluators that the writer has thought out the research plan meticulously and has the resources to ensure timely completion.
Purpose of Research Proposals
A research proposal is a sales pitch and therefore should be detailed enough to convince your readers, who could be supervisors, ethics committees, universities, etc., that what you’re proposing has merit and is feasible . Research proposals can help students discuss their dissertation with their faculty or fulfill course requirements and also help researchers obtain funding. A well-structured proposal instills confidence among readers about your ability to conduct and complete the study as proposed.
Research proposals can be written for several reasons:³
- To describe the importance of research in the specific topic
- Address any potential challenges you may encounter
- Showcase knowledge in the field and your ability to conduct a study
- Apply for a role at a research institute
- Convince a research supervisor or university that your research can satisfy the requirements of a degree program
- Highlight the importance of your research to organizations that may sponsor your project
- Identify implications of your project and how it can benefit the audience
What Goes in a Research Proposal?
Research proposals should aim to answer the three basic questions—what, why, and how.
The What question should be answered by describing the specific subject being researched. It should typically include the objectives, the cohort details, and the location or setting.
The Why question should be answered by describing the existing scenario of the subject, listing unanswered questions, identifying gaps in the existing research, and describing how your study can address these gaps, along with the implications and significance.
The How question should be answered by describing the proposed research methodology, data analysis tools expected to be used, and other details to describe your proposed methodology.
Research Proposal Example
Here is a research proposal sample template (with examples) from the University of Rochester Medical Center. 4 The sections in all research proposals are essentially the same although different terminology and other specific sections may be used depending on the subject.

Structure of a Research Proposal
If you want to know how to make a research proposal impactful, include the following components:¹
1. Introduction
This section provides a background of the study, including the research topic, what is already known about it and the gaps, and the significance of the proposed research.
2. Literature review
This section contains descriptions of all the previous relevant studies pertaining to the research topic. Every study cited should be described in a few sentences, starting with the general studies to the more specific ones. This section builds on the understanding gained by readers in the Introduction section and supports it by citing relevant prior literature, indicating to readers that you have thoroughly researched your subject.
3. Objectives
Once the background and gaps in the research topic have been established, authors must now state the aims of the research clearly. Hypotheses should be mentioned here. This section further helps readers understand what your study’s specific goals are.
4. Research design and methodology
Here, authors should clearly describe the methods they intend to use to achieve their proposed objectives. Important components of this section include the population and sample size, data collection and analysis methods and duration, statistical analysis software, measures to avoid bias (randomization, blinding), etc.
5. Ethical considerations
This refers to the protection of participants’ rights, such as the right to privacy, right to confidentiality, etc. Researchers need to obtain informed consent and institutional review approval by the required authorities and mention this clearly for transparency.
6. Budget/funding
Researchers should prepare their budget and include all expected expenditures. An additional allowance for contingencies such as delays should also be factored in.
7. Appendices
This section typically includes information that supports the research proposal and may include informed consent forms, questionnaires, participant information, measurement tools, etc.
8. Citations

Important Tips for Writing a Research Proposal
Writing a research proposal begins much before the actual task of writing. Planning the research proposal structure and content is an important stage, which if done efficiently, can help you seamlessly transition into the writing stage. 3,5
The Planning Stage
- Manage your time efficiently. Plan to have the draft version ready at least two weeks before your deadline and the final version at least two to three days before the deadline.
- What is the primary objective of your research?
- Will your research address any existing gap?
- What is the impact of your proposed research?
- Do people outside your field find your research applicable in other areas?
- If your research is unsuccessful, would there still be other useful research outcomes?
The Writing Stage
- Create an outline with main section headings that are typically used.
- Focus only on writing and getting your points across without worrying about the format of the research proposal , grammar, punctuation, etc. These can be fixed during the subsequent passes. Add details to each section heading you created in the beginning.
- Ensure your sentences are concise and use plain language. A research proposal usually contains about 2,000 to 4,000 words or four to seven pages.
- Don’t use too many technical terms and abbreviations assuming that the readers would know them. Define the abbreviations and technical terms.
- Ensure that the entire content is readable. Avoid using long paragraphs because they affect the continuity in reading. Break them into shorter paragraphs and introduce some white space for readability.
- Focus on only the major research issues and cite sources accordingly. Don’t include generic information or their sources in the literature review.
- Proofread your final document to ensure there are no grammatical errors so readers can enjoy a seamless, uninterrupted read.
- Use academic, scholarly language because it brings formality into a document.
- Ensure that your title is created using the keywords in the document and is neither too long and specific nor too short and general.
- Cite all sources appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
- Make sure that you follow guidelines, if provided. This includes rules as simple as using a specific font or a hyphen or en dash between numerical ranges.
- Ensure that you’ve answered all questions requested by the evaluating authority.
Key Takeaways
Here’s a summary of the main points about research proposals discussed in the previous sections:
- A research proposal is a document that outlines the details of a proposed study and is created by researchers to submit to evaluators who could be research institutions, universities, faculty, etc.
- Research proposals are usually about 2,000-4,000 words long, but this depends on the evaluating authority’s guidelines.
- A good research proposal ensures that you’ve done your background research and assessed the feasibility of the research.
- Research proposals have the following main sections—introduction, literature review, objectives, methodology, ethical considerations, and budget.

Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. How is a research proposal evaluated?
A1. In general, most evaluators, including universities, broadly use the following criteria to evaluate research proposals . 6
- Significance —Does the research address any important subject or issue, which may or may not be specific to the evaluator or university?
- Content and design —Is the proposed methodology appropriate to answer the research question? Are the objectives clear and well aligned with the proposed methodology?
- Sample size and selection —Is the target population or cohort size clearly mentioned? Is the sampling process used to select participants randomized, appropriate, and free of bias?
- Timing —Are the proposed data collection dates mentioned clearly? Is the project feasible given the specified resources and timeline?
- Data management and dissemination —Who will have access to the data? What is the plan for data analysis?
Q2. What is the difference between the Introduction and Literature Review sections in a research proposal ?
A2. The Introduction or Background section in a research proposal sets the context of the study by describing the current scenario of the subject and identifying the gaps and need for the research. A Literature Review, on the other hand, provides references to all prior relevant literature to help corroborate the gaps identified and the research need.
Q3. How long should a research proposal be?
A3. Research proposal lengths vary with the evaluating authority like universities or committees and also the subject. Here’s a table that lists the typical research proposal lengths for a few universities.
| Arts programs | 1,000-1,500 | |
| University of Birmingham | Law School programs | 2,500 |
| PhD | 2,500 | |
| 2,000 | ||
| Research degrees | 2,000-3,500 |
Q4. What are the common mistakes to avoid in a research proposal ?
A4. Here are a few common mistakes that you must avoid while writing a research proposal . 7
- No clear objectives: Objectives should be clear, specific, and measurable for the easy understanding among readers.
- Incomplete or unconvincing background research: Background research usually includes a review of the current scenario of the particular industry and also a review of the previous literature on the subject. This helps readers understand your reasons for undertaking this research because you identified gaps in the existing research.
- Overlooking project feasibility: The project scope and estimates should be realistic considering the resources and time available.
- Neglecting the impact and significance of the study: In a research proposal , readers and evaluators look for the implications or significance of your research and how it contributes to the existing research. This information should always be included.
- Unstructured format of a research proposal : A well-structured document gives confidence to evaluators that you have read the guidelines carefully and are well organized in your approach, consequently affirming that you will be able to undertake the research as mentioned in your proposal.
- Ineffective writing style: The language used should be formal and grammatically correct. If required, editors could be consulted, including AI-based tools such as Paperpal , to refine the research proposal structure and language.
Thus, a research proposal is an essential document that can help you promote your research and secure funds and grants for conducting your research. Consequently, it should be well written in clear language and include all essential details to convince the evaluators of your ability to conduct the research as proposed.
This article has described all the important components of a research proposal and has also provided tips to improve your writing style. We hope all these tips will help you write a well-structured research proposal to ensure receipt of grants or any other purpose.
References
- Sudheesh K, Duggappa DR, Nethra SS. How to write a research proposal? Indian J Anaesth. 2016;60(9):631-634. Accessed July 15, 2024. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5037942/
- Writing research proposals. Harvard College Office of Undergraduate Research and Fellowships. Harvard University. Accessed July 14, 2024. https://uraf.harvard.edu/apply-opportunities/app-components/essays/research-proposals
- What is a research proposal? Plus how to write one. Indeed website. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/research-proposal
- Research proposal template. University of Rochester Medical Center. Accessed July 16, 2024. https://www.urmc.rochester.edu/MediaLibraries/URMCMedia/pediatrics/research/documents/Research-proposal-Template.pdf
- Tips for successful proposal writing. Johns Hopkins University. Accessed July 17, 2024. https://research.jhu.edu/wp-content/uploads/2018/09/Tips-for-Successful-Proposal-Writing.pdf
- Formal review of research proposals. Cornell University. Accessed July 18, 2024. https://irp.dpb.cornell.edu/surveys/survey-assessment-review-group/research-proposals
- 7 Mistakes you must avoid in your research proposal. Aveksana (via LinkedIn). Accessed July 17, 2024. https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/7-mistakes-you-must-avoid-your-research-proposal-aveksana-cmtwf/
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
How to write a phd research proposal.
- What are the Benefits of Generative AI for Academic Writing?
- How to Avoid Plagiarism When Using Generative AI Tools
- What is Hedging in Academic Writing?
How to Write Your Research Paper in APA Format
The future of academia: how ai tools are changing the way we do research, you may also like, dissertation printing and binding | types & comparison , what is a dissertation preface definition and examples , how to write your research paper in apa..., how to choose a dissertation topic, how to write an academic paragraph (step-by-step guide), maintaining academic integrity with paperpal’s generative ai writing..., research funding basics: what should a grant proposal..., how to write an abstract in research papers..., how to write dissertation acknowledgements.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
The goal of a research proposal is twofold: to present and justify the need to study a research problem and to present the practical ways in which the proposed study should be conducted. The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews. They must provide persuasive evidence that a need exists for the proposed study. In addition to providing a rationale, a proposal describes detailed methodology for conducting the research consistent with requirements of the professional or academic field and a statement on anticipated outcomes and benefits derived from the study's completion.
Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005.
How to Approach Writing a Research Proposal
Your professor may assign the task of writing a research proposal for the following reasons:
- Develop your skills in thinking about and designing a comprehensive research study;
- Learn how to conduct a comprehensive review of the literature to determine that the research problem has not been adequately addressed or has been answered ineffectively and, in so doing, become better at locating pertinent scholarship related to your topic;
- Improve your general research and writing skills;
- Practice identifying the logical steps that must be taken to accomplish one's research goals;
- Critically review, examine, and consider the use of different methods for gathering and analyzing data related to the research problem; and,
- Nurture a sense of inquisitiveness within yourself and to help see yourself as an active participant in the process of conducting scholarly research.
A proposal should contain all the key elements involved in designing a completed research study, with sufficient information that allows readers to assess the validity and usefulness of your proposed study. The only elements missing from a research proposal are the findings of the study and your analysis of those findings. Finally, an effective proposal is judged on the quality of your writing and, therefore, it is important that your proposal is coherent, clear, and compelling.
Regardless of the research problem you are investigating and the methodology you choose, all research proposals must address the following questions:
- What do you plan to accomplish? Be clear and succinct in defining the research problem and what it is you are proposing to investigate.
- Why do you want to do the research? In addition to detailing your research design, you also must conduct a thorough review of the literature and provide convincing evidence that it is a topic worthy of in-depth study. A successful research proposal must answer the "So What?" question.
- How are you going to conduct the research? Be sure that what you propose is doable. If you're having difficulty formulating a research problem to propose investigating, go here for strategies in developing a problem to study.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Failure to be concise . A research proposal must be focused and not be "all over the map" or diverge into unrelated tangents without a clear sense of purpose.
- Failure to cite landmark works in your literature review . Proposals should be grounded in foundational research that lays a foundation for understanding the development and scope of the the topic and its relevance.
- Failure to delimit the contextual scope of your research [e.g., time, place, people, etc.]. As with any research paper, your proposed study must inform the reader how and in what ways the study will frame the problem.
- Failure to develop a coherent and persuasive argument for the proposed research . This is critical. In many workplace settings, the research proposal is a formal document intended to argue for why a study should be funded.
- Sloppy or imprecise writing, or poor grammar . Although a research proposal does not represent a completed research study, there is still an expectation that it is well-written and follows the style and rules of good academic writing.
- Too much detail on minor issues, but not enough detail on major issues . Your proposal should focus on only a few key research questions in order to support the argument that the research needs to be conducted. Minor issues, even if valid, can be mentioned but they should not dominate the overall narrative.
Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Sanford, Keith. Information for Students: Writing a Research Proposal. Baylor University; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences, Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Structure and Writing Style
Beginning the Proposal Process
As with writing most college-level academic papers, research proposals are generally organized the same way throughout most social science disciplines. The text of proposals generally vary in length between ten and thirty-five pages, followed by the list of references. However, before you begin, read the assignment carefully and, if anything seems unclear, ask your professor whether there are any specific requirements for organizing and writing the proposal.
A good place to begin is to ask yourself a series of questions:
- What do I want to study?
- Why is the topic important?
- How is it significant within the subject areas covered in my class?
- What problems will it help solve?
- How does it build upon [and hopefully go beyond] research already conducted on the topic?
- What exactly should I plan to do, and can I get it done in the time available?
In general, a compelling research proposal should document your knowledge of the topic and demonstrate your enthusiasm for conducting the study. Approach it with the intention of leaving your readers feeling like, "Wow, that's an exciting idea and I can’t wait to see how it turns out!"
Most proposals should include the following sections:
I. Introduction
In the real world of higher education, a research proposal is most often written by scholars seeking grant funding for a research project or it's the first step in getting approval to write a doctoral dissertation. Even if this is just a course assignment, treat your introduction as the initial pitch of an idea based on a thorough examination of the significance of a research problem. After reading the introduction, your readers should not only have an understanding of what you want to do, but they should also be able to gain a sense of your passion for the topic and to be excited about the study's possible outcomes. Note that most proposals do not include an abstract [summary] before the introduction.
Think about your introduction as a narrative written in two to four paragraphs that succinctly answers the following four questions :
- What is the central research problem?
- What is the topic of study related to that research problem?
- What methods should be used to analyze the research problem?
- Answer the "So What?" question by explaining why this is important research, what is its significance, and why should someone reading the proposal care about the outcomes of the proposed study?
II. Background and Significance
This is where you explain the scope and context of your proposal and describe in detail why it's important. It can be melded into your introduction or you can create a separate section to help with the organization and narrative flow of your proposal. Approach writing this section with the thought that you can’t assume your readers will know as much about the research problem as you do. Note that this section is not an essay going over everything you have learned about the topic; instead, you must choose what is most relevant in explaining the aims of your research.
To that end, while there are no prescribed rules for establishing the significance of your proposed study, you should attempt to address some or all of the following:
- State the research problem and give a more detailed explanation about the purpose of the study than what you stated in the introduction. This is particularly important if the problem is complex or multifaceted .
- Present the rationale of your proposed study and clearly indicate why it is worth doing; be sure to answer the "So What? question [i.e., why should anyone care?].
- Describe the major issues or problems examined by your research. This can be in the form of questions to be addressed. Be sure to note how your proposed study builds on previous assumptions about the research problem.
- Explain the methods you plan to use for conducting your research. Clearly identify the key sources you intend to use and explain how they will contribute to your analysis of the topic.
- Describe the boundaries of your proposed research in order to provide a clear focus. Where appropriate, state not only what you plan to study, but what aspects of the research problem will be excluded from the study.
- If necessary, provide definitions of key concepts, theories, or terms.
III. Literature Review
Connected to the background and significance of your study is a section of your proposal devoted to a more deliberate review and synthesis of prior studies related to the research problem under investigation . The purpose here is to place your project within the larger whole of what is currently being explored, while at the same time, demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. Think about what questions other researchers have asked, what methodological approaches they have used, and what is your understanding of their findings and, when stated, their recommendations. Also pay attention to any suggestions for further research.
Since a literature review is information dense, it is crucial that this section is intelligently structured to enable a reader to grasp the key arguments underpinning your proposed study in relation to the arguments put forth by other researchers. A good strategy is to break the literature into "conceptual categories" [themes] rather than systematically or chronologically describing groups of materials one at a time. Note that conceptual categories generally reveal themselves after you have read most of the pertinent literature on your topic so adding new categories is an on-going process of discovery as you review more studies. How do you know you've covered the key conceptual categories underlying the research literature? Generally, you can have confidence that all of the significant conceptual categories have been identified if you start to see repetition in the conclusions or recommendations that are being made.
NOTE: Do not shy away from challenging the conclusions made in prior research as a basis for supporting the need for your proposal. Assess what you believe is missing and state how previous research has failed to adequately examine the issue that your study addresses. Highlighting the problematic conclusions strengthens your proposal. For more information on writing literature reviews, GO HERE .
To help frame your proposal's review of prior research, consider the "five C’s" of writing a literature review:
- Cite , so as to keep the primary focus on the literature pertinent to your research problem.
- Compare the various arguments, theories, methodologies, and findings expressed in the literature: what do the authors agree on? Who applies similar approaches to analyzing the research problem?
- Contrast the various arguments, themes, methodologies, approaches, and controversies expressed in the literature: describe what are the major areas of disagreement, controversy, or debate among scholars?
- Critique the literature: Which arguments are more persuasive, and why? Which approaches, findings, and methodologies seem most reliable, valid, or appropriate, and why? Pay attention to the verbs you use to describe what an author says/does [e.g., asserts, demonstrates, argues, etc.].
- Connect the literature to your own area of research and investigation: how does your own work draw upon, depart from, synthesize, or add a new perspective to what has been said in the literature?
IV. Research Design and Methods
This section must be well-written and logically organized because you are not actually doing the research, yet, your reader must have confidence that you have a plan worth pursuing . The reader will never have a study outcome from which to evaluate whether your methodological choices were the correct ones. Thus, the objective here is to convince the reader that your overall research design and proposed methods of analysis will correctly address the problem and that the methods will provide the means to effectively interpret the potential results. Your design and methods should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
Describe the overall research design by building upon and drawing examples from your review of the literature. Consider not only methods that other researchers have used, but methods of data gathering that have not been used but perhaps could be. Be specific about the methodological approaches you plan to undertake to obtain information, the techniques you would use to analyze the data, and the tests of external validity to which you commit yourself [i.e., the trustworthiness by which you can generalize from your study to other people, places, events, and/or periods of time].
When describing the methods you will use, be sure to cover the following:
- Specify the research process you will undertake and the way you will interpret the results obtained in relation to the research problem. Don't just describe what you intend to achieve from applying the methods you choose, but state how you will spend your time while applying these methods [e.g., coding text from interviews to find statements about the need to change school curriculum; running a regression to determine if there is a relationship between campaign advertising on social media sites and election outcomes in Europe ].
- Keep in mind that the methodology is not just a list of tasks; it is a deliberate argument as to why techniques for gathering information add up to the best way to investigate the research problem. This is an important point because the mere listing of tasks to be performed does not demonstrate that, collectively, they effectively address the research problem. Be sure you clearly explain this.
- Anticipate and acknowledge any potential barriers and pitfalls in carrying out your research design and explain how you plan to address them. No method applied to research in the social and behavioral sciences is perfect, so you need to describe where you believe challenges may exist in obtaining data or accessing information. It's always better to acknowledge this than to have it brought up by your professor!
V. Preliminary Suppositions and Implications
Just because you don't have to actually conduct the study and analyze the results, doesn't mean you can skip talking about the analytical process and potential implications . The purpose of this section is to argue how and in what ways you believe your research will refine, revise, or extend existing knowledge in the subject area under investigation. Depending on the aims and objectives of your study, describe how the anticipated results will impact future scholarly research, theory, practice, forms of interventions, or policy making. Note that such discussions may have either substantive [a potential new policy], theoretical [a potential new understanding], or methodological [a potential new way of analyzing] significance. When thinking about the potential implications of your study, ask the following questions:
- What might the results mean in regards to challenging the theoretical framework and underlying assumptions that support the study?
- What suggestions for subsequent research could arise from the potential outcomes of the study?
- What will the results mean to practitioners in the natural settings of their workplace, organization, or community?
- Will the results influence programs, methods, and/or forms of intervention?
- How might the results contribute to the solution of social, economic, or other types of problems?
- Will the results influence policy decisions?
- In what way do individuals or groups benefit should your study be pursued?
- What will be improved or changed as a result of the proposed research?
- How will the results of the study be implemented and what innovations or transformative insights could emerge from the process of implementation?
NOTE: This section should not delve into idle speculation, opinion, or be formulated on the basis of unclear evidence . The purpose is to reflect upon gaps or understudied areas of the current literature and describe how your proposed research contributes to a new understanding of the research problem should the study be implemented as designed.
ANOTHER NOTE : This section is also where you describe any potential limitations to your proposed study. While it is impossible to highlight all potential limitations because the study has yet to be conducted, you still must tell the reader where and in what form impediments may arise and how you plan to address them.
VI. Conclusion
The conclusion reiterates the importance or significance of your proposal and provides a brief summary of the entire study . This section should be only one or two paragraphs long, emphasizing why the research problem is worth investigating, why your research study is unique, and how it should advance existing knowledge.
Someone reading this section should come away with an understanding of:
- Why the study should be done;
- The specific purpose of the study and the research questions it attempts to answer;
- The decision for why the research design and methods used where chosen over other options;
- The potential implications emerging from your proposed study of the research problem; and
- A sense of how your study fits within the broader scholarship about the research problem.
VII. Citations
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used . In a standard research proposal, this section can take two forms, so consult with your professor about which one is preferred.
- References -- a list of only the sources you actually used in creating your proposal.
- Bibliography -- a list of everything you used in creating your proposal, along with additional citations to any key sources relevant to understanding the research problem.
In either case, this section should testify to the fact that you did enough preparatory work to ensure the project will complement and not just duplicate the efforts of other researchers. It demonstrates to the reader that you have a thorough understanding of prior research on the topic.
Most proposal formats have you start a new page and use the heading "References" or "Bibliography" centered at the top of the page. Cited works should always use a standard format that follows the writing style advised by the discipline of your course [e.g., education=APA; history=Chicago] or that is preferred by your professor. This section normally does not count towards the total page length of your research proposal.
Develop a Research Proposal: Writing the Proposal. Office of Library Information Services. Baltimore County Public Schools; Heath, M. Teresa Pereira and Caroline Tynan. “Crafting a Research Proposal.” The Marketing Review 10 (Summer 2010): 147-168; Jones, Mark. “Writing a Research Proposal.” In MasterClass in Geography Education: Transforming Teaching and Learning . Graham Butt, editor. (New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2015), pp. 113-127; Juni, Muhamad Hanafiah. “Writing a Research Proposal.” International Journal of Public Health and Clinical Sciences 1 (September/October 2014): 229-240; Krathwohl, David R. How to Prepare a Dissertation Proposal: Suggestions for Students in Education and the Social and Behavioral Sciences . Syracuse, NY: Syracuse University Press, 2005; Procter, Margaret. The Academic Proposal. The Lab Report. University College Writing Centre. University of Toronto; Punch, Keith and Wayne McGowan. "Developing and Writing a Research Proposal." In From Postgraduate to Social Scientist: A Guide to Key Skills . Nigel Gilbert, ed. (Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2006), 59-81; Wong, Paul T. P. How to Write a Research Proposal. International Network on Personal Meaning. Trinity Western University; Writing Academic Proposals: Conferences , Articles, and Books. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Writing a Research Proposal. University Library. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
- << Previous: Writing a Reflective Paper
- Next: Generative AI and Writing >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Business How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
How to Write a Research Proposal: A Step-by-Step
Written by: Danesh Ramuthi Nov 29, 2023

A research proposal is a structured outline for a planned study on a specific topic. It serves as a roadmap, guiding researchers through the process of converting their research idea into a feasible project.
The aim of a research proposal is multifold: it articulates the research problem, establishes a theoretical framework, outlines the research methodology and highlights the potential significance of the study. Importantly, it’s a critical tool for scholars seeking grant funding or approval for their research projects.
Crafting a good research proposal requires not only understanding your research topic and methodological approaches but also the ability to present your ideas clearly and persuasively. Explore Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates to begin your journey in writing a compelling research proposal.
What to include in a research proposal?
In a research proposal, include a clear statement of your research question or problem, along with an explanation of its significance. This should be followed by a literature review that situates your proposed study within the context of existing research.
Your proposal should also outline the research methodology, detailing how you plan to conduct your study, including data collection and analysis methods.
Additionally, include a theoretical framework that guides your research approach, a timeline or research schedule, and a budget if applicable. It’s important to also address the anticipated outcomes and potential implications of your study. A well-structured research proposal will clearly communicate your research objectives, methods and significance to the readers.

How to format a research proposal?
Formatting a research proposal involves adhering to a structured outline to ensure clarity and coherence. While specific requirements may vary, a standard research proposal typically includes the following elements:
- Title Page: Must include the title of your research proposal, your name and affiliations. The title should be concise and descriptive of your proposed research.
- Abstract: A brief summary of your proposal, usually not exceeding 250 words. It should highlight the research question, methodology and the potential impact of the study.
- Introduction: Introduces your research question or problem, explains its significance, and states the objectives of your study.
- Literature review: Here, you contextualize your research within existing scholarship, demonstrating your knowledge of the field and how your research will contribute to it.
- Methodology: Outline your research methods, including how you will collect and analyze data. This section should be detailed enough to show the feasibility and thoughtfulness of your approach.
- Timeline: Provide an estimated schedule for your research, breaking down the process into stages with a realistic timeline for each.
- Budget (if applicable): If your research requires funding, include a detailed budget outlining expected cost.
- References/Bibliography: List all sources referenced in your proposal in a consistent citation style.

How to write a research proposal in 11 steps?
Writing a research proposal template in structured steps ensures a comprehensive and coherent presentation of your research project. Let’s look at the explanation for each of the steps here:
Step 1: Title and Abstract Step 2: Introduction Step 3: Research objectives Step 4: Literature review Step 5: Methodology Step 6: Timeline Step 7: Resources Step 8: Ethical considerations Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance Step 10: References Step 11: Appendices
Step 1: title and abstract.
Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes. The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Step 2: Introduction
In this section, introduce the topic of your research, emphasizing its significance and relevance to the field. Articulate the research problem or question in clear terms and provide background context, which should include an overview of previous research in the field.
Step 3: Research objectives
Here, you’ll need to outline specific, clear and achievable objectives that align with your research problem. These objectives should be well-defined, focused and measurable, serving as the guiding pillars for your study. They help in establishing what you intend to accomplish through your research and provide a clear direction for your investigation.
Step 4: Literature review
In this part, conduct a thorough review of existing literature related to your research topic. This involves a detailed summary of key findings and major contributions from previous research. Identify existing gaps in the literature and articulate how your research aims to fill these gaps. The literature review not only shows your grasp of the subject matter but also how your research will contribute new insights or perspectives to the field.
Step 5: Methodology
Describe the design of your research and the methodologies you will employ. This should include detailed information on data collection methods, instruments to be used and analysis techniques. Justify the appropriateness of these methods for your research.
Step 6: Timeline
Construct a detailed timeline that maps out the major milestones and activities of your research project. Break the entire research process into smaller, manageable tasks and assign realistic time frames to each. This timeline should cover everything from the initial research phase to the final submission, including periods for data collection, analysis and report writing.
It helps in ensuring your project stays on track and demonstrates to reviewers that you have a well-thought-out plan for completing your research efficiently.
Step 7: Resources
Identify all the resources that will be required for your research, such as specific databases, laboratory equipment, software or funding. Provide details on how these resources will be accessed or acquired.
If your research requires funding, explain how it will be utilized effectively to support various aspects of the project.
Step 8: Ethical considerations
Address any ethical issues that may arise during your research. This is particularly important for research involving human subjects. Describe the measures you will take to ensure ethical standards are maintained, such as obtaining informed consent, ensuring participant privacy, and adhering to data protection regulations.
Here, in this section you should reassure reviewers that you are committed to conducting your research responsibly and ethically.
Step 9: Expected outcomes and significance
Articulate the expected outcomes or results of your research. Explain the potential impact and significance of these outcomes, whether in advancing academic knowledge, influencing policy or addressing specific societal or practical issues.
Step 10: References
Compile a comprehensive list of all the references cited in your proposal. Adhere to a consistent citation style (like APA or MLA) throughout your document. The reference section not only gives credit to the original authors of your sourced information but also strengthens the credibility of your proposal.
Step 11: Appendices
Include additional supporting materials that are pertinent to your research proposal. This can be survey questionnaires, interview guides, detailed data analysis plans or any supplementary information that supports the main text.
Appendices provide further depth to your proposal, showcasing the thoroughness of your preparation.

Research proposal FAQs
1. how long should a research proposal be.
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the requirements of the academic institution, funding body or specific guidelines provided. Generally, research proposals range from 500 to 1500 words or about one to a few pages long. It’s important to provide enough detail to clearly convey your research idea, objectives and methodology, while being concise. Always check
2. Why is the research plan pivotal to a research project?
The research plan is pivotal to a research project because it acts as a blueprint, guiding every phase of the study. It outlines the objectives, methodology, timeline and expected outcomes, providing a structured approach and ensuring that the research is systematically conducted.
A well-crafted plan helps in identifying potential challenges, allocating resources efficiently and maintaining focus on the research goals. It is also essential for communicating the project’s feasibility and importance to stakeholders, such as funding bodies or academic supervisors.

Mastering how to write a research proposal is an essential skill for any scholar, whether in social and behavioral sciences, academic writing or any field requiring scholarly research. From this article, you have learned key components, from the literature review to the research design, helping you develop a persuasive and well-structured proposal.
Remember, a good research proposal not only highlights your proposed research and methodology but also demonstrates its relevance and potential impact.
For additional support, consider utilizing Venngage’s Proposal Maker and Research Proposals Templates , valuable tools in crafting a compelling proposal that stands out.
Whether it’s for grant funding, a research paper or a dissertation proposal, these resources can assist in transforming your research idea into a successful submission.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker
How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Short on time? Get an AI generated summary of this article instead
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project .
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement , devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes , demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:
Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Once you have outlined your goals, objectives, steps, and tasks, it’s time to drill down on selecting research methods . You’ll want to leverage specific research strategies and processes. When you know what methods will help you reach your goals, you and your teams will have direction to perform and execute your assigned tasks.
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews : this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies : this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting : participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups : use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies : ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys : get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing : tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing : ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project . Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty . But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 22 August 2024
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 August 2024
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Design for Business
- Most Recent
- Presentations
- Infographics
- Data Visualizations
- Forms and Surveys
- Video & Animation
- Case Studies
- Digital Marketing
- Design Inspiration
- Visual Thinking
- Product Updates
- Visme Webinars
- Artificial Intelligence
8 Research Proposal Examples & Template to Use

Written by: Raja Mandal

So you have a groundbreaking research idea you've spent months or even years developing, and now you're ready to take the next step.
How do you get funding for your research, and how should you approach potential funders? The answer is to create a convincing research proposal.
Unfortunately, most research proposals often get rejected. According to the European Research Council, the success rate for repeat proposal applications was only 14.8% in 2023 .
Pitching a novel research concept isn’t enough. To increase your chances of securing funding, your research proposal must check the right boxes in terms of clarity, feasibility, aesthetic appeal and other factors.
If you’re looking for inspiration to create a persuasive and feasible proposal, you’re in the right place. In this article, we have compiled a list of research proposal examples to help you create yours.
These examples will help you understand how to organize your proposal, what information to include and how to present it in a way that encourages others to support your project.
Let's dive in!
Table of Contents
What is a research proposal, what to include in a research proposal, 8 research proposal examples & templates, research proposal faqs.
- A research proposal is a document that outlines your proposed research project, explaining what you plan to study, why it's important and how you will conduct your research.
- A well-structured research proposal includes a title page, abstract and table of contents, introduction, literature review, research design and methodology, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, timeline and budget.
- Visme's research proposal examples and templates offer a great starting point for creating engaging and well-structured proposals.
- Choose a template from Visme's research proposal examples and customize it to fit your needs.
- With Visme’s proposal maker , you can create a research proposal that stands out. Access a drag-and-drop editor and advanced features like AI tools , collaboration features, brand wizard and more.
A research proposal is a structured document that outlines the core idea of your research, the methods you intend to use, the required resources and the expected results.
Think of it as a sales pitch for your research. It answers some big questions: What are you planning to explore? Why is it important to conduct the research? What are your research objectives and the methods you’ll use to achieve them? What are the potential outcomes or contributions of this research to the field?
A research proposal serves two primary purposes. First, it convinces funding bodies or academic committees to support your research project expected to bring new ideas and insights. Second, it provides a roadmap for your research journey, helping you stay focused, organized and on track.
Now, we'll discuss what to include in a research proposal. You'll learn about the important parts of a research proposal template and how they help present your research idea clearly.
Here’s an infographic that you can use to understand the elements of a research proposal quickly.

1. Title Page
Start your research proposal with a title page that clearly states your research. The title page is like a book cover, giving the first impression of your project. Therefore, you must ensure the design is engaging enough to attract your audience at first glance.
Include the following details on your title page:
- Title of your research
- Contact Details
- Name of the department or organization
- Date of submission

2. Abstract and Table of Contents
After the title page comes the abstract and the table of contents.
The abstract is a concise summary of your project that briefly outlines your research question, the reasons behind the study and the methods you intend to use. It is a quick way for readers to understand your proposal without reading the entire document.
The table of contents is a detailed list of the sections and subsections in your proposal, with page numbers. It helps readers navigate through your document and quickly locate different parts they're interested in.

3. Introduction
The introduction of your research proposal sets the tone for the rest of the document. It should grab the reader's attention and make them want to learn more. It's your chance to make a strong case for why your research is worth investigating and how it can fill a gap in current knowledge or solve a specific problem.
Make sure that your introduction covers the following:
- Background Information: Set the stage with a brief snapshot of existing research and why your topic is relevant.
- Research Problem: Identify the specific problem or knowledge gap that your study will address.
- Research Questions or Hypotheses: Present the central question or hypothesis that guides your research focus.
- Aims and Objectives: Outline your research's main goal and the steps you'll take to achieve it.
- Significance and Contribution: Explain how your research will add value to the field and what impact it could have.
4. Literature Review
A literature review is a list of the scholarly works you used to conduct your research. It helps you demonstrate your current knowledge about the topic.
Here's how this part works:
- Summary of Sources: Talk about the main ideas or findings from your research materials and explain how they connect to your research questions.
- Finding Gaps: Show where the current research falls short or doesn't give the full picture—this is where your research comes in!
- Key Theories: Tell the readers about any theories or ways of thinking that help shape your research.
- Learning from Methods: Discuss what previous researchers worked on and how their methods might guide your research.
- Recognizing Authors and Studies: Honor the pioneers whose work has had a major influence on your topic.
5. Research Design and Methodology
This section outlines your plan for answering your research question. It explains how you intend to gather and analyze information, providing a clear roadmap of the investigation process.
Here are the key components:
Population and Sample
Describe the entire group you're interested in (the population). This could be all teachers in a specific state or all social media platform users. After that, you will need to explain how you will choose a smaller group, known as a sample, to study directly. This sample should be selected to accurately represent the larger population you are interested in studying.
To choose the right sampling method, you need to assess your population properly. For instance, to obtain general insights, you can use random sampling to select individuals without bias. If the population consists of different categories, such as professionals and students, you can use stratified sampling to ensure that each category is represented in the sample.
Other popular sampling methods include systematic, convenience, purposive, cluster, and probability sampling techniques.
Research Approach
There are three main approaches for the research: qualitative (focusing on experiences and themes), quantitative (using numbers and statistics), or mixed methods (combining both). Your choice will depend on your research question and the kind of data you need.
Data Collection
This section details the specific methods you'll use to gather information. Will you distribute surveys online or in person? Conduct interviews? Perhaps you'll use existing data sets. Here, you'll also explain how you'll ensure the data collection process is reliable and ethical.
Data Analysis
Once you have collected your data, the next step is to analyze it to obtain meaningful insights. The method you choose depends on the available data type.
If you have quantitative data, you can employ statistical tests to analyze it. And if you're dealing with qualitative data, coding techniques can help you spot patterns and themes in your collected data.

6. Contribution to Knowledge
In this section, you need to explain how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge in your field. You should describe whether your study will fill a knowledge gap, challenge conventional ideas or beliefs or offer a fresh perspective on a topic.
Clearly outline how your work will advance your field of study and why this new knowledge is essential.
7. Research Schedule and Timeline
Create a timeline with important milestones, such as finishing your literature review, completing data collection and finalizing your analysis.
This shows that you've carefully considered the scope of your project and can manage your time effectively. Furthermore, account for possible delays and be prepared to adapt your schedule accordingly.
To create this timeline, consider using a visual tool like a Gantt chart or a simple spreadsheet. These tools will help you organize individual tasks, assign deadlines, and visualize the project's overall progress.
Choose a Gantt chart template from Visme's library and customize it to create your timeline quickly. Here's an example template:

The budget section is your opportunity to show them that you've carefully considered all necessary expenses and that your funding request is justified.
Here's how you can approach this part:
- Understand the Rules: Before making calculations, thoroughly review the funding agency's guidelines. Pay attention to what types of expenses are allowed or excluded and whether there are any budget caps.
- Personnel: Salaries and benefits for yourself, research assistants, or collaborators.
- Equipment: Specialized tools, software, or lab supplies.
- Travel: Transportation, lodging and meals if data collection requires travel.
- Dissemination: Costs for publishing results or presenting at conferences.
- Provide Justifications: Don't just list a cost. Briefly explain why each expense is crucial for completing your research.
- Be Thorough and Realistic: Research prices for specific items using quotes or online comparisons. Don't underestimate expenses, as this can raise troubles about the project's feasibility.
- Don't Forget Contingencies: Include a small buffer (around 5% of your total budget) for unexpected costs that might arise.

Using these research proposal examples and templates, you can create a winning proposal in no time. You will find templates for various topics and customize every aspect of them to make them your own.
Visme’s drag-and-drop editor, advanced features and a vast library of templates help organizations and individuals worldwide create engaging documents.
Here’s what a research student who uses Visme to create award-winning presentations has to say about the tool:
Chantelle Clarke
Research Student
Now, let’s dive into the research proposal examples.
1. Research Proposal Presentation Template

This research proposal presentation template is a powerful tool for presenting your research plan to stakeholders. The slides include specific sections to help you outline your research, including the research background, questions, objectives, methodology and expected results.
The slides create a coherent narrative, highlighting the importance and significance of your research. Overall, the template has a calming and professional blue color scheme with text that enables your audience to grasp the key points.
If you need help creating your presentation slides in a fraction of the time, check out Visme's AI presentation maker . Enter your requirements using text prompts, and the AI tool will generate a complete presentation with engaging visuals, text and clear structure. You can further customize the template completely to your needs.
2. Sales Research Proposal Template

Sales research gives you a deeper understanding of their target audience. It also helps you identify gaps in the market and develop effective sales strategies that drive revenue growth. With this research proposal template, you can secure funding for your next research project.
It features a sleek and professional grayscale color palette with a classic and modern vibe. The high-quality images in the template are strategically placed to reinforce the message without overwhelming the reader. Furthermore, the template includes a vertical bar graph that effectively represents budget allocations, enabling the reader to quickly grasp the information.
Use Visme's interactive elements and animations to add a dynamic layer to your research proposals. You can animate any object and add pop-ups or link pages for a more immersive experience. Use these functionalities to highlight key findings, demonstrate trends or guide readers through your proposal, making the content engaging and interactive.
3. General Funding Research Proposal Template

This proposal template is a great tool for securing funding for any type of research project. It begins with a captivating title page that grabs attention. The beautiful design elements and vector icons enhance the aesthetic and aid visual communication.
This template revolves around how a specific user group adopts cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. The goal is to assess awareness, gauge interest and understand key factors affecting cryptocurrency adoption.
The project methodology includes survey design, data collection, and market research. The expected impact is to enhance customer engagement and position the company as a customer-centric brand.
Do you need additional help crafting the perfect text for your proposal? Visme's AI writer can quickly generate content outlines, summaries and even entire sections. Just explain your requirements to the tool using a text prompt, and the tool will generate it for you.
4. Product Research Proposal Template

Creating a product that delights users begins with detailed product research. With this modern proposal template, you can secure buy-in and funding for your next research.
It starts with a background that explains why the research is important. Next, it highlights what the research is set to achieve, how the research will be conducted, how much it will cost, the timeline and the expected outcomes. With a striking color scheme combining black, yellow, and gray, the template grabs attention and maintains it until the last page.
What we love about this template is the smart use of visuals. You'll find a flowchart explaining the methodology, a bar graph for the budget, and a timeline for the project. But that’s just the tip of the iceberg regarding the visual elements you’ll find in Visme.
Visme offers data visualization tools with 30+ data widgets, such as radial gauges, population arrays, progress bars and more. These tools can help you turn complex data into engaging visuals for your research proposal or any other document.
For larger data sets, you can choose from 20+ types of charts and graphs , including bar graphs , bubble charts , Venn diagrams and more.
5. Tech Research Proposal Template

If you’re a tech researcher, we’ve got the perfect template for you. This research proposal example is about predictive analytics in e-commerce. However, you can customize it for any other type of research proposal.
It highlights the project's objectives, including the effectiveness of predictive analysis, the impact of product recommendations and supply chain optimization. The methods proposed for achieving these objectives involve A/B testing and data analysis, a comprehensive budget and a 12-month timeline for clear project planning.
The title page has a unique triptych-style layout that immediately catches the reader's attention. It has plenty of white space that enhances readability, allowing your audience to focus on the critical points.
Submitting to different funding agencies? You don’t have to manually make changes to your document. Visme's dynamic fields can help save time and eliminate repetitive data entry.
Create custom fields like project names, addresses, contact information and more. Any changes made to these fields will automatically populate throughout the document.
6. Marketing Research Proposal Template

Artificial intelligence (AI) is taking the world by storm and the marketing niche isn’t left out. With this eye-catching template, you can attract attention to your proposed marketing research project for an AI-driven platform.
The main goal of the research is to evaluate the platform's feasibility and marketing potential. To achieve this goal, the scope of work includes a comprehensive analysis of the market and competitors and pilot testing. The proposal also contains a budget overview that clearly outlines the allocation of funds, ensuring a well-planned and transparent approach.
Using Visme's Brand Design Tool , you can easily customize this template to suit your branding with just one click. Simply enter your URL into the brand wizard, and the tool will automatically extract your company logo, brand colors, and brand fonts . Once saved, you or your team members can apply the branding elements to any document. It's that simple!
7. Environmental Research Proposal Template

The environmental research proposal example focuses on carbon emissions, identifies their contributing factors, and suggests sustainable practices to address them. It uses an appropriate sample size and data collection techniques to gather and evaluate data and provide sustainable recommendations to reduce industrial carbon footprints and waste.
From a design standpoint, the green and white color combination matches the theme of nature and environmental friendliness. In addition to its aesthetic appeal, the proposal includes relevant images that support ecological advocacy, making it informative and visually aligned with its purpose.
A key feature of this template is its detailed breakdown of the project's timeline. It uses a Gantt chart to clearly present stages, milestones and deadlines.
Collaborate with your team members to customize these research proposal templates using Visme’s collaborative design features . These features allow you to leave feedback, draw annotations and even make live edits. Invite your teammates via email or a shareable link and allow them to work together on projects.
8. General Approval Research Proposal Template

This research proposal template is a total game-changer - you can use it for any research proposal and customize it however you want. It features a modern and refreshing color scheme that immediately makes it stand out, providing a contemporary look that can adapt to any project's needs.
The template's layout is thoughtfully designed with primary fields that users can easily personalize by changing text, adjusting colors, or swapping images. No matter the research topic, you can tailor the template to fit your specific needs.
Once you're done customizing your research proposal template on Visme, you can download, share and publish it in different ways. For offline usage, you may download the proposal in PDF, PNG, or JPG format. To share it online, you can use a private or public link or generate a code snippet that you can embed anywhere on the web.
Want to create other types of proposals? Here are 29 proposal templates that you can easily customize in Visme.
Q. What Are the Five Steps of Writing a Research Proposal?
Follow these steps to write a solid research proposal:
- Choose a topic within your field of study that can be explored and investigated.
- Research existing literature and studies to build a foundational understanding and prepare your research question.
- Outline your research proposal: introduction, literature review, proposed methodology, budget and timeline.
- Conduct more detailed studies to strengthen your proposition, refine your research question and justify your methodology.
- Follow your outline to write a clear and organized proposal, then review and edit for accuracy before submitting.
If you want to learn more about creating an expert research proposal , we highly recommend checking out our in-depth guide.
Q. How Long Is a Research Proposal?
Research proposals can range from 1,000 to 5,000 words. For smaller projects or when specific requirements aren't provided, aim for a concise and informative proposal that effectively outlines your research plan.
However, the ideal length depends on these factors:
- Projects with complex methodologies or multiple phases may require longer proposals to explain the scope and procedures in detail.
- Universities, academic institutions and funding agencies often have guidelines of a specific length. Always check their requirements beforehand.
- When writing a proposal, adjust the level of study based on the audience. Academic proposals may require comprehensive explanations, while business or non-profit proposals require a more streamlined approach.
Q. How Long Does It Take to Write a Research Proposal?
The time it takes to write a research proposal depends on a few factors:
- Complex research with extensive data collection or analysis will naturally take longer to plan and write about.
- If you're new to writing research proposals, expect to spend more time learning the format and best practices.
- If you've already conducted some research or a thorough literature review, the writing process might go faster.
- Funding applications often have strict deadlines that will dictate your timeline.
Set aside several weeks to a couple of months for researching, writing, and revising your proposal. Start early to avoid stress and produce your best work.
Q. What Not to Do for a Research Proposal?
There are several factors that can make a research proposal weak. Here are some of the most common errors that you should avoid while preparing your research proposal:
- Don’t choose a topic that’s too broad. Focus on a specific area you can thoroughly explore within your proposal’s limits.
- Don’t ignore the rules for formatting and submitting your proposal. Always adhere to the requirements set by your institution or funding body.
- Don’t forget to conduct a thorough literature review. It's crucial to show your grasp of existing research related to your topic.
- Don't be vague about your methods. Ensure they're clearly defined and suitable for answering your research question.
- Don't overlook errors in grammar, typos or structure. A well-proofread proposal reflects professionalism, so review it carefully before submitting it.
Craft Professional & Engaging Proposals with Visme
Writing a compelling research proposal takes effort, but with the right tools, the process becomes a breeze. Use the research proposal examples and templates in this article as a launching point to write your own proposal.
The best part? Visme provides easy-to-use tools with a vast collection of customizable templates, design elements and powerful features.
Whether you're a seasoned researcher or a student, Visme has the resources to help you create visually appealing and well-structured research proposals. In addition to research proposals, Visme helps you create many other document types, such as presentations , infographics , reports and more.
Ready to create your own research proposal? Check out Visme's proposal maker and start crafting professional and engaging proposals in minutes!
Create professional research proposals with Visme

Trusted by leading brands
Recommended content for you:

Create Stunning Content!
Design visual brand experiences for your business whether you are a seasoned designer or a total novice.
About the Author
Raja Antony Mandal is a Content Writer at Visme. He can quickly adapt to different writing styles, possess strong research skills, and know SEO fundamentals. Raja wants to share valuable information with his audience by telling captivating stories in his articles. He wants to travel and party a lot on the weekends, but his guitar, drum set, and volleyball court don’t let him.
Research Proposal: A step-by-step guide with template
Making sure your proposal is perfect will drastically improve your chances of landing a successful research position. Follow these steps.
There’s no doubt you have the most cutting-edge research idea to date, backed up by a solid methodology and a credible explanation proving its relevance! There are thousands of research ideas that could change the world with many new ideologies.
The truth is, none of this would matter without support. It can be daunting, challenging, and uncertain to secure funding for a research project. Even more so when it isn’t well-thought-out, outlined, and includes every detail.
An effective solution for presenting your project, or requesting funding, is to provide a research proposal to potential investors or financiers on your behalf.
It’s crucial to understand that making sure your proposal is perfect will drastically improve your chances of landing a successful research position. Your research proposal could result in the failure to study the research problem entirely if it is inadequately constructed or incomplete.
It is for this reason that we have created an excellent guide that covers everything you need to know about writing a research proposal, and includes helpful tips for presenting your proposal professionally and improving its likelihood of acceptance!
What Is a Research Proposal?

Generally, a research proposal is a well-crafted, formal document that provides a thorough explanation of what you plan to investigate. This includes a rationale for why it is worth investigating, as well as a method for investigating it.
Research proposal writing in the contemporary academic environment is a challenging undertaking given the constant shift in research methodology and a commitment to incorporating scientific breakthroughs.
An outline of the plan or roadmap for the study is the proposal, and once the proposal is complete, everything should be smooth sailing. It is still common for post-graduate evaluation panels and funding applications to submit substandard proposals.
By its very nature , the research proposal serves as a tool for convincing the supervisor, committee, or university that the proposed research fits within the scope of the program and is feasible when considering the time and resources available.
A research proposal should convince the person who is going to sanction your research, or put another way, you need to persuade them that your research idea is the best.
Obviously, if it does not convince them that it is reasonable and adequate, you will need to revise and submit it again. As a result, you will lose significant time, causing your research to be delayed or cut short, which is not good.
A good research proposal should have the following structure
A dissertation or thesis research proposal may take on a variety of forms depending on the university, but most generally a research proposal will include the following elements:
- Titles or title pages that give a description of the research
- Detailed explanation of the proposed research and its background
- Outline of the research project
- An overview of key research studies in the field
- Description the proposed research design (approach)
So, if you include all these elements, you will have a general outline. Let’s take a closer look at how to write them and what to include in each element so that the research proposal is as robust as the idea itself.
A step-by-step guide to writing a research proposal
#1 introduction.
Researchers who wish to obtain grant funding for a project often write a proposal when seeking funding for a research-based postgraduate degree program, or in order to obtain approval for completing a thesis or PhD. Even though this is only a brief introduction , we should be considering it the beginning of an insightful discussion about the significance of a topic that deserves attention.
Your readers should understand what you are trying to accomplish after they read your introduction. Additionally, they should be able to perceive your zeal for the subject matter and a genuine interest in the possible outcome of the research.
As your introduction, consider answering these questions in three to four paragraphs:
- In what way does the study address its primary issue?
- Does that subject matter fall under the domain of that field of study?
- In order to investigate that problem, what method should be used?
- What is the importance of this study?
- How does it impact academia and society overall?
- What are the potential implications of the proposed research for someone reviewing the proposal?
It is not necessary to include an abstract or summary for the introduction to most academic departments and funding sources. Nevertheless, you should confirm your institution’s requirements.
#2 Background and importance
An explanation of the rationale for a research proposal and its significance is provided in this section. It is preferable to separate this part from the introduction so that the narrative flows seamlessly.
This section should be approached by presuming readers are time-pressed but want a general overview of the whole study and the research question.
Please keep in mind that this isn’t an exhaustive essay that contains every detail of your proposed research, rather a concise document that will spark interest in your proposal.
While you should try to take into account the following factors when framing the significance of your proposed study, there are no rigid rules.
- Provide a detailed explanation of the purpose and problem of the study. Multidimensional or interdisciplinary research problems often require this.
- Outline the purpose of your proposed research and describe the advantages of carrying out the study.
- Outline the major issues or problems to be discussed. These might come in the form of questions or comments.
- Be sure to highlight how your research contributes to existing theories that relate to the problem of the study.
- Describe how your study will be conducted, including the source of data and the method of analysis.
- To provide a sense of direction for your study, define the scope of your proposal.
- Defining key concepts or terms, if necessary, is recommended.
The steps to a perfect research proposal all get more specific as we move forward to enhance the concept of the research. In this case, it will become important to make sure that your supervisor or your funder has a clear understanding of every aspect of your research study.
#3 Reviewing prior literature and studies
The aim of this paragraph is to establish the context and significance of your study, including a review of the current literature pertinent to it.
This part aims to properly situate your proposed study within the bigger scheme of things of what is being investigated, while, at the same time, showing the innovation and originality of your proposed work.
When writing a literature review, it is imperative that your format is effective because it often contains extensive information that allows you to demonstrate your main research claims compared to other scholars.
Separating the literature according to major categories or conceptual frameworks is an excellent way to do this. This is a more effective method than listing each study one by one in chronological order.
In order to arrange the review of existing relevant studies in an efficient manner, a literature review is often written using the following five criteria:
- Be sure to cite your previous studies to ensure the focus remains on the research question. For more information, please refer to our guide on how to write a research paper .
- Study the literature’s methods, results, hypotheses, and conclusions. Recognize the authors’ differing perspectives.
- Compare and contrast the various themes, arguments, methodologies, and perspectives discussed in the literature. Explain the most prominent points of disagreement.
- Evaluate the literature. Identify persuasive arguments offered by scholars. Choose the most reliable, valid, and suitable methodologies.
- Consider how the literature relates to your area of research and your topic. Examine whether your proposal for investigation reflects existing literature, deviates from existing literature, synthesizes or adds to it in some way.
#4 Research questions and objectives
The next step is to develop your research objectives once you have determined your research focus.
When your readers read your proposal, what do you want them to learn? Try to write your objectives in one sentence, if you can. Put time and thought into framing them properly.
By setting an objective for your research, you’ll stay on track and avoid getting sidetracked.
Any study proposal should address the following questions irrespective of the topic or problem:
- What are you hoping to accomplish from the study? When describing the study topic and your research question, be concise and to the point.
- What is the purpose of the research? A compelling argument must also be offered to support your choice of topic.
- What research methods will you use? It is essential to outline a clear, logical strategy for completing your study and make sure that it is doable.
Some authors include this section in the introduction, where it is generally placed at the end of the section.
#5 Research Design and Methods
It is important to write this part correctly and organize logically even though you are not starting the research yet. This must leave readers with a sense of assurance that the topic is worthwhile.
To achieve this, you must convince your reader that your research design and procedures will adequately address the study’s problems. Additionally, it seeks to ensure that the employed methods are capable of interpreting the likely study results efficiently.
You should design your research in a way that is directly related to your objectives.
Exemplifying your study design using examples from your literature review, you are setting up your study design effectively. You should follow other researchers’ good practices.
Pay attention to the methods you will use to collect data, the analyses you will perform, as well as your methods of measuring the validity of your results.
If you describe the methods you will use, make sure you include the following points:
- Develop a plan for conducting your research, as well as how you intend to interpret the findings based on the study’s objectives.
- When describing your objectives with the selected techniques, it is important to also elaborate on your plans.
- This section does not only present a list of events. Once you have chosen the strategy, make sure to explain why it is a good way to analyse your study question. Provide clear explanations.
- Last but not least, plan ahead to overcome any challenges you might encounter during the implementation of your research design.
In the event that you closely follow the best practices outlined in relevant studies as well as justify your selection, you will be prepared to address any questions or concerns you may encounter.
We have an amazing article that will give you everything you need to know about research design .
#6 Knowledge Contribution and Relevance
In this section, you describe your theory about how your study will contribute to, expand, or alter knowledge about the topic of your study.
You should discuss the implications of your research on future studies, applications, concepts, decisions, and procedures. It is common to address the study findings from a conceptual, analytical, or scientific perspective.
If you are framing your proposal of research, these guide questions may help you:
- How could the results be interpreted in the context of contesting the premises of the study?
- Could the expected study results lead to proposals for further research?
- Is your proposed research going to benefit people in any way?
- Is the outcome going to affect individuals in their work setting?
- In what ways will the suggested study impact or enhance the quality of life?
- Are the study’s results going to have an impact on intervention forms, techniques, or policies?
- What potential commercial, societal, or other benefits could be derived from the outcomes?
- Policy decisions will be influenced by the outcomes?
- Upon implementation, could they bring about new insights or breakthroughs?
Throughout this section, you will identify unsolved questions or research gaps in the existing literature. If the study is conducted as proposed, it is important to indicate how the research will be instrumental in understanding the nature of the research problem.
#7 Adherence to the Ethical Principles
In terms of scientific writing style, no particular style is generally acknowledged as more or less effective. The purpose is simply to provide relevant content that is formatted in a standardized way to enhance communication .
There are a variety of publication styles among different scholarly disciplines. It is therefore essential to follow the protocol according to the institution or organization that you are targeting.
All scholarly research and writing is, however, guided by codes of ethical conduct. The purpose of ethical guidelines, if they are followed, is to accomplish three things:
1) Preserve intellectual property right;
2) Ensure the rights and welfare of research participants;
3) Maintain the accuracy of scientific knowledge.
Scholars and writers who follow these ideals adhere to long-standing standards within their professional groups.
An additional ethical principle of the APA stresses the importance of maintaining scientific validity. An observation is at the heart of the standard scientific method, and it is verifiable and repeatable by others.
It is expected that scholars will not falsify or fabricate data in research writing. Researchers must also refrain from altering their studies’ outcomes to support a particular theory or to exclude inconclusive data from their report in an effort to create a convincing one.
#8 The budget
The need for detailed budgetary planning is not required by all universities when studying historical material or academic literature, though some do require it. In the case of a research grant application, you will likely have to include a comprehensive budget that breaks down the costs of each major component.
Ensure that the funding program or organization will cover the required costs, and include only the necessary items. For each of the items, you should include the following.
- To complete the study in its entirety, how much money would you require?
- Discuss the rationale for such a budget item for the purpose of completing research.
- The source of the amount – describe how it was determined.
When doing a study, you cannot buy ingredients the way you normally would. With so many items not having a price tag, how can you make a budget? Take the following into consideration:
- Does your project require access to any software programs or solutions? Do you need to install or train a technology tool?
- How much time will you be spending on your research study? Are you required to take time off from work to do your research?
- Are you going to need to travel to certain locations to meet with respondents or to collect data? At what cost?
- Will you be seeking research assistants for the study you propose? In what capacity and for what compensation? What other aspects are you planning to outsource?
It is possible to calculate a budget while also being able to estimate how much more money you will need in the event of an emergency.
#9 Timeline
A realistic and concise research schedule is also important to keep in mind. You should be able to finish your plan of study within the allotted time period, such as your degree program or the academic calendar.
You should include a timeline that includes a series of objectives you must complete to meet all the requirements for your scholarly research. The process starts with preliminary research and ends with final editing. A completion date for every step is required.
In addition, one should state the development that has been made. It is also recommended to include other relevant research events, for instance paper or poster presentations . In addition, a researcher must update the timeline regularly, as necessary, since this is not a static document.
#10 A Concluding Statement
Presenting a few of the anticipated results of your research proposal is an effective way to conclude your proposal.
The final stage of the process requires you to reveal the conclusion and rationale you anticipate reaching. Considering the research you have done so far, your reader knows that these are anticipated results, which are likely to evolve once the whole study is completed.
In any case, you must let the supervisors or sponsors know what implications may be drawn. It will be easier for them to assess the reliability and relevance of your research.
It will also demonstrate your meticulousness since you will have anticipated and taken into consideration the potential consequences of your research.
The Appendix section is required by some funding sources and academic institutions. This is extra information that is not in the main argument of the proposal, but appears to enhance the points made.
For example, data in the form of tables, consent forms, clinical/research guidelines, and procedures for data collection may be included in this document.
Research Proposal Template
Now that you know all about each element that composes an ideal research proposal, here is an extra help: a ready to use research proposal example. Just hit the button below, make a copy of the document and start working!

Avoid these common mistakes
In an era when rejection rates for prestigious journals can reach as high as 90 percent, you must avoid the following common mistakes when submitting a proposal:
- Proposals that are too long. Stay to the point when you write research proposals. Make your document concise and specific. Be sure not to diverge into off-topic discussions.
- Taking up too much research time. Many students struggle to delineate the context of their studies, regardless of the topic, time, or location. In order to explain the methodology of the study clearly to the reader, the proposal must clearly state what the study will focus on.
- Leaving out significant works from a literature review. Though everything in the proposal should be kept at a minimum, key research studies must need to be included. To understand the scope and growth of the issue, proposals should be based on significant studies.
- Major topics are too rarely discussed, and too much attention is paid to minor details. To persuasively argue for a study, a proposal should focus on just a few key research questions. Minor details should be noted, but should not overshadow the thesis.
- The proposal does not have a compelling and well-supported argument. To prove that a study should be approved or funded, the research proposal must outline its purpose.
- A typographical error, bad grammar or sloppy writing style. Even though a research proposal outlines a part of a larger project, it must conform to academic writing standards and guidelines.

A final note
We have come to the end of our research proposal guide. We really hope that you have found all the information you need. Wishing you success with the research study.
We at Mind the Graph create high quality illustrative graphics for research papers and posters to beautify your work. Check us out here .
Related Articles

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Fabricio Pamplona
Fabricio Pamplona is the founder of Mind the Graph - a tool used by over 400K users in 60 countries. He has a Ph.D. and solid scientific background in Psychopharmacology and experience as a Guest Researcher at the Max Planck Institute of Psychiatry (Germany) and Researcher in D'Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR, Brazil). Fabricio holds over 2500 citations in Google Scholar. He has 10 years of experience in small innovative businesses, with relevant experience in product design and innovation management. Connect with him on LinkedIn - Fabricio Pamplona .
Content tags
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Research Proposal – Types, Template and Example
Table of Contents

Research Proposal
Research proposal is a document that outlines a proposed research project . It is typically written by researchers, scholars, or students who intend to conduct research to address a specific research question or problem.
Types of Research Proposal
Research proposals can vary depending on the nature of the research project and the specific requirements of the funding agency, academic institution, or research program. Here are some common types of research proposals:
Academic Research Proposal
This is the most common type of research proposal, which is prepared by students, scholars, or researchers to seek approval and funding for an academic research project. It includes all the essential components mentioned earlier, such as the introduction, literature review , methodology , and expected outcomes.
Grant Proposal
A grant proposal is specifically designed to secure funding from external sources, such as government agencies, foundations, or private organizations. It typically includes additional sections, such as a detailed budget, project timeline, evaluation plan, and a description of the project’s alignment with the funding agency’s priorities and objectives.
Dissertation or Thesis Proposal
Students pursuing a master’s or doctoral degree often need to submit a proposal outlining their intended research for their dissertation or thesis. These proposals are usually more extensive and comprehensive, including an in-depth literature review, theoretical framework, research questions or hypotheses, and a detailed methodology.
Research Project Proposal
This type of proposal is often prepared by researchers or research teams within an organization or institution. It outlines a specific research project that aims to address a particular problem, explore a specific area of interest, or provide insights for decision-making. Research project proposals may include sections on project management, collaboration, and dissemination of results.
Research Fellowship Proposal
Researchers or scholars applying for research fellowships may be required to submit a proposal outlining their proposed research project. These proposals often emphasize the novelty and significance of the research and its alignment with the goals and objectives of the fellowship program.
Collaborative Research Proposal
In cases where researchers from multiple institutions or disciplines collaborate on a research project, a collaborative research proposal is prepared. This proposal highlights the objectives, responsibilities, and contributions of each collaborator, as well as the overall research plan and coordination mechanisms.
Research Proposal Outline
A research proposal typically follows a standard outline that helps structure the document and ensure all essential components are included. While the specific headings and subheadings may vary slightly depending on the requirements of your institution or funding agency, the following outline provides a general structure for a research proposal:
- Title of the research proposal
- Name of the researcher(s) or principal investigator(s)
- Affiliation or institution
- Date of submission
- A concise summary of the research proposal, typically limited to 200-300 words.
- Briefly introduce the research problem or question, state the objectives, summarize the methodology, and highlight the expected outcomes or significance of the research.
- Provide an overview of the subject area and the specific research problem or question.
- Present relevant background information, theories, or concepts to establish the need for the research.
- Clearly state the research objectives or research questions that the study aims to address.
- Indicate the significance or potential contributions of the research.
- Summarize and analyze relevant studies, theories, or scholarly works.
- Identify research gaps or unresolved issues that your study intends to address.
- Highlight the novelty or uniqueness of your research.
- Describe the overall approach or research design that will be used (e.g., experimental, qualitative, quantitative).
- Justify the chosen approach based on the research objectives and question.
- Explain how data will be collected (e.g., surveys, interviews, experiments).
- Describe the sampling strategy and sample size, if applicable.
- Address any ethical considerations related to data collection.
- Outline the data analysis techniques or statistical methods that will be applied.
- Explain how the data will be interpreted and analyzed to answer the research question(s).
- Provide a detailed schedule or timeline that outlines the various stages of the research project.
- Specify the estimated duration for each stage, including data collection, analysis, and report writing.
- State the potential outcomes or results of the research.
- Discuss the potential significance or contributions of the study to the field.
- Address any potential limitations or challenges that may be encountered.
- Identify the resources required to conduct the research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- Specify any collaborations or partnerships necessary for the successful completion of the study.
- Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
———————————————————————————————–
Research Proposal Example Template
Here’s an example of a research proposal to give you an idea of how it can be structured:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Well-being: A Mixed-Methods Study
This research proposal aims to investigate the impact of social media on the well-being of adolescents. The study will employ a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews to gather comprehensive data. The research objectives include examining the relationship between social media use and mental health, exploring the role of peer influence in shaping online behaviors, and identifying strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents. The findings of this study will contribute to the understanding of the effects of social media on adolescent well-being and inform the development of targeted interventions.
1. Introduction
1.1 Background and Context:
Adolescents today are immersed in social media platforms, which have become integral to their daily lives. However, concerns have been raised about the potential negative impact of social media on their well-being, including increased rates of depression, anxiety, and body dissatisfaction. It is crucial to investigate this phenomenon further and understand the underlying mechanisms to develop effective strategies for promoting healthy social media use among adolescents.
1.2 Research Objectives:
The main objectives of this study are:
- To examine the association between social media use and mental health outcomes among adolescents.
- To explore the influence of peer relationships and social comparison on online behaviors.
- To identify strategies and interventions to foster positive social media use and enhance adolescent well-being.
2. Literature Review
Extensive research has been conducted on the impact of social media on adolescents. Existing literature suggests that excessive social media use can contribute to negative outcomes, such as low self-esteem, cyberbullying, and addictive behaviors. However, some studies have also highlighted the positive aspects of social media, such as providing opportunities for self-expression and social support. This study will build upon this literature by incorporating both quantitative and qualitative approaches to gain a more nuanced understanding of the relationship between social media and adolescent well-being.
3. Methodology
3.1 Research Design:
This study will adopt a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews. The quantitative phase will involve administering standardized questionnaires to a representative sample of adolescents to assess their social media use, mental health indicators, and perceived social support. The qualitative phase will include in-depth interviews with a subset of participants to explore their experiences, motivations, and perceptions related to social media use.
3.2 Data Collection Methods:
Quantitative data will be collected through an online survey distributed to schools in the target region. The survey will include validated scales to measure social media use, mental health outcomes, and perceived social support. Qualitative data will be collected through semi-structured interviews with a purposive sample of participants. The interviews will be audio-recorded and transcribed for thematic analysis.
3.3 Data Analysis:
Quantitative data will be analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis to examine the relationships between variables. Qualitative data will be analyzed thematically to identify common themes and patterns within participants’ narratives. Integration of quantitative and qualitative findings will provide a comprehensive understanding of the research questions.
4. Timeline
The research project will be conducted over a period of 12 months, divided into specific phases, including literature review, study design, data collection, analysis, and report writing. A detailed timeline outlining the key milestones and activities is provided in Appendix A.
5. Expected Outcomes and Significance
This study aims to contribute to the existing literature on the impact of social media on adolescent well-being by employing a mixed-methods approach. The findings will inform the development of evidence-based interventions and guidelines to promote healthy social media use among adolescents. This research has the potential to benefit adolescents, parents, educators, and policymakers by providing insights into the complex relationship between social media and well-being and offering strategies for fostering positive online experiences.
6. Resources
The resources required for this research include access to a representative sample of adolescents, research assistants for data collection, statistical software for data analysis, and funding to cover survey administration and participant incentives. Ethical considerations will be taken into account, ensuring participant confidentiality and obtaining informed consent.
7. References
Research Proposal Writing Guide
Writing a research proposal can be a complex task, but with proper guidance and organization, you can create a compelling and well-structured proposal. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Understand the requirements: Familiarize yourself with the guidelines and requirements provided by your institution, funding agency, or program. Pay attention to formatting, page limits, specific sections or headings, and any other instructions.
- Identify your research topic: Choose a research topic that aligns with your interests, expertise, and the goals of your program or funding opportunity. Ensure that your topic is specific, focused, and relevant to the field of study.
- Conduct a literature review : Review existing literature and research relevant to your topic. Identify key theories, concepts, methodologies, and findings related to your research question. This will help you establish the context, identify research gaps, and demonstrate the significance of your proposed study.
- Define your research objectives and research question(s): Clearly state the objectives you aim to achieve with your research. Formulate research questions that address the gaps identified in the literature review. Your research objectives and questions should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Develop a research methodology: Determine the most appropriate research design and methodology for your study. Consider whether quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods approaches will best address your research question(s). Describe the data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations associated with your research.
- Create a research plan and timeline: Outline the various stages of your research project, including tasks, milestones, and deadlines. Develop a realistic timeline that considers factors such as data collection, analysis, and report writing. This plan will help you stay organized and manage your time effectively throughout the research process.
- A. Introduction: Provide background information on the research problem, highlight its significance, and introduce your research objectives and questions.
- B. Literature review: Summarize relevant literature, identify gaps, and justify the need for your proposed research.
- C . Methodology: Describe your research design, data collection methods, sampling strategy, data analysis techniques, and any ethical considerations.
- D . Expected outcomes and significance: Explain the potential outcomes, contributions, and implications of your research.
- E. Resources: Identify the resources required to conduct your research, such as funding, equipment, or access to data.
- F . References: Include a list of cited references in the appropriate citation style.
- Revise and proofread: Review your proposal for clarity, coherence, and logical flow. Check for grammar and spelling errors. Seek feedback from mentors, colleagues, or advisors to refine and improve your proposal.
- Finalize and submit: Make any necessary revisions based on feedback and finalize your research proposal. Ensure that you have met all the requirements and formatting guidelines. Submit your proposal within the specified deadline.
Research Proposal Length
The length of a research proposal can vary depending on the specific guidelines provided by your institution or funding agency. However, research proposals typically range from 1,500 to 3,000 words, excluding references and any additional supporting documents.
Purpose of Research Proposal
The purpose of a research proposal is to outline and communicate your research project to others, such as academic institutions, funding agencies, or potential collaborators. It serves several important purposes:
- Demonstrate the significance of the research: A research proposal explains the importance and relevance of your research project. It outlines the research problem or question, highlights the gaps in existing knowledge, and explains how your study will contribute to the field. By clearly articulating the significance of your research, you can convince others of its value and potential impact.
- Provide a clear research plan: A research proposal outlines the methodology, design, and approach you will use to conduct your study. It describes the research objectives, data collection methods, data analysis techniques, and potential outcomes. By presenting a clear research plan, you demonstrate that your study is well-thought-out, feasible, and likely to produce meaningful results.
- Secure funding or support: For researchers seeking funding or support for their projects, a research proposal is essential. It allows you to make a persuasive case for why your research is deserving of financial resources or institutional backing. The proposal explains the budgetary requirements, resources needed, and potential benefits of the research, helping you secure the necessary funding or support.
- Seek feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to receive feedback and guidance from experts in your field. It allows you to engage in discussions and receive suggestions for refining your research plan, improving the methodology, or addressing any potential limitations. This feedback can enhance the quality of your study and increase its chances of success.
- Establish ethical considerations: A research proposal also addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will ensure participant confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. By demonstrating your awareness and commitment to ethical research practices, you build trust and credibility in your proposed study.
Importance of Research Proposal
The research proposal holds significant importance in the research process. Here are some key reasons why research proposals are important:
- Planning and organization: A research proposal requires careful planning and organization of your research project. It forces you to think through the research objectives, research questions, methodology, and potential outcomes before embarking on the actual study. This planning phase helps you establish a clear direction and framework for your research, ensuring that your efforts are focused and purposeful.
- Demonstrating the significance of the research: A research proposal allows you to articulate the significance and relevance of your study. By providing a thorough literature review and clearly defining the research problem or question, you can showcase the gaps in existing knowledge that your research aims to address. This demonstrates to others, such as funding agencies or academic institutions, why your research is important and deserving of support.
- Obtaining funding and resources: Research proposals are often required to secure funding for your research project. Funding agencies and organizations need to evaluate the feasibility and potential impact of the proposed research before allocating resources. A well-crafted research proposal helps convince funders of the value of your research and increases the likelihood of securing financial support, grants, or scholarships.
- Receiving feedback and guidance: Presenting a research proposal provides an opportunity to seek feedback and guidance from experts in your field. By sharing your research plan and objectives with others, you can benefit from their insights and suggestions. This feedback can help refine your research design, strengthen your methodology, and ensure that your study is rigorous and well-informed.
- Ethical considerations: A research proposal addresses ethical considerations associated with your study. It outlines how you will protect the rights and welfare of participants, maintain confidentiality, obtain informed consent, and adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations. This emphasis on ethical practices ensures that your research is conducted responsibly and with integrity.
- Enhancing collaboration and partnerships: A research proposal can facilitate collaborations and partnerships with other researchers, institutions, or organizations. When presenting your research plan, you may attract the interest of potential collaborators who share similar research interests or possess complementary expertise. Collaborative partnerships can enrich your study, expand your resources, and foster knowledge exchange.
- Establishing a research trajectory: A research proposal serves as a foundation for your research project. Once approved, it becomes a roadmap that guides your study’s implementation, data collection, analysis, and reporting. It helps maintain focus and ensures that your research stays on track and aligned with the initial objectives.
When to Write Research Proposal
The timing of when to write a research proposal can vary depending on the specific requirements and circumstances. However, here are a few common situations when it is appropriate to write a research proposal:
- Academic research: If you are a student pursuing a research degree, such as a Ph.D. or Master’s by research, you will typically be required to write a research proposal as part of the application process. This is usually done before starting the research program to outline your proposed study and seek approval from the academic institution.
- Funding applications: When applying for research grants, scholarships, or funding from organizations or institutions, you will often need to submit a research proposal. Funding agencies require a detailed description of your research project, including its objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. Writing a research proposal in this context is necessary to secure financial support for your study.
- Research collaborations: When collaborating with other researchers, institutions, or organizations on a research project, it is common to prepare a research proposal. This helps outline the research objectives, roles and responsibilities, and expected contributions from each party. Writing a research proposal in this case allows all collaborators to align their efforts and ensure a shared understanding of the project.
- Research project within an organization: If you are conducting research within an organization, such as a company or government agency, you may be required to write a research proposal to gain approval and support for your study. This proposal outlines the research objectives, methodology, resources needed, and expected outcomes, ensuring that the project aligns with the organization’s goals and objectives.
- Independent research projects: Even if you are not required to write a research proposal, it can still be beneficial to develop one for your independent research projects. Writing a research proposal helps you plan and structure your study, clarify your research objectives, and anticipate potential challenges or limitations. It also allows you to communicate your research plans effectively to supervisors, mentors, or collaborators.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Grant Proposal – Example, Template and Guide

How To Write A Research Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Business Proposal – Step-by-Step...

Proposal – Types, Examples, and Writing Guide

How To Write A Grant Proposal – Step-by-Step...

How To Write A Proposal – Step By Step Guide...

Research Proposal Example/Sample
Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template
If you’re getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals , you’ve come to the right place.
In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals , one for a Master’s-level project, and one for a PhD-level dissertation. We also start off by unpacking our free research proposal template and discussing the four core sections of a research proposal, so that you have a clear understanding of the basics before diving into the actual proposals.
- Research proposal example/sample – Master’s-level (PDF/Word)
- Research proposal example/sample – PhD-level (PDF/Word)
- Proposal template (Fully editable)
If you’re working on a research proposal for a dissertation or thesis, you may also find the following useful:
- Research Proposal Bootcamp : Learn how to write a research proposal as efficiently and effectively as possible
- 1:1 Proposal Coaching : Get hands-on help with your research proposal

PS – If you’re working on a dissertation, be sure to also check out our collection of dissertation and thesis examples here .
FAQ: Research Proposal Example
Research proposal example: frequently asked questions, are the sample proposals real.
Yes. The proposals are real and were approved by the respective universities.
Can I copy one of these proposals for my own research?
As we discuss in the video, every research proposal will be slightly different, depending on the university’s unique requirements, as well as the nature of the research itself. Therefore, you’ll need to tailor your research proposal to suit your specific context.
You can learn more about the basics of writing a research proposal here .
How do I get the research proposal template?
You can access our free proposal template here .
Is the proposal template really free?
Yes. There is no cost for the proposal template and you are free to use it as a foundation for your research proposal.
Where can I learn more about proposal writing?
For self-directed learners, our Research Proposal Bootcamp is a great starting point.
For students that want hands-on guidance, our private coaching service is recommended.

Psst… there’s more!
This post is an extract from our bestselling short course, Research Proposal Bootcamp . If you want to work smart, you don't want to miss this .
14 Comments
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a PhD in Management at Altantic International University. I checked on the coaching services, but it indicates that it’s not available in my area. I am in South Sudan. My proposed topic is: “Leadership Behavior in Local Government Governance Ecosystem and Service Delivery Effectiveness in Post Conflict Districts of Northern Uganda”. I will appreciate your guidance and support
GRADCOCH is very grateful motivated and helpful for all students etc. it is very accorporated and provide easy access way strongly agree from GRADCOCH.
Proposal research departemet management
I am at the stage of writing my thesis proposal for a masters in Analysis of w heat commercialisation by small holders householdrs at Hawassa International University. I will appreciate your guidance and support
please provide a attractive proposal about foreign universities .It would be your highness.
comparative constitutional law
Kindly guide me through writing a good proposal on the thesis topic; Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Financial Inclusion in Nigeria. Thank you
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the topic of impacts of artisanal gold panning on the environment
I am in the process of research proposal for my Master of Art with a topic : “factors influence on first-year students’s academic adjustment”. I am absorbing in GRADCOACH and interested in such proposal sample. However, it is great for me to learn and seeking for more new updated proposal framework from GRADCAOCH.
Kindly help me write a research proposal on the effectiveness of junior call on prevention of theft
kindly assist me in writing the proposal in psychology education
Please,Kindly assist my in my phd thesis writing on personal and socio cultural factors as determinate of family planning adoption
I’m interested to apply for a mhil program in crop production. Please need assistance in proposal format.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
Writing a research proposal: planning and communicating your research ideas effectively
- January 2008
- Library and Information Research 32(102)

- University of Brighton
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- LIRG Journal

- Frederick Douglass Staten
- Janet Clapton

- Noeleen Schenk
- Alison Jane Pickard
- Peter Brophy

- Colin Robson
- R Collingwood
- M Denscombe
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up

How to write a research proposal
Drafting your first research proposal can be intimidating if you’ve never written (or seen) one before. Our grad students and admissions staff have some advice on making a start.
Before you make a start
Is it a requirement for your course.
For some research courses in sciences you’ll join an existing research group so you don’t need to write a full research proposal, just a list of the groups and/or supervisors you want to work with. You might be asked to write a personal statement instead, giving your research interests and experience.
Still, for many of our research courses — especially in humanities and social sciences — your research proposal is one of the most significant parts of your application. Grades and other evidence of your academic ability and potential are important, but even if you’re academically outstanding you’ll need to show you’re a good match for the department’s staff expertise and research interests. Every course page on the University website has detailed information on what you’ll need to send with your application, so make sure that’s your first step before you continue:
There are many ways to start, I’ve heard stories about people approaching it totally differently. Yannis (DPhil in Computer Science)
How to begin?
There isn’t one right way to start writing a research proposal. First of all, make sure you’ve read your course page - it’ll have instructions for what to include in your research proposal (as well as anything to avoid), how your department will assess it, and the required word count.
Start small, think big
A research degree is a big undertaking, and it’s normal to feel a bit overwhelmed at first. One way to start writing is to look back at the work you’ve already done. How does your proposed research build on this, and the other research in the area? One of the most important things you’ll be showing through your research project is that your project is achievable in the time available for your course, and that you’ve got (or know how you’ll get) the right skills and experience to pull off your plan.
They don’t expect you to be the expert, you just have to have good ideas. Be willing to challenge things and do something new. Rebecca (DPhil in Medieval and Modern Languages)
However, you don’t have to know everything - after all, you haven’t started yet! When reading your proposal, your department will be looking at the potential and originality of your research, and whether you have a solid understanding of the topic you’ve chosen.
But why Oxford?
An Admissions Officer at one of our colleges says that it’s important to explain why you’re applying to Oxford, and to your department in particular:
“Really, this is all dependent on a department. Look at the department in depth, and look at what they offer — how is it in line with your interests?”
Think about what you need to successfully execute your research plans and explain how Oxford’s academic facilities and community will support your work. Should I email a potential supervisor? Got an idea? If your course page says it’s alright to contact a supervisor (check the top of the How to apply section), it’s a good idea to get in touch with potential supervisors when you come to write your proposal.
You’re allowed to reach out to academics that you might be interested in supervising you. They can tell you if your research is something that we can support here, and how, and give you ideas. Admissions Officer
You’ll find more information about the academics working in your area on your department’s website (follow the department links on your course page ). John (DPhil in Earth Sciences) emailed a professor who had the same research interests as he did.
“Luckily enough, he replied the next day and was keen to support me in the application.”
These discussions might help you to refine your ideas and your research proposal.
Layal says, “I discussed ideas with my supervisor — what’s feasible, what would be interesting. He supported me a lot with that, and I went away and wrote it.”
It’s also an opportunity to find out more about the programme and the department:
“Getting in touch with people who are here is a really good way to ask questions.”
Not sure how to find a potential supervisor for your research? Visit our How-to guide on finding a supervisor .
Asking for help
My supervisors helped me with my research proposal, which is great. You don’t expect that, but they were really helpful prior to my application. Nyree (DPhil in Archaeological Science)
Don’t be afraid to ask for advice and feedback as you go. For example, you could reach out to a supervisor from your current or previous degree, or to friends who are also studying and could give you some honest feedback.
More help with your application
You can find instructions for the supporting documents you’ll need to include in your application on your course page and in the Application Guide.
Applicant advice hub
This content was previously available through our Applicant advice hub . The hub contained links to articles hosted on our Graduate Study at Oxford Medium channel . We've moved the articles that support the application process into this new section of our website.
- Application Guide: Research proposal
Can't find what you're looking for?
If you have a query about graduate admissions at Oxford, we're here to help:
Ask a question
Privacy Policy
Postgraduate Applicant Privacy Policy
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes and Tegan George. Revised on 13 June 2023.
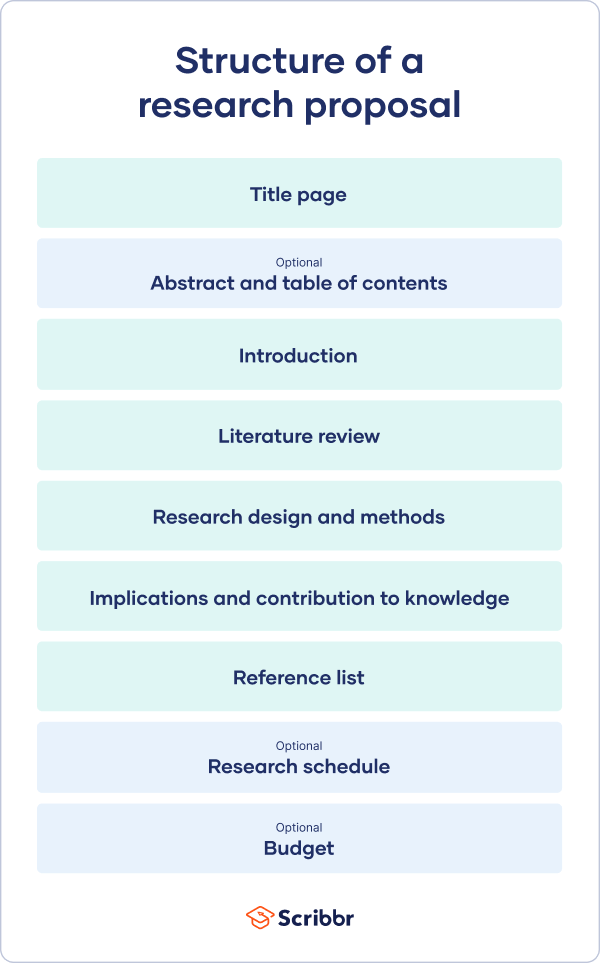
A research proposal describes what you will investigate, why it’s important, and how you will conduct your research.
The format of a research proposal varies between fields, but most proposals will contain at least these elements:
Introduction
Literature review.
- Research design
Reference list
While the sections may vary, the overall objective is always the same. A research proposal serves as a blueprint and guide for your research plan, helping you get organised and feel confident in the path forward you choose to take.
Table of contents
Research proposal purpose, research proposal examples, research design and methods, contribution to knowledge, research schedule, frequently asked questions.
Academics often have to write research proposals to get funding for their projects. As a student, you might have to write a research proposal as part of a grad school application , or prior to starting your thesis or dissertation .
In addition to helping you figure out what your research can look like, a proposal can also serve to demonstrate why your project is worth pursuing to a funder, educational institution, or supervisor.
| Show your reader why your project is interesting, original, and important. | |
| Demonstrate your comfort and familiarity with your field. Show that you understand the current state of research on your topic. | |
| Make a case for your . Demonstrate that you have carefully thought about the data, tools, and procedures necessary to conduct your research. | |
| Confirm that your project is feasible within the timeline of your program or funding deadline. |
Research proposal length
The length of a research proposal can vary quite a bit. A bachelor’s or master’s thesis proposal can be just a few pages, while proposals for PhD dissertations or research funding are usually much longer and more detailed. Your supervisor can help you determine the best length for your work.
One trick to get started is to think of your proposal’s structure as a shorter version of your thesis or dissertation , only without the results , conclusion and discussion sections.
Download our research proposal template
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We’ve included a few for you below.
- Example research proposal #1: ‘A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management’
- Example research proposal #2: ‘ Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use’
Like your dissertation or thesis, the proposal will usually have a title page that includes:
- The proposed title of your project
- Your supervisor’s name
- Your institution and department
The first part of your proposal is the initial pitch for your project. Make sure it succinctly explains what you want to do and why.
Your introduction should:
- Introduce your topic
- Give necessary background and context
- Outline your problem statement and research questions
To guide your introduction , include information about:
- Who could have an interest in the topic (e.g., scientists, policymakers)
- How much is already known about the topic
- What is missing from this current knowledge
- What new insights your research will contribute
- Why you believe this research is worth doing
As you get started, it’s important to demonstrate that you’re familiar with the most important research on your topic. A strong literature review shows your reader that your project has a solid foundation in existing knowledge or theory. It also shows that you’re not simply repeating what other people have already done or said, but rather using existing research as a jumping-off point for your own.
In this section, share exactly how your project will contribute to ongoing conversations in the field by:
- Comparing and contrasting the main theories, methods, and debates
- Examining the strengths and weaknesses of different approaches
- Explaining how will you build on, challenge, or synthesise prior scholarship
Following the literature review, restate your main objectives . This brings the focus back to your own project. Next, your research design or methodology section will describe your overall approach, and the practical steps you will take to answer your research questions.
| ? or ? , , or research design? | |
| , )? ? | |
| , , , )? | |
| ? |
To finish your proposal on a strong note, explore the potential implications of your research for your field. Emphasise again what you aim to contribute and why it matters.
For example, your results might have implications for:
- Improving best practices
- Informing policymaking decisions
- Strengthening a theory or model
- Challenging popular or scientific beliefs
- Creating a basis for future research
Last but not least, your research proposal must include correct citations for every source you have used, compiled in a reference list . To create citations quickly and easily, you can use our free APA citation generator .
Some institutions or funders require a detailed timeline of the project, asking you to forecast what you will do at each stage and how long it may take. While not always required, be sure to check the requirements of your project.
Here’s an example schedule to help you get started. You can also download a template at the button below.
Download our research schedule template
| Research phase | Objectives | Deadline |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Background research and literature review | 20th January | |
| 2. Research design planning | and data analysis methods | 13th February |
| 3. Data collection and preparation | with selected participants and code interviews | 24th March |
| 4. Data analysis | of interview transcripts | 22nd April |
| 5. Writing | 17th June | |
| 6. Revision | final work | 28th July |
If you are applying for research funding, chances are you will have to include a detailed budget. This shows your estimates of how much each part of your project will cost.
Make sure to check what type of costs the funding body will agree to cover. For each item, include:
- Cost : exactly how much money do you need?
- Justification : why is this cost necessary to complete the research?
- Source : how did you calculate the amount?
To determine your budget, think about:
- Travel costs : do you need to go somewhere to collect your data? How will you get there, and how much time will you need? What will you do there (e.g., interviews, archival research)?
- Materials : do you need access to any tools or technologies?
- Help : do you need to hire any research assistants for the project? What will they do, and how much will you pay them?
Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement.
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
A PhD, which is short for philosophiae doctor (doctor of philosophy in Latin), is the highest university degree that can be obtained. In a PhD, students spend 3–5 years writing a dissertation , which aims to make a significant, original contribution to current knowledge.
A PhD is intended to prepare students for a career as a researcher, whether that be in academia, the public sector, or the private sector.
A master’s is a 1- or 2-year graduate degree that can prepare you for a variety of careers.
All master’s involve graduate-level coursework. Some are research-intensive and intend to prepare students for further study in a PhD; these usually require their students to write a master’s thesis . Others focus on professional training for a specific career.
Critical thinking refers to the ability to evaluate information and to be aware of biases or assumptions, including your own.
Like information literacy , it involves evaluating arguments, identifying and solving problems in an objective and systematic way, and clearly communicating your ideas.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. & George, T. (2023, June 13). How to Write a Research Proposal | Examples & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved 3 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-proposal-explained/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, what is a literature review | guide, template, & examples, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
- Utility Menu
GA4 tracking code

- All URAF Opportunities
- CARAT (Opportunities Database)
- URAF Application Instructions
- URAF Calendar of Events and Deadlines
Writing Research Proposals
The research proposal is your opportunity to show that you—and only you!—are the perfect person to take on your specific project. After reading your research proposal, readers should be confident that…
- You have thoughtfully crafted and designed this project;
- You have the necessary background to complete this project;
- You have the proper support system in place;
- You know exactly what you need to complete this project and how to do so; and
- With this funding in hand, you can be on your way to a meaningful research experience and a significant contribution to your field.
Research proposals typically include the following components:
- Why is your project important? How does it contribute to the field or to society? What do you hope to prove?
- This section includes the project design, specific methodology, your specific role and responsibilities, steps you will take to execute the project, etc. Here you will show the committee the way that you think by explaining both how you have conceived the project and how you intend to carry it out.
- Please be specific in the project dates/how much time you need to carry out the proposed project. The scope of the project should clearly match the timeframe in which you propose to complete it!
- Funding agencies like to know how their funding will be used. Including this information will demonstrate that you have thoughtfully designed the project and know of all of the anticipated expenses required to see it through to completion.
- It is important that you have a support system on hand when conducting research, especially as an undergraduate. There are often surprises and challenges when working on a long-term research project and the selection committee wants to be sure that you have the support system you need to both be successful in your project and also have a meaningful research experience.
- Some questions to consider are: How often do you intend to meet with your advisor(s)? (This may vary from project to project based on the needs of the student and the nature of the research.) What will your mode of communication be? Will you be attending (or even presenting at) lab meetings?
Don’t be afraid to also include relevant information about your background and advocate for yourself! Do you have skills developed in a different research experience (or leadership position, job, coursework, etc.) that you could apply to the project in question? Have you already learned about and experimented with a specific method of analysis in class and are now ready to apply it to a different situation? If you already have experience with this professor/lab, please be sure to include those details in your proposal! That will show the selection committee that you are ready to hit the ground running!
Lastly, be sure to know who your readers are so that you can tailor the field-specific language of your proposal accordingly. If the selection committee are specialists in your field, you can feel free to use the jargon of that field; but if your proposal will be evaluated by an interdisciplinary committee (this is common), you might take a bit longer explaining the state of the field, specific concepts, and certainly spelling out any acronyms.
- Getting Started
- Application Components
- Interviews and Offers
- Building On Your Experiences
- Applying FAQs
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.60(9); 2016 Sep
How to write a research proposal?
Department of Anaesthesiology, Bangalore Medical College and Research Institute, Bengaluru, Karnataka, India
Devika Rani Duggappa
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or ‘blueprint’ for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project should flow smoothly. Even today, many of the proposals at post-graduate evaluation committees and application proposals for funding are substandard. A search was conducted with keywords such as research proposal, writing proposal and qualitative using search engines, namely, PubMed and Google Scholar, and an attempt has been made to provide broad guidelines for writing a scientifically appropriate research proposal.
INTRODUCTION
A clean, well-thought-out proposal forms the backbone for the research itself and hence becomes the most important step in the process of conduct of research.[ 1 ] The objective of preparing a research proposal would be to obtain approvals from various committees including ethics committee [details under ‘Research methodology II’ section [ Table 1 ] in this issue of IJA) and to request for grants. However, there are very few universally accepted guidelines for preparation of a good quality research proposal. A search was performed with keywords such as research proposal, funding, qualitative and writing proposals using search engines, namely, PubMed, Google Scholar and Scopus.
Five ‘C’s while writing a literature review

BASIC REQUIREMENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
A proposal needs to show how your work fits into what is already known about the topic and what new paradigm will it add to the literature, while specifying the question that the research will answer, establishing its significance, and the implications of the answer.[ 2 ] The proposal must be capable of convincing the evaluation committee about the credibility, achievability, practicality and reproducibility (repeatability) of the research design.[ 3 ] Four categories of audience with different expectations may be present in the evaluation committees, namely academic colleagues, policy-makers, practitioners and lay audiences who evaluate the research proposal. Tips for preparation of a good research proposal include; ‘be practical, be persuasive, make broader links, aim for crystal clarity and plan before you write’. A researcher must be balanced, with a realistic understanding of what can be achieved. Being persuasive implies that researcher must be able to convince other researchers, research funding agencies, educational institutions and supervisors that the research is worth getting approval. The aim of the researcher should be clearly stated in simple language that describes the research in a way that non-specialists can comprehend, without use of jargons. The proposal must not only demonstrate that it is based on an intelligent understanding of the existing literature but also show that the writer has thought about the time needed to conduct each stage of the research.[ 4 , 5 ]
CONTENTS OF A RESEARCH PROPOSAL
The contents or formats of a research proposal vary depending on the requirements of evaluation committee and are generally provided by the evaluation committee or the institution.
In general, a cover page should contain the (i) title of the proposal, (ii) name and affiliation of the researcher (principal investigator) and co-investigators, (iii) institutional affiliation (degree of the investigator and the name of institution where the study will be performed), details of contact such as phone numbers, E-mail id's and lines for signatures of investigators.
The main contents of the proposal may be presented under the following headings: (i) introduction, (ii) review of literature, (iii) aims and objectives, (iv) research design and methods, (v) ethical considerations, (vi) budget, (vii) appendices and (viii) citations.[ 4 ]
Introduction
It is also sometimes termed as ‘need for study’ or ‘abstract’. Introduction is an initial pitch of an idea; it sets the scene and puts the research in context.[ 6 ] The introduction should be designed to create interest in the reader about the topic and proposal. It should convey to the reader, what you want to do, what necessitates the study and your passion for the topic.[ 7 ] Some questions that can be used to assess the significance of the study are: (i) Who has an interest in the domain of inquiry? (ii) What do we already know about the topic? (iii) What has not been answered adequately in previous research and practice? (iv) How will this research add to knowledge, practice and policy in this area? Some of the evaluation committees, expect the last two questions, elaborated under a separate heading of ‘background and significance’.[ 8 ] Introduction should also contain the hypothesis behind the research design. If hypothesis cannot be constructed, the line of inquiry to be used in the research must be indicated.
Review of literature
It refers to all sources of scientific evidence pertaining to the topic in interest. In the present era of digitalisation and easy accessibility, there is an enormous amount of relevant data available, making it a challenge for the researcher to include all of it in his/her review.[ 9 ] It is crucial to structure this section intelligently so that the reader can grasp the argument related to your study in relation to that of other researchers, while still demonstrating to your readers that your work is original and innovative. It is preferable to summarise each article in a paragraph, highlighting the details pertinent to the topic of interest. The progression of review can move from the more general to the more focused studies, or a historical progression can be used to develop the story, without making it exhaustive.[ 1 ] Literature should include supporting data, disagreements and controversies. Five ‘C's may be kept in mind while writing a literature review[ 10 ] [ Table 1 ].
Aims and objectives
The research purpose (or goal or aim) gives a broad indication of what the researcher wishes to achieve in the research. The hypothesis to be tested can be the aim of the study. The objectives related to parameters or tools used to achieve the aim are generally categorised as primary and secondary objectives.
Research design and method
The objective here is to convince the reader that the overall research design and methods of analysis will correctly address the research problem and to impress upon the reader that the methodology/sources chosen are appropriate for the specific topic. It should be unmistakably tied to the specific aims of your study.
In this section, the methods and sources used to conduct the research must be discussed, including specific references to sites, databases, key texts or authors that will be indispensable to the project. There should be specific mention about the methodological approaches to be undertaken to gather information, about the techniques to be used to analyse it and about the tests of external validity to which researcher is committed.[ 10 , 11 ]
The components of this section include the following:[ 4 ]
Population and sample
Population refers to all the elements (individuals, objects or substances) that meet certain criteria for inclusion in a given universe,[ 12 ] and sample refers to subset of population which meets the inclusion criteria for enrolment into the study. The inclusion and exclusion criteria should be clearly defined. The details pertaining to sample size are discussed in the article “Sample size calculation: Basic priniciples” published in this issue of IJA.
Data collection
The researcher is expected to give a detailed account of the methodology adopted for collection of data, which include the time frame required for the research. The methodology should be tested for its validity and ensure that, in pursuit of achieving the results, the participant's life is not jeopardised. The author should anticipate and acknowledge any potential barrier and pitfall in carrying out the research design and explain plans to address them, thereby avoiding lacunae due to incomplete data collection. If the researcher is planning to acquire data through interviews or questionnaires, copy of the questions used for the same should be attached as an annexure with the proposal.
Rigor (soundness of the research)
This addresses the strength of the research with respect to its neutrality, consistency and applicability. Rigor must be reflected throughout the proposal.
It refers to the robustness of a research method against bias. The author should convey the measures taken to avoid bias, viz. blinding and randomisation, in an elaborate way, thus ensuring that the result obtained from the adopted method is purely as chance and not influenced by other confounding variables.
Consistency
Consistency considers whether the findings will be consistent if the inquiry was replicated with the same participants and in a similar context. This can be achieved by adopting standard and universally accepted methods and scales.
Applicability
Applicability refers to the degree to which the findings can be applied to different contexts and groups.[ 13 ]
Data analysis
This section deals with the reduction and reconstruction of data and its analysis including sample size calculation. The researcher is expected to explain the steps adopted for coding and sorting the data obtained. Various tests to be used to analyse the data for its robustness, significance should be clearly stated. Author should also mention the names of statistician and suitable software which will be used in due course of data analysis and their contribution to data analysis and sample calculation.[ 9 ]
Ethical considerations
Medical research introduces special moral and ethical problems that are not usually encountered by other researchers during data collection, and hence, the researcher should take special care in ensuring that ethical standards are met. Ethical considerations refer to the protection of the participants' rights (right to self-determination, right to privacy, right to autonomy and confidentiality, right to fair treatment and right to protection from discomfort and harm), obtaining informed consent and the institutional review process (ethical approval). The researcher needs to provide adequate information on each of these aspects.
Informed consent needs to be obtained from the participants (details discussed in further chapters), as well as the research site and the relevant authorities.
When the researcher prepares a research budget, he/she should predict and cost all aspects of the research and then add an additional allowance for unpredictable disasters, delays and rising costs. All items in the budget should be justified.
Appendices are documents that support the proposal and application. The appendices will be specific for each proposal but documents that are usually required include informed consent form, supporting documents, questionnaires, measurement tools and patient information of the study in layman's language.
As with any scholarly research paper, you must cite the sources you used in composing your proposal. Although the words ‘references and bibliography’ are different, they are used interchangeably. It refers to all references cited in the research proposal.
Successful, qualitative research proposals should communicate the researcher's knowledge of the field and method and convey the emergent nature of the qualitative design. The proposal should follow a discernible logic from the introduction to presentation of the appendices.
Financial support and sponsorship
Conflicts of interest.
There are no conflicts of interest.
FLEET LIBRARY | Research Guides
Rhode island school of design, create a research plan: research plan.
- Research Plan
- Literature Review
- Ulrich's Global Serials Directory
- Related Guides
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan
1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question
2. Research methodology - describes your approach to the research question
3. Literature review, critical evaluation and synthesis - systematic approach to locating,
reviewing and evaluating the work (text, exhibitions, critiques, etc) relating to your topic
4. Communication - geared toward an intended audience, shows evidence of your inquiry
Research conceptualization refers to the ability to identify specific research questions, problems or opportunities that are worthy of inquiry. Research conceptualization also includes the skills and discipline that go beyond the initial moment of conception, and which enable the researcher to formulate and develop an idea into something researchable ( Newbury 373).
Research methodology refers to the knowledge and skills required to select and apply appropriate methods to carry through the research project ( Newbury 374) .
Method describes a single mode of proceeding; methodology describes the overall process.
Method - a way of doing anything especially according to a defined and regular plan; a mode of procedure in any activity
Methodology - the study of the direction and implications of empirical research, or the sustainability of techniques employed in it; a method or body of methods used in a particular field of study or activity *Browse a list of research methodology books or this guide on Art & Design Research
Literature Review, critical evaluation & synthesis
A literature review is a systematic approach to locating, reviewing, and evaluating the published work and work in progress of scholars, researchers, and practitioners on a given topic.
Critical evaluation and synthesis is the ability to handle (or process) existing sources. It includes knowledge of the sources of literature and contextual research field within which the person is working ( Newbury 373).
Literature reviews are done for many reasons and situations. Here's a short list:
| to learn about a field of study to understand current knowledge on a subject to formulate questions & identify a research problem to focus the purpose of one's research to contribute new knowledge to a field personal knowledge intellectual curiosity | to prepare for architectural program writing academic degrees grant applications proposal writing academic research planning funding |
Sources to consult while conducting a literature review:
Online catalogs of local, regional, national, and special libraries
meta-catalogs such as worldcat , Art Discovery Group , europeana , world digital library or RIBA
subject-specific online article databases (such as the Avery Index, JSTOR, Project Muse)
digital institutional repositories such as Digital Commons @RISD ; see Registry of Open Access Repositories
Open Access Resources recommended by RISD Research LIbrarians
works cited in scholarly books and articles
print bibliographies
the internet-locate major nonprofit, research institutes, museum, university, and government websites
search google scholar to locate grey literature & referenced citations
trade and scholarly publishers
fellow scholars and peers
Communication
Communication refers to the ability to
- structure a coherent line of inquiry
- communicate your findings to your intended audience
- make skilled use of visual material to express ideas for presentations, writing, and the creation of exhibitions ( Newbury 374)
Research plan framework: Newbury, Darren. "Research Training in the Creative Arts and Design." The Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts . Ed. Michael Biggs and Henrik Karlsson. New York: Routledge, 2010. 368-87. Print.
About the author
Except where otherwise noted, this guide is subject to a Creative Commons Attribution license
source document
Routledge Companion to Research in the Arts
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: Aug 15, 2024 1:29 AM
- URL: https://risd.libguides.com/researchplan
- {{item.title}} {{item.title}} 0" aria-label="Find options under this page" @click="mobchildshow(true, item.title)" class="more-menu">
- {{subitem.title}}
Writing a research proposal
How to write a research proposal.
For many subjects, writing a research proposal is a key part of your postgraduate research degree application. This is your opportunity to demonstrate your knowledge and how you want to contribute to the subject.
We use the proposal to match your interest with an appropriate supervisor to make sure you have the best support during your degree. We are looking for originality and relevance when assessing the overall quality of your application, including your suitability for this level of study.
We highly recommend that you explore which academic researchers are working in your subject area and contact them first with any questions, this is a good opportunity to firm up your ideas, further explore the topic and talk with others in your field.
What is a research proposal?
A research proposal is a concise and coherent document, usually between 1500 – 2000 words, maximum 4 x A4 pages. You should outline your proposed research project, why it is of relevance (rationale), what research questions are you going to ask, what you hope to achieve (aims and objectives) and how you plan to carry out your research (methodology).
Step-by-step
This page is your comprehensive guide to writing a research proposal and will cover seven key elements of a proposal:
Working title
You should include a title for your thesis in the proposal.
Your title may change as you further your research, but at this stage it's important to state succinctly what your research will cover.
Introduction
Briefly identify your idea, what is your ‘research question’?
It could be the theory you want to test, or a more open question. It would be useful to give examples, 3-5 research questions from recently completed PhDs in a relevant field. You should discuss the context around your research topic, such as current debates and issues. The important thing here is that you introduce your research project with clarity and in a way that stimulates your reader’s interest.
Demonstrate the significance of your research project.
To do this, explain why your research is important, what makes it original and how it will contribute to existing knowledge within its field.
Aims and objectives
What are you hoping to achieve with your research?
Try and produce four or five bullet points of objectives for each aim, which demonstrate your understanding of how to meet your research aims. You can use the SMART acronym to support you in creating objectives, which involves making your objectives: specific, measurable, achievable, realistic and time specific.
Literature Review
Demonstrate your knowledge and awareness of relevant literature
A literature review is a discussion and evaluation of academic literature or a relevant body of knowledge (for practice-based research). You should use this section of your proposal to show that you are familiar with work in your chosen topic area and that your research will contribute something new and/or meaningful to it.
Methodology
Explain how you plan to carry out your research
The methodology section of your research proposal is where you explain how you plan to carry out your research. This should include the research techniques and methods you will use, why these are most appropriate and how you will implement them. You should also include a discussion of the research strategy (general approach) you will adopt, with appropriate justification, including the analytical approach. The section should also contain the range of research findings that will be gathered from the research and how you will analyse or evaluate this. For practice based research, include how will your portfolio of artefacts, code, software, compositions, computer games etc. articulate the originality of your research?
Reference all the materials you used in the preparation your proposal
You may also list references that you didn't directly draw upon, to demonstrate awareness of literature relating to your proposed material.
Support from academic staff in drafting your research proposal
Your research proposal will be read by academics with an interest in your field of research. You are therefore encouraged to contact members of academic staff informally prior to submitting your application to discuss to your research proposal. This can often speed up the applications process, as you can identify the member(s) of staff you have spoken to on your research degree application form.
Use the Huddersfield Research Portal to browse academic staff profiles and search using key words to find staff members who share your research interests.
Changing aspects of your research proposal after gaining a place as a research student
Your research proposal is your starting point, and we understand that as your idea develop s , your proposed research is likely to change. As such, you will not be obliged to adhere to the specifics of your proposal if you are offered a place as a research degree candidate at Huddersfield. However, as the proposal is the foundation of your working relationship with your supervisor(s), you will need to discuss any changes with them first.
Useful tips for writing a research proposal
- Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to be overly complicated.
- Share your proposal: Ask someone you trust (a friend, family member, tutor) to read your proposal and provide some feedback. Do they understand what your research is about? Do they think your aims and objectives are achievable? Does your research engage them?
- Align your proposal topic with University research themes: Whilst it is important to choose a research topic that you are passionate about, your proposal will be assessed (in part) on its fit with our University research themes. You therefore need to choose a topic which aligns with topics of interest to the University or academic school you hoping to work within and make it clear how your project matches up with them.
- Be realistic in your proposal: Your proposal is assessed not only on its quality, originality and fit with our research themes but also the likelihood of completion, so make sure that the scope of your research project is reasonable and realistic .
- Take your time when writing your proposal: There are a lot of elements to a high-quality research proposal, so take the time to ensure that you meet them all. At the University of Huddersfield, there are three opportunities for enrolling onto a research degree programme during the academic year (October, January, and April), meaning less time pressure when working on your proposal and application.
Once you have written your proposal, what next?
Once you have written your research proposal you will need to complete an application form. Look at our how to apply webpage for more information.

How to apply for a research degree
Our step-by-step guide will help you to make the most out of your application for a research degree

Scholarships and funding
Explore our funding options, including scholarships and Doctoral Loans.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
The University of Chicago The Law School
Abrams environmental law clinic—significant achievements for 2023-24, protecting our great lakes, rivers, and shorelines.
The Abrams Clinic represents Friends of the Chicago River and the Sierra Club in their efforts to hold Trump Tower in downtown Chicago accountable for withdrawing water illegally from the Chicago River. To cool the building, Trump Tower draws water at high volumes, similar to industrial factories or power plants, but Trump Tower operated for more than a decade without ever conducting the legally required studies to determine the impact of those operations on aquatic life or without installing sufficient equipment to protect aquatic life consistent with federal regulations. After the Clinic sent a notice of intent to sue Trump Tower, the State of Illinois filed its own case in the summer of 2018, and the Clinic moved successfully to intervene in that case. In 2023-24, motions practice and discovery continued. Working with co-counsel at Northwestern University’s Pritzker Law School’s Environmental Advocacy Center, the Clinic moved to amend its complaint to include Trump Tower’s systematic underreporting each month of the volume of water that it intakes from and discharges to the Chicago River. The Clinic and co-counsel addressed Trump Tower’s motion to dismiss some of our clients’ claims, and we filed a motion for summary judgment on our claim that Trump Tower has committed a public nuisance. We also worked closely with our expert, Dr. Peter Henderson, on a supplemental disclosure and on defending an additional deposition of him. In summer 2024, the Clinic is defending its motion for summary judgment and challenging Trump Tower’s own motion for summary judgment. The Clinic is also preparing for trial, which could take place as early as fall 2024.
Since 2016, the Abrams Clinic has worked with the Chicago chapter of the Surfrider Foundation to protect water quality along the Lake Michigan shoreline in northwest Indiana, where its members surf. In April 2017, the U. S. Steel plant in Portage, Indiana, spilled approximately 300 pounds of hexavalent chromium into Lake Michigan. In January 2018, the Abrams Clinic filed a suit on behalf of Surfrider against U. S. Steel, alleging multiple violations of U. S. Steel’s discharge permits; the City of Chicago filed suit shortly after. When the US government and the State of Indiana filed their own, separate case, the Clinic filed extensive comments on the proposed consent decree. In August 2021, the court entered a revised consent decree which included provisions advocated for by Surfrider and the City of Chicago, namely a water sampling project that alerts beachgoers as to Lake Michigan’s water quality conditions, better notifications in case of future spills, and improvements to U. S. Steel’s operations and maintenance plans. In the 2023-24 academic year, the Clinic successfully litigated its claims for attorneys’ fees as a substantially prevailing party. Significantly, the court’s order adopted the “Fitzpatrick matrix,” used by the US Attorney’s Office for the District of Columbia to determine appropriate hourly rates for civil litigants, endorsed Chicago legal market rates as the appropriate rates for complex environmental litigation in Northwest Indiana, and allowed for partially reconstructed time records. The Clinic’s work, which has received significant media attention, helped to spawn other litigation to address pollution by other industrial facilities in Northwest Indiana and other enforcement against U. S. Steel by the State of Indiana.
In Winter Quarter 2024, Clinic students worked closely with Dr. John Ikerd, an agricultural economist and emeritus professor at the University of Missouri, to file an amicus brief in Food & Water Watch v. U.S. Environmental Protection Agency . In that case pending before the Ninth Circuit, Food & Water Watch argues that US EPA is illegally allowing Concentrated Animal Feeding Operations, more commonly known as factory farms, to pollute waterways significantly more than is allowable under the Clean Water Act. In the brief for Dr. Ikerd and co-amici Austin Frerick, Crawford Stewardship Project, Family Farm Defenders, Farm Aid, Missouri Rural Crisis Center, National Family Farm Coalition, National Sustainable Agriculture Coalition, and Western Organization of Resource Councils, we argued that EPA’s refusal to regulate CAFOs effectively is an unwarranted application of “agricultural exceptionalism” to industrial agriculture and that EPA effectively distorts the animal production market by allowing CAFOs to externalize their pollution costs and diminishing the ability of family farms to compete. Attorneys for the litigants will argue the case in September 2024.
Energy and Climate
Energy justice.
The Abrams Clinic supported grassroots organizations advocating for energy justice in low-income communities and Black, Indigenous, and People of Color (BIPOC) communities in Michigan. With the Clinic’s representation, these organizations intervened in cases before the Michigan Public Service Commission (MPSC), which regulates investor-owned utilities. Students conducted discovery, drafted written testimony, cross-examined utility executives, participated in settlement discussions, and filed briefs for these projects. The Clinic’s representation has elevated the concerns of these community organizations and forced both the utilities and regulators to consider issues of equity to an unprecedented degree. This year, on behalf of Soulardarity (Highland Park, MI), We Want Green, Too (Detroit, MI), and Urban Core Collective (Grand Rapids, MI), Clinic students engaged in eight contested cases before the MPSC against DTE Electric, DTE Gas, and Consumers Energy, as well as provided support for our clients’ advocacy in other non-contested MPSC proceedings.
The Clinic started this past fall with wins in three cases. First, the Clinic’s clients settled with DTE Electric in its Integrated Resource Plan case. The settlement included an agreement to close the second dirtiest coal power plant in Michigan three years early, $30 million from DTE’s shareholders to assist low-income customers in paying their bills, and $8 million from DTE’s shareholders toward a community fund that assists low-income customers with installing energy efficiency improvements, renewable energy, and battery technology. Second, in DTE Electric’s 2023 request for a rate hike (a “rate case”), the Commission required DTE Electric to develop a more robust environmental justice analysis and rejected the Company’s second attempt to waive consumer protections through a proposed electric utility prepayment program with a questionable history of success during its pilot run. The final Commission order and the administrative law judge’s proposal for final decision cited the Clinic’s testimony and briefs. Third, in Consumers Electric’s 2023 rate case, the Commission rejected the Company’s request for a higher ratepayer-funded return on its investments and required the Company to create a process that will enable intervenors to obtain accurate GIS data. The Clinic intends to use this data to map the disparate impact of infrastructure investment in low-income and BIPOC communities.
In the winter, the Clinic filed public comments regarding DTE Electric and Consumers Energy’s “distribution grid plans” (DGP) as well as supported interventions in two additional cases: Consumers Energy’s voluntary green pricing (VGP) case and the Clinic’s first case against the gas utility DTE Gas. Beginning with the DGP comments, the Clinic first addressed Consumers’s 2023 Electric Distribution Infrastructure Investment Plan (EDIIP), which detailed current distribution system health and the utility’s approximately $7 billion capital project planning ($2 billion of which went unaccounted for in the EDIIP) over 2023–2028. The Clinic then commented on DTE Electric’s 2023 DGP, which outlined the utility’s opaque project prioritization and planned more than $9 billion in capital investments and associated maintenance over 2024–2028. The comments targeted four areas of deficiencies in both the EDIIP and DGP: (1) inadequate consideration of distributed energy resources (DERs) as providing grid reliability, resiliency, and energy transition benefits; (2) flawed environmental justice analysis, particularly with respect to the collection of performance metrics and the narrow implementation of the Michigan Environmental Justice Screen Tool; (3) inequitable investment patterns across census tracts, with emphasis on DTE Electric’s skewed prioritization for retaining its old circuits rather than upgrading those circuits; and (4) failing to engage with community feedback.
For the VGP case against Consumers, the Clinic supported the filing of both an initial brief and reply brief requesting that the Commission reject the Company’s flawed proposal for a “community solar” program. In a prior case, the Clinic advocated for the development of a community solar program that would provide low-income, BIPOC communities with access to clean energy. As a result of our efforts, the Commission approved a settlement agreement requiring the Company “to evaluate and provide a strawman recommendation on community solar in its Voluntary Green Pricing Program.” However, the Company’s subsequent proposal in its VGP case violated the Commission’s order because it (1) was not consistent with the applicable law, MCL 460.1061; (2) was not a true community solar program; (3) lacked essential details; (4) failed to compensate subscribers sufficiently; (5) included overpriced and inflexible subscriptions; (6) excessively limited capacity; and (7) failed to provide a clear pathway for certain participants to transition into other VGP programs. For these reasons, the Clinic argued that the Commission should reject the Company’s proposal.
In DTE Gas’s current rate case, the Clinic worked with four witnesses to develop testimony that would rebut DTE Gas’s request for a rate hike on its customers. The testimony advocated for a pathway to a just energy transition that avoids dumping the costs of stranded gas assets on the low-income and BIPOC communities that are likely to be the last to electrify. Instead, the testimony proposed that the gas and electric utilities undertake integrated planning that would prioritize electric infrastructure over gas infrastructure investment to ensure that DTE Gas does not over-invest in gas infrastructure that will be rendered obsolete in the coming decades. The Clinic also worked with one expert witness to develop an analysis of DTE Gas’s unaffordable bills and inequitable shutoff, deposit, and collections practices. Lastly, the Clinic offered testimony on behalf of and from community members who would be directly impacted by the Company’s rate hike and lack of affordable and quality service. Clinic students have spent the summer drafting an approximately one-hundred-page brief making these arguments formally. We expect the Commission’s decision this fall.
Finally, both DTE Electric and Consumers Energy have filed additional requests for rate increases after the conclusion of their respective rate cases filed in 2023. On behalf of our Clients, the Clinic has intervened in these cases, and clinic students have already reviewed thousands of pages of documents and started to develop arguments and strategies to protect low-income and BIPOC communities from the utility’s ceaseless efforts to increase the cost of energy.
Corporate Climate Greenwashing
The Abrams Environmental Law Clinic worked with a leading international nonprofit dedicated to using the law to protect the environment to research corporate climate greenwashing, focusing on consumer protection, green financing, and securities liability. Clinic students spent the year examining an innovative state law, drafted a fifty-page guide to the statute and relevant cases, and examined how the law would apply to a variety of potential cases. Students then presented their findings in a case study and oral presentation to members of ClientEarth, including the organization’s North American head and members of its European team. The project helped identify the strengths and weaknesses of potential new strategies for increasing corporate accountability in the fight against climate change.
Land Contamination, Lead, and Hazardous Waste
The Abrams Clinic continues to represent East Chicago, Indiana, residents who live or lived on or adjacent to the USS Lead Superfund site. This year, the Clinic worked closely with the East Chicago/Calumet Coalition Community Advisory Group (CAG) to advance the CAG’s advocacy beyond the Superfund site and the adjacent Dupont RCRA site. Through multiple forms of advocacy, the clinics challenged the poor performance and permit modification and renewal attempts of Tradebe Treatment and Recycling, LLC (Tradebe), a hazardous waste storage and recycling facility in the community. Clinic students sent letters to US EPA and Indiana Department of Environmental Management officials about how IDEM has failed to assess meaningful penalties against Tradebe for repeated violations of the law and how IDEM has allowed Tradebe to continue to threaten public and worker health and safety by not improving its operations. Students also drafted substantial comments for the CAG on the US EPA’s Lead and Copper Rule improvements, the Suppliers’ Park proposed cleanup, and Sims Metal’s proposed air permit revisions. The Clinic has also continued working with the CAG, environmental experts, and regulators since US EPA awarded $200,000 to the CAG for community air monitoring. The Clinic and its clients also joined comments drafted by other environmental organizations about poor operations and loose regulatory oversight of several industrial facilities in the area.
Endangered Species
The Abrams Clinic represented the Center for Biological Diversity (CBD) and the Hoosier Environmental Council (HEC) in litigation regarding the US Fish and Wildlife Service’s (Service) failure to list the Kirtland’s snake as threatened or endangered under the Endangered Species Act. The Kirtland’s snake is a small, secretive, non-venomous snake historically located across the Midwest and the Ohio River Valley. Development and climate change have undermined large portions of the snake’s habitat, and populations are declining. Accordingly, the Clinic sued the Service in the US District Court for the District of Columbia last summer over the Service’s denial of CBD’s request to have the Kirtland’s snake protected. This spring, the Clinic was able to reach a settlement with the Service that requires the Service to reconsider its listing decision for the Kirtland’s snake and to pay attorney fees.
The Clinic also represented CBD in preparation for litigation regarding the Service’s failure to list another species as threatened or endangered. Threats from land development and climate change have devastated this species as well, and the species has already been extirpated from two of the sixteen US states in its range. As such, the Clinic worked this winter and spring to prepare a notice of intent (NOI) to sue the Service. The Team poured over hundreds of FOIA documents and dug into the Service’s supporting documentation to create strong arguments against the Service in the imminent litigation. The Clinic will send the NOI and file a complaint in the next few months.
Students and Faculty
Twenty-four law school students from the classes of 2024 and 2025 participated in the Clinic, performing complex legal research, reviewing documents obtained through discovery, drafting legal research memos and briefs, conferring with clients, conducting cross-examination, participating in settlement conferences, and arguing motions. Students secured nine clerkships, five were heading to private practice after graduation, and two are pursuing public interest work. Sam Heppell joined the Clinic from civil rights private practice, bringing the Clinic to its full complement of three attorneys.
- House Republican Agendas and Project 2025 Would Increase Poverty and Hardship, Drive Up the Uninsured Rate, and Disinvest From People, Communities, and the Economy
CBPP Staff [1]
Executive Summary
Over the last several months, groups of House Republicans and the Heritage Foundation have released policy agendas that, taken together, would create a harsher country with higher poverty and less opportunity, where millions of people would face higher costs for health care, child care, and housing, and millions more would lose health coverage — all while wealthy households and corporations benefit from an unfair tax code that provides them with outsized tax breaks. These skewed priorities would exacerbate inequities in income, wealth, health, and hardship across lines of race and ethnicity, widening already glaring differences that have their roots in racism and other forms of discrimination.
Looking at three proposals — the House Republican Study Committee’s (RSC) budget plan, the Republican House Budget Committee’s (HBC) budget resolution, and the Heritage Foundation’s Project 2025 agenda — brings the implications of influential conservative policymakers’ and a think tank’s broader fiscal policy agenda into sharper focus. That agenda features:
Policies that raise costs and take away health coverage, food assistance, and other help affording the basics from people when they need them. These policies will create significant economic and health insecurity for millions of people while increasing poverty, hardship, and the number of people lacking health coverage. They will shortchange children’s futures, make it harder for millions of seniors to afford prescription drugs, and take away help that households need to afford food, housing, and child care.
For example, the RSC budget calls for $4.5 trillion in cuts over ten years in Medicaid, the Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace coverage, [2] cutting these health coverage funds by more than half. The HBC budget plan, meanwhile, calls for $2.2 trillion in cuts to health coverage — all from Medicaid, the associated committee report suggests. [3] This cut would amount to 30 percent on average over ten years, and 40 percent in 2034. Nearly 74 million people receive health coverage through Medicaid, so cuts of this magnitude would result in millions losing access to comprehensive coverage.
Similarly, the RSC budget calls for cutting average Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) benefits by about 22 percent by rescinding the updated 2021 Thrifty Food Plan, which adjusted SNAP benefits to reflect the cost of a healthy diet based on today’s dietary guidelines and food consumption patterns. [4] This cut would affect 41 million people participating in SNAP, formerly known as food stamps. (HBC and Project 2025 also sharply criticize the Thrifty Food Plan increase but are not clear about rescinding it. [5] ) And Project 2025 calls for gutting summer food assistance programs that children in families with low incomes rely on when school is out, which could include the new Summer EBT program that is expected to provide grocery benefits to more than 21 million children this summer. [6]
The HBC budget plan cuts the “income security” category of programs by almost $1 trillion over ten years; the accompanying report targets SNAP, the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) and Child Tax Credit, and Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (or TANF, which provides flexible funding that states use for a range of benefits and services to low-income families with children). If income security cuts are largely limited to these programs, benefits would be slashed by more than half by 2034. [7]
The RSC budget has very deep cuts in this part of the budget as well. It includes a cut that would convert Supplemental Security Income (SSI), a 50-year-old program that provided income assistance to 7.5 million low-income seniors and disabled people in 2022, to a block grant and end guaranteed cash aid through the program.
Many of the proposals in these agendas would shift large costs onto states, forcing them to either kick in far more money — a particular hardship for states with lower per capita incomes — or cut benefits and services to their residents.
- Massive disinvestment in public services, which will limit opportunity, hurt communities, undermine efforts to address climate change, erode basic government functions, and damage the economy. For example, both the HBC and RSC budget plans call for enormous cuts in the part of the budget that funds a wide range of federal services, activities, and assistance — from education investments that build the skills of our future workforce, to transportation infrastructure that supports commerce and safety, to the nation’s weather forecasting system and scientific and medical research. In addition, all three plans would repeal or let expire climate provisions of the bipartisan Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. And all three plans call for repealing the Inflation Reduction Act’s groundbreaking investments in clean energy. [8]
- A doubling down on skewed, expensive, and ineffective tax cuts. The RSC and HBC budget plans call for extending all of the 2017 law’s expiring individual income tax cuts, [9] which would cost nearly $4 trillion over ten years (2026-2035), [10] and making additional business tax breaks permanent, which would cost nearly a trillion more. [11] Project 2025 goes even further, calling for a host of new tax cuts for wealthy households and corporations, including for multinational corporations that use overseas tax havens. The HBC budget plan shows none of the costs of extending the expiring 2017 tax cuts in its budget figures, but creates a new procedure allowing unlimited tax cuts. [12]
- Harsh treatment of immigrants, hurting families, shortchanging children’s futures, undermining immigrants’ contributions to communities and the economy, and hurting the country as a whole. Project 2025, the RSC budget plan, and the HBC budget plan call for a host of harmful policies that would take help away from families that include immigrants when they fall on hard times. Among other proposals, these plans seek to frighten immigrants and their families from participating in the Census, paying their taxes, and receiving benefits for which they are eligible. [13]
Behind these eye-popping budget numbers are millions of real people who will see health coverage, food assistance, and other forms of support taken away. (See Figure 1.) This will make it even harder for them to afford the basics, leading to serious hardships such as homelessness or overcrowded living, food insecurity, hunger, and untreated health conditions.

It is also notable what is missing from these agendas. Despite rhetoric from some Republicans about the need to support families — and children in particular — these sweeping agendas do not call for new or increased investments to help families afford child care or rent, to expand the Child Tax Credit, or to bolster the EITC for workers without children. And they do nothing to ensure that all workers have access to paid family and medical leave so they can take time off to welcome a new child, attend to a health issue, or care for a family member who needs them.
These agendas, particularly Project 2025, cover multiple areas and this report does not analyze them in full. It provides key examples of fiscal, economic, and health policies within the agendas and, critically, how the plans have broad similarities. Key areas, such as the agendas’ impact on the functioning of the Justice Department, on abortion rights and reproductive freedom, on civil rights protections, and on the potential politicization of federal agencies and the civil service, are critically important but outside the scope of this analysis.
Raising Health Care Costs and Taking Coverage and Other Help Away From People Who Need It
The three policy agendas all share a common thread — taking away help that families use to afford the basics such as food, child care, housing, and health care. The cuts would hit families with low and moderate incomes especially hard while leaving many high-income people largely unscathed. But because investing in areas such as health care and child care has long-term payoffs for the country and economy as a whole, ultimately everyone would lose.

Medicaid Cuts Would Take Away Health Coverage From Millions of People
As noted, HBC would cut Medicaid by $2.2 trillion over ten years; [14] RSC would cut Medicaid, CHIP, and ACA marketplace assistance by $4.5 trillion, likely by cutting Medicaid even more deeply than the HBC proposals and by making cuts to marketplace policies described below. [15] The size of the cuts in Project 2025 is less clear but also extremely large. (See Figure 2.)
The ACA’s changes to Medicaid and individual market coverage drove a precipitous decline in the uninsured rate. That is particularly true for people of color, who have historically experienced higher uninsured rates due to systemic racism, discrimination in employment and education, and other factors that diminish income and access to employer-based health insurance. Between 2013 and 2022, uninsured rates for people under age 65 dropped from 23.8 percent to 14.1 percent among American Indian and Alaska Native people, from 29.7 percent to 17.8 percent among Latino people, and from 18.7 percent to 9.9 percent among Black people. [16] Rolling back or eliminating key ACA improvements — including the Medicaid expansion — and gutting other key Medicaid and marketplace protections would disproportionately harm people of color.
Medicaid proposals in the three agendas include:
- Capping or block-granting Medicaid and providing less funding than is needed to maintain the current program, thereby cutting the number of people who can receive coverage, the services provided, or both (HBC, RSC, and Project 2025); [17]
- Sharply cutting the share of Medicaid costs the federal government covers while giving states new authority to cut both the number of people and the health benefits Medicaid covers (HBC, RSC, and Project 2025); [18]
- Taking away financing options states now use to pay their share of Medicaid costs, making enrollment and services cuts even more likely (RSC and Project 2025); [19]
- Increasing the costs states must bear if they continue or adopt the Medicaid expansion, or explicitly allowing states to shift funds from adult health care coverage to other populations such as children or people with disabilities, with the goal of reducing coverage for adults and potentially pushing some states that have adopted the Medicaid expansion to end it (HBC; Project 2025; and RSC, which has more of these details spelled out); [20]
- Taking Medicaid coverage away from people who don’t meet rigid work requirements, which evidence from states [21] has shown doesn’t increase employment and takes coverage away from large numbers of enrollees — including many who are working or who should be exempt given their health conditions (HBC, RSC, and Project 2025); [22] and
- Allowing states to raise Medicaid premiums (Project 2025) [23] and make its benefit package far less comprehensive (RSC and Project 2025). [24]
Gutting ACA Would Raise Health Insurance Costs Sharply and Leave Millions Uninsured
Both Project 2025 and the RSC budget would raise health insurance premiums for millions of people and weaken or eliminate the ACA’s most popular consumer and financial protections. Insurers in the individual market could charge higher premiums to people with pre-existing conditions and remove limits that protect people from very high out-of-pocket health care spending. The HBC and RSC proposals would also cut financial assistance for ACA marketplace coverage, [25] where more than 20 million people get their health coverage and more than 9 in 10 receive premium tax credits that reduce the cost of their premiums. [26] The agendas would also strip away anti-discrimination protections that apply to all health programs and activities receiving federal financial assistance. While it is not presented as repealing the ACA, dismantling the ACA piecemeal like this would have a similar impact, with millions losing coverage.
Project 2025 and the RSC budget would:
- Cut federal premium tax credits, raising people’s costs. The RSC plan would reduce and ultimately eliminate the financial assistance that most people in ACA marketplace plans receive to help them afford their premiums, deductibles, and other costs under comprehensive health insurance plans, shifting some funding into a block grant. [27] Project 2025 criticizes federal marketplace financial assistance [28] and references a separate Heritage Foundation paper that calls for establishing capped federal allotments for states in place of the current ACA subsidies. [29] The ACA financial assistance — especially with the improvements enacted in 2021 — has helped drive a marked increase in insurance coverage rates, particularly among Black people, Hispanic people, and people with low incomes. [30]
- Allowing existing improvements to premium tax credits to expire after 2025 — as the HBC budget plan and RSC proposal would do [31] — would mean premium spikes for nearly all marketplace enrollees. For example, a typical 60-year-old couple making $80,000 (405 percent of the poverty level) would see their marketplace premiums more than triple to over $24,000 per year. (See Figure 3 for estimates by state.) [32] In addition, an estimated 4 million people would become uninsured, with the greatest coverage losses occurring among Black and Hispanic people in states that have not expanded Medicaid. [33] Eliminating the PTCs entirely, [34] meanwhile, would lead to even greater coverage losses, increase people’s premium costs even further, and throw stable insurance markets into disarray. For example, without a PTC, a 40-year-old person making $29,000 (roughly 200 percent of the poverty level) would see their annual marketplace premiums increase from $570 to $5,700. [35]

Eviscerate federal protections for people with pre-existing conditions. The RSC and Project 2025 plans would roll back federal insurance protections for people in marketplace plans in favor of separating healthy people and those with pre-existing conditions into different markets that operate under different rules.
The RSC proposal would allow insurers to charge higher premiums for individual market coverage (both inside and outside the ACA marketplace) to people with pre-existing conditions and exclude certain benefits from plans they buy. [36] The proposal says people with chronic and complex conditions would get coverage through separate state-run high-risk pools, [37] but these existed prior to the ACA and had high premiums, gaps in benefits, and limited enrollment because of their cost. [38]
Project 2025 proposes “regulatory relief” that amounts to eliminating many critical federal health reforms; it doesn’t specify which ones but calls for the federal government to create a second insurance market not subject to ACA standards, [39] which would attract healthier enrollees, with the likely result that premiums for those with pre-existing conditions would become unaffordable. This would disproportionately harm Black people: due to racial inequities in social and economic factors — such as being likelier to live in communities with less access to health care or to have lower incomes that make it harder to afford healthy food — they have a higher prevalence of several common chronic conditions. [40]
Both the RSC plan and Project 2025 would increase the availability of health plans that are currently exempt from ACA standards and protections, such as short-term health plans. [41] This is another strategy to lead people with fewer health care needs away from the ACA marketplace’s comprehensive health plans, resulting in a sicker risk pool and higher premiums for those enrolled in marketplace plans. [42]
- Roll back federal protections that explicitly prohibit insurers and health care providers from discriminating against LGBTQ+ people and people who have had abortions or miscarriages. Section 1557 of the ACA prohibits Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) programs, as well as insurance companies and health care providers that receive HHS funding, from discriminating against members of certain protected groups. Project 2025 seeks to end protections that currently apply to LGBTQ+ individuals, pregnant people, and people who have had an abortion or miscarriage. [43]
Taking Food, Other Assistance Away From Low-Income Households Would Increase Poverty, Hunger
Both the RSC and HBC plans call for large cuts to the part of the budget that funds income and food assistance programs such as SNAP. The HBC plan, for example, calls for $962 billion in cuts over ten years to “income security” programs, and its accompanying report indicates that SNAP, TANF, and the tax refunds provided through the EITC and Child Tax Credit would be targeted for cuts. [44] If income security cuts are largely limited to these programs, benefits would be slashed by more than half by 2034. [45]
All three agendas — HBC, RSC, and Project 2025 — call explicitly for significant cuts to SNAP. This is the nation’s largest and most important anti-hunger program, providing families with funds on an electronic benefit card that they use to purchase food at the grocery store. Taken together, these cuts would reduce or take away entirely food assistance for millions of people.
More than 44 million people in the United States live in households that experience food insecurity. Due to past and ongoing racism and discrimination, households that are American Indian or Alaska Native, Black, Hispanic, or multiracial experience much higher than average levels of food insecurity. [46] SNAP is highly effective at reducing food insecurity, and there is emerging evidence that SNAP may mitigate racial inequities in food insecurity and poverty. [47] But the proposed cuts to SNAP could weaken its effectiveness and exacerbate these inequities.
The proposed cuts include the following:

- The RSC budget calls for SNAP benefits to be cut by an average of 22 percent by undoing the recent, congressionally mandated re-evaluation of the Thrifty Food Plan — a long-overdue step that resulted in an upward revision to SNAP benefits to more accurately reflect both the cost of a modest but healthy diet and U.S. food consumption patterns. [48] This update to the Thrifty Food Plan lifts over 2 million SNAP participants above the poverty line, with the greatest poverty-reducing impact for Black and Hispanic individuals. [49] Undoing the revision would reverse this progress and cut benefits to some 41 million SNAP enrollees, including nearly 17 million children, slashing the average SNAP benefit from about $6.20 per person per day to only $4.80 in 2025. (See Figure 4.) Both Project 2025 and the HBC budget resolution also sharply criticize the 2021 re-evaluation of the Thrifty Food Plan. [50]
Meeting one’s life-sustaining needs should not be contingent on meeting a work requirement. But both the RSC budget and Project 2025 call for expanding the number of SNAP enrollees whose benefits would be taken away if they aren’t able to meet rigid work requirements — a policy already in place for most adults aged 18 through 54 who don’t receive disability benefits and don’t live with children. [51]
Most SNAP participants who can work, do. [52] These requirements are premised on the false assumption that people who receive SNAP do not work and must be compelled to do so — an assumption rooted in a host of unfounded prejudices based on race, gender, disability status, and class. Rigorous studies have shown that the current work requirement policy is ineffective at increasing employment. Instead, it takes food assistance away from people with very low incomes and increases food insecurity and hardship. [53]
Policies that take food assistance away from people who don’t meet a rigid work requirement ignore the realities of the low-paid labor market, such as irregular hours and a lack of paid sick days that lead to frequent job loss; the impact of work-limiting health conditions and caregiving responsibilities on a participant’s ability to find and keep consistent work; and substantial ongoing labor market discrimination.
The report accompanying the HBC budget resolution also calls for expanding ineffective work requirements. [54]
- Both the RSC budget and Project 2025 propose eliminating a long-standing SNAP option — a popular one, used in more than 40 states led by governors of both parties — that modestly raises SNAP’s income eligibility limits for certain households, including many households with earnings . [55] This policy, known as broad-based categorical eligibility, extends SNAP eligibility to many working families with low incomes for whom affording food is difficult because they face high costs for necessities like housing or child care. This option also allows states to adopt a less restrictive asset test to qualify for SNAP, allowing low-income households to build modest savings without losing food assistance. Eliminating this option would terminate SNAP for millions of people with low incomes and would take food assistance away primarily from working families, older adults, and people with disabilities. Punishing asset building would particularly harm people of color who participate in SNAP, who face structural disadvantages to building wealth and getting ahead.
The attacks on food and other assistance to low-income families aren’t limited to SNAP. For example:
- Project 2025 would also end most summer food assistance programs, designed to mitigate food insecurity when school is out and children don’t get school meals . [56] Many children who receive free or reduced-price school meals struggle to access nutritious food when school lets out for the summer. Studies have shown that households with school-aged children experience higher rates of food hardship during the summer. [57] Project 2025 could take away food assistance from roughly 21 million children in low-income families who are expected to receive grocery benefits this year through the new Summer EBT program, which was established by Congress in 2022 on a bipartisan basis to address this seasonal spike in child hunger. Project 2025 would also gut the Summer Food Service Program, which provides meals to more than 2 million children on average each day when school is out.
- Project 2025 and the RSC budget would make it harder and more stigmatizing for children in low-income communities to get free school meals. Currently, schools in every state serving large numbers of children in low-income families can provide free school meals to all children in the school, reducing administrative costs and eliminating the stigma associated with targeted participation. Almost 20 million children nationwide attend a school that uses this option. [58] Both Project 2025 and RSC would end this policy. [59]
- Project 2025 calls for ending Head Start , which provides early learning and other services to about 800,000 preschoolers, toddlers, and infants. [60] More than a third (37 percent) of the children enrolled in Head Start are Latine, nearly 30 percent (28 percent) are Black, about one-quarter are white, 3 percent are American Indian and Alaskan Native, and 3 percent are Asian, Native Hawaiian, or Pacific Islander. [61]
- The RSC budget calls for effectively ending guaranteed income assistance through SSI , which provided cash assistance to 7.5 million very low-income seniors and people with disabilities in 2022 (the last year data are available). [62] The plan calls for converting the funding (at what level is unclear) to a block grant to states, jeopardizing basic assistance for people whom the federal government for 50 years has recognized need income assistance they can count on. [63] (See Figure 5.)

Project 2025 calls for taking away housing assistance from people who can’t meet a work requirement or who reach an arbitrary time limit on how long they can receive assistance, even if they still need help to afford rent and avoid eviction. It would also end effective strategies for addressing homelessness that pair rental assistance with personalized supportive services, in favor of policies that research has found are less effective. [64] Like in other areas, these policies would disproportionately harm people of color, and especially Black people, who are far more likely than white people to experience homelessness and eviction. Discrimination was and is prevalent in housing as in other sectors, with one of the most consequential examples being federal “redlining” policies that made it far more difficult for Black people to become homeowners.
Project 2025 and the RSC budget would eliminate or weaken fair housing tools and enforcement, allowing for greater discrimination in housing that would exacerbate existing inequities. [65]
Enormous Costs Shifted to States, Widening Gaps Between Wealthier and Poorer States
All three agendas would cut funding that goes to states and localities, both in “mandatory” programs such as Medicaid and SNAP and in “discretionary” programs funded through the annual appropriations process, from transportation to public health to child care (see next section). As discussed above, the HBC, Project 2025, and RSC plans include proposals explicitly designed to shift costs from the federal government to states, including block-granting Medicaid or cutting the share of the program funded by the federal government. [66] The RSC budget also proposes block-granting SNAP and combining child nutrition programs, including the National School Lunch Program, School Breakfast Program, Child and Adult Care Food Program, Summer Food Service Program, and Special Milk Program, into a single block grant, likely with reduced funding. [67]
Under the RSC proposal, which would replace the long-standing Medicaid matching rate formula with a 50 percent rate for all states, the sharpest increases in Medicaid costs would generally occur in states whose residents have lower incomes and experience higher poverty rates — the states that can least afford the cost shift. [68] These states would experience the biggest cuts under the RSC proposal because, under current law, the federal government pays a larger share of Medicaid costs in states that have lower per capita incomes, recognizing the challenges these states face in financing health care costs. These are the same states that will struggle to make up for cuts in other areas, such as education or child care (discussed below), making it particularly hard for them to backfill for federal Medicaid funds, likely widening gaps between wealthier and poorer states in areas such as quality of education or health care access and coverage.
Finally, as noted, the RSC calls for converting the SSI program from one that now provides seniors and people with disabilities with federally funded cash assistance they can count on every month, to instead be a block grant to states, presumably with reduced funding. If funding proved inadequate, low-income seniors or people with disabilities would either receive less help or states would have to pick up the tab.
Massive Disinvestment in People, Communities, and the Building Blocks of Our Economy
The federal budget funds a host of investments in people, communities, and the economy as well as core functions of government through programs and initiatives funded through the appropriations process. This part of the budget (whose amounts are set annually) funds efforts such as: medical and basic scientific research; the weather forecasting system; education from preschool through college; housing; child care; tax system customer service and enforcement of our tax laws; disease monitoring and response to public health crises; the processing of applications and benefits in Social Security; anti-fraud staff in Medicare; investments in roads, bridges, public transit, and ports; and environmental clean-up and enforcement.
This part of the budget is called “discretionary” to connote that the spending is not fixed in law and that Congress has the discretion to set funding levels each year. But these kinds of investments are not optional for the safety, well-being, and thriving of our country and its economy, now and into the future.
Moreover, many of these investments — some targeted and others more broad based — promote opportunity for people and communities that have been under-resourced for decades due to federal, state, and local policy, especially Black, Latino, and Indigenous communities, people with disabilities, and people with low incomes living in rural and urban communities alike. These include additional funding for schools that serve large numbers of children in low-income families, college financial aid that paves the way to higher education, and funds for child care and preschool and for affordable housing development and rental assistance. [69]
Despite these critical functions, both the RSC budget and the HBC budget resolution call for massive disinvestment in this part of the budget — non-defense discretionary spending. [70] Indeed, the HBC budget would cut this part of the budget by $3.1 trillion over the decade. The RSC budget would cut even more, $4.1 trillion over the decade, [71] by making the cuts occur immediately rather than phasing them in.
Under both plans, non-defense discretionary spending would fall from its current level of 3.3 percent of GDP to about 1.4 or 1.5 percent after a decade — levels not seen since the Coolidge Administration a century ago. The programs targeted for these cuts are almost entirely unspecified, but if veterans’ health care is shielded, then under either of these plans, by 2034 spending for the remaining programs would fall by half .
Even though the plans do not offer many specifics, the cuts are so large that there is simply no way that all critically important public services could be protected. The result would likely be damaging cuts in our education and child care investments that build the human capital of our future workforce and allow parents to work, our transportation infrastructure that is critical to moving goods and services and keeping people safe, and our weather forecasting system that is essential for basic safety and commerce. And it would mean cutting staffing for agencies that help people access Social Security, ensure that Medicare providers are providing good care and playing by the rules, and enforce environmental laws and mitigate hazardous conditions. All of these public services are critical to people, families, communities, and the basic functioning of society.
The cuts the three agendas do specify include, for example, Project 2025’s elimination of Head Start (discussed above), which is funded in this part of the budget. Other examples include the following:
- Project 2025 calls for the Department of Education to be eliminated over time , with some programs transferred elsewhere and the rest abolished. [72] It would phase out over ten years the largest federal K-12 program, “Title I Education for the Disadvantaged,” which provides critical funding for school districts in communities experiencing high levels of poverty. Given the disproportionate child poverty rates among Black, Latine, and Indigenous children, this cut would exacerbate educational inequities. The RSC budget would eliminate a number of grants to school systems, and while it wouldn’t do so for Title I outright, that program would be at risk under RSC’s proposal that allows states to opt to receive all of their federal education funds through a block grant. [73] Both Project 2025 and RSC would make it harder for students to afford college by cutting financial aid.
- The RSC budget would take away assistance that millions of low-income households use to pay for heating, and in some states cooling, their homes, by eliminating the Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program (LIHEAP). [74]
- The RSC and HBC budgets would eliminate federal funds for the Legal Services Corporation, which provides financial support for roughly 130 nonprofit legal aid agencies nationwide. [75] Those agencies provide legal assistance to low-income families in handling non-criminal legal matters such as housing, child custody, domestic abuse, divorce, access to health care, employment law, and debt collection.
- The RSC budget calls for “significantly” reducing the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) budget, which the agency uses to reduce pollution, clean up hazardous waste, develop and enforce environmental standards, and help finance facilities for wastewater and drinking water treatment. [76] Among other things, the RSC budget calls for termination of surface water protection programs, which protect coastal waters and sources of drinking water such as rivers and lakes. The budget claims that states are better equipped to manage those waters, yet many of them flow or lie between states. Project 2025 and the HBC plan also call for cuts in EPA funding. [77]
- The RSC budget calls for elimination of all Energy Department funding for researching, developing, demonstrating, and deploying technologies for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting energy efficiency . [78] It would repeal clean energy provisions of the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act, including those supporting electric vehicles and low-emission school buses. [79] Project 2025 also calls for rescinding all remaining renewable energy funding appropriated in the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act. [80] The HBC plan criticized the infrastructure law and would not extend it, hampering efforts to combat climate change. [81] And, relatedly, all three plans call for repealing the Inflation Reduction Act’s investments in clean energy. [82]
- The RSC budget would eliminate both capital and operating funding for Amtrak , along with any further funding for high-speed rail. It would also end capital investment grants for mass transit and “RAISE” competitive grants for surface transportation infrastructure projects. [83]
- The RSC budget would both reduce the annual funding level for the IRS and repeal all that remains of funding provided in the Inflation Reduction Act to rebuild the IRS’ capacity to provide good customer service and enforce the tax laws and collect revenue that is due (discussed more below). [84]
- The RSC budget would eliminate funding for programs that are critical for states and localities to build and rehabilitate affordable housing and cut funding in half for fair housing education and enforcement . [85]
This is a recipe not for a thriving nation but for one retreating from its basic obligations to keep people safe and healthy and our economy strong. The impacts will at first fall most heavily on low- and middle-income people, who are least able to rely on private resources to replace basic government functions. Ultimately, though, these investments are critical for our economy and nation as a whole.
Doubling Down on Skewed, Expensive, and Failed Tax Policies
At the same time that these policy agendas call for massive disinvestment in public services and taking health coverage, food assistance, and other forms of assistance away from people who face challenges affording the basics, all three plans double down on expensive tax cuts mostly benefiting wealthy people and corporations. Project 2025 even calls for tax increases on low- and middle-income people.
Due to racial barriers to economic opportunity, households of color are overrepresented among households with incomes in the low end of the distribution, while non-Hispanic white households are heavily overrepresented among households with incomes at the top of the distribution. [86] Each of the three proposals would disproportionately benefit high-income households and exacerbate racial inequities.
For example, each agenda would double down on the 2017 tax cuts, whose core provisions are tilted heavily toward high-income households. [87] (See Figure 6.)

- The report accompanying the HBC budget resolution calls for extending all of the expiring 2017 tax cuts (at a cost of $4 trillion from 2026-2035) and making permanent costly business tax cuts . [88] But HBC does not include these costs in its budget resolution numbers, instead relying on language in the resolution allowing for consideration of these and other tax cuts regardless of cost. [89]
- The RSC budget calls for the continuation of all of the 2017 law’s individual income tax cuts and adds substantial tax cuts for corporations, wealthy shareholders, and large estates on top. [90] These include: repealing the estate tax, which less than 0.2 percent of estates now pay; lowering already low taxes on capital gains by indexing capital gains before calculating taxes; [91] repealing the Inflation Reduction Act provision that better ensures that large, highly profitable corporations pay at least some taxes; providing new tax breaks to already low-taxed corporations based on the amount they spend on certain investments; and expanding tax breaks for pass-through businesses, which saw large tax windfalls in the 2017 tax law from a special deduction that exempts from tax up to 20 percent of pass-through business income. [92]
- Changes to the tax brackets so that many low- and middle-income households would pay more while high-income households pay substantially less, by raising the lowest tax rate and lowering the highest tax rate. [94] Wealthy households would further benefit from cutting capital gains tax rates from 20 percent to 15 percent and eliminating a 3.8 percent surtax (known as the net investment income tax) on capital gains and other forms of unearned income. (See Figure 7.)
- Reducing the already too-low corporate tax rate even further, all the way to 18 percent. The 2017 tax law already gave corporations huge tax cuts by lowering the rate to 21 percent. This would provide a further tax cut of roughly $400 billion over ten years to large corporations on top of their 2017 windfall. [95]
- Giving new tax breaks to corporations that shift profits overseas.
- Cutting the estate tax, which only applies to the largest estates, and cutting the taxes shareholders pay when corporations distribute profits.
- Project 2025 also proposes long-term tax reforms that would dramatically shift the onus of taxation to middle- and low-income households. [96] Some of these proposals are vague, but they include shifting to a national sales tax (known as a consumption tax), which generally imposes far greater tax liability on middle- and low-income households who, compared to wealthy households, need to spend a larger share of their income on goods and services and who save a smaller share as they make ends meet. Project 2025 also proposes anti-democratic supermajority requirements on Congress to raise revenues, a tactic conservative states use to push taxes lower (there is no supermajority requirement to cut taxes), which would make it hard for the nation to respond to new needs or even raise revenues to lower deficits.
All three agendas call for repealing the Inflation Reduction Act’s funding for the IRS. [97] This funding is helping the IRS dramatically improve its customer service, operate the direct file mechanism so people can file their taxes directly with the IRS for free, and modernize and dramatically improve its tax enforcement efforts, which are already paying off in cracking down on wealthy tax cheats. [98]
Notably missing from these policy agendas is a positive tax agenda that would reflect some of the populist rhetoric some Republicans are employing about the need to support families and workers. These agendas would roll back rather than continue the expanded premium tax credits that have dramatically reduced the cost of health coverage for millions of people and expanded coverage, [99] and they don’t include Child Tax Credit and EITC expansions that would help middle- and lower-income families raising children and workers in lower-paid jobs.
Moreover, even as Project 2025 would raise taxes on middle- and low-income households, these families would all see sharp reductions in basic public services they benefit from, from quality schools and universities, to medical breakthroughs, to Medicaid, which serves nearly 74 million people.
Policies That Harm Immigrants and Their Families and Hurt Our Country as a Whole
Immigrants and their families are important parts of our communities. They bring vitality to our neighborhoods, they do important and often difficult work, they are business owners, and they contribute to the fabric of our nation in countless ways. Immigration has boosted our nation’s labor force at a time when the native-born population is aging, providing critical energy to our economy and helping to improve the financing of Social Security and Medicare over the coming decades. A recent Congressional Budget Office report highlights these economic contributions, showing that over a ten-year period (2024-2034), increased immigration would result in a GDP increase of $8.9 trillion and a decrease in the federal deficit by $900 billion. [100] CBO projects that in 2034, GDP will be an estimated 3.2 percent higher than it would be without these immigrants. [101]
Despite these contributions, the HBC budget plan, the RSC budget, and Project 2025 all treat immigrants — including those with a lawful immigration status — and their families harshly, putting concrete, harmful policies behind the ugly anti-immigrant rhetoric too prevalent in our public discourse.
For example, all three plans would reinstate the Trump Administration’s harsh public charge immigration policy, which essentially sought to create a wealth test for lawful immigration, preventing people from immigrating to the U.S. if they are not already economically successful. [102] The rule included an income test that could have blocked up to 99.2 percent of the population of South Asia, 98.5 percent of the population of Sub-Saharan Africa, and 79.0 percent of the population of Latin America and the Caribbean from immigrating to the U.S. [103] The rule ignores the record of achievement and upward mobility that immigrants and their descendants have shown for generations in the U.S.
The public charge changes also created fear among immigrants and their families that receiving benefits that Congress has made them eligible for would hurt their ability to remain in the country or have family members come. When proposed during the Trump Administration, the policy was shown to have a chilling effect on families’ willingness to access food assistance and health coverage that they qualified for. That includes forgoing help that their children — often citizens — needed. [104]
Even harsher, the RSC budget calls for a radical departure to how we treat immigrants who have lawful status, proposing to deny all public benefits (the precise scope is not clear) to anyone who is not a citizen, including immigrants who have lawful immigration status. [105] We already bar most lawful permanent residents from accessing public benefits such as Medicaid and SNAP during their first five years with that status in the U.S. People who have no documented status are blocked entirely for almost all benefits (with narrow exceptions such as Medicaid payment to health providers when people need emergency services in life-threatening circumstances). [106] But this proposal would further restrict benefits for immigrants, leaving many without any supports if they fall on hard times.
Republican health coverage proposals would increase number of uninsured, raise people’s costs, more revenue is required to meet the nation’s commitments, needs, and challenges, house republican budget reflects disturbing vision for the country, the 2017 trump tax law was skewed to the rich, expensive, and failed to deliver on its promises, policy basics federal budget.
- Deficits, Debt, and Interest
- Fiscal Stimulus
- Introduction to the Federal Budget Process
- Non-Defense Discretionary Programs
- The “Pay-As-You-Go” Budget Rule
- Where Do Our Federal Tax Dollars Go?
[1] This report’s authors: Sharon Parrott, Allison Orris, Claire Heyison, Sarah Lueck, Katie Bergh, Dorothy Rosenbaum, Joseph Llobrera, Catlin Nchako, Sonya Acosta, Will Fischer, David Reich, Richard Kogan, Samantha Jacoby, Chuck Marr, and Shelby Gonzales.
[2] See pp. 96 and 176 of Republican Study Committee, “Fiscal Sanity to Save America: Republican Study Committee FY 2025 Budget Proposal” (hereinafter RSC budget proposal), March 20, 2024, https://hern.house.gov/uploadedfiles/final_budget_including_letter_word_doc-final_as_of_march_25.pdf . For a detailed analysis of the agendas’ health proposals, see Allison Orris and Claire Heyison, “Republican Health Coverage Proposals Would Increase Number of Uninsured, Raise People’s Costs,” CBPP, September 3, 2024, https://www.cbpp.org/research/health/republican-health-coverage-proposals-would-increase-number-of-uninsured-raise .
[3] See pp. 11 and 44-45 of House of Representatives Committee on the Budget, “Concurrent Resolution on the Budget — Fiscal Year 2025, Report to Accompany H. Con. Res. 117” (hereinafter HBC report), report 118-568, June 27, 2024, https://www.congress.gov/congressional-report/118th-congress/house-report/568/1?outputFormat=pdf&s=1&r=4&q=%7B%22search%22%3A%22HCR+117%22%7D . CBPP calculations relative to Congressional Budget Office’s (CBO) February 2024 baseline, available at CBO, “The Budget and Economic Outlook: 2024-2034,” February 7, 2024, https://www.cbo.gov/publication/59710 .
[4] See p. 42 of the RSC budget proposal.
[5] Heritage Foundation, “Mandate for Leadership” (hereinafter Project 2025), 2023, https://static.project2025.org/2025_MandateForLeadership_FULL.pdf , pp. 300-301; 118 th Congress, Second Session, “H. Con. Res. 117 [Report No. 118–568]” (hereinafter HBC budget proposal), Section 412, June 27, 2024, https://www.congress.gov/118/bills/hconres117/BILLS-118hconres117rh.pdf .
[6] As with SNAP, the grocery benefits are distributed through a debit-style, electronic benefit transfer (EBT) card. For the proposal see pp. 303 of Project 2025.
[7] See pp. 11 and 52-53 of the HBC report. CBPP calculations are relative to CBO’s February 2024 baseline, and take into account that some of the total savings in the income security category reflect cuts to civil service retirement, which is another program the HBC report targets.
[8] The climate provisions in the Inflation Reduction Act are primarily in the form of tax credits.
[9] See p. 29 of the RSC budget proposal and pp. 71-72 of the HBC report.
[10] CBPP estimates based on CBO estimates. See Congressional Budget Office, “Budgetary Outcomes Under Alternative Assumptions About Spending and Revenues,” May 8, 2024, https://www.cbo.gov/publication/60114 . We use the ten-year period 2026-2035 because extending the Trump tax cuts would reduce tax liability starting in 2026. And in 2025, when Congress will debate how to handle the scheduled expirations, it will be looking at the 2026-2035 ten-year budget window.
[11] Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget, “TCJA Extension Could Add $4 to $5 Trillion to Deficits,” June 13, 2024, https://www.crfb.org/blogs/tcja-extension-could-add-4-5-trillion-deficits#appendix .
[12] See Section 302 of the HBC budget proposal.
[13] See pp. 145 and 680 of Project 2025, pp. 84-85 of the RSC budget proposal, and pp. 52-53 of the HBC report.
[14] See pp. 11 and 44-45 of the HBC report. CBPP calculations relative to CBO’s February 2024 baseline. While the cuts could also affect CHIP and ACA marketplace coverage, the accompanying report discusses cuts only to Medicaid.
[15] See pp. 96 and 176 of the RSC budget proposal.
[16] CBPP analysis of 2013 and 2022 American Community Survey data. The American Indian and Alaska Native (AIAN) category includes people who may be AIAN alone or in combination with other races and ethnicities. The Latino category includes people of any race. The Black and white categories include only people who identify as a single race and not Latino. (The use of “Latino” does not necessarily reflect how everyone who is part of this community would describe themselves. Elsewhere in this report we also use “Hispanic,” and “Latine” for gender inclusivity.)
[17] See p. 45 of the HBC report, pp. 95-96 of the RSC budget proposal, and p. 466 of Project 2025. For analysis of prior attempts to cap and block-grant Medicaid, see Aviva Aron-Dine, “Medicaid ‘Block Grant’ Guidance Will Likely Encourage States to Undermine Coverage,” CBPP, January 29, 2020, https://www.cbpp.org/blog/medicaid-block-grant-guidance-will-likely-encourage-states-to-undermine-coverage ; and Gideon Lukens and Allison Orris, “Changing Medicaid’s Funding Structure to a Per Capita Cap Would Shift Costs to States, Force Deep Cuts, and Leave Millions Uninsured,” CBPP, March 27, 2023, https://www.cbpp.org/research/health/changing-medicaids-funding-structure-to-a-per-capita-cap-would-shift-costs-to .
[18] See p. 45 of the HBC report, p. 96 of the RSC budget proposal, and pp. 467-469 of Project 2025.
[19] See p. 96 of the RSC budget proposal and p. 467 of Project 2025.
[20] See p. 45 of the HBC report, pp. 466-467 of Project 2025, and pp. 95-96 of the RSC budget proposal.
[21] Laura Harker, “Pain But No Gain: Arkansas’ Failed Medicaid Work-Reporting Requirements Should Not Be a Model,” CBPP, August 8, 2023, https://www.cbpp.org/research/health/pain-but-no-gain-arkansas-failed-medicaid-work-reporting-requirements-should-not-be ; Laura Harker, “6 Months Into Georgia Pathways Program, Over 400,000 People Still Lack Health Coverage; Expanding Medicaid Would Improve Access for Low-Income Georgians,” CBPP, January 25, 2024, https://www.cbpp.org/blog/6-months-into-georgia-pathways-program-over-400000-people-still-lack-health-coverage-expanding .
[22] See p. 45 of the HBC report, pp. 38 and 96 of the RSC budget proposal, and pp. 468-469 of Project 2025.
[23] See p. 468 of Project 2025.
[24] See pp. 95-96 of the RSC budget proposal and pp. 468-469 of Project 2025.
[25] See p. 4 of the HBC report and pp. 87-88 of the RSC budget proposal.
[26] Jared Ortaleza et al. , “Inflation Reduction Act Health Insurance Subsidies: What is Their Impact and What Would Happen if They Expire?” KFF, July 26, 2024, https://www.kff.org/affordable-care-act/issue-brief/inflation-reduction-act-health-insurance-subsidies-what-is-their-impact-and-what-would-happen-if-they-expire/ .
[27] See pp. 87-88 of the RSC budget proposal.
[28] See pp. 469-470 of Project 2025.
[29] The Heritage Foundation paper, and the Health Policy Consensus Group proposal it cites, propose converting the PTC into state block grants. These grants would be based on current subsidy levels. While the proposal does not specify how block grants would be adjusted over time, prior repeal plans set adjustments to increase funding cuts year over year. States would not be obligated to accept block grant funding and could instead choose to provide no or limited premium assistance for individual market coverage. See Edmund F. Haislmaier and Abigail Slagle, “Premiums, Choices, Deductibles, Care Access, and Government Dependence Under the Affordable Care Act: 2021 State-by-State Review,” Heritage Foundation, November 2, 2021, https://www.heritage.org/sites/default/files/2021-11/BG3668.pdf .
[30] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, “Health Insurance Marketplaces: 10 Years of Affordable Private Plan Options,” March 22, 2024, https://aspe.hhs.gov/sites/default/files/documents/00d1eccb776ac4abde9979aa793e2c7a/aspe-10-years-of-marketplace.pdf ; Ortaleza et al.
[31] See p. 4 of the HBC report and pp. 87-88 of the RSC budget proposal.
[32] Estimate is based on age-adjusted 2024 average benchmark premiums and 2023 poverty guidelines, which are used to determine premium tax credits for 2024 marketplace coverage. Gideon Lukens, “Health Insurance Costs Will Rise Steeply if Premium Tax Credit Improvements Expire,” CBPP, June 4, 2024, https://www.cbpp.org/research/health/health-insurance-costs-will-rise-steeply-if-premium-tax-credit-improvements-expire .
[33] Jessica Banthin, Michael Simpson, and Mohammed Akel, “The Impact of Enhanced Premium Tax Credits on Coverage by Race and Ethnicity,” Urban Institute, August 12, 2024, https://www.urban.org/research/publication/impact-enhanced-premium-tax-credits-coverage-race-and-ethnicity .
[34] The RSC proposal “adopts regulatory reforms developed by the RSC’s Health Care Task Force . . . and set forth in its report: A Framework for Personalized, Affordable Care. Republican Study Committee.” This report proposes eliminating the PTC and rolling back the ACA’s Medicaid expansion, and repurposing those funds for state “guaranteed coverage pools.” See p. 89 of the RSC budget proposal.
[35] KFF, “Health Insurance Marketplace Calculator,” updated October 27, 2023, https://www.kff.org/interactive/subsidy-calculator/ .
[36] See pp. 89-90 of the RSC budget proposal.
[37] See p. 90 of the RSC budget proposal.
[38] Edwin Park, “Trump, House GOP High-Risk Pool Proposals a Failed Approach,” CBPP, November 17, 2016, https://www.cbpp.org/blog/trump-house-gop-high-risk-pool-proposals-a-failed-approach .
[39] See pp. 469-470 of Project 2025.
[40] Nambi Ndugga, Latoya Hill, and Samantha Artiga, “Key Data on Health and Health Care by Race and Ethnicity,” KFF, June 11, 2023, https://www.kff.org/key-data-on-health-and-health-care-by-race-and-ethnicity .
[41] See pp. 91-92 of the RSC budget proposal and pp. 468 and 470 of Project 2025.
[42] Sarah Lueck, “Commentary: Growing Evidence Shows Need for Stronger Rules for Short-Term Health Plans,” CBPP, October 23, 2020, https://www.cbpp.org/research/health/commentary-growing-evidence-shows-need-for-stronger-rules-for-short-term-health .
[43] See pp. 475 and 495-496 of Project 2025.
[44] See p. 12 of the HBC report.
[45] See pp. 11 and 52-53 of the HBC report. CBPP calculations are relative to CBO’s February 2024 baseline, and take into account that some of the total savings in the income security category reflect cuts to civil service retirement, which is another program the HBC report targets.
[46] Lauren Hall, “Food Insecurity Increased in 2022, With Severe Impact on Households With Children and Ongoing Racial Disparities,” CBPP, October 26, 2023, https://www.cbpp.org/blog/food-insecurity-increased-in-2022-with-severe-impact-on-households-with-children-and-ongoing .
[47] Laura Samuel et al. , “Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program Access and Racial Disparities in Food Insecurity,” JAMA Network Open, Vol. 6, No. 6, June 2023, https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.20196 ; Benjamin Glasner et al. , “The Effectiveness of the Food Stamp Program at Reducing Differences in the Intergenerational Persistence of Poverty,” Washington Center for Equitable Growth, May 2023, https://equitablegrowth.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/053023-WP-The-Effectiveness-of-the-Food-Stamp-Program-at-Reducing-Racial-Differences-in-the-Intergenerational-Persistence-of-Poverty.pdf ; Alfonso Flores-Lagunes et al. , “Moving Policies toward Racial and Ethnic Equality: The Case of the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program,” American Journal of Agricultural Economics, Vol. 106, No. 2, May 2023, https://doi.org/10.1111/ajae.12402 .
[48] See p. 42 of the RSC budget proposal.
[49] Joseph Llobrera, “Recent Increase in SNAP Purchasing Power Invests in Children’s Health and Well-Being,” CBPP, August 29, 2022, https://www.cbpp.org/research/food-assistance/recent-increase-in-snap-purchasing-power-invests-in-childrens-health-and ; Laura Wheaton and Danielle Kwon, “Effect of the Reevaluated Thrifty Food Plan and Emergency Allotments on Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program Benefits and Poverty,” Urban Institute, August 1, 2022, https://www.urban.org/research/publication/effect-reevaluated-thrifty-food-plan-and-emergency-allotments-supplemental .
[50] See pp. 300-301 of Project 2025 and Section 412 of the HBC budget proposal.
[51] Under the Fiscal Responsibility Act, 53- and 54-year-olds will become newly subject to this work requirement beginning October 1, 2024. See pp. 41-42 of the RSC budget proposal and pp. 299-300 of Project 2025.
[52] Joseph Llobrera, “Most Working-Age SNAP Participants Work But Job Instability Overstates Joblessness in Some Analyses,” CBPP, May 19, 2023, https://www.cbpp.org/blog/most-working-age-snap-participants-work-but-job-instability-overstates-joblessness-in-some .
[53] Tori Coan and Shawn Fremstad, “The Dismal Economics of SNAP’s Work-Hours Test and Time Limit,” Center for Economic and Policy Research, April 18, 2023, https://cepr.net/report/the-dismal-economics-of-snaps-work-hours-test-and-time-limit/ .
[54] See p. 52 of the HBC report.
[55] See pp. 42-43 of the RSC budget proposal and p. 300 of Project 2025.
[56] Project 2025 proposes providing summer meals to children in low-income families only if they are taking summer-school classes, which would substantially cut the Summer Food Service Program (which provides meals) and could mean eliminating the Summer EBT program (which provides grocery benefits to enable low-income households with children to purchase food). See p. 303 of Project 2025.
[57] Mark Nord and Kathleen Romig, “Hunger in the Summer: Seasonal food insecurity and the National School Lunch and Summer Food Service programs,” Journal of Children and Poverty, Vol. 12, No. 2, 2006, pp. 141-158, https://doi.org/10.1080/10796120600879582 ; Jin Huang, Ellen Barnidge, and Youngmi Kim, “Children Receiving Free or Reduced-Price School Lunch Have Higher Food Insufficiency Rates in Summer,” Journal of Nutrition, Vol. 145, No. 9, September 2015, pp. 2161-68, https://doi.org/10.3945/jn.115.214486 .
[58] Allyson Pérez and Crystal FitzSimons, “Community Eligibility: The Key to Hunger-Free Schools, School Year 2022-2023,” Food Research and Action Center, May 2023, https://frac.org/wp-content/uploads/cep-report-2023.pdf .
[59] See p. 303 of Project 2025 and p. 46 of the RSC budget proposal.
[60] U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, “Head Start Program Facts: Fiscal Year 2022,” https://eclkc.ohs.acf.hhs.gov/data-ongoing-monitoring/article/head-start-program-facts-fiscal-year-2022 .
[62] Social Security Administration, “SSI Recipients by State and County, 2022,” https://www.ssa.gov/policy/docs/statcomps/ssi_sc/2022/table01.html .
[63] RSC budget, p. 45.
[64] Project 2025, p. 509.
[65] Project 2025, p. 509, and RSC, p. 171.
[66] Another proposal, from the conservative Paragon Institute, would not only reduce the enhanced matching rate for the Medicaid expansion but also shift costs to some states by dropping the current Medicaid matching rate floor from 50 percent to 40 percent. The institute justifies its proposal by arguing that its policies would reorient spending in support of traditional populations, such as children and people with disabilities, but the proposal fails to acknowledge deep cuts states could make across their programs given the extreme cost shift to states they propose. Brian Blase and Drew Gonshorowski, “Medicaid Financing Reform: Stopping Discrimination Against the Most Vulnerable and Reducing Bias Favoring Wealthy States,” Paragon Health Institute, July 2024, https://paragoninstitute.org/medicaid/medicaid-financing-reform-stopping-discrimination-against-the-most-vulnerable-and-reducing-bias-favoring-wealthy-states/ .
[67] See pp. 41-42 and 46 of the RSC budget proposal.
[68] The RSC proposal would shrink the federal government’s commitment to sharing in Medicaid costs in the 40 states and the District of Columbia that would otherwise have a standard Medicaid matching rate over 50 percent in fiscal year 2025. U.S. territories presumably would face a cut as well, since their matching rates now exceed 50 percent. KFF, “Federal Medical Assistance Percentage (FMAP) for Medicaid and Multiplier,” FY 2025, https://www.kff.org/medicaid/state-indicator/federal-matching-rate-and-multiplier/?currentTimeframe=0&sortModel=%7B%22colId%22:%22Location%22,%22sort%22:%22asc%22%7D .
[69] Also see Jabari Cook et al., “House Appropriations Bills Take Steps to Use the Federal Budget as a Tool for Antiracism,” CBPP, February 23, 2022, https://www.cbpp.org/research/house-appropriations-bills-take-steps-to-use-the-federal-budget-as-a-tool-for-antiracism .
[70] While Project 2025 includes a number of proposals for non-defense discretionary programs, it did not provide overall estimates for this budget category (unlike the HBC and RSC plans, which included full budget estimates).
[71] Cuts are measured from CBO’s February 2024 baseline but with the discretionary levels adjusted to reflect final appropriations for 2024 and the level of agreed-on adjustments to the 2025 non-defense discretionary cap that accompanied the enactment of that cap, which adds $652 billion in outlays over the decade. See the appendix of Richard Kogan et al., “More Revenue Is Required to Meet the Nation’s Commitments, Needs, and Challenges,” CBPP, June 17, 2024, https://www.cbpp.org/research/federal-budget/more-revenue-is-required-to-meet-the-nations-commitments-needs-and .
[72] Project 2025, Chapter 11, “Department of Education,” pp. 319-362.
[73] RSC budget, pp. 164-5.
[74] RSC budget, p. 163.
[75] RSC budget, p. 146; HBC report, p. 60.
[76] RSC budget, p. 155.
[77] Project 2025, Chapter 13, “Environmental Protection Agency,” pp. 417-448, and HBC report, p. 30.
[78] RSC budget, pp. 149-151.
[79] RSC budget, pp. 169-170.
[80] Project 2025, p. 365.
[81] HBC report, p. 35.
[82] RSC budget, p. 17; HBC report, p. 67; and Project 2025, p. 365. Note that the climate provisions in the Inflation Reduction Act are not funded by appropriations, but rather are in the form of tax incentives and mandatory spending.
[83] RSC budget, pp. 170-71.
[84] RSC budget, p. 151.
[85] RSC budget, pp. 171-172.
[86] For example, Latino and Black households represented 24 percent of all households in 2019, but they represented 32 percent of the least wealthy 60 percent of households and less than 1 percent of the wealthiest 1 percent. University of California at Berkeley, “Study: Survey of Consumer Finances (SCF) Combined Extract Data 1989-2019,” https://sda.berkeley.edu/sdaweb/analysis/?dataset=scfcomb2019 .
[87] White households in the highest-earning 1 percent receive 23.7 percent of the law’s total tax cuts, far more than the 13.8 percentage share that the bottom 60 percent of households of all races receive. Chye-Ching Huang and Roderick Taylor, “How the Federal Tax Code Can Better Advance Racial Equity,” CBPP, July 25, 2019, https://www.cbpp.org/research/federal-tax/how-the-federal-tax-code-can-better-advance-racial-equity .
[88] See pp. 71-72 of the HBC report.
[89] See Section 302 of HBC budget proposal.
[90] See pp. 29-33 of the RSC budget proposal.
[91] See Chye-Ching Huang and Kathleen Bryant, “Indexing Capital Gains for Inflation Would Worsen Fiscal Challenges, Give Another Tax Cut to the Top,” CBPP, September 6, 2018, https://www.cbpp.org/research/federal-tax/indexing-capital-gains-for-inflation-would-worsen-fiscal-challenges-give .
[92] Chuck Marr, Samantha Jacoby, and George Fenton, “The Pass-Through Deduction Is Skewed to the Rich, Costly, and Failed to Deliver on Its Promises,” CBPP, June 6, 2024, https://www.cbpp.org/research/federal-tax/the-pass-through-deduction-is-skewed-to-the-rich-costly-and-failed-to-deliver .
[93] See p. 696 of Project 2025.
[94] Brendan Duke, “Project 2025’s Tax Plan Would Raise Taxes on the Middle Class and Cut Taxes for the Wealthy,” Center for American Progress, August 27, 2024, https://www.americanprogress.org/article/project-2025s-tax-plan-would-raise-taxes-on-the-middle-class-and-cut-taxes-for-the-wealthy/ .
[95] CBPP calculations based on CBO, “Increase the Corporate Income Tax Rate by 1 Percentage Point,” December 7, 2022, https://www.cbo.gov/budget-options/58701 .
[96] See p. 698 of Project 2025.
[97] See p. 699 of Project 2025, p. 27 of the RSC budget proposal, and pp. 61 and 62 of the HBC report.
[98] Kayla Williams, “Tax Day Highlights IRS Progress and Need to Protect and Replenish Funding,” CBPP, April 10, 2024, https://www.cbpp.org/blog/tax-day-highlights-irs-progress-and-need-to-protect-and-replenish-funding .
[99] See pp. 87-88 of the RSC budget proposal, pp. 469-470 of Project 2025, and p. 4 of the HBC report.
[100] Congressional Budget Office, “An Update to the Budget and Economic Outlook: 2024 to 2034,” June 18, 2024, https://www.cbo.gov/publication/60039 .
[101] Congressional Budget Office, “Effects of the Immigration Surge on the Federal Budget and the Economy,” July 2024, https://www.cbo.gov/system/files/2024-07/60165-Immigration.pdf .
[102] See p. 145 of Project 2025, pp. 84-85 of the RSC budget proposal, and p. 52 of the HBC report.
[103] Danilo Trisi, “Trump Administration’s Overbroad Public Charge Definition Could Deny Those Without Substantial Means a Chance to Come to or Stay in the U.S.,” CBPP, May 30, 2019, https://www.cbpp.org/research/poverty-and-inequality/trump-administrations-overbroad-public-charge-definition-could-deny .
[104] Hamutal Bernstein et al. , “Amid Confusion over the Public Charge Rule, Immigrant Families Continued Avoiding Public Benefits in 2019,” Urban Institute, May 2020, https://www.urban.org/sites/default/files/publication/102221/amid-confusion-over-the-public-charge-rule-immigrant-families-continued-avoiding-public-benefits-in-2019_3.pdf .
[105] See p. 49 of the RSC budget proposal.
[106] Project 2025 also includes a range of harsh immigration policy measures, such as ending lawful immigration statuses for certain victims of trafficking and domestic violence, but those policies are beyond the scope of this analysis.
More from the Authors

Recent Work:
- In Case You Missed It . . .
- In Case You Missed It . . .

COMMENTS
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of ...
Make sure you can ask the critical what, who, and how questions of your research before you put pen to paper. Your research proposal should include (at least) 5 essential components: Title - provides the first taste of your research, in broad terms. Introduction - explains what you'll be researching in more detail.
Here is an explanation of each step: 1. Title and Abstract. Choose a concise and descriptive title that reflects the essence of your research. Write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. It should provide a brief overview of your proposal. 2.
Key Takeaways. Developing a research proposal involves the following preliminary steps: identifying potential ideas, choosing ideas to explore further, choosing and narrowing a topic, formulating a research question, and developing a working thesis. A good topic for a research paper interests the writer and fulfills the requirements of the ...
Research proposals, like all other kinds of academic writing, are written in a formal, objective tone. Keep in mind that being concise is a key component of academic writing; formal does not mean flowery. Adhere to the structure outlined above. Your reader knows how a research proposal is supposed to read and expects it to fit this template.
Before conducting a study, a research proposal should be created that outlines researchers' plans and methodology and is submitted to the concerned evaluating organization or person. Creating a research proposal is an important step to ensure that researchers are on track and are moving forward as intended. A research proposal can be defined as a detailed plan or blueprint for the proposed ...
The design elements and procedures for conducting research are governed by standards of the predominant discipline in which the problem resides, therefore, the guidelines for research proposals are more exacting and less formal than a general project proposal. Research proposals contain extensive literature reviews.
What is a research proposal? Simply put, a research proposal is a structured, formal document that explains what you plan to research (your research topic), why it's worth researching (your justification), and how you plan to investigate it (your methodology).. The purpose of the research proposal (its job, so to speak) is to convince your research supervisor, committee or university that ...
Step 1: Title and Abstract. Select a concise, descriptive title and write an abstract summarizing your research question, objectives, methodology and expected outcomes . The abstract should include your research question, the objectives you aim to achieve, the methodology you plan to employ and the anticipated outcomes.
Here's an example outline of a research plan you might put together: Project title. Project members involved in the research plan. Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan's intent) Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective) Objective 2. Objective 3.
A research proposal is a document that outlines your proposed research project, explaining what you plan to study, why it's important and how you will conduct your research. A well-structured research proposal includes a title page, abstract and table of contents, introduction, literature review, research design and methodology, contribution to ...
A dissertation or thesis research proposal may take on a variety of forms depending on the university, but most generally a research proposal will include the following elements: Titles or title pages that give a description of the research. Detailed explanation of the proposed research and its background. Outline of the research project.
The research proposal holds significant importance in the research process. Here are some key reasons why research proposals are important: Planning and organization: A research proposal requires careful planning and organization of your research project. It forces you to think through the research objectives, research questions, methodology ...
Research Proposal Example/Sample. Detailed Walkthrough + Free Proposal Template. If you're getting started crafting your research proposal and are looking for a few examples of research proposals, you've come to the right place. In this video, we walk you through two successful (approved) research proposals, one for a Master's-level ...
A quality example of a research proposal shows one's above-average analytical skills, including the ability to coherently synthesize ideas and integrate lateral and vertical thinking. Communication skills. The proposal also demonstrates your proficiency to communicate your thoughts in concise and precise language.
research proposal. It covers the when, why and how to aspects of research. proposals, and uses examples to illustrate the most effective way to communicate. research ideas. It is, in part ...
For some research courses in sciences you'll join an existing research group so you don't need to write a full research proposal, just a list of the groups and/or supervisors you want to work with. You might be asked to write a personal statement instead, giving your research interests and experience. Still, for many of our research courses ...
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: 'A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management'.
Writing Research Proposals. The research proposal is your opportunity to show that you—and only you!—are the perfect person to take on your specific project. After reading your research proposal, readers should be confident that…. You have thoughtfully crafted and designed this project; You have the necessary background to complete this ...
Writing the proposal of a research work in the present era is a challenging task due to the constantly evolving trends in the qualitative research design and the need to incorporate medical advances into the methodology. The proposal is a detailed plan or 'blueprint' for the intended study, and once it is completed, the research project ...
Style: If space allows, provide a clear project title. Structure your text - if allowed use section headings. Present the information in short paragraphs rather than a solid block of text. Write short sentences. If allowed, provide images/charts/diagrams to help break up the text.
If you want to learn how to write your own plan for your research project, consider the following seven steps: 1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can ...
A research plan is a framework that shows how you intend to approach your topic. The plan can take many forms: a written outline, a narrative, a visual/concept map or timeline. It's a document that will change and develop as you conduct your research. Components of a research plan. 1. Research conceptualization - introduces your research question.
Useful tips for writing a research proposal. Maintain a focus in your proposal: Your research proposal should be clear and concise, outlining your research idea and its benefits to your chosen field of study, in a way that the reader can clearly understand. Remember, your proposal is just the starting point and an outline and does not need to ...
1 Introduction Action research is a progressive method to enhance the dynamics of workplaces by a cyclical approach of planning, acting, observing, and reflecting. This plan presents results of research facilitated by course learning journeys and organizes those results into an action plan for improvement of our work environment. This section recapitulates the original research proposal and ...
The strategic plan from the White House National Science and Technology Council — shared first with POLITICO's E&E News — outlines the administration's research and development priorities ...
Protecting Our Great Lakes, Rivers, and Shorelines The Abrams Clinic represents Friends of the Chicago River and the Sierra Club in their efforts to hold Trump Tower in downtown Chicago accountable for withdrawing water illegally from the Chicago River. To cool the building, Trump Tower draws water at high volumes, similar to industrial factories or power plants, but Trump Tower operated for ...
Allowing existing improvements to premium tax credits to expire after 2025 — as the HBC budget plan and RSC proposal would do [31] — would mean premium spikes for nearly all marketplace enrollees. For example, a typical 60-year-old couple making $80,000 (405 percent of the poverty level) would see their marketplace premiums more than triple ...