Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA

How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA
In this citation guide, you will learn how to reference and cite an undergraduate thesis, master’s thesis, or doctoral dissertation. This guide will also review the differences between a thesis or dissertation that is published and one that has remained unpublished. The guidelines below come from the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (2020a), pages 333 and 334. Please note that the association is not affiliated with this guide.
Alternatively, you can visit EasyBib.com for helpful citation tools to cite your thesis or dissertation .
Guide Overview
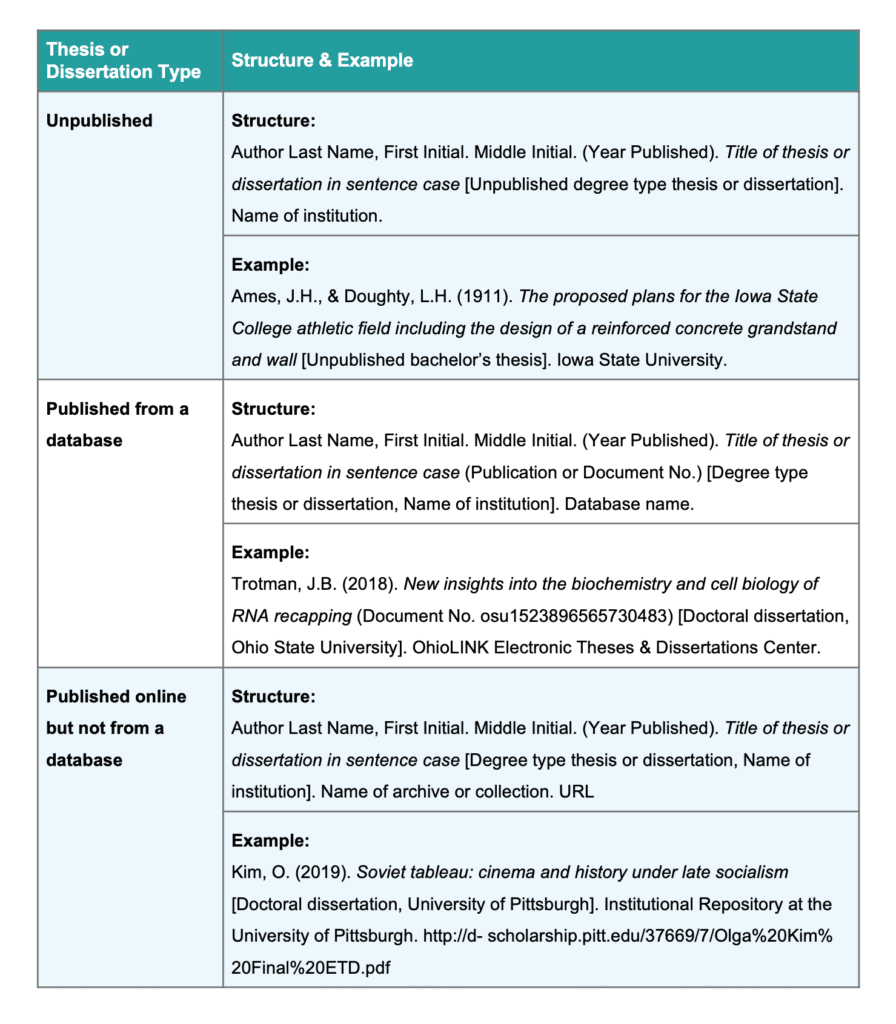
Citing an unpublished thesis or dissertation, citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation: reference overview, what you need.
Since unpublished theses can usually only be sourced in print form from a university library, the correct citation structure includes the university name where the publisher element usually goes.
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case [Unpublished degree type thesis or dissertation]. Name of institution.
Ames, J. H., & Doughty, L. H. (1911). The proposed plans for the Iowa State College athletic field including the design of a reinforced concrete grandstand and wall [Unpublished bachelor’s thesis]. Iowa State University.
In-text citation example:
- Parenthetical : (Ames & Doughty, 1911)
- Narrative : Ames & Doughty (1911)
If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It’s similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences:
- The institution is presented in brackets after the title
- The archive or database name is included
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case (Publication or Document No.) [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Database name.
Examples 1:
Knight, K. A. (2011). Media epidemics: Viral structures in literature and new media (Accession No. 2013420395) [Doctoral dissertation, University of California, Santa Barbara]. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.

Trotman, J.B. (2018). New insights into the biochemistry and cell biology of RNA recapping (Document No. osu1523896565730483) [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University]. OhioLINK Electronic Theses & Dissertations Center.
In the example given above, the dissertation is presented with a Document Number (Document No.). Sometimes called a database number or publication number, this is the identifier that is used by the database’s indexing system. If the database you are using provides you with such a number, then include it directly after the work’s title in parentheses.
If you are interested in learning more about how to handle works that were accessed via academic research databases, see Section 9.3 of the Publication Manual.
In-text citation examples :
- Parenthetical citation : (Trotman, 2018)
- Narrative citation : Trotman (2018)
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year Published). Title in sentence case [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Name of archive or collection. URL
Kim, O. (2019). Soviet tableau: cinema and history under late socialism [Doctoral dissertation, University of Pittsburgh]. Institutional Repository at the University of Pittsburgh. https://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/37669/7/Olga%20Kim%20Final%20ETD.pdf
Stiles, T. W. (2001). Doing science: Teachers’ authentic experiences at the Lone Star Dinosaur Field Institute [Master’s thesis, Texas A&M University]. OAKTrust. https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/ETD-TAMU-2001-THESIS-S745
It is important to note that not every thesis or dissertation published online will be associated with a specific archive or collection. If the work is published on a private website, provide only the URL as the source element.
In-text citation examples:
- Parenthetical citation : (Kim, 2019)
- Narrative citation : Kim (2019)
- Parenthetical citation : (Stiles, 2001)
- Narrative citation : Stiles (2001)
| Unpublished | Author last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). [Unpublished degree type thesis or dissertation]. Name of institution | Ames, J.H., & Doughty, L.H (1911). [Unpublished bachelor’s thesis]. Iowa State University. |
| Published from a database | Author last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). (Publication or Document No.) [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Database name. | Trotman, J.B. (2018). (Document No. osu1523896565730483) [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University]. OhioLINK Electronic Thesis & Dissertations Center |
| Published online but not from a database | Author last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Name of archive or collection. URL | Kim, O. (2019). [Doctoral dissertation, University of Pittsburgh]. Institutional Repository at the University of Pittsburgh. http://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/37669/7/Olga%20Kim%20Final%20ETD.pdf |
We hope that the information provided here will serve as an effective guide for your research. If you’re looking for even more citation info, visit EasyBib.com for a comprehensive collection of educational materials covering multiple source types.
If you’re citing a variety of different sources, consider taking the EasyBib citation generator for a spin. It can help you cite easily and offers citation forms for several different kinds of sources.
To start things off, let’s take a look at the different types of literature that are classified under Chapter 10.6 of the Publication Manual :
- Undergraduate thesis
- Master’s thesis
- Doctoral dissertation
You will need to know which type you are citing. You’ll also need to know if it is published or unpublished .
When you decide to cite a dissertation or thesis, you’ll need to look for the following information to use in your citation:
- Author’s last name, and first and middle initials
- Year published
- Title of thesis or dissertation
- If it is unpublished
- Publication or document number (if applicable; for published work)
- Degree type (bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral)
- Thesis or dissertation
- Name of institution awarding degree
- DOI (https://doi.org/xxxxx) or URL (if applicable)
Since theses and dissertations are directly linked to educational degrees, it is necessary to list the name of the associated institution; i.e., the college, university, or school that is awarding the associated degree.
To get an idea of the proper form, take a look at the examples below. There are three outlined scenarios:
- Unpublished thesis or dissertation
- Published thesis or dissertation from a database
- Thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database
American Psychological Association. (2020a). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
American Psychological Association. (2020b). Style-Grammar-Guidelines. https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/citations/basic-principles/parenthetical-versus-narrative
Published August 10, 2012. Updated March 24, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite a published thesis in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, publication year, title of the thesis, institute name, archive name, and URL (uniform resource locator). The templates for an in-text citation and reference list entry of a thesis, along with examples, are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
Use the author surname and the publication year in the in-text citation.
Author Surname (Publication Year)
Cartmel (2007)
Parenthetical:
(Author Surname, Publication Year)
(Cartmel, 2007)
Reference list entry template and example:
The title of the thesis is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose the thesis and the institute awarding the degree inside brackets following the publication year. Then add the name of the database followed by the URL.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the thesis [Master’s thesis, Institute Name]. Name of the Database. URL
Cartmel, J. (2007). Outside school hours care and schools [Master’s thesis, Queensland University of Technology]. EPrints. http://eprints.qut.edu.au/17810/1/Jennifer_Cartmel_Thesis.pdf
To cite an unpublished dissertation in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, year, title of the dissertation, and institute name. The templates for in-text citation and reference list entry of an online thesis, along with examples, are given below:
Author Surname (Year)
Averill (2009)
(Author Surname, Year)
(Averill, 2009)
The title of the dissertation is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose “Unpublished doctoral dissertation” inside brackets following the year. Then add the name of the institution awarding the degree.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the dissertation [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Name of the Institute.
Averill, R. (2009). Teacher–student relationships in diverse New Zealand year 10 mathematics classrooms: Teacher care [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Victoria University of Wellington.
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
APA 7th referencing style
- About APA 7th
- Printing this guide
- In-text references
- Direct quotations
- Reference list
- Author information
- Additional referencing information
- Using headings
- Book chapter
- Brochure and pamphlets
- ChatGPT and other generative AI tools
- Conferences
- Dictionary or encyclopaedia
- Government legislation
- Journal article
- Lecture notes and slides
- Legal sources
- Newspaper or magazine article
- Other web sources
- Patents and standards
- Personal communication
- Press (media) release
- Secondary source (indirect citation)
- Social media
- Software and mobile apps
- Specialised health information
- Television program
Thesis - from website
Thesis - from database.
- Works in non-English languages
- Works in non-English scripts, such as Arabic or Chinese
| Elements of the reference | Author - last name, initial(s). (Year). [Doctoral dissertation or Master's thesis, Institution]. Archive name. http://www.xxxxxx | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-text reference | (Axford, 2007) Axford (2007) found that .... | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference list | Axford, J.C. (2007). [Doctoral dissertation, University of Queensland]. UQ eSpace. http://espace.library.uq.edu.au/view/UQ:158747 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EndNote reference type | Thesis Add Archive Name to Name of Database field. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elements of the reference | Author - last name, initials. (Year). (Publication No. - if available) [Doctoral dissertation or master's thesis, Institution]. Database Name. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In-text reference | (Leigh, 2010) Leigh (2010) reported that .... | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reference list | Leigh, J. (2010). (Publication No. 305210119) [Doctoral dissertation, Indiana State University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| EndNote reference type | Thesis Add Publication Number to Document Number field. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
- << Previous: Television program
- Next: Video >>
- Last Updated: Aug 5, 2024 4:04 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.uq.edu.au/referencing/apa7
APA Style 6th Edition: Citing Your Sources
- Basics of APA Formatting
- In Text Quick View
- Block Quotes
- Books & eBooks
- Thesis/Dissertation
Standard Format
Various examples.
- Conference Presentations
- Course Documents
- Social Media
- Government Documents
- Academic Integrity and Plagiarism
- Additional Resources
- Sample Reference Page
Dissertation or thesis available from a database service:
Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of publication). Title of dissertation or thesis (Doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis). Retrieved from Name of database. (Accession or Order No.)
For an unpublished dissertation or thesis:
Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of creation). Title of dissertation or thesis (Unpublished doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis). Name of Institution, Location.
| Thesis, from a commercial database | Nicometo, D. N. (2015). (Order No. 1597712). Retrieved from ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global. (1717577238). |
| Dissertation, from an institutional database | Andrea, H. (2014). (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from https://etd.ohiolink.edu/ |
| Unpublished master’s thesis | Curry, J. (2016). (Unpublished master’s thesis). Pacific Oaks College, Pasadena, CA. |
See Ch 7 pp. 207-208 APA Manual for more examples and formatting rules
Formatting:
- Italicize the title
- Identify whether source is doctoral dissertation or master’s thesis in parentheses after the title
- << Previous: Articles
- Next: Websites >>
- Last Updated: Sep 22, 2022 11:20 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/APA-citation-style
APA (7th Edition) Referencing Guide
- Information for EndNote Users
- Authors - Numbers, Rules and Formatting
- In-Text Citations
- Reference List
- Books & eBooks
- Book chapters
- Journal Articles
- Conference Papers
- Newspaper Articles
- Web Pages & Documents
- Specialised Health Databases
- Using Visual Works in Assignments & Class Presentations
- Using Visual Works in Theses and Publications
- Using Tables in Assignments & Class Presentations
- Custom Textbooks & Books of Readings
- ABS AND AIHW
- Videos (YouTube), Podcasts & Webinars
- Blog Posts and Social Media
- First Nations Works
- Dictionary and Encyclopedia Entries
- Personal Communication
- Theses and Dissertations
Theses and dissertations
- Film / TV / DVD
- Miscellaneous (Generic Reference)
- AI software
- APA Format for Assignments
- What If...?
- Other Guides
- EscAPA7de - the APA escape room
- One Minute Video Series (APA)
A thesis is an unpublished document produced by student as part of the requirements for the degree. They come at various levels (e.g. Honours, Masters, PhD, etc). Check with your lecturer before using a thesis for your assignment.
| Format | Author, A. A. (Date). [Type of thesis, name of institution awarding degree]. Name of archive or site. URL
Author, A. A. (Date). [Type of thesis, name of institution awarding degree]. Database Name. : Author, A. A. (Date). [Type of thesis]. Name of institution awarding the degree.
Author, A. A. (Date). [Unpublished type of thesis]. Name of institution awarding the degree. |
| Examples | [Doctoral thesis, James Cook University]. ResearchOnline@JCU. https://researchonline.jcu.edu.au/47533/ Hawkins, E. J. (1999). [Unpublished master's thesis]. James Cook University. |
- << Previous: Personal Communication
- Next: Film / TV / DVD >>
- Last Updated: Sep 4, 2024 4:17 PM
- URL: https://libguides.jcu.edu.au/apa


- Harvard Library
- Research Guides
- Harvard Graduate School of Design - Frances Loeb Library
Write and Cite
- Theses and Dissertations
- Academic Integrity
- Using Sources and AI
- Academic Writing
- From Research to Writing
- GSD Writing Services
- Grants and Fellowships
- Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
What is a thesis?
What is a dissertation, getting started, staying on track.
A thesis is a long-term project that you work on over the course of a semester or a year. Theses have a very wide variety of styles and content, so we encourage you to look at prior examples and work closely with faculty to develop yours.
Before you begin, make sure that you are familiar with the dissertation genre—what it is for and what it looks like.
Generally speaking, a dissertation’s purpose is to prove that you have the expertise necessary to fulfill your doctoral-degree requirements by showing depth of knowledge and independent thinking.
The form of a dissertation may vary by discipline. Be sure to follow the specific guidelines of your department.
- PhD This site directs candidates to the GSAS website about dissertations , with links to checklists, planning, formatting, acknowledgments, submission, and publishing options. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus . Consult with your committee chair about specific requirements and standards for your dissertation.
- DDES This document covers planning, patent filing, submission guidelines, publishing options, formatting guidelines, sample pages, citation guidelines, and a list of common errors to avoid. There is also a link to guidelines for the prospectus .
- Scholarly Pursuits (GSAS) This searchable booklet from Harvard GSAS is a comprehensive guide to writing dissertations, dissertation-fellowship applications, academic journal articles, and academic job documents.
Finding an original topic can be a daunting and overwhelming task. These key concepts can help you focus and save time.
Finding a topic for your thesis or dissertation should start with a research question that excites or at least interests you. A rigorous, engaging, and original project will require continuous curiosity about your topic, about your own thoughts on the topic, and about what other scholars have said on your topic. Avoid getting boxed in by thinking you know what you want to say from the beginning; let your research and your writing evolve as you explore and fine-tune your focus through constant questioning and exploration.
Get a sense of the broader picture before you narrow your focus and attempt to frame an argument. Read, skim, and otherwise familiarize yourself with what other scholars have done in areas related to your proposed topic. Briefly explore topics tangentially related to yours to broaden your perspective and increase your chance of finding a unique angle to pursue.
Critical Reading
Critical reading is the opposite of passive reading. Instead of merely reading for information to absorb, critical reading also involves careful, sustained thinking about what you are reading. This process may include analyzing the author’s motives and assumptions, asking what might be left out of the discussion, considering what you agree with or disagree with in the author’s statements and why you agree or disagree, and exploring connections or contradictions between scholarly arguments. Here is a resource to help hone your critical-reading skills:
http://writing.umn.edu/sws/assets/pdf/quicktips/criticalread.pdf
Conversation
Your thesis or dissertation will incorporate some ideas from other scholars whose work you researched. By reading critically and following your curiosity, you will develop your own ideas and claims, and these contributions are the core of your project. You will also acknowledge the work of scholars who came before you, and you must accurately and fairly attribute this work and define your place within the larger discussion. Make sure that you know how to quote, summarize, paraphrase , integrate , and cite secondary sources to avoid plagiarism and to show the depth and breadth of your knowledge.
A thesis is a long-term, large project that involves both research and writing; it is easy to lose focus, motivation, and momentum. Here are suggestions for achieving the result you want in the time you have.
The dissertation is probably the largest project you have undertaken, and a lot of the work is self-directed. The project can feel daunting or even overwhelming unless you break it down into manageable pieces and create a timeline for completing each smaller task. Be realistic but also challenge yourself, and be forgiving of yourself if you miss a self-imposed deadline here and there.
Your program will also have specific deadlines for different requirements, including establishing a committee, submitting a prospectus, completing the dissertation, defending the dissertation, and submitting your work. Consult your department’s website for these dates and incorporate them into the timeline for your work.
Accountability
Sometimes self-imposed deadlines do not feel urgent unless there is accountability to someone beyond yourself. To increase your motivation to complete tasks on schedule, set dates with your committee chair to submit pre-determined pieces of a chapter. You can also arrange with a fellow doctoral student to check on each other’s progress. Research and writing can be lonely, so it is also nice to share that journey with someone and support each other through the process.
Common Pitfalls
The most common challenges for students writing a dissertation are writer’s block, information-overload, and the compulsion to keep researching forever.
There are many strategies for avoiding writer’s block, such as freewriting, outlining, taking a walk, starting in the middle, and creating an ideal work environment for your particular learning style. Pay attention to what helps you and try different things until you find what works.
Efficient researching techniques are essential to avoiding information-overload. Here are a couple of resources about strategies for finding sources and quickly obtaining essential information from them.
https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/subject_specific_writing/writing_in_literature/writing_in_literature_detailed_discussion/reading_criticism.html
https://students.dartmouth.edu/academic-skills/learning-resources/learning-strategies/reading-techniques
Finally, remember that there is always more to learn and your dissertation cannot incorporate everything. Follow your curiosity but also set limits on the scope of your work. It helps to create a folder entitled “future projects” for topics and sources that interest you but that do not fit neatly into the dissertation. Also remember that future scholars will build off of your work, so leave something for them to do.
Browsing through theses and dissertations of the past can help to get a sense of your options and gain inspiration but be careful to use current guidelines and refer to your committee instead of relying on these examples for form or formatting.
DASH Digital Access to Scholarship at Harvard.
HOLLIS Harvard Library’s catalog provides access to ProQuest Dissertations & Theses Global .
MIT Architecture has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Rhode Island School of Design has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
University of South Florida has a list of their graduates’ dissertations and theses.
Harvard GSD has a list of projects, including theses and professors’ research.
- << Previous: Reading, Notetaking, and Time Management
- Next: Publishing >>
- Last Updated: Sep 4, 2024 4:48 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.harvard.edu/gsd/write
Harvard University Digital Accessibility Policy
- Library Guides

APA 7th Referencing
Apa 7th referencing: theses.

- In-text referencing
- Compiling a Reference list
- Citing tables and figures
- DOIs and Live hyperlinks
- Secondary sources
- Journal Articles
- Reports & Grey Literature
- Conference Materials
- Datasets, Software & Tests
- Social Media
- Images, tables & figures
- Sound & video
- Legislation & Cases
- Personal Communications
- Standards & Patents
- Course Notes or Course Presentations
- Generative AI
- Sample Reference List
On this page
Basic format to reference a thesis or dissertation.
- Referencing theses: Examples
The basics of a reference list entry for a thesis or dissertation:
- Author. The surname is followed by first initials.
- Year (in round brackets).
- Title (in italics ).
- Level of Thesis or Dissertation [in square brackets].
- University, also in [square brackets] following directly after the Level of Thesis, for e.g. [Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University]
- Database or Archive Name
- The first line of each citation is left adjusted. Every subsequent line is indented 5-7 spaces.
Mosek, E. (2017). Team flow: The missing piece in performance [Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University]. Victoria University Research Repository. http://vuir.vu.edu.au/35038/

| Material Type | In-Text Example | Reference List Example |
|---|---|---|
| According to Mosek (2017) “flow was considered a highly functional state” ( p. 6) . | [Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University]. Victoria University Research Repository. http://vuir.vu.edu.au/35038/
| |
| … research is required to fill in gaps in our knowledge (Smith, 2018). | (Publication No. 10746190) [Doctoral dissertation, Drake University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
| |
| Tsao (2016) compared populations in Kentucky and Taiwan. | [Master’s thesis, University of Kentucky]. UKnowledge. https://uknowledge.uky.edu/foodsci_etds/47/ If an author's first name is hyphenated, as in Shu-Feng Tsao above, retain the hyphen and include a full stop after each initial but no space. |
- << Previous: Standards & Patents
- Next: Course Notes or Course Presentations >>
- Last Updated: Aug 12, 2024 3:24 PM
- URL: https://libraryguides.vu.edu.au/apa-referencing
Fast and free citation generator APA 6th and 7th ed. • MLA 8th ed. • Chicago 16th ed.
- Create Title Page
- Style Guide
- Manage Bibliographies

Mindfullness & COVID-19
- General Format Rules
- In-Text Citations
- General Rules – Reference List
- Encyclopedia & Dictionary
- Government Publication
- Social media
- Dissertation/Thesis
- Online Video
- Audio/Podcast
- Lecture notes
APA 6 Style Guide
| Blue text | Replace with information from source |
| Purple bold text | Text required by the APA style |
| [Gray text in brackets] | Tips |
Thesis/Dissertation – APA Reference List
Capitalization.
- The document title is in sentence case – Only the first word and proper nouns in the title are capitalized. Always capitalize the first word, the first word after a colon or a dash.
- The title of the thesis or dissertation is in title case – Each word in the name is capitalized, except for articles (a, an, the), prepositions (against, between, in, of, to), conjunctions (and, but, for, nor, or, so, yet), and the infinitive 'to'.
Thesis/Dissertation – Unpublished/Print version
For papers written in United States list City and State. For countries outside United States list City and Country.
Author , A . A . ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Unpublished doctoral dissertation [OR] Unpublished master's thesis). Academic Institution , City , State [OR] Country .
- Considine, M. (1986). Australian insurance politics in the 1970s: Two case studies . (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). University of Melbourne, Melbourne, Australia.
- Kassover,A. (1987). Treatment of abusive males: Voluntary vs. court-mandated referrals (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). Nova University, Fort Lauderdale, FL.
Thesis/Dissertation – From a commercial database (e.g., ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database)
Author , A ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from Name of database . ( Accession or Order Number )
Cooley, T. (2009). Design, development, and implementation of a Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN): The Hartford Job Corps Academy case study (Doctoral dissertation). Available from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses database. (UMI No. 3344745)
Thesis/Dissertation – Institutional Database (i.e. University website)
For U.S. thesis do not include university or locations. Include the university and location (City and Country) for a non-U.S. online thesis.
Author , A . A . ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis). Retrieved from http:// url.com
- Adams, R. J. (1973). Building a foundation for evaluation of instruction in higher education and continuing education (Doctoral dissertation). Retrieved from http://www.ohiolink.edu/etd/
- Barua, S. (2010). Drought assessment and forecasting using a nonlinear aggregated drought index (Doctoral dissertation, Victoria University, Melbourne, Australia). Retrieved from http://vuir.vu.edu.au/1598
Thesis/Dissertation – Web
For U.S. thesis do not include locations. Include the location (City and Country) for a non-U.S. online thesis.
Author , A . A . ( Year ). Title of dissertation/thesis (Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis, Institution issuing degree). Retrieved from http:// www.url.com
- Bruckman, A. (1997). MOOSE Crossing: Construction, community, and learning in a networked virtual world for kids (Doctoral dissertation, Massachusetts Institute of Technology). Retrieved from http://www-static.cc.gatech.edu/~asb/thesis

- AUT Library
- Library Guides
- Referencing styles and applications
APA 7th Referencing Style Guide
- Theses and dissertations
- Referencing & APA style
- In-text citation
- Elements of a reference
- Format & examples of a reference list
- Conferences
- Reports & grey literature
- Figures (graphs and images)
Terminology - Thesis, dissertation or exegesis?
Published theses and dissertations, unpublished theses and dissertations.
- Audio works
- Films, TV & video
- Visual works
- Generative artificial intelligence (AI)
- Computer software, games & apps
- Lecture notes & Intranet resources
- Legal resources
- Personal communications
- PowerPoint slides
- Social media
- Specific health examples
- Standards & patents
- Websites & webpages
- Footnotes and appendices
- Frequently asked questions
Thesis and dissertation can mean different things depending on where the degree is awarded. Always check the title page, or subsequent pages, to determine exactly what the work is and use the information for your reference.
Auckland University of Technology (and other NZ universities)
- Thesis is either for a doctoral or a master's degree.
- Dissertation is either for a master's or a bachelor's degree with honours.
- Exegesis is the written component of a practice-based thesis where the major output is a creative work; e.g., a film, artwork, novel.
Other parts of the world
- In North America and some other countries, dissertation is used for a doctoral degree and thesis for a master's degree.
Theses available in a database, a university archive or from a personal website.
Reference format
|
| |||
| Author, A. A. | (Year). | (Publication No. ) [Doctoral dissertation/Doctoral thesis/Master's dissertation/Master's thesis, Institution Name]. | Database Name. URL Archive Name. URL |
Theses published online (e.g. in institutional repositories)
| Miller, T. (2019). [Master's thesis, Auckland University of Technology]. Tuwhera. |
| Kelly, C. B. D. (2018). [Doctoral thesis, The University of Waikato]. The University of Waikato Research Commons. |
Theses from ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global
| Becker, J. C. (2013). (Publication No. 3577776) [Doctoral dissertation, Graduate Council of Texas State University - San Marcos]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global. |
Find how to cite in text on the In-text citation page.
Unpublished thesis or dissertations are usually sourced directly from the university in print form.
Reference format
|
| |||
| Author, A. A. | (Year). | [Unpublished doctoral or master's thesis or dissertation]. | Name of the Institution awarding the degree. |
| Stewart, Y. (2000). [Unpublished master's thesis]. Auckland University of Technology. |
- << Previous: Tables
- Next: Audiovisual media >>
- Last Updated: Aug 8, 2024 9:47 AM
- URL: https://aut.ac.nz.libguides.com/APA7th

Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis References
This page contains a reference example for an unpublished dissertation or thesis.
Harris, L. (2014). Instructional leadership perceptions and practices of elementary school leaders [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Virginia.
- Parenthetical citation : (Harris, 2014)
- Narrative citation : Harris (2014)
- When a dissertation or thesis is unpublished, include the description “[Unpublished doctoral dissertation]” or “[Unpublished master’s thesis]” in square brackets after the dissertation or thesis title.
- In the source element of the reference, provide the name of the institution that awarded the degree.
- The same format can be adapted for other unpublished theses, including undergraduate theses, by changing the wording of the bracketed description as appropriate.
- If you find the dissertation or thesis in a database or in a repository or archive, follow the published dissertation or thesis reference examples .
Unpublished dissertation or thesis references are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 10.6 and the Concise Guide Section 10.5
APA 7th Edition Citation Examples
- Volume and Issue Numbers
- Page Numbers
- Undated Sources
- Citing a Source Within a Source
- In-Text Citations
- Academic Journals
- Encyclopedia Articles
- Book, Film, and Product Reviews
- Online Classroom Materials
- Conference Papers
- Technical + Research Reports
- Court Decisions
- Treaties and Other International Agreements
- Federal Regulations: I. The Code of Federal Regulations
- Federal Regulations: II. The Federal Register
- Executive Orders
- Charter of the United Nations
- Federal Statutes
Format for dissertations and theses
Dissertations and theses database.
- Interviews, E-mail Messages + Other Personal Communications
- Social Media
- Business Sources
- PowerPoints
- AI: ChatGPT, etc.
Author last name, first initial. (Year). Title of dissertation/thesis (Publication No.) [Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis, University]. Database. URL
- Author: List the last name, followed by the first initial (and second initial). See Authors for more information.
- Year: List the year between parentheses, followed by a period.
- Title of dissertation/thesis: In italics. Capitalize the first word of the title, subtitle, and proper nouns.
- Publication number: Can be found in Dissertations and Theses database, listed in the item record as “Dissertation/thesis number.”
- Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis: List whether it is a dissertation or a thesis.
- University: List the university associated with the dissertation/thesis.
- Database: List database the dissertation/thesis was found in, if found in a database.
- URL: List URL if found on the free Web rather than in a database.
See specific examples below.
Dissertations:
Pecore, J. T. (2004). Sounding the spirit of Cambodia: The living tradition of Khmer music and dance-drama in a Washington, DC community (Publication No. 3114720) [Doctoral dissertation, University of Maryland]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
Master's Theses:
Hollander, M. M. (2017). Resitance to authority: Methodological innovations and new lessons from the Milgram experiment (Publication No. 10289373) [Master's thesis, University of Wisconsin - Madison]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
APA calls for the citation to include a unique identifying number for the dissertation, labeling it “Publication No.” That number can be found in Dissertations and Theses database, listed in the item record as “Dissertation/thesis number.”
Karamanos, X. (2020). The influence of professional development models on student mathematics performance in New Jersey public elementary schools [Doctoral dissertation, Seton Hall University]. Seton Hall University Dissertations and Theses (ETDs). https://scholarship.shu.edu/dissertations/2732
Bordo, V. C. (2011). Making a case for the use of foreign language in the educational activities of nonprofit arts organizations [Master's thesis, University of Akron]. OhioLINK Electronic Theses & Dissertations Center. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=akron1311135640
Caprette, C. L. (2005). Conquering the cold shudder: The origin and evolution of snake eyes [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University].
Angelova, A. N. (2004). Data pruning [Master's thesis, California Institute of Technology].
See Publication Manual , 10.6.
- << Previous: Federal Statutes
- Next: Images >>
- Last Updated: Mar 18, 2024 12:55 PM
- URL: https://libguides.umgc.edu/apa-examples
Citation guides
All you need to know about citations
How to cite a master's thesis in APA
- Google Docs
To cite a master's thesis in a reference entry in APA style 6th edition include the following elements:
- Author(s) of the thesis: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to seven authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For eight or more authors include the first six names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's name.
- Year of publication: Give the year in brackets followed by a full stop.
- Title of the master's thesis: Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized.
- URL: Give the full URL where the document can be retrieved from.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of a master's thesis in APA style 6th edition:
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the master's thesis (Master's thesis). Retrieved from URL
If the thesis is available from a database, archive or any online platform use the following template:
- Author(s) of the thesis: Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to 20 authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For 21 or more authors include the first 19 names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's name.
- Title of the Master's thesis: Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized.
- Publication number: Give the identification number of the thesis, if available.
- Name of the degree awarding institution: Give the name of the institution.
- Name of Platform: Give the name of the database, archive or any platform that holds the thesis.
- URL: If the thesis was found on a database, omit this element.
Here is the basic format for a reference list entry of a master's thesis in APA style 7th edition:
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the Master's thesis ( Publication number ) [Master's thesis, Name of the degree awarding institution ]. Name of Platform . URL
If the thesis has not been published or is available from a database use the following template:
- Location: Give the location of the institution. If outside the United States also include the country name.
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the master's thesis (Unpublished master's thesis). Name of the degree awarding institution , Location .
If the thesis is not published, use the following template:
Author(s) of the thesis . ( Year of publication ). Title of the master's thesis [Unpublished master's thesis]. Name of the degree awarding institution .
APA reference list examples
Take a look at our reference list examples that demonstrate the APA style guidelines for a master's thesis citation in action:
A master's thesis found in an online platform
Bauger, L . ( 2011 ). Personality, passion, self-esteem and psychological well-being among junior elite athletes in Norway ( Master's Thesis ). Retrieved from https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/29a9/ef96c34e577211246b83b11813a2585033c5.pdf
Bauger, L . ( 2011 ). Personality, passion, self-esteem and psychological well-being among junior elite athletes in Norway [ Master's Thesis , University of Tromsø ]. Semantic Scholar . https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/29a9/ef96c34e577211246b83b11813a2585033c5.pdf
An unpublished master's thesis
Aube, K. E . ( 2019 ). A comparison of water main failure prediction models in San Luis Obispo, CA ( Unpublished master's thesis ). Cal Poly , San Luis Obispo, CA .
Aube, K. E . ( 2019 ). A comparison of water main failure prediction models in San Luis Obispo, CA [ Unpublished master's thesis ]. Cal Poly .

This citation style guide is based on the official Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association ( 6 th edition).
More useful guides
- APA Referencing: Theses
- Citation Help for APA: Master's Thesis or Project
- APA Thesis, dissertation or exegesis?
More great BibGuru guides
- MLA: how to cite a photo
- AMA: how to cite a film
- Chicago: how to cite a song
Automatic citations in seconds
Citation generators
Alternative to.
- NoodleTools
- Getting started
From our blog
- 📚 How to write a book report
- 📝 APA Running Head
- 📑 How to study for a test
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
How to Cite Sources | Citation Generator & Quick Guide
Citing your sources is essential in academic writing . Whenever you quote or paraphrase a source (such as a book, article, or webpage), you have to include a citation crediting the original author.
Failing to properly cite your sources counts as plagiarism , since you’re presenting someone else’s ideas as if they were your own.
The most commonly used citation styles are APA and MLA. The free Scribbr Citation Generator is the quickest way to cite sources in these styles. Simply enter the URL, DOI, or title, and we’ll generate an accurate, correctly formatted citation.
Generate accurate citations with Scribbr
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text.
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When do you need to cite sources, which citation style should you use, in-text citations, reference lists and bibliographies.
Scribbr Citation Generator
Other useful citation tools
Citation examples and full guides, frequently asked questions about citing sources.
Citations are required in all types of academic texts. They are needed for several reasons:
- To avoid plagiarism by indicating when you’re taking information from another source
- To give proper credit to the author of that source
- To allow the reader to consult your sources for themselves
A citation is needed whenever you integrate a source into your writing. This usually means quoting or paraphrasing:
- To quote a source , copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks .
- To paraphrase a source , put the text into your own words. It’s important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don’t want to do this manually.
Citations are needed whether you quote or paraphrase, and whatever type of source you use. As well as citing scholarly sources like books and journal articles, don’t forget to include citations for any other sources you use for ideas, examples, or evidence. That includes websites, YouTube videos , and lectures .
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries

Usually, your institution (or the journal you’re submitting to) will require you to follow a specific citation style, so check your guidelines or ask your instructor.
In some cases, you may have to choose a citation style for yourself. Make sure to pick one style and use it consistently:
- APA Style is widely used in the social sciences and beyond.
- MLA style is common in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography , common in the humanities
- Chicago author-date , used in the (social) sciences
- There are many other citation styles for different disciplines.
If in doubt, check with your instructor or read other papers from your field of study to see what style they follow.
In most styles, your citations consist of:
- Brief in-text citations at the relevant points in the text
- A reference list or bibliography containing full information on all the sources you’ve cited
In-text citations most commonly take the form of parenthetical citations featuring the last name of the source’s author and its year of publication (aka author-date citations).
An alternative to this type of in-text citation is the system used in numerical citation styles , where a number is inserted into the text, corresponding to an entry in a numbered reference list.
There are also note citation styles , where you place your citations in either footnotes or endnotes . Since they’re not embedded in the text itself, these citations can provide more detail and sometimes aren’t accompanied by a full reference list or bibliography.
| (London: John Murray, 1859), 510. |
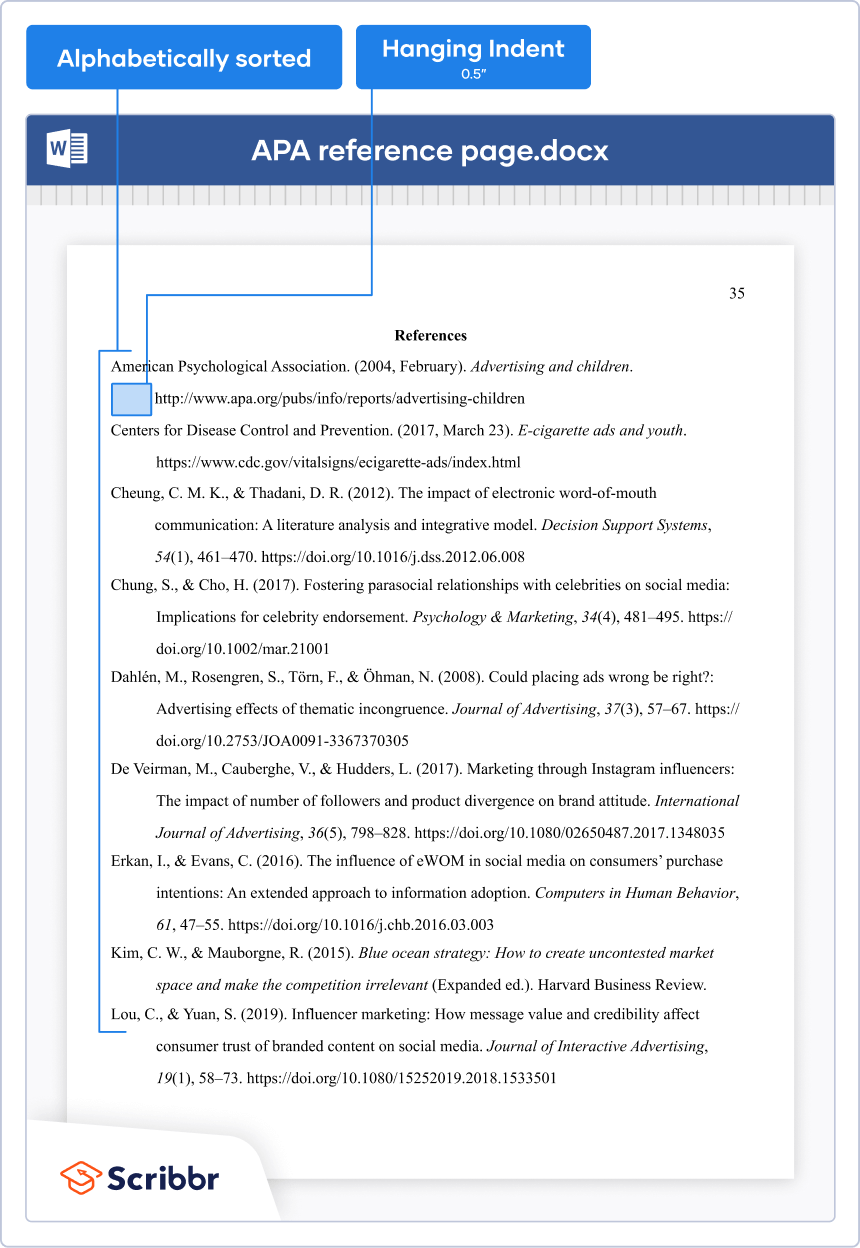
A reference list (aka “Bibliography” or “Works Cited,” depending on the style) is where you provide full information on each of the sources you’ve cited in the text. It appears at the end of your paper, usually with a hanging indent applied to each entry.
The information included in reference entries is broadly similar, whatever citation style you’re using. For each source, you’ll typically include the:
- Author name
- Publication date
- Container (e.g., the book an essay was published in, the journal an article appeared in)
- Location (e.g., a URL or DOI , or sometimes a physical location)
The exact information included varies depending on the source type and the citation style. The order in which the information appears, and how you format it (e.g., capitalization, use of italics) also varies.
Most commonly, the entries in your reference list are alphabetized by author name. This allows the reader to easily find the relevant entry based on the author name in your in-text citation.
In numerical citation styles, the entries in your reference list are numbered, usually based on the order in which you cite them. The reader finds the right entry based on the number that appears in the text.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Because each style has many small differences regarding things like italicization, capitalization , and punctuation , it can be difficult to get every detail right. Using a citation generator can save you a lot of time and effort.
Scribbr offers citation generators for both APA and MLA style. Both are quick, easy to use, and 100% free, with no ads and no registration required.
Just input a URL or DOI or add the source details manually, and the generator will automatically produce an in-text citation and reference entry in the correct format. You can save your reference list as you go and download it when you’re done, and even add annotations for an annotated bibliography .
Once you’ve prepared your citations, you might still be unsure if they’re correct and if you’ve used them appropriately in your text. This is where Scribbr’s other citation tools and services may come in handy:
Plagiarism Checker
Citation Checker
Citation Editing
Plagiarism means passing off someone else’s words or ideas as your own. It’s a serious offense in academia. Universities use plagiarism checking software to scan your paper and identify any similarities to other texts.
When you’re dealing with a lot of sources, it’s easy to make mistakes that could constitute accidental plagiarism. For example, you might forget to add a citation after a quote, or paraphrase a source in a way that’s too close to the original text.
Using a plagiarism checker yourself before you submit your work can help you spot these mistakes before they get you in trouble. Based on the results, you can add any missing citations and rephrase your text where necessary.
Try out the Scribbr Plagiarism Checker for free, or check out our detailed comparison of the best plagiarism checkers available online.
Scribbr Plagiarism Checker
Scribbr’s Citation Checker is a unique AI-powered tool that automatically detects stylistic errors and inconsistencies in your in-text citations. It also suggests a correction for every mistake.
Currently available for APA Style, this is the fastest and easiest way to make sure you’ve formatted your citations correctly. You can try out the tool for free below.
If you need extra help with your reference list, we also offer a more in-depth Citation Editing Service.
Our experts cross-check your in-text citations and reference entries, make sure you’ve included the correct information for each source, and improve the formatting of your reference page.
If you want to handle your citations yourself, Scribbr’s free Knowledge Base provides clear, accurate guidance on every aspect of citation. You can see citation examples for a variety of common source types below:
And you can check out our comprehensive guides to the most popular citation styles:
At college level, you must properly cite your sources in all essays , research papers , and other academic texts (except exams and in-class exercises).
Add a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize information or ideas from a source. You should also give full source details in a bibliography or reference list at the end of your text.
The exact format of your citations depends on which citation style you are instructed to use. The most common styles are APA , MLA , and Chicago .
The abbreviation “ et al. ” (Latin for “and others”) is used to shorten citations of sources with multiple authors.
“Et al.” is used in APA in-text citations of sources with 3+ authors, e.g. (Smith et al., 2019). It is not used in APA reference entries .
Use “et al.” for 3+ authors in MLA in-text citations and Works Cited entries.
Use “et al.” for 4+ authors in a Chicago in-text citation , and for 10+ authors in a Chicago bibliography entry.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles
- APA vs. MLA | The Key Differences in Format & Citation
- The Basics of In-Text Citation | APA & MLA Examples
More interesting articles
- Citation examples for common sources types
- Et Al. | Meaning & Use in APA, MLA & Chicago
- Hanging Indent | Word & Google Docs Instructions
- How to Cite a Book | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Journal Article | APA, MLA, & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Lecture | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Newspaper Article | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite a Website | MLA, APA & Chicago Examples
- How to Cite a Wikipedia Article | APA, MLA & Chicago
- How to Cite a YouTube Video | MLA, APA & Chicago
- How to Cite an Image | Photographs, Figures, Diagrams
- How to Cite an Interview | APA, MLA & Chicago Style
- Parenthetical Citation | APA, MLA & Chicago Examples
- What Are Endnotes? | Guide with Examples
- What Are Footnotes? | Guide with Word Instructions
- What Does Ibid. Mean? | Definition & Examples
- What is a DOI? | Finding and Using Digital Object Identifiers
- What Is an Annotated Bibliography? | Examples & Format
Scribbr APA Citation Checker
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!
Cite A Dissertation in Harvard style
Powered by chegg.
- Select style:
- Archive material
- Chapter of an edited book
- Conference proceedings
- Dictionary entry
- Dissertation
- DVD, video, or film
- E-book or PDF
- Edited book
- Encyclopedia article
- Government publication
- Music or recording
- Online image or video
- Presentation
- Press release
- Religious text
Use the following template or our Harvard Referencing Generator to cite a dissertation. For help with other source types, like books, PDFs, or websites, check out our other guides. To have your reference list or bibliography automatically made for you, try our free citation generator .
Reference list
Place this part in your bibliography or reference list at the end of your assignment.
In-text citation
Place this part right after the quote or reference to the source in your assignment.
Popular Harvard Citation Guides
- How to cite a Book in Harvard style
- How to cite a Website in Harvard style
- How to cite a Journal in Harvard style
- How to cite a DVD, video, or film in Harvard style
- How to cite a Online image or video in Harvard style
Other Harvard Citation Guides
- How to cite a Archive material in Harvard style
- How to cite a Artwork in Harvard style
- How to cite a Blog in Harvard style
- How to cite a Broadcast in Harvard style
- How to cite a Chapter of an edited book in Harvard style
- How to cite a Conference proceedings in Harvard style
- How to cite a Court case in Harvard style
- How to cite a Dictionary entry in Harvard style
- How to cite a Dissertation in Harvard style
- How to cite a E-book or PDF in Harvard style
- How to cite a Edited book in Harvard style
- How to cite a Email in Harvard style
- How to cite a Encyclopedia article in Harvard style
- How to cite a Government publication in Harvard style
- How to cite a Interview in Harvard style
- How to cite a Legislation in Harvard style
- How to cite a Magazine in Harvard style
- How to cite a Music or recording in Harvard style
- How to cite a Newspaper in Harvard style
- How to cite a Patent in Harvard style
- How to cite a Podcast in Harvard style
- How to cite a Presentation or lecture in Harvard style
- How to cite a Press release in Harvard style
- How to cite a Religious text in Harvard style
- How to cite a Report in Harvard style
- How to cite a Software in Harvard style
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Reference List: Common Reference List Examples
Article (with doi).
Alvarez, E., & Tippins, S. (2019). Socialization agents that Puerto Rican college students use to make financial decisions. Journal of Social Change , 11 (1), 75–85. https://doi.org/10.5590/JOSC.2019.11.1.07
Laplante, J. P., & Nolin, C. (2014). Consultas and socially responsible investing in Guatemala: A case study examining Maya perspectives on the Indigenous right to free, prior, and informed consent. Society & Natural Resources , 27 , 231–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941920.2013.861554
Use the DOI number for the source whenever one is available. DOI stands for "digital object identifier," a number specific to the article that can help others locate the source. In APA 7, format the DOI as a web address. Active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list. Also see our Quick Answer FAQ, "Can I use the DOI format provided by library databases?"
Jerrentrup, A., Mueller, T., Glowalla, U., Herder, M., Henrichs, N., Neubauer, A., & Schaefer, J. R. (2018). Teaching medicine with the help of “Dr. House.” PLoS ONE , 13 (3), Article e0193972. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193972
For journal articles that are assigned article numbers rather than page ranges, include the article number in place of the page range.
For more on citing electronic resources, see Electronic Sources References .
Article (Without DOI)
Found in a common academic research database or in print.
Casler , T. (2020). Improving the graduate nursing experience through support on a social media platform. MEDSURG Nursing , 29 (2), 83–87.
If an article does not have a DOI and you retrieved it from a common academic research database through the university library, there is no need to include any additional electronic retrieval information. The reference list entry looks like the entry for a print copy of the article. (This format differs from APA 6 guidelines that recommended including the URL of a journal's homepage when the DOI was not available.) Note that APA 7 has additional guidance on reference list entries for articles found only in specific databases or archives such as Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, UpToDate, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global, and university archives. See APA 7, Section 9.30 for more information.
Found on an Open Access Website
Eaton, T. V., & Akers, M. D. (2007). Whistleblowing and good governance. CPA Journal , 77 (6), 66–71. http://archives.cpajournal.com/2007/607/essentials/p58.htm
Provide the direct web address/URL to a journal article found on the open web, often on an open access journal's website. In APA 7, active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list.
Weinstein, J. A. (2010). Social change (3rd ed.). Rowman & Littlefield.
If the book has an edition number, include it in parentheses after the title of the book. If the book does not list any edition information, do not include an edition number. The edition number is not italicized.
American Nurses Association. (2015). Nursing: Scope and standards of practice (3rd ed.).
If the author and publisher are the same, only include the author in its regular place and omit the publisher.
Lencioni, P. (2012). The advantage: Why organizational health trumps everything else in business . Jossey-Bass. https://amzn.to/343XPSJ
As a change from APA 6 to APA 7, it is no longer necessary to include the ebook format in the title. However, if you listened to an audiobook and the content differs from the text version (e.g., abridged content) or your discussion highlights elements of the audiobook (e.g., narrator's performance), then note that it is an audiobook in the title element in brackets. For ebooks and online audiobooks, also include the DOI number (if available) or nondatabase URL but leave out the electronic retrieval element if the ebook was found in a common academic research database, as with journal articles. APA 7 allows for the shortening of long DOIs and URLs, as shown in this example. See APA 7, Section 9.36 for more information.
Chapter in an Edited Book
Poe, M. (2017). Reframing race in teaching writing across the curriculum. In F. Condon & V. A. Young (Eds.), Performing antiracist pedagogy in rhetoric, writing, and communication (pp. 87–105). University Press of Colorado.
Include the page numbers of the chapter in parentheses after the book title.
Christensen, L. (2001). For my people: Celebrating community through poetry. In B. Bigelow, B. Harvey, S. Karp, & L. Miller (Eds.), Rethinking our classrooms: Teaching for equity and justice (Vol. 2, pp. 16–17). Rethinking Schools.
Also include the volume number or edition number in the parenthetical information after the book title when relevant.
Freud, S. (1961). The ego and the id. In J. Strachey (Ed.), The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud (Vol. 19, pp. 3-66). Hogarth Press. (Original work published 1923)
When a text has been republished as part of an anthology collection, after the author’s name include the date of the version that was read. At the end of the entry, place the date of the original publication inside parenthesis along with the note “original work published.” For in-text citations of republished work, use both dates in the parenthetical citation, original date first with a slash separating the years, as in this example: Freud (1923/1961). For more information on reprinted or republished works, see APA 7, Sections 9.40-9.41.
Classroom Resources
Citing classroom resources.
If you need to cite content found in your online classroom, use the author (if there is one listed), the year of publication (if available), the title of the document, and the main URL of Walden classrooms. For example, you are citing study notes titled "Health Effects of Exposure to Forest Fires," but you do not know the author's name, your reference entry will look like this:
Health effects of exposure to forest fires [Lecture notes]. (2005). Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
If you do know the author of the document, your reference will look like this:
Smith, A. (2005). Health effects of exposure to forest fires [PowerPoint slides]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
A few notes on citing course materials:
- [Lecture notes]
- [Course handout]
- [Study notes]
- It can be difficult to determine authorship of classroom documents. If an author is listed on the document, use that. If the resource is clearly a product of Walden (such as the course-based videos), use Walden University as the author. If you are unsure or if no author is indicated, place the title in the author spot, as above.
- If you cannot determine a date of publication, you can use n.d. (for "no date") in place of the year.
Note: The web location for Walden course materials is not directly retrievable without a password, and therefore, following APA guidelines, use the main URL for the class sites: https://class.waldenu.edu.
Citing Tempo Classroom Resources
Clear author:
Smith, A. (2005). Health effects of exposure to forest fires [PowerPoint slides]. Walden University Brightspace. https://mytempo.waldenu.edu
Unclear author:
Health effects of exposure to forest fires [Lecture notes]. (2005). Walden University Brightspace. https://mytempo.waldenu.edu
Conference Sessions and Presentations
Feinman, Y. (2018, July 27). Alternative to proctoring in introductory statistics community college courses [Poster presentation]. Walden University Research Symposium, Minneapolis, MN, United States. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/symposium2018/23/
Torgerson, K., Parrill, J., & Haas, A. (2019, April 5-9). Tutoring strategies for online students [Conference session]. The Higher Learning Commission Annual Conference, Chicago, IL, United States. http://onlinewritingcenters.org/scholarship/torgerson-parrill-haas-2019/
Dictionary Entry
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Leadership. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary . Retrieved May 28, 2020, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/leadership
When constructing a reference for an entry in a dictionary or other reference work that has no byline (i.e., no named individual authors), use the name of the group—the institution, company, or organization—as author (e.g., Merriam Webster, American Psychological Association, etc.). The name of the entry goes in the title position, followed by "In" and the italicized name of the reference work (e.g., Merriam-Webster.com dictionary , APA dictionary of psychology ). In this instance, APA 7 recommends including a retrieval date as well for this online source since the contents of the page change over time. End the reference entry with the specific URL for the defined word.
Discussion Board Post
Osborne, C. S. (2010, June 29). Re: Environmental responsibility [Discussion post]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
Dissertations or Theses
Retrieved From a Database
Nalumango, K. (2019). Perceptions about the asylum-seeking process in the United States after 9/11 (Publication No. 13879844) [Doctoral dissertation, Walden University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
Retrieved From an Institutional or Personal Website
Evener. J. (2018). Organizational learning in libraries at for-profit colleges and universities [Doctoral dissertation, Walden University]. ScholarWorks. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=6606&context=dissertations
Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis
Kirwan, J. G. (2005). An experimental study of the effects of small-group, face-to-face facilitated dialogues on the development of self-actualization levels: A movement towards fully functional persons [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Saybrook Graduate School and Research Center.
For further examples and information, see APA 7, Section 10.6.
Legal Material
For legal references, APA follows the recommendations of The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation , so if you have any questions beyond the examples provided in APA, seek out that resource as well.
Court Decisions
Reference format:
Name v. Name, Volume Reporter Page (Court Date). URL
Sample reference entry:
Brown v. Board of Education, 347 U.S. 483 (1954). https://www.oyez.org/cases/1940-1955/347us483
Sample citation:
In Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the Supreme Court ruled racial segregation in schools unconstitutional.
Note: Italicize the case name when it appears in the text of your paper.
Name of Act, Title Source § Section Number (Year). URL
Sample reference entry for a federal statute:
Individuals With Disabilities Education Act, 20 U.S.C. § 1400 et seq. (2004). https://www.congress.gov/108/plaws/publ446/PLAW-108publ446.pdf
Sample reference entry for a state statute:
Minnesota Nurse Practice Act, Minn. Stat. §§ 148.171 et seq. (2019). https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/cite/148.171
Sample citation: Minnesota nurses must maintain current registration in order to practice (Minnesota Nurse Practice Act, 2010).
Note: The § symbol stands for "section." Use §§ for sections (plural). To find this symbol in Microsoft Word, go to "Insert" and click on Symbol." Look in the Latin 1-Supplement subset. Note: U.S.C. stands for "United States Code." Note: The Latin abbreviation " et seq. " means "and what follows" and is used when the act includes the cited section and ones that follow. Note: List the chapter first followed by the section or range of sections.
Unenacted Bills and Resolutions
(Those that did not pass and become law)
Title [if there is one], bill or resolution number, xxx Cong. (year). URL
Sample reference entry for Senate bill:
Anti-Phishing Act, S. 472, 109th Cong. (2005). https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/senate-bill/472
Sample reference entry for House of Representatives resolution:
Anti-Phishing Act, H.R. 1099, 109th Cong. (2005). https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/1099
The Anti-Phishing Act (2005) proposed up to 5 years prison time for people running Internet scams.
These are the three legal areas you may be most apt to cite in your scholarly work. For more examples and explanation, see APA 7, Chapter 11.
Magazine Article
Clay, R. (2008, June). Science vs. ideology: Psychologists fight back about the misuse of research. Monitor on Psychology , 39 (6). https://www.apa.org/monitor/2008/06/ideology
Note that for citations, include only the year: Clay (2008). For magazine articles retrieved from a common academic research database, leave out the URL. For magazine articles from an online news website that is not an online version of a print magazine, follow the format for a webpage reference list entry.
Newspaper Article (Retrieved Online)
Baker, A. (2014, May 7). Connecticut students show gains in national tests. New York Times . http://www.nytimes.com/2014/05/08/nyregion/national-assessment-of-educational-progress-results-in-Connecticut-and-New-Jersey.html
Include the full date in the format Year, Month Day. Do not include a retrieval date for periodical sources found on websites. Note that for citations, include only the year: Baker (2014). For newspaper articles retrieved from a common academic research database, leave out the URL. For newspaper articles from an online news website that is not an online version of a print newspaper, follow the format for a webpage reference list entry.
OASIS Resources
Oasis webpage.
OASIS. (n.d.). Common reference list examples . Walden University. https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/apa/references/examples
For all OASIS content, list OASIS as the author. Because OASIS webpages do not include publication dates, use “n.d.” for the year.
Interactive Guide
OASIS. (n.d.). Embrace iterative research and writing [Interactive guide]. Walden University. https://academics.waldenu.edu/oasis/iterative-research-writing-web
For OASIS multimedia resources, such as interactive guides, include a description of the resource in brackets after the title.
Online Video/Webcast
Walden University. (2013). An overview of learning [Video]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
Use this format for online videos such as Walden videos in classrooms. Most of our classroom videos are produced by Walden University, which will be listed as the author in your reference and citation. Note: Some examples of audiovisual materials in the APA manual show the word “Producer” in parentheses after the producer/author area. In consultation with the editors of the APA manual, we have determined that parenthetical is not necessary for the videos in our courses. The manual itself is unclear on the matter, however, so either approach should be accepted. Note that the speaker in the video does not appear in the reference list entry, but you may want to mention that person in your text. For instance, if you are viewing a video where Tobias Ball is the speaker, you might write the following: Tobias Ball stated that APA guidelines ensure a consistent presentation of information in student papers (Walden University, 2013). For more information on citing the speaker in a video, see our page on Common Citation Errors .
Taylor, R. [taylorphd07]. (2014, February 27). Scales of measurement [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PDsMUlexaMY
OASIS. (2020, April 15). One-way ANCOVA: Introduction [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/_XnNDQ5CNW8
For videos from streaming sites, use the person or organization who uploaded the video in the author space to ensure retrievability, whether or not that person is the speaker in the video. A username can be provided in square brackets. As a change from APA 6 to APA 7, include the publisher after the title, and do not use "Retrieved from" before the URL. See APA 7, Section 10.12 for more information and examples.
See also reference list entry formats for TED Talks .
Technical and Research Reports
Edwards, C. (2015). Lighting levels for isolated intersections: Leading to safety improvements (Report No. MnDOT 2015-05). Center for Transportation Studies. http://www.cts.umn.edu/Publications/ResearchReports/reportdetail.html?id=2402
Technical and research reports by governmental agencies and other research institutions usually follow a different publication process than scholarly, peer-reviewed journals. However, they present original research and are often useful for research papers. Sometimes, researchers refer to these types of reports as gray literature , and white papers are a type of this literature. See APA 7, Section 10.4 for more information.
Reference list entires for TED Talks follow the usual guidelines for multimedia content found online. There are two common places to find TED talks online, with slightly different reference list entry formats for each.
TED Talk on the TED website
If you find the TED Talk on the TED website, follow the format for an online video on an organizational website:
Owusu-Kesse, K. (2020, June). 5 needs that any COVID-19 response should meet [Video]. TED Conferences. https://www.ted.com/talks/kwame_owusu_kesse_5_needs_that_any_covid_19_response_should_meet
The speaker is the author in the reference list entry if the video is posted on the TED website. For citations, use the speaker's surname.
TED Talk on YouTube
If you find the TED Talk on YouTube or another streaming video website, follow the usual format for streaming video sites:
TED. (2021, February 5). The shadow pandemic of domestic violence during COVID-19 | Kemi DaSilvalbru [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PGdID_ICFII
TED is the author in the reference list entry if the video is posted on YouTube since it is the channel on which the video is posted. For citations, use TED as the author.
Walden University Course Catalog
To include the Walden course catalog in your reference list, use this format:
Walden University. (2020). 2019-2020 Walden University catalog . https://catalog.waldenu.edu/index.php
If you cite from a specific portion of the catalog in your paper, indicate the appropriate section and paragraph number in your text:
...which reflects the commitment to social change expressed in Walden University's mission statement (Walden University, 2020, Vision, Mission, and Goals section, para. 2).
And in the reference list:
Walden University. (2020). Vision, mission, and goals. In 2019-2020 Walden University catalog. https://catalog.waldenu.edu/content.php?catoid=172&navoid=59420&hl=vision&returnto=search
Vartan, S. (2018, January 30). Why vacations matter for your health . CNN. https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/why-vacations-matter/index.html
For webpages on the open web, include the author, date, webpage title, organization/site name, and URL. (There is a slight variation for online versions of print newspapers or magazines. For those sources, follow the models in the previous sections of this page.)
American Federation of Teachers. (n.d.). Community schools . http://www.aft.org/issues/schoolreform/commschools/index.cfm
If there is no specified author, then use the organization’s name as the author. In such a case, there is no need to repeat the organization's name after the title.
In APA 7, active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list.
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Common Reference List Examples
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Reference List
- Next Page: Common Military Reference List Examples
- Office of Student Disability Services

Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Dissertation | A Guide to Structure & Content
A dissertation or thesis is a long piece of academic writing based on original research, submitted as part of an undergraduate or postgraduate degree.
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter).
The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes:
- An introduction to your topic
- A literature review that surveys relevant sources
- An explanation of your methodology
- An overview of the results of your research
- A discussion of the results and their implications
- A conclusion that shows what your research has contributed
Dissertations in the humanities are often structured more like a long essay , building an argument by analysing primary and secondary sources . Instead of the standard structure outlined here, you might organise your chapters around different themes or case studies.
Other important elements of the dissertation include the title page , abstract , and reference list . If in doubt about how your dissertation should be structured, always check your department’s guidelines and consult with your supervisor.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Acknowledgements, table of contents, list of figures and tables, list of abbreviations, introduction, literature review / theoretical framework, methodology, reference list.
The very first page of your document contains your dissertation’s title, your name, department, institution, degree program, and submission date. Sometimes it also includes your student number, your supervisor’s name, and the university’s logo. Many programs have strict requirements for formatting the dissertation title page .
The title page is often used as cover when printing and binding your dissertation .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
The acknowledgements section is usually optional, and gives space for you to thank everyone who helped you in writing your dissertation. This might include your supervisors, participants in your research, and friends or family who supported you.
The abstract is a short summary of your dissertation, usually about 150-300 words long. You should write it at the very end, when you’ve completed the rest of the dissertation. In the abstract, make sure to:
- State the main topic and aims of your research
- Describe the methods you used
- Summarise the main results
- State your conclusions
Although the abstract is very short, it’s the first part (and sometimes the only part) of your dissertation that people will read, so it’s important that you get it right. If you’re struggling to write a strong abstract, read our guide on how to write an abstract .
In the table of contents, list all of your chapters and subheadings and their page numbers. The dissertation contents page gives the reader an overview of your structure and helps easily navigate the document.
All parts of your dissertation should be included in the table of contents, including the appendices. You can generate a table of contents automatically in Word.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
If you have used a lot of tables and figures in your dissertation, you should itemise them in a numbered list . You can automatically generate this list using the Insert Caption feature in Word.
If you have used a lot of abbreviations in your dissertation, you can include them in an alphabetised list of abbreviations so that the reader can easily look up their meanings.
If you have used a lot of highly specialised terms that will not be familiar to your reader, it might be a good idea to include a glossary . List the terms alphabetically and explain each term with a brief description or definition.
In the introduction, you set up your dissertation’s topic, purpose, and relevance, and tell the reader what to expect in the rest of the dissertation. The introduction should:
- Establish your research topic , giving necessary background information to contextualise your work
- Narrow down the focus and define the scope of the research
- Discuss the state of existing research on the topic, showing your work’s relevance to a broader problem or debate
- Clearly state your objectives and research questions , and indicate how you will answer them
- Give an overview of your dissertation’s structure
Everything in the introduction should be clear, engaging, and relevant to your research. By the end, the reader should understand the what , why and how of your research. Not sure how? Read our guide on how to write a dissertation introduction .
Before you start on your research, you should have conducted a literature review to gain a thorough understanding of the academic work that already exists on your topic. This means:
- Collecting sources (e.g. books and journal articles) and selecting the most relevant ones
- Critically evaluating and analysing each source
- Drawing connections between them (e.g. themes, patterns, conflicts, gaps) to make an overall point
In the dissertation literature review chapter or section, you shouldn’t just summarise existing studies, but develop a coherent structure and argument that leads to a clear basis or justification for your own research. For example, it might aim to show how your research:
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Takes a new theoretical or methodological approach to the topic
- Proposes a solution to an unresolved problem
- Advances a theoretical debate
- Builds on and strengthens existing knowledge with new data
The literature review often becomes the basis for a theoretical framework , in which you define and analyse the key theories, concepts and models that frame your research. In this section you can answer descriptive research questions about the relationship between concepts or variables.
The methodology chapter or section describes how you conducted your research, allowing your reader to assess its validity. You should generally include:
- The overall approach and type of research (e.g. qualitative, quantitative, experimental, ethnographic)
- Your methods of collecting data (e.g. interviews, surveys, archives)
- Details of where, when, and with whom the research took place
- Your methods of analysing data (e.g. statistical analysis, discourse analysis)
- Tools and materials you used (e.g. computer programs, lab equipment)
- A discussion of any obstacles you faced in conducting the research and how you overcame them
- An evaluation or justification of your methods
Your aim in the methodology is to accurately report what you did, as well as convincing the reader that this was the best approach to answering your research questions or objectives.
Next, you report the results of your research . You can structure this section around sub-questions, hypotheses, or topics. Only report results that are relevant to your objectives and research questions. In some disciplines, the results section is strictly separated from the discussion, while in others the two are combined.
For example, for qualitative methods like in-depth interviews, the presentation of the data will often be woven together with discussion and analysis, while in quantitative and experimental research, the results should be presented separately before you discuss their meaning. If you’re unsure, consult with your supervisor and look at sample dissertations to find out the best structure for your research.
In the results section it can often be helpful to include tables, graphs and charts. Think carefully about how best to present your data, and don’t include tables or figures that just repeat what you have written – they should provide extra information or usefully visualise the results in a way that adds value to your text.
Full versions of your data (such as interview transcripts) can be included as an appendix .
The discussion is where you explore the meaning and implications of your results in relation to your research questions. Here you should interpret the results in detail, discussing whether they met your expectations and how well they fit with the framework that you built in earlier chapters. If any of the results were unexpected, offer explanations for why this might be. It’s a good idea to consider alternative interpretations of your data and discuss any limitations that might have influenced the results.
The discussion should reference other scholarly work to show how your results fit with existing knowledge. You can also make recommendations for future research or practical action.
The dissertation conclusion should concisely answer the main research question, leaving the reader with a clear understanding of your central argument. Wrap up your dissertation with a final reflection on what you did and how you did it. The conclusion often also includes recommendations for research or practice.
In this section, it’s important to show how your findings contribute to knowledge in the field and why your research matters. What have you added to what was already known?
You must include full details of all sources that you have cited in a reference list (sometimes also called a works cited list or bibliography). It’s important to follow a consistent reference style . Each style has strict and specific requirements for how to format your sources in the reference list.
The most common styles used in UK universities are Harvard referencing and Vancouver referencing . Your department will often specify which referencing style you should use – for example, psychology students tend to use APA style , humanities students often use MHRA , and law students always use OSCOLA . M ake sure to check the requirements, and ask your supervisor if you’re unsure.
To save time creating the reference list and make sure your citations are correctly and consistently formatted, you can use our free APA Citation Generator .
Your dissertation itself should contain only essential information that directly contributes to answering your research question. Documents you have used that do not fit into the main body of your dissertation (such as interview transcripts, survey questions or tables with full figures) can be added as appendices .
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked.
- What Is a Dissertation? | 5 Essential Questions to Get Started
- What is a Literature Review? | Guide, Template, & Examples
- How to Write a Dissertation Proposal | A Step-by-Step Guide
More interesting articles
- Checklist: Writing a dissertation
- Dissertation & Thesis Outline | Example & Free Templates
- Dissertation binding and printing
- Dissertation Table of Contents in Word | Instructions & Examples
- Dissertation title page
- Example Theoretical Framework of a Dissertation or Thesis
- Figure & Table Lists | Word Instructions, Template & Examples
- How to Choose a Dissertation Topic | 8 Steps to Follow
- How to Write a Discussion Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Conclusion
- How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
- List of Abbreviations | Example, Template & Best Practices
- Operationalisation | A Guide with Examples, Pros & Cons
- Prize-Winning Thesis and Dissertation Examples
- Relevance of Your Dissertation Topic | Criteria & Tips
- Research Paper Appendix | Example & Templates
- Thesis & Dissertation Acknowledgements | Tips & Examples
- Thesis & Dissertation Database Examples
- What is a Dissertation Preface? | Definition & Examples
- What is a Glossary? | Definition, Templates, & Examples
- What Is a Research Methodology? | Steps & Tips
- What is a Theoretical Framework? | A Step-by-Step Guide
- What Is a Thesis? | Ultimate Guide & Examples
- How it works

How to Write a Dissertation Dedication – Types & Examples
Published by Alvin Nicolas at August 30th, 2024 , Revised On September 2, 2024
Imagine you’re writing a research paper, a thesis, or a dissertation. You instantly feel that you should thank those people in your life who are not even helping you in your writing process, but who you are pleased and honoured to have in life. This is when you would consider writing a dedication dissertation. It helps you to thank and show love to the people you value and cherish in your life.
Moreover, dedication also allows the person to add personal and emotional value to their esteemed work. It significantly impacts the motivation and inspiration of the person to work hard and achieve their goals efficiently. A dedication at the start of the dissertation significantly also adds to the appeal of the dissertation and makes the readers think about the writer’s generosity and ingenuity.
This blog comprehensively discusses what a dissertation dedication is, dedication dissertation examples, and the effective steps to write one. You can write a dissertation dedication efficiently by understanding all these important steps.
What is Dissertation Dedication?
A dissertation dedication is a line, paragraph, or page at the start of a master’s or PhD thesis or dissertation. It is a personal type of acknowledgement and appreciation to the people in the writer’s life who provided him with sufficient motivation and inspiration to keep up with his dissertation.
By adding a dedication section to their book, writers show their love and obligation to those who supported them and cheered them up during their work. This makes them not just academic geniuses but also emotionally vulnerable and generous people.
Moreover, when dedicatees read their names and the love writer shows them in the dissertation, they feel pleased and honoured. It also provides them with the fulfilling sensation that their support and prayers have led to a beneficial fruit of success.
- I dedicate this book to my wife…
- I dedicate this project to my supervisor….
Dissertation Dedication and Poem
Dedication in a dissertation does not always have to be a line or a paragraph; it can also be a poem. Sometimes, writers add a poem to dedicate their dissertation to anyone. They can write the poem themselves in their own words or select a line or two from famous poems by reputable poets and writers.
Adding a poem in the dedication section shows not only the writer’s emotional vulnerability and softness but also their creativity and devotion to literacy pieces.
Can You Dedicate Your Dissertation to Someone?
Yes, you can dedicate your dissertation to anyone by naming them and appreciating their presence in your life and by your side. There are many amazing ways that you can dedicate your dissertation to someone. Whether you want to dedicate your dissertation to your parents, colleagues, classmates, teachers, or husband, you can effortlessly add their names and the part they played in your life.
This blog brings you different types of dedication you can add to your dissertation.
Types of Dissertation Dedication
Here are the types of dissertation dedication given in the following:
Dedication to Family
Dedication to the family is added under the dedication when writers want to appreciate and cherish the presence of their parents, siblings, and cousin.
- I would like to dedicate this dissertation to my parents [names], who were there when no one was.
- I dedicate my dissertation to my sister [name], who supported me through thick and thin.
Dedication to Friends
Sometimes, writers want to thank and dedicate their work to their friends who supported them and helped them through thick and thin.
I dedicate my dissertation to my best friend [name], who stood up for me during the process.
Dedication to Special Person
Dedication to a special person or loved one can also be added to the dissertation to show love and dedication to that person.
I would like to dedicate this dissertation to my girlfriend [name], who supported me at my lowest.
Dedication to Mentor or Advisor
Students also tend to dedicate their theses or dissertations to their mentors and advisors, who advised them and helped them address issues promptly.
I dedicate my dissertation to my advisor [name], who advised me and helped me make this successful.
Dedication to Colleagues or Peers
When writers complete their dissertations with the assistance of their colleagues and peers, they also tend to dedicate their projects to them.
I dedicate my dissertation to my colleague and good friend [name], without whose support this would never have been completed.
Dedication to Institution
Being and working in a particular institution also compels the writers to dedicate their dissertations to that institution.
I dedicate this dissertation to this amazing institution [name] that made me feel at home, nurtured me, and sprouted this seed.
Dedication to Additional People
Sometimes writers give dedication to those additional people who were there around them during work who maybe haven’t cheered them up but their presence meant a lot.
I would also like to dedicate this dissertation to [name1] and [name2]…. Whose presence meant a lot to me.
Dedication to the Deceased One
If a loved one has recently or in the past died, the writers also tend to dedicate their dissertation to that person.
I dedicate this dissertation to my grandmother [name], who is not with us but is always with us in our memories.
Dedication to the Almighty
Dedication to the Almighty allows the writers to be thankful to God and divine forces that help them and remove any hurdles from their lives.
To the God Almighty, who is most beneficial and most merciful, who blessed me with the power to fulfil this task.
Dedication to Inspirational Personality
Sometimes writers also dedicate their dissertations to inspirational personalities who inspired them by adding their famous quotes to the dedication.
I dedicate my dissertation to Martin Luther King whose endurance and patience brought the emancipation of the Black.
Dedication Vs. Acknowledgements in Dissertation
Here is the difference between dedication and acknowledgement in a dissertation:
| Dedication | Acknowledgement |
|---|---|
| Dedication is the writer’s personal acknowledgement and appreciation for the people he values in life. | Acknowledgement is the recognition and appreciation of those people who supported the writer in completing his dissertation. |
| It contains appreciation for family, friends, colleagues, and special people. | It contains thanks to the members, advisors, and individuals who helped complete the dissertation. |
| It has an emotional and personal value. | It has a professional value. |
| It comes before the acknowledgement. | It comes after the dedication. |
How to Write a Dedication for a Dissertation?
Here are the steps that will significantly help you to write your dissertation dedication efficiently:
Step 1: Choose the Person You Want To Dedicate To
The first step to writing a dissertation dedication is to choose the people you want to dedicate to. This could be your family, friend, colleague, or personal mentor. Remember to think about who was there for you during your writing process. Make a list of people if you want to add multiple dedicatees.
Step 2: Describe the Person
The second step of writing a dissertation syndication is describing the person that you have chosen to give dedication to. You should describe the relation that you have with that person and what he/she did to make your dissertation successful.
Step 3: Name the Person
After describing the person, name the person you chose to dedicate your dissertation. Naming the person will let readers know about the identity of the dedicatees, no matter if they have met them or not.
Step 4: Keep the Tone Honest and Sincere
It is also important to be honest and sincere while writing the dedication for your dissertation. The people who were there for you, who supported you through everything deserve to be cheered and appreciated in the most sincere and loving way possible.
Step 5: Maintain the Order for Multiple Personnel
When you have chosen multiple personnel to dedicate your life to, it is essential to appreciate their order according to their relation to and association with you. The person who is closer comes at the start. This also lets the readers know whose presence you cherish the most.
Step 6: Maintain the Length
It is essential to maintain the length of the dedication. Avoid overwriting and over-explaining in the deviation. It will unexpectedly lose the interest of readers to read the extensive paragraph of appreciation for someone. Write in a length that makes a powerful impact.
Step 7: Review, Revise, and Finalise
When you have successfully written the dedication for someone you chose to dedicate to your dissertation, it’s time to review it. Review to identify any mistakes and ensure the appropriate use of words. After making the necessary changes, finalise it.
Dissertation dedication Sample
Here is a sample of the dissertation dedication:
|
|
Dedication Dissertation Examples
These are the examples of dissertation dedication that can significantly help you write an amazing dedication your dissertation:
|
I dedicate this dissertation to my beloved family. I love you all too much. I especially thank and appreciate my parents, Martha and George Johansson, who supported me in this course and made me believe that I dream well and I can achieve well. Their spiritual and mental strength helped me and guided me through everything. I also thank my sister Kloe, who always made me believe that I am enough. I just have to believe in myself, and everything will come my way. I also dedicate this dissertation to my best friend Josh, who was always there for me when no one was, who taught me how to swim through deeper waters and how to stand when you have no strength left in your limbs. I also dedicate this dissertation to my therapist, Mr.Henry Neilson, who was always there through thick and thin. He made me realise that ups and downs are inevitable in life. You have to accept both sides in order to make peace with yourself and with the world. Finally, I dedicate this dissertation to God Almighty, who granted me all my strengths and weaknesses, all sickness and health, and all happiness and sorrow. |
|
I dedicate this dissertation to my parents, Henry Alwyn and Taylor Hathaway, who were always there for me every step of the way. Their advice of resilience and hard work made me believe I can do and achieve everything in my life if I am determined and believe in myself. To my brother Abernathy, who always made me laugh with his silly jokes and made me realise that whatever happens in life, the most powerful move that you can make is to smile. I also dedicate this dissertation to my talented sister Catherine, who taught me that creativity is within you; you just have to pull it out by using her exquisite textile designs. I also dedicate this dissertation to my best friend and colleague, Elijah Benjamin, who embodies true devotion and love for his work. He believed perfection is not about controlling something; it’s about letting go. Last but not least, to my girlfriend Emily, who was there to love me, pamper me, and provide her gentle touch and warmth. I love you, darling. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can i dedicate my dissertation to someone.
Yes, you can dedicate your dissertation to someone by naming and describing their part in supporting and completing your research process .
How to write a dedication for a dissertation?
- Choose the Person
- Describe the Person
- Name the Person
How much time should I dedicate to the dissertation?
You should dedicate 300-400 hours to a dissertation
You May Also Like
When writing your dissertation, an abstract serves as a deal maker or breaker. It can either motivate your readers to continue reading or discourage them.
Do dissertations scare you? Struggling with writing a flawless dissertation? Well, congratulations, you have landed in the perfect place. In this blog, we will take you through the detailed process of writing a dissertation. Sounds fun? We thought so!
USEFUL LINKS
LEARNING RESOURCES

COMPANY DETAILS

- How It Works

Online Students
For All Online Programs
International Students
On Campus, need or have Visa
Campus Students
For All Campus Programs
What a Thesis Paper is and How to Write One

From choosing a topic and conducting research to crafting a strong argument, writing a thesis paper can be a rewarding experience.
It can also be a challenging experience. If you've never written a thesis paper before, you may not know where to start. You may not even be sure exactly what a thesis paper is. But don't worry; the right support and resources can help you navigate this writing process.
What is a Thesis Paper?

A thesis paper is a type of academic essay that you might write as a graduation requirement for certain bachelor's, master's or honors programs. Thesis papers present your own original research or analysis on a specific topic related to your field.
“In some ways, a thesis paper can look a lot like a novella,” said Shana Chartier , director of information literacy at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU). “It’s too short to be a full-length novel, but with the standard size of 40-60 pages (for a bachelor’s) and 60-100 pages (for a master’s), it is a robust exploration of a topic, explaining one’s understanding of a topic based on personal research.”
Chartier has worked in academia for over 13 years and at SNHU for nearly eight. In her role as an instructor and director, Chartier has helped to guide students through the writing process, like editing and providing resources.
Chartier has written and published academic papers such as "Augmented Reality Gamifies the Library: A Ride Through the Technological Frontier" and "Going Beyond the One-Shot: Spiraling Information Literacy Across Four Years." Both of these academic papers required Chartier to have hands-on experience with the subject matter. Like a thesis paper, they also involved hypothesizing and doing original research to come to a conclusion.
“When writing a thesis paper, the importance of staying organized cannot be overstated,” said Chartier. “Mapping out each step of the way, making firm and soft deadlines... and having other pairs of eyes on your work to ensure academic accuracy and clean editing are crucial to writing a successful paper.”
How Do I Choose a Topic For My Thesis Paper?

What your thesis paper is for will determine some of the specific requirements and steps you might take, but the first step is usually the same: Choosing a topic.
“Choosing a topic can be daunting," said Rochelle Attari , a peer tutor at SNHU. "But if (you) stick with a subject (you're) interested in... choosing a topic is much more manageable.”
Similar to a thesis, Attari recently finished the capstone for her bachelor’s in psychology . Her bachelor’s concentration is in forensics, and her capstone focused on the topic of using a combined therapy model for inmates who experience substance abuse issues to reduce recidivism.
“The hardest part was deciding what I wanted to focus on,” Attari said. “But once I nailed down my topic, each milestone was more straightforward.”
In her own writing experience, Attari said brainstorming was an important step when choosing her topic. She recommends writing down different ideas on a piece of paper and doing some preliminary research on what’s already been written on your topic.
By doing this exercise, you can narrow or broaden your ideas until you’ve found a topic you’re excited about. " Brainstorming is essential when writing a paper and is not a last-minute activity,” Attari said.
How Do I Structure My Thesis Paper?
Thesis papers tend to have a standard format with common sections as the building blocks.
While the structure Attari describes below will work for many theses, it’s important to double-check with your program to see if there are any specific requirements. Writing a thesis for a Master of Fine Arts, for example, might actually look more like a fiction novel.
According to Attari, a thesis paper is often structured with the following major sections:
Introduction
- Literature review
- Methods, results
Now, let’s take a closer look at what each different section should include.
Your introduction is your opportunity to present the topic of your thesis paper. In this section, you can explain why that topic is important. The introduction is also the place to include your thesis statement, which shows your stance in the paper.
Attari said that writing an introduction can be tricky, especially when you're trying to capture your reader’s attention and state your argument.
“I have found that starting with a statement of truth about a topic that pertains to an issue I am writing about typically does the trick,” Attari said. She demonstrated this advice in an example introduction she wrote for a paper on the effects of daylight in Alaska:
In the continental United States, we can always count on the sun rising and setting around the same time each day, but in Alaska, during certain times of the year, the sun rises and does not set for weeks. Research has shown that the sun provides vitamin D and is an essential part of our health, but little is known about how daylight twenty-four hours a day affects the circadian rhythm and sleep.
In the example Attari wrote, she introduces the topic and informs the reader what the paper will cover. Somewhere in her intro, she said she would also include her thesis statement, which might be:
Twenty-four hours of daylight over an extended period does not affect sleep patterns in humans and is not the cause of daytime fatigue in northern Alaska .
Literature Review
In the literature review, you'll look at what information is already out there about your topic. “This is where scholarly articles about your topic are essential,” said Attari. “These articles will help you find the gap in research that you have identified and will also support your thesis statement."
Telling your reader what research has already been done will help them see how your research fits into the larger conversation. Most university libraries offer databases of scholarly/peer-reviewed articles that can be helpful in your search.
In the methods section of your thesis paper, you get to explain how you learned what you learned. This might include what experiment you conducted as a part of your independent research.
“For instance,” Attari said, “if you are a psychology major and have identified a gap in research on which therapies are effective for anxiety, your methods section would consist of the number of participants, the type of experiment and any other particulars you would use for that experiment.”
In this section, you'll explain the results of your study. For example, building on the psychology example Attari outlined, you might share self-reported anxiety levels for participants trying different kinds of therapies. To help you communicate your results clearly, you might include data, charts, tables or other visualizations.
The discussion section of your thesis paper is where you will analyze and interpret the results you presented in the previous section. This is where you can discuss what your findings really mean or compare them to the research you found in your literature review.
The discussion section is your chance to show why the data you collected matters and how it fits into bigger conversations in your field.
The conclusion of your thesis paper is your opportunity to sum up your argument and leave your reader thinking about why your research matters.
Attari breaks the conclusion down into simple parts. “You restate the original issue and thesis statement, explain the experiment's results and discuss possible next steps for further research,” she said.
Find Your Program
Resources to help write your thesis paper.
While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn’t have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier.
If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
- Citation Handbooks: An online citation guide or handbook can help you ensure your citations are correct. APA , MLA and Chicago styles have all published their own guides.
- Citation Generators: There are many citation generator tools that help you to create citations. Some — like RefWorks — even let you directly import citations from library databases as you research.
- Your Library's Website: Many academic and public libraries allow patrons to access resources like databases or FAQs. Some FAQs at the SNHU library that might be helpful in your thesis writing process include “ How do I read a scholarly article? ” or “ What is a research question and how do I develop one? ”
It can also be helpful to check out what coaching or tutoring options are available through your school. At SNHU, for example, the Academic Support Center offers writing and grammar workshops , and students can access 24/7 tutoring and 1:1 sessions with peer tutors, like Attari.
"Students can even submit their papers and receive written feedback... like revisions and editing suggestions," she said.
If you are writing a thesis paper, there are many resources available to you. It's a long paper, but with the right mindset and support, you can successfully navigate the process.
“Pace yourself,” said Chartier. “This is a marathon, not a sprint. Setting smaller goals to get to the big finish line can make the process seem less daunting, and remember to be proud of yourself and celebrate your accomplishment once you’re done. Writing a thesis is no small task, and it’s important work for the scholarly community.”
A degree can change your life. Choose your program from 200+ SNHU degrees that can take you where you want to go.
Meg Palmer ’18 is a writer and scholar by trade who loves reading, riding her bike and singing in a barbershop quartet. She earned her bachelor’s degree in English, language and literature at Southern New Hampshire University (SNHU) and her master’s degree in writing, rhetoric and discourse at DePaul University (’20). While attending SNHU, she served as the editor-in-chief of the campus student newspaper, The Penmen Press, where she deepened her passion for writing. Meg is an adjunct professor at Johnson and Wales University, where she teaches first year writing, honors composition, and public speaking. Connect with her on LinkedIn .
Explore more content like this article

What is the Difference Between Bachelor’s and Master’s Degrees?

Academic Referencing: How to Cite a Research Paper

What is Considered Plagiarism And How to Avoid It
About southern new hampshire university.

SNHU is a nonprofit, accredited university with a mission to make high-quality education more accessible and affordable for everyone.
Founded in 1932, and online since 1995, we’ve helped countless students reach their goals with flexible, career-focused programs . Our 300-acre campus in Manchester, NH is home to over 3,000 students, and we serve over 135,000 students online. Visit our about SNHU page to learn more about our mission, accreditations, leadership team, national recognitions and awards.

- Otis College of Art and Design
- Otis College LibGuides
- Millard Sheets Library
Theories and Trends in Contemporary Art, Media, and Culture
- Reference Materials
- Research Strategies This link opens in a new window
Crafting Your Thesis Statement
References for rhetoric and the art of writing, the importance of editing and drafting.
- Grammarly for Education
A good paper includes a clear and concise thesis statement. Your thesis statement should come towards the beginning of your paper, ideally within the first paragraph of your introduction.
To craft a strong thesis statement, you will need to articulate:
- a claim related to this topic;
- reasoning supporting your claim.
Your topic and claim should have specificity. Beware of having too narrow or broad of a topic; if it is too narrow, this will make it difficult to find relevant sources to construct your argument, and if it's broad, this will make it difficult to cover all aspects of the topic in enough depth.
Rhetoric (or the art of communicating effectively) is a critical component of good writing. This involves elements like sentence structure (syntax), vocabulary, grammar, and organization or arrangement of the ideas and concepts included in your paper.
The sources featured below focus on the topic of rhetoric or writing more broadly:

Revising and editing your writing will make it better. Aim to give yourself enough time to step away from your project and return with a fresh perspective, as this can make any errors or strange phrasings more readily apparent.
Drafting is an important part of good writing. Like any kind of art and design making, no one is really satisfied with their first attempt. Everyone wants good feedback, suggestions for improvement, glaring errors or omissions pointed out. The same is true for writing. Good writers are not born, they are the result of practice, drafting and feedback. Getting feedback on your drafts will definitely improve the quality of your written communication, critical thinking, and information literacy.
While it is useful and important to re-read your own work, we also have tools and resources geared towards helping you learn to improve your writing. For more, see below:

- << Previous: Research Strategies
- Next: Citations >>
- Last Updated: Sep 4, 2024 12:18 PM
- URL: https://otis.libguides.com/theories-trends-contemporary
Otis College of Art and Design | 9045 Lincoln Blvd. Los Angeles, CA 90045 | MyOtis
Millard Sheets Library | MyOtis | 310-665-6930 | Ask a Librarian
How to Write First Class Honours on CV: A Guide
If you’ve achieved a first class honours CV, you’ll want to showcase it on your CV. Gaining the highest possible grade for your undergraduate degree is no mean feat, and in a competitive job market it can help set you apart from the average candidate. In this article, we discuss how to write first class honours on your CV, with tips and examples to highlight your educational achievements for maximum impact.
Writing First Class Honours on Your CV
The best way to write your degree on your CV depends on the stage of your career and how important qualifications are to the roles you’re applying for. For junior, entry-level and graduate positions, the outcome of your degree will carry more weight than roles later in your career, after you’ve established a body of relevant work experience. As such, if you have a first class honours degree, you’ll really want to draw attention to it early in your career.
Formatting Your Degree Entry
The key to listing your first class honours degree on your CV is clarity and formatting. Follow a clear, organised structure to the education on your CV so the reader can quickly and easily understand your degree, specialisms and performance. Take a look at the CV examples below for guidance on how to structure your degree listing:
[Degree type], [Degree name], (Degree class), [Institution name], [Graduation date or dates of study]
- [Bullet points highlighting specialist areas of study, awards or societies you were a member of]
BSc (Hons) Business and Management (First Class Honours), University of Kent, Canterbury, September 2019 – July 2022
- Specialised in business accounting and data analysis
- Awarded Linda Davidson Prize for Best Dissertation for my study ‘Harnessing Big Data Analytics for Strategic Decision-Making in Business Management’
Using Correct Degree Abbreviations
When writing your degree in your education section, first specify the type of degree using standardised abbreviations. Some of the most common degree abbreviations are:
- BA for Bachelor of Arts
- BSc for Bachelor of Science
- MA for Master of Arts
- MSc for Master of Science
- MBA for Master of Business Administration
- PhD for Doctor of Philosophy
If your degree was an Honours degree, remember also to include this by adding ‘(Hons)’ beside your degree abbreviation. Honours degrees are typically a higher level of qualification than standard degrees, so it definitely adds value to your applications.
Using the Correct Format for ‘First Class Honours’
For clarity, and to avoid confusion, reference your degree grade in full as ‘First Class Honours’. This makes it stand out to employers reading your CV. If preferred, you could use a hyphen and list your degree as ‘First-Class Honours’.
Other ways to write your degree level include ‘First’ or ‘1st’. You might choose to use these if you’re short on space in your CV, but it’s usually better to write your grade out in full so it grabs the attention of the reader.
Another consideration is whether to include your overall degree score in your CV. Degrees are scored out of 100, with scores of 70 and above earning a first class degree. However, if you scored closer to 100 than 70, you might wish to mention this as it can help to set you apart even further from other strong candidates.
Including Academic Achievements on Your CV
Listing your academic achievements on your CV are one of the best ways you can prove you’re a suitable candidate for the job. Combined with your work experience, skills and career achievements, academic achievements can help showcase the necessary credentials to get you through to the interview stage.
The significance of academic achievements on your CV will depend on various factors. One of these is your career stage. If you’re a recent graduate or you’re applying for a first major role, academic achievements tend to take on more significance. This is because you’ll have limited work experience to prove yourself to employers. Equally, if you’re writing an academic CV for postgraduate studies or a role within a university, your degree is likely to take centre stage.
Another variable in the significance of academic achievements on your CV is the type of role you’re applying for. Some jobs might have a degree grade threshold, such as upper second class honours (2:1) or first class honours (1st). In these circumstances, it’s essential to add your degree grade to your application.
In addition, there are plenty of professions that require a specific type of degree or professional qualification to be eligible for the role. In these cases, your CV education section takes on greater importance. Whether the requirement is for a degree in a certain subject, or a professional qualification such as a Legal Practice Course or, for accountancy, the ACA, make sure you draw attention to these on your CV.
Using Academic Achievements to Your Advantage
Whether your academic achievements include a first class honours degree, an award or some other indicator of high achievement, such as a scholarship or fellowship, it can be powerful to include them on your CV. First class degrees indicate a level of dedication, intelligence and mastery of your subject area, as well as showing employers that you have a strong work ethic.
You can use other types of academic achievement to create a point of difference between yourself and other candidates. This could be particularly strong grades in certain subjects or modules of your degree, or winning awards for dissertations or other projects. Whether you received a first class degree or excelled in some other area of your studies, it’s important to make the most of it in your CV.
Other Places to Reference Your Degree on Your CV
While the most common and obvious place to mention your first class degree on your CV is the education section, this needn’t be the only place you mention it. If your degree is of particular importance to the job you’re applying for, you may reference it in your CV summary. You could even reference your degree in your cover letter . Just choose a cover letter template that gives you the chance to add details about your degree and other achievements.
Special Cases for Listing Your Degree on Your CV
There are certain special cases where you might need to treat the listing of your degree differently on your CV. If you’re still studying and you’re applying for jobs, your university student CV will either need to include a provisional grade, or simply state that your degree is ‘ongoing’. Nevertheless, it’s still worth mentioning the degree you’re studying towards. If you’re a student applying for further studies, your college student cover letter and personal statement are the ideal place to mention your degree, in addition to your CV.
Another special case for listing your first class degree is if the role requires foreign language skills , and your degree is in the required foreign language. In this case, you could mention your languages degree as early as your CV header, among your personal information. Alternatively, you could mention it in the additional information section, under languages.
If you studied towards a degree but never completed it, you may still wish to mention the studies you undertook, if they’re particularly relevant to the job. Mentioning an incomplete degree can help you avoid gaps in your CV. In this case, list your degree in the same way as you would a complete course, but instead of listing your grade, add ‘(incomplete)’. In the bullet points underneath this entry, or in your cover letter, you could reference your reasons for not completing the course, along with any relevant modules you completed.
Expert Tip:
Mentioning your first class honours degree can help you to gain an advantage with your applications. As well as listing your grades, include modules and specialist subjects that you excelled in during your studies, so employers can gain a strong understanding of your academic skills and achievements.
Common Mistakes To Avoid with Adding Your Degree to Your CV
Avoid making these common mistakes to ensure your degree makes the best possible impact on your CV:
- Over-emphasising your degree: a first class honours degree is a major achievement, but on its own it probably won’t be enough to get you the job. Make sure you dedicate enough attention to other valuable experience and skills.
- Using overly complex degree abbreviations: if your degree has an unusual abbreviation, it might be best to leave it out to avoid confusing the reader.
- Using inconsistent formatting: make sure the presentation and formatting of your education section is consistent. Capitalise ‘First Class Honours’ and other degree grades and use bullet points to add detail about your studies.
"Combined with your work experience, skills and career achievements, academic achievements can help showcase the necessary credentials to get you through to the interview stage."
Key Takeaways for Adding First Class Honours to Your CV
Understanding how to list your first class honours degree on your CV can help you to effectively communicate your academic achievement to employers. This can make the difference for various jobs, especially when the field of applicants is particularly competitive. Jobseeker offers CV templates that showcase your skills, experience and qualifications with clean, professional designs. Sign up today to access a wealth of tools and CV articles . You can also find cover letter articles to help you draft this important part of your applications.
Get ahead of the competition
Make your job applications stand-out from other candidates.

The Layout of Your CV

Tips for Creating a CV in Word

Showing Teamwork Skills on Your CV: A Guide
We Trust in Human Precision
20,000+ Professional Language Experts Ready to Help. Expertise in a variety of Niches.
API Solutions
- API Pricing
- Cost estimate
- Customer loyalty program
- Educational Discount
- Non-Profit Discount
- Green Initiative Discount1
Value-Driven Pricing
Unmatched expertise at affordable rates tailored for your needs. Our services empower you to boost your productivity.
- Special Discounts
- Enterprise transcription solutions
- Enterprise translation solutions
- Transcription/Caption API
- AI Transcription Proofreading API
Trusted by Global Leaders
GoTranscript is the chosen service for top media organizations, universities, and Fortune 50 companies.
GoTranscript
One of the Largest Online Transcription and Translation Agencies in the World. Founded in 2005.
Speaker 1: Writing your thesis used to be this really lonely academic process where you sit in a library or wherever you want to be and you're just like, oh, oh, what am I writing? Oh, this is so sad, am I writing that the right way? But now with AI tools, it's become easier than ever to keep that creative juice flowing and use it as like a research assistant as you're writing. This is what I would do. The first thing I'd like to do is head over to ChatGPT or you could even use Perplexity or whatever sort of like large language model you like. But this is why I use ChatGPT is because if I'm undertaking a large project, I'm going up here and I'm clicking on Customize ChatGPT and it's this dialog box that is really, really useful because here you can add custom instructions. So here it says, what would you like ChatGPT to know about you to provide better responses? And they've got some thought starters there. So if you're starting a big research project like writing your thesis, writing a dissertation, you should actually go in and change how you want GPT to interact with you. So where are you based? That's not super important. What do you do for work? Now that's very, very important. What you do for work at the moment is you are a thesis writer. You need to be that specific to make sure that it gets all of the information in a useful format for you. And then you've got what are your hobbies and interests? Not super useful. And then what subjects can you talk about for hours? What are some goals you have? So here you just need to talk about the fact that you're writing a thesis, that you need help writing that thesis by bouncing off ideas and sort of like correcting any academic writing, that sort of stuff. And then down here, how would you like ChatGPT to respond? How formal or casual should ChatGPT? Now this is super powerful. You can say, I want it to be academically focused. I want academic language that is suitable for a thesis or dissertation. How long or short should they be? You want longer responses if you're writing your thesis or dissertation, because then it will give you more to work with, more to think about, more to add, more to subtract, more to edit. That's the stuff you really want. How should you be addressed? It doesn't matter. Should ChatGPT have opinions on topics or remain neutral? You don't want any opinions. You want to stick to fact-based stuff. So you can say in there, stick to facts. Stick to scientific data. Do not give me opinions on anything that you think about this writing. That sort of stuff should all be included in your customized ChatGPT option, and I haven't seen this anywhere else other than ChatGPT, which is why it is my go-to at the moment. So this is the sort of stuff you can do. So make this paragraph sound more academic. Now as you're writing, when I was writing my thesis, this one, where is it? Look at this. I would sit there for hours thinking about how to look the best way to write this, and I would get stuck in my own mind, ruminating over the same sentences. Here, now you can use ChatGPT as that kind of writing assistant. So make this paragraph sound more academic, and then I post it in the paragraph, and it's given me an option. Figure X illustrates the morphology of silver nanowire only and silver nanowire carbon nanotube, nanocomposite films, blah, blah, blah. And so I obviously had to come up with the first draft. The thing about your thesis is you can't get ChatGPT to write about your results unless you put those results in as a figure, but even then, you need to be the one that really drives that first draft, in my opinion. And so now we've got this, the AFM data presented in blah, blah, blah. So that will make it sound much more academic, and you can go through and be like, yes, I like this bit, I don't like this bit, but that's how I would use it. The second way I would use ChatGPT is by making sure that I'm using the appropriate academic language. Now, when you're entering a research field, there's all this language you need to get used to, but it doesn't come naturally, or at least it didn't to me. So if I wanted to talk about a certain aspect of my study, quite often I'd have to go and read about it to go, oh, that's how they explain it. Now, that's super easy because you can use a prompt like this. What is the best way to describe the process of delamination? So I wanted to say that something delaminated, but I want to know about the language, about the use of different terminologies that I could use in my own report or my dissertation. So here, delamination is the process where layers in a composite material separate. So I need to make sure that I mention composite material and that it's likely to distress and fatigue or imperfection. So all of these are ways that I can talk about delamination that I didn't know about before. Stress concentration, that is very important for me. Fatigue, propagation, separation. So those are the steps that I need to make sure I address if I'm writing about delamination of my transparent electrodes. And this makes it so easy to sound more professional, to sound more academic, to make sure you're using the right terms and you're not just sort of like using high school level terminology to be like, oh yeah, it kind of splits and separates here. You can start to go in and talk about all of that for the propagation, separation. You can talk about stress concentration, fatigue and imperfections, all of that sort of stuff. Now you have the language at your fingertips to talk about anything academic that you want. Sometimes as you're writing your thesis and dissertation, there's just that one sort of like perfect reference that you need to find. And it's really hard to find it because it's just lost to the world. This is where I use things like Site Assistant or Syspace. So Site Assistant, if you go to site.ai, which is here and then you click up here into Assistant, you click there and then you get access to this AI research partner and you can ask a question. But go down here, go to settings first. So here you can actually sort of change how it responds. So I want to make sure that, let's have a look. Okay, I always want to use references. I want both huge structures response, yes. If I've got a certain year range for a paper, you know, if I want something more recent, I can put it in here. But I make sure that that is set appropriately for the sort of response I want. And if you're writing your PhD thesis or your dissertation for your master's, whatever it is, you have to make sure that you are getting appropriate responses that will match what you want to say and for a thesis, you want that to be as academic and referenced as possible. So I'll go in here and I'll ask questions. As I'm sort of, you know, typing up my thesis, I'll be like, oh, I need a little reference just to say this. Or I know that there was this paper that said this, I can go in and find it using an AI research partner where I can go and find those references. Another one I would use, and this is probably one I use more often is Syspace. And I'll go in and once again, I will ask a question here. If I've got a specific PDF, I can ask questions about that PDF. I'm going to extract data, I can paraphrase, I can do everything that I really want to do in Syspace for a thesis or dissertation, which is why it's my go-to. So as I'm writing my thesis, I'm sort of juggling those two things, creating really sort of rigorous academic language, but also I'm trying to find evidence at the same time to support what I'm saying. For example, with the delamination thing, I can go find examples about delamination in the literature, something that I wouldn't have necessarily done during my literature review. And it just sort of like works together. You're just sort of like writing, referencing, writing, referencing, reading, reading, reading, referencing, you know, you've got to read these references, by the way. The last way that's really valuable for enhancing your academic writing is by using AI proofreaders. There's two that I really like. The first one is Trinker. Trinker by Enargo here is a really great way to actually check your academic writing. I've tested it on a range of different papers that I've had in the past. This is what they look like. So once you get it sort of like checked by Trinker, you do get a tracked changes word document. And that is just like your supervisor, at least my supervisor used to give back to me. So it is a nice first step for checking all of your academic writing. I really like it. And then, you know, it's got little comments down the side here. It's got the track changes. That is exactly what I want when I am looking through that first draft or trying to make it better. You get up to 30,000 words in one go. One credit will use 5,000 words. So you do get quite a generous free limit with Trinker. But if you're checking your thesis or your dissertation, you need to make sure that you're checking it all in one go or you're sort of like putting it in in sections or putting it in in chapters. The last thing I really like is PaperPal. PaperPal, this is their edit PaperPal section. This is their web interface, but you can also install it on Word. Go check out my other video where I talk about using PaperPal in more detail. But the one thing I like about this is you can paste in sections and then you get all of these checks along the side here. So you can see that this one, you know, it doesn't like that and it's changing it to the green. And then it's got this one from these images. It is clear. Yes, okay. So by using these tools, you'll be making sure that your supervisor isn't distracted by those silly little mistakes. They're actually addressing the underlying science and research that you want to address. Those are the most important changes. I used to get backstabbed all the time being like full stop here. Make sure you do the thing there. The, the, the, the, the, the. And I was like, yes, I get it. I get it. I get how bad at putting full stops. But what do you think of the actual science in here? That was far more useful because that's the thing that actually gets you a PhD or gets you through your master's, not the position of certain full stops or, you know, commas or semi-colons, however you use them. If you like this video, go check out this one where I talk about AI enhanced academic writing where there's more tools to make sure that your academic writing is chef's kiss.

- Twitter - X /
- US & World
Brazilian Supreme Court panel upholds X ban, while Starlink refuses to comply
Four more justices have bolstered the ban’s legal standing, which could still face another vote by all 11 justices..
By Richard Lawler , a senior editor following news across tech, culture, policy, and entertainment. He joined The Verge in 2021 after several years covering news at Engadget.
Share this story
:format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25535561/STK160_X_TWITTER_2__C.jpg)
A panel of five Brazilian Supreme Court justices voted on Monday to uphold a decision ( PDF ) requiring the National Telecommunications Agency (Anatel) to limit access to X, the service formerly known as Twitter. Justice Alexandre de Moraes issued the ban on Friday in response to X owner Elon Musk’s refusal to comply with court orders to block certain accounts and to identify a legal representative in the country. Four other justices have now backed the decision.
Poder360 and O Globo report that three justices, Cristiano Zanin, Flávio Dino, and Cármen Lúcia, fully supported de Moraes’ ruling, while a fourth, Luiz Fux, noted reservations about a fine for people who circumvent the ban with a VPN, saying only people who post criminal messages like those expressing Nazism or fascism should be fined.
- Brazil bans X: all the latest news
- Brazil’s X ban is sending lots of people to Bluesky
As far as the ban’s effect, competing platforms have reported large numbers of new accounts made by Brazilian users. News organization Poder360 noted that its X account will now be managed exclusively from Portugal to respect the judge’s decision.
Meanwhile, Starlink has told Brazil’s telecom regulator, Anatel, that it will not comply with the ban until the court unfreezes its assets. So far, X is reportedly still accessible via the service. The New York Times reports that de Moraes has blocked Starlink from making Brazilian transactions while the court seeks to collect $3 million in unpaid fines by X. The satellite-based internet service is operated by SpaceX, which is also partially owned by Musk.
Poder360 reports that the court order gave internet providers and app stores five days to take measures to block access to X in the country, establishing a deadline of Wednesday, September 4th.
What to expect from Apple’s ‘It’s Glowtime’ iPhone 16 event
The remarkable paper pro is as outrageous as it is luxurious, sony is taking concord offline on september 6th after disastrous launch, canva says its ai features are worth the 300 percent price increase, hyundai’s first ev with native tesla supercharging is the new ioniq 5.
More from this stream Brazil bans X: all the latest news
Does threads have the wrong vibe for the displaced brazilian internet, nevertheless, they persisted., bluesky has gained a million new users in the last three days., come (back) to brazil.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
To cite an unpublished dissertation (one you got directly from the author or university in print form), add "Unpublished" to the bracketed description, and list the university at the end of the reference, outside the square brackets. APA format. Author last name, Initials. (Year).
A dissertation or thesis is considered published when it is available from a database such as ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global or PDQT Open, an institutional repository, or an archive. If the database assigns publication numbers to dissertations and theses, include the publication number in parentheses after the title of the ...
Citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database. If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It's similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences: Structure: Author's last name, F. M. (Year published).
Thesis, from a commercial database. Lope, M. D. (2014). Perceptions of global mindedness in the international baccalaureate middle years programme: The relationship to student academic performance and teacher characteristics (Order No. 3682837) [Doctoral dissertation, University of Maryland].ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global.
How to Cite a Published Dissertation or Thesis in APA. To cite a published dissertation in APA 7th edition, you need to include: Author, A. A. (Year). Title of doctoral dissertation or master's thesis (Publication number, if available) [Doctoral dissertation or master's thesis, Institution]. Publisher.
EndNote reference type: Thesis. Add Archive Name to Name of Database field. Thesis - from database. Elements of the reference: Author - last name, initials. (Year). Title of thesis - italicised (Publication No. - if available) [Doctoral dissertation or master's thesis, Institution]. Database Name. In-text reference
How to cite a dissertation in APA. Give the last name and initials (e. g. Watson, J. D.) of up to seven authors with the last name preceded by an ampersand (&). For eight or more authors include the first six names followed by an ellipsis (…) and add the last author's name. Give the full URL where the document can be retrieved from.
Dissertation or thesis available from a database service: Author Surname, First Initial. Second Initial. (year of publication). Title of dissertation or thesis (Doctoral dissertation or master's thesis). Retrieved from Name of database. (Accession or Order No.) For an unpublished dissertation or thesis: Author Surname, First Initial. Second ...
A thesis is an unpublished document produced by student as part of the requirements for the degree. They come at various levels (e.g. Honours, Masters, PhD, etc). Check with your lecturer before using a thesis for your assignment.
A thesis is a long-term, large project that involves both research and writing; it is easy to lose focus, motivation, and momentum. Here are suggestions for achieving the result you want in the time you have. The dissertation is probably the largest project you have undertaken, and a lot of the work is self-directed.
Basic format to reference a thesis or dissertation. The basics of a reference list entry for a thesis or dissertation: Author. The surname is followed by first initials. Year (in round brackets). Title (in italics). Level of Thesis or Dissertation [in square brackets]. The first line of each citation is left adjusted.
Thesis/Dissertation - APA Reference List Capitalization. The document title is in sentence case - Only the first word and proper nouns in the title are capitalized. Always capitalize the first word, the first word after a colon or a dash. The title of the thesis or dissertation is in title case - Each word in the name is capitalized, except for articles (a, an, the), prepositions ...
Thesis is either for a doctoral or a master's degree. Dissertation is either for a master's or a bachelor's degree with honours. Exegesis is the written component of a practice-based thesis where the major output is a creative work; e.g., a film, artwork, novel.
APA in-text citations The basics. In-text citations are brief references in the running text that direct readers to the reference entry at the end of the paper. You include them every time you quote or paraphrase someone else's ideas or words to avoid plagiarism.. An APA in-text citation consists of the author's last name and the year of publication (also known as the author-date system).
When a dissertation or thesis is unpublished, include the description " [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]" or " [Unpublished master's thesis]" in square brackets after the dissertation or thesis title. In the source element of the reference, provide the name of the institution that awarded the degree. The same format can be adapted ...
Format: Author last name, first initial. (Year). Title of dissertation/thesis (Publication No.) [Doctoral dissertation/Master's thesis, University].Database. URL. Elements: Author: List the last name, followed by the first initial (and second initial).See Authors for more information.; Year: List the year between parentheses, followed by a period. Title of dissertation/thesis: In italics.
Year of publication: Give the year in brackets followed by a full stop. Title of the Master's thesis: Only the first letter of the first word and proper nouns are capitalized. Publication number: Give the identification number of the thesis, if available. Name of the degree awarding institution: Give the name of the institution.
To quote a source, copy a short piece of text word for word and put it inside quotation marks. To paraphrase a source, put the text into your own words. It's important that the paraphrase is not too close to the original wording. You can use the paraphrasing tool if you don't want to do this manually.
Using reference in a dissertation that belong to the past five to ten years are acceptable; however, using references of the 1980s or 1990s is not recommended. The main reason being changes in time, settings, environment, participants, etc. All these factors contribute a lot towards accurate conclusions, thus they are regarded as essential when ...
Cite A Dissertation in Harvard style. Use the following template or our Harvard Referencing Generator to cite a dissertation. For help with other source types, like books, PDFs, or websites, check out our other guides. To have your reference list or bibliography automatically made for you, try our free citation generator.
Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis. Kirwan, J. G. (2005). An experimental study of the effects of small-group, face-to-face facilitated dialogues on the development of self-actualization levels: A movement towards fully functional persons [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Saybrook Graduate School and Research Center.
The structure of a dissertation depends on your field, but it is usually divided into at least four or five chapters (including an introduction and conclusion chapter). The most common dissertation structure in the sciences and social sciences includes: An introduction to your topic. A literature review that surveys relevant sources.
David and Ruth discuss how to handle references and citations in your dissertation or thesis. They explain 7 of the most commonly made mistakes in terms of r...
A dissertation dedication is a line, paragraph, or page at the start of a master's or PhD thesis or dissertation. It is a personal type of acknowledgement and appreciation to the people in the writer's life who provided him with sufficient motivation and inspiration to keep up with his dissertation.
Resources to Help Write Your Thesis Paper. While your thesis paper may be based on your independent research, writing it doesn't have to be a solitary process. Asking for help and using the resources that are available to you can make the process easier. If you're writing a thesis paper, some resources Chartier encourages you to use are:
A good paper includes a clear and concise thesis statement. Your thesis statement should come towards the beginning of your paper, ideally within the first paragraph of your introduction. To craft a strong thesis statement, you will need to articulate: a topic; a claim related to this topic; reasoning supporting your claim.
For clarity, and to avoid confusion, reference your degree grade in full as 'First Class Honours'. This makes it stand out to employers reading your CV. If preferred, you could use a hyphen and list your degree as 'First-Class Honours'. Other ways to write your degree level include 'First' or '1st'.
As I'm sort of, you know, typing up my thesis, I'll be like, oh, I need a little reference just to say this. Or I know that there was this paper that said this, I can go in and find it using an AI research partner where I can go and find those references. ... So as I'm writing my thesis, I'm sort of juggling those two things, creating really ...
The Last Screenwriter is a 2024 Swiss science fiction drama film directed by Peter Luisi and written by ChatGPT.It is one of the first films written using artificial intelligence.The film concerns a human screenwriter who encounters an AI scriptwriting system and finds that it matches his skills.
A panel of five Brazilian Supreme Court justices voted on Monday to uphold a decision requiring the National Telecommunications Agency (Anatel) to limit access to X, the service formerly known as ...