- Scroll to top
- Light Dark Light Dark


Cart review
No products in the cart.
7 Essential Steps: How to Write a Research Brief That Gets Results
- Author Survey Point Team
- Published February 17, 2024

In this blog, we’ll explore seven essential steps to learn how to write a research brief that not only guides your project but also resonates with your audience. Research briefs are the unsung heroes of successful projects. Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or a newbie, crafting a well-structured brief can significantly impact the quality of your work.
Crafting a research brief that yields results is crucial. Explore the seven essential steps to write an effective research brief, ensuring success in your projects. Learn from experts and avoid common pitfalls.
Embarking on a research journey requires a well-crafted roadmap. A research brief serves as the compass, guiding you through the intricate terrain of data and insights. In this article, we will explore the seven essential steps to create a research brief that not only meets but exceeds expectations, ensuring the desired results.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Research Briefs
Why Research Briefs Matter
Research briefs are the cornerstone of successful projects. They set the tone, define objectives, and guide researchers toward meaningful outcomes. A well-structured brief not only saves time but also ensures the collected data aligns with the project goals.
How to Write a Research Brief: Understanding Your Objective
Defining Clear Research Goals
The first step in creating a research brief is understanding the project’s objective. Clearly define what you aim to achieve, ensuring every subsequent decision aligns with this overarching goal. Clarity at this stage is paramount.
Target Audience Analysis
Identifying and Understanding Your Audience
Knowing your audience is key to effective communication. Dive deep into demographic details, preferences, and behaviors. Tailor your research brief to resonate with the intended audience, enhancing its impact.
Crafting a Clear Research Question
Formulating Effective Research Queries
A well-defined research question is the compass that guides your entire project. Craft a question that is clear, concise, and directly aligns with your objectives. This foundational step ensures focused and purposeful research.
Literature Review
Building a Solid Foundation
Before venturing into uncharted territories, review existing literature. This not only provides valuable insights but also prevents redundancy. Acknowledge the work of others and identify gaps your research can fill.
Research Methodology
Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the appropriate research methodology is pivotal. Whether qualitative or quantitative, the chosen approach should align with your objectives. Justify your choice, considering the nature of your research question.
How to Write a Research Brief: Data Collection
Ensuring Quality Information
Collecting data is where the rubber meets the road. Implement a robust data collection strategy, ensuring the information gathered is relevant, accurate, and aligns with your research question. Quality over quantity is the mantra.
Analysis and Interpretation
Extracting Meaningful Insights
Analysis is the heart of research. Interpret the collected data, drawing meaningful conclusions. Your insights should directly contribute to answering your research question and, consequently, achieving your objective.
Crafting a Compelling Title
Making Your Research Brief Stand Out
A captivating title is the first impression your research brief makes. It should be concise, intriguing, and reflective of the study’s essence. Crafting a compelling title sets the stage for your audience’s engagement.
The Power of Effective Communication
Conveying Your Message Clearly
Beyond the data, effective communication is crucial. Present your findings in a clear, concise manner. Utilize visuals, charts, and graphs to enhance understanding. Make your research brief accessible to a broad audience.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes That Can Derail Your Research
Avoiding common pitfalls is as important as following the right steps. Identify and steer clear of potential pitfalls that could compromise the integrity and effectiveness of your research brief. Learn from others’ mistakes to enhance your own success.
Real-life Success Stories
Learnings from Notable Research Briefs
Drawing inspiration from successful research briefs can provide valuable insights. Explore real-life success stories, understand the strategies employed, and apply these lessons to elevate the impact of your own research briefs.
How to Write a Research Brief: FAQ
Can I write multiple research questions? Certainly, but ensure they all align with your main objective. Quality over quantity is crucial in research.
How do I choose between qualitative and quantitative methods? Consider the nature of your research question. Qualitative methods delve into depth, while quantitative methods focus on breadth.
Is a literature review necessary for all research briefs? Yes, a literature review establishes the context for your research and prevents duplication of efforts.
How do I make my title captivating? A captivating title is concise, intriguing, and reflective of your study’s essence. Use language that sparks curiosity.
What are common pitfalls in research briefs? Common pitfalls include unclear objectives, biased data collection, and inadequate analysis. Be vigilant to avoid these pitfalls.
Can I use the same research methodology for every project? Adapt your research methodology to align with each project’s unique objectives. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach.
Wrapping Up the Research Brief Journey In conclusion, crafting a research brief that gets results requires a strategic approach. By following the seven essential steps outlined in this article, you can navigate the complexities of research with confidence. Remember, a well-prepared brief not only guides your journey but ensures the destination is one of success.
Survey Point Team
Related posts.

- Posted by Survey Point Team
How K12 Data Analytics Can Help You Achieve Your School’s Goals in 2024

Discover Why Data Science is Right for You: 7 Compelling Reasons to Dive In Today

Python vs R for Data Analysis: Which One Should Learn in 2024?

Medical Student Research Journal
Michigan state university college of human medicine.

Guidelines – Brief Report
Brief reports are similar to original research in that they follow the same rigor, format and guidelines, but are designed for small-scale research or research that is in early stages of development. These may include preliminary studies that utilize a simple research design or a small sample size and that have produced limited pilot data and initial findings that indicate need for further investigation. Brief reports are much shorter than manuscripts associated with a more advanced, larger-scale research project. They are not meant to be used for a short version of an article about research that would otherwise qualify for a full original research manuscript or for publishing material on research that lacks significance, is not rigorous or, if expanded, would not qualify for a full article or for research.
Order of Sections
Introduction
- Illustrations (Figure/Tables)
Manuscript Limits
- Total Length: up to 1500 words (not including abstract, illustrations, and references)
- Abstract Length: up to 150 words
- Table/Figure Limits: up to 3 tables and figures
- References: up to 40 references
The title page should carry the following information:
- Article Title (concise information about the study, limited to 100 characters)
- Author Names (Mark D. Smith B.S. 1* , Jeremy Michael Howes M.S. 2 , Jessica P. Masters M.D. Ph. D. 1,2 )
- Institutional Affiliations of all authors in order of appearance in author names ( 1 College of Human Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA. 2 Dept. of Internal Medicine, Michigan State University, East Lansing, MI, USA)
- Contact information for corresponding author(s) including address, email, phone, and fax. The corresponding author should indicate clearly whether his or her e-mail address can be published. Corresponding author(s) is indicated with asterisk by name in author listing; the medical students should be corresponding author.
- Short Title (50 character limit shorter title for headers)
- Key Phrases – Relevant words or short phrases that aid search engines or indexes in finding your work (use MeSH headings if possible). Use key phrases that are not present in the title. Maximum of 6, e.g. (Pemphigus, Bullous Skin Disorder, Autoimmune, Blistering, Skin Diseases, Monoclonal Antibody)
- Disclaimers, if any
- Word Count: Abstract and Body (excluding abstract, illustrations, and references)
- Table and Figure Count
- Source(s) of support in the form of grants, equipment, drugs, or all of these
- Conflict of Interest Statement
Abstracts are the only substantive portion of the article indexed in many electronic databases, and the only portion many readers read. Authors must be careful that they accurately reflect the content of the article in the abstract. This description should include:
- Context or background for the study
- Purpose, basic procedures, main findings, and principal conclusions
- Emphasis on new and important aspects of the study or observations
- No references, illustrations, or references to illustrations are allowed in the abstract
- The abstract should be structured with similar headings as in the main article (e.g. introduction, patient profile, interventions, conclusions)
Provide a context or background for the study including the nature of the problem and its significance to medical learners and scientists. State the specific purpose or research objective tested by the study; the research objective is often more sharply focused when stated as a question. Both the main and secondary objectives should be clear, and any pre-specified subgroup analyses should be described. Provide only directly pertinent references, and do not include data or conclusions from the work being reported.
The methods section should include information on materials, methods and procedures in sufficient detail such that the study can be repeated and/or validated. The methods section should include only information that was available at the time the plan or protocol for the study was being written; all information obtained during the study belongs in the results section. The methods section is comprised of the following subheadings (if applicable):
Selection and Description of Participants
Describe your selection of the observational or experimental participants clearly, including eligibility and exclusion criteria and a description of the source population. Explain the use of variables such as gender and age when they are included in a study report–for example, authors should explain why only participants of certain ages were included or why women were excluded. The guiding principle should be clarity about how and why a study was done in a particular way.
Technical Information
Identify the methods, apparatus (give the manufacturer’s name, city, and state in parentheses), and procedures in sufficient detail to allow others to reproduce the results. Give references to established methods, including statistical methods, describe new or substantially modified methods, give the reasons for using them, and evaluate their limitations.
Describe statistical methods with enough detail to enable a knowledgeable reader with access to the original data to verify the reported results. Avoid relying solely on statistical hypothesis testing, such as p-values, which fail to convey important information about effect size, but include averages with confidence intervals if available, in addition to the p-values. Define statistical terms, abbreviations, and most symbols. Specify the computer software used.
Present your results in logical sequence in the text, tables, and illustrations, giving the main or most important findings first. Do not repeat all the data in the tables or illustrations in the text; emphasize or summarize only the most important observations. Extra or supplementary materials and technical detail can be placed in an appendix. Restrict tables and figures to those needed to explain the argument of the paper and to assess supporting data. Avoid interpreting the data, as this section is pure information that the reader can interpret for themselves; the authors’ own interpretation of the data is meant for the discussion section of the manuscript.
Emphasize the new and important aspects of the study and the conclusions that follow from them. For experimental studies, it is useful to begin the discussion by summarizing briefly the main findings, then explore possible mechanisms or explanations for these findings, compare and contrast the results with other relevant studies, state the limitations of the study, and explore the implications of the findings for future research and for clinical practice.
Limitations : Because every experiment or project can always be improved, a healthy discussion of the limitations of the study should be included. All manuscripts should include a brief discussion on the adequacy of the research methods to draw a valid conclusion. Authors should comment on changes that would improve the methods of the study or reasons why the methods are able to draw a strong conclusion. The discussion of limitations should not be a separate heading or sub-heading in the actual manuscript, but should be a flowing part of the discussion section.
Please see the directions for formatting References .
Illustrations (Figures and Tables)
Should follow the same format as mentioned in the General Guidelines .
Copyright Notice
The Medical Student Research Journal is a scholarly journal by medical students supported by Michigan State University College of Human Medicine.
Authors grant unrestricted copyright license to MSRJ while retaining full copyright to their works. This means authors may distribute their work at their discretion, but may not alter the final product as published by MSRJ. Permissions for reproduction of final published article are granted by MSRJ, while pre-publication works are distributable at authors’ discretion.
Michigan State University logos used with permission.
Privacy Statement
The names and email addresses entered in this journal site will be used exclusively for the stated purposes of this journal and will not be made available for any other purpose or to any other party.
Disclosures Please view our disclosures available on the general guidelines here .
This page was last updated on 2/15/2014 KCP.
- Business & Enterprise
- Education, Learning & Skills
- Energy & Environment
- Financial Services
- Health & Wellbeing
- Higher Education
- Work & Welfare
- Behavioural insights
- Business Spotlight – IFF’s business omnibus
- Customer experience research
- Customer satisfaction measurement
- National statistics and complex surveys
- Stakeholder research
- Tenant satisfaction measures
- Our approach
- Trusted partner
- Equality, diversity & inclusion at IFF
- Sustainability at IFF
- Charity giving
- Meet the team
- News & resources
- Case studies
How to write an effective research brief
Whether you’re launching a simple survey or planning a large-scale project the quality of your brief will hugely impact on the value you get from the research. While it can take a little time and effort creating a research brief, it will undoubtedly be time well spent – getting you better results and return on your investment and saving you valuable resources on further clarification. At best, a poor brief will be a time drain on you and your team. At worst, the findings will fail to meet your objectives, costing you time and money.
We’ve seen a lot of research briefs over the years. Some of which have been well thought through and clear, helping us prepare a detailed proposal and deliver an effective project and subsequent results. And others which have been not so good, lacking clarity or detail.
Using this experience, we’ve put together a ‘how to’ guide on writing an effective research brief, to help you ensure success on your next project.
1. Preparation is key
As with any project, before you start it’s crucial you think through what you want and need to deliver. Here are some things you should consider:
- Why are you conducting the research? What exactly are you looking to understand?
- Who are you looking to understand better? Who do you need to speak to answer your research questions?
- Who are your internal stakeholders? Have you discussed the project needs with the people in your organisation who will use the findings or who are invested in the research?
- How will the findings be used?
- When do you need the findings?
- Have you agreed a budget with either your procurement team, or the relevant person in your organisation?
2. Be clear on your objectives
This is one of the most important parts of your brief to convey to the reader what you want out of the project and ensure you get results which deliver.
Projects should have around three or four overarching aims which set out what the project ultimately wants to achieve.
These might be things like:
- Assess the impact of……
- Examine views of…..
- Evaluate the effectiveness of….
In addition to project objectives, you should also include the key questions you want the research to answer. These should support you in meeting the aims of the research.
For example, if the project aim is to assess the impact of an intervention, your research questions might include:
- Who did the intervention target?
- What did the project deliver?
- What elements were successful, and why?
- What were the main enablers and barriers?
3. Remember your audience
Research agencies or organisations who will be responding to your brief might not know anything about your business. So, make sure you include enough background information in your brief to enable them to understand your needs and deliver effectively. And avoid use of jargon or acronyms which could lead to errors or confusion.
4. Structure your research brief
Before you start to populate your brief it’s worth considering all the information and sections you need to include, to structure your thinking and ensure you don’t miss anything important.
This might include some, or all, of the following:
- Background info
- Introduction
- Aims and objectives
- Research Question(s)
- Issues / Risks
- Methodology
- Timing and Outputs
- Project Management
5. Make it thorough, yet succinct
While it’s crucial to include all the relevant information to enable bidders to respond effectively, no one wants to read reams and reams of information. To avoid the key information getting lost in the details use annexes to add supplementary information which could be useful.
6. Consider how prescriptive you want to be on the methodology
The extent to which you want to specify the methodology will depend on the project you aim to deliver. There are benefits and risks to being overly prescriptive or offering free reign. If you outline in precise detail how you want the research to be conducted, you will hamper any original ideas from those invited to tender and might limit the impact on the research. Whereas, if you’re less prescriptive, allowing room for creativity, you risk not getting the project or results you want, or receiving proposals on a scale which you can’t resource.
Generally, it is useful to allow those invited to tender some scope to develop the methodology they propose to use. Exceptions might be where previous work has to be very precisely replicated or some other very precise commitment about the nature of findings has been given to stakeholders.
7. Define your timelines
As a minimum, you need to include when you want the project to start and end. But you should also include the timetable for procurement. When planning this, don’t underestimate the time and resource needed to run a procurement exercise. Make sure your evaluators are available when you need them and have enough time blocked out in their diary.
You’ll likely also want to include milestones for when you expect outputs to be delivered, such as deadlines for a draft report (providing opportunity for review and feedback) and the final report; allowing sufficient time between the two to enable your stakeholders to consult, for you to feedback and for the contractor to revise the report.
8. Set expectations on cost
You will most likely have budgetary constraints, with a figure for what you are prepared to spend. To save you and your bidders time, and to set realistic expectations, you should include an indication within your brief. This will prevent you receiving proposals which are way out of the ballpark; enable bidders to plan a project which delivers on (or at least close to) budget; and will prevent any nasty surprises, further down the line.
By following these tips you’ll be well on your way to creating an effective research brief which delivers on time and on budget.
If you’d like more guidance download our “step-by-step” guide, which includes a template and information for what to include in each section to ensure success.
Download the guide now.
Brief Report
A Brief Report is a focused article of original research intended to advance its field of study. It may contain up to 5 Figures or Tables presenting original data.
The article should also be conclusive and self-explanatory and may contain Supplementary Material such as Figures, Tables and Video files. In the studies involving noncoding RNA molecules the Authors should consider the following issues:
- The rationale to study a particular noncoding RNA needs to be specified in the introduction.
- Studies concerning the function of these RNAs via mediating a single target or pathway should include studies on additional multiple targets/pathways to prove functional specificity.
- Their proposed function should be verified via the studies of the gain and/or loss of function. Detailed studies of signalling pathway(s) regulated by specific RNA should be carried out.
- Details of the initial screen used to identify RNA species involvement in pathway/disease (number of subjects, statistical tests employed, percent change from controls) should be provided if applicable.
Please review the Editorial Policies around the use of human subjects/material/data and animal research before writing your Ethics Declarations. All human research must be done in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and all animal research (vertebrates and regulated invertebrates) in accordance with the Basel Declaration . Such research must be approved by the appropriate ethics committee and that information must be present in your Ethics Declaration. In the Ethics Declaration, you should provide:
- the number and date of ethics approval and information for that local ethics committee as confirming that they follow the Declaration of Helsinki for human research.
- the number and dates of the ethics approval for animal research.
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters strongly encourages that all datasets on which the conclusions of the paper rely should be available to readers. We encourage authors to ensure that their datasets are either deposited in publicly available repositories (where available and appropriate) or presented in the main manuscript or additional supporting files whenever possible. Please see Springer Nature’s information on recommended repositories. Where a widely established research community expectation for data archiving in public repositories exists, submission to a community-endorsed, public repository is mandatory. A list of data where deposition is required, with the appropriate repositories, can be found on the Editorial Policies Page .
For any submissions which include images from gels or western blots, authors are required to include their raw image files as supplementary files during submission. Failure to do so could cause delays in reviewing the manuscript. In addition, when blots are the subject of quantitation via scanning at least 3 blots performed independently has to be used. At least 3 copies of the originals should be attached. All images are checked by software for detection of duplication or manipulation before acceptance.
Language quality check
Authors should be aware that Springer Nature offers a free service whereby authors can have their manuscript checked for grammatical and readability before submissions. We encourage authors to make use of this tool to improve the quality of their manuscript.
Graphical abstract image
A graphical abstract image must be uploaded during submission. This is a picture which will appear underneath the Abstract on the journal website. It should be relevant to the topic covered and serve to attract readers' attention to the article. The graphical abstract image may be one of the images included in the article or any other image the authors feel to be appropriate. It must have landscape orientation, approximately 920 pixels width x 300 pixels height, and should be uploaded as a JPEG, PNG or SVG file. Please note that graphical abstract images must comply with BMC's copyright policy.
The Editors strongly encourage authors to limit the use of abbreviations or acronyms within the title of their manuscripts. Exceptions for widely-used terms within the scientific community (such as DNA or RNA) permitted.
Preparing your manuscript
The information below details the section headings that you should include in your manuscript and what information should be within each section.
Please note that your manuscript must include a 'Declarations' section including all of the subheadings (please see below for more information).
The title page should:
- "A versus B in the treatment of C: a randomized controlled trial", "X is a risk factor for Y: a case control study", "What is the impact of factor X on subject Y: A systematic review"
- or for non-clinical or non-research studies a description of what the article reports
- if a collaboration group should be listed as an author, please list the Group name as an author. If you would like the names of the individual members of the Group to be searchable through their individual PubMed records, please include this information in the “Acknowledgements” section in accordance with the instructions below
- Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT , do not currently satisfy our authorship criteria . Notably an attribution of authorship carries with it accountability for the work, which cannot be effectively applied to LLMs. Use of an LLM should be properly documented in the Methods section (and if a Methods section is not available, in a suitable alternative part) of the manuscript.
- indicate the corresponding author
The Abstract should not exceed 350 words. Please minimize the use of abbreviations and do not cite references in the abstract. Reports of randomized controlled trials should follow the CONSORT extension for abstracts. The abstract must include the following separate sections:
- Background: the context and purpose of the study
- Methods: how the study was performed and statistical tests used
- Results: the main findings
- Conclusions: brief summary and potential implications
- Trial registration: If your article reports the results of a health care intervention on human participants, it must be registered in an appropriate registry and the registration number and date of registration should be stated in this section. If it was not registered prospectively (before enrollment of the first participant), you should include the words 'retrospectively registered'. See our editorial policies for more information on trial registration
Three to ten keywords representing the main content of the article.
The Background section should explain the background to the study, its aims, a summary of the existing literature and why this study was necessary or its contribution to the field.
The methods section should include:
- the aim, design and setting of the study
- the characteristics of participants or description of materials
- a clear description of all processes, interventions and comparisons. Generic drug names should generally be used. When proprietary brands are used in research, include the brand names in parentheses
- the type of statistical analysis used, including a power calculation if appropriate
This should include the findings of the study including, if appropriate, results of statistical analysis which must be included either in the text or as tables and figures.
This section should discuss the implications of the findings in context of existing research and highlight limitations of the study.
Conclusions
This should state clearly the main conclusions and provide an explanation of the importance and relevance of the study reported.
List of abbreviations
If abbreviations are used in the text they should be defined in the text at first use, and a list of abbreviations should be provided.
Declarations
All manuscripts must contain the following sections under the heading 'Declarations':
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication, availability of data and materials, competing interests, authors' contributions, acknowledgements.
- Authors' information (optional)
Please see below for details on the information to be included in these sections.
If any of the sections are not relevant to your manuscript, please include the heading and write 'Not applicable' for that section.
Manuscripts reporting studies involving human participants, human data or human tissue must:
- include a statement on ethics approval and consent (even where the need for approval was waived)
- include the name of the ethics committee that approved the study and the committee’s reference number if appropriate
Studies involving animals must include a statement on ethics approval and for experimental studies involving client-owned animals, authors must also include a statement on informed consent from the client or owner.
See our editorial policies for more information.
If your manuscript does not report on or involve the use of any animal or human data or tissue, please state “Not applicable” in this section.
If your manuscript contains any individual person’s data in any form (including any individual details, images or videos), consent for publication must be obtained from that person, or in the case of children, their parent or legal guardian. All presentations of case reports must have consent for publication.
You can use your institutional consent form or our consent form if you prefer. You should not send the form to us on submission, but we may request to see a copy at any stage (including after publication).
See our editorial policies for more information on consent for publication.
If your manuscript does not contain data from any individual person, please state “Not applicable” in this section.
All manuscripts must include an ‘Availability of data and materials’ statement. Data availability statements should include information on where data supporting the results reported in the article can be found including, where applicable, hyperlinks to publicly archived datasets analysed or generated during the study. By data we mean the minimal dataset that would be necessary to interpret, replicate and build upon the findings reported in the article. We recognise it is not always possible to share research data publicly, for instance when individual privacy could be compromised, and in such instances data availability should still be stated in the manuscript along with any conditions for access.
Authors are also encouraged to preserve search strings on searchRxiv https://searchrxiv.org/ , an archive to support researchers to report, store and share their searches consistently and to enable them to review and re-use existing searches. searchRxiv enables researchers to obtain a digital object identifier (DOI) for their search, allowing it to be cited.
Data availability statements can take one of the following forms (or a combination of more than one if required for multiple datasets):
- The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [NAME] repository, [PERSISTENT WEB LINK TO DATASETS]
- The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
- The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due [REASON WHY DATA ARE NOT PUBLIC] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
- The data that support the findings of this study are available from [third party name] but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of [third party name].
- Not applicable. If your manuscript does not contain any data, please state 'Not applicable' in this section.
More examples of template data availability statements, which include examples of openly available and restricted access datasets, are available here .
BioMed Central strongly encourages the citation of any publicly available data on which the conclusions of the paper rely in the manuscript. Data citations should include a persistent identifier (such as a DOI) and should ideally be included in the reference list. Citations of datasets, when they appear in the reference list, should include the minimum information recommended by DataCite and follow journal style. Dataset identifiers including DOIs should be expressed as full URLs. For example:
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A, Nakhjiri N, Farahmand A. Global integrated drought monitoring and prediction system (GIDMaPS) data sets. figshare. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.853801
With the corresponding text in the Availability of data and materials statement:
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [NAME] repository, [PERSISTENT WEB LINK TO DATASETS]. [Reference number]
If you wish to co-submit a data note describing your data to be published in BMC Research Notes , you can do so by visiting our submission portal . Data notes support open data and help authors to comply with funder policies on data sharing. Co-published data notes will be linked to the research article the data support ( example ).
All financial and non-financial competing interests must be declared in this section.
See our editorial policies for a full explanation of competing interests. If you are unsure whether you or any of your co-authors have a competing interest please contact the editorial office.
Please use the authors initials to refer to each authors' competing interests in this section.
If you do not have any competing interests, please state "The authors declare that they have no competing interests" in this section.
All sources of funding for the research reported should be declared. If the funder has a specific role in the conceptualization, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript, this should be declared.
The individual contributions of authors to the manuscript should be specified in this section. Guidance and criteria for authorship can be found in our editorial policies .
Please use initials to refer to each author's contribution in this section, for example: "FC analyzed and interpreted the patient data regarding the hematological disease and the transplant. RH performed the histological examination of the kidney, and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript."
Please acknowledge anyone who contributed towards the article who does not meet the criteria for authorship including anyone who provided professional writing services or materials.
Authors should obtain permission to acknowledge from all those mentioned in the Acknowledgements section.
See our editorial policies for a full explanation of acknowledgements and authorship criteria.
If you do not have anyone to acknowledge, please write "Not applicable" in this section.
Group authorship (for manuscripts involving a collaboration group): if you would like the names of the individual members of a collaboration Group to be searchable through their individual PubMed records, please ensure that the title of the collaboration Group is included on the title page and in the submission system and also include collaborating author names as the last paragraph of the “Acknowledgements” section. Please add authors in the format First Name, Middle initial(s) (optional), Last Name. You can add institution or country information for each author if you wish, but this should be consistent across all authors.
Please note that individual names may not be present in the PubMed record at the time a published article is initially included in PubMed as it takes PubMed additional time to code this information.
Authors' information
This section is optional.
You may choose to use this section to include any relevant information about the author(s) that may aid the reader's interpretation of the article, and understand the standpoint of the author(s). This may include details about the authors' qualifications, current positions they hold at institutions or societies, or any other relevant background information. Please refer to authors using their initials. Note this section should not be used to describe any competing interests.
Footnotes can be used to give additional information, which may include the citation of a reference included in the reference list. They should not consist solely of a reference citation, and they should never include the bibliographic details of a reference. They should also not contain any figures or tables.
Footnotes to the text are numbered consecutively; those to tables should be indicated by superscript lower-case letters (or asterisks for significance values and other statistical data). Footnotes to the title or the authors of the article are not given reference symbols.
Always use footnotes instead of endnotes.
Examples of the Vancouver reference style are shown below.
See our editorial policies for author guidance on good citation practice
Web links and URLs: All web links and URLs, including links to the authors' own websites, should be given a reference number and included in the reference list rather than within the text of the manuscript. They should be provided in full, including both the title of the site and the URL, as well as the date the site was accessed, in the following format: The Mouse Tumor Biology Database. http://tumor.informatics.jax.org/mtbwi/index.do . Accessed 20 May 2013. If an author or group of authors can clearly be associated with a web link, such as for weblogs, then they should be included in the reference.
Example reference style:
Article within a journal
Smith JJ. The world of science. Am J Sci. 1999;36:234-5.
Article within a journal (no page numbers)
Rohrmann S, Overvad K, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Jakobsen MU, Egeberg R, Tjønneland A, et al. Meat consumption and mortality - results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Medicine. 2013;11:63.
Article within a journal by DOI
Slifka MK, Whitton JL. Clinical implications of dysregulated cytokine production. Dig J Mol Med. 2000; doi:10.1007/s801090000086.
Article within a journal supplement
Frumin AM, Nussbaum J, Esposito M. Functional asplenia: demonstration of splenic activity by bone marrow scan. Blood 1979;59 Suppl 1:26-32.
Book chapter, or an article within a book
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. In: Bourne GH, Danielli JF, Jeon KW, editors. International review of cytology. London: Academic; 1980. p. 251-306.
OnlineFirst chapter in a series (without a volume designation but with a DOI)
Saito Y, Hyuga H. Rate equation approaches to amplification of enantiomeric excess and chiral symmetry breaking. Top Curr Chem. 2007. doi:10.1007/128_2006_108.
Complete book, authored
Blenkinsopp A, Paxton P. Symptoms in the pharmacy: a guide to the management of common illness. 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1998.
Online document
Doe J. Title of subordinate document. In: The dictionary of substances and their effects. Royal Society of Chemistry. 1999. http://www.rsc.org/dose/title of subordinate document. Accessed 15 Jan 1999.
Online database
Healthwise Knowledgebase. US Pharmacopeia, Rockville. 1998. http://www.healthwise.org. Accessed 21 Sept 1998.
Supplementary material/private homepage
Doe J. Title of supplementary material. 2000. http://www.privatehomepage.com. Accessed 22 Feb 2000.
University site
Doe, J: Title of preprint. http://www.uni-heidelberg.de/mydata.html (1999). Accessed 25 Dec 1999.
Doe, J: Trivial HTTP, RFC2169. ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2169.txt (1999). Accessed 12 Nov 1999.
Organization site
ISSN International Centre: The ISSN register. http://www.issn.org (2006). Accessed 20 Feb 2007.
Dataset with persistent identifier
Zheng L-Y, Guo X-S, He B, Sun L-J, Peng Y, Dong S-S, et al. Genome data from sweet and grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). GigaScience Database. 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.5524/100012 .
Figures, tables and additional files
See General formatting guidelines for information on how to format figures, tables and additional files.
Submit manuscript
- Editorial Board
- Instructions for Editors
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- Follow us on Twitter
Affiliated with

Annual Journal Metrics
Citation Impact 2023 Journal Impact Factor: 9.2 5-year Journal Impact Factor: 8.1 Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 1.476 SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 2.229
Speed 2023 Submission to first editorial decision (median days): 11 Submission to acceptance (median days): 105
Usage 2023 Downloads: 642,615 Altmetric mentions: 1,059
- More about our metrics
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters
ISSN: 1689-1392
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

Brief Report
Brief reports are suitable for the presentation of research that extends previously published research, including the reporting of additional data and confirmatory results in other settings, as well as small-scale studies. Authors must clearly acknowledge any work upon which they are building, both published and unpublished. Journal of Big Data strongly encourages that all datasets on which the conclusions of the paper rely should be available to readers. We encourage authors to ensure that their datasets are either deposited in publicly available repositories (where available and appropriate) or presented in the main manuscript or additional supporting files whenever possible. Please see Springer Nature’s information on recommended repositories.
Authors who need help depositing and curating data may wish to consider uploading their data to Springer Nature’s Research Data Support or contacting our Research Data Support Helpdesk . Springer Nature’s Research Data Support provides data deposition and curation to help authors follow good practice in sharing and archiving of research data, and can be accessed via an online form. The services provide secure and private submission of data files, which are curated and managed by the Springer Nature Research Data team for public release, in agreement with the submitting author. These services are provided in partnership with figshare. Checks are carried out as part of a submission screening process to ensure that researchers who should use a specific community-endorsed repository are advised of the best option for sharing and archiving their data. Use of Research Data Support is optional and does not imply or guarantee that a manuscript will be accepted.
The Abstract of the manuscript should not exceed 350 words and must be structured into separate sections:
- Background, the context and purpose of the study;
- Findings, the main results;
- Conclusions, brief summary and potential implications.
Please minimize the use of abbreviations and do not cite references in the abstract.
Preparing your manuscript
The title page should:
- present a title that includes, if appropriate, the research design or for non-research studies: a description of what the article reports
- if a collaboration group should be listed as an author, please list the group name as an author and include the names of the individual members of the group in the “Acknowledgements” section in accordance with the instructions below
- Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT , do not currently satisfy our authorship criteria . Notably an attribution of authorship carries with it accountability for the work, which cannot be effectively applied to LLMs. Use of an LLM should be properly documented in the Methods section (and if a Methods section is not available, in a suitable alternative part) of the manuscript
- indicate the corresponding author
The abstract should briefly summarize the aim, findings or purpose of the article. Please minimize the use of abbreviations and do not cite references in the abstract.
Three to ten keywords representing the main content of the article.
This should contain the body of the article, and may also be broken into subsections with short, informative headings.
List of abbreviations
If abbreviations are used in the text they should be defined in the text at first use, and a list of abbreviations should be provided.
Declarations
All manuscripts must contain the following sections under the heading 'Declarations':
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication, availability of data and materials, competing interests, authors' contributions, acknowledgements.
- Authors' information (optional)
Please see below for details on the information to be included in these sections.
If any of the sections are not relevant to your manuscript, please include the heading and write 'Not applicable' for that section.
Manuscripts reporting studies involving human participants, human data or human tissue must:
- include a statement on ethics approval and consent (even where the need for approval was waived)
- include the name of the ethics committee that approved the study and the committee’s reference number if appropriate
Studies involving animals must include a statement on ethics approval and for experimental studies involving client-owned animals, authors must also include a statement on informed consent from the client or owner.
See our editorial policies for more information.
If your manuscript does not report on or involve the use of any animal or human data or tissue, please state “Not applicable” in this section.
If your manuscript contains any individual person’s data in any form (including individual details, images or videos), consent to publish must be obtained from that person, or in the case of children, their parent or legal guardian. All presentations of case reports must have consent to publish.
You can use your institutional consent form if you prefer. You should not send the form to us on submission, but we may request to see a copy at any stage (including after publication).
See our editorial policies for more information on consent for publication.
If your manuscript does not contain data from any individual person, please state “Not applicable” in this section.
All manuscripts must include an ‘Availability of data and materials’ statement. Data availability statements should include information on where data supporting the results reported in the article can be found including, where applicable, hyperlinks to publicly archived datasets analysed or generated during the study. By data we mean the minimal dataset that would be necessary to interpret, replicate and build upon the findings reported in the article. We recognise it is not always possible to share research data publicly, for instance when individual privacy could be compromised, and in such instances data availability should still be stated in the manuscript along with any conditions for access.
Data availability statements can take one of the following forms (or a combination of more than one if required for multiple datasets):
- The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [NAME] repository, [PERSISTENT WEB LINK TO DATASETS]
- The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
- The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due [REASON WHY DATA ARE NOT PUBLIC] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
- The data that support the findings of this study are available from [third party name] but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of [third party name].
- Not applicable. If your manuscript does not contain any data, please state 'Not applicable' in this section.
More examples of template data availability statements, which include examples of openly available and restricted access datasets, are available here .
SpringerOpen also requires that authors cite any publicly available data on which the conclusions of the paper rely in the manuscript. Data citations should include a persistent identifier (such as a DOI) and should ideally be included in the reference list. Citations of datasets, when they appear in the reference list, should include the minimum information recommended by DataCite and follow journal style. Dataset identifiers including DOIs should be expressed as full URLs. For example:
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A, Nakhjiri N, Farahmand A. Global integrated drought monitoring and prediction system (GIDMaPS) data sets. figshare. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.853801
With the corresponding text in the Availability of data and materials statement:
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [NAME] repository, [PERSISTENT WEB LINK TO DATASETS]. [Reference number]
If you wish to co-submit a data note describing your data to be published in BMC Research Notes , you can do so by visiting our submission portal . Data notes support open data and help authors to comply with funder policies on data sharing. Co-published data notes will be linked to the research article the data support ( example ).
All financial and non-financial competing interests must be declared in this section.
See our editorial policies for a full explanation of competing interests. If you are unsure whether you or any of your co-authors have a competing interest please contact the editorial office.
Please use the authors’ initials to refer to each authors' competing interests in this section.
If you do not have any competing interests, please state "The authors declare that they have no competing interests" in this section.
All sources of funding for the research reported should be declared. If the funder has a specific role in the conceptualization, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript, this should be declared.
The individual contributions of authors to the manuscript should be specified in this section. Guidance and criteria for authorship can be found in our editorial policies .
Please use initials to refer to each author's contribution in this section, for example: "FC analyzed and interpreted the patient data regarding the hematological disease and the transplant. RH performed the histological examination of the kidney, and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript."
Please acknowledge anyone who contributed towards the article who does not meet the criteria for authorship including anyone who provided professional writing services or materials.
Authors should obtain permission to acknowledge from all those mentioned in the Acknowledgements section.
See our editorial policies for a full explanation of acknowledgements and authorship criteria.
If you do not have anyone to acknowledge, please write "Not applicable" in this section.
Group authorship (for manuscripts involving a collaboration group): if you would like the names of the individual members of a collaboration Group to be searchable through their individual PubMed records, please ensure that the title of the collaboration Group is included on the title page and in the submission system and also include collaborating author names as the last paragraph of the “Acknowledgements” section. Please add authors in the format First Name, Middle initial(s) (optional), Last Name. You can add institution or country information for each author if you wish, but this should be consistent across all authors.
Please note that individual names may not be present in the PubMed record at the time a published article is initially included in PubMed as it takes PubMed additional time to code this information.
Authors' information
This section is optional.
You may choose to use this section to include any relevant information about the author(s) that may aid the reader's interpretation of the article, and understand the standpoint of the author(s). This may include details about the authors' qualifications, current positions they hold at institutions or societies, or any other relevant background information. Please refer to authors using their initials. Note this section should not be used to describe any competing interests.
Footnotes should be designated within the text using a superscript number. It is not allowed to use footnotes for references/citations.
Examples of the Vancouver reference style are shown below.
See our editorial policies for author guidance on good citation practice.
Web links and URLs: All web links and URLs, including links to the authors' own websites, should be given a reference number and included in the reference list rather than within the text of the manuscript. They should be provided in full, including both the title of the site and the URL, as well as the date the site was accessed, in the following format: The Mouse Tumor Biology Database. http://tumor.informatics.jax.org/mtbwi/index.do . Accessed 20 May 2013. If an author or group of authors can clearly be associated with a web link, such as for weblogs, then they should be included in the reference.
Example reference style:
Article within a journal
Smith JJ. The world of science. Am J Sci. 1999;36:234-5.
Article within a journal (no page numbers)
Rohrmann S, Overvad K, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Jakobsen MU, Egeberg R, Tjønneland A, et al. Meat consumption and mortality - results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Medicine. 2013;11:63.
Article within a journal by DOI
Slifka MK, Whitton JL. Clinical implications of dysregulated cytokine production. Dig J Mol Med. 2000; doi:10.1007/s801090000086.
Article within a journal supplement
Frumin AM, Nussbaum J, Esposito M. Functional asplenia: demonstration of splenic activity by bone marrow scan. Blood 1979;59 Suppl 1:26-32.
Book chapter, or an article within a book
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. In: Bourne GH, Danielli JF, Jeon KW, editors. International review of cytology. London: Academic; 1980. p. 251-306.
OnlineFirst chapter in a series (without a volume designation but with a DOI)
Saito Y, Hyuga H. Rate equation approaches to amplification of enantiomeric excess and chiral symmetry breaking. Top Curr Chem. 2007. doi:10.1007/128_2006_108.
Complete book, authored
Blenkinsopp A, Paxton P. Symptoms in the pharmacy: a guide to the management of common illness. 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1998.
Online document
Doe J. Title of subordinate document. In: The dictionary of substances and their effects. Royal Society of Chemistry. 1999. http://www.rsc.org/dose/title of subordinate document. Accessed 15 Jan 1999.
Online database
Healthwise Knowledgebase. US Pharmacopeia, Rockville. 1998. http://www.healthwise.org. Accessed 21 Sept 1998.
Supplementary material/private homepage
Doe J. Title of supplementary material. 2000. http://www.privatehomepage.com. Accessed 22 Feb 2000.
University site
Doe, J: Title of preprint. http://www.uni-heidelberg.de/mydata.html (1999). Accessed 25 Dec 1999.
Doe, J: Trivial HTTP, RFC2169. ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2169.txt (1999). Accessed 12 Nov 1999.
Organization site
ISSN International Centre: The ISSN register. http://www.issn.org (2006). Accessed 20 Feb 2007.
Dataset with persistent identifier
Zheng L-Y, Guo X-S, He B, Sun L-J, Peng Y, Dong S-S, et al. Genome data from sweet and grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). GigaScience Database. 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.5524/100012 .
General formatting information
Manuscripts must be written in concise English. For help on scientific writing, or preparing your manuscript in English, please see Springer's Author Academy .
Quick points:
- Use double line spacing
- Include line and page numbering
- Use SI units: Please ensure that all special characters used are embedded in the text, otherwise they will be lost during conversion to PDF
- Do not use page breaks in your manuscript
File formats
The following word processor file formats are acceptable for the main manuscript document:
- Microsoft word (DOC, DOCX)
- Rich text format (RTF)
- TeX/LaTeX
Please note: editable files are required for processing in production. If your manuscript contains any non-editable files (such as PDFs) you will be required to re-submit an editable file if your manuscript is accepted.
For more information, see ' Preparing figures ' below.
Additional information for TeX/LaTeX users
You are encouraged to use the Springer Nature LaTeX template when preparing a submission. A PDF of your manuscript files will be compiled during submission using pdfLaTeX and TexLive 2021. All relevant editable source files must be uploaded during the submission process. Failing to submit these source files will cause unnecessary delays in the production process.
Style and language
For editors and reviewers to accurately assess the work presented in your manuscript you need to ensure the English language is of sufficient quality to be understood. If you need help with writing in English you should consider:
- Getting a fast, free online grammar check .
- Visiting the English language tutorial which covers the common mistakes when writing in English.
- Asking a colleague who is proficient in English to review your manuscript for clarity.
- Using a professional language editing service where editors will improve the English to ensure that your meaning is clear and identify problems that require your review. Two such services are provided by our affiliates Nature Research Editing Service and American Journal Experts . SpringerOpen authors are entitled to a 10% discount on their first submission to either of these services. To claim 10% off English editing from Nature Research Editing Service, click here . To claim 10% off American Journal Experts, click here .
Please note that the use of a language editing service is not a requirement for publication in Journal of Big Data and does not imply or guarantee that the article will be selected for peer review or accepted. 为便于编辑和评审专家准确评估您稿件中陈述的研究工作,您需要确保文稿英语语言质量足以令人理解。如果您需要英文写作方面的帮助,您可以考虑:
- 获取快速、免费的在线 语法检查 。
- 查看一些有关英语写作中常见语言错误的 教程 。
- 请一位以英语为母语的同事审阅您的稿件是否表意清晰。
- 使用专业语言编辑服务,编辑人员会对英语进行润色,以确保您的意思表达清晰,并提出需要您复核的问题。例如我们的附属机构 Nature Research Editing Service 以及合作伙伴 American Journal Experts 都可以提供此类专业服务。SpringerOpen作者享受首次订单10%优惠,该优惠同时适用于两家公司。您只需点击以下链接即可开始。使用 Nature Research Editing Service的编辑润色10%的优惠服务,请点击 这里 。使用 American Journal Experts的10%优惠服务,请点击 这里 。
请注意,使用语言编辑服务并非在期刊上发表文章的必要条件,这也并不意味或保证文章将被选中进行同行评议或被接受。 エディターと査読者があなたの論文を正しく評価するには、使用されている英語の質が十分であることが必要とされます。英語での論文執筆に際してサポートが必要な場合には、次のオプションがあります:
- 高速なオンライン 文法チェック を無料で受ける。
- 英語で執筆する際のよくある間違いに関する 英語のチュートリアル を参照する。
- 英語を母国語とする同僚に、原稿内の英語が明確であるかをチェックしてもらう。
- プロの英文校正サービスを利用する。校正者が原稿の意味を明確にしたり、問題点を指摘し、英語を向上させます。 Nature Research Editing Service と American Journal Experts の2つは弊社と提携しているサービスです。SpringerOpenのジャーナルの著者は、いずれかのサービスを初めて利用する際に、10%の割引を受けることができます。Nature Research Editing Serviceの10%割引を受けるには、 こちらをクリックしてください 。. American Journal Expertsの10%割引を受けるには、 こちらをクリックしてください 。
英文校正サービスの利用は、このジャーナルに掲載されるための条件ではないこと、また論文審査や受理を保証するものではないことに留意してください。 영어 원고의 경우, 에디터 및 리뷰어들이 귀하의 원고에 실린 결과물을 정확하게 평가할 수 있도록, 그들이 충분히 이해할 수 있을 만한 수준으로 작성되어야 합니다. 만약 영작문과 관련하여 도움을 받기를 원하신다면 다음의 사항들을 고려하여 주십시오:
- 영어 튜토리얼 페이지 에 방문하여 영어로 글을 쓸 때 자주하는 실수들을 확인합니다.
- 귀하의 원고의 표현을 명확히 해줄 영어 원어민 동료를 찾아서 리뷰를 의뢰합니다
- 리뷰에 대비하여, 원고의 의미를 명확하게 해주고 리뷰에서 요구하는 문제점들을 식별해서 영문 수준을 향상시켜주는 전문 영문 교정 서비스를 이용합니다. Nature Research Editing Service 와 American Journal Experts 에서 저희와 협약을 통해 서비스를 제공하고 있습니다. SpringerOpen에서는 위의 두 가지의 서비스를 첫 논문 투고를 위해 사용하시는 경우, 10%의 할인을 제공하고 있습니다. Nature Research Editing Service이용시 10% 할인을 요청하기 위해서는 여기 를 클릭해 주시고, American Journal Experts 이용시 10% 할인을 요청하기 위해서는 여기 를 클릭해 주십시오.
영문 교정 서비스는 게재를 위한 요구사항은 아니며, 해당 서비스의 이용이 피어 리뷰에 논문이 선택되거나 게재가 수락되는 것을 의미하거나 보장하지 않습니다.
Data and materials
For all journals, SpringerOpen strongly encourages all datasets on which the conclusions of the manuscript rely to be either deposited in publicly available repositories (where available and appropriate) or presented in the main paper or additional supporting files, in machine-readable format (such as spread sheets rather than PDFs) whenever possible. Please see the list of recommended repositories in our editorial policies.
For some journals, deposition of the data on which the conclusions of the manuscript rely is an absolute requirement. Please check the Instructions for Authors for the relevant journal and article type for journal specific policies.
For all manuscripts, information about data availability should be detailed in an ‘Availability of data and materials’ section. For more information on the content of this section, please see the Declarations section of the relevant journal’s Instruction for Authors. For more information on SpringerOpen's policies on data availability, please see our editorial policies .
Formatting the 'Availability of data and materials' section of your manuscript
The following format for the 'Availability of data and materials section of your manuscript should be used:
"The dataset(s) supporting the conclusions of this article is(are) available in the [repository name] repository, [unique persistent identifier and hyperlink to dataset(s) in http:// format]."
The following format is required when data are included as additional files:
"The dataset(s) supporting the conclusions of this article is(are) included within the article (and its additional file(s))."
For databases, this section should state the web/ftp address at which the database is available and any restrictions to its use by non-academics.
For software, this section should include:
- Project name: e.g. My bioinformatics project
- Project home page: e.g. http://sourceforge.net/projects/mged
- Archived version: DOI or unique identifier of archived software or code in repository (e.g. enodo)
- Operating system(s): e.g. Platform independent
- Programming language: e.g. Java
- Other requirements: e.g. Java 1.3.1 or higher, Tomcat 4.0 or higher
- License: e.g. GNU GPL, FreeBSD etc.
- Any restrictions to use by non-academics: e.g. licence needed
Information on available repositories for other types of scientific data, including clinical data, can be found in our editorial policies .
What should be cited?
Only articles, clinical trial registration records and abstracts that have been published or are in press, or are available through public e-print/preprint servers, may be cited.
Unpublished abstracts, unpublished data and personal communications should not be included in the reference list, but may be included in the text and referred to as "unpublished observations" or "personal communications" giving the names of the involved researchers. Obtaining permission to quote personal communications and unpublished data from the cited colleagues is the responsibility of the author. Either footnotes or endnotes are permitted. Journal abbreviations follow Index Medicus/MEDLINE.
Any in press articles cited within the references and necessary for the reviewers' assessment of the manuscript should be made available if requested by the editorial office.
Preparing figures
When preparing figures, please follow the formatting instructions below.
- Figure titles (max 15 words) and legends (max 300 words) should be provided in the main manuscript, not in the graphic file.
- Tables should NOT be submitted as figures but should be included in the main manuscript file.
- Multi-panel figures (those with parts a, b, c, d etc.) should be submitted as a single composite file that contains all parts of the figure.
- Figures should be numbered in the order they are first mentioned in the text, and uploaded in this order.
- Figures should be uploaded in the correct orientation.
- Figure keys should be incorporated into the graphic, not into the legend of the figure.
- Each figure should be closely cropped to minimize the amount of white space surrounding the illustration. Cropping figures improves accuracy when placing the figure in combination with other elements when the accepted manuscript is prepared for publication on our site. For more information on individual figure file formats, see our detailed instructions.
- Individual figure files should not exceed 10 MB. If a suitable format is chosen, this file size is adequate for extremely high quality figures.
- Please note that it is the responsibility of the author(s) to obtain permission from the copyright holder to reproduce figures (or tables) that have previously been published elsewhere. In order for all figures to be open access, authors must have permission from the rights holder if they wish to include images that have been published elsewhere in non open access journals. Permission should be indicated in the figure legend, and the original source included in the reference list.
Figure file types
We accept the following file formats for figures:
- EPS (suitable for diagrams and/or images)
- PDF (suitable for diagrams and/or images)
- Microsoft Word (suitable for diagrams and/or images, figures must be a single page)
- PowerPoint (suitable for diagrams and/or images, figures must be a single page)
- TIFF (suitable for images)
- JPEG (suitable for photographic images, less suitable for graphical images)
- PNG (suitable for images)
- BMP (suitable for images)
- CDX (ChemDraw - suitable for molecular structures)
Figure size and resolution
Figures are resized during publication of the final full text and PDF versions to conform to the SpringerOpen standard dimensions, which are detailed below.
Figures on the web:
- width of 600 pixels (standard), 1200 pixels (high resolution).
Figures in the final PDF version:
- width of 85 mm for half page width figure
- width of 170 mm for full page width figure
- maximum height of 225 mm for figure and legend
- image resolution of approximately 300 dpi (dots per inch) at the final size
Figures should be designed such that all information, including text, is legible at these dimensions. All lines should be wider than 0.25 pt when constrained to standard figure widths. All fonts must be embedded.
Figure file compression
Vector figures should if possible be submitted as PDF files, which are usually more compact than EPS files.
- TIFF files should be saved with LZW compression, which is lossless (decreases file size without decreasing quality) in order to minimize upload time.
- JPEG files should be saved at maximum quality.
- Conversion of images between file types (especially lossy formats such as JPEG) should be kept to a minimum to avoid degradation of quality.
If you have any questions or are experiencing a problem with figures, please contact the customer service team at [email protected] .
Preparing tables
When preparing tables, please follow the formatting instructions below.
- Tables should be numbered and cited in the text in sequence using Arabic numerals (i.e. Table 1, Table 2 etc.).
- Tables less than one A4 or Letter page in length can be placed in the appropriate location within the manuscript.
- Tables larger than one A4 or Letter page in length can be placed at the end of the document text file. Please cite and indicate where the table should appear at the relevant location in the text file so that the table can be added in the correct place during production.
- Larger datasets, or tables too wide for A4 or Letter landscape page can be uploaded as additional files. Please see [below] for more information.
- Tabular data provided as additional files can be uploaded as an Excel spreadsheet (.xls ) or comma separated values (.csv). Please use the standard file extensions.
- Table titles (max 15 words) should be included above the table, and legends (max 300 words) should be included underneath the table.
- Tables should not be embedded as figures or spreadsheet files, but should be formatted using ‘Table object’ function in your word processing program.
- Color and shading may not be used. Parts of the table can be highlighted using superscript, numbering, lettering, symbols or bold text, the meaning of which should be explained in a table legend.
- Commas should not be used to indicate numerical values.
If you have any questions or are experiencing a problem with tables, please contact the customer service team at [email protected] .
Preparing additional files
As the length and quantity of data is not restricted for many article types, authors can provide datasets, tables, movies, or other information as additional files.
All Additional files will be published along with the accepted article. Do not include files such as patient consent forms, certificates of language editing, or revised versions of the main manuscript document with tracked changes. Such files, if requested, should be sent by email to the journal’s editorial email address, quoting the manuscript reference number.
Results that would otherwise be indicated as "data not shown" should be included as additional files. Since many web links and URLs rapidly become broken, SpringerOpen requires that supporting data are included as additional files, or deposited in a recognized repository. Please do not link to data on a personal/departmental website. Do not include any individual participant details. The maximum file size for additional files is 20 MB each, and files will be virus-scanned on submission. Each additional file should be cited in sequence within the main body of text.
Submit manuscript
- Editorial Board
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- Follow us on Twitter
Annual Journal Metrics
Citation Impact 2023 Journal Impact Factor: 8.6 5-year Journal Impact Factor: 12.4 Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 3.853 SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 2.068
Speed 2023 Submission to first editorial decision (median days): 56 Submission to acceptance (median days): 205
Usage 2023 Downloads: 2,559,548 Altmetric mentions: 280
- More about our metrics
- ISSN: 2196-1115 (electronic)
Writing up a Research Report
- First Online: 10 November 2021
Cite this chapter

- Stefan Hunziker 3 &
- Michael Blankenagel 3
3434 Accesses
A research report is one big argument how and why you came up with your conclusions. To make it a convincing argument, a typical guiding structure has developed. In the different chapters, distinct issues need to be addressed to explain to the reader why your conclusions are valid. The governing principle for writing the report is full disclosure: to explain everything and ensure replicability by another researcher.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Barros, L. O. (2016). The only academic phrasebook you’ll ever need. Createspace Independent Publishing Platform.
Google Scholar
Field, A. (2016). An adventure in statistics. The reality enigma . SAGE.
Field, A. (2020). Discovering statistics using IBM SPSS statistics (5th ed.). SAGE.
Früh, M., Keimer, I., & Blankenagel, M. (2019). The impact of Balanced Scorecard excellence on shareholder returns. IFZ Working Paper No. 0003/2019. Retrieved June 09, 2021, from https://zenodo.org/record/2571603#.YMDUafkzZaQ .
Yin, R. K. (2013). Case study research: Design and methods (5th ed.). SAGE.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Wirtschaft/IFZ – Campus Zug-Rotkreuz, Hochschule Luzern, Zug-Rotkreuz, Zug , Switzerland
Stefan Hunziker & Michael Blankenagel
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Stefan Hunziker .
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Fachmedien Wiesbaden GmbH, part of Springer Nature
About this chapter
Hunziker, S., Blankenagel, M. (2021). Writing up a Research Report. In: Research Design in Business and Management. Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_4
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-658-34357-6_4
Published : 10 November 2021
Publisher Name : Springer Gabler, Wiesbaden
Print ISBN : 978-3-658-34356-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-658-34357-6
eBook Packages : Business and Economics (German Language)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Submit your Research
- My Submissions
- Article Guidelines
- Article Guidelines (New Versions)
- Data Guidelines
- Posters and Slides Guidelines
- Document Guidelines
- Article Processing Charges
- Peer Review
- The Peer Review Process
- The Editorial Team’s Role
- Understanding Peer Review Reports and Statuses
- Revising and Responding to Reviewers
- Finding Article Reviewers
- Reviewer Criteria
- Hints and Tips for Finding Reviewers
- Dos and Don’ts for Suggesting Reviewers
Guidelines for Article Preparation for Submission
- Data and Software Availability
- Reporting Guidelines
- Ethics and Consent
- Author Contributions
- Competing Interests
- Grant Information
- Acknowledgments
- Supplementary Material
- References and footnotes
- Figures and Tables
- Units, Symbols and Mathematical Scripts
- Authors’ Role in the Peer Review Process
- Introduction
- Conclusions/Discussion
- Initial ace validity testing
- Preliminary pilot testing
- Reliability testing (internal consistency, test-retest, inter-rater)
- Any changes implemented resulting from preliminary testing
- Title of file. (Description of data in file).
- Data file 1. Datasets.xlsx
- Title of file. (Description of data in file.)
- Software available from: URL for the website where software can be downloaded from, if applicable.
- Source code available from: URL for versioning control system (for example GitHub).
- Archived source code at time of publication: DOI and citation for project in Zenodo (please select the appropriate DOI for the version which underlies your article).
- License: Must be an open license and preferably an OSI-approved license .
- Randomized controlled trials ( CONSORT )
- Observational studies ( STROBE )
- Qualitative research ( COREQ ; SRQR )
- In vivo animal studies ( ARRIVE )
- Authors should ensure that the terms sex and gender are used correctly throughout the article.
- Title/abstract : it should be clear if the results can only be applied to one sex or gender.
- Introduction : if sex and gender differences are expected in the results, these should be stated.
- if sex and gender differences were taken into consideration for the design of the study these should be stated. If they were not taken into consideration, the rationale should be given.
- explanation of how sex of participants was defined should be stated, either based on self-report, assigned following external or internal examination of body characteristics, or through genetic testing or other means.
- Results : data should be presented disaggregated by sex and gender.
- Discussion : implications of sex and gender differences in the results should be discussed. If sex or gender analysis was not conducted, the rationale should be given.
| Conceptualization | Ideas; formulation or evolution of overarching research goals and aims. |
| Data Curation | Management activities to annotate (produce metadata), scrub data and maintain research data (including software code, where it is necessary for interpreting the data itself) for initial use and later reuse. |
| Formal Analysis | Application of statistical, mathematical, computational, or other formal techniques to analyze or synthesize study data. |
| Funding Acquisition | Acquisition of the financial support for the project leading to this publication. |
| Investigation | Conducting a research and investigation process, specifically performing the experiments, or data/evidence collection. |
| Methodology | Development or design of methodology; creation of models. |
| Project Administration | Management and coordination responsibility for the research activity planning and execution. |
| Resources | Provision of study materials, reagents, materials, patients, laboratory samples, animals, instrumentation, computing resources, or other analysis tools. |
| Software | Programming, software development; designing computer programs; implementation of the computer code and supporting algorithms; testing of existing code components. |
| Supervision | Oversight and leadership responsibility for the research activity planning and execution, including mentorship external to the core team. |
| Validation | Verification, whether as a part of the activity or separate, of the overall replication/reproducibility of results/experiments and other research outputs. |
| Visualization | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically visualization/data presentation. |
| Writing – Original Draft Preparation | Creation and/or presentation of the published work, specifically writing the initial draft (including substantive translation). |
| Writing – Review & Editing | Preparation, creation and/or presentation of the published work by those from the original research group, specifically critical review, commentary or revision – including pre- or post-publication stages. |
- Abbreviations and journal names should align with discipline specific standards.
- Preprints can be cited and listed in the reference list.
- Unpublished abstracts, papers that have been submitted to a journal but not yet accepted, and personal communications should instead be included in the text; they should be referred to as ‘personal communications’ or ‘unpublished work’ and the researchers involved should be named. Authors are responsible for getting permission to quote any personal communications from the cited individuals.
- Web links should be included as hyperlinks within the main body of the article, and not as references.
- Datasets published or deposited elsewhere (for example, in a general repository) should be listed in the “References” section and the citation to the dataset should follow one of these examples .
- Special care should be taken with mathematical scripts, especially subscripts and superscripts and differentiation between the letter “ell” and the figure one, and the letter “oh” and the figure zero.
- It is important to differentiate between mathematical symbols and letters to ensure that these are consistent throughout. Regardless of which symbol you use to represent which constant or unknown (e.g. K could be Kelvin, Kinetic energy, spring constant or a number of others), please make sure the formatting, such as roman or italic, and capitalization of the symbol is consistent throughout and only used to represent ONE constant or unknown for example: C (heat capacity) and c (speed of light); K and k; X, x and × (multiplication) etc.
- In both displayed equations and in text, scalar variables must be in italics, with non-variable matter in upright type.
- For simple fractions in the text, the solidus “/” should be used instead of a horizontal line, care being taken to insert parentheses where necessary to avoid ambiguity. Exceptions are the proper fractions available (e.g., ¼, ½, ¾).
- The solidus is not generally used for units (e.g. m s⁻¹ not m/s). But note can be where convention stipulates electrons/s, counts/channel, etc.
- Displayed equations referred to in the text should be numbered serially ((1), (2), etc.) on the right-hand side. Short expressions not referred to by any number will usually be incorporated into the text.
- The following styles are preferred: roman bold sans serif r for tensors, bold serif italic r for vectors, roman bold serif r for matrices, and medium-weight italic serif r for scalar variables. In mathematical expressions, the use of “d” for differential should be made clear, and coded in roman, not italic. i.e. use the equation function in Word.
- Braces, brackets, and parentheses are used in the order {[( )] }, except where mathematical convention dictates otherwise (e.g., square brackets for commutators and anticommutators; braces for the exponent in exponentials).
- For units and symbols, the SI system should be used. Where measurements are given in other systems, please insert conversions.
- The key with mathematical symbols and expressions is to ensure consistency above all else throughout the document.
The email address should be the one you originally registered with F1000.
You registered with F1000 via Google, so we cannot reset your password.
To sign in, please click here .
If you still need help with your Google account password, please click here .
You registered with F1000 via Facebook, so we cannot reset your password.
If you still need help with your Facebook account password, please click here .
If your email address is registered with us, we will email you instructions to reset your password.
If you think you should have received this email but it has not arrived, please check your spam filters and/or contact for further assistance.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Critical Analysis – Types, Examples and Writing...

Research Results Section – Writing Guide and...

Research Paper Title Page – Example and Making...

Research Techniques – Methods, Types and Examples


Tables in Research Paper – Types, Creating Guide...

Thesis – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case AskWhy Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Research Reports: Definition and How to Write Them

Reports are usually spread across a vast horizon of topics but are focused on communicating information about a particular topic and a niche target market. The primary motive of research reports is to convey integral details about a study for marketers to consider while designing new strategies.
Certain events, facts, and other information based on incidents need to be relayed to the people in charge, and creating research reports is the most effective communication tool. Ideal research reports are extremely accurate in the offered information with a clear objective and conclusion. These reports should have a clean and structured format to relay information effectively.
What are Research Reports?
Research reports are recorded data prepared by researchers or statisticians after analyzing the information gathered by conducting organized research, typically in the form of surveys or qualitative methods .
A research report is a reliable source to recount details about a conducted research. It is most often considered to be a true testimony of all the work done to garner specificities of research.
The various sections of a research report are:
- Background/Introduction
- Implemented Methods
- Results based on Analysis
- Deliberation
Learn more: Quantitative Research
Components of Research Reports
Research is imperative for launching a new product/service or a new feature. The markets today are extremely volatile and competitive due to new entrants every day who may or may not provide effective products. An organization needs to make the right decisions at the right time to be relevant in such a market with updated products that suffice customer demands.
The details of a research report may change with the purpose of research but the main components of a report will remain constant. The research approach of the market researcher also influences the style of writing reports. Here are seven main components of a productive research report:
- Research Report Summary: The entire objective along with the overview of research are to be included in a summary which is a couple of paragraphs in length. All the multiple components of the research are explained in brief under the report summary. It should be interesting enough to capture all the key elements of the report.
- Research Introduction: There always is a primary goal that the researcher is trying to achieve through a report. In the introduction section, he/she can cover answers related to this goal and establish a thesis which will be included to strive and answer it in detail. This section should answer an integral question: “What is the current situation of the goal?”. After the research design was conducted, did the organization conclude the goal successfully or they are still a work in progress – provide such details in the introduction part of the research report.
- Research Methodology: This is the most important section of the report where all the important information lies. The readers can gain data for the topic along with analyzing the quality of provided content and the research can also be approved by other market researchers . Thus, this section needs to be highly informative with each aspect of research discussed in detail. Information needs to be expressed in chronological order according to its priority and importance. Researchers should include references in case they gained information from existing techniques.
- Research Results: A short description of the results along with calculations conducted to achieve the goal will form this section of results. Usually, the exposition after data analysis is carried out in the discussion part of the report.
Learn more: Quantitative Data
- Research Discussion: The results are discussed in extreme detail in this section along with a comparative analysis of reports that could probably exist in the same domain. Any abnormality uncovered during research will be deliberated in the discussion section. While writing research reports, the researcher will have to connect the dots on how the results will be applicable in the real world.
- Research References and Conclusion: Conclude all the research findings along with mentioning each and every author, article or any content piece from where references were taken.
Learn more: Qualitative Observation
15 Tips for Writing Research Reports
Writing research reports in the manner can lead to all the efforts going down the drain. Here are 15 tips for writing impactful research reports:
- Prepare the context before starting to write and start from the basics: This was always taught to us in school – be well-prepared before taking a plunge into new topics. The order of survey questions might not be the ideal or most effective order for writing research reports. The idea is to start with a broader topic and work towards a more specific one and focus on a conclusion or support, which a research should support with the facts. The most difficult thing to do in reporting, without a doubt is to start. Start with the title, the introduction, then document the first discoveries and continue from that. Once the marketers have the information well documented, they can write a general conclusion.
- Keep the target audience in mind while selecting a format that is clear, logical and obvious to them: Will the research reports be presented to decision makers or other researchers? What are the general perceptions around that topic? This requires more care and diligence. A researcher will need a significant amount of information to start writing the research report. Be consistent with the wording, the numbering of the annexes and so on. Follow the approved format of the company for the delivery of research reports and demonstrate the integrity of the project with the objectives of the company.
- Have a clear research objective: A researcher should read the entire proposal again, and make sure that the data they provide contributes to the objectives that were raised from the beginning. Remember that speculations are for conversations, not for research reports, if a researcher speculates, they directly question their own research.
- Establish a working model: Each study must have an internal logic, which will have to be established in the report and in the evidence. The researchers’ worst nightmare is to be required to write research reports and realize that key questions were not included.
Learn more: Quantitative Observation
- Gather all the information about the research topic. Who are the competitors of our customers? Talk to other researchers who have studied the subject of research, know the language of the industry. Misuse of the terms can discourage the readers of research reports from reading further.
- Read aloud while writing. While reading the report, if the researcher hears something inappropriate, for example, if they stumble over the words when reading them, surely the reader will too. If the researcher can’t put an idea in a single sentence, then it is very long and they must change it so that the idea is clear to everyone.
- Check grammar and spelling. Without a doubt, good practices help to understand the report. Use verbs in the present tense. Consider using the present tense, which makes the results sound more immediate. Find new words and other ways of saying things. Have fun with the language whenever possible.
- Discuss only the discoveries that are significant. If some data are not really significant, do not mention them. Remember that not everything is truly important or essential within research reports.
Learn more: Qualitative Data
- Try and stick to the survey questions. For example, do not say that the people surveyed “were worried” about an research issue , when there are different degrees of concern.
- The graphs must be clear enough so that they understand themselves. Do not let graphs lead the reader to make mistakes: give them a title, include the indications, the size of the sample, and the correct wording of the question.
- Be clear with messages. A researcher should always write every section of the report with an accuracy of details and language.
- Be creative with titles – Particularly in segmentation studies choose names “that give life to research”. Such names can survive for a long time after the initial investigation.
- Create an effective conclusion: The conclusion in the research reports is the most difficult to write, but it is an incredible opportunity to excel. Make a precise summary. Sometimes it helps to start the conclusion with something specific, then it describes the most important part of the study, and finally, it provides the implications of the conclusions.
- Get a couple more pair of eyes to read the report. Writers have trouble detecting their own mistakes. But they are responsible for what is presented. Ensure it has been approved by colleagues or friends before sending the find draft out.
Learn more: Market Research and Analysis
MORE LIKE THIS

Target Population: What It Is + Strategies for Targeting
Aug 29, 2024
Microsoft Customer Voice vs QuestionPro: Choosing the Best
Statistical Methods: What It Is, Process, Analyze & Present
Aug 28, 2024

Velodu and QuestionPro: Connecting Data with a Human Touch
Other categories.
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Tuesday CX Thoughts (TCXT)
- Uncategorized
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence
- SpringerLink shop
Types of journal articles
It is helpful to familiarise yourself with the different types of articles published by journals. Although it may appear there are a large number of types of articles published due to the wide variety of names they are published under, most articles published are one of the following types; Original Research, Review Articles, Short reports or Letters, Case Studies, Methodologies.
Original Research:
This is the most common type of journal manuscript used to publish full reports of data from research. It may be called an Original Article, Research Article, Research, or just Article, depending on the journal. The Original Research format is suitable for many different fields and different types of studies. It includes full Introduction, Methods, Results, and Discussion sections.
Short reports or Letters:
These papers communicate brief reports of data from original research that editors believe will be interesting to many researchers, and that will likely stimulate further research in the field. As they are relatively short the format is useful for scientists with results that are time sensitive (for example, those in highly competitive or quickly-changing disciplines). This format often has strict length limits, so some experimental details may not be published until the authors write a full Original Research manuscript. These papers are also sometimes called Brief communications .
Review Articles:
Review Articles provide a comprehensive summary of research on a certain topic, and a perspective on the state of the field and where it is heading. They are often written by leaders in a particular discipline after invitation from the editors of a journal. Reviews are often widely read (for example, by researchers looking for a full introduction to a field) and highly cited. Reviews commonly cite approximately 100 primary research articles.
TIP: If you would like to write a Review but have not been invited by a journal, be sure to check the journal website as some journals to not consider unsolicited Reviews. If the website does not mention whether Reviews are commissioned it is wise to send a pre-submission enquiry letter to the journal editor to propose your Review manuscript before you spend time writing it.
Case Studies:
These articles report specific instances of interesting phenomena. A goal of Case Studies is to make other researchers aware of the possibility that a specific phenomenon might occur. This type of study is often used in medicine to report the occurrence of previously unknown or emerging pathologies.
Methodologies or Methods
These articles present a new experimental method, test or procedure. The method described may either be completely new, or may offer a better version of an existing method. The article should describe a demonstrable advance on what is currently available.
Back │ Next
26+ SAMPLE Brief Report in PDF | MS Word
Brief report | ms word, 26+ sample brief report , what is a brief report, the standard sections of a brief report, brief reports vs. long reports, how to make a brief report, how long should a brief report be, what is the simplest format of a brief report, what are the types of reports.

Brief Report Template

Research Brief Report

Basic Brief Report

Meeting Brief Report

Brief Report of Training Workshop

Brief Report in PDF

Cooperative Farm Brief Report

Brief Survey Report

University Assessment Brief Report
Standard Brief Report

Respiratory Virus Activity Brief Report

Faculty Brief Report

Project Brief Report

Brief Report Format

Simple Brief Report

Conversation Brief Report

Technology Assessment Brief Report

Brief Report Annual Meeting

Brief Report Series
Data Brief Reporting Schedule

Transparency Camp Brief Report
Brief Report on Service Learning
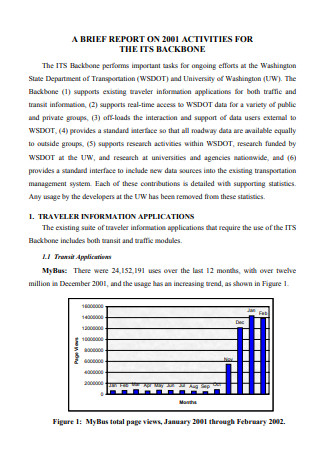
Formal Brief Report

Brief Report Example

Printable Brief Report

Needs and Opportunities Brief Report

Committee Brief Report
Why are brief reports important, polarizing length, disparity in scope, informal vs. formal reports, preliminary vs. final studies, step 1: gather enough background about your subject, step 2: use a sample brief report template, step 3: denote the brief report’s important sections, step 4: be direct to the point, step 5: observe an easy-to-follow format and structure.
- Long and brief reports
- Formal and informal reports
- Vertical and lateral reports
- Proposal reports
- Functional reports
- Periodic reports
- Informational and analytical reports
Share This Post on Your Network
You may also like these articles, medical report.

In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the essentials of creating an effective Medical Report. Whether you are a healthcare professional or need to understand how to document medical…
Training Report

In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of creating an effective Training Report. Whether you are new to this process or looking to enhance your existing…
browse by categories
- Questionnaire
- Description
- Reconciliation
- Certificate
- Spreadsheet
Information
- privacy policy
- Terms & Conditions
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
Article Types
All articles are assigned a type, depending on the content of the article. This is useful to readers, informing them of the style of content to expect (original research, review, communication, etc.) and for indexing services when applying filters to search results. This section details the most common article types, although is not exhaustive. Editors have the final say on which type should be assigned to a published article. Scientists are encouraged to publish their experimental, theoretical, descriptive studies and observations in as much detail as possible so the results can be reproduced. Manuscripts that are not comprehensive may be found not suitable for peer review.
These are original research manuscripts. The work should report scientifically sound experiments and provide a substantial amount of new information. The article should include the most recent and relevant references in the field. The structure should include an Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Materials and Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusions (optional) sections. Please refer to the journal webpages for specific instructions and templates.
Brief Report
Brief reports are short, observational studies that report preliminary results or a short complete study or protocol. Brief reports usually contain two figures and/or a table; however, the Materials and Methods sections should be detailed to ensure reproducibility of the presented work. The structure is similar to that of an article.
Case Report
Common in medical journals, case reports present detailed information on the symptoms, signs, diagnosis, treatment (including all types of interventions), and outcomes of an individual patient. They usually describe new or uncommon conditions that serve to enhance medical care or highlight diagnostic approaches. The structure of case reports differs from articles and includes an Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Detailed Case Description, Discussion, and Conclusions. Special care should be taken when submitting case reports to ensure that appropriate permission for publication has been obtained from patients featuring in the paper. A sample blank consent form can be found on the ‘Instructions for Authors’ pages of the relevant journals. Please refer to the journal websites for more information, because not all MDPI journals publish case reports.
Communication
Communications are short articles that present groundbreaking preliminary results or significant findings that are part of a larger study over multiple years. They can also include cutting-edge methods or experiments, and the development of new technology or materials. The structure is similar to an article.
Conference Report
Conference reports are records of the events of a conference, seminar, or meeting. They should provide a comprehensive overview of a meeting or session, along with relevant background information for the reader. The structure should contain Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Conference Sections, and Concluding Remarks. They can also include all accepted meeting abstracts.
These are non-peer-reviewed texts used to announce the launch of a new journal, a new section, a new Editor-in-Chief, a Special Issue, or an invited editorial. The main text should provide a brief introduction of the purpose and aim of the Editorial—to present the new journal, close the Special Issue, report on a pressing topic, etc. Editorials should not include unpublished or original data, although must provide a Conflict of Interest statement. Editorials prepared for the launch of new journals may also include a short biography of the Editor-in-Chief.
Essays are an article type commonly used in humanities and social sciences to present provocative arguments aimed to stimulate the readers’ re-thinking of certain issues. The structure is similar to that of a review. Arguments should be supported by relevant references.
Hypothesis articles introduce a new hypothesis or theory, or a novel interpretation of that theory. They should provide: (1) a novel interpretation of recent data or findings in a specific area of investigation; (2) an accurate presentation of previously posed hypotheses or theories; (3) the hypothesis presented which should be testable in the framework of current knowledge; and (4) the possible inclusion of original data as well as personal insights and opinions. If new data are presented, the structure should follow that of an article. If no new data are included, the structure can be more flexible, but should still include an Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Relevant sections, and Concluding Remarks.
Interesting Images
This article type presents interesting images selected for educational, diagnostic, illustrative or aesthetic purposes. The number of images included is at the discretion of the author and there are no restrictions on use of color or image size; however, high-resolution images with sharp features must be provided. The structure of Interesting Images includes an unstructured Abstract and Keywords with no regular manuscript text (introduction/methods/results/discussion). Images should be accompanied by detailed legends focusing on the features of the image and their relevance, not a report of a case study. Reference citations should appear in the legends. There are no length restrictions on the legends.
Opinions are short articles that reflect the author’s viewpoints on a particular subject, technique, or recent findings. They should highlight the strengths and weaknesses of the topic presented in the opinion. The structure is similar to a review; however, they are significantly shorter and focused on the author’s view rather than a comprehensive, critical review.
Perspective
Perspectives are usually an invited type of article that showcase current developments in a specific field. Emphasis is placed on future directions of the field and on the personal assessment of the author. Comments should be situated in the context of existing literature from the previous 3 years. The structure is similar to a review.
Project Report
Project reports are short and/or rapid announcements of project results and implications. They should include a research strategy or approach, the activities, technologies, and details of the project undertaken, conclusions, and recommendations for the future direction of work in the field. The structure is similar to an article, but permits a higher degree of flexibility.
Protocols provide a detailed step-by-step description of a method. They should be proven to be robust and reproducible and should accompany a previously published article that uses this method. Any materials and equipment used should be explicitly listed. Conditions, quantities, concentrations, etc., should be given. Critical timepoints and steps, as well as warnings, should be emphasized in the text. The structure should include an Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Experimental Design, Materials and Equipment, Detailed Procedure, and Expected Results.
Registered Report
Registered reports are scientific articles which are peer reviewed before the research is performed and the data are collected. The ideas that meet high scientific standards, such as rigor, soundness, significant importance, and implications for the scientific community are then provisionally accepted for publication before data collection starts. Detailed guidelines for registered reports can be accessed here: https://www.mdpi.com/about/article_types/registered_reports .
Technical Note
Technical notes are brief articles focused on a new technique, method, or procedure. These should describe important modifications or unique applications for the described method. Technical notes can also be used for describing a new software tool or computational method. The structure should include an Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Materials and Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusions.
Reviews offer a comprehensive analysis of the existing literature within a field of study, identifying current gaps or problems. They should be critical and constructive and provide recommendations for future research. No new, unpublished data should be presented. The structure can include an Abstract, Keywords, Introduction, Relevant Sections, Discussion, Conclusions, and Future Directions. A Scoping Review type can be submitted as a Review. The structure is similar to that of a review. Scoping reviews should strictly follow the PRISMA extension for scoping reviews checklist ( https://www.prisma-statement.org/scoping ) and submit the checklist as non-published material during submission. Templates for the flow diagram can be downloaded from the PRISMA website and the diagram should be included in the main text. We strongly encourage authors to register their detailed protocols, before data extraction commences, in a public registry such as the Open Science Framework ( https://osf.io/ ) or Inplasy ( https://inplasy.com/ ). Authors must include a statement about following the PRISMA guidelines and registration information (if available) in the Methods section.
Book Review
Book reviews are short literary criticisms analyzing the content, style, and merit of a recently published book. Full book details should be provided at the beginning of the article. The structure should only include an Introduction and be a discussion of critical points with no sections or conclusions.
Systematic Review
Systematic review articles present a detailed investigation of previous research on a given topic that use clearly defined search parameters and methods to identify, categorize, analyze, and report aggregated evidence on a specific topic. The structure is similar to a review; however, they should include a Methods section. Systematic reviews should strictly follow the PRISMA checklist ( https://www.prisma-statement.org/prisma-2020-statement ) and include a completed PRISMA flow diagram as part of the main text or Supplementary Materials. Templates for the flow diagram can be downloaded from the PRISMA website. We strongly encourage authors to register their detailed protocols before data extraction commences, in a public registry such as PROSPERO ( https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/ ). Authors must include a statement about following the PRISMA guidelines and registration information (if available) in the Methods section.
Abstract and Proceeding Paper
These types of articles contain peer reviewed research output from conferences and can be submitted to one of MDPI’s proceedings journals: https://www.mdpi.com/about/proceedings .
Abstracts could be a short single paragraph summarizing the main topic and findings presented at the conference, or the extension of a typical abstract that contains a moderately detailed account of the work. They should be submitted to a conference in advance and provide details in support of a presentation made at the conference. The main text usually has no sections, but may include tables, figures, and references. The length should not exceed four pages.
Proceeding papers report new evidence or conclusions, and are expanded versions of work presented in a conference presentation. Conference proceedings can be incomplete findings that report on an idea, technique, or important results, thus providing readers with a brief overview of recent work or specific projects of significant interest. The structure is similar to a standard research article, and should include sections such as an Introduction, Methods, Results, Conclusions, etc. It is recommended that the length should not exceed eight pages.
All published items will be assigned a digital object identifier (DOI) and be citable, and posters, videos, or PPT presentations can be published together as the Supplementary Materials.
For updating published papers, please see the descriptions for Corrections, Retractions, Comments and Replies, and Expressions of Concern online at Research and Publication Ethics .
Further Information
Mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

- What are research briefings?
- How it works
- The Oxford Review Store
- The DEI (Diversity, Equity and Inclusion) Impact Series
- What is DEI? The Oxford Review Guide to Diversity, Equity and Inclusion.
- The Oxford Review DEI (Diversity, Equity and Inclusion) Dictionary
- The Essential Guide to Evidence-Based Practice
- The Oxford Review Encyclopaedia of Terms
- Video Research Briefings
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Competitive Intelligence From The Oxford Review
- The Oxford Review Mission / Aim
- How to use The Oxford Review to do more than just be the most knowledgeable person in the room
- Charities The Oxford Review Supports
- Terms and conditions
- Member Login
What are research briefings
Get free research briefings from the OR
What is a research briefing?
And how to be easily the most knowledgable person in the room.

In this briefing about research briefings I look at:
- What a research briefing is
- What a good research briefing should contain
- Who uses them
- How professionals use them
- How to know the quality of the research briefing and the study you are being briefed on
A research briefing is a summary of a single piece of proper research or a series of research studies on a similar topic. A briefing is a concise and understandable consolidation of just the main points of longer, more complex, academic and often impenetrable research.
What makes a good research briefing?
A good research briefing will have a number of attributes The point of a research briefing is that it should be useful to the reader in some way. A briefing and indeed the actual research is really only any use if it has some impact beyond ‘that’s interesting’. It needs to add something to the reader so the information / findings of the research need to be:
- Reader centric - the briefing needs to be on a topic of interest and use to the reader
- Useful - this is usually because the reader can use the information to actually do something as a result of reading the briefing
- Brief! People are busy so the briefing has to get the right information to the reader as quickly as possible
- Understandable - It needs to be based on the readers reading comprehension, experience, expertise and knowledge levels The point of a search briefing is to remove jargon and academic lagged and make it readily understandable
- Accurate - the briefing has to fairly represent the main findings of the research without bias or distortion
Additionally, a good briefing will review the research as objectively as possible to give an indication of any weaknesses in the research. Every study has weaknesses, there is no 100% watertight research. Having a fair appreciation of these weaknesses enables people to make better decisions about the study and the applicability and usability to the reader’s situation.
Not all studies have the same level of validity and reliability, indeed some are just rubbish and have little value. For example, a survey of the opinions of two people is very different to a study observing the behaviour of thousands. Understanding this is important.
Why do professionals use research briefings?
Ask yourself, in terms of the amount, how do you keep up to date with what’s happening in your professional area. How you gain new knowledge and insights and where do you get ideas from? It is probably a mix of the following:
- Work colleagues
- LinkedIn, Twitter, Facebook or other social media
- Professional forums and groups
- Magazines and newsletters
- Surveys and opinion polls
- Proper research papers or research briefings
- Conferences
- University or college or other courses
Now rank that mix, where do most of your updates, knowledge, insights and ideas come from week-to-week in order? Which is your most used source of practice evidence and inspiration? And how much of that information and knowledge is based on verifiable evidence? (See here for an article about the difference between opinion- and evidence-based knowledge) Properly designed, a good properly curated and accurate briefing based on proper research can get you the most up-to-date findings from the best research studies in a matter of minutes. Not only that a good research briefing service can make sure you only get the content you need.
This means that you stay up to date and impressively well-informed without becoming overwhelmed and in only a few minutes a week.
Get regular research brie fings - free...
Where does the data for a research briefing come from?
Good research briefings should come from good published research study.
So for a starter, research briefings should be using peer-reviewed sources (research that has been reviewed by other researchers and experts for accuracy, validity and reliability).
Anyone can publish a blog. Anyone can write a self-published book. Anyone can say they have done a survey. But how accurate or biased is it? How big is the sample in the study? Is it the opinions of just a few people or observations and proper statistical analysis of larger populations? Are the results generalisable (apply to most situations) or is it a case study that just applies to one situation or context?
A good research briefing will review and help you decide on the quality of the research, what its weakness are and not just report the findings.
What are research briefings based on?
That depends on who is doing the briefing. We can only talk about the OR Briefings...
All of our briefings come from properly published academic peer-reviewed sources. We not only get you to the findings fast, but we also review and fully reference the study, so you know where it has come from and how reliable it is. This is important information if you are going to have confidence in what you are investing your precious time on.
We also interview many of the researchers and send them out to members as podcasts.
How can I tell the quality of a research briefing?
We can’t talk for anyone else, but as mentioned above we review the research of every single study we provide briefings about. At the end of every briefing we let you know about the:
- Research Quality – we tell you what the strengths and weaknesses are of the study and give it a score out of 5 for fast reference
- Confidence – Given what other studies on this topic are saying and the weaknesses of the study, how confident are we that you can rely on the findings. Again we give it a score out of 5 and let you know why we have given it that score
- Usefulness – How useful and practical is this study, to whom and for what.
- Comments – We make general comments about the study or studies referenced in the briefing to help you decide how best to use it.
What subjects do you do research briefings on?
At the moment we do research briefings around anything broadly connected to organisations and people. We tend to focus on topics connected to (but we are not restricted to):
- Project Management and Agile Working
- Organisational Development and Design
- Organisational Change and Transformation
- Human Resources (HR), Human Capital (HC) and Human Resource Management (HRM)
- Learning, e-learning and Knowledge Management
- Coaching and mentoring
- Problem Solving and Decision-Making
- Work Psychology
Who uses research briefings?
The range of our members include:
- Operational managers
- HR Directors, managers and professionals
- Learning Directors, managers and professionals
- Organisational development, change and transformation professionals
- Consultants
- Professors, Academics and Lecturers / teachers
- The United Nations
- The National Health Service (UK)
- UK Parliament
- The Scrum Alliance of America
- The Bank of England
- The Bank of Russia
- Consultancy teams and companies
and many others
How do people use research briefings?
People use our research briefings for a wide number of purposes including:
- For their own CPD
- Training and development of others
- With coaching clients
- Team development - many companies have a group membership so every member of the team get the briefings
- Team members pick a briefing a week to discuss either at team meeting or on slack or other Social media
- As the basis of blogs, newsletters and email marketing. The briefings are an excellent way to position yourself as right up-to-date, well-informed and importantly evidence-based
- To solve real life work problems and make their practice evidence-based
- To help with leadership and management issues
- To get work-based practices onto an evidence-based practice
- To create and support organisational change
- To integrate into and update consultancy practice
- Keep entire organisations up to date
- Use in knowledge management systems
- With members in membership sites
Types of research briefing
There are a number of different types of research briefing including:
- A document such written briefing, Powerpoint set etc. webpage or PDF
- An infographic
- An audio file / podcast
- A video research briefing as a presentation
- A live seminar, workshop either in person or as an online webinar and this can either be live or pre-recorded
What do I get if I join?
- Weekly research briefings sent direct to you every week
- A copy of the Oxford Review containing between twelve and sixteen additional research briefings every month
- Research Infographics
- Video research briefings
- Special reports / short literature reviews on topics that appear to be getting a lot of research attention or if there has been a recent shift in the thinking or theory
- Human resources (not legal aspects)
- Organisational development
- Organisational change
- Organisational learning
- Learning and development
- Knowledge management
- Decision making and problem solving
- Request specific research / brief literature reviews
- Access to the entire archive of previous research briefings, copies of the Oxford Review, infographics, video research briefings and special reports.
- Access to Live Reports – continually updated as new research on the topic is released
- Members only podcasts – research briefings in audio
- Access to a member only forum and communities of practice, including live workshops every two weeks
- Access to The Oxford Review courses
How do I join?
In order to keep the integrity of the members community and ensure that we are bringing in like-minded research/evidence-based or research/evidence-interested members, we ask that you have a quick chat with us beforehand so you can ask any questions and we can find out a little about you and your interests:
To arrange a quick chat click here
Our members guide what research we search for and source. What we have found over the years is that people who speak to us in person are much more likely to interact and tell us what they are looking for.
99% of everything you are trying to do...

...has already been done by someone else, somewhere - and meticulously researched.
Get the latest research briefings, infographics and more from The Oxford Review - Free.
Success! Now check your email to confirm your subscription.
There was an error submitting your subscription. Please try again.
Brief report
Brief reports are suitable for the presentation of research that extends previously published research, including the reporting of additional controls and confirmatory results in other settings, as well as negative results. Authors must clearly acknowledge any work upon which they are building, both published and unpublished.
Preparing your manuscript
The information below details the section headings that you should include in your manuscript and what information should be within each section.
Please note that your manuscript must include a 'Declarations' section including all of the subheadings (please see below for more information).
The title page should:
- "A versus B in the treatment of C: a randomized controlled trial", "X is a risk factor for Y: a case control study", "What is the impact of factor X on subject Y: A systematic review"
- or for non-clinical or non-research studies: a description of what the article reports
- if a collaboration group should be listed as an author, please list the group name as an author. If you would like the names of the individual members of the group to be searchable through their individual PubMed records, please include this information in the “Acknowledgements” section in accordance with the instructions below
- Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT , do not currently satisfy our authorship criteria . Notably an attribution of authorship carries with it accountability for the work, which cannot be effectively applied to LLMs. Use of an LLM should be properly documented in the Methods section (and if a Methods section is not available, in a suitable alternative part) of the manuscript
- indicate the corresponding author
Please minimize the use of abbreviations and do not cite references in the abstract. The abstract should briefly summarize the aim, findings or purpose of the article. The Abstract should not exceed 250 words.
Three to ten keywords representing the main content of the article.
This should contain the body of the article, and may also be broken into subsections with short, informative headings.
List of abbreviations
If abbreviations are used in the text they should be defined in the text at first use, and a list of abbreviations should be provided.
Declarations
All manuscripts must contain the following sections under the heading 'Declarations':
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication, availability of data and materials, competing interests, authors' contributions, acknowledgements.
- Authors' information (optional)
Please see below for details on the information to be included in these sections.
If any of the sections are not relevant to your manuscript, please include the heading and write 'Not applicable' for that section.
Manuscripts reporting studies involving human participants, human data or human tissue must:
- include a statement on ethics approval and consent (even where the need for approval was waived)
- include the name of the ethics committee that approved the study and the committee’s reference number if appropriate
Studies involving animals must include a statement on ethics approval and for experimental studies involving client-owned animals, authors must also include a statement on informed consent from the client or owner.
See our editorial policies for more information.
If your manuscript does not report on or involve the use of any animal or human data or tissue, please state “Not applicable” in this section.
If your manuscript contains any individual person’s data in any form (including any individual details, images or videos), consent for publication must be obtained from that person, or in the case of children, their parent or legal guardian. All presentations of case reports must have consent for publication.
You can use your institutional consent form or our consent form if you prefer. You should not send the form to us on submission, but we may request to see a copy at any stage (including after publication).
See our editorial policies for more information on consent for publication.
If your manuscript does not contain data from any individual person, please state “Not applicable” in this section.
All manuscripts must include an ‘Availability of data and materials’ statement. Data availability statements should include information on where data supporting the results reported in the article can be found including, where applicable, hyperlinks to publicly archived datasets analysed or generated during the study. By data we mean the minimal dataset that would be necessary to interpret, replicate and build upon the findings reported in the article. We recognise it is not always possible to share research data publicly, for instance when individual privacy could be compromised, and in such instances data availability should still be stated in the manuscript along with any conditions for access.
Authors are also encouraged to preserve search strings on searchRxiv https://searchrxiv.org/ , an archive to support researchers to report, store and share their searches consistently and to enable them to review and re-use existing searches. searchRxiv enables researchers to obtain a digital object identifier (DOI) for their search, allowing it to be cited.
Data availability statements can take one of the following forms (or a combination of more than one if required for multiple datasets):
- The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [NAME] repository, [PERSISTENT WEB LINK TO DATASETS]
- The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
- The datasets generated and/or analysed during the current study are not publicly available due [REASON WHY DATA ARE NOT PUBLIC] but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
- Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analysed during the current study.
- The data that support the findings of this study are available from [third party name] but restrictions apply to the availability of these data, which were used under license for the current study, and so are not publicly available. Data are however available from the authors upon reasonable request and with permission of [third party name].
- Not applicable. If your manuscript does not contain any data, please state 'Not applicable' in this section.
More examples of template data availability statements, which include examples of openly available and restricted access datasets, are available here .
BioMed Central strongly encourages the citation of any publicly available data on which the conclusions of the paper rely in the manuscript. Data citations should include a persistent identifier (such as a DOI) and should ideally be included in the reference list. Citations of datasets, when they appear in the reference list, should include the minimum information recommended by DataCite and follow journal style. Dataset identifiers including DOIs should be expressed as full URLs. For example:
Hao Z, AghaKouchak A, Nakhjiri N, Farahmand A. Global integrated drought monitoring and prediction system (GIDMaPS) data sets. figshare. 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.853801
With the corresponding text in the Availability of data and materials statement:
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available in the [NAME] repository, [PERSISTENT WEB LINK TO DATASETS]. [Reference number]
If you wish to co-submit a data note describing your data to be published in BMC Research Notes , you can do so by visiting our submission portal . Data notes support open data and help authors to comply with funder policies on data sharing. Co-published data notes will be linked to the research article the data support ( example ).
All financial and non-financial competing interests must be declared in this section.
See our editorial policies for a full explanation of competing interests. If you are unsure whether you or any of your co-authors have a competing interest please contact the editorial office.
Please use the authors initials to refer to each authors' competing interests in this section.
If you do not have any competing interests, please state "The authors declare that they have no competing interests" in this section.
All sources of funding for the research reported should be declared. If the funder has a specific role in the conceptualization, design, data collection, analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript, this should be declared.
The individual contributions of authors to the manuscript should be specified in this section. Guidance and criteria for authorship can be found in our editorial policies .
Please use initials to refer to each author's contribution in this section, for example: "FC analyzed and interpreted the patient data regarding the hematological disease and the transplant. RH performed the histological examination of the kidney, and was a major contributor in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript."
Please acknowledge anyone who contributed towards the article who does not meet the criteria for authorship including anyone who provided professional writing services or materials.
Authors should obtain permission to acknowledge from all those mentioned in the Acknowledgements section.
See our editorial policies for a full explanation of acknowledgements and authorship criteria.
If you do not have anyone to acknowledge, please write "Not applicable" in this section.
Group authorship (for manuscripts involving a collaboration group): if you would like the names of the individual members of a collaboration Group to be searchable through their individual PubMed records, please ensure that the title of the collaboration Group is included on the title page and in the submission system and also include collaborating author names as the last paragraph of the “Acknowledgements” section. Please add authors in the format First Name, Middle initial(s) (optional), Last Name. You can add institution or country information for each author if you wish, but this should be consistent across all authors.
Please note that individual names may not be present in the PubMed record at the time a published article is initially included in PubMed as it takes PubMed additional time to code this information.
Authors' information
This section is optional.
You may choose to use this section to include any relevant information about the author(s) that may aid the reader's interpretation of the article, and understand the standpoint of the author(s). This may include details about the authors' qualifications, current positions they hold at institutions or societies, or any other relevant background information. Please refer to authors using their initials. Note this section should not be used to describe any competing interests.
Footnotes can be used to give additional information, which may include the citation of a reference included in the reference list. They should not consist solely of a reference citation, and they should never include the bibliographic details of a reference. They should also not contain any figures or tables.
Footnotes to the text are numbered consecutively; those to tables should be indicated by superscript lower-case letters (or asterisks for significance values and other statistical data). Footnotes to the title or the authors of the article are not given reference symbols.
Always use footnotes instead of endnotes.
Examples of the Vancouver reference style are shown below.
See our editorial policies for author guidance on good citation practice
Web links and URLs: All web links and URLs, including links to the authors' own websites, should be given a reference number and included in the reference list rather than within the text of the manuscript. They should be provided in full, including both the title of the site and the URL, as well as the date the site was accessed, in the following format: The Mouse Tumor Biology Database. http://tumor.informatics.jax.org/mtbwi/index.do . Accessed 20 May 2013. If an author or group of authors can clearly be associated with a web link, such as for weblogs, then they should be included in the reference.
Example reference style:
Article within a journal
Smith JJ. The world of science. Am J Sci. 1999;36:234-5.
Article within a journal (no page numbers)
Rohrmann S, Overvad K, Bueno-de-Mesquita HB, Jakobsen MU, Egeberg R, Tjønneland A, et al. Meat consumption and mortality - results from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition. BMC Medicine. 2013;11:63.
Article within a journal by DOI
Slifka MK, Whitton JL. Clinical implications of dysregulated cytokine production. Dig J Mol Med. 2000; doi:10.1007/s801090000086.
Article within a journal supplement
Frumin AM, Nussbaum J, Esposito M. Functional asplenia: demonstration of splenic activity by bone marrow scan. Blood 1979;59 Suppl 1:26-32.
Book chapter, or an article within a book
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. In: Bourne GH, Danielli JF, Jeon KW, editors. International review of cytology. London: Academic; 1980. p. 251-306.
OnlineFirst chapter in a series (without a volume designation but with a DOI)
Saito Y, Hyuga H. Rate equation approaches to amplification of enantiomeric excess and chiral symmetry breaking. Top Curr Chem. 2007. doi:10.1007/128_2006_108.
Complete book, authored
Blenkinsopp A, Paxton P. Symptoms in the pharmacy: a guide to the management of common illness. 3rd ed. Oxford: Blackwell Science; 1998.
Online document
Doe J. Title of subordinate document. In: The dictionary of substances and their effects. Royal Society of Chemistry. 1999. http://www.rsc.org/dose/title of subordinate document. Accessed 15 Jan 1999.
Online database
Healthwise Knowledgebase. US Pharmacopeia, Rockville. 1998. http://www.healthwise.org. Accessed 21 Sept 1998.
Supplementary material/private homepage
Doe J. Title of supplementary material. 2000. http://www.privatehomepage.com. Accessed 22 Feb 2000.
University site
Doe, J: Title of preprint. http://www.uni-heidelberg.de/mydata.html (1999). Accessed 25 Dec 1999.
Doe, J: Trivial HTTP, RFC2169. ftp://ftp.isi.edu/in-notes/rfc2169.txt (1999). Accessed 12 Nov 1999.
Organization site
ISSN International Centre: The ISSN register. http://www.issn.org (2006). Accessed 20 Feb 2007.
Dataset with persistent identifier
Zheng L-Y, Guo X-S, He B, Sun L-J, Peng Y, Dong S-S, et al. Genome data from sweet and grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). GigaScience Database. 2011. http://dx.doi.org/10.5524/100012 .
Figures, tables and additional files
See General formatting guidelines for information on how to format figures, tables and additional files.
Submit manuscript
- Editorial Board
- Manuscript editing services
- Instructions for Authors
- Instructions for Editors
- Sign up for article alerts and news from this journal
- OA Funding Support
Annual Journal Metrics
Citation Impact 2023 Journal Impact Factor: 4.0 5-year Journal Impact Factor: 4.4 Source Normalized Impact per Paper (SNIP): 1.235 SCImago Journal Rank (SJR): 1.351
Speed 2023 Submission to first editorial decision (median days): 6 Submission to acceptance (median days): 131
Usage 2023 Downloads: 2,725,853 Altmetric mentions: 4,628
- More about our metrics
Harm Reduction Journal
ISSN: 1477-7517
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
NTRS - NASA Technical Reports Server
Available downloads, related records.
- Buy crypto Express buy Visa, Mastercard, and others P2P trading Buy/Sell with zero trading fees via 100+ payment methods
- Discover Markets View the latest crypto prices, volume, and data Opportunities Discover hot and new crypto
Trading instruments
Powerful tools
- Grow Earn Don’t just HODL. Earn Simple Earn On-chain Earn Structured Products Loan Borrow to earn, borrow to spend Jumpstart Discover new, high-quality projects around the world
X Layer network
- Institutional Institutional home The world’s most powerful suite of crypto trading solutions APIs Seamless and ultra-low latency API connectivity VIP Loan Improve capital efficiency Broker Program Access world-class market depth with high commissions Managed Trading Sub-accounts Manage sub-accounts, trade easily and safely with more profits Historical market data Candlesticks, aggregate trades, order book data and more Institutional Insights Our latest institutional trading research, news, and more
- More Products OKB Security of funds Status Proof of Reserves Others Campaign center My rewards Referral Affiliates OKX Ventures Trade on TradingView Listing application
- Log in Sign up
- Support Support center My tickets Connect with OKX
Our Research Brief with Economist Impact is Live: Digital Assets as the New Alternative for Institutional Investors
A message from OKX Global Chief Commercial Officer Lennix Lai. Opinions are that of the author and do not reflect OKX's official view. Not financial advice.
I'm pleased to share the launch of our new research brief, " Digital assets as the new alternative for institutional investors: market dynamics, opportunities and challenges ," commissioned by OKX Institutional and authored by Economist Impact. This comprehensive study features insights and analysis from industry leaders such as Citi, Skybridge Capital and VanEck, and delves into the transformative potential of digital assets for institutional investors with a focus on four key areas: institutional asset allocation, custody, regulatory developments and risk management.
The projected value of tokenized assets is expected to surpass $10 trillion by 2030 , unlocking an undeniable opportunity.* This shift is set to unlock unprecedented potential and, as our research brief shows, there is already significant institutional momentum for growth.
As institutional investors are increasingly entering the digital asset space, the report is designed to guide them on seizing opportunities while effectively mitigating challenges.
Key findings*
Asset allocation - 69% of institutional investors intend to increase their allocations to crypto and other digital assets within the next 2-3 years, with projections indicating that these assets could represent 7.2% of institutional portfolios by 2027.
Custody - 80% of traditional and crypto hedge funds utilizing digital assets employ third-party custodians, highlighting a strong reliance on specialized solutions for secure asset management. Moreover, the institutional digital asset custody market is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 23% through 2028. These findings underscore the industry's evolution to a point where there is strong demand for segregation of duties related to trade execution and asset custody.
Regulation - The current convergence of developing regulatory frameworks will soon address market uncertainty and enhance consumer protection, and lead to greater opportunities for investors. Examples of increased regulatory clarity can be found in several key financial centers across the globe such as Singapore and the UAE, while the approval of 11 Spot Bitcoin ETFs by the SEC in the US has significantly increased the accessibility of Bitcoin to institutional investors, which in turn has boosted demand and liquidity.
Risk management - Despite the differences between the traditional financial and digital asset classes, many tools that are commonly used in traditional finance are also used in crypto. Value-at-risk models, scenario analysis and reverse stress testing as well as real-time monitoring are some examples of this implementation.
As our research shows, digital assets are set to become a staple of institutional portfolios in the future. Increasingly mature blockchain technology and digital security infrastructure, ongoing efforts to achieve global regulatory clarity, deep liquidity pools and digital innovations such as tokenized real-world assets drive adoption, interest and investment.
At OKX, we’re committed to supporting this evolution by offering the tools and robust infrastructure that institutions need to confidently pursue their trading strategies. We hope this report serves as an invaluable guide for understanding the shifting dynamics of digital assets in institutional portfolios.
OKX Global Chief Commercial Officer
*Insights referenced in this release are cited in the research brief, and are comprised of (1) viewpoints from the Economist Impact roundtable session in Dubai, UAE; (2) interviews with industry experts; (3) desktop research, and industry surveys and studies. Sources for all referenced insights can be found in the research brief


An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
Office of the Assistant Secretary for Planning and Evaluation
Nursing Home Closures Did Not Increase in 2020 and 2021, Despite Financial Challenges Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic Issue Brief
Nursing homes experienced unprecedented financial challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic, raising concerns about a potential increase in nursing home closures. The COVID-19 pandemic resulted in lower occupancy rates and revenue in nursing homes, raised operating costs with new expenditures on personal protective equipment, cleaning supplies, and COVID-19 tests, and exacerbated existing staffing shortages, resulting in increased costs to attract and retain workers. We conducted this study to understand the impact of COVID-19 pandemic on nursing home closures and found that closures did not increase during 2020 and 2021. There is, however, some evidence that nursing homes that were more impacted by COVID-19 were more likely to close. Nursing home characteristics associated with higher likelihood of closure included size, occupancy rate, and percentage of residents with Medicare as the primary payer. Explanations for the absence of additional closures during 2020 and 2021 include several strategies by nursing home providers to mitigate staffing shortages, including freezing admissions and closing portions of facilities, and federal and state financial assistance to nursing homes that likely prevented or delayed closure.
This research was conducted under contract #HHSP233201500039I between HHS/ASPE’s Office of Behavioral Health, Disability, and Aging Policy (BHDAP) and Research Triangle Institute. Additional research in this area is available at the ASPE Aging & Disability page and the ASPE COVID-19 page .
*This content is in the process of Section 508 review. If you need immediate assistance accessing this content, please submit a request to Brenda Veazey, [email protected] . Content will be updated pending the outcome of the Section 508 review.
Available Reports:
- Nursing Home Closures Did Not Increase in 2020 and 2021, Despite Financial Challenges Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic Issue Brief (nh-closure-financial-challenges-covid)
Related Products:
- Changes in Ownership of Skilled Nursing Facilities from 2016 to 2021: Variations by Size, Occupancy Rate, Penalty Amount, and Type of Ownership Research Brief
- Ownership of Skilled Nursing Facilities: An Analysis of Newly-Released Federal Data
- Changes in Ownership of Skilled Nursing Facilities (2016-2021): Analysis Using Newly Released CMS Data Research Brief
- Tracking the Impact of Ownership Changes in Hospice Care Provided in Medicare Beneficiaries: Final Report
- Trends in Nursing Home-Hospice Contracting and Common Ownership between Hospice Agencies and Nursing Homes: Final Report
Content Search
Kakuma - disaster risk mitigation strategy 2023.
- Kenya Red Cross
Attachments

Executive summary
The Kakuma Risk Mitigation Strategy, a collaborative effort between the Kenya Red Cross, UN-Habitat, and various stakeholders operating in Kalobeyei, addresses the critical need for effective measures to mitigate the impacts of floods and drought in the region. This strategic initiative has been developed in response to the increasing vulnerability of communities in Kakuma and Kalobeyei to climate-related challenges.
Kakuma and Kalobeyei settlements are located in an area prone to effects of climate change and natural disasters. Despite UNHCR and government efforts to integrate refugees and host communities, natural disasters can also be a source of potential conflict. Without drastic action to mitigate the impacts of climate change, both host and refugee communities' vulnerability to disasters will increase compromising their security and placing them at risk of secondary displacement.
The strategy is an integral component in the overall county and national planning arrangements. It foundationally aligns with national and county government disaster risk management framework ensuring coherence with broader resilience-building efforts at the higher administrative levels.
The strategy development involved in-depth analyses and stakeholder consultations culminating in a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by both the host and refugee communities. A variety of participatory methods including, stakeholder workshops, focused-group discussions, and key informant interviews leveraging Indigenous and Traditional Knowledge were conducted to gather input from relevant parties. The participatory climate risk assessment (PCRA) approach was utilized to cover various aspects of the strategy including hazard mapping, prioritization of hazards, vulnerability assessment, participatory scenario planning, evaluation of local responses to impacts, and formulation of community adaptation goals and strategies.
Central to this strategy is the establishment of a community-led early warning system designed to enhance preparedness and response to climate-related hazards. By aligning the implementation process with stakeholders approaches and encouraging community involvement, the strategy seeks to empower local communities to actively mitigate risks and adapt to changing environmental conditions.
The success of the proposed risk mitigation strategy relies on close collaboration with relevant government actors and the UN-Habitat office to ensure effective implementation and continuous support. The strategy emphasizes the generation of quarterly and final detailed project reports to track progress, achievements, and challenges. This iterative reporting process allows for timely adjustments and improvements, ensuring the adaptive management of the strategy.
Related Content
Global prioritisation exercise (gpe) for humanitarian research and innovation national consultation: kenya, june 2024.
Ethiopia + 25 more
Africa Region | Hunger crisis - Emergency Appeal No. MGR60001 - Revised Operational Strategy
Brief: el niño floods worsen humanitarian needs in kenya (march 2024).
Kenya + 1 more
Kenya: IFRC network mid-year report, January - June 2023 (13 December 2023)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Research Brief Basics. Definition and Purpose: A research brief is a short, targeted summary of a research study or project. Its primary purposes are to: Inform decision-makers who might not have time for in-depth reports. Influence policy by highlighting key research outcomes.
Research briefs are the cornerstone of successful projects. They set the tone, define objectives, and guide researchers toward meaningful outcomes. A well-structured brief not only saves time but also ensures the collected data aligns with the project goals. How to Write a Research Brief: Understanding Your Objective. Defining Clear Research Goals
Research Report is a written document that presents the results of a research project or study, including the research question, methodology, results, and conclusions, in a clear and objective manner. ... The introduction sets the stage for the research report and provides a brief overview of the research question or problem being investigated ...
Guidelines - Brief Report. Brief reports are similar to original research in that they follow the same rigor, format and guidelines, but are designed for small-scale research or research that is in early stages of development. These may include preliminary studies that utilize a simple research design or a small sample size and that have ...
2. Be clear on your objectives. This is one of the most important parts of your brief to convey to the reader what you want out of the project and ensure you get results which deliver. Projects should have around three or four overarching aims which set out what the project ultimately wants to achieve.
A Brief Report is a focused article of original research intended to advance its field of study. It may contain up to 5 Figures or Tables presenting original data. The article should also be conclusive and self-explanatory and may contain Supplementary Material such as Figures, Tables and Video files.
A research report is one type that is often used in the sciences, engineering and psychology. Here your aim is to write clearly and ... Abstract/Synopsis - This gives a very brief overview of the report in a condensed form. For more specific details on how to write this, please refer to the Learning Guide Writing an Abstract. STEP 7
This process of distilling a long research paper down to a brief report is also the key to getting papers published in top-tier journals. Chapter 41 looks more closely at how to say more with fewer words. In some sense, only the main report from a major study truly justifies a full report. Most other research papers in the medical literature ...
Criteria. Brief reports are suitable for the presentation of research that extends previously published research, including the reporting of additional data and confirmatory results in other settings, as well as small-scale studies. Authors must clearly acknowledge any work upon which they are building, both published and unpublished.
A research report is one big argument how and why you came up with your conclusions. To make it a convincing argument, a typical guiding structure has developed. ... You offer user guidance or an essay map, a thesis statement, or a research question. Brief and relevant background information shows how your topic fits into a larger framework and ...
These will improve the visibility of your article. 5. Main Body. The format of the main body of the article is flexible: it should be concise, making it easy to read and review, and presented in a format that is appropriate for the type of study presented. A Brief Report should be no more than 2500 words .
Reports scientific results of original research in such areas as economic policy, ethics, law, and health care delivery. ... Brief Report. Describes 1-3 patients or a single family. See Example ...
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. ... Limitations: The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self ...
Abstract. This guide for writers of research reports consists of practical suggestions for writing a report that is clear, concise, readable, and understandable. It includes suggestions for terminology and notation and for writing each section of the report—introduction, method, results, and discussion. Much of the guide consists of ...
A research brief is a concise, non-technical summary of the key takeaways from a research study. Briefs communicate research insights to the public, thereby translating research and evidence-based practices into real-world settings. ... On Being Brief: Skills and Supports for Translating Research to Practice via Brief Reports. Have you ever ...
Research Report Summary: The entire objective along with the overview of research are to be included in a summary which is a couple of paragraphs in length. All the multiple components of the research are explained in brief under the report summary.
esources; or brief validation studies of existing tools.Brief reports will typically be 2,000 to 3,000 words, including the main text, tables/figures, and references. Reference to background literature should be kept at a maximum of 15 entrie. , as the focus is on the methods, analysis, and results. The internal format of the brie.
These papers communicate brief reports of data from original research that editors believe will be interesting to many researchers, and that will likely stimulate further research in the field. As they are relatively short the format is useful for scientists with results that are time sensitive (for example, those in highly competitive or ...
What Is a Brief Report? From the word "brief" itself, you already have a sense of what a brief report is—a short research report of any event, project, case, or research. Although brief reports have similar rules and formats to basic or longer research reports, the major difference is that brief reports are often used for smaller-scale projects.
Brief Report. Brief reports are short, observational studies that report preliminary results or a short complete study or protocol. Brief reports usually contain two figures and/or a table; however, the Materials and Methods sections should be detailed to ensure reproducibility of the presented work. The structure is similar to that of an article.
1 Choose a topic based on the assignment. Before you start writing, you need to pick the topic of your report. Often, the topic is assigned for you, as with most business reports, or predetermined by the nature of your work, as with scientific reports. If that's the case, you can ignore this step and move on.
Request specific research / brief literature reviews; Access to the entire archive of previous research briefings, copies of the Oxford Review, infographics, video research briefings and special reports. Access to Live Reports - continually updated as new research on the topic is released; Members only podcasts - research briefings in audio
Brief reports are suitable for the presentation of research that extends previously published research, including the reporting of additional controls and confirmatory results in other settings, as well as negative results. Authors must clearly acknowledge any work upon which they are building, both published and unpublished.
Increasing research in western countries has yielded longitudinal evidence about the psychosocial benefits of SSM for sexual minority individuals, but they have rarely included sexual minority ...
Pulmonary Spindle Cell Carcinoma Mimicking Granulomatous Inflammation: A Rare Case Report and Brief Review of the Literature. Qian Liu 1 Department of Oncology, Xiangyang No. 1 People's Hospital, Hubei University of Medicine, ... and molecular biology research have led to the notion that PSCC originates from primitive epithelial stem cells ...
This paper discusses the current focus of NASA's Advanced Space Suit Pressure Garment Technology Development team's efforts, the status of that work, and a summary of longer term technology development priorities and activities. The Exploration Extra-vehicular Activity Mobility Unit (xEMU) has been the team's primary effort over the past several years.
Issue briefs and reports. Our programs and centers deliver in-depth, highly relevant issue briefs and reports that break new ground, shift opinions, and set agendas on public policy, with a focus on advancing debates by integrating foundational research and analysis with concrete policy solutions.
This shift is set to unlock unprecedented potential and, as our research brief shows, there is already significant institutional momentum for growth. As institutional investors are increasingly entering the digital asset space, the report is designed to guide them on seizing opportunities while effectively mitigating challenges. Key findings*
Available Reports: Nursing Home Closures Did Not Increase in 2020 and 2021, Despite Financial Challenges Caused by the COVID-19 Pandemic Issue Brief (nh-closure-financial-challenges-covid) ... (2016-2021): Analysis Using Newly Released CMS Data Research Brief; Tracking the Impact of Ownership Changes in Hospice Care Provided in Medicare ...
Attachments. Download Report (PDF | 1.42 MB); Executive summary. The Kakuma Risk Mitigation Strategy, a collaborative effort between the Kenya Red Cross, UN-Habitat, and various stakeholders ...