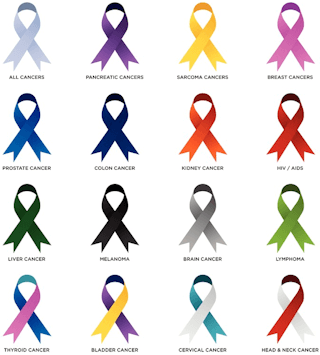
Awareness Ribbon Colors: Meanings and Causes Chart
Introduction, how many awareness ribbons are there.
Many groups, foundations, and organizations have adopted ribbons as symbols of support or awareness. As a result, various causes may often share the same, or similar, ribbon color(s). With new awareness days, weeks, and months , and ribbon colors, designs and symbols being created for causes, conditions, and cancer awareness , we're not certain how many there are, but as seen below, there are a lot!
Important Notes:
- Disabled World does not guarantee these ribbons' accuracy, legal status, or causes. Before using any ribbon colors and designs for any reason, thoroughly research all current existing ribbon designations and causes.
- As many awareness ribbon colors may have multiple associated meanings, we only list ribbons regarding health/disabilities.
- Due to different groups, organizations, countries, and people often creating different colored ribbons for the same cause, we may have a condition/disease listed several times under various ribbon colors.
- If you know a ribbon or cause we have listed is not correct - or if you know of an awareness ribbon color or cause we have missed - please see: How to correct, register, or submit an awareness ribbon color or design .

Main Digest
Covid-19 coronavirus awareness ribbon.
In these times of social isolation or distancing, you may like to either suggest a design for a COVID-19 Awareness Ribbon, send us an image of your COVID-19 Awareness Ribbon design, or ask your child if they wish to design an awareness ribbon. Your description and design could convey; sentiments of those affected by COVID-19, remembrance of those who passed due to the Coronavirus, or gratitude for the doctors, nurses, delivery personnel, and many other workers who have, and are, placing their lives on the line every second of the day to save lives and help others stay safe. More information can be found at: Disabled World COVID-19 Awareness Ribbon Design Submissions .
Jump to Different Awareness Ribbon Colors
Black awareness ribbons.
- September 11th (9/11)
- Melanoma awareness
- Virginia Tech Mourning/Remembrance
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis (Primary Biliary Cirrhosis)
- Sleep Apnea
- Sleep Disorders
Blue Awareness Ribbons
- Addiction Recovery
- Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
- Autoimmune Diseases (All)
- Beat Bullying (UK)
- Brachial Plexus Injuries - (Also Silver Ribbon with a bell)
- National Non Smoking Week (Canada)
- Charge Syndrome (Royal Blue)
- Colon Cancer
- Colorectal Cancer
- Cri du Chat Syndrome
- Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
- Epstein-Barr Virus
- Erb's Palsy
- Familial Polyposis
- Foster Care Awareness
- Guillain Barre Syndrome
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa (U.K.)
- Human Trafficking - (Including Human Sex Trafficking)
- Hydranencephaly awareness
- Huntington's Disease
- Leukodystrophies
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta (IO)
- Pompe Disease
- Restless Legs Syndrome
- Transverse Myelitis
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome
- Tuberous Sclerosis
- Usher Syndrome
- Von Hippel-Lindau (VHL)
- Walker-Warburg Syndrome Awareness
- West Nile Virus
Light Blue Ribbons
- Addisons Disease
- Behcets Disease
- Chronic Illness
- Cushing Syndrome
- DiGeorge Syndrome
- Edwards Syndrome (Trisomy 18)
- Graves Disease
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Klinefelter's Syndrome
- Men's Health
- Prostate cancer awareness
- Shprintzen Syndrome
- Thyroid Disease
- Twin to Twin Transfusion Syndrome (TTTS) awareness (2 daisies in center for identical twins, 3 for triplets - may be white, light pink, light blue)
- Velo-Cardio Facial Syndrome
Navy-Blue Ribbons
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
- Colon Cancer and Colorectal Cancer (Or Brown Ribbon)
- Crohn's Disease
- Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome (CVS)
- Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis (LCH)
- Koolen-de Vries Syndrome
- Krabbe Disease
- Mastocytosis
- Rectal Cancer
- Restless Legs Syndrome (RLS)
Royal Blue Ribbons
- Child Abuse Awareness
- Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME) / Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
- Syringomyelia
Robin Egg Blue Ribbons
- Pierre Robin Syndrome, Pierre Robin Malformation, Pierre Robin Sequence, Pierre Robin Anomaly, Pierre Robin Anomalad).
Blue Ribbons (2 Tone)
- Hydrocephalus Awareness - Light blue and dark blue ribbon with a drop of water on it.
Blue/Gray Ribbon with Red Blood Drop
- Type 1 Diabetes (Juvenile Diabetes)
Blue Jeans Denim Ribbon
- Genetic Disorder Awareness
Indigo Ribbon
- Crimes against targeted individuals of organized stalking and electronic harassment awareness.
- Achalasia Awareness
- Anti-Tobacco
- Colorectal Cancers (Dark blue is official ribbon color)
- Familia Polyposis
- Adults with Disabilities Awareness and support
- Amyloidosis support
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome
- AV Malformation
- Cystic Hygroma
- Disabled Adults
- Factor V Leiden
- Hemangioma and Vascular Malformation
- Hereditary Hemochromatosis
- Hughes Syndrome
- Lymphatic Malformation
- Meningococcal Meningitis
- Multiple Myeloma
- Post-Polio Syndrome
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Sturge-Weber Syndrome
- Thrombophilia
- Williams Syndrome
- Herpes Simplex Virus Awareness - HSV 1 is the oral version of the virus, and HSV 2 is the genital type. HSV is NOT part of standard STD screening, is highly contagious, and there is no cure.
- Spinal Cord Injuries (SCI)
- Spinal Diseases and Disorders
Gray / Grey
- Alpha-1 Antitrypsin Deficiency
- Asthma awareness
- Brain cancer awareness
- Brain Tumors
- Borderline Personality Disorder Awareness
- Diabetes awareness (Or blue circle, as designated by International Diabetes Federation)
- Adrenal Cancer
- Aging Research Awareness
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bone Marrow Donation
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans (BOS)
- Cerebral Palsy
- Childhood Depression
- Craniosynostosis Awareness
- Eye Injury Prevention
- Fanconi's Syndrome
- Fibrodysplasia Ossifican's Progressiva
- Functional Gastrointestinal and Motility Disorders (FGIMDs)
- Gastroparesis
- Growth and rebuilding
- Kidney Cancer
- Living Organ Donation
- Manic Depression
- Mental Health
- Mental Illness
- Nephrotic Syndrome
- Neural Tube Defects
- Neurofibromatosis
- Organ Transplant and Donation
- Mitochondrial Disease Awareness
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
- Spinal Cord Injury
- Stem Cell Research
- Superficial Siderosis (Color hex code = #429F46)
- Tissue Donation
- Tourette's Syndrome
- Traumatic Brain Injury
- Cyclin-dependent kinase-like 5 (CDKL5)
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
- Gastroschisis
- Kabuki Syndrome
- Lyme Disease
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma
- Sandhoff Disease
Light Green
- Celiac Disease
- Chronic pelvic Pain
- Human Papilloma Virus
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STD)
- Autosomal Recessive Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Congenital hepatic Fibrosis
- Genetic Disorders
- Ivemark Syndrome
- Bone Tumor Awareness (musculoskeletal tumors and lesions, benign/malignant)
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH)
- Dysautonomia
- Interstitial Cystitis
- Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Anti Bullying Awareness
- Agoraphobia
- Anxiety Disorder
- Batten Disease awareness
Cervical Cancer
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia awareness
- Dissociative Disorders (All)
- Ectodermal Dysphasia
- Fibular Hemimelia (FH)
- Food Allergies
- Fragile X Syndrome
- Gynecological cancer
- Interstitial Cystitis and Bladder Pain Syndrome awareness and support
- Knee Injury Awareness
- Marker X Syndrome
- Martin-Bell Syndrome
- Military Sexual Trauma awareness
- Myasthenia Gravis awareness
- Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Ovarian Cancer
- Panic Disorder
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome awareness and support
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
- Proximal Femoral Focal Deficiency (PFFD)
- Sexual Assault
- Scleroderma (Stiff Skin Syndrome)
- Sexual Assault and Sexual Violence awareness and support
- Trigeminal Neuralgia (TN)
- Tsunami Victims
- Uterine Cancer
- Vulvar Cancer
- Hepatitis B and Liver Cancer - The Jade Ribbon Campaign was launched by Asian Liver Center at Stanford University in 2001.
Sea Green/Sea Foam Blue Ribbons
- Family Estrangement: The ribbon color is seafoam-blue (Pantone 628 Cp Color, HEX #C8E3E2, rgb(200,227,226))
- Stuttering: The awareness color ribbon for stuttering is Sea Green (Sea Foam Blue).
- Alveolar Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Childhood cancer awareness
- Embryonal Rhabdomyosarcoma
- Neuroblastoma and Osteosarcoma
- Amplified Musculoskeletal Pain Syndrome (AMPS)
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- Agent Orange
- Autoinflammatory Disorders
- Cultural Diversity
- Functional Neurological Disorder (FND)
- Kidney Cancer - Renal Cell Carcinoma
- Malnutrition
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD) - Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS).
- Self Injury Awareness
- Sensory Processing Disorder
- Spinal Cancer
- Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Endometrial Cancer
- Vaginal Cancer
- Appendix Cancer - Extremely rare condition, affecting an estimated 600 to 1,000 Americans each year. Primary lymphomas can occur in the appendix.
Pearl, White or Clear Ribbons
- Dating Violence Awareness
- Lung Cancer
- Lung Disease
- Mesothelioma
- Waldenstrom's Macroglobulinemia
- Bone Cancer
- Bone Disease
- Congenital Cataracts
- Gay-Teen Suicide Awareness
- Invisible Illness
- Multiple Hereditary Exostoses
- Osteoporosis
- Postpartum Depression
- Severe Combined Immune Deficiency Disease (SCID) and SCID Newborn Screening
- Retinoblastoma Cancer (eye)
- Right to Life
- Breast cancer awareness
- Birth Parents
- Nursing Mothers
- Breast Reconstruction Awareness (BRA)
- Alzheimer's Disease awareness
- Cerebrospinal Fluid Leak (CSF)
- Chiari Malformation awareness
- Childhood Hemiplegia and stroke awareness
- Chronic and Acute Pain
- Crohn's (Crohn's and Colitis Foundation of America (CCFA) uses orange and blue in promotional materials)
- Colitis Awareness Campaign
- Cystic Fibrosis awareness
- Domestic Violence Awareness Campaign
- Elder Abuse Awareness
- Fibromyalgia awareness
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa Awareness Ribbon
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) Awareness
- Leiomyosarcoma
- Lupus awareness
- Macular Degeneration
- March of Dimes
- Meningitis Survivors
- Mesh Awareness
- Mucolididoses
- Neuropathy Awareness
- Pancreatic cancer awareness
- Pancreatitis
- Porphyria - Erythropoietic Protoporphyria (EPP) and X-Linked Protoporphyria (XLP)
- Premature Birth (Also Pink and Blue according to some organizations)
- Retinitis Pigmentosa
- Rett Syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Scheuermann's Disease
- Sjorgren's Syndrome
- Spirit Day and victims of homophobia
Thyroid Cancer
- Trisomy 9 Awareness
- Cancer awareness (all kinds)
- Craniosynostosis awareness
- Epilepsy awareness
- Gynecological Cancer
- Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis
- Infantile Spasms
- Acid Reflux (GERD)
- Eating disorders awareness
- Eosinophilic Disorders
- Esophageal cancer
- Gastric Cancer
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome(IBS)
- Pulmonary hypertension awareness
- Small Intestine Cancer and Stomach Cancer
- Hodgkin's lymphoma awareness
- Testicular Cancer
- Testicular Cancer . There is debate about the color for testicular cancer awareness and ribbons, however orchid, a purple/violet color, has long been recognized as the official color for testicular cancer.
Purple and Silver Ribbons
- Purple and Silver are the colors representing International Overdose Awareness Day (IOAD). Silver is the awareness color for drug overdose (fatal or nonfatal), and purple is the awareness color for opioid addiction.
- AIDS and HIV awareness
- Adult Onset Still's Disease (AOSD)
- Aperts Syndrome
- Brain Aneurysm Awareness - (www.bafound.org)
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans
- Burn Victims
- Cardiovascular Disease
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Congenital Heart Disease
- Congestive Heart Failure
- Courage and Inspiration
- Diamond Blackfan Anemia
- Epidermolysis Bullosa
- Evans Syndrome
- Factor XI Deficiency
- Heart Disease
- High Blood Pressure
- Hypertension
- Long Q-T Syndrome
- Marfan Syndrome
- Poland Syndrome
- Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD) - Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS). Now uses the Multi-colored flame ribbon.
- Substance abuse awareness
- Supraventricular Tachycardia
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura
- Tuberculosis
- Vasculitis awareness
- Von Willebrand's Disease
- Wegener's Granulomatosis
- Wolf-Parkinson-White
- Brachial Nerve Plexus (BNP) - Silver Ribbon with a bell (Also Blue Ribbon)
- Brain Disabilities
- Brain disorders awareness
- Campaign for the Brain
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth (CMT)
- Cortical Visual Impairment (CVI) Awareness
- Disabled Children
- Elderly Abuse
- Encephalitis
- Essential Tremor
- Gynaecological Cancer awareness (NZ)
- Kienbock's Disease (Silver and Black)
- Medical Device Injury Awareness
- Niemann-Pick
- Ovarian cancer awareness (Australia)
- Parkinson's Disease
- Schizophrenia
- Sciatic Pain
- Stalking Awareness
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV)
- Adenosarcoma
- Bladder Cancer - (Also see: Purple, Blue and Marigold ribbon below)
- Bone cancer / Osteosarcoma
- Craniofacial Acceptance (CCAKids.org)
- Endometriosis awareness
- Ewings Sarcoma
- Liver Cancer
- Liver Disease
- Microcephaly
- Missing Children
- Myxoid Liposarcoma
- Osteosarcoma
- Spina Bifida
- Suicide Prevention (Also see Blue/Purple - Teal/Purple - Turquoise/Purple ribbon)
Awareness Symbols Causes and Meanings
Rainbow butterfly symbol.
The rainbow butterfly symbol, based on the "rainbow infinity" neurodiversity symbol, grew from conversations on an ADHD Facebook group about what signs and symbols people with ADHD felt best represented them. The butterfly symbol pictured below resonated with many, symbolizing how ADHD minds often flit from one thing to the next. The rainbow butterfly symbol pictured is a current popular version.

Autism Infinity Symbol
The Autism Infinity Symbol is becoming a popular alternative to the puzzle pieces autism symbols, as well as a symbol for Neurodiversity .

Blue Star Symbol
Represents the fight against colorectal cancer . The hope is the Blue Star Universal Symbol will be integrated into existing group awareness efforts and incorporated into materials as a representation of the collective fight against colorectal cancer.
Checkered Eye Symbol
The checkered eye is a wearable symbol indicating its wearer has a vision disability. It is a simple line drawing of an eye, the center (iris) is black and white checkers. The symbol bears the Checkered Eye and the text "LOW VISION".
Black and White Checkered Ribbon
Black and white checkered awareness ribbon denotes "Blindness is a Spectrum".
Cloud Ribbon
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia awareness. Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) is a birth defect, occurring while the fetus is developing.
Dark Blue and Orange/Orchid
The awareness ribbon colors for Psoriatic Arthritis (PsA) is Dark Blue for Arthritis, and Orange/Orchid for Psoriasis.
Diabetes Awareness
Blue Diabetes Circle Awareness. The awareness ribbon color for Diabetes was gray. However, diabetes is now symbolized by the blue circle, as designated by the International Diabetes Federation.
Purple Ribbon with White Spots in Figure 8 Format
Lichen Sclerosus awareness ribbon for a chronic skin disease. The shade of purple may change, but the white spots and figure 8 shape is the main identifier.
Long Covid Awareness Ribbon

The three colors of the long covid awareness ribbon represent; past, present, and future of Long COVID:
- Gray: Loss and Grief
- Teal: Hope and Support
- Black: Loneliness and Isolation
Multi-colored Puzzle Ribbon
Multi-colored puzzle ribbon with the words "Developmental Disabilities Awareness - Normal is Over-rated" on one side.
Teal Lichen Sclerosus Ribbon
Folded teal colored Lichen Sclerosus Awareness ribbon (U.K.) with the black printed words "Lichen Sclerosus" on one end and "Awareness" on the other end.
FOXG1 - Orange Ribbon with Fox Tail
FOXG1 is a severe neurological condition characterized by seizures, small head size, inability to control body movements, and lack of speech.
Multi-colored Flame
Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS) - Formerly known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy (RSD).
Pink Ribbon - Red Ribbon
Pink Ribbon Red Ribbon will expand the availability of vital cervical cancer screening and treatment and breast care education.
Rainbow Ribbons
- Adrenocortical Carcinoma
- Rainbow Ribbon (Pastel Colors) - Researchers have found that puzzle pieces carry a negative connotation. A rainbow ribbon for autism represents the diversity of people on the spectrum and hearkens to the neurodiversity movement.
Reddish Ribbon
Prurigo Nodularis (PN) awareness ribbon features a reddish color fading to "pinkish" with dots at the ends and the words Prurigo Nodularis printed on one side.
Trisomy Awareness
Trisomy Awareness ribbon - Created by the Support Organization for Trisomy to represent all forms of Trisomy.
Mosaic Trisomies
The ribbon features a mosaic pattern of red, blue, and yellow colors, with the words "Mosaic Trisomy Awareness" printed on it.
Blue Butterfly
The blue butterfly symbol is used to raise awareness of Turner Syndrome
Mint Green and Golden Yellow Butterfly
The Mint green and golden yellow butterfly symbol is used to raise awareness of Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome (BWS).
Multiple Colored Ribbons Causes and Meanings
Beige - giraffe print ribbons.
Tethered spinal cord syndrome - Closely associated with spina bifida.
Black with Silver Sparkled Striped Zebra Ribbons
Stiff Person Syndrome
Black and Teal Zebra Print Ribbon
Erdheim-Chester Disease
Black and White Striped Ribbons
Black and White Striped Breast Implant Illness (BII) awareness ribbon with the words "Breast Implant Illness" printed black on white background.
Blue and Green Ribbons
Psuedotumor Cerebri
Blue, Orange, Green and Yellow Ribbons
Intestinal Malrotation - A congenital birth defect affecting the positioning of a person's intestines.
Blue and Red Ribbons
- Congenital Heart Defects and Disease
- Hypo plastic left heart Syndrome
- Olser Weber Rendu Syndrome (HHT)
- Noonan's Syndrome
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Rare Lung Diseases
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SADS)
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF)

Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) awareness ribbon submitted by Josh Ingram, founder and president of the Fill Your Lungs Foundation. The current ribbon for regular pulmonary fibrosis is half red and half blue. This represents oxygenated and deoxygenated blood traveling in and out of the lungs. Fill Your Lungs Foundation used the same colors, but made one distinct change - the symbol of a question mark depicted in red. This alludes to the unknown cause of IPF, the factor that separates it from its counterpart (PF). The design has been widely accepted and used as the awareness ribbon for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis - even being published on the cover of a UK edition of "Pulmonary Fibrosis Weekly" magazine.
Blue and Purple
- Pediatric Stroke
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- (Striped blue and purple ribbon) - Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD)
Blue and Teal
The Spina Bifida Association ribbon color is blue and teal and represents all forms of Spina Bifida including Occult Spinal Dysraphism, Spina Bifida Occulta, Meningocele and Myelomeningocele.
Blue/Purple - Teal/Purple - Turquoise/Purple
Suicide awareness and prevention (also see yellow ribbon).
Blue/Yellow Ribbons
- Down Syndrome
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome - (TOS)
- Spina Bifida and Hydrocephalus - Ribbon incorporates combined colors of both Spina Bifida (Yellow) and Hydrocephalus (Two-Tone Blue ribbon with water drop on the side).
Bone/Beige Trimmed in Royal Blue Ribbon
Hip Dysplasia
Brown with Pink Dots Ribbon
The Persistent Cloaca ribbon is brown to symbolize bowel issues, and the pink dots symbolize occurrence in females only.
Burgundy and Ivory
- Oral head and Neck cancers
- Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Throat Cancer
- Laryngeal Cancer
- Pharyngeal Cancer
Burgundy and Purple
Arachnoiditis - Purple is for neuropathy and burgundy for meningitis.
Cow Print Ribbons
Omphalocele Awareness
Gold and Blue with Diamond Ribbon
Bohring-Opitz Syndrome
Gold and Silver Ribbons
- Hearing Disorders
- Hearing Impairments
- Meniere's Disease
Gray and Cream
Spondylolisthesis Awareness Ribbon - The colors for the ribbon are Cool Gray 10 for the Silver that represents Titanium (the metal used for spinal fusions when having surgery for spondylolisthesis) and spinal conditions. The PMS 726 is the cream color of the ribbon, and this represents spondylolisthesis.
Light Green/Dark Blue
Body-focused Repetitive Behavior (BFRB) - General term for related complex disorders including hair pulling, skin picking, nail-biting.
Grey and Burgundy Ribbons
Arachnoid Cysts
Grey Ribbon with Red Heart
Hypotonia awareness ribbon.
Multi-colored with the words "Hypotonia Awareness - One Inchstone at a Time".
Idiopathic Hypersomnia Awareness
Idiopathic Hypersomnia - Disease characterized primarily by severe excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS).
Oral Cancer Awareness Ribbons

Ivory with Rose Ribbons
The official awareness ribbon color for Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is Ivory and also includes a rose picture.
Lime Green with DNA Strand Ribbon
MEF2C Haploinsufficiency Syndrome - Neurodevelopmental disorder associated with intellectual disability, autistic features, epilepsy, and abnormal movements.
Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly
The Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly ribbon is royal blue with a yellow border, and yellow letters MFDM on the left bottom portion of the ribbon. The ribbon design combines craniofacial and microcephaly colors.
Orange and Green
Synergy Saturday and Healthy Self - A weekly wellness project and health awareness initiative with free health screenings, risk assessments, giveaways, and health education handouts for poor health and poverty alleviation - synergysaturday.com
Orange and Navy Blue
Human Rights for Family Caregivers Awareness
Orchid and Orange
Pink and blue.
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism
- Birth defects
- Genital integrity
- Male Breast Cancer
- Hyperemesis Graviduram
- Hyperammonemia
- Infant loss awareness
- Infertility awareness
- Inflammatory breast cancer awareness
- Pregnancy Loss
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
- Premature Birth (Also purple according to some organizations)
- Twin to Twin transfusion syndrome
- Turner Syndrome (Various groups of TS have their colors, but every group uses the butterfly symbol .)
- Pediatric bronchiolitis obliterans
Pink / Blue
Clubfoot - A clubfoot, or talipes equinovarus (TEV), is a birth defect. The foot is twisted in (inverted) and down. Without treatment, persons afflicted often appear to walk on their ankles, or on the sides of their feet. Ponseti International Association (PIA) has designated June 3rd as World Clubfoot Day.
Pink Purple and Teal Ribbons
Purple and black.
- Tracheostomy Awareness - The ribbon is two-tone, with one side being purple and the other black.
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis (NEC) Awareness - Right half of the ribbon is purple, and the left half is black.
Purple / Blue
GNA01 Gene Mutation Disorder - The awareness ribbon is colored purple and blue, with the words "Epilepsy" written on the purple part and "Movement Disorder" written on the blue part.
Purple / Green
Sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (SOD) - Purple/Green Ribbon with the words "Sod Awareness" printed in white on the purple side.
Purple and Green Ribbons
- Stickler Syndrome - Also known as hereditary progressive arthro-ophthalmopathy.
- Schizencephaly - Purple for epilepsy and green for cerebral palsy.
Purple, Blue, Marigold, Ribbons
Bladder Cancer Awareness
Purple and Teal with White Stars Ribbon
The Necrotizing fasciitis - Purple and teal with white stars representing those who lost the battle with this disease.
Purple, Teal and Green
Medullary Sponge Kidney ( Cacchi-Ricci disease ).
Purple and White
Sarcoidosis - Snowflake signifies no two Sarcoidosis Sufferers are affected in the same way.
Purple and Yellow
Autoimmune Hepatitis .
Puzzle Ribbon
- Autism awareness
- Asperger's Syndrome
Quilt Design Ribbon
Dissociative Identity Disorder (DID) - Multiple Personality Disorder (MPD) - The ribbon is based on a crazy quilt design made of various colors and shapes of fabric. An alternative design preferred by some is based on multi-colored stained glass.
Red and White
- Aplastic Anemia
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Red and Zebra Striped Ribbons
Hashimoto's Encephalitis, Hashimoto's Encephalopathy, Non-vasculitic Autoimmune Meningoencephalitis, Steroid-responsive Encephalopathy associated with Autoimmune Thyroiditis.
Red with White Border Ribbon
Chronic Venous Insufficiency Awareness
Red / Orange
Rare Adipose Disorders, Dercum's Disease (Adiposis Dolorosa), Madelung's Disease (Launois-Bensaude Syndrome), Multiple Familial Lipomatosis MFL and Multiple Symmetrica.
Red and Gold
Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia (NAIT) Awareness (NAITP or NAIT or NATP or NAT for short, or fetal and neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia, FNAIT, feto-maternal alloimmune thrombocytopenia, FMAITP or FMAIT).
Red White and Black
Pernicious Anaemia and B12 Deficiency - Two awareness ribbons are listed for Pernicious anemia, both ribbons are colored red, white, and black. The second ribbon has the words "Pernicious Anaemia" written on the black part, and B12 Deficiency on the red part. Pernicious Anaemia is believed to be an autoimmune disease . Courtesy of Georgia Dent ([email protected]), Ribbon design is copyrighted.
Red and Yellow
- Hepatitis C
- HIV/HCV Co-Infection
Silver and Blue
Corpus Callosum
Silver, Red and Zebra
Autoimmune Encephalitis
Green Lanyard or Ribbon with Sunflowers
The Sunflower Lanyard and Awareness Ribbon is a growing initiative to aid the wearer with hidden or invisible disabilities receive more support in public places such as airports, shopping centers, and transport facilities.
Teal and Black
International Association for Premenstrual Disorders (IAPMD) Awareness
Teal and White
White with blue outline.
Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
White with Navy Stripe
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis - (Aran-Duchenne, Gehrig's Disease, Lou Gehrig's Disease, Motor Neuron Disease)
Yellow and Multicolor Ribbons
Gilbert's Syndrome
White Ribbon with Red Spots
- Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria (Hives) - Itchy red or skin-colored welts. The condition is considered chronic hives if the welts appear for more than 6 weeks - and recur frequently over months or years. Chronic Idiopathic Urticaria can be very uncomfortable and interfere with sleep and daily activities. Antihistamines and anti-itch medications provide relief for many people.
- Granuloma Annulare Awareness - Granuloma annulare is a chronic skin condition that causes raised reddish or skin-colored bumps (lesions) in a ring pattern, usually on the hands and feet.
Zebra Ribbons (Black and White)
- Carcinoid and Neuroendocrine tumor awareness
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome
- Endocrine Cancer
- Primary Immunodeficiency
- Rare Disease awareness
- Vaccine Awareness
Inclusion Awareness Ribbon

Dr. Joanna Baker-Rogers (Director, Busy Life Ltd, www.Busy-life.co.uk) submitted an Awareness Ribbon design for Inclusion - one that raises awareness of how everyone should be included in everything, regardless of race, ability, gender, etc. She chose the three primary colors, as these are the colors that every other color is made from. Applying this to inclusion means that everyone is included. This is not the same as diversity. Diversity means including marginalized, minority groups. Inclusion means including everyone; for example, non-disABLED people who constitute the majority of the population. The RGB codes are:
- Red = 255 000 000
- Blue = 000 122 246
- Yellow = 255 229 050
How Do I Register an Awareness Ribbon Color or Design?
Awareness Ribbons are not a centralized idea, there isn't really an official place to go to register a design, or color. Currently, awareness ribbons are considered to be in the public domain in most countries, and a simple ribbon of a particular color is generally not considered sufficiently original and creative enough to be copyrighted by a person - or group. However, in a few cases, several particular designs have been granted a special trademark status. E.g. Canada has granted "official mark" status for the pink (breast cancer) awareness ribbons to the Canadian Breast Cancer Foundation.
If you are designing your own awareness ribbon and need color ideas, refer to our comprehensive list of HEX and RGB color codes .
How Do I Submit an Awareness Ribbon Color or Design?
You are welcome to submit an awareness ribbon color and design to add to our list provided it meets the following criteria:
- When submitting an awareness ribbon, or design, please provide an example(s) of where the ribbon is currently used, e.g., web-page address, organization etc.
- Do NOT post, or redesign, awareness ribbons that are trademarked - (TM), (R). Some ribbons, including style, color, and design are copyrighted, you should thoroughly research the ribbon design you are wishing to submit to avoid possible copyright infringement.
- To avoid listing several ribbons or designs for the same cause, the awareness ribbon or design you wish to submit MUST be recognized as the most popular one chosen for the cause it represents - Different styles and colors recognized by different countries are OK.
To submit an awareness ribbon, or if you know a ribbon, or cause, we have listed is not correct, or if you know of an awareness ribbon color, or cause, we have missed, please contact us .
Awareness Bracelet Colors
An awareness band, awareness bracelet, or wristband, is defined as a bracelet of various colors on which a slogan is sometimes written, usually sold to raise awareness for charitable causes. These plastic wristbands are available in nearly every color, or colors, and are constructed from material such as silicone, fabric, rubber, or plastic. Awareness bracelets sometimes carry embossed messages demonstrating the wearer's support of a certain cause, or charitable organization. Awareness bracelets generally use the same, or similar colors to awareness ribbons.
Related Information
- Cancer Awareness: Color Chart of Ribbon Colors for Cancers - List, table and printable chart outlining the colors of awareness ribbons that represent different types of cancer and their causes.
- Mood Colors: Meaning and Associations of Color Psychology - Chart showing various colors, the color meaning and what it symbolizes, for those who may be seeking ideas in designing new colored awareness bracelets and ribbons.
- Calendar of US and International Awareness Days, Weeks and Months - List of U.S. National and U.N. International commemorative observance and awareness days, weeks, months to commemorate medical research or ethical cause of importance.
- Notable LGBT Awareness Dates and Events - List of important LGBT+ community awareness remembrance dates and coming events in respect to sexual orientation, gender identity, transgenderism, transsexualism, and intersexuality.
- U.N. International Awareness and Commemorative Dates - List of International days of observance established by the United Nations (UN), World Health Organization (WHO) and United Nations Educational Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO).
- List of U.S. Presidential Proclamation Dates - List of annual awareness and observance dates including days, weeks and months, as recognized by U.S. presidential proclamation.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Types of Speech Impediments
Phynart Studio / Getty Images
Articulation Errors
Ankyloglossia, treating speech disorders.
A speech impediment, also known as a speech disorder , is a condition that can affect a person’s ability to form sounds and words, making their speech difficult to understand.
Speech disorders generally become evident in early childhood, as children start speaking and learning language. While many children initially have trouble with certain sounds and words, most are able to speak easily by the time they are five years old. However, some speech disorders persist. Approximately 5% of children aged three to 17 in the United States experience speech disorders.
There are many different types of speech impediments, including:
- Articulation errors
This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment of the different types of speech disorders.
Speech impediments that break the flow of speech are known as disfluencies. Stuttering is the most common form of disfluency, however there are other types as well.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Disfluencies
These are some of the characteristics of disfluencies:
- Repeating certain phrases, words, or sounds after the age of 4 (For example: “O…orange,” “I like…like orange juice,” “I want…I want orange juice”)
- Adding in extra sounds or words into sentences (For example: “We…uh…went to buy…um…orange juice”)
- Elongating words (For example: Saying “orange joooose” instead of "orange juice")
- Replacing words (For example: “What…Where is the orange juice?”)
- Hesitating while speaking (For example: A long pause while thinking)
- Pausing mid-speech (For example: Stopping abruptly mid-speech, due to lack of airflow, causing no sounds to come out, leading to a tense pause)
In addition, someone with disfluencies may also experience the following symptoms while speaking:
- Vocal tension and strain
- Head jerking
- Eye blinking
- Lip trembling
Causes of Disfluencies
People with disfluencies tend to have neurological differences in areas of the brain that control language processing and coordinate speech, which may be caused by:
- Genetic factors
- Trauma or infection to the brain
- Environmental stressors that cause anxiety or emotional distress
- Neurodevelopmental conditions like attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
Articulation disorders occur when a person has trouble placing their tongue in the correct position to form certain speech sounds. Lisping is the most common type of articulation disorder.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Articulation Errors
These are some of the characteristics of articulation disorders:
- Substituting one sound for another . People typically have trouble with ‘r’ and ‘l’ sounds. (For example: Being unable to say “rabbit” and saying “wabbit” instead)
- Lisping , which refers specifically to difficulty with ‘s’ and ‘z’ sounds. (For example: Saying “thugar” instead of “sugar” or producing a whistling sound while trying to pronounce these letters)
- Omitting sounds (For example: Saying “coo” instead of “school”)
- Adding sounds (For example: Saying “pinanio” instead of “piano”)
- Making other speech errors that can make it difficult to decipher what the person is saying. For instance, only family members may be able to understand what they’re trying to say.
Causes of Articulation Errors
Articulation errors may be caused by:
- Genetic factors, as it can run in families
- Hearing loss , as mishearing sounds can affect the person’s ability to reproduce the sound
- Changes in the bones or muscles that are needed for speech, including a cleft palate (a hole in the roof of the mouth) and tooth problems
- Damage to the nerves or parts of the brain that coordinate speech, caused by conditions such as cerebral palsy , for instance
Ankyloglossia, also known as tongue-tie, is a condition where the person’s tongue is attached to the bottom of their mouth. This can restrict the tongue’s movement and make it hard for the person to move their tongue.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia is characterized by difficulty pronouncing ‘d,’ ‘n,’ ‘s,’ ‘t,’ ‘th,’ and ‘z’ sounds that require the person’s tongue to touch the roof of their mouth or their upper teeth, as their tongue may not be able to reach there.
Apart from speech impediments, people with ankyloglossia may also experience other symptoms as a result of their tongue-tie. These symptoms include:
- Difficulty breastfeeding in newborns
- Trouble swallowing
- Limited ability to move the tongue from side to side or stick it out
- Difficulty with activities like playing wind instruments, licking ice cream, or kissing
- Mouth breathing
Causes of Ankyloglossia
Ankyloglossia is a congenital condition, which means it is present from birth. A tissue known as the lingual frenulum attaches the tongue to the base of the mouth. People with ankyloglossia have a shorter lingual frenulum, or it is attached further along their tongue than most people’s.
Dysarthria is a condition where people slur their words because they cannot control the muscles that are required for speech, due to brain, nerve, or organ damage.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Dysarthria
Dysarthria is characterized by:
- Slurred, choppy, or robotic speech
- Rapid, slow, or soft speech
- Breathy, hoarse, or nasal voice
Additionally, someone with dysarthria may also have other symptoms such as difficulty swallowing and inability to move their tongue, lips, or jaw easily.
Causes of Dysarthria
Dysarthria is caused by paralysis or weakness of the speech muscles. The causes of the weakness can vary depending on the type of dysarthria the person has:
- Central dysarthria is caused by brain damage. It may be the result of neuromuscular diseases, such as cerebral palsy, Huntington’s disease, multiple sclerosis, muscular dystrophy, Huntington’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, or Lou Gehrig’s disease. Central dysarthria may also be caused by injuries or illnesses that damage the brain, such as dementia, stroke, brain tumor, or traumatic brain injury .
- Peripheral dysarthria is caused by damage to the organs involved in speech. It may be caused by congenital structural problems, trauma to the mouth or face, or surgery to the tongue, mouth, head, neck, or voice box.
Apraxia, also known as dyspraxia, verbal apraxia, or apraxia of speech, is a neurological condition that can cause a person to have trouble moving the muscles they need to create sounds or words. The person’s brain knows what they want to say, but is unable to plan and sequence the words accordingly.
Symptoms and Characteristics of Apraxia
These are some of the characteristics of apraxia:
- Distorting sounds: The person may have trouble pronouncing certain sounds, particularly vowels, because they may be unable to move their tongue or jaw in the manner required to produce the right sound. Longer or more complex words may be especially harder to manage.
- Being inconsistent in their speech: For instance, the person may be able to pronounce a word correctly once, but may not be able to repeat it. Or, they may pronounce it correctly today and differently on another day.
- Grasping for words: The person may appear to be searching for the right word or sound, or attempt the pronunciation several times before getting it right.
- Making errors with the rhythm or tone of speech: The person may struggle with using tone and inflection to communicate meaning. For instance, they may not stress any of the words in a sentence, have trouble going from one syllable in a word to another, or pause at an inappropriate part of a sentence.
Causes of Apraxia
Apraxia occurs when nerve pathways in the brain are interrupted, which can make it difficult for the brain to send messages to the organs involved in speaking. The causes of these neurological disturbances can vary depending on the type of apraxia the person has:
- Childhood apraxia of speech (CAS): This condition is present from birth and is often hereditary. A person may be more likely to have it if a biological relative has a learning disability or communication disorder.
- Acquired apraxia of speech (AOS): This condition can occur in adults, due to brain damage as a result of a tumor, head injury , stroke, or other illness that affects the parts of the brain involved in speech.
If you have a speech impediment, or suspect your child might have one, it can be helpful to visit your healthcare provider. Your primary care physician can refer you to a speech-language pathologist, who can evaluate speech, diagnose speech disorders, and recommend treatment options.
The diagnostic process may involve a physical examination as well as psychological, neurological, or hearing tests, in order to confirm the diagnosis and rule out other causes.
Treatment for speech disorders often involves speech therapy, which can help you learn how to move your muscles and position your tongue correctly in order to create specific sounds. It can be quite effective in improving your speech.
Children often grow out of milder speech disorders; however, special education and speech therapy can help with more serious ones.
For ankyloglossia, or tongue-tie, a minor surgery known as a frenectomy can help detach the tongue from the bottom of the mouth.
A Word From Verywell
A speech impediment can make it difficult to pronounce certain sounds, speak clearly, or communicate fluently.
Living with a speech disorder can be frustrating because people may cut you off while you’re speaking, try to finish your sentences, or treat you differently. It can be helpful to talk to your healthcare providers about how to cope with these situations.
You may also benefit from joining a support group, where you can connect with others living with speech disorders.
National Library of Medicine. Speech disorders . Medline Plus.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Language and speech disorders .
Cincinnati Children's Hospital. Stuttering .
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick statistics about voice, speech, and language .
Cleveland Clinic. Speech impediment .
Lee H, Sim H, Lee E, Choi D. Disfluency characteristics of children with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder symptoms . J Commun Disord . 2017;65:54-64. doi:10.1016/j.jcomdis.2016.12.001
Nemours Foundation. Speech problems .
Penn Medicine. Speech and language disorders .
Cleveland Clinic. Tongue-tie .
University of Rochester Medical Center. Ankyloglossia .
Cleveland Clinic. Dysarthria .
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Apraxia of speech .
Cleveland Clinic. Childhood apraxia of speech .
Stanford Children’s Hospital. Speech sound disorders in children .
Abbastabar H, Alizadeh A, Darparesh M, Mohseni S, Roozbeh N. Spatial distribution and the prevalence of speech disorders in the provinces of Iran . J Med Life . 2015;8(Spec Iss 2):99-104.
By Sanjana Gupta Sanjana is a health writer and editor. Her work spans various health-related topics, including mental health, fitness, nutrition, and wellness.

Diversity, Equity, Inclusion (DEI) and Multicultural Resources: Awareness Ribbon Colors & Months
- General DEI
- Journals & Magazines
- Multimedia Resources
- Intercultural Communication
- Valentine's Day This link opens in a new window
- Mardi Gras This link opens in a new window
- St. Patrick's Day (March 17) This link opens in a new window
- Easter and Passover This link opens in a new window
- Independence Day This link opens in a new window
- Christmas This link opens in a new window
- Constitution Day and Citizenship Day This link opens in a new window
- Juneteenth This link opens in a new window
- Hanukkah This link opens in a new window
- Women's History Month This link opens in a new window
- African American Music Appreciation Month This link opens in a new window
- LGBtQIA+ Pride Month This link opens in a new window
- Asian American and Pacific Islander Heritage Month This link opens in a new window
- Black History Month This link opens in a new window
- Caribbean American Heritage Month This link opens in a new window
- Filipino American History Month This link opens in a new window
- Hispanic & Latinx Heritage Month This link opens in a new window
- Jewish American Heritage Month This link opens in a new window
- Native American Indian Heritage Month This link opens in a new window
- Polish American Heritage Month This link opens in a new window
- Arab American Heritage Month This link opens in a new window
- African American Studies This link opens in a new window
- Asian Studies This link opens in a new window
- Caribbean Studies This link opens in a new window
- Judaic Studies This link opens in a new window
- Latin American Studies This link opens in a new window
- Native American Studies This link opens in a new window
- Polish Studies This link opens in a new window
- Women Studies This link opens in a new window
- Awareness Ribbon Colors & Months
- Want to Contribute?
- Citing Your Sources This link opens in a new window
- Library Resources and Services This link opens in a new window
- Software in the Library
- Get Help This link opens in a new window
Dual Color Ribbons

Red & Yellow Ribbon
The red and yellow ribbon, also known as the coronavirus awareness ribbon, made its debut in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. This ribbon is used to represent not just COVID-19, but coronavirus in general. The full list of red & yellow ribbon meanings includes:
- Coronavirus
- HIV/HCV Co-Infection (April)
- Hepatitis C (May)

Black & Gold Ribbon
A black and gold awareness ribbon is used to represent a platelet donation, which is collected by the Red Cross and used to help people who are undergoing medical treatments like chemotherapy. The full list of black & gold ribbon meanings includes:
- Platelet Donation

Black & Navy Ribbon
While you most often see black and navy ribbons as a tribute to police officers lost in the line of duty, you’ll also see this color combo used to raise awareness for ocular melanoma. The full list of black & navy ribbon meanings includes:
- Ocular Melanoma
- Police Officers Lost in the Line of Duty

Black & White Ribbon
A black and white awareness ribbon is used to represent acute disseminated encephalomyelitis as well as vaccine injuries. The full list of black & white ribbon meanings includes:
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
- Vaccine Injury

Blue & Black Ribbon
Blue & Black awareness ribbon with another color takes on a different meaning. For instance, blue and black symbolizes the loss of, or memory of, a brother, father, son, or male loved one. The full list of blue & black ribbon meanings includes:
- Loss of, on in memory of, a brother, father, son, or male loved one

Blue & Gray Ribbon
The blue and gray ribbon is used to represent awareness and support of those battling Type 1 Diabetes.
The full list of blue & gray ribbon meanings includes:
- Diabetes (Type 1)

Blue & Orange Ribbon
The blue and orange ribbon symbolizes the memory of Frankie Delgado who died at the age of 4 from a phenomenon known as “dry drowning.” This rare condition occurs when there’s too much water in the lungs. The full list of blue & orange ribbon meanings includes:
- Dry Drowning (In Memory of Baby Frankie)
- #FrankieDryDrowningAwareness

Blue & Silver Ribbon
The blue and silver ribbon is associated with many causes that affect children including fetal alcohol syndrome and Type 1 Juvenile Diabetes. The full list of blue & silver ribbon meanings includes:
- Brachial Plexus Injuries
- Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
- Juvenile Diabetes (Type 1)

Blue & White Ribbon
Blue and white ribbons are used for causes related to teen cancer and femoral acetabular impingement, a condition in which an extra bone grows along the hip joint. The full list of blue & white ribbon meanings includes:
- Lou Gehrig's Disease (May)
- Teen Cancer
- Femoral Acetabular Impingement

Green & Blue Ribbon
The color combo of blue and green on an awareness ribbon represents many genetic disorders and viruses including cytomegalovirus and neurofibromatosis. The full list of green & blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Adrenoleukodystrophy
- Cytomegalovirus
- Neurofibromatosis
- Neurofibromatosis Type 1

Green & Orange Ribbon
The two colors on this awareness ribbon are fitting as green and orange represents a dual diagnosis. This can be any combination of diseases or symptoms. The full list of green & orange ribbon meanings includes:
- Dual Diagnosis

Lavender & Orange Ribbon
Lavender is used to represent cancer in general, but when it’s paired with orange, it helps raise awareness for skin conditions like eczema and psoriasis. The full list of lavender & orange ribbon meanings includes:
- Psoriatic Arthritis

Peach & Gray Ribbon
If you see peach and gray together on a ribbon, it’s symbolizing an end to clergy sexual abuse.
The full list of peach & gray ribbon meanings includes:
- Clergy Sexual Abuse

Pink & Black Ribbon
If you combine pink with another color, like black, it takes on its own meaning. This color combo is associated with the loss of, or memory of, a sister, mother, daughter, or female loved one. The full list of pink & black ribbon meanings includes:
- Loss of, in memory of, a sister, mother, daughter or female loved one

Pink & Blue Ribbon
The pink and blue ribbon are used in sad circumstances of child loss, birth defects, prematurity, and a number of other causes. The full list of pink & blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism (March)
- Baby Safe Haven
- Birth Defects (January)
- Breat Cancer (male) (April)
- Genital Integrity
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum (October)
- Infant Diseases
- Infertility (April)
- Miscarriage/Stillbirth (October)
- Mourning the Loss of a Baby or Infant
- Premature Birth (November)
- Prostate and Breast Cancer (Combined)
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) (Ocober)

Pink & Red Ribbon
While you might think of Valentine’s Day, pink and red mean so much more when they’re paired together in a ribbon. They represent women living with HIV and how they’re five times more likely to develop cervical cancer. The full list of pink & red ribbon meanings includes:
- Women living with HIV are 5 times more likely to develop cervical cancer

Pink & Teal Ribbon
The colorful pairing of pink and teal is used to support many causes related to Breast Cancer Awareness, such as different forms of breast cancer and the combination of ovarian and breast cancer. The full list of pink & teal ribbon meanings includes:
- BRCA1 (Breast Cancer)
- BRCA2 (Breast Cancer)
- Hereditary Breast Cancer (September)
- Ovarian and Breast Cancer (Combined)

Purple & Blue Ribbon
Blue is a popular color to pair with purple. This awareness ribbon is used for rheumatoid arthritis, cult awareness, preeclampsia, and many other causes. The full list of purple & blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Adult-Onset Still’s Disease
- Alternating Hemiplegia
- Childhood Stroke
- Cult Awareness
- Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD)
- Pediatric Stroke (May)
- Preeclampsia
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (February)
- Rheumatoid Disease
- Smith-Magenis Syndrome

Purple & Red Ribbon
At this point in time, a purple and red ribbon is used to support only two causes. These include migraines and Raynaud’s Disease, which is a condition where some parts of the body feel numb and cold in certain situations. The full list of purple & red ribbon meanings includes:
- Raynaud’s Disease/Phenomenon

Purple & Teal Ribbon
Teal and purple ribbons are used to represent many important situations that need attention. These include domestic violence, sexual assault, and suicide. The full list of purple & teal ribbon meanings includes:
- Domestic Violence
- Sexual Assault
- Suicide (September)
- Surviving Family Members of Suicide

Red & Black Ribbon
Red and black may represent the Chicago Bulls, but on an awareness ribbon, these colors symbolize important movements and causes like Black Lives Matter and Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome (SDS). The full list of red & black ribbon meanings includes:
- Black Lives Matter
- In Memory of Murder Victims
- Murder Victims
- Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome (SDS)

Red & Blue Ribbon
Red and blue mixed together usually makes purple, but if they’re combined on an awareness ribbon, they represent various heart defects and syndromes as well as other ailments such as pulmonary fibrosis. The full list of red & blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Congenital Heart Diseases (February)
- Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome
- Hypoplastic Right Heart Syndrome
- Noonan Syndrome
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Tricuspid Atresia

Red & Gray Ribbon
The red and gray ribbon currently only has one cause it represents: polymicrogyria, which is a condition of abnormal brain development before birth. The full list of red & gray ribbon meanings includes:
- Polymicrogyria

Red & Orange Ribbon
The red and orange ribbon is associated with myeloproliferative disorders, which is a group of slow-growing blood cancers in the bone marrow. The full list of red & orange ribbon meanings includes:
- Myelofibrosis
- Myeloproliferative Disorders
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN)

Red & Pearl Ribbon
If you combine red with a pearl color, you’ve got a ribbon that represents latex allergies. This condition causes itchiness, hives, and in some severe cases, anaphylaxis. The full list of red & pearl ribbon meanings includes:
- Latex Allergy

Red, White, & Blue Ribbon
The red, white, & blue ribbon is all about American patriotism and is used as a remembrance for the attacks on September 11th as well as a symbol of military and troop support. The full list of red, white, & blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Military and Troop Support
- Remembering September 11, 2001

Silver & Gold Ribbon
The metallic mix of silver and gold is used to represent various hearing disorders like deafness and hyperacusis. It’s also used for diseases that affect the ears like tinnitus. The full list of silver & gold ribbon meanings includes:
- Hearing Disorders
- Hearing Impairment
- Hearing Loss
- Hyperacusis
- Meniere’s Disease

Teal & White Ribbon
The teal and white awareness ribbon is used as an agent of hope for those struggling with cervical cancer. Many organizations have used this ribbon to create change. The full list of teal & white ribbon meanings includes:
- Cervical Cancer (January)

Yellow & Blue Ribbon
Yellow and blue on a ribbon help raise awareness for Down Syndrome and a variety of other causes. The full list of yellow & blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Bohring-Optiz Syndrome
- CMT (Charcot-Marie-Tooth) (September)
- Cushing Sydrome
- Dercum’s Disease (Adiposis Dolorosa)
- Down Syndrome (October)
- Ukraine Support

Yellow & Purple Ribbon
A yellow and purple ribbon is used to raise awareness for illnesses that affect internal organs and characteristic facial features. The full list of yellow & purple ribbon meanings includes:
- Autoimmune Hepatitis
- Bladder Cancer
- Sotos Syndrome
Other Types of Awareness Ribbons

Kente Cloth Ribbon
The Kente cloth is a type of silk and cotton fabric that’s native to Ghana. On an awareness ribbon, this pattern is used to raise support for women of color who are suffering from breast cancer. The full list of kente cloth ribbon meanings includes:
- Women of Color Breast Cancer

Blue & White Pinstripes Ribbon
A blue ribbon with white stripes has the same spirit as the ice bucket challenge. It supports causes related to ALS and Lou Gehrig’s Disease. The full list of blue & white pinstripes ribbon meanings includes:
- Lou Gehrig’s Disease
- Motor Neuron Diseases

Red & White Pinstripes Ribbon
The color combo of red & white pinstripes is used to represent many causes, not limited to oral cancer, aplastic anemia, and deep vein thrombosis. The full list of red & white pinestripes ribbon meanings includes:
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma
- Aplastic Anemia
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Head and Neck Cancer
- Oral Cancer
- Pulmonary Dysplasia
- Septo-Optic Dysplasia
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma

Polka Dot Ribbon
The polka dot awareness ribbon is used to represent those who are suffering from blindness. This condition affects more than 3.4 million people in the United States. The full list of polka dot ribbon meanings includes:

Puzzle Piece Ribbon
The puzzle piece ribbon is used to raise awareness for every type of autism on the spectrum. According to the Autism Society, the pattern reflects the complex nature of this developmental disorder. The full list of puzzle piece ribbon meanings includes:
- Asperger’s Syndrome
- Autism Spectrum Disorders (April)

Rainbow Ribbon
The rainbow awareness ribbon is used to support those who are fighting for marriage equality and LGBTQ rights. This is an ongoing battle for an estimated 4.5% of the U.S. population who identify as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender. The full list of rainbow ribbon meanings includes:
- LGBTQ Pride
- LGBTQ Rights
- Marriage Equality

Zebra Ribbon
The zebra print is used to raise awareness for rare diseases and disorders. It’s also used for specific conditions like carcinoid cancer and Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome. The full list of zebra ribbon meanings includes:
- Carcinoid Cancer (November)
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (May)
- Neuroendocrine Cancer (November)
- Rare Diseases and Disorders (February)
Solid Ribbon Colors

Pink Ribbons
Pink is a power color as it’s used to support a number of worthwhile causes, including breast cancer awareness, Paget’s disease, and overall women’s health. The full list of pink ribbon meanings includes:
- Birth Parents
- Breast Cancer Awareness (October)
- Eosinophilic Diseases
- “Fight Like a Girl”
- Nursing Mothers (August)
- Paget’s Disease
- Respecting Birth Parents & Nursing Parents
- Women’s Health

Hot Pink Ribbon
A dark shade of hot pink is used for many different causes, such as cleft palate, eosinophilic diseases, and gendercide. The full list of hot pink ribbon meanings includes:
- Cleft Palate
- Eosinophilic Disease
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer
- Stop Gendercide

Peach Ribbon
A lighter, peach ribbon is used to raise awareness for a variety of cancers and other causes. The full list of peach ribbon meanings includes:
- Endometrial Cancer (September)
- Invisible Illness
- Uterine Cancer (September)
- Vaginal Cancer

Yellow Ribbon
The yellow awareness ribbon is used to show support for our troops and to bring attention to Prisoners of War or Missing in Action, (POW/MIA), adoption, and many different types of cancer. Yellow is also the suicide prevention color. The full list of yellow ribbon meanings includes:
- Adenosarcoma (November)
- Amber Alert (January)
- Bladder Cancer (May)
- Adoptive Parents (November)
- Bone Cancer
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning (January)
- Craniofacial Acceptance
- Endometriosis (March)
- Epithelioid Sarcoma
- Ewing Sarcoma (July)
- Microcephaly
- Missing Persons (May)
- Myxoid Liposarcoma
- Obesity (September)
- Osteosarcoma
- Prisoners of War (September)
- Refugees Welcome
- Sarcoma (July)
- Spina Bifida (October)
- Suicide Prevention (May)
- The Disappeared

Amber Ribbon
Amber is a precious gem and a darker shade of yellow. On an awareness ribbon, it stands to symbolize appendix cancer and pseudomyxoma peritonei. The full list of amber ribbon meanings includes:
- Appendix Cancer
- Pseudomyxoma Peritonei

Red gets a lot of use in the world of awareness ribbons. This bold color stands to symbolize addiction, blood cancer, heart disease, tuberculosis, and zika virus among many other causes. The full list of red ribbon meanings includes:
- Addiction (September)
- Adult Onset Still’s Disease (AOSD)
- AIDS (July)
- Alcohol Dependence
- Apert Syndrome
- Bleeding Disorders
- Blood Cancer
- Blood Clotting Disorders
- Bronchiolitis Obliterans
- Burn Victims
- Cardiomyopathy
- Cardiovascular Disease (February)
- Cavernous Angioma
- Clotting Factor Deficiencies
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome
- Congenital Heart Defects
- Congenital Heart Disease
- Congenital Heart Failure
- Congestive Heart Failure (February)
- Courage and Inspiration
- DARE – Red Ribbon Week (April)
- Diamond-Blackfan Anemia
- Disaster Relief
- Distracted Driving
- Driving Under the Influence Prevention (April)
- Drug Addiction
- Epidermolysis Bullosa (October)
- Erythromelalgia
- Evans Syndrome (February)
- Factor XI Deficiency
- Fanconi Anemia
- Female Genital Mutilation
- Giant Cell Arteritis
- Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (GPA)
- Heart Defects
- Heart Disease & Stroke (September)
- Hemolytic Anemia
- Hemophilia (March)
- High Blood Pressure (May)
- HIV/AIDS (December)
- Human Trafficking – #REDSANDPROJECT
- Hypertension (November)
- Long Q-T Syndrome (September)
- Marfan Syndrome (February)
- Mothers Against Drunk Driving MADD (April)
- Poland Syndrome
- Prinzmetal Angina
- Red Ribbon Week
- Sickle Cell Anemia
- Sinus Tachycardia
- Substance Abuse (April)
- Support Our Troops
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (TTP)
- Trafficking in Persons – Red Sand Project
- Tuberculosis (March)
- Von Willebrand Disease (VWD) (March)
- Wegener’s Granulomatosis
- Women’s Heart Health

Burgundy Ribbon
Burgundy is a darker, wine-colored shade of red. This awareness ribbon color symbolizes disabled adults, headaches, meningitis, and many other causes. The full list of burgundy ribbon meanings includes:
- Adhesions (September)
- Amyloidosis
- Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome (June)
- AV Malformation (September)
- Brain Aneurysm (September)
- Cesarean (April)
- Congenital Vascular Cavernous Malformation
- Cystic Hygroma
- Disabled Adults (October)
- Factor V Leiden (March)
- Hemangioma & Vascular Malformation (May)
- Hemiplegic Migraine
- Hemochromatosis
- Hereditary Hemochromatosis (May)
- Hirschsprung’s Disease
- Hospice Care (November)
- Hughes Syndrome (May)
- Lymphatic Malformation (May)
- Meningitis (August)
- Multiple Myeloma (March)
- Parkes Weber Syndrome
- PHACES (March)
- Port-Wine Stain Birthmark
- Post-Polio Syndrome (October)
- Sickle Cell Anemia (September)
- Sturge-Weber Syndrome (June)
- Thrombopphilia (March)
- William's Syndrome (May)

Blue Ribbon
Blue ribbon awareness is a symbol of hope for many people. This color represents over 100 causes, including bullying, malaria, sex trafficking, rheumatism, and water safety. The full list of blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) (October)
- Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome (AGS)
- Alexander Disease
- Alopecia Areata (September)
- Angelman’s Syndrome
- Ankylosing Spondylitis (April)
- Apraxia (May)
- Arthritis (May)
- Arthrogryposis
- Ataxia Telangiectasia
- Autoimmune Autonomic Neuropathy
- Autonomic Dysfunction
- Behcet’s Disease (Silk Road Disease)
- Brahcial Plexus Injuries (October)
- Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease (CPPD)
- Canada’s National Non-Smoking Week
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease
- Charge Syndrome
- Child Abuse Prevention & Awareness (April)
- Chondromalacia Patella
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (March)
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy (CIDP)
- Coffin-Siris Syndrome
- Colon Cancer (March)
- Colorectal Cancer (March)
- Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy
- CRI DU CHAT Syndrome
- Crime Victims Rights (April)
- Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome
- Dandy-Walker Syndrome
- Dermatomyositis
- Dermatomyositis (Juvenile)
- Drowning (August)
- Dystonia (September)
- Epstein-Barr Virus (September)
- Equal Access to Education
- Erb’s Palsy (October)
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (March)
- Familial Dysautonomia
- Fibromuscular Dysplasia
- Fibrous Dysplasia
- Free Speech – Freedom of the Press (October)
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome (May)
- Human Trafficking (January)
- Huntington’s Disease (May)
- Hurricane Awareness (May)
- Hydrocephalus (September)
- Hydrocephaly
- Hypotension (POTS)
- Hystiocytosis Awareness (September)
- Histiocytosis
- Ichthyosis (May)
- Inclusion Body Myositis
- Infant Airway Defects
- Infectious Arthritis
- Inflammatory Arthritis
- Juvenile Arthritis
- Juvenile Dermatomyositis (JD)
- Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Klinefelter’s Syndrome
- Langerhans Cells Histiocytosis (September)
- Laryngomalacia
- Leukodystrophy (September)
- McCune-Albright Syndrome
- Me/CFIDS (May)
- Metachromatic Leukodystrophy
- Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- Myositis Neurocardiogenic Syncope (May)
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta
- Palindromic Rheumatism
- Panhypopituitarism
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome
- Polymyalgia Rheumatica
- Polymyositis
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
- Reactive Arthritis
- Rectal Cancer (March)
- Reiter’s Syndrome
- Restless Legs Syndrome
- Reye’s Syndrome (September)
- Save the Music in Our Schools
- Save the Waves
- Sensor Processing Disorder
- Sex Slavery
- Sex Trafficking
- Short Bowel Syndrome (March)
- Spinal Stenosis
- Spondylarthritis
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (August)
- Syringomyelia
- Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- Tachycardia
- Targeting Individuals of Bullying
- Teen Pregnancy Prevention
- Temporal Arteritis
- Transverse Myelitis (June)
- Trash-Free Seas
- Treacher Collins Syndrome (TCS)
- Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
- Unidentified Missing Persons
- Usher Syndrome
- Vocal Cord Dysfunction
- Water Quality (August)
- Water Safety (May)

Blue Jeans Ribbon
While blue jeans may make you think of pants, this look is also used to raise awareness. These ribbons are designed to support causes associated with congenital and genetic diseases. The full list of blue jeans vribbon meanings includes:
- Congenital and Genetic Diseases

Light Blue Ribbon
A light blue awareness ribbon is used to support a number of causes and organizations, including prostate cancer, acid attacks, and foster care. The full list of light blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Acid Attacks
- Addison’s Disease (May)
- Adrenal Insufficiency
- Behcets Disease (May)
- Chronic Illness (September)
- Cushing Syndrome (April)
- DiGeorge Syndrome
- Foster Care (May)
- Grave’s Disease (January)
- Lymphedema (March)
- Men’s Health (June)
- Pro-Choice (March)
- Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome
- Prostate Cancer (September)
- Spay and Neuter Pets (March)
- Thyroid Disease (January)
- Tracheomalacia
- Trisomy 18/ Edwards’ Syndrome (March)
- Twin-to-Twin Transfusion Syndrome (December)

Perwinkle Blue Ribbon
Periwinkle, which is a blueish purplish color, is used on awareness ribbons as a symbol for causes related to anorexia, irritable bowel syndrome, and different types of cancer. The full list of perwinkle blue ribbon meanings includes:
- Acid Reflux Disease (November)
- Anorexia Nervosa (February)
- Eating Disorders (February)
- Esophageal Cancer (April)
- Gastric Cancer (November)
- Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (April)
- Pulmonary Hypertension (November)
- Small Intestine Cancer
- Stomach Cancer (November)

Turquoise Ribbon
Nearly 21 million people in the United States struggle with substance abuse. The turquoise ribbon is a sign of hope as it represents causes that support addiction recovery. It is also used to represent those who have a medical condition known as dysautonomia. The full list of turquoise ribbon meanings includes:
- Addiction Recovery
- Dysautonomia

Teal Ribbon
A teal ribbon is used to raise awareness for ovarian cancer, rape, food allergies, Tourette Syndrome, and many other causes. The full list of teal ribbon meanings includes:
- Agoraphobia
- Anaphylaxis
- Anti Bullying Awareness (October)
- Anxiety Disorders & Panic Attacks
- Batten Disease
- Child Sexual Abuse and Assault
- Dissociative Identity Disorder
- Ectodermal Dysplasia
- Food Allergies
- Fragile X Syndrome
- Gambling Addiction
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder
- Gynecologic Cancer & Ovarian Cancer (September)
- Heterotaxy Syndrome
- Interstitial Cystitis & Bladder Pain Syndrome (September)
- Juvenile Scleroderma
- Military Sexual Assault
- Myasthenia Gravis
- No Body Shaming
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder
- Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder
- Occipital Neuralgia
- Polycystic Kidney Disease
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
- Premature Ovarian Failure
- Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder
- Progressive Supranuclear Palsy
- Scleroderma
- Sexual Assault on College Campuses
- Sexual Violence
- Social Anxiety
- Stress Disorders
- Systemic Sclerosis
- Tourette Syndrome
- Trigeminal Neuralgia
- Women Murdered by Domestic Violence

Green Ribbon
The green ribbon is used to represent bipolar disorder and over 45 other causes including global warming, text-free driving, cerebral palsy, and genocide. The full list of green ribbon meanings includes:
- Achondroplasia
- Adrenal Cancer
- Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome
- Bile Duct Cancer (February)
- Biliary Atresia
- Bipolar Disorder (February)
- Bone Marrow Disease
- Bone Marrow Donor (November)
- Brain Injury
- Cerebral Palsy (May)
- Cholangiocarcinoma (February)
- Chromosome 12, Microdeletion
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy
- Cirrhosis of the Liver
- Cloves Syndrome
- Depression (October)
- Dermatillomania
- Dwarfism (October)
- Environmental Concerns (April)
- Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (April)
- Gallbladder Cancer
- Gastroparesis (August)
- Gastroschisis
- Glaucoma (January)
- Global Warming
- Gun Control (June)
- Human Papilloma Virus (May)
- In Favor of Medical Marijuana
- Infantile Scoliosis
- Ivemark Syndrome
- Kabuki Syndrome
- Kidney Disease/Renal Cell Carcinoma (March)
- Literacy (October)
- Liver Cancer & Liver Disease (September)
- Liver Melanoma
- Manic Depression (October)
- Major Depressive Disorder
- Mental Health (May)
- Mental Illness (October)
- Mental Retardation (March)
- Missing Children
- Mitochondrial Disease and Disorders (September)
- Natural Disasters (September)
- Nephrotic Syndrome (March)
- Organ Transplant & Organ Donation (April)
- Spinal Cord Injury (May)
- Stem Cell Donation (August)
- Tethered Spinal Cord Syndrome
- Text-Free Driving (Distracted Driving)
- Traumatic Brain Injury (March)
- Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome (May)

Light Green Ribbon
A light green ribbon is primarily used to raise awareness for sexually transmitted diseases, but it also represents causes related to chronic pelvic pain and Celiac Disease. The full list of light green ribbon meanings includes:
- Celiac Disease (May)
- Chronic Pelvic Pain (September)
- Human Papilloma Virus (HPV) (May)
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) (April)

Lime Green Ribbon
The depression awareness color is lime green. This bright, vibrant color is also used for childhood depression, mood disorders, and as the mental health ribbon. The full list of lime green ribbon meanings includes:
- Auditory Processing Disorder
- Childhood Depression
- Childhood Mental Health
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (February)
- Dysthymic Disorder
- Essential Tremor (March)
- Maternal Mental Health
- Mental Health
- Mental Illness
- Mood Disorders
- Multiple Chemical Sensitivity
- Muscular Dystrophy
- Lyme Disease (May)
- Lymphoma (September)
- Muscular Dystrophy (May)
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma (September)
- Pans/Pandas
- Postpartum Depression
- Postpartum Disorders
- Reactive Attachment Disorder
- Sandhoff Disease (September)
- Spinal Cord Disorders
- Substance-Related Disorders
- Trichotillomania
- Williams Syndrome

Sea Green Ribbon
The sea green awareness ribbon is used to represent speech impediments like stuttering, stammering, and lisping. The full list of sea green ribbon meanings includes:

Black Ribbon
The black ribbon symbol is often associated with mourning, but this color is also used for sleeping disorders and gang prevention. The full list of black ribbon meanings includes:
- Accidents (June)
- Amish Support
- Anti-Terrorism
- B.R.A.V.E. (Black Ribbon Against Violence)
- Gang Prevention
- Hypersomnia
- Melanoma (May)
- Mourning (October)
- Narcolepsy (March)
- National Tragedies
- POW/MIA (September)
- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (October)
- Skin Cancer
- Sleep Apnea (October)
- Sleep Disorders (March)
- Students for Gun Control
- Trauma (May)

Purple Ribbon
The purple awareness ribbon is very popular. It’s used as a symbol of hope for pancreatic cancer, cystic fibrosis, epilepsy, and over 70 other causes. The full list of purple ribbon meanings includes:
- Aicardi Syndrome
- Alzheimer’s Disease (November)
- Animal Protection and Welfare (April)
- Arachnoiditis
- Arnold Chiari Malformation (September)
- Binge Eating Disorder
- Bulimia Nervosa
- Caregiver Appreciation
- Chronic Pain
- Chronic Pain in Women
- Chronic Pancreatitis
- Chronic Vestibular Migraine
- Cornelia De Lange Syndrome
- Craniosynostosis
- Crohn’s Disease & Colitis (May)
- CSF Leak (Spinal)
- Cystic Fibrosis (May)
- Diabetic Neuropathy
- Domestic Violence (October)
- Dravet Syndrome
- Drowning Impact
- Drug Overdose
- Eating Disorders
- Elder Abuse
- Epilepsy (November)
- Fat Shaming and Skinny Shaming
- Fibromyalgia (May)
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
- Hemicrania Continua
- Hereditary Neuropathies
- Homelessness (November)
- Hurler Syndrome
- Hurler-Scheie Syndrome
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) (September)
- Infantile Spasms
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- International Women’s Day
- Lewy Body Dementia
- Lupus (May)
- Macular Degeneration (February)
- Maroteaux Lamy Syndrome
- Moebius Syndrome
- Morquio Syndrome
- Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) (October)
- Multiple System Atrophy
- Neuropathy – Hereditary
- Opioid Addiction
- Pancreatic Cancer (November)
- Pancreatitis (Chronic)
- Pediatric SLE
- Peripheral Neuropathy
- Pudendal Neuralgia
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (May)
- Relay for Life
- Religious Tolerance
- Rett Syndrome
- Sarcoidosis
- Scheie Syndrome
- Seizure Disorders
- Sjogren’s Syndrome (April)
- Sly Syndrome
- Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Teens
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Turner Syndrome
- Ulcerative Colitis

Orchid Ribbon
The orchid ribbon is a lighter shade of purple that’s used to represent testicular cancer. The full list of orchid ribbon meanings includes:
Testicular Cancer

Violet Ribbon
A dark shade of violet is used to support causes related to Hodgkin’s Disease, which is a cancer that occurs in the immune system and is often treatable. The full list of violet ribbon meanings includes:
- Hodgkin’s Disease (September)
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma

Lavender Ribbon
Lavender is a lighter shade of purple that, when used on an awareness ribbon, represents any cancer that doesn’t have its own dedicated color already. The full list of lavender ribbon meanings includes:
- Cancer for which a color has not been designated (June)
- Caregiver Awareness (November)
- General Cancer
- Hypokalemic Periodic Paralysis
- Infantile Spasms (December)
- Rett Syndrome (October)
- Epilepsy Awareness (November)

Brown Ribbon
Despite its harmful effects, 14 of every 100 adults in the United States still smoke cigarettes. The brown ribbon is a call-to-action that represents quitting once and for all. The full list of brown ribbon meanings includes:
- Familial Polyposis (March)
- Great American Smokeout
- Immigration (June)
- Smoking Cessation (November)

Cloud Ribbon
The cloud ribbon is a sign of hope for those suffering from congenital diaphragmatic hernias. If you’re not familiar, this is a defect in the diaphragm that causes crowding near the heart and lungs making it difficult to breathe. The full list of cloud ribbon meanings includes:
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia

Cream Ribbon
A cream-colored or beige ribbon is used for illnesses that affect the spine, hip joints, and nervous system. These include degenerative disc disease, developmental dysplasia of the hip, and spinal muscular atrophy. The full list of cream ribbon meanings includes:
- Degenerative Disc Disease
- Developmental Dysplasia/Dislocation of the Hip
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy

Gold Ribbon
A gold awareness ribbon is used to symbolize causes related to childhood cancer, neuroblastoma, and retinoblastoma. The latter two conditions are cancers that are found in the adrenal glands and retinas respectively. The full list of gold ribbon meanings includes:
- Childhood Cancer (September)
- COPD (November)
- Neuroblastoma
- Retinoblastoma

Graphite Ribbon
A dark gray, or graphite, awareness ribbon is used to support the many people affected by lead poisoning. In fact, 1.2 million children were affected in the United States alone and only half of them got the treatment they needed. The full list of graphite ribbon meanings includes:
- Lead-Free Kids
- Lead Poisoning

Gray Ribbon
A gray ribbon is used to raise awareness for a variety of illnesses and conditions that affect both adults and children, such as asthma, brain tumors, and diabetes. The full list of gray ribbon meanings includes:
- Allergies (May)
- Aphasia (June)
- Asthma (May)
- Brain Cancer (May)
- Brian Tumors (May)
- Diabetes (November)
- Glioblastoma
- Hyperglycemia
- Hypoglycemia
- Parkinson's Disease (April)
- Personality Disorders

Orange Ribbon
You may not see it as often as pink or red, but orange is still a really popular color for awareness ribbons. It’s used to represent ADHD awareness, multiple sclerosis, motorcycle safety, and many other causes. The full list of orange ribbon meanings includes:
- ADHD (October)
- Agent Orange (August)
- Amniotic Band Syndrome
- Animal Cruelty - Animal Welfare (February)
- Asylum Seekers – Cultural Diversity
- Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
- Cultural Diversity (October)
- Equality and Liberty
- Familial Mediterranean Fever
- Gun Violence Prevention (June)
- Human Rights
- Humane Treatment of Animals
- Humane Treatment of Refugees
- Hunger (October)
- Kidney Cancer (march)
- Leukemia (September)
- Limb Difference
- Malnutrition
- Motorcycle Safety (May)
- Multiple Sclerosis (March)
- Necrotizing Fasciitis
- No Kid or Pets Unattended in Cars
- Prader-Willi Syndrome
- Racial Tolerance
- Reflect Sympathetic Dystrophy
- RSD/CRPS (November)
- Self-Injury
- Skin Cancer (Non-Melanoma) (May)
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma
- Tay-Sachs Disease
- World Hunger/Poverty

Pearl Ribbon
A pearl is typically thought of as a gemstone that’s found in shelled mollusks or animals. When it’s used on an awareness ribbon, however, it represents lung or bronchial cancer and many other causes. The full list of pearl ribbon meanings includes:
- Bronchial Cancer
- Bronchiectasis
- Chronic Lung Disease
- Lung Cancer (November)
- Lung Disease
- Mesothelioma
- Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia

Silver Ribbon
Silver is a popular color for awareness ribbons. It’s used to represent a large number of causes including brain disorders, limb loss, and schizophrenia. The full list of silver ribbon meanings includes:
- Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum
- Bell’s Palsy
- Borderline Personality Disorder
- Brain Disabilities
- Brain Disorders
- Disabled Children (October)
- Dyslexia (October)
- Encephalitis (May)
- Facial Paralysis
- Locked-In Syndrome
- Neurological Disorders
- Parkinson’s Disease
- Schizoaffective Disorder
- Schizoid Personality Disorder
- Schizophrenia (May)
- Stalker Awareness (January)

White Ribbon
A neutral white ribbon is used to provide support for many causes and illnesses, including adoption, bone cancer, osteoporosis, and teen abstinence. Most recently, it’s been used globally to represent the coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic. It supports patients and families who have been affected by the virus, as well as healthcare workers who are risking their lives to help others. The full list of white ribbon meanings includes:
- Adoption (November)
- Bone Cancer (August)
- Bone Diseases (August)
- Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE)
- International End of Violence Against Women
- Make Poverty History
- Osteoporosis (May)
- Stalking (January)
- Teen Abstinence (May)
- Victims of Terrorism
- White Matter Brain Disorder
- White Ribbon Campaign for Men Against Violence
- << Previous: Diversity Awareness Calendar
- Next: Want to Contribute? >>
- Last Updated: Jun 26, 2024 5:26 PM
- URL: https://iot.libguides.com/DEI
Call Us Today: (224) 219-1924
Grow with us in a FUN & functional way!
e-mail: [email protected]

Speech Impediment: Definition, Causes, Types and Treatment
02 may speech impediment: definition, causes, types and treatment.
One of life’s joys as a parent is watching your kids grow and change. You see them learn new things, meet new friends, and explore the world around them. But sometimes, you also witness them struggle – like when they have their first fight with a friend or don’t do as well as they wanted to on a test. And while it’s never easy to see your child suffer, one of the hardest things to watch is when your child has difficulty communicating. If your child has a speech impediment, you know that feeling all too well. It can be frustrating and heartbreaking to see your little one struggling to be understood. But take heart – you’re not alone. Many children have difficulties with speech, and with the right pediatric speech therapist in Chicago , your child can learn to overcome their impediment. This blog post will define a speech impediment, discuss some of the most common types and causes, and provide information on treatment options.
What is a speech impediment?
A speech impediment is a condition that affects a person’s ability to produce sound correctly. The term can refer to any difficulties that impede a person’s speech, from mild sound errors to severe problems with articulation. All individuals with speech impediments have difficulty producing certain sounds, depending on one sound. Some people may only have trouble with one sound, while others may have difficulty producing multiple sounds.
What causes speech impediments?
Some people are born with speech impediments, while others develop them later in life. There are many different causes of speech impediment, as you will see below.
1. Congenital defects Congenital defects are abnormalities that are present at birth. They can affect any part of the body, including the mouth and vocal cords. In some cases, congenital defects can cause problems with the tongue moving or the formation of teeth. Many different types of congenital defects can cause a speech impediment, including : Cleft lip and palate is a condition where there is an opening in the lip and/or roof of the mouth. This opening can cause problems with the way the mouth forms words, as well as with eating and drinking. Cleft lip and palate can also cause hearing problems. Vocal cord paralysis is a condition where the vocal cords are unable to move correctly. This can make it difficult to produce sound, as well as to breathe properly. Tongue-tie is a condition where the tongue is tethered to the floor of the mouth. This can make it difficult to move the tongue and can cause problems with eating, drinking, and speaking.
2. Neurological disorders Neurological disorders are conditions that affect the nervous system. These disorders can cause problems with the way the brain sends signals to the muscles, which can lead to difficulties with movement and speech. Some of the more common neurological disorders include: Cerebral palsy is a condition that affects movement and muscle coordination. It is caused by damage to the brain, usually before or during birth. Cerebral palsy can cause problems with the way a person walks, talks, and eats. Multiple sclerosis is a disease of the nervous system that causes the immune system to attack the nerves. This can lead to problems with muscle control and vision, hearing, and speech.
3. Hearing loss Hearing loss can be caused by many different things, including exposure to loud noise, certain medications, and aging. Hearing loss can make it difficult to understand what other people are saying, which can lead to problems with speech. There are many different types of hearing loss, and the severity can vary from person to person. Some people with hearing loss may only have trouble hearing certain sounds, while others may not be able to hear anything at all. Hearing loss can be temporary or permanent. Temporary hearing loss can be caused by things like earwax buildup or infection. Permanent hearing loss can be caused by things like damage to the inner ear or a genetic disorder.
4. Language disorders Language disorders are conditions that affect a person’s ability to understand or use language. These disorders can make it difficult to produce or comprehend speech. Some of the more common language disorders include dyslexia and aphasia.
5. Emotional disorders Emotional disorders are conditions that affect a person’s emotions or mood. These disorders can cause problems with speech due to anxiety or stress. Some of the more common emotional disorders include anxiety disorders and depression. lip
Types of speech disorder
There are many different types of speech disorders, and the symptoms can vary from person to person. Some of the more common types of speech disorders include:
1. Articulation disorder An articulation disorder is a problem with the way the mouth, teeth, or tongue move to make sounds. This can make it difficult to produce certain sounds correctly. People with articulation disorders may have trouble saying certain words correctly, or they may leave out parts of words when they speak.
2. Fluency disorder A fluency disorder is a problem with the flow of speech. People with fluency disorders may have trouble putting their thoughts into words, and they may stutter when they speak. Stuttering is a type of fluency disorder that is characterized by pauses, repetitions, or prolongations of sounds.
3. Resonance disorder A resonance disorder is a problem with the way sound resonates in the mouth and throat. This can make it difficult to produce certain sounds correctly. People with resonance disorders may have trouble producing vowel sounds, or they may speak with a nasal tone.
4. Voice disorder A voice disorder is a problem with the way the voice sounds. This can be caused by things like vocal cord damage or misuse of the voice. People with voice disorders may have trouble speaking loudly or speaking in a hoarse or breathy voice.

Treatment of speech impediments
There are many different treatments for speech disorders, and the best treatment will depend on the individual and the cause of the disorder. Some of the more common treatments include:
1. Speech therapy Speech therapy is a type of treatment that helps people with speech disorders improve their abilities. Speech therapists can help people with articulation disorders learn to produce sounds correctly, people with fluency disorders reduce their stuttering, and people with resonance disorders improve their vowel production.
2. Surgery Surgery can be used to correct some anatomical defects that cause speech disorders. For example, surgery can be used to correct cleft lip and palate, vocal cord paralysis, and tongue tie.
3. Medication Medication can be used to treat some neurological disorders that cause speech disorders. For example, medication can be used to treat conditions like cerebral palsy and multiple sclerosis.
4. Hearing aids Hearing aids can be used to treat hearing loss that causes speech disorders. Hearing aids amplify sound so that people with hearing loss can better understand what other people are saying.
5. Communication devices Communication devices can be used to help people with language disorders or severe speech disorders communicate. These devices can include things like picture boards and computer software that helps people generate speech.
6. Counseling Counseling can be used to treat emotional disorders that cause speech disorders. Counseling can help people manage their anxiety and stress and learn coping mechanisms to deal with their disorders.
7. Alternative treatments There are many different alternative treatments for speech disorders. Some of these treatments include acupuncture, aromatherapy, and massage therapy. It is important to speak with a doctor before starting any alternative treatment.
Speech disorders can cause a variety of problems for people, ranging from difficulty understanding what other people are saying to difficulty producing speech. There are many different causes of speech disorders, and the best treatment will depend on the individual and the cause of the disorder. Visit https://functionalspeechtherapy.com/ to learn more about pediatric speech disorders and treatment options.
Functional Speech Therapy Co., 960 Route 22, Unit 216 Fox River Grove Illinois 60021, (224) 219-1924
Find us on Social Media https://www.facebook.com/FUNctionalSpeechClinic/ https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCJyXslNcwUw-ABZ5myhERTQ https://www.instagram.com/functional\_speechtherapy
No Comments
Sorry, the comment form is closed at this time.
- Brain & Nervous System
What to Know About Speech Impairment

A speech impairment affects people who have problems speaking in a regular tone of voice or tempo. Speech impairments make it hard for people to communicate properly, and they can happen in both children and adults.
These disorders can cause frustration and embarrassment to the person suffering from them.
What is Speech Impairment?
People who have speech impairments have a hard time pronouncing different speech sounds. They might distort the sounds of some words and leave other sounds out completely.
There are three general categories of speech impairment:
- Fluency disorder. This type can be described as continuity, smoothness, rate, and effort in speech production.
- Voice disorder. A voice disorder means you have an atypical tone of voice. It could be an unusual pitch, quality, resonance, or volume.
- Articulation disorder. If you have an articulation disorder, you might distort certain sounds. You could also fully omit sounds.
Stuttering , or stammering, is a common fluency disorder that affects about 3 million Americans. It usually affects young children who are just learning to speak, but it can continue on into adulthood.
Speech and language impairments are two words that are often used interchangeably, but they are two very different types of problems.
Speech means talking. It uses the jaw muscles, tongue, lips, and vocal chords. Language is a set of words and symbols made to communicate a message. Language and speech disorders can affect you separately, or both can happen at the same time.
Types of Speech Impairments
Speech impairments can begin in childhood and carry on through your adult years. Others can happen due to trauma, or after a medical event like a stroke.
The types of speech impairments are:
- Childhood apraxia of speech. This can happen to children when it’s time for them to start talking. The brain’s signals don’t communicate with the mouth, so the child can’t move their lips and tongue in the way they’re mean to.
- Dysarthria. This type of speech impairment happens when the muscles you use to talk are too weak, and can’t form words properly.
- Orofacial myofunctional disorders (OMD). OMDs are characterized by an abnormal pattern of facial muscle use. OMD interferes with how the facial muscles, including the tongue, are used. People who suffer from OMD might also struggle to breathe through their nose.
- Speech sound disorders. It’s normal for children to struggle to pronounce certain sounds as they learn to talk. But after ages four or five, constant mispronunciation might signal a problem. It can continue into adulthood, or some people get it after a stroke.
- Stuttering. Stuttering can mean repeating words or sounds like “uh” and “um” (disfluencies) involuntarily. Stuttering can be intensified by strong emotions or stress.
- Voice. A voice disorder can mean you “lost” your voice because you stressed it too much. It can also mean a chronic cough or paralysis of the vocal cords, among others.
Health Issues That Affect Speech Impairment
Other than childhood speech impairments, there are a range of reasons you could get one in your adult years. They can happen due to a traumatic event, illness, or surgery.
Dysarthria , aphasia, and voice disturbances can happen in adulthood, and are usually due to these medical events.
Aphasia. Aphasia is the loss of ability to understand words, spoken or written. There are many types of aphasia . It can happen after a stroke or if a tumor reaches the part of the brain where language is processed.
Medical issues that can cause aphasia:
- Head trauma
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- Brain tumor
- Alzheimer’s disease
Dysarthria. Dysarthria is usually caused by a nerve problem. The person suffering from it loses the ability to make certain sounds or might have poor pronunciation. It can also affect your ability to control the tongue, larynx, lips, and vocal chords.
Medical issues that can cause dysarthria:
- Facial trauma
- Diseases that affect your nervous system
- Side effects of certain medication
- Alcoholic intoxication
- Dentures that don’t fit properly
- Transient ischemic attack (TIA)
Voice disturbances. Traumatic events or extreme stress placed on the vocal cords can cause you to “lose” your voice or have a vocal disturbance. Disease can also affect the way your voice sounds.
Cancerous or noncancerous growths or nodules on the vocal cords can make your voice sound different.
Understanding Speech Impairments
Having a speech impairment can be a very frustrating and embarrassing experience for the person experiencing it. It’s important to be patient and understanding when communicating.
Try the following tips to improve communication and foster an accepting environment with someone who has a speech impairment:
- Speak slowly and use hand gestures
- Keep a pen and paper handy in case it’s needed to communicate
- Maintain a calm environment free of stimulating sounds
- Use simple phrases when you speak
- Use your normal tone of voice
Consulting with a mental health care provider can help with feelings of anger and depression that can accompany speech impairments.

Top doctors in ,
Find more top doctors on, related links.
- Brain & Nervous System News & Features
- Brain & Nervous System Reference
- Brain & Nervous System Slideshows
- Brain & Nervous System Quizzes
- Brain & Nervous System Videos
- Find a Neurologist
- Living Better With MS
- Alzheimer's Disease
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob Disease
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- Lou Gehrig’s Disease (ALS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Parkinson's Disease
- Restless Legs Syndrome
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy
- More Related Topics

- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Master’s Degrees
- Doctorate Degrees
- Certificate Programs
- Nursing Degrees
- Cybersecurity
- Human Services
- Science & Mathematics
- Communication
- Liberal Arts
- Social Sciences
- Computer Science
- Admissions Overview
- Tuition and Financial Aid
- Incoming Freshman and Graduate Students
- Transfer Students
- Military Students
- International Students
- Early Access Program
- About Maryville
- Our Faculty
- Our Approach
- Our History
- Accreditation
- Tales of the Brave
- Student Support Overview
- Online Learning Tools
- Infographics
Home / Blog
Speech Impediment Guide: Definition, Causes, and Resources
December 8, 2020

Tables of Contents
What Is a Speech Impediment?
Types of speech disorders, speech impediment causes, how to fix a speech impediment, making a difference in speech disorders.
Communication is a cornerstone of human relationships. When an individual struggles to verbalize information, thoughts, and feelings, it can cause major barriers in personal, learning, and business interactions.
Speech impediments, or speech disorders, can lead to feelings of insecurity and frustration. They can also cause worry for family members and friends who don’t know how to help their loved ones express themselves.
Fortunately, there are a number of ways that speech disorders can be treated, and in many cases, cured. Health professionals in fields including speech-language pathology and audiology can work with patients to overcome communication disorders, and individuals and families can learn techniques to help.

Commonly referred to as a speech disorder, a speech impediment is a condition that impacts an individual’s ability to speak fluently, correctly, or with clear resonance or tone. Individuals with speech disorders have problems creating understandable sounds or forming words, leading to communication difficulties.
Some 7.7% of U.S. children — or 1 in 12 youths between the ages of 3 and 17 — have speech, voice, language, or swallowing disorders, according to the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). About 70 million people worldwide, including some 3 million Americans, experience stuttering difficulties, according to the Stuttering Foundation.
Common signs of a speech disorder
There are several symptoms and indicators that can point to a speech disorder.
- Unintelligible speech — A speech disorder may be present when others have difficulty understanding a person’s verbalizations.
- Omitted sounds — This symptom can include the omission of part of a word, such as saying “bo” instead of “boat,” and may include omission of consonants or syllables.
- Added sounds — This can involve adding extra sounds in a word, such as “buhlack” instead of “black,” or repeating sounds like “b-b-b-ball.”
- Substituted sounds — When sounds are substituted or distorted, such as saying “wabbit” instead of “rabbit,” it may indicate a speech disorder.
- Use of gestures — When individuals use gestures to communicate instead of words, a speech impediment may be the cause.
- Inappropriate pitch — This symptom is characterized by speaking with a strange pitch or volume.
In children, signs might also include a lack of babbling or making limited sounds. Symptoms may also include the incorrect use of specific sounds in words, according to the American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA). This may include the sounds p, m, b, w, and h among children aged 1-2, and k, f, g, d, n, and t for children aged 2-3.
Back To Top
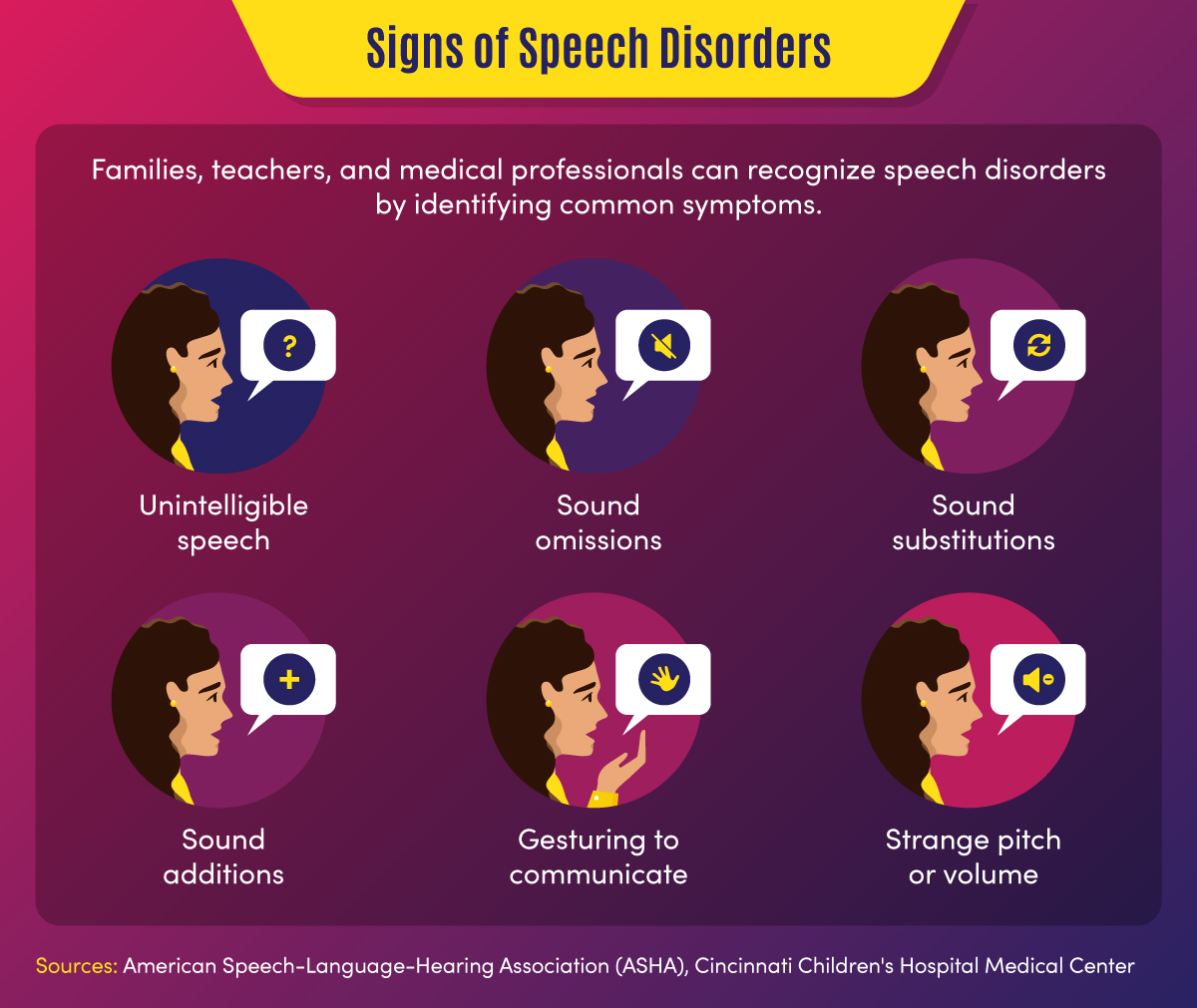
Categories of Speech Impediments
Speech impediments can range from speech sound disorders (articulation and phonological disorders) to voice disorders. Speech sound disorders may be organic — resulting from a motor or sensory cause — or may be functional with no known cause. Voice disorders deal with physical problems that limit speech. The main categories of speech impediments include the following:
Fluency disorders occur when a patient has trouble with speech timing or rhythms. This can lead to hesitations, repetitions, or prolonged sounds. Fluency disorders include stuttering (repetition of sounds) or (rapid or irregular rate of speech).
Resonance disorders are related to voice quality that is impacted by the shape of the nose, throat, and/or mouth. Examples of resonance disorders include hyponasality and cul-de-sac resonance.
Articulation disorders occur when a patient has difficulty producing speech sounds. These disorders may stem from physical or anatomical limitations such as muscular, neuromuscular, or skeletal support. Examples of articulation speech impairments include sound omissions, substitutions, and distortions.
Phonological disorders result in the misuse of certain speech sounds to form words. Conditions include fronting, stopping, and the omission of final consonants.
Voice disorders are the result of problems in the larynx that harm the quality or use of an individual’s voice. This can impact pitch, resonance, and loudness.
Impact of Speech Disorders
Some speech disorders have little impact on socialization and daily activities, but other conditions can make some tasks difficult for individuals. Following are a few of the impacts of speech impediments.
- Poor communication — Children may be unable to participate in certain learning activities, such as answering questions or reading out loud, due to communication difficulties. Adults may avoid work or social activities such as giving speeches or attending parties.
- Mental health and confidence — Speech disorders may cause children or adults to feel different from peers, leading to a lack of self-confidence and, potentially, self-isolation.
Resources on Speech Disorders
The following resources may help those who are seeking more information about speech impediments.
Health Information : Information and statistics on common voice and speech disorders from the NIDCD
Speech Disorders : Information on childhood speech disorders from Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center
Speech, Language, and Swallowing : Resources about speech and language development from the ASHA
Children and adults can suffer from a variety of speech impairments that may have mild to severe impacts on their ability to communicate. The following 10 conditions are examples of specific types of speech disorders and voice disorders.
1. Stuttering
This condition is one of the most common speech disorders. Stuttering is the repetition of syllables or words, interruptions in speech, or prolonged use of a sound.
This organic speech disorder is a result of damage to the neural pathways that connect the brain to speech-producing muscles. This results in a person knowing what they want to say, but being unable to speak the words.
This consists of the lost ability to speak, understand, or write languages. It is common in stroke, brain tumor, or traumatic brain injury patients.
4. Dysarthria
This condition is an organic speech sound disorder that involves difficulty expressing certain noises. This may involve slurring, or poor pronunciation, and rhythm differences related to nerve or brain disorders.
The condition of lisping is the replacing of sounds in words, including “th” for “s.” Lisping is a functional speech impediment.
6. Hyponasality
This condition is a resonance disorder related to limited sound coming through the nose, causing a “stopped up” quality to speech.
7. Cul-de-sac resonance
This speech disorder is the result of blockage in the mouth, throat, or nose that results in quiet or muffled speech.
8. Orofacial myofunctional disorders
These conditions involve abnormal patterns of mouth and face movement. Conditions include tongue thrusting (fronting), where individuals push out their tongue while eating or talking.
9. Spasmodic Dysphonia
This condition is a voice disorder in which spasms in the vocal cords produce speech that is hoarse, strained, or jittery.
10. Other voice disorders
These conditions can include having a voice that sounds breathy, hoarse, or scratchy. Some disorders deal with vocal folds closing when they should open (paradoxical vocal fold movement) or the presence of polyps or nodules in the vocal folds.
Speech Disorders vs. Language Disorders
Speech disorders deal with difficulty in creating sounds due to articulation, fluency, phonology, and voice problems. These problems are typically related to physical, motor, sensory, neurological, or mental health issues.
Language disorders, on the other hand, occur when individuals have difficulty communicating the meaning of what they want to express. Common in children, these disorders may result in low vocabulary and difficulty saying complex sentences. Such a disorder may reflect difficulty in comprehending school lessons or adopting new words, or it may be related to a learning disability such as dyslexia. Language disorders can also involve receptive language difficulties, where individuals have trouble understanding the messages that others are trying to convey.

Resources on Types of Speech Disorders
The following resources may provide additional information on the types of speech impediments.
Common Speech Disorders: A guide to the most common speech impediments from GreatSpeech
Speech impairment in adults: Descriptions of common adult speech issues from MedlinePlus
Stuttering Facts: Information on stuttering indications and causes from the Stuttering Foundation
Speech disorders may be caused by a variety of factors related to physical features, neurological ailments, or mental health conditions. In children, they may be related to developmental issues or unknown causes and may go away naturally over time.
Physical and neurological issues. Speech impediment causes related to physical characteristics may include:
- Brain damage
- Nervous system damage
- Respiratory system damage
- Hearing difficulties
- Cancerous or noncancerous growths
- Muscle and bone problems such as dental issues or cleft palate
Mental health issues. Some speech disorders are related to clinical conditions such as:
- Autism spectrum disorder
- Down syndrome or other genetic syndromes
- Cerebral palsy or other neurological disorders
- Multiple sclerosis
Some speech impairments may also have to do with family history, such as when parents or siblings have experienced language or speech difficulties. Other causes may include premature birth, pregnancy complications, or delivery difficulties. Voice overuse and chronic coughs can also cause speech issues.
The most common way that speech disorders are treated involves seeking professional help. If patients and families feel that symptoms warrant therapy, health professionals can help determine how to fix a speech impediment. Early treatment is best to curb speech disorders, but impairments can also be treated later in life.
Professionals in the speech therapy field include speech-language pathologists (SLPs) . These practitioners assess, diagnose, and treat communication disorders including speech, language, social, cognitive, and swallowing disorders in both adults and children. They may have an SLP assistant to help with diagnostic and therapy activities.
Speech-language pathologists may also share a practice with audiologists and audiology assistants. Audiologists help identify and treat hearing, balance, and other auditory disorders.
How Are Speech Disorders Diagnosed?
Typically, a pediatrician, social worker, teacher, or other concerned party will recognize the symptoms of a speech disorder in children. These individuals, who frequently deal with speech and language conditions and are more familiar with symptoms, will recommend that parents have their child evaluated. Adults who struggle with speech problems may seek direct guidance from a physician or speech evaluation specialist.
When evaluating a patient for a potential speech impediment, a physician will:
- Conduct hearing and vision tests
- Evaluate patient records
- Observe patient symptoms
A speech-language pathologist will conduct an initial screening that might include:
- An evaluation of speech sounds in words and sentences
- An evaluation of oral motor function
- An orofacial examination
- An assessment of language comprehension
The initial screening might result in no action if speech symptoms are determined to be developmentally appropriate. If a disorder is suspected, the initial screening might result in a referral for a comprehensive speech sound assessment, comprehensive language assessment, audiology evaluation, or other medical services.
Initial assessments and more in-depth screenings might occur in a private speech therapy practice, rehabilitation center, school, childcare program, or early intervention center. For older adults, skilled nursing centers and nursing homes may assess patients for speech, hearing, and language disorders.
How Are Speech Impediments Treated?
Once an evaluation determines precisely what type of speech sound disorder is present, patients can begin treatment. Speech-language pathologists use a combination of therapy, exercise, and assistive devices to treat speech disorders.
Speech therapy might focus on motor production (articulation) or linguistic (phonological or language-based) elements of speech, according to ASHA. There are various types of speech therapy available to patients.
Contextual Utilization — This therapeutic approach teaches methods for producing sounds consistently in different syllable-based contexts, such as phonemic or phonetic contexts. These methods are helpful for patients who produce sounds inconsistently.
Phonological Contrast — This approach focuses on improving speech through emphasis of phonemic contrasts that serve to differentiate words. Examples might include minimal opposition words (pot vs. spot) or maximal oppositions (mall vs. call). These therapy methods can help patients who use phonological error patterns.
Distinctive Feature — In this category of therapy, SLPs focus on elements that are missing in speech, such as articulation or nasality. This helps patients who substitute sounds by teaching them to distinguish target sounds from substituted sounds.
Core Vocabulary — This therapeutic approach involves practicing whole words that are commonly used in a specific patient’s communications. It is effective for patients with inconsistent sound production.
Metaphon — In this type of therapy, patients are taught to identify phonological language structures. The technique focuses on contrasting sound elements, such as loud vs. quiet, and helps patients with unintelligible speech issues.
Oral-Motor — This approach uses non-speech exercises to supplement sound therapies. This helps patients gain oral-motor strength and control to improve articulation.
Other methods professionals may use to help fix speech impediments include relaxation, breathing, muscle strengthening, and voice exercises. They may also recommend assistive devices, which may include:
- Radio transmission systems
- Personal amplifiers
- Picture boards
- Touch screens
- Text displays
- Speech-generating devices
- Hearing aids
- Cochlear implants
Resources for Professionals on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide information for speech therapists and other health professionals.
Assistive Devices: Information on hearing and speech aids from the NIDCD
Information for Audiologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for audiologists from ASHA
Information for Speech-Language Pathologists: Publications, news, and practice aids for SLPs from ASHA
Speech Disorder Tips for Families
For parents who are concerned that their child might have a speech disorder — or who want to prevent the development of a disorder — there are a number of activities that can help. The following are tasks that parents can engage in on a regular basis to develop literacy and speech skills.
- Introducing new vocabulary words
- Reading picture and story books with various sounds and patterns
- Talking to children about objects and events
- Answering children’s questions during routine activities
- Encouraging drawing and scribbling
- Pointing to words while reading books
- Pointing out words and sentences in objects and signs
Parents can take the following steps to make sure that potential speech impediments are identified early on.
- Discussing concerns with physicians
- Asking for hearing, vision, and speech screenings from doctors
- Requesting special education assessments from school officials
- Requesting a referral to a speech-language pathologist, audiologist, or other specialist
When a child is engaged in speech therapy, speech-language pathologists will typically establish collaborative relationships with families, sharing information and encouraging parents to participate in therapy decisions and practices.
SLPs will work with patients and their families to set goals for therapy outcomes. In addition to therapy sessions, they may develop activities and exercises for families to work on at home. It is important that caregivers are encouraging and patient with children during therapy.
Resources for Parents on How to Fix a Speech Impediment
The following resources provide additional information on treatment options for speech disorders.
Speech, Language, and Swallowing Disorders Groups: Listing of self-help groups from ASHA
ProFind: Search tool for finding certified SLPs and audiologists from ASHA
Baby’s Hearing and Communication Development Checklist: Listing of milestones that children should meet by certain ages from the NIDCD
If identified during childhood, speech disorders can be corrected efficiently, giving children greater communication opportunities. If left untreated, speech impediments can cause a variety of problems in adulthood, and may be more difficult to diagnose and treat.
Parents, teachers, doctors, speech and language professionals, and other concerned parties all have unique responsibilities in recognizing and treating speech disorders. Through professional therapy, family engagement, positive encouragement and a strong support network, individuals with speech impediments can overcome their challenges and develop essential communication skills.
Additional Sources
American Speech-Language-Hearing Association, Speech Sound Disorders
Identify the Signs, Signs of Speech and Language Disorders
Intermountain Healthcare, Phonological Disorders
MedlinePlus, Speech disorders – children
National Institutes of Health, National Institutes on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, “Quick Statistics About Voice, Speech, Language”
Bring us your ambition and we’ll guide you along a personalized path to a quality education that’s designed to change your life.
Take Your Next Brave Step
Receive information about the benefits of our programs, the courses you'll take, and what you need to apply.

- breynolds430
- Nov 1, 2023
Common Types Of Speech Impediments Explained
Updated: Dec 1, 2023

Speech impediments—a phrase is often thrown but hardly understood. They aren't character flaws or something to brush off lightly. Communication issues can make life tough for people who deal with them daily. Understanding speech impediment issues helps us show empathy and support for those with them.
Remember, living with a speech impediment isn't a choice—cope or conquer it is. As we learn more, we understand they are more than stutters or lisps. They're silent battles fought every day. This is an opportunity for us to lend support through enhanced understanding and shared respect.
In our daily interactions, we can make a significant impact. We can do this by listening, respecting their struggles, and appreciating their courage. Remember, understanding is the cradle of support. We learn, we grow, and together, we conquer.
Understanding Speech Impediments
Speech impediments involve troubles with voice or actual speech sounds—consonants, vowels, or both. They interfere with one's ability to communicate or articulate thoughts effectively. Some pose a significant hurdle socially, academically, or occupationally. To better support and relate to those with speech impediments, it helps to understand the different types and levels of challenges they face.
Navigating Stutters
Stutters usually stir up visual imagery of duplicated words or parts of words. However, stuttering is more complicated. It also includes longer sounds and pauses that disrupt speech fluency. You'll witness people begging for that elusive word to go off the tip of the tongue.
But what's the culprit? The answer is neurological. The brain and muscles working together for speech are not synchronized. People who stutter know what they want to say but need help to speak fluently.
Decoding Lisps
A lisp is another everyday speech impediment. The infliction is primarily with the letters S and Z. People with a lisp pronounce these sounds as "th." Witness someone say "thun" instead of Sun? That's a lisp playing its mischief.
Lisps originate from incorrect tongue placements in the mouth. If your tongue hits the front teeth when saying S and Z, that's called a lisp.
Apraxia of speech is another form of speech impediment and is quite nasty in its play. Apraxia of speech is different from stutters or lisps. Instead, it's an issue with the motor skill programming involved in speech.
People with apraxia struggle to coordinate the speech muscles in their brains. They understand the language perfectly and know what they wish to say. But the necessary complex motor movements evade them, disrupting smooth speech.
Another impediment to consider is dysarthria, resulting from nerve or muscle damage. It hinders speaking when these parts don't work well. Controlling the tongue and managing breath becomes difficult.
Dysarthria is different from stuttering. It needs help struggling to form words correctly. Dysarthria patients know what to say but struggle to say the words physically.
Phonological Disorders
This speech problem depends on knowing and using speech sound rules. Typically, younger children grapple with such issues while learning language rules. But when these problems persist and impact intelligibility, it's labeled a phonological disorder.
Individuals struggling with phonological disorders encounter set sound patterns they seemingly can't break. To outsiders, pronunciation errors may come across as child-like talk. But in reality, it's a complex issue requiring professional attention.
Selective Mutism
Selective mutism is when someone struggles to speak in specific social situations while being acceptable to others. It's often linked to shyness or social anxiety. Selective mutism usually begins in childhood and is often connected to extreme shyness or social anxiety.
Selective mutism can disrupt learning in school due to its impact on communication. In certain situations, someone with selective mutism can't speak due to anxiety, even if they know how to use language.
Vocal Cord Paralysis
Vocal cord paralysis is a speech problem caused by nerve damage from surgery, accidents, strokes, or tumors. The result? Difficulty in swallowing and even breathing. Speech production is severely affected when the vocal cords do not open and close smoothly.
People with vocal cord paralysis often have a hoarse or whispered speech. The pitch could be too high or low, making it easier to transition between pitches. But safety is also a concern due to difficulty swallowing, leading to recurring pneumonia and lung problems.
Articulation and Phonological Troubles
Finally, we touch on speech sound disorders, comprising articulation and phonological disorders. People with articulation disorders struggle to produce certain sounds, which makes their words hard to understand. Sounds are often switched or left out, making it harder to understand each other.
Phonological disorders, as we've discussed, relate to predictable, regular patterns of sound errors. Children with phonological disorders often substitute sounds made at the back of the mouth, such as "k" and "g," with front-mouth sounds like "t" and "d." In such cases, 'cat' might become 'tat,' and 'game' turns into 'dame.'
They learn sound patterns while learning language rules but don't stop using them as they age. This pattern then molds into a phonological disorder, impacting clear communication.

10 Most Common Speech-Language Disorders & Impediments
As you get to know more about the field of speech-language pathology you’ll increasingly realize why SLPs are required to earn at least a master’s degree . This stuff is serious – and there’s nothing easy about it.
In 2016 the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders reported that 7.7% of American children have been diagnosed with a speech or swallowing disorder. That comes out to nearly one in 12 children, and gets even bigger if you factor in adults.
Whether rooted in psycho-speech behavioral issues, muscular disorders, or brain damage, nearly all the diagnoses SLPs make fall within just 10 common categories…
Types of Speech Disorders & Impediments
Apraxia of speech (aos).
Apraxia of Speech (AOS) happens when the neural pathway between the brain and a person’s speech function (speech muscles) is lost or obscured. The person knows what they want to say – they can even write what they want to say on paper – however the brain is unable to send the correct messages so that speech muscles can articulate what they want to say, even though the speech muscles themselves work just fine. Many SLPs specialize in the treatment of Apraxia .
There are different levels of severity of AOS, ranging from mostly functional, to speech that is incoherent. And right now we know for certain it can be caused by brain damage, such as in an adult who has a stroke. This is called Acquired AOS.
However the scientific and medical community has been unable to detect brain damage – or even differences – in children who are born with this disorder, making the causes of Childhood AOS somewhat of a mystery. There is often a correlation present, with close family members suffering from learning or communication disorders, suggesting there may be a genetic link.
Mild cases might be harder to diagnose, especially in children where multiple unknown speech disorders may be present. Symptoms of mild forms of AOS are shared by a range of different speech disorders, and include mispronunciation of words and irregularities in tone, rhythm, or emphasis (prosody).
Stuttering – Stammering
Stuttering, also referred to as stammering, is so common that everyone knows what it sounds like and can easily recognize it. Everyone has probably had moments of stuttering at least once in their life. The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders estimates that three million Americans stutter, and reports that of the up-to-10-percent of children who do stutter, three-quarters of them will outgrow it. It should not be confused with cluttering.
Most people don’t know that stuttering can also include non-verbal involuntary or semi-voluntary actions like blinking or abdominal tensing (tics). Speech language pathologists are trained to look for all the symptoms of stuttering , especially the non-verbal ones, and that is why an SLP is qualified to make a stuttering diagnosis.
The earliest this fluency disorder can become apparent is when a child is learning to talk. It may also surface later during childhood. Rarely if ever has it developed in adults, although many adults have kept a stutter from childhood.
Stuttering only becomes a problem when it has an impact on daily activities, or when it causes concern to parents or the child suffering from it. In some people, a stutter is triggered by certain events like talking on the phone. When people start to avoid specific activities so as not to trigger their stutter, this is a sure sign that the stutter has reached the level of a speech disorder.
The causes of stuttering are mostly a mystery. There is a correlation with family history indicating a genetic link. Another theory is that a stutter is a form of involuntary or semi-voluntary tic. Most studies of stuttering agree there are many factors involved.
Dysarthria is a symptom of nerve or muscle damage. It manifests itself as slurred speech, slowed speech, limited tongue, jaw, or lip movement, abnormal rhythm and pitch when speaking, changes in voice quality, difficulty articulating, labored speech, and other related symptoms.
It is caused by muscle damage, or nerve damage to the muscles involved in the process of speaking such as the diaphragm, lips, tongue, and vocal chords.
Because it is a symptom of nerve and/or muscle damage it can be caused by a wide range of phenomena that affect people of all ages. This can start during development in the womb or shortly after birth as a result of conditions like muscular dystrophy and cerebral palsy. In adults some of the most common causes of dysarthria are stroke, tumors, and MS.
A lay term, lisping can be recognized by anyone and is very common.
Speech language pathologists provide an extra level of expertise when treating patients with lisping disorders . They can make sure that a lisp is not being confused with another type of disorder such as apraxia, aphasia, impaired development of expressive language, or a speech impediment caused by hearing loss.
SLPs are also important in distinguishing between the five different types of lisps. Most laypersons can usually pick out the most common type, the interdental/dentalised lisp. This is when a speaker makes a “th” sound when trying to make the “s” sound. It is caused by the tongue reaching past or touching the front teeth.
Because lisps are functional speech disorders, SLPs can play a huge role in correcting these with results often being a complete elimination of the lisp. Treatment is particularly effective when implemented early, although adults can also benefit.
Experts recommend professional SLP intervention if a child has reached the age of four and still has an interdental/dentalised lisp. SLP intervention is recommended as soon as possible for all other types of lisps. Treatment includes pronunciation and annunciation coaching, re-teaching how a sound or word is supposed to be pronounced, practice in front of a mirror, and speech-muscle strengthening that can be as simple as drinking out of a straw.
Spasmodic Dysphonia
Spasmodic Dysphonia (SD) is a chronic long-term disorder that affects the voice. It is characterized by a spasming of the vocal chords when a person attempts to speak and results in a voice that can be described as shaky, hoarse, groaning, tight, or jittery. It can cause the emphasis of speech to vary considerably. Many SLPs specialize in the treatment of Spasmodic Dysphonia .
SLPs will most often encounter this disorder in adults, with the first symptoms usually occurring between the ages of 30 and 50. It can be caused by a range of things mostly related to aging, such as nervous system changes and muscle tone disorders.
It’s difficult to isolate vocal chord spasms as being responsible for a shaky or trembly voice, so diagnosing SD is a team effort for SLPs that also involves an ear, nose, and throat doctor (otolaryngologist) and a neurologist.
Have you ever heard people talking about how they are smart but also nervous in large groups of people, and then self-diagnose themselves as having Asperger’s? You might have heard a similar lay diagnosis for cluttering. This is an indication of how common this disorder is as well as how crucial SLPs are in making a proper cluttering diagnosis .
A fluency disorder, cluttering is characterized by a person’s speech being too rapid, too jerky, or both. To qualify as cluttering, the person’s speech must also have excessive amounts of “well,” “um,” “like,” “hmm,” or “so,” (speech disfluencies), an excessive exclusion or collapsing of syllables, or abnormal syllable stresses or rhythms.
The first symptoms of this disorder appear in childhood. Like other fluency disorders, SLPs can have a huge impact on improving or eliminating cluttering. Intervention is most effective early on in life, however adults can also benefit from working with an SLP.
Muteness – Selective Mutism
There are different kinds of mutism, and here we are talking about selective mutism. This used to be called elective mutism to emphasize its difference from disorders that caused mutism through damage to, or irregularities in, the speech process.
Selective mutism is when a person does not speak in some or most situations, however that person is physically capable of speaking. It most often occurs in children, and is commonly exemplified by a child speaking at home but not at school.
Selective mutism is related to psychology. It appears in children who are very shy, who have an anxiety disorder, or who are going through a period of social withdrawal or isolation. These psychological factors have their own origins and should be dealt with through counseling or another type of psychological intervention.
Diagnosing selective mutism involves a team of professionals including SLPs, pediatricians, psychologists, and psychiatrists. SLPs play an important role in this process because there are speech language disorders that can have the same effect as selective muteness – stuttering, aphasia, apraxia of speech, or dysarthria – and it’s important to eliminate these as possibilities.
And just because selective mutism is primarily a psychological phenomenon, that doesn’t mean SLPs can’t do anything. Quite the contrary.
The National Institute on Neurological Disorders and Stroke estimates that one million Americans have some form of aphasia.
Aphasia is a communication disorder caused by damage to the brain’s language capabilities. Aphasia differs from apraxia of speech and dysarthria in that it solely pertains to the brain’s speech and language center.
As such anyone can suffer from aphasia because brain damage can be caused by a number of factors. However SLPs are most likely to encounter aphasia in adults, especially those who have had a stroke. Other common causes of aphasia are brain tumors, traumatic brain injuries, and degenerative brain diseases.
In addition to neurologists, speech language pathologists have an important role in diagnosing aphasia. As an SLP you’ll assess factors such as a person’s reading and writing, functional communication, auditory comprehension, and verbal expression.
Speech Delay – Alalia
A speech delay, known to professionals as alalia, refers to the phenomenon when a child is not making normal attempts to verbally communicate. There can be a number of factors causing this to happen, and that’s why it’s critical for a speech language pathologist to be involved.
The are many potential reasons why a child would not be using age-appropriate communication. These can range anywhere from the child being a “late bloomer” – the child just takes a bit longer than average to speak – to the child having brain damage. It is the role of an SLP to go through a process of elimination, evaluating each possibility that could cause a speech delay, until an explanation is found.
Approaching a child with a speech delay starts by distinguishing among the two main categories an SLP will evaluate: speech and language.
Speech has a lot to do with the organs of speech – the tongue, mouth, and vocal chords – as well as the muscles and nerves that connect them with the brain. Disorders like apraxia of speech and dysarthria are two examples that affect the nerve connections and organs of speech. Other examples in this category could include a cleft palette or even hearing loss.
The other major category SLPs will evaluate is language. This relates more to the brain and can be affected by brain damage or developmental disorders like autism. There are many different types of brain damage that each manifest themselves differently, as well as developmental disorders, and the SLP will make evaluations for everything.
Issues Related to Autism
While the autism spectrum itself isn’t a speech disorder, it makes this list because the two go hand-in-hand more often than not.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that one out of every 68 children in our country have an autism spectrum disorder. And by definition, all children who have autism also have social communication problems.
Speech-language pathologists are often a critical voice on a team of professionals – also including pediatricians, occupational therapists, neurologists, developmental specialists, and physical therapists – who make an autism spectrum diagnosis .
In fact, the American Speech-Language Hearing Association reports that problems with communication are the first detectable signs of autism. That is why language disorders – specifically disordered verbal and nonverbal communication – are one of the primary diagnostic criteria for autism.
So what kinds of SLP disorders are you likely to encounter with someone on the autism spectrum?
A big one is apraxia of speech. A study that came out of Penn State in 2015 found that 64 percent of children who were diagnosed with autism also had childhood apraxia of speech.
This basic primer on the most common speech disorders offers little more than an interesting glimpse into the kind of issues that SLPs work with patients to resolve. But even knowing everything there is to know about communication science and speech disorders doesn’t tell the whole story of what this profession is all about. With every client in every therapy session, the goal is always to have the folks that come to you for help leave with a little more confidence than when they walked in the door that day. As a trusted SLP, you will build on those gains with every session, helping clients experience the joy and freedom that comes with the ability to express themselves freely. At the end of the day, this is what being an SLP is all about.
Ready to make a difference in speech pathology? Learn how to become a Speech-Language Pathologist today
- Emerson College - Master's in Speech-Language Pathology online - Prepare to become an SLP in as few as 20 months. No GRE required. Scholarships available.
- Arizona State University - Online - Online Bachelor of Science in Speech and Hearing Science - Designed to prepare graduates to work in behavioral health settings or transition to graduate programs in speech-language pathology and audiology.
- NYU Steinhardt - NYU Steinhardt's Master of Science in Communicative Sciences and Disorders online - ASHA-accredited. Bachelor's degree required. Graduate prepared to pursue licensure.
- Calvin University - Calvin University's Online Speech and Hearing Foundations Certificate - Helps You Gain a Strong Foundation for Your Speech-Language Pathology Career.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Heart Disease
- Digestive Health
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Diet & Nutrition
- Health Insurance
- Public Health
- Patient Rights
- Caregivers & Loved Ones
- End of Life Concerns
- Health News
- Thyroid Test Analyzer
- Doctor Discussion Guides
- Hemoglobin A1c Test Analyzer
- Lipid Test Analyzer
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) Analyzer
- What to Buy
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Medical Expert Board
Overcoming Speech Impediment: Symptoms to Treatment
There are many causes and solutions for impaired speech
- Types and Symptoms
- Speech Therapy
- Building Confidence
Speech impediments are conditions that can cause a variety of symptoms, such as an inability to understand language or speak with a stable sense of tone, speed, or fluidity. There are many different types of speech impediments, and they can begin during childhood or develop during adulthood.
Common causes include physical trauma, neurological disorders, or anxiety. If you or your child is experiencing signs of a speech impediment, you need to know that these conditions can be diagnosed and treated with professional speech therapy.
This article will discuss what you can do if you are concerned about a speech impediment and what you can expect during your diagnostic process and therapy.
FG Trade / Getty Images
Types and Symptoms of Speech Impediment
People can have speech problems due to developmental conditions that begin to show symptoms during early childhood or as a result of conditions that may occur during adulthood.
The main classifications of speech impairment are aphasia (difficulty understanding or producing the correct words or phrases) or dysarthria (difficulty enunciating words).
Often, speech problems can be part of neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders that also cause other symptoms, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) or autism spectrum disorder .
There are several different symptoms of speech impediments, and you may experience one or more.
Can Symptoms Worsen?
Most speech disorders cause persistent symptoms and can temporarily get worse when you are tired, anxious, or sick.
Symptoms of dysarthria can include:
- Slurred speech
- Slow speech
- Choppy speech
- Hesitant speech
- Inability to control the volume of your speech
- Shaking or tremulous speech pattern
- Inability to pronounce certain sounds
Symptoms of aphasia may involve:
- Speech apraxia (difficulty coordinating speech)
- Difficulty understanding the meaning of what other people are saying
- Inability to use the correct words
- Inability to repeat words or phases
- Speech that has an irregular rhythm
You can have one or more of these speech patterns as part of your speech impediment, and their combination and frequency will help determine the type and cause of your speech problem.
Causes of Speech Impediment
The conditions that cause speech impediments can include developmental problems that are present from birth, neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease , or sudden neurological events, such as a stroke .
Some people can also experience temporary speech impairment due to anxiety, intoxication, medication side effects, postictal state (the time immediately after a seizure), or a change of consciousness.
Speech Impairment in Children
Children can have speech disorders associated with neurodevelopmental problems, which can interfere with speech development. Some childhood neurological or neurodevelopmental disorders may cause a regression (backsliding) of speech skills.
Common causes of childhood speech impediments include:
- Autism spectrum disorder : A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social and interactive development
- Cerebral palsy : A congenital (from birth) disorder that affects learning and control of physical movement
- Hearing loss : Can affect the way children hear and imitate speech
- Rett syndrome : A genetic neurodevelopmental condition that causes regression of physical and social skills beginning during the early school-age years.
- Adrenoleukodystrophy : A genetic disorder that causes a decline in motor and cognitive skills beginning during early childhood
- Childhood metabolic disorders : A group of conditions that affects the way children break down nutrients, often resulting in toxic damage to organs
- Brain tumor : A growth that may damage areas of the brain, including those that control speech or language
- Encephalitis : Brain inflammation or infection that may affect the way regions in the brain function
- Hydrocephalus : Excess fluid within the skull, which may develop after brain surgery and can cause brain damage
Do Childhood Speech Disorders Persist?
Speech disorders during childhood can have persistent effects throughout life. Therapy can often help improve speech skills.
Speech Impairment in Adulthood
Adult speech disorders develop due to conditions that damage the speech areas of the brain.
Common causes of adult speech impairment include:
- Head trauma
- Nerve injury
- Throat tumor
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Essential tremor
- Brain tumor
- Brain infection
Additionally, people may develop changes in speech with advancing age, even without a specific neurological cause. This can happen due to presbyphonia , which is a change in the volume and control of speech due to declining hormone levels and reduced elasticity and movement of the vocal cords.
Do Speech Disorders Resolve on Their Own?
Children and adults who have persistent speech disorders are unlikely to experience spontaneous improvement without therapy and should seek professional attention.
Steps to Treating Speech Impediment
If you or your child has a speech impediment, your healthcare providers will work to diagnose the type of speech impediment as well as the underlying condition that caused it. Defining the cause and type of speech impediment will help determine your prognosis and treatment plan.
Sometimes the cause is known before symptoms begin, as is the case with trauma or MS. Impaired speech may first be a symptom of a condition, such as a stroke that causes aphasia as the primary symptom.
The diagnosis will include a comprehensive medical history, physical examination, and a thorough evaluation of speech and language. Diagnostic testing is directed by the medical history and clinical evaluation.
Diagnostic testing may include:
- Brain imaging , such as brain computerized tomography (CT) or magnetic residence imaging (MRI), if there’s concern about a disease process in the brain
- Swallowing evaluation if there’s concern about dysfunction of the muscles in the throat
- Electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies (aka nerve conduction velocity, or NCV) if there’s concern about nerve and muscle damage
- Blood tests, which can help in diagnosing inflammatory disorders or infections
Your diagnostic tests will help pinpoint the cause of your speech problem. Your treatment will include specific therapy to help improve your speech, as well as medication or other interventions to treat the underlying disorder.
For example, if you are diagnosed with MS, you would likely receive disease-modifying therapy to help prevent MS progression. And if you are diagnosed with a brain tumor, you may need surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation to treat the tumor.
Therapy to Address Speech Impediment
Therapy for speech impairment is interactive and directed by a specialist who is experienced in treating speech problems . Sometimes, children receive speech therapy as part of a specialized learning program at school.
The duration and frequency of your speech therapy program depend on the underlying cause of your impediment, your improvement, and approval from your health insurance.
If you or your child has a serious speech problem, you may qualify for speech therapy. Working with your therapist can help you build confidence, particularly as you begin to see improvement.
Exercises during speech therapy may include:
- Pronouncing individual sounds, such as la la la or da da da
- Practicing pronunciation of words that you have trouble pronouncing
- Adjusting the rate or volume of your speech
- Mouth exercises
- Practicing language skills by naming objects or repeating what the therapist is saying
These therapies are meant to help achieve more fluent and understandable speech as well as an increased comfort level with speech and language.
Building Confidence With Speech Problems
Some types of speech impairment might not qualify for therapy. If you have speech difficulties due to anxiety or a social phobia or if you don’t have access to therapy, you might benefit from activities that can help you practice your speech.
You might consider one or more of the following for you or your child:
- Joining a local theater group
- Volunteering in a school or community activity that involves interaction with the public
- Signing up for a class that requires a significant amount of class participation
- Joining a support group for people who have problems with speech
Activities that you do on your own to improve your confidence with speaking can be most beneficial when you are in a non-judgmental and safe space.
Many different types of speech problems can affect children and adults. Some of these are congenital (present from birth), while others are acquired due to health conditions, medication side effects, substances, or mood and anxiety disorders. Because there are so many different types of speech problems, seeking a medical diagnosis so you can get the right therapy for your specific disorder is crucial.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Language and speech disorders in children .
Han C, Tang J, Tang B, et al. The effectiveness and safety of noninvasive brain stimulation technology combined with speech training on aphasia after stroke: a systematic review and meta-analysis . Medicine (Baltimore). 2024;103(2):e36880. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000036880
National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders. Quick statistics about voice, speech, language .
Mackey J, McCulloch H, Scheiner G, et al. Speech pathologists' perspectives on the use of augmentative and alternative communication devices with people with acquired brain injury and reflections from lived experience . Brain Impair. 2023;24(2):168-184. doi:10.1017/BrImp.2023.9
Allison KM, Doherty KM. Relation of speech-language profile and communication modality to participation of children with cerebral palsy . Am J Speech Lang Pathol . 2024:1-11. doi:10.1044/2023_AJSLP-23-00267
Saccente-Kennedy B, Gillies F, Desjardins M, et al. A systematic review of speech-language pathology interventions for presbyphonia using the rehabilitation treatment specification system . J Voice. 2024:S0892-1997(23)00396-X. doi:10.1016/j.jvoice.2023.12.010
By Heidi Moawad, MD Dr. Moawad is a neurologist and expert in brain health. She regularly writes and edits health content for medical books and publications.
Common Speech Impediments: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, And Support
Speech impediments include a variety of both language and speech disorders, some of which can be addressed through online speech therapy with speech-language pathologists. They can arise because of heredity and genetics, developmental delays, or even damage to Broca’s area—the part of the brain that’s involved in language skills and speech skills. They may also be linked to other conditions like autism spectrum disorder, cerebral palsy, dyslexia, or even hearing loss. It depends on the type and the cause, but most speech impediments and speech impairments can be treated through speech therapy.
That said, recognizing when a speech impediment may be present can help you get yourself or your child the treatment and support they may need for improved academic and/or social functioning and self-confidence.

Common symptoms of a speech impediment
There are many different types of speech impediments a person can have, so the symptoms can vary. However, it’s important to understand what symptoms may indicate a speech disorder so that you can seek treatment if necessary.
Symptoms of a speech disorder
- Elongating words
- Quiet or muffled speech
- Blinking frequently
- Distorted sounds while talking
- Frequent changes in pitch
- Poor voice quality
- Visible frustration when trying to communicate
- Overall difficulty communicating and expressing thoughts and ideas
- Inability to repeat words
- Inability to pronounce words the same way twice
- A phobia of speaking in public
- Speaking slowly and carefully
- Speech delay
- Frequent pauses when talking
- Limited vocabulary over several years, delayed language development
Some speech and language disorders are consistent with underlying mental health conditions such as autism. You can visit licensed health professionals or speech therapists to receive an accurate diagnosis and find out how to treat a speech impediment or language disorder, and its underlying cause, if applicable.
Categories of a speech disorder
Speech impediments or communication disorders can take many forms, from speech sound disorders to voice-related disorders. While speech sound disorders mostly result from sensory or motor causes, voice-related disorders deal with physical problems regarding speech. Read on for a list of some of the most common categories of speech impediments.
Voice disorders
Voice disorders primarily arise due to issues regarding the health and structure of the larynx or the voice box. They can impact pitch, resonance, volume, and voice quality. Symptoms of a voice disorder may include having a hoarse, quivering, strained, choppy, or weak and whispery voice, which can make it difficult to produce speech sounds.
The root cause of these disorders can be either organic, like alterations to respiratory, laryngeal, or vocal tract mechanisms, or functional, like improper use of the voice. Some risk factors that may contribute to vocal health challenges include allergies, psychological stress, age, excessive alcohol or drug use, screaming, scarring from neck surgery, or even gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD). Examples of voice disorders include laryngitis, vocal cord paralysis/weakness, polyps or nodes present on the vocal cords, leukoplakia, or muscle tension dysphonia.
Fluency disorders
A person may be diagnosed with a fluency disorder if they have trouble with speech timing and rhythm which makes it difficult to create a normal speech pattern. These disorders are characterized by interruptions in the typical flow of speaking, including abnormal repetitions, hesitation, and prolongations. Their cause is unknown, but it may be genetic. Symptoms can also be exacerbated by stress and anxiety. Stuttering is the most common example of fluency disorders.
Symptoms of a fluency disorder may include dragging out syllables, speaking breathlessly, repetition of words, speaking slowly, and being tense while speaking. Secondary symptoms may include fidgeting, mumbling, saying “um” or “uh” often, not using certain problematic words, rearranging words in sentences, and anxiety around speaking. Treatment options vary depending on the specific disorder. With stuttering, for example, slowing down, practicing, using speech monitors, attending speech therapy, and receiving cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) are all potential treatment options.
Articulation disorders and phonological disorders
Articulation and phonological disorders are two types of speech disorders classified as speech sound disorders that may impact communication. An articulation disorder includes speech that commonly exhibits errors such as substitution, omission, distortion, and/or addition (SODA). Although the actual causes of articulation disorders aren’t well understood, contributing factors may include brain injuries, a cleft palate/cleft lip, or nerve damage. Phonological disorders typically involve producing sounds correctly but using them in the wrong place and are more predictable than articulation errors. There may also be a genetic factor that contributes to both disorders and other families may be impacted as well. A licensed speech-language pathologist (SLP) can determine if an individual may have an articulation disorder or a phonological disorder. Ongoing speech therapy is typically the recommended treatment method.
Speech impediments versus language impairments
A speech impediment is typically characterized by difficulty creating sound due to factors like fluency disorders or other voice problems. These disorders may arise from underlying mental health issues, neurological problems, or physical factors or conditions impacting speech muscles.
Language impairments, on the other hand, are more about difficulty processing, reading, and writing and can be connected to an issue processing receptive language. They’re common in children, especially when they first start school. Language impairments relate to meaning, whereas speech impediments relate to sound. It’s also very common for a language impairment disorder to present alongside a learning disability like dyslexia.

An example of speech disorder: Apraxia
Apraxia of speech is a speech sound disorder that affects the pathways of the brain. It’s characterized by a person having difficulty expressing their thoughts accurately and consistently. It involves the brain being able to form the words and knowing exactly what to say, but the person then being unable to properly execute the required speech movements to deliver accurate sounds. In mild cases, a person will only have small limitations in their ability to form speech sounds. In severe cases, alternate communication methods may need to be used.
An SLP is the type of provider who can diagnose apraxia. To diagnose speech disorders, including both childhood apraxia (sometimes called verbal apraxia) and acquired apraxia, they may ask the individual to perform simple speech tasks like repeating a particular word several times or repeating a list of words that increase in length. Apraxia generally needs to be monitored by both parents and an SLP over time for an accurate diagnosis to be possible.
There are various treatment options for apraxia, the most common being one-on-one meetings with a speech pathologist. They’ll likely help you or your child build helpful strategies and skills to help strengthen problem areas and communicate more clearly. Some other treatment methods include improving speech intelligibility or using alternate forms of communication, like electronic speech or manual signs and gestures.
An example of communication disorder: Aphasia
The National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders describes aphasia as a communication disorder that results in a person’s inability to speak, write, and/or understand language. Like other communication disorders, it may occur because of damage to the portions of the brain that are involved in language, which is common in those who have experienced a stroke. It may also come on gradually in those who have a tumor or a progressive neurological disease like Alzheimer’s. Symptoms may include saying or writing sentences that don’t make sense, a reduction in a person’s ability to understand a conversation, and substituting certain sounds and words for others.
Brain injuries in patients with Aphasia
Since this disorder is usually caused by damage to parts of the brain, it will typically first be recognized in an MRI or CT scan that can confirm the presence of a brain injury. The extent and type of aphasia can generally only be determined by observing the affected part of the brain and determining how extensively it has been damaged, which is often done with the help of an SLP.
Treatment options for aphasia can be restorative (aimed at restoring impaired function) or compensatory (aimed at compensating for deficits).
An example of nervous system disorder: Dysarthria
Dysarthria is usually caused by brain damage or facial paralysis that affects the muscles of the jaw, tongue, or throat, which may result in deficits in a person’s speech. It may also be caused by other conditions like Lou Gehrig’s disease, Parkinson’s, or a stroke. It’s considered a nervous system disorder, subclassified as a motor speech disorder. It’s commonly seen in those who already have other speech disorders, such as aphasia or apraxia. Symptoms of dysarthria include slurred speech, speaking too slowly, speaking too quickly, speaking very softly, being unable to move one’s lips or jaw, and having monotonous speech.
Exercises to counter muscle weakness
Dysarthria can be diagnosed by an expert in speech-language pathology through an exam and tests like MRI, CT, electromyography, or the Denver articulation screening examination. Treatment depends upon the severity and rate of progression of the disorder. Some potential examples include tactics like slowing down while talking, doing exercises to help strengthen jaw muscles, moving the lips and tongue more, and learning strategies for speaking more loudly. Hand gestures and speech machines may also help.
Seek treatment if you’re having difficulty with verbal communication
It is important to treat speech disorders; the consequences of an untreated speech or language impediment can vary widely depending on the type, symptoms, and severity, as well as the age and life situation of the individual. In general, it’s usually helpful to seek professional advice on treating speech disorders as soon as you notice or suspect an impediment present in yours or your child’s speech. Especially for moderate to severe cases, some potential effects of leaving these common speech disorders untreated can include:
- Poor academic performance/dropping out of school
- Decrease in quality of life
- Social anxiety and an inability to connect with people
- Damaged relationships
- Social isolation
- Hospitalization

Support options and resources
Meeting with an SLP is usually the recommended first step for someone who believes they or their child may have a speech impediment. If you have a teenager with dyslexia, there are resources for dyslexic teens that can give supportive information about the condition. Healthcare providers may also provide helpful insights and ask about your family members’ history when it comes to speech and language-related issues as they can be hereditary.
Therapeutic support for speech impediments
While these professionals can help with the physical aspects of a variety of speech and language impediments, you or your child may also benefit from emotional support in relation to the mental health effects of having an impediment. A therapist may be able to provide this type of guidance. If your child is experiencing a speech impediment, a counselor may be able to work with them to process their feelings of frustration and learn healthy coping mechanisms for stress. They can help you manage the same feelings if you receive a speech or language impediment diagnosis, or may be able to support you in your journey of parenting a child with a speech or language impediment diagnosis.
In addition to support at home, teenagers with a diagnosed speech impairment or impediment can receive special education services at school. The Centers for Disease Control notes that under the Individuals with Disabilities Act (IDEA) and Section 504, schools must provide support and accommodations for students with speech disorders. For some children, support groups can provide outlets for social connections and advice for coping.
Accessible healthcare options online
Meeting with a therapist in person is an option if there are providers in your area. That said, many people find it less intimidating or more comfortable to meet with a therapist virtually. For example, a teen who is experiencing a speech or language impediment may feel better interacting with a counselor through the online chat feature that virtual therapy platforms like TeenCounseling provide. It may allow them to express themselves more clearly than they could face-to-face or over the phone. Parents who need support in caring for a child with a speech or language impediment may find the availability and convenience of meeting with a therapist through an online therapy service like BetterHelp to be most beneficial. Research suggests that online and in-person therapy offer similar benefits for a variety of conditions, so you can choose the format that’s best for you.
Counselor reviews
See below for reviews of TeenCounseling therapists written by parents who sought help for their children through this service.
“Kathleen has been good for my daughter to talk to. I am thankful for her to give my daughter someone else's perspective other than her parents. Thank you.”
“I love Ms. Jones. She doesn’t over-talk or judge you. She gives really good advice and if you're confused she knows how to break it down or explain whatever it is so you can understand. If you need to talk about anything, she’s always an open ear and responds quickly. Not only does she give you points from others' perspectives but she steps into yours so she can understand why certain things are the way they are. In my first session, I was nervous and I think she could tell. She’ll crack a joke every now and then to make me feel more comfortable. She’s just such a bundle of joy and a good counselor to have.”
Speech and language impediments can vary widely in terms of types, causes, symptoms, and severity. These are diagnosed by professionals in the field of speech and language pathology or by a medical doctor. A therapist can provide emotional support for those who are having difficulty coping with their own or their child’s diagnosis or other related challenges.
What are the 3 speech impediments?
Speech impediments can manifest in a variety of ways. Three of the most common are listed below:
- Voice disorders affect the tone, pitch, quality, and volume of a person’s voice. A person with a voice disorder may have difficulty speaking or being heard clearly by others. Voice disorders can be either functional or organic. Functional disorders occur due to improper use of the parts of the throat that produce speech, such as overuse of the voice leading to vocal fatigue. Organic voice disorders result from physical anatomical changes, such as nodules on the vocal cords.
- Fluency disorders affect the rate, rhythm, and cadence of speech. Those with fluency disorders may speak in a disjointed, choppy, or prolonged fashion, making them difficult for others to understand clearly. While many types of fluency disorders exist, stuttering is likely the best-known. Speech often requires precise timing to convey a message accurately, which fluency disorders can disrupt.
- Speech sound disorders are a broad category of disorders that interferes with a person’s ability to produce sounds and words correctly. Speech sound disorders can present very differently from person to person. Sometimes word sounds are omitted or added where not appropriate, and sometimes word sounds are distorted or substituted completely. A typical example of a speech sound disorder is the substitution of “r” for “w” in words like “rabbit” (becoming “wabbit”). Many children experience that substitution, but it does not become a disorder until the child does not outgrow it.
Other types of disorders can cause problems with expressive communication or tongue-tie those experiencing them, such as developmental language disorder. Language disorders also cause concerns related to expressive communication, but the concerns are due to a lack of understanding of one or more components of language, not an inability to produce or use word sounds.
What do you call a speech impediment?
Speech impediments are typically referred to as speech disorders . Speech refers to the ability to form speech sounds using the vocal cords, mouth, lips, and tongue. Speech also requires that a rhythm and cadence be maintained. Speech disorders indicate a problem producing intelligible speech; word sounds may be omitted or misplaced, the rhythm of the speech may be difficult to follow, or a person’s voice might be strangely pitched or too soft to hear clearly.
It is important not to confuse speech disorders with language disorders . Language disorders arise due to difficulty understanding what words mean, how word sounds fit together, or how to use spoken language to communicate. Language problems may affect how a person speaks, but the root cause of the concern is linked to their understanding of language, not their ability to produce intelligible speech.
How do I know if I have a speech impediment?
If you’re experiencing a sudden onset of impaired speech with no apparent cause, seek medical attention immediately. Strokes, traumatic brain injuries, and other serious medical conditions can cause sudden changes in speaking ability. Gradual changes in speaking ability may also indicate an underlying medical problem. If you’re concerned that your speaking ability has been gradually deteriorating, consider making an appointment with a healthcare provider in the near future.
Most people with a speech disorder are diagnosed in childhood. Parents often identify speech-related concerns in early childhood based on their child’s speech patterns. The child’s pediatrician may also refer the child to a speech-language pathologist, a professional specializing in evaluating and treating speech disorders. If problems persist until the child is in school, teachers and other school officials might initiate a referral for an evaluation if they believe speech concerns are present. Children often receive speech and language therapy that resolves or improves their speech problems.
Speech disorders also appear in adulthood, often due to injury or illness. It is also possible, although rare, for speech problems to be misdiagnosed or missed outright during a person’s childhood. In that case, the speech disorder may have been present since childhood and symptoms persisted into adulthood.
If you’re finding it difficult to communicate verbally with others, have an easily identifiable speech problem (like stuttering), or receive feedback that others have trouble understanding you, consider making an appointment with your doctor for an evaluation and referral to the appropriate healthcare providers.
What are 5 causes of speech impairment?
Speech and language disorders can result from conditions that interfere with the development of perceptual, structural, motor, cognitive, or socioemotional functions. The cause of many speech disorders is unknown, but research has indicated several underlying factors that may be responsible:
- Pre-existing genetic conditions, like Down’s syndrome or Fragile X syndrome. Evidence suggests that genes may play a role even if genetic abnormalities do not result in a diagnosable genetic condition.
- Physical abnormalities, such as damage or improper development of the respiratory system, facial muscles, or cranial nerves.
- Hearing problems, which can delay a child’s acquisition of speech.
- Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder, may interfere with speech development. There is also evidence to suggest that those with attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder may have a more challenging time acquiring speech skills.
- Neurological conditions such as cerebral palsy.
Mental health concerns can also cause problems communicating with others. For example, an underlying anxiety disorder may lead to selective mutism , wherein a child speaks only under certain circumstances.
Is speech impediment a disability?
A speech-language disorder is considered a “ communication disability ” under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). The ADA requires government and businesses to establish “effective communication” with people who have communication disabilities. Effective communication can be established in several ways. For those with a speech disorder, accommodation may be as simple as ensuring the person can get hold of writing materials if they need to express themselves quickly. In some cases, organizations may use a transliterator, or person trained to recognize unclear speech and repeat it clearly.
Because speech disorders are known to lead to academic struggles in K-12 and higher education settings, they are categorized as a disability under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Improvement Act (IDEIA) . The IDEIA sets guidelines for all schools in the United States, public or not public, guaranteeing each child a right to accommodations and interventions for their speech disorder.
Can I fix my speech impediment?
Whether or not a speech disorder can be completely eliminated depends heavily on individual factors. The cause of the disorder, its severity, and the type of speech dysfunction all play a role in determining whether a particular disorder can be completely resolved. While it is not possible to guarantee that a speech disorder can be “cured,” nearly all disorders are treatable, and improvement is likely possible.
Can you treat a speech impediment?
Yes, many speech disorders are highly treatable. Most people receive treatment as children when most speech disorders become apparent. For children, speech-language pathologists will identify the specific speech disorder, search for an underlying cause, and design an intervention that targets that child’s speech problem. For example, a child who struggles with articulation errors and producing word sounds consistently may benefit from a contextual utilization approach . Contextual utilization leverages the fact that one sound is easier or more difficult to pronounce depending on which other sounds surround it.
Speech disorders that emerge in adulthood may be more challenging to treat due to underlying factors, such as brain injury. Suppose an adult experiences a traumatic brain injury that affects their speaking ability. In that case, a speech-language pathologist may help them find alternative communication methods, such as using a computer. They may also help them directly restore some of their speaking ability by leading them through exercises that improve nerve function and muscle control.
Is a speech impediment mental?
Speech disorders can be caused by various factors, many of which have nothing to do with the brain. However, there is a relationship between psychiatric mental health concerns and difficulty with spoken communication . Although researchers are still unsure of the exact cause, studies have identified a significant link between speech disorders and mental health disorders like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depression.
Neurodevelopmental disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder, are also associated with an increased risk of developing a speech disorder. Although the link between neurodevelopmental disorders and speech disorders is not fully understood, evidence suggests that treating the speech disorder is still possible.
Finally, speech disorders can also be caused by illness or injury in the brain, such as cancer, an infection, or traumatic brain injury. Although these are not considered mental or developmental disorders, they may affect brain function and mental acuity. Speaking is a complex process, and there are many ways it can be affected.
Is autism a speech impediment?
Autism spectrum disorder is not a speech disorder, but it is heavily associated with communication problems. Those on the autism spectrum often use repetitive or rigid language and may not follow communication norms. They may repeat phrases continuously, use a modified tone of voice, or introduce information that has little to do with the conversation at hand.
Those on the autism spectrum are often able to form word sounds properly. The communication deficits of autism spectrum disorder are more closely related to language disorders than speech disorders. Speech disorders are associated with difficulty producing or using word sounds correctly, whereas language disorders are associated with a lack of understanding of one or more language components.
Autism spectrum disorder is also characterized by difficulties using pragmatic communication, or communication that is appropriate to a specific social situation. Although not a disorder of speech, a limited ability to recognize the socioemotional content of speech can significantly impact interpersonal communication and social interactions.
- Navigating Depression In Teens And Young People Medically reviewed by Elizabeth Erban , LMFT, IMH-E
- ADHD Signs In Women, Men, And Children Medically reviewed by Julie Dodson , MA
- Relationships and Relations

No products in the cart.
Login/Sign Up
Awareness Colors, Causes and Definitions | Meanings of Each Awareness Cause
Personalized Cause - Awareness Color Chart By Colors, Causes and Meanings
This chart has similar content, in a different format, to our Awareness Cause and Color Reference Guide in the header of our site under Find Your Ribbon."
Both charts help you navigate to specific colors or causes.
Please bookmark this list so you have a handy reference guide for awareness colors when you need to support a loved one.
Welcome to Personalized Cause's chart of Awareness Ribbons Colors and Causes and their specific meanings and definitions. Personalized Cause offers awareness ribbon pins in personalized and non-personalized ribbon pin versions (no minimums), personalized and non-personalized fabric ribbons in bulk , and silicone wristbands in personalized and non-personalized variations with the wording KNOW MORE . The personalized wristbands are available in bulk.
The Awareness Ribbons Colors and Causes chart listed here apply to all of our products. We designed each of our products to coordinate in color across our entire product offering. Each product, including ribbons, pins and wristbands use a specified Pantone color. That way, you can purchase consistently colored items, at various price points, according to the demographic you serve or your own personal needs.
Please browse our Awareness Ribbons Colors and Causes which are grouped by color or image, keeping in mind that this list is for information purposes only. Please do not reproduce our copyrighted cause list by color without our written permission.
Amber Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Appendiceal Cancer / Appendiceal Tumors / Appendix Cancer: Appendix Cancer is very rare and typically found incidentally during appendectomies in about 1% of cases. Appendix Cancer is a rare disease. The alternate awareness ribbons for Appendix Cancer are Blue Jeans and Zebra.
- Flint Michigan Water Crisis: The Flint Michigan water crisis is a public health crisis that started in 2014 after the drinking water for the city of Flint, Michigan was contaminated with lead and possibly Legionella bacteria.
- Pseudomyxoma Peritonei: Pseudomyxoma Peritonei is a rare disease characterized by the presence of mucin in the peritoneal cavity. While the most common cause of PMP is Appendix Cancer, several types of tumors can cause Pseudomyxoma Peritonei. Pseudomyxoma peritonei is a Rare Disease. The alternate awareness ribbons are Blue Jeans and Zebra.
Animal Paw Prints Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Animal Abuse Prevention: Preventing animal cruelty and abuse is in all of our best interests. Studies show that cruelty to animals is a sign that other abuse may be taking place in the home. Those same studies show that children who witness animal abuse are at a greater risk of becoming animal abusers themselves. The alternate color for animal abuse prevention is purple.
- Animal Fostering Parent / Family: Animal Fostering creates more space in shelters for other animals in need. Whether a shelter is crowded or not, each animal in a shelter requires time and resources that could be stretched further if those animals were in foster homes. Foster caregivers help animal shelters and rescues extend their resources.
- Animal Loss Due to Animal Abuse: Animal death due to animal abuse includes hoarding, lack of shelter or veterinary care, tethering and abandonment, as well as other forms of abuse. The alternate color for animal loss due to animal abuse is purple and black.
- Animal Protection and Welfare: Animals deserve to live their lives free from suffering and exploitation. The alternate color for animal protection and welfare is purple.
- Animal Rescue Mom / Dad / Family: Overburdened shelters take in millions of stray, abused and lost animals every year. By adopting an animal, you're making room for others. You are giving more animals a second chance and the cost of your adoption goes directly toward helping shelters better care for the animals they take in.
- Cancer (Cats and Dogs): Cats and dogs can get cancer. A veterinary oncologist is a veterinarian that specializes in the diagnosis and treatment of cancer in pets. A veterinary oncologist has undergone an additional 3–4 years of residency training in cancer medicine after attaining their Doctor of Veterinary Medicine degree.
- Cat and Dog Blood Donors / Veterinary Transfusion Medicine: Just like humans, animals may require blood transfusions. Trauma, autoimmune diseases, bone marrow surgery, cancer, and abdominal surgery are just a few reasons blood is needed to save the life of a beloved dog or cat.
- Diabetes (Cats and Dogs): In dogs, the prevalence of Diabetes is about 1 in 500. The common age of diagnosis is 7-9 years. Female dogs are three times more likely than males to get Diabetes. Dogs are more likely to have insulin-dependent diabetes, similar to Type I Diabetes in humans. In cats, the prevalence of diabetes is about 1 in 200 cats.
- Feline Leukemia Virus / FeLV (Cats): Feline Leukemia virus (FeLV) is one of the most common infectious diseases in cats, affecting between 2 and 3% of all cats in the United States.
- Heart Worm (Cats and Dogs): Heart Worm Disease results in severe lung disease, heart failure, other organ damage, and death in pets. This mainly occurs in dogs, cats, and ferrets. Heart Worm is caused by a parasitic worm called Dirofilaria immitis . The worms are spread through the bite of a mosquito.
- High Rise Syndrome (Cats): High-Rise Syndrome refers to the injuries that cats may sustain if they fall from a steep height. Cases of High-Rise Syndrome tend to spike during warm weather months when windows are open and outdoor spaces, like terraces, are in use more often.
- Humane Treatment of Animals: Animals deserve to be treated humanely. It is our responsibility as humans to treat them with compassion and benevolence. The alternate color for Humane Treatment of Animals is orange.
- Kennel Cough (Cats and Dogs): Kennel Cough is a highly contagious, common airway infection that can be caused by several viruses and bacteria. Its most distinctive symptom is a loud, hacking cough.
- Loss of a Loved Pet / In Memory of a Loved Pet: When we lose a beloved pet, the loss can bring grief and intense sorrow. Honoring and remembering a pet with an animal paw prints ribbon pin is a way to keep your pet close to your heart.
- Parvovirus (Dogs): Parvo in puppies is caused by the canine parvovirus. This virus is highly contagious and spreads through direct contact with an infected dog or indirect contact with a contaminated object.
- Rabies (Cats and Dogs): Rabies is a viral disease that can infect all warm-blooded animals, including cats and people, although some species are somewhat naturally resistant to the disease.
- Ringworm (Cats): Ringworm in cats is a highly contagious fungal infection of the skin. It is more common in kittens and long-haired cats, but can affect any breed and age.
- Spay and Neuter Pets: Spaying is the common term used to describe the surgical procedure known as an ovariohysterectomy. In this procedure, the female's ovaries and uterus are removed completely. Neutering and castration are the common terms used to describe the surgical procedure during which both testicles are removed in order to sterilize a male cat or dog. The alternate color for spay and neuter pets is light blue.
- Upper Respiratory Infection (Cats) Feline upper respiratory infection is the common term for a respiratory infection. Synonyms for this condition include Feline Infectious Respiratory Disease and Feline Upper Respiratory Disease Complex.
- Worms (Cats and Dogs): Healthy-looking pets can still carry worms , so it's important to worm them regularly.
Black A wareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Accidents/Unintentional Injuries: Injuries have traditionally been known as "accidents" or random and unavoidable events. Injuries are instead described as preventable events with major consequences on public health and represent a significant global issue.
- Black Ribbon Against Violence / BRAVE: Black Ribbon Against Violence Everywhere is the meaning behind this black ribbon.
- Black Ribbon Day / European Day of Remembrance for Victims of Stalinism and Nazism: The European Day of Remembrance for Victims of Stalinism and Nazism, known as Black Ribbon Day in some countries, is an international day of remembrance for victims of totalitarian regimes, specifically Stalinism, Communism, Nazism and Fascism. Black Ribbon Day symbolizes the rejection of “extremism, intolerance and oppression”.
- Black Ribbon Foundation: The Black Ribbon Foundation of Australia seeks to eliminate any public perception toward the gender/sex bias surrounding domestic violence. Its full title is Black Ribbon - Awareness of Men Suffering Domestic Violence. The foundation was created to help all victims of domestic violence equally, regardless of gender.
- Black Ribbons for Funerals / Memorials / Mourning: Traditionally, black has been the color that communicates bereavement. For this reason, it is often used in funeral services. Many cultures have their own traditional color other than black. In some cultures, the ribbon is torn to represent the tear in your heart when losing a loved one.
- Funerals/Mourning: The “color of mourning” has varied, though most cultures recognize black as being the preferred standard for funeral attire.
- Gang Prevention: Gang Prevention programs target youth at risk of gang involvement and help reduce the number of youth who join gangs.
- Hypersomnia: Hypersomnia, or excessive sleepiness, is a condition in which a person has trouble staying awake during the day. People who have hypersomnia can fall asleep at any time; for instance, at work or while they are driving. According to the National Sleep Foundation , up to 40% of people have some symptoms of hypersomnia from time to time.
- Insomnia: Insomnia is defined as difficulty initiating or maintaining sleep, or both, despite adequate opportunity and time to sleep. This can lead to impaired daytime functioning. Insomnia may be a cause of or result of poor quality and/or quantity of sleep. In general, women are affected more frequently than men.
- Malignant Melanoma (Skin Cancer): Melanoma is a cancer that develops in melanocytes, the pigment cells present in the skin. It can be more serious than the other forms of skin cancer because of a tendency to spread to other parts of the body and cause serious illness and death. About 50,000 new cases of Melanoma are diagnosed in the United States every year.
- Mass Shooting Memorial / Community in Mourning: There's no single consensus on the definition of a mass shooting although it is often defined as an incident in which four or more people are shot or killed, not including the shooter. Communities in mourning suffer the shock of losing loved ones, and experience the random nature of mass shootings.
- Mass Shooting Victims / Mass Shooting Survivors: Studies show that long-term outcomes for survivors of mass shootings are improved with the help of community connections and continuing access to mental health support.
- Melanoma, Adult: Melanoma occurs when the pigment-producing cells that give color to the skin become cancerous. Symptoms might include a new, unusual growth or a change in an existing mole. Melanomas can occur anywhere on the body.
- Melanoma, Childhood (Skin Cancer): Even though Melanoma is rare, it is the most common skin cancer in children. It occurs more often in adolescents aged 15 to 19 years of age. The alternate color for melanoma in children is gold.
- Memorial Ribbons: A black ribbon may be worn, seen on websites, or used on social media to provide support to those who have lost a loved one. A memorial black ribbon may also be used to honor a deceased individual.
- Mourning: As opposed to grief, which refers to how someone may feel the loss of a loved one, mourning is the outward expression of that loss. Mourning usually involves culturally determined rituals that help mourners make sense of the end of their loved one's life and give structure to what can feel like a very confusing time. While the internal pain of grief is a more universal phenomenon, how people mourn is influenced by their personal, familial, cultural, religious, and societal beliefs and customs.
- Narcolepsy: Narcolepsy is a chronic disease of the central nervous system. Symptoms include excessive daytime sleepiness, sudden loss of muscle tone, distorted perceptions, inability to move or talk, disturbed nocturnal sleep, and automatic behavior.
- National Tragedies: A tragedy is an event of great loss, usually of human life. Examples of recent national tragedies include: The World Trade Center bombing, the assassination President Kennedy, the truck bombing of the Oklahoma City Federal Building by Timothy McVeigh and, most recently, school shootings.
- POW/MIA Recognition Day: Congress designated the third Friday of September as National POW/MIA Recognition Day and ordered prominent display of the POW/MIA flag on this day and several other days. The alternate color for POW/MIA Remembrance is camo (camouflage).
- Sleep Apnea: Sleep Apnea is a serious sleep disorder that happens when breathing stops and starts while sleeping. If Sleep Apnea goes untreated, it can cause loud snoring, daytime tiredness, or more serious problems like heart trouble or high blood pressure.
- Sleep Disorders: Sleep Disorders are conditions that prevent a person from getting restful sleep and, as a result, can cause daytime sleepiness and dysfunction. There are approximately eighty different types of sleep disorders which affect approximately 70 million Americans. The most important sleep disorders are Insomnia, Sleep Apnea, Restless Legs Syndrome and Narcolepsy.
Black and Blue A wareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Loss of a Brother / In Memory of a Brother
- Loss of a Father / In Memory of a Father
- Loss of a Male Loved One / In Memory of a Male Loved One
- Loss of a Son / In Memory of a Son
Black and Gold Awareness R ibbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Platelet Donation: Platelets are tiny, colorless, disc-shaped particles circulating in the blood and are essential for normal blood clotting. Platelets are critically important to the survival of many patients with clotting problems (aplastic anemia, leukemia) or cancer, and patients who undergo organ transplants or major surgeries. Platelets can only be stored for five days after being collected. Maintaining an adequate supply of this lifesaving, perishable product is an ongoing challenge. Some donations can generate two or three adult-sized platelet transfusion doses from one donation. The alternate color for platelet donation is red.
- School Bus Accidents: Each year, an average of 137 people are killed in school transportation-related crashes, and hundreds more are injured. When it comes to school bus safety, the safest place to be is actually on the bus . Motorists, pedestrians, and bicyclists, make up 93% of the fatalities in these types of accidents each year.
Black and Navy Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Intraocular Melanoma, Adult (Eye Cancer): Intraocular Melanoma is a rare cancer that forms in the eye. It usually has no early signs or symptoms. As with Melanoma of the skin, risk factors include having fair skin and light-colored eyes.
- Intraocular Melanoma, Childhood (Eye Cancer): Intraocular Melanoma begins in the middle of three layers of the wall of the eye. The middle layer, where Intraocular Melanoma forms, is called the uvea or uveal tract. The alternate color for Intraocular Melanoma in children is gold.
- Loss of an Adult Child / In Memory of an Adult Child
- Ocular Melanoma: Ocular Melanoma is a cancer in pigment-producing cells of the eye called melanocytes.
- Police Officers Lost in the Line of Duty: This color represents any law enforcement officer who has died as a direct or indirect result of a personal injury sustained in the line of duty. This includes law enforcement officers who, while in an off-duty capacity, act in direct response to an emergency situation involving the general public or a violation of the law.
- Uveal Melanoma: Ocular Melanoma or, more specifically, Uveal Melanoma is the most common primary intraocular cancer in adults.
Black and Pink Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Loss of a Daughter / In Memory of a Daughter
- Loss of a Female Loved One / In Memory of a Female Loved One
- Loss of a Mother / In Memory of a Mother
- Loss of a Sister / In Memory of a Sister
- Sleep Apnea in Women: The signs and symptoms of Sleep Apnea in women can be different from those in men. Women with Sleep Apnea may not report the typical symptom of sleepiness commonly reported by men with Sleep Apnea.
Black and Red Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Black Lives Matter: The Black Lives Matter movement began as a social media response to an acquittal in the 2013 shooting death of African-American teen Trayvon Martin. The acquittal sparked outrage around the country leading to mass demonstrations against racially-motivated injustice and racism among law enforcement. Every June 1 marks the start of Black Lives Matter Month, an opportunity for all Americans to make a stand against racism and racially-motivated violence. Founded as a hashtag in 2013, Black Lives Matter has grown into thousands of decentralized chapters advocating for equality and justice for the Black community, and protesting against violence against Black people at the hands of law enforcement.
- I Am An Immigrant: The I Am An Immigrant campaign encourages all Americans to celebrate the monumental contributions that immigrants have made, and continue to make, every day. Online campaigns include #ToImmigrantsWithLove, #ImmigrantHeritageMonth, and #CelebrateImmigrants, allowing space for immigrants and their allies to share stories demonstrating how immigration benefits communities, the economy, and our country.
- I Stand With Immigrants: The I Stand With Immigrants Initiative , powered by FWD.us , leads narrative campaigns that empower immigrants and their allies to share stories and drive action that demonstrate immigration is good for our communities, economy, and country. The goal is to encourage everyone to explore their individual heritage and celebrate both our distinct and shared experiences.
- Immigrant Heritage: June is Immigrant Heritage Month. The celebration formally began in 2014 and seeks to give immigrants and refugees the opportunity to explore and celebrate their background as well as create awareness about how diversity and immigration are both essential elements of a community's social fabric.
- In Memory of Murder Victims: The annual National Day of Remembrance for Murder Victims gives people the opportunity to remember those lost to homicide, and honor their memories.
- Murder Victims: In addition to pins to remember victims of homicide, black and red pins show support for survivors of homicide victims.
- Murdered Children: In 2007, Congress designated September 25 as the National Day of Remembrance for Murder Victims. Robert and Charlotte Hullinger, of Cincinnati, formed Parents of Murdered Children following the 1978 murder of their 19-year-old daughter, Lisa, while she was studying in Germany. The annual day of observance is on the date Lisa was murdered. The annual National Day of Remembrance for Murder Victims provides the opportunity to remember those lost to homicide, and honor their memories. The purpose of this event is to focus on the impact of murder on families, and communities, and ways to support and serve survivors.
- Police Shooting Victims: Sometimes outmoded and abusive police practices prevail largely because no one has ever questioned them. In such cases, the simple act of spotlighting a problem can have a powerful effect that leads to reform.
- Sepsis: Sepsis is defined as "life-threatening organ dysfunction due to a dysregulated host response to infection." The new criteria are based on just three symptoms: Altered mental status, fast respiratory rate and low blood pressure.
- Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome: Shwachman-Diamond syndrome is an inherited condition that affects many parts of the body, particularly the bone marrow, pancreas, and skeletal system. Most cases of Shwachman-Diamond Syndrome are caused by mutations in the SBDS gene.
- Undocumented Students: According to the Migration Policy Institute’s most recent data, only 25 percent of undocumented citizens 25 years or older have received a high school equivalent degree. Those youth frequently encounter challenges when applying for college or employment. The College Board estimates that only 5 to 10 percent of undocumented students actually attend college. Although federal law does not prohibit undocumented students from attending U.S. colleges or universities, most states do not allow them to pay in-state tuition and they are not eligible for most federal loans, financial aid, and scholarships.
Black and White Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis: Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis is a neurological condition characterized by a brief but intense attack of inflammation in the brain and spinal cord. This may lead to damage of the layer of insulation around the nerves (myelin) within affected areas. ADEM often follows viral infection, or less often, vaccinations for measles, mumps, or rubella (MMR). Symptoms usually appear rapidly, beginning with fever, fatigue, headache, nausea and vomiting.
- Vaccine Injury: Any vaccine can cause side effects, but for the most part, the side effects are minor. Common side effects are pain, swelling, and redness at the injection site, low-grade fever, shivering, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, and joint aches. The side effects for all of the different vaccines can be found on the CDC web site (https://www.cdc.gov/vaccines/vac-gen/side-effects.htm). There are rare serious side effects that can be serious or even fatal. However, many more people died of vaccine-preventable diseases prior to vaccines than ever suffer serious complications of vaccines.
- Anti Corruption: Corruption is the use of public office for private gain. It includes crimes such as extortion, bribery, racketeering, or embezzlement. It also includes unethical acts and patronage such as revolving doors for government employees and capture of the regulatory process by the powerful and connected.
Black and White Pinstripes Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Breast Implant Illness / Breast Implant Injury: Breast Implant Illness is a period of sickness affecting the body caused by silicone or saline breast implants. Symptoms of breast implant illness vary from body to body due to personal differences, the type of breast implants and the progression of the illness. However, it appears that some symptoms show up earlier and more consistently such as fatigue, cognitive dysfunction (brain fog, memory loss), joint and muscle pain, hair loss, recurring infections and problems with thyroid and adrenals, or other endocrine glands.
- Silicone Poisoning / Silicone Toxicity from Breast Implants: Breast Implant Illness is a collection of symptoms that occur in people with breast implants. There is no official medical diagnosis for Breast Implant Illness. Symptoms may include fatigue, joint pain, brain fog, dry eyes and many other health concerns. Healthcare providers diagnose BII by ruling out other health conditions.
Blood Drop Type 1 Diabetes T1D Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 / Juvenile Diabetes / Type 1 Diabetes / T1D: Diabetes is a disease that occurs when blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high. Blood glucose is the main source of energy and comes from the food. Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. Sometimes the body doesn’t make enough, or any, insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. Glucose then stays in the blood and doesn’t reach the body's cells. The alternate color for T1D is blue and gray.
Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening lung condition that prevents enough oxygen from getting to the lungs and into the blood. Symptoms may include difficulty breathing, low blood pressure and organ failure, rapid breathing and shortness of breath.
- Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome: Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome is an inherited disease that mainly affects the brain, immune system, and the skin. Loss of white matter in the brain and abnormal deposits of calcium in the brain lead to an early-onset severe brain dysfunction that usually results in severe intellectual and physical disability. Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome is a Congenital and Genetic Disease. The alternate awareness ribbon for Aicardi-Goutieres Syndrome is Blue Jeans.
- Alexander Disease: Alexander Disease is a type of leukodystrophy characterized by the destruction of the myelin sheath and abnormal protein deposits known as Rosenthal fibers. Most cases of Alexander disease begin before age 2 years of age in the infantile form. Alexander Disease is a Congenital and Genetic Disease. The alternate awareness ribbon for Alexander Disease is Blue Jeans.
- Alopecia Areata: Alopecia Areata is an acquired skin disease that can affect all hair-bearing skin. Alopeca Areata is characterized by localized areas of non-scarring alopecia (hair loss).
- Anal Cancer: Anal Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the anus. Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) is the major risk factor for Anal Cancer.
- Angelman Syndrome: Angelman Syndrome is a genetic disorder that primarily affects the nervous system. Characteristic features include developmental delay, intellectual disability, severe speech impairment, problems with movement and balance, epilepsy, and a small head size. Individuals with Angelman Syndrome typically have a happy, excitable demeanor with frequent smiling, laughter, and hand-flapping movements. Angelman Syndrome is a Congenital and Genetic Disease. The alternate awareness ribbon for Angelman Syndrome is Blue Jeans.
- Ankylosing Spondylitis: Ankylosing Spondylitis is a form of arthritis featuring chronic inflammation of the spine and the sacroiliac joints. Over time, chronic inflammation of the spine (spondylitis) can lead to a complete fusion of the vertebrae, a process referred to as ankylosis. Ankylosis causes loss of mobility of the spine.
- Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita: Arthrogryposis Multiplex Congenita refers to the development of multiple joint contractures affecting two or more areas of the body prior to birth.
- Antisynthetase Syndrome: Antisynthetase Syndrome is a rare, chronic disorder that can affect multiple systems of the body. The disorder is immune-mediated, which means there is inflammation resulting from abnormal functioning of the immune system and the presence of specific autoantibodies that target a specific protein in the body.
- Apraxia: Aphasia is a neurological disorder caused by damage to the portions of the brain responsible for language. Primary signs of Apraxia include difficulty in expressing oneself when speaking, trouble understanding speech, and difficulty with reading and writing. Aphasia is not a disease, but a symptom of brain damage.
- Arthritis: Arthritis literally means inflammation of one or more joints. Arthritis is a joint inflammation disorder. Arthritis is frequently accompanied by joint pain. Joint pain is referred to as arthralgia.
- At-Risk Youth: An At-Risk youth is a child who is less likely to transition successfully into adulthood.
- Ataxia Telangiectasia: Ataxia Telangiectasia is a rare condition that affects the nervous system, the immune system, and many other parts of the body. Ataxia Telangiectasia is typically characterized by uncoordinated muscle movements, uncontrollable movements of the limbs, a weakened immune system with frequent infections, and an increased risk of cancers such as leukemia and lymphoma.
- Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy: Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy is a rare autoimmune disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and damages certain parts of the autonomic nervous system. Signs and symptoms may include severe orthostatic hypotension (low blood pressure upon standing). fainting, constipation, fixed and dilated pupils, urinary retention, and/or dry mouth and eyes.
- Autoimmune Autonomic Neuropathy: Autoimmune Autonomic Neuropathy is a disorder of difficulties maintaining blood pressure, usually combined with gastrointestinal problems and dry eyes or non-reactive pupils.
- Autonomic Dysfunction: Autonomic Dysfunction can affect a small part of the Autonomic Nervous System or the entire Autonomic Nervous System. Some symptoms of an autonomic nerve disorder include dizziness orthostatic hypotension, an inability to alter heart rate with exercise, or exercise intolerance.
- Back Pain: The back is a common target of several types of arthritis. Most back pain is due to strain, injury or posture problems affecting the ligaments or muscles of the spine. However, it may also be due to arthritis, scoliosis, inflamed nerves or a problem in a different part of the body.
- Bullying: Bullying is unwanted, aggressive behavior among school-aged children that involves a real or perceived power imbalance. The behavior is repeated, or has the potential to be repeated, over time. Bullying can also occur in teen-age or adult populations.
- Bursitis: Bursitis is a painful condition that affects the small, fluid-filled sacs that cushion the bones, tendons and muscles near the joints. Bursitis occurs when these sacs become inflamed. The most common locations for Bursitis are in the shoulder, elbow and hip.
- Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease: Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease occurs when crystals form deposits in the joint and surrounding tissues. The crystal deposits cause inflammation in the joint, which can damage the joint cartilage. The disease may take the form of osteoarthritis, a chronic rheumatoid arthritis-like inflammatory arthritis, or an acutely painful inflammatory condition called Pseudogout.
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome: Carpal Tunnel Syndrome is caused by irritation of the median nerve at the wrist. Irritation of the median nerve causes tingling and numbness of the thumb, index, and the middle fingers.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease: Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease is a group of disorders that affect the peripheral nerves. There are over forty types of Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease.
- CHARGE Syndrome: CHARGE Syndrome is a rare disorder that arises during early fetal development and affects multiple organ systems. Other characteristics of CHARGE Syndrome may not become apparent until later in life.
- Child Abuse / Child Neglect: Child Abuse is any injury that is intentionally inflicted on a child by a caregiver or during discipline. Neglect, physical, and sexual abuse are types of Child Abuse that typically result in reporting to and intervention by authorities.
- Child Exploitation: Child Exploitation can affect any child or young person, male or female, under the age of 18. The main types of Child Exploitation experienced by young people are criminal and sexual exploitation. The alternate color for Child Exploitation is white.
- Child Labor: Child Labor refers to the exploitation of children through any form of work that deprives children of their childhood, interferes with their ability to attend school regularly, and is mentally, physically, socially and morally harmful.
- Chondromalacia Patellae: Chondromalacia Patellae, also known as “runner’s knee,” is a condition where the cartilage on the undersurface of the patella (kneecap) deteriorates and softens. This condition is common among young, athletic individuals, but may also occur in older adults who have arthritis of the knee.
- Chronic Epstein Barr Virus: Chronic Active Epstein-Barr Virus infection is a very rare complication of an Epstein Barr Virus infection. Symptoms may include fever, swollen lymph nodes, and an enlarged liver and/or spleen. More serious complications may include anemia, nerve damage, liver failure, and/or interstitial pneumonia. Symptoms may be constant or come and go, and tend to get worse over time.
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: Chronic Fatigue Syndrome is defined by two major criteria, chronic severe fatigue for at least six months not caused by a diagnosable disease or relieved with rest and at least four other specific symptoms that occur simultaneously or after the development of severe fatigue. These include cognitive impairment, muscle and/or joint pain, new types of headaches, tender lymph nodes, sore throat, un-refreshing sleep, and malaise after exercise. In 2015, the Institute of Medicine proposed a new name for this syndrome, Systemic Exertion Intolerance Disease.
- Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy: Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy is a neurological disorder that causes progressive weakness and impaired sensory function in the legs and arms. Symptoms include tingling or numbness in the toes and fingers, weakness of the arms and legs, loss of deep tendon reflexes, fatigue, and abnormal sensations. CIDP is thought to be caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking and damaging the myelin sheath of the peripheral nerves. Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating Polyneuropathy is closely related to Guillain-Barre Syndrome and is considered the "chronic counterpart" of Guillain-Barre Syndrome.
- Coffin-Siris Syndrome: Coffin-Siris Syndrome is a genetic condition that causes variable degrees of learning disability, developmental delays, underdeveloped “pinky” toenails or fingernails, and distinct facial features.
- Colon Cancer, Adult: Colorectal Cancer is a malignant tumor arising from the inner wall of the large intestine (colon) or rectum. It is the third leading cause of cancer in both men and women in the U.S. Common risk factors for colorectal cancer include increased age, African-American race, a family history of colorectal cancer, colon polyps, and long-standing ulcerative colitis. Most colorectal cancers develop from polyps. Removal of colon polyps can aid in the prevention of colorectal cancer. Colon polyps and early cancer may have no cancer-specific signs or symptoms.
- Colon Cancer, Childhood: Carcinoma of the large bowel is rare in children . It is seen in 1 case per 1 million people younger than 20 years in the United States annually. Fewer than 100 cases are diagnosed in children each year in the United States. The alternate color for childhood colon cancer is gold.
- Colorectal Cancer, Adult: Colorectal Cancer often begins as a growth called a polyp inside the colon or rectum. Finding and removing polyps can prevent colorectal cancer. Worldwide, colorectal cancer is the third most common form of cancer.
- Colorectal Cancer, Childhood: Childhood Colorectal Cancer may be part of an inherited syndrome. Some colorectal cancers in young people are linked to a gene mutation that causes polyps to form that may turn into cancer later. The risk of colorectal cancer is increased by having certain inherited conditions. The alternate color for colorectal cancer in children is gold.
- Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy: Congenital Generalized Lipodystrophy is a rare disease characterized by a generalized lack of fat (adipose tissue) in the body. It is part of a group of diseases known as lipodystrophies.
- Cri du Chat Syndrome: Cri du chat Syndrome, or cat cry syndrome, is a genetic condition. Infants with this condition often have a high-pitched cry that sounds like that of a cat. The disorder is characterized by intellectual disability and delayed development, small head size, low birth weight, weak muscle tone in infancy, and distinctive facial features. While Cri Du Chat syndrome is a genetic condition, most cases are not inherited.
- Crime Victims Rights: Victims' rights are legal rights afforded to victims of crime. These may include the right to restitution, the right to a victims' advocate, the right not to be excluded from criminal justice proceedings, and the right to speak at criminal justice proceedings.
- Cryopyrin Associated Periodic Syndromes: Cryopyrin Associated Periodic Syndromes, also called Cryopyrin Associated Autoinflammatory Syndrome are three diseases related to a defect in the same gene. These diseases include Neonatal Onset Multi-System Inflammatory Disease, Muckle-Wells Syndrome and Familial Cold Auto-Inflammatory Syndrome. The differences are in their severity and the organs involved. The alternate color for Cryopyrin Associated Periodic Syndrome is orange.
- Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome: Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome is a condition characterized by recurrent, prolonged episodes of severe nausea and vomiting. Episodes of vomiting may last hours or days. Most people with Cyclic Vomiting Syndrome are symptom-free in between episodes. The condition can begin at any age, but it most often begins in childhood.
- Dandy-Walker Malformations / Dandy Walker: Dandy-Walker Complex is a group of disorders that affect the development of the brain. The changes in brain development are present from birth (congenital). Dandy-Walker Complex affects the formation of the area of the brain known as the cerebellum, which is responsible for coordinating movement, and the fluid-filled spaces around it. The alternate color for Dandy-Walk Malformations/Dandy Walker is Blue Jeans.
- Dermatomyositis, Adult: Dermatomyositis is one of a group of acquired muscle diseases called inflammatory myopathies, which are characterized by chronic muscle inflammation accompanied by muscle weakness and a skin rash. Dermatomyositis may occur at any age, but is most common in adults in their late 40s to early 60s, or children between 5 and 15 years of age. There is no cure for dermatomyositis, but the symptoms can be treated.
- Dermatomyositis, Childhood: Juvenile Dermatomyositis is a rare childhood disease that causes muscle weakness and skin rash. Juvenile Dermatomyositis affects about 3,000-5,000 children in the United States. Most cases occur between the ages of 5 and 10.
- Dysautonomia: Dysautonomia is an umbrella term used to describe several different medical conditions that cause a malfunction of the autonomic nervous system. The autonomic nervous system controls the "automatic" functions of the body. People living with various forms of Dysautonomia have trouble regulating the autonomic nervous system, which can result in lightheadedness, fainting, unstable blood pressure, abnormal heart rates, malnutrition, and in severe cases, death.
- Dyspraxia: Dyspraxia, a form of developmental coordination disorder, affects fine and/or gross motor coordination in children and adults. It may also affect speech. Dyspraxia is a lifelong condition.
- Dystonia: Dystonia is a disorder characterized by involuntary muscle contractions that cause slow repetitive movements or abnormal postures. Some forms of Dystonia are genetic but the cause for the majority of cases is not known.
- Education: Education helps students to develop critical skills, problem-solving skills and cognitive skills. Education allows students to become self-sufficient and Independent. Education helps students contribute to the well-being of society and create equal opportunities for both men and women.
- Enthesitis: Enthesitis is the medical term for inflammation of one or more entheses. Entheses are sites at which tendons and ligaments attach to bones. Enthesitis can cause symptoms such as joint pain and stiffness and problems with mobility. The condition can develop as a result of overuse, injuries, or underlying diseases.
- Enthesitis-Related Arthritis: Enthesitis-Related Arthritis is a disease predominantly affecting the joints and entheses of the lower extremities and has the potential to eventually affect the sacroiliac joints and spine evolving to Juvenile Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Epstein-Barr Virus: The Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV) is a herpes virus that is found worldwide and is a common cause of infectious mononucleosis. The cause of an Epstein-Barr Infection (mononucleosis) is EBV. Risk factors include intimate contacts with body secretions, especially saliva, and objects that may be exposed to body secretions of infected people. The Epstein-Barr Virus is contagious and is spread from person to person.
- Equal Access to Education: All students, regardless of race, color, national origin or zip code, deserve a high-quality education that includes resources such as academic and extracurricular programs, strong teaching, technology and instructional materials, and safe school facilities.
- Erb's Palsy: Erb’s Palsy, also known as Erb-Duchenne Palsy, is a nerve disorder that occurs as a result of an injury during birth. Erb’s Palsy affects about one or two out of every 1,000 children born.
- Familial Adenomatous Polyposis: Familial Adenomatous Polyposis is an inherited condition that causes cancer of the large intestine (colon) and rectum. People usually develop hundreds to thousands of noncancerous polyps in the colon as early as their teenage years. Over time, these polyps can become cancerous, leading to early-onset colorectal cancer at an average age of 39 years. Some people have a milder form of the condition called Attenuated Familial Adenomatous Polyposis which is generally characterized by fewer colon polyps and a delay in the development of colon cancer by 10-15 years.
- Familial Dysautonomia: Familial Dysautonomia is a genetic disorder. The disorder disturbs cells in the autonomic nervous system, which controls involuntary actions such as digestion, breathing, production of tears, and the regulation of blood pressure and body temperature. It also affects the sensory nervous system, which controls activities related to the senses, such as taste and the perception of pain, heat, and cold.
- Familial Mediterranean Fever: Familial Mediterranean Fever is a genetic auto-inflammatory disorder that causes recurrent fevers and painful inflammation of the abdomen, lungs and joints. Familial Mediterranean Fever is an inherited disorder that typically occurs in people of Mediterranean origin, including those of North African, Jewish, Arab, Armenian, Turkish, Greek or Italian ancestry.
- Fibromuscular Dysplasia: Fibromuscular Dysplasia is characterized by abnormal development or growth of cells in the walls of blood vessels (arteries) that can cause vessel narrowing. The carotid arteries are commonly affected. Arteries within the brain and kidneys can also be affected. Some people experience no symptoms of the disease while others may experience high blood pressure, dizziness or vertigo, chronic headache, ringing in the ears, weakness or numbness in the face, neck pain, or changes in vision.
- Fibrous Dysplasia: Fibrous Dysplasia is a skeletal disorder characterized by the replacement of normal bone with fibrous bone tissue. Fibrous dysplasia can affect any bone in the body. Though many people with this disorder do not have any symptoms, others may have bone pain, bones deformities, or an increased risk of fractures.
- Fifth Disease: Fifth Disease is a mild viral illness that most commonly affects children. It is called Fifth Disease because it is the fifth of the five viral rash diseases of childhood (the other four being measles, rubella, chicken pox and roseola).
- First Responders: A first responder is a person with specialized training who is among the first to arrive and provide assistance at the scene of an emergency, such as an accident, natural disaster, or terrorism. First Responders typically include law enforcement officers, paramedics, emergency medical technicians, and firefighters. First Responders also include those on the front line of the Covid Pandemic.
- Free Speech: Free Speech is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or a community to articulate their opinions and ideas without fear of retaliation, censorship, or legal sanction.
- Freedom of the Press: Freedom of the Press, protected by the First Amendment, is critical to a democracy in which the government is accountable to the people.
- Gout: Gout is a type of arthritis that causes sudden joint inflammation, usually in a single joint. Gout is caused by too much uric acid in the bloodstream and accumulation of uric acid crystals in tissues of the body.
- Guillain-Barre Syndrome: Guillain-Barré Syndrome is a rare syndrome in which the body’s immune system attacks part of the peripheral nervous system. Symptoms of Guillain-Barre Syndrome include muscle weakness, numbness, and tingling, which can increase in intensity until the muscles cannot be used at all (paralysis). The exact cause of Guillain-Barré Syndrome is unknown.
- Hand Washing: Since 2008, Global Hand Washing Day has been celebrated annually on October 15 to promote Hand Washing with soap and water as an easy, effective, and affordable way to prevent disease and save lives. It can dramatically reduce the risk of diarrhea and pneumonia, which can cause serious illness and death.
- Histiocytosis: Histiocytosis is a rare blood disease caused by abnormal increase in the number of immune cells called histiocytes. Histiocytosis is not technically a cancer. But, because it is so similar to cancer, it is primarily treated by oncologists with chemotherapy and/or steroids.
- Human Slavery (Modern Slavery): Modern Slavery is defined as the recruitment, movement, harboring or receiving of children, women or men through the use of force, coercion, abuse of vulnerability, deception or other means for the purpose of exploitation. Children are among the most vulnerable to slavery. There are 8.4 million children currently suffering exploitation all over the world. At least 4.8 million are enduring sexual exploitation. There are an estimated 20.1 million people in forced labor. They are coerced through violence, intimidation or subtler techniques such as debt-accumulation or the retention of documents.
- Human Trafficking: Human Trafficking is modern-day slavery and involves the use of force, fraud, or coercion to obtain some type of labor or commercial sex act. Every year, millions of men, women, and children are trafficked in countries around the world, including the United States. It is estimated that Human Trafficking generates many billions of dollars of profit per year, second only to drug trafficking as the most profitable form of transnational crime. Human Trafficking is a hidden crime as victims rarely come forward to seek help because of language barriers, fear of their traffickers, and/or fear of law enforcement.
- Huntington's Disease: Huntington Disease is an inherited condition that causes progressive degeneration of neurons in the brain. Signs and symptoms usually develop between ages 35 to 44 years and may include uncontrolled movements, loss of intellectual abilities, and various emotional and psychiatric problems.
- Hydrocephalus: Hydrocephalus is a condition in which the primary characteristic is excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain. The fluid is actually cerebrospinal fluid, a clear fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. The excessive accumulation of fluid results in an abnormal widening of spaces in the brain (ventricles) and potentially places harmful pressure on the tissues of the brain.
- Hypotension: For some people, low blood pressure causes no problems. However, for many people, abnormally low blood pressure (hypotension) can cause dizziness and fainting. In severe cases, low blood pressure can be life-threatening. A blood pressure reading below 90 for the top number (systolic) or 60 for the bottom number (diastolic) is generally considered Low Blood Pressure.
- Ichthyosis: Ichthyosis is a general term for a family of rare genetic skin diseases characterized by dry, thickened, scaling skin.
- Inclusion Body Myositis: Inclusion Body Myositis is a progressive muscle disorder characterized by muscle inflammation, weakness, and atrophy. The symptoms and rate of progression vary from person to person. Common symptoms include progressive weakness of the legs, arms, fingers, and wrists.
- Infant Airway Defects: Airway disorders can affect how babies and children breathe, eat, swallow, and sleep. These conditions may be diagnosed before birth or develop over time as the result of an infection or traumatic injury. Blocked airways can also occur suddenly. If your child experiences a sudden blockage in their airway from an object, allergic reaction, or any other reason, call 911 immediately.
- Infectious Arthritis: Infectious Arthritis is joint pain, soreness, stiffness and swelling caused by a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection that spreads from another part of the body. Depending on the type of infection, one or more joints may be affected.
- Intestinal Malrotation or Volvulus: Intestinal Malrotation is a condition that is congenital (present at birth) and results from a problem in the normal formation of the fetal intestines. There is a disruption in the usual steps that the intestines follow to arrive at the correct position within the abdomen. Malrotation causes the parts of the intestine to settle in the wrong part of the abdomen, which can cause them to become blocked or twist.
- Invisible Disabilities: Invisible Disabilities, or hidden disability, is an umbrella term that captures a spectrum of hidden disabilities or challenges, primarily neurological. Invisible disabilities, or hidden disabilities, are defined as disabilities that are not immediately apparent. Some people with visual or auditory disabilities who do not wear glasses or hearing aids, or discreet hearing aids, may not be obviously disabled. Some people who have vision loss may wear contacts.
- Juvenile Arthritis Also known as Pediatric Rheumatic Disease, Juvenile Arthritis is an umbrella term used to describe the many autoimmune and inflammatory conditions or Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases that can develop in children under the age of 16. Although the various types of juvenile arthritis share many common symptoms, like pain, joint swelling, redness and warmth, each type of Juvenile Arthritis is distinct and has its own special concerns and symptoms. Some types of Juvenile Arthritis affect the musculoskeletal system, but joint symptoms may be minor or nonexistent. Juvenile Arthritis can also involve the eyes, skin, muscles and gastrointestinal tract.
- Juvenile Dermatomyositis: Juvenile Dermatomyositis is a disease in children that causes skin rash and muscle inflammation, resulting in weak muscles. Juvenile Dermatomyositis is a type of autoimmune disease. In autoimmune diseases such as JDM, cells fight the body's own tissues and cells, causing inflammation and, in some cases, tissue damage.
- Klinefelter Syndrome (47,XXY): Klinefelter Syndrome, also known as the XXY condition, is a term used to describe males who have an extra X chromosome in most of their cells. Instead of having the usual XY chromosome pattern that most males have, these men have an XXY pattern. Even though all men with Klinefelter Syndrome have the extra X chromosome, not every XXY male has all of those symptoms.
- Langerhans Cell Histiocystosis: Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis is a disorder that primarily affects children, but is also found in adults. People with Langerhans Cell Histiocytosis produce too many Langerhans cells or histiocytes, a form of white blood cells found in healthy people that are supposed to protect the body from infection. In people with LCH, these cells multiply excessively and build up in certain areas of the body, causing tumor formations called granulomas.
- Laryngomalacia: Laryngomalacia is best described as floppy tissue above the vocal cords that falls into the airway when a child breathes in. It is the most frequent cause of noisy breathing (stridor) in infants and children. It is also the most common birth defect of the voice box (larynx).
- Leukodystrophy: Leukodystrophy is a type of rare genetic disorder that affects the brain, spinal cord, and other nerves in the body. It is caused by destruction of the white matter of the brain. The leukodystrophies are a group of disorders caused by mutations in the genes involved in making myelin. Myelin is needed to protect the nerves and the nerves cannot function normally without it.
- Malaria: Malaria is a serious and sometimes fatal disease caused by a parasite that commonly infects a certain type of mosquito which feeds on humans. Infection with malaria parasites may result in a wide variety of symptoms, ranging from absent or very mild symptoms to severe disease and even death. People who get malaria are typically very sick with high fevers, shaking chills, and flu-like illness. In general, malaria is a curable disease if diagnosed and treated promptly and correctly.
- McCune-Albright Syndrome: McCune-Albright Syndrome is a disorder that affects the skin, skeleton, and certain hormone-producing tissues. Cafe-au-lait spots of the skin are common and are usually the first apparent sign of McCune-Albright Syndrome. McCune-Albright Syndrome is not inherited.
- Metachromatic Leukodystrophy: Metachromatic Leukodystrophy is an inherited condition characterized by the accumulation of fats called sulfatides in cells, especially cells of the nervous system. This accumulation results in progressive destruction of white matter of the brain. Affected individuals experience progressive deterioration of intellectual functions and motor skills, such as the ability to walk. They also develop loss of sensation in the extremities, incontinence, seizures, paralysis, inability to speak, blindness, and hearing loss.
- Misophonia: Misophonia, translated as “hatred of sound,” is a chronic condition that causes intense emotional reactions to specific sounds. Symptoms usually start in childhood or early teenage years, and severity increases over time. The cause of Misophonia is not known.
- Myalgic Encephalomyelitis / Chronic Fatigue Syndrome / ME / CFIDS: Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (ME) is defined by distinctive neuro-muscular symptoms including prolonged muscle weakness after minor exertion, neurological symptoms indicative of cerebral dysfunction, circulatory impairment, and a chronic relapsing course. Symptoms vary and fluctuate and are usually chronic. The cause is still unknown, but most investigators believe that the disorder is most likely the result of an abnormal immune system response to an infection or virus.
- Myositis / Polymyositis / Dermatomyositis: Myositis is a term meaning inflammation in the muscles. There are several types of myositis, the most common being polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Polymyositis causes muscle weakness around the middle of the body and affects both sides of the body. Dermatomyositis causes muscle weakness as well as a skin rash.
- Neurocardiogenic Syncope (Vasovagal Syncope): Neurocardiogenic syncope (also known as vasovagal syncope) is a benign condition characterized by a self limited episode of systemic hypotension. Neurocardiogenic Syncope is caused by an abnormal or exaggerated autonomic response to various stimuli, of which the most common are standing and emotion.
- Osteoarthritis: Sometimes called Degenerative Joint Disease or “wear and tear” arthritis, Osteoarthritis is the most common chronic condition of the joints. It occurs when the cartilage or cushion between joints breaks down leading to pain, stiffness and swelling.
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Osteogenesis Imperfecta is a group of genetic disorders that primarily affect the bones. People with this condition have bones that break easily, often from little or no trauma, however, severity varies among affected people. Multiple fractures are common, and in severe cases, can even occur before birth. Milder cases may involve only a few fractures over a person's lifetime.
- Paget's Disease of the Bone: Paget's Disease is a chronic bone disorder that typically results in enlarged, deformed bones due to excessive breakdown and formation of bone tissue. This causes bones to weaken. It can also cause bone pain, arthritis, deformities or fractures.
- Palindromic Rheumatism: Palindromic Rheumatism is a rare episodic form of inflammatory arthritis. Between attacks, symptoms disappear and the affected joints go back to normal, with no lasting damage. Half of the people who have palindromic rheumatism eventually develop rheumatoid arthritis, which does cause permanent joint damage.
- Panhypopituitarism: Panhypopituitarism is a rare condition in which the pituitary gland stops making most or all hormones. Pituitary hormones help control the way many parts of the body work. Symptoms of the condition depend on the hormones that are missing. This condition may be caused by a tumor on or near the pituitary gland, infection, stroke, injury, surgery, or radiation therapy. It may also be inherited.
- Paralysis: Paralysis is the loss of voluntary movement. Paralysis that affects only one muscle or limb is partial paralysis, also known as palsy; paralysis of all muscles is total paralysis.
- Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome: Patellofemoral Pain Syndrome is a broad term used to describe pain in the front of the knee and around the patella, or kneecap. It is sometimes called "runner's knee" or "jumper's knee" because it is common in people who participate in sports.
- Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS): Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS) is a condition characterized by too little blood returning to the heart when moving from a lying down to a standing up position (orthostatic intolerance). Orthostatic Intolerance causes lightheadedness or fainting that can be eased by lying back down. In people with POTS, these symptoms are also accompanied by a rapid increase in heart rate. Although POTS can affect men and women of all ages, most cases are diagnosed in women between the ages of 15 and 50.
- Pseudogout: Pseudogout often resembles gout and, like gout, is caused by the formation of crystals in the joints. Instead of being composed of uric acid, as true gout crystals are, the crystals in Pseudogout are composed of a salt called calcium pyrophosophate dihydrate (CPPD). The condition is also called CPPD Disease.
- Reactive Arthritis: Reactive Arthritis, formerly known as Reiter's Syndrome, is a form of inflammatory arthritis that develops in response to an infection in another part of the body. Reactive Arthritis is an inflammatory type of Arthritis which affects the joints, and may affect the eyes, skin and urinary tract (bladder, vagina, urethra).
- Rectal Cancer: Rectal Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the rectum. Colorectal Cancer often begins as a growth called a polyp inside the colon or rectum.
- Reiter's Syndrome (Reactive Arthritis): Reactive Arthritis was formerly known as Reiter's Syndrome. Reactive Arthritis is a type of arthritis that occurs because of an infection.
- Restless Leg Syndrome: Restless Leg Syndrome is a condition marked by a strong urge to mover the legs and unpleasant leg sensations while resting and sleeping. The leg pain of Restless Leg Syndrome typically eases with motion of the legs and becomes more noticeable at rest.
- Reye Syndrome: Reye Syndrome is a rare but often severe and even fatal illness that primarily occurs in children and adolescents. Children diagnosed with Reye Syndrome generally present with vomiting and mental-status changes. The illness can resolve spontaneously or progress to coma and death. Although the cause is still unclear, studies have identified that there is a relationship between some viral infections and the use of aspirin medications. The CDC recommended educating parents about the dangers of treating children with aspirin in the 1980s, and now the disease occurs very rarely.
- Rheumatism: The term “rheumatism” was used historically to describe a number of rheumatic conditions. It is no longer used by medical professionals, who stress the importance of obtaining a specific diagnosis in order to get proper treatment. The alternate color for rheumatism is purple and blue.
- Save the Music in Our Schools: Research from a variety of sources indicates that all students do not have equitable access to music education. Music In Our Schools Month ® or “MIOSM®” is NAfME’s annual celebration during March which engages music educators, students, and communities from around the country in promoting the benefits of high quality music education programs in schools.
- Save the Waves: Save The Waves protects coastal ecosystems around the world in partnership with local communities, utilizing a unique combination of protected areas, economics, and direct action.
- Sensory Processing Disorder: Besides sound, touch, taste, sight and smell, there are also two other less known senses. They are proprioception, or a sense of body awareness, and vestibular sense, which involves movement, balance, and coordination. Kids with sensory processing issues experience too much or too little stimulation through these senses.
- Sex Slavery / Sex Trafficking:
- Human trafficking is a form of modern-day slavery. This crime occurs when a trafficker uses force, fraud or coercion to control another person for the purpose of engaging in commercial sex acts or soliciting labor or services against his/her will. Force, fraud, or coercion need not be present if the individual engaging in commercial sex is under 18 years of age.
- 1 (888) 373-7888 / TTY: 711 for the National Human Trafficking Hotline SMS: 233733 (Text "HELP" or "INFO")
- Hours: 24 hours, 7 days a week Languages: English, Spanish and 200 more languages
- Short Bowel Syndrome: Short Bowel Syndrome is a disorder characterized by malabsorption of nutrients due to problems involving the small intestine. In children the main causes include necrotizing enterocolitis, intestinal atresias, and intestinal volvulus.
- Sperm and Testicular Autoimmunity: Anti-sperm antibodies fight sperm. This happens when the immune system mistakenly targets sperm in a man's semen as an invader and damages or kills it.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal Stenosis is narrowing of the spinal column due to arthritis that leads to a bony overgrowth of vertebrae and a thickening of ligaments. If a significant overgrowth occurs, the narrowing can press on the nerves in the spine. The alternate color for Spinal Stenosis is cream.
- Spondylitis (See Ankylosing Spondylitis): Ankylosing Spondylitis has no known specific cause, though genetic factors seem to be involved. In particular, people who have a gene called HLA-B27 are at a greatly increased risk of developing Ankylosing Spondylitis. However, only some people with the gene develop the condition.
- Spondyloarthritis: Spondyloarthritis is an umbrella term for inflammatory diseases that involve both the joints and the entheses (the sites where the ligaments and tendons attach to the bones). The most common of these diseases is Ankylosing Spondylitis.
- Stevens-Johnson Syndrome: Stevens-Johnson Syndrome is a very severe reaction that mainly affects the skin, mucous membranes, and eyes. It is often triggered by particular medications. This syndrome is an emergency medical condition that usually requires hospitalization and can be life-threatening. Symptoms may include fever and flu-like symptoms, followed by painful blistering of the skin and mucous membranes.
- Surfriders: The Surfrider Foundation, based in San Clemente, California, is dedicated to the protection and enjoyment of the world's ocean, waves and beaches, for all people, through a powerful activist network.
- Syringomyelia: Syringomyelia is a condition in which a cyst, called a syrinx, forms within the spinal cord. This cyst expands and elongates over time, destroying the center of the spinal cord.
- Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis: Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis is the most common type of arthritis in children where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s tissues, causing inflammation in joints and potentially other areas of the body.
- Targeted Individuals of Bullying / Harassment / Stalking: Children can be bullied. No single factor puts a child at risk of being bullied (targeted) by others. Depending on the environment, some groups, such as lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgendered (LGBTQ+) youth, youth with disabilities, and socially isolated youth, may be at an increased risk of being bullied or targeted. Adults can also be bullied, especially in the workplace.
- Teen Pregnancy Prevention: Teen Pregnancy Prevention is a major public health concern because it directly affects the immediate and long-term well-being of mother, father, and child. Teen pregnancy and childbirth contribute significantly to dropout rates among high school females, increased health and foster care costs, and a wide range of developmental problems for children born to teen mothers.
- Tendinitis: Tendinitis is inflammation or irritation of a tendon, the thick fibrous cords that attach muscle to bone. The condition causes pain and tenderness just outside a joint.
- Transverse Myelitis: Transverse Myelitis is a neurological disorder caused by inflammation of the spinal cord, which carries nerve signals from the brain to the rest of the body. Most commonly, the upper spinal cord is affected, causing impaired leg movement, and problems controlling the bowel and bladder. The onset of symptoms may be acute or subacute. The cause of Transverse Myelitis may be unknown or associated with a wide variety of underlying health problems, including infections, immune system disorders, and other inflammatory disorders.
- Trash Free Seas: Ocean trash affects the health of wildlife, people and local economies. Trash in the water and on the shore can be mistaken as food by wildlife, or entangle animals with lethal consequences. Plastic also attracts and concentrates other pollutants from surrounding seawater, posing a contamination risk to those species that then eat it.
- Treacher Collins Syndrome: Treacher Collins Syndrome is a genetic disease that alters the development of bones and other tissues in the face. Signs and symptoms vary from almost unnoticeable face changes to severe facial and ear alterations, cleft palate and a restricted airway.
- Tuberous Sclerosis Complex: Tuberous Sclerosis is a genetic disorder characterized by the growth of numerous noncancerous (benign) tumors in many parts of the body. Common signs and symptoms include patches of unusually light-colored skin, areas of raised and thickened skin, and growths under the nails.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Type 2 Diabetes is an impairment in the way the body regulates and uses sugar (glucose) as fuel. This long-term, chronic condition results in too much sugar circulating in the bloodstream. Eventually, high blood sugar levels can lead to disorders of the circulatory, nervous and immune systems.
- Unidentified Missing Persons: The National Missing and Unidentified Persons System ( NamUs ) is a national clearinghouse and resource center for missing, unidentified, and unclaimed person cases throughout the United States.
- Usher Syndrome: Usher Syndrome is a genetic disorder characterized by abnormalities in the inner ear, hearing loss or deafness and progressive vision loss due to Retinitis Pigmentosa.
- Vocal Cord Dysfunction: Vocal Cord Dysfunction means that the vocal cords do not act normally. Instead of vocal cords opening up when you breathe in and out, the vocal cords close.
- Water Safety: Water Safety awareness combines a range of strategies and activities designed to keep children safe when in, on, or around water.
Blue and Gray Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 / Juvenile Diabetes / Type 1 Diabetes / T1D: Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 (T1D) is a condition in which cells in the pancreas stop producing insulin, causing abnormally high blood sugar levels. Lack of insulin results in the inability of the body to use glucose for energy and control the amount of sugar in the blood. T1D can occur at any age, but usually develops by early adulthood, most often in adolescence. The alternate color for T1D is the blood drop diabetes ribbon pin.
Blue and Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Adrenoleukodystrophy: Adrenoleukodystrophy, is a deadly genetic disease that most severely affects boys and men. This brain disorder destroys myelin, the protective sheath that surrounds the brain's neurons, the nerve cells that allow thinking and muscle control. The most devastating form of Adrenoleukodystrophy appears in childhood, generally between the ages of four and ten years old.
- Cytomegalovirus: Cytomegalovirus is a common virus in the same family as herpesvirus. Cytomegalovirus is spread by direct contact of body fluids, such as saliva, blood, urine, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. Thus breastfeeding, blood transfusions, organ transplants, and sexual contact are possible modes of transmission. Most healthy people do not experience any symptoms when infected with CMV, and it does not pose a serious health concern. A majority of adults have antibodies consistent with past infection.
- Neurofibromatosis Type 1: Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1) is a genetic disease that causes tumors to develop in the nervous system. Neurofibromatosis Type 1 causes skin changes, bone abnormalities, optic gliomas, and tumors on the nerve tissue or under the skin. Signs and symptoms are usually present at birth.
- Neurofibromatosis Type 2: Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2) causes acoustic neuromas, hearing loss, ringing in the ears, poor balance, brain and/or spinal tumors, and cataracts at a young age. It often starts in the teen years.
- Schwannomatosis : The third type of Neurofibromatosis is Schwannomatosis, which causes schwannomas, pain, numbness, and weakness. Schwannomas are rarely cancerous, but can lead to nerve damage and loss of muscle control.
Blue and White Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Adolescent Cancer (Teen Cancer): Teens and young adults with cancer are a group with special needs and have different cancers from young children and older adults. They also have unique social preferences. One study found that adolescent and young adult patients ranked the opportunity to meet other young adult survivors higher than receiving support from family and friends.
- Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome: Hip Impingement Syndrome, also known as Femoral Acetabular Impingement Syndrome, usually affects young and middle-aged adults. Pain is caused because two areas are contacting or impinging on each other, resulting in pain.
Blue and White Pinstripes Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis / ALS / Lou Gehrig’s Disease: Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord. Motor neurons reach from the brain to the spinal cord and from the spinal cord to the muscles throughout the body. The progressive degeneration of the motor neurons in ALS eventually leads to their death. When the motor neurons die, the ability of the brain to initiate and control muscle movement is lost. With voluntary muscle action progressively affected, patients in the later stages of the disease may become totally paralyzed.
- Congenital SMA with Arthrogryposis: Congenital SMA with Arthrogryposis is a rare disorder. Manifestations include severe contractures, scoliosis, chest deformity, respiratory problems, unusually small jaws, and drooping of the upper eyelids.
- Kennedy Disease / Kennedy’s Disease: Kennedy’s Disease, also known as Progressive Spinobulbar Muscular Atrophy, is an X-linked recessive disease. Daughters of individuals with Kennedy’s Disease are carriers and have a fifty percent chance of having a son affected with the disease. The onset of symptoms is variable and the disease may first be recognized between 15 and 60 years of age.
- Lou Gehrig's Disease: Lou Gehrig's Disease, also known as ALS, was first found in 1869. It was not until 1939 that Lou Gehrig brought national and international attention to the disease. Ending the career of one of the most beloved baseball players of all time, the disease is still most closely associated with the name, Lou Gehrig. Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects nerve cells in the brain and the spinal cord.
- Motor Neuron Diseases: Motor Neuron Diseases are a group of progressive neurological disorders that destroy motor neurons, the cells that control essential voluntary muscle activity such as speaking, walking, breathing, and swallowing. Over time, the ability to control voluntary movement can be lost.
- Post Polio Syndrome: Post Polio Syndrome is s a condition that can strike polio survivors decades after their recovery from poliomyelitis. Polio is an acute viral disease that destroys motor neurons. Many people who are affected early in life recover and develop new symptoms many decades later.
- Primary Lateral Sclerosis: Primary Lateral Sclerosis affects the upper motor neurons of the arms, legs, and face. It occurs when specific nerve cells in the motor regions of the cerebral cortex gradually degenerate, causing the movements to be slow and effortful.
- Progressive Bulbar Palsy (Progressive Bulbar Atrophy) involves the brain stem, the bulb-shaped region containing lower motor neurons needed for swallowing, speaking, chewing, and other functions.
- Progressive Muscular Atrophy: Progressive Muscular Atrophy is marked by slow but progressive degeneration of only the lower motor neurons.
- Pseudobulbar Palsy: Pseudobulbar Palsy is a condition characterized by the inability to control facial movements and is caused by a variety of neurological disorders.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Spinal Muscular Atrophy is a hereditary disease affecting the lower motor neurons. In SMA, insufficient levels of the SMN protein lead to degeneration of the lower motor neurons, producing weakness and wasting of the skeletal muscles. SMA in children is classified into three types, based on ages of onset, severity, and progression of symptoms. The alternate color for SMA is cream.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type I: Werdnig-Hoffmann Disease is evident by the time a child is 6 months old. The alternate color for SMA Type I is cream.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type II: The intermediate form, usually begins between 6 and 18 months of age. The alternate color for SMA Type II is cream.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type III: Kugelberg-Welander Disease appears between 2 and 17 years of age. The alternate color for SMA Type III is cream.
Braille Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Blindness (Visually Handicapped/Visually Challenged): Blindness is a loss of useful sight. Blindness can be temporary or permanent. There are many causes of blindness. The correct terms for referring to blindness include visually handicapped and visually challenged.
Brown Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Childhood Diarrhea: Dehydration is the major concern with Childhood Diarrhea. In most cases, treatment includes replacing lost fluids. Antibiotics may be prescribed when bacterial infections are the cause.
- Effects of Nicotine on Young Adults: Youth and young adults are uniquely at risk for long-term, long-lasting effects of exposing their developing brains to nicotine. These risks include nicotine addiction, mood disorders, and permanent lowering of impulse control.
- Flavors Hook Kids: The tobacco industry uses fun flavors and tech devices to hook kids on nicotine. Why kids? A developing brain is easier to addict.
- Great American Smoke Out: The Great American Smoke Out is an opportunity for smokers to commit to healthy, smoke-free lives – not just for a day, but year round. The Great American Smoke Out provides an opportunity for individuals, community groups, businesses, health care providers, and others to encourage people to use the date to make a plan to quit, or plan in advance and initiate a smoking cessation plan on the day of the event. The Great American Smoke Out event challenges people to stop smoking and helps people learn about the many tools they can use to help them quit and stay quit.
- Health Risks of E Cigarettes / Vaping Health Risks of Smokeless Tobacco: The majority of vape liquids contain nicotine. In addition to being highly addictive, nicotine alters the neurotransmitters in the brain. Vaping has been found to slow brain development in teens and affect memory, decision-making, concentration, self-control, and mood .
- Nicotine = Brain Poison: Nicotine is poison for the adolescent brain. Nicotine changes the way connections form in the brain. Nicotine can interfere with attention and learning. Nicotine can increase anxiety, mood swings, and irritability.
- No Butts: California Smokers' Helpline is a free telephone counseling program that can help you #quitsmoking or using #tobacco. Call 1-800-NO-BUTTS.
- Public Hygiene: Public hygiene is the science and practices to make our surroundings clean from the spread of communicable diseases. It is equally important for personal hygiene to keep the environment clean and free of germs.
- Public Sanitation: Poor Public sanitation is linked to transmission of diarrhea diseases such as cholera and dysentery, as well as typhoid, intestinal worm infections and polio. It contributes to the spread of antimicrobial resistance.
- Smoking Cessation: Quitline Services Call 1-800-QUIT-NOW (1-800-784-8669) if you want help quitting. This is a free telephone support service that can help those who want to stop smoking or using tobacco. Callers are routed to their state quit lines, which offer several types of quit information and services.
- Sports Related Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy: Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a progressive brain condition that's thought to be caused by repeated blows to the head and repeated episodes of concussion. It is particularly associated with contact sports, such as boxing or football. Most of the available studies are based on ex-athletes.
- Unsafe Drinking Water: Safe and readily available water is important for public health, whether it is used for drinking, domestic use, food production or recreational purposes. Improved water supply and sanitation, and better management of water resources, can boost countries’ economic growth and contribute greatly to poverty reduction. In 2010, the UN General Assembly explicitly recognized the human right to water and sanitation. Everyone has the right to sufficient, continuous, safe, acceptable, physically accessible and affordable water for personal and domestic use.
Burgundy Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm: An Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm is an enlarged area in the lower part of the major vessel that supplies blood to the body (aorta). The aorta runs from the heart through the center of the chest and abdomen.
- Adhesions: Adhesions are bands of scar-like tissue that form between two surfaces inside the body and cause them to stick together. Pain from adhesions is caused by the increased muscle contraction of the gut trying to force its contents through the narrowed segment . Adhesions can result in long term abdominal pain (chronic pain syndrome), which can be difficult to treat.
- Amyloidosis: Amyloidosis is a term that represents several different types of diseases where an abnormal protein called amyloid is produced. These amyloid protein fibers can attach and deposit into organs, tissues, nerves and other places in the body. When that happens, normal function of the area can be affected. Amyloidosis is considered a rare disease by the U.S. Office of Rare Diseases (ORD), a segment of the National Institutes of Health (NIH). It is also referred to as an “orphan” disease. As a classified rare disease by the U.S. government, this means that it is estimated that all of the types of Amyloidosis combined affects less than 200,000 people in the U.S. population.
- Antiphospholipid Syndrome: Antiphospholipid Syndrome is a disorder of the immune system that is characterized by excessive clotting of blood and/or certain complications of pregnancy and the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies (such as anti-cardiolipin or lupus anticoagulant antibodies) in the blood. Clotting disorders associated with Antiphospholipid Syndrome include stroke, blood clots deep within the legs and clots in the lungs.
- Aortic Aneurysm: Aortic Aneurysm is an abnormal bulge that occurs in the wall of the major blood vessel (aorta) that carries blood from the heart to the body. Aortic Aneurysms can occur anywhere in the aorta and may be tube-shaped or round.
- Aortic Dissection: Aortic Dissection is a serious condition in which a tear occurs in the inner layer of the body's main artery (aorta). Blood rushes through the tear, causing the inner and middle layers of the aorta to split (dissect). If the blood goes through the outside aortic wall, aortic dissection is often deadly.
- Arteriovenous Malformations: Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is a rare disease characterized by tangled blood vessels that connect arteries and veins. These tangles disrupt normal blood flow and oxygen circulation and can develop anywhere in the body but are most commonly found afflicting a person’s brain or spine.
- Bacterial Meningitis: Bacteria or a virus can cause meningitis. Viral meningitis is more common, but Bacterial Meningitis is more serious. It can lead to brain damage, paralysis, or stroke. In some cases, it can be fatal.
- Brain Aneurysm: Brain Aneurysms, also referred to as Cerebral Aneurysms or Intracranial Aneurysms, are a weak bulging spot on the wall of a brain artery. Over time, the blood flow within the artery pounds against the thinned portion of the wall and aneurysms form silently from wear and tear on the arteries. As the artery wall becomes gradually thinner from the dilation, the blood flow causes the weakened wall to swell outward. This pressure may cause the aneurysm to rupture and allow blood to escape into the space around the brain. A ruptured brain aneurysm commonly requires advanced surgical treatment.
- Coagulation Disorders: Coagulation Disorders are conditions that affect the blood's clotting activities. Hemophilia, Von Willebrand disease, clotting factor deficiencies, hyper-coagulable states and Deep Venous Thrombosis (DVT) are all coagulations disorders. Hemophilia and Von Willebrand disease are among the best known. The alternate color for Coagulation Disorders is red.
- Congenital Megacolon (Hirschsprung's Disease): Congenital Megacolon is a condition of the large intestine (colon) that causes difficulty passing stool. Hirschsprung's Disease involves missing nerve cells in the muscles of part or all of the large intestine (colon). Present at birth, it causes difficulty passing stool. Surgery is needed to bypass the affected part of the colon or remove it entirely.
- Congenital Vascular Cavernous Malformation: Cavernous Malformations are dilated blood vessels that are characterized by multiple distended "caverns" of blood-filled vasculature through which the blood flows very slowly. Cavernous aMlformations are primarily located in the brain, but can also be found in the spinal cord, on the skin, and more rarely in the retina.
- Cystic Hygroma: A Cystic Hygroma is a fluid-filled sac that results from a blockage in the lymphatic system. It is most commonly located in the neck or head area, but can be located anywhere in the body. When it is identified on pregnancy ultrasound, there is an increased risk for miscarriage. In some cases, it is not discovered until a person is older.
- Disabled Adults: More than 21 million US adults 18–64 years of age have a disability.
- Factor V Leiden Thrombophilia: Factor V Leiden Thrombophilia is a genetic disorder that makes it more likely to develop a blood clot. It is estimated that 95% of people with Factor V Leiden never develop a clot. When a clot does form, the clot most often occurs in the leg or lungs.
- Headache: The head is one of the most common sites of pain in the body. Head pain can be classified as being one of three types: 1) primary headache, 2) secondary headache, and 3) cranial neuralgias, facial pain, and other headaches. Common primary headaches include tension, migraine, and cluster headaches.
- Hemangioma: Hemangioma is a birthmark that most commonly appears as a rubbery, bright red nodule of extra blood vessels in the skin. A hemangioma grows during the first year of life, and then recedes over time. A child who had a hemangioma during infancy usually has little visible trace of the growth by age 10.
- Hemiplegic Migraine: Hemiplegic Migraine is a rare type of migraine with aura that occurs with motor weakness during the aura. Signs and symptoms vary but may include visual disturbances, sensory loss, difficulty with speech, weakness on one side of the body, confusion, and impaired consciousness.
- Hemochromatosis: Hemochromatosis is one of the most common genetic disorders in the United States. It is an inherited condition in which the body absorbs and stores too much iron. The extra iron builds up in several organs, especially the liver, and can cause serious damage. Without treatment, the disease can cause these organs to fail.
- Hirschsprung Disease: Hirschsprung Disease is a congenital disease where the large intestine does not have nerve cells needed to expel stools (feces) normally from the body. About one in 5000 newborns have Hirschsprung Disease.
- Hughes Syndrome: Hughes Syndrome, or Antiphospholipid Antibody Syndrome, is an autoimmune condition that causes thickening of the circulating blood. The immune system produces abnormal blood proteins called antiphospholipid antibodies, which cause blood platelets to clump together. Hughes Syndrome is sometimes called ‘sticky blood syndrome’ because people with this condition are more likely to form clots in blood vessels. People with certain autoimmune diseases such as Systemic Lupus eErythematosus (SLE) are at increased risk of having Hughes Syndrome.
- Meningitis: Meningitis is an inflammation of the meninges. The meninges are the three membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord. Meningitis can occur when fluid surrounding the meninges becomes infected. The most common causes of meningitis are viral and bacterial infections.
- Meningococcal Meningitis: Meningitis caused by the bacteria Neisseria meningitidis is called Meningococcal Meningitis. With meningococcal meningitis, the bacteria infect the lining of the brain and spinal cord and cause swelling.
- Multiple Myeloma/Plasma Cell Neoplasms: Multiple Myeloma is a form of cancer that occurs due to abnormal and uncontrolled growth of plasma cells in the bone marrow. When present, the most common symptom is anemia, which can be associated with fatigue and shortness of breath.
- Parkes Weber Syndrome: Parkes Weber Syndrome is a rare congenital condition characterized by a large number of abnormal blood vessels. Parkes Weber Syndrome typically includes a capillary malformation on the skin, excessive growth of bone and soft tissue of the affected limb, and multiple abnormal connections between arteries and veins which can potentially lead to heart failure.
- Platelet Disorders: Platelet Disorders are conditions that occur when the platelet count in the blood is too high or too low or platelets do not work properly. Platelets are tiny blood cells that are made in the bone marrow from larger cells. During injury, platelets form a plug, called a blood clot, to seal a wound. Blood clots help stop or slow down bleeding.
- Polio Survivor: Surviving paralytic polio can be a life-changing experience. Individuals may be permanently physically disabled to varying degrees.
- Port-Wine Stain Birthmark: Port-Wine Stains are a kind of vascular birthmark, meaning that they're related to the skin's blood vessels. A Port-Wine Stain Birthmark happens when chemical signals in tiny blood vessels don't "turn off," and those blood vessels get bigger. The extra blood turns the skin red.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Sickle Cell Anemia is one of a group of inherited disorders known as Sickle Cell Disease. It affects the shape of red blood cells, which carry oxygen to all parts of the body. In Sickle Cell Anemia, some red blood cells are shaped like sickles or crescent moons. These sickle cells become rigid and sticky, which can slow or block blood flow. The alternate color for Sickle Cell Anemia is red.
- Tuberculous Meningitis: Tuberculous Meningitis is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis . This is the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. The bacteria spread to the brain and spine from another place in the body, usually the lung. Tuberculous Meningitis is very rare in the United States.
Camo Military Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Loss of a Military Husband / In Memory of a Military Husband
- Loss of a Military Wife / In Memory of a Military Wife
- Loss of a Soldier / In Memory of a Soldier
- Military and Troop Support: Support our troops is a slogan commonly used in the United States and Canada in reference to each country's military forces or troops. The slogan has been used during recent conflicts, including the Gulf War and the Iraq War.
- Military Families: Military F amilies are defined as those with Immediate family members related by blood, marriage, or adoption to a current member of the U.S. armed forces, including one who is deceased .
- Military Personnel Injured in Active Duty: Common combat injuries include second and third degree burns, broken bones, shrapnel wounds, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, nerve damage, paralysis, loss of sight and hearing, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and limb loss. The alternate color for Military Personnel Injured in Active Duty is purple.
- Parents of Fallen Soldiers: Gold star families include spouses, children, parents, siblings or others whose loved one died in service to our nation. They are a vital part of our country's military community and history.
- POW / MIA: POW/MIA Recognition Day is commemorated on the third Friday of every September, a date that’s not associated with any particular war. In 1979, Congress and the president passed resolutions making it official after the families of the more than 2,500 Vietnam War POW/MIAs pushed for full accountability. The alternate color for POW/MIA Recognition Day is black.
Cloud Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia: Congenital Diaphragmatic Hernia (CDH) is a condition present before birth characterized by abnormal development of the diaphragm. The severity of CDH may range from a thinned area in part of the diaphragm, to its complete absence. CDH may allow the stomach and intestines to move through an opening into the chest cavity, crowding the heart and lungs.
Copper Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Menkes Syndrome: Menkes Disease or Menkes Syndrome is an inherited disorder in which the body has a problem absorbing copper. The disease affects both mental and physical development.
Cranberry Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Chronic Bladder Infections: A chronic urinary tract infection is a repeated or prolonged bacterial infection of the bladder or urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
- Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Disorder: Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ) Syndrome is pain in the jaw joint that can be caused by a variety of medical problems. The temporomandibular joint connects the lower jaw to the skull in front of the ear. Certain facial muscles that control chewing are also attached to the lower jaw.
Cream Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Degenerative Disc Disease: Not actually a disease, Degenerative Disc Disease refers to a condition in which pain is caused from a disc that loses integrity. Several factors can cause discs to degenerate, including age.
- Developmental-Dysplasia of Hip: In babies and children with Developmental-Dysplasia of the Hip, the hip joint has not formed normally. The ball is loose in the socket and may be easy to dislocate. Although Developmental-Dysplasia of Hip is most often present at birth, it may also develop during a child's first year of life.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy: Spinal Muscular Atrophy is a hereditary disease affecting the lower motor neurons. In Spinal Muscular Atrophy, insufficient levels of the SMN protein lead to degeneration of the lower motor neurons, producing weakness and wasting of the skeletal muscles. SMA in children is classified into three types, based on ages of onset, severity, and progression of symptoms. The alternate color for Spinal Muscular Atrophy is blue and white pinstripes.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type I: Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type I (Werdnig-Hoffmann Disease) is evident by the time a child is 6 months old. The alternate color for SMA Type I is blue and white pinstripes.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type II: Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type II is the intermediate form, usually begins between 6 and 18 months of age. The alternate color for SMA Type II is blue and white pinstripes.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type III: Spinal Muscular Trophy Type III (Kugelberg-Welander Disease) appears between 2 and 17 years of age. The alternate color for SMA Type III is blue and white pinstripes.
- Spinal Stenosis: Spinal Stenosis is narrowing of the spinal canal. Spinal Stenosis can put pressure on the spinal cord and the nerves within the spine. It commonly occurs in the neck and lower back. The condition is often caused by age-related wear and tear. The alternate color for Spinal Stenosis is blue.
Denim Blue Jeans Awareness Ribbons: Causes and colors symbolize, stand for and support :
- Congenital Diseases and Disorders: Congenital Diseases and Disorders or Congenital Anomalies are defined as structural or functional anomalies that occur during intrauterine life. Also called birth defects, congenital disorders, or congenital malformations, these conditions develop prenatally and may be identified before or at birth, or later in life.
- Genetic Diseases and Disorders: Genetic Diseases and Disorders are a disease caused in whole or part by a change in the DNA sequence away from the normal sequence. Genetic Disorders can be caused by a mutation in one gene, by mutations in multiple genes, by a combination of gene mutations and environmental factors, or by damage to chromosomes.
- Global Genes® - Rare and Genetic Diseases: Denim Blue Jeans Awareness Ribbon for Rare Diseases as Designated by Global Genes® .: Global Genes® is a leading rare disease patient advocacy organization with the mission to eliminate the challenges of rare disease. Through their work, they build awareness, educate the global community, and provide critical connections and resources that equip advocates to become activists for their disease. Global Genes® promotes the needs of the rare disease community as a whole under a unifying symbol of hope – the Blue Denim Genes Ribbon ™. Genes and jeans are a natural fit. Both are universal, come in pairs and are unique to the individual. The blue jeans ribbon is a simple concept that anyone can embrace and a powerful way to raise awareness for rare disease. Learn more about genetic diseases at NIH's National Human Genome Research Institute .
Figure 8 Infinity Neurodiversity Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Neurodiversity: Neurodiversity and neurological differences need to be recognized and respected as any other human variation. These differences can include those labeled with Dyspraxia, Dyslexia, Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder, Dyscalculia, Autistic Spectrum, Tourette Syndrome, and others.
Fuchsia Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Eosinophilic Diseases: Eosinophils are a normal cellular component of the blood and certain tissues, including the spleen, lymph nodes, thymus, and the submucosal areas of the gastrointestinal, respiratory, and genitourinary tracts. Counts of 0 to 450 eosinophils per cubic millimeter of blood are considered within normal limits. Eosinophilic Disorders occur when eosinophils are found in above-normal amounts in various parts of the body.
- Eosinophilic Esophagitis: Eosinophilic Esophagitis is an allergic condition that happens in the esophagus. The esophagus becomes inflamed and does not contract properly. It can get narrowed and develop rings or abscesses. The symptoms happen when the immune system makes white blood cells in reaction to an allergen.
- Feminism: Feminism is the belief in the social, political, and economic equality of the sexes. Feminist activism is the struggle for that equality. Core beliefs include: Sexism exists; Sexism against women (misogyny) is enduring, pervasive, systemic, cultural, and ingrained; Men and women should have equal rights and opportunities; Women are intellectual and social equals to men; Women should be recognized and treated as equals to men.
- Gestational Pemphigoid: Gestational Pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune skin disorder that occurs during pregnancy. Gestational Pemphigoid belongs to the pemphigoid group of autoimmune skin diseases that cause blistering of the skin and mucosal membranes
- Herpes Gestationis / Pemphigoid Gestationis: Herpes Gestationis, also known as Pemphigoid Gestationis, is a rare, autoimmune disease that occurs during the second or third trimester, but it has been reported in the first trimester. It flares at delivery and usually resolves spontaneously over weeks or months after delivery.
- Keep Abortion Legal / I Stand With Planned Parenthood®: No one is free unless they control their own body. Abortion is an essential part of sexual and reproductive health care. Both in-clinic and medication abortions are very safe. Nearly a fourth of women in America will have an abortion by age 45. Abortion has been practiced for thousands of years in cultures throughout the world. The ability to control one's own personal medical decisions, including whether to end a pregnancy, is a fundamental human right. Restricting abortion access is dangerous and inhumane.
- Self Love: Self Love is regard for one's own well-being and happiness (chiefly considered as a desirable rather than narcissistic characteristic).
Gold Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Childhood: Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many immature lymphocytes. Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The alternate color for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is orange.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Childhood: Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia, also called Acute Myelogenous Leukemia or AML, is a type of blood cancer. It is a quickly progressing disease in which too many abnormal white blood cells are found in the bone marrow, the soft, spongy center of long bones. In Acute Myeloid Leukemia, myeloid stem cells become immature white blood cells called myeloblasts or “blasts.” These blasts do not become healthy white blood cells. Instead, they build up in the bone marrow, so there is less room for healthy white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets. In addition, these abnormal cells are unable to fight off infection. The alternate color for Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia is orange.
- Adrenocortical Carcinoma, Childhood: Adrenocortical Tumor is a cancer of the adrenal glands. These glands produce many hormones. The disease is called "functioning ACT" if it causes more hormones to be made than normal, or "nonfunctioning ACT" if it does not. In children, about nine out of 10 adrenocortical tumors are "functioning." In adolescents (teens), only about five out of 10 adrenocortical tumors are "functioning." Thelternate color for Adrenocortical Carcinoma in children is green.
- Astrocytomas, Childhood: Astrocytomas are tumors that start in star-shaped brain cells called astrocytes. An astrocyte is a type of glial cell. Glial cells hold nerve cells in place, bring food and oxygen to them, and help protect them from disease, such as infection. Astrocytoma is the most common type of glioma diagnosed in children. It can form anywhere in the central nervous system. Brain and spinal cord tumors can be benign or malignant. The alternate color for Astrocytomas in children is gray.
- Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumors, Childhood: Brain and spinal cord tumors can be benign or malignant. Central nervous system Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor is a very rare, fast-growing tumor of the brain and spinal cord. It usually occurs in children aged three years and younger, although it can occur in older children and adults. About half of these tumors form in the cerebellum or brain stem. The alternate color for Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumors in children is gray.
- Bladder Cancer, Childhood: In children, bladder cancer is not likely to spread and the prognosis is usually excellent after surgery to remove the tumor. The alternate color for Bladder Cancer in children is purple, blue and marigold.
- Brain Stem Glioma, Childhood: Gliomas are tumors formed from glial cells. Glial cells in the brain hold nerve cells in place, bring food and oxygen to them, and help protect them from disease, such as infection. Most Childhood Brain Stem Gliomas form in a part of the brain stem called the pons. The alternate color for Childhood Brain Stem Glioma is gray.
- Brain Tumors, Childhood: Brain Tumors occur when there is a genetic alteration in the normal cells in the brain. The alteration causes the cells to undergo a series of changes that result in a growing mass of abnormal cells. Primary brain tumors involve a growth that starts in the brain, rather than spreading to the brain from another part of the body. Brain tumors may be low grade (less aggressive) or high grade (very aggressive). The cause of Primary Brain Tumors is unknown. Central Nervous System Tumors are the most common solid tumor in children. The alternate color for brain tumors in children is gray.
- Breast Cancer, Childhood: Breast Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the breast. Breast Cancer may occur in both male and female children. Breast cancer is the most common cancer among females aged 15 to 39 years. The alternate color for breast cancer in children is pink.
- Breast Feeding – The Gold Standard: Breastfeeding provides unmatched health benefits for babies and mothers. It is the clinical gold standard for infant feeding and nutrition, with breast milk uniquely tailored to meet the health needs of a growing baby. It is important to create supportive and safe environments for mothers who choose to breastfeed.
- Bronchial Adenoma, Childhood: Bronchial Adenoma is a rare type of cancer that starts in the mucous glands and ducts of the lung airways or windpipe, and in the salivary glands. Although the word "adenoma" means a noncancerous tumor, most Bronchial Adenomas are cancer and can spread to other parts of the body. The alternate color for Bronchial Adenoma in children is pearl.
- Bronchial Tumors, Childhood: The alternate color for Bronchial Tumors in children is pearl. Tracheobronchial Tumors begin in the cells that line the surface of the lung. Most Tracheobronchial Tumors in children are benign and occur in the trachea or large airways of the lung. Sometimes, a slow-growing Tracheobronchial Tumor becomes cancer that may spread to other parts of the body.
- Bronchogenic Carcinoma, Childhood: Primary lung cancer is extremely rare in children. Adenocarcinoma is the most common type of bronchogenic carcinoma in children and adults.The alternate color for Bronchogenic Carcinoma in children is pearl.
- Cancers of Childhood, Unusual: Childhood Cancer is a rare disease with about 15,000 cases diagnosed annually in the United States in individuals younger than 20 years. The U.S. Rare Diseases Act of 2002 defines a rare disease as one that affects populations smaller than 200,000 persons and, by definition, all pediatric cancers are considered rare. The Rare Diseases Act of 2002 amended the Pubic Health Service Act to: (1) establish an Office of Rare Diseases at the National Institutes of Health; and (2) provide for rare disease regional centers of excellence.
- Carcinoid Tumors, Childhood: Carcinoid Tumors are a specific type of neuroendocrine tumor. Carcinoid Tumors most often develop in the GI tract, in organs such as the stomach or intestines, or in the lungs. Sometimes neuroendocrine tumors in children form in the appendix. The tumor is often found during surgery to remove the appendix. The alternate color for Carcincoid Tumors in children is zebra.
- Cardiac (Heart) Tumors, Childhood: Most tumors that form in the heart are not cancerous. Before birth and in newborns, the most common benign heart tumors are teratomas. An inherited condition called Tuberous Sclerosis can cause heart tumors to form in a fetus or newborn. Malignant tumors that begin in the heart are even more rare than benign heart tumors in children. The alternate color for cardiac (heart) tumors in children is red.
- Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors, Childhood: Germ cells are a type of cell that form as a fetus develops. These cells later become sperm in the testicles or eggs in the ovaries. Sometimes while the fetus is forming, germ cells travel to other parts of the body and grow into germ cell tumors. Germ Cell Tumors that form in the brain or spinal cord are called CNS Germ Cell Tumors. The alternate color for Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors in children is gray.
- Central Nervous System Tumors and Cancer, Childhood: A Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumor begins when healthy cells in the brain or the spinal cord change and grow out of control, forming a mass. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. The alternate color for Central Nervous System Tumors and cancer in children is gray.
- Cervical Cancer, Childhood: Cervical Cancer is rarely seen in children and teens. Cases of cervical cancer in women under 20 are seen in only about 0.2 percent of females. In very rare cases in the past, some cervical cancer was seen in girls whose mothers were treated with a drug called diethylstilbestrol (DES), which was used to prevent miscarriage. DES has not been used with pregnant women since the early 1970s. The alternate color for Cervical Cancer in children is teal and white.
- Childhood Cancers: Although pediatric cancer death rates have declined by nearly 70 percent over the past four decades, cancer remains the leading cause of death from disease among children. The most common types of cancer diagnosed in children ages 0 to 14 years are Leukemias, Brain and other Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumors, and Lymphomas.
- Chordoma, Childhood: Chordoma is a very rare type of bone tumor that forms anywhere along the spine from the base of the skull to the tailbone. Childhood Chordoma is linked to the condition Tuberous Sclerosis, a genetic disorder in which tumors that are benign form in the kidneys, brain, eyes, heart, lungs, and skin. The alternate color for Chordoma in children is yellow.
- Colorectal Cancer, Childhood: Childhood Colorectal Cancer may be part of an inherited syndrome. Some colorectal cancers in young people are linked to a gene mutation that causes polyps to form what may turn into cancer later. The alternate color for colorectal cancer in children is blue.
- Craniopharyngioma, Childhood: Childhood Craniopharyngiomas are rare tumors usually found near the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. The alternate color for Craniopharyngioma in children is gray.
- Dermatomyositis, Childhood: Juvenile Dermatomyositis is a rare childhood disease that causes muscle weakness and skin rash. Juvenile Dermatomyositis is a rare disease that causes inflammation of the blood vessels, muscles and skin. It affects about 3,000-5,000 kids in the United States. Most cases occur between the ages of 5 and 10. The alternate color for Juvenile Dermatomyositis is blue.
- Embryonal Tumors, Central Nervous System, Childhood: Central Nervous System (CNS) Embryonal Tumors form in embryonic cells that remain in the brain after birth. Most CNS Embryonal Tumors in children are malignant. Malignant Brain Tumors are likely to grow quickly and spread into other parts of the brain. Benign Brain Tumors grow and press on nearby areas of the brain. They rarely spread to other parts of the brain. The alternate color for Embryonal Tumors of the Central Nervous System in children is gray.
- Ependymoma, Childhood: Childhood Ependymoma is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord. Brain and spinal cord tumors can be benign or malignant. Ependymomas form from ependymal cells that line the ventricles and passageways in the brain and the spinal cord. The alternate color for Ependymomas in children is gray.
- Esophageal Cancer, Childhood: Esophageal Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the esophagus. Most Esophageal Tumors in children begin in the thin, flat calls that line the esophagus. The alternate color for Esophageal Cancer in children is periwinkle.
- Extracranial Germ Cell Tumor, Childhood: Extracranial Germ Cell Tumors are tumors that develop from germ cells and can form in many parts of the body. They are most common in teenagers and can often be cured. Childhood Extracranial Germ Cell Tumors form from germ cells in parts of the body other than the brain.
- Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumor, Childhood: Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors develop from germ cells. Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors form outside the gonads (testicles and ovaries). When cells that are meant to form sperm in the testicles or eggs in the ovaries travel to other parts of the body, they may grow into Extragonadal Germ Cell Tumors.
- Gastric (Stomach) Cancer, Childhood Gastric (stomach) Cancer occurs when cancer cells form in the lining of the stomach. The alternate color for gastric (stomach) cancer in children is periwinkle.
- Germ Cell Tumors, Childhood: Germ Cell Tumors are malignant (cancerous) or nonmalignant (benign, non-cancerous) tumors that are comprised mostly of germ cells. Germ cells are the cells that develop in the embryo and become the cells that make up the reproductive system in males and females. Most ovarian tumors and testicular tumors are of germ cell origin.
- Heart Tumors, Childhood: Most tumors that form in the heart are benign. Before birth and in newborns, the most common benign heart tumors are teratomas. An inherited condition called Tuberous Sclerosis can cause heart tumors to form in a fetus or newborn. Malignant tumors that begin in the heart are even more rare than benign heart tumors in children. The alternate color for heart tumors in children is red .
- Hepatoblastoma: Hepatoblastoma is a rare tumor that originates in cells in the liver. It is the most common cancerous (malignant) liver tumor in early childhood. Most Hepatoblastoma Tumors begin in the right lobe of the liver.
- Hodgkin Disease/Hodgkin Lymphoma, Childhood: Hodgkin Lymphoma, also called Hodgkin’s Lymphoma and Hodgkin Disease, is a cancer of the lymphoid system. The lymphoid system is made up of various tissues and organs, including the lymph nodes, tonsils, bone marrow, spleen, and thymus. These organs produce, store and carry white blood cells to fight infection and disease. Approximately 1,180 children and adolescents each year are diagnosed with Hodgkin Lymphoma in the United States. It has been reported in infants and very young children, but it is considered rare before the age of five. The majority of Hodgkin Lymphoma cases are in teenagers (age 15-19). Hodgkin Lymphoma is the most common cancer of teenagers and young adults. The alternate color for Hodgkin Disease/Hodgkin Lymphoma in children is violet.
- Intraocular Melanoma, Childhood: Intraocular Melanoma begins in the middle of three layers of the wall of the eye. The alternate color for Intraocular Melanoma in children is black and navy.
- Liver Cancer, Childhood: Hepatoblastoma is a solid tumor cancer of the liver. This primary liver tumor which accounts for half of all liver tumors in children is rare with approximately 50 to 70 new cases diagnosed in the United States each year. It occurs slightly more often in boys than girls. Like most childhood cancers, scientists do not know the cause of Liver Cancer. Some children however are at an increased risk of being diagnosed with Hepatoblastoma due to other genetic conditions. These include: Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome, Familial Adenomatous Polyposis, and Aicardi Syndrome. The alternate color for Liver Cancer in children is green.
- Lung Cancer, Childhood: In children, the most common lung tumors are Tracheobronchial Tumors and Pleuropulmonary Blastoma. Tracheobronchial Tumors begin in the cells that line the surface of the lung. Most Tacheobronchial Tumors in children are benign and occur in the trachea or large airways of the lung. Pleuropulmonary Blastomas form in the tissue of the lung and pleura. The alternate color for lung cancer in children is pearl.
- Melanoma, Childhood: Even though Melanoma is rare, it is the most common skin cancer in children. It occurs more often in adolescents aged 15 to 19 years. The alternate color for Melanoma in children is black.
- Mesothelioma, Childhood: Mesothelioma is a rare cancer most commonly diagnosed in people in their 60s and 70s, but doctors have reported roughly 300 cases worldwide in young adults, children and even infants. In most cases of mesothelioma diagnosed in youth and childhood, there is no history of exposure to asbestos, which is a much more common cancer among adults. The alternate color for mesothelioma in children is pearl.
- Midline Tract Carcinoma with NUT Gene Changes: Childhood Midline Tract Carcinoma is a disease in which cancer cells form in the respiratory tract or other places along the middle of the body. Midline Tract Carcinoma is sometimes caused by a change in the NUT gene. Midline Tract Cancer may form when part of the DNA from chromosome 15 (called the NUT gene) joins with the DNA from another chromosome or when there are other changes to the NUT gene.
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndrome, Childhood: Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndromes are inherited disorders that affect the endocrine system. Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia Syndromes may cause the growth of too many normal cells or tumors that may be benign or malignant. The two main types of MEN syndromes are MEN1 Syndrome (Werner Syndrome) and MEN2 (Sipple Syndrome).
- Neuroblastoma, Childhood: Neuroblastoma is a tumor that develops from a nerve in a child, usually before the age of 5. It occurs in the abdomen near the adrenal glands, but it can also occur in other parts of the body. It is considered an aggressive tumor because it often spreads to other parts of the body (metastasizes).
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Childhood: Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (sometimes called NHL, or just Lymphoma) is a cancer that starts in cells called lymphocytes. Lymphocytes are part of the body’s immune system. NHL is not common in children, but it can occur. The alternate color for childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is Lime Green.
- Ovarian Cancer, Childhood: Ovarian Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the ovary. Most ovarian tumors in children are benign. They occur most often in females aged 15 to 19 years. There are several types of Malignant Ovarian Tumors: Germ Cell Tumors that start in egg cells in females; Epithelial Tumors that start in the tissue covering the ovary; and Stromal Tumors that begin in stromal cells, which make up tissues that surround and support the ovaries. The alternate color for Ovarian Cancer in children is teal.
- Pancreatic Cancer, Childhood: Pancreatic Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the pancreas. There are four types of pancreatic cancer in children including: Solid Pseudopapillary Tumor of the Pancreas, Pancreatoblastoma, Islet Cell Tumors, and Pancreatic Carcinoma. The alternate color for pancreatic cancer in children is purple.
- Paraganglioma, Childhood: Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma are rare tumors that come from the same type of nerve tissue. Paraganglioma forms outside the adrenal glands near the carotid artery, along nerve pathways in the head and neck, and in other parts of the body. Some Paragangliomas make extra catecholamines called adrenaline and noradrenaline.
- Pheochromocytoma, Childhood: Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma are rare tumors that come from the same type of nerve tissue. Pheochromocytoma forms in the adrenal glands. Some Pheochromocytomas release extra adrenaline and noradrenaline into the blood and cause symptoms. The alternate color for pheochromocytoma in children is green or zebra.
- Retinoblastoma, Childhood: Retinoblastoma is a rare type of eye cancer in the retina that typically develops before the age of 5. It usually affects only one eye, but 1/3 of children with retinoblastoma develop cancer in both eyes. The first sign is typically a visible whiteness in the pupil called "cat's eye reflex," which is particularly noticeable in photographs taken with a flash. Other signs and symptoms include strabismus; persistent eye pain, redness or irritation; and blindness or poor vision in the affected eye(s). The alternate color for retinoblastoma in children is white.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, Childhood (Soft Tissue Sarcoma): Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which cancer cells form in soft tissues of the body. In children, the tumors form most often in the arms, legs, or trunk. Soft tissue sarcoma in children may respond differently to treatment, and may have a better prognosis than soft tissue sarcoma in adults. The alternate color for Rhabdomyosarcoma in children is yellow.
- Skin Cancer: Skin Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. There are three types of skin cancer: Melanoma, Squamous Cell Skin Cancer and Basal Cell Skin Cancer. Even though Melanoma is rare, it is the most common skin cancer in children. The alternate color for skin cancer in children is orange.
- Stomach (Gastric) Cancer, Childhood: Stomach cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the lining of the stomach. The alternate color for stomach (gastric) cancer in children is periwinkle.
- Testicular Cancer, Childhood: Testicular Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. There are two types of testicular tumors: Germ Cell Tumors that start in sperm cells in males; and Non-Germ Cell Tumors that begin in the tissues that surround and support the testicles. These tumors may be benign or malignant. The alternate color for Testicular Cancer in children is orchid.
- Unknown Primary Cancer, Childhood: Adenocarcinomas, Melanomas, and Embryonal Tumors are common tumor types that appear and it is not known where the cancer first formed. Embryonal Tumors such as Rhabdomyosarcomas and Neuroblastomas are most common in children.
- Unusual Cancers, Childhood: Unusual Cancers of Childhood are cancers rarely seen in children. Cancer in children and adolescents is rare. Since 1975, the number of new cases of childhood cancer has slowly increased. Since 1975, the number of deaths from childhood cancer has decreased by more than half. Unusual cancers are so rare that most children's hospitals are likely to see less than a handful of some types in several years. Because the unusual cancers are so rare, there is not a lot of information about what treatment works best. A child's treatment is often based on what has been learned from treating other children. Sometimes, information is available only from reports of the diagnosis, treatment, and follow-up of one child or a small group of children who were given the same type of treatment.
- Vaginal Cancer, Childhood: Vaginal Cancer forms in the vagina. The vagina is the canal leading from the cervix to the outside of the body. At birth, a baby passes out of the body through the vagina (also called the birth canal). The alternate color for vaginal cancer in children is teal.
- Wilms' Tumor and Other Childhood Kidney Tumors, Childhood: Kidney Cancer can develop in adults and children. The main types of Kidney Cancer are Renal Cell Cancer, Transitional Cell Cancer, and Wilms' Tumor. Certain inherited conditions increase the risk of kidney cancer. The alternate color for Wilms' Tumor and other childhood Kidney Cancer is orange.
Graphite Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Higher Education, Not Higher Education Debt: All people deserve equitable access to a high quality education, regardless of race, class, gender, sexual orientation, immigration status, or any social identity. Unfortunately, the already unaffordable and still skyrocketing cost of higher education is risking our nation’s future. A college degree is required for most jobs that offer a livable wage in America. Making higher education unaffordable and sustainable jobs inaccessible without a degree only further perpetuates the cycles of intergenerational poverty. The goal is to ensure that quality higher education is affordable and accessible to all, without the burden of debt or financial hardship.
- Homeless College Students: The root causes of homelessness and food insecurity on college campuses are complex, as many of the factors are interrelated. Key contributing factors include financial insecurity, housing insecurity, work or family obligations, and student loan debt.
- Lead Free Kids: Exposure to lead can seriously harm a child’s health. Even at low levels, lead exposure can cause damage to the brain and nervous system, slowing growth and development and lowering IQ. Exposure to lead can lead to problems with hearing and speech, behavior, paying attention, and learning.
- Lead Poisoning: Lead Poisoning is entirely preventable. The key is stopping children from coming into contact with lead and treating children who have been poisoned by lead.
- Living Wage for Teachers: Though Business.org found teachers earn 11 percent more than the average salary across the nation, making $65,090 a year while the national average salary is $58,260, one survey found 80 percent of Americans feel teachers are underpaid.
- Student Loan Debt: Forty-five million Americans have student loan debt - that's about one in 7 Americans (13.5%), according to an analysis of January 2022 census data. Those ages 25-to-34 are the most likely to hold student loan debt, but the greatest amount is owed by those 35 to 49, more than $600 billion, federal data show. Among all borrowers, women typically borrow more for college compared to men (and attain more degrees), according to 2020 data by the American Association of University Women. And Black students borrow more often and greater amounts compared with all other races and ethnicities, according to federal data.
Gray Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Acute Flaccid Myelitis: Acute Flaccid Myelitis is a rare but serious condition. It affects the nervous system, specifically the area of the spinal cord called gray matter, which causes the muscles and reflexes in the body to become weak.
- Allergies: Allergies occur when the immune system reacts to a foreign substance — such as pollen, bee venom or pet dander — or a food that doesn't cause a reaction in most people. The immune system produces substances known as antibodies.
- Allergy-Induced Asthma: The same substances that trigger hay fever (allergic rhinitis) symptoms, such as pollen, dust mites and pet dander, may also cause asthma signs and symptoms. In some people, skin or food allergies can cause asthma symptoms. This is called allergic asthma or allergy-induced asthma.
- Aphasia: Aphasia, a disturbance in the formulation and comprehension of language, is due to damage to brain tissue areas responsible for language. Aphasia may occur suddenly or develop over time, depending on the type and location of brain tissue damage. Causes of Aphasia are mainly due to strokes, severe head trauma, brain tumors, and brain infections.
- Asthma and Allergies: Asthma and allergies often go hand-in-hand. Asthma is a disease of the bronchial tubes, which carry air in and out of the lungs. There are several different types of asthma. Allergic-asthma is a type of asthma that is triggered by an allergy (for example, pollen or mold spores). According to the American Academy of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology , many of the 25 million Americans with asthma also have allergies, and this is called Allergic Asthma.
- Astrocytomas, Childhood: Astrocytomas are tumors that start in star-shaped brain cells called astrocytes. Astrocytoma is the most common type of glioma diagnosed in children. It can form anywhere in the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord). Brain and spinal cord tumors can be benign or malignant. The alternate color for Astrocytomas in children is gold.
- Atypical Teratoid / Rhabdoid Tumors, Adult: Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor is predominantly a childhood tumor and has only been rarely reported in adults. Therefore, treatment regimens are often extrapolated from the pediatric experience.
- Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor, Childhood: Brain and spinal cord tumors can be benign or malignant. Central Nervous System (CNS) Atypical Teratoid/Thabdoid Tumor is a very rare, fast-growing tumor of the brain and spinal cord. It usually occurs in children aged three years and younger, although it can occur in older children and adults. The alternate color for Atypical Teratoid/Rhabdoid Tumor in children is gold.
- Brain Cancer: Brain Cancer can arise from many different types of brain cells or occur when cancer cells from another part of the body spread (metastasize) to the brain.
- Brain Fog: “Brain fog” isn’t a medical condition. It’s a term used for certain symptoms that can affect the ability to think. A person may feel confused or disorganized or find it hard to focus or put your thoughts into words. Certain medical conditions can cause Brain Fog. These include taking certain medications, Covid-19, lupus, and pregnancy.
- Brain Stem Glioma, Childhood: Gliomas are tumors formed from glial cells. Glial cells in the brain hold nerve cells in place, bring food and oxygen to them, and help protect them from disease. The brain stem is the part of the brain that controls breathing, heart rate, and the nerves and muscles used in seeing, hearing, walking, talking, and eating. The alternate color for Childhood Brain Stem Glioma is gold.
- Brain Tumors, Adult: Primary Brain Tumors can be either malignant (contain cancer cells) or benign (do not contain cancer cells). A Primary Brain Tumor is a tumor which begins in the brain tissue. If a cancerous tumor starts elsewhere in the body, it can spread cancer cells, which grow in the brain. These type of tumors are called secondary or metastatic brain tumors.
- Brain Tumors, Childhood: A Brain Tumor occurs when there is a genetic alteration in the normal cells in the brain. The alteration causes the cells to undergo a series of changes that result in a growing mass of abnormal cells. Primary Brain Tumors involve a growth that starts in the brain, rather than spreading to the brain from another part of the body. The alternate color for Brain Tumors in children is gold.
- Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors, Childhood (Neurological Cancer: Germ Cells are a type of cell that form as a fetus develops. These cells later become sperm in the testicles or eggs in the ovaries. Sometimes while the fetus is forming, germ cells travel to other parts of the body and grow into Germ Cell Tumors. The alternate color for Central Nervous System Germ Cell Tumors in children is gold.
- Central Nervous System Tumors and Cancer, Adult: Unlike cancers that start in other parts of the body, tumors that start in the brain or spinal cord rarely spread to distant organs. Even so, Brain or Spinal Cord Tumors are rarely considered benign (non-cancerous). These tumors can still cause damage by growing and spreading into nearby areas, where they can destroy normal brain tissue. And unless they are completely removed or destroyed, most Brain or Spinal Cord Tumors will continue to grow and eventually be life-threatening.
- Central Nervous System Tumors and Cancer, Childhood: Central Nervous System (CNS) Tumors begins when healthy cells in the brain or the spinal cord change and grow out of control, forming a mass. A tumor can be cancerous or benign. A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A benign tumor means the tumor can grow but will not spread. The alternate color for Central Nervous System Tumors and Cancer in children is gold.
- Craniopharyngioma, Adult: Craniopharyngiomas are slow growing benign tumors of the sellar and parasellar region with an overall incidence rate of approximately 1.3 per million. During adulthood there is a peak incidence between 40 and 44 years.
- Craniopharyngioma, Childhood: Childhood Craniopharyngiomas are rare tumors usually found near the pituitary gland and the hypothalamus. The alternate color for Craniopharyngioma in children is gold.
- Embryonal Tumors, Central Nervous System, Childhood: Central Nervous System (CNS) Embryonal Tumors form in embryonic cells that remain in the brain after birth. CNS Embryonal Tumors tend to spread through the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) to other parts of the brain and spinal cord. The tumors may be malignant (cancer) or benign (no cancer). The alternate color for Embryonal Tumors, Central Nervous System in children, is gold.
- Ependymoma, Adult: Ependymomas in adults are rare, accounting for only 3% of all primary central nervous system tumors diagnosed each year in the United States. Although Ependymomas may arise in various regions throughout the central nervous system, the frequency of location varies by age. Spinal Cord Ependymomas are most prevalent in adults, whereas this location is quite rare in the pediatric population.
- Ependymoma, Childhood: Ependymoma is a tumor that appears most often in the brain and sometimes in the spinal cord. It is a type of glioma , meaning it starts in the support cells of the brain. This cancer occurs more frequently in children, accounting for 5-10% of all pediatric brain tumors, but it can also affect adults. The alternate color for Childhood Ependymoma is gold.
- Glioblastoma: Glioblastoma is a malignant (cancerous) brain tumor that develops from a specific type of brain cell called an astrocyte. These cells help support and nourish neurons (nerve cells of the brain) and form scar tissue that helps repair brain damage in response to injury. Glioblastomas are often very aggressive and grow into surrounding brain tissue.
- Glioblastoma Multiforme: Glioblastoma, also referred to as a grade IV Astrocytoma, is a fast-growing and aggressive brain tumor. It invades the nearby brain tissue, but generally does not spread to distant organs.
- Hyperglycemia: Hyperglycemia or high blood sugar is an abnormally high blood glucose (blood sugar) level in the blood. Hyperglycemia is a hallmark sign of diabetes (both Type 1 Dabetes and Type 2 Diabetes) and Pre-diabetes. Diabetes is the most common cause of high blood sugar. Other conditions that can cause high blood sugar are pancreatitis, Cushing's syndrome, unusual hormone-secreting tumors, pancreatic cancer, certain medications, and severe illnesses.
- Hypoglycemia: Hypoglycemia is the medical term for low blood sugar. It typically occurs as a side effect of medications for Diabetes. The normal range of blood glucose is from 70 to 100 mg/dL in an individual without diabetes, Most people will feel the effects and symptoms of low blood sugar when blood glucose levels are lower than 50 mg/dL. Symptoms and signs include nervousness, dizziness, trembling, sweating, hunger, weakness, and palpitations.
- Personality Disorders: Personality Disorders are a group of mental illnesses. They involve long-term patterns of thoughts and behaviors that are unhealthy and inflexible. The behaviors cause serious problems with relationships and work. People with personality disorders have trouble dealing with everyday stresses and problems. They often have stormy relationships with other people.
- Pituitary Tumors: Pituitary Tumors are usually not cancer and are called pituitary adenomas. They grow slowly and do not spread. Rarely, pituitary tumors are cancer and they can spread to distant parts of the body. Pituitary Tumors represent from 10% to 25% of all intracranial neoplasms.
Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize. stand for and support :
- Achondroplasia: Achondroplasia is a disorder of bone growth that prevents the changing of cartilage to bone.
- Adrenal Cancer: Adrenal Cancer is a condition that occurs when abnormal cells form in or travel to the adrenal glands. A cancerous tumor of the adrenal gland is called an Adrenal Cortical Carcinoma. A noncancerous tumor of the adrenal gland is called a benign adenoma.
- Adrenocortical Carcinoma Cancer, Adult: Adrenocortical Carcinoma is a rare tumor. Although it mainly occurs in adults, children can be affected, too. Historically, only about 30% of these malignancies are confined to the adrenal gland at the time of diagnosis. However, recently, more have been diagnosed at early stages, most likely due to the widespread use of high-quality imaging techniques.
- Adrenocortical Carcinoma, Childhood: Adrenocortical Tumor is a cancer of the adrenal glands, which are triangle-shaped glands located on both kidneys. These glands produce many chemicals, called hormones. The alternate color for Adrenocortical carcinoma in children is gold.
- Anencephaly: Anencephaly is a type of neural tube defect characterized by abnormal development of the brain and the bones of the skull. Anencephaly occurs when the 'cephalic' or head end of the neural tube fails to close, causing the absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp. Infants with this disorder are born without a forebrain (the front part of the brain) and a cerebrum (the thinking and coordinating part of the brain). The remaining brain tissue is often exposed (not covered by bone or skin).
- Anti GBM / Anti TBM Nephritis: Anti-GBM/Anti-TBM Nephritis is a rare autoimmune disorder caused by autoantibodies that attack the walls of small blood vessels (capillaries) in the kidney. Anti-GBM Disease that only affects the kidneys is called Anti-GBM Glomerulonephritis.
- Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility: Autoimmune Gastrointestinal Dysmotility is a limited form of dysautonomia that affects digestive tract motility. Although rare, the condition can be debilitating, with individuals experiencing nausea and dramatic weight loss.
- Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome: Beckwith-Wiedemann Syndrome is a growth disorder that can affect several parts of the body. Babies and children are larger than normal usually until age 8, when growth slows down, resulting in an average height in adults.
- Bile Duct Cancer/Cholangiocarcinoma: Cancer of the bile duct (also called Cholangiocarcinoma) is extremely rare. The true incidence of bile duct cancer is unknown because establishing an accurate diagnosis is difficult.
- Biliary Atresia: Biliary Atresia is a rare, progressive obliterative cholangiopathy of the extrahepatic bile ducts, occurring in the embryonic/ perinatal period. This leads to severe and persistent jaundice with an unfavorable course in the absence of treatment.
- Bipolar Disorder: Bipolar Disorder, also called Bipolar I Disorder and previously called Manic Depression, is a condition that involves mood swings with at least one episode of mania and may also include repeated episodes of depression. Bipolar Disorder afflicts up to 4 million people in the United States and is the fifth leading cause of disability worldwide.
- Bone Marrow Disease: Bone Marrow Disease causes problems with the stem cells or how they develop. For example, in Leukemia, a cancer of the blood, the bone marrow makes abnormal white blood cells. In Aplastic Anemia, the bone marrow doesn't make red blood cells. In Myeloproliferative Disorders, the bone marrow makes too many white blood cells.
- Bone Marrow Donation/Bone Marrow Donor: To become a donor it just takes a small vial of blood or cheek swab to be typed as a bone marrow/stem cell donor. There are many people who are desperately waiting to find a donor match. You may be able to save someone’s life. There are donor registry sites throughout the country.
- Brain Injury: Traumatic Brain Injuries account for thousands of deaths each year in the U.S. As well, significant numbers of people suffer temporary and permanent disability due to brain injury. Head injury does not necessarily mean brain injury. Bleeding in the brain usually occurs at the time of injury and can continue increasing pressure within the skull. However, symptoms may develop immediately or progress gradually over time.
- Cerebral Palsy: Cerebral Palsy refers to a group of neurological disorders that can affect the brain and/or spinal cord.
- Cholangiocarcinoma: Cholangiocarcinoma is bile duct cancer. Liver cancer includes hepatocellular carcinoma and bile duct cancer (cholangiocarcinoma). Risk factors include chronic infection with hepatitis B or C and cirrhosis of the liver.
- Chemical Sensitivity: While certain chemicals are known to cause toxicity or adverse reactions including allergies, some people have sensitivities to a wide spectrum of environmental agents. These people have been dubbed to have Multiple Chemical Sensitivities or Idiopathic Environmental Intolerance.
- Chromosome 12q, Deletion: Chromosome 12q, Deletion is a chromosome abnormality that occurs when there is a missing copy of the genetic material located on the long arm (q) of chromosome 12. The severity of the condition and the signs and symptoms depend on the size and location of the deletion and which genes are involved.
- Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE):n Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE) is a degenerative brain disease found in athletes, military veterans, and others with a history of repetitive brain trauma. In CTE, a protein called Tau forms clumps that slowly spread throughout the brain, killing brain cells. CTE has been seen in people as young as 17, but symptoms do not generally begin appearing until years after the onset of head impacts.
- Cirrhosis of the Liver: Cirrhosis is a serious degenerative disease that occurs when healthy cells in the liver are damaged and replaced by scar tissue, usually as a result of alcohol abuse or chronic hepatitis. As liver cells give way to tough scar tissue, the organ loses its ability to function properly.
- Climate Change: Climate Change refers to long-term shifts in temperatures and weather patterns. These shifts may be natural, but since the 1800s, human activities have been the main driver of climate change, primarily due to the burning of fossil fuels (like coal, oil, and gas) which produces heat-trapping gases.
- CLOVES Syndrome: CLOVES Syndrome is a rare condition that is primarily characterized by congenital overgrowth of fatty tissue, malformations of the vascular system, epidermal nevi, and spinal or skeletal abnormalities. The severity of the condition and the associated signs and symptoms vary significantly from person to person.
- Dermatillomania (Skin Picking Disorder): People that suffer from Dermatillomania exhibit symptoms that include repetitive touching, rubbing, scratching, picking at, and digging into their skin. Some people do this to remove irregularities or perceived imperfections while others do it obsessively for other reasons.
- Dwarfism: Dwarfism is a condition that is characterized by short stature, usually resulting in an adult height of 4'10" or shorter. Dwarfism can and most often does occur in families where both parents are of average height.
- Environmental Protection: Environmental protection is the practice of protecting the natural environment by individuals, organizations and governments. Its objectives are to conserve natural resources and the existing natural environment and, where possible, to repair damage and reverse trends.
- Eye Cancer/Ocular Cancer: Two types of cancers can be found in the eye. The first is primary Intraocular Cancer. In adults, Melanoma is the most common Primary Intraocular Cancer, followed by Primary Intraocular Lymphoma. In children, Retinoblastoma is the most common primary Intraocular Cancer, and Medulloepithelioma is the next most common, but is still extremely rare. Secondary Intraocular Cancers start somewhere else in the body and then spread to the eye. These are not truly “eye cancers,” but they are actually more common than Primary Intraocular Cancers. The most common cancers that spread to the eye are breast and lung cancers. Most often these cancers spread to the part of the eyeball called the uvea.
- Eye Injury Prevention: Wear personal protective eyewear, such as goggles, face shields, safety glasses, or full face respirators. The eye protection chosen for specific work situations depends upon the nature and extent of the hazard, the circumstances of exposure, other protective equipment used, and personal vision needs.
- Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva: Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva is a disorder in which skeletal muscle and connective tissue, such as tendons and ligaments, are gradually replaced by bone (ossified). This condition leads to bone formation outside the skeleton that restricts movement.
- Gallbladder Cancer: Gallbladder Cancer is a rare disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the gallbladder.
- Gastroparesis: Gastroparesis means weakness of the muscles of the stomach. Gastroparesis results in poor grinding of food in the stomach into small particles and slow emptying of food from the stomach into the small intestine.
- Gastroschisis: Gastroschisis is a birth defect that occurs when a baby's intestines extend outside of the body through a hole next to the belly button. This type of defect is known as an abdominal wall defect. Sometimes other organs are also involved.
- Genocide: Genocide is a term used to describe violence against members of a national, ethnic, racial or religious group with the intent to destroy the entire group. The word came into general usage only after World War II, when the full extent of the atrocities committed by the Nazi regime against European Jews during that conflict became known. In 1948, the United Nations declared genocide to be an international crime; the term would later be applied to the horrific acts of violence committed during conflicts in the former Yugoslavia and in the African country of Rwanda in the 1990s.
- Glaucoma: Glaucoma is an eye disease that is often associated with elevated intraocular pressure, in which damage to the optic nerve can lead to loss of vision and even blindness. Glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness in the world.
- Global Warming: Global Warming is happening now. Globally, the average surface temperature has increased more than one degree Fahrenheit since the late 1800s. Most of that increase has occurred over just the past three decades.
- Glomerulonephritis: Glomerulonephritis is inflammation of the tiny filters in the kidneys (glomeruli). The excess fluid and waste that glomeruli remove from the bloodstream exit the body as urine. Glomerulonephritis can come on suddenly (acute) or gradually (chronic).
- Goodpasture Syndrome: Goodpasture Syndrome is a rare disorder in which the body mistakenly makes antibodies that attack the lungs and kidneys. It most often occurs in people ages 20 to 30 or older than age 60.
- Hepatocellular (Liver) Cancer: Liver Cancer includes Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Bile Duct Cancer (Cholangiocarcinoma). Risk factors for Hepatocellular Carcinoma include chronic infection with Hepatitis B or C and Cirrhosis of the Liver.
- IgA Nephropathy: IgA Nephropathy is an autoimmune disease that affects the filters (glomeruli) of the kidneys . IgA is an immunoglobulin, which is a part of an individual’s healthy immune system. The IgA immunoglobulin normally attaches itself to an infection found in the body, triggering an immune response.
- Infantile Scoliosis: Infantile Scoliosis is an idiopathic condition that affects children before the age of 3. Infantile Scoliosis is characterized by the presence of an abnormal curve of the spine to the right or the left.
- Ivemark Syndrome: Ivemark Syndrome is a rare congenital condition that affects multiple organ systems of the body. Ivemark Syndrome is characterized by the absence or underdevelopment of the spleen, heart malformations, and the abnormal arrangement of the internal organs of the chest and abdomen.
- Kabuki Syndrome: Kabuki Syndrome is a rare disorder that affects multiple parts of the body. It is present from birth. Features often include a characteristic facial appearance, skeletal abnormalities, short stature, heart defects, and intellectual disability.
- Kidney Disease / Renal Disease: Most people who get Liver Cancer get it in the setting of Chronic Liver Disease. Incidence rates of Hepatocellular Cancer are rising in the United States due to increasing prevalence of Cirrhosis caused by Chronic Hepatitis C and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Chronic Kidney Disease, also called Chronic Kidney Failure, describes the gradual loss of kidney function.
- Ligneous Conjunctivitis: Ligneous Conjunctivitis is a rare form of chronic, recurrent conjunctivitis characterized by fibrinous pseudomembranes on the palpebral conjunctivae. It may be associated with Systemic Pseudomembranous.
- Literacy: Beyond its conventional concept as a set of reading, writing and counting skills, literacy is now understood as a means of identification, understanding, interpretation, creation, and communication in an increasingly digital, text-mediated, information-rich and fast-changing world.
- Liver Cancer, Adult Primary: Primary Liver Cancer starts in the liver. Metastatic Liver Cancer starts somewhere else and spreads to the liver.
- Liver Cancer, Childhood: Childhood Liver Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the liver. Liver Cancer is rare in children and adolescents. There are two main types of Childhood Liver Cancer: Hepatoblastoma: A type of liver cancer that usually does not spread outside the liver. This type usually affects children younger than 3 years old. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A type of liver cancer that often spreads to other places in the body. This type usually affects children older than 14 years old. The alternate color for childhood liver cancer is gold.
- Liver Disease: Liver Disease is any disturbance of liver function that causes illness. Liver Disease is also referred to as hepatic disease. Liver disease is a broad term that covers all the potential problems that cause the liver to fail to perform its designated functions. Usually, more than 75% or three quarters of liver tissue needs to be affected before a decrease in function occurs.
- Liver Melanoma (Metastatic Melanoma): The most dangerous aspect of Melanoma is its ability, in later stages, to spread to other parts of the body. The term metastatic melanoma, or Stage IV melanoma, is used when melanoma cells of any kind have spread through the lymph nodes to distant sites.
- Major Depressive Disorder: Major Depressive Disorder, also referred to as clinical depression, is a significant medical condition that can affect many areas of one's life. It impacts mood and behavior as well as various physical functions. Major Depressive Disorder is one of the most common mental disorders in the United States. In 2015, nearly 7 percent of Americans over age 18 had an episode of MDD.
- Missing Children:
- The missing children issue is complex and multifaceted. Children may become missing due to abduction by non-family members or abduction by family members. Children may become missing as a result of running away from home. Children may also become missing involuntarily for reasons other than abduction such as becoming lost, injured or under other circumstances.
- Website: https://www.amberalert.gov/
- Website: https://twitter.com/AMBERAlert
- Call 1-800-THE-LOST or 1- 800) 843-5678. Available 24/7, 365
- Medical Marijuana Advocate The term medical marijuana refers to using the whole, unprocessed marijuana plant or its basic extracts to treat symptoms of illness and other conditions. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has not recognized or approved the marijuana plant as medicine. However, scientific study of the chemicals in marijuana, called cannabinoids, has led to two FDA-approved medications that contain cannabinoid chemicals in pill form. Continued research may lead to more medications. Because the marijuana plant contains chemicals that may help treat a range of illnesses and symptoms, many people argue that it should be legal for medical purposes. In fact, a growing number of states have legalized marijuana for medical use.
- Mitochondrial Diseases / Mitochondrial Disorders (Dysfunction) Mitochondrial Diseases are chronic, genetic, often inherited disorders that occur when mitochondria fail to produce enough energy for the body to function properly. Mitochondrial Diseases can be present at birth, but can also occur at any age. Mitochondrial Diseases can affect almost any part of the body, including the cells of the brain, nerves, muscles, kidneys, heart, liver, eyes, ears or pancreas. Mitochondrial Dysfunction occurs when the mitochondria do not work as well as they should due to another disease or condition.
- Mooren's Ulcer: It has been postulated that Mooren's Ulcer may result from an autoimmune etiology . Sensitization to calgranulin C, an antigen expressed by corneal stromal keratinocytes, may occur after trauma or infection of the cornea, causing the unveiling of this hidden corneal antigen.
- Natural Disasters: A natural disaster is a major adverse event resulting from natural processes of the Earth. Examples include floods, hurricanes, tornadoes, volcanic eruptions, earthquakes, tsunamis, and other geologic processes. A natural disaster can cause loss of life or property damage, and typically leaves some economic damage in its wake, the severity of which depends on the affected population's resilience, or ability to recover and also on the infrastructure available.
- Nephrotic Syndrome Nephrotic Syndrome is a kidney disorder that causes the body to excrete too much protein in the urine. Nephrotic Syndrome is usually caused by damage to the clusters of small blood vessels in the kidneys that filter waste and excess water from the blood. Nephrotic Syndrome causes swelling, particularly in the feet and ankles, and increases the risk of other health problems.
- Neural Tube Defects: Neural Tube Defects occur when the neural tube does not close properly. The neural tube forms the early brain and spine. These types of birth defects develop very early during pregnancy, often before a woman knows she is pregnant. The two most common Neural Tube Defects are Spina Bifida (a spinal cord defect) and A nencephaly (a brain defect).
- Neuromyelitis Optica Spectrum Disorder / Devic's Disease: Neuromyelitis Optica, also known as Devic's disease, is a rare condition in which the immune system damages the spinal cord and the nerves of the eyes (optic nerves). Neuromyelitis Optica can affect anyone at any age, but it is more common in women than men.
- Nutrition: Nutrition is about eating a healthy and balanced diet . Food and drink provide the energy and nutrients needed to be healthy.
- Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid: Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid refers to Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid that clinically presents as a chronic scarring conjunctivitis. Involvement of other mucosal sites and non-mucosal skin may also occur in Ocular Cicatricial Pemphigoid.
- Optic Neuritis: Optic Neuritis occurs when swelling (inflammation) damages the optic nerve. The optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibers that transmits visual information from the eye to the brain. Common symptoms of Optic Neuritis include pain with eye movement and temporary vision loss in one eye.
- Organ Donation / Organ Donor A national computer system and strict standards are in place to ensure ethical and fair distribution of organs. Organs are matched by blood and tissue typing, organ size, medical urgency, waiting time and geographic location. Organs and tissue that can be donated include: heart, kidneys, lungs, pancreas, liver, intestines, corneas, skin, tendons, bone, nerve and heart valves.
- Organ Transplant Recipient: Organ donation is the process of surgically removing an organ or tissue from one person (the organ donor) and placing it into another person (the recipient). Transplantation is necessary because the recipient's organ has failed or has been damaged by disease or injury.
- Pars Planitis: Pars Planitis is a disease of the eye that is characterized by inflammation of the narrowed area ( pars plana ) between the colored part of the eye (iris) and the choroid. This may lead to blurred vision; dark, floating spots in the vision; and progressive vision loss.
- Pheochromocytoma, Adult Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor that can be non-cancerous or malignant. Pheochromocytomas form in the adrenal glands. Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor that forms in the center of the adrenal gland. Usually Pheochromocytoma affects one adrenal gland, but it may affect both adrenal glands. Sometimes there is more than one tumor in one adrenal gland. The alternate color for Pheochromocytoma is zebra.
- Pheochromocytoma, Childhood Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor. Pheochromocytoma forms in the adrenal glands. Some Pheochromocytomas release extra adrenaline and noradrenaline into the blood and cause symptoms. The alternate color for Pheochromocytoma in children is gold or zebra.
- Physical Fitness: Physical Fitness is a state of health and well-being and, more specifically, the ability to perform aspects of sports, occupations and daily activities. Physical Fitness is generally achieved through proper nutrition, moderate-vigorous physical exercise, and sufficient rest along with a formal recovery plan.
- Pollution: Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment . These harmful materials are called pollutants. Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash. They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories.
- Primary Biliary Cholangitis / Primary Biliary Cirrhosis: Bile is a substance produced by the liver to facilitate digestion. In Primary Biliary Cirrhosis, the bile ducts develop inflammation and eventually collapse. This causes liver damage and may eventually lead to cirrhosis.
- Primary Central Nervous System (CNS) Lymphoma: Primary Central Nervous System (CNS) Lymphoma is a disease in which malignant cells form in the lymph tissue of the brain and/or spinal cord. Primary CNS Lymphoma can start in the brain, spinal cord, or meninges (the layers that form the outer covering of the brain). Because the eye is so close to the brain, Primary CNS Lymphoma can also start in the eye (called Ocular Lymphoma).
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis is a chronic liver disease in which the bile ducts inside and outside the liver become inflamed and scarred, and eventually narrowed or blocked. When this happens, bile builds up in the liver and causes further liver damage.
- Recycling: Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. The recovery of energy from waste materials is often included in this concept. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the properties it had in its original state.
- Retroperitoneal Fibrosis: Retroperitoneal Fibrosis is a rare condition characterized by the presence of inflammatory and fibrous tissue in the retro-peritoneum (the tissue that lines the abdominal wall and covers most of the organs in the abdomen). The tissue is generally localized around the infrarenal portion of the abdominal aorta and the iliac arteries, often encasing the ureters or other abdominal organs.
- Runaway and Homeless Youth: Each year, thousands of U.S. youth run away from home, are asked to leave their homes or become homeless. Through the Runaway and Homeless Youth Program (RHY), FYSB supports street outreach, emergency shelters and longer-term transitional living and maternity group home programs to serve and protect these young people.
- Sandy Hook Promise: Sandy Hook Promise is a national nonprofit organization founded and led by several family members whose loved ones were killed at Sandy Hook Elementary School on December 14, 2012. Based in Newtown, Connecticut, their intent is to honor all victims of gun violence by turning their tragedy into a moment of transformation. By empowering youth to “know the signs” and uniting all people who value the protection of children, they can take meaningful actions in schools, homes, and communities to prevent gun violence and stop the tragic loss of life
- Scleritis: The sclera is the white part of the eye . When the sclera is swollen, red, tender, or painful , it is called scleritis. It is common for people with scleritis to have another disease, like rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune disease. This underlying disease causes many of the symptoms of scleritis.
- Scoliosis: Scoliosis is an abnormal curve in the spine. There are several types of scoliosis based on the cause and age when the curve develops. The majority of people have no known cause. The most common symptom of Scoliosis is curvature of the spine. Scoliosis risk factors include age (9- to 15-year-olds), female sex, and family history.
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that is related to changes in seasons. SAD begins and ends at about the same times every year. Most people's symptoms start in the fall and continue into the winter months, sapping energy and making sufferers feel moody. Less often, Seasonal Affective Disorder causes depression in the spring or early summer. Spinal Cord Injury: The most common cause of Spinal Cord Injury is trauma. Spinal Cord Injury is most common in young, white men. Spinal Cord Injury can be either complete or incomplete. In complete injuries there is no function below the level of injury. In incomplete injuries, there is some function remaining below the level of injury.
- Stem Cell Donation: People who want to donate stem cells or join a volunteer registry can speak with a health care provider or contact the National Marrow Donor Program to find the nearest donor center. Potential donors are asked questions to make sure they are healthy enough to donate and don’t pose a risk of infection to the recipient. For more information about donor eligibility guidelines, contact Be the Match or the donor center in your area. Be the Match (formerly the National Marrow Donor Program) Toll-free number: 1-800-MARROW or (1-800-627-7692) Website: www.bethematch.org
- Sympathetic Ophthalmia: Sympathetic ophthalmia is a rare, bilateral granulomatous uveitis that occurs after either surgical or accidental trauma to one eye.
- Telehealth: Telehealth is the distribution of health-related services and information via electronic information and telecommunication technologies. It allows long-distance patient and clinician contact, care, advice, reminders, education, intervention, monitoring, and remote admissions.
- Tethered Cord Syndrome: Tethered Cord Syndrome is a rare neurological condition. The severity of the condition and the associated signs and symptoms vary from person to person. In some cases, symptoms may be present at birth (congenital), while others may not experience symptoms until later in adulthood. Features of the condition may include foot and spinal abnormalities, weakness in the legs, loss of sensation in the lower limbs, lower back pain, scoliosis, and urinary incontinence.
- Tissue Donation: Tissue donation is a common lifesaving option for people who wish to be donors, as there are very few medical reasons a person would not be eligible to donate tissue. Corneas or whole eyes, bone, skin, tendons, ligaments, heart valves and other cardiovascular tissues can be transplanted. Great care is taken in the recovery of tissues to ensure presentation of the body for funeral purposes. Generally, donation will not delay funeral arrangements, and tissue donation does not interfere with an open-casket funeral for the donor.
- Tolosa Hunt Syndrome: Tolosa-Hunt Syndrome is a rare disorder characterized by severe periorbital headaches, along with decreased and painful eye movements. Symptoms usually affect only one eye. In most cases, affected individuals experience intense sharp pain and decreased eye movements. Symptoms often will subside without intervention and may recur without a distinct pattern.
- Traumatic Brain Injury: Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI) happens when a bump, blow, jolt, or other head injury causes damage to the brain. Every year, millions of people in the U.S. suffer brain injuries. More than half are bad enough that people must go to the hospital. The worst injuries can lead to permanent brain damage or death. Half of all TBIs are from motor vehicle accidents. Military personnel in combat zones are also at risk.
- Uveitis: Uveitis is a form of eye inflammation. It affects the middle layer of tissue in the eye wall. Uveitis warning signs often come on suddenly and get worse quickly. They include eye redness, pain and blurred vision.
- Vision Impairment: Vision Impairment means that a person's eyesight cannot be corrected to a “normal” level. Vision impairment may be caused by a loss of visual acuity, where the eye does not see objects as clearly as usual.
- Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome (VHL): Von Hippel-Lindau Syndrome is an inherited disorder characterized by the abnormal growth of both benign and cancerous tumors and cysts in many parts of the body. Tumors usually first appear in young adulthood.
Hot Pink Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Bubonic Plague: Bubonic Plague is the most common form of plague and is caused by the bite of an infected flea. Plague bacillus , Y. pestis , enters at the bite and travels through the lymphatic system to the nearest lymph node where it replicates itself. The lymph node then becomes inflamed, tense and painful, and is called a 'bubo'.
- Cleft Lip and Cleft Palate: A Cleft Lip can range from a little notch in the colored part of the lip to a complete separation of the upper lip that extends up and into the nose. This can affect one side of the mouth or both sides, and can be complete (the cleft goes up into the nose) or incomplete. A Cleft Lip can also affect the gum where the teeth come through. This can range from a small notch to a complete separation of the gum into two parts. A Cleft Palate is a gap in the roof of the mouth. A cleft can affect the soft palate or both the soft and hard palate. A person can have a Cleft Lip, a Cleft Palate, or a Cleft Lip and Palate. A Cleft Palate by itself is often called an isolated Cleft Palate.
- Conjunctivitis / Pink Eye: Conjunctivitis, or Pink Eye, is an irritation or inflammation of the conjunctiva, which covers the white part of the eyeball. It can be caused by allergies or a bacterial or viral infection. Conjunctivitis can be extremely contagious, and is spread by contact.
- Inflammatory Breast Cancer: Inflammatory Breast Cancer is a rare and very aggressive disease in which cancer cells block lymph vessels in the skin of the breast. This type of breast cancer is called “inflammatory” because the breast often looks swollen and red, or inflamed. Inflammatory Breast Cancer is rare, accounting for 1 to 5 percent of all breast cancers diagnosed in the United States. Most Inflammatory Breast Cancers are invasive ductal carcinomas, which means they developed from cells that line the milk ducts of the breast and then spread beyond the ducts.
- Plague: Plague is a disease that affects humans and other mammals. It is caused by the bacterium, Yersinia pestis . Humans usually get plague after being bitten by a rodent flea that is carrying the plague bacterium or by handling an animal infected with plague.
- Pneumonic Plague: Pneumonic plague occurs when Y.pestis infects the lungs. This type of plague can spread from person to person through the air.
- Stop Gendercide: The Stop Gendercide Now Campaign consists of a public awareness campaign and a petition to put pressure on the governments of countries with significant sex ratio imbalances: To introduce measures to ensure that the killing, fatal neglect or abandonment of baby girls because they are girls is ended.
Kente Cloth Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- African American Breast Cancer Incidence: African American women’s mortality rates are 41 percent higher than their caucasian counterparts. The same research indicates that African American women are often diagnosed at later stages, sometimes with more aggressive forms of cancer and at younger ages. This trend is the result of compounding social, cultural, financial and geographic barriers.
- Closing the Breast Cancer Gap / Breast Health Equity: Racial disparities in breast cancer mortality among African American women is an issue that has been well documented over the past 40 years. While early studies largely attributed poor survival in this group to low socioeconomic status, cumulative evidence suggests that ethnic disparities in breast cancer survival are influenced by multiple factors existing along a continuum—from breast cancer prevention to post-treatment surveillance.
- Men of Color Breast Cancer: A study has found that Black men have higher rates of all types of breast cancer compared to white men in the United States. This is different than the rates in women in the United States, where Black women have higher rates of triple-negative breast cancer — cancer that is progesterone-receptor-negative, estrogen-receptor-negative, and HER2-negative — but lower rates of hormone-receptor-positive breast cancer compared to white women.
- Women of Color Breast Cancer / WOC Breast Cancer: Although the mortality rates have declined in some ethnic populations, the overall cancer incidence among African American and Hispanic populations has continued to grow.
Lavender Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- All Cancers: A term for diseases in which abnormal cells divide without control and can invade nearby tissues. Cancer cells can also spread to other parts of the body through the blood and lymph systems. There are several main types of cancer. Carcinoma is a cancer that begins in the skin or in tissues that line or cover internal organs. Sarcoma is a cancer that begins in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue. Leukemia is a cancer that begins in blood-forming tissue, such as the bone marrow, and causes too many abnormal blood cells to be made. Lymphoma and multiple myeloma are cancers that begin in the cells of the immune system. Central nervous system cancers are cancers that begin in the tissues of the brain and spinal cord. Also called malignancy.
- Cancer, For which a primary color has not been designated - Unspecified Cancer. Sometimes, an awareness color for a specific cancer has not been decided or assigned: Cancer is not just one disease but many diseases. There are more than 100 different types of cancer. Most cancers are named for where they start. For example, lung cancer starts in the lung, and breast cancer starts in the breast. The spread of cancer from one part of the body to another is called metastasis. Symptoms and treatment depend on the cancer type and how advanced it is.
- Choriocarcinoma / Placental Cancer: A malignant, fast-growing tumor that develops from trophoblastic cells (cells that help an embryo attach to the uterus and help form the placenta). Almost all choriocarcinomas form in the uterus after fertilization of an egg by a sperm, but a small number form in a testis or an ovary.
- Stress: Stress is a normal human reaction that happens to everyone. In fact, the human body is designed to experience stress and react to it. When a person experiences changes or challenges (stressors), the body produces physical and mental responses. That’s stress. Stress becomes a problem when stressors continue without relief or periods of relaxation.
- Stress Induced Illnesses: Prolonged stress puts the body in a continuous state readiness for physical action. When the body has no time to re-establish equilibrium, it becomes overworked and the immune system weakens, making a person susceptible to sickness. Many essential bodily processes are disrupted and the risk of health problems increases.
Lavender and White Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Beta Foster Care: Beta Foster Care (BFC) is a private non-profit foster family agency licensed by the State of California Department of Social Services Community Care Licensing. BFC trains and certifies qualified adults for foster care under state regulations and manages the appropriate placement of children into these foster homes.
- Lichen Planus: Lichen Planus occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks cells of the skin or mucous membranes. On skin, Lichen Planus appears as purplish, itchy, flat-topped bumps. On mucous membranes, such as in the mouth, it forms lacy white patches, sometimes with painful sores.
Light Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Achalasia: Achalasia occurs when nerves in the esophagus become damaged. As a result, the esophagus becomes paralyzed and dilated over time and eventually loses the ability to squeeze food down into the stomach. Food then collects in the esophagus, sometimes fermenting and washing back up into the mouth, which can taste bitter. The alternate color for Achalasia is light green.
- Acid Attacks: Acid throwing, also called an acid attack, is a form of violent assault defined as the act of throwing acid or a similarly corrosive substance onto the body of another with the intention to disfigure, maim, torture, or kill. Perpetrators of acid attacks throw corrosive liquids at their victims, usually at their faces, burning them, and damaging skin tissue, often exposing and sometimes dissolving the bones.
- Addison's Disease: Addison's Disease is a chronic condition that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce any or enough of the hormones cortisol and aldosterone.
- Adrenal Insufficiency: Adrenal Insufficiency is an endocrine disorder that occurs when the adrenal glands do not produce enough of certain hormones. Secondary Adrenal Insufficiency occurs when the pituitary gland fails to produce enough adrenocorticotropin (ACTH), a hormone that stimulates the adrenal glands to produce the hormone cortisol.
- Autoimmune Dysautonomia: Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy is a very rare form of dysautonomia in which the bodies own immune system damages a receptor in the autonomic ganglia (part of the peripheral autonomic nerve fiber). The alternate color for Autoimmune Dysautonomia is turquoise.
- Behcet’s Disease / Behcet’s Syndrome: Behcet's Disease, also called Behcet's Syndrome, is a rare disorder that causes blood vessel inflammation throughout your body. The disease can lead to numerous signs and symptoms that can seem unrelated at first. They can include mouth sores, eye inflammation, skin rashes and lesions, and genital sores.
- Chromasome 5q Duplication: Chromosome 5q Duplication is a chromosome abnormality that occurs when there is an extra copy of genetic material on the long arm (q) of chromosome 5. The severity of the condition and the signs and symptoms depend on the size and location of the duplication and which genes are involved.
- Chronic Diseases / Chronic Illnesses: A chronic disease is one lasting three months or more, by the definition of the U.S. National Center for Health Statistics. Chronic diseases generally cannot be prevented by vaccines or cured by medication, nor do they just disappear.
- DiGeorge Syndrome: DiGeorge Syndrome is a primary immunodeficiency disease associated with susceptibility to infections due to decreased T cell production and function due to an absent or poorly developed thymus. The thymus is the “school house” where T-cells are educated to fight infection and prevent autoimmunity. DiGeorge Syndrome is caused by abnormal cell and tissue development during fetal growth.
- Dysphagia: Dysphagia is difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia means it takes more time and effort to move food or liquid from the mouth to the stomach. Dysphagia may also be associated with pain. In some cases, swallowing may be impossible.
- Edwards Syndrome: Edwards Syndrome, also known as Trisomy 18, is a very severe genetic condition that affects the way a child's body develops and grows. Children diagnosed with Trisomy 18 have a low birth weight, multiple birth defects and defining physical characteristics.
- Foster Care: Foster Care is a temporary arrangement in which adults provide for the care of a child or children whose birthparent is unable to care for them. Foster care can be informal or arranged through the courts or a social service agency. The goal for a child in the Foster Care system is usually reunification with the birth family, but may be changed to adoption when this is seen as in the child's best interest. While foster care is temporary, adoption is permanent.
- Graves’ Disease: Graves' Disease is an autoimmune disease that damages the thyroid gland. Graves' Disease affects more women than men. It is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid gland). The alternate color for Graves' Disease is paisley.
- Hashimoto’s Thyroid Disease: Hashimoto's Disease is an autoimmune disorder. The immune system creates antibodies that attack thyroid cells as if they were bacteria, viruses or some other foreign body. The immune system wrongly enlists disease-fighting agents that damage cells and lead to cell death. The alternate color for Hashimoto's Thyroid Disease is paisley.
- Hyperaldosteronism: Hyperaldosteronism is a disorder in which the adrenal gland releases too much of the hormone aldosterone into the blood. Hyperaldosteronism can be primary or secondary.
- Lymphedema: Lymphedema is the name of a type of swelling. Lymphedema occurs when lymph builds up in the body's soft tissues. Lymph is a fluid that contains white blood cells that defend against germs. It can build up when the lymph system is damaged or blocked. It typically builds up in the arms or legs.
- Men's Health: Compared to women, men are more likely to smoke and drink, make unhealthy or risky choices and put off regular checkups and medical care. There are also health conditions that only affect men, such as prostate cancer and low testosterone. Many of the major health risks that men face, such as colon cancer or heart disease, can be prevented and treated with early diagnosis. Screening tests can find diseases early, when they are easier to treat.
- Movember: Movember is an annual event involving the growing of moustaches during the month of November to raise awareness of men's health issues, such as prostate cancer, testicular cancer, and men's suicide. The Movember Foundation runs the Movember charity event, housed at Movember.com.
- Penile Cancer: Penile Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the penis. Penile Cancer usually forms on or under the foreskin. Human papillomavirus (HPV) causes about one-third of penile cancer cases. When found early, penile cancer is usually curable.
- Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome: Pitt-Hopkins Syndrome is a genetic syndrome that causes developmental delays, moderate to severe intellectual disability, behavioral differences, distinctive facial features, and breathing problems such as episodes of rapid breathing and breath-holding. Other features may include symptoms of autism spectrum disorder, sleep disturbances, seizures, constipation, nearsightedness, and minor skeletal abnormalities.
- Pro-Choice: The United States abortion-rights movement (also known as the United States pro-choice movement) is a sociopolitical movement in the United States supporting the view that a woman should have the legal right to an elective abortion, meaning the right to terminate her pregnancy. This pro-choice stance is part of a broader global abortion-rights movement. The pro-choice movement consists of a variety of organizations, with no single centralized decision-making body. A key point in abortion rights in the United States was the U.S. Supreme Court's 1973 decision in Roe v. Wade, which struck down most state laws restricting abortion, thereby decriminalizing and legalizing elective abortion in a number of states. Roe v. Wade was overturned by the Supreme Court in 2022.
- Prostate Cancer: The prostate is a gland that is part of the male reproductive system, wrapping around the male urethra at its exit from the bladder. Prostate Cancer is common in men over 50 and the risk of developing Prostate Cancer increases with age. Certain populations are at increased risk for developing Prostate Cancer, particularly African-Americans and men with a father or brother diagnosed with Prostate Cancer at a younger age.
- Spay and Neuter Pets: By spaying or neutering your pet, you’ll help control the pet homelessness crisis, which results in millions of healthy dogs and cats being euthanized in the United States each year simply because there are not enough homes to go around. There are also medical and behavioral benefits to spaying (female pets) and neutering (male pets) your animals. The alternate color for Spay and Neutering pets is Animal Paw Prints.
- Thyroid Conditions and Diseases: The thyroid produces thyroid hormone, which controls many activities in the body. Diseases of the thyroid cause it to make either too much or too little of the hormone. The alternate color for Thyroid Conditions and Diseases is paisley.
- Tracheomalacia: Tracheomalacia is the collapse of the airway when breathing. This means that when a child exhales, the trachea narrows or collapses so much that it may feel hard to breathe. This may lead to a vibrating noise or cough. Tracheomalacia can result in recurring respiratory illnesses or make it difficult to recover from a respiratory illness. In the long term, it can lead to progressive lung injury.
- Trisomy 5q: Chromosome 5q duplication is a chromosome abnormality that occurs when there is an extra copy of genetic material on the long arm (q) of chromosome 5. The severity of the condition and the signs and symptoms depend on the size and location of the duplication and which genes are involved.
- Trisomy 13: Trisomy 13 is a type of chromosome disorder characterized by having 3 copies of chromosome 13 in cells of the body, instead of the usual 2 copies. In some affected people, only a portion of cells contains the extra chromosome 13 (called mosaic trisomy 13), whereas other cells contain the normal chromosome pair.
- Trisomy 18 Syndrome / Edwards Syndrome: Trisomy 18, also known as Edwards Syndrome, is a chromosome disorder characterized by having 3 copies of chromosome 18 instead of the usual 2 copies.
- Velo Cardio Facial Syndrome: Velo Cardio Facial Syndrome is a genetic condition that is sometimes hereditary. Velo Cardio Facial Syndrome is characterized by a combination of medical problems that vary from child to child.
Light Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Achalasia: Achalasia occurs when nerves in the esophagus become damaged. As a result, the esophagus becomes paralyzed and dilated over time and eventually loses the ability to squeeze food down into the stomach. Food then collects in the esophagus, sometimes fermenting and washing back up into the mouth, which can taste bitter. The alternate color for Achalasia is light blue.
- Celiac Disease: In people with celiac disease, inflammation occurs in the small intestinal mucosa when it is exposed to gluten in the diet. Celiac Disease is thought to be an autoimmune disorder and may have a familial or genetic component. Because the intestine becomes inflamed, it may also lose its ability to absorb nutrients from the diet, leading to other associated illnesses.
- Chronic Pelvic Pain: Chronic Pelvic Pain is pain in the pelvic area that lasts for six months or longer. Chronic pain can come and go, or it can be constant. Sometimes Chronic Pelvic Pain follows a regular cycle. For example, it may occur during menstruation. It also can occur only at certain times, such as before or after eating, while urinating, or during sex.
- Chancroid Syndrome: Chancroid Syndrome is caused by the bacterium Haemophilus ducreyi and results in painful, superficial ulcers, often with regional lymphadenopathy. Chancroid Syndrome occurs in Asia, Africa, and the Caribbean, and is an important cofactor of HIV transmission. The genital ulcer from chancroid is painful and tender.
- Dermatitis Herpetiformis: Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a chronic, intensely itchy, blistering skin manifestation of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, commonly known as Celiac Disease. Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a rash that affects about 10 percent of people with Celiac Disease. Dermatitis Herpetiformis is found mainly in adults and is more common in men and people of northern European descent.
- Human Papilloma Virus (HPV): Human Papilloma Virus, or HPV, is the most common sexually transmitted infection (STI) in the United States. About 80% of women will get at least one type of HPV at some point in their lifetime. It is usually spread through vaginal, oral, or anal sex. Many women do not know they have HPV, because it usually has no symptoms and typically goes away on its own. Some types of HPV can cause illnesses such as genital warts or cervical cancer. There is a vaccine to help prevent HPV.
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease / PID: Pelvic Inflammatory Disease is an infection of the female reproductive organs. It most often occurs when sexually transmitted bacteria spread from the vagina to the uterus, fallopian tubes or ovaries.
- Refractory Celiac Disease: Refractory Celiac Disease is a complex autoimmune disorder much like the more common Celiac Disease but, unlike Celiac Disease, it is resistant or unresponsive to at least twelve months of treatment with a strict gluten-free diet.
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases / STDs / Sexually Transmitted Infections / STIs: Sexually Transmitted Diseases are characteristically transmitted by sexual contact, such as gonorrhea, syphilis, genital herpes, and chlamydia.
Lime Green awareness ribbons colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- AIDS-Related Lymphoma: AIDS-related lymphoma is a type of cancer that affects the lymph system, which is part of the body's immune system.
- AIDS-Related Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a broad term for cancer that begins in cells of the lymph system. The two main types are Hodgkin lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Primary CNS lymphoma may occur in patients who have acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) or other disorders of the immune system or who have had a kidney transplant.
- Anhedonia: Anhedonia refers to the reduced ability to experience pleasure. It is a feature of several types of psychiatric disorders and maladaptive behaviors.
- Auditory Processing Disorder: Auditory Processing Disorder is a hearing problem that affects about 5% of school-aged children. Children with this condition cannot process what they hear in the same way other children do because their ears and brain do not fully coordinate. Something interferes with the way the brain recognizes and interprets sounds, especially speech.
- Babesiosis: Babesiosis is caused by microscopic parasites that infect red blood cells and are spread by certain ticks. In the United States, tick-borne transmission is most common in particular regions and seasons. It mainly occurs in parts of the Northeast and upper Midwest and usually peaks during the warm months.
- Burkitt Lymphoma: Burkitt Lymphoma is a form of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma in which cancer starts in immune cells called B-cells. Recognized as the fastest growing human tumor, Burkitt Lymphoma is associated with impaired immunity.
- Childhood Mental Health: Mental Health in childhood means reaching developmental and emotional milestones, and learning healthy social skills and how to cope when there are problems.
- Childhood Mental Illness: Among the more common mental disorders that can be diagnosed in childhood are Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), anxiety (fears or worries), and behavior disorders.
- Chronic Lyme Disease (Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome): Lyme Disease is caused by infection with the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi . Although most cases of Lyme disease can be cured with oral antibiotics, patients can sometimes have symptoms of pain, fatigue, or difficulty thinking that lasts for more than six months after they finish treatment. This condition is called Post-Treatment Lyme Disease Syndrome.
- Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma: Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome are diseases in which lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) become malignant and affect the skin. Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome are types of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma.
- Depression: A Depressive Disorder is a clinical syndrome, meaning a group of symptoms. Depressive Disorders feature not only negative thoughts, moods, and behaviors but also specific changes in bodily functions (like, eating, sleeping, energy and sexual activity, as well as potentially developing aches or pains). Because depression can lead to self-harm including suicide, it is important to note that one of every 25 suicide attempts results in death. Some types of depression, especially Bipolar Depression, run in families. While there are many social, psychological, and environmental risk factors for developing Depression, some are particularly prevalent in one gender or the other, or in particular age or ethnic groups. There can be some differences in signs and symptoms of depression depending upon age, gender, and ethnicity.
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy is a progressive form of Muscular Dystrophy that occurs primarily in males, though in rare cases may affect females. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy causes progressive weakness and loss of skeletal and heart muscles.
- Dysthymic Disorder: Dysthymic Disorder, or dysthymia, is a mood or affective disorder. It is a chronic, mild depression that lasts for a long period of time.
- Lyme Disease: Lyme Disease is a tick-borne disease. Lyme Disease is not contagious from an affected person to someone else. Lyme Disease can cause abnormalities in the skin, joints, heart, and nervous system.
- Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a general term for a group of cancers that originate in the lymph system (the tissues and organs that produce, store, and carry white blood cells that fight infections and other diseases). The two main kinds of Lymphoma are Hodgkin Lymphoma, which spreads in an orderly manner from one group of lymph nodes to another and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, which spreads through the lymphatic system in a non-orderly manner. Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma can occur in children, teens, and adults. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma becomes more common as people get older. Unlike most cancers, rates of Hodgkin Lymphoma are highest among teens and young adults (ages 15 to 39 years) and again among older adults (ages 75 years or older). White people are more likely than black people to develop Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and men are more likely than women to develop Lymphoma.
- Maternal Mental Health: Worldwide about 10% of pregnant women and 13% of women who have just given birth experience a mental disorder, primarily depression. In developing countries this is even higher. In severe cases mothers’ suffering might be so severe that they may even commit suicide. Maternal Mental Disorders are treatable. Effective interventions can be delivered even by well-trained non-specialist health providers.
- Mental Disorders: Mental Disorders comprise a broad range of problems, with different symptoms. However, they are generally characterized by some combination of abnormal thoughts, emotions, behavior and relationships with others. Examples include schizophrenia, depression, intellectual disabilities and disorders due to drug abuse. Most of these disorders can be successfully treated.
- Mental Health: Mental Health is defined as a state of well-being in which individuals realize their own potential, can cope with the normal stresses of life, can work productively and are able to make a contribution to the community.
- Mental Illness: Mental illness, also called mental health disorders, refers to a wide range of mental health conditions - disorders that affect mood, thinking and behavior. Examples of mental illness include depression, anxiety disorders, schizophrenia, eating disorders and addictive behaviors.
- Minority Mental Health: As hard as it is for anyone to get proper mental health care in the United States, it’s even harder for racial, ethnic, religious and gender minorities. Not only are there the problems most of us experience, including issues with insurance, long wait times, difficulty finding specialists, deductibles and co-pays, but there are added burdens of access and quality-of-care.
- Mood Disorders: Mood Disorder, also known as mood (affective) disorders, is a group of conditions where a disturbance in the person's mood is the main underlying feature. Mood Disorders fall into the basic groups of elevated mood, such as mania or hypomania; depressed mood, of which the best-known and most researched is major depressive disorder (commonly called clinical depression), unipolar depression, or major depression and moods which cycle between mania and depression, known as Bipolar Disorder. There are several sub-types of Depressive Disorders or Psychiatric Syndromes featuring less severe symptoms such as Dysthymic Disorder and Cyclothymic Disorder. Mood Disorders may also be substance-induced or occur in response to a medical condition.
- Multiple Chemical Sensitivity: Multiple Chemical Sensitivity can include a wide range of symptoms, which some people link to their environment. It's also known as Environmental Illness,” Sick Building Syndrome,” or MCS. Doctors may call it Idiopathic Environmental Intolerance.
- Muscular Dystrophy: Muscular Dystrophy is a term that refers to a number of diseases that cause progressive loss of muscle mass resulting in weakness and, sometimes, loss of mobility. There are many different kinds of Muscular Dystrophy, each affecting different groups of muscles. In some types of Muscular Dystrophy, symptoms begin in childhood. In other forms, symptom onset doesn’t occur until adulthood.
- Mycosis Fungoides: Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome are types of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. In Mycosis Fungoides, T-cell lymphocytes become cancerous and affect the skin. In Sezary Syndrome, cancerous T-cell lymphocytes affect the skin and are in the blood. Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome are the two most common types of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
- Myotonic Muscular Dystrophy: Myotonic Dystrophy is a form of Muscular Dystrophy that affects muscles and many other organs in the body. The word myotonic is the adjective for the word myotonia, an inability to relax muscles at will. The term muscular dystrophy means progressive muscle degeneration, with weakness and shrinkage of the muscle tissue.
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Adult: Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is cancer that originates in the lymphatic system, the disease-fighting network spread throughout the body. In Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, tumors develop from lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell. Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is more common than the other general type of lymphoma, Hodgkin Lymphoma. Many different subtypes of Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma exist. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma are among the most common subtypes.
- Non Hodgkin Lymphoma / Non Hodgkin’s Lymphoma, Childhood: Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (sometimes called NHL, or just lymphoma) is a cancer that starts in cells called lymphocytes, which are part of the body’s immune system. NHL is not common in children, but it can occur. An alternate color for childhood Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma is gold.
- Parry Romberg Syndrome: Parry-Romberg Syndrome, also called Romberg Syndrome or progressive facial hemiatrophy, is a condition where the tissue of one side of the face gradually wastes away. Over time, the soft tissue (muscle and fat) gradually shrinks, the facial bones may change, and the skin may become thin.
- Pediatric Acute Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome / PANS: Pediatric Acute-Onset Neuropsychiatric Syndrome (PANS) is a clinical diagnosis given to children who have a dramatic, sometimes overnight, onset of neuropsychiatric symptoms including obsessions/compulsions or food restriction. They are often diagnosed with Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) or an eating disorder, but the sudden onset of symptoms separates PANS from these other disorders. In addition, they may have symptoms of depression, irritability, anxiety, and difficulty with schoolwork. The cause of PANS is unknown in most cases but is thought to be triggered by infections, metabolic disturbances, and other inflammatory reactions.
- Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorder Associated with Streptococcus / PANDAS: PANDAS is an acronym for Pediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorder Associated with Streptococcus. It is used to describe a condition in children whose symptoms of Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) or a tic disorder (i.e. Tourette syndrome) are worsened by group A streptococcal infections. The underlying cause of PANDAS is unclear, but studies suggest that a strep infection causes an abnormal immune response resulting in neuropsychiatric symptoms.
- Postpartum Depression: Postpartum Depression is moderate to severe depression in a woman after giving birth. Postpartum Depression may occur soon after delivery or up to a year later. Most of the time, it occurs within the first three months after delivery.
- Postpartum Disorders: Postpartum Disorders describe the range of emotional, physical, and behavioral challenges often experienced by new mothers. Symptoms can range from mild to severe. While many new mothers experience a mild, brief bout of "baby blues," others suffer from Postpartum Depression, a much more serious condition. In some cases, new mothers may have Postpartum Psychosis, which is rare but severe and incapacitating.
- Reactive Attachment Disorder: Reactive Attachment Disorder is a rare but serious condition in which an infant or young child does not establish healthy attachments with parents or caregivers. Reactive Attachment Disorder may develop if the child's basic needs for comfort, affection and nurturing are not met and loving, caring, stable attachments with others are not established.
- Sezary Syndrome: Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome are diseases in which lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell) become malignant and affect the skin. Mycosis Fungoides and Sezary Syndrome are types of Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. In Sezary Syndrome, cancerous T-cells are found in the blood.
- Spasticity: Spasticity is a state of increased tone of a muscle and an increase in the deep tendon reflexes. For example, with spasticity of the legs (spastic paraplegia) there is an increase in tone of the leg muscles so they feel tight and rigid and the knee jerk reflex is exaggerated.
- Spinal Cord Disorders: Spinal Cord Disorders cause various patterns of deficits depending on which nerve tracts within the cord or which spinal roots outside the cord are damaged. Disorders affecting spinal nerves, but not directly affecting the cord, cause sensory or motor abnormalities or both only in the areas supplied by the affected spinal nerves.
- Substance-Related Disorders: Recent estimates indicate that nearly 21 million adults in the United States have a Substance-Related Addictive Disorder. Substance-Related Disorders are categorized by 10 separate classes of substances: alcohol, caffeine, cannabis, hallucinogens, inhalants, opioids, sedatives, stimulants, tobacco, and other (or unknown) substances. These drugs all activate the reward system in the brain, which produces feelings of pleasure in the user.
- Trichotillomania: Trichotillomania, also called Hair-Pulling Disorder, is a mental disorder that involves recurrent, irresistible urges to pull out hair from the scalp, eyebrows or other areas of the body, despite trying to stop.
- Wage Gap: The gender wage gap refers to the difference in earnings between women and men. Experts have calculated this gap in a multitude of ways, but the varying calculations point to a consensus: Women consistently earn less than men, and the gap is wider for most women of color. Analyzing the most recent Census Bureau data from 2018, women of all races earned, on average, just 82 cents for every $1 earned by men of all races. This calculation is the ratio of median annual earnings for women working full time, year round to those of their male counterparts, and it translates to a gender wage gap of 18 cents. When talking about the wage gap for women, it is important to highlight that there are significant differences by race and ethnicity. The Wage Gap is larger for most women of color.
- Williams Syndrome: Williams Syndrome is a genetic condition that affects many parts of the body. Signs and symptoms include mild to moderate intellectual disability, unique personality traits, distinctive facial features, and heart and blood vessel problems. Williams Syndrome is caused by a person missing more than 25 genes from a specific area of chromosome 7 (deletion).
Lime Green and Aqua Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Adult Stem Cell Donor: Donating bone marrow stem cells requires stem cells drawn from either the blood or bone marrow to be given to someone else. This is known as a stem cell transplant, bone marrow transplant or hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Stem cells used in transplants come from three sources. These sources are the spongy tissue at the center of some bones (bone marrow), the bloodstream (peripheral blood) and umbilical cord blood from newborns. The source that is used depends on the purpose of the transplant.
- Healthy Aging: Many factors influence healthy aging. Some of these, such as genetics, are not in our control. Others, like exercise, a healthy diet, going to the doctor regularly, and taking care of our mental health, are within our reach.
Lime Green and Fuchsia Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Flu: Flu is a common viral infection that can be deadly, especially in high-risk groups. The flu attacks the lungs, nose, and throat. Young children, older adults, pregnant women, and people with chronic disease or weak immune systems are at high risk. Symptoms include fever, chills, muscle aches, cough, congestion, runny nose, headaches, and fatigue. The flu is treated primarily with rest and fluid to let the body fight the infection on its own. An annual vaccine can help prevent the flu and limit its complications. Flu is spread by airborne respiratory droplets (coughs or sneezes); touching a contaminated surface; saliva (kissing or shared drinks); S kin- to-skin contact (handshakes or hugs).
- Flu Prevention / Flu Vaccine: Flu vaccination can reduce flu illnesses, doctors' visits, and missed work and school due to flu, as well as prevent flu-related hospitalizations. CDC recommends that everyone six months of age and older get a flu vaccine every year. An annual flu vaccine is the first and best way to protect against flu.
Maroon and Gray Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Arachnoid Cysts Arachnoid Cysts are cerebrospinal fluid covered by arachnoidal cells and collagen that may develop between the surface of the brain and the cranial base or on the arachnoid membrane. The arachnoid membrane is one of the three meningeal layers that cover the brain and spinal cord.
Olive Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Army Cyber Security Awareness Campaign: The Army Cybersecurity Awareness Campaign is a year-long, 24/7 enduring effort to promote awareness and cybersecurity best practices by Soldiers, Civilians, contractors, and families. The campaign launches during Cybersecurity Awareness Month in October.
- Childless-Not-By-Choice: Involuntary childlessness (also known as childless-not-by-choice, or childless by circumstance) refers to people who have wanted to be parents, but who have not been able to due to a number of different reasons.
- Families Belong Together / Stop Separation of Parents from Children at the Border: Families Belong Together is a campaign of the National Domestic Workers Alliance formed in response to the 2018 family separation crisis. Families Belong Together works with nearly 250 organizations representing Americans from all backgrounds who have joined together to fight family separation and promote dignity, unity and compassion for all children and families. In addition, they work with advocates on either side of the border to draw attention to abuses in the immigration system, hold elected officials accountable, and change the narrative about migrants and migrant families in popular culture and media.
- STAND-TO! / The Official Focus of the U.S. Army: STAND-TO! was an information paper-based web platform that supported the U.S. Army’s strategic communication objectives. Beginning May 2022, STAND-TO! was no longer published on Army.mil and/or distributed to its subscribers. Continue to learn about the U.S. Army on www.army.mil and follow @USArmy on their social media platforms.
Orange Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Adult Adult Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, also called Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia, is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow.
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Childhood: Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated. Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many immature lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Leukemia may affect red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. The alternate color for Childhood Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia is gold.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Adult: Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. It is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults. Acute Myeloid Leukemia is also called Acute Myelogenous Leukemia, Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia, Acute Granulocytic Leukemia, and Acute Non-Lymphocytic Leukemia.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Childhood: Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia, also called Acute Myelogenous Leukemia or AML, is a type of blood cancer. It is a quickly progressing disease in which too many abnormal white blood cells are found in the bone marrow, the soft, spongy center of long bones. In Acute Myeloid Leukemia, myeloid stem cells (a type of blood stem cell) become immature white blood cells called myeloblasts or “blasts.” These blasts do not become healthy white blood cells. Instead, build up in the bone marrow, so there is less room for healthy white blood cells, red blood cells and platelets. In addition, these abnormal cells are unable to fight off infection. The alternate color for Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia is gold.
- Agent Orange: Agent Orange was a tactical herbicide the U.S. military used to clear leaves and vegetation for military operations mainly during the Vietnam War. Veterans who were exposed to Agent Orange may have certain related cancers or other illnesses.
- Amniotic Band Syndrome: Amniotic Band Syndrome refers to a condition in which bands develop from the inner lining of the amnion. The amnion is the sac that surrounds the baby in the womb. As the baby develops in the womb, the bands may attach to and affect the development of different areas of the body.
- Asylum Seekers: An asylum seeker is a person who flees his or her home country, spontaneously enters another country and applies for asylum, i.e. the right to international protection, in this other country. An asylum seeker may be a refugee, a displaced person or a migrant, such as an economic migrant.
- Attention Deficit Disorder / ADD: ADD, or attention-deficit disorder, is an old term, now out of date, for the disorder now called ADHD, or Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. It was called ADD up until 1987, when the word “hyperactivity” was added to the name.
- Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD): Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder is a chronic condition including attention difficulty, hyperactivity (ADHD), and impulsiveness.
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Skin: Skin Cancer is the most common type of cancer. The main types of skin cancer are Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, and Melanoma. Squamous cells are thin, flat cells that form the top layer of the epidermis. Basal cells are the round cells under the squamous cells. Melanoma is much less common than the other types but much more likely to invade nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body. Most deaths from skin cancer are caused by Melanoma.
- Balo's Disease: Balo's Disease is a rare demyelinating disorder of the central nervous system (CNS) in which the myelin (the fatty substance covering nerve fibers) is damaged. Balo's Disease shares features with other demyelinating diseases and is generally regarded as a rare variant of multiple sclerosis (MS).
- Basal Cell Carcinoma of the Skin: Basal Cell Carcinoma is a type of skin cancer that most often develops on areas of skin exposed to the sun, such as the face. On brown and Black skin, basal cell carcinoma often looks like a bump that's brown or glossy black and has a rolled border. Basal Cell Carcinoma is a type of skin cancer.
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes too many lymphocytes (a type of white blood cell). Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia is a blood and bone marrow disease that usually gets worse slowly. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia is one of the most common types of leukemia in adults. It often occurs during or after middle age. It rarely occurs in children.
- Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (also called CML or chronic granulocytic leukemia) is a slowly progressing blood and bone marrow disease that usually occurs during or after middle age, and rarely occurs in children.
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: COPD, or Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, is a long-term lung disease that refers to both chronic bronchitis and emphysema. COPD symptoms include persistent cough with mucus and shortness of breath.
- Complex Regional Pain Syndrome / CRPS / Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome / RSDS: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome, also known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome, is a rare disorder of the sympathetic nervous system that is characterized by chronic, severe pain. The sympathetic nervous system is the part of the autonomic nervous system that regulates involuntary functions of the body such as increasing heart rate, constricting blood vessels, and increasing blood pressure. Excessive or abnormal responses of portions of the sympathetic nervous system are thought to be responsible for the pain associated with Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome.
- Cultural Diversity: Cultural Diversity is the inclusion of diverse people. The phrase cultural diversity can also refer to having different cultures respect each other's differences.
- Diversity: Diversity means understanding that each individual is unique, and recognizing individual differences. These differences can be along the dimensions of race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, socio-economic status, age, physical abilities, religious beliefs, political beliefs, or other ideologies.
- Easterseals: Through their national network of affiliates, Easterseals provides essential services and on-the-ground support to more than 1.5 million people each year — from early childhood programs for the critical first five years, to autism services, to medical rehabilitation and employment programs, to veterans’ services, and more. Their public education, policy, and advocacy initiatives positively shape perceptions and address the urgent and evolving needs of the one in four Americans living with disabilities.
- Food Insecurity and Hunger / Food Deserts: The U.S. Department of Agriculture defines food deserts as areas where people live more than 1 mile from a supermarket in urban areas, or ten miles away in rural areas. This often translates into families shopping at ‘mini-marts’ or gas stations for their routine groceries. These local businesses generally sell ‘junk’ food and have significantly higher prices for this food (which is rarely fresh). Food deserts have a disproportionate impact on urban Latino and African American communities, and rural Indigenous Peoples and Caucasian communities. Food insecurity is much more profound within these food deserts.
- Gun Control: Gun Control is a broad term that covers any sort of restriction on what kinds of firearms can be sold and bought, who can possess or sell them, where and how they can be stored or carried, what duties a seller has to vet a buyer, and what obligations both the buyer and the seller have to report transactions to the government. Sometimes, the term is also used to cover related matters, like limits on types of ammunition and magazines, or technology, like the type that allows guns to fire only when gripped by their owners. In recent years, Gun Control debates have focused primarily on background checks for buyers, allowing people to carry weapons in public, and whether to allow the possession of assault rifles. Firearm injuries are a serious public health problem. In 2020, there were 45,222 firearm-related deaths in the United States. That is about 124 people dying from a firearm-related injury each day. More than half of firearm-related deaths were suicides and more than 4 out of every 10 were firearm homicides.
- Gun Violence Prevention: Gun Violence Prevention is a proactive plan to prevent active shooter incidents and, more broadly, address gun violence in all its forms. Many of today’s youth have grown up in the shadow of mass shootings, including at Columbine High School, Sandy Hook Elementary, and Marjorie Stoneman Douglas High School. Active shooter drills are commonly practiced, starting in elementary school. Educators are increasingly expected to transform from nurturers to first responders at a moment’s notice, having to react and decide the best ways to protect their students based on the circumstances. Further, Gun Violence affects people of all ages and races in the U.S. but has a disproportionate impact on young adults, males and racial/ethnic minorities. Guns are a weapon of choice for mass homicides and suicide. Gun violence costs the U.S. $229 billion, or an average of $700 per gun in America.
- Hairy Cell Leukemia: Hairy Cell Leukemia is a cancer of the blood and bone marrow. This rare type of leukemia gets worse slowly or does not get worse at all. The disease is called Hairy Cell Leukemia because the leukemia cells look "hairy" when viewed under a microscope.
- Human Rights: Human Rights are rights inherent to all human beings, regardless of race, sex, nationality, ethnicity, language, religion, or any other status. Human rights include the right to life and liberty, freedom from slavery and torture, freedom of opinion and expression, the right to work and education, and many more.
- Humane Treatment of Animals: There are no federal animal welfare laws regulating the treatment of the billions of "food animals" while they're on the farm. Further, while all 50 states have cruelty statutes, most explicitly exempt common farming practices, no matter how abusive. Each one of us has the ability to help farm animals every time we sit down to eat. Whether it be avoiding the most abusive animal products, such as eggs from caged birds, reducing the amount of animal products we eat, or replacing our animal consumption with vegetarian foods, we each can use our consumer dollars to improve farm animals' lives. The alternate color for Humane Treatment of Animals is animal paw prints.
- Humane Treatment of Refugees: Today, intense and unrelenting conflicts have driven more people from their homes than ever before. 65 million people are displaced globally, including 21 million refugees, half of them children. The immense scale of the global refugee crisis is challenging policymakers across the world to offer protection and dignity to a dramatically higher number of people while preventing deaths at sea and addressing local concerns about border protection.
- Hunger: 821 million people in the world do not get the food they need to live a healthy life. 66 million primary school-age children attend classes hungry across the developing world. Malnutrition in all its forms, from wasting to obesity, directly affects one in three people.
- Idiopathic Inflammatory Demyelinating Diseases: Idiopathic Inflammatory Demyelinating Diseases represent a broad spectrum of Central Nervous System Disorders that can be differentiated on the basis of severity, clinical course, and lesion distribution, as well as imaging, laboratory and pathologic findings. Multiple sclerosis (MS) is the most common Demyelinating Disease of the central nervous system. In this disorder, the immune system attacks the myelin sheath or the cells that produce and maintain it. This attack causes inflammation and injury to the nerve sheath and ultimately to the nerve fibers that it surrounds.
- Kidney Cancer (Renal Cell): Kidney Cancer is a disease in which the cells in certain tissues of the kidney start to grow uncontrollably and form tumors. Renal cell carcinoma, which occurs in the cells lining the kidneys (epithelial cells), is the most common type of kidney cancer.
- Leukemia: Leukemia is a malignant progressive disease in which the bone marrow and other blood-forming organs produce increased numbers of immature or abnormal leukocytes. These suppress the production of normal blood cells, leading to anemia and other symptoms.
- Limb Difference: Limb Difference is the partial or complete absence of or malformation of limbs (arms and legs). There are two main types of limb difference: congenital limb difference and acquired limb difference. Congenital Limb Difference is also referred to as Limb Reduction" or Congenital Amputation or Amelia and occurs when someone is born missing all or part of their upper and/or lower limbs. Acquired Limb Differences is also known as Amputation and occurs when someone has a limb removed for medical reasons, or accidentally due to trauma.
- Malnutrition: Malnutrition refers to deficiencies, excesses or imbalances in a person’s intake of energy and/or nutrients. The term malnutrition covers two broad groups of conditions. One is undernutrition, which includes stunting (low height for age), wasting (low weight for height), underweight (low weight for age) and micronutrient deficiencies or insufficiencies (a lack of important vitamins and minerals). The other is overweight, obesity and diet-related noncommunicable diseases (such as heart disease, stroke, diabetes and cancer).
- Mass Shooting Prevention / Gun Control: For the last 20 years, students, educators, and parents have lived with the reality of increasingly frequent school shootings. The worst period for this violence has been in the 2021–2022 school year, which saw nearly quadruple the average number of gunfire incidents since 2013. From an average of 49 incidents in every school year since 2013, this past school year saw 193 incidents of gunfire on the grounds of preschools and K–12 schools. Meanwhile, America’s gun violence epidemic, in the form of mass shootings, gun homicides and suicides, and unintentional shootings, has been infecting America’s schools. The failure to address the root causes of school gun violence from all angles has lasting consequences for millions of American children.
- Merkel Cell Carcinoma (Skin Cancer): Merkel Cell Carcinoma is a rare type of skin cancer that usually appears as a flesh-colored or bluish-red nodule, often on the face, head or neck. Merkel Cell Carcinoma is also called Neuroendocrine Carcinoma of the skin. Merkel Cell Carcinoma most often develops in older people. Long-term sun exposure or a weak immune system may increase the risk of developing Merkel Cell Carcinoma. Merkel Cell Carcinoma tends to grow fast and to spread quickly to other parts of your body.
- Motorcycle Safety: In 2020, 82,528 motorcyclists were recorded injured, 5,579 motorcyclists were killed, totaling 14% of all traffic fatalities in that same year according to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). Riding a motorcycle is not without risk. Injuries and fatalities are not uncommon. But taking precautions on the road and preparing properly can reduce the severity of the risk. In states without universal helmet laws, 57% of motorcyclists killed were not wearing helmets compared to 11% in states with helmet laws, reports the NHTSA. They estimate that 1,872 motorcyclists’ lives were saved by wearing a helmet in 2017. Practicing responsible riding and wearing the appropriate protective gear can help you make sure you can keep riding for many years to come.
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is a potentially disabling disease of the brain and spinal cord (Central Nervous System). In MS, the immune system attacks the protective sheath (myelin) that covers nerve fibers and causes communication problems between the brain and the rest of the body. Eventually, the disease can cause the nerves themselves to deteriorate or become permanently damaged.
- Myelogenous Leukemia, Chronic: Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia is a disease in which the bone marrow makes too many white blood cells. Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia (also called CML or Chronic Granulocytic Leukemia) is a slowly progressing blood and bone marrow disease that usually occurs during or after middle age. It rarely occurs in children. In Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia, too many blood stem cells become a type of white blood cell called granulocytes. These granulocytes are abnormal and do not become healthy white blood cells. They are also called leukemia cells. The leukemia cells can build up in the blood and bone marrow so there is less room for healthy white blood cells, red blood cells, and platelets. When this happens, infection, anemia, or easy bleeding may occur.
- Myeloid Leukemia, Acute: Adult Acute Myeloid Leukemia is a type of cancer in which the bone marrow makes abnormal myeloblasts (a type of white blood cell), red blood cells, or platelets. This type of cancer usually gets worse quickly if it is not treated. It is the most common type of Acute Leukemia in adults. Acute Myeloid Leukemia is also called Acute Myelogenous Leukemia, Acute Myeloblastic Leukemia, Acute Granulocytic Leukemia, and Acute Nonlymphocytic Leukemia.
- Necrotizing Fasciitis: Necrotizing Fasciitis is a rare infection that is often described in media reports as a condition involving "flesh-eating bacteria." It can be fatal if not treated promptly. Necrotizing Fasciitis spreads quickly and aggressively in an infected person. It causes tissue death at the infection site and beyond.
- No Kid Hungry: No Kid Hungry is the only national campaign committed to ending childhood hunger in the U.S. There is no possible excuse for children to go hungry in this country. Yet it happens - every day, in every community. According to the latest estimates, as many as 9 million children in the United States live in "food insecure" homes. This means that those households don't have enough food for every family member to lead a healthy life.
- No Kids or Pets Unattended in Cars: Every day, children and pets are left unattended in or around vehicles, a danger most people greatly underestimate. This emerging public health issue causes death and injury due to the dangerous social practice of leaving children and pets unattended in or around vehicles.
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer: Non-Melanoma skin cancer refers to all the types of cancer that occur in the skin that are not melanoma. Several types of skin cancer fall within the broader category of Non-Melanoma skin cancer, with the most common types being Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma.
- Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer, Childhood: Risk factors for Childhood Basal Cell Carcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the skin include being exposed to natural sunlight or artificial sunlight (such as from tanning beds), having a fair complexion, actinic keratosis, Gorlin Syndrome, past treatment with radiation, and a weakened immune system. The alternate color for Childhood Non-Melanoma Skin Cancer is gold.
- Orange Ribbon for At-Risk Animals: Registered with the US Patent and Trademark Office, the Orange Ribbon for Animals is the official awareness ribbon for at-risk animals in the United States.
- Pemphigus Vulgaris : Pemphigus Vulgaris is a rare long-term condition caused by a problem with the immune system. It causes blisters in the mouth and on the skin. It can be very serious, but treatment can help control it.
- Prader-Willi Syndrome: Prader-Willi Syndrome is a genetic condition that affects many parts of the body. Infants with Prader-Willi Syndrome have severe hypotonia, feeding difficulties, and slow growth. In later infancy or early childhood, affected children typically begin to eat excessively and become obese. Other signs and symptoms often include short stature, hypogonadism, developmental delays, cognitive impairment, and distinctive behavioral characteristics such as temper tantrums, stubbornness, and obsessive-compulsive tendencies.
- Racial Tolerance: Racial Tolerance can be described as “a respect, acceptance and appreciation of the rich diversity of our world's cultures, forms of expression and ways of being human. Tolerance is harmony in difference.”
- Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy: Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS), also known as Reflex Sympathetic Dystrophy Syndrome (RSDS), involves a disturbance in the sympathetic nervous system. The sympathetic nervous system is the network of nerves located alongside the spinal cord that controls certain bodily functions, such as opening and closing blood vessels or sweat glands. CRPS causes musculoskeletal pain and skin changes, primarily in the hands and feet.
- Renal Cell Cancer (Kidney Cancer): Renal Cell Cancer (also called kidney cancer or renal cell adenocarcinoma) is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells are found in the lining of tubules (very small tubes) in the kidney. Kidney Cancer can develop in adults and children. The main types of Kidney Cancer are Renal Cell Cancer, Transitional Cell Cancer, and Wilms' Tumor. Certain inherited conditions increase the risk of Kidney Cancer. Cancer that starts in the ureters or the renal pelvis (the part of the kidney that collects urine and drains it to the ureters) is different from Renal Cell Cancer.
- Safe Rides: SafeRides is the best choice for friends or family going to nightclubs, bars, pub crawls, wine tours, as well as for trips to concerts, games, birthdays and bachelor / bachelorette parties.
- Self-Harm (Self-Injury): Self-Harm or Self-Injury means hurting oneself on purpose. One common method is cutting oneself with a knife. But any time someone deliberately hurts herself is classified as Self-Harm. Some people feel an impulse to burn themselves, pull out hair or pick at wounds to prevent healing. Extreme injuries can result in broken bones.
- Skin Cancer: Skin Cancer is the most common type of cancer. Skin Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. The main types of skin cancer are Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, and Melanoma. Melanoma is much less common than the other types but much more likely to invade nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body. Most deaths from skin cancer are caused by melanoma.
- Skin Cancer, Childhood: Skin Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the skin. The skin is the body’s largest organ. There are three types of Skin Cancer: Melanoma, Squamous Cell Skin Cancer and Basal Cell Skin Cancer. Even though Melanoma is rare, it is the most common Skin Cancer in children. It occurs more often in adolescents aged 15 to 19 years. The alternate color for Skin Cancer in children is gold.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Skin: Skin Cancer is the most common type of cancer. The main types of Skin Cancer are Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Basal Cell Carcinoma, and Melanoma. Melanoma is much less common than the other types but much more likely to invade nearby tissue and spread to other parts of the body. Most deaths from Skin Cancer are caused by Melanoma.
- Tay-Sachs Disease: Tay-Sachs Disease is a rare, inherited neurodegenerative disease. People with Tay-Sachs Disease do not have enough of an enzyme called beta-hexosaminidase A. The less enzyme a person has, the more severe the disease and the earlier that symptoms appear. There are 3 forms of Tay-Sachs Disease, distinguished by the general age of onset.
- Transitional Cell Cancer of the Renal Pelvis and Ureter (Kidney) Cancer: Kidney Cancer can develop in adults and children. The main types of Kidney Cancer are Renal Cell Cancer, Transitional Cell Cancer, and Wilms' Tumor. Certain inherited conditions increase the risk of Kidney Cancer. Renal Cell Cancer is a more common type of Kidney Cancer.
- Ureter and Renal Pelvis, Transitional Cell Cancer, Kidney (Renal Cell) Cancer: Kidney Cancer can develop in adults and children. The main types of Kidney Cancer are Renal Cell Cancer, Transitional Cell Cancer, and Wilms' Tumor. Transitional Cell Cancer of the renal pelvis and ureters is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the renal pelvis and ureter. Certain inherited conditions increase the risk of Kidney Cancer.
- Wilms' Tumor and Other Childhood Kidney Tumors: Kidney Cancer can develop in adults and children. The main types of Kidney Cancer are Renal Cell Cancer, Transitional Cell Cancer, and Wilms' Tumor. Certain inherited conditions increases the risk of Kidney Cancer. Childhood kidney tumors are diseases in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the kidney. There are many types of childhood kidney tumors, which include: Wilms' Tumor, Renal Cell Cancer, Rhabdoid Tumor of the Kidney, Clear Cell Sarcoma of the Kidney, Congenital Mesoblastic Nephroma, Ewing Sarcoma of the Kidney, Primary Renal Myoepithelial Carcinoma, Cystic Partially Differentiated Nephroblastoma, Multiocular Cystic Nephroma, Primary Renal Synovial Sarcoma, and Anaplastic Sarcoma of the Kidney. Nephroblastomatosis is not cancer but may become Wilms' Tumor. The alternate color for Wilms' Tumor in children is gold.
- World Hunger: Although the number of undernourished people has dropped by over 20% since 1992 (216 million fewer than in 1990-92) today there are 821 million people who do not have enough to eat. This is more than the 795 million in 2014, although still down from about 900 million in 2000. 98% of the world’s undernourished people live in developing countries. 767 million people, or 1 in 10 people in the world, live under $1.90 a day, and half of the extreme poor (389 million) live in Sub-Saharan Africa. 328 million children are living in extreme poverty.
- World Poverty: 328 million children are living in extreme poverty.
Orange and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Union for International Cancer Control, World Cancer Day: The Union for International Cancer Control (UICC) unites and supports the cancer community to reduce the global cancer burden, to promote greater equity, and to ensure that cancer control continues to be a priority in the world health and development agenda.
- Marshall County HS Shooting: The Marshall County High School shooting occurred at Marshall County High School in Benton, Kentucky, on January 23, 2018.
Orange and Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Dual Diagnosis Dual diagnosis (also referred to as co-occurring disorders) is a term for when someone experiences a mental illness and a substance use disorder simultaneously. Either disorder, substance use or mental illness, can develop first. People experiencing a mental health condition may turn to alcohol or other drugs as a form of self-medication to improve the mental health symptoms they experience. However, research shows that alcohol and other drugs worsen the symptoms of mental illnesses.
- Ritual Abuse: Ritual Abuse is abuse that occurs in the context linked to some symbols or group activity that have religious, magical or supernatural connotation and where the invocation of these symbols or activities, repeated over time, is used to frighten and intimate. All of this is conducted for the purpose of control so that the abusers can systematically abuse others.
Orange and Lavender Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Eczema: Eczema is a common skin condition marked by itchy and inflamed patches of skin. It is also known as Atopic Dermatitis. It is more common in babies and young children, and often occurs on the faces of infants. It also often appears inside the elbows and behind the knees of children, teenagers, and adults. In rare cases, atopic dermatitis can first appear during puberty or adulthood. It affects males and females equally.
- Psoriasis: Psoriasis is a chronic, inflammatory skin disease. Psoriasis is related to inherited genes and the immune system. Plaque Psoriasis is the most common form of Psoriasis.
- Psoriatic Arthritis: Psoriatic Arthritis is a form of arthritis that affects some people who have Psoriasis, a condition that features red patches of skin topped with silvery scales. Most people develop Psoriasis first and are later diagnosed with Psoriatic Arthritis, but the joint problems can sometimes begin before skin lesions appear.
Orange and Purple Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Failed Back Surgery Syndrome: Failed Back Surgery Syndrome refers to a subset of patients who have new or persistent pain after spinal surgery for back or leg pain. The pain can be reduced but still present, or may get worse within a few months after surgery due to a buildup of scar tissue around spinal nerve roots, along with persistent tissue pain and muscle spasm. The term refers to a condition of continuing pain and is not meant to imply there was necessarily a problem during surgery. While published reports estimate the incidence of Failed Back Surgery Syndrome to be between 20 – 40%, the likelihood is considered greater with repeated surgery, and the condition will be more prevalent in regions where spinal surgery is more common.
Orange and Red Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms including ET, MF, PV / MPN: Myeloproliferative neoplasms are types of blood cancer that begin with an abnormal mutation (change) in a stem cell in the bone marrow. The change leads to an overproduction of any combination of white cells, red cells and platelets. The alternate color for Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms is red.
- Kawasaki Disease: Kawasaki Disease is a rare childhood condition that involves inflammation of the blood vessels, especially the coronary arteries. It is a disease of infants and young children, usually age 2 years and younger, with boys afflicted more often than girls. Although all racial groups are affected, children of Asian ancestry are more likely to develop the disease.
- Myelodysplastic Syndromes: Myelodysplastic syndromes are a group of cancers in which immature blood cells in the bone marrow do not mature or become healthy blood cells. The alternate color for Myelodysplastic Syndromes is red.
- Myelofibrosis: Myelofibrosis is a disorder of the spongy tissue inside the bone (bone marrow) that contains the stem cells that will form blood cells. In Myelofibrosis, the bone marrow is replaced by fibrous (scar) tissue. When the bone marrow is scarred, it cannot make enough blood cells. This leads to anemia, weakness, fatigue, and often, swelling of the liver and spleen.
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms, Chronic, including ET, MF, and PV: Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms are blood cancers that occur when the body makes too many white or red blood cells, or platelets. This overproduction of blood cells in the bone marrow can create problems for blood flow and lead to various symptoms. MPNs were called Myeloproliferative Diseases until 2008 when the World Health Organization reclassified them as cancers and renamed them Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. There are three main types of MPNs: Polycythemia Vera (PV), Essential Thrombocythemia (ET), Myelofibrosis (MF). Certain Leukemias, including Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia, are also now considered Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. The alternate colors are burgundy and red for Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms.
- Myeloproliferative Disorders: Myeloproliferative Disorders are blood cancers caused by changes in the stem cells inside bone marrow, the tissue that makes blood cells. These changes cause the body to make too many blood cells. This excess can be any type of blood cell — white, red, or platelets. A MPD diagnosis depends on which blood cell, or cells, the body overproduces. MPDs usually affect only one type of blood cell. Rarely do they affect more than one.
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms: Myeloproliferative Neoplasms are a group of diseases in which the bone marrow makes too many red blood cells, white blood cells, or platelets. Normally, the bone marrow makes blood stem cells (immature cells) that become mature blood cells over time.
- Parkland High School Shooting: On February 14, 2018, 19-year-old Nikolas Cruz opened fire on students and staff at Marjory Stoneman Douglas High School in the Miami suburban town of Parkland, Florida, murdering 17 people and injuring 17 others. The shooting prompted student survivors to found the March for Our Lives gun safety advocacy group, and led to changes in Florida gun laws, including raising the minimum age for firearms purchases to 21.
- Polycythemia Vera: Polycythemia eVra, or PV, is a rare, chronic blood cancer in which a person’s body makes too many red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Polycythemia Vera is part of a group of diseases called M yeloproliferative Neoplasms. Too many red blood cells can cause the blood to thicken. Thicker blood doesn’t flow normally through arteries and veins.
Orange and Yellow Awareness ribbons colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Stiff-Person Syndrome Stiff-Person Syndrome, also known as stiff-man syndrome, is a rare neurologic disorder of unclear cause characterized by progressive rigidity and stiffness. The stiffness primarily affects the trunk muscles and is superimposed by spasms, resulting in postural deformities.
Orchid Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Testicular Cancer, Adult: Testicular Cancer occurs in the testicles (testes), which are located inside the scrotum, a loose bag of skin underneath the penis. The testicles produce male sex hormones and sperm for reproduction. Compared to other types of cancer, testicular cancer is rare. But Testicular Cancer is the most common cancer in American males between the ages of 15 and 35. Nearly all Testicular Cancers begin in the germ cells, the cells in the testicles that produce immature sperm. What causes germ cells to become abnormal and develop into cancer is not known.
- Testicular Cancer, Childhood: Testicular Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of one or both testicles. There are two types of testicular tumors. The first is Germ Cell Tumors that start in sperm cells in males. The second is and Non-Germ Cell Tumors that begin in the tissues that surround and support the testicles. These tumors may be benign or malignant. The alternate color for Testicular Cancer in children is gold.
Paisley Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Goiter: A goiter commonly develops as a result of iodine deficiency or inflammation of the thyroid gland. Not all goiters cause symptoms. Symptoms that do occur might include swelling, and cough. Rarely, symptoms may include throat tightness or trouble breathing.
- Grave's Disease: Graves' Disease is an immune system disorder that results in the overproduction of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism). Although a number of disorders may result in hyperthyroidism, Graves' Disease is a common cause. Thyroid hormones affect many body systems, so signs and symptoms of Graves' Disease can be wide ranging.
- Hashimoto's Disease: Hashimoto's Disease is an autoimmune disorder. The immune system creates antibodies that attack thyroid cells as if they were bacteria, viruses or some other foreign body.
- Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: Hashimoto's Thyroiditis is also called Hashimoto's Disease. Hashimoto's Thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease, a disorder in which the immune system turns against the body's own tissues. In people with Hashimoto's, the immune system attacks the thyroid. This can lead to hypothyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid does not make enough hormones for the body's needs.
- Hyperthyroidism: Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) occurs when the thyroid gland produces too much of the hormone thyroxine. Hyperthyroidism can accelerate your body's metabolism, causing unintentional weight loss and a rapid or irregular heartbeat. Several treatments are available for Hyperthyroidism.
- Hypothyroidism: Hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) is a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough of certain important hormones. Women, especially those older than age 60, are more likely to have Hypothyroidism. Hypothyroidism upsets the normal balance of chemical reactions in the body. It seldom causes symptoms in the early stages, but over time, untreated Hypothyroidism can cause a number of health problems, such as obesity, joint pain, infertility and heart disease.
- Ord’s Thyroiditis: Ord's Thyroiditis is also known as Ord's Disease. This autoimmune condition is characterized by atrophy of the thyroid gland and Hypothyroidism. It is very similar to Hashimoto's Disease, apart from the shrinking of the thyroid gland instead of the development of a Goiter.
- Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis is swelling (inflammation) of the thyroid gland. It causes either unusually high or low levels of thyroid hormones in the blood. The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the neck. It produces hormones that control the body's growth and metabolism.
- Thyroid Nodules: The term Thyroid Nodule refers to an abnormal growth of thyroid cells that forms a lump within the thyroid gland. Although the vast majority of thyroid nodules are benign (noncancerous), a small proportion of thyroid nodules do contain thyroid cancer. In order to diagnose and treat thyroid cancer at the earliest stage, most thyroid nodules need some type of evaluation.
Peach Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Autoimmune Progesterone Dermatitis: Autoimmune Progesterone Dermatitis is a rare autoimmune response to endogenous progesterone that usually occurs in fertile females. Cutaneous or mucosal lesions develop cyclically during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle when progesterone levels are elevated.
- Endometrial Cancer: Endometrial Cancer is cancer that starts in the endometrium, the lining of the uterus (womb). Endometrial Cancer is the most common type of uterine cancer.
- Endometrial Stromal Cancer: Endometrial Stromal Sarcoma is the rarest type of uterine cancer that accounts for less than 1% of cancers of the female reproductive organs. These tumors tend to occur more often in premenopausal women between 40-50 years of age. This is younger than the average for uterine cancer in general (early 60s).
- Invisible Illness: An invisible illness is an umbrella term for any medical condition that is not easily visible to others. This includes chronic physical conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, fibromyalgia, and also mental illnesses.
- Pink Tax – Gender Based Price Discrimination: The Pink Tax is gender-specific pricing that results in higher costs for products marketed toward women. Identical products marketed for men often have lower prices compared to the women’s versions. Pink Tax products commonly use specific characteristics, such as colorful packaging, fruity scents, and floral designs to try to appeal to women. While the Pink Tax affects a wide range of products including children and adult clothing, toys, and soaps, it also impacts service industries, such as dry cleaners and hair salons.
- Uterine Cancer: There are two primary types of uterine cancer, which develop in different parts of the uterus. Endometrial Cancer develops in the lining of the uterus, called the endometrium. This is the most common type of uterine cancer, accounting for more than 95 percent of cases. Uterine Sarcoma is a more rare type of uterine cancer, and forms in the muscles or other tissues of the uterus.
- Uterine Sarcoma: Uterine Sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the muscles of the uterus or other tissues that support the uterus. Uterine Cancers can be of two types: Endometrial Cancer (common) and Uterine Sarcoma (rare). Uterine Sarcoma is different from cancer of the endometrium, a disease in which cancer cells start growing inside the lining of the uterus. Endometrial Cancer can often be cured. Uterine Sarcoma is often more aggressive and harder to treat.
Peach and Gray Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Clergy Sexual Abuse: Sexual abuse happens when someone in a ministerial role (clergy, religious or lay) engages in sexual contact or sexualized behavior with a congregant, employee, student or counseling client in the ministerial relationship.
Pearl Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Bronchial Adenoma, Adult: Bronchial Adenoma is a rare type of cancer that starts in the mucous glands and ducts of the lung airways (bronchi) or windpipe (trachea), and in the salivary glands. Although the word "adenoma" means a noncancerous tumor, most Bronchial Sdenomas are cancer and can spread to other parts of the body.
- Bronchial Adenoma, Childhood: Bronchial Adenoma is rare in children, but it is the most common primary lung tumor. The alternate color for Bronchial Adenoma in children is gold.
- Bronchial Cancer: Bronchial Adenoma is a rare type of cancer that starts in the mucous glands and ducts of the lung airways (bronchi) or windpipe (trachea), and in the salivary glands. Although the word "adenoma" means a noncancerous tumor, most Bronchial Sdenomas are cancer and can spread to other parts of the body.
- Bronchial Tumors, Adult: Most of the tumors that form in the trachea and bronchi in adults are cancerous, but a few are noncancerous. Squamous Cell Carcinoma, which usually arises in the lower part of the trachea, is the most common type of malignant Tracheal Tumor.
- Bronchial Tumors, Childhood Tracheobronchial Tumors begin in the cells that line the surface of the lung. Most Tracheobronchial Tumors in children are benign and occur in the trachea or large airways of the lung. Sometimes, a slow-growing Tracheobronchial Tumor becomes cancer that may spread to other parts of the body. The alternate color for Bronchial Tumors in childhood is gold.
- Bronchiectasis: Bronchiectasis is a chronic condition that causes the walls of the bronchi to thicken from inflammation and infection. People with Bronchiectasis have periodic flare-ups of breathing difficulties, called exacerbations.
- Bronchogenic Carcinoma, Adult: Cancer that begins in the tissue that lines or covers the airways of the lungs, including Small Cell and Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.
- Bronchogenic Carcinoma, Childhood: Pleuropulmonary Blastoma is a type of childhood lung cancer that forms in the tissues of the lung and pleura or the organs between the lungs. The alternate color for Bronchogenic Carcinoma in childhood is gold.
- Chronic Lung Disease: Chronic Lung Disease is a general term for long-term respiratory problems in premature babies. It is also known as Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia. Chronic Lung Disease results from lung injury to newborns who must use a mechanical ventilator and extra oxygen for breathing. The lungs of newborn (and especially premature) babies are fragile and are easily damaged. With injury, the tissues inside the lungs become inflamed and can break down, causing scarring. This scarring can result in difficulty breathing and increased oxygen needs.
- Congenital Lobar: Congenital Lobar Emphysema, also called Congenital Lobar Overinflation, is a rare anomaly of fetal lung development in which an obstruction of the airways leads to an enlarged, overinflated lobe or lobes of the lung.
- Emphysema: Emphysema is a lung condition that causes shortness of breath. In people with Emphysema, the air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) are damaged. Over time, the inner walls of the air sacs weaken and rupture, creating larger air spaces instead of many small ones. This reduces the surface area of the lungs and, in turn, the amount of oxygen that reaches the bloodstream.
- Emphysema Interstitial Lung Disease: Combined Pulmonary Fibrosis and Emphysema is a possible new addition to a growing list of smoking-related lung disease characterized by the coexistence of usual Interstitial Pneumonia or Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia with Emphysema in tobacco smokers.
- Lung Cancer (Non-Small Cell and Small Cell): Lung Cancer begins in the lungs and may spread to lymph nodes or other organs in the body. Lung Cancers usually are grouped into two main types called Small Cell and Non-Small Cell. These types of lung cancer grow differently and are treated differently. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer is more common than Small Cell Lung Cancer.
- Lung Cancer, Adult: Lung Cancer often has no symptoms until it has spread (metastasized). This is because there are few specialized nerves (pain receptors) in the lungs. When symptoms do occur, they vary depending on the type of Lung Cancer and location and size of the tumor. A series of tests are necessary to diagnose Lung Cancer. Further testing can identify the type and stage of cancer, which help determine treatment options.
- Lung Cancer, Childhood: In children, the most common lung tumors are Tracheobronchial Tumors and Pleuropulmonary Blastoma. Tracheobronchial Tumors begin in the cells that line the surface of the lung. Most Tracheobronchial Tumors in children are benign and occur in the trachea or large airways of the lung. Sometimes, a slow-growing Tracheobronchial Tumor becomes cancer that may spread to other parts of the body. Pleuropulmonary Blastomas form in the tissue of the lung and pleura. The alternate color for lung cancer in children is gold.
- Lung Disease Linked to Vaping: EVALI is a serious medical condition in which a person's lungs become damaged from substances contained in e-cigarettes and vaping products. Vaping involves using a device known as an e-cigarette to heat up a small amount of liquid, turning it into a vapor that can be inhaled.
- Mesothelioma, Malignant: Mesothelioma is an aggressive cancer that affects the lining of the lungs, heart, or abdomen. Caused by the inhalation of asbestos fibers, mesothelioma is often diagnosed in older individuals who worked with asbestos products.
- Mesothelioma, Adult: Malignant Mesothelioma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the chest or abdomen. Being exposed to asbestos can affect the risk of Malignant Mesothelioma. Signs and symptoms of Malignant Mesothelioma include shortness of breath and pain under the rib cage.
- Mesothelioma, Childhood: Mesothelioma is a rare cancer most commonly diagnosed in people in their 60s and 70s, but doctors have reported roughly 300 cases worldwide in young adults, children and even infants. In most cases of Mesothelioma diagnosed in childhood, there is no history of exposure to asbestos, which is a much more common cancer among adults. The alternate color for Mesothelioma in children is gold.
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the lungs. Lung Cancer includes two main types: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Small Cell Lung Cancer. Smoking causes most lung cancers, but nonsmokers can also develop lung cancer.
- Pneumonia: Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in one or both lungs. The air sacs may fill with fluid or pus (purulent material), causing cough with phlegm or pus, fever, chills, and difficulty breathing. A variety of organisms, including bacteria, viruses and fungi, can cause pneumonia.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer Lung Cancer includes two main types: Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer and Small Cell Lung Cancer. The types of Small Cell Lung Cancer are named for the kinds of cells found in the cancer and how the cells look when viewed under a microscope: Small Cell Carcinoma (Oat Cell Cancer) or Combined Small Cell Carcinoma.
- Thymoma and Thymic Carcinoma The thymus, a small organ that lies in the upper chest under the breastbone, is part of the lymph system. It makes white blood cells, called lymphocytes, that protect the body against infections. There are different types of tumors of the thymus. Thymomas and Thymic Carcinomas are rare tumors of the cells that are on the outside surface of the thymus. The tumor cells in a thymoma look similar to the normal cells of the thymus, grow slowly, and rarely spread beyond the thymus. On the other hand, the tumor cells in a Thymic Carcinoma look very different from the normal cells of the thymus, grow more quickly, and have usually spread to other parts of the body when the cancer is found. Thymic Carcinoma is more difficult to treat than thymoma.
- Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia is a rare type of cancer that begins in the white blood cells. With Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia, the bone marrow produces too many abnormal white blood cells that crowd out healthy blood cells. The abnormal white blood cells produce a protein that accumulates in the blood, impairs circulation and causes complications. Waldenstrom Macroglobulinemia is considered a type of Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma. It is sometimes called Lymphoplasmacytic Lymphoma.
Pearl and White Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Lung Cancer Acquired in Ways Other Than Smoking: While cigarette smoking is an undisputed cause of Lung Cancer, not all cases of lung cancer occur in smokers or former smokers. Each year, over 170,000 Americans develop Lung Cancer, and approximately ten per cent of Lung Cancers, or 17,000 cases, occur in non-smokers. Although not every non-smoker suffering from Lung Cancer will have an identifiable risk factor for development of the disease, a number of conditions and circumstances have been identified that will increase a non-smoker's chance of developing Lung Cancer. These include passive smoking, radon gas, exposure to asbestos, hereditary factors, and air pollution.
- Passive Smoking: When others breathe in your secondhand smoke, or passive smoking, it isn't just unpleasant for them, it can damage their health too. People who regularly breathe in secondhand smoke are more likely to get the same diseases as smokers, including Lung Cancer and heart disease.
- Secondhand Smoke: Secondhand Smoke exposure occurs when people who do not smoke breathe in smoke exhaled by people who smoke or from burning tobacco products. Since the 1964 Surgeon General's Report, 2.5 million adults who do not smoke have died from health problems caused by Secondhand Smoke exposure.
Periwinkle Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Anorexia Nervosa: Anorexia Nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by weight loss (or lack of appropriate weight gain in growing children); difficulties maintaining an appropriate body weight for height, age, and stature; and, in many individuals, distorted body image. People with Anorexia generally restrict the number of calories and the types of food they eat. Some people with the disorder also exercise compulsively, purge via vomiting and laxatives, and/or binge eat.
- Duodenal Cancer: Duodenal Cancer is a mass of irregular, fast-growing cells (tumor) in the first portion of the small intestine. This tumor may prevent the intestine from properly digesting food and block food from passing through the intestines. In early stages, Duodenal Cancer may present with no symptoms.
- Esophageal Cancer, Adult: Esophageal Cancer is cancer that forms in tissues lining the esophagus. Two types of Esophageal Cancer are Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cancer that begins in flat cells lining the esophagus) and Adenocarcinoma (cancer that begins in cells that make and release mucus and other fluids).
- Esophageal Cancer, Childhood: Esophageal Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the esophagus. Most Esophageal Tumors in children begin in the thin, flat cells that line the esophagus. The alternate color for Esophageal Cancer in children is gold.
- Gastric Cancer (Stomach Cancer), Adult: Gastric Cancer, also called Stomach Cancer, is a malignant tumor of the stomach. Gastric Cancer can develop in any part of the stomach and can spread from the stomach to other organs.
- Gastric Cancer (Stomach Cancer), Childhood: Gastric (stomach) Cancer occurs when cancer cells form in the lining of the stomach. The alternate color for Gastric Cancer in children is gold.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease / GERD: Gastroesophageal R eflux Disease (GERD) occurs when stomach acid repeatedly flows back into the tube connecting your mouth and stomach (esophagus). This backwash (acid reflux) can irritate the lining of your esophagus. Many people experience acid reflux from time to time.
- Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer: Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer is a rare inherited condition associated with an increased risk of Gastric Cancer. Diffuse Gastric Cancer is a specific type of Stomach Cancer, sometimes also called “signet ring cell gastric cancer” or “linitis plastic.” It tends to affect much of the stomach rather than staying in one area of the stomach. Approximately 20% of all Stomach Cancers are diffuse Gastric Cancers, and a small number of these are due to Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer. The average age for someone with HDGC to be diagnosed with Stomach Cancer is 38, although it can be diagnosed much earlier or later than that.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS): Irritable Bowel Syndrome, or IBS, or Spastic Colon, is a type of gastrointestinal disorder. There are different forms of this functional disease. IBS with diarrhea (IBS-D) is characterized by chronic or recurrent diarrhea, while IBS with constipation (IBS-C) is characterized by abdominal pain or discomfort associated with constipation. Some people experience alternating symptoms of diarrhea or constipation.
- Pulmonary Hypertension: Pulmonary Hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that affects the arteries in the lungs and the right side of the heart. In one form of Pulmonary Hypertension, tiny arteries in the lungs, called pulmonary arterioles, and capillaries become narrowed, blocked or destroyed. This makes it harder for blood to flow through the lungs, and raises pressure within tbe lungs' arteries. As the pressure builds, the heart's lower right chamber (right ventricle) must work harder to pump blood through the lungs, eventually causing the heart muscle to weaken and fail. Some forms of Pulmonary Hypertension are serious conditions that become progressively worse and sometimes fatal.
- Small Intestine Cancer: Small Intestine Cancer starts when cells in the small intestine start to grow out of control. The small intestine is part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, also known as the digestive tract. The GI tract processes food for energy and rids your body of solid waste. Although the small intestine makes up the largest part of the GI tract, small intestine cancers are much less common than most other types of GI cancers (such as colon, rectal, stomach, and esophagus cancers) in the United States.
- Stomach Cancer: Stomach Cancer occurs when cancer cells form in the lining of the stomach. Risk factors include smoking, infection with H. pylori bacteria, and certain inherited conditions. Gastric Cancer begins in the cells lining the mucosal layer and spreads through the outer layers as it grows.
- Stomach Cancer, Childhood: Stomach Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the lining of the stomach. The alternate color for stomach (gastric) cancer in children is gold.
Pink Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Breast Cancer, Adult: Breast Cancer starts when cells in the breast begin to grow out of control. These cells usually form a tumor that can often be seen on an x-ray or felt as a lump. The tumor is malignant (cancer) if the cells can grow into (invade) surrounding tissues or spread (metastasize) to distant areas of the body. Breast Cancer occurs almost often in women, but men can get Breast Cancer, too.
- Breast Cancer, Childhood: Breast Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the breast. Breast Cancer may occur in both male and female children. Breast Cancer is the most common cancer among females aged 15 to 39 years. Breast Cancer in this age group is more aggressive and more difficult to treat than in older women. Most breast tumors in children are Fibroadenomas, which are benign (not cancer). Rarely, these tumors become large Phyllodes Tumors (cancer) and begin to grow quickly. The alternate color for Breast Cancer in children is gold.
- Breast Cancer and Pregnancy: Breast Cancer is the second most common cancer in women after Skin Cancer. Mammograms can detect breast cancer early, possibly before it has spread. Sometimes Breast Cancer occurs in women who are pregnant or have just given birth. Breast Cancer occurs about once in every 3,000 pregnancies. It occurs most often in women aged 32 to 38 years. Because many women are choosing to delay having children, it is likely that the number of new cases of Breast Cancer During Pregnancy will increase.
- Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS): Ductal Carcinoma in Situ (DCIS) is Non-Invasive Breast Cancer. Ductal means that the cancer starts inside the milk ducts, carcinoma refers to any cancer that begins in the skin or other tissues (including breast tissue) that cover or line the internal organs, and in situ means "in its original place." Ductal Carcinoma in Situ is called "non-invasive" because it hasn't spread beyond the milk duct into any normal surrounding breast tissue.
- Metastatic Breast Cancer: Metastatic Breast Cancer (also called stage IV) is breast cancer that has spread to another part of the body, most commonly the liver, brain, bones, or lungs.
- Paget's Disease of the Breast: Paget's Disease of the Breast (also known as Paget's Disease of the Nipple and Mammary Paget Disease) is a rare type of cancer involving the skin of the nipple and, usually, the darker circle of skin around it, which is called the areola. Most people with Paget Disease of the breast also have one or more tumors inside the same breast. These breast tumors are either Ductal Carcinoma in Situ or Invasive Breast Cancer.
- Pregnancy and Breast Cancer: The prevalence of Pregnancy-Associated Breast Cancer may be increasing owing to delayed childbearing, and despite its low incidence, Breast Cancer is the second most common cancer in pregnant women.
- Women's Health Women's Health refers to the branch of medicine that focuses on the treatment and diagnosis of diseases and conditions that affect a woman's physical and emotional well-being.
Pink and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Amniotic Fluid Embolism: Amniotic Fluid Embolism is a rare but serious condition that occurs when amniotic fluid, the fluid that surrounds a baby in the uterus during pregnancy or fetal material such as fetal cells, enters the mother's bloodstream.
- Baby, Infant and Child Loss: The death and loss of a child is frequently called the ultimate tragedy. Pregnancy and Infant Loss Remembrance Day is a day of remembrance for pregnancy loss and infant death, which includes, but is not limited to: miscarriage, stillbirth, SIDS, and the death of a newborn. Pink and blue pins can also be used to recognize mourning for the infant or child by engraving a name, date or message.
- Baby Safe Haven: Safe Haven Infant Protection Laws enable a person to give up an unwanted infant anonymously. As long as the baby has not been abused, the person may do so without fear of arrest or prosecution. The purpose of Safe Haven is to protect unwanted babies from being hurt or killed because they were abandoned. Abandoning a baby puts the child in extreme danger. Too often, it results in the child’s death. It is also illegal, with severe consequences. But with Safe Haven, this tragedy doesn’t ever have to happen again.
- Baby Sleeping Suffocation / Infant Sleeping Suffocation / Bed Sharing is Bad for Baby: Bed-sharing increases a baby's risk of dying from SIDS, especially in preterm infants (preemies), babies who had a low birth weight, and healthy full-term infants younger than 4 months old. Other things that increase this risk of death while bed-sharing include: a baby sleeping on a couch alone or with a parent.
- Barriers to Breastfeeding: Breastfeeding has maternal, infant, and societal benefits. However, many parents experience obstacles to achieving their breastfeeding goals, leading to reduced rates of breastfeeding initiation and continuation. Despite efforts to increase rates of breastfeeding initiation and continuation, inequities still persist. The factors that influence an individual’s desire and ability to breastfeed are varied and include individual parent considerations, practitioner influences, hospital barriers ,societal factors, such as workplace and parental leave policies, access to lactation support, and social support of their breastfeeding goals.
- Birth Defects: A birth defect is a problem that happens while a baby is developing in the mother's body. Most birth defects happen during the first 3 months of pregnancy. One out of every 33 babies in the United States is born with a birth defect.
- Break Time for Nursing Mothers: Federal law requires employers to provide reasonable break time for an employee to express breast milk for her nursing child for one year after the child's birth each time such employee has need to express the milk ( Section 7 of the FLSA ). Employers are also required to provide a place, other than a bathroom, that is shielded from view and free from intrusion from coworkers and the public, which may be used by an employee to express breast milk.
- Breast Cancer, Male: Male Breast Cancer is a rare cancer that forms in the breast tissue of men. Though Breast Cancer is most commonly thought of as a disease that affects women, breast cancer does occur in men. Male breast cancer is most common in older men, though it can occur at any age. A history of breast cancer in a close male relative (father, brother or uncle) increases a woman's risk of Breast Cancer.
- Breast Feeding in Public / Free the Nipple: The female nipple ban no longer exists for breastfeeding mothers, which should make many people who have been pushing Facebook (Meta) to address a nudity double standard at least partially happy.
- Cot Death: Cot Death is also called Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS). It is the sudden and unexpected death of a baby who seems healthy during sleep. Cot Death can happen in a cot, pram, bed, car seat, baby seat or anywhere a baby is sleeping. Name is typically used outside the United States.
- Genital Integrity: The primary goals of advocating for genital integrity are protecting human rights and advocating for those who feel they have been violated. The Genital Integrity movement may someday enable humans to see ourselves better, and to see how certain perceptions of "male" and "female” directly lead to forced genital cutting. In nearly every case of forced genital cutting – male, female, and intersex – a child or adolescent is forced by an adult to endure an alteration of his or her body. Even intersex babies born with "ambiguous genitalia" are not unhealthy; they merely do not conform to cultural definitions of male or female genital norms.
- Hyperemesis Gravidarum: Hyperemesis Gravidarum is a condition characterized by severe nausea, vomiting, weight loss, and electrolyte disturbance. The majority of pregnant women experience some type of morning sickness (70 – 80%). Recent studies show that at least 60,000 cases of extreme morning sickness called Hyperemesis Gravidarum are reported by those who treated in a hospital but the numbers are expected to be much higher than this since many women are treated at home or by out patient care with their health care provider.
- Infant Diseases: Childhood Disease and Disorder, is described as an illness, impairment, or abnormal condition that affects primarily infants and children—i.e., those in the age span that begins with the fetus and extends through adolescence.
- Infertility: Infertility means not being able to become pregnant after a year of trying. If a woman can get pregnant but keeps having miscarriages or stillbirths, that's also called infertility. After one year of having unprotected sex, about 15 percent of couples are unable to get pregnant. About a third of the time, infertility can be traced to the woman. In another third of cases, it is because of the man. The rest of the time, it is because of both partners or no cause can be found.
- Intersex: Being intersex is a naturally occurring variation in humans, and it isn’t a medical problem — therefore, medical interventions (like surgeries or hormone therapy) on children usually aren’t medically necessary. Being intersex is also more common than most people realize. It’s hard to know exactly how many people are intersex, but estimates suggest that about 1-2 in 100 people born in the U.S. are intersex.
- March of Dimes: The March of Dimes mission is to lead the fight for the health of all moms and babies . Their goals are to end the preventable maternal health risks and deaths, end preventable preterm birth and infant death, and close the health equity gap. The alternate color for March of Dimes is purple.
- Male Breast Cancer: Male Breast Cancer is a rare cancer that forms in the breast tissue of men. Though Breast Cancer is most commonly thought of as a disease that affects women, Breast Cancer does occur in men. Male Breast Cancer is most common in older men, though it can occur at any age. Men diagnosed with male breast cancer at an early stage have a good chance for a cure. Treatment typically involves surgery to remove the breast tissue. Other treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, may be recommended based on your particular situation.
- Miscarriage: Miscarriage is the spontaneous loss of a pregnancy before the 20 weeks. About 10 to 20 percent of known pregnancies end in miscarriage. But the actual number is likely higher because many miscarriages occur so early in pregnancy that a woman doesn't realize she's pregnant.
- Mourning the Loss of an Infant / Mourning the Loss of a Baby: You may never really get over the loss of a baby, but you can move through your grief to healing. Find the resources, support and strength you need to heal among a community of people who share an unspoken connection through their struggles, battles, wins and losses.
- Loss of, or in memory of, a baby or infant: After a pregnancy or infant loss, many parents wrestle with finding ways to honor their baby and keep his or her memory alive. The desire to maintain a connection to the baby is a normal and healthy part of grieving. This process looks different for everyone and takes time.
- Nursing Mothers' Rights: Section 7 of the FLSA requires employers to provide reasonable break time for an employee to express breast milk for her nursing child for one year after the child's birth each time such employee has need to express the milk. Employers are also required to provide a place, other than a bathroom, that is shielded from view and free from intrusion from coworkers and the public, which may be used by an employee to express breast milk. The break time requirement became effective when the Affordable Care Act was signed into law on March 23, 2010. Further, all fifty states, the District of Columbia, Puerto Rico and the Virgin Islands have laws that specifically allow women to breastfeed in any public or private location.
- Parental Alienation: Parental alienation is a strategy whereby one parent intentionally displays to the child unjustified negativity aimed at the other parent. The purpose of this strategy is to damage the child's relationship with the other parent and to turn the child's emotions against that other parent.
- Premature Birth: A premature birth is a birth that takes place more than three weeks before the baby's estimated due date. In other words, a premature birth is one that occurs before the start of the 37th week of pregnancy. The alternate color for Premature Birth is purple.
- Prematurity: Preterm is defined as babies born alive before 37 weeks of pregnancy are completed. There are subcategories of preterm birth, based on gestational age. They are: extremely preterm (less than 28 weeks), very preterm (28 to 32 weeks), and moderate to late preterm (32 to 37 weeks). The alternate color for Premie Babies is purple.
- Prostate and Breast Cancer: A history of prostate cancer in 1 or more first-degree relatives (father or brother) may also increase a woman's risk of Breast Cancer, especially if the Prostate Cancer was found at a young age.
- Pyloric Stenosis: Pyloric Stenosis is an uncommon condition in infants that blocks food from entering the small intestine. Normally, a muscular valve (pylorus) between the stomach and small intestine holds food in the stomach until it is ready for the next stage in the digestive process.
- Stillbirth: A Stillbirth is the death or loss of a baby before or during delivery. Both miscarriage and Stillbirth describe pregnancy loss, but they differ according to when the loss occurs. In the United States, a miscarriage is usually defined as loss of a baby before the 20th week of pregnancy, and a Stillbirth is loss of a baby after 20 weeks of pregnancy.
- Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS): Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS) is the unexplained death, usually during sleep, of a seemingly healthy baby less than a year old. SIDS is sometimes known as crib death or cot death because the infants often die in their cribs. Although the cause is unknown, it appears that SIDS might be associated with defects in the portion of an infant's brain that controls breathing and arousal from sleep.
- Sudden Unexplained Death in Childhood: Sudden Unexplained Death in Childhood (SUDC) is the sudden death of a child 12 months of age or older that remains unexplained after a thorough case investigation, including performance of a complete autopsy, examination of the death scene, and review of the clinical history. These deaths elude scientific understanding. SUDC cannot be predicted or prevented at this time. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, in 2018, 392 children between the ages of 1-18 years died suddenly without a clear cause of death determined. Most of these children were toddlers, aged 1-4 years; an incidence of 1.4 deaths per 100,000 toddler aged children. Research and awareness of SUDC remains limited.
Pink and Gold Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Phyllodes Tumor: Phyllodes Tumors of the breast are rare, accounting for less than 1% of all breast tumors. The name "phyllodes," which is taken from the Greek language and means "leaflike," refers to that fact that the tumor cells grow in a leaflike pattern. Other names for these tumors are Phylloides Tumor and Cystosarcoma Phyllodes. Phyllodes Tumors tend to grow quickly, but they rarely spread outside the breast. Although most Phyllodes Tumors are benign (not cancerous), some are malignant (cancerous) and some are borderline (in between noncancerous and cancerous). All three kinds of Phyllodes Tumors tend to grow quickly, and they require surgery to reduce the risk of a Phyllodes Tumor coming back in the breast (local recurrence). Phyllodes Tumors can occur at any age, but they tend to develop when a woman is in her 40s. Benign Phyllodes Tumors are usually diagnosed at a younger age than Malignant Phyllodes Tumors. Phyllodes Tumors are extremely rare in men.
Pink and Red Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Cervical Cancer in Women with HIV: Compared to the general population, people infected with HIV are currently about 500 times more likely to be diagnosed with Kaposi Sarcoma, 12 times more likely to be diagnosed with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, and, among women, 3 times more likely to be diagnosed with Cervical Cancer.
- Ebola: Ebola is a virus that causes severe bleeding, organ failure, and can lead to death. Humans may spread the virus to other humans through contact with bodily fluids such as blood. Initial symptoms include fever, headache, muscle pain, and chills. Later, a person may experience internal bleeding resulting in vomiting or coughing blood.
- Gum Disease: In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums can become swollen and red, and they may bleed. In its more serious form, called periodontitis, the gums can pull away from the tooth, bone can be lost, and the teeth may loosen or even fall out. Periodontal disease is mostly seen in adults.
- Wound Care: Wound Care involves every stage of wound management . This includes diagnosing wound type, considering factors that affect wound healing, and the proper treatments for wound management. Once the wound is diagnosed and all factors are considered, a treatment facility can determine the best treatment options.
Pink and Teal Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- BRCA1/2 (BReast CAncer genes 1 and 2): BRCA1 and BRCA2 (BReast CAncer genes 1 and 2) are the best-known genes linked to Breast Cancer risk. Everyone has these genes, but some people have an inherited mutation in one or both that increases the risk of breast cancer. BRCA1/2 mutations can be passed from either parent and can affect the risk of cancers in both women and men. A person who has a BRCA1/2 mutation is sometimes called a BRCA1/2 carrier. Like other gene mutations, BRCA1/2 mutations are rare in the general population. In the U.S., about 1 in 400 people have a BRCA1/2 mutation. However, prevalence varies by ethnic group. Among Ashkenazi Jewish women and men, about 1 in 40 carry a BRCA1/2 mutation.
- Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer: Hereditary Breast and Ovarian Cancer is an inherited genetic condition. This means that the cancer risk is passed from generation to generation in a family. 2 genes are associated with the majority of HBOC families: BRCA1 and BRCA2. BRCA stands for BReast CAncer. Other, less common genes have also been associated with an increased risk of developing breast and other cancers. Men with these gene mutations also have an increased risk of Breast Cancer and Prostate Cancer. Not all families with multiple cases of Breast and Ovarian Cancer have mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2.
- Hereditary Breast Cancer: A small percentage of all Breast Cancers cluster in families. These cancers are described as hereditary and are associated with inherited gene mutations. Hereditary Breast Cancers tend to develop earlier in life than non-inherited (sporadic) cases, and new (primary) tumors are more likely to develop in both breasts.
- Ovarian and Breast Cancer Combined: There is a genetic link between the ovaries and the breasts. The ovaries and the breasts are also connected through a genetic component. Most notably, researchers have established that BRCA1 and BRCA2 gene mutations can increase the risk of both breast cancer and ovarian cancer.
Purple Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Aicardi Syndrome: Aicardi Syndrome is a rare neurological disorder. The severity of the syndrome and the associated signs and symptoms vary from person to person. The three main features of Aicardi Syndrome are: Complete or partial absence of the nerve tissue that allows the right and left sides of the brain to communicate (corpus callosum); Seizures beginning in infancy (infantile spasms), that may become hard to control (refractory epilepsy); Defects or holes in the light sensitive tissue at the back of the eye (retina) known as chorioretinal lacunae.
- Alzheimer's Disease: Alzheimer’s Disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and, eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. In most people with the disease, those with the late-onset type, symptoms first appear in their mid-60s. Early-onset Alzheimer’s occurs between a person’s 30s and mid-60s and is very rare. Alzheimer’s Disease is the most common cause of dementia among older adults.
- Animal Abuse Prevention: Animal cruelty includes intentional, malicious acts of animal abuse and less clear-cut situations where the needs of an animal are neglected. Violence against animals has been linked to a higher likelihood of criminal violence and domestic abuse. It is our responsibility to prevent animal abuse. The alternate color for Animal Abuse Prevention is animal paw prints.
- Animal Protection and Welfare: In its simplest form, Animal Welfare refers to the relationships people have with animals and the duty they have to assure that the animals under their care are treated humanely and responsibly. The alternate color for Animal Protection and Welfare is animal paw prints.
- Anti N Methyl D Aspartate Receptor Encephalitis: Anti-NMDA Receptor Encephalitis is a neurologic disease first identified by Dr.Josep Dalmau and colleagues at the University of Pennsylvania in 2007. It is an autoimmune disease, where the body creates antibodies against the NMDA receptors in the brain.
- Arachnoiditis: Arachnoiditis is a pain disorder caused by inflammation of the arachnoid, one of the membranes that surrounds and protects the nerves of the spinal cord. The inflammation may occur due to irritation from chemicals, infection, direct injury to the spine, chronic compression of spinal nerves, or complications from spinal surgery or other spinal procedures. It may result in scar tissue and adhesions, which cause the spinal nerves to “stick” together. If Arachnoiditis affects the function of nerves, it can cause symptoms such as numbness, tingling, and a characteristic stinging and burning pain in the lower back or legs. In some people. it may affect the bladder, bowel, and sexual function. Very severe Arachnoiditis can result in paralysis of the legs.
- Arnold Chiari Malformation: Chiari Malformation is a condition in which brain tissue extends into the spinal canal. It occurs when part of the skull is misshapen or smaller than is typical, pressing on the brain and forcing it downward.
- Autoimmune Enteropathy: Autoimmune Enteropathy is a rare disorder in which the immune system causes damage to the lining of the intestines. Symptoms can occur shortly after birth with poor growth as well as severe and long-lasting diarrhea.
- Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease: Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease is an inflammatory condition of the inner ear. It occurs when the body's immune system attacks cells in the inner ear that are mistaken for a virus or bacteria. Autoimmune Inner Ear Disease is a rare disease occurring in less than one percent of the 28 million Americans with a hearing loss.
- Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome: Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder of the immune system first described by NIH scientists in the mid-1990s that affects both children and adults. In Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome, unusually high numbers of white blood cells called lymphocytes accumulate in the lymph nodes, liver, and spleen and can lead to enlargement of these organs. Autoimmune Lymphoproliferative Syndrome can also cause anemia (low level of red blood cells), thrombocytopenia (low level of platelets), and neutropenia (low level of neutrophils, the most common type of white blood cell in humans). These problems can increase the risk of infection and hemorrhage.
- Autoimmune Neutropenia: Autoimmune Neutropenia is described as a reduced number of neutrophils resulting from increased peripheral destruction by antineutrophil antibodies from autoimmune disorders. These autoantibodies are directed against cell membrane antigens present on IgG Fc receptors.
- Autoimmune Oophoritis: Autoimmune Oophoritis is a rare cause of primary ovarian insufficiency. It happens when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the ovaries causing inflammation, atrophy and fibrosis. These changes stop the ovaries from working normally.
- Autoimmune Orchitis: Autoimmune Orchitis is a relevant cause of decreased fecundity in males, and it is defined as a direct aggression to the testis with the concomitant presence of anti-sperm antibodies (ASA). The presence of these specific antibodies has been observed in approximately 5-12% of infertile male partners.
- Autoimmune Pancreatitis: Autoimmune Pancreatitis is a chronic inflammation that is thought to be caused by the body's immune system attacking the pancreas and that responds to steroid therapy. Two subtypes of AIP are now recognized, type 1 and type 2.
- Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome: Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome is a rare, inherited disease in which the immune system mistakenly attacks many of the body's tissues and organs. The mucous membranes and adrenal and parathyroid glands are commonly affected, though other tissues and organs may become involved as well.
- Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type II: Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type II, also known as Schmidt Syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disorder in which there is a steep drop in production of several essential hormones by the glands that secrete these hormones.
- Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type III: Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndrome Type II, also known as Schmidt Syndrome, is a rare autoimmune disorder in which there is a steep drop in production of several essential hormones by the glands that secrete these hormones.
- Autoimmune Retinopathy: Autoimmune Retinopathy is a rare and still poorly understood immune-mediated disease that may cause inflammation from circulating autoantibodies against the retina. It may be related to history of autoimmune disease in the patient or in a family member or the presence of neoplastic disease in the individual.
- Autoimmune Thrombocytopenic Purpura / ATP: Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura is a blood disorder characterized by a decrease in the number of platelets in the blood. Platelets are cells in the blood that help stop bleeding. A decrease in platelets can cause easy bruising, bleeding gums, and internal bleeding.
- Autoimmune Thyroiditis: Thyroiditis is when the thyroid gland becomes irritated. Hashimoto's Thyroiditis is the most common type of this health problem. It is an autoimmune disease. It occurs when the body makes antibodies that attack the cells in the thyroid. The thyroid then can't make enough of the thyroid hormone.
- Autoimmune Urticaria: Chronic Autoimmune Urticaria is caused by anti-FcεRI and less frequently, by anti-IgE autoantibodies that lead to mast cell and basophil activation, thereby giving rise to the release of histamine and other pro-inflammatory mediators.
- Autoimmune Uveitis: Uveitis often happens in people who have an autoimmune condition. This is where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. Autoimmune conditions known to cause uveitis include Ankylosing Spondylitis, a condition where the spine and other areas of the body become inflamed.
- Axonal and Neuronal Neuropathy: Axonal and Neuronal Neuropathy is a variant of Guillain-Barré Syndrome, an autoimmune disease. It is characterized by acute paralysis and loss of reflexes without sensory loss.
- Binge Eating Disorder: Binge Eating Disorder is a severe, life-threatening, and treatable eating disorder characterized by recurrent episodes of eating large quantities of food (often very quickly and to the point of discomfort), a feeling of a loss of control during the binge, experiencing shame, distress or guilt afterwards, and not regularly using unhealthy compensatory measures (e.g., purging) to counter the binge eating. It is the most common eating disorder in the United States.
- Body Shaming: Body Shaming occurs among both men and women of all different shapes and body sizes. Body Shaming has included both criticisms of being “too fat” , or “too skinny” , often picking on flaws that completely irrelevant. Many magazines, social media platforms, and advertisements contribute to body shaming in ways that have started to normalize these damaging behaviors. Many TV shows and movies have fallen into this pattern as well, where the “fat” character is often the subject of criticism and comic relief. With the trending behaviors of celebrity fat shaming on social media, it is important to understand the potential consequences that may arise.
- Bulimia Nervosa: Bulimia Nervosa, commonly called Bulimia, is a serious, potentially life-threatening eating disorder. People with Bulimia may secretly binge, eating large amounts of food with a loss of control over the eating, and then purge, trying to get rid of the extra calories in an unhealthy way. To get rid of calories and prevent weight gain, people with Bulimia may use different methods. For example, people may regularly self-induce vomiting or misuse laxatives, weight-loss supplements, diuretics or enemas after bingeing. Or one may use other ways to eliminate calories and prevent weight gain, such as fasting, strict dieting or excessive exercise.
- Cancer Survivors: The American Cancer Society uses the term Cancer Survivor to refer to anyone who has ever been diagnosed with cancer no matter where they are in the course of their disease.
- Caregiver Appreciation: Currently, over 1/3 of the United States population is composed of caregivers and the numbers are rising. Family caregivers are the foundation of long-term care nationwide. November is recognized as National Caregiver Appreciation Month, a month-long tribute to recognize those individuals providing caregiving support to a family member or loved one.
- Cerebral Spinal Fluid Leak: Cerebral Spinal Fluid Leak results when the fluid around the brain (called cerebral spinal fluid) leaks through a hole through the skull bone. This fluid can either drain from the ear or the nose, depending on where the skull bone is damaged.
- Chiari Malformations: Chiari Malformations are structural defects in the cerebellum, the part of the brain that controls balance. When the indented bony space at the lower rear of the skull is smaller than normal, the cerebellum and brainstem can be pushed downward. The resulting pressure on the cerebellum can block the flow of cerebrospinal fluid (the liquid that surrounds and protects the brain and spinal cord) and can cause a range of symptoms including dizziness, muscle weakness, numbness, vision problems, headache, and problems with balance and coordination.
- Children of Fallen Soldiers: Approximately 25,000 children have lost an active-duty parent in the military over the last 35 years. 97% of casualties are men, leaving behind single mothers to care for their families. Of those families, 60% report having trouble making ends meet. The alternate color for Children of Fallen Soldiers is camoflauge. (camo).
- Chronic and Intractable Pain: Intractable Pain is typically considered to be a severe form of Chronic Pain. But unlike Chronic Pain from arthritic knees or similar cause, intractable pain isn't easily treated or relieved.
- Chronic Pain: Usually pain is regarded as chronic when it lasts or recurs for more than 3 to 6 months. Chronic Pain is a frequent condition, affecting an estimated 20% of people worldwide and accounting for 15% to 20% of physician visits.
- Chronic Pain in Women: Pain conditions affecting women have a significant global impact. Yet, there is still a lack of awareness/recognition of pain issues affecting women. Chronic Pain affects a higher proportion of women than men around the world. However, women are less likely to receive treatment. Research has shown that women generally experience more recurrent pain, more severe pain and longer lasting pain than men.
- Chronic Pancreatitis: Chronic Pancreatitis is inflammation of the pancreas that does not heal or improve, it gets worse over time and leads to permanent damage. Chronic Pancreatitis eventually impairs a patient’s ability to digest food and make pancreatic hormones. Industrialized countries have estimated an annual incidence rate of 5-12/100,000 people who will develop Chronic Pancreatitis. The prevalence of Chronic Pancreatitis is 50/100,000 people. Chronic Pancreatitis often develops in patients between the ages of 30 and 40, and is more common in men than women.
- Chronic Vestibular Migraine: A Vestibular Migraine is a nervous system problem that causes repeated dizziness (or vertigo) in people who have a history of migraine symptoms. Unlike traditional migraines, one may not always have a headache. There are many names for this type of problem, which include Migraine-Associated Vertigo, Migrainous Vertigo, and Migraine-Related Vestibulopathy.
- Cicatricial Pemphigoid: Cicatricial Pemphigoid is a rare, chronic autoimmune blistering disorder which can produce scarring. It can affect the skin only, mucous membranes only, or both the skin and mucous membranes. When only mucous membranes are involved, the disease is often referred to as mucous membrane pemphigoid.
- Colitis: Colitis means inflammation of the colon. The colon, also known as the large intestine or large bowel, constitutes the last part of the digestive tract. The colon is a long, muscular tube that receives digested food from the small intestine. It removes water from the undigested food, stores the undigested food, and then eliminates it from the body through bowel movements.
- Cornelia de Lange Syndrome (CdLS): Cornelia de Lange syndrome (CdLS) is a developmental disorder that affects many parts of the body. The severity of the condition and the associated signs and symptoms can vary widely, but may include distinctive facial characteristics, growth delays, intellectual disability and limb defects.
- Craniosynostosis: Craniosynostosis is a birth defect in which one or more of the fibrous joints between the bones of the baby's skull (cranial sutures) close prematurely (fuse), before the baby's brain is fully formed. Brain growth continues, giving the head a misshapen appearance. Craniosynostosis usually involves fusion of a single cranial suture, but can involve more than one of the sutures in the baby's skull (complex craniosynostosis). In rare cases, craniosynostosis is caused by certain genetic syndromes (syndromic craniosynostosis).
- Crohn's Disease: Crohn’s Disease causes inflammation in part of the digestive system. Crohn's Disease can affect any part of it, but most often it affects the small intestine and colon. Crohn's Disease and another disease, called Ulcerative Colitis, belong to a group of diseases known as Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
- Cystic Fibrosis: Cystic Fibrosis is an inherited disorder that causes severe damage to the lungs, digestive system and other organs in the body. Cystic Fibrosis affects the cells that produce mucus, sweat and digestive juices. These secreted fluids are normally thin and slippery. But in people with Cystic Fibrosis, a defective gene causes the secretions to become sticky and thick. Instead of acting as a lubricant, the secretions plug up tubes, ducts and passageways, especially in the lungs and pancreas.
- Dementia: Dementia is not a specific disease. Instead, Dementia describes a group of symptoms affecting memory, thinking and social abilities severely enough to interfere with daily functioning. Though Dementia generally involves memory loss, memory loss has different causes. So memory loss alone does not mean one has Dementia. Alzheimer's Disease is the most common cause of a progressive Dementia in older adults, but there are a number of causes of Dementia. Depending on the cause, some Dementia symptoms can be reversed.
- Dental Hygiene: Oral Hygiene is the practice of keeping the mouth clean and disease-free . It involves brushing and flossing your teeth as well as visiting your dentist regularly for dental X-rays, exams and cleanings.
- Diabetic Neuropathy: Diabetic Neuropathy is a type of nerve damage that can occur if one has diabetes. High blood sugar (glucose) can injure nerves throughout the body. Diabetic Neuropathy most often damages nerves in the legs and feet. Depending on the affected nerves, symptoms of Diabetic Neuropathy can range from pain and numbness in the legs and feet to problems with the digestive system, urinary tract, blood vessels and heart. Some people have mild symptoms. But for others, Diabetic Neuropathy can be quite painful and disabling.
- Discoid Lupus Erythematosus: Discoid Lupus Erythematosus is a type of C utaneous Lupus Erythematosus . Cutaneous refers to skin. Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus includes types of lupus that affect the skin. People with Discoid Lupus get round sores, usually on their face or scalp. Another name for Discoid Lupus is Chronic Cutaneous Lupus.
- Domestic Violence: Domestic Violence and emotional abuse are behaviors used by one person in a relationship to control the other. Partners may be married or not married; heterosexual, gay, or lesbian; living together, separated or dating. Violence can be criminal and includes physical assault (hitting, pushing, shoving, etc.), sexual abuse (unwanted or forced sexual activity), and stalking. Although emotional, psychological and financial abuse are not criminal behaviors, they are forms of abuse and can lead to criminal violence.
- Dravet Syndrome: Dravet Syndrome is a severe form of epilepsy that is part of a group of diseases known as SCN1A-Related Seizure Disorders. The condition appears during the first year of life as frequent fever-related seizures. As the condition progresses, other types of seizures typically occur, including Myoclonus and Status Epilepticus. A family history of either epilepsy or febrile seizures exists in 15 percent to 25 percent of cases. Intellectual development begins to deteriorate around age 2, and affected individuals often have a lack of coordination, poor development of language, hyperactivity, and difficulty relating to others.
- Drowning Impact: Drowning Impact Awareness Month began in August 2004. June, July, and August are peak times for child drownings. Back-to-school distractions in August make it a high risk month for child drowning. Drowning is a top cause of injury-related death for children, especially the one to five year old age group. Every child drowning is preventable. Prevention is the cure, and awareness is free.
- Drug Overdose: Drug Overdoses can be accidental or intentional. They occur when a person takes more than the medically recommended dose. However, some people may be more sensitive to certain medications, so the low (more dangerous) end of a drug may be toxic for them; a dose that is still within the range of acceptable medical use may be too much for their bodies to handle. Illicit drugs, used to get high, may be taken in overdose amounts when a person's metabolism cannot detoxify the drug fast enough to avoid unintended side effects.
- Eating Disorders: Eating Disorders are serious conditions related to persistent eating behaviors that negatively impact one's health, emotions and ability to function in important areas of life. The most common Eating Disorders are Anorexia Nervosa, Bulimia Nervosa and Binge-Eating Disorder.
- Elder Abuse: Elder Abuse is an intentional act, or failure to act, by a caregiver or another person in a relationship involving an expectation of trust that causes or creates a risk of harm to an older adult. (An older adult is defined as someone age 60 or older.)
- Epilepsy: Epilepsy is a central nervous system disorder in which brain activity becomes abnormal, causing seizures or periods of unusual behavior, sensations, and sometimes loss of awareness. Seizure symptoms can vary widely. Some people with Epilepsy simply stare blankly for a few seconds during a seizure, while others repeatedly twitch their arms or legs. Having a single seizure does not mean you have epilepsy. At least two unprovoked seizures are generally required for an epilepsy diagnosis.
- Erythema Nodosum: Erythema Nodosum is characterized by tender, red bumps, usually found symmetrically on the shins. Up to 55 percent of cases have no clear identifiable cause. Sometimes, Erythema Nodosum is not a separate disease. Rather, it is a sign of some other infection, disease, or of a sensitivity to a drug.
- Fat Shaming and Skinny Shaming: According to the Urban Dictionary, Fat Shaming is the act of poking fun of someone for being overweight, or telling someone they are worthless, useless, lazy, or disgusting because they are overweight. Conversely, Skinny Shaming is when someone is naturally skinny and people tell them that they need to eat a cheeseburger. Basically, Skinny Shaming someone for being skinny is because you think that they are choosing to be skinny when in fact, they aren't. This is often confused with pointing out someone is Anorexic.
- Fibromyalgia: Fibromyalgia is a condition associated with widespread chronic pain, fatigue, memory problems and mood changes. Fibromyalgia is not a single disease, but a constellation of symptoms that can be managed. It is not life threatening and does not lead to muscle or joint damage. Researchers suspect that different factors, alone or in combination, may contribute to the development of the disease. An infectious illness, physical trauma, emotional trauma or hormonal changes may trigger the development of generalized pain, fatigue and sleep disturbances that characterize the condition.
- First Responders (Fallen): This cause remembers fallen First Responders, any Police, Fire, EMS, or Dispatcher who at any time has dedicated their life to helping their fellow man.
- Fistulas: A fFstula is an abnormal connection between two body parts, such as an organ or blood vessel and another structure. Fistulas are usually the result of an injury or surgery. Infection or inflammation can also cause a Fistula to form.
- Frontotemporal Dementia: Frontotemporal Dementia is an uncommon type of dementia that causes problems with behavior and language. Dementia is the name for problems with mental abilities caused by gradual changes and damage in the brain. Frontotemporal Dementia affects the front and sides of the brain (the frontal and temporal lobes).
- Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration: Frontotemporal Lobar Degeneration is a general term that describes a group of disorders based on their neuropathology that cause damage and dysfunction of the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain.
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors may be malignant (cancer) or benign (not cancer). They are most common in the stomach and small intestine but may be found anywhere in or near the GI tract. Soft tissue sarcoma is a broad term for cancers that start in soft tissues (muscle, tendons, fat, lymph and blood vessels, and nerves). These cancers can develop anywhere in the body but are found mostly in the arms, legs, chest and abdomen. The alternate color for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST), Soft Tissue Sarcoma, is yellow.
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Gestational Trophoblastic Disease is a group of rare tumors that involve abnormal growth of cells inside a woman's uterus. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease does not develop from cells of the uterus like Cervical Cancer or Endometrial (uterine lining) Cancer do. Instead, these tumors start in the cells that would normally develop into the placenta during pregnancy. (The term gestational refers to pregnancy.)
- Gender Equality: Gender Equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing different behaviors, aspirations and needs equally, regardless of gender.
- Gestational Trophoblastic Disease: Gestational Trophoblastic Disease is the name given to a group of tumors that form during abnormal pregnancies. Gestational Trophoblastic Disease is rare, affecting about one in every 1,000 pregnant women in the U.S. While some GTD tumors are malignant (cancerous) or have the potential to turn cancerous, the majority are benign (noncancerous).
- Hemicrania Continua: Hemicrania Continua is a type of primary headache disorder, which means the headache is not caused by another medical condition. Symptoms of Hemicrania Continua include constant mild to moderate pain on one side of the head (unilateral) with periods of more intense, severe, migraine-like pain (exacerbations). These severe pain periods can last from 20 minutes to days. The frequency of exacerbations also varies greatly. The headache stays on the same side of the head and usually without pain free periods.
- Henoch Schonlein Purpura: Henoch-Schönlein Purpura causes blood vessels to get inflamed (irritated and swollen). This inflammation is called vasculitis. It usually affects the small blood vessels in the skin (capillaries). It can also affect blood vessels in the bowel and the kidneys. When the blood vessels get inflamed, they can bleed into the skin, causing a rash that is called Purpura. The intestines and the kidneys may also bleed.
- Hereditary Myopathy: Hereditary Myopathy with early respiratory failure is an inherited disease that affects muscles used for movement and muscles that are needed for breathing. The major signs and symptoms of Hereditary Myopathy usually appear in adulthood, often in the mid-thirties.
- Hereditary Neuropathies: Hereditary Neuropathies are passed on genetically from parent to child. They’re sometimes called Inherited Neuropathies. Neuropathies can also be nonhereditary, or acquired. Acquired Neuropathies are caused by other conditions, such as diabetes, thyroid disease, or alcohol use disorder. Idiopathic Neuropathies have no apparent cause.
- Homelessness: The definition of homelessness is divided into four categories. These categories include: 1) literally homeless; 2) imminent risk of homelessness; 3) homeless under other Federal statues; and 4) fleeing/attempting to flee domestic violence.
- Hurler-Scheie Syndrome: Hurler-Scheie Syndrome is the intermediate form of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1 between the two extremes Hurler Syndrome and Scheie Syndrome. It is a rare lysosomal storage disease, characterized by skeletal deformities and a delay in motor development.
- Hurler Syndrome: Hurler Syndrome is the most severe form of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1, a rare lysosomal storage disease, characterized by skeletal abnormalities, cognitive impairment, heart disease, respiratory problems, enlarged liver and spleen, characteristic facies and reduced life expectancy.
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP): Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP) is a disorder that can lead to easy or excessive bruising and bleeding. The bleeding results from unusually low levels of platelets, the cells that help blood clot. Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura, which is also called Immune Thrombocytopenia, affects children and adults. Children often develop ITP after a viral infection and usually recover fully without treatment. In adults, the disorder is often long term.
- IgG4 Related Sclerosing Disease: IgG4-Related Sclerosing Disease is a systemic disease characterized by extensive IgG4-positive plasma cells and T-lymphocyte infiltration of various organs.
- Infantile Spasms: Infantile Spasms is a rare seizure disorder that occurs in young children, usually under one year of age. About 1,200 children in the US are diagnosed each year with Infantile Spasms. It often has a very subtle appearance so it is difficult for parents to recognize that it is a serious problem. A young child having Infantile Spasms may just have little head drops that do not appear to be anything serious. However, it is a much more serious seizure disorder than the generalized convulsion. Not only is it difficult for the parent to realize that this is a seizure disorder, it is also challenging for pediatricians. Infantile Spasms are so uncommon that most pediatricians will see only one or two Infantile Spasm cases during all their years of practice.
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease: Inflammatory Bowel Disease is an umbrella term used to describe disorders that involve chronic inflammation of the digestive tract. Types of IBD include Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease. Both Ulcerative Colitis and Crohn's Disease usually involve severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, fatigue and weight loss.
- Intermediate Uveitis: Intermediate Uveitis is a chronic, relapsing disease of insidious onset. According to the Standardization of Uveitis Nomenclature working group criteria, Intermediate Uveitis is defined as an intraocular inflammation mainly focused on the vitreous and peripheral retina.
- International Overdose Awareness Day: International Overdose Awareness Day (Overdose Day) is a global event held on August 31 each year since 2001. Its purpose is to raise awareness of overdoses, reduce the stigma of drug-related deaths and acknowledge the grief felt by families and friends.
- International Women's Day: International Women's Day (March 8) is a global day celebrating the social, economic, cultural and political achievements of women. The day also marks a call to action for accelerating gender parity. Internationally, purple is a color for symbolizing women.
- Islet Cell Tumors, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Pancreatic Cancer can develop from two kinds of cells in the pancreas; exocrine cells and neuroendocrine cells, such as islet cells. The exocrine type is more common and is usually found at an advanced stage. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine tumors (Islet Cell Tumors) are less common but have a better prognosis. The alternate color for Islet Cell Tumors, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors, is zebra.
- Lambert Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome: Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome is a very rare condition that affects the signals sent from the nerves to the muscles. It means the muscles are unable to tighten (contract) properly, resulting in muscle weakness and a range of other symptoms.
- Lewy Body Dementia: Lewy Body Dementia, also known as dementia with Lewy bodies, is the second most common type of progressive Dementia after Alzheimer's Disease Dementia. Protein deposits, called Lewy bodies, develop in nerve cells in the brain regions involved in thinking, memory and movement (motor control). Lewy Body Dementia causes a progressive decline in mental abilities. People with Lewy Body Dementia may experience visual hallucinations, and changes in alertness and attention. Other effects include Parkinson's Disease-like symptoms such as rigid muscles, slow movement and tremors.
- Lupus / Systemic Lupus Erythematosus / SLE Lupus: Lupus is a chronic, autoimmune disease that affects various parts of the body, including joints, kidneys and other organs, skin, blood and even the brain.
- Lupus in Children and Teens: Lupus is an autoimmune disease. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system turns against the body it's designed to protect for unknown reasons. Lupus can affect nearly every organ system in the body, including the skin, joints, kidneys, heart, lungs and central nervous system. Most often when people speak of childhood lupus, they are referring to Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE). Lupus is a lot more common in young people than is generally believed. The best estimate is that SLE affects between 5,000 and 10,000 children in the United States. Adolescent girls develop lupus much more frequently than do boys, but in younger children before puberty, girls are affected only a little more frequently than are boys.
- Lupus Nephritis: Lupus Nephritis occurs when lupus autoantibodies affect structures in your kidneys that filter out waste. This causes kidney inflammation and may lead to blood in the urine, protein in the urine, high blood pressure, impaired kidney function or even kidney failure.
- Macular Degeneration: Macular Degeneration is the leading cause of vision loss, affecting more than 10 million Americans – more than cataracts and glaucoma combined. At present, Macular Degeneration is considered an incurable eye disease. Macular Degeneration is caused by the deterioration of the central portion of the retina, the inside back layer of the eye that records the images one sees and sends them via the optic nerve from the eye to the brain. The retina’s central portion, known as the macula, is responsible for focusing central vision in the eye, and it controls one's ability to read, drive a car, recognize faces or colors, and see objects in fine detail.
- March of Dimes: The mission of the March of Dimes is s to lead the fight for the health of all moms and babies. Their goals is to end the preventable maternal health risks and deaths, end preventable preterm birth and infant death, and close the health equity gap. The alternate color for March of Dimes is pink and blue.
- Maroteaux Lamy Syndrome / Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VI / MPS VI (Alternate Color: Pink and Blue): Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome is a form of mucopolysaccharidosis with the clinical onset before age 3 that is characterized by an inability to metabolize dermatan sulfate. This leads to abnormal accumulation of dermatan sulfate, resulting in mild to severe changes in muscle, bone, skin, and other tissues, particularly the heart.
- Microscopic Colitis: Microscopic colitis is an inflammation of the large intestine (colon) that causes persistent watery diarrhea. The disorder gets its name from the fact that it's necessary to examine colon tissue under a microscope to identify it, since the tissue may appear normal with a colonoscopy or flexible sigmoidoscopy.
- Military Personnel Injured in Active Duty: If this happens, you’ll receive a phone call. If at all possible, the phone call will be from your service member themself. If that’s not possible a military official will call you with as many details as they have and then give you regular updates by phone until they are no longer necessary. If they cannot reach you. they will contact your unit to try to reach you through whatever means necessary. The alternate color for Military Personnel Injured in Active Duty is Red, White and Blue or Camoflauge (Camo).
- Moebius Syndrome: Moebius Syndrome is a rare neurological condition that primarily affects the muscles that control facial expression and eye movement. The signs and symptoms of this condition are present from birth. Weakness or paralysis of the facial muscles is one of the most common features of Moebius Syndrome.
- Morquio Syndrome: Morquio Syndrome is a rare inherited birth defect that is estimated to occur in one of every 200,000 births. The disease may not be visible at birth. Symptoms usually begin between ages 1 and 3. Morquio Syndrome is a progressive disease. Morquio Syndrome is part of a group of diseases called mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS). Morquio is also known as MPS IV. In children with Morquio Syndrome, the body cannot break down sugar chains called glycosaminoglycans that help build bone, cartilage, eye corneas, skin and connective tissue (such as tendons, ligaments, etc.)
- Mucopolysaccharidoses: Mucopolysaccharidoses are a group of metabolic disorders caused by the absence or malfunctioning of lysosomal enzymes needed to break down molecules called glycosaminoglycans. These long chains of sugar carbohydrates occur within the cells that help build bone, cartilage, tendons, corneas, skin and connective tissue.
- Mucopolysaccharidosis I: Mucopolysaccharidosis Type I (MPS I) is a rare disease in which the body is missing or does not have enough of an enzyme needed to break down long chains of sugar molecules. These chains of molecules are called glycosaminoglycans (formerly called mucopolysaccharides).
- Mucopolysaccharidosis II (MPS II) is an inherited disorder of carbohydrate metabolism that occurs almost exclusively in males. It is characterized by distinctive facial features, a large head, hydrocephalus, enlargement of the liver and spleen (hepatosplenomegaly), umbilical or inguinal hernia, and hearing loss.
- Mucopolysaccharidosis III: Children with MPS III usually appear healthy at birth, but developmental delay is usually evident by age 2-5 years. Mental and motor development peak by 3-6 years of age, after which intellectual decline usually occurs. Behavioral problems such as hyperactivity and irritability may become obvious earlier. Severe behavioral disturbance is a very common feature of Sanfilippo Syndrome, and one of the more difficult aspects of the disorder to manage.
- Multifocal Motor Neuropathy: Multifocal motor neuropathy is a progressive disorder, this means that the signs and symptoms tend to worsen slowly over time. The main symptom is progressive muscle weakness of the arms and legs. Unlike other neurological disorders affecting the arms and legs, there usually is not any sensory deficits.
- Multiple System Atrophy: Multiple System Atrophy is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a combination of symptoms that affect both the autonomic nervous system (the part of the nervous system that controls involuntary action such as blood pressure or digestion) and movement.
- Myofascial Pain Syndrome: Myofascial Pain Syndrome is a chronic condition that causes pain in the musculoskeletal system. This pain is confined to a particular area. For example, you might only feel the pain and tenderness in your right shoulder and neck. The pain is typically associated with trigger points in muscles. These trigger points radiate pain to the affected area when pressure is applied to them, and sometimes spontaneously with no pressure. Sometimes this pain can be in what seems to be an unrelated part of the body.
- Natowicz Syndrome: Mucopolysaccharidosis type IX (MPS IX, Natowicz Syndrome, Hyaluronidase Deficiency) is a rare lysosomal storage disease characterized by high hyaluronan concentration in the serum resulting from deficiency in hyaluronidase 1 (HYAL1, MIM:607071) which normally hydrolyses 1-4 linkages between N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) and D-glucuronate (GlcA) residues. Symptoms of MPS IX are periodically painful soft tissue masses around the joints, acquired short stature and erosion of the hip joint, although joint movement and intelligence are normal.
- Near Homelessness: Homelessness and poverty are inextricably linked. Poor people are frequently unable to pay for housing, food, childcare, health care, and education. Difficult choices must be made when limited resources cover only some of these necessities. Often it is housing, which absorbs a high proportion of income that must be dropped. If you are poor, you are essentially an illness, an accident, or a paycheck away from living on the streets.
- Neonatal Lupus: Neonatal lupus is an autoimmune disease in which passive transfer of autoantibodies from the mother to the fetus results in fetal and neonatal disease. The major manifestations are cardiac and cutaneous findings.
- Opioid Epidemic; The opioid epidemic goes back to the 1990s, with the release of OxyContin and mass marketing of prescription painkillers, as well as campaigns like "Pain as the Fifth Vital Sign" that pushed doctors to treat pain as a serious medical problem. Doctors subsequently prescribed opioids in droves, leading to a proliferation of pills that eventually ended up with not just patients but also teens rummaging through their parents' medicine cabinets, other family and friends of patients, and the black market. This contributed to the spread of opioid painkiller misuse and addiction, which over time also led to greater misuse of illicitly produced opioids like heroin and fentanyl. Drug overdose deaths have climbed every year since the late 1990s as a result. During the State of the Union address in 2018, lawmakers wore purple ribbons in an effort to raise awareness of the opioid epidemic.
- Pancreatic Cancer, Adult: Pancreatic cancer is a disease in which malignant cells are found in the tissues of the pancreas. Also called exocrine cancer.
- Pancreatic Cancer, Childhood: Pancreatic Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the pancreas. Many different kinds of tumors can form in the pancreas. Some tumors are benign (not cancer). There are four types of PancreaticCcancer in children including: Solid Pseudopapillary tumor of the pancreas, Pancreatoblastoma, Islet cell Tumors, and Pancreatic Carcinoma. The alternate color for pancreatic cancer in children is gold.
- Parsonage Turner Syndrome: Parsonage-Turner Syndrome is an uncommon neurological disorder characterized by rapid onset of severe pain in the shoulder and arm. This acute phase may last for a few hours to a few weeks and is followed by wasting and weakness of the muscles (amyotrophy) in the affected areas.
- Pediatric Hemiplegia: Infantile or Congenital Hemiplegia refers to brain injuries that occur before or at birth and lead to Hemiplegia. Juvenile hemiplegia is seen in patients who sustained injuries above the age of 1 year. Hemiplegia is the physical manifestation of an injury to a specific area of the brain that controls motor function. The alternate color for Congenital Hemiplegia is purple and blue.
- Pediatric SLE: Lupus is a chronic, autoimmune disease that affects various parts of the body, including joints, kidneys and other organs, skin, blood and even the brain. Children and teens with SLE may have fatigue, pain or swelling in joints, skin rashes, fevers, hair loss, mouth sores or skin color changes due to the cold (Raynaud's phenomenon). Fatigue is one of the most prominent and life-affecting symptoms. Joint pain, another prominent symptom, is what most commonly initiates the first doctor visit.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Peripheral Neuropathy refers to the conditions that result when nerves that carry messages to and from the brain and spinal cord from and to the rest of the body are damaged or diseased. The peripheral nerves make up an intricate network that connects the brain and spinal cord to the muscles, skin, and internal organs.
- Pick’s Disease: Pick's Disease is a type of frontotemporal dementia, a neurodegenerative disease. That means the affected neurons (brain or nerve cells) gradually stop working. As brain cells in the affected areas fail, those areas atrophy (shrink or wither), and you lose the abilities those areas once controlled.
- Polyglandular Syndromes Type I, II, III: Polyglandular Syndromes Type I, II, III is characterized by sequential or simultaneous deficiencies in the function of several endocrine glands that have a common cause. Etiology (cause, set of causes) is most often autoimmune.
- Postherpetic Neuralgia: Postherpetic Neuralgia is the most common complication of shingles. The condition affects nerve fibers and skin, causing burning pain that lasts long after the rash and blisters of shingles disappear. The chickenpox (herpes zoster) virus causes shingles.
- Premature Birth: A Premature Birth is a birth that takes place more than three weeks before the baby's estimated due date. In other words, a premature birth is one that occurs before the start of the 37th week of pregnancy. Premature babies, especially those born very early, often have complicated medical problems. Typically, complications of prematurity vary. But the earlier your baby is born, the higher the risk of complications.
- Preemie Baby: Prematurity happens when a baby is born before 37 weeks’ gestation (time spent developing in the mother's womb). Babies who are part of a multiple birth, such as twins, are more likely to be born prematurely.
- Progressive Inflammatory Neuropathy: Progressive Inflammatory Neuropathy is a disease that was identified in a report, released on January 31, 2008, by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. The first known outbreak of this neuropathy occurred in southeastern Minnesota in the United States.
- Pudendal Neuralgia: Pudendal Neuralgia is a type of long-term (chronic) pelvic pain that originates from damage or irritation of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve is one of the main nerves in the pelvis, supplying areas such as the lower buttocks, the perineum, the rectum, vulva, labia and clitoris in women, and scrotum and penis in men.
- Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Pulmonary arterial hypertension is one form of a broader condition known as pulmonary hypertension, which means high blood pressure in the lungs. In Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension, increased pressure in the vessels is caused by obstruction in the small arteries in the lung, for a variety of reasons.
- Relay for Life: Relay For Life is a community based fundraising event of the American Cancer Society. Each year, more than 5,000 Relay For Life events take place in over twenty countries. Events are held in local communities, campus universities and in virtual worlds.
- Religious Tolerance: Religious tolerance is an important element of peace because religious convictions are part of human identity.
- Rett Syndrome: Rett Ayndrome is a rare genetic neurological and developmental disorder that affects the way the brain develops, causing a progressive inability to use muscles for eye and body movements and speech. It occurs almost exclusively in girls. Most babies with Rett Ayndrome seem to develop normally at first, but after about 6 months of age, they lose skills they previously had, such as the ability to crawl, walk, communicate or use their hands. Over time, children with Rett Ayndrome have increasing problems with the use of muscles that control movement, coordination and communication. Rett syndrome can also cause seizures and intellectual disability.
- Sanfilippo Syndrome: Sanfilippo Syndrome is a rare genetic condition that causes fatal brain damage. It is referred to as a childhood disease because most patients never reach adulthood. The lack of enzyme prevents the body from going through its natural recycling process, causing cellular malfunction. The disease has four subtypes (A, B, C and D). Each subtype corresponds to a specific deficient enzyme.
- Sarcoidosis: Sarcoidosis, also called Sarcoid, is an inflammatory disease marked by the formation of granulomas (small nodules of immune cells) in the lungs, lymph nodes, and other organs. Sarcoidosis may be acute and go away by itself, or it may be chronic and progressive.
- Scheie Syndrome: Scheie Syndrome is the mildest form of Mucopolysaccharidosis Type 1, a rare lysosomal storage disease, characterized by skeletal deformities and a delay in motor development.
- Seizure Disorders: Seizure Disorders are one of a great many medical conditions that are characterized by episodes of uncontrolled electrical activity in the brain (seizures). Some Seizure Disorders are hereditary, but others are caused by birth defects or environmental hazards, such as lead poisoning.
- Sjogren's Syndrome: Sjögren’s Syndrome is a chronic, autoimmune disease that causes dryness of the eyes, mouth and other body parts. In an autoimmune disease, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue, leading to inflammation in the body. In Sjögren’s Syndrome, the infection-fighting cells of the immune system (lymphocytes) attack the normal cells of glands that produce moisture in the eyes, mouth and other tissues. These are called exocrine glands. This action damages these glands, making them unable to produce moisture.
- Sly Syndrome: Sly Syndrome is a disorder of mucopolysaccharide metabolism characterized by short stature, coarsening of the facial features, clouding of the cornea, striking enlargement of the liver and spleen, skeletal abnormalities, and intellectual deterioration resulting in moderately severe mental retardation.
- Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome: Superior Mesenteric Artery Syndrome is a rare digestive system disorder. The superior mesenteric artery provides blood to the small intestine, cecum, and colon. It crosses over the first part of the small intestine, called the duodenum. Symptoms occur when the artery obstructs the duodenum.Superior mesenteric artery syndrome may be referred to at SMA Syndrome or as SMAS, and by a variety of other names including Cast Syndrome, Wilkie Syndrome, Arteriomesenteric Duodenal Obstruction, and Chronic Duodenal Ileus.
- Susac Syndrome: Susac Syndrome is an autoimmune endotheliopathy, a disorder in which the body's immune system mistakenly attacks the inside lining (endothelium) of the walls of the very tiny blood vessels that supply blood to the brain, retina, and inner ear. The exact, underlying reason why this occurs is unknown.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): Lupus is a chronic, autoimmune disease. People with lupus have an overactive and misdirected immune system. Lupus is systemic, meaning that it affects a wide part of the body, including the joints, kidneys, skin, blood, brain and other organs. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) accounts for about 70 percent of all lupus cases. While SLE generally is considered the most serious form of lupus, cases range from very mild to severe. SLE affects various parts of the body and can cause joint pain, fatigue, hair loss, sensitivity to light, fever, rash and kidney problems. It is estimated that more than 1.5 million Americans have lupus. African American women are three times more likely than white women to have it. Hispanic, Asian and Native American women also have a higher incidence of lupus. People of all ages, races and sexes can get lupus, but 9 out of 10 adults with the disease are women between the ages of 15 and 45.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in Children and Teens: Lupus is an autoimmune disease. Lupus is a lot more common in young people than is generally believed. The best estimate is that SLE affects between 5,000 and 10,000 children in the United States. Adolescent girls develop lupus much more frequently than do boys, but in younger children before puberty, girls are affected only a little more frequently than are boys.
- Thoracic Outlet Syndrome: Thoracic Outlet Syndrome is a condition whereby symptoms are produced from compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, because of an inadequate passageway through an area (thoracic outlet) between the base of the neck and the armpit.
- Turner Syndrome: Turner Syndrome is a chromosomal condition that alters development in females. Women with this condition tend to be shorter than average and are usually unable to conceive a child (infertile) because of an absence of ovarian function.
- Ulcerative Colitis: Ulcerative Colitis is an inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers (sores) in the digestive tract. Ulcerative Colitis affects the innermost lining of the large intestine (colon) and rectum. Symptoms usually develop over time, rather than suddenly.
- Victims of Homophobia: Homophobic and transphobic violence has been reported in all regions of the world. It ranges from aggressive, sustained psychological bullying to physical assault, torture, kidnapping and targeted killings. Sexual violence has also been widely reported, including so-called “corrective” or “punitive” rape, in which men rape women assumed to be lesbian on the pretext of trying to “cure” their victims of homosexuality.
- Vitiligo: Vitiligo is a disease that causes the loss of skin color in blotches. The extent and rate of color loss from vitiligo is unpredictable. It can affect the skin on any part of the body. It may also affect hair and the inside of the mouth. Normally, the color of hair and skin is determined by melanin. Vitiligo occurs when the cells that produce melanin die or stop functioning. Vitiligo affects people of all skin types, but it may be more noticeable in people with darker skin.
- Vulvar Cancer: Vulvar Cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the vulva. Vulvar cancer forms in a woman's external genitalia. Vulvar cancer usually forms slowly over years, most often on the vaginal lips or the sides of the vaginal opening. Infection with human papillomavirus (HPV) causes about half of all Vulvar Cancers.
Purple and Black Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support::
- Animal Loss Due to Animal Abuse: Animal abuse can take many forms: it includes not only obvious forms of abuse such as killing or physically hurting animals, but also includes keeping wild animals in captivity. It’s possible to abuse animals through our actions, as well through our lack of action. Cats and dogs linger in shelters and may be euthanized before ever finding homes;,many species of wildlife face hunting pressure from humans, and are increasingly affected by climate change; most animals in the food system are kept in crowded, filthy conditions, and are killed after only a fraction of their natural lifespans. These are just a few examples of what animal abuse is. The alternate color for Animal Loss Due to Animal Abuse is Animal Paw Prints.
- Fentanyl Abuse and Overdose: Deaths involving synthetic opioids other than methadone (primarily fentanyl) continued to rise with 56,516 overdose deaths reported in 2020.
- Paranormal Activity: Paranormal Activity are phenomena described in popular culture, folk, and other non-scientific bodies of knowledge, whose existence within these contexts is described to lie beyond normal experience or scientific explanation.
Purple and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand up and support:
- Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy: Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy is a variant type of Guillain-Barre Syndrome. Acute Motor Axonal Neuropathy is a non-inflammatory disease whereby axons of motor nerve cells are selectively targeted and destroyed by the body's own immune system. The myelin sheath surrounding the axon is unaffected.
- Alternating Hemiplegia of Childhood: Alternating Hemiplegia is a rare neurological disorder that develops in childhood, most often before the child is 18 months old. The disorder is characterized by recurrent episodes of paralysis that involve one or both sides of the body, multiple limbs, or a single limb.
- Childhood Stroke / Pediatric Stroke: Pediatric Stroke is a rare condition affecting one in every 4,000 newborns and an additional 2,000 older children each year. Stroke is a type of blood vessel (cerebrovascular) disorder. Strokes can be categorized as ischemic (caused by insufficient blood flow) and hemorrhagic (caused by bleeding into the brain).
- Cults: In modern English, a cult is a social group that is defined by its unusual religious, spiritual, or philosophical beliefs and rituals, or its common interest in a particular personality, object, or goal. This sense of the term is controversial, having divergent definitions both in popular culture and academia, and has also been an ongoing source of contention among scholars across several fields of study. The word "cult" is usually considered a pejorative.
- Felty Syndrome: Felty syndrome is a disorder that includes rheumatoid arthritis, a swollen spleen, decreased white blood cell count, and repeated infections. It is rare.
- Hidradenitis Suppurativa: Hidradenitis Suppurativa is a condition that causes small, painful lumps to form under the skin. The lumps usually develop in areas where your skin rubs together, such as the armpits, groin, buttocks and breasts.
- Inflammatory Arthritis: Inflammatory Arthritis is a group of diseases characterized by inflammation of the joints and often other tissues. These include Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA), Psoriatic Arthritis, Ankylosing Spondylitis, Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) and Systemic Lupus Srythematosus (SLE) (lupus), among others.
- Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis: JIA is arthritis that affects one or more joints for at least 6 weeks in a child age 16 or younger. Unlike Adult Rheumatoid Arthritis, which is ongoing (chronic) and lasts a lifetime, children often outgrow JIA. But the disease can affect bone development in a growing child.
- Mixed Connective Tissue Disease: Mixed Connective Tissue Disease is a rare autoimmune disorder featuring signs and symptoms of three different disorders: Lupus, Scleroderma and Polymyositis. An autoimmune disorder is one in which the body’s immune system turns against the body it was designed to protect for unknown reasons.
- Pediatric Hemiplegia: Infantile or Congenital Hemiplegia refers to brain injuries that occur before or at birth and lead to hemiplegia. Juvenile Hemiplegia is seen in patients who sustained injuries above the age of 1 year. Hemiplegia is the physical manifestation of an injury to a specific area of the brain that controls motor function. The alternate color for Pediatric Hemiplegia is purple.
- Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases: Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases, also called Juvenile Arthritis, is an umbrella term used to describe the many autoimmune and inflammatory conditions that can develop in children ages 16 and younger. Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases affect nearly 300,000 children in the United States. That’s more than Juvenile Diabetes and Cystic Fibrosis combined. Although they share many common telltale symptoms, like pain, joint swelling, redness and warmth, they are distinct and each have their own special concerns and symptoms. Some Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases affect the musculoskeletal system, but joint symptoms may be a minor or nonexistent component. Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases can involve the eyes, skin, muscles and gastrointestinal tract as well. The alternate color for Pediatric Rheumatic Diseases is blue.
- Pediatric Stroke (Childhood Stroke): Identifying pediatric stroke and finding the cause of a stroke is vital to providing the right treatment and preventing more injury. Doctors can find a cause in about two-thirds of the cases. A common cause of Ischemic Strokes is that a blood clot forms in the heart and travels to the brain. This can be caused by Congenital Heart Problems such as abnormal valves or infections. In these cases children may need surgery or antibiotics.
- Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Polymyalgia Rheumatica is an inflammatory disorder typically seen in older adults that causes widespread aching, stiffness and flu-like symptoms. It is more common in women than men, and is seen more often in Caucasians than any other race. The average age of onset is 70 years, and it is rarely seen in people younger than 50. Polymyalgia Rheumatica is a self-limiting condition, lasting from one to five years; however, it varies from person to person. Approximately 15 percent of people with Polymyalgia Rheumatica develop a potentially dangerous condition called giant cell arteritis (also known as temporal arteritis). The alternate color for Polymyalgia Rheumatica is red.
- Preeclampsia: Preeclampsia is a pregnancy complication characterized by high blood pressure and signs of damage to another organ system, most often the liver and kidneys. Preeclampsia usually begins after 20 weeks of pregnancy in women whose blood pressure had been normal. Left untreated, preeclampsia can lead to serious, even fatal, complications for both the mother and baby.
- Relapsing Polychondritis: Relapsing Polychondritis is an immune-mediated condition associated with inflammation in cartilaginous structures and other tissues throughout the body, particularly the ears, nose, eyes, joints, and respiratory tract.
- Rheumatism: Rheumatic Disease is an umbrella term that refers to arthritis and several other conditions that affect the joints, tendons, muscle, ligaments, bones, and muscles (arthritis refers to disorders that mainly affect the joints). Rheumatic Diseases, like Osteoarthritis, can lead to severe joint pain from the breakdown of cartilage, the firm but soft tissue that protects a joint, when not managed well. The alternate color for Rheumatism is blue.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system, which normally protects its health by attacking foreign substances like bacteria and viruses, mistakenly attacks the joints. This creates inflammation that causes the tissue that lines the inside of joints (the synovium) to thicken, resulting in swelling and pain in and around the joints. The synovium makes a fluid that lubricates joints and helps them move smoothly. The alternate color for Rheumatoid Arthritis is a blue.
- Rheumatic Disease: Rheumatic Disease is an umbrella term that refers to arthritis and several other conditions that affect the joints, tendons, muscle, ligaments, bones, and muscles (arthritis refers to disorders that mainly affect the joints). Rheumatic Diseases, like Osteoarthritis, can lead to severe joint pain from the breakdown of cartilage, the firm but soft tissue that protects a joint, when not managed well.
- Smith-Magenis Syndrome: Smith-Magenis Syndrome is a developmental disorder that affects many parts of the body. The major features of this condition include mild to moderate intellectual disability, delayed speech and language skills, distinctive facial features, sleep disturbances, and behavioral problems. Most people with SMS have a deletion of genetic material in each cell from a specific region of chromosome 17.
Purple, Blue and Marigold Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support :
- Bladder Cancer, Adult: Cancer that forms in tissues of the bladder (the organ that stores urine). Most bladder cancers are Transitional Cell Carcinomas (cancer that begins in cells that normally make up the inner lining of the bladder). Other types include Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cancer that begins in thin, flat cells) and Adenocarcinoma (cancer that begins in cells that make and release mucus and other fluids). The cells that form Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Adenocarcinoma develop in the inner lining of the bladder as a result of chronic irritation and inflammation.
- Bladder Cancer, Childhood: In children, Bladder Cancer is usually low grade (not likely to spread) and the prognosis is usually excellent after surgery to remove the tumor. The alternate color for bladder cancer in children is gold.
Purple and Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors symbolize, stand for and support:
- Hospice Care / Palliative Care: Palliative Care is specialized medical care for people living with a serious illness, such as cancer or heart failure. Patients in Palliative Care may receive medical care for their symptoms, or palliative care, along with treatment intended to cure their serious illness. Palliative care is meant to enhance a person's current care by focusing on quality of life for them and their family. Like Palliative Care, Hospice provides comprehensive comfort care as well as support for the family, but, in Hospice, attempts to cure the person's illness are stopped. Hospice is provided for a person with a terminal illness whose doctor believes he or she has six months or less to live if the illness runs its natural course.
- Traditional Feminism: Traditional Feminism developed in the late 1800's through the early 1900's. It was a movement that sought for women to be treated as equal to men. Such political issues included women's suffrage, equal pay, equal employment opportunities, etc. When women were allowed jobs in the 19th Century they were still deprived of some equal rights like: no equal pay, no high position, and sometimes no equal treatment. Throughout the 1950’s, women heard advice from the time they were born until they reached adulthood. The new suburban lifestyle in magazines such as Ladies Home Journal and Good Housekeeping and television shows such as "Father Knows Best" and "The Donna Reed Show" reinforced this image that prompted many women to leave college early and pursue the "cult of the housewife." Women also didn’t get any benefits in society in the 1950’s, so if they weren’t married, they would have to find a husband. Most Women also didn’t have jobs. Traditional Feminists believe a stay-at-home mother is as valuable as a working father or mother. They also believe that staying at home to manage a home and a family should be seen just as important and valuable as working outside of the home. The pressure our society has put on women to "do it all" - succeed in a career, have and maintain an immaculate home, remain healthy and "sexy" and raise children is degrading to the job of homemaking and child rearing.
Purple, Red and White Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Raynaud's Phenomenon: Raynaud’s Phenomenon is a condition that affects blood flow to the arms and legs, also called the extremities. It occurs when the blood vessels that feed the fingers and toes get smaller in reaction to cold or emotional stress (this event is called a vasospastic attack).
- Raynaud’s Syndrome: Raynaud's Syndrome (Raynaud's Disease) causes smaller arteries that supply blood flow to the skin to narrow in response to cold or stress. The affected body parts, usually fingers and toes, might turn white or blue and feel cold and numb until blood flow improves, usually when you get warm.
Purple, Teal and Magenta Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Parathyroid Cancer: Parathyroid Cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of a parathyroid gland. Having certain inherited disorders can increase the risk of developing Parathyroid Cancer. Signs and symptoms of parathyroid cancer include weakness, feeling tired, and a lump in the neck.
- Fentanyl Deaths and Overdoses: Fentanyl Deaths and Overdoses involving synthetic opioids other than methadone (primarily fentanyl) continued to rise with 56,516 overdose deaths reported in 2020.
Purple and Yellow Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: Autoimmune Hepatitis is liver inflammation that occurs when your body's immune system turns against liver cells. The exact cause of Autoimmune Hepatitis is unclear, but genetic and environmental factors appear to interact over time in triggering the disease. Untreated Autoimmune Hepatitis can lead to scarring of the liver (cirrhosis) and eventually to liver failure. When diagnosed and treated early, however, Autoimmune Hepatitis often can be controlled with drugs that suppress the immune system.
- Chemical Injuries: A chemical lesion is the local result of the reaction that corrosive or irritant chemical products have with biological tissue. The chemical lesion is characterized by partial or total destruction of the biological tissue.
- Lupus and Endometriosis: An increased risk for Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) was found among patients with endometriosis, according to study results published in Scientific Reports .
- Progressive Feminism: Progressive Feminists fight for gender equality and some believe that males must be more involved in the feminist movement for it to be more effective. Progressive Feminists want to teach the generation ahead about gender equality at a very young age by teaching it at home and trying to implement it into schools. Treating women as equals does not mean that we ignore differences — men and women tend to have different strengths and weaknesses, different likes and dislikes, and will often choose different career paths, family roles, television shows, books, and movies. In fact, men and women tend to like that they’re different and celebrate those differences.
- Sotos Syndrome: Sotos Syndrome is a condition characterized mainly by distinctive facial features; overgrowth in childhood; and learning disabilities or delayed development. Facial features may include a long, narrow face; a high forehead; flushed (reddened) cheeks; a small, pointed chin; and down-slanting palpebral fissures. Affected infants and children tend to grow quickly; they are significantly taller than their siblings and peers and have a large head. Other signs and symptoms may include intellectual disability; behavioral problems; problems with speech and language; and/or weak muscle tone (hypotonia).
Puzzle Pieces Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Asperger's Syndrome: Asperger Syndrome is part of the Autism Spectrum Disorder, a group of disorders that affects the development of social and communication skills. Unlike many children with Austim Spectrum Disorder, children with Asperger Syndrome do not have early language delays, and often have well developed language skills and normal to above average intelligence. However, they may use unusual speech patterns and have a hard time understanding irony, humor, and sarcasm or gestures and social cues important to normal conversation. Many children with Asperger Syndrome develop an obsessive interest in one topic or object. They may use high-level vocabulary or complex statistics in conversation.
- Autism Spectrum Disorder: Autism, or Autism Spectrum Disorder, refers to a broad range of conditions characterized by challenges with social skills, repetitive behaviors, speech and nonverbal communication. There is not one autism but many subtypes, and each person with Autism can have unique strengths and challenges. A combination of genetic and environmental factors influence the development of Autism. Autism affects an estimated 1 in 59 children. Many people with Autism also have sensory issues. These can include aversions to certain sights, sounds and other sensations. Autism’s hallmark signs usually appear by age 2 to 3. Often, it can be diagnosed as early as 18 months. Some associated development delays can appear even earlier.
- Autism Spectrum Disorders: Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental disability caused by differences in the brain. Some people with Autism Spectrum Disorder have a known difference, such as a genetic condition. Other causes are not yet known. Scientists believe there are multiple causes of Autism Spectrum Disorder that act together to change the most common ways people develop. We still have much to learn about these causes and how they impact people with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
Rainbow Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Gender Fluidity: Gender Fluidity means that a person is flexible in regard to the gender with which they identify. Their gender identity or expression is not fixed and may encompass one gender, multiple genders, or no gender. Their gender identity and expression may also change over time.
- LGBTQ+ Pride: Pride, as opposed to shame and social stigma, is the predominant outlook that bolsters most LGBTQ+ rights movements throughout the world. LGBT is an acronym meaning lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender. The term sometimes is extended to LGBTQ, or even LGBTQIA, to include queer, intersex and asexual groups. Queer is an umbrella term for non-straight people; intersex refers to those whose sex is not clearly defined because of genetic, hormonal or biological differences; and asexual describes those who don't experience sexual attraction. These terms may also include gender fluid people, or those whose gender identity shifts over time or depending on the situation.
- Marriage Equality: Marriage Equality means the fundamental human right and equal rights of men and women of legal adult age of any nationality, race or religion to marry and found a family with the free and full consent of their intended spouse of their chosen sex and are entitled to equal rights to marriage, during marriage and if a marriage should end, in marriage law and legislation.
- National Coming Out Day: National Coming Out Day is an annual LGBT awareness day observed on October 11, to support lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender people (the LGBT community) in "coming out" of the closet. First celebrated in the US in 1988, the initial idea was grounded in the feminist and gay liberation spirit of the personal being political, and the emphasis on the most basic form of activism being coming out to family, friends and colleagues, and living life as an openly lesbian or gay person. The founders belief was that homophobia thrives in an atmosphere of silence and ignorance and that once people know that they have loved ones who are lesbian or gay, they are far less likely to maintain homophobic or oppressive views.
- Non Binary: When we use the word transgender, we are referring to an inclusive umbrella term that consists of binary trans people (trans men and trans women), as well as non-binary people and people who cross dress. Non-binary people feel their gender identity cannot be defined within the margins of gender binary. Instead, they understand their gender in a way that goes beyond simply identifying as either a man or woman.
Red Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Acquired Hemophilia: Acquired Hemophilia is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by bleeding that occurs in patients with no personal or family history of diseases related to clotting/coagulation. Autoimmune Disorders occur when the body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy cells or tissue.
- Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome / AIDS: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). By damaging the immune system, HIV interferes with the body's ability to fight infection and disease.
- Acquired Pure Red Cell Aplasia: Acquired Pure Red Cell Aplasia is a bone marrow disorder characterized by a reduction of red blood cells (erythrocytes) produced by the bone marrow. Signs and symptoms may include fatigue, lethargy, and/or abnormal paleness of the skin (pallor) due to the anemia the caused by the disorder. In most cases, the cause of acquired PRCA is unknown (idiopathic). In other cases it may occur secondary to autoimmune disorders, tumors of the thymus gland (thymomas), hematologic cancers, solid tumors, viral infections, or certain drugs.
- Addiction: Addiction is a primary, chronic disease of brain reward, motivation, memory and related circuitry. Addiction affects neurotransmission and interactions within reward structures of the brain, such that motivational hierarchies are altered and addictive behaviors, which may or may not include alcohol and other drug use, supplant healthy, self-care related behaviors. Addiction also affects brain reward structures, such that the memory of previous exposures to rewards (such as food, sex, alcohol and other drugs) leads to a biological and behavioral response to external cues, in turn triggering craving and/or engagement in addictive behaviors.
- Adult-Onset Still's Disease: Adult-Onset Still's Disease s a form of Still's Disease, a rare systemic Auto-inflammatory Disease characterized by the classic triad of persistent high spiking fevers, joint pain, and a distinctive salmon-colored bumpy rash. The disease is considered a diagnosis of exclusion.
- AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome): Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). By damaging the immune system, HIV interferes with the body's ability to fight the organisms that cause disease. HIV is a sexually transmitted infection (STI). It can also be spread by contact with infected blood or from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breast-feeding. Without medication, it may take years before HIV weakens the immune system to the point of AIDS. There's no cure for HIV/AIDS, but there are medications that can dramatically slow the progression of the disease. These drugs have reduced AIDS deaths in many developed nations.
- Alcohol Dependence: Alcohol Dependence may include a drinker's increase in tolerance, withdrawal syndrome, unsuccessful attempts to cut down or even quit drinking altogether, lose control of their alcohol use and consistently drink more and for longer than intended. The cardinal features of Alcohol Dependence are compulsion (inability to refrain from taking that drink), loss of control over alcohol (can't quit) and continued drinking no matter what the consequences.
- Anemia of Chronic Disease: Anemia of chronic disease happens when you have an autoimmune disease or other illness lasts longer than three months and that causes inflammation. Chronic inflammation can affect the body's ability to use iron needed to make enough red blood cells. Anemia happens when you don't have enough red blood cells.
- Anti Neutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody Associated Vasculitis: Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody (ANCA)-associated vasculitis (AAV) is a complex systemic autoimmune disease presenting with the inflammation of small and medium vessels that results in vascular destruction and tissue necrosis.
- Atrial Fibrillation (AFib): Atrial fibrillation (A-fib) is an irregular and often very rapid heart rhythm (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots in the heart. A-fib increases the risk of stroke, heart failure and other heart-related complications. During Atrial Fibrillation, the heart's upper chambers (the atria) beat chaotically and irregularly, out of sync with the lower chambers (the ventricles) of the heart. For many people, A-fib may have no symptoms. However, A-fib may cause a fast, pounding heartbeat (palpitations), shortness of breath or weakness. Episodes of Atrial Fibrillation may come and go, or they may be persistent. Although A-fib itself usually isn't life-threatening, it's a serious medical condition that requires proper treatment to prevent stroke.
- Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia: Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia is a rare immune disorder. It happens when your body mistakes red blood cells as foreign substances and attacks them. Treatments include medication, surgery or, in rare cases, a blood transfusion. Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia is highly manageable, but can be fatal if left untreated. Prompt care is critical.
- Benign Mucosal Pemphigoid: Cicatricial Pemphigoid (also known as Benign Mucosal Pemphigoid, Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid, or Benign Mucous Membrane Pemphigoid) is a rare chronic autoimmune blistering disease characterized by erosive skin lesions of the mucous membranes and skin that results in scarring of at least some sites of involvement.
- Blackfan Diamond Anemia / Diamond Blackfan Anemia: Diamond-Blackfan Anemia is a rare blood disorder that occurs when the bone marrow fails to make red blood cells, which are essential for carrying oxygen from the lungs to all the other parts of the body.
- Bleeding Disorders: Bleeding Disorders are a group of conditions that result when the blood cannot clot properly. In normal clotting, platelets, a type of blood cell, stick together and form a plug at the site of an injured blood vessel. Proteins in the blood called clotting factors then interact to form a fibrin clot, essentially a gel plug, which holds the platelets in place and allows healing to occur at the site of the injury while preventing blood from escaping the blood vessel. While too much clotting can lead to conditions such as heart attacks and strokes, the inability to form clots can be very dangerous as well, as it can result in excessive bleeding. Bleeding can result from either too few or abnormal platelets, abnormal or low amounts of clotting proteins, or abnormal blood vessels.
- Blood Cancer: Blood Cancer, also called Hematologic Cancer, is cancer that begins in blood-forming tissue, such as the bone marrow, or in the cells of the immune system. Examples of Blood Cancer are leukemia, lymphoma, and Multiple Myeloma.
- Blood Clotting Disorders: Coagulation (blood clotting) Disorders are disruptions in the body’s ability to control blood clotting. Coagulation Disorders can result in either a hemorrhage (too little clotting that causes an increased risk of bleeding) or thrombosis (too much clotting that causes blood clots to obstruct blood flow). These Clotting Disorders develop due to several conditions.
- Blood Donation s: You must wait at least eight weeks (56 days) between donations of whole blood and 16 weeks (112 days) between Power Red donations. Whole blood donors can donate up to 6 times a year. Platelet Apheresis donors may give every 7 days up to 24 times per year.
- Bullous Pemphigoid: Bullous pemphigoid is a rare skin condition that causes large, fluid-filled blisters. They develop on areas of skin that often flex — such as the lower abdomen, upper thighs or armpits. Bullous Pemphigoid is most common in older adults.
- Burns: Burns are tissue damage that results from heat, overexposure to the sun or other radiation, or chemical or electrical contact. Burns can be minor medical problems or life-threatening emergencies.
- Cardiac Tumors / Heart Tumors, Adult: The majority of diagnosed Cardiac Tumors are benign. In adults, a somewhat mushy, gelatinous type of tumor called a Myxoma is the most common.
- Cardiac (Heart) Tumors, Childhood - Unusual Cancers of Children: Most tumors that form in the heart are benign (not cancer). Before birth and in newborns, the most common benign heart tumors are Teratomas. In infants and children, Rhabdomyomas predominate, typically associated with the syndrome Tuberous Sclerosis. An inherited condition called Tuberous Sclerosis can cause heart tumors to form in a fetus or newborn. Malignant Tumors that begin in the heart are even more rare than benign heart tumors in children.
- Cardiomyopathy: Cardiomyopathy is a disease of the heart muscle that makes it harder for the heart to pump blood to the rest of the body. Cardiomyopathy can lead to heart failure. The main types of Cardiomyopathy include dilated, Hypertrophic and Restrictive Cardiomyopathy. Treatment, which might include medications, surgically implanted devices or, in severe cases, a heart transplant, depends on which type of Cardiomyopathy you have and how serious it is.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Cardiovascular Disease generally refers to conditions that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina) or stroke. Other heart conditions, such as those that affect your heart's muscle, valves or rhythm, also are considered forms of heart disease.
- Cavernous Angioma: A Cavernous Angioma is a blood vessel abnormality characterized by large, adjacent capillaries with little or no intervening brain. The blood flow through these vessels is slow. Cavernous Angiomas can occur anywhere in the central nervous system. The disease occurs in 0.4 percent of the population, and 18.7 percent of these patients have multiple lesions.
- Chagas Disease: Chagas Disease is named after the Brazilian physician Carlos Chagas, who discovered the disease in 1909. It is caused by the parasite Trypanosoma cruzi , which is transmitted to animals and people by insect vectors and is found only in the Americas (mainly, in rural areas of Latin America where poverty is widespread).
- Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms including ET, MF, PV / MPN: Myeloproliferative Neoplasms are types of Blood Cancer that begin with an abnormal mutation (change) in a stem cell in the bone marrow. The change leads to an overproduction of any combination of white cells, red cells and platelets. The alternate color for – (Alternate Color: Orange and Red)
- Churg Strauss Syndrome / Eosinophilic Granulomatosis: Churg-Strauss Syndrome is a disorder marked by blood vessel inflammation. This inflammation can restrict blood flow to organs and tissues, sometimes permanently damaging them. This condition is also known as Eosinophilic Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (EGPA).
- Clotting Factor Deficiencies: Rare Clotting Factor Deficiencies are a group of inherited bleeding disorders caused by a problem with one or several clotting factors. Clotting factors are proteins in the blood that control bleeding. Many different clotting factors work together in a series of chemical reactions to stop bleeding. This is called the clotting process. Problems with Factor VIII and Factor IX are known as hemophilia A and B, respectively. Rare clotting factor deficiencies are bleeding disorders in which one of the other Clotting Factors (i.e. factors I, II, V, V + VIII, VII, X, XI, or XIII) is missing or not working properly. Less is known about these disorders because they are diagnosed so rarely. In fact, many have only been discovered in the last 40 years.
- Clotting Factor Deficiencies: If any of the clotting factors is missing or is not working properly, the coagulation cascade is blocked. When this happens, the blood clot does not form and the bleeding continues longer than it should. Deficiencies of F actor VIII and Factor IX are known as Hemophilia A and B, respectively.
- Coagulation Disorders: Coagulations Disorders are conditions that affect the blood's clotting activities. Hemophilia, Von Willebrand Disease, Clotting Factor Deficiencies, Hypercoagulable States and Deep Venous Thrombosis are all Coagulations Disorders. Hemophilia and Von Willebrand Disease are among the best known. The alternate color for oagulation Disorders is burgundy.
- Cogan’s Syndrome: Cogan's Syndrome is a rare inflammatory disease characterized by inflammation of the inner ears and eyes. It can lead to vision difficulties, hearing loss and dizziness. Commonly there is also inflammation in other organs as well, particularly the heart and large blood vessels, nervous system and bowels.
- Cold Agglutinin Disease: Cold Agglutinin Disease is a rare autoimmune disorder characterized by the premature destruction of red blood cells (hemolysis).
- Congestive Heart Failure: Congestive Heart Failure is a chronic progressive condition that affects the pumping power of the heart muscles. While often referred to simply as “heart failure,” CHF specifically refers to the stage in which fluid builds up around the heart and causes it to pump inefficiently.
- COVID-19: COVID-19 is caused by a Coronavirus called SARS-CoV-2. Older adults and people who have severe underlying medical conditions like heart or lung disease or diabetes seem to be at higher risk for developing more serious complications from COVID-19 illness.
- Coxsackie Myocarditis: Coxsackie Myocarditis is inflammation and weakness of the heart muscle caused by a viral infection (Coxsackie virus) that reaches the heart. Myocarditis can damage the heart muscle causing it to become thick and swollen. The heart muscle may be directly damaged by the virus or the bacteria that infect it.
- DARE - Red Ribbon Week: Red Ribbon Week is an alcohol, tobacco, and other drug and violence prevention awareness campaign observed annually in October in the United States.
- Designated Driver - MADD: Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD) is a nonprofit organization in the United States and Canada that seeks to stop drunk driving, support those affected by drunk driving, prevent underage drinking, and strive for stricter impaired driving policy, whether that impairment is caused by alcohol or any other drug. The terms "designated driver" and "designated driving" (commonly known as DD), refer to the selection of a person who remains sober as the responsible driver of a vehicle while others have been allowed to drink alcoholic beverages.
- Diamond Blackfan Anemia: Diamond Blackfan Anemia is a rare inherited bone marrow failure syndrome, characterized by a failure of the bone marrow (the center of the bone where blood cells are made) to produce red blood cells. This failure causes Diamond Blackfan Anemia patients to become severely anemic.
- Disaster Relief: Disaster relief (or emergency management) refers to the process of responding to a catastrophic situation, providing humanitarian aid to persons and communities who have suffered from some form of disaster.
- Dressler’s Syndrome: Dressler Syndrome is inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart (pericarditis). It's believed to occur as the result of the immune system responding to damage to heart tissue or damage to the sac around the heart (pericardium). The damage can result from a heart attack, surgery or traumatic injury.
- Driving Under the Influence Prevention: For more than 40 years, preventionists across the country have observed National Impaired Driving Prevention Month in December to raise awareness that impaired driving can be deadly and to put strategies in place for all of us to make it home safely.
- Drug Addiction: The National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA) provides a comprehensive definition of drug addiction, stating, “addiction is defined as a chronic, relapsing brain disease that is characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite harmful consequences.” Addiction is recognized as a brain disease because drugs literally cause changes to the brain.
- Epidermolysis Bullosa: Epidermolysis Bullosa is a group of rare diseases that cause fragile, blistering skin. The blisters may appear in response to minor injury, even from heat, rubbing, scratching or adhesive tape. In severe cases, the blisters may occur inside the body, such as the lining of the mouth or the stomach. Most types of Epidermolysis Bullosa are inherited. The condition usually shows up in infancy or early childhood. Some people don't develop signs and symptoms until adolescence or early adulthood.
- Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita : Epidermolysis Bullosa Acquisita is a rare, sporadic, subepithelial, mucocutaneous blistering disease that usually develops in adulthood. EBA is classically described as a mechanobullous disorder characterized by skin fragility, noninflammatory tense bullae, milia, and scarring.
- Erythromelalgia: Erythromelalgia is a rare condition that primarily affects the feet and, less commonly, the hands. It is characterized by intense, burning pain of affected extremities, severe redness, and increased skin temperature that may be episodic or almost continuous in nature.
- Erythromelalgia : Erythromelalgia is a rare condition that causes episodes of burning pain and redness in the feet, and sometimes the hands, arms, legs, ears and face. Symptoms of Erythromelalgia can begin at any age. Some people may have had it from early childhood, while some are only affected as adults.
- Essential Mixed Cryoglobulinemia : Essential Mixed Cryoglobulinemia is often found in people who have a chronic (long-lasting) inflammatory condition, such as an autoimmune disease or hepatitis C. Most people with Mixed Cryoglobulinemia have a chronic hepatitis C infection. Cryoglobulins are antibodies.
- Evans Syndrome : Evans Syndrome is a rare disorder in which the body's immune system produces antibodies that mistakenly destroy red blood cells, platelets and sometimes certain white blood cell known as neutrophils. This leads to abnormally low levels of these blood cells in the body (cytopenia).
- Factor VII Deficiency : Factor VII (seven) deficiency is a disorder caused by a lack of a protein called factor VII in the blood. It leads to problems with blood clotting (coagulation). Blood clotting normally occurs when there is damage to a blood vessel.
- Factor X Deficiency : Factor X Deficiency is a rare genetic blood disorder that causes the normal clotting process (coagulation) to take longer than normal.
- Factor XI Deficiency : Factor XI deficiency is a disorder that can cause abnormal bleeding due to a shortage (deficiency) of the aFctor XI protein, which is involved in blood clotting. This condition is classified as either partial or severe based on the degree of deficiency of the Factor XI protein.
- Factor XII Deficiency : Factor XII deficiency is a rare genetic blood disorder that causes prolonged clotting (coagulation) of blood in a test tube without the presence of prolonged clinical bleeding tendencies. It is caused by a deficiency of the Factor XII (Hageman factor), a plasma protein (glycoprotein).
- Factor XIII Deficiency : Factor XIII Deficiency is an extremely rare inherited blood disorder characterized by abnormal blood clotting that may result in abnormal bleeding. Signs and symptoms occur as the result of a deficiency in the blood clotting factor 13, which is responsible for stabilizing the formation of a blood clot.
- Fanconi Anemia: Fanconi Anemia is a rare, inherited blood disorder that leads to bone marrow failure. The disorder also is called Fanconi's Anemia. Fanconi Anemia prevents the bone marrow from making enough new blood cells for the body to work normally.
- Female Genital Mutilation: Female Genital Mutilation (FGM) comprises all procedures that involve partial or total removal of the external female genitalia, or other injury to the female genital organs for non-medical reasons. The practice is mostly carried out by traditional circumcisers, who often play other central roles in communities, such as attending childbirths. In many settings, health care providers perform Female Genital Mutilation due to the erroneous belief that the procedure is safer when medicalized. WHO strongly urges health professionals not to perform such procedures. Female Genital Mutilation is recognized internationally as a violation of the human rights of girls and women. It reflects deep-rooted inequality between the sexes, and constitutes an extreme form of discrimination against women. It is nearly always carried out on minors and is a violation of the rights of children. The practice also violates a person's rights to health, security and physical integrity, the right to be free from torture and cruel, inhumane or degrading treatment, and the right to life when the procedure results in death.
- Giant Cell Arteritis / Temporal Arteritis: Giant Cell Arteritis or Temporal Arteritis, is an inflammatory disease affecting the large blood vessels of the scalp, neck and arms. Inflammation causes a narrowing or blockage of the blood vessels, which interrupts blood flow. The disease is commonly associated with Polymyalgia Rheumatica. Caucasian women over the age of 50, most commonly between the ages of 70 and 80 years, have the highest risk of developing giant cell arteritis. Although women are more likely than men to develop Giant Cell Arteritis, research suggests that men are more likely to suffer potentially blinding eye involvement.
- Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis (see Wegener's Granulomatosis):
- Heart Defects: Congenital Heart Defects are structural problems arising from abnormal formation of the heart or major blood vessels. At least 18 distinct types of Congenital Heart Defects are recognized, with many additional anatomic variations. Ongoing progress in diagnosis and treatment (surgery and heart catheterization) makes it possible to treat most defects, even those once thought to be hopeless.
- Heart Disease: Heart Disease describes a range of conditions that affect the heart. Diseases under the heart disease umbrella include blood vessel diseases, such as coronary artery disease; heart rhythm problems (arrhythmias); and heart defects you're born with (congenital heart defects), among others. The term "heart disease" is often used interchangeably with the term "cardiovascular disease." Cardiovascular disease generally refers to conditions that involve narrowed or blocked blood vessels that can lead to a heart attack, chest pain (angina) or stroke. Other heart conditions, such as those that affect the heart's muscle, valves or rhythm, also are considered forms of heart disease.
- Heart Disorders: The major heart disorders include: Heart Attack. A heart attack, or myocardial infarction, usually tops the list of cardiovascular diseases in the United States. Others include Stroke, Heart Failure, Arrhythmia. and Heart Valve Complications.
- Heart Tumors, Adult: The most common types of benign heart tumors are: Myxoma – most common primary cardiac tumor. Myxoma accounts for approximately 50% of Primary Cardiac Tumors. Papillary Fibroelastoma is the most common Cardiac Tumor to affect the cardiac valves.
- Heart Tumors, Childhood: Most tumors that form in the heart are benign (not cancer). Before birth and in newborns, the most common benign heart tumors are Teratomas. An inherited condition called Tuberous Sclerosis can cause heart tumors to form in a fetus or newborn. Malignant tumors that begin in the heart are even more rare than benign heart tumors in children. The alternate color for heart tumors in children is gold.
- Hemolytic Anemia: Hemolytic Anemia is a disorder in which red blood cells are destroyed faster than they can be made. The destruction of red blood cells is called hemolysis. Red blood cells carry oxygen to all parts of the body. If one has a lower than normal amount of red blood cells, one has anemia. When one has anemia, the blood can’t bring enough oxygen to all the tissues and organs. Without enough oxygen, the body can’t work as well as it should. Hemolytic Anemia can be inherited or acquired.
- Hemophilia: Hemophilia is a rare disorder in which the blood doesn't clot normally because it lacks sufficient blood-clotting proteins (clotting factors). With Hemophilia, one may bleed for a longer time after an injury than if the blood clotted normally. Small cuts usually aren't much of a problem. The greater health concern is deep bleeding inside the body, especially in the knees, ankles and elbows. That internal bleeding can damage organs and tissues, and may be life-threatening. Hemophilia is an inherited (genetic) disorder. Treatment includes regular replacement of the specific clotting factor that is reduced.
- Hemophilia A: Hemophilia A is a hereditary bleeding disorder caused by a lack of blood clotting factor VIII. Without enough factor VIII, the blood cannot clot properly to control bleeding.
- Hemophilia B: Hemophilia B is a hereditary bleeding disorder caused by a lack of blood clotting factor IX. Without enough factor IX, the blood cannot clot properly to control bleeding.
- Hemophilia C: Hemophilia C is an inherited blood disorder. It happens when you don't have one of the 13 clotting factors, or blood proteins, that help slow or stop blood flow. In hemophilia C, you don't have the clotting factor or blood protein XI, sometimes called Factor 11, because you didn't inherit the F11 gene.
- Hereditary Nonspherocytic Hemolytic Anemia: Hereditary Nonspherocytic hemolytic anemia refers to a group of conditions for which the main feature is the premature destruction of red blood cells. Red blood cells move oxygen throughout the body. Premature destruction of red blood cells is called Hemolytic Anemia.
- Hereditary Spherocytic Hemolytic Anemia: Hereditary Spherocytosis is an inherited disease that affects the red blood cells. Characteristic symptoms of Hereditary Spherocytosis are the destruction of red blood cells in the spleen and their removal from the blood stream (Hemolytic Anemia), a yellow tone to the skin (Jaundice), and an enlarged spleen (Splenomegaly).
- High Cholesterol: High Cholesterol is closely linked with many other medical problems. That means it can cause some serious problems to start (like coronary artery disease). But it can also happen as a result of other diseases, especially ones that trigger inflammation in your body (like lupus). People with high cholesterol often develop high blood pressure as well.
- HIV/AIDS: Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is a chronic, potentially life-threatening condition caused by the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). By damaging the immune system, HIV interferes with the body's ability to fight the organisms that cause disease. HIV is a sexually transmitted infection. It can also be spread by contact with infected blood or from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breast-feeding. Without medication, it may take years before HIV weakens the immune system to the point that one has AIDS.
- Human Trafficking: Human Trafficking is the trade of humans for the purpose of forced labour, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation for the trafficker or others. This may encompass providing a spouse in the context of forced marriage, or the extraction of organs or tissues, including for surrogacy and ova removal.
- 1 (888) 373-7888 National Human Trafficking Hotline
- SMS: 233733 (Text "HELP" or "INFO")
- Hours: 24 hours, 7 days a week
- Languages: English, Spanish and 200 more languages
- Website: humantraffickinghotline.org
- Hypertension: Hypertension, or High Blood Pressure is a common condition in which the long-term force of the blood against your artery walls is high enough that it may eventually cause health problems, such as heart disease. Blood pressure is determined both by the amount of blood your heart pumps and the amount of resistance to blood flow in your arteries. The more blood your heart pumps and the narrower your arteries, the higher your blood pressure. One can have high blood pressure (hypertension) for years without any symptoms. Even without symptoms, damage to blood vessels and the heart continues and can be detected. Uncontrolled high blood pressure increases the risk of serious health problems, including heart attack and stroke. High Blood Pressure generally develops over many years, and it affects nearly everyone eventually. Fortunately, high blood pressure can be easily detected.
- Impaired Driving: Impaired Driving is dangerous. It is the cause of more than half of all car crashes. Impaired Driving means operating a motor vehicle while affected by alcohol, legal or illegal drugs, sleepiness, distractions such as using a cell phone or texting, and having a medical condition which affects one's driving.
- Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis: Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis is a cutaneous, small-vessel vasculitis of the dermal capillaries and venules. This condition can be idiopathic or can be associated with infections, neoplasms, autoimmune disorders, and drugs.
- Linear IgA Disease: Linear IgA Bullous Dermatosis, also known as Linear IgA Disease, is a rare, idiopathic or drug-induced autoimmune blistering disease characterized by the linear deposition of IgA at the dermoepidermal junction.
- MADD / Mothers Against Drunk Driving: Mothers Against Drunk Driving is a non-profit organization in the United States, Canada and Brazil that seeks to stop drunk driving, support those affected by drunk driving, prevent underage drinking, and strive for stricter impaired driving policy, whether that impairment is caused by alcohol or any other drug.
- Marfan Syndrome: Marfan Syndrome is a genetic disorder that affects the body’s connective tissue. Connective tissue holds all the body’s cells, organs and tissue together. It also plays an important role in helping the body grow and develop properly. Because connective tissue is found throughout the body, Marfan Syndrome can affect many different parts of the body, as well. Features of the disorder are most often found in the heart, blood vessels, bones, joints, and eyes.
- Megaloblastic Anemia: Megaloblastic Anemia is a type of anemia characterized by very large red blood cells. In addition to the cells being large, the inner contents of each cell are not completely developed. This malformation causes the bone marrow to produce fewer cells, and sometimes the cells die earlier than the 120-day life expectancy.
- Microscopic Polyangiitis: Microscopic Polyangiitis is a condition that causes small blood vessels to be inflamed. It's a rare type of vasculitis. The disease can damage the blood vessels and cause problems in organs around the body. Microscopic Polyangitis most often affects people in their 50s and 60s, but it can happen at any age.
- Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD): Mothers Against Drunk Driving (MADD) is a nonprofit organization in the United States and Canada that seeks to stop drunk driving, support those affected by drunk driving, prevent underage drinking, and strive for stricter impaired driving policy, whether that impairment is caused by alcohol or any other drug.
- Myeloproliferative Neoplasms (MPN), Chronic, including ET, MF, and PV: Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms are blood cancers that occur when the body makes too many white or red blood cells, or platelets. This overproduction of blood cells in the bone marrow can create problems for blood flow and lead to various symptoms. MPNs were called Myeloproliferative Diseases until 2008 when the World Health Organization reclassified them as cancers and renamed them Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. There are three main types of MPNs: Polycythemia vera (PV), Essential Thrombocythemia (ET), Myelofibrosis (MF). Certain leukemias, including Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia, are also now considered Myeloproliferative Neoplasms. The alternate colors for Myeloproliferative Neoplasms are burgundy, and orange and red for Chronic Myeloproliferative Neoplasms.
- Myocarditis: Myocarditis is inflammation of the heart muscle. Pericarditis is inflammation of the outer lining of the heart. In both cases, the body's immune system causes inflammation in response to an infection or some other trigger.
- National Red Ribbon Campaign / National Red Ribbon Week / DARE: National Family Partnership provides drug awareness by sponsoring the annual National Red Ribbon Campaign™. Since its beginning in 1985, the Red Ribbon has touched the lives of millions of people around the world. In response to the murder of DEA Agent Enrique Camarena, angered parents and youth in communities across the country began wearing Red Ribbons as a symbol of their commitment to raise awareness of the killing and destruction cause by drugs in America. In 1988, National Family Partnership sponsored the first National Red Ribbon Celebration. Today, the Red Ribbon serves as a catalyst to mobilize communities to educate youth and encourage participation in drug prevention activities.
- Neonatal Alloimmune Thrombocytopenia / NAIT: NeonatalAalloimmune Thrombocytopenia, (NAIT) is caused by maternal antibodies raised against alloantigens carried on fetal platelets. Although many cases are mild, NAIT is a significant cause of morbidity and mortality in newborns and is the most common cause of intracranial haemorrhage in full-term infants.
- Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria: Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria is a rare, acquired, life-threatening disease of the blood. The disease is characterized by destruction of red blood cells, blood clots, and impaired bone marrow function. Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria is closely related to aplastic anemia.
- Pernicious Anemia: Anemia is a condition in which the body does not have enough healthy red blood cells. Red blood cells provide oxygen to body tissues. There are many types of anemia. Pernicious Anemia is a decrease in red blood cells that occurs when the intestines cannot properly absorb vitamin B12.
- Platelet Donation: Blood donation is a voluntary procedure that can help save the lives of others. There are several types of blood donation, which help meet different medical needs. Platelet Donation collects only platelets, the cells that help stop bleeding by clumping and clotting in blood vessels. Donated platelets are commonly given to people with leukemia, people receiving chemotherapy and babies with severe infections. The alternate color for Platelet Donation is black and gold.
- Poland Syndrome: Poland Syndrome, named after British surgeon Alfred Poland, is a rare birth defect characterized by underdevelopment or absence of the chest muscle on one side of the body, and usually also webbing of the fingers of the hand on the same side.
- Polyarteritis Nodosa: Polyarteritis Nodosa is a rare multi-system disorder characterized by widespread inflammation, weakening, and damage to small and medium-sized arteries.
- Polymyalgia Rheumatica: Polymyalgia Rheumatica is an inflammatory disorder that causes muscle pain and stiffness, especially in the shoulders and hips. Signs and symptoms of Polymyalgia Rheumatica usually begin quickly and are worse in the morning. The alternate color for Polymyalgia Rheumatica is purple and blue.
- Postmyocardial Infarction Syndrome: Postmyocardial Infarction Syndrome is inflammation of the sac surrounding the heart. It is believed to occur as the result of the immune system responding to damage to heart tissue or damage to the sac around the heart. The damage can result from a heart attack, surgery or traumatic injury. Symptoms include chest pain, which can feel like chest pain from a heart attack.
- Postpericardiotomy Syndrome: Postpericardiotomy Syndrome is a clinical syndrome consisting of worsening or new formation of pericardial and/or pleural effusion, pericardial rub, chest pain with or without dyspnea, fever, and elevated inflammatory markers.
- Prinzmetal Angina (PVA): Prinzmetal's Variant Angina is characterized by recurrent episodes of chest pain that usually occur when a person is at rest, between midnight and early morning. "Typical" angina, by contrast, is often triggered by physical exertion or emotional stress. Episodes of Prinzmetal Variant Angina can be very painful, and may last from several minutes to thirty minutes. In some cases the pain may spread from the chest to the head, shoulder, or arm.
- Pulmonary Embolism: Pulmonary Embolism occurs when a blood clot gets stuck in an artery in the lung, blocking blood flow to part of the lung. Blood clots most often start in the legs and travel up through the right side of the heart and into the lungs. This is called Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT).
- Pyoderma Gangrenosum: Pyoderma Gangrenosum is a rare condition that causes large, painful sores to develop on your skin, most often on the legs. The exact causes of Pyoderma Gangrenosum are unknown, but it appears to be a disorder of the immune system.
- Red Ribbon Week - National Red Ribbon Campaign™: Red Ribbon Week takes place every year on October 23-31. The National Family Partnership organized the first Nationwide Red Ribbon Campaign. National Family Partnership provides drug awareness by sponsoring the annual National Red Ribbon Campaign™. Since its beginning in 1985, the Red Ribbon has touched the lives of millions of people around the world. In response to the murder of DEA Agent Enrique Camarena, angered parents and youth in communities across the country began wearing Red Ribbons as a symbol of their commitment to raise awareness of the killing and destruction cause by drugs in America.
- Red Sand Project: #RedSandProject is a participatory artwork that raises awareness about vulnerabilities that can lead to human trafficking and exploitation.
- Rheumatic Fever: Rheumatic Fever is an inflammation in the heart, joints, skin or central nervous system that can occur following inadequately treated strep throat or scarlet fever. These diseases are caused by an infection with group A streptococcus bacteria. Proper treatment of strep can prevent rheumatic fever.
- Rosacea: Rosacea is a common skin condition that causes redness and visible blood vessels in the face. It may also produce small, red, pus-filled bumps. These signs and symptoms may flare up for a period of weeks to months and then diminish for a while. Rosacea can be mistaken for acne, an allergic reaction or other skin problems.
- Schnitzler Syndrome: The Schnitzler Syndrome is a rare and acquired systemic disease which bears in common many features with a group of inherited diseases referred to as auto-inflammatory syndromes. Its main clinical features include fever, an urticarial rash, muscle, bone and/or joint pain and enlarged lymph nodes.
- Sickle Cell Anemia: Sickle Cell Anemia is an inherited form of anemia, a condition in which there aren't enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen throughout your body. Normally, red blood cells are flexible and round, moving easily through the blood vessels. In Sickle Cell Anemia, the red blood cells become rigid and sticky and are shaped like sickles or crescent moons. These irregularly shaped cells can get stuck in small blood vessels, which can slow or block blood flow and oxygen to parts of the body. The alternate color for Sickle Cell Anemia is burgundy.
- Sideroblastic Anemias: Sideroblastic Anemia is a rare blood disorder that affects how the body produces red blood cells. Those with Sideroblastic Anemia lack red blood cells and too much iron in the system because the body is not making use of iron in the red blood cells.
- Sinus Tachycardia: Tachycardia is a condition that makes the heart beat more than 100 times per minute. There are three types of Sinus Tachycardia. Sinus Tachycardia happens when the heart’s natural pacemaker sends out electrical signals faster than normal. The heart beats fast, but it beats the way it should.
- Stroke: A stroke, sometimes called a "brain attack," occurs when blood flow to an area in the brain is cut off. The brain cells, deprived of the oxygen and glucose needed to survive, die. If a Stroke is not caught early, permanent brain damage or death can result.
- Substance Abuse: Substance Abuse refers to the harmful or hazardous use of psychoactive substances, including alcohol and illicit drugs. Psychoactive Substance use can lead to dependence syndrome - a cluster of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that develop after repeated substance use and that typically include a strong desire to take the drug, difficulties in controlling its use, persisting in its use despite harmful consequences, a higher priority given to drug use than to other activities and obligations, increased tolerance, and sometimes a physical withdrawal state.
- Sudden Arrhythmic Death Syndrome / SADS: Sudden Arrhythmic Death Syndrome is when someone dies suddenly and unexpectedly from a cardiac arrest, but the cause of the cardiac arrest cannot be found. A Cardiac Arrest is when the heart suddenly stops pumping blood around the body. This stops breathing and starves your brain of oxygen.
- Supraventricular Tachycardia / SVT: Supraventricular Tachycardia happens when the electrical system that controls the heart rhythm is not working properly. This causes the heart to suddenly beat much faster. It can then slow down abruptly.
- Tachycardia: Tachycardia is the medical term for a heart rate over 100 beats a minute. Many types of irregular heart rhythms (arrhythmias) can cause tachycardia. A fast heart rate is not always a concern. For instance, the heart rate typically rises during exercise or as a response to stress.
- Takayasu’s Arteritis: Takayasu's A rteritis is a rare type of vasculitis, a group of disorders that causes blood vessel inflammation. In Takayasu's Arteritis, the inflammation damages the large artery that carries blood from the heart to the rest of the body and its main branches.
- Temporal Arteritis: Giant Cell Arteritis, or Temporal Arteritis, is an inflammatory disease affecting the large blood vessels of the scalp, neck and arms. Inflammation causes a narrowing or blockage of the blood vessels, which interrupts blood flow. The disease is commonly associated with Polymyalgia Rheumatica.
- Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura is a rare blood disorder. In TTP, blood clots form in small blood vessels throughout the body. The clots can limit or block the flow of oxygen-rich blood to the body's organs, such as the brain, kidneys, and heart. As a result, serious health problems can develop. The increased clotting that occurs in TTP also uses up platelets in the blood. Platelets are blood cell fragments that help form blood clots. These cell fragments stick together to seal small cuts and breaks on blood vessel walls and stop bleeding. With fewer platelets available in the blood, bleeding problems can occur.
- Trafficking in Persons: Human Trafficking is the trade of humans for the purpose of forced labor, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation for the trafficker of others. This may encompass providing a spouse in the context of forced marriage, or the extraction of organs or tissues, including for surrogacy and ova removal.
- Tuberculosis: Tuberculosis, or TB, as it’s commonly called, is a contagious infection that usually attacks the lungs. It can also spread to other parts of the body, like the brain and spine. A type of bacteria called Mycobacterium tuberculosis causes it.
- Urticarial Vasculitis: Urticarial Vasculitis is among a family of rare diseases characterized by inflammation of the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and damage vital organs and tissues.
- Vasculitis: Vasculitis is inflammation of your blood vessels. It causes changes in the blood vessel walls, including thickening, weakening, narrowing or scarring. These changes can restrict blood flow, resulting in organ and tissue damage. There are many types of Vasculitis, and most of them are rare. Vasculitis might affect just one organ, or several. The condition can be short term or long lasting.
- Von Willebrand's Disease: Von Willebrand disease is a lifelong bleeding disorder in which the blood doesn't clot well. Most people with the disease are born with it, though its warning signs may not show up for years. Some people may suspect they have a bleeding disorder when they have heavy bleeding after a dental procedure or, for women, during a menstrual period. Most people with this condition inherited it from a parent. A faulty gene causes problems with a protein important to the blood-clotting process.
- Wegener's Granulomatosis: Wegener's Granulomatosis is a very rare disease that affects many different organs and systems of the body. One of the main features of the disease is an inflammation of the blood vessels (vasculitis). The inflammation narrows the blood vessels and reduces the blood flow to the affected organs. This destroys tissues and damages vital organs.
- Women's Heart Health: In the United States, 1 in 4 women dies from heart disease. The most common cause of Heart Disease in both men and women is narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries, the blood vessels that supply blood to the heart itself. This is called Coronary Artery Disease, and it happens slowly over time. It is the major reason people have heart attacks. The older a woman gets, the more likely she is to get Heart Disease. But women of all ages should be concerned about Heart Disease. All women can take steps to prevent it by practicing healthy lifestyle habits.
- World Pandemic, including Coronavirus: A pandemic is a global disease outbreak. It differs from an outbreak or epidemic because it affects a wider geographical area, often worldwide; infects a greater number of people than an epidemic; is often caused by a new virus or a strain of virus that has not circulated among people for a long time. Humans usually have little to no immunity against it. The virus spreads quickly from person-to-person worldwide. A Pandemic causes much higher numbers of deaths than epidemics and often creates social disruption, economic loss, and general hardship.
- Zika Virus is a virus transmitted by mosquitoes which typically causes asymptomatic or mild infection (fever and rash) in humans, identified originally in Africa and later in other tropical regions, including South America, where it may be associated with an increased incidence of microcephaly in babies born to mothers infected during pregnancy.
Red and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Accessible Healthcare for All / Not a Party Issue / A Human Issue: As a matter of human dignity, everyone is entitled to health care. Like any basic element of life, health care sustains us and should always be accessible and affordable for everyone—where they need it, when they need it, no exceptions and no interruptions. The consequences of being uninsured are significant. Because uninsured patients do not receive the right care in the right place, they are up to four times as likely as insured patients to require avoidable hospitalizations and emergency care.
- Congenital Heart Block: Congenital Heart Block, or Atrioventricular Block, is characterized by interference of the transfer of the electrical nerve impulses that regulate the normal and rhythmic pumping action of the heart muscle. The severity of such conduction abnormalities varies among affected individuals.
- Congenital Heart Defects: Congenital Heart Defects are present at birth and can affect the structure of a baby’s heart and the way it works. They can affect how blood flows through the heart and out to the rest of the body. Congenital Heart Defects can vary from mild (such as a small hole in the heart) to severe (such as missing or poorly formed parts of the heart).
- Congenital Heart Diseases: A Congenital Heart Defect or Congenital Heart Disease is a malformation of the heart, aorta, or other large blood vessels that is the most frequent form of major birth defect in newborns. Congenital Heart Disease, or a Congenital Heart Defect, is a heart abnormality present at birth. There are numerous types of Congenital Heart Defects. They can range from simple conditions that do not cause symptoms to complex problems that cause severe, life-threatening symptoms. According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, there are currently 1 million adults and 1 million children in the United States living with Congenital Heart Defects.
- Fibrosing Alveolitis: Fibrosing Alveolitis is a disease of unknown cause mainly involving the gas-exchanging portions of the lungs. It may occur in isolation and be called cryptogenic or idiopathic, in which case the clinical manifestations are mainly respiratory, or it may be associated with other disorders, such as Rheumatoid Arthritis.
- Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia: Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia is a disorder in which some blood vessels do not develop properly. A person with Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia may form blood vessels without the capillaries (tiny blood vessels that pass blood from arteries to veins) that are usually present between arteries and veins.
- Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS): Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) is a birth defect that affects normal blood flow through the heart. As the baby develops during pregnancy, the left side of the heart does not form correctly. Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome is one type of congenital heart defect. Because a baby with this defect needs surgery or other procedures soon after birth, Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome is considered a critical congenital heart defect.
- Hypoplastic Right Heart Syndrome: Hypoplastic Right Heart Syndrome is the underdevelopment of the right side of the heart, particularly the ventricle. The ventricle is the muscular lower chamber of the heart. Normally, the right ventricle pushes blood out of the heart and to the lungs where it can pick up oxygen. The blood with oxygen then moves to the left side of the heart which pumps the blood to the rest of the body. Hypoplastic Right Heart Syndrome makes it difficult or impossible to pass blood to the lungs. This decreases the amount of oxygen for the rest of the body. The underdeveloped muscle of the right ventricle can also be easily exhausted by normal heart functions. Other structures of the right side of the heart may also be underdeveloped and decrease the flow of blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Noonan Syndrome: Noonan Syndrome is a genetic disorder that prevents normal development in various parts of the body. A person can be affected by Noonan Syndrome in a wide variety of ways. Noonan Syndrome is caused by a genetic mutation and is acquired when a child inherits a copy of an affected gene from a parent. It can also occur as a spontaneous mutation, meaning there's no family history involved.
- Pulmonary Fibrosis: Pulmonary Fibrosis is a lung disease that occurs when lung tissue becomes damaged and scarred. This thickened, stiff tissue makes it more difficult for the lungs to work properly. As Pulmonary Fibrosis worsens, one becomes progressively more short of breath. The scarring associated with Pulmonary Fibrosis can be caused by a multitude of factors.
- Tricuspid Atresia: Tricuspid Atresia is a rare congenital heart malformation characterized by the congenital agenesis of tricuspid valve leading to severe hypoplasia of the right ventricle.
- UNICEF: UNICEF, originally called the United Nations International Children's Emergency Fund in full, now officially United Nations Children's Fund, is an agency of the United Nations responsible for providing humanitarian and developmental aid to children worldwide.
Red and Gray Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Ohio State University Suicide Prevention Program : Anyone can help prevent suicide by learning the risks, warning signs, and how to intervene. REACH © is the name of the OSU Suicide Prevention in-person gatekeeper training program designed to help the OSU community prevent suicide by teaching faculty, staff, and students how to: R ecognize warning signs, E ngage with empathy, A sk directly about suicide, C ommunicate hope, H elp suicidal individuals access care and treatment. OSUSPP only offers in-person REACH © Trainings to university and student affiliated organizations, departments, colleges, and programs. Participants who finish the training receive certificates and pins verifying their completion of the program.
- Polymicrogyria: Polymicrogyria is a condition characterized by abnormal development of the brain before birth. Specifically, the surface of the brain develops too many folds which are unusually small. The signs and symptoms associated with the condition vary based on how much of the brain and which areas of the brain are affected. Bilateral forms tend to cause more severe neurological problems.
Red and Pearl Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- COVID-19 (Red for the virus, pearl for the lungs): If COVID-19 pneumonia progresses, more of the air sacs can become filled with fluid leaking from the tiny blood vessels in the lungs. Eventually, shortness of breath sets in, and can lead to Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS), a form of lung failure.
- Latex Allergy: Latex Allergy is a reaction to certain proteins found in natural rubber latex, a product made from the rubber tree. With a Latex Allergy, the body mistakes latex for a harmful substance. Latex Allergy may cause itchy skin and hives or even anaphylaxis, a potentially life-threatening condition that can cause throat swelling and severe difficulty breathing.
Red and Purple Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Autoimmune Myocarditis: Autoimmune Myocarditis is an autoimmune disease that affects the heart. The condition is characterized by inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium). Some people with Autoimmune Myocarditis have no noticeable symptoms of the condition.
- Chronic Migraine: A migraine can cause severe throbbing pain or a pulsing sensation, usually on just one side of the head. It's often accompanied by nausea, vomiting, and extreme sensitivity to light and sound. Migraine attacks can cause significant pain for hours to days and can be so severe that the pain is disabling. Warning symptoms known as aura may occur before or with the headache. These can include flashes of light, blind spots, or tingling on one side of the face or in the arm or leg.
- Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumor: Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumors are tumors that grow in the abdomen and pelvic area of the body. Desmoplastic Small Round Cell Tumors are a type of soft tissue sarcoma, which is a type of cancer that forms in the connective tissue of the body.
- Lupus Vasculitis: Lupus Vasculitis is one of the secondary vasculitides occurring in the setting of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE) in approximately 50% of patients. It is most commonly associated with small vessels, but medium-sized vessels can also be affected, whereas large vessel involvement is very rare.
Red and White Pinstripes Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Acquired Aplastic Anemia: Acquired Aplastic Anemia is a rare, serious blood disorder, due to bone marrow failure to produce blood cells. Bone marrow is the spongy substance found in the center of the bones of the body, in adults mainly the spine, pelvis, and large bones of the legs.
- Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma: An Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma is a rare type of cancer that usually begins in the salivary glands.
- Aplastic Anemia: Aplastic Anemia is a condition in which the bone marrow is unable to produce blood cells.
- Bone Marrow Failure: Bone Marrow Failure develops when the bone marrow is unable to produce enough healthy blood cells for an individual's needs. The bone marrow is the soft, spongy center of the bones that is the body's factory where all blood cells are produced. These include: Red blood cells, which carry oxygen throughout the body.
- Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT): Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) occurs when a blood clot (thrombus) forms in one or more of the deep veins in the body, usually in the legs. Deep Vein Thrombosis can cause leg pain or swelling, but also can occur with no symptoms.
- Esthesioneuroblastoma: Head and Neck Cancers include cancers in the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose, and salivary glands. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) increase the risk of Head and Neck Cancers. Esthesioneuroblastoma, also known as Olfactory Neuroblastoma, is an uncommon malignant tumor of the upper nasal cavity and anterior skull base.
- Head and Neck Cancer: Head and Neck Cancer is cancer that arises in the head or neck region (in the nasal cavity, sinuses, lips, mouth, salivary glands, throat, or larynx).
- Hypopharyngeal Cancer: Head and Neck Cancers include cancers in the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose and salivary glands. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) increase the risk of Head and Neck Cancers.
- Laryngeal Cancer: Head and Neck Cancer includes cancers in the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose, and salivary glands. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) increase the risk of Head and Neck Cancers. Most Laryngeal Cancers form in squamous cells, the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the larynx. Laryngeal Cancer is a type of Head and Neck Cancer.
- Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer: Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer is a type of Head and Neck Cancer. Head and Neck Cancers include cancers in the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose, and salivary glands. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with Human Papillomavius (HPV) increase the risk of Head and Neck Cancers. Most lip and oral cavity cancers start in squamous cells, the thin, flat cells that line the lips and oral cavity. These are called squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer cells may spread into deeper tissue as the cancer grows. Squamous Cell Carcinoma usually develops in areas of leukoplakia (white patches of cells that do not rub off)
- Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer with Occult Primary: When Squamous Cell Cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the neck or around the collarbone, it is called Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer. The treatment for Metastatic Cancer is the same as treatment for the primary tumor. For example, when Lung Cancer spreads to the neck, the cancer cells in the neck are Lung Cancer cells and they are treated the same as the cancer in the lung. Sometimes doctors cannot find where in the body the cancer first began to grow. When tests cannot find a primary tumor, it is called an occult (hidden) primary tumor. In many cases, the primary tumor is never found.
- Mouth Cancer: Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the lips or mouth. The oral cavity includes the front two thirds of the tongue; the gums; the lining of the inside of the cheeks; the bottom of the mouth under the tongue; the roof of the mouth; the small area behind the wisdom teeth. Most Lip and Oral Cavity Cancers start in squamous cells, the thin, flat cells that line the lips and oral cavity. These are called Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancer cells may spread into deeper tissue as the cancer grows. Squamous Cell Carcinoma usually develops in areas of leukoplakia (white patches of the cells that do not rub off).
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer: Nasopharyngeal Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the nasopharynx. The nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat behind the nose.
- Oral Cancer, Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer and Oropharyngeal Cancer: Oral Cancer is cancer that forms in tissues of the oral cavity or the part of the throat at the back of the mouth. Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the lips and mouth. Most Lip and Oral Cavity Cancers start in squamous cells, the thin flat cells that line the lips and oral cavity. These are called Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cancer cells may spread into deeper tissue as the cancer grows. Squamous Cell Carcinoma usually develops in areas of leukoplakia (white patches of cells that do not rub off). Lip and Oral Cavity Cancer is a type of Head and Neck Cancer.
- Osler's Disease: Osler's Disease, also known as Hereditary Hemorrhagic Telangiectasia and Osler-Weber-Rendu Syndrome, is an autosomal dominant disorder leading to abnormal blood vessel formation in the skin, mucous membranes and often in organs, such as the lungs, liver and brain (arteriovenous malformations).
- Papillomatosis, Adult: Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis is a rare disorder characterized by the development of small, wart-like growths in the respiratory tract.
- Papillomatosis, Childhood: Laryngeal Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the larynx. Laryngeal Cancer is a type of head and neck cancer. Most Laryngeal Cancers form in squamous cells, the thin, flat cells lining the inside of the larynx.
- Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer: Different types of cells in the paranasal sinus and nasal cavity may become malignant. The most common type of Paranasal Sinus and Nasal Cavity Cancer is Squamous Cell Carcinoma. This type of cancer forms in the squamous cells (thin, flat cells) lining the inside of the paranasal sinuses and the nasal cavity.
- Pharyngeal Cancer: Head and Neck Cancers include cancers in the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose, and salivary glands. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) increase the risk of head and neck cancers.
- Pulmonary Embolism: Pulmonary Embolism is a blockage in one of the pulmonary arteries in the lungs. In most cases, Pulmonary Embolism is caused by blood clots that travel to the lungs from the legs or, rarely, other parts of the body (Deep Vein Thrombosis).
- Salivary Gland Cancer: More than half of all salivary gland tumors are benign (not cancerous) and do not spread to other tissues. Salivary Gland Cancer is a type of Head and Neck Cancer. Head and Neck Cancers include cancers in the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose, and salivary glands. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) increase the risk of Head and Neck Cancers.
- Septo-Optic Dysplasia: Septo-Optic Dysplasia is a disorder of early brain development. Although its signs and symptoms vary, this condition is traditionally defined by three characteristic features: Underdevelopment of the optic nerves; abnormal formation of structures along the midline of the brain; and pituitary hypoplasia.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Squamous Cell Carcinoma, also called Epidermoid Carcinoma, is cancer that begins in squamous cells. Squamous cells are thin, flat cells that look like fish scales, and are found in the tissue that forms the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body, and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. Most cancers of the anus, cervix, head and neck, and vagina are squamous cell carcinomas.
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ: Squamous Cell Carcinoma in Situ is a condition in which abnormal cells are found in the tissues that form the surface of the skin, the lining of the hollow organs of the body (such as the bladder and uterus), and the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts.
- Squamous Neck Cancer with Occult Primary, Metastatic: Metastatic Squamous Neck Cancer with Occult Primary is a disease in which squamous cell cancer spreads to lymph nodes in the neck and it is not known where the cancer first formed in the body. Cancer can begin in squamous cells anywhere in the body and metastasize through the blood or lymph system to other parts of the body.
- Throat Cancer: Head and Neck Cancers include cancers of the larynx, throat, lips, mouth, nose, and salivary glands. Tobacco use, heavy alcohol use, and infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) increase the risk of Head and Neck Cancers. Nasopharyngeal Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the nasopharynx. The nasopharynx is the upper part of the throat behind the nose. Oropharyngeal cancer is a disease in which malignant cancer cells form in the tissues of the oropharynx. The oropharynx is the middle part of the throat, behind the mouth. Hypopharyngeal Cancer is a disease in which cancer cells form in the tissues of the hypopharynx. The hypopharynx is the bottom part of the pharynx (throat).
- Tongue Cancer: Tongue cancer is a form of cancer that begins in the cells of the tongue. Several types of cancer can affect the tongue, but Tongue Cancer most often begins in the thin, flat squamous cells that line the surface of the tongue. The type of cells involved in Tongue Cancer helps determine prognosis and treatment.
Red and White Polka Dots Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Grover’s Disease: Grover's Disease is a skin disorder characterized by a rash of small, raised skin-colored or reddish spots, which are usually itchy. While the rash caused by Grover's Disease may last for just two to four weeks and then disappear, the rash can sometimes persist for months or even years.
- Measles: Measles is an acute viral respiratory illness. It is characterized by a fever (as high as 105°F) and malaise, cough, coryza, and conjunctivitis. The rash usually appears about 14 days after a person is exposed.
- Mucha-Habermann Disease: Mucha-Habermann Disease, also known as Pityriasis Lichenoides et Varioliformis Acuta or PLEVA, is a rare skin disorder. The lesions most often appear on the trunk and the arms and legs. Lesions tend to develop in small groups. Mucha-Habermann Disease most often affects children or young adults.
- Pityriasis Lichenoides et Varioliformis Acuta / PLEVA: Pityriasis Lichenoides et Varioliformis Acuta (PLEVA), otherwise known as Mucha-Habermann Disease, is an uncommon cutaneous inflammatory disorder that most frequently affects young adults and children.
- Urticaria: Urticaria, also known as hives, weals, welts or nettle rash, is a raised, itchy rash that appears on the skin. It may appear on one part of the body or be spread across large areas. The rash is usually very itchy and ranges in size from a few millimeters to the size of a hand.
Red and Yellow Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Hepatitis C: Hepatitis C is a viral infection that causes liver inflammation, sometimes leading to serious liver damage. The Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) spreads through contaminated blood. Until recently, Hepatitis C treatment required weekly injections and oral medications that many HCV-infected people couldn't take because of other health problems or unacceptable side effects. Today, chronic HCV is usually curable with oral medications taken every day for two to six months. Still, about half of people with HCV don't know they're infected, mainly because they have no symptoms, which can take decades to appear. For that reason, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends a one-time screening blood test for everyone at increased risk of the infection. The largest group at risk includes everyone born between 1945 and 1965, a population five times more likely to be infected than those born in other years.
- HIV / HCV Co Infection: People with HIV who have underlying liver disease are at risk for severe disease from Hepatitis A infection, and widespread Hepatitis A outbreaks associated with person-to-person transmission have been occurring in the United States since 2016. Therefore, CDC and ACIP recommend Hepatitis A vaccination for this population.
Red, White and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Fireworks Safety: If not handled properly, fireworks can cause burns and eye injuries in kids and adults. The best way to protect your family is not to use any fireworks at home. Attend public fireworks displays, and leave the lighting to the professionals. Lighting fireworks at home isn't legal in many areas, so if you still want to use them, be sure to check with your local police department first.
- Loss of a Military Husband / In Memory of a Military Husband: If a family service member died in military service, a family replaces the blue service star with a gold star. The gold star lets the community know that their family service member died or was killed while serving their country. The alternate color for loss of a Military Husband / In Memory of a Military Husband is camo (camouflage).
- Loss of a Military Wife / In Memory of a Military Wife: If a family service member died in military service, a family replaces the blue service star with a gold star. The gold star lets the community know that their family service member died or was killed while serving their country. The alternate color for loss of a Military Wife / In Memory of a Military Wife is camo (camouflage).
- Loss of a Soldier / In Memory of a Soldier: If a family service member died in military service, a family replaces the blue service star with a gold star. The gold star lets the community know that their family service member died or was killed while serving their country. The alternate color for loss of a Soldier / In Memory of a Soldier is camo (camouflage).
- Military and Troop Support: Military and Troop Support, or Deployed Soldier Support, shows support for their efforts and freedom throughout the world.
- Military Families: Being a part of a military family is always a balancing act. Sometimes, “the job” must come first, and other times family is the top priority. But at the end of the day, when a service member joins the military, their family joins with them. Service members, military spouses and military kids all understand that this life comes with unique challenges and scary moments but working together as a family means that the service member can fulfill the oath they made to defend their country and its people. The alternate color for Military Families is camo (camouflage).
- Military Personnel Injured in Active Duty: Reported injuries in female military personnel versus male military personnel were compared to male. There are differences between the sexes in average fitness levels and injury reporting behaviors. The difference in rates of reported injuries was greatest during basic training, and reduced thereafter, possibly due in part to a reduced difference in fitness between the sexes or increased opportunity to self-determine workloads relative to fitness levels. The alternate colors for Military Personnel Injured in Active Duty are purple and camo (camouflage).
- Parents of Fallen Soldiers: When the unfortunate news of a family member’s death is delivered, the blue star of military service is replaced by a gold star. If you ever see a gold star banner, you know the family has had a loved one who made the ultimate sacrifice for their country. Sometimes a service banner might have a mix of blue and gold stars. This means that only some of their loved ones came home safely. The alternate Color for Parents of Fallen Soldiers is camo (camouflage).
- Patriotism: The dictionary definition for patriotism as "love for or devotion to one's country." Wearing a red, white and blue awareness ribbon demonstrates patriotism.
- Remembering 9/11: 9/11 attacks were a series of airline hijackings and suicide attacks committed in 2001 by 19 militants associated with the Islamic extremist group al-Qaeda against targets in the United States. 9/11 was the deadliest terrorist attack on American soil in United States history.
- Remembering September 11, 2001: September 11 attacks, also known as 9/11 attacks, were the deadliest terrorist attack on U.S. soil. The attacks involved the hijacking of four planes, three of which were used to strike significant U.S. sites. The September 11 attacks caused extensive death and destruction. Approximately 2,750 people were killed in New York, 184 at the Pentagon, and 40 in Pennsylvania, where one of the hijacked planes crashed after the passengers attempted to retake the plane.
Road Distracted Driving Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Distracted Driving / Texting While Driving: Distracted Driving is any activity that diverts attention from driving, including talking or texting on your phone, eating and drinking, talking to people in your vehicle, fiddling with the stereo, entertainment or navigation system — anything that takes your attention away from the task of safe driving. Texting is the most alarming distraction. Sending or reading a text takes your eyes off the road for 5 seconds. At 55 mph, that's like driving the length of an entire football field with your eyes closed. You cannot drive safely unless the task of driving has your full attention. Any non-driving activity you engage in is a potential distraction and increases your risk of having an accident.
Royal Blue and Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Congenital Cytomegalovirus: Congenital Cytomegalovirus is a condition that can occur when an infant is infected with a virus called cytomegalovirus (CMV) before birth. Congenital means the condition is present at birth.
- Intercranial Hypertension: Intracranial Hypertension literally means that the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) within the skull is too high. Intracranial means “within the skull.” Hypertension means “high fluid pressure.”
Sea Green Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Stammering: Stammering and Stuttering are two different words that are used to describe the same condition. The cause of Stammering is unknown, but research shows that a combination of factors is involved. Stammering affects four times as many men as women.
- Stuttering: Generally speaking Stuttering is used more commonly in North America and Australia, while in Britain they tend to use the word Stammering.
Silver Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum : Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum is a rare birth defect in which there is a complete or partial absence of the corpus callosum, the band of white matter connecting the two hemispheres in the brain. This congenital defect occurs when the corpus callosum fails to develop normally, typically during pregnancy.
- Amalgam Illness / Mercury Toxicity A wide variety of debilitating and supposedly incurable conditions may actually be due to chronic mercury poisoning. These conditions are seldom cured because mercury poisoning is believed to be rare.
- Bell's Palsy: Bell's Palsy causes sudden, temporary weakness in the facial muscles. This makes half of the face appear to droop. Consequently, a smile is one-sided, and the eye on that side resists closing. Bell's Palsy, also known as Facial Palsy, can occur at any age. The exact cause is unknown. It's believed to be the result of swelling and inflammation of the nerve that controls the muscles on one side of the face. It may also be due to a reaction that occurs after a viral infection. For most people, Bell's Palsy is temporary.
- Bickerstaff’s Encephalitis: Bickerstaff Brainstem Encephalitis is a rare, autoimmune disease of the peripheral and central nervous system (i.e., brainstem). BBE is considered a variant of other immune-mediated polyneuropathies, such as Guillain Barré Syndrome and Miller Fisher Syndrome.
- Borderline Personality Disorder: Borderline Personality Disorder, also known as Emotionally Unstable Personality Disorder, is a long-term pattern of abnormal behavior characterized by unstable relationships with other people, unstable sense of self, and unstable emotions.
- Brain Disabilities: Neurological Disabilities include a wide range of disorders, such as epilepsy, learning disabilities, neuromuscular disorders, autism, ADD, brain tumors, and cerebral palsy. Some neurological conditions are congenital, emerging before birth.
- Brain Diseases: Brain diseases come in different forms. Infections, trauma, stroke, seizures, and tumors are some of the major categories of brain diseases.
- Brain Disorders: A neurological disorder is any disorder of the nervous system. Structural, biochemical or electrical abnormalities in the brain, spinal cord or other nerves can result in a range of symptoms. Examples of symptoms include paralysis, muscle weakness, poor coordination, loss of sensation, seizures, confusion, pain and altered levels of consciousness. There are many recognized neurological disorders, some relatively common, but many rare.
- Developmental Learning Disorders: Learning disorders generally affect people of average or above average intelligence. As a result, the disorder appears as a gap between expected skills, based on age and intelligence, and academic performance . Common learning disorders affect a child's abilities in reading, written expression, math or nonverbal skills.
- Disabled Children: A child can be considered to be disabled if he or she has significant problems with communication, comprehension, vision, hearing or physical functioning .
- Dyslexia: Dyslexia is a specific learning disability that is neurobiological in origin. It is characterized by difficulties with accurate and/or fluent word recognition and by poor spelling and decoding abilities. These difficulties typically result from a deficit in the phonological component of language that is often unexpected in relation to other cognitive abilities and the provision of effective classroom instruction. Secondary consequences may include problems in reading comprehension and reduced reading experience that can impede growth of vocabulary and background knowledge.
- Encephalitis: Encephalitis is inflammation of the brain. There are several causes, but the most common is viral infection. Encephalitis often causes only mild flu-like signs and symptoms, such as a fever or headache, or no symptoms at all. Sometimes the flu-like symptoms are more severe. Encephalitis can also cause confused thinking, seizures, or problems with senses or movement. Rarely, Encephalitis can be life-threatening.
- Facial Paralysis: Facial Paralysis is a loss of facial movement due to nerve damage. One's facial muscles may appear to droop or become weak. Facial Paralysis can happen on one or both sides of the face. Common causes of Facial Paralysis include infection or inflammation of the facial nerve.
- Herpes Simplex Encephalitis: Herpes Simplex Encephalitis is an acute or subacute illness that causes both general and focal signs of cerebral dysfunction.
- Japanese Encephalitis: Japanese Encephalitis Virus is a flavivirus related to dengue, yellow fever and West Nile viruses, and is spread by mosquitoes. Juvenile Encephalitis Virus is the main cause of viral encephalitis in many countries of Asia with an estimated 68,000 clinical cases every year.
- Limb Loss: Amputation is the removal of a limb by trauma, medical illness, or surgery. As a surgical measure, it is used to control pain or a disease process in the affected limb, such as malignancy or gangrene. In some cases, it is carried out on individuals as a preventative surgery for such problems.
- Locked-In Syndrome: Locked-in syndrome is a rare neurological disorder in which there is complete paralysis of all voluntary muscles except for the ones that control the movements of the eyes. Individuals with Locked-In syndrome are conscious and awake, but have no ability to produce movements (outside of eye movement) or to speak. Cognitive function is usually unaffected.
- Neurological Disorders: Neurological disorders are diseases of the brain, spine and the nerves that connect them. There are more than 600 diseases of the nervous system, such as brain tumors, epilepsy, Parkinson's disease and stroke as well as less familiar ones such as Frontotemporal Dementia.
- Parkinson's Disease: Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects predominately dopamine-producing neurons in a specific area of the brain called substantia nigra. Symptoms generally develop slowly over years.
- Perivenous Encephalomyelitis: Perivenous Demyelination is the pathological hallmark of Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis. Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis (ADEM) is characterized by a brief but widespread attack of inflammation in the brain and spinal cord that damages myelin, the protective covering of nerve fibers.
- Schizoaffective Disorder: Schizoaffective Disorder is a mental disorder in which a person experiences a combination of Schizophrenia symptoms, such as hallucinations or delusions, and mood disorder symptoms, such as depression or mania. The two types of schizoaffective Disorder, both of which include some symptoms of schizophrenia, are: Bipolar type, which includes episodes of mania and sometimes major depression; and Depressive type, which includes only major depressive episodes.
- Schizoid Personality Disorder: Schizoid Personality Disorder is a personality disorder characterized by a lack of interest in social relationships, a tendency towards a solitary or sheltered lifestyle, secretiveness, emotional coldness, detachment, and apathy.
- Schizophrenia: Schizophrenia is a chronic brain disorder that affects less than one percent of the U.S. population. When Schizophrenia is active, symptoms can include delusions, hallucinations, trouble with thinking and concentration, and lack of motivation.
Silver and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Brachial Plexus Injuries: The Brachial Plexus is the network of nerves that sends signals from the spinal cord to the shoulder, arm and hand. A Brachial Plexus Injury occurs when these nerves are stretched, compressed, or damaged extensively.
- Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders: Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders is an umbrella term describing the range of effects that can occur in an individual whose mother drank alcohol during pregnancy. These effects may include physical, mental, behavioral, and/or learning disabilities with possible lifelong implications.
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome: Fetal Alcohol Syndrome is a condition in a child that results from alcohol exposure during the mother's pregnancy. Fetal Alcohol Syndrome causes brain damage and growth problems. The problems caused by Fetal Alcohol Syndrome vary from child to child, but defects caused by Fetal Alcohol Syndrome are not reversible. An alternate spelling is Foetal Alcohol Syndrome.
- Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders / Foetal Alcohol Syndrome: The alternate spelling for Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders / Fetal Alcohol Syndrome isis Foetal Alcohol Syndrome / Foetal Alcohol Syndrome. Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorders are a group of conditions that can occur in a person who was exposed to alcohol before birth. These effects can include physical problems and problems with behavior and learning. Often, a person with an Foetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder has a mix of these problems.
- Type 1 Diabetes (T1D): Type 1 Diabetes (T1D), once known as Juvenile Diabetes or Insulin-Dependent Diabetes, is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin. Insulin is a hormone needed to allow sugar (glucose) to enter cells to produce energy. Different factors, including genetics and some viruses, may contribute to Type 1 Diabetes (T1D). Although Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) usually appears during childhood or adolescence, it can develop in adults. Despite active research, Type 1 Diabetes has no cure. The alternate color for Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) is the blue and gray blood drop awareness ribbon pin.
Silver and Gold Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Deafness: Deafness is partial or complete hearing loss. Levels of hearing impairment vary from a mild to a total loss of hearing. There are four levels of deafness or hearing impairment. These are: Mild deafness or mild hearing impairment where people may find it hard to understand the words other people are saying, especially if there is a lot of background noise; Moderate deafness or moderate hearing impairment where the person finds following a conversation very difficult without using a hearing aid; Severe deafness where the person is severely deaf and must either lip-read or use sign language in order to communicate, even if they have a hearing aid; Profound deafness where some people cannot hear anything at all.
- Hearing Disorders: There are four major types of hearing loss, including Auditory Processing Disorders, Conductive Hearing Loss, Sensorineural Hearing Loss, and Mixed Hearing Loss.
- Hearing Impairments: Hearing loss affects people of all ages and can be caused by many different factors. The three basic categories of hearing loss are sensorineural hearing loss, conductive hearing loss and mixed hearing loss.
- Hearing Loss: Hearing Loss is a common problem caused by noise, aging, disease, and heredity. People with Hearing Loss may find it hard to have conversations with friends and family. They may also have trouble understanding a doctor’s advice, responding to warnings, and hearing doorbells and alarms.
- Hyperacusis: Hyperacusis (or hyperacousis) is a highly debilitating hearing disorder characterized by an increased sensitivity to certain frequencies and volume ranges of sound. A person with severe hyperacusis has difficulty tolerating everyday sounds, which become painful or loud. Hyperacusis is often coincident with tinnitus. Both conditions have a prevalence of about 10–15% and hearing loss as a major risk factor.
- Meniere's Disease: Meniere's Disease is a disorder of the inner ear that causes episodes in which one feels as if they're spinning (vertigo), and has fluctuating hearing loss with a progressive, ultimately permanent loss of hearing, ringing in the ear (tinnitus), and sometimes a feeling of fullness or pressure in your ear. In most cases, Meniere's Disease affects only one ear.
- Tinnitus: Tinnitus is the perception of noise or ringing in the ears. A common problem, tinnitus affects about 1 in 5 people. Tinnitus isn't a condition itself, it's a symptom of an underlying condition, such as age-related hearing loss, ear injury or a circulatory system disorder.
- VACTERL Association: VACTERL Association is a non-random association of birth defects that affects multiple parts of the body. The term VACTERL is an acronym with each letter representing the first letter of one of the more common findings seen in affected individuals: (V) = vertebral abnormalities; (A) = anal atresia; (C) = cardiac (heart) defects; (T) = tracheal anomalies including tracheoesophageal (TE) fistula; (E) = esophageal atresia; (R) = renal (kidney) and radial (thumb side of hand) abnormalities; and (L) = other limb abnormalities. Intelligence is usually normal.
- VACTERL with Hydrocephalus: VACTERL with Hydrocephalus (VACTERL-H) is a rare genetic disorder in which the non-random congenital malformations of VACTERL association co-occur with hydrocephalus. Hydrocephalus is a condition in which accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in and around the brain and spinal cord causes increased pressure on the brain tissue.
Teal Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Adrenal Cortical Cancer: Adreno Cortical Carcinoma is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the outer layer of the adrenal gland. Having certain genetic conditions increases the risk of Adreno Cortical Carcinoma. Symptoms of Adreno Cortical Carcinoma include pain in the abdomen.
- Adult Survivors of Child Sexual Abuse: Many adult survivors manage things by working hard to “forget” or not think about their prior sexual abuse. Unfortunately, some adult survivors avoid working through their traumas by hurting themselves with drugs and alcohol, excessive exercise, unhealthy relationships with food, or harming themselves in other ways. These means of coping help the survivor to avoid the pain of past memories of abuse. The alternate color for Adult Survivors of Child Sexual Abuse is white.
- Agoraphobia: Agoraphobia is a type of Anxiety Disorder in which you fear and avoid places or situations that might cause you to panic and make you feel trapped, helpless or embarrassed. You fear an actual or anticipated situation, such as using public transportation, being in open or enclosed spaces, standing in line, or being in a crowd. The anxiety is caused by fear that there's no easy way to escape or get help if the anxiety intensifies. Most people who have agoraphobia develop it after having one or more panic attacks, causing them to worry about having another attack and avoid the places where it may happen again. People with agoraphobia often have a hard time feeling safe in any public place, especially where crowds gather.
- Anaphylaxis: Anaphylaxis is a serious allergic response that often involves swelling, hives, lowered blood pressure and in severe cases, shock. If anaphylactic shock is not treated immediately, it can be fatal. A major difference between Anaphylaxis and other allergic reactions is that Anaphylaxis typically involves more than one system of the body.
- Anxiety Disorders: Anxiety Disorders are a group of mental illnesses, and the distress they cause can keep you from carrying on with your life normally. Anxiety Disorder is an umbrella term that includes different conditions: Panic Disorder, Social Anxiety Disorder, specific phobias and Generalized Anxiety Disorder.
- Batten Disease (Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis): Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis refers to a group of conditions that affect the nervous system. Signs and symptoms vary widely between the forms but generally include a combination of dementia, vision loss, and epilepsy. Although Neuronal Ceroid Lipofuscinosis was historically classified according to the age of onset and clinical symptoms, the most recent classification system is primarily based on the underlying genetic cause.
- Child Sexual Abuse and Assault: Sexual Abuse can include many different things, from touching a victim in a sexual manner to forcing a victim to touch the perpetrator in a sexual way to making a victim look at sexual body parts or watch sexual activity. Sexual Abuse of a child is a criminal act. The term sexual assault can describe a range of criminal acts that are sexual in nature, from unwanted touching and kissing, to rubbing, groping or forcing the victim to touch the perpetrator in sexual ways. Sexual assault overlaps with rape because the term includes rape. The alternate color for Child Sexual Abuse and Assault is white.
- CREST Syndrome: CREST Syndrome is characterized by: Calcinosis: Calcium skin deposits. Raynaud's phenomenon: A condition in which the blood vessels of the fingers and toes spasm when triggered by factors, such as cold, stress or illness. Cold, painful or numb fingers and toes result, which in severe cases may become gangrenous.
- Dissociative Identity Disorder: Dissociative Identity Disorder is thought to be a complex psychological condition that is likely caused by many factors, including severe trauma during early childhood. The dissociative aspect is thought to be a coping mechanism. In other words, the person literally dissociates himself from a situation or experience that's too violent, traumatic, or painful to assimilate with his conscious self.
- Ectodermal Dysplasia: Ectodermal Dysplasias are a group of more than 180 disorders that affect the outer layer of tissue of the embryo that helps make up the skin, sweat glands, hair, teeth, and nails. Symptoms of Ectodermal Dysplasia can range from mild to severe and may include teeth abnormalities; brittle, sparse or absent hair; abnormal fingernails; inability to perspire; various skin problems; and other symptoms.
- Fallopian Tube Cancer: Ovarian Epithelial Cancer, Fallopian Tube Cancer, and Primary Peritoneal Cancer form in the same kind of tissue and are treated in the same way. These cancers are often advanced at diagnosis. Less common types of Ovarian Tumors include Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors and Ovarian Low Malignant Potential Tumors.
- Food Allergies: Food Allergies or Food Intolerances affect nearly everyone at some point. But only about 5% of children have clinically proven allergic reactions to foods. In teens and adults, Food Allergies occur in about 4% of the total population. This difference between the clinically proven prevalence of food allergy and the public perception of the problem is in part due to reactions called "food intolerances" rather than Food Allergies. A food allergy, or hypersensitivity, is an abnormal response to a food that is triggered by the immune system.
- Fragile X Syndrome: Fragile X Syndrome is a genetic condition involving changes in part of the X chromosome. This condition causes a range of developmental problems including learning disabilities and cognitive impairment. It is the most common form of inherited intellectual disability in males and a significant cause of intellectual disability in females.
- Gambling Addiction: Gambling is a diverse activity, so different types of gambling addiction exist. It is not always obvious when someone is addicted to gambling. Contrary to popular belief, the act of gambling is not restricted to slot machines, cards and casinos. Purchasing a lottery ticket, entering a raffle or making a bet with a friend are also forms of gambling. Gambling addiction can occur when a person feels that they are in financial ruin and can only solve their problems by gambling what little they have in an attempt to get a large sum of money. Unfortunately, this almost always leads to a cycle in which the gambler feels they must win back their losses, and the cycle goes on until the person is forced to seek rehabilitation to break their habit.
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Generalized Anxiety Disorder is characterized by persistent and excessive worry about a number of different things. People with Generalized Anxiety Disorder may anticipate disaster and may be overly concerned about money, health, family, work, or other issues. Individuals with Generalized Anxiety Disorder find it difficult to control their worry. They may worry more than seems warranted about actual events or may expect the worst even when there is no apparent reason for concern.
- Graves’ Ophthalmopathy: Graves' Ophthalmopathy signs and symptoms include bulging eyes, redness and retracting eyelids. About 30% of people with Graves' Disease show some signs and symptoms of Graves' Ophthalmopathy. In Graves' Ophthalmopathy, inflammation and other immune system events affect muscles and other tissues around your eyes.
- Gynecologic Cancer: Gynecologic Cancer is cancer of the female reproductive tract, including the cervix, endometrium, fallopian tubes, ovaries, uterus, and vagina.
- Heterotaxy Syndrome: Heterotaxy is a condition characterized by internal organs that are not arranged as would be expected in the chest and abdomen. Organs are expected to be in a particular position inside of the body, known as situs solitus. Heterotaxy occurs when the organs are not in this typical orientation, but are instead in different positions in the body. This most commonly causes complications with the heart, lungs, liver, spleen, and intestines.
- Hirsutism: Hirsutism is a condition in women that results in excessive growth of dark or coarse hair in a male-like pattern, on the face, chest and back. With Hirsutism, extra hair growth often arises from excess male hormones (androgens), primarily testosterone.
- Interstitial Cystitis: Interstitial Cystitis, also called painful bladder syndrome, is a chronic condition causing bladder pressure, bladder pain and sometimes pelvic pain. The pain ranges from mild discomfort to severe. Although signs and symptoms of Interstitial Cystitis may resemble those of a chronic urinary tract infection, there's usually no infection.
- Juvenile Scleroderma: Scleroderma, which literally means “hard skin,” describes a group of conditions that causes the skin to tighten and harden. There are two basic forms: Localized Scleroderma and Systemic Scloerosis. Juvenile Scleroderma can occur at any age and in any race, but it is more common in girls. It is a rare disease.
- Lichen Sclerosus: Lichen Sclerosus is a condition that causes patchy, discolored, thin skin. It usually affects the genital and anal areas. Anyone can get Lichen Sclerosus but postmenopausal women are at higher risk. It isn't contagious and can't be spread through sexual contact.
- Marker X Syndrome: Fragile X S yndrome, also known as Martin-Bell S yndrome, Marker X S yndrome, and FRAXA S yndrome. It is the most common form of inherited mental retardation. Fragile X S yndrome is caused by a mutation in the FMR1 gene, located on the X chromosome.
- Martin Bell Syndrome: A genetic condition causing intellectual disability Fragile X syndrome causes mild to severe intellectual disability. It affects both males and females, but females usually have milder symptoms. Symptoms include delays in talking, anxiety, and hyperactive behavior. Some people have seizures. Physical features might include large ears, a long face, a prominent jaw and forehead, and flat feet.Therapy can be used to treat learning disabilities.
- Military Sexual Assault: The military has long struggled with addressing sexual assault among troops. Concerns spiked in 2013 when the Pentagon released a report that estimated the number of sexual assaults increased 35 percent from 2010 to 2012 to 26,000 victims.
- Morphea: Morphea Scleroderma is a skin condition characterized by hardened, discolored, and thickened patches of skin on various areas of the body without internal organ involvement. The exact cause of morphea is unknown. However, it is considered an autoimmune disease and is associated with various predisposing factors.
- MRSA: Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA) infection is caused by a type of staph bacteria that's become resistant to many of the antibiotics used to treat ordinary staph infections. Most MRSA infections occur in people who've been in hospitals or other health care settings, such as nursing homes and dialysis centers. Another type of MRSA infection has occurred in the wider community — among healthy people. This form, community-associated MRSA, often begins as a painful skin boil. It's spread by skin-to-skin contact. At-risk populations include groups such as high school wrestlers, child care workers and people who live in crowded conditions.
- Myasthenia Gravis: Myasthenia Gravis is a chronic condition that causes muscles to tire and weaken easily. This waxing-and-waning weakness of muscles, worsening with use and improving with rest, is a hallmark of this particular disease. The disease most commonly affects muscles that control eye and eyelid movement. The majority will go on to develop weakness in other muscle groups within one or two years.
- #metoo: The Me Too movement (or #MeToo movement), with many local and international alternative names, is a movement against sexual harassment and sexual assault. #MeToo spread virally in October 2017 as a hashtag on social media in an attempt to demonstrate the widespread prevalence of sexual assault and harassment, especially in the workplace.
- No Body Shame: No Body Shame is a global movement to help people of every variety live their lives fully, passionately, and free of shame.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder: Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is a type of mental illness. People with OCD can have either obsessive thoughts and urges or compulsive, repetitive behaviors. Some have both obsessions and compulsions. OCD is not about habits like biting your nails or always thinking negative thoughts. The disorder can affect your job, school, and relationships and keep you from living a normal life. Your thoughts and actions are beyond your control.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder: Obsessive-Compulsive Personality Disorder is a personality disorder that’s characterized by extreme perfectionism, order and neatness. People with OCPD will also feel a severe need to impose their own standards on their outside environment.
- Occipital Neuralgia: Occipital Neuralgia is a condition in which the nerves that run from the top of the spinal cord up through the scalp, called the occipital nerves, are inflamed or injured. One might feel pain in the back of the head or the base of the skull.
- Ovarian Cancer, Adult: Ovarian Cancer is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in tissues of the ovary. Most Ovarian Cancers are either Ovarian Epithelial Cancers (cancer that begins in the cells on the surface of the ovary) or malignant germ cell tumors (cancer that begins in egg cells). Fallopian Tube Cancer and Primary Peritoneal Cancer are similar to Ovarian Epithelial Cancer and are staged and treated the same way.
- Ovarian Cancer, Childhood: Ovarian Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the ovary. Most ovarian tumors in children are benign (not cancer). They occur most often in females aged 15 to 19 years. The alternate color for ovarian cancer in children is gold.
- Ovarian Epithelial Cancer: Epithelial Ovarian Cancer is the most common type of Ovarian Cancer. About 90 out of 100 tumors of the ovary (90%) are epithelial. Epithelial Ovarian Cancer means the cancer started in the surface layer covering the ovary. Serous Epithelial Ovarian Cancer is the most common type, making up about two thirds of the cases diagnosed. Doctors now think that most high grade serous Ovarian Cancers actually start in cells at the far end of the fallopian tube, rather than the surface of the ovary. These early cancer cells then spread to the ovary and grow. About 10% are undifferentiated or unclassifiable. These tumors have cells that are very undeveloped, so it is not possible to tell from which type of cell the cancer started.
- Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor: Ovarian Germ Cell Tumor is a disease in which malignant cells form in the germ cells of the ovary. Germ Cell Tumors begin in the reproductive cells (egg or sperm) of the body. Ovarian Germ Cell Tumors usually occur in teenage girls or young women and most often affect just one ovary.
- Ovarian Low Malignant Potential Tumor: Ovarian Low Malignant Potential Tumor is a disease in which abnormal cells form in the tissue covering the ovary. Ovarian Low Malignant Potential Tumors have abnormal cells that may become cancer, but usually do not. This disease usually remains in the ovary.
- Panic Disorder: Panic Disorder is diagnosed in people who experience spontaneous seemingly out-of-the-blue panic attacks and are very preoccupied with the fear of a recurring attack. Panic Attacks occur unexpectedly, sometimes even when waking up from sleep. Panic Disorder usually begins in adulthood, but children can also have panic disorder and many children experience panic-like symptoms (“fearful spells”).
- Polycystic Kidney Disease : Polycystic Kidney Disease is an inherited disorder in which clusters of cysts develop primarily within the kidneys, causing the kidneys to enlarge and lose function over time. Cysts are noncancerous round sacs containing fluid. The cysts vary in size, and they can grow very large. Having many cysts or large cysts can damage the kidneys.
- Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome (PCOS): Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder common among women of reproductive age. Women with PCOS may have infrequent or prolonged menstrual periods or excess male hormone (androgen) levels. The ovaries may develop numerous small collections of fluid and fail to regularly release eggs.
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): Post Traumatic Stress Disorder is a mental health condition that's triggered by a terrifying event, either experiencing it or witnessing it. Symptoms may include flashbacks, nightmares and severe anxiety, as well as uncontrollable thoughts about the event.
- Premature Ovarian Failure / Premature Ovarian Insufficiency: Premature Ovarian Failure, also known as Primary Ovarian Insufficiency, is a loss of normal function of the ovaries before age 40. If the ovaries fail, they don't produce normal amounts of the hormone estrogen or release eggs regularly. Infertility is a common result. Premature Ovarian Failure is sometimes referred to as premature menopause, but the two conditions aren't the same. Women with premature ovarian failure can have irregular or occasional periods for years and might even become pregnant. Women with premature menopause stop having periods and can't become pregnant.
- Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder: Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder is a much more severe form of Premenstrual Syndrome. It may affect women of childbearing age. The main symptoms that distinguish Premenstrual Mood Dysphoric Disorder from other mood disorders or menstrual conditions is when symptoms start and how long they last. Symptoms of PMDD are so severe that it affects one's ability to function at home, work and in relationships. Primary Peritoneal Cancer: Primary Peritoneal Cancer is a relatively rare cancer that develops most commonly in women. Primary Peritoneal Cancer is a close relative of epithelial ovarian cancer, which is the most common type of malignancy that affects the ovaries. The cause of Primary Peritoneal Cancer is unknown
- Progressive Supranelear Palsy : Progressive Supranuclear Palsy is a degenerative neurologic disease due to damage to nerve cells in the brain. Signs and symptoms vary but may include loss of balance, blurred vision, problems controlling eye movement, changes in mood, behavior and judgment, cognitive decline, and slowing and slurred speech.
- Rape: Rape is forced sexual intercourse, sexual assault, or sexual intercourse between an adult and a minor. Rape may be heterosexual (involving members of opposite sexes) or homosexual (involving members of the same sex). Rape involves insertion of an erect penis or an inanimate object into the female vagina or the male anus. Legal definitions of rape may also include forced oral sex and other sexual acts.
- Scleroderma: Scleroderma is a group of rare diseases that involve the hardening and tightening of the skin and connective tissues, the fibers that provide the framework and support for your body. In some people, Scleroderma affects only the skin. But in many people, Scleroderma also harms structures beyond the skin, such as blood vessels, internal organs and the digestive tract. Signs and symptoms vary, depending on which structures are affected.
- Sexual Assault: The term Sexual Assault refers to sexual contact or behavior that occurs without explicit consent of the victim. Some forms of sexual assault include: Attempted rape, fondling or unwanted sexual touching, forcing a victim to perform sexual acts, such as oral sex or penetrating the perpetrator’s body, or penetration of the victim’s body, also known as rape.
- Sexual Assault on College Campuses: Sexual Assault on College Campuses is a common problem that often goes unreported. It includes any unwanted sexual activity, from unwanted touching to rape. Alcohol and drugs often play a role in sexual assault on campuses.
- Sexual Violence: Sexual Violence is a serious public health and human rights problem with both short- and long-term consequences on both women's physical, mental, and sexual and reproductive health. Whether sexual violence occurs in the context of an intimate partnership, within the larger family or community structure, or during times of conflict, it is a deeply violating and painful experience for the survivor. Men and boys who have been sexually assaulted may experience the same effects of sexual assault as other survivors, and they may face other challenges that are more unique to their experience.
- Social Anxiety: The latest government epidemiological data show social anxiety affects about 7% of the population at any given time. The chances of developing social anxiety disorder at any time during the lifespan stands slightly above 13%. Social Anxiety is the fear of social situations that involve interaction with other people.
- Stress Disorders: Trauma- and stress-related disorders result from exposure to a traumatic or stressful event. Specific disorders include acute stress disorder and post-traumatic stress disorder. These disorders cause similar symptoms but differ in how long they last.
- Systemic Scleroderma: Systemic Scleroderma is an autoimmune disorder that affects the skin and internal organs. Autoimmune disorders occur when the immune system malfunctions and attacks the body's own tissues and organs. The word "scleroderma" means hard skin in Greek, and the condition is characterized by the buildup of scar tissue.
- Systemic Sclerosis: Systemic Sclerosis is a multi-system disease which results in fibrosis and vascular abnormalities in association with autoimmune changes, affecting the connective tissue in many parts of the body. These lead to the breakdown of the skin, subcutaneous tissue, muscles and internal organs (e.g. digestive tract, heart, lungs, and kidneys).
- Tourette Syndrome: Tourette Syndrome is a disorder that involves repetitive movements or unwanted sounds (tics) that cannot be easily controlled. Males are about three to four times more likely than females to develop Tourette syndrome.
- Trigeminal Neuralgia: Trigeminal Neuralgia is a chronic pain condition that affects the trigeminal nerve, which carries sensation from the face to the brain. Even mild stimulation of the face, such as from brushing one's teeth or putting on makeup, may trigger a jolt of excruciating pain. Trigeminal Neuralgia affects women more often than men, and it's more likely to occur in people who are older than 50.
- Vaginal Cancer, Adult: Vaginal Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the vagina. Vaginal Cancer is not common. Infection with Human Papillomavirus (HPV) causes two-thirds of the cases of Vaginal Cancer. Vaccines that protect against infection with HPV may reduce the risk of vaginal cancer.
- Vagina Cancer, Childhood: Vaginal Cancer forms in the vagina. The vagina is the canal leading from the cervix to the outside of the body. The alternate color for childhood vaginal cancer is gold.
- Vulvar Sclerosus: Vulvar Lichen Sclerosus is a chronic skin condition that affects the vulva (the skin surrounding the opening of the vagina) and anus and is followed by itching and pain.
- Women Murdered by Domestic Violence: Thirty-five percent of women worldwide have experienced either physical and/or sexual intimate partner violence or non-partner sexual violence, according to the United Nations. According to a Global Study on Homicide, of all women globally who were the victims of homicide in 2012, an estimated half were killed by intimate partners or family members. Each year, over 10 million women and men are victims of intimate partner violence, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Teal and Purple Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Domestic Violence and Sexual Assault: Perpetrators who are physically violent toward their intimate partners are often sexually abusive as well. Women who are disabled, pregnant, or attempting to leave their abusers are at greatest risk for intimate partner rape.
- End Violence Against Women International: End of Violence Against Women International's Vision Statement: We envision a world where gender-based violence is unacceptable, where perpetrators are held accountable, and victims receive the compassion, support, and justice they deserve.
- International Military Suicide: Historically, military suicide rates have been lower than those rates found in the general population. Rising suicide rates among Service members and Veterans over the past decade have raised public and professional concerns.
- LGBTQ+ Suicide Prevention: The LGBTQ+ community is diverse and made up of different experiences, identities, and challenges. However, members of the community are disproportionately at-risk for suicide and other mental health struggles. Over 80% of LGBTQ+ youth have been assaulted or threatened, and every instance of victimization in an LGBTQ+ person’s life more than doubles the likelihood of self-harming. The alternate color for LGBTQ+ Suicide Prevention is teal, purple and rainbow.
- Suicide: Nearly 1 million people die by suicide globally each year. Suicide is one of the top ten leading causes of death across all age groups. Worldwide, suicide ranks among the three leading causes of death among adolescents and young adults.
- Suicide Prevention: Suicide Prevention is a collection of efforts to reduce the risk of suicide. Suicide is often preventable, and the efforts to prevent it may occur at the individual, relationship, community, and society level. The alternate color for Suicide Prevention is yellow.
- Surviving Family Members of Suicide: In North America, the term suicide survivor has come to mean someone who is bereaved after the death by suicide of someone they know.
Teal, Purple and Rainbow Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- LGBTQ+ Suicide Prevention:
- The LGBTQ+ community is diverse and made up of different experiences, identities, and challenges. However, members of the community are disproportionately at-risk for suicide and other mental health struggles. Over 80% of LGBTQ+ youth have been assaulted or threatened, and every instance of victimization in an LGBTQ+ person’s life more than doubles the likelihood of self-harming. The alternate color for LGBTQ+ Suicide Prevention is teal and purple.
Teal and White Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Cervical Cancer, Adult: Cervical Cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. Various strains of the Human Papillomavirus (HPV), a sexually transmitted infection, play a role in causing most cervical cancer.
- Cervical Cancer, Childhood: Cervical Cancer is rarely seen in children and teens. Cases of Cervical Cancer in women under 20 were seen in only about 0.2 percent of females. In very rare cases in the past, some Cervical Cancer was seen in girls whose mothers were treated with a drug called diethylstilbestrol (DES), which was used to prevent miscarriage. But DES has not been used with pregnant women since the early 1970s. The alternate color for Cervical Cancer in children is gold.
Teal and Yellow Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize:
- Body Dysmorphic Disorder: Body Dysmorphic Disorder, occasionally called Dysmorphophobia, is a mental disorder characterized by the obsessive idea that some aspect of one's own body part or appearance is severely flawed and warrants exceptional measures to hide or fix their dysmorphic part on their person.
- Support for Ukraine: More than 5.5 million children are in need of humanitarian assistance as they continue to suffer the deadly consequences of a brutal war not of their making. The war has sparked displacement on a scale and speed not seen since World War II, with far-reaching impact across the region and beyond. By late October 2022, more than 7.7 million individual refugees from Ukraine had been recorded across Europe, while millions more people had been internally displaced in Ukraine.
Turquoise Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Addiction Recovery: Recovery is a complex and dynamic process encompassing all the positive benefits to physical, mental and social health that can happen when people with an addiction to alcohol or drugs, or their family members, get the help they need.
- Autoimmune Dysautonomia: Autoimmune Autonomic Ganglionopathy is a very rare form of dysautonomia in which the bodies own immune system damages a receptor in the autonomic ganglia (part of the peripheral autonomic nerve fiber). The alternate color for Autoimmune Dysautonomia is light blue.
Violet Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Hodgkin Disease/Hodgkin Lymphoma During Pregnancy: Lymphoma is the fourth most frequent malignancy diagnosed during pregnancy, occurring in approximately 1:6000 of deliveries. Its occurrence may increase due to the current trend to postpone pregnancy until later in life and the suggested high incidence of AIDS-related Non-Hodgkin's Lymphoma in developing countries.
- Hodgkin Lymphoma / Hodgkin’s Lymphoma / Hodgkin’s Disease, Adult: Hodgkin Disease, also called Hodgkin Lymphoma) is a cancer of the immune system that is marked by the presence of a type of cell called the Reed-Sternberg cell. The two major types of Hodgkin disease are classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Nodular Lymphocyte-Predominant Hodgkin Lymphoma. Symptoms include the painless enlargement of lymph nodes, spleen, or other immune tissue. Other symptoms include fever, weight loss, fatigue, or night sweats. Also called Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Hodgkin Lymphoma / Hodgkin’s Lymphoma / Hodgkin’s Disease, Childhood: Hodgkin Lymphoma, also called Hodgkin’s Lymphoma and Hodgkin Disease, is a cancer of the lymphoid system. The lymphoid system is made up of various tissues and organs, including the lymph nodes, tonsils, bone marrow, spleen, and thymus. These organs produce, store and carry white blood cells to fight infection and disease. Approximately 1,180 children and adolescents each year are diagnosed with Hodgkin Lymphoma in the United States. It has been reported in infants and very young children, but it is considered rare before the age of five. The majority of Hodgkin Lymphoma cases are in teenagers (age 15-19). Hodgkin Lymphoma is the most common cancer of teenagers and young adults. The alternate color for Hodgkin Disease/Hodgkin Lymphoma in children is gold.
White Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Adoption: Related to human children, “adoption” means “the act or process of adopting a child.” But, legally, adoption does not just refer to children, although that is its most popular use. In fact, adults over the age of 18 can legally be adopted as well.
- Adult Survivors of Child Sexual Abuse: Typically, when the word “survivor” is used with an illness like cancer, a person has received treatment and has gone through a healing process. For “adult survivors of child sexual abuse,” the term actually means that the adult experienced sexual abuse in childhood. It does not necessarily mean they have received appropriate treatment and gone through an adequate healing process. In fact, the vast majority of “adult survivors” of Child Sexual Abuse have not had access to care to appropriately foster that treatment and healing process. Their lives typically carry the traces of that abuse and trauma well into their adulthood.
- Albinism: The term albinism typically refers to oculocutaneous albinism, a group of inherited disorders where there is little or no production of the pigment melanin. The type and amount of melanin your body produces determines the color of your skin, hair and eyes.
- Bone Diseases: Generalized osteoporosis is the most common form of bone disease, affecting most of the skeleton. Osteoporosis can also occur in localized parts of the skeleton as a result of injury or conditions that reduce muscle forces on the bone, such as limb paralysis. A lifelong lack of calcium plays a role in the development of osteoporosis. Low calcium intake contributes to diminished bone density, early bone loss and an increased risk of fractures.
- Child Exploitation: Child Exploitation takes many forms. Child Sexual Exploitation is a form of child sexual abuse in which a person(s), of any age takes advantage of a power imbalance to force or entice a child into engaging in sexual activity in return for something received by the child and/or those perpetrating or facilitating the abuse. The alternate color for Child Exploitation is blue.
- Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis: Chronic Recurrent Multifocal Osteomyelitis, or Chronic Nonbacterial Osteomyelitis, is a disorder that causes bone pain due to inflammation in the bones not caused by infection. One or multiple bones can be affected.
- Child Sexual Abuse / Child Sexual Assault: It is any sexual activity between adults and minors or between two minors when one forces it on the other. This includes sexual touching and non-touching acts like exhibitionism, exposure to pornography, photography of a child for sexual gratification, solicitation of a child for prostitution, voyeurism and communication in a sexual way by phone, Internet or face-to-face. It is a crime punishable by law that must be reported. The alternate color for Child Sexual Abuse / Child Sexual Assault is teal.
- Congenital Cataracts: A Congenital Cataract is when the lens of the eye is cloudy instead of clear at birth, making it hard to see. The lens is the tissue inside the eye that helps focus the light coming into the eye. Congenital Cataracts can happen in one or both eyes.
- Dental Health: Dental and oral health is an essential part of your overall health and well-being. Poor oral hygiene can lead to dental cavities and gum disease, and has also been linked to heart disease, cancer, and diabetes.
- Hernia: A Hernia is a gap in this muscular wall that allows the contents inside the abdomen to protrude outward. There are different types of Hernias, but the most common Hernias occur in the belly or groin areas.
- Holocaust Remembrance : The internationally recognized date for Holocaust Remembrance Day corresponds to the 27th day of Nisan on the Hebrew calendar. It marks the anniversary of the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising.
- Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy: Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy is a type of brain damage that occurs when an infant's brain doesn't receive enough oxygen and blood. It is a dangerous condition that requires immediate medical intervention.
- International End of Violence Against Women: This campaign, led by the UN Secretary-General and UN Women since 2008, aims to prevent and eliminate violence against women and girls around the world, calling for global action to increase awareness, promote advocacy and create opportunities for discussion on challenges and solutions.
- Make Poverty History: Make Poverty History is the name of organizations in a number of countries, which focus on issues relating to 8th Millennium Development Goal such as aid, trade and justice. They generally form a coalition of aid and development agencies which work together to raise awareness of global poverty and achieve policy change by governments. The movement exists or has existed in Australia, Canada, Denmark, Finland, New Zealand, Nigeria, Norway, Romania, South Africa, Ireland, the United Arab Emirates, the United States of America, and the United Kingdom. The various national campaigns are part of the international Global Call to Action Against Poverty campaign.
- Medical Professionals on the Front Line (COVID-19) : These individuals, who work across many different health care fields including doctors and nurses, nursing home managers, front desk clerks, as well as those who assist with patient care such as bathing, eating, cleaning, exercising, or housekeeping, have been on the front lines of an industry providing care for the sickest adults. The spread of COVID-19 throughout the country overwhelmed many health care settings with intensive care units at capacity and other facilities struggling to keep both patients and employees safe. Now, with three COVID-19 vaccines currently being distributed to adults across the country, this project takes a look at the toll of the last year on frontline health care workers.
- Multiple Hereditary Exostoses: Hereditary Multiple Exostosis, also known as Diaphyseal Aclasis, is a genetic condition often passed down to a child by one parent, but it can also be caused by a genetic mutation, meaning it can occur on its own by a change.
- Osteoporosis: Osteoporosis is a condition of fragile bone with an increased susceptibility to fracture. Osteoporosis weakens bone and increases risk of bones breaking. Bone mass (bone density) decreases after 35 years of age, and bone loss occurs more rapidly in women after menopause.
- Peace: Peace is a concept of societal friendship and harmony in the absence of hostility and violence. In a social sense, peace is commonly used to mean a lack of conflict and freedom from fear of violence between individuals or groups.
- Poverty: Frequently, Poverty is defined in either relative or absolute terms. Absolute Poverty measures poverty in relation to the amount of money necessary to meet basic needs such as food, clothing, and shelter. The concept of Absolute Poverty is not concerned with broader quality of life issues or with the overall level of inequality in society. The concept therefore fails to recognize that individuals have important social and cultural needs. This, and similar criticisms, led to the development of the concept of Relative Poverty. Relative Poverty defines poverty in relation to the economic status of other members of the society: people are poor if they fall below prevailing standards of living in a given societal context. An important criticism of both concepts is that they are largely concerned with income and consumption.
- Retinoblastoma, Childhood: Retinoblastoma is a rare type of eye cancer in the retina that typically develops before the age of 5. It usually affects only one eye, but one-third of children with Retinoblastoma develop cancer in both eyes. The first sign is typically a visible whiteness in the pupil called "cat's eye reflex" or leukocoria, which is particularly noticeable in photographs taken with a flash. Other signs and symptoms include strabismus; persistent eye pain, redness or irritation; and blindness or poor vision in the affected eye(s). The alternate color for Retinoblastoma in children is gold.
- Safe Motherhood: Safe Motherhood means ensuring that all women have access to the information and services they need to go safely through pregnancy and childbirth. It includes: Education on safe motherhood, prenatal care (care during pregnancy) and counseling with focus on high risk pregnancies.
- Teen Sexual Abstinence: Teen Sexual Abstinence is a choice to not participate in any genital contact. The choice is usually made for a specific moral, religious, legal, or health reason. It is the act of not having sex – the personal definition of which can range from no sexual contact to everything but intercourse. Abstinence is the only 100 percent guarantee of protection against pregnancy. Abstinence is the best way to protect yourself from being infected with a STIs.
- Victims of Terrorism: Terrorism is defined as the deliberate creation and exploitation of fear through violence or the threat of violence in the pursuit of political change. All terrorist acts involve violence or the threat of violence. Terrorism is specifically designed to have far-reaching psychological effects beyond the immediate victim(s) or object of the terrorist attack. Terrorism is designed to create power where there is none or to consolidate power where there is very little. Through the publicity generated by their violence, terrorists seek to obtain the leverage, influence, and power they otherwise lack to effect political change on either a local or an international scale.
- White Matter Brain Disorder / White Matter Brain Disease: White Matter Brain Disorder / Why Matter Brain Disease is the wearing away of tissue in the largest and deepest part of your brain due to aging. This tissue contains millions of nerve fibers, or axons, that connect other parts of the brain and spinal cord and signal your nerves to talk to one another. A fatty material called myelin protects the fibers and gives white matter its color. This type of brain tissue helps people think fast, walk straight, and keeps a person from falling. When it becomes diseased, the myelin breaks down.
- White Ribbon Campaign for Men Against Violence: Men and boys wearing the White Ribbon declare that they will never commit, excuse, or remain silent about men's violence against women. White Ribbon is one of the world’s largest male-led campaigns to end men’s violence against women. It started in 1991 in Canada, and is now active in many countries across the globe. Every year it is growing stronger as more men and boys realize that women’s and girls’ safety is their issue too.
Y ellow Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Adenosarcoma: A tumor that is a mixture of an adenoma (a tumor that starts in the gland-like cells of epithelial tissue) and a sarcoma (a tumor that starts in bone, cartilage, fat, muscle, blood vessels, or other connective or supportive tissue).
- Adoptive Parents: An adoptive parent is someone who provides a permanent home to a child or children through a legal process. The key word is "permanent." The end result is no different than giving birth to a child. Becoming an adoptive parent comes with all the joys, heartache, laughter, frustration, responsibilities and rights that a natural or biological parent-child relationship brings.
- AIDS-Related Kaposi Sarcoma: Kaposi Sarcoma is a cancer that causes lesions (abnormal tissue) to grow in the skin; the mucous membranes lining the mouth, nose and throat; lymph nodes; or other organs. Kaposi Sarcoma is different from other cancers in that lesions may begin in more than one place in the body at the same time.
- Bone Cancer (includes Ewing Sarcoma, Osteosarcoma and Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma): Bone Cancer is rare and includes several types. Some Bone Cancer, including Osteosarcoma and Ewing Sarcoma, are seen most often in children and young adults. Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma of bone is a rare tumor of the bone. It is treated like Osteosarcoma.
- Bone Diseases: Bone Diseases can make bones easy to break. Different kinds of bone problems include: Low bone density and osteoporosis, which make your bones weak and more likely to break; Osteogenesis Imperfecta makes your bones brittle; Paget's disease of bone makes them weak. Bones can also develop cancer and infections. Other Bone Diseases are caused by poor nutrition, genetics, or problems with the rate of bone growth or rebuilding.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: Carbon Monoxide is a colorless, odorless gas produced by burning material containing carbon. Early symptoms of Carbon Monoxide Poisoning such as headaches, nausea, and fatigue, are often mistaken for the flu because the deadly gas goes undetected in a home. Prolonged exposure can lead to brain damage and even death. Because carbon monoxide is an odorless, tasteless, and colorless gas, it is known as the "silent killer."
- Catalan Independence / Republic of Catalonia Freedom: The Catalan declaration of independencewas a resolution that was passed by the Parliament of Catalonia on October 27, 2017, which declared the independence of Catalonia from Spain and the founding of an independent Catalan Republic. The declaration did not receive recognition from the international community.
- Chondrosarcoma: Chondrosarcoma is a rare type of cancer that usually begins in the bones, but can sometimes occur in the soft tissue near bones. Chondrosarcoma happens most often in the pelvis, hip and shoulder. More rarely, it can happen in the bones of the spine.
- Chordoma, Adult: Chordoma is a rare type of bone cancer that happens most often in the bones of the spine or the skull. It most often forms where the skull sits atop the spine (skull base) or at the bottom of the spine (sacrum).
- Chordoma, Childhood: Chordoma is a very rare type of bone tumor that forms anywhere along the spine from the base of the skull to the tailbone. In children and adolescents, Chordomas develop more often in the base of the skull, making them hard to remove completely with surgery. Childhood Chordoma is linked to the condition Tuberous Sclerosis, a genetic disorder in which tumors that are benign (not cancer) form in the kidneys, brain, eyes, heart, lung, and skin. The alternate color for Chordoma in childhood is gold.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis is the presence of tissue that normally grows inside the uterus (womb) in an abnormal anatomical location. Endometriosis is very common and may not produce symptoms, or it may lead to painful menstruation. It has also been associated with infertility. Endometriosis occurs most commonly within the Fallopian tubes and on the outside of the tubes and ovaries, the outer surface of the uterus and intestines, and anywhere on the surface of the pelvic cavity. It can also be found, less often, on the surface of the liver, in old surgery scars or, very rarely, in the lung or brain.
- Epithelioid Sarcoma: A rare type of cancer that usually begins as a slow-growing, firm lump in the deep soft tissue or skin of the arms, hands, or fingers. It may also occur in the legs, trunk, or head and neck. The lump is usually painless and there may be an ulcer in the skin covering the lump. Epithelioid Sarcoma may spread to nearby tissue, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body. It often recurs (comes back) after treatment. Epithelioid Sarcoma usually occurs in young adults. It is a type of soft tissue sarcoma.
- Ewing Sarcoma: Ewing Sarcoma is a type of cancer that forms in bone or soft tissue. It is also called Peripheral Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor and pPNET.
- Falls: Many falls do not cause injuries. But one out of five falls does cause a serious injury such as a broken bone or a head injury. These injuries can make it hard for a person to get around, do everyday activities, or live on their own.
- Gastrointestinal Stomal Tumors (GIST): Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors may be malignant (cancer) or benign (not cancer). They are most common in the stomach and small intestine but may be found anywhere in or near the GI tract. Soft tissue sarcoma is a broad term for caners that start in soft tissues. These cancers can develop anywhere in the body but are found mostly in the arms, legs, chest, and abdomen. The alternate color for Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors is purple.
- Gastritis: Gastritis is a general term for a group of conditions with one thing in common: Inflammation of the lining of the stomach. The inflammation of Gastritis is most often the result of infection with the same bacterium that causes most stomach ulcers or the regular use of certain pain relievers.
- Giving Prisoners a Second Chance at Life: Formerly incarcerated persons deserve a second chance to prove they can become productive members of society. Overcoming barriers to employment, education, and housing are paramount to successful reintegration.
- Kapoli Sarcoma: Kapoli Sarcoma is a cancer that causes lesions (abnormal tissue) to grow in the skin; the mucous membranes lining the mouth, nose, and throat; lymph nodes; or other organs. The lesions are usually purple and are made of cancer cells, new blood vessels, red blood cells, and white blood cells. Kaposi Sarcoma is different from other cancers in that lesions may begin in more than one place in the body at the same time.
- Leprosy: Hansen's Disease (also known as leprosy) is an infection caused by slow-growing bacteria called Mycobacterium leprae . It can affect the nerves, skin, eyes, and lining of the nose (nasal mucosa). With early diagnosis and treatment, the disease can be cured.
- Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma of Bone and Osteosarcoma: Osteosarcoma and Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma of the bone are diseases in which malignant cells form in bone. Osteosarcoma usually starts in osteoblasts, which are a type of bone cell that becomes new bone tissue. Osteosarcoma is most common in adolescents. It commonly forms in the ends of the long bones of the body, which include bones of the arms and legs. In children and adolescents, it often forms in the long bones, near the knee. Rarely, Osteosarcoma may be found in soft tissue or organs in the chest or abdomen. Osteosarcoma is the most common type of bone cancer.
- Microcephaly: Microcephaly is a rare neurological condition in which a person's head is significantly smaller than expected based on standardized charts. Some cases of Microcephaly are detected at birth, while others develop in the first few years of life.
- Missing Persons: Anyone whose whereabouts cannot be established is considered as missing until located, and their well-being or otherwise confirmed. All reports of missing people sit within a continuum of risk from ‘no apparent risk (absent)’ through to high-risk cases that require immediate, intensive action.
- Myxoid Liposarcoma: Myxoid/Round Cell Liposarcoma is one of several types of liposarcoma. Liposarcoma is a rare cancer that grows in the cells that store fat in the body. Myxoid Liposarcoma usually grows in the arms and legs. These tumors grow slowly, and they can spread to other parts of the body.
- Obesity: A person has traditionally been considered to be obese if they are more than 20 percent over their ideal weight. That ideal weight must take into account the person's height, age, sex, and build. Obesity has been more precisely defined by the National Institutes of Health (the NIH) as a BMI of 30 and above. (A BMI of 30 is about 30 pounds overweight.) Obesity is often multifactorial, based on both genetic and behavioral factors. Accordingly, treatment of obesity usually requires more than just dietary changes. Exercise, counseling and support, and sometimes medication can supplement diet to help patients conquer weight problems. Extreme diets, on the other hand, can actually contribute to increased obesity.
- Osteosarcoma: Osteosarcoma is a type of bone cancer that begins in the cells that form bones. Osteosarcoma is most often found in the long bones — more often the legs, but sometimes the arms — but it can start in any bone. In very rare instances, it occurs in soft tissue outside the bone.
- Osteosarcoma and Malignant Fibrous Histiocytoma of Bone: Osteosarcoma is a cancer of the bone that usually affects the large bones of the arm or leg. It occurs most commonly in young people and affects more males than females. Osteosarcoma is also called Osteogenic Sarcoma. Malignant fibrous histiocytoma of bone is a rare tumor of the bone. Ewing Sarcoma is another kind of bone cancer.
- Refugees Welcome Campaign (Welcoming Refugees): The goal of the Refugees Welcome campaign is to provide opportunities for refugees to share their experiences with faith and community groups to build friendships among diverse cultures and faiths, strengthen public and private welcome of our refugee neighbors, promote refugee integration and leadership and celebrate refugees’ community contributions.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, Adult: Rhabdomyosarcoma is a rare type of cancer that forms in soft tissue, specifically skeletal muscle tissue or sometimes hollow organs such as the bladder or uterus. Rhabdomyosarcoma can occur at any age, but it most often affects children.
- Rhabdomyosarcoma, Childhood: Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in soft tissues of the body. Soft tissue sarcoma may be found anywhere in the body. In children, the tumors form most often in the arms, legs, or trunk (chest and abdomen). Soft tissue sarcoma in children may respond differently to treatment, and may have a better prognosis than soft tissue sarcoma in adults. The alternate color for Rhabdomyosarcoma in children is gold.
- Sarcoma: Soft tissue sarcoma is a broad term for cancers that start in soft tissues (muscle, tendons, fat, lymph and blood vessels, and nerves). These cancers can develop anywhere in the body but are found mostly in the arms, legs, chest, and abdomen. Childhood soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant cells form in soft tissues of the body.
- Soft Tissue Sarcoma: Soft Tissue Sarcoma is a broad term for cancers that start in soft tissues (muscles, tendons, fat, lymph and blood vessels, and nerves). These cancers can develop anywhere in the body but are found mostly in the arms, legs, chest, and abdomen. Adult soft tissue sarcoma is a disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the soft tissues of the body.
- Spina Bifida: Spina Bifida is a birth defect that occurs when the spine and spinal cord don't form properly. It falls under the broader category of Neural Tube Defects. The neural tube is the embryonic structure that eventually develops into the baby's brain and spinal cord and the tissues that enclose them. Normally, the neural tube forms early in pregnancy, and it closes by the 28th day after conception. In babies with Spina Bifida, a portion of the neural tube fails to develop or close properly, causing defects in the spinal cord and in the bones of the spine. Spina Bifida can range from mild to severe, depending on the type of defect, size, location and complications.
- Suicide Prevention: Suicide Prevention means diminishing the risk of suicide. It may not be possible to eliminate entirely the risk of suicide but it is possible to reduce this risk. The alternate color for Suicide Prevention is teal and purple.
- Support Our Troops: Support our Troops is a slogan commonly used in the United States and Canada in reference to each country's military forces or troops. The slogan has been used during recent conflicts, including the Gulf War and the Iraq War.
- The Disappeared: Victims of enforced disappearance are people who have literally disappeared; from their loved ones and their community. They go missing when state officials (or someone acting with state consent) grabs them from the street or from their homes and then deny it, or refuse to say where they are. Sometimes disappearances may be committed by armed non-state actors, like armed opposition groups. And it is always a crime under international law.
- Urethral Cancer: Urethral Cancer is a disease in which malignant cells form in the tissues of the urethra. Urethral Cancer is rare and is more common in men than in women. Urethral Cancer can metastasize (spread) quickly to tissues around the urethra and has often spread to nearby lymph nodes by the time it is diagnosed.
- Vascular Tumors: Soft tissue sarcomas are malignant tumors that arise in any of the mesodermal tissues of the extremities (50%), trunk and retroperitoneum (40%), or head and neck (10%). The reported international incidence rates range from 1.8 to 5 cases per 100,000 individuals per year. The risk of sporadic Soft Tissue Sarcomas is increased by previous radiation therapy, and in the case of lymphangiosarcoma, by chronic lymphedema.
- Welcoming Refugees: An environment that promotes solidarity, diversity and openness is essential for resettlement to grow sustainably. The arrival of refugees can trigger positive social and economic changes, transform civic culture and local institutions, and promote social cohesion, particularly when local communities are engaged in welcoming them.
Yellow and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Adiposis Dolorosa / Dercum’s Disease: Dercum disease - also known as Adiposis Dolorosa, Anders' syndrome and Dercum-Vitaut syndrome - is a rare condition that is characterized by multiple, painful fatty lipomas (benign, fatty tumors) that occur chiefly in post-menopausal, obese women of middle age.
- Bohring-Opitz Syndrome: Bohring-Opitz Syndrome is a rare genetic condition characterized by intrauterine growth restriction, failure to thrive, sleep apnea, developmental delay, hypotonia, flexion of the elbows and wrists, excessive hair growth, Wilms' tumor, microcephaly, brain malformations, and distinctive facial features.
- Cushing Syndrome: Cushing Syndrome is an extremely complex hormonal condition that involves many areas of the body. Common symptoms are thinning of the skin, weakness, weight gain, bruising, hypertension, diabetes, thin weak bones, facial puffiness and, in women, cessation of menstrual periods. Ironically, one of the most common causes of Cushing syndrome is the administration of "cortisol-like medications" for the treatment of diverse diseases. All other cases of Cushing syndrome are due to the excess production of cortisol by the adrenal gland.
- Dercum's Disease (Adiposis Dolorosa): Adiposis Dolorosa is a rare condition characterized by the growth of multiple, painful, lipomas (benign, fatty tumors). The lipomas may occur anywhere on the body and can cause severe pain. Other symptoms may include weakness, fatigue, and memory disturbances. It usually occurs in adults, and women are more commonly affected than men.
- Developmental Disabilities: Developmental disabilities are a group of conditions due to an impairment in physical, learning, language, or behavior areas. These conditions begin during the developmental period, may impact day-to-day functioning, and usually last throughout a person's lifetime.
- Down Syndrome: Down Syndrome is a genetic disorder caused when abnormal cell division results in an extra full or partial copy of chromosome 21. This extra genetic material causes the developmental changes and physical features of Down Syndrome. Down Syndrome varies in severity among individuals, causing lifelong intellectual disability and developmental delays. It's the most common genetic chromosomal disorder and cause of learning disabilities in children.
- Fatty Oxidation Disorders: Fatty Acid Xxidation Disorders are inborn errors of metabolism due to disruption of either mitochondrial β-oxidation or the fatty acid transport using the carnitine transport pathway.
- Opsoclonus Myoclonus Syndrome: Opsoclonus Myoclonus is a rare neurological disorder characterized by an unsteady, trembling gait, myoclonus (brief, shock-like muscle spasms), and opsoclonus (irregular, rapid eye movements). Other symptoms may include difficulty speaking, poorly articulated speech, or an inability to speak.
- Support for Ukraine: The United States is working with Allies and partners to support Ukraine in their fight for sovereignty and freedom. The U.S. has provided Ukraine with billions of dollars in security assistance since the beginning of Russia’s unprovoked assault on February 24, 2022.
Zebra Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Carcinoid Cancer, Adult Carcinoid Tumors are a type of slow-growing cancer that can arise in several places throughout the body. Carcinoid Tumors, which are one subset of tumors called Neuroendocrine Tumors, usually begin in the digestive tract or in the lungs. Carcinoid Tumors can produce and release hormones into the body that cause signs and symptoms such as diarrhea or skin flushing.
- Carcinoid Cancer, Childhood: A Carcinoid Tumor is a specific type of Neuroendocrine Tumor. Carcinoid tumors most often develop in the GI tract, in organs such as the stomach or intestines, or in the lungs. Sometimes Neuroendocrine Tumors in children form in the appendix. The tumor is often found during surgery to remove the appendix. The alternate color for Carcinoid Cancer in children is gold.
- Carcinoid Syndrome
- Carcinoid Tumors, Adult
- Carcinoid Tumors, Childhood – (Alternate Color: Gold)
- Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome: The Ehlers-Danlos syndromes are a group of connective tissue disorders that can be inherited and are varied both in how they affect the body and in their genetic causes. They are generally characterized by joint hypermobility (joints that stretch further than normal), skin hyperextensibility (skin that can be stretched further than normal), and tissue fragility.
- Gastrointestinal Carcinoid Tumor: Gastrointestinal Cardinoid tumors are slow-growing tumors that form in the GI tract, mainly in the rectum, small intestine, or appendix.
- Islet Cell Tumors, Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors: Pancreatic Cancer can develop from two kinds of cells in the pancreas; exocrine cells and neuroendocrine cells, such as Islet cells. The exocrine type is more common and is usually found at an advanced stage. Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (Islet Cell Tumors) are less common but have a better prognosis. The alternate color for Islet Cell Tumors, pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors is purple.
- Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (Islet Cell Tumors) Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors form in hormone-making cells (Islet cells) of the pancreas. Pancreatic Cancer can develop from two kinds of cells in the pancreas; exocrine cells and neuroendocrine cells, such as Islet cells. The exocrine type is more common and is usually found at an advanced stage. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (islet cell tumors) are less common but have a better prognosis. Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Tumors (NETs) may be benign or malignant. When pancreatic NETs are malignant, they are called Pancreatic Endocrine Cancer or Islet Cell Carcinoma.
- Pheochromocytoma: Pheochromocytoma and Paraganglioma are rare tumors that can be benign or malignant. Pheochromocytomas form in the adrenal glands, and Paragangliomas usually along nerve pathways in the head, neck, and spine. Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor that forms in the center of the adrenal gland. Usually, Pheochromocytoma affects one adrenal gland, but it may affect both adrenal glands. Sometimes there is more than one tumor in one adrenal gland. The alternate color for Pheochromocytoma is green.
- Pheochromocytoma, Childhood: Pheochromocytoma and paraganglioma are rare tumors that come from the same type of nerve tissue. Pheochromocytoma forms in the adrenal glands. Some pheochromocytomas release extra adrenaline and noradrenaline into the blood and cause symptoms. The alternate color for childhood Pheochromocytoma is green or gold.
- Rare Diseases and Disorders In the United States, a Rare Disease is defined as a condition that affects fewer than 200,000 people. This definition was created by Congress in the Orphan Drug Act of 1983 . Rare Diseases became known as Orphan Diseases because drug companies were not interested in adopting them to develop treatments. The Orphan Drug Act created financial incentives to encourage companies to develop new drugs for Rare Diseases. The Rare Disease definition was needed to establish which conditions would qualify for the new incentive programs. Other countries have their own official definitions of a Rare Disease. In the European Union, a disease is defined as rare when it affects fewer than 1 in 2,000 people. There may be as many as 7,000 Rare Diseases. The total number of Americans living with a Rare Disease is estimated at between 25-30 million. This estimate has been used by the Rare Disease community for several decades to highlight that while individual diseases may be rare, the total number of people with a Rare Disease is large. In the United States, only a few types of Rare Diseases are tracked when a person is diagnosed. These include certain infectious diseases, birth defects, and cancers. It also includes the diseases on state newborn screening tests. Because most Rare Diseases are not tracked, it is hard to determine the exact number of rare diseases or how many people are affected.
Zebra, Pink and Blue Awareness Ribbons: Colors and causes symbolize, stand for and support:
- Undiagnosed Diseases: The Common Fund’s Undiagnosed Diseases Network is a research study to improve the level of diagnosis of rare and undiagnosed conditions. In the United States, it has been estimated that approximately 25 million Americans suffer from a rare disorder. The Undiagnosed Diseases Network established a nationwide network of clinicians and researchers who use both basic and clinical research to uncover the underlying disease mechanisms associated with these conditions. In its first 20 months, the UDN accepted 601 participants undiagnosed by traditional medical practices. Of those who completed their UDN evaluation during this time, 35% were given a diagnosis. Many of these diagnoses were rare genetic diseases including 31 previously unknown syndromes. The UDN is currently accepting applications . Contact Undiagnosed Diseases Network at https://undiagnosed.hms.harvard.edu/apply/
Ahead of speech, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. says in a Pennsylvania court filing that he will be endorsing Donald Trump
PHOENIX -- Ahead of speech, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. says in a Pennsylvania court filing that he will be endorsing Donald Trump.
Trending Reader Picks

RFK Jr. suspends his presidential bid and backs Donald Trump before appearing with him at his rally
- Aug 22, 11:28 PM

Suspect charged with murder and animal cruelty in fatal carjacking of 80-year-old dog walker
- Aug 23, 7:50 PM

Georgia lawmakers say the top solution to jail problems is for officials to work together
- Aug 23, 1:44 PM

Nikki Haley in Taiwan says an isolationist policy is not healthy while expressing support for Trump
- Aug 24, 3:18 AM
Trump-backed Alaska Republican withdraws from US House race after third-place finish in primary
- Aug 23, 2:14 PM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events
- Crime & Courts
- VCS Outdoors
- National Politics
- News Columnists
- Conejo Valley
- Port Hueneme
- Santa Paula
- Simi Valley
What's wrong with RFK Jr's voice? Spasmodic dysphonia explained

During Robert F. Kennedy Jr.'s now-suspended 2024 presidential race , many people noticed his raspy and often halting voice.
The son and nephew of slain political leaders has a rare disorder called spasmodic dysphonia — a spasm of the vocal muscles.
Kennedy is one of an estimated 50,000 people in North America with SD, as it is often referred to, a neurological condition that creates a vocal tremble in mostly middle-aged people that usually lasts for the rest of their lives.
There is no cure, but treatments can temporarily reduce symptoms.
Here's what to know about spasmodic dysphonia:
RFK Jr. and spasmodic dysphonia
Spasmodic dysphonia has recently been spotlighted due to Robert F. Kennedy Jr.’s presidential campaign. While the candidate has had the disorder for almost 30 years, his raspy, trembling voice has received more attention with a host of stump speeches, media appearances, and advertisements over his now-suspended presidential campaign.
In an interview this spring with the Los Angeles Times, Kennedy said his voice doesn’t tire or get worse as he speaks. It just sounds like he’s always on the verge of breaking down.
How is spasmodic dysphonia treated?
To date, no known cure for spasmodic dysphonia exists. However, several forms of treatment — including speech therapy, drugs and surgery — are available to alleviate or control the symptoms of the vocal spasms on a temporary or long-lasting basis.
Dr. Andrew Blitzer, a New Jersey ear, nose, and throat specialist, developed a now-common treatment for SD that involves injecting Botox into the throat muscles to control the vocal cords, the USA TODAY Network reported. Although it doesn't treat the neurological condition, it helps abate the symptoms for three to four months on average.
The problem has long been diagnosing the condition. Many of Dr. Blitzer's first patients had been seen by an average of 13 doctors and other medical personnel, from psychiatrists to speech pathologists, before they were diagnosed with SD. The situation has improved now that SD is taught more in medical schools and during ENT residencies. Still, many of Dr. Blitzer's patients come from across the U.S. and even overseas to have him treat them.
"You can make a big difference in people's lives by giving them their voice back," he said. "It's such a small procedure, but it makes a big difference."
Why did RFK Jr. drop out of the presidential race?
Robert F. Kennedy Jr. says he will suspend his campaign in the 2024 presidential race and throw his support behind Republican nominee Donald Trump, USA TODAY reported.
In a virtual address on Friday, Kennedy clarified that he plans to remove his name from the ballot in about 10 battleground states, "where my presence would be a spoiler," a process he has already begun in states including Arizona and Pennsylvania.
Speculation that Kennedy would drop out began earlier this week after his running mate Nicole Shanahan said in an interview Tuesday the campaign had been weighing a decision .
Trump earlier this week called Kennedy “a brilliant" and "very smart guy" — a far cry from April, when he called him “far more liberal than anyone running as a Democrat" and feared that Kennedy's independent candidacy might cost him votes in the general election.
Vice President Kamala Harris' campaign, in response to Kennedy's suspension, offered their ticket as an option to voters "tired of Donald Trump and looking for a new way forward."
“In order to deliver for working people and those who feel left behind, we need a leader who will fight for you, not just for themselves, and bring us together, not tear us apart," Campaign Chair Jen O’Malley Dillon said in a statement. "Vice President Harris wants to earn your support."
USA TODAY contributed to this report.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Pernicious Anaemia and B12 Deficiency - Two awareness ribbons are listed for Pernicious anemia, both ribbons are colored red, white, and black. The second ribbon has the words "Pernicious Anaemia" written on the black part, and B12 Deficiency on the red part. Pernicious Anaemia is believed to be an autoimmune disease.
Check out our speech impediment selection for the very best in unique or custom, handmade pieces from our wall hangings shops. ... Awareness Shirt,Support Son Stuttering Awareness Shirt,Stuttering Awareness Warrior Gift,Stuttering Sea Green Ribbon Tee (4.4k) Sale Price $13.65 $ 13.65 $ 19.50 Original Price $19.50 ...
However, some speech disorders persist. Approximately 5% of children aged three to 17 in the United States experience speech disorders. There are many different types of speech impediments, including: Disfluency. Articulation errors. Ankyloglossia. Dysarthria. Apraxia. This article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment of the different ...
The green ribbon is used to represent bipolar disorder and over 45 other causes including global warming, text-free driving, cerebral palsy, and genocide. ... The sea green awareness ribbon is used to represent speech impediments like stuttering, stammering, and lisping. The full list of sea green ribbon meanings includes: Lisping; Stammering;
Speech disorders, impairments, or impediments, are a type of communication disorder in which normal speech is disrupted. [1] This can mean fluency disorders like stuttering, cluttering or lisps.Someone who is unable to speak due to a speech disorder is considered mute. [2] Speech skills are vital to social relationships and learning, and delays or disorders that relate to developing these ...
1. Speech therapy. Speech therapy is a type of treatment that helps people with speech disorders improve their abilities. Speech therapists can help people with articulation disorders learn to produce sounds correctly, people with fluency disorders reduce their stuttering, and people with resonance disorders improve their vowel production. 2.
There are three general categories of speech impairment: Fluency disorder. This type can be described as continuity, smoothness, rate, and effort in speech production. Voice disorder. A voice ...
stroke. traumatic brain injury. degenerative neurological or motor disorder. injury or illness that affects your vocal cords. dementia. Depending on the cause and type of speech impairment, it may ...
Use of gestures — When individuals use gestures to communicate instead of words, a speech impediment may be the cause. Inappropriate pitch — This symptom is characterized by speaking with a strange pitch or volume. In children, signs might also include a lack of babbling or making limited sounds.
A lisp is a functional speech disorder commonly called a speech impediment. A lisp is characterized by difficulty making specific speech sounds, such as /s/ and /z/. Incorrect tongue placement is the primary reason behind a lisp, resulting in difficulty articulating the /s/ and /z/ sounds. are not universally agreed upon.
See the Speech Sound Disorders Evidence Map for summaries of the available research on this topic.. The scope of this page is speech sound disorders with no known cause—historically called articulation and phonological disorders—in preschool and school-age children (ages 3-21).. Information about speech sound problems related to motor/neurological disorders, structural abnormalities, and ...
Speech disorders affect the vocal cords, muscles, nerves, and other structures within the throat. Causes may include: vocal cord damage. brain damage. muscle weakness. respiratory weakness ...
Apraxia. Apraxia of speech is another form of speech impediment and is quite nasty in its play. Apraxia of speech is different from stutters or lisps. Instead, it's an issue with the motor skill programming involved in speech. People with apraxia struggle to coordinate the speech muscles in their brains. They understand the language perfectly ...
Spasmodic Dysphonia (SD) is a chronic long-term disorder that affects the voice. It is characterized by a spasming of the vocal chords when a person attempts to speak and results in a voice that can be described as shaky, hoarse, groaning, tight, or jittery. It can cause the emphasis of speech to vary considerably.
Common causes of childhood speech impediments include: Autism spectrum disorder: A neurodevelopmental disorder that affects social and interactive development. Cerebral palsy: A congenital (from birth) disorder that affects learning and control of physical movement. Hearing loss: Can affect the way children hear and imitate speech.
MAGA-affiliated accounts on social media have mocked Tim Walz's 17-year-old neurodivergent son Gus for crying during his father's speech at the Democratic National Convention on Wednesday.. Gus ...
Overall difficulty communicating and expressing thoughts and ideas. Inability to repeat words. Inability to pronounce words the same way twice. A phobia of speaking in public. Speaking slowly and carefully. Speech delay. Frequent pauses when talking. Limited vocabulary over several years, delayed language development.
Awareness Ribbons Colors, Causes and Meanings. Search our awareness pins, ribbons and wristbands. ... Sleep Apnea is a serious sleep disorder that happens when breathing stops and starts while sleeping. If Sleep Apnea goes untreated, it can cause loud snoring, daytime tiredness, or more serious problems like heart trouble or high blood pressure ...
Ahead of speech, Robert F. Kennedy Jr. says in a Pennsylvania court filing that he will be endorsing Donald Trump. By The Associated Press. August 23, 2024, 2:10 PM. 1:10.
Robert F. Kennedy, Jr. has a condition called spasmodic dysphonia, which causes the sound of a raspy voice due to spasms in the vocal cords.
speech-language pathologist. no more than 90 days before the AME exam. It must include: • Detailed summary of the history of the condition; • Current medications, dosage, and side effects (if any); • Physical exam findings; • Results of any testingperformed; • Diagnosis; • Assessment; • Plan (prognosis); and • Follow-up. 2.