Your Article Library
C. v. raman: essay on c. v. raman (760 words).
ADVERTISEMENTS:
Read this comprehensive essay on Chandrasekhar Venkata Raman (1888 A.D. – 1970 A.D.) !
The Great Indian physicist Chandrasekhar Venkata Raman, popularly known as C.V Raman, was born on 7 th November, 1888 at Trichirapalli in Tamil Nadu. His father was a physics teacher and so it was natural that Raman developed love for this subject. He was a brilliant student from the very beginning. As a brilliant and promising lad, he passed his matriculation examination at the young age of 12 from Madras University.
His parents wanted to sent him England for higher studies but his poor health did not allow it. He studied at Hindu College, Visakhapatnam and Presidency College, Madras. He obtained his post-graduation degree in physics in 1907 with the top position. During his student period he conducted many researches and published his papers in many reputed magazines.

His interest in physics was deep and lasting and so he continued his research work in his spare time in the laboratory of the Association. He published his research results in the leading journals of Calcutta, now Kolkata which were in regard to the subject of propagation of light. These original research papers were of great scientific significance.
When these came to the notice of the then Vice -Challenger of Calcutta University, Sir Ashutosh Mukharjee, he appointed him Professor of physics in the University. During his stay at the University he continued his research with much more devotion and won immense honour and recognition as a physicist.
He was elected the Fellow of the Royal Society of London in 1924. He discovered the “Raman Effect” in 1928. For it he was awarded the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1930. He became the first Indian to win this prestigious honour. With this award, his reputation increased by leaps and bounds and many Universities and institutions of repute honoured him with Ph D and D.Sc. degrees.
In December, 1927 he was busy in laboratory when the news came that the well-known physicist A.M. Compton was awarded the Nobel Prize for demonstrating that the nature of X-rays undergoes a change when passed through a matter.
This effect came to be known as the “Compton Effect.” Encouraged by this discovery, Raman continued his experiments and ultimately proved that light rays can also be scattered. His discovery enabled for the first time, the mapping of possible levels of energy gains of molecules and atoms of a substance and thus discovered their molecules and atomic structure. This discovery of the scattering of light led to the development of a simple alternative to infra-red spectroscopy, namely, Raman Spectroscopy.
Raman Effect happens when molecules of a medium scatter light energy particles known as photons. The spectrum varies with the nature of the transparent medium used to scatter the light. Raman Effect has proved to be of great scientific value and with its help the structure of more than 200 compounds has been known. He also gave us the scientific explanation for the blue colour of the sky and the ocean.
He explained that the blue color of the ocean was as a result of the scattering of sunlight by the molecules of the water. He travelled widely abroad delivering lectures about his discoveries and researches. In 1933 he became the Director of the Indian Institute of Sciences, Bangalore. In 1943 he founded the Raman Research Institute at Bangalore. He was knighted in 1927. He was awarded the Bharat Ratna in 1954 and the International Lenin Prize in 1957.
Raman was a born genius and a self-made man and scientist with deep religious convictions. His interests were wide and deep and so were his contributions to the human knowledge and development. Besides optics, he was deeply interested in acoustics—the science and study of sound.
His contributions to the mechanical theory of bowed, stringed and other musical instruments like violin, sitar, cello, piano, veena, Tanpura and mridangam have been very significant. He explained in detail how these musical instruments produce harmonious tones and notes. He died on November 21, 1970 at the ripe age of 82 at Bangalore and his mortal remains were consigned to flames in the campus of the Raman Research Institute.

Related Articles:
- Meghnad Saha: Essay on Meghnad Saha
- Homi Jehangir Bhabha: Essay on Homi Jehangir Bhabha
No comments yet.
Leave a reply click here to cancel reply..
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center

Who is C.V. Raman?
- Is mathematics a physical science?
- Why does physics work in SI units?

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- The Nobel Prize - Biography of Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman
- ACS Publications - Recent Advances in Enhancement of Raman Scattering Intensity for Biological Applications
- Famous Scientists - C. V. Raman
- IndianetZone - Biography of Chandrasekhar Venkata Raman
- Indian Academy of Sciences - Prof. C. V. Raman
- C.V. Raman - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)

C.V. Raman was an Indian physicist who won the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1930 for his discovery of what became known as the Raman effect . He significantly influenced the growth of science in India through his teaching, his support of nearly every Indian research institution of his time, and his founding of the Indian Academy of Sciences.
What did C.V. Raman discover?
C.V. Raman discovered the Raman effect , which occurs when light that shines through a material is scattered and its wavelength changes from that of the original incident light because of its interactions with the molecules in the material.
Why did C.V. Raman win the Nobel Prize?
C.V. Raman was awarded the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the Raman effect , in which light that passes through a material is scattered and the wavelength of the scattered light is changed because it has caused an energy state transition in the material’s molecules .
Recent News
C.V. Raman (born November 7, 1888, Trichinopoly , India—died November 21, 1970, Bangalore) was an Indian physicist whose work was influential in the growth of science in India . He was the recipient of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1930 for the discovery that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the light that is deflected changes in wavelength. This phenomenon is now called Raman scattering and is the result of the Raman effect .
After earning a master’s degree in physics at Presidency College, University of Madras , in 1907, Raman became an accountant in the finance department of the Indian government. He became professor of physics at the University of Calcutta in 1917. Studying the scattering of light in various substances, in 1928 he found that when a transparent substance is illuminated by a beam of light of one frequency, a small portion of the light emerges at right angles to the original direction, and some of this light is of different frequencies than that of the incident light. These so-called Raman frequencies are the energies associated with transitions between different rotational and vibrational states in the scattering material.

Raman was knighted in 1929, and in 1933 he moved to the Indian Institute of Science, at Bangalore , as head of the department of physics. In 1947 he was named director of the Raman Research Institute there and in 1961 became a member of the Pontifical Academy of Science. He contributed to the building up of nearly every Indian research institution in his time, founded the Indian Journal of Physics and the Indian Academy of Sciences, and trained hundreds of students who found important posts in universities and government in India and Myanmar (Burma). He was the uncle of Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar , who won the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics, with William Fowler .
- Skip to main content
- Skip to secondary menu
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
A Plus Topper
Improve your Grades
CV Raman Essay | Essay on CV Raman for Students and Children in English
February 12, 2024 by sastry
CV Raman Essay: Steeped in intellectual thought with an illustrious eye for detail, he represented India’s scientific temper. He is the first Asian and the foremost Indian to win the Nobel Prize in Physics. Most importantly, he did this at a time when India was little known in the field of Sciences. A man of immense calibre and a pool of talent, he can be none other than Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. – The Intellectual Gem
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on CV Raman for Kids and Students in English
Given below are two essays in English for students and children about the topic of ‘CV Raman’ in both long and short form. The first essay is a long essay on the CV Raman of 400-500 words. This long essay about CV Raman is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on CV Raman of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
Long Essay on CV Raman 500 Words in English
Below we have given a long essay on CV Raman of 500 words is helpful for classes 7, 8, 9 and 10 and Competitive Exam Aspirants. This long essay on the topic is suitable for students of class 7 to class 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants.
Born at Trichinopoly in Tamil Nadu on 7th November, 1888, his father was a lecturer in Mathematics and Physics, in Mrs AV Narasimha Rao College, Visakhapatnam, and later joined Presidency College, Madras. His maternal grandfather was a Sanskrit scholar, well versed in ‘navya nyaya’ or modern logic.
So, from an early age, he was immersed in an academic atmosphere. He was a diligent student. He entered the Presidency College, Madras, in 1902, and in 1904 passed his BA examination, winning the first place and a gold medal in Physics. In 1907, he gained his MA degree, obtaining the highest distinctions. His earliest researches in optics and acoustics—the two fields of investigation to which he dedicated his entire career were carried out while he was a student. Since at that time a scientific career did not appear to offer the best possibilities, Raman joined the Indian Finance Department in 1907. Though the duties of his office took most of his time, Raman found opportunities for carrying on experimental researches in the laboratory of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Sciences at Calcutta.
In 1917, he was offered the newly endowed Palit Chair of Physics at Calcutta University, and decided to accept it. Raman’s main research was focussed on acoustics and musical instruments, and led to his election as fellow of the Royal Society in 1924. It was during a trip to England in 1921 that he was fascinated by the blue colour of the Mediterranean.
With a very simple experiment, he convinced himself that the blue colour of the sea was not only due to the reflection of the sky, as proposed by Lord Rayleigh, but mainly due to the scattering of light by water molecules. On his return to Calcutta, he began a systematic study of the scattering of light by different liquids, culminating in the discovery of a totally new kind of radiation, predicted by the quantum theory and named after him.
There Raman radiations carry vital information about the internal structure of the scattering molecules, and have proved to be of immense importance in studying molecular structures. His efforts finally paid off when he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, the first to be ever won by an Indian. Thereafter, he became the Honorary Secretary of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Sciences. After 15 years in Calcutta, he became Professor at the Indian Institute of Science at Bangalore (1933-1948) and in 1948, he became the Director of the Raman Institute of Research at Bangalore, established and endowed by himself. He also founded the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926, of which he was the Editor.
Raman sponsored the establishment of the Indian Academy of Sciences and served as its President since its inception. He was also the President of the Current Science Association, Bangalore, which publishes Current Science. (India)
Raman has done credible work in his field and his early memoirs appeared as Bulletins of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Sciences. These dealt with the maintenance of vibrations and the theory of musical instruments of the violin family. In 1922, he published his work on the ‘Molecular Diffraction of Light’, the first of a series of investigations with his collaborators which ultimately led to the discovery, on 28th February, 1928, of the radiation effect, which is named after him. This work bagged him the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Some other investigations which propelled the world of science during his time were the experimental and the theoretical studies on the diffraction of light by acoustic waves of Ultrasonic and Hypersonic frequencies. In 1932, he and Suri Bhagavantam discovered quantum photon spin. During his term at IISc, he admitted the talented electrical engineering student, GN Ramachandran, who went on to become a recognised X-ray crystallographer.

Short Essay on CV Raman 200 Words in English
Below we have given a short essay on CV Raman is for Classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. This short essay on the topic is suitable for students of class 6 and below.
In 1948, Raman, through studying the spectroscopic behaviour of crystals, approached fundamental problems of crystal dynamics in a new manner. His laboratory has been dealing with the structures and properties of diamond, the structure of optical behaviour of numerous iridescent substances like opal and pearls.
This luminous star in the firmament of the scientific fraternity has been honoured with a large number of honorary doctorates and memberships of scientific societies. He was elected as a fellow of the Royal Society in 1924 and knighted in 1929. In 1941, he was awarded the Franklin Medal. In 1954, he was conferred upon, the Bharat Ratna. He got the Lenin Peace Prize in 1957.
Another big honour was that the American Chemical Society and IACS recognised his discovery as an International Historic Chemical Landmark. India celebrates National Science Day every year on 28th February to remember the discovery of Raman effect that took place in 1928.
At the end of October, 1970, he collapsed in his laboratory. Doctors gave him four hours to live. He survived and asked to be shifted from the hospital to the gardens of his institute. He passed away on 21 st November, 1970. His life was a testimony to hard work, patience and perseverance for achieving one’s goals. One should also be level headed and not go overboard on attaining success. With him, dawned an era of high quality science, and he showed the light for others to follow.
CV Raman Essay Word Meanings for Simple Understanding
- Illustrious – very famous and much admired, especially because of what you have achieved
- Diligent – showing care and effort in your work or duties
- Optics – the scientific study of sight and light
- Acoustics – the shape, design, etc. of a room or theatre that make it good or bad for carrying sound
- Endowed – to give a large sum of money to a school, a college or another institution to provide it with an income
- Inception – the start of an institution, an organisation, etc.
- Propelled – to move, drive or push something forward or in a particular direction
- Diffraction – breaking up of stream of light into a series of dark and light bands or the different colours of the spectrum
- Spectroscopic – a piece of equipment for forming and looking at spectra
- Iridescent – showing many bright colours that seem to change in different lights
- Picture Dictionary
- English Speech
- English Slogans
- English Letter Writing
- English Essay Writing
- English Textbook Answers
- Types of Certificates
- ICSE Solutions
- Selina ICSE Solutions
- ML Aggarwal Solutions
- HSSLive Plus One
- HSSLive Plus Two
- Kerala SSLC
- Distance Education

- Vishal's account
Essay On C V Raman – 10 Lines, Short and Long Essay For Children & Students

Key Points to Remember When Writing an Essay on C V Raman
10 lines on c v raman, a paragraph on c v raman, short essay on c v raman, long essay on c v raman for kids, what will your child learn from the essay on c v raman.
Writing an essay is like setting on a journey of discovery, especially for school kids. It’s a wonderful way to explore new ideas, express thoughts, and learn about remarkable personalities who have shaped our world. Today, we’ll delve into an essay on CV Raman in English, a topic that not only educates but also inspires young minds. C V Raman, a name synonymous with brilliance in the field of science, has been a source of fascination and inspiration for students across the globe. Writing an essay for school kids on such a luminary not only enhances their knowledge but also kindles a spark of curiosity and admiration for the wonders of science and the people behind these discoveries. So, let’s begin our delightful journey through the life and accomplishments of Sir C V Raman, a Nobel laureate whose work continues to illuminate the world of physics.
Writing an essay on a distinguished personality like Sir C V Raman can be an enlightening experience. It’s crucial to present information in a way that’s both informative and captivating, especially for young minds. Here are some key points to keep in mind to make your essay on CV Raman engaging and informative:
- Understand the Subject: Before you begin writing, make sure you have a good grasp of who C V Raman was. Research his life, his discoveries, and why he is such a significant figure in science.
- Structure Your Essay: Organize your essay with a clear introduction, body, and conclusion. The introduction should set the tone and give a brief overview of CV Raman. The body should cover his life, achievements, and contributions in detail, while the conclusion should summarize his impact and legacy.
- Use Simple Language: Remember, your audience is primarily school children. Use simple, easy-to-understand language.
- Incorporate Interesting Facts: To make your essay more engaging, include interesting facts about CV Raman’s life and discoveries. This could be anecdotes about his experiments or lesser-known facts about his personal life.
- Explain Scientific Concepts Clearly: If you discuss the Raman Effect or other scientific concepts, explain them in a way that is easy for children to understand. Use analogies or simple examples.
- Highlight His Achievements: Discuss the awards and recognitions received by CV Raman, including the Nobel Prize in Physics, to inspire and motivate young readers.
- Mention His Legacy: Conclude by talking about how CV Raman’s work continues to influence modern science. This could include his impact on research or how he inspires current scientists .
- Proofread and Edit: Ensure your essay is free from grammatical errors and is well-edited. A well-written essay is more engaging and easier to understand.
- Add Personal Reflections: If possible, include personal reflections or thoughts on how CV Raman’s work or character inspires you. This adds a personal touch to your essay, making it more relatable for young readers.
Exploring the life of a great scientist can be both educational and exciting, especially for younger students. In our 10 lines about CV Raman, we aim to capture the essence of his achievements in a concise yet engaging way. This section is particularly tailored as an essay for lower primary classes, offering a simple yet informative glimpse into the life of this renowned physicist.

- C V Raman was a renowned Indian physicist, born on November 7, 1888, in Tiruchirapalli, India.
- He showed an early interest in science and was a brilliant student throughout his academic career.
- Raman completed his college education at a very young age and started his research in the field of physics.
- He is most famous for his groundbreaking work in the field of light scattering, known as the ‘Raman Effect’.
- For his discovery of the Raman Effect, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930.
- His work helped scientists understand more about how light interacts with matter.
- Apart from the Nobel Prize, he received numerous other awards and honors for his contributions to science.
- Raman was also a professor and mentor, inspiring many young scientists in India and abroad.
- He founded the Raman Research Institute in Bangalore, where he continued his research until his death.
- C V Raman passed away on November 21, 1970, but his legacy continues to inspire scientists and students around the world.
Delving into the lives of eminent scientists not only enriches our knowledge but also inspires us. In this section, we’ll craft an essay in 100 words about Sir C V Raman, focusing on his major contributions and the impact he had on the world of science. This succinct paragraph aims to capture the essence of Raman’s life, making it an ideal read for anyone looking to understand his significance in a brief yet comprehensive manner.
Sir C V Raman, an Indian physicist and Nobel laureate, was a pioneering figure in the world of science. Born in 1888, he displayed exceptional academic brilliance from a young age. His most notable contribution, the ‘Raman Effect’, which he discovered in 1928, revolutionized the understanding of light and matter interaction. This groundbreaking discovery earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, making him the first Asian to receive this honor in the field of science. Raman was not only a scientist but also an educator, inspiring many through his teachings and research. His legacy continues to influence contemporary physics, making him a towering figure in scientific history. His life and work remain a source of inspiration for aspiring scientists worldwide, illustrating the power of curiosity and perseverance.
Exploring the achievements of great scientists is not only informative but also deeply inspiring. In this short essay in 200 words, we aim to shed light on the life and legacy of Sir C V Raman, an extraordinary physicist whose discoveries have left an indelible mark on science. This concise essay is designed to provide a comprehensive overview of his life’s work and its significance.
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, more commonly known as C V Raman, was a figure who revolutionized the understanding of light and its behavior. Born in 1888 in the then British India, Raman displayed an early passion for science, leading him to a career that would be marked by extraordinary achievements. His most significant contribution came in the form of the ‘Raman Effect’, a phenomenon in light scattering that he discovered in 1928. This discovery not only earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, but it also put India on the global map of scientific research.
Raman’s work extended beyond just theoretical physics; he was deeply involved in practical research and teaching. He founded the Raman Research Institute in Bangalore, where he nurtured future generations of scientists. His passion for science was contagious, inspiring many young minds to pursue careers in research. Raman’s legacy is not limited to his scientific contributions; he left behind a legacy of curiosity, dedication, and a relentless pursuit of knowledge. His life story is a testament to the power of perseverance and passion in achieving greatness. As we reflect on his contributions, Raman’s story continues to inspire and motivate scientists and students alike, making him an enduring figure in the annals of scientific history.
Exploring the life of a legendary scientist like Sir C V Raman is an exciting adventure into the world of discovery and innovation. This long essay, spanning 400-600 words, is specifically crafted for kids to understand and appreciate the extraordinary journey of C V Raman. From his early years to his groundbreaking discoveries and notable achievements, this essay provides a comprehensive look into the life of a man who changed the way we understand light.
Early Life and Education
C V Raman was born on November 7, 1888, in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, India. From a young age, Raman exhibited a deep interest in science and an exceptional intellectual capacity. He breezed through his schooling, often topping his class and showing a particular fondness for physics and mathematics. His academic brilliance led him to Presidency College, Madras, where he completed his degree in physics at the age of 16. Despite the lack of advanced scientific facilities in India at the time, Raman’s passion for physics didn’t wane. He initially took a job in the Indian Finance Department but continued to engage in scientific research in his free time, demonstrating his unwavering dedication to science.
Greatest Discoveries
The most significant of C V Raman’s discoveries was undoubtedly the ‘Raman Effect’. This phenomenon, discovered in 1928, dealt with the scattering of light and revealed new insights into the nature of light. Raman discovered that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the deflected light changes in wavelength. This discovery was groundbreaking as it provided a new tool for analyzing the molecular structure of materials. The ‘Raman Effect’ has since become a fundamental principle in the field of spectroscopy, impacting various scientific disciplines.
Achievements of C V Raman
The Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to him in 1930 for his groundbreaking discovery of the Raman Effect, marking him as the inaugural Asian laureate in the field of science. But his accolades don’t stop there. In 1954, Raman received the Bharat Ratna, the most prestigious civilian honor in India. He also received knighthood in 1929. Beyond these honors, Raman’s greatest achievement was perhaps his role in enhancing scientific research in India. He established the Indian Academy of Sciences and the Raman Research Institute, which became hubs for scientific study and research in India, nurturing numerous young scientists and making significant contributions to the field of physics.
C V Raman passed away on November 21, 1970, at the age of 82. His death marked the end of an era in Indian science. However, his legacy continues to live on through his discoveries, his contributions to scientific institutions, and the inspiration he provides to generations of scientists. Raman’s life story is not just about scientific discovery; it is a story of perseverance, passion, and an unquenchable thirst for knowledge. His journey from a curious child to a Nobel laureate serves as an inspiration to children and adults alike, reminding us that with dedication and hard work, anyone can reach the stars.
Through this essay, kids can learn not only about the scientific achievements of C V Raman but also about the qualities that make a great scientist. His story teaches us the importance of curiosity, persistence, and the desire to explore the unknown. C V Raman’s life is a beacon of inspiration, encouraging young minds to dream big and pursue their passions with determination.
Through the essay on C V Raman, children will embark on an inspiring journey that transcends mere facts and dates. In this brief summary of CV Raman’s life, readers will discover the significance of persistence, the impact of curiosity, and the transformative potential of an individual’s unwavering commitment to scientific exploration, resulting in revolutionary breakthroughs with global implications. This essay not only educates young minds about a legendary scientist but also instills values of hard work, passion, and the endless possibilities that come with pursuing one’s dreams.
1. How to explain Raman Effects to your child?
The Raman Effect can be explained to children as a special way light behaves, changing slightly when it passes through different materials, like a secret code that tells us what the material is made of.
2. How to use Raman Effects in day-to-day life?
Raman Effect is used in everyday life mainly through technologies in devices like barcode scanners and in scientific research to understand the composition of materials.
The essay on C V Raman offers a comprehensive insight into the life of a pioneering scientist, blending scientific achievements with valuable life lessons. It serves as a source of inspiration for children, highlighting the importance of curiosity, perseverance, and the pursuit of knowledge. Through this exploration, young minds are encouraged to dream big and understand the impact one individual can have on the world through dedication and passion for science.
References:
1. Singh. R, C. V. Raman and the Discovery of the Raman Effect (Physics in Perspective); Research Gate; https://www.researchgate.net/publication/226927241_C_V_Raman_and_the_Discovery_of_the_Raman_Effect ; December 2002
2. C.V. Raman and the Raman Effect; American Chemical Society; https://www.acs.org/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/ramaneffect.html
3. Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, 1888-1970 – Journals; Royal Society; https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/pdf/10.1098/rsbm.1971.0022
4. Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman Biographical; The Nobel Prize; https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/physics/1930/raman/biographical/
5. Jayaraman. A; Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman; Indian Academy of Sciences; https://www.ias.ac.in/public/Resources/Other_Publications/e-Publications/003/Chandrasekhara_Venkata_Raman.pdf
Essay on Srinivasa Ramanujan for Kids Essay on Savitribai Phule for Children
- RELATED ARTICLES
- MORE FROM AUTHOR

Essay On Nelson Mandela: 10 Lines, Short and Long Essay

Water Conservation for Kids - Facts & Tips to Save Water

List Of Christmas Words That Start With A

Interesting Ocean Facts for Kids

Beautiful Friendship Day Wishes, Quotes and Messages for Kids

40 Questions to Ask at Parent-Teacher Conference
Popular on parenting.

245 Rare Boy & Girl Names with Meanings

Top 22 Short Moral Stories For Kids

170 Boy & Girl Names That Mean 'Gift from God'

800+ Unique & Cute Nicknames for Boys & Girls
Latest posts, happy raksha bandhan gifs for a special sibling celebration.

90 Hilarious Winter Jokes for Kids to Make Holiday More Fun

60 Best Back to School Jokes for Kids to Start the Year With a Smile

100+ Heartfelt Thank You Messages and Quotes for Parents
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience and security.
Enhanced Page Navigation
- Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman - Biographical
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman
Biographical.

His earliest researches in optics and acoustics – the two fields of investigation to which he has dedicated his entire career – were carried out while he was a student.
Since at that time a scientific career did not appear to present the best possibilities, Raman joined the Indian Finance Department in 1907; though the duties of his office took most of his time, Raman found opportunities for carrying on experimental research in the laboratory of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science at Calcutta (of which he became Honorary Secretary in 1919).
In 1917 he was offered the newly endowed Palit Chair of Physics at Calcutta University, and decided to accept it. After 15 years at Calcutta he became Professor at the Indian Institute of Science at Bangalore (1933-1948), and since 1948 he is Director of the Raman Institute of Research at Bangalore, established and endowed by himself. He also founded the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926, of which he is the Editor. Raman sponsored the establishment of the Indian Academy of Sciences and has served as President since its inception. He also initiated the Proceedings of that academy, in which much of his work has been published, and is President of the Current Science Association, Bangalore, which publishes Current Science (India) .
Some of Raman’s early memoirs appeared as Bulletins of the Indian Associationfor the Cultivation of Science (Bull. 6 and 11, dealing with the “Maintenance of Vibrations”; Bull. 15, 1918, dealing with the theory of the musical instruments of the violin family). He contributed an article on the theory of musical instruments to the 8th Volume of the Handbuch der Physik , 1928. In 1922 he published his work on the “Molecular Diffraction of Light”, the first of a series of investigations with his collaborators which ultimately led to his discovery, on the 28th of February, 1928, of the radiation effect which bears his name (“A new radiation”, Indian J. Phys. , 2 (1928) 387), and which gained him the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Other investigations carried out by Raman were: his experimental and theoretical studies on the diffraction of light by acoustic waves of ultrasonic and hypersonic frequencies (published 1934-1942), and those on the effects produced by X-rays on infrared vibrations in crystals exposed to ordinary light. In 1948 Raman, through studying the spectroscopic behaviour of crystals, approached in a new manner fundamental problems of crystal dynamics. His laboratory has been dealing with the structure and properties of diamond, the structure and optical behaviour of numerous iridescent substances (labradorite, pearly felspar, agate, opal, and pearls).
Among his other interests have been the optics of colloids, electrical and magnetic anisotropy, and the physiology of human vision.
Raman has been honoured with a large number of honorary doctorates and memberships of scientific societies. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society early in his career (1924), and was knighted in 1929.
This autobiography/biography was written at the time of the award and first published in the book series Les Prix Nobel . It was later edited and republished in Nobel Lectures . To cite this document, always state the source as shown above.
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman – died on November 21, 1970.
Nobel Prizes and laureates
Nobel prizes 2023.

Explore prizes and laureates
Water: The Elixer Of Life By C. V. Raman – Summary and Questions
Table of Contents
Water: The Elixer Of Life – C.V.Raman
Introduction: Water is a vital ingredient for survival of all living beings. Imagine a day without water no water to drink, wash, or to cook! People can survive without food for days but not without water. About 70% of earth’s surface is covered with water. Of this 97% is saline and 2% is fresh which is present in the form of ice caps, glaciers, icebergs or in the atmosphere. Only 1% can be used for drinking. We are heading towards a freshwater crisis that is leading to poor access to safe water for millions of people. Hence, conserving water has become the need of the hour, along with an efficient management system, to ensure a steady supply for the future.
About C.V. Raman
Please enable JavaScript
Water, an elixir of life
Humankind has always searched in vain for an imaginary elixir of life, the divine amrita. A draught of this elixir was thought to confer immortality <em>Immortality</em> is the indefinite continuation of a person's existence, even after death. It is the quality or condition of being immortal. It also means enduring fame. " data-gt-translate-attributes='[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]' tabindex=0 role=link>immortality . But Raman feels that the true elixir of life is water. This single liquid can change the entire scene. He remembers that he was standing on the line which separates the Libyan Desert from the valley of the Nile in Egypt. On one side was a vast area covered with sand and without a speck of green or a single living thing. On the other side was one of the greatest, most fertile and densely populated areas. It was teeming with life and vegetation. The only thing which made the difference was water. It was the water of the river Nile. Geologist tells that the entire soil of river, Nile is the creation of the river itself. Its ancient civilization was created and sustained by the life-giving water of the Nile.
We take granted this common substance in everyday life. But we forget that water is the most potent and wonderful thing on the earth. It has played a very important role In shaping the course of earth’s history. It continues to play the leading role in the drama of life on earth. Nothing can add so much to the beauty of the countryside as water. In south India, the rain-fed tanks are very common. They are shallow but the bottom of the tank is not visible due to silt-laden water. These tanks play a vital role in south India agriculture. Much of rice is grown under them.
One of the most remarkable facts about water is its power to carry silt in suspension. This suspension is the reason for the different colours of the water in a rain-fed tank. Swiftly flowing water can carry fairly large and heavy particles. The finest particles remain with the water and are carried to a large distance. When silt-laden water mixes with the saltwater of the sea, there is rapid precipitation of the suspended matter. The colour of the water changes successively from the muddy red or brown of silt through varying shades of yellow and green finally to the blue of the deep sea. A large land is formed by silt thus deposited. Such land is very fertile. The flow of water plays a great part in this process; sometimes it can be destructive also.
Water is the basis of all life. Every animals and plant contain water in this body. No activity is possible without water. Water is necessary for animal life. The moist in the soil is necessary for the growth of plants and trees. So, the conservation and utilization of water is most important for human welfare.
A vast area of land could be turned into a fertile and prosperous country by courageous and well-planned action. The systematic planting of suitable trees is the urgent need of India. Such plantation would, directly and indirectly, prove a source of wealth to the country. They would check soil erosion and conserve the rainfall of the country. Water is the commonest of liquid, but it is also the most uncommon of liquid with amazing properties. These properties are responsible for its unique power of maintaining animal and plant life. The investigation of the nature and properties of water is, therefore, of the highest scientific interest.
Questions and Answers
Ans. Water is the true elixir of life. This is a common substance. So, we take it granted in our everyday life. It is the most wonderful thing on Earth. It continues to play a leading role in the drama of life on Earth.
The conservation and utilization of water is fundamental to human welfare. One of the most remarkable facts about water is its power to carry silt suspension. Our agriculture depends on seasonal rainfall. So, collection and utilization of rainwater is very important. Water is the commonest of the liquids. These uncommon properties are responsible for its unique power of maintaining animal and plant life.
Question.2. Write about the power and beauty of the element, water.
One of the most remarkable facts about water is its power to carry silt in suspension. The flow of water plays a great role in the geographical process. It can sometimes play a destructive role and wash away the soil. Great tracts of land have been formed by silt deposited by water. The problem of soil erosion is caused by water. Vast areas of land could be turned into fertile or infertile. This is the power and beauty of water.
The sudden burst of excessively heavy rain results into a large run of surplus water which causes soil erosion. The slope of land, removal of the natural protective coat of vegetation, ruts for flow of water with speed and no check to such flow are also the causes for soil erosion.
Question.4. What are the usual measures used to check soil erosion?
Vast areas of land could be turned into a fertile and prosperous country by well-planned action. The systematic planting of suitable trees in every possible place is most urgent in India. They would check soil erosion and conserve the rainfall of the country.
Ans. C.V. Raman gives the example of rain-fed tanks which play a very vital role in south Indian agriculture. In Mysore, much of the rice is grown under them. The colour of the water in rain-fed tanks changes according to the land from which the water comes. Swiftly flowing water can carry large and heavy particles. The finest particles remain floating in the water. Large areas of land can be converted into fertile land due to silt-laden water.
Collection and utilization of rainwater is very important because our Indian agriculture depends on rainfall. Much of the rainwater flows down into the river and the sea. So a large quantity of water is lost. The proper use of this flowing water is a great national problem. Planting of trees is urgent need of India. They would help to save the rainwater of the country from flowing away to waste.
Have something to say Cancel reply
Discover more from smart english notes.
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.

Essay on CV Raman
Students are often asked to write an essay on CV Raman in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on CV Raman
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, known as CV Raman, was born on November 7, 1888, in Tamil Nadu, India. He was a brilliant student and showed a great interest in science from a young age.
Achievements
Raman is famous for his work in the field of light scattering. His discovery, known as the ‘Raman Effect’, earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, making him the first Asian to receive this honor in science.
Raman’s work revolutionized our understanding of light and its interactions. His contributions to science continue to inspire students worldwide.
250 Words Essay on CV Raman
Introduction.
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, widely known as C.V. Raman, was an eminent Indian physicist who made significant contributions to the field of light scattering. His groundbreaking work earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, making him the first Asian scientist to receive this honor.
Raman’s Early Life and Education
The raman effect.
Raman’s most notable work is the discovery of the Raman Effect in 1928. This phenomenon, where light changes its wavelength and color when passing through different materials, revolutionized the field of spectroscopy. It provided a new method for studying and identifying substances based on their light scattering properties, with far-reaching implications in various scientific disciplines.
Legacy and Impact
C.V. Raman’s work transcends his lifetime, with the Raman Effect becoming a cornerstone in modern physics. His legacy also lies in his role as a science communicator and educator, inspiring future generations of Indian scientists. Despite the limited resources of his time, Raman’s unyielding curiosity and dedication to science serve as a beacon for aspiring researchers worldwide.
In conclusion, C.V. Raman’s contributions to science, particularly the discovery of the Raman Effect, have had a profound and lasting impact. His life and work continue to inspire and guide the scientific community, cementing his place in the annals of scientific history.
500 Words Essay on CV Raman
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, popularly known as C.V. Raman, was an eminent physicist who left an indelible mark on the scientific landscape of India and the world. His groundbreaking work in the field of light scattering, known as the Raman Effect, earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930. He was the first Asian and non-white to receive a Nobel Prize in any branch of science.
Early Life and Education
C.V. Raman was born on November 7, 1888, in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu. He was a prodigious child and completed his schooling at a very young age. Raman graduated with a gold medal in Physics from Presidency College, Madras, in 1907. Despite his keen interest in science, he initially embarked on a career in the Indian Finance Department due to the lack of opportunities in the scientific field in India at that time.
The Path to Discovery
On February 28, 1928, Raman discovered that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the deflected light changes in wavelength. This phenomenon, now known as the Raman Effect, provided the foundation for Raman spectroscopy, a tool commonly used today for identifying the molecular composition of materials. This discovery was a significant leap in the field of quantum physics.
Nobel Laureate and Later Life
Raman was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 for his discovery. He was knighted in 1929 for his contributions to science. In 1943, Raman established the Raman Research Institute in Bangalore, where he served as the director and remained active in research until his death in 1970.
C.V. Raman’s life and work exemplify the pursuit of knowledge and the power of curiosity. His groundbreaking research in the field of light scattering changed the course of scientific research and continues to have significant implications in various scientific fields. His story is not just about his scientific achievements but also about his commitment to nurturing scientific research in India. His legacy continues to inspire generations of scientists and researchers, encouraging them to think beyond the ordinary and make extraordinary contributions to the world of science.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
UPSC Coaching, Study Materials, and Mock Exams
Enroll in ClearIAS UPSC Coaching Join Now Log In
Call us: +91-9605741000
CV Raman: The Visionary Scientist
Last updated on March 11, 2024 by ClearIAS Team

Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, more commonly known as CV Raman, was a pioneering Indian physicist whose work in the field of light scattering earned him the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics. Read here to learn more about his life.
National Science Day is celebrated in India on February 28th every year since 1986 to mark the discovery of the Raman Effect by Indian physicist Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman on this day in 1928.
This celebration not only commemorates Raman’s groundbreaking discovery, for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 but also aims to spread the message of the importance of science and its application in the daily life of the people.
Table of Contents
The early life of CV Raman
Born on November 7, 1888, in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, Raman displayed a prodigious intellect from an early age, finishing his secondary education by the age of 11.
He graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree from Presidency College, Madras, in 1904, and subsequently completed his Master’s in Physics in 1907.
- Despite beginning his career in the Indian Finance Department as a civil servant, Raman’s passion for science never waned.
- He conducted research at the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS) in Kolkata during his spare time, which led to significant discoveries in acoustics and optics.
CV Raman made his first trip to London in 1921, where his reputation in the study of optics and especially acoustics was already known to the English physicists J. J. Thomson and Lord Rutherford.
UPSC CSE 2025: Study Plan ⇓
(1) ⇒ UPSC 2025: Prelims cum Mains
(2) ⇒ UPSC 2025: Prelims Test Series
(3) ⇒ UPSC 2025: CSAT
Note: To know more about ClearIAS Courses (Online/Offline) and the most effective study plan, you can call ClearIAS Mentors at +91-9605741000, +91-9656621000, or +91-9656731000.
- Raman’s specialty had been the study of the vibrations and sounds of stringed instruments such as the violin, the Indian veena, and tambura, and two uniquely Indian percussion instruments, the tabla, and the mridangam.
But it was the return trip from London to Bombay aboard the SS Narkunda that would change forever the direction of Raman’s future.
- During the fifteen-day voyage, his restless and probing mind became fascinated with the deep blue color of the Mediterranean.
- Unable to accept Lord Rayleigh’s explanation that the color of the sea was just a reflection of the color of the sky, Raman proceeded to outline his thoughts on the matter while still at sea and sent a letter to the editors of the journal Nature when the ship docked in Bombay.
A short time later Raman was able to show conclusively that the color of the sea was the result of the scattering of sunlight by the water molecules.
- Ironically, it was the same argument that Rayleigh had invoked when explaining the color of the sky – the blue was the result of the scattering of sunlight by the molecules in the air.
Also read: Indian Scientists: From Ancient to Modern Era
Nobel Prize and the Raman Effect
CV Raman’s most celebrated discovery, the Raman Effect, came in 1928. It demonstrated that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the deflected light changes wavelength and amplitude.
- This discovery was groundbreaking because it confirmed the quantum nature of light and was the first strong evidence of the quantum behavior of molecules.
- Raman used a simple apparatus to show that when light passes through a transparent substance, it scatters, and the scattered light contains frequencies not present in the original light, a phenomenon that could not be explained by classical physics.
For this discovery, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, becoming the first Asian and the first non-white to receive a Nobel Prize in the sciences.
What is the Raman effect?
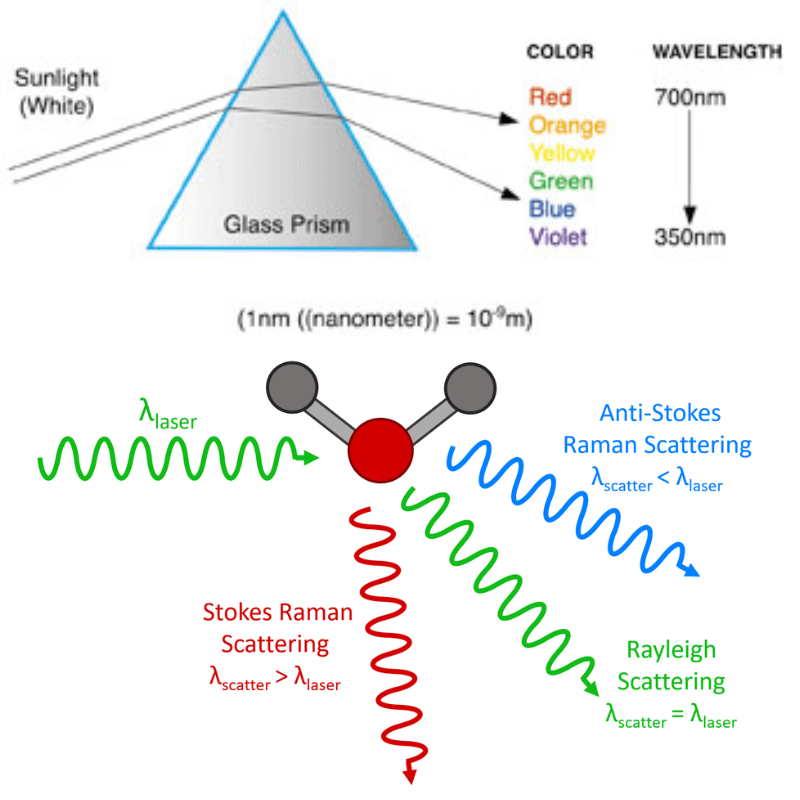
The Raman Effect occurs when light interacts with the molecules of a material, causing a change in the energy and wavelength of the scattered light.
- When monochromatic light (light of a single wavelength, usually from a laser) is directed at a material, most of the light scatters elastically (Rayleigh scattering), meaning it retains its original energy and wavelength.
- However, a small fraction of the light (approximately 1 in 10 million photons) scatters inelastically, either gaining or losing energy in the process. This inelastic scattering is the Raman Effect.
Stokes and Anti-Stokes Scattering
The energy change in the scattered light corresponds to the vibrational energies of the molecules in the material.
- If the scattered light loses energy (shifts to a longer wavelength), it is called Stokes scattering.
- Conversely, if the scattered light gains energy (shifts to a shorter wavelength), it is called Anti-Stokes scattering.
- The difference in energy between the incident and scattered light directly relates to the vibrational energy levels of the molecules in the sample.
The discovery of the Raman Effect was a milestone in experimental physics and quantum theory.
- It provided the first experimental evidence of the quantum nature of light and molecules, supporting the theoretical predictions of quantum mechanics.
- The Raman Effect showed that light-matter interactions could result in the exchange of energy, leading to a deeper understanding of molecular energy levels and the electromagnetic spectrum.
Application of Raman effect
In the first seven years after its discovery, the Raman Effect was the subject of more than 700 papers in the scientific literature, mostly by physicists who were using the technique to study the vibration and rotation of molecules and relating those phenomena to the molecular structure.
By the late 1930s, the Raman Effect had become the principal method of non-destructive chemical analysis for both organic and inorganic compounds.
- The unique spectrum of Raman scattered light for any particular substance served as a “fingerprint” that could be used for qualitative analysis, even in a mixture of materials.
- Raman spectroscopy could be applied not only to liquids but also to gases and solids.
- The use of Raman spectroscopy as a basic analytical tool changed sharply after World War II.
- During the war, infrared spectroscopy was enhanced by the development of sensitive detectors and advances in electronics.
Other applications:
- Material Science : It helps in characterizing materials, understanding their structure, and studying phase transitions.
- Biological Studies : Raman spectroscopy is used in the medical field to diagnose diseases, analyze biochemical changes in cells, and study drug interactions at the molecular level.
- Pharmaceuticals : It assists in drug development and quality control by identifying the molecular composition and crystalline forms of drugs.
- Environmental Science : It is employed in detecting pollutants and analyzing environmental changes.
Academic and Research Contributions
After his Nobel win, Raman’s reputation and influence grew. He served as the director of the Indian Institute of Science (IISc) in Bangalore from 1933 to 1937.
He established the Raman Research Institute in Bangalore in 1948, where he worked until he died in 1970.
He also founded the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926, of which he is the Editor. Raman sponsored the establishment of the Indian Academy of Sciences and has served as President since its inception.
His research at these institutions spanned various domains of physics, including crystal dynamics, musical instruments, and the properties of diamonds.
Raman’s legacy is not just in his scientific discoveries but also in his role as a leader in Indian science. He was instrumental in promoting scientific research in India, inspiring generations of scientists.
Despite facing several challenges, including limited resources and recognition from the global scientific community initially, Raman’s perseverance and dedication to science shone brightly. His work laid the groundwork for numerous scientific advancements, including the study of molecular energy levels, chemical analysis techniques, and even the investigation of quantum mechanics.
Sir CV Raman passed away on November 21, 1970, leaving behind a rich legacy of scientific inquiry and discovery. His life and work continue to inspire scientists around the world, underscoring the importance of curiosity, perseverance, and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
Related article:
- Indian Scientists
- Jagadish Chandra Bose
- Women in STEM
-Article by Swathi Satish

Top 10 Best-Selling ClearIAS Courses
Upsc prelims cum mains (pcm) gs course: unbeatable batch 2025 (online), rs.75000 rs.29000, upsc prelims marks booster + 2025 (online), rs.19999 rs.14999, upsc prelims test series (pts) 2025 (online), rs.9999 rs.4999, csat course 2025 (online), current affairs course 2025 (online), ncert foundation course (online), essay writing course for upsc cse (online), ethics course for upsc cse (online), upsc interview marks booster course (online), rs.9999 rs.4999.

About ClearIAS Team
ClearIAS is one of the most trusted learning platforms in India for UPSC preparation. Around 1 million aspirants learn from the ClearIAS every month.
Our courses and training methods are different from traditional coaching. We give special emphasis on smart work and personal mentorship. Many UPSC toppers thank ClearIAS for our role in their success.
Download the ClearIAS mobile apps now to supplement your self-study efforts with ClearIAS smart-study training.
Reader Interactions
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Don’t lose out without playing the right game!
Follow the ClearIAS Prelims cum Mains (PCM) Integrated Approach.
Join ClearIAS PCM Course Now
UPSC Online Preparation
- Union Public Service Commission (UPSC)
- Indian Administrative Service (IAS)
- Indian Police Service (IPS)
- IAS Exam Eligibility
- UPSC Free Study Materials
- UPSC Exam Guidance
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Syllabus
- UPSC Online
- UPSC Prelims
- UPSC Interview
- UPSC Toppers
- UPSC Previous Year Qns
- UPSC Age Calculator
- UPSC Calendar 2024
- About ClearIAS
- ClearIAS Programs
- ClearIAS Fee Structure
- IAS Coaching
- UPSC Coaching
- UPSC Online Coaching
- ClearIAS Blog
- Important Updates
- Announcements
- Book Review
- ClearIAS App
- Work with us
- Advertise with us
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
- Talk to Your Mentor
Featured on

and many more...
ClearIAS Programs: Admissions Open
Thank You 🙌
UPSC CSE 2025: Study Plan
Subscribe ClearIAS YouTube Channel

Get free study materials. Don’t miss ClearIAS updates.
Subscribe Now
IAS/IPS/IFS Online Coaching: Target CSE 2025

Cover the entire syllabus of UPSC CSE Prelims and Mains systematically.

- Classroom Programme
- Interview Guidance
- Online Programme
- Drishti Store
- My Bookmarks
- My Progress
- Change Password
- From The Editor's Desk
- How To Use The New Website
- Help Centre
Achievers Corner
- Topper's Interview
- About Civil Services
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus
- GS Prelims Strategy
- Prelims Analysis
- GS Paper-I (Year Wise)
- GS Paper-I (Subject Wise)
- CSAT Strategy
- Previous Years Papers
- Practice Quiz
- Weekly Revision MCQs
- 60 Steps To Prelims
- Prelims Refresher Programme 2020
Mains & Interview
- Mains GS Syllabus
- Mains GS Strategy
- Mains Answer Writing Practice
- Essay Strategy
- Fodder For Essay
- Model Essays
- Drishti Essay Competition
- Ethics Strategy
- Ethics Case Studies
- Ethics Discussion
- Ethics Previous Years Q&As
- Papers By Years
- Papers By Subject
- Be MAINS Ready
- Awake Mains Examination 2020
- Interview Strategy
- Interview Guidance Programme
Current Affairs
- Daily News & Editorial
- Daily CA MCQs
- Sansad TV Discussions
- Monthly CA Consolidation
- Monthly Editorial Consolidation
- Monthly MCQ Consolidation
Drishti Specials
- To The Point
- Important Institutions
- Learning Through Maps
- PRS Capsule
- Summary Of Reports
- Gist Of Economic Survey
Study Material
- NCERT Books
- NIOS Study Material
- IGNOU Study Material
- Yojana & Kurukshetra
- Chhatisgarh
- Uttar Pradesh
- Madhya Pradesh
Test Series
- UPSC Prelims Test Series
- UPSC Mains Test Series
- UPPCS Prelims Test Series
- UPPCS Mains Test Series
- BPSC Prelims Test Series
- RAS/RTS Prelims Test Series
- Daily Editorial Analysis
- YouTube PDF Downloads
- Strategy By Toppers
- Ethics - Definition & Concepts
- Mastering Mains Answer Writing
- Places in News
- UPSC Mock Interview
- PCS Mock Interview
- Interview Insights
- Prelims 2019
- Product Promos
Drishti IAS Blog
- Sir C. V. Raman: The Pioneer Of Modern Science In India

Sir C. V. Raman: The Pioneer Of Modern Science In India Blogs Home
- 07 Nov 2022
-(1).png)
At a time of distress when the entire nation was struggling to be free from the shackles of oppression and cruelty, a man of science was busy making space for India on the globe.
“Look at the resplendent colours on the soap bubbles! Why is the sea blue? What makes diamond glitter? Ask the right questions, and nature will open the doors to her secrets.”
These are the words of Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, also known as Sir C V Raman, whose inquisitiveness and incessant efforts to find the answers made him the first Asian physicist to receive the Nobel prize in 1930. 7th November marks the birth anniversary of this revered scientist who discovered the Raman Effect. His discovery enabled the scientific community to move forward and better understand various natural phenomena.
Sir C V Raman was born in 1888 in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu. His father was Chandrashekhar Ramanathan. He was a lecturer of Mathematics and Physics at the Presidency College at the University of Madras. He graduated at the age of 16 from the same college. He was a brilliant student and a gold medalist. After obtaining Masters' in Physics, he secured a government job in Indian Finance Department. He continued experimental research in acoustics and optics in the laboratory of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science (IACS). He also published his work in leading Physics journals.
In 1917, he left his government job and became a Palit Professor of Physics at the University of Calcutta. He continued studying acoustics, the sounds of stringed instruments like violin and veena and percussion instruments like tabla and mridangam. His work earned him a good reputation among his peers in the country and internationally. On his first trip to London in 1921, he received a warm welcome from English Physicists J. J. Thomson and Lord Rutherford.
While returning to India from London via sea route, the blue colour of the sea caught his attention. Dissatisfied with Lord Railey’s explanation that the colour of the sea was blue due to the reflection of the colour of the sky, he decided to investigate the reason behind it. With his mentee K. S. Krishnan , he started studying light scattering.
His sincerity, dedication, and contribution towards the discipline of physics got recognition from the Royal Society of London when he was elected a fellow of the society in 1924. He got invited to the California Institute of Technology (Caltech) in the United States by Nobel Laureate Robert Millikan, where he spent four months studying the scattering of light. On 28th February 1928, he finally got his answer when he discovered Raman Effect, according to which the light changes its wavelength and frequency when it gets deflected by molecules. The day has been commemorated as National Science Day every year since 1987
Sir Raman was already a renowned name in the field of science but discovering the Raman effect strengthened his position in the community. He received a knighthood from the Royal Society of London in 1929, and the following year he became the first Indian scientist to be honoured with the Nobel Prize. He also headed the Indian Institute of Science (IISc), Bangalore as the first Indian director.
Sir Raman was educated in India; he did most of his research work here and went on to earn the reputation of an internationally celebrated physicist. Ernest Rutherford, who discovered the nucleus, referred to Raman’s Spectroscopy in his presidential address to the Royal Society of London.
Sir Raman dreamt of building a society in India like the Royal Society of London and other entities in the world to inculcate scientific temperament in the Indian youth. In 1934 he founded the Indian Academy of Science (IAS) in Bangalore to further the cause of science. After retiring from IISc, Sir Raman founded Raman Research Institute (RRI) to continue his research. He remained the director of RRI until his death on 21st November 1970.
He expressed his disappointment in Indian talent leaving the country to find better opportunities abroad when he said:
“My life has been an utter failure. I thought I would try to build true science in this country, but all we have is a legion of camp followers for the west.”
But he remained open to working with western physicists like Max Born and Erwin Schrodinger, both of who were Nobel Laureates. He persuaded German scientist Max Born to come to India and work for the country. He stayed for some time at IISc, but Sir Raman’s efforts to prolong his stay could not fructify.
Sir C. V. Raman was honoured on numerous platforms for his incredible contribution to advancing the sciences. After India became independent, he became the first national professor of India. He was awarded Bharat Ratna in 1954. He remains one of the few recipients to receive both the Bharat Ratna and the Nobel Prize. He received Lenin Peace Prize in 1957 in Kremlin. Several buildings and roads are also named after him in Russia.
Today, the Raman effect is used in medicine, surgery, and medical diagnosis like cancer detection. It is being used in remote sensing, geology, and mineralogy. It is used for ensuring quality control in the pharmaceutical industry. Police are also using it for forensic work. The most visible public use of Raman spectroscopy can be seen at airports, metro stations, malls, or other places of security where scanners are used to detect explosives and drugs.
Sir C. V. Raman’s discovery has proved to be a significant stepping stone to the world of science. He left us half a century ago, and his discovery will also be a century old in a few years. Still, his ideas will always remain relevant and encourage curious minds to unravel the secrets of nature.
Priyanka Todariya
https://www.acs.org/content/acs/en/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/ramaneffect.htmlhttps://www.ias.ac.in/ https://www.jagranjosh.com/general-knowledge/chandrasekhara-venkata-raman-cv-raman-biography-1573042778-1 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Mme5K68m28Q
Comments (0)


- Contact For Teachers : Please mail us [email protected] For Students : Please mail us [email protected]
- Join Us Become a Teacher Join our Sales Team Become an Affiliate Careers
- Community Blog Podcasts SparkShop Communication Skill Test
- Download our App
- CommSkillTest
- TRAINING BROCHURE
- BOOK YOUR FREE TRIAL
Please Provide these Details to receive app download link
Thu, 12 Aug, 2021
CV Raman: The Renowned Scientist Behind the Discovery of Raman Effect!
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (CV Raman) was an Indian scientist and physicist. Born on 7th November 1888, his contribution to the field of science got him a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930. He discovered the ‘ Raman Effect ’, which is a unique form of ‘modified scattering of light’. He was awarded Fellowship of Royal Society of London in 1924, along with a Knights Bachelor in 1930.
Born in a family of Hindu Tamil Brahmins, he was one of the eight siblings. He displayed his higher level of intelligence at a very young age, making him a child prodigy.
He completed his secondary school at 11 and higher secondary school at 13 years of age. By 16, he graduated Physics Bachelor’s degree with honours, as a topper of his class. He had published his first research paper on ‘diffraction of light’, even before his graduation. He then went on to pursue his master’s degree. By the age of 19, he was appointed as Assistant Accountant General in the Indian Finance Service, Calcutta.
The IACS (Indian Association for the Cultivation of Sciences) was the first research institute in India. This institute allowed CV Raman to research extensively about acoustics and optics. This research got him his well-deserved fame among the international scientific community. Eventually, he was offered the position of ‘Palit Professor’ for the Physics Dept. at the University of Calcutta’s Rajabazar Science College.
When he visited Europe for the first time, watching the Mediterranean Sea inspired him. He sought to disprove that Rayleigh-scattered light is the reason why the sea was observed to be blue-colored. In 1923, Compton proved that EM waves could also be described as particles .
When Ramanathan learnt this in 1927, he continued his research with K. S. Krishnan. During his research with his associate K. S. Krishnan, Raman discovered interesting properties of light.
K. S. Krishnan observed that all types of liquids produced polarised fluorescence. This was within the visible spectrum of light. CV Raman noted this, called it modified scattering, and sent the manuscript to ‘Nature’ scientific magazine.
Raman invented a spectrograph for detecting this phenomenon. They placed a violet filter on sunlight and scattered it through a liquid. This produced Rayleigh’s scattered light and a weak light of different colour. They then placed a green filter and noticed green light scattered by the liquid. This was Raman’s scattered light. It was a secondary type of radiation, and more than 60 other liquids displayed the same output. This discovery was one of the initial reliable proofs of the ‘quantum nature of light’.
PlanetSpark provides the best public speaking courses for your child. Book a FREE class without any further delay and make your child a great public speaker NOW!
People who read this blog, also read this:
Mahatma Gandhi - The father of India
A Speech Commemorating Jawaharlal Nehru
Related Articles
Mon, 12 Aug, 2019
7 Benefits of PlanetSpark’s Essay Writing Course for Intermediate Children in English!
Sun, 04 Jul, 2021
Essay On Trees for Class 4 Kids: Exploring Their Importance and Beauty!
Tue, 01 Feb, 2022
Effective Paragraph & Essay Writing Prompts for 4th Graders!
- Student Blogs
- Privacy
- Terms
- Public Speaking for Kids
- Creative Writing for Kids
- Spoken English for Kids
- How to Raise a Smart Kid
- Critical and Creative Thinking Skills
- Develop Reading Habits
- English Conversation for Kids
- Types of Reading Skills
Follow the Spark
- Become a Teacher
- Join our Sales Team
- Become An Affiliate
- Watch Live Class
- Customer Support
Get Trial Class
Please enter your phone number to proceed.
- Fundamentals NEW
- Biographies
- Compare Countries
- World Atlas
Related resources for this article
- Primary Sources & E-Books
(1888–1970). The Indian physicist C.V. Raman helped the growth of science in his country. He received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1930 for the discovery that when light passes through a transparent material, some of the light changes in wavelength. This phenomenon is now called Raman scattering.
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman was born on November 7, 1888, in Trichinopoly, India. He became professor of physics at the University of Calcutta in 1917. While studying the scattering of light in various substances, Raman made an important discovery in 1928. He found that when a beam of light of one frequency passes through a transparent substance, a small portion of the light emerges at right angles to the original direction. Some of this light is of different frequencies than that of the original light beam. These so-called Raman frequencies are the energies associated with transitions between different rotational and vibrational states in the scattering material.
Raman was knighted in 1929, and in 1933 he moved to the Indian Institute of Science at Bangalore as head of the department of physics. In 1947 he was named director of the Raman Research Institute there. In 1961 Raman became a member of the Pontifical Academy of Sciences. He contributed greatly to increasing the vitality of nearly every Indian research institution in his time. Raman founded the Indian Journal of Physics and the Indian Academy of Sciences and trained hundreds of students who found posts in universities and government in India and Myanmar (Burma). Raman died on November 21, 1970, in Bangalore. He was the uncle of Subrahmanyan Chandrasekhar , who was a cowinner of the 1983 Nobel Prize for Physics.
It’s here: the NEW Britannica Kids website!
We’ve been busy, working hard to bring you new features and an updated design. We hope you and your family enjoy the NEW Britannica Kids. Take a minute to check out all the enhancements!
- The same safe and trusted content for explorers of all ages.
- Accessible across all of today's devices: phones, tablets, and desktops.
- Improved homework resources designed to support a variety of curriculum subjects and standards.
- A new, third level of content, designed specially to meet the advanced needs of the sophisticated scholar.
- And so much more!
Want to see it in action?
Start a free trial
To share with more than one person, separate addresses with a comma
Choose a language from the menu above to view a computer-translated version of this page. Please note: Text within images is not translated, some features may not work properly after translation, and the translation may not accurately convey the intended meaning. Britannica does not review the converted text.
After translating an article, all tools except font up/font down will be disabled. To re-enable the tools or to convert back to English, click "view original" on the Google Translate toolbar.
- Privacy Notice
- Terms of Use
- general knowledge
C.V. Raman Biography: Early Life,Family, Education, Career, Awards and Achievements
Cv rama biography: november 7 marks the birth anniversary of the great scientist cv raman. he was a physicist, nobel laureate, and bharat ratna recipient who was instrumental in india’s growth in the fields of science and physics. let us read more about c.v. raman, his childhood days, education, family, discoveries, awards, and achievements. .

National Science Day 2023: Every year, November 7 commemorates the birth of Indian physicist Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. He discovered the Raman Effect on February 28, 1928, and for this discovery, he was honoured with the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930.
This article includes instances from his birth, early life, career, various achievements, and more.
C.V Raman: Biography
C.V. Raman, or Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, was born on November 7, 1888, at Tiruchirappalli in southern India. His father was a lecturer in mathematics and physics. At a young age, he was exposed to an academic environment. His contribution to science and innovative research helped India and the world.
|
|
Dr. Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (C.V. Raman): Early Life and Family
Dr. C.V. Raman was born on November 7, 1888, in a South Indian Brahmin family in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu. His father's name was Chandrasekhara Ramanathan Iyer. He was a lecturer in mathematics and physics at a college in Vishakhapatnam. His mother's name was Parvathi Ammal.
C. V. Raman has been an intelligent student since his early childhood. At the age of 11, he passed his matriculation and 12th grade on a scholarship. In 1902, he joined the Presidency College and received his graduate degree in 1904. At that time, he was the only student who received the first division. He has a Master's in Physics from the same college and broke all the previous records. In 1907, he married Lokasundari Ammal and had two sons, namely Chandrasekhar and Radhakrishnan.
Dr. Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (C.V. Raman): Career
Because of his father's interest, he appeared for the Financial Civil Services (FCS) examination and topped it. In 1907, he went to Calcutta (now Kolkata) and joined as an assistant accountant general. But in his spare time, he went to the laboratory to do research at the Indian Association for Cultivation of Sciences. Let us tell you that, his job was very hectic, and he also continued his research work at night due to his core interest in science.
Though the facilities available in the laboratory were very limited, he continued his research and published his findings in leading international journals, including 'Nature', 'The Philosophical Magazine', 'Physics Review', etc. At that time, his research was focused on the areas of vibrations and acoustics.
He got an opportunity to join the University of Calcutta in 1917 as the first Palit Professor of Physics. After 15 years at Calcutta, he became a Professor at the Indian Institute of Science at Bangalore from 1933 to 1948 and since 1948, he has been the Director of the Raman Institute of Research at Bangalore which was established and endowed by him only.
Dr. Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (C.V. Raman): Works and Discovery
He established the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926 where he was the editor. He also sponsored the establishment of the Indian Academy of Sciences and served as the President since its inception. He was the President of the Current Science Association in Bangalore, which publishes Current Science (India).
In 1928, he wrote an article on the theory of musical instruments for the 8th Volume of the Handbuch der Physik. He published his work on the "Molecular Diffraction of Light" in 1922 which led to his ultimate discovery of the radiation effect on February 28, 1928, and earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930. He became the first Indian to receive a Nobel Prize.
Other research carried out by Dr. C.V. Raman was on the diffraction of light by acoustic waves of ultrasonic and hypersonic frequencies and the effects produced by X-rays on infrared vibrations in crystals exposed to ordinary light.
In 1948, he also studied the fundamental problems of crystal dynamics. His laboratory has been dealing with the structure and properties of diamonds, and the structure and optical behaviour of numerous iridescent substances like pearls, agate, opal, etc.
He was also interested in the optics of colloids, electrical and magnetic anisotropy, and the physiology of human vision.
No doubt, he was honoured with a large number of doctorates and memberships in scientific societies. In 1924, he was also elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society early in his career and was knighted in 1929.
As briefly described he is best known for discovering the 'Raman Effect' or the theory related to the scattering of light. He showed that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the deflected light changes its wavelength.
Dr. Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (C.V. Raman): Awards and Honours
- In 1924, he was elected as a Fellow of the Royal Society early in his career and was knighted in 1929.
- He won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930.
- He was awarded the Franklin Medal in 1941.
- He was awarded the Bharat Ratna in 1954, the highest civilian award in India.
- In 1957, he was awarded the Lenin Peace Prize.
- The American Chemical Society and the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science in 1998 recognised Raman's discovery as an International Historic Chemical Landmark.
- On 28 February every year, India celebrates National Science Day to commemorate the discovery of the Raman Effect in 1928 in his honour.
In 1970, he received a major heart attack while working in the laboratory. He took his last breath at the Raman Research Institute on 21st November 1970.
Dr. C.V. Raman was one of the great legends from India whose hard work and determination made India proud and became the first Indian to receive a Nobel Prize in Physics. He proved that, if a person wants to pursue his/her desires nobody can stop. His interest in science and dedication towards research work made him discover the Raman Effect. He will always be remembered as a great Scientist, Physicist, and Nobel laureate.
Get here current GK and GK quiz questions in English and Hindi for India , World, Sports and Competitive exam preparation. Download the Jagran Josh Current Affairs App .
- Why is National Science Day celebrated? + NationalScience Day is observed on 28 February to commemorate the discovery of the 'Raman Effect'. In 1986, the Government of India designated 28 February as National Science Day (NSD). On this Day, Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, also known as CV Raman announced the discovery of the 'Raman Effect' for which he was awarded the Nobel Prize in 1930.
- When is National Science Day observed? + Every year on 28 February, National Science Day is celebrated to pay tribute to the Nobel Laureate Dr. C.V. Raman.
- When did C.V. Raman die? + Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (C.V. Raman) died on 21 November 1970.
- When and Why was C.V. Raman awarded with Nobel Prize? + Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (C.V. Raman) won Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 for his work on the scattering of light and for the discovery of the effect named after him that is the Raman Effect.
- What is the full name of C.V. Raman? + C.V. Raman full name is Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. He was born at Tiruchirappalli in Southern India on 7 November 1888.
- August Important Days 2024
- Independence Day Quiz 2024
- Independence Day 2024
- Vinesh Phogat Disqualified
- Vinesh Phogat Biography
- Paris Olympics 2024 India Medal Tally
- How to Use Meta AI
- India PM List 2024
- Nirmala Sitharaman
- Finance Ministers List 2024
- India Events
Latest Education News
Optical Illusion IQ Test: Only 1% Geniuses Can Spot The Boomerang Hidden Among Bananas In 8 Seconds!
Bihar BSEB Sakshmta 2 Pariksha Admit Card 2024: बिहार सक्षमता परीक्षा के एडमिट कार्ड यहाँ से करें Download
ISC Physical Education Specimen Paper 2024 (PDF) – CISCE Class 12 Physical Education Sample Paper
BPSC TRE 3.0 OMR Sheet 2024 Out at bpsc.bih.nic.in: Raise Objection till Aug 28
Today Current Affairs Quiz In Hindi: 16 अगस्त 2024- UN में भारत के नए राजदूत
MP Board Class 10 Maths Syllabus 2024-25: Download Detailed Syllabus With Marking Scheme
UPSC Full Form with Complete Details
झारखंड आबकारी कांस्टेबल एडमिट कार्ड 2024 OUT: अभी यहां से डाउनलोड करें एग्जाम Hall Ticket
MPBSE Class 11 Accountancy Syllabus 2024-25: Download MP Board Marking Scheme PDF
Who is Nalin Prabhat: IPS Officer to take over as next DGP of J&K, Read Biography, Profile
BSEB Bihar Sakshamta Pariksha 2 Admit Card 2024 OUT at bsebsakshamta.com: Download Link Here
UP Police Constable Exam City Slip,Admit Card 2024 [Live Update] :आज शाम 5 बजे से डाउनलोड करें यूपी पुलिस की सिटी स्लिप, Download Link
AP ICET 2024 Phase 1 Seat Allotment Results on August 20 at icet-sche.aptonline.in
Math Puzzle: Only highly intelligent readers can solve this math puzzle in 10 seconds!
Jharkhand Excise Constable Admit Card 2024 Out at jssc.nic.in, Direct Link to Hall Ticket, Check PET Schedule
Essay on Raksha Bandhan: Short and Long Essays for School Students in English
UP Police Exam City Slip 2024: Download UPPRPB Constable Pre Admit Card at uppbpb.gov.in
MPBSE Class 11 Chemistry Syllabus 2024-25: Download MP Board Marking Scheme PDF
ISC Political Science Specimen Paper 2024-25 Free PDF Download: CISCE Class 12 Political Science Sample Paper
Find 3 differences between the honeybee pictures in 14 seconds!
Short Essay on CV Raman (Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman)
Jump ahead to:
CV raman biography in essay more than 100 words in english here we have 10 lines about CV Raman or more. This paragraph is all about CV Raman (Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman)
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman was born at Trichinopoly in Southern India ON November 7th, 1888 . His father was a lecturer in mathematics and physics so that from the first he was immersed in an academic atmosphere.
He entered Presidency College, Madras in 1902 , and in 1904 passed his B.A. examination , winning the first place and the gold medal in physics, in 1907 he gained his M.A. degree , obtaining the highest distinctions . His earliest researches in optics and acoustics – the two fields of investigation to which he has dedicated his entire career – were carried out while he was a student.
Since at that time a scientific career did not appear to present the best possibilities, Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman joined the Indian Finance Department in 1907 : though the duties of his office took most of his time, Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman found opportunities for carrying on experimental research in laboratory of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science at Calcutta (of which he became Honorary Secretary in 1919 ).
Short Essay on C.V Raman in English paragraph

In 1971 he was offered the newly endowed Palit Chair of Physics at Calcutta University and decided to accept it. After 15 years at Calcutta , he became Professor at the Indian Institute of Science at Banglore (1933-1948), and since 1948 he is Director of the Raman Institute of research at Banglore , established and endowed by himself.
He also founded the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926 , of which he is the Editor. Raman sponsored the Establishment of the Indian Academy of Sciences and has served as President since its inception.
He also initiated the Proceedings of that academy, in which much of his work has been published, and in President of the Current Science Association, Bangalore, which publishes Current Science (India).
10 lines about CV Raman
Some of Raman’s early memoirs appeared as (10 lines about CV Raman)
- Bulletins of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Science.
- He contributed an article on the theory of musical instrument to the 8th Volume of the Handbuch der Physik, 1928.
- In 1922 he published his work on the “Molecular Diffraction of Light” , the first of the series of investigations with his collaborators which ultimately led to his discovery,
- on the 28th of February , 1928 of the radiation effect which bears his name ( “A new radiation”, Indian J.Phys., 2 (1928) 387), and which gained him to 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics.
- Other investigations carried out by Raman were: his experimental and theoretical studies on the diffraction of light by acoustic waves of ultrasonic and hypersonic frequencies (published 1934-1942), and those on the effects produced by X-ray on infrared vibration in crystals exposed to ordinary light.
- In 1948 Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, through studying the spectroscopic behaviour of crystals, approached in a new manner fundamental problems of crystal dynamics,
- His laboratory has been dealing with the structure and properties of diamond, the structure and optical behaviour of numerous iridescent substances ( labradorite, pearly felspar, agate, opal, and pearls ).
- Among his other interests have been the optics of colloids, electrical and magnetic anisotropy, and the physiology of human vision.
- Raman has been honoured with a large number of honorary doctorates and memberships of scientific societies.
- He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society early in his career (1924) , and was knighted in 1929.
CV Raman PDF (Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman)
Audio by ttsmp3
1 thought on “Short Essay on CV Raman (Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman)”
Thanks for visit our site, If you want to know more about how to write Short Essay on CV Raman (Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman). For any query about this topic comment below.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Notify me of new posts by email.
Pen2Print Services
Get Pen2Print services from our Educational Platform for scholars.
- _Published Books
- Conferences
- Conference Proceedings
- Edited Books
- Cover Design
Search more articles
Short essay on 'chandrasekhara venkata raman' (c v raman) (200 words).

Featured post
How to write effective literature review.
A literature review is an essential component of any research project or academic paper. It involves identifying, evaluating, and summarizin...

- Book Chapters

- IS TEXTING THE NEXT BIG THING IN RECRUITING? At first glance texting and interviewing candidates seems to go together as well as ketchup and lobster. But if you think about it just a mi...

- A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Biography: Early Life, Education, Career, Books, Awards and More Our Missile Man Dr. A.P.J. Abdul Kalam was an Indian scientist and politician who played a leading role in the development of India's ...

Services Tags
- Audio Books
- Book Chapter Publication
- Book Chapters Publication
- Book Publication
- Book Publishing
- Book review
- Book Series
- Book-Chapters
- Book-Cover-Design
- Call for Book Chapters
Call for Papers
- Conference-Proceedings
- Content Writing
- Copywriting
- Creative Writing
- Edited-Books
- Pen2Print Publication
- Pen2print Services
- Physical Educational Books
- Publications
- Research Papers
- Research Publication
- Website Development
- Writing Services
Readers of the Forum
Search this website.
Our YouTube channel crossed 10k subs!
- Publication
Popular Posts

- IS TEXTING THE NEXT BIG THING IN RECRUITING?

Get More Services
Welcome to Books and Book Chapters, if you wish to get your scholarly books and book chapters published then you are at the right place.

Send mail to [email protected]
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- C V Raman Biography

Writing a Biographical Essay of a Historical Figure
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, was an Indian physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 for his work on light scattering and the discovery of a new form of scattering called Raman scattering or the Raman effect. The compositions of solids, liquids, and gases can all benefit from this effect. It can also be used to diagnose diseases and track manufacturing processes.
Biography is an account of a person’s life by another person. It is a descriptive work written in detail. Biographical pieces can be in various forms, like a video or book and they can be of any length, like a book or an essay. An authorized biography is written with the permission of the subject and an unauthorized one is not. However, biographies of historical figures written for purely academic purposes do not require consent from the subject or people who hold the rights of consent for the subject.
Choosing the Right Level
Biographies can be written by students of all classes. The higher the class, the more details go into the essay. The biography by a fifth-grader will be smaller and less detailed than that written by a ninth-grader. The demand for making it more interesting and decorating it with aptly placed figures of speech grows with grade.
Choosing the Right Source
Biography is not fiction or a made-up story. It is the arrangement of boring dates and facts into a beautiful landscape that would be the subject’s life. For the facts to be accurate and true, trustworthy sources must be consulted, like a known book or reliable websites that contain life information.
Choosing the Right Information
Having selected the right source of information, it can get mind-boggling to choose what information to keep and what not to mention in the essay. It is better to have too much information than too little so that the best out of them can be chosen. A biography should answer some basic questions about the person. The place and date of his birth and death. Information about his immediate family. Important milestones of his life, like schooling, occupation, marriage, kids, appointments, or discoveries. His accomplishments during his lifetime. And then the legacy he leaves behind, like his impact on society or education and the historical significance.
How to Arrange the Information?
Biographies are descriptions of someone’s life, so setting the tone and making it sound interesting relies freely on the writer’s shoulders. The student can make life sound fun and lively, or gripping and intense. This is where the talent of a writer shines through, so use all of the writing tools at hand and make the best of them.
The Person Behind the Facts
The personality of the subject should shine through the essay. Select appropriate adjectives to build upon the character of the person. If interesting anecdotes highlight the kind of person he was, use them to build upon his personality.
Legacy in Conclusion
The achievement of his life and his notable works need to be mentioned, as well as how he affects posterity. In conclusion, the importance of his work and legacy should be highlighted.
It should be remembered that however tempting it feels to include interesting details and fun facts, the word limit should be kept in mind. This is what should rule which facts go and which do not in the essay. The introduction, body, and conclusion need to be clearly arranged. A biographical essay is not a story-telling spree, so the spirit of an essay should be intact.
The best essays are easy to read and the flow from one part to another is seamless. It might sound contradictory to keep a seamless flow while keeping the three parts of an essay demarcated, but it is not impossible and this is the delicate balance that can only be achieved by persistent practice. Language is not much different from Maths or Science in this aspect – practice makes perfect.
Information About C V Raman
Sir C V Raman’s birthday- November 7, 1888
Sir C V Raman’s death day- November 21, 1970
Alma mater- The University of Madras (M.A.)
Known for Raman effect
Spouse- Lokasundari Ammal (1908–1970)
Children- Chandrasekhar Raman and Venkatraman Radhakrishnan
About C V Raman’s Family and Background
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman was born to a Tamil Brahmin family in Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu, on November 7, 1888. Raman's forefathers were agriculturists who settled in the Tanjore district near Porasakudi Village and Mangudi. Chandrasekhara Iyer, his father, attended a school in Kumbakonam and graduated with honours in 1881. He eventually earned a Bachelor of Arts degree in Physics from Tiruchirapalli's Society of the Promotion of the Gospel College in 1891. In the same college, Chandrasekara became a lecturer. He married Parvathi Ammal after passing the Matriculation exam and they had eight children: five sons and three daughters. Chandrasekaran, Raman's father, moved to Visakhapatnam when he was four years old to work as a lecturer at Mrs. A.V. Narasimha Rao College. He taught Physics, arithmetic, and physical geography at the university. Chandrasekaran was regarded as physically and mentally powerful due to his involvement in athletics, physical culture, and Indian Carnatic music, among other things. Raman, unlike his father, was not physically powerful, but he was a brilliant thinker. He excelled in school and displayed early signs of exceptional ability, receiving praise from his teachers as well as numerous prizes and scholarships. While still in school, Raman developed an interest in Physics. He once designed a dynamo on his own and was fascinated with how physical principles and machines worked. C. V. Raman graduated from high school at the age of eleven, receiving first place in the Matriculation Examination (top marks). He then enrolled in the AVN College to prepare for the Intermediate Exam. He received more accolades this time, and he received top scores on the university test. In 1903, he received a scholarship to study for a BA degree at the Presidency College in Chennai (then Madras), where he was the youngest student. At the time, the Presidency College was the best in Southern India. When Raman was in college, the majority of his professors were Europeans. Raman's interest in Physics grew even stronger during this period, and he also developed a strong liking for English. Raman earned first place in the university's BA exams in 1904, and gold medals in English and Physics. Raman's teachers encouraged him to continue his education in England, but the Madras Civil Surgeon refused, arguing that the young Raman was too weak to endure the English climate. Raman, on the other hand, completed his MA in Physics at Presidency College and did not travel abroad until he was thirty-three years old.
About C V Raman’s Early Career and Marriage
In January 1907, Raman sat for and passed his Master's examination, earning top marks and a slew of awards and prizes. While he desired to focus on science (particularly research), there were no research opportunities in India (specifically for Indians). Owing to his deteriorating health at the time, he was unable to travel to England. As a result, Raman's thoughts turned to work for the government, which is known to be clean, stable, and even prestigious. Even in this situation, he desired to enter the prestigious Indian Civil Service (ICS), the highest level of government service, but this meant training in England and taking the exam there—an option that was also ruled out due to medical reasons. The Financial Civil Service (FCS), where Raman's brother C.S. Iyer was already a member, which was his next preference. The FCS served as a forerunner to today's Indian Audit and Accounts Service. Raman passed the FCS examination in 1907 and married Lokasundari before taking up an official job. This period of his life unfolded unusually. Typically, parents arranged Indian marriages, which includes finding a suitable horoscope match for their infant. This included looking at the positions of the stars on their birth date, as well as other horoscopic statistics. The boy and his parents then pay a visit to the girl's house to see if she likes them; during this period, the girl is normally asked to give a musical performance. The date for their marriage is fixed if all arrangements are in agreement and the girl's family provides adequate dowry. Raman's marriage went in a different direction. Mr. Ramaswamy Sivan, a freemason, theosophist, and radical thinker, was a friend of Raman's as a college student. Mr. Sivan's house was a frequent stop for Raman, and one day he heard music from an Indian classical instrument, the veena, played by Lokasundari, Sivan's sister-in-law, who was visiting from Madurai. Lokasundari was a natural at playing the veena, and Raman was instantly drawn to her. Sivan discussed this idea with Raman, who immediately accepted it since Lokasundari was of marriageable age at the time and her family was looking for a suitable groom. Raman then continued to seek permission from his parents. However, it was later discovered that Lokasundari, thought of the same caste as Raman (Brahmin), belonged to a separate subset—a match that was strictly forbidden at the time. Raman's father, who is a rather liberal man, agreed that Raman could choose his bride, even if she came from a different subset. The rest of the family, including Raman's mother, was unhappy, however. Despite these challenges, Raman followed his heart and kept on doing things his way. In mid-1907, Raman was appointed Assistant Accountant-General in Calcutta, even though he was still a teenager. His pay, including the marriage allowance, was Rs. 400 at the time. Raman and Lokasundari set out for Calcutta, the capital of British India at the time. Raman took advantage of Calcutta's vibrant and scientific environment, allowing him to fully articulate his scientific creativity—Calcutta was then regarded as the East's premier science city. Raman was sent to Nagpur and Rangoon in addition to Calcutta; no matter where he was posted, Raman still found a way to perform experiments at home.
C V Raman Contribution to Science
Raman productively used the time he had with Professor Jones while studying Physics at Presidency College, designing and creating experiments to address the boundless questions he had. Only the most basic laboratory instruments (enough for classwork) were available in the Physics lab at the time, but Raman made use of them all. Raman's questions were frequently those for which there were no answers in the literature. As a result, the nature of science came naturally to him, prompting him to perform experiments throughout his life. Raman experimented with asymmetric diffraction of light though he was well aware of light in a wave shape and the principle of diffraction. Professor Jones was given his observations on this experiment, which he collected and gave to him for feedback. Professor Jones, on the other hand, remained silent for many months. Raman was aware of the Philosophical Magazine at the time, possibly those subscribed to by the Connemara Public Library, which was about five kilometers from Presidency College (it is not certain how Raman came to know of this magazine). This paper was written in 1906, and Raman, who was only 18 at the time and had not yet graduated from high school, was the sole author with no acknowledgments. Raman's achievement was all the more remarkable because Presidency College was not a research institution, and Raman's paper was the first to emerge from there. Almost immediately after Raman's first publication, Johns Hopkins University's R.W. Wood published another. Wood later sent a cable to Nature announcing the Raman Effect's discovery. Raman left the government in 1917 to take up the newly established Palit Professorship in Physics at the University of Calcutta. Simultaneously, he continued his study at the IACS, where he eventually rose to the position of Honorary Secretary. Raman referred to this period in his career as his "golden age." At the IACS and the University of Calcutta, he was surrounded by a group of gifted students. In 1929, he presided over the 16th session of the Indian Science Congress. Raman worked on the acoustics of musical instruments in addition to his Nobel Prize-winning work on light scattering. Based on superposition velocities, he developed a theory of transverse vibration of bowed strings. In comparison to Helmholtz's method, this does a great job of describing bowed string vibration. He was also the first to explore the harmonic essence of Indian drum sounds like the tabla and mridangam. Raman was appointed director of the newly established Indian Institute of Science (IISc) in Bangalore in 1933. The IISc was established in 1909 with the aim of conducting original research and providing science and engineering education. Before Raman's appointment, all of IISc's directors, as well as the majority of its faculty, were British. He remained a Professor of Physics for another two years. The new government of Independent India named him the country's first National Professor in 1947. In 1948, he retired from the Indian Institute of Science and a year later founded the Raman Research Bangalore, Karnataka, where he served as director until he died in 1970.
C V Raman’s Discovery
Raman was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 for his research on light scattering and the discovery of the Raman effect. The inelastic scattering of a photon is known as "Raman scattering" or "Raman effect." This phenomenon is the basis for Raman spectroscopy.
What led to C V Raman’s Invention of Raman Effect?
C V Raman Discovery of the Physics of Musical sound- Understanding the Physics of musical Sound was one of Raman's passions. The Sensations of Tone by Hermann Von Helmholtz, which he came across when he entered IACS, inspired him. Between 1916 and 1921, he researched and published a lot of his observations. Based on the superposition of velocities, he developed the principle of transverse vibration of bowed string instruments. The wolf tone in violins and cellos was one of his earliest experiments. He investigated the acoustics of various violins and related instruments, as well as water splashes and Indian stringed instruments. "Experiments with mechanically-played violins" was one of his works. C V Raman Discovery behind the Blue colour of the sea- In 1919, Raman began investigating light scattering as part of his broadening foray into optics. His first amazing discovery was the mechanics of seawater's blue colour. In September 1921, he reflected on the Mediterranean Sea's blue colour while sailing home from England on the S.S. Narkunda. He tested the seawater with basic optical instruments, including a pocket-sized spectroscope and a Nicol prism. No.56 Lord Rayleigh's explanation in 1910, "The much-revered dark blue of the deep sea has little to do with the colour of water, but is the blue of the sky seen by refraction," was the strongest of many theories on the colour of the sea. C V Raman Inventions: Most photons are elastically dispersed as light is scattered from an atom or molecule. The incident photons have the same energy (frequency) as scattered photons, and therefore the same wavelength. Excitations of optical frequencies distinct from, and normally lower than, the frequency of the incident photons scatter a small fraction of scattered light (roughly one in ten million photons). Raman scattering may occur in gas when a molecule's vibrational, rotational, or electronic energy changes. "The character of scattered radiations allows us to obtain an insight into the ultimate structure of the scattering," Raman explained. Raman published his thesis on "Molecular Diffraction of Light" in 1922, the first of a series of investigations with his collaborators that eventually led to his discovery of the radiation effect that bears his name (on February 28, 1928). In 1928, C. V. Raman and K. S. Krishnan, as well as Grigory Landsberg and Leonid Mandelstam, independently identified the Raman effect. Raman's discovery was hailed by physicists as evidence of the quantum theory. The vibrational Raman effect is of primary interest to chemists. The Raman Effect was named a National Historic Chemical Landmark by the American Chemical Society in 1998, in recognition of its importance as a method for studying the structure of liquids, gases, and solids. The Raman Effect is distinct from the fluorescence mechanism. The incident light is completely absorbed in the latter case, and the system is transferred to an energetically excited state from which it can only transition to various lower states after a certain period (resonance lifetime). Both processes emit a photon with a different frequency than the incident photon, and the molecule is brought to a higher or lower energy level. However, the Raman Effect can occur for any frequency of incident light, which is a significant difference. The Raman Effect, in contrast to the fluorescence effect, is not a resonant effect.
C V Raman’s Contribution as an Author
C V Raman’s discoveries led him to write a set of books which are listed below-
Vol. 1 -Scattering of Light (Ed. S Ramaseshan)
Vol. 2 -Acoustic
Vol. 3 -Optica
Vol. 4 -Optics of Minerals and Diamond
Vol. 5 -Physics of Crystals
Vol. 6 -Floral Colours and Visual Perception
C V Raman’s Achievements and Awards
Many honorary doctorates and memberships in scientific societies were bestowed upon Raman. He was a member of the Deutsche Akademie in Munich, the Swiss Physical Society in Zürich, the Royal Philosophical Society in Glasgow, the Royal IrishAcademy, the Hungarian Academy of Sciences, the Academy of Sciences of The Soviet Union, the Optical Society of America, and the Mineralogical Society of America, the Romanian Academy of Sciences, the Catgut Acoustical Society of America, and the Czechoslovak Academy of Sciences. He was elected a Fellow of the Royal Society in 1924. He did, however, resign from the fellowship in 1968 for unknown reasons, making him the only Indian FRS to do so. In 1929, he was the President of the Indian Science Congress's 16th session. From 1933 until his death, he was the first President of the Indian Academy of Sciences. In 1961, he was elected to the Pontifical Academy of Sciences.
Though still employed by the Indian Finance Service, Raman won the Curzon Research Award in 1912. While still working for the Indian Finance Service, he received the Woodburn Research Medal in 1913. The Accademia Nazionale delle Scienze in Rome awarded him the Matteucci Medal in 1928. He was knighted in 1930. The Viceroy of India, Lord Irwin, conferred him a Knight Bachelor in a special ceremony at the Viceroy's House (now Rashtrapati Bhavan) in New Delhi after his inclusion in the 1929 Birthday was postponed. He was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 for "research on light scattering and the discovery of the phenomenon named after him."He was the first Asian and non-white person to win a Nobel Prize for Science. Rabindranath Tagore (another Indian) had previously won the Nobel Prize for Literature in 1913. He was awarded the Hughes Medal of the Royal Society in 1930. The Franklin Institute in Philadelphia awarded him the Franklin Medal in 1941. He received the Bharat Ratna award in 1954. (along with politician and former Governor-General of India C. Rajagopalachari and philosopher Sir Sarvepalli Radhakrishnan). He received the Lenin Peace Prize in 1957.

FAQs on C V Raman Biography
1. What is the discovery of C V Raman about?
On a boat trip back from England in 1921, Indian physicist C.V. Raman began work on a line of research that would lead to the discovery of a new scattering effect, now known as the Raman effect, in February 1928. The Raman effect is significant in Physics and Chemistry.
2. Why write a biography about CV Raman?
Writing a biography is a good way to practice research and describe a person and his legacy to mankind. CV Raman is an apt topic for biography because he was a historical figure of great importance and his legacy in the field of Mathematics and Physics is big and easily available for research.
3. Are there ways of talking about a subject other than a biographical essay?
A biographical essay is just one of the many ways of describing a person’s life. Some other forms are a documentary, a biographical movie, the life of a person written as a play or story – it can be short or long – the options are as endless as one’s creativity. Refer to the official website of Vedantu or download the app for an elaborate explanation.
4. What are the tools that one can use to make a boring biography interesting?
Writing tools that can brighten up a boring biography are figures of speech, including relevant quotes, presenting the facts in a story-telling manner, etc
5. Was CV Raman a scientist or a mathematician?
CV Raman was a Nobel Prize-winning Physicist whose exemplary work in Optics won him a place in the annals of history.
6. C V Raman is Famous For?
The Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to C.V. Raman in 1930 for his discovery of the Raman effect, in which light passing through a substance is dispersed and the wavelength of the scattered light is altered due to an energy state transfer in the material's molecules.
CBSE Library

CV Raman Essay | Essay on CV Raman for Students and Children in English
CV Raman Essay: Steeped in intellectual thought with an illustrious eye for detail, he represented India’s scientific temper. He is the first Asian and the foremost Indian to win the Nobel Prize in Physics. Most importantly, he did this at a time when India was little known in the field of Sciences. A man of immense calibre and a pool of talent, he can be none other than Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. – The Intellectual Gem
You can read more Essay Writing about articles, events, people, sports, technology many more.
Long and Short Essays on CV Raman for Kids and Students in English
Given below are two essays in English for students and children about the topic of ‘CV Raman’ in both long and short form. The first essay is a long essay on the CV Raman of 400-500 words. This long essay about CV Raman is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on CV Raman of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
Long Essay on CV Raman 500 Words in English
Below we have given a long essay on CV Raman of 500 words is helpful for classes 7, 8, 9 and 10 and Competitive Exam Aspirants. This long essay on the topic is suitable for students of class 7 to class 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants.
Born at Trichinopoly in Tamil Nadu on 7th November, 1888, his father was a lecturer in Mathematics and Physics, in Mrs AV Narasimha Rao College, Visakhapatnam, and later joined Presidency College, Madras. His maternal grandfather was a Sanskrit scholar, well versed in ‘navya nyaya’ or modern logic.
So, from an early age, he was immersed in an academic atmosphere. He was a diligent student. He entered the Presidency College, Madras, in 1902, and in 1904 passed his BA examination, winning the first place and a gold medal in Physics. In 1907, he gained his MA degree, obtaining the highest distinctions. His earliest researches in optics and acoustics—the two fields of investigation to which he dedicated his entire career were carried out while he was a student. Since at that time a scientific career did not appear to offer the best possibilities, Raman joined the Indian Finance Department in 1907. Though the duties of his office took most of his time, Raman found opportunities for carrying on experimental researches in the laboratory of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Sciences at Calcutta.
In 1917, he was offered the newly endowed Palit Chair of Physics at Calcutta University, and decided to accept it. Raman’s main research was focussed on acoustics and musical instruments, and led to his election as fellow of the Royal Society in 1924. It was during a trip to England in 1921 that he was fascinated by the blue colour of the Mediterranean.
With a very simple experiment, he convinced himself that the blue colour of the sea was not only due to the reflection of the sky, as proposed by Lord Rayleigh, but mainly due to the scattering of light by water molecules. On his return to Calcutta, he began a systematic study of the scattering of light by different liquids, culminating in the discovery of a totally new kind of radiation, predicted by the quantum theory and named after him.
There Raman radiations carry vital information about the internal structure of the scattering molecules, and have proved to be of immense importance in studying molecular structures. His efforts finally paid off when he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930, the first to be ever won by an Indian. Thereafter, he became the Honorary Secretary of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Sciences. After 15 years in Calcutta, he became Professor at the Indian Institute of Science at Bangalore (1933-1948) and in 1948, he became the Director of the Raman Institute of Research at Bangalore, established and endowed by himself. He also founded the Indian Journal of Physics in 1926, of which he was the Editor.
Raman sponsored the establishment of the Indian Academy of Sciences and served as its President since its inception. He was also the President of the Current Science Association, Bangalore, which publishes Current Science. (India)
Raman has done credible work in his field and his early memoirs appeared as Bulletins of the Indian Association for the Cultivation of Sciences. These dealt with the maintenance of vibrations and the theory of musical instruments of the violin family. In 1922, he published his work on the ‘Molecular Diffraction of Light’, the first of a series of investigations with his collaborators which ultimately led to the discovery, on 28th February, 1928, of the radiation effect, which is named after him. This work bagged him the 1930 Nobel Prize in Physics.
Some other investigations which propelled the world of science during his time were the experimental and the theoretical studies on the diffraction of light by acoustic waves of Ultrasonic and Hypersonic frequencies. In 1932, he and Suri Bhagavantam discovered quantum photon spin. During his term at IISc, he admitted the talented electrical engineering student, GN Ramachandran, who went on to become a recognised X-ray crystallographer.

Short Essay on CV Raman 200 Words in English
Below we have given a short essay on CV Raman is for Classes 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6. This short essay on the topic is suitable for students of class 6 and below.
In 1948, Raman, through studying the spectroscopic behaviour of crystals, approached fundamental problems of crystal dynamics in a new manner. His laboratory has been dealing with the structures and properties of diamond, the structure of optical behaviour of numerous iridescent substances like opal and pearls.
This luminous star in the firmament of the scientific fraternity has been honoured with a large number of honorary doctorates and memberships of scientific societies. He was elected as a fellow of the Royal Society in 1924 and knighted in 1929. In 1941, he was awarded the Franklin Medal. In 1954, he was conferred upon, the Bharat Ratna. He got the Lenin Peace Prize in 1957.
Another big honour was that the American Chemical Society and IACS recognised his discovery as an International Historic Chemical Landmark. India celebrates National Science Day every year on 28th February to remember the discovery of Raman effect that took place in 1928.
At the end of October, 1970, he collapsed in his laboratory. Doctors gave him four hours to live. He survived and asked to be shifted from the hospital to the gardens of his institute. He passed away on 21 st November, 1970. His life was a testimony to hard work, patience and perseverance for achieving one’s goals. One should also be level headed and not go overboard on attaining success. With him, dawned an era of high quality science, and he showed the light for others to follow.
CV Raman Essay Word Meanings for Simple Understanding
- Illustrious – very famous and much admired, especially because of what you have achieved
- Diligent – showing care and effort in your work or duties
- Optics – the scientific study of sight and light
- Acoustics – the shape, design, etc. of a room or theatre that make it good or bad for carrying sound
- Endowed – to give a large sum of money to a school, a college or another institution to provide it with an income
- Inception – the start of an institution, an organisation, etc.
- Propelled – to move, drive or push something forward or in a particular direction
- Diffraction – breaking up of stream of light into a series of dark and light bands or the different colours of the spectrum
- Spectroscopic – a piece of equipment for forming and looking at spectra
- Iridescent – showing many bright colours that seem to change in different lights
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

2 Minute Speech on C.V. Raman in English
Greetings and good morning everyone, today I am going to give a speech on C.V. Raman. C.V. Raman, also known as the Great Indian Physicist Chandrasekhar Venkata Raman, was born in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, on November 7, 1888. Raman naturally developed a passion for physics because his father was a teacher of the discipline. He was a standout student from the start. He passed his matriculation test from Madras University at the tender age of 12 as a bright and promising young man.
In 1924, he was chosen as a Fellow of the Royal Society of London. In 1928, he discovered the “Raman Effect”, and in 1930, he was given the Physics Nobel Prize.
Related Posts:

45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Meet top uk universities from the comfort of your home, here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

- Trending Events /
Top 10 Life Learnings from CV Raman Quotes

- Updated on
- Nov 7, 2023

CV Raman or Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman is one of India’s most renowned physicists who discovered the Raman Effect. He was the first Indian to win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930. Dr CV Raman was very good at academics as he sought inspiration from his father who was a reputed lecturer of mathematics and physics . He was born in Tiruchirappalli on 7 November 1888. National Science Day celebrated on 28 February is dedicated to celebrating the discovery of CV Raman in science. On his birth anniversary read this article to learn about some inspirational life lessons through CV Raman Quotes!
Also Read: CV Raman Biography
❓Who was Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman?
Born on November 7, 1888, in the city of Tiruchirapalli of Tamil Nadu, CV Raman was the second of eight children in his family. His father Chandrasekaran Ramanathan Iyer was a teacher of Mathematics and Physics. His mother Parvathi Ammal was taught by her husband to read and write. The family was financially unstable at the time of Raman’s birth, however, the situation improved when he was four years old as his father became a lecturer. Eventually, the family then moved to Visakhapatnam. From a very young age, CV Raman showcased exceptional talent in studies. He was very interested in reading books and Science as a subject always fascinated the young Raman.
One of the most distinguished scientists of the 20th century, C V Raman became the first national professor of India after the country gained independence. Apart from this, he also won the Nobel Prize in 1930 for his groundbreaking work in the field of physics.
Also Read: How to Prepare for UPSC in 6 Months?
🗨️ CV Raman Quotes
CV Raman established and supported the Indian Institute of Science. He also served as a professor at the University. His quotes are inspiring the young scientists to discover something unique and contribute to the field of science.
Here are some inspirational CV Raman quotes:
“Treat me right and you will see the light…Treat me wrong and you will be gone!”
“I am the master of my failure. If I never fail, how will I ever learn?”
“If someone judges you, they are wasting space in their mind. The best part is it’s their problem.”
“I strongly believe that fundamental science cannot be driven by instructional, industrial government or military pressures.”
“It was poverty and the poor laboratories that gave me the determination to do the very best I could.”
“The essence of science is independent thinking, hard work, and not equipment. When I got my Nobel Prize, I had spent hardly 200 rupees on my equipment.”
“I would like to tell the young men and women before me not to lose hope and courage. Success can only come to you by courageous devotion to the task lying in front of you.”
“You can’t always choose who comes into your life but you can learn what lesson they teach you Success can come to you by courageous Devotion to the task lying in front of you.”
“The essence of the scientific spirit is to realize what a wonderful world it is that we live in.”
“Ask the right questions, and nature will open the door to her secrets.”
🎂 CV Raman Birthday
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman the first Indian to win Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 and also a Bharat Ratna in 1954 discovered the Raman Effect that explains the phenomenon of scattering of light. Every year, India celebrates National Science Day to commemorate the discovery of CV Raman on 28 February.
Here are some tweets on CV Raman’s Birthday:
On his birth anniversary, we remember Sir C. V. Raman, renowned for winning the Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the 'Raman Effect'. Today, we pay our tributes to the Bharat Ratna Awardee for his enormous contribution to the field of Science. pic.twitter.com/fB61gBJOUd — Congress (@INCIndia) November 7, 2023
My tributes to physicist and Nobel Laureate, Sir #CVRaman , on his birth anniversary today. His life and work continue to inspire students of science. 🙏🏻 #RamanEffect pic.twitter.com/YU8Oi3LLGY — Rajeev Chandrasekhar 🇮🇳 (@Rajeev_GoI) November 7, 2023
Also Read: Nobel Laureates of India
Relevant Searches
The famous line of Dr CV Raman is “Treat me right and you will see the light…Treat me wrong and you will be gone!”
CV Raman invented the Raman Effect which is the scattering of light. It tells about the scattering of light due to changes in the wavelength when it interacts with the molecules in the striking material.
“I would like to tell the young men and women before me not to lose hope and courage. Success can only come to you by courageous devotion to the task lying in front of you.”
For more information on such interesting topics, visit our Important Days website and follow Leverage Edu .
Kajal Thareja
Hi, I am Kajal, a pharmacy graduate, currently pursuing management and is an experienced content writer. I have 2-years of writing experience in Ed-tech (digital marketing) company. I am passionate towards writing blogs and am on the path of discovering true potential professionally in the field of content marketing. I am engaged in writing creative content for students which is simple yet creative and engaging and leaves an impact on the reader's mind.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *

Connect With Us
45,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
January 2024
September 2024
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Have something on your mind?

Make your study abroad dream a reality in January 2022 with
India's Biggest Virtual University Fair

Essex Direct Admission Day
Why attend .

Don't Miss Out

COMMENTS
100 Words On Essay On CV Raman. Since his father taught physics and mathematics at AV Narasimha Rao College in Visakhapatnam, CV Raman was raised in an academic environment. Raman was a dedicated student. He enrolled in the Presidency College in Madras in 1902, and in 1904 he successfully completed his BA programme, earning first place and a ...
Read this comprehensive essay on Chandrasekhar Venkata Raman (1888 A.D. - 1970 A.D.) ! The Great Indian physicist Chandrasekhar Venkata Raman, popularly known as C.V Raman, was born on 7 th November, 1888 at Trichirapalli in Tamil Nadu. His father was a physics teacher and so it was natural that Raman developed love for this subject.
C.V. Raman (born November 7, 1888, Trichinopoly, India—died November 21, 1970, Bangalore) was an Indian physicist whose work was influential in the growth of science in India. He was the recipient of the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1930 for the discovery that when light traverses a transparent material, some of the light that is deflected ...
The first essay is a long essay on the CV Raman of 400-500 words. This long essay about CV Raman is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on CV Raman of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
C. V. Raman was born in Tiruchirappalli in the Madras Presidency of British India (now Tiruchirapalli, Tamil Nadu, India) to Tamil Iyer Brahmin parents, [4] [5] Chandrasekhar Ramanathan Iyer and Parvathi Ammal. [6] He was the second of eight siblings. [7] His father was a teacher at a local high school, and earned a modest income. He recalled: "I was born with a copper spoon in my mouth.
Writing an essay is like setting on a journey of discovery, especially for school kids. It's a wonderful way to explore new ideas, express thoughts, and learn about remarkable personalities who have shaped our world. Today, we'll delve into an essay on CV Raman in English, a topic that not only educates but also inspires young minds.
C handrasekhara Venkata Raman was born at Tiruchirappalli in Southern India on November 7th, 1888. His father was a lecturer in mathematics and physics so that from the first he was immersed in an academic atmosphere. He entered Presidency College, Madras, in 1902, and in 1904 passed his B.A. examination, winning the first place and the gold medal in physics; in 1907 he gained his M.A. degree ...
Question.2. Write about the power and beauty of the element, water. Ans. Water is the true elixir of life. It is the basis of life on Earth. Every animal and plant contains water. It is necessary for their life. Our agriculture is depended on water. To explain the power of water C.V.Raman has given an example.
Students are often asked to write an essay on CV Raman in their schools and colleges. And if you're also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic. ... 500 Words Essay on CV Raman Introduction. Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, popularly known as C.V. Raman, was an eminent physicist who left an ...
The early life of CV Raman. Born on November 7, 1888, in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, Raman displayed a prodigious intellect from an early age, finishing his secondary education by the age of 11. He graduated with a Bachelor of Arts degree from Presidency College, Madras, in 1904, and subsequently completed his Master's in Physics in 1907.
Abstract and Figures. In 1928 the Indian physicist C. V. Raman (1888-1970) discovered the effect named after him virtually simultaneously with the Russian physicists G. S. Landsberg (1890-1957 ...
7th November marks the birth anniversary of this revered scientist who discovered the Raman Effect. His discovery enabled the scientific community to move forward and better understand various natural phenomena. Sir C V Raman was born in 1888 in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu. His father was Chandrashekhar Ramanathan.
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman (CV Raman) was an Indian scientist and physicist. Born on 7th November 1888, his contribution to the field of science got him a Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930. He discovered the ' Raman Effect ', which is a unique form of 'modified scattering of light'. He was awarded Fellowship of Royal Society of ...
Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman was born on November 7, 1888, in Trichinopoly, India. He became professor of physics at the University of Calcutta in 1917. While studying the scattering of light in various substances, Raman made an important discovery in 1928. He found that when a beam of light of one frequency passes through a transparent ...
In this video you will see essay on C.V. Raman.This C.V. Raman biography is important for students.C.V. Raman is one of the famous scientist of India. Watch ...
Dr. Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman or C.V Raman was known for his discovery Raman Effect and received Nobel Prize in 1930. He became the first Indian to receive Nobel Prize in Physics. Let us read ...
This paragraph is all about CV Raman (Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman) Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman was born at Trichinopoly in Southern India ON November 7th, 1888. His father was a lecturer in mathematics and physics so that from the first he was immersed in an academic atmosphere. He entered Presidency College, Madras in 1902, and in 1904 ...
' Sir C. V. Raman' was born on 7 November 1888 at Thiruvanaikoil, Tiruchirappalli, Madras Province, India. His full name was Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman. He was the son of R. Chandrasekhara Iyer and Parvati Ammal (Saptarshi Parvati). His father was a lecturer in mathematics and physics at Presidency College in Madras.
Writing a Biographical Essay of a Historical Figure. Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, was an Indian physicist who won the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930 for his work on light scattering and the discovery of a new form of scattering called Raman scattering or the Raman effect. ... CV Raman is an apt topic for biography because he was a ...
The first essay is a long essay on the CV Raman of 400-500 words. This long essay about CV Raman is suitable for students of class 7, 8, 9 and 10, and also for competitive exam aspirants. The second essay is a short essay on CV Raman of 150-200 words. These are suitable for students and children in class 6 and below.
#cvraman #ramaneffect #preparestudies #handwriting #english Write a short essay on C.V Raman10 lines on Lal Bahadur Shastri : https://youtu.be/QRTkVY-75YM10 ...
Greetings and good morning everyone, today I am going to give a speech on C.V. Raman. C.V. Raman, also known as the Great Indian Physicist Chandrasekhar Venkata Raman, was born in Tiruchirappalli, Tamil Nadu, on November 7, 1888. Raman naturally developed a passion for physics because his father was a teacher of the discipline.
CV Raman or Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman is one of India's most renowned physicists who discovered the Raman Effect. He was the first Indian to win the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1930. Dr CV Raman was very good at academics as he sought inspiration from his father who was a reputed lecturer of mathematics and physics.He was born in Tiruchirappalli on 7 November 1888.