- What is a bee?
- Types Of Bees
- Why Are Bees Good Pollinators?
- Bee Identification
- Bee Nest FAQs
- Bee Life Cycle
- Bee Stings: Facts
- Found A Bee?
- Save The Bees
- Enemies Of Bees
- Apiphobia - Fear Of Bees
- Waxing lyrical
- Books About Bees
- Stuff For Kids
- Conservation Articles
- About Bumble Bees
- Bumble Bee Life Cycle
- Bumble Bee Queen
- Cuckoo Species
- Foraging Behaviour
- Bumble Bee Nests
- North American Bumble Bees
- British Bumble Bees
- About Honey Bees
- Honey Bee Life Cycle
- Honey Bee Colonies
- Honey Bee Queen
- Honey Bee Facts
- Swarm Removal
- Honey Bee Anatomy
- About Honey
- How Do Bees Make Honey?
- Honey & Health
- What Is Manuka Honey?
- Honey & Beauty
- Bees And Pollen
- List: BKAs of North America
- Beekeeping Links
- In Eco-sensitive areas
- Business Plan
- Leafcutter Bees
- Mining Bees
- Wool Carder Bee
- Pantaloon Bees
- Carpenter bees
- Small Carpenter bees
- Sharp-tail Bees
- Mourning Bees
- Plasterer Bees
- Long-horned Bee
- Oil-collecting Bees
- Hairy-footed Flower Bee
- Yellow-faced Bee
- Orange-legged furrow bee
- Smeathman’s furrow bee
- Resin Bees (Heriades)
- About Wasps
- Types of Wasp
- Bees Vs Wasps
- Wasp Stings
- Gardening For Bees
- Garden Flowers Guide
- Flowering Shrubs
- Herbs For Bees
- Bulbs & Corms
- Wildflowers
- Flower Shapes
- Bee Garden Tips
- Small Gardens

Creating A Beekeeping Business Plan
Updated: 30th April 2021
Here are some factors to consider if you are drawing up a beekeeping business plan (and a free template for you to use), whether you wish to become a honey producer, or are wanting to offer a variety of products and services related to beekeeping, honey bees and hives.
On the one hand, you may be able to earn a living from keeping bees, but like all businesses, there are potential pitfalls.
PDF Template At the bottom of this page, you'll find a PDF business plan template you can adapt and use for your own purposes.
Below, we will first look at the following topics:
- Initial considerations
- Income routes
- Finances (costs, sales, cash flow, profit & loss)
- Researching your beekeeping business plan (What? Who? Where? How? Why?)
- SWOT analysis
- General administration
If you require a loan to help you get started, then you will need to demonstrate to the lender that you have thought about the business in detail.
Consider things from the lender’s perspective: if you were in his or her shoes, would you loan money to this new beekeeping business based on the plan and information you are being presented with?
In addition, you need to work through the details yourself, so that you can have confidence, minimize your risks and have a genuine chance of success.
Drawing Up A Beekeeping Business Plan – some initial considerations:
It sounds obvious, but.....are you an experienced beekeeper?
If not, best get some experience first, and ensure you:
- know what you are doing;
- you are happy handling the bees;
- you know what to do in a crisis;
- you don’t suddenly discover you have a severe allergy to stings ;
- you have full knowledge of how to keep and provide for your bees (see ' apiary design ' - where will they forage, how will you protect the hives against disease, predators, even vandalism, the elements and so on);
- Understand any legal consideration in starting an apiary .
How Can Beekeepers Earn Income From Keeping Bees?
You may have a firm idea already of how beekeeping is going to earn an income for you, but it's also worth trying to think outside the box, and look at offering a multiple range of products (and maybe even services), in order to build your income across the seasons.

However, whether you decide to focus only on being a honey producer, or selling a wider range of product and services, you’ll need to estimate your potential earnings, and add these to your business plan.
Here are some ideas of what your business might include:
- Selling honey.
- Selling other bee products, such as beeswax .
- Selling services, such as pollination. Investigate it carefully, because selling pollination services can be a tricky business these days if the crops are treated with pesticides such as the infamous neonicotinoids .
- Selling beekeeping courses at your apiary or online, CDs and books you have written yourself.
- If you have land, would you be interested in running a nursery or cut flower business alongside your beekeeping business? You'll need to think about flowers for the bees to forage on anyway, and having visited such a business, there was a huge amount of flower available for bees, despite cutting.
- Selling beekeeping supplies, such as bee hives, items of equipment, or beekeeping suits and hats .
- Are you able to build a brand, such that you could offer other 'add ons' for sale from an online shop - from honey sticks to socks, who knows?
In thinking about your business, put a great deal of thought into whether it is something you can start up as a hobby (perhaps whilst continuing with your day job), and build it from there.
As I write, I am aware that some large commercial honey sellers run training schemes whereby you can earn whilst you learn. As far as I can make out, the salary is modest, but if you are especially keen, it may be a way for you to get valuable experience if that is what you need.
However, do check first regarding whether or not you are then tied to supplying the company with honey etc for a set period of time, and whether this suits you, and also whether you are happy to supply honey in this way. In addition, check whether you would have to sign an agreement forbidding you to set up a business entirely of your own.
Some beekeepers prefer to set up small-scale, organic practices, charging a premium for their products, selling directly to the public or specialist delicatessens.
A Beekeeping Business Plan Needs To Cover Finances: costs, sales, cash flow, profit & loss
Consider these costs:
- Initial set up costs (hives, honey bees including nucs , beekeeping equipment and clothing, premises, insurances), building a website and hosting if needed and so on.
- Product related costs & inventory, such as honey jars and labels .
- General business running costs: travel, any items relating to the care of the bees, postage and packing, phone, rent, stationery etc.
- Will you spend any money on marketing, such as advertising honey or beekeeping courses in the local paper, or will you engage in internet advertising? Be sure to build in a mechanism that allows you to assess the cost effectiveness of any marketing activity, if possible.
- Cost of finance (interest and charges).
- Also consider your home and family incomings and outgoings. Are you considering giving up a regular, paid job in order to run a beekeeping business, and if so, for how long can you survive - including in a poor year?
- Will you need to adapt your land in some way, to cater for bees on your property? If so, be sure to factor in the costs and timings. You should calendarize these costs, and also add a realistic sales forecast as far as possible. Although you will need it to go along to the bank or lender, forecasting is of course very difficult, and may need to be adjusted from time to time. How much, if you implement your marketing plan (we’ll get to that in a minute), could you sell on a monthly basis? Itemize each activity: how much honey will you sell, how many courses will you fill etc.
Financial challenges can hit any business.
- How will you cope with payment schedules? For example, if you supply 200 jars of honey to a store, when will you be paid, and can you cope with late payments? Cash flow is one of the major challenges for any business, but especially new ones. Not being able to pay your bills because somebody didn’t pay you, can create misery and force businesses to close.
- What is your profit margin? Remember it needs to cover ALL of your costs, with enough to earn the income you need, and hopefully leave some for emergencies.
Researching Your Beekeeping Business
Find out as much as you can about the market, products, services, prices, your customers, relevant law, prior to committing yourself.
Ask yourself the What? Who? Where? and How? Why? questions.
For example (no doubt, you can come up with more):
- What are customers buying, what do they want and are there any unexploited niches you can fill?? Whatever you are selling, are there any legal or labelling requirements or standards?)
- What should the packaging look like? ( Bottles or jars and labels for jars).
- Who is buying your products and how should they be approached, when, and what are their needs/wants? (think in terms of the public, retailers, wholesalers).
- At what prices are comparable bee products being sold in your area? Are there many competitors? How much supply is there versus demand? Can you compete?
- Where will the customers need to go to buy the products? Internet? Shops? Market? Where will you reach them? Would your prefer to sell bulk honey to a major buyer or network?
- Where will you buy your own supplies from?
When?
- When will customers purchase from you, and how does this impact your business? Do you have to warn customers in advance/how long do advanced booking periods need to be, and...
- When will you be paid and when do you have to pay suppliers?
- How will you persuade customers to buy and how will you generate awareness? How often will your customers purchase from you?
- How much will it all cost, and how much do you need to sell to create a viable beekeeping business?
- How will your product be different? For example, will yours be the only organic meadow honey in the area, or perhaps the only raw comb honey?
- Why will anyone wish to buy your products? Don’t be offended by this question. This question is deliberately asked so that you think of things from your customer’s perspective.
Having considered these questions, what actions need to be taken, when, by whom and at what cost?
Marketing And Your Beekeeping Business Plan
There are many cost effective ways to sell and promote your products.
- You can sell directly to the public at the local food market, promote on social media for a low cost. In some city shopping centers, it's possible to purchase a one day trading permit, and set up a stall selling produce - but check local regulations, especially around permits, food selling, pitch size etc. After that, assess whether it is worth trying out a stand for a day or a few days.
- Look out for honey festivals, and find out whether you can get a stand to promote your goods and business. Remember to look into the cost and find out how many people are likely to attend.
- You can also sell via specialist networks or to major buyers and brand owners, who already have established channels to sell their products in stores. Such companies may purchase your honey and apply their own label to the product.
- Social media can be a great way to promote your goods, and advertising can be cost effective - but see what you can achieve without the advertising first! Remember that you can also use You Tube to advertise goods on the existing videos of other you tubers, to send potential customers directly to your website. You can make a few videos and upload them to generate interest too, of course! Think about your message and target market very carefully to ensure you waste as little money as possible.
- Can you call in favors and assistance from friends, relatives and local business?
- You can start a blog or website relatively cheaply, and you may be able to generate some free PR with your local newspaper.
- If you are planning to distribute far and wide, you may wish to get your name out there generally, by teaming up with bloggers, on-line news sources and so on. Find an interesting angle, something you can talk about in an engaging way.
- Depending on what it is you sell, you may also consider joining an affiliate scheme, thus harnessing the power of people on the web to promote on your behalf - in exchange for a small percentage of the sale. Check all the details before you sign up.
- Remember to think about your target purchaser and the impact this may have on your labelling and packaging. For example, if you are targeting the gift market, your presentation might be different than if you are targeting the gourmet food market. Don't underestimate the power of packaging and label design !
- Consider also setting up an online store via Amazon and/or Ebay - this does not prevent you from having a store on your own website. The point about Amazon and Ebay are that they are widely trusted. You could also investigate other platforms, such as Etsy. You then need to explore ways to increase your visibility through these channels.
A SWOT Analysis For A Beekeeping Business
It’s worth doing a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats) for your beekeeping business plan, as with any other business plan.
Make a list, and decide whether there are actions you can take. Don’t run before you can walk, or over-stretch yourself, however.
Here are some examples (let me stress that - examples only! )
| Lifelong experience of beekeeping – generations of beekeepers in the family. | Use this in marketing, to talk about a caring family business with generations of expertise. Customers are buying from people, not a faceless organisation. |
| Limited business experience of book keeping – only ever provided a few jars of honey for friends. | Enrol on a small business course or book keeping course, buy a simple on-line software package, or check on line for suitable courses. Check with the local council for free, helpful resources. |
| Free access to 100 acres of organic farm and meadowland | (Depending on regulations in your country). Label the honey product ‘organic’ and 'meadow honey' or 'wildflower honey', and sell in to speciality organic food stores and delicatessens, with appropriate pricing and packaging. |
| Diseases | Keep bees and hives in good condition, and practice high standards of beekeeping husbandry. Insure hives against losses due to diseases. |
General Administration
This is often forgotten, but.....
- How will you manage the paperwork for paying taxes etc? If you need assistance, you'll need to factor in the cost of that assistance.
- Remember to keep comprehensive records, and in good order. File receipts and paperwork. Take copies of crucial documents. Take back-up copies of any computer generated admin.
- Have a visible calendar and/or diary to ensure you file any important paperwork on time, such as taxes and any legal documents, to avoid fines.
- Be an organized beekeeper, for example, with an appropriate hive painting system.
More Beekeeping Business Tips
Hopefully you will be able to keep your set up and business running costs to a minimum.
- With a bit of luck, you won’t be renting property, but if for any reason you must rent space, then try to ensure favourable terms and conditions. Avoid arrangements that will be difficult to get out of, that demand penalties for early termination of agreements or very long notice periods. Also, look out for hidden clauses on lease agreements - especially clauses that are easily missed in the body of the test, or at the very end (or both). Go through the lease agreement with a fine-toothed comb, and check again before signing to ensure no unwanted clauses have crept in to the agreement.
- Check the regulations with regard to beekeeping in your area.
- Is there sufficient forage for the bees?
- Keep on top of payments from customers, and be a good customer yourself.
- Have more than one income stream if possible.
You can use the - free beekeeping business plan template a PDF download (please note, it will open in a new window) to help you get started, but ensure that you add any legal considerations applicable to your own country.
Are Cuprinol and Creosote safe to use on a bee hive?
The Flow Hive - is there a problem with plastic in bee hives?
Where Can I Sell My Used Bee Hives?
How to clean used beekeeping equipment
Are honey bees domesticated?

Pssst ... spread the word!

COPYRIGHT 2010 - 2024: WWW.BUZZABOUTBEES.NET ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Privacy Policy Affiliates Policy Disclaimer Contact Me

Starting Honey Beekeeping Business Plan (PDF)

In a world where sustainable and environmentally conscious businesses are gaining increasing traction, few opportunities are as compelling as starting a honey beekeeping business. Apiculture, the rearing of honey bees at a commercial scale has become a fast growing business venture all over the world. The maintenance of honeybees and hives has been providing farmers and hobbyists with a variety of business opportunities such as the production of honey, beeswax, and other edible bee products in addition to crop pollination services, and the sale of bees to other beekeepers. Due to the increase in the demand for natural and healthy alternatives to artificial sweeteners, starting a beekeeping farming project is a lucrative business for small and large scale farmers. This article will outline how to start the honey beekeeping business, and the honey bee farming business plan – PDF, Word and Excel.
Honey beekeeping is a lucrative business project that is providing income for a lot of people. There are some important things you need to consider before you setup such a business. You need to gather the correct resources, decide on the size of your honey bee farming project this includes the number of your bee hives/colonies; location of honey beekeeping business, as well as your target market. These factors will be determined by the amount of capital you have. If you do not have a lot of capital, you can always start small and grow your honey bee farming business overtime. You also need to carry out market research (Who are you going to sell the honey to? At what price?) and write a honey beekeeping business plan before you start the project.
Market Research
It’s important that you carry out a comprehensive market research before starting a honey beekeeping business. It’s essential to delve into understanding the pricing dynamics of honey within your target market. This entails identifying not only the current market prices but also any variations that may occur seasonally or due to regional factors. Explore various distribution options, such as farmers’ markets, local stores, online platforms, and wholesale distribution. Evaluate which channels align best with your business goals. Moreover, you should gain insights into who your potential customers are and their buying habits. Determine how frequently they order honey products and in what quantities, whether it’s for personal consumption, resale, or industrial use. This knowledge will enable you to align your pricing strategy with market demand, ensuring competitive pricing that resonates with your customer base and maximizes your business’s revenue potential.
Furthermore, a thorough competitive analysis is essential. Research existing honey producers in your area and beyond, scrutinizing their products, pricing, marketing tactics, and customer feedback. This knowledge will allow you to pinpoint gaps in the market that your beekeeping business can fill, helping you stand out in the marketplace. Staying attuned to local and global honey market trends, regulations, seasonal variations, and pricing strategies are additional facets of market research that are crucial for your success.
Financial projections are a critical component of market research when starting a honey beekeeping business. These projections involve estimating and forecasting the financial performance of your venture, including startup costs, operational expenses, revenue forecasts, and potential profits. By meticulously analyzing the data gathered during your research, you can create a realistic financial roadmap that will help you make informed decisions and secure necessary funding. Financial projections provide a clear picture of your business’s financial viability and sustainability, ensuring that you have a solid plan in place to manage your resources effectively and achieve your long-term goals in the honey beekeeping industry.
Land for Honey Beekeeping Business
When setting up your honey beekeeping business, you obviously require land. You can keep the bees in urban, suburban, and rural areas but remember that certain types of land and land factors will be much more favourable for bees and beekeeping than others. The land where bees are kept is referred to as an apiary or bee yard. The location of the apiary is of the essence in honey beekeeping business as it determines the success of the honey bee farming venture. Nectar and pollen sources must be close to the bee hives. This is because pollen plays a crucial role in brood rearing, honey production and nectar comprises a basic energy source for bees. Bees can be kept at varied locations; none the less, large concentrations of floral sources as well as populous colonies are needed to produce good honey output. The natural source of nectar and pollen are flowering trees and plants.
You need to consider water availability, climate, forage, as well as the possibility of predators when selecting where your bees live and produce honey. Although honey bees can adapt to different types of environments do not forget that climatic conditions have an effect on the bees. That means if your environment gets cold, you should avoid keeping your hives in areas with poor air flow (such areas create cool, moist conditions) as that will negatively affect your bees during the cold winter. Sun exposure and dry conditions are great for the hives but you should not let the hives overheat. Shaded locations hinder flight of bee workers as well as finding the queen and sighting eggs within the cells. Bees generally tend to become irritable and difficult to handle in poorly located areas. As such, an ideal spot with maximum sunshine through the day should be selected. Make sure that there is a proper water source nearby so that your bees do not have to use up a lot of energy to fly to a far source. You can set up your own water source but make sure that it’s at least 15 feet away from the hive so that the bees can orient themselves around it. Not to forget forage, ensure that there is a constant supply of pollen and nectar from spring to fall from various fruits, vegetables, flowers, herbs, and other plants around your colony. In addition, in order for the honey beekeeping business to be successful, it is necessary for land to be dry with superior air drainage. Windy areas should be avoided; the same applies to exposed hill tops or river banks with a potential of flooding. Take care that selected land for the honey bee farming business is free from pesticides that may cause harm to insects, particularly when they are kept in farming land used for grain among other plants. Your honey bee farming business plan should take into account the cost of purchasing or renting the land.
Good bee hives are essential when operating a profitable beekeeping business. There are many different types of bee hives developed for honey beekeeping. Example of beehives include f ixed comb hives, top-bar hives, frame hives, Kenyan top bar hive and the Langstroth hive. When a lot of people think of a beehives, most of them picture a Langstroth, this is because this is one of the oldest beehive invented around the 1850’s. The design has changed over the years, but this beehive is still convenient for your beekeeping enterprise. The key innovation with this beehive is the use of convenient vertically-hanging frames that allow bees to build their comb. You can also consider a Warre beehive, that looks like a mini-Langstroth for your project. The Warre has a series of simple slats from the top of each box which allows the bees to build their comb vertically downwards. The Top Bar Hive is another beehive you can consider for your honey beekeeping business. This is the most recent design, which is more comfortable and presents the bees with a convenient height. There are no heavy, honey-laden boxes to lift, only individual frames of comb. From these most common beehives, you can select one that is suitable for your project. Beehives are often made out of wood which offers durability, flexibility and convenience. Wood housing also improves the colony’s efficiency to regulate hive interior temperature and humidity. It is advisable to externally paint the hive bodies and supers white or any other colour that has an action of radiating direct heat from the sun. In addition, painted housing tends to last longer hence the suggestion. The costs of purchasing the beehives should be included in the beekeeping business plan.
Equipment For Beekeeping Business
When it comes to equipment, there is some basic equipment that you must have for your beekeeping project in addition to a beehive. You must have wooden frames that hold sheets of beeswax, plus a smoker to calm bees and reduce stinging. You can use a pine straw, grass and burlap to make a good smoker fuel. Invest in a veil and gloves to protect your head and arms from stings. Other p rotective clothing required for honey beekeeping includes bee suit/overalls and gumboots. You will also need feeders to hold sugar syrup that you can feed to your bees. A hive tool set (bee brush, hive opener and stainless-steel knife) is also required. Processing equipment required depend on the size of the honey beekeeping business. Honey processing equipment include storage containers, refractometer, centrifuge honey extractor and honey press. The costs of the equipment should be included in the honey beekeeping business plan.
Honey Bee Colony
You obviously need bees when starting the beekeeping business. There are different ways to acquire the bees. Some of these include buying from an existing colony, starting from a small “nucleus” colony that you can buy from another beekeeper, capturing a swarm or splitting an existing colony. You can start with a honey bee colony that is bought from a reputable producer. That would be a good way to ensure that the colony you have is healthy and of a particular breed. The entire honey bee farming business is centred on the honey bee colony. Honey bees live in colonies. Therefore, make sure that you purchase bees from reputable and accredited breeders. There are other to factors to consider when buying the colony, which include the temperament, docility, colour, productivity and disease resistance of the queen. Each colony will be having about 10,000 to 60,000 bees. The honey bee colony is made up of three types of bees. A bee colony is comprised of a queen (fertile female), a few hundred drones (males) and thousands of workers (sterile females). A honey bee colony is comprised of a single queen. The role of the queen is to lay eggs. Queen bees are raised from the same eggs as worker bees, but are provided with more food for increased productivity. She lays the most eggs during the first year, about 2500 to 3000 per day. Bees referred to as workers carry out different operations within the colony. They collect nectar and pollen, make honey and wax, feed the queen, tend to eggs, build and repair the comb. They are also responsible for cleaning and controlling temperature within the colony. The male bees are called drones and their sole purpose is to mate with the queen. So each hive will be comprised of one bee colony. Thus the size of your honey beekeeping business will be determined by the number of bee hives/bee colonies that you have. The honey bee farming business plan should include the costs of acquiring the bee colonies.
Feed For Bees
Feed and nutrition is an important aspect for the success of the bee farming business. Honey bees need essential nutrients for survival and reproduction. Like many other animals, they need carbohydrates, which is the sugar in nectar or honey, amino acids which are obtained from protein from pollen, lipids fatty acids, sterols, vitamins, minerals as well as water. It is important that these nutrients are present in the right quantities for the honey bees to survive and thrive. You may need to supplement food to honey bees to prevent them from starving. Make sure that you do not feed bees with honey unless it is from your own disease-free hives. However, it is important to emphasize that feeding bees shouldn’t be the norm. It is not uncommon to see an overuse of the feeder with new bee keepers. Feeding bees is only supplementary and should be treated as a way to address very specific cases.
Bees mainly obtain nutrients from pollen and honey. Bees do not need to be fed regularly, as long as flowers are available, bees will feed themselves. Supplementary feed is however sometimes necessary and can be in form of cane or beet sugar and isomerized corn syrup. Bees collect a number of substances to ensure survival and productivity:
- nectar – converted into honey and stored in beeswax cells
- pollen – provides most of the protein, amino acids, fats, vitamins and mineral requirements of diet
- water – for maintaining the temperature and humidity of the hive and diluting stored honey
- propolis –naturally occurring glue like substance used in sealing cracks and crevices in the hive
Health & Disease Management in Honey Beekeeping
Maintaining the health of your honey bee colonies is paramount to the success of your beekeeping business. Honey bees, like any other living organisms, are susceptible to various diseases and pests that can threaten their well-being. Effective health and disease management strategies are crucial to ensure the vitality of your colonies and the quality of your honey production.
Regular hive inspections should be implemented to monitor the overall health of your bee colonies, allowing for early detection of issues. Integrated Pest Management (IPM) techniques should be adopted to address common threats like Varroa mites, small hive beetles, and wax moths while minimizing the use of chemicals. Promote disease prevention through good hygiene practices, including maintaining clean hives and ensuring proper ventilation. Pay close attention to the health of the queen bee, as it plays a vital role in colony strength. Provide bees with a balanced diet through diverse forage sources and supplement their nutrition when necessary. Detailed record-keeping of hive inspections and treatments is essential to track colony health history. Additionally, continuous education and training are crucial to staying informed about the latest research and best practices in honey bee health management. A proactive approach to health and disease management is vital for the long-term sustainability of your honey beekeeping business, ensuring robust and thriving hives that contribute to successful honey production.
Honey Beekeeping Business Model
The honey beekeeping business model revolves around the careful management of bee colonies. At the outset, you acquire bee colonies that will reproduce and grow in numbers over time. These colonies are the heart of your operation, as they work tirelessly to produce honey, one of the primary revenue sources for your business. The acquisition of suitable land is also essential to provide a conducive environment for your bees to forage and thrive. Moreover, investing in quality equipment, particularly bee hives, is critical for housing and maintaining your bee colonies effectively.
The core of your honey beekeeping business lies in the production and harvest of honey, a valuable product that you will sell to generate revenue. Additionally, there are other valuable byproducts like beeswax that can also be harvested and sold, contributing to your income stream. While there are expenses associated with the business, such as feed for the bees, costs related to the harvesting process, and expenditures for packaging and marketing, the revenue generated from selling honey and byproducts tends to far exceed these input costs and operational expenses. This favorable balance between revenue and expenses results in a healthy profit margin, making honey beekeeping an attractive and sustainable business venture with the potential for long-term success and profitability.
The number of employees required depends on the size of the bee farming business. You will need beekeepers who will be responsible for the bee hive management, feeding the bees, monitoring the apiary, harvesting and packaging the honey. The honey beekeeping farming business plan should cater for the costs of paying all your employees.
Capital for Honey Beekeeping Business
The amount depends on the scale of the honey beekeeping operations. You can get a loan from the bank, or funding from investors, to use as capital to start your honey bee farming business. If you plan to raise capital from investors and a loan from the bank, you need a good beekeeping business plan. If you don’t have access to investors and bank loan, you can use your personal savings and start small, and grow your business overtime. Honey bee farming is profitable, so if you reinvest the profits you get, you can quickly grow. Even if you are not planning to get a loan, you should still get a honey bee farm business plan to guide you in starting and operating the business. It is essential for you to have a honey beekeeping farming business plan before you venture into the beekeeping business, so that you know all the costs involved and you make an informed decision.
Marketing Plan
Crafting a robust marketing plan is a pivotal step in the journey of promoting your honey beekeeping business effectively. Your marketing strategy should not only showcase the exceptional quality of your honey but also underscore the distinctive features of your beekeeping practices, such as sustainability and purity. To achieve this, it’s essential to consider various elements in your marketing plan. First and foremost, establishing a compelling brand identity is crucial. Create a visually appealing logo, choose an engaging business name, and weave a captivating brand narrative that accentuates the authenticity, purity, and eco-consciousness of your honey production. Identifying your target audience is equally vital. Whether you’re targeting health-conscious consumers, local retailers, or businesses seeking honey as a premium ingredient, defining your audience enables you to tailor your marketing messages and select the most effective channels.
In the digital age, a robust online presence is indispensable. Develop a professional website that provides comprehensive information about your honey products, pricing, and easy purchase options. Leverage social media platforms to chronicle your beekeeping journey, share educational content, and engage with potential customers. Locally, participating in farmers’ markets, craft fairs, and community events can help introduce your honey to the local community. Offering samples and educating consumers about the benefits of your honey can be highly effective in building initial trust and recognition.
A thoughtful approach to packaging and labeling, customer testimonials, collaborations with local businesses, content marketing, promotions, and customer engagement all play pivotal roles in the success of your marketing plan. Continuously monitoring the effectiveness of your strategies through analytics tools and being flexible enough to adjust your plan based on data and feedback will help you fine-tune your marketing efforts. By developing a comprehensive marketing plan, you not only raise awareness of your honey beekeeping business but also foster connections with your target audience, ultimately building a loyal customer base that values the quality and values behind your honey products.

The end product of the beekeeping business is honey. Bees form honey from the nectar which they collect from flowers. So at harvest time, beekeepers will harvest the honey from the beehives. Honey is an excellent, stable sweetener and energy source for humans. For this reason, it is often sold in its natural form. It is also an essential ingredient in the confectionary and cosmetology industry. Another valuable byproduct from beekeeping is beeswax. The wax from bees is used to make products such as bath soap, shoes polish and candles. The market for honey is huge, potential customers include individuals, supermarkets , wholesalers, restaurants and organisations. The honey beekeeping business plan should obviously include a proper marketing strategy for the business.
Keys to Profitability in Your Honey Bee Farming Business
Achieving profitability in your honey beekeeping business is a multi-faceted endeavor that hinges on strategic planning, efficient management, and a deep understanding of the honey market. To ensure the financial success of your venture, consider several critical factors. First and foremost, efficient hive management is essential. Regular hive inspections, disease prevention, and maintaining the health of your bee colonies are paramount. Healthy, disease-free colonies are more likely to produce abundant honey, which directly impacts your profitability.
Moreover, stringent cost control is necessary to optimize your bottom line. Keep a close watch on expenses associated with feed, equipment, and hive maintenance, and seek opportunities to streamline operations and reduce unnecessary costs. Producing high-quality honey is another key to profitability. Ensuring that your bees have access to diverse, pesticide-free forage sources results in honey with unique flavors and characteristics, allowing you to command higher prices in the market.
Effective marketing efforts play a pivotal role as well. Develop a strong brand, leverage online platforms to expand your reach, and explore collaborations with local businesses to enhance your market presence. Effective marketing can drive sales and boost revenue. Additionally, consider diversifying your product offerings, such as selling beeswax, pollen, or honey-based skincare products, as this can create multiple income streams. As your honey beekeeping business grows, carefully scale up your operations in alignment with your resources. Build and nurture strong customer relationships, stay informed about industry advancements, manage your finances diligently, and implement sustainable beekeeping practices. By incorporating these keys to profitability into your business strategy, you can pave the way for a successful and financially rewarding venture that ensures the well-being of your bee colonies and the longevity of your business.
Advantages of Honey Beekeeping Business
One notable advantage of beekeeping is its relatively low startup costs. Compared to many other businesses, beekeeping requires minimal initial investment. The essential equipment is cost-effective, and the primary financial commitment lies in acquiring bee colonies and bee hives. This affordability makes beekeeping accessible to a wide range of individuals, allowing them to enter the industry with relatively modest capital resources. Furthermore, beekeeping offers multiple income streams. While honey is the primary product, beekeepers can diversify their offerings to include beeswax, royal jelly, pollen, and various bee-related products. Additionally, providing pollination services to local farmers is another lucrative avenue that beekeepers can explore.
Another significant advantage of the honey beekeeping business lies in its exceptional profitability. Honey, a prized natural sweetener and health food, commands robust prices in the market. What further enhances profitability is the business’s low operating costs. While beekeepers must invest in equipment, hive maintenance, and bee colonies, the ongoing expenses are relatively minimal. This favorable balance between high market prices for honey and cost-efficient operations makes beekeeping a financially lucrative venture, attracting entrepreneurs seeking both sustainability and profitability in their business endeavors.
The increasing demand for honey serves as another compelling advantage. Consumers are gravitating towards pure, locally sourced, and sustainably produced honey, creating a thriving market for beekeepers. This heightened demand, coupled with the potential for multiple income streams, positions beekeeping as a financially rewarding endeavor. The business is flexible, allowing beekeepers to adapt their operations to their resources and schedules. Whether you’re starting small as a hobbyist or envisioning a larger-scale operation, beekeeping can accommodate various settings and grow alongside your expertise and confidence.
Pre-Written Honey Bee Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel): Comprehensive Version, Short Funding/Bank Loan Version and Automated Financial Statements
For an in-depth analysis of the honey beekeeping farming business, we encourage you to purchase our well-researched and comprehensive honey beekeeping business plan. We introduced the business plans after discovering that many were venturing into the honey production business without enough knowledge and understanding of how to run the honey bee farming business, how to keep the bees, lack of understanding of the financial side of the business, lack of understanding of : the industry, the risks involved , costs and profitability of the business; which often leads to disastrous losses.
The StartupBiz Global honey beekeeping business plan will make it easier for you to launch and run your honey bee farming business successfully, fully knowing what you are going into, and what’s needed to succeed in the business. It will be easier to plan and budget as you will be aware of all the costs involved in setting up and running the beekeeping business.
Uses of the Honey Beekeeping Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
The honey bee farm business plan can be used for many purposes including:
- Raising capital from investors/friends/relatives
- Applying for a bank loan
- Start-up guide to launch your honey beekeeping business
- As a honey bee farming business proposal
- Assessing profitability of the honey beekeeping business
- Finding a business partner
- Assessing the initial start-up costs so that you know how much to save
- Manual for current business owners to help in business and strategy formulation
Contents of the Honey Bee Farming Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
The honey beekeeping farming business plan include, but not limited to:
- Marketing Strategy
- Financial Statements (monthly cash flow projections, income statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, break even analysis, payback period analysis, start-up costs, financial graphs, revenue and expenses, Bank Loan Amortization)
- Risk Analysis
- Industry Analysis
- Market Analysis
- SWOT & PEST Analysis
- Operational Requirements (Including technical aspects of how to keep the bees, equipment requirements etc)
- Operational Strategy
- Why some people in the honey beekeeping business fail, so that you can avoid their mistakes
- Ways to raise capital to start your honey bee farming business
The Pre-written honey bee farming business plan package consist of 4 files
- Honey Beekeeping Business Plan – PDF file (Comprehensive Version – 100 Pages)
- Honey Bee Farming Business Plan – Editable Word File (Comprehensive Version – 100 Pages)
- Honey Bee Farming Business Plan Funding/Bank Loan Version- Editable Word File (Short version for applying for a loan/funding – 44 pages)
- Honey Beekeeping Business Plan Automated Financial Statements – (Editable Excel File)
The business plan can be used in any country and can be easily edited. The financial statements are automated. This implies that you can change eg the number of bee hives, selling price of the honey etc, and all the other financial statements will automatically adjust to reflect the change.
Click below to download the Contents Page of the Honey Bee Farming Business Plan (PDF)

Testimonial 1
StartupBiz Global provided a very professional and comprehensive business plan which I used for my business. The business plan was easy to edit, and I was able to get the funding which I wanted. I highly recommend their business plans.
Testimonial 6
I purchased a business plan from you, and I’m glad to inform you that I was able to get my loan, and I’m starting my poultry farming business on the 1 st of July. This was made possible because of your business plan. Thank you very much, you made my dream come true.
Testimonial 8
Just wanted to say I am very happy with the business plan and I will gladly recommend your products, thank you very much and have a great day.
Testimonial 7
I found Startupbiz Global online when I was in desperate need of a business plan. I was overwhelmed by the quality of the business plan, it’s comprehensive and well researched! I did not have to wait to get the business plan, I got it instantly after payment. I highly recommend Startupbiz Global, and would happily use them again in the future.
Testimonial 3
I was extremely lucky to come across StartupBiz Global. Their business plan exceeded my expectations, and most importantly I was able to secure a loan from my bank. Thank you guys, now my dreams are coming true!
Testimonial 2
Many thanks for your incredibly efficient service and thorough business plan. I am very impressed with the business plan. Before I bought the business plan, I tried to do my own business plan – it was such a nightmare and it turned out badly, also not to mention the stress it caused me. I wish I knew about your website earlier!
Testimonial 5
I was able to understand the business side of farming because of your business plan. You did extensive research; the business plan was well prepared and fully detailed. It made everything clear, and I have somewhere to start now. I am confident that I am going to succeed in my business because of the guidance from your business plan.
Testimonial 4
The business plan which I purchased from your website saved me TIME and MONEY! The layout of the business plan was excellent. The financial statements were detailed and easy for me to edit. I will come back to purchase another business plan soon.
Get the Honey Beekeeping Business Plan (PDF, Word And Excel)
Click Buy Now below to purchase using Paypal, Credit Card, or Debit Card. After you have purchased, you will immediately see the download link for the business plan package on the screen. You will also immediately get an email with the business plan download link. The Pre-written business plan package (PDF, Word, and Excel) costs $30 only!

If you want to purchase multiple business plans at once then click here: Business Plans Store.
The business plan package is a zipped compressed file containing the PDF, Word and Excel documents. To open the package after downloading it, just right click, and select Extract All. If you have any problems in downloading and opening the files, email us on [email protected] and we will assist you.
We wish you the best in your honey bee farming business! Check out our collection of business plans , and more business ideas .
Related Posts

Top 8 Profitable Solar Energy Business Ideas

Top 9 Green Business Ideas

Latest Innovations In Poultry Farming

Starting Catering Services Business Plan (PDF)

Join our mailing list to receive the latest posts and updates from our website.
You have Successfully Subscribed!

Beekeeping & Honey Bee Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Honey Beekeeping Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their beekeeping business.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating a business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write a honey bee farm business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Honey Bee Farm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your honey bee farm as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your beekeeping business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Beekeeping Business
If you’re looking to start a honey bee farm or grow your existing beekeeping business , you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your honey bee farm to improve your chances of success. Your business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Beekeeping Business
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a beekeeping business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for beekeeping businesses.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a honey bee farm or beekeeping business.
If you want to start a honey bee farm or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of beekeeping business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a honey bee farm that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of beekeeping businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the beekeeping industry.
- Discuss the type of beekeeping business you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of honey bee farm you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of honey bee farms:
- Honey farm: specializing in producing and selling honey.
- Pollination services: renting out bee hives to farmers.
- Selling bees: raising and selling honey bees to individuals and farmers.
- Selling raw beeswax: beeswax is a byproduct of the honey-making process. Many beekeepers make money by selling the excess beeswax.
In addition to explaining the type of beekeeping business you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the amount of honey produced, the number of colonies obtained, reaching X number of clients served, etc.
- Your legal business Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the beekeeping industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the honey bee farm industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your beekeeping business plan:
- How big is the beekeeping industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your honey bee farm? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, schools, families, and corporations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of beekeeping you operate. Clearly, individuals would respond to different marketing promotions than corporations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Honey Bee Farm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other beekeeping businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes other types of honey or sweet treats for consumers other methods of pollination for farmers.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of honey bee farms are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you make it easier for your customers to engage with your business?
- Will you offer products or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a beekeeping business, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of honey bee farm that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide honey, beeswax, bee rental, or bee sales?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your plan, you are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your honey bee farm. Document where your farm is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your honey bee farm located near a busy retail district, your backyard, adjacent to another type of farm, or a standalone piece of land? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your honey bee farm marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your honey bee farm, including answering calls, caring for bees, collecting and packaging honey, and meeting with customers.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to obtain your Xth colony, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your honey bee farm to a new location.
Management Team
To demonstrate your honey bee farm’s potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing honey bee farms. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing a honey bee farm.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, are you selling honey for $5 per jar? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your honey bee farm, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a honey bee farm:
- Cost of beekeeping equipment and beekeeping supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, and computer software
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your honey bee farm location lease or a list of testimonials from satisfied customers.
Writing a business plan for your honey bee farm is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert. You will understand the honey bee farm industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful honey bee farm.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Honey Bee Farm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s business plan services can give you a winning business plan.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- Sample Business Plans
- Food, Beverage & Restaurant
Beekeeping Business Plan
High demand, low startup costs, and a recurring revenue model make starting a beekeeping business a lucrative and rewarding profession.
Anyone can start a new business, but you need a detailed business plan when it comes to raising funding, applying for loans, and scaling it like a pro!
Need help writing a business plan for your beekeeping business? You’re at the right place. Our beekeeping business plan template will help you get started.

Free Business Plan Template
Download our free beekeeping business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
How to Write a Beekeeping Business Plan?
Writing a beekeeping business plan is a crucial step toward the success of your business. Here are the key steps to consider when writing a business plan:
1. Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section planned to offer an overview of the entire business plan. However, it is written after the entire business plan is ready and summarizes each section of your plan.
Here are a few key components to include in your executive summary:
- Introduce your Business: Start your executive summary by briefly introducing your business to your readers.
- This section may include the name of your beekeeping business, its location, when it was founded, the type of beekeeping business (E.g. honey production firm, pollination services, bee breeding, queen bee production, beekeeping education & training), etc.
- Market opportunity: Summarize your market research, including market size, growth potential, and marketing trends. Highlight the opportunities in the market and how your business will fit in to fill the gap.
- Products and Services: Highlight the beekeeping services you offer your clients. The USPs and differentiators you offer are always a plus.
- For instance, you may include hive management, bee package sales, hive rental, honey extraction, etc as some of your services.
- Marketing & Sales Strategies: Outline your sales and marketing strategies—what marketing platforms you use, how you plan on acquiring customers, etc.
- Financial Highlights: Briefly summarize your financial projections for the initial years of business operations. Include any capital or investment requirements, associated startup costs, projected revenues, and profit forecasts.
- Call to action: Summarize your executive summary section with a clear CTA, for example, inviting angel investors to discuss the potential business investment.
Ensure your executive summary is clear, concise, easy to understand, and jargon-free.
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Business Overview
The business overview section of your business plan offers detailed information about your company. The details you add will depend on how important they are to your business. Yet, business name, location, business history, and future goals are some of the foundational elements you must consider adding to this section:
- Business Description: Describe your business in this section by providing all the basic information:
- Honey production
- Pollination services
- Bee breeding
- Queen bee production
- Beekeeping equipment & supplies
- Beekeeping education and training
- Bee rescue and removal
- Explain where your business is located and why you selected the place.
- Owners: List the names of your beekeeping company’s founders or owners. Describe what shares they own and their responsibilities for efficiently managing the business.
- Mission Statement: Summarize your business’ objective, core principles, and values in your mission statement. This statement needs to be memorable, clear, and brief.
- Business History: If you’re an established beekeeping business, briefly describe your business history, like—when it was founded, how it evolved over time, etc.
- Additionally, If you have received any awards or recognition for excellent work, describe them.
- Future Goals: It’s crucial to convey your aspirations and vision. Mention your short-term and long-term goals; they can be specific targets for revenue, market share, or expanding your services.
This section should provide a thorough understanding of your business, its history, and its future plans. Keep this section engaging, precise, and to the point.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should offer a thorough understanding of the industry with the target market, competitors, and growth opportunities. You should include the following components in this section.
- Target market: Start this section by describing your target market. Define your ideal customer and explain what types of services they prefer. Creating a buyer persona will help you easily define your target market to your readers.
- For instance, hobbyist beekeepers, commercial beekeepers, honey consumers, farmers’ markets, or retail stores would be an ideal target audience for a beekeeping business.
- Market size and growth potential: Describe your market size and growth potential and whether you will target a niche or a much broader market.
- The revenue market size of the beekeeping business was $616.9 million in 2022 which is expected to grow only.
- Competitive Analysis: Identify and analyze your direct and indirect competitors. Identify their strengths and weaknesses, and describe what differentiates your beekeeping services from them. Point out how you have a competitive edge in the market.
- Market Trends: Analyze emerging trends in the industry, such as technology disruptions, changes in customer behavior or preferences, etc. Explain how your business will cope with all the trends.
- For instance, local and organic honey has a booming market; explain how you plan on dealing with this potential growth opportunity.
- Regulatory Environment: List regulations and licensing requirements that may affect your beekeeping company, such as registration & licensing, hive placement & zoning, pest control & pesticide regulations, pollination services, occupational health & safety, etc.
Here are a few tips for writing the market analysis section of your beekeeping business plan:
- Conduct market research, industry reports, and surveys to gather data.
- Provide specific and detailed information whenever possible.
- Illustrate your points with charts and graphs.
- Write your business plan keeping your target audience in mind.
4. Beekeeping Services
The product and services section should describe the specific services and products that will be offered to customers. To write this section should include the following:
- Hive management
- Bee package sales
- Hive rental
- Queen bee production and sales
- Swarm capture and removal
- Beekeeping equipment sales
- Hive transportation
- Beekeeping consultation
- Describe each service: Provide a detailed description of each service you provide, any supporting service you provide with the main service, and everything about it.
- For instance, for hive rental service: the number of hives available, the length of rental periods, and any additional services or assistance offered (such as hive maintenance or hive transportation) should be there in the details.
- Quality measures: This section should explain how you maintain quality standards and consistently provide the highest quality service.
- This may include hive health management, honey quality control, pollination services, bee breeding practices, food safety & hygiene, continuous training & education, etc.
- Additional Services: Mention if your beekeeping company offers any additional services. You may include beekeeping workshops & training, hive installation & consultation, hive rental & maintenance, honey extraction & processing, beekeeping equipment sales, etc.
In short, this section of your beekeeping plan must be informative, precise, and client-focused. By providing a clear and compelling description of your offerings, you can help potential investors and readers understand the value of your business.
5. Sales And Marketing Strategies
Writing the sales and marketing strategies section means a list of strategies you will use to attract and retain your clients. Here are some key elements to include in your sales & marketing plan:
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Define your business’s USPs depending on the market you serve, the equipment you use, and the unique services you provide. Identifying USPs will help you plan your marketing strategies.
- For example, local or sustainable honey, hive rental & beekeeping services, specialty honey varieties, etc could be some of the great USPs for a beekeeping company.
- Pricing Strategy: Describe your pricing strategy—how you plan to price your services and stay competitive in the local market. You can mention any discounts you plan on offering to attract new customers.
- Marketing Strategies: Discuss your marketing strategies to market your services. You may include some of these marketing strategies in your business plan—social media marketing, local networking, content marketing, and print marketing.
- Sales Strategies: Outline the strategies you’ll implement to maximize your sales. Your sales strategies may include direct sales calls, sampling, partnering with other businesses, offering referral programs, etc.
- Customer Retention: Describe your customer retention strategies and how you plan to execute them. For instance, introducing loyalty programs, discounts on bulk purchases, personalized service, etc.
Overall, this section of your honey bee farm business plan should focus on customer acquisition and retention.
Have a specific, realistic, and data-driven approach while planning sales and marketing strategies for your beekeeping business, and be prepared to adapt or make strategic changes in your strategies based on feedback and results.
6. Operations Plan
The operations plan section of your business plan should outline the processes and procedures involved in your business operations, such as staffing requirements and operational processes. Here are a few components to add to your operations plan:
- Staffing & Training: Mention your business’s staffing requirements, including the number of employees or beekeepers needed. Include their qualifications, the training required, and the duties they will perform.
- Operational process: Outline the processes and procedures you will use to run your beekeeping business. Your operational processes may include hive setup & placement, bee feeding, hive inspection & maintenance, swarm prevention & management, etc.
- Equipment & Machinery: Include the list of equipment and machinery required for beekeeping, such as hive components, beekeeping tools, protective gear, honey extraction equipment, bee feeding equipment, transportation & hive management, etc.
- Explain how these technologies help you maintain quality standards and improve the efficiency of your business operations.
Adding these components to your operations plan will help you lay out your business operations, which will eventually help you manage your business effectively.
7. Management Team
The management team section provides an overview of your beekeeping business’s management team. This section should provide a detailed description of each manager’s experience and qualifications, as well as their responsibilities and roles.
- Founders/CEO: Mention the founders and CEO of your beekeeping company, and describe their roles and responsibilities in successfully running the business.
- Key managers: Introduce your management and key members of your team, and explain their roles and responsibilities.
- It should include, key executives(e.g. COO, CMO.), senior management, and other department managers (e.g. operations manager, general manager, beekeeping manager.) involved in the beekeeping business operations, including their education, professional background, and any relevant experience in the industry.
- Organizational structure: Explain the organizational structure of your management team. Include the reporting line and decision-making hierarchy.
- Compensation plan: Describe your compensation plan for the management and staff. Include their salaries, incentives, and other benefits.
- Advisors/Consultants: Mentioning advisors or consultants in your business plans adds credibility to your business idea.
- So, if you have any advisors or consultants, include them with their names and brief information consisting of roles and years of experience.
This section should describe the key personnel for your beekeeping services, highlighting how you have the perfect team to succeed.
8. Financial Plan
Your financial plan section should provide a summary of your business’s financial projections for the first few years. Here are some key elements to include in your financial plan:
- Profit & loss statement: Describe details such as projected revenue, operational costs, and service costs in your projected profit and loss statement. Make sure to include your business’s expected net profit or loss.
- Cash flow statement: The cash flow for the first few years of your operation should be estimated and described in this section. This may include billing invoices, payment receipts, loan payments, and any other cash flow statements
- Balance sheet: Create a projected balance sheet documenting your beekeeping business’s assets, liabilities, and equity.
- Break-even point: Determine and mention your business’s break-even point—the point at which your business costs and revenue will be equal.
- This exercise will help you understand how much revenue you need to generate to sustain or be profitable.
- Financing needs: Calculate costs associated with starting a beekeeping business, and estimate your financing needs and how much capital you need to raise to operate your business. Be specific about your short-term and long-term financing requirements, such as investment capital or loans.
Be realistic with your financial projections, and make sure you offer relevant information and evidence to support your estimates.
9. Appendix
The appendix section of your plan should include any additional information supporting your business plan’s main content, such as market research, legal documentation, financial statements, and other relevant information.
- Add a table of contents for the appendix section to help readers easily find specific information or sections.
- In addition to your financial statements, provide additional financial documents like tax returns, a list of assets within the business, credit history, and more. These statements must be the latest and offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
- Provide data derived from market research, including stats about the industry, user demographics, and industry trends.
- Include any legal documents such as permits, licenses, and contracts.
- Include any additional documentation related to your business plan, such as product brochures, marketing materials, operational procedures, etc.
Use clear headings and labels for each section of the appendix so that readers can easily find the necessary information.
Remember, the appendix section of your bee farm business plan should only include relevant and important information supporting your plan’s main content.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
This sample beekeeping business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful beekeeping plan, including all the essential components of your business.
After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our beekeeping business plan pdf .
Related Posts
Fishing Farming Business Plan
Farmers Market Business Plan
10 Popular Business Planning Software
Poultry Farming Business Plan
Cover Page Design for Business Plan
Customer Analysis Guide for Business Plan
Frequently asked questions, why do you need a beekeeping business plan.
A business plan is an essential tool for anyone looking to start or run a successful beekeeping business. It helps to get clarity in your business, secures funding, and identifies potential challenges while starting and growing your business.
Overall, a well-written plan can help you make informed decisions, which can contribute to the long-term success of your beekeeping company.
How to get funding for your beekeeping business?
There are several ways to get funding for your beekeeping business, but self-funding is one of the most efficient and speedy funding options. Other options for funding are:
- Bank loan – You may apply for a loan in government or private banks.
- Small Business Administration (SBA) loan – SBA loans and schemes are available at affordable interest rates, so check the eligibility criteria before applying for it.
- Crowdfunding – The process of supporting a project or business by getting a lot of people to invest in your business, usually online.
- Angel investors – Getting funds from angel investors is one of the most sought startup options.
Apart from all these options, there are small business grants available, check for the same in your location and you can apply for it.
Where to find business plan writers for your beekeeping business?
There are many business plan writers available, but no one knows your business and ideas better than you, so we recommend you write your beekeeping business plan and outline your vision as you have in your mind.
What is the easiest way to write your beekeeping business plan?
A lot of research is necessary for writing a business plan, but you can write your plan most efficiently with the help of any beekeeping business plan example and edit it as per your need. You can also quickly finish your plan in just a few hours or less with the help of our business plan software .
How do I write a good market analysis in a beekeeping business plan?
Market analysis is one of the key components of your business plan that requires deep research and a thorough understanding of your industry.
We can categorize the process of writing a good market analysis section into the following steps:
- Stating the objective of your market analysis—e.g., investor funding.
- Industry study—market size, growth potential, market trends, etc.
- Identifying target market—based on user behavior and demographics.
- Analyzing direct and indirect competitors.
- Calculating market share—understanding TAM, SAM, and SOM.
- Knowing regulations and restrictions
- Organizing data and writing the first draft.
Writing a marketing analysis section can be overwhelming, but using ChatGPT for market research can make things easier.
How detailed should the financial projections be in my beekeeping business plan?
The level of detail of the financial projections of your beekeeping business may vary considering various business aspects like direct and indirect competition, pricing, and operational efficiency. However, your financial projections must be comprehensive enough to demonstrate a comprehensive view of your financial performance.
Generally, the statements included in a business plan offer financial projections for at least the first three or five years of business operations.
Can a good beekeeping business plan help me secure funding?
Indeed. A well-crafted beekeeping business will help your investors better understand your business domain, market trends, strategies, business financials, and growth potential—helping them make better financial decisions.
So, if you have a profitable and investable business, a comprehensive business plan can certainly help you secure your business funding.
What's the importance of a marketing strategy in a beekeeping business plan?
Marketing strategy is a key component of your beekeeping business plan. Whether it is about achieving certain business goals or helping your investors understand your plan to maximize their return on investment—an impactful marketing strategy is the way to do it!
Here are a few pointers to help you understand the importance of having an impactful marketing strategy:
- It provides your business an edge over your competitors.
- It helps investors better understand your business and growth potential.
- It helps you develop products with the best profit potential.
- It helps you set accurate pricing for your products or services.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Honey Bee Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Honey Bee Farm Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Honey Bee Farm business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Honey Bee Farms.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Honey Bee Farm business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm is a startup honey bee business located in Churchtown, Ohio. The company is founded by Tony and Galene Hausen, farm owners and former employees of a large honey bee corporation that mined honey from bee farms. Tony and Galene have gained a great deal of experience after ten years as employees and now want to establish this startup honey bee farm on their own farm property to continue harvesting superior honey from the bees that have been on their family farm for over one hundred years.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will provide a variety of honeys and honey-based products, each designed to be sold at wholesale or retail to a variety of customers who appreciate the wholesome goodness of natural organic honey. The Sweet Bee Honey Farm will concentrate on offering the finest honey worthy of the most expensive retail sales.
Product Offering
The following are the products that Sweet Honey Bee Farm will provide:
- Pure honey, including wildflower, clover, orange blossom, and more. The honey is raw and unprocessed, free from additives or preservatives,
- Honey on the Comb: for those who appreciate the raw beauty of honeycomb, they will offer comb honey, where the honey remains in its natural beeswax comb, untouched by human processing,
- Infused honey that includes a selection of flavored honey varieties, infused with natural ingredients like lavender, cinnamon, or ginger. Infusions create a delightful twist to the traditional honey taste.
- Beeswax products, including candles, lip balms, and skincare items
Customer Focus
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will target retail customers at their Sweet Honey Bee Shop. In addition, they will target online customers via their fully-developed website. They will target grocery buyers and specialty gourmet buyers within their chosen industries.
Management Team
Tony and Galene Hausen will be the co-owners of the company. Galene will oversee all staff and manage client relations. Tony will work on product development and business expansion. They have spent the past year recruiting Sarah Thompson, their former administrative assistant, who will take on the role of Office Manager. They have also recruited Greg Naynold, the former farm manager at their employer company. He will now become the Senior Farm Manager.
Tony and Galene Hausen both share over ten years of experience in the keeping of honey bees and the harvesting of their honey. They worked as the Production Manager and Human Resources Manager respectively, where they honed their craft and made extensive contacts with customers and clients in the wholesale industries related to honey.
Sarah Thompson is a graduate of the University of Ohio with a bachelor’s degree in administration. She worked for the former employer as an administrative assistant for two years, where her organizational skills won the praise of all who knew her. Sarah will be the Office Manager who will manage the office administration, client files, and accounts payable.
Greg Maynold has been a farm manager and beekeeper for over twenty years. He will experienced in all facets of beekeeping and worked with Tony and Galene for ten years. His skill level is unparalleled in beekeeping and farming. He will become the Senior Farm Manager, overseeing all honey bee production and processing, as well as overseeing the fields and crops produced on the farm.
Success Factors
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly-qualified team of Sweet Honey Bee Farm
- Comprehensive menu of organic products, sourced directly from the farm.
- Sweet Honey Bee Farm will establish a retail shop, offering one-of-a-kind honey products and other organic foods.
- Sweet Honey Bee Farm offers the best pricing in town. Their pricing structure is the most cost effective compared to the competition.
Financial Highlights
Sweet Honey Bee Farm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its Sweet Honey Bee Farm. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and marketing costs. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office space build-out: $20,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $10,000
The following graph outlines the financial projections for Sweet Honey Bee Farm.
Company Overview
Who is sweet honey bee farm.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm is a newly established, full-service honey bee farm in Churchtown, Ohio. Sweet Honey Bee Farm will provide the most pure, organic honeys and honey products in the country. In addition, Sweet Honey Bee Farm will actively seek online consumers and larger contracts with grocery chain and specialty gourmet stores. Sweet Honey Bee Farm will provide a comprehensive menu of honey products for any consumer to utilize. Their full-service approach includes a comprehensive menu of delicious, custom honey products.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will be able to serve consumers throughout the country via their website and farm business. The team of professionals are highly qualified and experienced in honey bee management and harvesting of honey. Sweet Honey Bee Farm removes all headaches and issues of finding pure, organic honey and honey products, while delivering the best customer service.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm History
Since incorporation, Sweet Honey Bee Farm has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered Sweet Honey Bee Farm, LLC to transact business in the state of Ohio.
- Has a contract in place for a 10,000 square foot office near the Sweet Honey Bee Farm
- Reached out to numerous contacts to purchase honey from the Sweet Honey Bee Farm
- Began recruiting a staff of six and office personnel to work at the Sweet Honey Bee Farm
Sweet Honey Bee Farm Products
The following will be the services Sweet Honey Bee Farm will provide:
Industry Analysis
The honey bee farming industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $739 billion. The growth will be driven by an increased awareness of the importance of honey bees, particularly as pollinators in agriculture. The growth will be driven, as a result of this awareness, to a heightened consumer outreach toward honey and honey bee farming methods. The growth of the industry will also be led by the growing demand for naturally healthful food products. The costs will likely be reduced as more honey bee farms are established, which may cause the increased growth to be slightly lower. Additional costs that will be reduced will be those for housing and maintaining honey bee boxes due to technological advances that will lead to greater outcomes using less manpower and creative tech production methods.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will target retail customers in the greater Ohio state at their Sweet Honey Bee Farm Shop. In addition, they will target online customers nationally via their fully-developed website. They will target grocery buyers and specialty gourmet buyers within their chosen industries.
| Total | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 1,680,988 | 100% |
| Male | 838,675 | 49.9% |
| Female | 842,313 | 50.1% |
| 20 to 24 years | 114,872 | 6.8% |
| 25 to 34 years | 273,588 | 16.3% |
| 35 to 44 years | 235,946 | 14.0% |
| 45 to 54 years | 210,256 | 12.5% |
| 55 to 59 years | 105,057 | 6.2% |
| 60 to 64 years | 87,484 | 5.2% |
| 65 to 74 years | 116,878 | 7.0% |
| 75 to 84 years | 52,524 | 3.1% |
Customer Segmentation
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Retail customers via the Sweet Honey Bee Farm Shop
- National online customers via the website
- Wholesale buyers of grocery chains
- Wholesale buyers of specialty gourmet stores
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Purely Perfect Honey Company
Purely Perfect Honey Company is located near Cincinnati, Ohio. The company was established in 1990 by Hank Ramey as a small shop attached to his farm. The development of a greater interest in honey bees and the products they produce led to a larger audience for the Purely Perfect Honey Company. In 2015, the company began to change their processes and systems to claim they had “Eco-Friendly Practices.” To conform to this title, they made a commitment to sustainable and eco-friendly practices, including water conservation and waste reduction. The current farms that harvest honey use no harmful pesticides or chemicals that could endanger the honey bees or the environment. Biodiversity is heavily enforced and practiced at the Purely Perfect Honey Company and the farms that contribute honey to the company are inspected quarterly for their harvesting of honey and the practices employed on each farm.
Gradley’s Gourmet Shops
Gradley’s Gourmet Shops are a chain of ten stores that sell specialty gourmet foods and food products. They produce honey from supplier farms and sell the honey as “pure and organic.” The chain sells honey that has been flavored with various infusions and the stores sell honey and butter soaps, herbal honey teas, honeycomb in glass jars, and honey-baked breads. These specialty gourmet items are priced on the high end of the spectrum due to retailer costs and the nature of the ingredients used to prepare and package the honey-based goods.
Gradley’s Gourmet Shops was founded by Teresa Gradley and her father, Mason Gradley in 1999. As a team, they sourced farm products, including produce, that are fresh, nutritious and comply with environmentally-sustainable farming practices. Gradley’s has been a chain that is growing due to increased awareness of nature foods and the way food is processed; however, the stores in the chain are small and some face closure as a result of poor marketing practices and inexperienced staff members.
Thacker Bee Farm
Thacker Bee Farm was established in 2019 by Jamie Lawson. While not technically a farm, Jamie chose to name her online retail company after a family home headquartered in Churchtown, Ohio. The website featuring honey bee products and honey also includes the brand positioning as “natural products” of all kinds. Grocery items, soaps, medicinals and herbal supplements are offered to online customers. Shipping of products and food is done by the store staff.
Although claiming the name, “organic and sustainable,” Thacker Bee Farm is selling products from farms around the country and using products from various bee genuses. Some of the natural products, including the herbal supplements are mass produced and bottled under the Thacker Bee Farm name; however, they are not generated at a farm. Some products are purchased from China and resold under the Thacker Bee Farm label.
Competitive Advantage
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Highly-qualified team of skilled employees who are able to harvest honey successfully and then package and sell honey and honey-based products to consumers either in person or online.
- Honey infusions, flavored honeys, honey soaps, and other honey products guarantee authenticity, as all products are made on the Sweet Honey Bee Farm.
- Unbeatable pricing to its clients; they will offer the lowest pricing in the city.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Sweet Honey Bee Farm is as follows:
Word of Mouth/Referrals
The owners of Sweet Honey Bee Farm have built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by providing exceptional service and expertise for their customers. The customers have already indicated they will follow them to the new company and help spread the word of Sweet Honey Bee Farm.
Professional Associations and Networking
Tony and Galene Hausen will attend community association meetings, trade group events, and trade shows to encounter opportunities to grow Sweet Honey Bee Farm. This includes industry sector shows where they can source products and sell their own to buyers.
Print Advertising
Two weeks prior to opening their store, a direct mail piece will be sent to all residents of Churchtown, Ohio, inviting them to attend the launch. Included in the offer will be discount pricing to be given during the first month of business.
Website/SEO Marketing
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will fully utilize their website. The website will be well organized, informative, and list all the products that Sweet Honey Bee Farm provides. In addition, buttons will be employed for purchases and shipping instructions will be included with each order made. Automated processing will email confirmations to customers for products ordered. The website will list their contact information and tell the back story of their farm and how they’ve developed it. The website will engage in SEO marketing tactics so that anytime someone types in the Google or Bing search engine “organic honey” or “honey farm near me,” Sweet Honey Bee Farm will be listed at the top of the search results.
The pricing of Sweet Honey Bee Farm will be moderate and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive excellent value when purchasing their services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Sweet Honey Bee Farm. Operation Functions:
- Tony and Galene Hausen will be the co-owners of the company. Galene will oversee all staff and manage client relations. Tony will work on product development and business expansion. They have spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Sarah Thompson will be the Office Manager who will manage the office administration, client files, and accounts payable.
- Greg Maynold will be the Senior Farm Manager, overseeing all honey bee production and processing, as well as overseeing the fields and crops produced on the farm.
Milestones:
Sweet Honey Bee Farm will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease office space
- 5/15/202X – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the Sweet Honey Bee Farm
- 6/1/202X – Finalize contracts for Sweet Honey Bee Farm clients
- 6/15/202X – Begin networking at industry events
- 6/22/202X – Begin moving into Sweet Honey Bee Farm office
- 7/1/202X – Sweet Honey Bee Farm opens its doors for business
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Sweet Honey Bee Farm are the fees they will charge to customers and wholesale clients for their services.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff Sweet Honey Bee Farm. The expenses will be the payroll cost, rent, utilities, office supplies, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Sweet Honey Bee Farm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its honey bee farm. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and association memberships. The breakout of the funding is below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Customers and Clients Per Month: 180
- Average Revenue per Month: $28,000
- Office Lease per Year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |

Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Honey Bee Farm Business Plan FAQs
What is a honey bee farm business plan.
A honey bee farm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your honey bee farm business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Honey Bee Farm business plan using our Honey Bee Farm Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Honey Bee Farm Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of honey bee farm businesses , some examples include: Honey farm, Pollination services, Selling bees, and Selling raw beeswax.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Honey Bee Farm Business Plan?
Honey Bee Farm businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Honey Bee Farm Business?
Starting a honey bee farm business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Honey Bee Farm Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed honey bee farm business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your honey bee farm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your honey bee farm business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Honey Bee Farm Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your honey bee farm business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your honey bee farm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Honey Bee Farm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your honey bee farm business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your honey bee farm business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful honey bee farm business:
- How to Start a Bee Farm
Sample Honey Bee Farming Business Plan
Honey bee farming business plan sample.
Do you think you should start a honey farm? Honey bees manufacture lots of honey in their hives which can serve as a source of income or for personal consumption. Apiculture the practice of rearing bees in hives can serve as a good commercial business as honey is heavily consumed.
A lot of products obtained from bees such as beeswax, honey and so on are in demand nowadays which can fetch a high profit or you can decide on a non-profit small scale farm for family and relatives.
Bee keeping has turned out to be among the most profitable businesses in the agro allied sector with increasing interests among entrepreneurs to invest. Although a very lucrative venture, it comes with its own challenges.
To surmount the challenges presented, entrepreneurs need to set up a framework that will ensure that the challenges faced or to be faced by their business are properly handled and surmounted.
An important tool necessary for the success of a honey bee farm business is the business plan. This article presents a sample honey bee farm business plan because of its importance to the stability of the business.
It provides guidelines which if well followed will result in the stability, profitability and growth of the entrepreneur’s honey bee farm.
HONEY FARMING BUSINESS OPPORTUNITIES
In this section however, we will discuss on how to start a honey farm. There are various steps to be carried out before operating a fully functional honey farm ( apiary );
- NATURE OF THE HONEY FARM
The first step to start a honey farm is to understand the philosophy of bees. The honey bee colony is an inexplicable and self reliant entity that can house over one hundred thousand members consisting of the unfertile female bees who carry out the major work in the hive which includes the feeding and cleaning of the queen and gathering nectars for honey production and the beeswax for the hive.
The male or drone bees in the hive unlike the worker bees only move around, consume honey and mate. The queen rests at the center of the hive, it produces eggs until it becomes inefficient and is then taken out by the worker bees.
So after you may have understood what goes on in a beehive, you must decide the type of bees you want to start a honey farm with. Gentle bees such as the buckfast bees are recommended for beginners because they’re easier to watch over and maintain.
There are a few ways to collect bees for a honey farm, you can either decide to catch a stray spring swam of bees or buy a fully instituted beehive from other bee farmers. When you have decided the bees you want to purchase, employ the services of a skilled apiarist to inspect and properly examine the hive and bees to ensure they are in good condition.
- RESEARCH BEEKEEPING REGULATIONS IN YOUR AREA
Before you start a honey farm, make sure there are no regulations and laws against placing the farm in your backyard. Register with the Beekeeping association of your state to gather information on these regulations.
- LOCATION OF BEEHIVE
When you want to start a honey farm, you may have considered urban areas as inappropriate locations to start a honey farm.
This assumption is wrong because bee hives can be placed in any location with healthy nectar producing flowers, you may decide to place your bee hive on the top of your roof or in a small portion of the backyard, there will be no problem as long as you have properly researched on the types of bees to purchase.
However, this choice of location is not advisable to those who are allergic to bee stings.
Also consider neighbors when choosing a location, place the hive in places where it will not disturb those living around or using the side walk.
- HARVESTING THE HONEY
First timers who have never tried out honey harvesting should ensure adequate protection and care to avoid accidents and mistakes. When putting out the time to start a honey farm, you should also consider learning the process of harvesting the honey.
A rundown of the process of honey harvesting;
- Open the hive, use a smoker to constrain the bees to the bottom of the hive and remove the sealed inner cover.
- The next step is to move the bees away from the hive. You should definitely not attempt to harvest the homey with the bees in the hive, the bees should be removed using any method you find most efficient.
- Uncap the sealed honey comb on each side of the collected frame.
- Extract the honey from the frame using manual or electrical extraction devices, the honey is allowed to fall to the bottom of the extractors drum.
- Open the faucet of the extractor’s drum and pass the honey through cheesecloth until all physical impurities are removed.
After these processes, the honey is ready to be bottled.
If you have never tried out bee farming before, it is advisable to study them a few times from a professional beekeeper who would show you a few techniques in honey farming.
When you start a honey farm, it is relatively easy to maintain compared to other forms of livestock farming as raring bees would not require you to clear out manure or fill, or clean water and food trough, bees gather their own food and rely solely upon themselves to survive.
Note that different types of flowers would produce different honey. It is important to move the hives from place to place to yield different honey from bees. Do not place beehives in cold wet places and be very cautious as beeswax stings causes irritations to the skin.
BEEKEEPING BUSINESS PLAN EXAMPLE
Here is a sample business plan for starting a honey bee farm. Table of Contents
Executive Summary
Products and Services
Vision Statement
Mission Statement
Target Market
Source of Revenue
Competitive Advantage
Payment Channels
Sales Projection
Publicity and Advert Strategies
Han’s Honey Bee Farms is a commercial honey bee farm to be located in Ohio . Fully licensed to carry out the production of bees and bee products, the Han’s Honey Bee Farms specializes in services that include the sale of live bees, collection of bee venom, royal jelly among several other bee products.
Our honey bee farm will not just produce for the local market in Ohio, but will produce for the domestic market (American) as well as for export or international market. Owned by Mr. Han Miller, who possesses extensive experience in the honey bee farm business, Han’s Honey Bee Farms will be driven by excellence and professionalism, with a well dedicated and motivated workforce that will drive the growth of this business.
Our workforce will be drawn from the very best hands within the industry to provide the much needed growth drive.
Our products will consist mainly of bee related products such as well packaged honey, collection of bee pollens, pollination activities as well as the sale of live bees.
Other services include consultancy and advisory services to smaller honey bee farms as well as teaching the skills of honey bee farming to interested individuals.
We at Han’s Honey Bee Farms intend to be among the top 5 major honey bee brands within the first 7 years from the commencement of business. This we intend to achieve by bringing together a workforce that shares our passion which will drive our growth plans.
Within this period, we intend to commence commercial export of our products to the international market.
We will be providing quality honey bee products and services to our esteemed clients through the adoption of best practices within the industry. Our outlets will be spread across all the states within the United States.
Due to our aggressive expansion plans we have, we will embark on deliberate efforts to increase our clients by reaching out to a diverse market that includes both commercial and individual clients. Our target market will consist mainly of agricultural products merchants, restaurants, hotels, beauty salons , food processing companies and households among others.
Our revenues will be generated primarily from the sale of the products and services on offer at our farms. Some of these products and services will consist of consultancy and advisory services to smaller honey bee farmers, the sale of our well packaged honey plus the production of bee wax. Others will include organizing seminars on bee and honey production. Revenue will also be realized from the sale of live bees.
A competitive advantage we will have over our competition is the favourable work environment needed for optimum productivity. Our workforce will thrive within a well laid out work environment with the necessary work conditions required for the best results.
Also, we will include a quality control unit that will ensure that only the best products reach the end consumer. Our remuneration will be among the best in the industry to ensure proper motivation of our workforce, resulting in the commitment of their best effort leading to growth and increased productivity.
We will be including diverse payment channels centred around the client, to ease the payment of services enjoyed some of these channels will include the receipt of cash payments, use of POS machine for payments and mobile banking. Others include the acceptance of cheques, bank draft and the use of mobile banking.
We have carried out studies within this industry which has shown a healthy growth projection for our business.
Using a three-year time frame, current economic indicators were used to arrive at these figures. However, unpredictable factors such as environmental disasters as earthquakes and economic downturn were discounted.
Below is a chart summarizing our three-year sales projection;
- First Year $150,000
- Second Year $280,000
- Third Year $510,000
We will be making use of effective publicity and advert strategies to reach the widest possible section of our consumers and clients. some of the strategies to be adopted include the placement of paid adverts in both electronic and print media, the use of billboards and the building of a website all showcasing our services.
This article focuses on providing a sample honey bee farm business plan to the interested entrepreneur who has little or no knowledge on how to write a good honey bee farm business plan.
Using the format provided here, the entrepreneur is ensured of success in producing a compelling and well written business plan.
HONEY BEE FARM BUSINESS PLAN OUTLINE
Business Name: Tony Roger and Son Bee Farm
- Our Products and Services
Business Structure
- Market Analysis
- Sales and Marketing Strategy
- Financial Plan
Tony Roger and sons bee farms is a registered bee farm company that will be located in Nevada, Las Vegas. We have already gotten a vast area of land that will be suitable to comfortably carry out our farming activities.
We at Tony Roger and Sons bee Farm Company are not just in this business to take advantage of the high demand for bee products. We are also in this business to contribute in the best way that we can to the economy of the United States. As a result of this, we will ensure that every product that has our label on it is of the highest standard possible.
At Tony Roger and Sons Bee Farm, we will be raising top quality bee products for the residents of Nevada, Las Vegas.
We will also supply other parts of the United States as well as major cities in Canada with products from our bee farm. Some of the many services that we will be making available to our potential customers are;
- Pollination Services
- The sale of live bees
- The sale of bee products such as honey and pollen
- The production of bee wax
- The production of bees
At Tony Roger and Sons bee farm, our vision is to be a household name in Las Vegas and also the United States at large. We want to be the first brand that comes to mind when a bee, as well as bee products, are thought of.
We at Tony Roger and Sons bee farm are not just okay with being one of the many bee farms that are located in the United States. We want to dominate the bee farming industry with our products.
We are also looking to become a franchise after being in operation for close to five years.
As newcomers in the bee farm industry, we intend to start out on a very small scale. However, we intend to grow very massively within a year. We want to compete very favorably with the much more established brands in this industry.
We know that all our dreams at Toney Roger and Sons bee farm will only remain dreams if the right structure is not placed. Therefore, to make our dream of becoming a reputable bee farm in the United States come true, we will be working with only the best hands in this industry. We will employ only individuals that are creative, goal-oriented and hardworking.
Also, we will ensure that our employees work under the very conducive environments that will help them to function at their best.
Market Analysis Market Trends
The rate at which health professionals make known the benefits of honey as a harmless sweetener has positively affected the bee farming industry. Since the preference of honey over sugar as a sweetener began, there has been a very high demand for honey. This demand has given the bee farming industry the much-needed boost to stay relevant.
Sales and Marketing Strategies
There are lots of bee farms that are scattered across the United States. Therefore to make it quickly to the top and also remain relevant, we have come up with certain strategies. These strategies include;
- We will offer our products to our potential customers at a relatively cheaper price
- We will make sure we have a strong internet presence
- We will advertise our brand as well as products in magazines that are centered on food and agriculture
Virtually everyone makes use of bee products. As a result of this, the market for the bee farming industry is very large. Therefore, to make the best out of this industry, we have carried out our research and have come up with the ideal target market. Those that make up our target market include;
- Restaurants
- Individuals
Financial Plan Source of Startup Capital
To get this business started, we will need a startup capital of $50,000. Already we have $30,000. The remaining amount that we need will be gotten from the bank in form of a loan.
The bee farming industry is a very lucrative one. This explains the high level of competition in this industry.
Although there is a high level of competition in this industry, we have carried out our research and have come up with just the factor to give us an edge in this business.
Our competitive advantage is this; we have a strong network with those that are involved in the sale of bee products in the United States, we also have the most recent tools for bee farming. This we know will help us get our products ready on time and also get them sold off in record time.
This is a bee production business plan for Tony Roger and Sons Bee Farm. It will be located in Nevada, Las Vegas.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
BeeKeepClub Resources and Guides for Beekeepers
How to start a honey business that’s profitable.
Michael Simmonds June 26, 2023 Blog 7 Comments
If you purchase an independently reviewed item through our site, we earn an affiliate commission. Read our affiliate disclosure .
Beekeeping is a fun hobby for many, but perhaps you want to take it a bit further – to turn it into a profitable business. Starting a honey business will require you to properly plan and prepare before starting any operation. You will need adequate resources to buy the materials and equipment you will need. It is also useful to have some knowledge about beekeeping and the know-how of running a business in general. This guide on how to start a honey business details all of what you will need before getting into this sweet venture. Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
Starting a Honey Business
It is highly recommended that you have some decent knowledge about beekeeping before starting a honey business . With the right setup, readiness to learn and motivation, you can start your operations. Go at it slowly at first and increase the size of your honey business as you go. If you have a large business in mind, start with a few beehives and then scale up when you have gained experience in beekeeping.
When starting the honey business , there are three main things to bear in mind:
- Providing shelter for the bees.
- How you will maintain the shelter in a suitable state for continued use by the bees.
- Harvesting honeybee products from the beehive.
These three things are crucial to beekeeping and any honey business at large.
Things to Consider Before Starting a Honey Business
A good honey business will be easier to run if you are in control of production and marketing to varying extents. It helps you get through buying equipment and preparing the honey for marketing much easier. Quality is very important in any business, and perhaps even more so in a honey business. Knowledge about beekeeping practices helps you get high yields of top-quality honey and beehive products. Joining local clubs and reading books about beekeeping, harvesting and working with honey are great for gaining knowledge about best practices and the equipment you should buy.
Purchasing the Necessary Equipment

You will need to have the necessary equipment in place before you can even think about getting started in beekeeping , much less starting a honey business . Equipment includes the beehives for the honeybee colonies you will have, and protective wear – beekeeping suits , veils and gloves . These protective equipment are important in allowing you to work around bees safely. Set aside some of your investment money for the purchase of other equipment and beehive treatments for the maintenance of healthy honeybee colonies.
Purchasing beekeeping equipment depends on the size of the honey business operation you are aiming for and the amount of investment money you have. With larger beekeeping operations, you generally have to buy more pieces of equipment such as beekeeping suits and hive tools for each labourer you employ in your apiary.
Depending on where you live, beehives may come in different designs. Popular designs include the Langstroth beehive, the top bar beehive, the Warre beehive, and the British National beehive. Beekeeping practices are also slightly different based on the climatic region you are in. If your region experiences large changes in temperatures over the seasons, prepare well for the cold seasons. Bees have less activity and fewer foraging areas in winter than in other seasons.
One of the most important pieces of equipment in beekeeping is the honey extractor. For large honey businesses , a large extractor that takes many frames at a time is the best option. You may also go for an extraction line that is manned by up to 3 people in a team. Commercial honey extractors allow you to extract honey from many beehive frames in a single day. You can delay the purchase of a honey extractor until it is time to harvest honey.
Getting a Honeybee Colony

You can’t have a honey business without the bees, so after procuring the necessary equipment, the next thing you need is a bee colony. You can buy a colony or catch a swarm yourself. It is important to get a healthy colony in order to establish strong honeybee colonies across your apiary. Beekeepers may also improve the genetics of their honeybee colonies by introducing new queen bees . Trapping a wild-swarming honeybee colony is a great way to improve the genetics in your apiary. With large apiaries, characteristics such as resistance to diseases and pests are very important as they save you large costs incurred in honeybee colony pest and disease control. Indeed, a severe mite of wax moth infestation is capable of wiping out entire honeybee colonies.
Trapping a wild bee swarm is a very fulfilling activity for beekeepers. Making and using a swarm trap is easy. You can also opt to buy a swarm trap instead. Lures to attract bees to the swarm trap are great for your chances of getting a swarm into your trap. Have a beehive ready for when you catch a swarm of bees. Moving bees to the beehive as soon as possible allows the swarming bees to start establishing a home , with less loss in swarm size. More bees in a freshly installed honeybee swarm help the swarm carry out beehive activities quickly and readily.
Beekeeping Books

Knowledge is key, and having a few books about beekeeping is very important. There are great authors with years of beekeeping experience who have published theirs. Beekeeping books have different skill level requirements. The best beekeepers have books for beginner to professional experience levels. As you become more experienced, you will find that each book takes on a new significance.
Top beekeeping books include “ The Backyard Beekeeper ” by Kim Flottum, “ Beekeeping for Dummies ” by Howland Blackiston, “ The Beekeeper’s Handbook ” by Diana Sammataro, “ First Lessons in Beekeeping ” by Keith Delaplane and “ Practical Beekeeping” by Clive de Bruyn.
Starting beekeeping with a few books to guide you makes it easy to set up the business. A book for beginners, with some intermediate and detailed guide on beekeeping should be enough for you just starting out. You can buy other books later to add to your knowledge of beekeeping. Some beekeepers go with a set of good-quality beginner books and two professional-level books.
Joining Local Clubs
Joining a beekeeping club is a great way to interact with beekeepers. You will pick up on a number of key beekeeping tips from other beekeepers. A beekeeping club is a great place to access books about beekeeping too. You can share your own books, learn about the best titles to buy, and borrow resources from other beekeepers.
You will get to know the best equipment for beekeeping and how useful it can be in your business. When need be, you can borrow or rent equipment from the other beekeepers before you purchase your own. If there is no club in your area, consider starting one if you know other beekeepers near you.
Protecting Honey Bee Colonies in Winter
Beekeepers use various methods to keep their colonies healthy over winter . Bee death in winter can cause weak colonies later on. Wintering bees feed on honey since they can’t leave the hive to get food elsewhere. They guard the hive and warm it. Bees may retreat to the inner parts of the hive and congregate around each other more during winter. If this happens and the hive entrance is left unguarded, bees may get bombarded with the infestations of pests. Robber bees, wasps and other insects that predate on bees or steal their honey may also attack through an unguarded hive entrance.
Regular inspection of beehives is important in a honey business . You should have and follow a schedule of beehive inspections. On warmer days during cold weather, you can feed bees . You can also opt to use insulated beehives that lose less heat during winter. Popular methods of beehive insulation include the use of insulation blankets and plastic insulation armour for beehives. These items for insulation are specially designed to allow ventilation of the beehive and the movement of bees into and out of the beehive.
A Commercial Beekeeping Business Plan

Your honey business will run better if you have a plan for it. You must first prepare and plan before you can succeed. A commercial beekeeping business plan helps you to better understand how to put the business together. It creates a framework on which you can start and grow the honey business . The business plan helps you think long-term about the business in addition and how best to manage expenses.
During the development of your commercial beekeeping business plan, carry out market research to investigate the market opportunity. This gives you insights into the marketplace – its competitiveness and your customers. Plan out the business strategically and capitalize on the business with significant investments to get value from your honey business .
A good business plan should define the goals for your business clearly. It also helps establish if the business is feasible. Establish the factors that are critical to your honey business in the beekeeping plan. How you evaluate the internal and external business environment for the honey business should also be found in the plan.
What should a Commercial Beekeeping Business Plan detail?
A commercial beekeeping business plan answers questions about what the business is, the products offered by the business, and resource availability and use in the business. It also gives a guide on how performance will be measured. It has the following sections among others:
- Mission and goals of the business. These guide the beekeeper in setting up the business and deciding what is important for the business.
- Apiary strategy and implementation strategy.
- Business financial plan of income and expenditure.
- An executive summary of the honey business . The vision and mission of the business may be included in the executive summary.
- Enterprise analysis and planning.
- A marketing plan.
- Break-even analysis.
A break-even analysis is important for the price determination of your beehive products. It allows you to set targets and know how much of beehive products you need to sell in order to make a profit. The analysis can be categorized into three parts: break-even sales units, break-even sales in monetary value (currency), and break-even time.
Establishing a Marketing Strategy

It is necessary to have a marketing strategy in the business plan of your honey business . The plan is an outline of prices, quantity objectives and the time required to generate returns for the business. It takes into account market conditions and the wants of the customers you target. In marketing, consider cash flow to the business, market prices and production risks that affect the business. Distribution of honey products can be done by individual beekeepers or through marketing firms. Some individual beekeepers sell honey through their networks and reach small markets.
Selling honey products through marketing firms utilizes their brand presence in the market while giving you an avenue to move large volumes. It is more suitable for beekeepers with large colony beekeeping operations to sell through firms than individually. A marketing budget detailed in a marketing plan shows sources of marketing resources and how they will be spent. It should feature in your commercial beekeeping business plan.
Benefits of a Commercial Beekeeping Business Marketing Plan
A marketing plan for a commercial honeybee business sets goals and outlines how best to achieve them. Beekeepers with clear and efficient marketing plans enter new markets, maintain the market and increase market share over time. They also guide the development of new honey business products to meet customer needs. With a solid marketing plan, you are able to raise your competitiveness in the business.
How you package your beehive products matters in your honey business . Well-packaged honey and other beehive products attract customers and help them relate the product with value. Packaging for honey should be food-safe. You may have varying sizes of packaging to suit the different quantity needs of your customers. Clear packaging in a honey business allows customers to see the contents of the package and builds trust with your brand.
Beekeeping Business Profits

The profits you realize in the beekeeping business vary by region and the amount of honey your honeybee colonies produce. On average, a beekeeper can expect to sell a pint (473 ml) of honey at USD$10 and a quart (o.94 L) at USD$17. Selling honey to bulk packers or processors gives you different prices than selling wholesale or retail prices. For your honey business to be profitable, you must keep costs down while making sure you get good honey yields per beehive.
Factors Affecting Profits
Factors that affect your honey business profits should be controlled. These include controlling pests and diseases of honeybees, purchasing assets early on in beekeeping and making the best use of available labour. Beekeepers that maximize these three factors enjoy good honey yields and great prices for their honey. Their honey businesses are profitable and can grow to large operations.
1. Pests, Diseases and Predators

Controlling pests and diseases of honeybees allows bee colonies to remain strong, and strong colonies are able to produce much more. Beekeepers who neglect disease and pest control in their honeybee colonies suffer low honey yields. Colonies that are diseased or suffering a pest infestation cannot produce brood and honey in large amounts. Some diseases and pests of honeybees lead to colony collapse where bees may all die or leave the beehive. Beekeepers should also take steps to ensure predators and large animals that attack bees do not gain access to the apiary. These animals such as bears , not only cause losses of honey in a beehive but may also damage the beehives in their pursuit of honey.
Beekeepers use a combination of methods to keep pests and diseases at bay. The application of chemicals in a beehive is one common way. It is recommended to deploy different chemical treatments over time when dealing with pests of honeybees so they do not develop resistance. You should also practice proper beehive hygiene and regular beehive inspections to prevent diseases from infecting your beehives. Join regional and local beekeeping associations and clubs to get up-to-date news about bee diseases in your area. Some diseases can spread across apiaries and cause heavy losses. If you get an early warning that a disease has been noted in your area, you should take preventive measures and be on increased alert so you notice the disease early if it infects your honeybee colonies.
2. Equipment Costs
When starting a honey business , it is best to purchase most of the assets you will need and which are useful for large operations. A means of transporting your honey is important for when you harvest. Other significant assets are beekeeping suits and a honey extractor. Of course, beehives for your honeybee colonies must also be purchased. You can start out with a pick-up truck, a large extractor and a beekeeping suit for each labourer you have. Over time, increase the number of beehives you have and add the other assets accordingly.
3. Labor Costs
Labour in a honey business can run up high costs for you. The common labour rate in beekeeping is $12 per hour. Setting up beehives and inspecting them are the least labour-intensive activities in a large apiary. Installing bees, treating beehives for pests, diseases and parasites, and harvesting honey can be very labour-intensive. For a honey business with many beehives, make sure to hire experienced labourers who work fast and make a few mistakes. You may pay slightly more for experienced labour, but it pays off in the long run.
How Many Hives Are Needed to Be Profitable?

Honey business operations have varying levels of profitability. Large operations promise better profits due to better use of assets. They also give more honey yields allowing beekeepers to achieve more revenue than smaller operations.
With proper beekeeping practices and high vigilance, a beekeeping operation of more than 25 beehives should give good profit ratios. Honey business operations of less than 25 beehives are not very profitable. Beekeepers running a honey business should keep financial records so they can easily assess their profitability.
Minimum Hives
The minimum safe number of hives to have in a honey business when starting is 50. With 50 beehives in your first year of operations, you will inject considerable capital into the business but get profitable quickly.
Having another job that can funnel cash into the honey business may be needed. Keep your debt low when you have less than 100 beehives in your honey business . After your first year with 50 beehives, look at increasing the number of beehives you have to 100 within 3 years.
A honey business operation of 100 hives or more is quite profitable. It is also easy to fuel growth using retained earnings from the business. Getting a substantial loan is possible when you have 100 hives in your honey business operation.
Returns on assets and liabilities are the biggest determinants of profitability in a honey business . They vary over time and may increase in some years while going lower in others. Older honey businesses tend to be more profitable than younger ones. This influences growth and as a result, older honey businesses have generally more beehives than younger businesses.
How Many Gallons of Honey Can You Get From a Hive in a Year?

The amount of honey you harvest is important for your honey business . Honey and other beehive products are often sold by weight. A single beehive can give a yield of anything between 20 and 60 pounds of honey. On average, beekeepers get more than 25 pounds of honey within a year.
Bees in a new beehive have low amounts of honey during honey harvest time. An abundance of honeybee forage also impacts how much honey beekeepers get from a hive. Strong colonies with many bees give better yields of beehive products. Beehive diseases and pests of bees also affect the amount of honey you can harvest from a single beehive.
Honey bee colonies have to maintain sufficient brood levels in order to have good colony strength. Honey is stored by bees in good times for use during hard times. When you harvest honey, you should leave some for the bees to use when conditions are not favourable for foraging.
How Honeybees Get High Honey Yields per Hive per Year
Skilled beekeepers have found out various ways to keep strong colonies and have high honey yields. They make sure to have bee colonies that are good at foraging and making honey. Planting flowers that bees love is one way of making sure to have a good honey harvest. You should also provide a water -drinking place if water places are far from your apiary.
Keeping Records
Records in beekeeping are an often overlooked part of the honey business . Beekeepers should keep two types of records: records of beehive activities and observations, and records of incomes and expenditures related to the honey business .
- You do not have to keep elaborate records or have financial accounting skills. Simple records that capture important information are adequate for general use.
- Properly kept records in your honey business help you make quick and accurate assessments of the profitability of the business.
Unfortunately, many beekeepers are not willing to share financial information or records of their honey businesses , despite being profitable.
Estimated Investment Needed for a 1,000 Colony Bee Operation
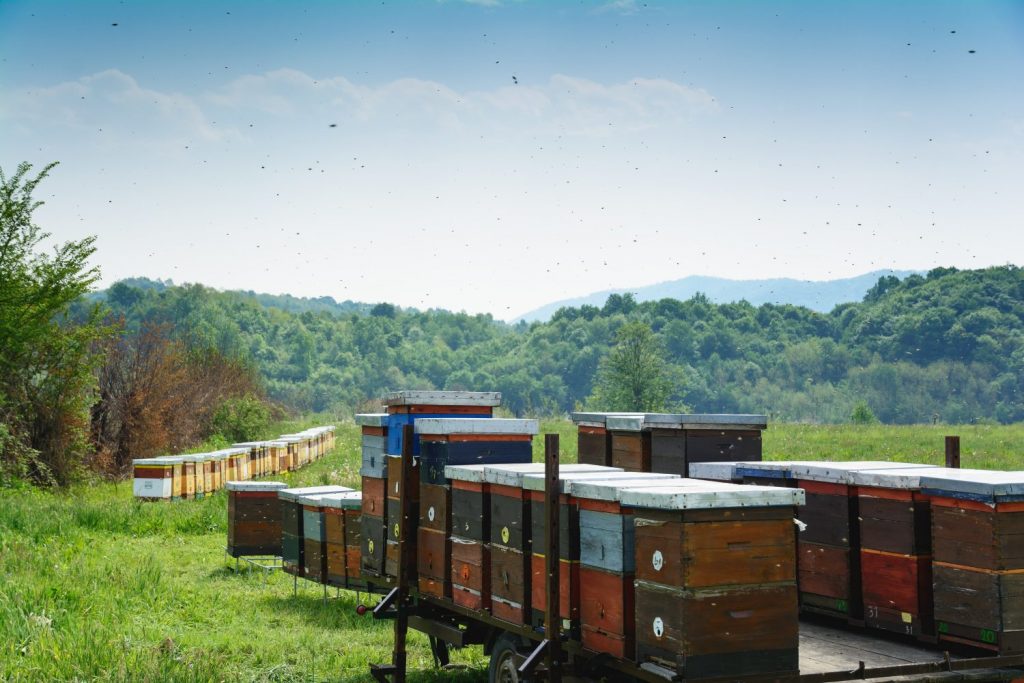

Beekeepers with honey businesses have varying size apiaries. A 1,000 colony bee operation is a large operation on average. The investment needed for such a honey business operation is considerably large. Basic investments in the operation vary in number. The investment also varies depending on the labour you use in the apiary. This estimated investment needed for a 1,000 colony bee operation in the USA is $500,000 to operate for at least 1 year. Once you harvest honey after the first year, the cost of keeping the apiary is going to be reduced. This is because you will not be buying any more equipment for setup anymore.
Beekeeping assets depreciate over time. The return on assets will however remain the same for as long as they are in use. Beekeepers should fuel the growth of their apiaries using retained earnings. They may also pump in money from another job they have. Loans are also a popular way of financing investment in a beekeeping business. A high debt ratio is not good for your honey business . You should thus keep liabilities at the lowest attainable levels while increasing your assets. A honey business with less than 25 beehives is often not very profitable, so start the business with more beehives if possible.
Your estimated investment for a 1,000 bee colony operation should be enough to buy beehives, protective clothing, pest and disease control and honey harvesting equipment . You will also need to buy bees for the beehives you start with.
Due to the large size of the apiary, a large honey business operation with 1,000 colonies requires you to have a mode of transportation . In most cases, a pick–up truck is adequate. It comes in handy when you are going out for a visit to the beehives and need to take some tools, equipment or beehive treatment materials with you. The truck also makes it easy for you to transport harvested honey from the apiary.
Start Small
Bringing together the 1,000 bee colonies can be done over a period of time. It allows you to spend small amounts of investment capital at a time. You also gain experience in beekeeping as you expand the operation.
When starting small first, go for a large honey extractor that can hold many frames at a time. 6-8 frame extractors are good for both small and large honey businesses . They extract honey quickly and can get through frames from many beehives quickly. After the apiary has grown bigger, you can install larger honey extractors.
Protective clothing that you buy typically lasts more than 1 year. Good quality protective clothing should protect you from bee stings, be usable in both hot and cold weather and be comfortable for you. Manufacturers of beekeeping suits, jackets and smocks use different materials and veil designs in their protective wear. Equipment for a honey business is a long-term investment. Get the best equipment you can buy and maintain them well to last long.
Other Beehive Products
In addition to honey, there are other products you harvest from a beehive. They include propolis and beeswax. Beekeepers also sell brood combs, bees and entire swarms from beehives. These additional beehive products add to the total monetary yield per hive in a year.
Selling honey after harvesting may require you to process it. Some buyers of honey prefer to have it still in the honeycomb when they are buying it. Others are fine with honey that has been extracted from the honeycomb. To give your honey consumers the best quality honey, do not add anything to harvested honey.
A Look at Commercial Honey Extractors
Large honey business operations magnify beekeeping activities . Harvesting honey and processing it through extraction is a single-day activity with few beehives. On apiaries with hundreds of beehives, you will need large honey extractors to go through beehive frames quickly. This requires beekeepers in large honey businesses to go for commercial honey extractors.
Commercial honey extractors are largely electric and utilize centrifugal force to extract honey from beehive frames. They capitalize on extracting honey from a large number of frames at a time to make sure you finish honey extraction as quickly as possible. Let us take a look at a few commercial honey extractors that are currently available to beekeepers.
Cowen Manufacturing 28-Frame Extractor

The 28-frame extractor is made and sold by Cowen Manufacturing. It is built in a production line design with racks and drip pans on both sides of an extraction section. It features extraction, uncapping, hot water, pumping and spinning systems to not only extract honey but also remove wax from the honey. The extractor is loaded with beehive frames containing honey on one side where they are uncapped.
Pushing frames onto the loading side of the extractor results in empty frames being pushed out of the extractor. More than one person is required to operate the extractor. With experience using the extractor and a two-man team, Cowen Manufacturing promises that you can go through anything between 100-150 super boxes in a single 8-hour shift with this extractor line. This 28-frame extractor line uses a 115-volt electric current and may require more than one plug.
Lyson 40-Frame Complete Mini Extracting Line

This 40-frame complete mini-extracting line comes with a built-in uncapper with a feeder and knives heated using water. It is a professional quality extractor that holds 40 frames at a time. It is easy to load the extractor using its manual frame cart. Each cart takes 20 frames. Loading and unloading times are minimized on this extractor to give you greater throughput. This is an ideal extraction line for medium-sized honey business operations.
Lyson Beekeeping is the maker of this extracting line. They are a Polish company that has won awards with for their beekeeping equipment. The 40-frame mini-extracting line comes with a motor controller for speed varying. It also includes a programmable controller with a colour LCD output. 8 programs are available for automatic control of the speed at which the extractor runs.
Cowen Manufacturing 60-Frame Air Ram Extractor

Medium commercial beekeepers are very well suited to the 60-frame air ram extractor. It is made and sold by Cowen Manufacturing. The extractor is a two-man honey extraction line and takes 60 frames at a time. It promises you extraction of honey from up to 300 honey super boxes in a day. The extractor line features a powered loading conveyer, automatic self-adjusting drive, stainless steel reel, and a food-safe tank for collecting honey.
Loading the 60-frame air ram extractor is done at one point where the frames are uncapped and then conveyed to the extraction section. The extractor line mechanically loads the frames into the extractor. The extractor in the line works automatically using electricity. Operation of the line is continuous with an average extraction cycle lasting 7-10 minutes.
Cowen Manufacturing 60-Frame Non-Air Extractor

The 60-frame non-air extractor is a variant of the same-sized extractor line by Cowen Manufacturing. It uses slightly different technology within the extraction line but takes the same number of frames at a time. The non-air extraction line is more economical and is great for large operations that have the capacity for growth.
This 60-frame extraction line variant is more manual than its air-ram counterpart. The brakes on this line are operated by foot, gates are opened using levers, frames are pushed into the reel using a crank apparatus, and the machine’s hood is hand-operated. The extraction line is a sensible investment for large operations which are still growing. It allows fast extraction of honey so that honey super boxes can be put back onto beehives quickly.
Kelley Beekeeping 72-Frame Stainless Steel Radial Extractor

This is a large radial extractor made by Kelley Beekeeping. It takes a large number of frames at a time so you spend less time in honey extraction. The extractor runs on electric power. It is built for commercial operations and heavy use. Beekeepers with hundreds of frames to process get the job done quickly with this extractor.
The 72-frame extractor is made using 22-gauge stainless steel on the sides. 18-gauge stainless steel is used at the bottom of the large drum of this extractor. The extractor has a diameter of 60 inches and is 35 inches high. Kelley Beekeeping has made this 72-frame extractor with a variable-speed AC motor for easy use. This extractor comes with a 3-inch brass flange. The honey gate and stand needed for the extractor are sold separately.
Dadant M00432 84-Frame Honey Master Extractor Segmented Reel

An extractor this big is a great choice for large-scale honey business operations that have reached their maximum planned sizes. The 84-frame honey master segmented reel extractor is made and sold by Dadant, a reputed beekeeping equipment supplier . It is made using type-304 stainless steel that is welded together. The extractor shows good craftsmanship in fabrication and reinforced leg structure. With an extraction cycle lasting a conservative 15 minutes, you can extract honey from more than 2,500 beehive frames in a day.
This large extractor comes with electronic speed control for its ¾ horsepower motor that runs on DC electric power. The extractor is built in an inverted cone design to allow drainage of all extracted honey. It has a 3-inch male pipe threaded to allow connection to other honey collection receptacles and pipes. The tank of this extractor has a diameter of 62 inches.
Cowen Manufacturing 120-Frame Air Ram Extractor

Cowen Manufacturing is the maker of this massive honey extractor. It is a 2-3 person extractor line that extracts honey from 120 frames at a time. It easily extracts its way through more than 70 honey super boxes in an hour. This is perhaps the best honey extractor for large commercial honey bee businesses. It is a valuable investment for a honey business that has reached its planned maximum size in colony numbers. The extractor is durable and affordable to maintain. It runs on AC electric power.
This 120-frame extractor line is loaded with beehive frames and uncaps them within the line. It then moves the frames along a conveyor system with a drip pan to the extraction tank. The extractor uses a lever-operated air ram to load uncapped frames into the extraction tank. After extraction, it removes the empty frame onto the unloading section of the line. An air-ram brake holds the extraction line’s stainless steel reel in place during loading and unloading.
Maintaining Honey Extractors
It is important to clean and grease honey extractors. Cleaning them with hot water is recommended. It keeps the extractors free of contaminants that may get into honey and make it unfit for consumption. Greasing keeps moving parts lubricated and properly functioning. Each of these commercial honey extractors has its maintenance manual that you should read and follow carefully. The extractors may use oils of varying viscosity ratings and compositions. Do not operate the extractors on wrong power ratings or when dissembled.
Storing Honey
You may store honey and package it later. You can market your honey locally or across larger regions. Listing in business directories both online and offline is great to market your honey business . Beekeepers also use other advertising methods for their honey business products.
Beekeepers also store honey in comb for some time and then extract it later. Honey in comb stays in its natural form for a long time. Stored honey in a container that is not opened frequently keeps it nutritious and high quality for a long time. Honey does not ferment due to its very high concentration of sugars. You may also put honey in cold storage without affecting its quality.
Use this guide on how to start a honey business for a better idea of what is needed to set up a successful beekeeping operation. It is easy to start your own beekeeping enterprise and run it. You can practice small-scale beekeeping or go large-scale, it’s up to you. Beekeepers with large apiaries often start small to gain experience in beekeeping and honey marketing. With experience and increased financial resources, they then expanded the honey business to the size they set out to achieve. This is one of the best ways to start and run a large honey business. You can also check an interesting article on starting a business and what is an LLC .
About Michael Simmonds
Thank you for sharing such nice content. An increase in health consciousness among people and a drive to find a better substitute for sugar drives the growth of the market. Apiculture products are highly nutritious and beneficial to health. This has led to rising in demand for pollination which in turn boosts the apiculture market.
Want to start a bee business
That’s great! You can use the information in this article as a guide to get started. All the best!

[…] require you to properly plan and prepare before starting any operation. You will need adequate resources to buy the materials and equipment you need. It is also useful to have some knowledge about […]
[…] to with some other sort of enterprise, you’ll need to plan to your beekeeping enterprise in Jamaica earlier on. This is step one that ensures points of the beekeeping enterprise are […]
[…] since this is the easiest way to acquire the required in-person tips and insights about the business of keeping bees. You should also consider enrolling for a beginner course. This can be done online or onsite […]
[…] method now not best aligns with Google’s highest practices but in addition guarantees your honey industry sticks out within the virtual panorama. Pay particular consideration to beefing up your on-line […]
Please Enable JavaScript in your Browser to Visit this Site.

How to Start a Honey Production Business
Main Sections In This Post Steps To Starting A Honey Production Business Points to Consider Knowledge Is Power Featured Video
In this post, you’ll find a step-by-step guide on how to start a honey production business.
In addition, we will give you an overview of what you can expect from operating a honey production business and help you make better decisions and gain clarity.
You can access the latest resources in our “Knowledge Is Power” section. Which can be used during the startup phase and once your honey production business is fully operational.
There is an abundance of information available to explore. If you like this post, consider sharing it with others and bookmarking it for future reference.
Let’s get started with the steps.
The Steps to Take To Start Your Honey Production Business
Below are the steps to starting a honey production business.
Each step is linked to a specific section, allowing you to jump to your desired section or scroll to follow the steps in order.
- An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
- Honey Production Business Overview
- Researching Your Honey Production Business
- Looking at Financials
- Creating Your Mission Statement
- Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
- Choose a Honey Production Business Name
- Register Your Company
- Create Your Corporate Identity
- Writing a Business Plan
- Banking Considerations
- Getting the Funds for Your Operation
- Software Setup
- Business Insurance Considerations
- Supplier and Service Provider Considerations
- Setting Your Prices
- Physical Setup
- Creating a Website
- Create an External Support Team
- Hiring Employees
- Getting Customers Through the Door
1. An Overview of What You’re Getting Into
a. ) Owning and Operating Your Own Business
Owning and operating a business is distinct from being an employee. It carries greater responsibility, often involving long hours and the need to address challenges independently.
The conventional nine-to-five workday no longer applies.
Before starting a business, it’s essential to assess whether the responsibilities of business ownership align with your preferences and capabilities. Take time to consider if this path is the right fit for you.”
See Considerations Before You Start Your Business to identify points for a new business owner.
b.) Pros and Cons of Owning a Business
Running a business carries both advantages and drawbacks. While the allure of entrepreneurship lies in its rewards, many underestimate the associated challenges.
Examining these challenges is vital for a comprehensive understanding of potential issues. This proactive approach enables better preparation and minimizes unexpected obstacles.
By acknowledging the problems you may encounter, you can develop strategies to address them effectively.
In the world of business, foresight and readiness are essential for navigating complexities, and fostering a more resilient and successful enterprise.
For more, see Pros and Cons of Starting a Small Business.
c.) Passion a Key Ingredient For Success
Passion: The Driving Force
The opportunity to work in a field aligned with your passion is indeed a blessing. Passion is the essential fuel that drives your success in the challenging realm of business ownership.
Passion Fuels Problem-Solving
When you’re deeply passionate about your honey production business, challenges become opportunities for innovation and problem-solving.
Your determination to find solutions sets you on a path to overcoming obstacles. Conversely, lacking passion might lead to seeking an exit when faced with difficulties.
The Crucial Role of Passion
The level of passion you possess for running a honey production business significantly determines your chances of success.
The Passion Test
Imagine a life with boundless wealth, possessions, and freedom. Would you still choose to operate a honey production business without monetary gain? Your affirmative answer signifies genuine passion and a commitment to the journey.
Passion vs. Alternatives
If your response is negative, it raises an important question: What alternative path would you prefer? Perhaps pursuing that alternative aligns better with your true passions than starting a honey production business.
In Conclusion
In summary, passion is the linchpin of success in owning and operating a honey production business. It not only propels you forward but also shapes your resilience in the face of challenges.
Passion is the compass guiding you toward a fulfilling and prosperous entrepreneurial journey.
For More, See How Passion Affects Your Business .
2. Gaining an Overview of Owning a Honey Production Business
Next, let’s spend some time on key issues to give you an overview of what to expect from owning and running a honey production business.
Note: This section contains an abundance of information that you will want to review. It will give you an overview of what to expect, and it’s worth reading this section.
a.) A Quick Overview of Owning a Honey Production Business
Understanding a Honey Production Business
A honey production business involves the cultivation and extraction of honey from beehives, creating a product that can be sold to consumers or other businesses.
It is a multifaceted endeavor that encompasses various tasks, from beekeeping to marketing the final product.
Day-to-Day Operations: Beekeeping and Beyond
Running and managing a honey production business demands a range of daily tasks, each integral to its success.
Beekeeping: At the core, beekeeping forms the foundation of a honey production business. This involves caring for beehives, ensuring the health and well-being of the bee population, and managing hives to optimize honey production.
Harvesting and Extraction: Regular honey harvesting is essential. Beekeepers must carefully extract honeycomb frames, remove beeswax, and employ extraction equipment to obtain raw honey.
Processing and Packaging: Once harvested, the raw honey undergoes processing to remove impurities and achieve the desired consistency. It is then meticulously packaged to maintain its quality.
Quality Control: Ensuring the quality and safety of the honey is paramount. Daily quality checks are necessary to meet industry standards and customer expectations.
Marketing and Sales: Effective marketing strategies are crucial for reaching customers. This involves promoting the honey product through various channels, such as online platforms, local markets, or partnerships with retailers.
Financial Management: Daily financial tasks include tracking expenses, monitoring sales, and managing budgets to ensure profitability.
Inventory Management: Keeping an eye on inventory levels is vital to meet customer demands without overstocking or running out of product.
Regulatory Compliance: Staying informed about and adhering to industry regulations and safety standards is an ongoing responsibility.
Customer Engagement: Maintaining communication with customers, addressing inquiries, and seeking feedback are essential for building and retaining a loyal customer base.
Environmental Stewardship: Sustainability practices, such as promoting pollinator-friendly environments, may also be part of daily operations to support the bee population.
In essence, running a honey production business involves a blend of hands-on beekeeping, quality control, marketing efforts, and the overall management of resources to ensure a steady supply of high-quality honey to the market.
These daily tasks, when executed effectively, contribute to the success and sustainability of the business.
b.) Honey Production Business Models
Exploring Honey Production Business Setups and Models
Honey production businesses can take on various setups and business models, each with its own characteristics and advantages. Understanding these options is essential for informed decision-making during the startup phase.
1. Beekeeping and Local Sales:
- Model: Beekeepers maintain beehives, harvest honey, and sell directly to local consumers, farmers’ markets, or small retailers.
- Advantages: Low overhead, direct interaction with customers, and potential for premium pricing due to locally sourced honey.
2. Commercial Honey Farming:
- Model: Large-scale honey production involves extensive beehive management, commercial extraction, and distribution to regional or national markets.
- Advantages: Economies of scale, higher production volume, and broader market reach.
3. Specialty Honey Products:
- Model: Producing unique honey-based products such as flavored honey, honeycomb, or honey-infused goods.
- Advantages: Niche market appeal, potential for premium pricing, and product diversification.
4. Pollination Services:
- Model: Offering beehive rentals to agricultural businesses for pollination services, with honey production as a secondary income source.
- Advantages: Stable income through pollination contracts and additional honey revenue.
5. Value-Added Processing:
- Model: Processing raw honey into various value-added products like cosmetics, health supplements, or honey-based beverages.
- Advantages: Diversification, higher profit margins, and entry into niche markets.
6. Online Retail and E-commerce:
- Model: Selling honey and related products through online platforms, reaching a broader customer base.
- Advantages: Global reach, convenience, and potential for scalability.
7. Agritourism and Educational Ventures:
- Model: Combining honey production with guided tours, workshops, and educational experiences for visitors.
- Advantages: Multiple income streams, brand building, and community engagement.
Choosing the Right Model:
Choosing a suitable business model from the beginning is crucial, as switching your model later is more challenging.
Focusing on a niche allows you to be more focused and tailor your offers to a specific group while becoming a specialist instead of trying to become everything for everyone type of business.
Identifying a business model that feels right for your honey production business is essential for a more accessible and planned startup phase.
It sets the foundation for long-term success and sustainability in this dynamic industry.
c.) Challenges You Could Face When Starting and Operating a Honey Production Business
Challenges During the Startup Phase of a Honey Production Business
Starting a honey production business can be rewarding, but it comes with its share of challenges that aspiring owners should be prepared for:
- Beekeeping Knowledge: Acquiring the necessary knowledge of beekeeping practices and hive management can be daunting for newcomers. Understanding bee behavior, disease prevention, and seasonal hive care is crucial.
- Bee Health: Maintaining healthy bee populations is essential. Bee diseases and pests can threaten hives, requiring vigilance and proactive measures to prevent losses.
- Equipment and Infrastructure: Investing in beehives, extraction equipment, protective gear, and suitable land can be costly. Proper infrastructure is vital for efficient honey production.
- Marketing and Branding: Building a brand and marketing honey products effectively can be challenging. Finding your unique selling point and reaching your target audience is crucial.
- Regulatory Compliance: Complying with local, state, and federal regulations governing beekeeping, food safety, and labeling can be complex and time-consuming.
- Weather and Environmental Factors: Weather conditions and environmental factors can significantly impact honey production. Droughts, extreme temperatures, and habitat changes can affect bee foraging and honey yields.
- Competition: The honey market can be competitive. Differentiating your product and finding your market niche is a constant challenge.
Challenges When the Honey Production Business is Operating
Once the honey production business is up and running, a new set of challenges arises:
- Seasonality: Honey production is seasonal, and managing cash flow during off-seasons can be a challenge. Diversifying product lines or income streams may be necessary.
- Bee Health Maintenance: Continuous monitoring and management of bee health remains essential. Diseases, parasites, and hive stress can still threaten bee colonies.
- Quality Control: Ensuring consistent honey quality and adhering to industry standards is an ongoing commitment. Maintaining product excellence is crucial for customer satisfaction.
- Market Fluctuations: Honey prices can fluctuate due to market dynamics and environmental factors. Business owners must adapt pricing strategies accordingly.
- Scaling Production: Expanding production while maintaining quality and sustainability can be complex. Scaling too quickly or inefficiently can strain resources.
- Customer Retention: Keeping a loyal customer base requires consistent product quality and effective customer service. Building and retaining customer trust is an ongoing endeavor.
- Environmental Sustainability: Promoting bee health and environmental sustainability is increasingly important. Implementing sustainable practices and supporting pollinator-friendly initiatives may be required.
- Regulatory Changes: Staying updated on evolving regulations and compliance requirements is necessary. Adapting to changes in food safety or labeling regulations is crucial.
Navigating these challenges, both during the startup phase and while operating a honey production business, demands resilience, dedication, and a proactive approach.
Overcoming these obstacles can lead to a successful and sustainable enterprise in the honey industry.
d.) Questions You Need to Consider for Your Honey Production Business
Questions to Consider for Your Honey Production Business
To embark on a successful journey in the honey production business, answering the following questions is essential.
These considerations will help you anticipate and address potential challenges and lay a strong foundation for your venture:
What Business Model Suits You?
- What type of honey production business model are you considering?
Skills and Competency:
- Do you have the skills needed to manage and operate a honey production business?
Sole Operator or Team?
- Will you do all the work alone, or will you hire employees?
Management Approach:
- Do you intend to manage your business, or are you planning to hire a manager?
Customer Acquisition:
- How will you get customers?
- Who are you competing against?
- How will you keep customers coming back?
Partnerships and Investment:
- Are you interested in finding partners or investors?
Financial Planning:
- How will you finance your startup costs?
- Have you considered how long it will take to become profitable?
Sustaining Early Operations:
- How will you support yourself during the early stage of operation, which can be financially challenging?
Product and Service Portfolio:
- What products and services will you offer?
- How do you know people will want what you have to offer?
Competitive Edge:
- What will you provide that sets you apart from your competition?
Market Positioning:
- How will you position your Honey Production Business—High-End, Average, or Discount operation?
These questions serve as the groundwork for your honey production business plan. They prompt critical thinking, guiding you in making informed decisions and mitigating potential pitfalls.
Careful consideration of these aspects will help you shape a clear business strategy and set achievable goals.
Whether you’re a newcomer or an experienced beekeeper, addressing these inquiries is a crucial step toward establishing a thriving and sustainable honey production business.
3. Research
Inside information honey production business research.
Essential Preliminary Research
Before embarking on any business endeavor, comprehensive research is paramount for a successful honey production venture.
Information Is Key
Quality information equips you with a clear understanding of the industry landscape. Without it, you risk unforeseen challenges.
Seek Wisdom from Experts
Engaging with experienced honey production business owners is invaluable. Their insights, gleaned from years of practice, offer a priceless perspective.
Unlocking Insights
Time spent with seasoned professionals grants access to a wealth of knowledge and valuable insights.
Navigating the Path
Identifying the right individuals to connect with is a critical step, and this article provides guidance on approaching them effectively.
For an in-depth exploration of this topic, refer to the article “An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start” for comprehensive insights and strategies.
See An Inside Look Into the Business You Want To Start for all the details.
Supply, Demand, and Your Location
Understanding the supply and demand dynamics in the honey production business is critical before diving in.
Demand Assessment:
Evaluating the demand for your honey products and services is a fundamental step. Quality and pricing alone aren’t enough; substantial demand must exist to justify your venture.
Risk of Low Demand:
Insufficient demand can lead to business closure shortly after opening, leaving substantial debt in its wake.
Market Saturation Analysis:
Consider market saturation in your chosen niche. In oversaturated markets, gaining a foothold is challenging unless you offer unique value not replicated by competitors.
Innovative Differentiation:
Ask yourself if your competitors can easily replicate your ideas. If so, established players might dominate market share.
Understanding Your Competition:
Assess your competition, focusing on their strengths and weaknesses. Avoid competing with entities that outmatch your capabilities.
Identifying Your Unique Value:
Differentiate by providing something your competitors don’t. Determine if this offering aligns with customer preferences and willingness to pay.
Strategic Location Selection:
Choosing a business location involves a balancing act. Ideal locations strike a balance between demand and manageable competition.
Affordability and Exposure:
Consider affordability and exposure. Highly populated areas offer visibility but may entail higher expenses. Calculate whether these expenses justify potential profits.
Sustainable Sales Volume:
In less populated, cheaper areas, ensure a sufficient customer base exists to sustain sales and business operations.
Careful evaluation of these supply and demand factors, along with strategic location selection, is pivotal for a success.
For more, see the Demand for Your Products and Services and Choosing The Best Location for Your Business.
Target Audience
Understanding Your Target Audience
Comprehending your target audience yields several advantages.
It enables product and service adaptation, allowing a more precise alignment with customer interests.
This focused approach promotes customer satisfaction and loyalty by delivering what they truly desire, rather than a broad range of products.
Target Market Ideas:
- Health-conscious consumers seeking natural sweeteners.
- Gourmet chefs and culinary enthusiasts valuing premium honey.
- Eco-conscious individuals supporting sustainable beekeeping.
- Local food markets and artisanal product enthusiasts.
- Nutrition-focused consumers interested in honey’s health benefits.
- Small-scale food and beverage producers requiring quality honey as an ingredient.
- Gift shoppers seeking unique, locally sourced products.
- Beekeeping hobbyists seeking supplies and expertise.
For more, see How To Understand Your Target Market.
4. Looking at Financials:
Understanding the numbers and making good decisions is a crucial factor in succeeding.
You will struggle to manage a successful operation without putting in the time and effort to understand and monitor the financials of your honey production business.
Let’s look at startup costs, operating costs, and profits.
Start-Up Costs:
Estimating Startup Costs
Accurate estimation of startup costs is pivotal for a seamless journey from planning to opening your honey production business.
Underestimation Pitfall:
Underestimating can lead to financial shortfalls, delaying your startup.
Overestimation Risks:
Conversely, overestimation may deter potential investors, making your venture seem high-risk.
Factors Influencing Costs:
Your startup expenses hinge on several factors:
- Operation size
- Chosen location
- Hiring employees or acquiring equipment
- Business premise (rented, leased, home-based, or online)
Estimation Process:
Create a comprehensive list of required items and gather price quotes. Additional expenses may surface during research.
Unique Ventures:
No one can provide an exact cost since each honey production setup differs.
Business Model Matters:
Start by defining your business model. Online setups are generally more cost-effective than brick-and-mortar or home-based operations.
Complex Variables:
Many variables affect costs, making thorough research and precise estimates imperative. Accurate estimations help determine the viability of your honey production business endeavor.
Sample Startup Cost For a Honey Production Business
The purpose of the list below is to focus on the items in the list more than the numbers because these are general samples, and your figures will be different.
Sample List of Estimated Startup Costs for a Mid-Sized Honey Production Business in the USA
Note: These estimates can vary significantly depending on location, scale, and specific business decisions.
1. Beekeeping Equipment:
- Beehives (20-50 hives): $5,000 – $15,000
- Hive tools, smokers, and protective gear: $1,000 – $2,500
- Extractors, honey tanks, and processing equipment: $3,000 – $7,000
2. Bees and Queen Bees:
- Bee packages or nucleus colonies (20-50 colonies): $2,000 – $5,000
- Queen bees: $50 – $100 per queen
3. Land and Location:
- Purchase or lease of land suitable for beekeeping: $10,000 – $50,000 (varies by region)
- Site preparation and fencing: $2,000 – $5,000
4. Business Registration and Licensing:
- State and local permits and licenses: $500 – $2,000
- Business insurance: $1,000 – $2,500
5. Marketing and Branding:
- Brand identity development: $1,000 – $2,500
- Marketing materials and website creation: $2,000 – $5,000
6. Initial Bee Food and Medication:
- Sugar syrup, pollen supplements, and medications: $500 – $1,500
7. Transportation:
- Beekeeping vehicle (used): $5,000 – $15,000
- Fuel and maintenance: $1,000 – $2,500
8. Staffing:
- Wages for seasonal workers (if applicable): $2,000 – $5,000
9. Education and Training:
- Beekeeping courses and workshops: $500 – $2,000
10. Miscellaneous Expenses: – Safety equipment and first aid supplies: $500 – $1,000 – Office supplies and administrative costs: $1,000 – $2,500
Total Estimated Startup Costs (Lower Value): $33,000
Total Estimated Startup Costs (Upper Value): $104,600
These estimates provide a range of potential startup costs for a mid-sized honey production business in the USA. Your numbers will vary based on individual circumstances and location.
For more, refer to my article on Estimating Startup Costs.
Monthly Operating Costs:
Your monthly expenses mirror the considerations discussed in startup costs. Several variables influence these ongoing operational expenses.
Staffing Impact:
Choosing between running your honey production business independently or with a full staff significantly shapes monthly outlays.
Location Significance:
The choice of location plays a crucial role. High-traffic areas often command higher expenses compared to less frequented areas.
Diverse Factors:
Monthly expenses encompass a range of variables, from loan repayments to marketing campaigns and repairs.
Prioritizing Efficiency:
To maintain peak business performance and navigate revenue fluctuations, it’s vital to minimize costs that don’t compromise quality, service, or productivity.
Balancing cost control while preserving essential aspects of your operation is key to sustained success.
Sample list of estimated monthly expenses for a MID-sized honey production business
Again, the purpose of the list below is to focus on the item in the list more than the numbers. The numbers are a general idea, and your numbers and list will differ.
Sample List of Estimated Monthly Expenses for a Mid-sized Honey Production Business in the USA
Note: These are sample estimates and can vary based on specific circumstances and location.
1. Employee Salaries and Wages:
- Beekeepers and seasonal workers: $3,500 – $7,000
2. Rent or Mortgage Payment:
- Land or facility rental or mortgage: $1,500 – $3,500
3. Utilities:
- Electricity, water, and gas: $500 – $1,000
4. Insurance:
- Business liability and property insurance: $200 – $500
5. Beekeeping Supplies:
- Replacement beekeeping equipment and maintenance: $300 – $600
6. Bee Food and Medications:
- Monthly bee food, treatments, and medications: $200 – $400
7. Marketing and Advertising:
- Online and local marketing efforts: $500 – $1,500
8. Transportation:
- Fuel, vehicle maintenance, and insurance: $300 – $800
9. Loan Payments:
- Monthly loan repayments (if applicable): $1,000 – $2,500
10. Miscellaneous Expenses: – Repairs and maintenance, office supplies: $300 – $600
Total Estimated Monthly Expenses (Lower Value): $7,000
Total Estimated Monthly Expenses (Upper Value): $17,900
These estimates provide a range of potential monthly expenses for a mid-sized honey production business in the USA.
Actual expenses will vary based on individual circumstances and location.
Considerations for Profits
While profit margins are known, your net profit hinges on how you manage your honey production business. High overhead can reduce profits even with substantial sales.
Your Unique Scenario:
Estimating your honey production business’s profit is a personalized endeavor. You know your business setup and operational approach best.
Positioning Matters:
Your business positioning, whether high-end, high-quality, or discount, directly influences profit margins.
Calculating Profit:
Estimate by calculating the cost per sale, monthly sales volume, and subtracting overhead costs to gauge potential profit.
Sales Strategy:
Consider sales volume alongside profit per sale. Striking a balance ensures expenses are covered, leaving room for a healthy profit.
Individual Variables:
Numerous factors impact profitability, and as the business owner, you are best equipped to estimate your potential earnings.
For More, See Estimating Profitability and Revenue.
Final Thoughts on Financials
Financial Vitality
The financial aspects of a honey production business are pivotal for sustainable operations. Beyond mere record-keeping for tax and legal compliance, active financial monitoring is paramount.
Profit and Expense Tracking:
Regularly monitoring profits and expenses through detailed reports unveils valuable trends and insights into your business’s financial health.
Detecting Anomalies:
Imagine a sudden drop in weekly sales. Monitoring allows swift investigation into potential causes such as market shifts, product or service issues, or new competitors.
Proactive Problem-Solving:
Without vigilant financial oversight, critical issues may remain hidden until they escalate beyond remedy.
Strategic Decision-Making:
Studying financial data empowers informed decisions, enabling timely adjustments to maintain business stability and profitability. Financial vigilance is the bedrock of a thriving honey production enterprise.
5. Create Your Mission Statement
Defining Purpose with a Mission Statement
A mission statement serves as the compass guiding your honey production business.
It succinctly articulates your purpose, helping you maintain focus and a clear sense of the primary value you offer to customers and the community.
Sample Mission Statements for a Honey Production Business:
- To sustainably produce high-quality honey, fostering environmental stewardship and supporting local beekeeping communities.
- Our mission is to deliver pure, natural honey products that promote health and well-being, sourced responsibly from our own hives.
- Dedicated to preserving the vital role of bees, we strive to provide the finest honey, pollination services, and education to enrich lives and ecosystems.
- We are committed to crafting artisanal honey products, celebrating the unique flavors of nature, and nurturing the vital connection between bees and people.
- At our core, we aim to share the sweetness of nature with the world, offering pure, unprocessed honey that embodies the essence of our pristine surroundings.
These mission statements illustrate the diverse ways a honey production business can define its purpose, from sustainability and community support to product quality and environmental stewardship.
For more, see How To Create a Mission Statement.
6. Creating A Unique Selling Proposition (USP)
Crafting Uniqueness with a USP
A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is the key to setting your honey production business apart. It identifies and creates that distinct quality or feature that makes your brand unique in the marketplace.
A well-defined USP not only helps you stand out but also resonates with customers, giving them a compelling reason to choose your honey over others.
Sample USPs for a Honey Production Business:
- Single-Origin Excellence: Our honey is sourced from a specific region, capturing unique flavors and terroir, delivering a taste of the land in every jar.
- Eco-Conscious Beekeeping: We prioritize sustainability, employing ethical beekeeping practices that protect pollinators and their ecosystems, ensuring pure, guilt-free honey.
- Varietal Honey Selection: Discover a diverse range of honey varieties, each with distinct tastes and health benefits, curated for culinary enthusiasts and health-conscious consumers.
- Artisanal Blending: Our expert honey artisans skillfully blend and infuse honey with natural ingredients, creating unparalleled gourmet experiences.
- Community Connection: Supporting local beekeepers and promoting bee education, we cultivate a sense of community and awareness around the importance of bees.
These USPs highlight the potential uniqueness of a honey production business, from environmental responsibility and product diversity to regional specificity and community engagement.
7. Choose a Business Name
Selecting a suitable name for your honey production business is crucial. It should strike a balance between catchiness and industry relevance.
Remember, this name will likely remain with your company throughout its existence, so take your time in choosing.
Memorability Matters:
Opt for a name that’s easy to pronounce and easy to remember. A memorable name can leave a lasting impression on potential customers.
Online Presence:
In today’s digital age, securing a matching domain name for your business’s online presence is essential for consistency and visibility.
Avoid Duplicates:
Ensure the name you desire isn’t already registered by another business to prevent legal complications.
Here Is a List of Sample Honey Production Business Names:
- BeeBliss Honey Co.
- Nature’s Nectar Harvest
- HiveCrafters
- PureBloom Honey
- GoldenBee Acres
- HoneyHarvest Provisions
- PollenCraft Honeyworks
- BuzzMasters Apiary
- HoneyCrest Creations
- Hive & Harmony Honey
- Wildflower Essence Honey
- The Honey Haven
- BeeBounty Farms
- GoldenGrove Apiaries
- HoneyBloom Ventures
- Apiary Allure
- BuzzWorthy Honey Co.
- PurePollen Honeyworks
- BeeHaven Delights
- SweetNectar Acres
- BuzzLuxe Beekeeping
- BeeJoyful Harvest
- Nature’sGold Bee Co.
- HoneyMeadow Provisions
- BeeZen Honeyworks
- GoldenPollen Apiary
- HiveGrace Creations
- SweetHarvest Hive
- PollenGlow Honey
- BeeGrove Essentials
This list serves as inspiration to spark your creativity and craft an original, fitting name for your honey production business.
For more, see the following articles:
- How To Register a Business Name
- Registering a Domain Name For Your Business
8. Register Your Company
Legal Compliance for Your Honey Production Business
Ensuring the legality of your honey production business is paramount for smooth operations and peace of mind.
Consulting with a professional can provide valuable guidance on legal structures, tax benefits, and liability protection.
Common Types of Registrations:
- Business Entity Registration: Register your business as a legal entity, such as a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation.
- Trade Name Registration: If operating under a business name different from your legal entity, register a “Doing Business As” (DBA) or trade name.
- Employer Identification Number (EIN): Obtain an EIN from the IRS for tax purposes, especially if you plan to hire employees.
- Sales Tax Permit: Depending on your location, you may need a sales tax permit to collect and remit sales tax on honey sales.
Permits and Licenses:
- Food Establishment Permit: Required for food production and sales, including honey.
- Apiary Registration: Register your beekeeping operations with the appropriate agricultural department or agency.
- Health Department Permits: If you process or package honey, check if you need health department permits.
- Local Business Licenses: Check with your local municipality for any required business licenses.
- Environmental Permits: If your beekeeping activities impact the environment, you may need environmental permits.
- Transportation Permits: If you transport bees or honey, verify if transportation permits are necessary.
- Import/Export Licenses: For international honey trade, explore import/export licensing requirements.
Navigating the legal landscape of a honey production business involves several facets, and professional advice and comprehensive research can ensure compliance and smooth operations.
Registration:
- How to Register Your Business
- How To Register a DBA
- How to Register a Trademark
- How to Get a Business License
Business Structures:
- How to Choose a Business Structure
- Pros & Cons of a Sole Proprietorship
- How To Form an LLC
- How To Register a Business Partnership
- How To Form a Corporation
- How To Choose a Business Registration Service
9. Create Your Corporate Identity
A Corporate ID is a visual representation of your business, encompassing elements like your logo, business cards, website, signage, stationery, and promotional materials.
Consistency in design across these components is key to leaving a professional and lasting impression on both new and existing customers.
You can see our pages for an overview of your logo , business cards , website , and business sign , or see A Complete Introduction to Corporate Identity Packages.
10. Writing a Business Plan
A well-crafted business plan is not just a formality but an essential document. It serves multiple purposes, acting as a guide during startup and full operation, a tool for securing financing, and a communication tool for potential investors.
Invest Time and Effort for a Vision
Creating an effective business plan is a task that demands time and effort. It involves articulating a vision for your fully operational business, requiring careful consideration of details.
While the process may seem intensive, the end result is worth it. A comprehensive plan provides a clear roadmap for both starting and running your business.
Diverse Creation Options
When developing your business plan, you have several options at your disposal. You can choose to start from scratch, seek the assistance of a professional, utilize a template, or employ business plan software.
Regardless of your chosen approach, active involvement in the process is crucial. Effective communication of your business’s nature and management strategy is key, especially when hiring a professional.
Adaptation and Optimization
Recognize that your business plan and operations are not set in stone. As you gain experience and respond to changes in the market, your business plan may require adjustments.
Periodic review and optimization of the document ensure that your business remains aligned with your goals and responsive to evolving circumstances. Stay flexible, and be ready to make necessary changes for sustained success.
Business Plan Template for a Honey Production Business
Note: This business plan template serves as a comprehensive guide for your honey production business. Customize each section to suit your specific goals, market, and operational requirements.
1. Executive Summary
Overview of your business, including the mission statement, business name, location, and key leadership.
- Mission Statement: Clearly define the purpose and values of your honey production business.
- Business Name and Location: Provide the chosen name and address of your business.
- Leadership Team: Introduce key team members and their roles.
2. Business Description
Detailed insights into your honey production business.
- Business Concept: Explain the core idea and unique selling proposition (USP) of your honey production venture.
- Market Analysis: Present research on the honey industry, target market, and competition.
3. Products and Services
In-depth information on the honey products and services you offer.
- Product Portfolio: Describe the types of honey and related products you produce.
- Quality Assurance: Explain the measures taken to ensure product quality.
4. Market Research
Comprehensive market analysis and strategies.
- Target Audience: Define your ideal customer demographics.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze key competitors and their strengths and weaknesses.
- Market Trends: Discuss industry trends and consumer preferences.
5. Marketing and Sales Strategy
Detailed plans for promoting and selling your honey products.
- Marketing Plan: Outline your marketing channels, strategies, and budget.
- Sales Approach: Describe your sales tactics and distribution methods.
6. Organization and Management
Information on your business’s structure and leadership.
- Legal Structure: Specify your business’s legal structure (e.g., LLC, sole proprietorship).
- Management Team: Present bios and responsibilities of key team members.
7. Financial Projections
Comprehensive financial data, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow projections.
- Start-up Costs: List initial expenses and funding requirements.
- Sales Forecast: Projected revenue and sales growth.
- Budget: Present a detailed budget for at least the first year.
8. Funding Requirements
If seeking external funding, provide details on the amount, source, and use of funds.
- Financing Needs: Specify the amount of funding required.
- Use of Funds: Describe how the funds will be utilized.
9. Risk Analysis
Identification and mitigation strategies for potential risks.
- Market Risks: Address risks related to market fluctuations.
- Operational Risks: Discuss potential challenges in production and distribution.
10. Appendices
Supplementary information and supporting documents.
- Resumes: Include detailed resumes of key team members.
- Market Research: Attach any market research data and analysis.
- Legal Documents: Include licenses, permits, and contracts.
- Financial Projections: Attach detailed financial projections.
- Other Relevant Documents: Include any additional documents relevant to your business plan.
Remember to revise and update your business plan regularly to reflect changes in your business environment and goals.
A well-crafted plan serves as a roadmap to guide your honey production business to success.
See How to Write a Business Plan for information on creating your business plan.
11. Banking Considerations
Selecting the Right Financial Partners
Opt for a local bank with a strong small business focus.
A dedicated business account ensures a clear separation between personal and business transactions, simplifying expense tracking and accurate tax reporting.
Cultivate a professional rapport with your banker, benefiting from their financial expertise and streamlined services.
Additionally, consider setting up a merchant account or online service to accept credit and debit card payments, enhancing sales and customer convenience.
For more, see How to Open a Business Bank Account. You may also want to look at What Is a Merchant Account and How to Get One.
12. Getting the Funds for Your Operation
Securing Financing for Your Honey Production Business
When seeking funds to kickstart your honey production business, consider these strategies:
- Traditional Lenders: Explore loans from banks and credit unions, especially those with experience in small business lending.
- Private Loans: Seek private investors or lenders who are willing to support your venture.
- Asset Liquidation: Evaluate the option of selling assets you own, like equipment or real estate , to generate initial capital.
- Government Grants: Research potential government grants or subsidies available for new businesses in the honey production sector.
Meeting with a Loan Officer: Key Considerations
Before meeting with a loan officer, prepare thoroughly:
- Understand your business plan and financial needs.
- Determine the loan amount and repayment terms you require.
- Check your credit score and address any issues.
- Be ready to discuss your personal and business financial history.
- Anticipate questions about collateral and your ability to repay.
Sample List of Documents for Business Loan Application:
- Business plan with financial projections.
- Personal and business tax returns.
- Financial statements (balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement).
- Business licenses and permits.
- Personal and business bank statements.
- Collateral information (if applicable).
- Personal identification and social security number.
- Resumes of key team members.
- Business credit report (if available).
Presenting a well-organized loan application package enhances your chances of securing the necessary funds for your honey production business.
For more, see the following:
- Getting a Small Business Loan
- SBA Small Business Grants
- Search: Honey Production Business Start-up Loans
- Search: Grants For a Honey Production Business
13. Software Setup
Choosing the Right Software
Selecting software for your honey production business involves careful considerations:
- Implementation Ease: Research software options thoroughly as it’s easier to start with the right system than switch later with data complications.
- Vendor Reliability: Opt for a company with a proven track record, ensuring dependable support for the long term.
- Demo Opportunities: Whenever possible, try out software demos before committing to ensure it meets your specific needs.
- User Feedback: Explore software reviews and forums for insights from other users to gauge performance and reliability.
- Financial Management: Consider software for expense tracking and financial document preparation to facilitate tax filing.
Consulting with your bookkeeper or accountant can provide valuable guidance in selecting the most suitable accounting software for your business.
Types of Software for Honey Production Business:
- Inventory Management Software: Tracks honey production and storage.
- Accounting Software: Manages finances, tracks expenses, and generates financial reports.
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software: Helps maintain customer relationships and sales records.
- Quality Control Software: Monitors product quality and safety.
- Website and E-commerce Software: Facilitates online sales and marketing.
- Supply Chain Management Software: Manages sourcing of honey and production materials.
- Marketing and Social Media Management Software: Aids in promoting the business and engaging with customers.
- Shipping and Logistics Software: Streamlines product delivery and distribution.
- Data Analytics Software: Analyzes market trends and consumer behavior.
- Production Software: Specifically designed for beekeeping and honey production operations.
Choosing the right combination of software tools can streamline operations and enhance efficiency in your honey production business.
Check out Google’s latest search results for software packages for a honey production business.
14. Get The Right Business Insurance
Securing Adequate Business Insurance
Ensuring your honey production business is adequately insured is vital to safeguard against unforeseen incidents.
Here are key considerations:
- Coverage Scope: Assess the different aspects of your business that require protection, including customers, employees, property, and more.
- Professional Liability Insurance: Protect yourself from potential lawsuits and claims by considering professional liability insurance, especially if you offer consulting or expert advice.
- Business Interruption Insurance: This coverage can be a lifeline in case of an incident that forces an involuntary shutdown, helping your business weather unexpected disruptions.
- Expert Guidance: Collaborate with a knowledgeable insurance broker who understands the intricacies of the honey production industry. They can tailor a policy that aligns with your specific needs and ensures comprehensive coverage.
- Regular Reviews: Periodically review and update your insurance coverage to account for changes in your business operations, growth, or potential new risks.
Having the right insurance coverage in place not only protects your business but also provides peace of mind, allowing you to focus on growing your honey production venture without undue worry over potential setbacks.
For more, see What to Know About Business Insurance . You can also browse the latest Google search results for honey production business insurance .
15. Suppliers and Service Providers
Selecting Reliable Suppliers and Service Providers
Building strong relationships with suppliers and service providers is pivotal for the success of your honey production business.
Here’s what you may need and why these relationships matter:
1. Honey Suppliers: Establishing a partnership with dependable honey suppliers ensures a consistent source of high-quality honey, a cornerstone of your product.
2. Beekeeping Equipment Suppliers: Reliable access to beekeeping tools and equipment is vital for smooth operations.
3. Packaging Suppliers: Trustworthy packaging suppliers provide containers and materials that maintain honey quality and appeal to customers.
4. Transportation Services: Efficient and reliable transportation services are essential for the distribution of your honey products.
5. Marketing and Advertising Services: Collaborating with professionals in marketing and advertising can help you reach a broader audience and promote your honey brand effectively.
6. Accounting and Financial Services: Financial experts can assist with bookkeeping, taxes, and financial planning, ensuring your business remains financially sound.
7. Legal Services: Legal advisors help navigate regulations, contracts, and intellectual property protection, safeguarding your business interests.
Building respectful and mutually beneficial relationships with these suppliers and service providers can lead to competitive prices, consistent product quality, and a streamlined business operation.
These partnerships contribute significantly to the overall success of your honey production business.
For More, See How To Choose a Supplier.
16. Setting Prices
Pricing Strategies for Your Honey Production Business
Researching pricing strategies is crucial when establishing your honey production business. Here’s why:
1. Competitive Advantage: Understanding your market allows you to set competitive prices, ensuring you stand out while attracting customers.
2. Profit Maximization: Setting the right prices ensures profitability, enabling you to cover expenses and reinvest in your business.
3. Customer Perception: Proper pricing communicates value. It’s essential to strike a balance between affordability and quality to appeal to your target market.
4. Sales Optimization: Accurate pricing can drive sales and revenue while avoiding the pitfalls of underpricing or losing customers due to overpricing.
5. Long-Term Sustainability: Maintaining appropriate pricing ensures your business remains financially stable, supporting growth and longevity.
By carefully researching and implementing effective pricing strategies, you can position your honey production business for success in a competitive market.
See the following for more:
- Setting the Price of Your Products and Services
- Search Results for Pricing Strategies for a Honey Production Business.
17. Physical Setup
Inventory Management
When running a honey production business, efficient inventory management is crucial.
1. Customer-Centric Selection: Prioritize stocking products your customers desire. Understand your target market’s preferences and provide value through a well-curated inventory.
2. Balance Inventory Levels: Striking the right balance in inventory levels is essential. Overstocking ties up capital that could be better used elsewhere, while understocking leads to lost sales opportunities.
3. Strategic Display: How you display your products significantly impacts sales. Experiment with different displays and record their effectiveness. Optimize your layout to maximize visibility and accessibility.
Expiry Date Awareness
For products with expiry dates, it’s crucial to manage inventory effectively:
1. Avoid Nearing Expiry: Prevent carrying products with approaching expiration dates. Regularly check your inventory to ensure you’re offering fresh products to your customers.
2. Maintain Balance: Finding the right balance between stocking enough to meet demand and avoiding excessive quantities with short shelf lives is vital.
Layout and Signage
A well-planned layout and effective signage enhance your honey production business:
1. Layout Overview: The layout should be designed for efficiency and customer convenience. Ensure smooth flow from production to display areas, optimizing space for both staff and customers.
2. Professional Signage: Professional signage adds credibility to your business. Install clear and informative signs, including your main business sign, parking lot signs, exit signs, and special area signage. Well-placed signs enhance the overall customer experience.
Office Organization
Managing your honey production business efficiently requires an organized office:
1. Productivity Boost: An organized office space increases productivity. Ensure your office is well-equipped with the necessary tools, resources, and technology to manage your business effectively.
2. Time Management: Time is a valuable resource. Streamline your office setup to save time on administrative tasks, allowing you to focus on core business activities.
A well-organized inventory, thoughtfully planned layout, effective signage, and an efficient office setup all contribute to the success of your honey production business.
See Here are Considerations for The Setup of Your Office for tips and ideas to make your office work for you. Also, have a look at our article About Company Signs.
18. Creating a Website
Establishing Your Online Presence
In today’s digital age, having a robust online presence, including a website, is indispensable for your honey production business:
1. Central Hub: Your website serves as the primary point of contact for potential customers. It provides essential information about your business, products, and services.
2. Ownership and Control: Unlike social media accounts, your website is fully owned and controlled by you. Registering your domain name and hosting your site gives you autonomy and ownership.
3. Marketing Tool: Utilize your website as a powerful marketing tool. Engage with your audience by creating informative blog posts that resonate with your customers.
Sharing industry insights and valuable tips not only builds trust but positions you as an industry expert in your customers’ eyes.
A well-designed website offers a competitive edge, helps establish credibility, and fosters customer trust, making it a critical component of your honey production business’s success.
For more, see How to Build a Website for Your Business .
19. Create an External Support Team
Building Your External Support Team
Establishing an external support team of professionals is a vital asset for your honey production business. Here’s why it matters:
1. Dependable Advisors: Your external support team consists of trusted individuals who provide advice and services on an as-needed basis. They are not on your payroll, which offers flexibility in utilizing their expertise.
2. Diverse Expertise: While you may already collaborate with some professionals, recognizing them as part of your team underscores their significance. Expanding your team’s diversity can bring in new skills and perspectives.
3. Time Investment: Building strong professional relationships takes time. Start with essential members, such as an accountant, lawyer, financial advisor, and marketing specialist, and gradually expand your network.
4. On-Demand Assistance: When your team is in place, you can rely on them for critical support when needed, whether for financial guidance, legal matters, marketing strategies, or technical expertise.
Your external support team is a valuable resource, enhancing your business’s resilience and ensuring you have the right experts at your disposal when challenges arise.
For more, see Building a Team of Professional Advisors for Your Business.
20. Hiring Employees
Expanding Your Team as Your Business Grows
While initially managing your honey production business alone can be cost-effective, growth may require you to hire employees.
1. Managing Costs: Operating solo initially helps keep expenses low, but growth may necessitate expanding your team.
2. Qualified Personnel: When hiring employees, prioritize individuals with relevant qualifications and strong work ethics .
3. Right Fit: Ensure every new hire is well-suited for their role and shares your commitment to the business’s success.
Job Positions and Services:
As your honey production business expands, consider these job positions or outsourced services:
- Honey Production Manager
- Sales and Marketing Specialist
- Quality Control Inspector
- Administrative Assistant
- Customer Service Representative
- Packaging and Inventory Manager
- Beekeeping Expert
- Accountant or Bookkeeper
- Web Developer or IT Support
- Legal Advisor or Consultant
- Supplier and Vendor Relationships Manager
This list provides a foundation for building a capable team to support your growing business effectively.
For more, see How and When to Hire a New Employee.
21. Getting Customers Through the Door
When you have reached this step, your business is set up and ready to go, with one more final step, which is important: getting customers through the door.
There are numerous ways to do this, like advertising, having a grand opening , word of mouth, etc.
Let’s dig a little deeper into the following sections.
a.) Marketing Considerations
Attracting the Right Customers for Your Honey Production Business
For your honey production business to thrive, attracting the right customers is crucial.
Here are some key points to consider:
1. Building Reputation: In the early stages, building a strong reputation is essential as your business is new and relatively unknown.
2. Ongoing Marketing: Marketing is an ongoing process that becomes more manageable and effective over time as you gain experience.
3. Marketing Investment: The more you invest in effective marketing techniques, the greater your revenue potential.
4. Expertise Not Always Required: While you don’t always need a marketing agency or expert, consider this option if it aligns with your business goals.
Simplifying Marketing:
Here are a few simple methods to raise awareness about your honey production business:
- Social Media: Create profiles on platforms like Instagram and Facebook to showcase your products and engage with potential customers.
- Local Events: Participate in local farmers’ markets or food festivals to introduce your honey to the community.
- Online Presence: Develop a user-friendly website with information about your honey, production methods, and contact details.
- Word of Mouth: Encourage satisfied customers to spread the word about your high-quality honey to their friends and family.
- Networking: Join industry-related groups and associations to connect with potential partners, suppliers, and customers.
- Collaborations: Partner with local businesses or artisans to cross-promote products and expand your customer base.
By utilizing these simple marketing methods, you can effectively spread the word about your honey production business and attract the right customers.
See How To Get Customers Through the Door and our marketing section to provide ideas to help you bring awareness to your business.
b.) The Market Can Guide You:
Drawing from years of business experience, here’s a piece of advice: pay close attention to your customers’ desires.
While you may have a specific product or service in mind for your honey production business, the market might indicate a demand for something slightly different.
You might be tempted to stick to your original plan, and that’s understandable, but it’s crucial not to ignore market signals.
If you consistently notice signs of demand for variations or new products or services, take a step back and consider them. Ignoring these signals could mean missing out on the opportunity for your business to thrive.
While your vision is vital, being adaptable and responsive to your customers’ changing preferences can be equally essential.
Ultimately, it’s your business, and the decisions are yours to make.
However, keeping an open mind and being willing to adjust to meet market demands can be a wise strategy for long-term success.
c.) Sample Ad Ideas:
- Discover the golden goodness of our locally sourced, artisanal honey. Taste the difference today!
- Our all-natural honey is packed with antioxidants and goodness. Elevate your well-being with each spoonful.
- Unwrap the sweetness of gifting with our exquisite honey collection. Share nature’s golden treasure!
- Experience the rich, authentic taste of honey straight from our sustainable hives. A pure delight!
- Support local beekeepers and enjoy premium honey. Good for you, great for our planet!
These ads aim to showcase the quality, health benefits, and uniqueness of the honey products, enticing potential customers to explore and purchase from the honey production business.
d.) B2B Ideas
Collaborative partnerships can be mutually beneficial for businesses.
Here are some businesses you could approach to work within a referral program and ideas on how to reward them.
- Approach health food stores to promote your honey as a natural sweetener for their organic products. In return, offer to display their promotional material in your store or on your website.
- Collaborate with bakeries to use your honey in their products. You can refer customers to them for fresh bread and pastries, while they can recommend your honey for sweetening.
- Partner with tea shops to offer honey as a natural sweetener for their teas. In exchange, they can promote your honey to their tea-loving clientele.
- Participate in farmers’ markets and cross-promote with nearby vendors. Refer customers to neighboring stalls, and they can do the same for your honey.
- Collaborate with health and wellness coaches who can recommend your honey as a healthy alternative to refined sugars. In return, refer clients to their services.
- Partner with cafes committed to sustainability. They can serve your honey with coffee and snacks, and you can promote their eco-friendly practices.
- Work with nutritionists who can advocate your honey for its health benefits. In return, refer clients seeking dietary guidance to their services.
- Approach yoga studios to offer your honey for post-workout smoothies and teas. They can direct their clients to your honey, and you can refer customers to their yoga classes.
- Collaborate with food cooperatives to have your honey featured in their organic product sections. You can cross-promote each other to members.
- Partner with family restaurants for them to use your honey in kids’ menu items. In exchange, promote their family-friendly atmosphere and menu.
Reward these businesses by offering referral fees for each customer they send your way, referring your clients to them, or engaging in co-marketing efforts that benefit both your business and theirs.
Building these strategic partnerships can expand your customer base and provide added value to your customers while supporting other local businesses.
Points To Consider
Next, let’s review essential points for more tips, insights, and considerations before starting your honey production business.
We will cover sections, including skills to consider, points to focus on, and equipment. Then you’ll reach the “Knowledge Is Power,” section, where you will want to use the resources for valuable information.
Key Points to Succeed in a Honey Production Business
Here are key points to succeed in both the setup and operation phases of a honey production business:
Setup Phase:
- Market Research: Thoroughly research your target market, competition, and consumer preferences to identify a niche.
- Business Plan: Create a comprehensive business plan outlining your goals, strategies, and financial projections.
- Legal Compliance: Ensure your business is registered, licenses obtained, and all legal requirements met.
- Funding: Secure adequate funding to cover startup costs, equipment, and initial inventory.
- Quality Control: Establish stringent quality control measures for honey production and packaging.
- Supplier Relationships: Build strong relationships with suppliers for consistent and quality honey sources.
- Equipment and Technology: Invest in modern honey extraction and processing equipment for efficiency.
- Branding and Packaging: Develop an appealing brand identity and packaging that stands out on the shelves.
- Marketing Plan: Create a marketing strategy for product promotion and customer acquisition.
- Distribution Channels: Set up effective distribution channels to reach your target markets.
Operation Phase:
- Quality Maintenance: Continuously monitor and maintain honey quality to meet customer expectations.
- Inventory Management: Keep a well-managed inventory to meet demand without overstocking.
- Customer Service: Provide excellent customer service, addressing inquiries and concerns promptly.
- Marketing & Promotion: Maintain marketing efforts to retain existing customers and attract new ones.
- Adaptation: Stay agile and adapt to changing market trends and customer preferences.
- Sustainability: Focus on sustainable honey production and eco-friendly practices.
- Cost Control: Manage operational costs efficiently to maintain profitability.
- Employee Training: Ensure your team is well-trained in honey production and customer service.
- Feedback Loop: Establish a feedback loop to gather customer feedback and make improvements.
- Financial Management: Keep a close eye on financials, monitor cash flow, and plan for growth.
Success in both phases relies on diligent planning, a commitment to quality, and adaptability to changing market dynamics.
Making Your Honey Production Business Stand Out
- Unique Honey Varieties: Offer a wide range of honey varieties, including rare and unique flavors such as lavender, eucalyptus, or wildflower, to attract customers seeking something different.
- Local Sourcing: Emphasize locally sourced honey, showcasing the connection to your region and supporting local beekeepers.
- Organic and Sustainable Practices: Highlight your commitment to organic and sustainable beekeeping practices, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers.
- Artisanal Packaging: Invest in distinctive, artisanal packaging that not only preserves honey quality but also makes your product visually appealing.
- Honey-Based Products: Diversify your product line with honey-based items like beeswax candles, honey-infused skincare, or honey mustard, offering customers more than just plain honey.
- Educational Experiences: Organize beekeeping workshops, farm tours, or honey tastings to educate customers about honey production and create memorable experiences.
- Subscription Boxes: Offering a honey subscription service that delivers unique honey varieties and honey-related products to customers regularly.
- Collaborations: Partner with local artisans or chefs to create exclusive honey-infused products or collaborate on limited-edition releases.
- Online Presence: Build a strong online presence, including a user-friendly website and active social media profiles to engage with customers and share your story.
- Customer Stories: Share stories of beekeepers, local suppliers, and the journey of honey production to connect with customers on a personal level.
- Health Benefits: Highlight the health benefits of raw honey, emphasizing its natural sweetness and potential medicinal properties.
- Customization: Offer personalized honey jars for special occasions, weddings, or corporate gifts, allowing customers to customize labels.
- Community Engagement: Engage with the local community by participating in farmers’ markets, community events, or partnering with local charities.
- Beekeeping Education: Provide resources on beekeeping practices and the importance of bees in pollination to raise awareness.
- Honey Tasting Events: Organize honey tasting events where customers can sample various honey varieties and learn about their unique flavors.
Ideas for Add-Ons for a Honey Production Business:
- Beekeeping Equipment: Sell beekeeping equipment and supplies, catering to hobbyist beekeepers and expanding your customer base.
- Honey-Related Merchandise: Offer honey-themed merchandise such as t-shirts , mugs , and kitchenware for fans of your brand.
- Honey-Infused Foods: Create a line of honey-infused food products like honey mustard, honey barbecue sauce, or honey-flavored snacks.
- Beekeeping Workshops: Organize beekeeping workshops and training sessions for beginners and advanced beekeepers, sharing your expertise.
- Apiary Tours: Offer guided tours of your apiary, allowing visitors to witness beekeeping practices firsthand.
- Bee-Friendly Plants: Sell bee-friendly plants and seeds that support pollinators, encouraging customers to create bee-friendly gardens.
- Honey Subscriptions: Offering a subscription service that delivers curated honey selections, recipes, and honey-related products to subscribers.
- Gift Baskets: Create gift baskets featuring an assortment of honey varieties, beeswax candles, and honey-infused products, ideal for gifting.
- Honey-Based Cosmetics: Develop a line of skincare and beauty products using honey and beeswax, tapping into the growing demand for natural cosmetics.
- Honey Tasting Kits: Assemble honey tasting kits with small jars of different honey varieties and tasting notes for a unique experience.
- Honey-Infused Beverages: Partner with local breweries or distilleries to produce honey-infused beers, meads, or spirits.
- Educational Books and Materials: Sell books, guides, and educational materials on beekeeping, honey production, and the importance of pollinators.
- Beekeeping Services: Offer beekeeping services, such as hive maintenance, swarm removal, or pollination services to local farms and gardens.
- Honey-Related Art and Crafts: Collaborate with local artists to create honey-themed art and crafts for sale at your store.
- Honey Certification Courses: Provide certification courses in beekeeping and honey production, attracting individuals interested in pursuing beekeeping as a profession.
These ideas can help your honey production business stand out and offer valuable add-ons that cater to a diverse customer base, fostering growth and success in the competitive market.
Equipment and Supplies
A List of Equipment and Supplies to Consider for a Honey Production Business:
- Beehives (Langstroth, Top Bar, or Warre)
- Hive covers and inner covers
- Hive frames with foundation
- Queen excluders
- Hive stands or pallets
- Entrance reducers
- Beekeeping suits or jackets
- Beekeeping veils or helmets
- Beekeeping gloves
- Beekeeping boots or gaiters
- Smoker and smoker fuel
- Hive tools (hive brush, frame grip, uncapping knife, etc.)
- Queen marking kit
- Hive feeders (entrance, frame, or top feeders)
- Swarm capture equipment (swarm box, bait hives, or swarm lures)
- Honey extractors (manual or motorized)
- Uncapping knife or roller
- Uncapping scratcher
- Honey settling tank or bucket
- Strainers and sieves
- Bottling tanks or containers
- Bottling equipment (jars, lids, labels, and filling equipment)
- Honey creaming machine (if producing creamed honey)
- Honey warming cabinet or warming trays
- Honey pumps and bottling lines (for larger operations)
- Honey pumps and filters (for removing impurities)
- Storage cabinets for beekeeping equipment
- Shelving units for storing honey jars and supplies
- Climate-controlled storage for honey
- Varroa mite treatments
- Hive beetle traps
- Bee supplements and feed (pollen patties, sugar syrup, etc.)
- Bee medications and treatments (if needed)
- Beehive transportation equipment (hive straps, pallets, or trailers)
- Vehicle suitable for hive transportation
- Honey refractometer (for measuring moisture content)
- Honey color grading kit (if selling different honey varieties)
- Custom honey labels
- Packaging materials (jars, lids, shrink bands, and honeycomb labels)
- Honey bottling and labeling equipment (for larger-scale operations)
- First aid kit
- Fire extinguisher (for honey extraction areas)
- Safety goggles and gloves
- Computers and software for record-keeping
- Accounting software or services
- Administrative supplies (desk, chairs, filing cabinets, etc.)
- Marketing materials (brochures, business cards, flyers , etc.)
- Point of sale (POS) system or cash register
- Online store setup (website, e-commerce platform, or online marketplace account)
- Beekeeping reference books and guides
- Educational materials for beekeeping workshops and courses
- Security cameras and alarms (for larger-scale operations)
- Fencing or bee barriers (to protect hives from predators)
- Rainwater harvesting system (for hive watering)
- Solar panels or alternative energy sources (for sustainable operations)
Please note that the specific equipment needed may vary depending on the scale of your honey production business and your beekeeping practices.
It’s essential to assess your requirements and budget accordingly when acquiring these items.
Honey Buyer Guides
Buyer guides serve as a valuable resource because they offer insights and perspectives that you, as a business owner, might not be aware of.
By paying attention to buyer guides, you can gain a deeper understanding of your customers’ needs, preferences, and pain points.
This knowledge allows you to fine-tune your honey production business, make necessary improvements, and ultimately provide better value to your clientele.
See the latest search results for honey buyer guides.
Assessing Your Skill Set:
Before diving into a honey production business, it’s essential to evaluate your skill set. Your abilities will play a significant role in your business’s success.
Take a closer look at your strengths and weaknesses in areas like beekeeping, business management, marketing, finance, and problem-solving.
Addressing Skill Gaps:
If you find gaps in your skill set, don’t fret.
You have options. You can either invest time and effort in learning and honing these skills or consider hiring experts who can complement your abilities.
Acquiring the necessary skills is crucial to tackle the challenges that may arise in the honey production industry.
Essential Skills for a Honey Production Business Owner:
- Beekeeping Expertise: A deep understanding of beekeeping techniques, hive management, and honey extraction is fundamental.
- Business Management: Efficiently running the business, including planning, organization, and decision-making, is vital.
- Marketing Skills: Promoting your honey and products to reach a broader audience and drive sales.
- Financial Acumen: Managing finances, budgeting, and keeping track of expenses and revenue.
- Problem-Solving Abilities: The capacity to troubleshoot issues that may arise in beekeeping or business operations.
Assessing and enhancing these skills will position you for success in the competitive world of honey production.
Considering the Future of Your Honey Production Business:
Contemplating the future of your honey production business is essential, even in a rapidly evolving landscape.
A well-defined vision serves as a guiding light, aiding in strategic decision-making and ensuring your business progresses in alignment with your aspirations.
It allows you to adapt and steer your enterprise towards the desired destination, despite the uncertainties of tomorrow.
In an ever-changing industry, a clear vision provides stability and purpose, enabling you to proactively shape the future rather than merely reacting to it.
Find a Honey Production Business For Sale
Exploring the acquisition of an existing honey production business offers distinct advantages and drawbacks worth considering before starting your own venture.
- Immediate Revenue: Taking over an established business means revenue starts flowing from day one.
- Skip Startup Phase: You avoid the challenges and uncertainties associated with starting from scratch.
- Proven Success: An existing business has a track record of profitability, expenses, and operational efficiency.
- Customer Base: You inherit an existing customer base, ensuring a ready market.
- Reputation: The business comes with an established reputation, potentially boosting trust and sales.
- Higher Cost: Acquiring a business typically involves purchasing goodwill, increasing the overall cost.
- Change Risks: Altering established practices can lead to customer losses and operational challenges.
- Inherited Reputation: Both positive and negative aspects of the business’s reputation become yours.
While an exact match for a honey production business for sale may not be available, exploring similar industry options can uncover valuable opportunities. Carefully weigh the pros and cons to determine if acquiring an existing business aligns with your goals.
The latest search results for a honey production business for sale and others in the same category.
Franchise Opportunities Related to a Honey Production Business
Considering a honey franchise has its merits and drawbacks, it’s essential to evaluate them before starting your honey production venture.
- Proven Business Model: Franchises offer a well-defined business plan created by the corporate office, reducing the guesswork.
- Reputation and Marketing: Benefit from an established brand and existing marketing efforts, potentially accelerating your business’s growth.
- Comprehensive Knowledge: You gain in-depth insights into the business’s operations before you start.
- Corporate Support: Franchisees receive support and guidance from the corporate office, aiding in problem-solving and business development.
- High Costs: Initial investment and ongoing franchise fees can be substantial.
- Limited Autonomy: Significant changes or business alterations often require corporate approval.
- Product and Service Constraints: Franchises typically restrict the products and services you can offer.
- Operational Restrictions: You must adhere strictly to the terms of the franchise agreement.
While there may not be a perfect honey production franchise, exploring related franchises can uncover opportunities you hadn’t considered. Evaluate the pros and cons carefully to determine if a franchise is the right path for your honey business venture.
See the latest search results for franchise opportunities related to this industry.
Knowledge Is Power if You Use It!
Knowledge empowers action. Abundant industry information, accessible through the provided links, aids both the startup and operational phases of your business.
Trends and Statistics
Examining industry trends and statistics is crucial for honey production businesses.
It enables informed decision-making, staying competitive, and adapting to market dynamics.
See the latest search results for trends and statistics related to the honey industry.
Honey Associations
Trade associations provide benefits like industry news updates and networking opportunities, aiding professionals in staying informed and connected.
See the search results related to honey associations and the benefits of Joining the Chamber of Commerce.
The Top Honey Producers
Analyzing an existing honey production business sparks innovation, identifies industry gaps for competitive advantage, and uncovers overlooked opportunities for improvement.
See the latest search results for the top honey producers.
The Future of the Honey
Researching the industry’s future is vital for aspiring honey producers. It provides insights into trends and challenges, aiding informed decision-making and long-term success planning.
See the search results for the future of honey production
Customer Expectations
Reviewing search results for customer expectations in honey consumption offers valuable insights.
It allows you to align with customer desires, and uncover potential issues.
See the search results related to customer expectations for honey consumption.
Expert Tips
Analyzing expert tips enhances skills for both novices and experts. Experts may discover efficient methods, while novices gain valuable knowledge to improve their abilities.
See the latest search results for honey production to gain tips and insights.
Honey Production Business Insights
Examining tips and insights can uncover innovative ideas, highlight pitfalls to avoid, and enhance your knowledge in the honey production industry.
See the latest search results about insights into running a honey production business.
Honey Publications
Publications provide valuable honey-related tips and insights, serving as a reliable source of information in the field.
See the search results for honey production publications.
Honey Forums
Exploring honey forums fosters industry connections and customer insight.
Engage in discussions to gain a deeper understanding of your customer base and their perspectives.
See the latest search results related to honey forums.
Online or local courses enhance skills and knowledge, benefiting your honey production business. Education is a valuable asset in this field.
See the latest courses that could benefit a honey production business owner . Also, see our management articles for tips and insights for managing your business.
Honey Blogs
Subscribing to leading honey blogs provides insights and keeps you industry-current.
Subscribe to those of value, trimming those outdated. Curate a valuable collection for a steady flow of information.
Look at the latest search results for top honey production blogs to follow.
Production-Based Business Tips
Examining advice and knowledge for success in honey production enables effective management, fostering sustainable, long-term success in your honey business.
Look at the latest search results for production tips and insights to follow.
The news serves as a valuable resource to stay informed about media-covered honey-related stories, helping you stay up-to-date on relevant information.
See the latest results for honey production news.
Watching YouTube videos about honey production provides an additional information source to enhance your understanding of the subject.
YouTube videos related to honey production.
Privacy Overview
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

BEEKEEPING Business Plan-AINEYA KENNEDY.docx

The apiculture business plan here is a detailed information on a natural beekeeping business plan for a community based organization. The plan also detailed the most products of beehive like, pollen, propolis, wax, royal Jelly and bee honey.
Related Papers
Alebachew Tilahun
Samir Abedelsaid
Beekeeping or apiculture is the preservation of honey bee colonies to get pure honey and helps in pollination. Beekeeping is a useful mean of strengthening livelihoods because it creates a variety of assets. The main focus of the study was to assess the impact of beekeeping training given by Society of facilitator and Trainer (SOFT) to females in Sargodha and Chakwal district. Capacity building of rural women in beekeeping was the focus and fifteen trainees’ beekeepers were selected randomly from each district for survey to assess the impact of beekeeping in their livelihood. The analysis suggests that there are some social and cultural barriers which restrict women to go out in the fields for the management practices of beekeeping. For future selection criteria of participants have to be focused and without the involvement of male member they can’t manage this whole activity in a better way. For young females it was very difficult to handle bees, proper colonies management, their s...
Abebe Mitikie
This study was conducted in Tehuleder district, Eastern part of Amhara region to characterize the beekeeping system, analyze the potentials and constraints for beekeeping and suggest possible solutions for existing problems, identify major honeybee flora and their flowering periods, and determine the major honey quality in different agro-ecology of the study area . Data were collected from 120 beekeepers having bee colonies and living in three different agro-ecologies. The study had two parts: part one was data collection among beekeepers with a semi-structured questioner by single- visit-multiple-subject formal survey method. From the total 120 sample beekeepers 92.5 % of them were male headed households, 95.8 % of them are married, mean age of the respondents was 48.97±11.03 years and they owned 105, 17 and 57 traditional, transitional and frame hived colonies respectively. The study result indicates that based on their level of technological advancement, three distinct types of beekeeping practices were used by the sample beekeepers in the area. These are traditional (local) hive based, transitional (Ethio-ribrab top bar) hive based and moveable frame (box) hive based beekeeping practices. Most of the beekeepers in the study area kept both traditional, transitional and frame beehives at their eave of the house, only 10.8% feed their colony at dearth, 95.5% of them increases colonies by catching the swarm colonies. The mean honey yield of traditional, transitional and framed type hives was 5.64, 12.7 and 16.9 kilogram per year, respectively and all of the respondents sell the unstrained honey directly to local market. Drought or rain dependent of the agriculture (76.7%), increased cost of production (75%), pests and predators (47.5%), application of pesticides and herbicides (43.3%) and lack of bee forages 32.5% are the major constraints to tackle the development of beekeeping in Tehuledere district. The second part of the study was the determination of honey quality produced in the study district. 24 honey samples was collected from crushed comb (traditional and transitional hive) honey and framed hive honey as two distinct groups from the represented 3 different agro-ecologies of the district directly from the apiary farm gates with tightly closed half a kilogram of plastic containers analyzed for eight honey quality parameters (moisture content, total reducing sugar, pH, acidity, diastase activity, sucrose content, HMF and mineral content) in the Food Chemistry and Analysis laboratory of School of Chemical and Food Engineering, Bahir Dar University, Ethiopia. The mean moisture content, mineral content, acidity, pH, HMF, diastase activity, sucrose content, and total reducing sugar, are 16.7%, 0.07%, 22.3 meq acid/kg, 3.85±0.46, 37.7 mg/kg, 14.4 Goth scale, 4.04 % and 64.3meq/kg respectively. All the eight determined parameters showed that 100 % of the sample means were situated in the acceptable range of the world honey quality standard set by Codex Almentarious, 2001. Package designing for implementation of improved practices, gaining of efficient seasonal trainings, plantation of drought tolerant bee forages, establishment of diversified beekeeping products collection and processing centers, integrating the responsible crop scientists, animal science experts and other administration organizations for efficient utilization of agrochemicals are recommended to enhance the sector.
European Scientific Journal ESJ
The study examined The Role of Beekeeping in Forest Conservation and Poverty Alleviation in Moshi Rural District. It was guided by the following research objectives firstly to examine the challenges of beekeeping, secondly to identify the market, products and technology used in beekeeping and lastly to examine the contributions of beekeeping on forest conservation and poverty alleviation in Moshi rural district. The study employed mixed research design where by 70 beekeepers were sampled. Both primary and secondary data were employed in this study. Different methods were used in data collection which included house hold questionaire, interviews, wealth ranking, observation and focus group discussion. Statistical package for social science (SPSS) version 16 and microsoft excel were used to analyze quantitative data. Findings revealed that 40% of sampled beekeepers agreed that beekeeping contributed to forest and biodiversity conservation through afforestation programs. which imply Results revealed that there is strong positive relationship (r = 0.718) between numbers of beehives and liters of honey produced in a year in Moshi rural district. Majority, 75% of the sampled beekeepers disagreed to the fact that beekeeping contributes to poverty alleviatio. This is because majority lacks skills, reliable market and appropriate technology. The findings further revealed that financial constraint is the most emerging challenge where by 62% of the respondents said they lack finaces to buy modern beehives.
IASET US , fauzia anjum , Wali Khan , EDITOR IASET
Beekeeping or apiculture provides nutritional, economic and ecological security to rural communities as an additional income generating activity. The study was conducted to analyze the impact of honeybee keeping on the sustainable livelihoods development in Bajuar agency, Khyber PakhtunKhwa Pakistan. Primary data have been collected from randomly selected 80 beekeepers with the help of pretested schedule through research designed questionnaire. Descriptive statistics; frequency, mean and percentages were employed in data analysis. On average landholding of the beekeepers was 18.46 acres per household ranging from zero to 320 acres and the honey productivity per household was 1295 kg ranges from 10-6000 Kg. The mean beehives holding were 60.45 per household ranges from 2-665 hives. The average annual household income per beekeeper has been observed to be higher (Rs.527275) followed by the non-beekeeping sources (Rs.180300). The Pre and Post Beekeeping mean annual expenditures of the sample size household was Rs.164200 and Rs.257912 respectively. The major constraints listed by the beekeepers were shortage of effective bee flora during bee hives migration, pest and diseases attack, lack of professional training, extension services, credit facility and transportation. Most of the beekeepers have been observed to be potential or expand its production and productivity on sustainable basis.
Impact Assessment of Beekeeping in sustainable rural livelihood
Journal of Social Sciences COES&RJ-JSS
Beekeeping or apiculture is the preservation of honey bee colonies to get pure honey and helps in pollination. Beekeeping is a useful mean of strengthening livelihoods because it creates a variety of assets. The main focus of the study was to assess the impact of beekeeping training given by Society of facilitator and Trainer (SOFT) to females in Sargodha and Chakwal district. Capacity building of rural women in beekeeping was the focus and fifteen trainees’ beekeepers were selected randomly from each district for survey to assess the impact of beekeeping in their livelihood. The analysis suggests that there are some social and cultural barriers which restrict women to go out in the fields for the management practices of beekeeping. For future selection criteria of participants have to be focused and without the involvement of male member they can’t manage this whole activity in a better way. For young females it was very difficult to handle bees, proper colonies management, their supplement feeding, honey extraction, movement of hives etc. Economically, beekeeping increased keepers’ income but this ratio was very low in the targeted area. Training had to be gender based for sustaining livelihood. There are some problems identified by the beekeepers. Finally the authors have drawn some recommendations for future beekeeping trainings. In not shell there was no positive impact of beekeeping training of rural women.
Viktor Fursov
Priyatelenko V.Ya., Fursov V.N., Ilienko E.V. Effective Vasyl Priyatelenko's three-storey beehive with unique frames. – Abstracts of 44-thInternational Beekeeping Congress “Apimondia”, Daewon, South Korea, 15-20. September, 2015. – 2015, p.253-254
Gluschenko-Nikodim V.P., Fursov V.N. Effective technology of Mother of God’s beekeeping, with high productivity of honeybee rearing. – Abstracts of 44-th International Beekeeping Congress “Apimondia”, Korea, 15-20. September, 2015. – 2015, p.263. (in English)
Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Andrzej K Kuropatnicki
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Claudia M Moreno
Shimelis Mengistu
Joel Buyinza
koleoso abdulateef
Awraris Getachew Shenkute
Irene Onyango , Shadrack Muya , George Michuki , Samuel Kabochi , Muo Kasina , Erastus Mbugua
Prof Dr Orhan Yılmaz
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- Agriculture Farming
- Livestock Farming
Project Reports
- Hydroponics
- Best Fertilizers
- Vertical Farming
- Sheep Farming
- Goat Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Fish Farming
- Pig Farming
- Dairy Farming
- Rabbit Farming
- Success Stories of Farmers
- Boost Fruit Yield
- District Wise Crop Production
- Schemes & Subsidies
- Agriculture Colleges
- Farm Insurance
- Disease Control And Management
Agriculture
Aquaculture
Horticulture
Agri Business
Buzzing Towards Success: Creating a Comprehensive Beekeeping Business Plan
Table of contents, land for honey beekeeping business, bee hives for beekeeping business, equipment for beekeeping business, honey bee colony in beekeeping, feed for bees in beekeeping business, labor for beekeeping business, capital for beekeeping business, market and demand for beekeeping business, key elements of a successful beekeeping business plan, executive summary of beekeeping business, market analysis of beekeeping business, beekeeping business operations and management, marketing and sales strategy for beekeeping business, financial projections and planning for beekeeping business.
As demand for natural and healthy alternatives to artificial sweeteners increases, beekeeping has become a popular and profitable business venture. Beekeeping provides farmers with various opportunities, including honey production, crop pollination services, and the sale of bees to other beekeepers.

However, starting a beekeeping business requires careful planning and considering resources, location, target market, and capital. To ensure success, conducting market research and developing a comprehensive beekeeping business plan before starting the project is important. This article will guide how to start a honey beekeeping business and create a successful business plan.
Comprehensive Beekeeping Business Plan
When starting a honey beekeeping business, finding the right location for your apiary is crucial to the success of your venture. The location of your bee yard can affect the quality and quantity of honey produced, as well as the health and productivity of your bees. You need to choose a location with a large concentration of flowering trees and plants and a reliable water source nearby.
The land should also have good air drainage and be free from pesticides that may harm your bees. Avoid windy areas, exposed hilltops, and river banks that may flood. Consider your area’s climate and ensure your bees can access shade and water during hot weather. The amount for purchasing or renting the land and its ongoing expenses should be factored into your beekeeping business plan.
Several types of beehives are available, such as fixed comb hives, top-bar hives, frame hives, Kenyan top-bar hives, Langstroth hives, and Warre beehives. The Langstroth beehive, developed in the 1850s, is the most well-known type, and the vertically-hanging frames make it easy for bees to build their comb. The Warre beehive is similar to the Langstroth but with simple slats that allow bees to build their comb downwards. The Top Bar Hive is the most recent design, providing a more convenient height and individual frames of comb.
Wood box material is the most commonly used material for beehives due to its durability, flexibility, and ability to regulate hive temperature and humidity. Painting the beehive with white or any other heat-radiating color can prolong its lifespan. The cost of purchasing beehives should be included in the business plan. Choosing the right beehive is essential for your beekeeping venture’s success, so take your time and choose wisely.
In addition to a beehive, several other equipment and supplies are necessary for a successful beekeeping business. Essential equipment includes wooden frames to hold beeswax sheets, a smoker to calm bees and reduce stinging, and a veil and gloves to protect against stings. You can use pine straw, grass, or burlap to fuel your smoker. Other protective clothing may also be required, such as bee suits/overalls and gumboots.
In case you missed it: 17 Key Rules for Effective Beekeeping Management: Basic Tips for Profitable Honeybee Farming
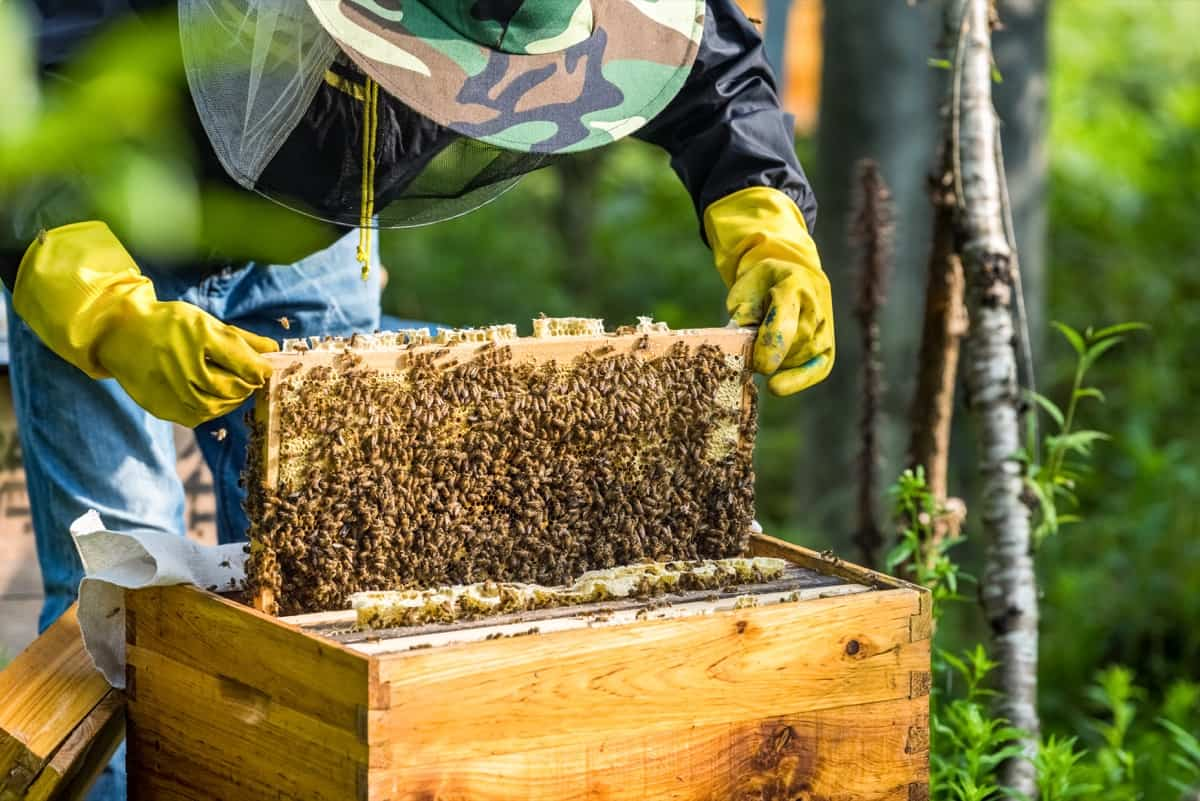

Feeders are necessary to hold sugar syrup that you can feed your bees. A hive tool set, including a bee brush, hive opener, and stainless-steel knife, is also important. The processing equipment required will depend on the size of your honey beekeeping business. This equipment includes storage containers, a refractometer, a centrifuge honey extractor, and a honey press.
Acquiring a honey bee colony is essential for a successful beekeeping business. There are several ways to obtain bees, such as purchasing from an existing colony or starting from a small nucleus colony purchased from another beekeeper. You can also capture a swarm or split an existing colony. Buying a colony from a reputable producer is a good way to ensure its health and breed. A colony consists of a queen, a few hundred drones, and thousands of workers.
The queen lays eggs, and worker bees carry out various tasks such as collecting nectar, making honey and wax, and cleaning the colony. Drones’ sole purpose is to mate with the queen. Each hive will contain one bee colony, so the number of bee colonies will determine the size of your beekeeping business. Factors to consider when purchasing a colony include the queen’s temperament, docility, color, productivity, and disease resistance. The business plan should include the cost of acquiring bee colonies.
Feeding and nutrition are essential for the success of the beekeeping business. Honey bees require a balanced diet of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, and water to survive and reproduce. The necessary nutrients are obtained from nectar, pollen, and honey. However, supplementary feeding may be necessary in certain cases to prevent bees from starving. Ensuring that the bees are fed the right nutrients appropriately is crucial. When feeding bees, avoid using honey from disease-infected hives.
Bee feeding should only be done in specific circumstances and not overused. Bees primarily obtain nutrients from nectar and pollen. They store nectar as honey and use pollen for protein, fats, vitamins, and mineral requirements. Water is also essential for regulating temperature and humidity in the hive and diluting stored honey. Bees also collect propolis, a natural substance that seals cracks and crevices in the hive. Beekeepers can use a cane, beet sugar, and isomerized corn syrup as supplementary feed for bees.
The size of a bee farming business determines the necessary number of employees, specifically beekeepers who will manage the hives, monitor the apiary, and handle honey harvesting and packaging.
In case you missed it: How to Start Honey Bee Farming/Beekeeping from Scratch: A Complete Guide for Beginners
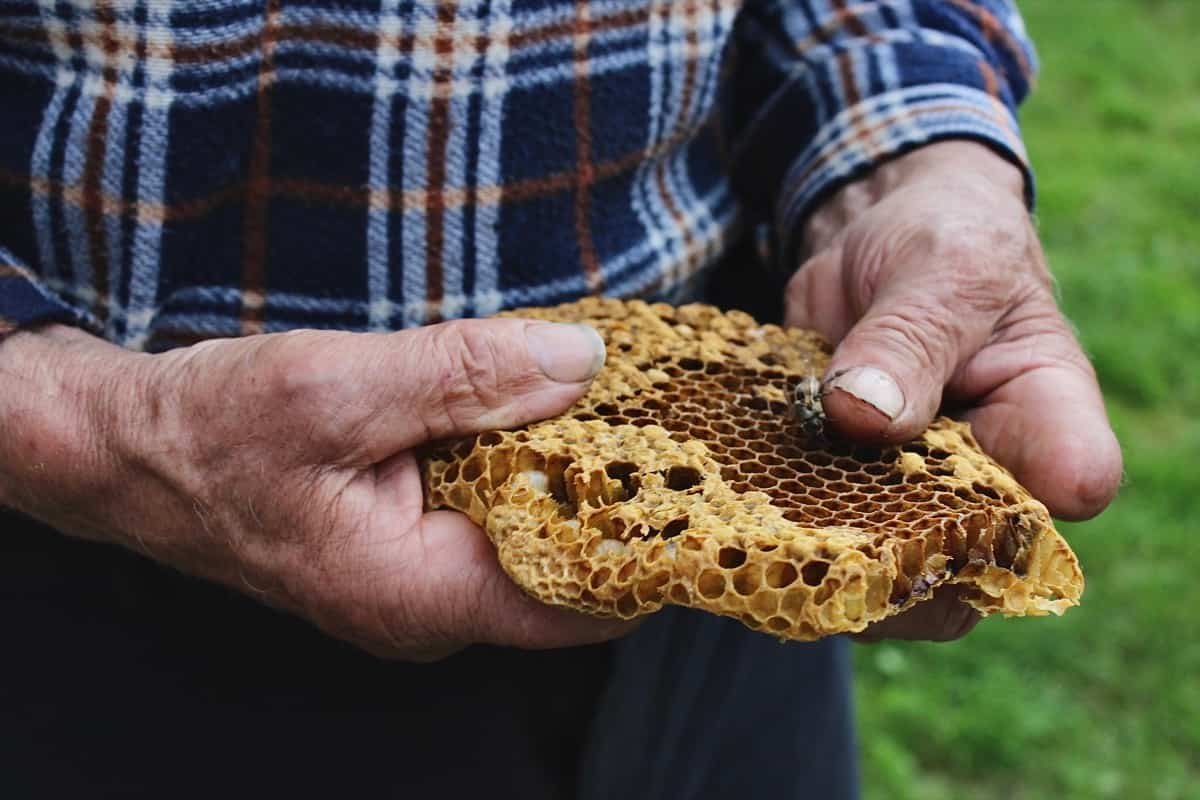

Entrepreneurs can obtain funding from banks or investors by presenting a comprehensive business plan. Those who lack access to such resources can rely on personal savings and gradually expand their business. Reinvesting profits can facilitate growth in the long run. Even without seeking loans, having a business plan is crucial to understanding the costs and making informed decisions. In short, a well-designed honey beekeeping business plan is essential for success, regardless of the funding source.
The main product of beekeeping is honey, a valuable and stable sweetener sold in its natural form and used in various industries, such as confectionery and cosmetology. Beekeepers also collect beeswax, which is used to make soap, polish, and candles. The market for honey is extensive, encompassing individuals, supermarkets, wholesalers, restaurants, and organizations.
The first step is to conduct thorough research on the market, potential customers, and competition. This information can help you identify your niche, target audience, and unique selling proposition. Next, you need to determine the scope of your business, including the scale, location, and necessary equipment and resources. Setting realistic financial projections and goals is also essential.
This involves estimating start-up costs, revenue, and expenses and identifying potential funding sources. Moreover, you should have a well-defined marketing strategy outlining reaching and engaging with customers. Your plan should also consider the legal and regulatory requirements of operating a beekeeping business, such as obtaining permits and adhering to safety and environmental standards.
The executive summary should provide a clear picture of the company’s goals, operations, and financial projections regarding a beekeeping business plan. Beekeeping is an industry that offers a range of opportunities for entrepreneurs, from honey production and beekeeping equipment sales to pollination services and beekeeping education. The executive summary of a beekeeping business plan should outline the business’s unique value proposition, such as its commitment to sustainability, high-quality honey production, or community education efforts.
The executive summary should also detail the company’s operational structure, including the size of the beekeeping operation, the number of hives, and the types of products and services offered. It should also highlight the company’s competitive advantages, such as its partnerships with local farmers or access to premium honey markets.
In case you missed it: How this Woman Made 2 Lakh per Month from Beekeeping: A Success Story of Honey Bee Farmer
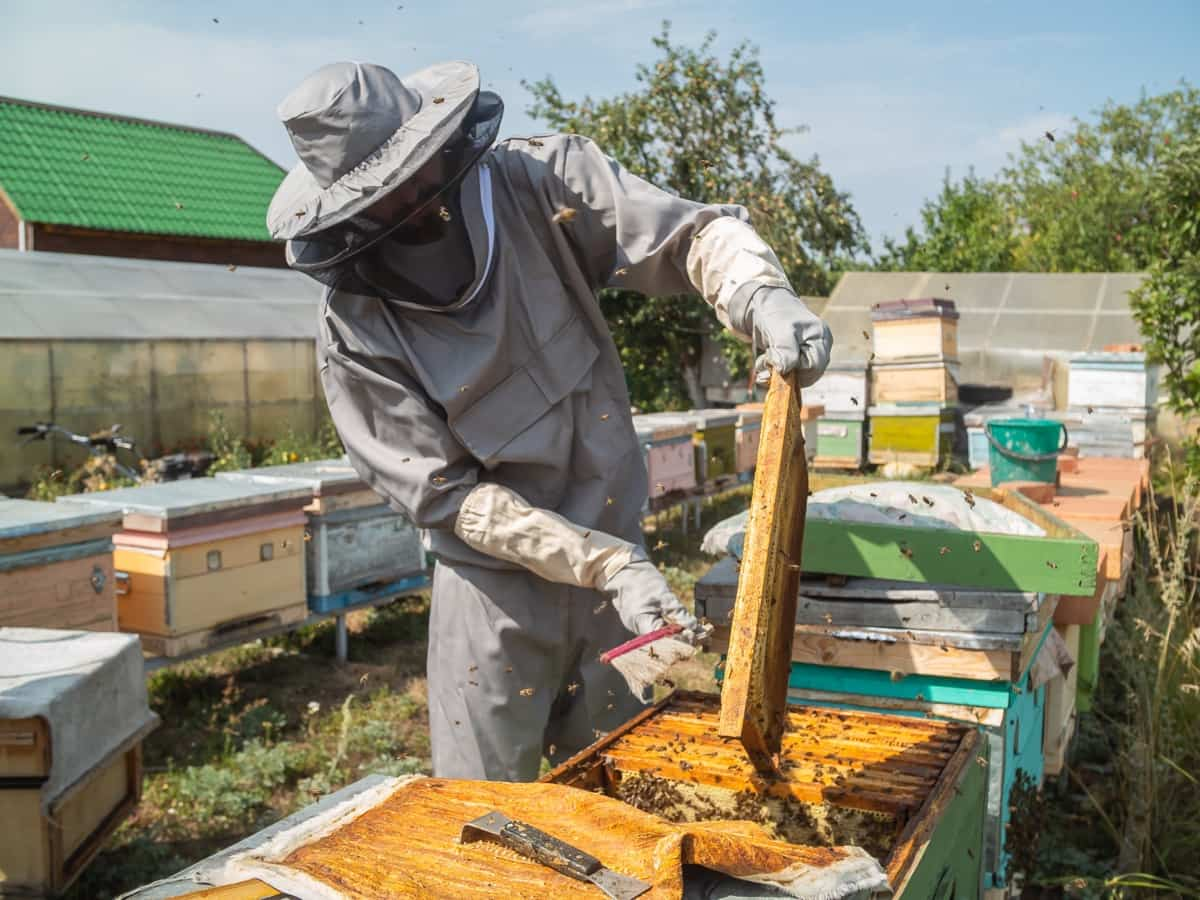

- The beekeeping industry has experienced steady growth over the past few years as demand for honey, beeswax, and other bee-related products continues to increase.
- The global market size was valued at USD 7.1 billion in 2020 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 6.0% from 2021 to 2028.
- The beekeeping business is highly dependent on weather conditions and the availability of flowers for bees to pollinate. This can cause fluctuations in the market and affect the supply and pricing of honey and other bee products.
- Beekeeping businesses can generate revenue by selling honey, beeswax, bee pollen, royal jelly, and other bee-related products.
- The beekeeping industry is increasing awareness of the health benefits of honey and other bee products. These products are used in various industries, including food and beverage, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals.
- The beekeeping industry is highly competitive, with many small-scale and large-scale players. To be successful, beekeeping businesses need to differentiate themselves through the quality of their products, branding, and marketing strategies.
- Beekeeping businesses can face challenges related to bee health and disease management, affecting bee colonies’ productivity and bee products.
Products and Services from Beekeeping Business
- Honey: Beekeepers collect honey from beehives and sell it as a natural sweetener.
- Beeswax: Beeswax is natural wax bees produce and can be used to make candles, soaps, and cosmetics.
- Royal Jelly: Royal jelly is a nutritious substance produced by honeybees and is sold as a dietary supplement.
- Propolis: Propolis is a resin-like substance produced by bees and is sold as a natural health supplement.
- Pollination: Beekeepers can rent their bees to farmers and orchard owners to pollinate crops, which increases yield and improves fruit quality.
- Swarm removal: Beekeepers can remove and relocate swarms of bees from residential or commercial properties.
- Beekeeping education: Beekeepers can offer classes or workshops on beekeeping, honey extraction, and related topics to educate and train people on the importance of bees and beekeeping.
- Honey extraction: Beekeepers can extract honey from beehives and sell it to wholesale or retail customers.
In case you missed it: Best Regenerative Agriculture Practices Every Grower Should Follow and Why It Is Important
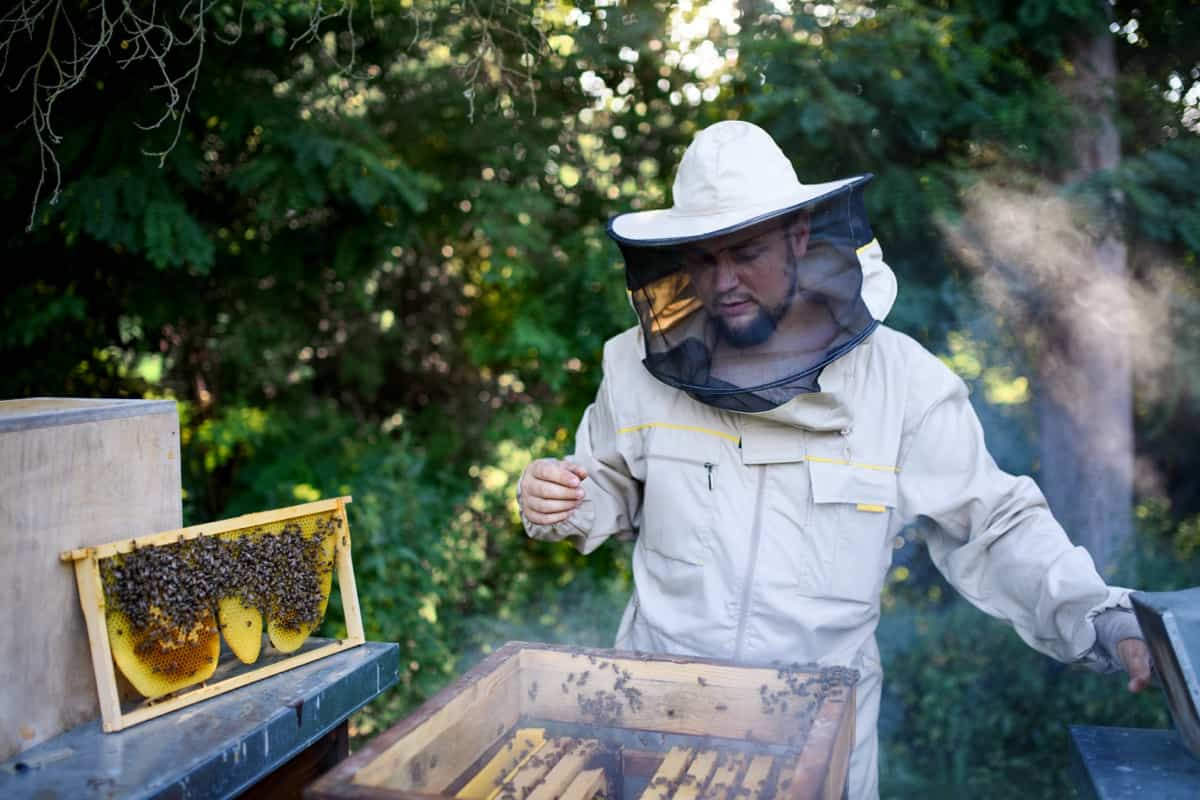

- The success of the beekeeping business depends on various factors, including the location, climate, availability of resources, and quality of management practices.
- To start a beekeeping business, you need to obtain the necessary permits, purchase or build beehives, purchase bees, and acquire beekeeping equipment such as protective gear, tools, and extractors.
- Beekeepers must monitor the health of their colonies regularly, provide adequate food and water, and manage pests and diseases that may affect their bees.
- The honey production season usually lasts from late spring to early summer, and beekeepers must harvest the honey and extract it from the comb to prevent spoilage.
- Beekeepers can sell their products directly to customers, through farmers’ markets, or to wholesalers or retailers.
- Beekeeping businesses’ marketing strategies include creating a brand, establishing a website or social media presence, attending trade shows, and collaborating with local businesses.
- Beekeepers must carefully manage their expenses, including equipment, labor, and bee feed costs to maintain profitability and sustainability.
- Identify your target audience (honey lovers, health-conscious consumers, etc.) and tailor your marketing message to them.
- Leverage social media platforms to showcase your product, share customer testimonials, and build brand awareness.
- Attend local farmer’s markets and craft fairs to sell your products and connect with potential customers.
- Offer promotions or discounts to incentivize purchases and encourage customer loyalty.
- Consider partnering with local restaurants or specialty food stores to sell your products.
- Email marketing keeps your customers informed about new products, promotions, and industry news.
- Analyze and adjust your marketing and sales strategy based on customer feedback and market trends.
- Financial projections will help determine the profitability of the beekeeping business and set realistic financial goals.
- The financial projections should include revenue forecasts, expenses, profit and loss statements, reports, and cash flow projections.
- In beekeeping businesses, expenses may include the purchase or leasing of land, beekeeping equipment and tools, protective gear, beehives, and bees.
- Other expenses may include marketing, advertising, insurance, licenses, and permits.
- It is also essential to consider the seasonal nature of the beekeeping business, as honey production is often highest in the summer months.
In case you missed it: 20 Eco-Friendly Farming Techniques to Achieve Sustainable Agriculture
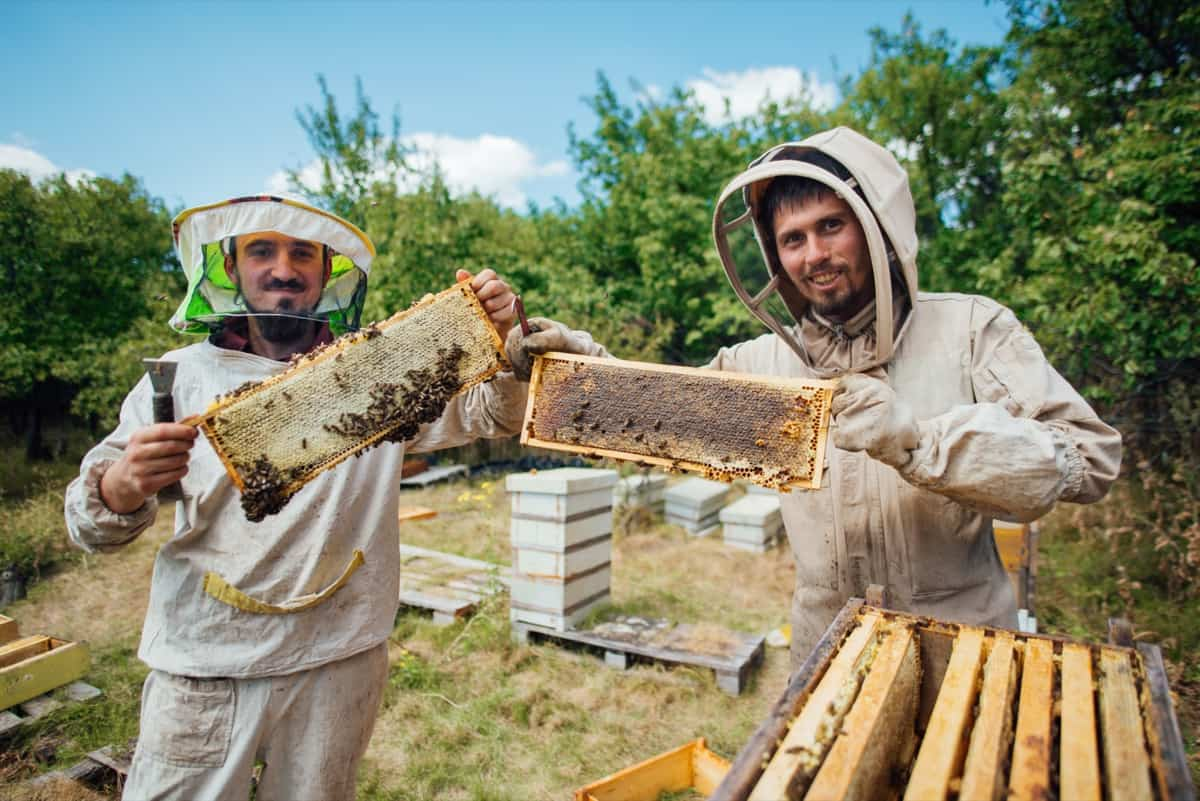

Beekeeping requires a detailed business plan. Financial predictions and planning assist in creating realistic financial objectives, managing spending and earnings, and making necessary modifications to keep on track. For a successful beekeeping business, consult professionals and experienced beekeepers.
Common Challenges in Strawberry Farming: A Beginners Guide
Maximizing yield in ridge gourd farming: best practices and tips .
- Sustainable Agriculture with CRFs (Controlled Release Fertilizers): A Game-changer for Crop Productivity
Organic Farming vs. Natural Farming (ZBNF): Key Principles and Differences
Strawberry nursery establishment and management, modi vision for indian agriculture, government support and policies for zbnf in india, deworming schedule for sheep: a beginners guide.
- Ultimate Guide to Beans Farming in Kenya: From Planting to Profits
Ultimate Guide to Natural Vegetable Farming
Natural farming for sustainable livestock management, dairy farm technology in india: the future of dairy husbandry, comprehensive guide to organic farming in villages, modern sheep farming technology: the future of sheep husbandry, goat farming technology: the future of goat husbandry.
- How to Build a Low-budget Goat Shed: Cheap Ideas and Tips
Goat Farming Training Programs in India: A Beginner’s Guide
Types of pesticides used in agriculture: a beginner’s guide, economical aquaculture: a guide to low-budget fish farming, 15 common planting errors that can doom your fruit trees.
- How to Make Houseplants Bushy: Effective Tips and Ideas
- Innovative Strategies for Boosting Coconut Pollination and Yield
- Pollination Strategies for Maximum Pumpkin Yield
- The Complete Guide to Chicken Fattening: Strategies for Maximum Growth
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
- Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
- How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Sustainable Agriculture with CRFs (Controlled Release Fertilizers): A Game-changer for...
Ultimate guide to beans farming in kenya: from planting to..., how to build a low-budget goat shed: cheap ideas and..., borewell drilling cost, pump price, and pipe cost, polyhouse subsidy, cost, profit, project report, tractor subsidy, bank loan, eligibility, schemes, process, malabar neem project report details guide, cold storage project report, cost and subsidy, mushroom farming project report, cost and profit analysis.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A Beekeeping Business Plan Needs To Cover Finances: costs, sales, cash flow, profit & loss. Consider these costs: Initial set up costs (hives, honey bees including nucs , beekeeping equipment and clothing, premises, insurances), building a website and hosting if needed and so on. Product related costs & inventory, such as honey jars and labels.
This article will outline how to start the honey beekeeping business, and the honey bee farming business plan - PDF, Word and Excel. Honey beekeeping is a lucrative business project that is providing income for a lot of people. There are some important things you need to consider before you setup such a business.
The amount needed to acquire / lease a farm land - $50,000. The Total Fee for incorporating the Business (commercial bee farm) in United States of America - $750. Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services (software, P.O.S machines and other software) - $3,300.
Marketing Plan. Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P's: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a beekeeping business, your marketing strategy should include the following: Product: In the product section, you should reiterate the type of honey bee farm that you documented in your company overview.
This sample beekeeping business plan will provide an idea for writing a successful beekeeping plan, including all the essential components of your business. After this, if you still need clarification about writing an investment-ready business plan to impress your audience, download our beekeeping business plan pdf .
5/1/202X - Finalize contract to lease office space. 5/15/202X - Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the Sweet Honey Bee Farm. 6/1/202X - Finalize contracts for Sweet Honey Bee Farm clients. 6/15/202X - Begin networking at industry events. 6/22/202X - Begin moving into Sweet Honey Bee Farm office.
An important tool necessary for the success of a honey bee farm business is the business plan. This article presents a sample honey bee farm business plan because of its importance to the stability of the business.. It provides guidelines which if well followed will result in the stability, profitability and growth of the entrepreneur's honey bee farm.
This causes fast & quality collection of honey. Also, if you want to migrate the bees hive, then migrate them near to any yard, in the start of flowering, just after that. Place honey collective hive to provide a site for your bees. It is likely more beneficial to place 5 hives for the Indian bees.
Business Description and Goals Cape Flats Honey is a new business that will initially focus on the retail of jars of pure honey and feral swarm relocation, defining the primary co-operative as a retail business. The honey to be sold will be pre-jarred wholesale honey purchased from the Honeybee Foundation. After labeling all jars with
Let's go through the content of each section in more detail! 1. The executive summary. In your honey bee farm's business plan, the first section is the executive summary — a captivating overview of your plan that aims to pique the reader's interest and leave them eager to learn more about your business.
Business Plan- AZONI Honey. Business Plan- AZONI Honey. Md. Zahidul Hasan. From a group research. ... Honey bee population worldwide is dwindling due to a number of interrelated factors among them pathogens such as viruses, bacteria, fungi and metazoan parasites. ... From the total 120 sample beekeepers 92.5 % of them were male headed ...
When starting the honey business, there are three main things to bear in mind: Providing shelter for the bees. How you will maintain the shelter in a suitable state for continued use by the bees. Harvesting honeybee products from the beehive. These three things are crucial to beekeeping and any honey business at large.
The business plan is your game. set objectives and guidelines. create a standard against actual results with your. identify problems quickly, unmanageable. keep on track. Because planning is so crucial important to examine every carefully and honestly. Be you are capable of and the your business.
Beekeeping Business Plan Example - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The Beekeeping Business Plan is a compass for beekeepers, ensuring happy hives, honey production, and market success. It's a roadmap to nurture buzzing companions and create a thriving, sweet venture in the world of beekeeping.
Beekeeping: At the core, beekeeping forms the foundation of a honey production business. This involves caring for beehives, ensuring the health and well-being of the bee population, and managing hives to optimize honey production. Harvesting and Extraction: Regular honey harvesting is essential.
Abstract. Honey as a natural product, is very important in human nutrition and human health. Bees are important for maintaining the ecosystem in the pollination process. The market has a high ...
beekeeping business plan - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. bankable business plan for beekeeping
The apiculture business plan here is a detailed information on a natural beekeeping business plan for a community based organization. The plan also detailed the most products of beehive like, pollen, propolis, wax, royal Jelly and bee honey. ... Beekeeping or apiculture is the preservation of honey bee colonies to get pure honey and helps in ...
business plan - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document provides details about a proposed business for honey production, processing, and packaging in Pakistan. It will involve setting up 1500 beehives in Punjab for honey production and processing and packaging facilities in Karachi. The total projected cost is 20.8 million Pakistani rupees.
Feed for Bees in Beekeeping Business. Feeding and nutrition are essential for the success of the beekeeping business. Honey bees require a balanced diet of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, vitamins, minerals, and water to survive and reproduce. The necessary nutrients are obtained from nectar, pollen, and honey.
BUSINESS PLAN for business activity: CONSTRUCTION OF SLOVENE BEEKEEPING SCHOOL KHAMRON- CAMBODIA Consulting during preparation of business plan: Author: MATEJ JENKO TOMAŽ OŠTIR ... bees, honey manufacturing and other profitable activities. Educational activities will be developing in two levels: theoretical and practical. ...
How to fill out a sample of honey bee: 01. First, gather the necessary materials such as a clean container, a net or brush to collect the bees, and a small jar or vial for preservation. 02. Find a suitable location where honey bees are present, such as a garden or apiary. 03.
Pdf-business-plan. its good to all. Course. Business law notes (Blaw3201) 29 Documents. Students shared 29 documents in this course. University Dire Dawa University ... Honey is the natural sweet substance produced by honey bees from the nectar of flowers. It. is also produced from blossoms or secretions of living parts of plants or excretions ...