Lean Six Sigma Training Certification
- Facebook Instagram Twitter LinkedIn YouTube
- (877) 497-4462


Online Root Cause Analysis Training
Our Root Cause Analysis Online training gives you the knowledge and skills needed to solve real-world problems whether you’re working alone or as part of a team. You will get a solid grasp of the relationship between causes and effects and suggest fact-based and data-driven solutions that will lead to course correction and the improvement of organizational processes.
The Online RCA training will benefit anyone who has been tasked with solving a problem in their organization. You will be able to be a functional member of the problem-solving team and aid in the creation, implementation and standardization of measures that lead to long-lasting gains. This means being able to detect the problem, gather facts (for a comprehensive analysis), create theories, identify the root cause and eliminate it indefinitely.
6Sigma.us RCA online training offers a globally recognized certificate that is obtainable over 90 days. You will learn all the tools and techniques under the RCA umbrella, as well as when and how to use them. You will even be provided with downloadable files and templates that can be modified and adapted to meet your problem-solving needs.
Interested in Online Root Cause Analysis Training?
What You Will Learn
The RCA concepts will help you identify answers to the following questions:
- How many problems are encountered each year? How many seem to recur?
- How many have an unknown cause? How many have a known cause?
- Is a team created to solve them? Does the team use a structured process?
Who Should Register Online Root Cause Analysis?
This program is for individuals, teams, and organizations that desire to institutionalize an operating system for structured problem-solving. Including but not limited to Operations Staff in manufacturing and service organizations, managers, process owners, and engineers.
Prerequisites
Topics covered:.
- What Root-Cause Analysis (RCA) is, why we need it and when to use it
- Problem-Solving Process Flowchart (8D Roadmap)
- Problems vs. Opportunities
- Preventative Practices
- Problem Detection & Specification
- Problem Anatomy = |Should – Actual|*Risk
- Causes to Determine
- Cause Structures
- Situation Appraisal
- Known vs. Unknown Cause
- Using Facts, Evidence & Assumptions
- Interim Actions
- Using a Team Approach
- Risk Analysis Tools
- Importance of Language
- Cause-Effect Mapping Methods
- Potential Cause Filters and Generators
- Human Error
- Choosing the Best Solution Profile
- Solution Validation
- Exercises & Case Studies
You will be introduced to the following concepts:
Present state scenario:.
1. A problem is detected 2. Everyone sees pieces of the true picture 3. Many pieces could be assumptions, not facts 4. Each piece generates theories and supporting evidence is gathered 5. Each theory is consistent with its piece and so becomes “worth looking into” 6. This feels right because everyone’s doing something to solve the problem
Present State Audit:
• A fragmented picture and assumption-based theories drive problem-solving activities • No procedure for bringing all the pieces together • No procedure for separating assumptions from facts • No procedure for using the facts to find the cause
Future State “Lean Problem-Solving” Scenario:
1. A problem is detected 2. Everyone knows what facts to gather to see the whole picture 3. Facts and evidence are used as a filter to reject the theories that don’t explain the facts 4. Theories that explain the facts are worth looking into 5. This feels right because every theory that gets rejected is time and money saved 6. The filter is also a “theory generator” that leads us to the cause 7. A solution profile is developed for sustainable results
What You Will Receive
- Access to the online Root Cause Analysis training for 90 days in our online Learning Center portal
- Access to the online RCA manual, delivered using LockLizard for secure access
- Downloadable library of RCA templates and files to use and modify as you see fit
- Certificate of completion upon successfully passing the final comprehensive exam
- Please note there are no refunds once the program has been started or 7 Days after purchase.
A printed copy of the slides used during the presentation can be purchased and shipped anywhere in the US for $70.
It was a very detailed and thorough course. I really liked it!
Abelardo Gutierrez del Toro | 5
This is a very good course. I loved how you could do it at your own pace since I am a Maintenance Manager and I have to work all hours.
Adam Davis | 5
Great way to learn Root Cause Analysis.
Bryan Vargas Santiago | 5
Good Course, Lots of material to cover and remember but once finished, all information tied together nicely.
Bryan Whitehead | 5
Was overall satisfied with this course
Edgar Dominguez | 5
Course was very good in helping me make changes to my daily processes.
Elliott Johnson | 5
The course was good and very helpfull on how to find the 5 why's on any situations that I may need to resolve in the future.
Evelio Solis | 5
at the beggining of this cours Ihave some problems understanding some words and have some issues ansuering my questions but finally Ican finished this courrse. thanks you much for all this educational material.
Maria Mendoza | 5
AWESOME EXPERIENCE
Michele Etienne | 5
The RCA course really helped provide the tools needed for sucessfull RCA towards my job. I am excited to apply it towards my work issues to help improve our OTD and products.
Veronica Rodriguez | 5
SixSigma.us Accreditation & Affiliations

Monthly Management Tips
- Be the first one to receive the latest updates and information from 6Sigma
- Get curated resources from industry-experts
- Gain an edge with complete guides and other exclusive materials
- Become a part of one of the largest Six Sigma community
- Unlock your path to become a Six Sigma professional
" * " indicates required fields
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
Root Cause Analysis: What It Is & How to Perform One

- 07 Mar 2023
The problems that affect a company’s success don’t always result from not understanding how to solve them. In many cases, their root causes aren’t easily identified. That’s why root cause analysis is vital to organizational leadership .
According to research described in the Harvard Business Review , 85 percent of executives believe their organizations are bad at diagnosing problems, and 87 percent think that flaw carries significant costs. As a result, more businesses seek organizational leaders who avoid costly mistakes.
If you’re a leader who wants to problem-solve effectively, here’s an overview of root cause analysis and why it’s important in organizational leadership.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Root Cause Analysis?
According to the online course Organizational Leadership —taught by Harvard Business School professors Joshua Margolis and Anthony Mayo— root cause analysis is the process of articulating problems’ causes to suggest specific solutions.
“Leaders must perform as beacons,” Margolis says in the course. “Namely, scanning and analyzing the landscape around the organization and identifying current and emerging trends, pressures, threats, and opportunities.”
By working with others to understand a problem’s root cause, you can generate a solution. If you’re interested in performing a root cause analysis for your organization, here are eight steps you must take.
8 Essential Steps of an Organizational Root Cause Analysis
1. identify performance or opportunity gaps.
The first step in a root cause analysis is identifying the most important performance or opportunity gaps facing your team, department, or organization. Performance gaps are the ways in which your organization falls short or fails to deliver on its capabilities; opportunity gaps reflect something new or innovative it can do to create value.
Finding those gaps requires leveraging the “leader as beacon” form of leadership.
“Leaders are called upon to illuminate what's going on outside and around the organization,” Margolis says in Organizational Leadership , “identifying both challenges and opportunities and how they inform the organization's future direction.”
Without those insights, you can’t reap the benefits an effective root cause analysis can produce because external forces—including industry trends, competitors, and the economy—can affect your company’s long-term success.
2. Create an Organizational Challenge Statement
The next step is writing an organizational challenge statement explaining what the gap is and why it’s important. The statement should be three to four sentences and encapsulate the challenge’s essence.
It’s crucial to explain where your organization falls short, what problems that poses, and why it matters. Describe the gap and why you must urgently address it.
A critical responsibility is deciding which gap requires the most attention, then focusing your analysis on it. Concentrating on too many problems at once can dilute positive results.
To prioritize issues, consider which are the most time-sensitive and mission-critical, followed by which can make stakeholders happy.
3. Analyze Findings with Colleagues
It's essential to work with colleagues to gain different perspectives on a problem and its root causes. This involves understanding the problem, gathering information, and developing a comprehensive analysis.
While this can be challenging when you’re a new organizational leader, using the double helix of leadership —the coevolutionary process of executing organizational leadership's responsibilities while developing the capabilities to perform them—can help foster collaboration.
Research shows diverse ideas improve high-level decision-making, which is why you should connect with colleagues with different opinions and expertise to enhance your root cause analysis’s outcome.
4. Formulate Value-Creating Activities
Next, determine what your company must do to address your organizational challenge statement. Establish three to five value-creating activities for your team, department, or organization to close the performance or opportunity gap you’ve identified.
This requires communicating organizational direction —a clear and compelling path forward that ensures stakeholders know and work toward the same goal.
“Setting direction is typically a reciprocal process,” Margolis says in Organizational Leadership . “You don't sit down and decide your direction, nor do you input your analysis of the external context into a formula and solve for a direction. Rather, setting direction is a back-and-forth process; you move between the value you'd like to create for customers, employees, investors, and your grasp of the context.”

5. Identify Necessary Behavior Changes
Once you’ve outlined activities that can provide value to your company, identify the behavior changes needed to address your organizational challenge statement.
“Your detective work throughout your root cause analysis exposes uncomfortable realities about employee competencies, organizational inefficiencies, departmental infighting, and unclear direction from leadership at multiple levels of the company,” Mayo says in Organizational Leadership .
Factors that can affect your company’s long-term success include:
- Ineffective communication skills
- Resistance to change
- Problematic workplace stereotypes
Not all root cause analyses reveal behaviors that must be eliminated. Sometimes you can identify behaviors to enhance or foster internally, such as:
- Collaboration
- Innovative thinking
- Creative problem-solving
6. Implement Behavior Changes
Although behaviors might be easy to pinpoint, putting them into practice can be challenging.
To ensure you implement the right changes, gauge whether they’ll have a positive or negative impact. According to Organizational Leadership , you should consider the following factors:
- Motivation: Do the people at your organization have a personal desire for and commitment to change?
- Competence: Do they have the skills and know-how to implement change effectively?
- Coordination: Are they willing to work collaboratively to enact change?
Based on your answers, decide what behavior changes are plausible for your root cause analysis.
7. Map Root Causes
The next step in your analysis is mapping the root causes you’ve identified to the components of organizational alignment. Doing so helps you determine which components to adjust or change to implement employee behavior changes successfully.
Three root cause categories unrelated to behavior changes are:
- Systems and structures: The formal organization component, including talent management, product development, and budget and accountability systems
- People: Individuals’ profiles and the workforce’s overall composition, including employees’ skills, experience, values, and attitudes
- Culture: The informal, intangible part of your organization, including the norms, values, attitudes, beliefs, preferences, common practices, and habits of its employees
8. Create an Action Plan
Using your findings from the previous steps, create an action plan for addressing your organizational problem’s root cause and consider your role in it.
To make the action plan achievable, ensure you:
- Identify the problem’s root cause
- Create measurable results
- Ensure clear communication among your team
“One useful way to assess your potential impact on the challenge is to understand your locus of control,” Mayo says in Organizational Leadership , “or the extent to which you can personally drive the needed change or improvement.”
The best way to illustrate your control is by using three concentric circles: the innermost circle being full control of resources, the middle circle representing your ability to influence but not control, and the outermost circle alluding to shifts outside both your influence and control.
Consider these circles when implementing your action plan to ensure your goals don’t overreach.

The Importance of Root Cause Analysis in Organizational Leadership
Root cause analysis is a critical organizational leadership skill for effectively addressing problems and driving change. It helps you understand shifting conditions around your company and confirm that your efforts are relevant and sustainable.
As a leader, you must not only effect change but understand why it’s needed. Taking an online course, such as Organizational Leadership , can enable you to gain that knowledge.
Using root cause analysis, you can identify the issues behind your organization’s problems, develop a plan to address them, and make impactful changes.
Are you preparing to transition to a new leadership role? Enroll in our online certificate course Organizational Leadership —one of our leadership and management courses —and learn how to perform an effective root cause analysis to ensure your company’s long-term success. To learn more about what it takes to be an effective leader, download our free leadership e-book .

About the Author

Principles of Root Cause Analysis
Formats ⟩ Live Virtual : 4 hrs./1 Day | In-Person : 6 hrs./1 Day
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a set of methodologies used to efficiently analyze problems and find key faults with those problems. In this course, we will teach you tools for finding the root causes of problems and focusing on what matters the most. You will learn skills for problem-solving, decision-making, impact analysis, fault finding, reliability, process control, and identifying symptoms, impacts, consequences, and effects.
Learning Objectives »
- Use a step-by-step approach to RCA.
- Question the cause of problems to find underlying issues.
- Avoid common pitfalls.
- Apply the 5W1H technique to generate clusters of questions.l
- Use a questioning technique to consider the consequences of change.
- Employ cause and effect diagrams to visually find faults.
- Apply the Pareto Principle to focus on what matters most.
- Use a powerful matrix to identify high-risk areas.
Course Agenda
Performance Review Strategy
- What is Root Cause Analysis?
- Steps for Effective RCA
- 8D or 8 Disciplines
- Types of Causes
- Best Practice of Guidelines
- Pitfalls of RCA
Root Cause Analysis Techniques
- Clustering Questions
- Appreciation Technique
Cause and Effect Diagram
- Steps for Diagramming Cause and Effect
- Guidelines for Diagramming
- Using an “AND” Operator
- Manufacturing
- Marketing Services
- Pareto Analysis
- Pareto Principle
- How to Use Pareto
Impact Analysis
- The Purpose of Instant Analysis
- Steps for Instant Analysis
- Reinforce Learning

Root Cause Problem Solving - Methods and Tools PD530931
Topics: Management and Organization Management and Organization , Failure analysis , Analysis methodologies

How do you solve a problem? Do you find yourself using quick and easy solutions or a structured methodology? Too often, organizations tend to seek quick solutions to a problem without adequately addressing its underlying cause. These decisions often result in solutions that don't work or aren't sustainable, often wasting time, effort, and money. To combat these issues and adopt a fresh approach, teams can use the methods and tools of root cause problem solving. By first viewing a problem as an opportunity for improvement, the team can then identify the problem's root cause or causes, and implement solutions to prevent the problem's reoccurrence.
This six module course introduces the Root Cause Problem Solving approach. It explains how using Root Cause analysis can help improve operational and financial performance by identifying root causes and implementing solutions to significant or recurring problems. This methodology is used by many major automotive manufacturers to improve quality and customer satisfaction, reduce operation costs, and provide greater employee knowledge of work processes.
Participants will become familiar with the eight steps of the Root Cause Problem Solving approach, learning the key actions completed in each step and interacting with examples and scenarios that demonstrate how each step functions to solve problems and keep them from reoccurring in an organization. Participants will also be supplied with tools that assist with the completion of each step that they can use in their own problem-solving efforts on-the-job.
By participating in this eLearning course, you'll be able to:
- Explain why root cause analysis using the 8-step problem solving methodology is more effective than non-structured problem solving efforts
- Define the difference between a problem, symptom, cause, and root cause
- Use tools and techniques to solve problems
- Evaluate the effectiveness of problems solving efforts
- Describe the role of problem solving in continuous improvement
Materials Provided
- 90 days of online single-user access (from date of purchase) to the six hour presentation
- Integrated knowledge checks to reinforce key concepts
- Follow-up to your content questions
- 1.0 CEUs*/Certificate of Achievement (upon completion of all course content and a score of 70% or higher on the learning assessment)
*SAE International is authorized by IACET to offer CEUs for this course.
Is this On Demand Course for You?
This course is applicable to those directly working in or responsible for performance improvement of any definable, repetitive process (e.g., manufacturing, design, logistics, purchasing, sales, or distribution), including: manufacturing managers, supervisors, and team leaders; manufacturing engineers; design engineers; quality engineers and technicians; technical managers; project team leaders; problem solving and quality improvement facilitators; anyone whose role includes problem solving: supervisors and lead personnel.
Testimonial
"Thank you for introducing me to the SAE Root Cause Problem Solving course. Quality has been my vocation for 11 years and this course opened my eyes to so many things I have been missing. It should be required for anyone in the quality business." Chuck Hartshorn Quality Manager
For More Details
Email [email protected] , or call 1-877-606-7323 (U.S. and Canada) or 724-776-4970 (outside US and Canada).
Module 1: Foundations for Adopting Root Cause Analysis
- Identifying Problems
- How to Approach Problem Solving Using a Process Approach
- Methods and Tools for Problem Solving: An 8 Step Approach
- Roles and Responsibilities in Problem Solving
- Setting Up a Problem Solving Team
Module 2: Describing the Problem and Implementing Containment
- How to Describe a Problem
- Symptoms vs. Causes
- Methods for Collecting and Analyzing Data
- Problem Statements
- Methods for Protecting the Customer
Module 3: Discovering Root Causes
- Recognizing Potential Causes
- Methods for Identifying Causes and Root Causes (cause-effect diagram, 5-why)
- Validating Potential Root Cause
Module 4: Designing a Solution and Implementing Permanent Corrective Action
- Strategies for Planning and Designing Effective Solutions
- Methods for Evaluating Potential Solutions
- Error Proofing Strategies
- Planning Implementation
- Project Management Strategies
- Completing System Changes
- Measuring and Verifying Effectiveness
Module 5: Preventing Reoccurrence
- Ensuring the Problem is Eliminated
- Holding the Solution in Place
- Leveraging What is Learned
- FMEA and Problem Solving
Module 6: Recognizing Efforts
- Methods of Team and Individual Recognition
- Capturing Lessons Learned and Moving Them Forward
- Problem Solving and Continuous Improvement
- Windows 7, 8, 10 (other operating systems and mobile platforms are not supported but may work)
- Internet Explorer 11, Mozilla Firefox 37, Google Chrome 42 (other browsers are not supported but may work)
- Broadband-1Mbps minimum
– If you’d like only an introduction or overview of the topic, this module can be purchased as a stand-alone course. – After completing the introductory module, you may purchase the remaining course modules as one package, without the need to repurchase the introductory module. – If you'd like to take the complete course, this purchase option includes all the course modules in one package. |
- Training Portal
- GET YOUR CAUSE MAPPING® TEMPLATE

- About Cause Mapping®
- What is Root Cause Analysis?
- Cause Mapping® Method
- Cause Mapping® FAQs
- Why ThinkReliability?
- Online Workshops
- On-Demand Training Catalog
- On-Demand Training Subscription
- Company Case Study
- Upcoming Webinars
- Webinar Archives
Public Workshops
- Private Workshops
- Cause Mapping Certified Facilitator Program
Our Services
- Facilitation, Consulting, and Coaching
- Root Cause Analysis Program Development
- Work Process Reliability™
- Cause Mapping® Template
- Root Cause Analysis Examples
- Video Library
- Articles and Downloads
- About ThinkReliability
- Client List
- Testimonials
- There are no suggestions because the search field is empty.
Join us for the next Cause Mapping Root Cause Analysis Public Workshop in HOUSTON, TX on September 10-12, 2024.
UPCOMING WEBINAR - - - - - - - - - -
August 23rd at 10:00 am, excel tips & tricks for using the cause mapping ® template, upcoming short course - - - - - - - - - -, november 8th, how to investigate: human error, upcoming workshop - - - - - - - - - -, september 10-12th, cause mapping ® root cause analysis for facilitators + documentation public workshop - houston, tx, your trusted authority on root cause analysis - - - - - - - - - -.
PROVEN METHODOLOGY
Cause Mapping ® root cause analysis is an extremely effective systems-thinking approach that utilizes visual communication to improve the way people collect, analyze, and use information to solve problems.
World-Class Training
Our root cause analysis training workshops teach you how to analyze and solve everything from day-to-day recurring problems to catastrophic events. All of our instructors have strong technical backgrounds with extensive practical experience from the field.
Expert Support
Do you have a problem or incident that needs to be investigated right now? Our expert facilitators can lead your investigation remotely or on site. With our experience and expertise, we deliver efficient and effective results. Give us a call and we can start today.

Learn the basics of Cause Mapping or advance your facilitation & investigation skills by attending our public root cause analysis training workshops.

Informational Webinars
Register today for one of our FREE live Webinars -- packed full of useful information and problem solving techniques for facilitating better investigations.

Cause Mapping Certification
Gain the confidence and proficiency necessary to lead complex high-risk incident investigations.

Company Case Studies
A cost-effective solution to provide additional training and support using Cause Maps to investigate and solve problems within your organization.

FACILITATION
Our expertise and efficiency at investigating incidents can immediately be applied to any of your problems.

RCA PROGRAM DEVELOPMENT
We will work closely with key stakeholders to evaluate and develop a customized RCA program that will drive results and integrate within the current processes at your site.

UPCOMING ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS TRAINING - - - - - - - - - -

April 26 at 10:00 AM
Introduction to Cause Mapping ® - Effective Root Cause Analysis
April 30 - May 2
Cause Mapping ® Root Cause Analysis for Facilitators + Documentation In-Person Public Workshop - Houston, TX
May 3 at 10:00 AM
How to Build an Investigation File as a Report
May 10 at 10:00 AM
Checklist Basics – A Key to Error Reduction

The best root cause analysis software you didn’t know you had!
Learn how to document an entire investigation using a tool that is already on your computer — Microsoft Excel!

From the Blog - - - - - - - - - -
Should the rca team include the person involved in the incident, how much detail is enough in an rca investigation, separating fact from fiction in the mcdonald’s hot coffee case.

- The Root - RCA blog
- Root Cause Analysis blog archive
- Patient Safety blog archive
- Learner Dashboard
© 2024 ThinkReliability. All Rights Reserved.

Root Cause Analysis (RCA) Methods for Effective Problem Solving
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 8, 2023 — 7 minutes to read
Imagine facing a problem in your organization that keeps recurring despite your best efforts to solve it. You might be addressing the symptoms, but not the underlying cause. This is where root cause analysis (RCA) comes into play. RCA is a systematic approach to identifying the root cause of problems or events, understanding how to fix or compensate for them, and applying the knowledge gained to prevent future issues or replicate successes. In this comprehensive guide to root cause analysis, you’ll learn various methods and techniques for conducting an RCA. You’ll understand how to gather and manage evidence, investigate the people, processes, and systems involved, and determine the key factors leading to the problem or event.
Whether you’re a project manager, a team leader, or simply someone looking to improve your problem-solving skills, this guide will help you grasp the fundamentals of RCA and apply them effectively in your work. As you delve deeper into the world of Root Cause Analysis, you’ll discover how it can turn challenges into opportunities for growth and pave the way for a more efficient and successful future.
Related: 3 Root Cause Analysis Templates (and Examples)
5 Whys: How to Uncover Root Causes [Examples]

Root Cause Analysis Fundamentals
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach to identify the underlying cause of a problem. By focusing on the root cause, you can effectively address the issue and prevent recurrence. Generally, RCA is used to investigate incidents, eliminate defects, and enhance systems or processes.
RCA aims to achieve the following objectives:
- Determine the root cause of a problem or issue, not just its symptoms.
- Identify and implement solutions that address the root cause and prevent its recurrence.
- Improve understanding of the systems, processes, or components involved to avoid similar issues in the future.
- Foster a proactive and continuous improvement mindset within your organization.
When conducting RCA, maintain an open mind and avoid making assumptions. Utilize critical thinking and involve team members from various disciplines to achieve a comprehensive understanding of the problem.
The RCA Process
Problem identification.
To effectively utilize Root Cause Analysis (RCA), first identify the problem at hand. Determine the specific issue, incident, or failure that needs to be investigated. Clearly define the problem and its impact on your organization’s operations in order to establish a focused and valuable analysis.
Data Collection
Gather relevant data about the problem, including when and where it occurred, who was involved, what processes and systems were affected, and any other important context. Be thorough and systematic in your data collection, and make use of any available documentation, interviews, or observations to build a comprehensive understanding.
Cause Identification
Analyze the collected data to pinpoint potential causes of the problem. This could start with brainstorming and then using tools such as cause-and-effect diagrams or the “5 Whys” technique to delve deeper into the issue. Determine the causes that are most likely to have contributed to the problem and classify them as either root causes or contributing factors.
Solution Implementation
Once you have identified the root cause(s) of the problem, develop and execute an action plan to address the issue. Design solutions that specifically target the root cause(s) to eliminate them from your processes, rather than simply addressing the symptoms of the problem. Implement the appropriate changes to your processes or systems and ensure that all stakeholders are aware of these changes.
Follow-up and Monitoring
After implementing the solutions, monitor the results to ensure they are effective in addressing the root cause(s) and preventing the problem from reoccurring. Collect and analyze data regularly to evaluate the impact of the implemented solutions on your organization’s performance. Adjust and refine the solutions if necessary, and maintain ongoing vigilance in order to identify any future problems that may arise from the same root cause(s).
RCA Techniques
The 5 Whys technique is a straightforward method for identifying the root cause of a problem. To employ this approach, you simply ask “why” five times, with each question delving deeper into the issue. The process helps trace the problem to its origin by examining each level of cause and effect. Here’s an example:
- Why did the machine stop working?
- Why did the fuse blow?
- Why did the motor overheat?
- Why was there insufficient lubrication on the motor?
- Why was the lubrication schedule not followed?
In this case, the root cause is the failure to adhere to the lubrication schedule.
Learn more: 5 Whys: How to Uncover Root Causes [Examples]
Fishbone Diagram
The Fishbone Diagram, also known as the Ishikawa Diagram or cause-and-effect diagram, is a visual tool that helps you organize and sort potential root causes. To create a Fishbone Diagram:
- Write down the problem statement at the head of the fishbone structure.
- Identify major categories of causes, such as people, process, equipment, and environment. Draw lines connecting them to the problem statement.
- Assign specific causes under each category and draw smaller lines connecting them to the respective major categories.
- Analyze the diagram to find trends, patterns, or potential areas of focus.
By organizing information in this way, you can better assess the causes and identify the root cause of the problem.
Learn more: Fishbone Diagram (Components, Factors, Examples) and Ishikawa Diagram: Examples and Applications
Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA) is a systematic approach to identify potential failures and evaluate the consequences. FMEA processes typically involve these steps:
- Identify potential failure modes, which are the ways something could go wrong.
- Determine the potential effects of each failure mode, and how it could impact the overall system or process.
- Assign a risk priority number (RPN) to each failure mode, considering factors such as likelihood, severity, and detectability.
- Develop actions and strategies to mitigate high-risk failure modes.
By using FMEA, you can proactively address possible issues before they escalate, and maintain a more reliable process or system.
Barrier Analysis
Barrier Analysis focuses on preventing problems by examining the barriers in place to control risks. The objective is to identify vulnerabilities in these barriers and develop strategies for improvement. The steps of Barrier Analysis include:
- Identify hazards and risks associated with your system or process.
- Define the barriers in place that protect against these hazards.
- Evaluate the effectiveness, strength, and reliability of each barrier.
- Identify gaps or weaknesses in the barriers.
- Develop and implement improvements to strengthen the barriers.
This method provides a clear understanding of how existing safety measures perform and how they can be improved to better protect against potential issues.
See also: 3 Root Cause Analysis Templates (and Examples)
What is Poka-Yoke? [Examples, Principles, Methods]
Benefits of Root Cause Analysis
Quality improvement.
Root cause analysis can significantly enhance the quality of your products or services. By systematically identifying the root causes of issues and implementing corrective actions, you’ll prevent recurring problems and reduce the number of defects. In turn, this will help you maintain customer satisfaction, reduce costs associated with rework or returns, and improve your reputation in the market.
Risk Reduction
Reducing risk is another advantage of root cause analysis. When you identify the underlying causes of problems, you can take necessary measures to eliminate or mitigate those risks. This proactive approach can protect your business from potential losses or disruptions, such as regulatory penalties, customer dissatisfaction, or harm to employees or the environment. By addressing the sources of risk, you can maintain a safer and more profitable business.
Process Optimization
Root cause analysis supports continuous improvement by highlighting inefficiencies and areas for optimization in your operations. By examining your processes beyond the symptoms of a specific issue, you can uncover opportunities to streamline workflows, reduce waste or downtime, and better utilize resources. Implementing these improvements not only resolves the immediate problem but also enhances overall productivity and efficiency in your organization.
To attain the benefits of root cause analysis, apply it consistently and rigorously. Ensure that you involve relevant stakeholders, gather necessary data, and employ a systematic approach to identifying and addressing root causes.
Challenges of Root Cause Analysis
Common pitfalls.
When conducting Root Cause Analysis (RCA), you might face common pitfalls that can reduce the effectiveness of your investigation. Some of these pitfalls include:
- Rushing the process : It is important to allocate appropriate time and resources to conduct a thorough RCA.
- Overlooking small details : Make sure to pay attention to all possible contributing factors when investigating a problem. Small details can often hold the key to the root cause.
- Focusing on blame : RCA should focus on identifying systemic issues and providing solutions rather than blaming individuals or departments.
Addressing Human Factors
Human factors play a critical role in many problems. When conducting RCA, it is crucial to consider the human factors that may have contributed to the issue. Here are some tips to help you address human factors in your RCA:
- Consider psychological factors : Assess the mental state of the people involved in the incident, including their level of stress, fatigue, and emotions.
- Evaluate communication and collaboration : Analyze how effectively teams were communicating and working together at the time of the incident.
- Assess training and competency : Determine if the people involved had the appropriate training and knowledge to handle the situation.
Keep a neutral and non-blaming tone while assessing human factors. The aim is to uncover systemic issues that can be improved upon.
Fishbone Diagram (Components, Factors, Examples)
Ishikawa Diagram: Examples and Applications
- Advantages of SWOT Analysis (6 Benefits and 4 Limitations)
- 8 Examples: Top Problem Solving Skills
- What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
Virtual RCA Training
Gain root cause analysis (rca) knowledge, skills, and tools and learn how to apply them to real-world events in an interactive & safe learning environment. contact us register course info, virtual instructor-led root cause analysis training.
TECHNOLOGY REQUIREMENTS
- Capability Development
Root Cause Analysis
Available as:
- In-house class
- Public class
Kepner-Tregoe's Root Cause Analysis (RCA) training equips individuals and teams with the tools to systematically find the root cause of problems and prevent them from reoccurring. As the world's leading troubleshooting company, KT has led major investigations in every industry and environment possible. This workshop brings that wealth of experience to the classroom so you can learn and practice root cause analysis skills and make an immediate impact back on the job.

What You Get:
- 2 days led by an expert instructor
- Access to digital tools and resources
- Troubleshooting skills you can use immediately on the job
- Certificate of completion
- Certification Credits : 1.4 CEUs
RM 2,800 for 3 or more Workshop Hours: 9:00am - 5:30pm (UTC+8)
Workshop Hours: 8am - 2pm (ET)
Workshop Hours: Noon - 6pm (ET)
Workshop Hours: 10am - 6pm (ET)
Pour toute question contactez Florence Lemerle [email protected]
To see the total select country, date and number of participants
To see the total select language, date and number of participants
In this county services are provided by the official KT licensee.
* Before applicable taxes
Class seats guaranteed with payment. Seat reservations held for 72 hours.
Contact us to inquire for more details or have the workshop customized upon your corporate needs.
Anyone who is required to troubleshoot, perform investigations or root cause analysis (RCA), manage incidents, or conduct problem solving. Functional troubleshooting roles often include service, support, and quality engineers; problem and incident managers; analysts, technicians, auditors, and others responsible for resolution of critical incidents and problems.
- Learn the best-in-class root cause analysis methodology…proven in all types of industries and organizations for over 60 years.
- Discover the power of KT Clear Thinking and walk away with a framework that integrates easily with Lean, Six Sigma, 8D, ITIL, CAPA, and other methodologies.
- Apply the skills learned to rapidly identify the cause of problems back on the job.
Skills Developed
- Understand whether you truly have a cause-unknown problem
- Obtain a clear, factual description of the problem through rigorous questioning techniques
- Create and test hypotheses, and confirm root cause before adopting a fix
- Identify where else the fix may cause problems and prevent unintended consequences
Return on Investment
- A major manufacturing issue was resolved at a medical device manufacturer
- An 18-month-old problem was eliminated at Tokyo Electron
- Downtime eliminated at a multi-billion dollar oil and gas company
- $150,000 in costs saved and major upheaval avoided at Duke Energy
“The Kepner-Tregoe problem-solving process continues to help FCA save time and money. It does this by upgrading an already valuable engineering expert into a problem-solving asset.”
— Chris Hernan, Reactive MBB and Instructor, FCA Group
“KT has changed the way we solve problems. We are now more consistent, efficient and data-driven as compared to before in RCA. While we are at the starting point of our journey, we believe the process will lead us to drive better results in the future. Thanks to KT for their continuous support during and after our engagement.”
— Vishnukanth Ladchumigandan, Engineering Director, Mattel (Malaysia) Sdn. Bhd. (Toys)
Contact Form
Showcase your skills.
The KT Badge Program is a visible recognition of your rational process skills. Your Kepner-Tregoe Digital Badges can be shown on your social media profile page, your email signature, and your personal website. And finally the authenticity of your KT badge can be validated on our website portal.
The Foundation Badge is the starting point and highlights that you have attended a KT training program. Once you have begun applying the KT technologies you will progress through the levels of Practitioner, Advanced, and ultimately, achieve recognition as a KT Expert.

Kepner-Tregoe Foundations Badge
If you have successfully participated in this workshop, you are eligible to receive the KT Foundations Badge.
Related Workshops
For inquiries, details, or a proposal!
Subscribe to the KT Newsletter
Request in-house class offer, there will be a popup title here.
Root Cause Analysis – The 5 Whys Technique
This elementary and often effective approach to problem-solving promotes deep thinking through questioning, and can be adapted quickly and applied to most problems. For example, asking “Why?” may be a favorite technique of your three-year-old child in driving you crazy, but it could teach you a valuable problem-solving technique.
“If you don’t ask the right questions, you don’t get the right answers. A question asked in the right way often points to its answer. Asking questions is the ABC of diagnosis. Only the inquiring mind solves problems.” – Edward Hodnett
The “5 Whys” is a simple problem-solving technique that helps you to get to the root of a problem quickly, which was originally developed by Sakichi Toyota. It was used within the Toyota Motor Corporation during the evolution of its manufacturing methodologies. It is a critical component of problem-solving training, delivered as part of the induction into the Toyota Production System.
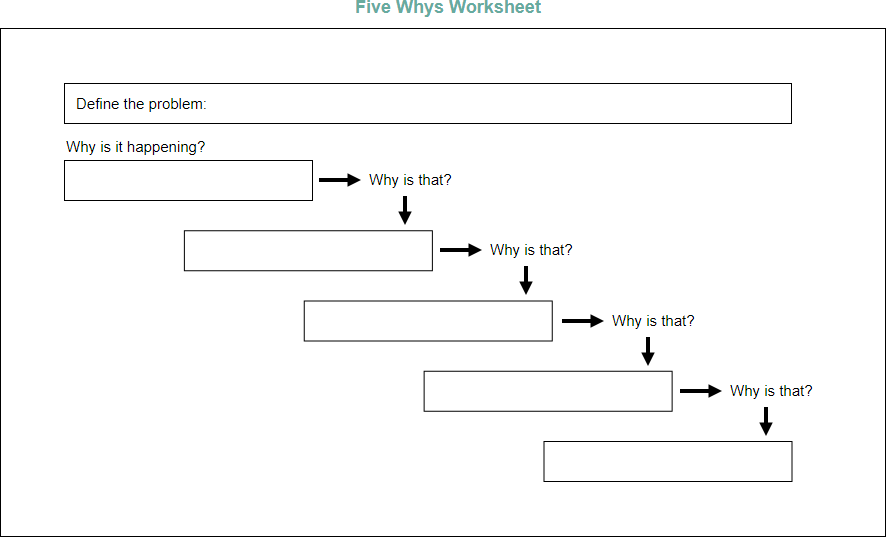
How to Conduct 5 Whys Analysis?
When you’re looking to solve a problem, start at the result and work backward (toward the root cause), continually asking: “Why?” You’ll need to repeat this over and over until the root cause of the problem becomes apparent.
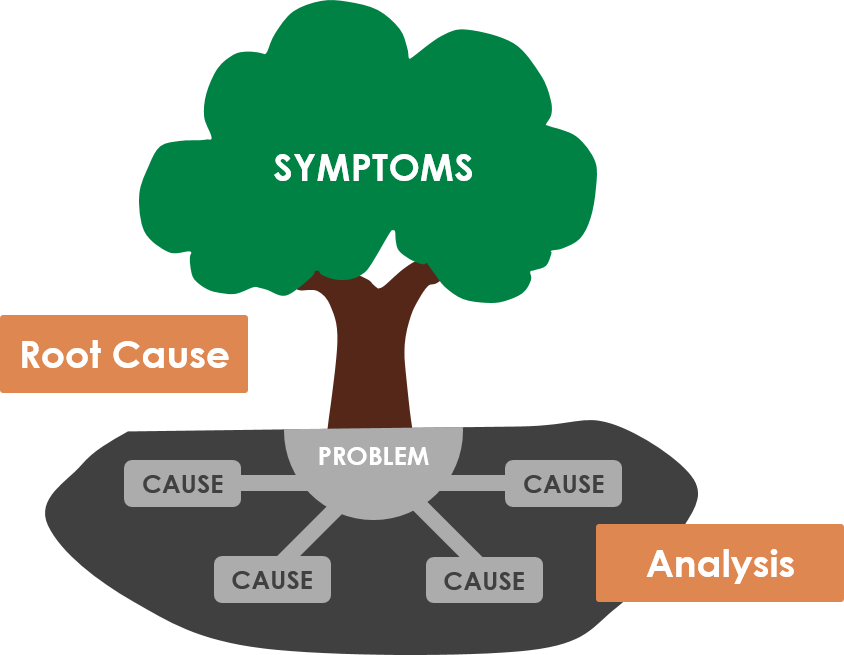
The 5 Whys strategy involves looking at any problem and asking: “Why?” and “What caused this problem?” Very often, the answer to the first “why” will prompt another “why” and the answer to the second “why” will prompt another and so on; hence the name the 5 Whys strategy.
The 5 Whys exercise is vastly improved when applied by a team and there are five basic steps to conducting it:
- Write down the specific problem. Writing the issue helps you formalize the problem and describe it completely. It also helps a team focus on the same problem.
- Ask “Why” the problem happens and write the answer down below the problem.
- If the answer you just provided doesn’t identify the root cause of the problem that you wrote down in Step 1, ask “Why” again and write that answer down.
- Loopback to step 3 until the team is in agreement that the problem’s root cause is identified. Again, this may take fewer or more times than five Whys.
- After settling on the most probable root cause of the problem and obtaining confirmation of the logic behind the analysis, develop appropriate corrective actions to remove the root cause from the system.
Edit this Diagram
5 Whys Example
The vehicle will not start. (The problem)
- Why? – The battery is dead. (First why)
- Why? – The alternator is not functioning. (Second why)
- Why? – The alternator belt has broken. (Third why)
- Why? – The alternator belt was well beyond its useful service life and not replaced. (Fourth why)
- Why? – The vehicle was not maintained according to the recommended service schedule. (Fifth why, a root cause)
Note: A 5 Whys analysis sometime could be taken further to a sixth, seventh, or higher level, but five iterations of asking why are generally sufficient to get to a root cause.
5-Whys Criticisms
Here are each of the criticisms as listed on the Wikipedia:
- Stopping at symptoms, not the root cause
- Limited by the investigator’s knowledge.
- Not asking the right Why questions.
- Not repeatable – Different people build different 5 Whys.
- The tendency to isolate a single root cause
©2024 by Visual Paradigm. All rights reserved.
- Terms of Service
- Privacy Policy
- Security Overview
Learn Problem Solving to Eliminate the Causes for Failures and Overload
Problem solving training for result-driven managers and functional specialists to effectively eliminate the root causes of variability, gaps, defects, frustrations, and stress., cases, when to use:.
- Frustration from never-ending fire-fighting
- Excessive defects, uncontrolled variability
- Stress from unhappy boss, customer, spouse
- Working too hard, too late, risking burnout
Clients, for whom:
- Department managers and team leaders
- Functional specialists, engineers, controllers
- Consultants and improvement champions
- Anyone struggling with too many problems
Process, how it works:
- Online training course with personal coaching
- Apply 5 shifts to successfully address any problem
- Eliminate causes at physical, human, system root
- Learn proven strategies; practical templates included
Benefits, what to gain:
- Status and recognition as expert problem solver
- Become indispensable to the organization
- Free time to spend with family, friends, hobby
- Strategy for better pay and career advancement
Course Content - What You Will Learn
- Systematically solve safety, quality, reliability issues
- Define issue statements based on data, observations
- Learn proven tools and techniques to tackle deviations
- Use basic PDCA and 5-Why analysis for simple issues
- Use Causal Factor Analysis (CFA) for disasters, accidents
- Use Fault Tree Analysis (FTA) for rule-based problems
- Identify cause-effect relationships between factors
- Provide evidence to confirm or reject assumptions
- Drill down causes at the physical, human, latent root
- Develop actions to remove, reduce, control causes
Why Did the Titanic Sink?
The 13 Reasons for Formal Problem Solving
- Undesirable condition
- Deviation, defect, failure
- Safety accident, incident, major risk
- Product failure due to strength, performance, reliability
- Line stop event
- Regulatory non-compliance
- Customer dissatisfaction or request
- Cost overrun
- Equipment breakdown
- Process failure
- Behavioral issue, noncompliant, disengaged
- Repetitive or transferable problem
- Detection failure
Ineffective Trouble Shooting
- Fire fighting
- Going from crisis to crisis
- Stagnant or declining performance
- No time for deeper analysis
- Look for the guilty party: ”Who did that?”
- Jumping from problem into actions
- Generate laundry list of actions to firefight symptoms
- Sub-optimizing one area, spot scope
- Focus on lagging metrics (yield, sales, profits) and hope processes will improve as a result
Effective Problem Solving

- Systems thinking
- Continuous improvement
- Systematic root cause elimination
- Better performance after each problem
- Allocate time to analyze, dialogue, conclude
- Seek deep understanding: “How did that happen?”
- Acting after understanding cause-effect relationships
- Addressing all factors of the failure tree
- Optimizing the value stream, enterprise scope
- Focus on improving processes (capability) that effect actual performance metrics
The Problem Solving Training Gets You Certified
The Beginner Problem Solving Training helps anyone to get started with systematic problem solving. Within a few days, you will learn the basic methods and tools, and apply them to solve a difficult situation in five steps: (1) Describe Gap, (2) Analyze Issues, (3) Identify Causes, (4) Address Causes, (5) Evaluate Results. Quizzes and self-evaluation forms help you to test your skills and evaluate solution the effectiveness of your solutions.
The Advanced Problem Solving Training is for managers, supervisors, and functional specialists to build their their problem-solving skills. The course focuses on systematic root-cause analysis and developing countermeasures to effectively contain, correct, and prevent failures from reoccurring. The advanced course is supported by a coach, helping students through the process, while providing feedback to get the analysis right.
The Expert Problem Solving Training is for engineers, managers, and quality professionals to build expert skills in systematic problem solving. The course covers the deep analysis of event-based problems, rule-based problems and human failures. The expert toolkit allows you tackling deviations and defects at the system level by eliminating, reducing, and controlling the entire set of causes, identified on the logic tree – assisted by an experienced coach.

Problem Solver | Basic Skills
Online course for beginners to build foundational skills to identify, describe, contain, correct, and prevent simple problems from reoccurring.

Problem Solver | Advanced Skills
Coaching-supported advanced course to strengthen problem-solving skills, to deeply analyze and effectively address identified root causes.

Problem Solver | Expert Skills
Coaching-supported expert course to solve complex problems by systematically reducing, eliminating, or controlling direct causes and root causes.
Basic Problem Solver
- 100% online and self-certified, without coaching
- Build basic skills in systematic problem solving
- Ideal for beginners from any function, any level
- Formally analyze and solve a basic problem
- Takes 2-5 days effort during a 1-month period
- Get access to basic videos, templates, toolkit
- Apply multi-5-why to identify root causes
- Formally implement a solution using PDCA
- Create financial benefits; typ. $3k or more
- Get your certificate "Problem Solver"
Advanced Problem Solver
- Coaching sessions for business case and impact
- Build advanced skills in problem-solving
- Ideal for managers, supervisors, specialists
- Solve an advanced problem and get feedback
- Takes 5-10 days effort during a 2-month period
- Get access to advanced videos, templates, tools
- Perform root cause analysis and test robustness
- Formally implement solutions, test effectiveness
- Create financial benefits; typ. $30k or more
- Get your certificate "Advanced Problem Solver"
Expert Problem Solver
- Coaching sessions, expert validation, live support
- Build expert skills in systematic problem solving
- For engineers. managers, quality professionals
- Solve a major problem, supported by a coach
- Takes 10-20 days effort during a 3-month period
- Get access to expert videos, templates, toolkit
- Identify physical, human, and latent causes
- Formally eliminate, reduce, control causes
- Create financial benefits; typ. $60k or more
- Get your certificate "Expert Problem Solver"

Root Cause Analysis (Problem Solving)
All organisations in both the manufacturing and service sectors experience problems in their operations. The problems may be technical in nature or may be people related; the problems may be detected within the manufacturing or service organisation or, more seriously, be identified and reported by the customer. It is important that a well-structured approach to the solution of problems is established. There are well proven methods available to assist organizations to get to the root cause of problems and to develop effective solutions.
Public Training Programmes
Customised In-Company Programmes
What's covered?
Introduction
- Introduction to the principles and disciplines of Root Cause Analysis
- The tools of Root Cause Analysis
- Explanation of the techniques of brainstorming in teams
- The tutor will present the participants with a detailed procedure that is to be followed when they work in teams in the Practical Session.
Practical Session with the Tutor acting as Team Facilitator ( Main part of the day)
- The group of participants will be divided into two teams of approximately 5-6 people, depending on the numbers attending. Each team will be allocated an example of a problem, and that they are to analyze in the practical session.
- Detailed specification of the problem
- Documentation of the background information and evidence that is available including the circumstances surrounding the problem
- Develop a process flow chart
- Brainstorming of the causes – the participants will document all possible causes under a number of headings including: Equipment, Methods, People, Materials, Environment
- The team will discuss each listed possible cause in detail so that each team member has sufficient understanding to enable them to decide on the likelihood of a link between the cause and the problem
- Short listing of the causes using system of voting provided by the tutor
- Further detailed analysis of the short list using the 5 Why’s technique.
- Conclusion as to the most likely root cause(s) of the problem
- Discussion on the preventive actions to be taken for each of the root causes
- Documentation of the problem, the root causes, and the recommended corrective/preventive actions
On completion of the team exercises, each team will make a presentation of their work and findings, and the course will finish with a general group discussion on the Root Cause Analysis methodology
All personnel who can contribute to the solution of problems that arise in the company’s operations, including Management, Technical and Administrative staff and operatives.
Participants achieve the following learning outcomes from the programme;
- Contribute in teams to the solution of problems that arise in their own work environment
- Use the problem solving tools to collect and analyse data
- Lead problem solving teams
- Demonstrate understanding of the structure of root cause analysis which leads to the satisfactory elimination of problems

With a background of thirty year’s practical experience, Albe...

Grainne is a highly experienced Continuous Improvement and Lean...
In-House Courses For In-House courses the tutor will contact you in advance to discuss the course programme in more detail in order to tailor it specifically for your organisation.
Course Manual Participants will be provided with a very comprehensive course reference manual, written by the course tutor, which includes worked examples of the use of the quality tools. The manual includes a detailed description of how a team should undertake an 8D analysis, which could be used as the basis of an In-House procedure, and also includes useful blank forms for use by problem solving teams.
Share this Programme
Share this:.
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
Related Programmes
You may be also interested in the following related programmes:
- Acceptance Sampling (including AQL selection)
- Failure Mode & Effect Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Green Belt – QQI Level 7
Course Code
Public price.
(includes course documentation)
Delivery Mode
What our learner's say, news & updates, process flow charts are an essential tool in root cause analysis.
There are several tools used in Root Cause Analysis. One of the most important is the Process Flow Chart. Problems arise when the process fails to performs it...
- 11 Feb 2025 Book Date
- 11 Feb 2025 Delivery: Virtual Training Location: Virtual Book Date


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Define problem-solving models used for root cause analysis, including 8D, PDCA, and DMAIC. Implement problem-solving techniques (poka-yoke, multi-voting, etc.) and plan, manage, and verify change. ... Internet-based, self-paced training modules, which may involve combinations of text, visuals, audio, interactive simulations and quizzes (see ...
Investigate root causes with cause-and-effect analysis, 5 Whys, FMEA, and other analytical tools. Assess and work with various data collection plans and methods, as well as data charts and control charts. Define problem-solving models used for root cause analysis, including 8D, PDCA, and DMAIC.
You will be able to be a functional member of the problem-solving team and aid in the creation, implementation and standardization of measures that lead to long-lasting gains. This means being able to detect the problem, gather facts (for a comprehensive analysis), create theories, identify the root cause and eliminate it indefinitely.
8 Essential Steps of an Organizational Root Cause Analysis. 1. Identify Performance or Opportunity Gaps. The first step in a root cause analysis is identifying the most important performance or opportunity gaps facing your team, department, or organization. Performance gaps are the ways in which your organization falls short or fails to deliver ...
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic process used to identify the fundamental causes of problems or events, preventing their recurrence. This course introduces RCA as a critical thinking methodology, equipping learners with the tools and techniques to dissect problems, understand their core issues, and implement effective solutions. This ...
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a set of methodologies used to efficiently analyze problems and find key faults with those problems. In this course, we will teach you tools for finding the root causes of problems and focusing on what matters the most. You will learn skills for problem-solving, decision-making, impact analysis, fault finding, reliability, process control, and identifying symptoms ...
Objectives. By participating in this eLearning course, you'll be able to: Explain why root cause analysis using the 8-step problem solving methodology is more effective than non-structured problem solving efforts. Define the difference between a problem, symptom, cause, and root cause. Use tools and techniques to solve problems.
With successful completion of Root Cause Analysis Training, learners will be able to effectively participate on a problem solving team beginning with defining the symptoms of the problem, then using data and investigative tools identify the root cause and finally employing decision matrices to select the most appropriate solution. Participants ...
PROACT® Root Cause Analysis (RCA) training provides problem solving skills and techniques to properly investigate, analyze and prevent failures and risks. Upon completion of this course, you will have the skill sets needed to complete a thorough and fact-driven RCA. Using the PROACT® Approach you will learn fact finding techniques ...
From hands-on root cause analysis training to turnkey investigation help, ThinkReliability is your go-to partner in problem solving. (281) 412-7766 [email protected]
Explore 7 powerful RCA techniques to enhance problem-solving. From Fishbone Diagrams to FMEA, unlock effective strategies for identifying root causes. Training. RCA 101 - 5-Why Analysis (Free Training) ... Root Cause Analysis Training. Your team needs a common methodology and plan to execute effective RCA's. With both in-person and on-demand ...
Definition. Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic approach to identify the underlying cause of a problem. By focusing on the root cause, you can effectively address the issue and prevent recurrence. Generally, RCA is used to investigate incidents, eliminate defects, and enhance systems or processes.
VIRTUAL INSTRUCTOR-LED ROOT CAUSE ANALYSIS TRAINING ... Our virtual courses deliver essential problem-solving tools and skills, including; writing a problem statement, cause & effect analysis, solution generation, team facilitation, and expert reporting. These key concepts are reinforced with expert instructor insights and practical exercises ...
Request in-house class offer. Kepner-Tregoe's Root Cause Analysis (RCA) training equips individuals and teams with the tools to systematically find the root cause of problems and prevent them from reoccurring. As the world's leading troubleshooting company, KT has led major investigations in every industry and environment possible.
It is a critical component of problem-solving training, delivered as part of the induction into the Toyota Production System. ... After settling on the most probable root cause of the problem and obtaining confirmation of the logic behind the analysis, develop appropriate corrective actions to remove the root cause from the system. Edit this ...
Step 1: Identify the Problem. Before diving into a 5 Whys analysis, it's crucial to clearly identify the problem or issue at hand. This step sets the stage for the entire process and ensures that the focus remains on addressing the right concern. Take the time to gather relevant data, observe patterns, and consult with team members or ...
Investigate root causes with cause-and-effect analysis, 5 Whys, FMEA, and other analytical tools. Assess and work with various data collection plans and methods, as well as data charts and control charts. Define problem-solving models used for root cause analysis, including 8D, PDCA, and DMAIC.
Problem solving training for result-driven managers and functional specialists to effectively eliminate the root causes of variability, gaps, defects, frustrations, and stress. Systematic problem solving is a foundational sill, and by working as a professional, you are required to address performance and behavioral issues to boost safety ...
Root cause analysis (RCA) is defined as a collective term that describes a wide range of approaches, tools, and techniques used to uncover causes of problems. Some RCA approaches are geared more toward identifying true root causes than others, some are more general problem-solving techniques, and others simply offer support for the core ...
Further detailed analysis of the short list using the 5 Why's technique. Conclusion as to the most likely root cause (s) of the problem. Discussion on the preventive actions to be taken for each of the root causes. Documentation of the problem, the root causes, and the recommended corrective/preventive actions.
Solving a large number of problems looks like something is getting done. But if we don't actually diagnose the real root cause of a problem we'll likely have the same exact problem over and over. Instead of a news editor just fixing every single omitted Oxford comma, she will prevent further issues by training her writers to use commas ...
The model follows a very simple seven-step process: [1] 1. Assemble a Team. Gather together people who are familiar with the specifics of the problem, and with the process that you're trying to fix. Include someone to act as a facilitator, who can keep the team focused on identifying effective counter-measures. 2.