ORIGINAL RESEARCH article
Work stress, mental health, and employee performance.

- 1 School of Business, Zhengzhou University, Zhengzhou, China
- 2 Henan Research Platform Service Center, Zhengzhou, China
The COVID-19 pandemic outbreak—as a typical emergency event—significantly has impacted employees' psychological status and thus has negatively affected their performance. Hence, along with focusing on the mechanisms and solutions to alleviate the impact of work stress on employee performance, we also examine the relationship between work stress, mental health, and employee performance. Furthermore, we analyzed the moderating role of servant leadership in the relationship between work stress and mental health, but the result was not significant. The results contribute to providing practical guidance for enterprises to improve employee performance in the context of major emergencies.

Introduction
Small- and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) are the key drivers of economic development as they contribute >50, 60, 70, 80, and 90% of tax revenue, GDP, technological innovation, labor employment, and the number of enterprises, respectively. However, owing to the disadvantages of small-scale and insufficient resources ( Cai et al., 2017 ; Flynn, 2017 ), these enterprises are more vulnerable to being influenced by emergency events. The COVID-19 pandemic outbreak—as a typical emergency event—has negatively affected survival and growth of SMEs ( Eggers, 2020 ). Some SMEs have faced a relatively higher risk of salary reduction, layoffs, or corporate bankruptcy ( Adam and Alarifi, 2021 ). Consequently, it has made employees in the SMEs face the following stressors during the COVID-19 pandemic: First, employees' income, promotion, and career development opportunities have declined ( Shimazu et al., 2020 ). Second, as most employees had to work from home, family conflicts have increased and family satisfaction has decreased ( Green et al., 2020 ; Xu et al., 2020 ). Finally, as work tasks and positions have changed, the new work environment has made employees less engaged and less fulfilled at work ( Olugbade and Karatepe, 2019 ; Chen and Fellenz, 2020 ).
For SMEs, employees are their core assets and are crucial to their survival and growth ( Shan et al., 2022 ). Employee work stress may precipitate burnout ( Choi et al., 2019 ; Barello et al., 2020 ), which manifests as fatigue and frustration ( Mansour and Tremblay, 2018 ), and is associated with various negative reactions, including job dissatisfaction, low organizational commitment, and a high propensity to resign ( Lu and Gursoy, 2016 ; Uchmanowicz et al., 2020 ). Ultimately, it negatively impacts employee performance ( Prasad and Vaidya, 2020 ). The problem of employee work stress has become an important topic for researchers and practitioners alike. In this regard, it is timely to explore the impact of work stress on SME problems of survival and growth during emergency events like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Although recent studies have demonstrated the relationship between work stress and employee performance, some insufficiencies persist, which must be resolved. Research on how work stress affects employee performance has remained fragmented and limited. First, the research into how work stress affects employee performance is still insufficient. Some researchers have explored the effects of work stress on employee performance during COVID-19 ( Saleem et al., 2021 ; Tu et al., 2021 ). However, they have not explained the intermediate path, which limits our understanding of effects of work stress. As work stress causes psychological pain to employees, in response, they exhibit lower performance levels ( Song et al., 2020 ; Yu et al., 2022 ). Thus, employees' mental health becomes an important path to explain the relationship mechanism between work stress and employee performance, which is revealed in this study using a stress–psychological state–performance framework. Second, resolving the mental health problems caused by work stress has become a key issue for SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic. As the core of the enterprise ( Ahn et al., 2018 ), the behavior of leaders significantly influences employees. Especially for SMEs, intensive interactive communication transpires between the leader and employees ( Li et al., 2019 ; Tiedtke et al., 2020 ). Servant leadership, as a typical leader's behavior, is considered an important determinant of employee mental health ( Haslam et al., 2020 ). Hence, to improve employees' mental health, we introduce servant leadership as a moderating variable and explore its contingency effect on relieving work stress and mental health.
This study predominantly tries to answer the question of how work stress influences employee performance and explores the mediating impact of mental health and the moderating impact of servant leadership in this relationship. Mainly, this study contributes to the existing literature in the following three ways: First, this research analyzes the influence of work stress on employee performance in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic, which complements previous studies and theories related to work stress. Second, this study regards mental health as a psychological state and examines its mediating impact on the relationship between work stress and employee performance, which complements the research path on how work stress affects employee performance. Third, we explore the moderating impact of servant leadership, which has been ignored in previous research, thus extending the understanding of the relationship between the work stress and mental health of employees in SMEs.
To accomplish the aforementioned tasks, the remainder of this article is structured as follows: First, based on the literature review, we propose our hypotheses. Thereafter, we present our research method, including the processes of data collection, sample characteristics, measurement of variables, and sample validity. Subsequently, we provide the data analysis and report the results. Finally, we discuss the results and present the study limitations.
Theoretical background and hypotheses
Work stress and employee performance.
From a psychological perspective, work stress influences employees' psychological states, which, in turn, affects their effort levels at work ( Lu, 1997 ; Richardson and Rothstein, 2008 ; Lai et al., 2022 ). Employee performance is the result of the individual's efforts at work ( Robbins, 2005 ) and thus is significantly impacted by work stress. However, previous research has provided no consistent conclusion regarding the relationship between work stress and employee performance. One view is that a significant positive relationship exists between work stress and employee performance ( Ismail et al., 2015 ; Soomro et al., 2019 ), suggesting that stress is a motivational force that encourages employees to work hard and improve work efficiency. Another view is that work stress negatively impacts employee performance ( Yunus et al., 2018 ; Nawaz Kalyar et al., 2019 ; Purnomo et al., 2021 ), suggesting that employees need to spend time and energy to cope with stress, which increases their burden and decreases their work efficiency. A third view is that the impact of work stress on employee performance is non-linear and may exhibit an inverted U-shaped relationship ( McClenahan et al., 2007 ; Hamidi and Eivazi, 2010 ); reportedly, when work stress is relatively low or high, employee performance is low. Hence, if work stress reaches a moderate level, employee performance will peak. However, this conclusion is derived from theoretical analyses and is not supported by empirical data. Finally, another view suggests that no relationship exists between them ( Tănăsescu and Ramona-Diana, 2019 ). Indubitably, it presupposes that employees are rational beings ( Lebesby and Benders, 2020 ). Per this view, work stress cannot motivate employees or influence their psychology and thus cannot impact their performance.
To further explain the aforementioned diverse views, positive psychology proposes that work stress includes two main categories: challenge stress and hindrance stress ( Cavanaugh et al., 2000 ; LePine et al., 2005 ). Based on their views, challenge stress represents stress that positively affects employees' work attitudes and behaviors, which improves employee performance by increasing work responsibility; by contrast, hindrance stress negatively affects employees' work attitudes and behaviors, which reduces employee performance by increasing role ambiguity ( Hon and Chan, 2013 ; Deng et al., 2019 ).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, SMEs have faced a relatively higher risk of salary reductions, layoffs, or corporate bankruptcy ( Adam and Alarifi, 2021 ). Hence, the competition among enterprises has intensified; managers may transfer some stress to employees, who, in turn, need to bear this to maintain and seek current and future career prospects, respectively ( Lai et al., 2015 ). In this context, employee work stress stems from increased survival problems of SMEs, and such an external shock precipitates greater stress among employees than ever before ( Gao, 2021 ). Stress more frequently manifests as hindrance stress ( LePine et al., 2004 ), which negatively affects employees' wellbeing and quality of life ( Orfei et al., 2022 ). It imposes a burden on employees, who need to spend time and energy coping with the stress. From the perspective of stressors, SMEs have faced serious survival problems during the COVID-19 pandemic, and consequently, employees have faced greater hindrance stress, thereby decreasing their performance. Hence, we propose the following hypothesis:
H1 . Work stress negatively influences employee performance in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Work stress and mental health
According to the demand–control–support (DCS) model ( Karasek and Theorell, 1990 ), high-stress work—such as high job demands, low job control, and low social support at work—may trigger health problems in employees over time (e.g., mental health problems; Chou et al., 2015 ; Park et al., 2016 ; Lu et al., 2020 ). The DCS model considers stress as an individual's response to perceiving high-intensity work ( Houtman et al., 2007 ), which precipitates a change in the employee's cognitive, physical, mental, and emotional status. Of these, mental health problems including irritability, nervousness, aggressive behavior, inattention, sleep, and memory disturbances are a typical response to work stress ( Mayerl et al., 2016 ; Neupane and Nygard, 2017 ). If the response persists for a considerable period, mental health problems such as anxiety or depression may occur ( Bhui et al., 2012 ; Eskilsson et al., 2017 ). As coping with work stress requires an employee to exert continuous effort and apply relevant skills, it may be closely related to certain psychological problems ( Poms et al., 2016 ; Harrison and Stephens, 2019 ).
The COVID-19 pandemic has disrupted the normal operating order of enterprises as well as employees' work rhythm. Consequently, employees might have faced greater challenges during this period ( Piccarozzi et al., 2021 ). In this context, work stress includes stress related to health and safety risk, impaired performance, work adjustment, and negative emotions, for instance, such work stress can lead to unhealthy mental problems. Hence, we propose the following hypothesis:
H2 . Work stress negatively influences mental health in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Mediating role of mental health
Previous research has found that employees' mental health status significantly affects their performance ( Bubonya et al., 2017 ; Cohen et al., 2019 ; Soeker et al., 2019 ), the main reasons of which are as follows: First, mental health problems reduce employees' focus on their work, which is potentially detrimental to their performance ( Hennekam et al., 2020 ). Second, mental health problems may render employees unable to work ( Heffernan and Pilkington, 2011 ), which indirectly reduces work efficiency owing to increased sick leaves ( Levinson et al., 2010 ). Finally, in the stress context, employees need to exert additional effort to adapt to the environment, which, consequently, make them feel emotionally exhausted. Hence, as their demands remain unfulfilled, their work satisfaction and performance decrease ( Khamisa et al., 2016 ).
Hence, we propose that work stress negatively impacts mental health, which, in turn, positively affects employee performance. In other words, we argue that mental health mediates the relationship between work stress and employee performance. During the COVID-19 pandemic, work stress—owing to changes in the external environment—might have caused nervous and anxious psychological states in employees ( Tan et al., 2020 ). Consequently, it might have rendered employees unable to devote their full attention to their work, and hence, their work performance might have decreased. Meanwhile, due to the pandemic, employees have faced the challenges of unclear job prospects and reduced income. Therefore, mental health problems manifest as moods characterized by depression and worry ( Karatepe et al., 2020 ). Negative emotions negatively impact employee performance. Per the aforementioned arguments and hypothesis 2, we propose the following hypothesis:
H3 . Mental health mediates the relationship between work stress and employee performance in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Moderating role of servant leadership
According to the upper echelons theory, leaders significantly influence organizational activities, and their leadership behavior influences the thinking and understanding of tasks among employees in enterprises ( Hambrick and Mason, 1984 ). Servant leadership is a typical leadership behavior that refers to leaders exhibiting humility, lending power to employees, raising the moral level of subordinates, and placing the interests of employees above their own ( Sendjaya, 2015 ; Eva et al., 2019 ). This leadership behavior provides emotional support to employees and increase their personal confidence and self-esteem and thus reduce negative effects of work stress. In our study, we propose that servant leadership reduces the negative effects of work stress on mental health in SMEs.
Servant leadership can reduce negative effects of work stress on mental health in the following ways: Servant leaders exhibit empathy and compassion ( Lu et al., 2019 ), which help alleviate employees' emotional pain caused by work stress. Song et al. (2020) highlighted that work stress can cause psychological pain among employees. However, servant leaders are willing to listen to their employees and become acquainted with them, which facilitates communication between the leader and the employee ( Spears, 2010 ). Hence, servant leadership may reduce employees' psychological pain through effective communication. Finally, servant leaders lend employees power, which makes the employees feel trusted. Employees—owing to their trust in the leaders—trust the enterprises as well, which reduces the insecurity caused by work stress ( Phong et al., 2018 ). In conclusion, servant leadership serves as a coping resource that reduces the impact of losing social support and thus curbs negative employee emotions ( Ahmed et al., 2021 ). Based on the aforementioned analysis, we find that servant leaders can reduce the mental health problems caused by work stress. Hence, we propose the following hypothesis:
H4 . Servant leadership reduces the negative relationship between work stress and mental health in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methodology
Data collection and samples.
To assess our theoretical hypotheses, we collected data by administering a questionnaire survey. The questionnaire was administered anonymously, and the respondents were informed regarding the purpose of the study. Owing to the impact of the pandemic, we distributed and collected the questionnaires by email. Specifically, we utilized the network relationships of our research group with the corporate campus and group members to distribute the questionnaires. In addition, to ensure the quality of the questionnaires, typically senior employees who had worked for at least 2 years at their enterprises were chosen as the respondents.
Before the formal survey, we conducted a pilot test. Thereafter, we revised the questionnaire based on the results of the trial investigation. Subsequently, we randomly administered the questionnaires to the target enterprises. Hence, 450 questionnaires were administered via email, and 196 valid questionnaires were returned—an effective rate of 43.6%. Table 1 presents the profiles of the samples.
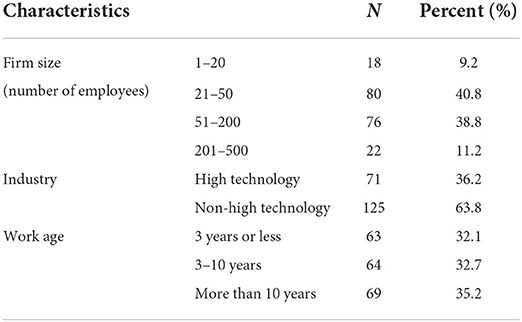
Table 1 . Profiles of the samples.
Table 1 shows the descriptive statistics of the sample. Based on the firm size, respondents who worked in a company with 1–20 employees accounted for 9.2%, those in a company with 21–50 employees accounted for 40.8%, those in a company with 51–200 employees accounted for 38.8%, and those in a company with 201–500 employees accounted for 11.2%. Regarding industry, the majority of the respondents (63.8%) worked for non-high-technology industry and 36.2% of the respondents worked for high-technology industry. Regarding work age, the participants with a work experience of 3 years or less accounted for 32.1%, those with work experience of 3–10 years accounted for 32.7%, and those with a work experience of more than 10 years accounted for 35.2%.
Core variables in this study include English-version measures that have been well tested in prior studies; some modifications were implemented during the translation process. As the objective of our study is SMEs in China, we translated the English version to Chinese; this translation was carried out by two professionals to ensure accuracy. Thereafter, we administered the questionnaires to the respondents. Hence, as the measures of our variables were revised based on the trial investigation, we asked two professionals to translate the Chinese version of the responses to English to enable publishing this work in English. We evaluated all the items pertaining to the main variables using a seven-point Likert scale (7 = very high/strongly agree, 1 = very low/strongly disagree). The variable measures are presented subsequently.
Work stress (WS)
Following the studies of Parker and DeCotiis (1983) and Shah et al. (2021) , we used 12 items to measure work stress, such as “I get irritated or nervous because of work” and “Work takes a lot of my energy, but the reward is less than the effort.”
Mental health (MH)
The GHQ-12 is a widely used tool developed to assess the mental health status ( Liu et al., 2022 ). However, we revised the questionnaire by combining the research needs and results of the pilot test. We used seven items to measure mental health, such as “I feel that I am unable (or completely unable) to overcome difficulties in my work or life.” In the final calculation, the scoring questions for mental health were converted; higher scores indicated higher levels of mental health.
Servant leadership (SL)
Following the studies by Ehrhart (2004) and Sendjaya et al. (2019) , we used nine items to measure servant leadership, including “My leader makes time to build good relationships with employees” and “My leader is willing to listen to subordinates during decision-making.”
Employee performance (EP)
We draw on the measurement method provided by Chen et al. (2002) and Khorakian and Sharifirad (2019) ; we used four items to represent employee performance. An example item is as follows: “I can make a contribution to the overall performance of our enterprise.”
Control variables
We controlled several variables that may influence employee performance, including firm size, industry, and work age. Firm size was measured by the number of employees. For industry, we coded them into two dummy variables (high-technology industry = 1, non-high-technology industry = 0). We calculated work experience by the number of years the employee has worked for the enterprise.
Common method bias
Common method bias may exist because each questionnaire was completed independently by each respondent ( Cai et al., 2017 ). We conducted a Harman one-factor test to examine whether common method bias significantly affected our data ( Podsakoff and Organ, 1986 ); the results revealed that the largest factor in our data accounted for only 36.219% of the entire variance. Hence, common method bias did not significantly affect on our study findings.
Reliability and validity
We analyzed the reliability and validity of our data for further data processing, the results of which are presented in Table 2 . Based on these results, we found that Cronbach's alpha coefficient of each variable was >0.8, thus meeting the requirements for reliability of the variables. To assess the validity of each construct, we conducted four separate confirmatory factor analyses. All the factor loadings exceeded 0.5. Overall, the reliability and validity results met the requirements for further data processing.
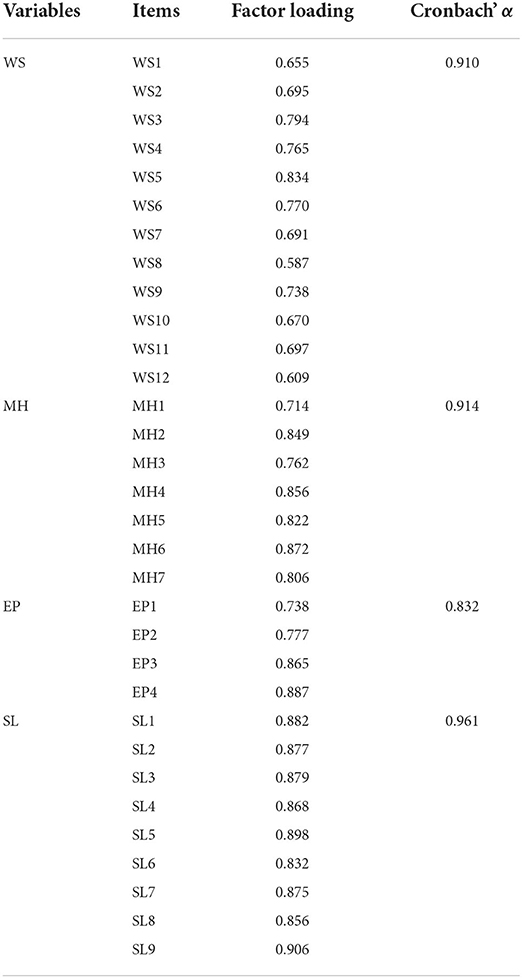
Table 2 . Results of confirmatory factor analysis and Cronbach's alpha coefficients.
To verify our hypotheses, we used a hierarchical linear regression method. Before conducting the regression analysis, we performed a Pearson correlation analysis, the results of which are presented in Table 3 .
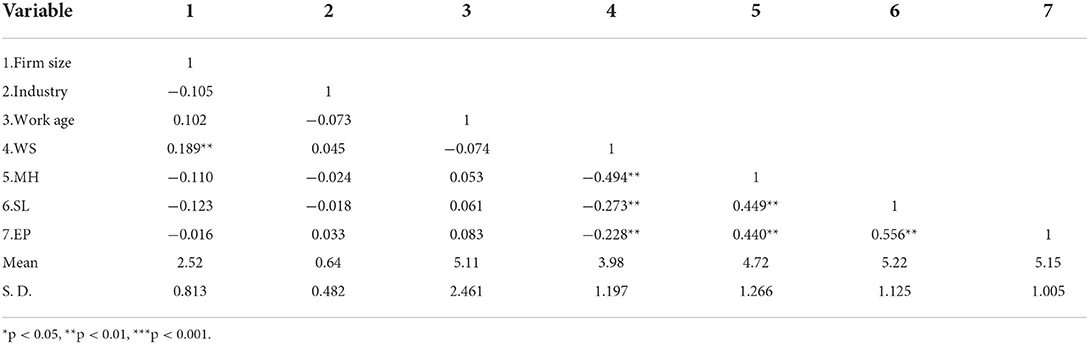
Table 3 . Descriptive statistics and correlation analysis.
In the regression analysis, we calculated the variance inflation factor (VIF) of each variable and found that the VIF value of each variable was <3. Hence, the effect of multiple co-linearity is not significant. The results of regression analysis are presented in Tables 4 , 5 .
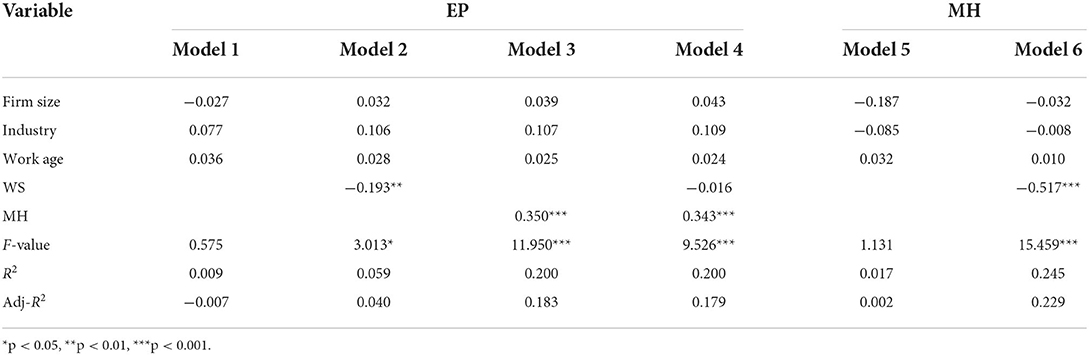
Table 4 . Results of linear regression analysis (models 1–6).
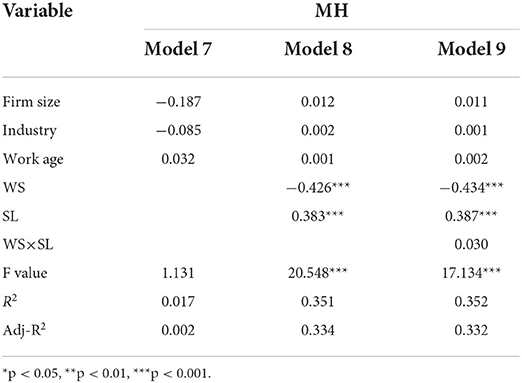
Table 5 . Results of linear regression analysis (models 7–9).
Table 4 shows that model 1 is the basic model assessing the effects of control variables on employee performance. In model 2, we added an independent variable (work stress) to examine its effect on employee performance. The results revealed that work stress negatively affects employee performance (β = −0.193, p < 0.01). Therefore, hypothesis 1 is supported. Model 5 is the basic model that examines the effects of control variables on mental health. In model 6, we added an independent variable (work stress) to assess its effect on mental health. We found that work stress negatively affects mental health (β = −0.517, p < 0.001). Therefore, hypothesis 2 is supported.
To verify the mediating effect of mental health on the relationship between work stress and employee performance, we used the method introduced by Kenny et al. (1998) , which is described as follows: (1) The independent variable is significantly related to the dependent variable. (2) The independent variable is significantly related to the mediating variable. (3) The mediating variable is significantly related to the dependent variable after controlling for the independent variable. (4) If the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable becomes smaller, it indicates a partial mediating effect. (5) If the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable is no longer significant, it indicates a full mediating effect. Based on this method, in model 4, mental health is significantly positively related to employee performance (β = 0.343, p < 0.001), and no significant correlation exists between work stress and employee performance (β = −0.016, p > 0.05). Hence, mental health fully mediates the relationship between work stress and employee performance. Therefore, hypothesis 3 is supported.
To verify the moderating effect of servant leadership on the relationship between work stress and mental health, we gradually added independent variables, a moderator variable, and interaction between the independent variables and moderator variable to the analysis, the results of which are presented in Table 5 . In model 9, the moderating effect of servant leadership is not supported (β = 0.030, p > 0.05). Therefore, hypothesis 4 is not supported.
For SMEs, employees are core assets and crucial to their survival and growth ( Shan et al., 2022 ). Specifically, owing to the COVID-19 pandemic, employees' work stress may precipitate burnout ( Choi et al., 2019 ; Barello et al., 2020 ), which influences their performance. Researchers and practitioners have significantly focused on resolving the challenge of work stress ( Karatepe et al., 2020 ; Tan et al., 2020 ; Gao, 2021 ). However, previous research has not clearly elucidated the relationship among work stress, mental health, servant leadership, and employee performance. Through this study, we found the following results:
Employees in SMEs face work stress owing to the COVID-19 pandemic, which reduces their performance. Facing these external shocks, survival and growth of SMEs may become increasingly uncertain ( Adam and Alarifi, 2021 ). Employees' career prospects are negatively impacted. Meanwhile, the pandemic has precipitated a change in the way employees work, their workspace, and work timings. Moreover, their work is now intertwined with family life. Hence, employees experience greater stress at work than ever before ( Gao, 2021 ), which, in turn, affects their productivity and deteriorates their performance.
Furthermore, we found that mental health plays a mediating role in the relationship between work stress and employee performance; this suggests that employees' mental status is influenced by work stress, which, in turn, lowers job performance. Per our findings, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, employees experience nervous and anxious psychological states ( Tan et al., 2020 ), which renders them unable to devote their full attention to their work; hence, their work performance is likely to decrease.
Finally, we found that leaders are the core of any enterprise ( Ahn et al., 2018 ). Hence, their leadership behavior significantly influences employees. Per previous research, servant leadership is considered a typical leadership behavior characterized by exhibiting humility, delegating power to employees, raising the morale of subordinates, and placing the interests of employees above their own ( Sendjaya, 2015 ; Eva et al., 2019 ). Through theoretical analysis, we found that servant leadership mitigates the negative effect of work stress on mental health. However, the empirical results are not significant possibly because work stress of employees in SMEs is rooted in worries regarding the future of the macroeconomic environment, and the resulting mental health problems cannot be cured merely by a leader.
Hence, due to the COVID-19 pandemic, employees experience work stress, which precipitates mental health problems and poor employee performance. To solve the problem of work stress, SMEs should pay more attention to fostering servant leadership. Meanwhile, organizational culture is also important in alleviating employees' mental health problems and thus reducing negative effects of work stress on employee performance.
Implications
This study findings have several theoretical and managerial implications.
Theoretical implications
First, per previous research, no consistent conclusion exists regarding the relationship between work stress and employee performance, including positive relationships ( Ismail et al., 2015 ; Soomro et al., 2019 ), negative relationships ( Yunus et al., 2018 ; Nawaz Kalyar et al., 2019 ; Purnomo et al., 2021 ), inverted U-shaped relationships ( McClenahan et al., 2007 ; Hamidi and Eivazi, 2010 ), and no relationship ( Tănăsescu and Ramona-Diana, 2019 ). We report that work stress negatively affects employee performance in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic; thus, this study contributes to the understanding of the situational nature of work stress and provides enriching insights pertaining to positive psychology.
Second, we established the research path that work stress affects employee performance. Mental health is a psychological state that may influence an individual's work efficiency. In this study, we explored its mediating role, which opens the black box of the relationship between work stress and employee performance; thus, this study contributes to a greater understanding of the role of work stress during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Finally, this study sheds light on the moderating effect of servant leadership, which is useful for understanding why some SMEs exhibit greater difficulty in achieving success than others during the COVID-19 pandemic. Previous research has explained the negative effect of work stress ( Yunus et al., 2018 ; Nawaz Kalyar et al., 2019 ; Purnomo et al., 2021 ). However, few studies have focused on how to resolve the problem. We identify servant leadership as the moderating factor providing theoretical support for solving the problem of work stress. This study expands the explanatory scope of the upper echelons theory.
Practice implications
First, this study elucidates the sources and mechanisms of work stress in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic. Employees should continuously acquire new skills to improve themselves and thus reduce their replaceability. Meanwhile, they should enhance their time management and emotional regulation skills to prevent the emergence of adverse psychological problems.
Second, leaders in SMEs should pay more attention to employees' mental health to prevent the emergence of hindrance stress. Employees are primarily exposed to stress from health and safety risks, impaired performance, and negative emotions. Hence, leaders should communicate with employees in a timely manner to understand their true needs, which can help avoid mental health problems due to work stress among employees.
Third, policymakers should realize that a key cause of employee work stress in SMEs is attributable to concerns regarding the macroeconomic environment. Hence, they should formulate reasonable support policies to improve the confidence of the whole society in SMEs, which helps mitigate SME employees' work stress during emergency events like the COVID-19 pandemic.
Finally, as work stress causes mental health problems, SME owners should focus on their employees' physical as well as mental health. Society should establish a psychological construction platform for SME employees to help them address their psychological problems.
Limitations and future research
This study has limitations, which should be addressed by further research. First, differences exist in the impact of the pandemic on different industries. Future research should focus on the impact of work stress on employee performance in different industries. Second, this study only explored the moderating role of servant leadership. Other leadership behaviors of leaders may also affect work stress. Future research can use case study methods to explore the role of other leadership behaviors.
This study explored the relationship between work stress and employee performance in SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic. Using a sample of 196 SMEs from China, we found that as a typical result of emergency events, work stress negatively affects employees' performance, particularly by affecting employees' mental health. Furthermore, we found that servant leadership provides a friendly internal environment to mitigate negative effects of work stress on employees working in SMEs.
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/supplementary material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author/s.
Ethics statement
Ethical review and approval was not required for the study on human participants in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. Written informed consent from the patients/participants or patients/participants legal guardian/next of kin was not required to participate in this study in accordance with the national legislation and the institutional requirements.
Author contributions
BC: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, and visualization. LW: formal analysis. BL: investigation, funding acquisition, and writing—review and editing. WL: resources, project administration, and supervision. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
This research was supported by the major project of Henan Province Key R&D and Promotion Special Project (Soft Science) Current Situation, Realization Path and Guarantee Measures for Digital Transformation Development of SMEs in Henan Province under the New Development Pattern (Grant No. 222400410159).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Adam, N. A., and Alarifi, G. (2021). Innovation practices for survival of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in the COVID-19 times: the role of external support. J. Innov. Entrepreneursh . 10, 1–22. doi: 10.1186/s13731-021-00156-6
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ahmed, I., Ali, M., Usman, M., Syed, K. H., and Rashid, H. A. (2021). Customer Mistreatment and Insomnia in Employees-a Study in Context of COVID-19. J. Behav. Sci. 31, 248–271.
Google Scholar
Ahn, J., Lee, S., and Yun, S. (2018). Leaders' core self-evaluation, ethical leadership, and employees' job performance: the moderating role of employees' exchange ideology. J. Bus. Ethics . 148, 457–470. doi: 10.1007/s10551-016-3030-0
Barello, S., Palamenghi, L., and Graffigna, G. (2020). Burnout and somatic symptoms among frontline healthcare professionals at the peak of the Italian COVID-19 pandemic. Psychiatry Res . 290, 113129. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2020.113129
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Bhui, K. S., Dinos, S., Stansfeld, S. A., and White, P. D. (2012). A synthesis of the evidence for managing stress at work: a review of the reviews reporting on anxiety, depression, and absenteeism. J. Environ. Public Health . 2012. doi: 10.1155/2012/515874
Bubonya, M., Cobb-Clark, D. A., and Wooden, M. (2017). Mental health and productivity at work: Does what you do matter?. Labour Econ . 46, 150–165. doi: 10.1016/j.labeco.2017.05.001
Cai, L., Chen, B., Chen, J., and Bruton, G. D. (2017). Dysfunctional competition and innovation strategy of new ventures as they mature. J. Bus. Res . 78, 111–118. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2017.05.008
Cavanaugh, M. A., Boswell, W. R., Roehling, M. V., and Boudreau, J. W. (2000). An empirical examination of self-reported work stress among US managers. J. Appl. Psychol . 85, 65–74. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.85.1.65
Chen, I. S., and Fellenz, M. R. (2020). Personal resources and personal demands for work engagement: Evidence from employees in the service industry. Int. J. Hosp. Manage . 90, 102600. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102600
Chen, Z. X., Tsui, A. S., and Farh, J. L. (2002). Loyalty to supervisor vs. organizational commitment: Relationships to employee performance in China. J. Occupa. Organ. Psychol . 75, 339–356. doi: 10.1348/096317902320369749
Choi, H. M., Mohammad, A. A., and Kim, W. G. (2019). Understanding hotel frontline employees' emotional intelligence, emotional labor, job stress, coping strategies and burnout. Int. J. Hosp. Manage . 82, 199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2019.05.002
Chou, L., Hu, S., and Lo, M. (2015). Job stress, mental health, burnout and arterial stiffness: a cross-sectional study among Taiwanese medical professionals. Atherosclerosis . 241, e135–e135. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2015.04.468
Cohen, J., Schiffler, F., Rohmer, O., Louvet, E., and Mollaret, P. (2019). Is disability really an obstacle to success? Impact of a disability simulation on motivation and performance. J. Appl. Soc. Psychol . 49, 50–59. doi: 10.1111/jasp.12564
Deng, J., Guo, Y., Ma, T., Yang, T., and Tian, X. (2019). How job stress influences job performance among Chinese healthcare workers: a cross-sectional study. Environ. Health Prevent. Med . 24, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12199-018-0758-4
Eggers, F. (2020). Masters of disasters? Challenges and opportunities for SMEs in times of crisis. J. Bus. Res . 116, 199–208. doi: 10.1016/j.jbusres.2020.05.025
Ehrhart, M. G. (2004). Leadership and procedural justice climate as antecedents of unit-level organizational citizenship behavior. Pers. Psychol . 57, 61–94. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-6570.2004.tb02484.x
Eskilsson, T., Slunga Järvholm, L., Malmberg Gavelin, H., Stigsdotter Neely, A., and Boraxbekk, C. J. (2017). Aerobic training for improved memory in patients with stress-related exhaustion: a randomized controlled trial. BMC psychiatry . 17, 1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12888-017-1457-1
Eva, N., Robin, M., Sendjaya, S., Van Dierendonck, D., and Liden, R. C. (2019). Servant leadership: a systematic review and call for future research. Leadersh. Q . 30, 111–132. doi: 10.1016/j.leaqua.2018.07.004
Flynn, A. (2017). Re-thinking SME disadvantage in public procurement. J. Small Bus. Enter. Dev . 24, 991–1008. doi: 10.1108/JSBED-03-2017-0114
Gao, Y. (2021). Challenges and countermeasures of human resource manage in the post-epidemic Period. Int. J. Manage Educ. Human Dev . 1, 036–040.
Green, N., Tappin, D., and Bentley, T. (2020). Working from home before, during and after the Covid-19 pandemic: implications for workers and organisations. N. Z. J. Employ. Relat . 45, 5–16. doi: 10.24135/nzjer.v45i2.19
Hambrick, D. C., and Mason, P. A. (1984). Upper echelons: the organization as a reflection of its top managers. Acad.Manage. Rev . 9, 193–206. doi: 10.2307/258434
Hamidi, Y., and Eivazi, Z. (2010). The relationships among employees' job stress, job satisfaction, and the organizational performance of Hamadan urban health centers. Soc. Behav. Pers. Int. J . 38, 963–968. doi: 10.2224/sbp.2010.38.7.963
Harrison, M. A., and Stephens, K. K. (2019). Shifting from wellness at work to wellness in work: Interrogating the link between stress and organization while theorizing a move toward wellness-in-practice. Manage. Commun. Q . 33, 616–649. doi: 10.1177/0893318919862490
Haslam, S. A., Reicher, S. D., and Platow, M. J. (2020). The New Psychology of Leadership: Identity, Influence and Power . London, UK: Routledge. doi: 10.4324/9781351108232
Heffernan, J., and Pilkington, P. (2011). Supported employment for persons with mental illness: systematic review of the effectiveness of individual placement and support in the UK. J. Mental Health . 20, 368–380. doi: 10.3109/09638237.2011.556159
Hennekam, S., Richard, S., and Grima, F. (2020). Coping with mental health conditions at work and its impact on self-perceived job performance. Employee Relat. Int. J . 42, 626–645. doi: 10.1108/ER-05-2019-0211
Hon, A. H., and Chan, W. W. (2013). The effects of group conflict and work stress on employee performance. Cornell Hosp. Q . 54, 174–184. doi: 10.1177/1938965513476367
Houtman, I., Jettinghof, K., and Cedillo, L. (2007). Raising Awareness of Stress at Work in Developing Countires: a Modern Hazard in a Traditional Working Environment: Advice to Employers and Worker Representatives . Geneva: World Health Organization.
Ismail, A., Saudin, N., Ismail, Y., Samah, A. J. A., Bakar, R. A., Aminudin, N. N., et al. (2015). Effect of workplace stress on job performance. Econ. Rev. J. Econ. Bus . 13, 45–57.
Karasek, R., and Theorell, T. (1990). Healthy Work: Stress, Productivity, and the Reconstruction of Working Life . New York: Basic Books.
Karatepe, O. M., Rezapouraghdam, H., and Hassannia, R. (2020). Job insecurity, work engagement and their effects on hotel employees' non-green and nonattendance behaviors. Int. J. Hosp. Manage . 87, 102472. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102472
Kenny, D., Kashy, D., and Bolger, N. (1998). Data analysis in social psychology. Handbook Soc. Psychol. 1, 233–268.
Khamisa, N., Peltzer, K., Ilic, D., and Oldenburg, B. (2016). Work related stress, burnout, job satisfaction and general health of nurses: a follow-up study. Int. J. Nurs. Pract . 22, 538–545. doi: 10.1111/ijn.12455
Khorakian, A., and Sharifirad, M. S. (2019). Integrating implicit leadership theories, leader–member exchange, self-efficacy, and attachment theory to predict job performance. Psychol. Rep . 122, 1117–1144. doi: 10.1177/0033294118773400
Lai, H., Hossin, M. A., Li, J., Wang, R., and Hosain, M. S. (2022). Examining the relationship between COVID-19 related job stress and employees' turnover intention with the moderating role of perceived organizational support: Evidence from SMEs in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health . 19, 3719. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19063719
Lai, Y., Saridakis, G., and Blackburn, R. (2015). Job stress in the United Kingdom: Are small and medium-sized enterprises and large enterprises different?. Stress Health . 31, 222–235. doi: 10.1002/smi.2549
Lebesby, K., and Benders, J. (2020). Too smart to participate? Rational reasons for employees' non-participation in action research. Syst. Pract. Action Res . 33, 625–638. doi: 10.1007/s11213-020-09538-5
LePine, J. A., LePine, M. A., and Jackson, C. L. (2004). Challenge and hindrance stress: relationships with exhaustion, motivation to learn, and learning performance. J. Appl. Psychol . 89, 883. doi: 10.1037/0021-9010.89.5.883
LePine, J. A., Podsakoff, N. P., and LePine, M. A. (2005). A meta-analytic test of the challenge stressor–hindrance stressor framework: an explanation for inconsistent relationships among stressors and performance. Acad. Manage J . 48, 764–775. doi: 10.5465/amj.2005.18803921
Levinson, D., Lakoma, M. D., Petukhova, M., Schoenbaum, M., Zaslavsky, A. M., Angermeyer, M., et al. (2010). Associations of serious mental illness with earnings: results from the WHO World Mental Health surveys. Br. J. Psychiatry . 197, 114–121. doi: 10.1192/bjp.bp.109.073635
Li, S., Rees, C. J., and Branine, M. (2019). Employees' perceptions of human resource Manage practices and employee outcomes: empirical evidence from small and medium-sized enterprises in China. Employee Relat. Int. J . 41, 1419–1433. doi: 10.1108/ER-01-2019-0065
Liu, Z., Xi, C., Zhong, M., Peng, W., Liu, Q., Chu, J., et al. (2022). Factorial validity of the 12-item general health questionnaire in patients with psychological disorders. Current Psychol . 1–9. doi: 10.1007/s12144-022-02845-1
Lu, A. C. C., and Gursoy, D. (2016). Impact of job burnout on satisfaction and turnover intention: do generational differences matter?. J. Hosp. Tour. Res . 40, 210–235. doi: 10.1177/1096348013495696
Lu, J., Zhang, Z., and Jia, M. (2019). Does servant leadership affect employees' emotional labor? A Soc. information-processing perspective. J. Bus. Ethics . 159, 507–518. doi: 10.1007/s10551-018-3816-3
Lu, L. (1997). Hassles, appraisals, coping and distress: a closer look at the stress process. Kaohsiung J. Med. Sci . 13, 503–510.
PubMed Abstract | Google Scholar
Lu, Y., Zhang, Z., Yan, H., Rui, B., and Liu, J. (2020). Effects of occupational hazards on job stress and mental health of factory workers and miners: a propensity score analysis. BioMed Res. Int . 2020. doi: 10.1155/2020/1754897
Mansour, S., and Tremblay, D. G. (2018). Work–family conflict/family–work conflict, job stress, burnout and intention to leave in the hotel industry in Quebec (Canada): moderating role of need for family friendly practices as “resource passageways”. Int. J. Human Res. Manage . 29, 2399–2430. doi: 10.1080/09585192.2016.1239216
Mayerl, H., Stolz, E., Waxenegger, A., Rásky, É., and Freidl, W. (2016). The role of personal and job resources in the relationship between psychoSoc. job demands, mental strain, and health problems. Front. Psychol . 7, 1214. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01214
McClenahan, C., Shevlin, M. G., Bennett, C., and O'Neill, B. (2007). Testicular self-examination: a test of the health belief model and the theory of planned behaviour. Health Educ. Res . 22, 272–284. doi: 10.1093/her/cyl076
Nawaz Kalyar, M., Shafique, I., and Ahmad, B. (2019). Job stress and performance nexus in tourism industry: a moderation analysis. Tour. Int. Interdiscip. J . 67, 6–21.
Neupane, S., and Nygard, C. H. (2017). Physical and mental strain at work: relationships with onset and persistent of multi-site pain in a four-year follow up. Int. J. Indus. Ergon . 60, 47–52. doi: 10.1016/j.ergon.2016.03.005
Olugbade, O. A., and Karatepe, O. M. (2019). Stressors, work engagement and their effects on hotel employee outcomes. Serv. Indus. J . 39, 279–298. doi: 10.1080/02642069.2018.1520842
Orfei, M. D., Porcari, D. E., D'Arcangelo, S., Maggi, F., Russignaga, D., Lattanzi, N., et al. (2022). COVID-19 and stressful adjustment to work: a long-term prospective study about homeworking for bank employees in Italy. Front. Psychol . 13, 843095. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.843095
Park, S. K., Rhee, M. K., and Barak, M. M. (2016). Job stress and mental health among nonregular workers in Korea: What dimensions of job stress are associated with mental health?. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health . 71, 111–118. doi: 10.1080/19338244.2014.997381
Parker, D. F., and DeCotiis, T. A. (1983). Organizational determinants of job stress. Organ. Behav. Human Perform . 32, 160–177. doi: 10.1016/0030-5073(83)90145-9
Phong, L. B., Hui, L., and Son, T. T. (2018). How leadership and trust in leaders foster employees' behavior toward knowledge sharing. Soc. Behav. Pers. Int. J . 46, 705–720. doi: 10.2224/sbp.6711
Piccarozzi, M., Silvestri, C., and Morganti, P. (2021). COVID-19 in manage studies: a systematic literature review. Sustainability . 13, 3791. doi: 10.3390/su13073791
Podsakoff, P. M., and Organ, D. W. (1986). Self-reports in organizational research: problems and prospects. J. Manage . 12, 531–544. doi: 10.1177/014920638601200408
Poms, L. W., Fleming, L. C., and Jacobsen, K. H. (2016). Work-family conflict, stress, and physical and mental health: a model for understanding barriers to and opportunities for women's well-being at home and in the workplace. World Med. Health Policy . 8, 444–457. doi: 10.1002/wmh3.211
Prasad, K., and Vaidya, R. W. (2020). Association among Covid-19 parameters, occupational stress and employee performance: an empirical study with reference to Agricultural Research Sector in Hyderabad Metro. Sustain. Humanosphere . 16, 235–253.
Purnomo, K. S. H., Lustono, L., and Tatik, Y. (2021). The effect of role conflict, role ambiguity and job stress on employee performance. Econ. Educ. Anal. J . 10, 532–542. doi: 10.15294/eeaj.v10i3.50793
Richardson, K. M., and Rothstein, H. R. (2008). Effects of occupational stress manage intervention programs: a meta-analysis. J. Occup. Health Psychol . 13, 69–93. doi: 10.1037/1076-8998.13.1.69
Robbins, S. P. (2005). Essentials of Organizational Behavior (8th ed.) . Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Saleem, F., Malik, M. I., and Qureshi, S. S. (2021). Work stress hampering employee performance during COVID-19: is safety culture needed? Front . Psychol . 12, 655839. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.655839
Sendjaya, S. (2015). Personal and Organizational Excellence Through Servant Leadership Learning to Serve, Serving to Lead, Leading to Transform . Berlin, Germany: Springer.
Sendjaya, S., Eva, N., Butar Butar, I., Robin, M., and Castles, S. (2019). SLBS-6: Validation of a short form of the servant leadership behavior scale. J. Bus. Ethics . 156, 941–956. doi: 10.1007/s10551-017-3594-3
Shah, S. H. A., Haider, A., Jindong, J., Mumtaz, A., and Rafiq, N. (2021). The impact of job stress and state anger on turnover intention among nurses during COVID-19: the mediating role of emotional exhaustion. Front. Psychol . 12. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.810378
Shan, B., Liu, X., Gu, A., and Zhao, R. (2022). The effect of occupational health risk perception on job satisfaction. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health . 19, 2111. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19042111
Shimazu, A., Nakata, A., Nagata, T., Arakawa, Y., Kuroda, S., Inamizu, N., et al. (2020). PsychoSoc. impact of COVID-19 for general workers. J. Occup. Health . 62, e12132. doi: 10.1002/1348-9585.12132
Soeker, M. S., Truter, T., Van Wilgen, N., Khumalo, P., Smith, H., Bezuidenhout, S., et al. (2019). The experiences and perceptions of individuals diagnosed with schizophrenia regarding the challenges they experience to employment and coping strategies used in the open labor market in Cape Town, South Africa. Work . 62, 221–231. doi: 10.3233/WOR-192857
Song, L., Wang, Y., Li, Z., Yang, Y., and Li, H. (2020). Mental health and work attitudes among people resuming work during the COVID-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health . 17, 5059. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17145059
Soomro, M. A., Memon, M. S., and Bukhari, N. S. (2019). Impact of stress on employees performance in public sector Universities of Sindh. Sukkur IBA J. Manage. Bus . 6, 114–129. doi: 10.30537/sijmb.v6i2.327
Spears, L. C. (2010). Character and servant leadership: ten characteristics of effective, caring leaders. J. Virtues Leadersh . 1, 25–30.
Tan, W., Hao, F., McIntyre, R. S., Jiang, L., Jiang, X., Zhang, L., et al. (2020). Is returning to work during the COVID-19 pandemic stressful? A study on immediate mental health status and psychoneuroimmunity prevention measures of Chinese workforce. Brain Behav. Immun . 87, 84–92. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.04.055
Tănăsescu, R. I., and Ramona-Diana, L. E. O. N. (2019). Emotional intelligence, occupational stress and job performance in the Romanian banking system: a case study approach. Manage Dyn. Knowl. Econ . 7, 323–335. doi: 10.25019/MDKE/7.3.03
Tiedtke, C., Rijk, D. E., Van den Broeck, A. A., and Godderis, L. (2020). Employers' experience on involvement in sickness absence/return to work support for employees with Cancer in small enterprises. J. Occup. Rehabil . 30, 635–645. doi: 10.1007/s10926-020-09887-x
Tu, Y., Li, D., and Wang, H. J. (2021). COVID-19-induced layoff, survivors' COVID-19-related stress and performance in hospital industry: the moderating role of social support. Int. J. Hosp. Manage . 95, 102912. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2021.102912
Uchmanowicz, I., Karniej, P., Lisiak, M., Chudiak, A., Lomper, K., Wiśnicka, A., et al. (2020). The relationship between burnout, job satisfaction and the rationing of nursing care—A cross-sectional study. J. Nurs. Manage . 28, 2185–2195. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13135
Xu, S., Wang, Y. C., Ma, E., and Wang, R. (2020). Hotel employees' fun climate at work: effects on work-family conflict and employee deep acting through a collectivistic perspective. Int. J. Hosp. Manage . 91, 102666. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhm.2020.102666
Yu, D., Yang, K., Zhao, X., Liu, Y., Wang, S., D'Agostino, M. T., et al. (2022). Psychological contract breach and job performance of new generation of employees: Considering the mediating effect of job burnout and the moderating effect of past breach experience. Front . Psychol . 13, 985604. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.985604
Yunus, N. H., Mansor, N., Hassan, C. N., Zainuddin, A., and Demong, N. A. R. (2018). The role of supervisor in the relationship between job stress and job performance. Int. J. Acad. Res. Bus. Soc. Sci . 8, 1962–1970. doi: 10.6007/IJARBSS/v8-i11/5560
Keywords: COVID-19, work stress, mental health, employee performance, social uncertainty
Citation: Chen B, Wang L, Li B and Liu W (2022) Work stress, mental health, and employee performance. Front. Psychol. 13:1006580. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.1006580
Received: 29 July 2022; Accepted: 10 October 2022; Published: 08 November 2022.
Reviewed by:
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Wang, Li and Liu. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY) . The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Biao Li, lib0023@zzu.edu.cn
Disclaimer: All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Research article
- Open access
- Published: 04 November 2020
Effects of a work-related stress model based mental health promotion program on job stress, stress reactions and coping profiles of women workers: a control groups study
- Ozlem Koseoglu Ornek ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-9101-6256 1 , 2 &
- Melek Nihal Esin 3
BMC Public Health volume 20 , Article number: 1658 ( 2020 ) Cite this article
21k Accesses
21 Citations
46 Altmetric
Metrics details
Work-related stress and its detrimental effects on human health have rapidly increased during the past several years. It causes many different stress reactions, related diseases and unhealthy behavior among workers, but especially women workers. Thus, the aim of this study was to examine the effects of the work-related stress model based Workplace Mental Health Promotion Programme on the job stress, social support, reactions, salivary immunoglobulin A and Cortisol levels, work absenteeism, job performance and coping profiles of women workers.
This study had a “pre-test post-test non-equivalent control groups” design and included 70 women workers (35 in each study group) selected by randomized sampling from two factories. The programme was delivered as an intervention including 12 weeks of follow-up. Reminder messages, videos, and WhatsApp texts were used at the follow-up stage. The research measurements were; the assessment form, the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire, the Brief Coping Profile Scale, salivary ELISA kits, and a self-reported check-list.
There were no differences in sociodemographic characteristics, general health or working conditions between the Intervention and control groups( p > .05). Three months after the intervention, there was a significant decrease in job stress( p ≤ .001), physical and mental reactions’ scores( p ≤ .001) and work absenteeism( p < .05), and there was an increase in job performance( p < .05), social support( p ≤ .001) among the intervention group. The programme showed positive effects on coping profiles( p < .05). After the intervention salivary-cortisol and IgA levels showed a statistically significant decrease( p < .05). A majority of effect sizes were very large (η p 2 > .14).
Conclusions
Work-ProMentH was found to be effective and useful in job stress management and promotion of effective coping profiles. It enables its users to holistically assess worker stress and to plan and examine intervention programmes via a systematic approach. There is a need for more empirical studies that may support the data of the present study, but it is thought that the intervention can be maintained for the long-term. We recommend that occupational health professionals at workplaces should consider using this model-based cost-effective intervention, which seems easy and practical to apply in real-life situations.
Trial registration
ISRCTN registration ID: ISRCTN14333710 (2020/10/03, retrospective registration).
Peer Review reports
Work-related stress (WRS) has become a crucial public health problem in recent decades, and its detrimental effects on human health have recently increased rapidly [ 1 , 2 ]. Thus, there is a large challenge to understand its reactions, related factors and outcomes. Many stress-related models have been developed to better explain and cope with the stress [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 , 7 ]. According to the WRS model, stress is defined as all reactions that take place and cause any change in individuals’ cognitive, physical, psychological and emotional structures as a result of a high perceived workload [ 6 ]. It has a flow process, and causes many different stress reactions, related diseases and unhealthy behaviours among workers. The reactions can involve physical, psychological, biological, and/or behavioural symptoms. Commonly observed physical symptoms include high blood pressure, a fast pulse, Cheyne Stokes respiration, headache, and tense muscles. Biological parameters consist mainly of immunological variables, such as T cell activation, decreased immunoglobulin A (IgA), and increased cortisol secretion [ 8 , 9 , 10 ]. Mental health symptoms may involve irritability, tension, aggressive behaviors, lack of concentration, and sleep, perception, and memory disorders [ 11 , 12 ]. If the reactions persist for an extended period, there may be irreversible health outcomes, such as chronic fatigue, cardiovascular diseases [ 13 , 14 ], musculoskeletal diseases [ 15 ], or mental health problems, such as anxiety or depression [ 16 , 17 ]. The development of such physical and mental health problems can also lead to extended sick leaves or absenteeism [ 18 , 19 ] and decreases in job quality, performance, and productivity; it can also threaten workers’ health and safety [ 6 , 20 ].
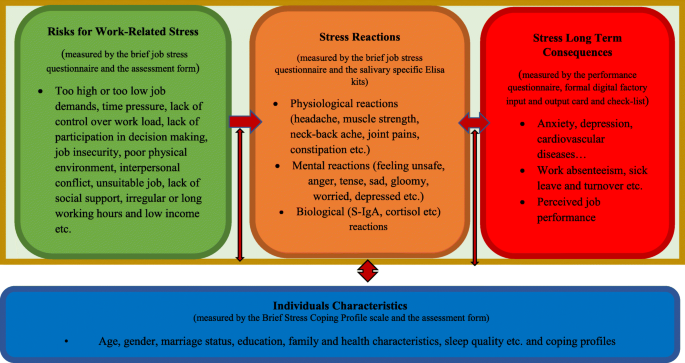
Working conditions and individual characteristics are the main related factors for developing WRS. The work-related stress model indicates that, stress and its reactions occur as a result of the relationship between individual characteristics such as age, education, gender, personality, experience and coping profiles, working conditions such as high or low job demands, irregular or long working hours, time pressure, job insecurity, lack of social support and psychological harassment, living conditions, and responses to stress. Therefore, the model consists of four main components: risks for work-related stress, individuals’ characteristics, stress reactions, and long-term consequences of stress. It defines the relationship within the components as a dynamic process. One of the most important advantages of the model is that it takes into account the individual differences of the workers. According to the model and various studies, short-term stress increases the motivation and productivity of workers but exposure to long-term stress resources causes various long-term health and behavioural problems. The model illustrates the long-term consequences of such stress reactions, which affect workers’ physical and mental health, job performance, work absenteeism, and other risky health behaviours. Generally, working conditions have a strong relationship with stress and its results (see Fig. 1 ) [ 6 , 21 , 22 , 23 ]. Related studies have provided important evidence on the interrelations between the model’s components. For example, individual characteristics, such as age, education level, gender, goals, social support [ 24 ], and family conditions, have significant effects on one’s ability to cope with stress [ 25 ]. Moreover, working conditions, such as long working hours, lack of control over one’s workload, time pressures, job insecurity, and an insufficient salary, have a strong influence on the development of job-related stress [ 26 ].
The evaluation of the Model of Work-related Stress’ components and their interrelations
It is widely acknowledged that perceived social support plays a significant role in decreasing WRS. It also has positive effects on job performance, work absenteeism, and productivity [ 24 , 27 , 28 , 29 ]. The higher the degree of social support workers have, the more easily they can be protected from occupational stress as well as from physical and mental health problems [ 30 ]. According to the studies with controlled study designs, interventions, such as exercise, education, consultations, or organizational programmes initiated by supervisors and administrators encourage feelings of solidarity and happiness. These kinds of feelings increase the amount of social support over the course of time [ 31 ].
The effects of stress vary between genders, placing females in a more disadvantaged and vulnerable category than their male counterparts due to biological and psychosocial systems. Gender discrimination, income inequality, and cultural barriers play an important role on this matter, especially in the developing and undeveloped countries [ 2 , 32 , 33 , 34 , 35 , 36 ]. Research on how stress affects different genders reveals that women are twice as likely as men to develop symptoms of stress. The identified underlying causes of this include the female biological and psychological systems, the impact of women’s many roles and responsibilities concerning family life, and their exposure to societal disparities. One’s cultural perspective also has a significant impact on preventing and coping with WRS [ 33 , 37 , 38 , 39 ]. However, working conditions and the economy have presented employees with more difficulties in recent years. Second, only to child workers, women are the most vulnerable population of employees. It is, therefore, crucial to prevent job stress, as much as possible, before it causes chronic problems for all workers, especially women workers. Women workers in particular have disadvantaged life and working conditions due to high social disparity, gender inequality, and a great responsibility to balance work and family life in undeveloped and antisocial-democratic society. Accordingly, primary protective mental health intervention should be implemented at work; however, such assistance has been found to be insufficient, and pre-test and post-test control studies are lacking in developing countries [ 40 ].
As a result, various approaches relating to prevention, protection, and promotion programmes covering stress management have been introduced and implemented in various countries [ 17 , 26 , 41 , 42 ]. However, a majority of intervention programmes are focused on limited specific topics (e.g. job stressor, psychological distress, sickness absenteeism, IgA) in developed countries. Therefore, this WRS model-based study was designed to plan and evaluate Workplace Mental Health Promotion Program (Work-ProMentH) using a broad, systematic approach to women workers’ health in a developing country. The WRS model enables its users to assess the causes and consequences of work-related health using a holistic approach and to plan and evaluate programmes in a systematic manner (see Fig. 1 ) [ 6 ]. Additionally, women workers were chosen as the specific research samples in the present study for the reasons mentioned above, and working in the textile and garment sectors is very common among the workers. This sector has the highest rate of women workers compared to other sectors in some countries such as Turkey. Generally, women who work in this sector have low levels of education, are unskilled and have poor economic status. Precarious working conditions such as job insecurity, unpredictable working hours, insufficient salary, and lack of a union are very common among the workers in this sector [ 43 , 44 , 45 ]. As a result, the aim of this study was to examine the effects of the newly developed WRS model-based Workplace Mental Health Promotion Program (Work-ProMentH) on the job-related stress of female workers, their physical and mental reactions to stress, social support, coping profiles, work absenteeism, and job performance; the women’s salivary immunoglobulin A (S-IgA) and cortisol (S-cortisol) levels were also measured.
Study design and objectives
The aim of this study, which featured a pre-test–post-test non-equivalent control group design, was to examine the effects of the WRS model-based Work-ProMentH on women workers’ job stress, physical and mental reactions, social support, coping profiles, work absenteeism, job performance, and salivary IgA (S-IgA) and cortisol (S-cortisol) levels. The research was carried out in 2 textile factories (A and B) since the intervention is considered to affect workers in the same factory. Factory B is defined as a subcomponent and partner of factory A. The factories mainly manufacture knitwear and export it abroad. Both factories have demonstrated adherence to the laws and regulations on occupational health and common international inspections. The factories also have the same occupational health physician and nurse. Additionally, the first researcher voluntarily worked 2 hours per week for more than a year before the study began to observe the work process, working conditions, and work environments.
The hypotheses we tested in this study are as follows
Compared to those who do not participate in the Work-ProMentH intervention, workers who do participate in the program will have decreased job stress, less severe physical and mental stress reactions, lower S-cortisol levels, less job absenteeism, increased S-IgA levels, more social support, better job performance, and improved coping profiles.
Participants
Criteria for inclusion in the study sample consisted of a job-stress subscale score above the median(med: 45), indicating a higher level of WRS, and no use of any medication that has effects on cortisol and IgA. Criteria for exclusion from the study population included the use of any medication that affects salivary cortisol and/or IgA levels, age under 18 years, diagnosed psychiatric health problems, or illiteracy. Out of 242 female workers assessed for eligibility, 101 (53 from factory A, and 48 from factory B) met the criteria and were included in the study. The factory where the programme was performed was selected by a draw (factory A). The study sample size was calculated by power analysis; the minimal study sample was found to be 58 (intervention group [IG]: 29, control group [CG]: 29). The acceptance of Type I errors was set at 5%, and that of Type II errors was set at 20% (α = 0.05, 1-β = 0.80). Drop-outs were expected rate for unknown reasons. Researchers selected 70 participants (35 in each study group) from factories A and B via systematic sampling. The study procedure is shown in Fig. 2 . All workers worked 5 days per week, beginning at 08:30 am, and finishing at 7:00 pm. Their lunch was provided by the factories. The mean age of the women workers in the IG was 33.54 ± 9.6 (19–54) years, and almost 49% of them graduated from elementary school. The mean age of the women workers in the CG was 31.11 ± 8.2 (20–52) years, and almost 60% of them graduated from elementary school. There was no difference between the groups’ main sociodemographic characteristics. The characteristics of the groups are reported in Table 1 .
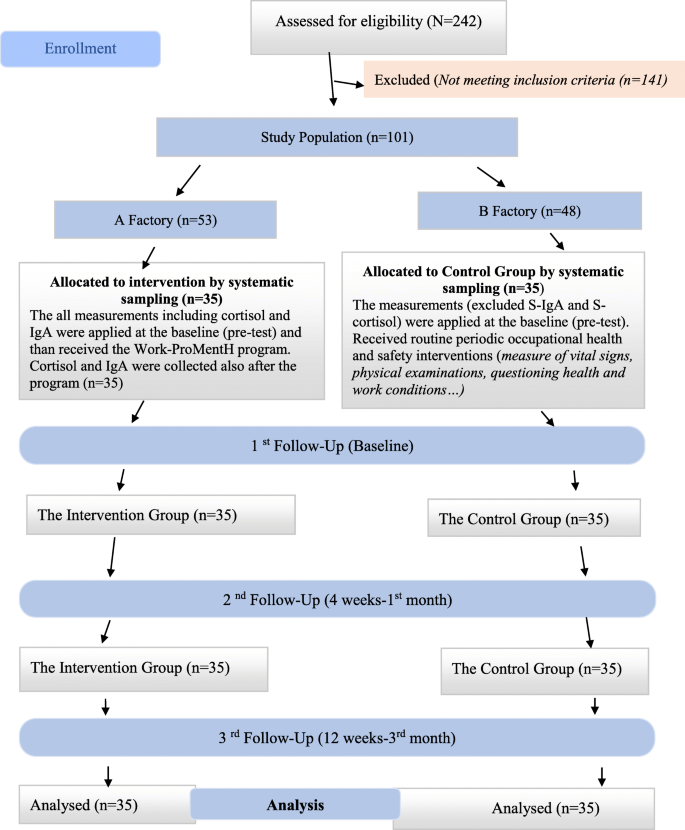
The Flow Diagram of the Study
The data were collected between February and April, 2016. During this process, 2 participants (due to marriage) and 3 participants (due to working conditions and health problems) were dropped from the CG between weeks 10 and 11 of the follow-up stage. The workers who dropped out were not considered missing as the intent-to-treat (ITT) principle was used in the data analysis process [ 46 ].
Measurements
The study examined five measurements that were selected and developed by researchers based on the components (Risks for work-related stress, Stress reactions, Stress long-term consequences, Individuals characteristics) of the causes and consequences in the WRS model to evaluate stress, stress reactions, long-term stress responses, and coping profiles. The risks for the work-related stress component of the model were measured by the brief job stress questionnaire and the assessment form; stress reactions were measured by the brief job stress questionnaire and salivary-specific ELISA kits; individual characteristics were measured by the Brief Stress Coping Profile scale and the assessment form; and stress long-term consequences were measured by the performance questionnaire, formal, digital factory input and output card and checklist (see Fig. 1 ).
The Descriptive Workers Assessment Form concerns sociodemographic characteristics (age, gender, education, birthplace, marital status, perception of economic condition, and classification of salary per month); health characteristics (perceptions about the participant’s health, quality of sleep, and any chronic disease(s) being medically controlled or treated); work characteristics (work hours, occupation, work schedule, and frequency and duration of work breaks and annual leave); and perceived job performance questions that were developed by the World Health Organization. Responses to the questions vary from 1 to 10 points, with 1 point representing the lowest job performance and 10 points representing the highest job performance [ 47 ].
The Brief Job Stress Questionnaire (BJSQ), a self-assessment form developed in Japan [ 48 ], consists of 57 items covering job stress (17 items such as “I have an extremely large amount of work to do”, “I can’t complete work in the required time”, “The atmosphere in my workplace is friendly”), physical (11 items such as “I have experienced stomach and/or intestine problems”, “I have experienced diarrhoea and/or constipation”, “I have had a stiff neck and/or shoulders”, “I have had lower back pain”) and psychological stress reactions (18 items such as “I have been inwardly annoyed or aggravated”, “I have felt tense”, “I have felt gloomy”), and social support (11 items) [ 49 ]. It has a 4-point Likert-type response option from “strongly disagree” =1 to “strongly disagree” =4. A higher subscale score indicates a high level of job stress, stress reactions, or social support [ 50 ]. The Turkish version of the BJSQ was used in this study, and the scale’s reliability and validity were measured before conducting the research. The reliability of the Turkish version of the BJSQ’s subscales was indicated by Cronbach’s alpha values of 0.66, 0.81, 0.82, and 0.81, respectively [ 51 ]. Additionally, the Cronbach’s alpha values of these subscales were found to be between 0.66 and 0.90 in this study. The BJSQ was used at the baseline and follow-up stages.
The Brief Stress Coping Profile (BSCP), comprising 18 related items on a 4-point Likert-type scale (often, sometimes, seldom, or never), is a self-rating scale for assessing workers’ coping profiles. The questionnaire was developed by Kageyama, Kobayashi, Kawashima, and Kanamaru (2004) [ 52 ] and features the following six subscales: active solution (items 1, 2, and 3; such as “I try to analyse the causes and solve the problem”), seeking help for the solution (items 4, 5, and 6; such as “I consult with someone I can trust”), changing mood (items 7, 8, and 9; such as “I try to do something that calms me down”), changing one’s point of view (items 10, 11, and 12; such as “I try to think this experience is good for me”), emotional expression involving others (items 13, 14, and 15; such as “I blame the person who is involved in the problem”), and avoidance and suppression (items 16, 17, and 18; such as “I do nothing but endure the situation”). Each of these subscales has 3 items and a score range of 3–12 points. A high subscale score indicates that the respondent frequently chooses that kind of coping method [ 53 ]. The Turkish version of the BSCP was used in this study, and the scale’s reliability and validity were measured before conducting the research. The reliability of the Turkish version of the BSCP were indicated by Cronbach’s alpha values of 0.69, 0.71, 0.66, 0.75, 0.78, and 0.77, respectively [ 54 ]. The BSCP was used at the baseline and follow-up stages.
Salivary-specific ELISA kits that are lucent and have a cover were used to evaluate cortisol and IgA levels in every participant’s saliva. When saliva is collected with the kit, it should be covered carefully and saved in a portable freeze at + 4°, and it has to be transferred to a laboratory with an International Accreditation. The analyses were conducted at baseline (at 08:45 am, February) and just after the IG intervention (at 10:15 am, February) in the morning. The eligibility criteria for collecting saliva-cortisol and saliva-IgA are as follows: there should not be any blood contamination from the mouth, there should not be any medication that affects cortisol used in the last week, and there should not be anything eaten 30 min before saliva collection.
The work absenteeism of all participants was checked through formal digital factory timecards and self-reported checklists. The absenteeism duration was calculated based on hours.
Workplace mental health promotion program intervention
The Work-ProMentH is a health-promotion programme based on the WRS model [ 6 ]. Before the Work-ProMentH intervention, the approval and follow-up procedures of the factories’ administration were explained to the IG and verified. The programme was applied once to the IG (35 women workers) at baseline in factory A at 9 am by the first researcher. A visual presentation and video training were provided, and a digital camera was used to video record workers while they were practising the programme, which consisted of stress management techniques, effective coping skills, and relaxation exercises. The programme also provided definitions for and explanations of stress and WRS, stress physiology, stress reactions, stress-related diseases, stress-related factors and effective coping and stress management skills, relaxation exercises, and deep breathing techniques. In the context of coping with stress, these exercises were taught, along with correct abdominal deep breathing skills, to the IG. During this interactive training, the WRS factors were defined and discussed interactively and in detail with the workers, who offered examples from their work experiences. During the training, the exercises were practised as a group and video recorded. The training lesson lasted 45 min and took place in a meeting room at the workplace. After the training, a brochure explaining the content and process of the programme and a video describing the exercises were given to the workers. The exercise times (10:00 a.m., 1:00 p.m., and 4:00 p.m.) were organized in cooperation with the workers, supervisors, and administrators while considering the employees’ work schedules. This was followed by direct observation, a weekly self-reported checklist, and recording via a factory-fixed camera for 12 weeks. The mobile phone application WhatsApp was used to send reminder messages and videos to the participants to reinforce the training during the follow-up stage. The effects of the programme were assessed in the first and third months in both groups, but S-IgA and S-cortisol levels were assessed only in the IG before and just after the intervention (see Fig. 2 ).
Statistical analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS version 22 for Windows (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Descriptive statistics of the demographic characteristics and health and work conditions of the workers are presented as numbers, percentages, and means ± standard deviations. A chi-square test and Mann-Whitney U test were applied for comparing the groups’ sociodemographic characteristics. An independent samples t test was performed to analyse the difference between the means of the groups, and a paired sample t test was conducted to analyse the difference between the pre-post mean scores of the variables. Repeated measures ANOVA was performed to detect the difference between related means of each group by time. The Bonferroni test was conducted to correct for multiple testing. Partial eta squared (η p 2 ) was then used for the overall effect. Using Cohen’s guidelines (1988), η p 2 = .01 was considered small, η p 2 = .06 was considered moderate, and η p 2 = .14 was considered a large effect [ 55 ]. Data were evaluated with a 95% confidence interval, and p < 0.05 was accepted as significant.
Primary outcomes
The sociodemographic characteristics, general health, working conditions, job stress, stress reactions, social support, job performance, work absenteeism, and coping profiles of the female workers were evaluated and compared before the Work-ProMentH was initiated. In addition, the IG’s S-IgA and S-cortisol levels were assessed prior to the programme’s start.
Demographic characteristics, general health, and work conditions
The mean age of the workers was 32.3 years (SD = 9.01, with a range of 19–54); more than 54% ( n = 38) had completed primary education, almost 46% of them were married, and over 62% of them had no children. Of all participants, 81.4% reported their health condition as “good,” and over 77% of those who reported their health condition as “good” were among the CG. All participants worked 5 days per week, 12 h per day, and took their breaks at the same time. None of them had permanent working contracts or were members of unions. Over 51% of them defined their economic condition as “good,” and almost 86% of those who defined their economic condition as “good” were among the IG. Over 88% of them worked for a minimum wage (800–1500 Turkish Lira = 510–748 U.S. dollars) in the factories. More than 57% of the IG and almost 63% of the CG began to work when they were younger than 18 years old. The mean working experience was 4.91 years (SD = 3.84) in the IG and 5.09 years (SD = 3.00) in the CG. A comparison of women workers in the IG and CG revealed no differences in sociodemographic characteristics, general health condition, work experience, or working conditions ( p > .05) (see Table 1 ).
Job stress, stress reactions, social support, job performance, work absenteeism, and coping profiles
The mean scores for job stress, physical symptoms (e.g., stomach, back, or arm pain), mental stress reactions (e.g., depression, irritability, annoyed mood), social support, job performance (hours/month), work absenteeism (hours/month), and coping profile in the IG and CG were compared. There were no differences between the IG and CG in terms of the scores for these variables ( p > .05) (see Table 2 ).
S-IgA and S-cortisol scores
S-IgA and S-cortisol levels were analysed in the IG. The mean S-IgA score was 110.32 ± 88.37, and the mean S-cortisol score was 83.67 ± 68.45 (see Table 2 ).
Secondary outcomes
Work-promenth intervention follow-up.
The IG received the Work-ProMentH with follow-up for a 3-month period. Female workers in the IG and CG were compared at baseline and in the first and third months with respect to the frequency of relaxation exercises, job stress, physical and mental reactions, S-IgA and S-cortisol levels, social support, coping profiles, job performance, and work absenteeism (see Table 1 ).
According to the findings at the follow-up, the mean scores in the IG for practising the relaxation exercises were 71.60 (SD = 33.39) in the first month and 129.45 (SD = 78.86) at the end of the third month. There was a significant increase in the mean scores for the groups’ performance of relaxation exercises ( p ≤ .001). During the first month, 62.9% ( n = 22) regularly implemented the programme compared with 51.4% ( n = 18) at the end of 3 months. At the end of the first month, the reasons for not implementing the intervention regularly were reported as follows: 75% “ had a heavy workload, ” 15.5% “felt sick,” 4.5% “were not able to concentrate,” and 5% “did not feel like doing it.” By the end of the third month, the reason “ did not feel like doing it ” increased to 17%, and “ felt sick ” decreased to 5%.
Intervention effects on job stress, stress reactions, social support, S-IgA and S-cortisol levels, job performance, and work absenteeism
According to the present findings from the Work-ProMentH follow-up, workers in the IG reported decreased job stress ( p ≤ .001; η p 2 = .77) and mental ( p = .001, η p 2 = .18) and physical ( p ≤ .001; η p 2 = .49) reactions. Scores on post-test follow-up 1 and 2 were significantly lower than the pre-test scores. There was also a significant increase in the IG workers’ perceived job performance ( p = .02; η p 2 = .12) and social support ( p ≤ .001; η p 2 = .62) and a significant decrease in their work absenteeism ( p = .029; η p 2 = .09). In terms of subjective job stress, IG post-test scores were significantly reduced compared with the pre-test scores; however, the CG post-test job-stress scores were slightly increased. A comparison of the IG and CG mean scores for all variables noted here before and after the Work-ProMentH follow-up revealed a significant difference in the third months’ results, except for those for mental reactions ( p = .487). A majority of effect sizes were very large (η p 2 > .14 was considered large).
The IG S-IgA enzyme and S-cortisol hormone levels were analysed before and after Work-ProMentH and showed statistically significant reductions ( p = .03 and p ≤ .001, respectively).
Intervention effects on coping profile
Overall, a significant effect of Work-ProMentH on coping profile was found. Table 3 shows a comparison of the coping profile mean values at the follow-up. There was a significant increase in the coping profile mean scores for active solution ( p = .014; η p 2 = .11), seeking help for the solution ( p = .032; η p 2 = .10), changing mood (p = .007; η p 2 = .13) and changing one’s point of view ( p = .004; η p 2 = .17); however, there were decreases in coping profile scores for emotional expression involving others ( p ≤ .001; η p 2 = .33) and avoidance and suppression ( p = .004; η p 2 = .21) at follow-up. According to these results, the profiles of the workers showed significant improvements at follow-up; however, a comparison of the IG and CG revealed that the programme did not demonstrate any statistically significant differences in active solution profiles.
The comprehensive evidence-based results of this pre-test and post-test-controlled study included a 12-week (3 months) follow up. Randomized sampling was used to select the study population, but the study was carried out in 2 textile factories since the intervention is considered to affect workers in the same factory. That may be a limitation of the study. The Work-ProMentH’s effects on the job stress, physical and psychological stress reactions, social support, S-cortisol and S-IgA levels, job performance, work absenteeism, and coping profile of female workers were assessed. In this process, the WRS model was used as a guide to evaluate the dynamic relations of these factors. The results of the present study show that the Work-ProMentH had meaningful effects on the job stress, physical and mental stress reactions, social support, S-cortisol levels, job performance, work absenteeism, and coping profiles of the IG participants. It was seen that the more the Work-ProMentH was practised, the greater its positive effects on the IG. However, when all these variables were compared between the IG and CG at follow-up, it was observed that the programme did not make any statistically significant differences in “mental reactions” and “active coping profiles.” An unexpected finding was that S-IgA levels were decreased after programme implementation.
We also considered worker attendance in the programme’s follow-up stage. It was found that the frequency of continuing the Work-ProMentH in the workplace decreased during the third month compared with that of the first month, although the performance rate was still high. The reasons for not fully participating (3 times per workday) in the programme were questioned. The most frequently self-reported reason was “heavy workload,” but the rate of the reason “feeling sick” decreased over time. This could be explained by the positive influence of the programme on coping profiles. Generally, the workers found it easy to complete the whole programme while they were at the workplace, except the first week. We think that positive reactions and feedback by the administrators/supervisors also played an important role in the results of the present study. Additionally, practising the programme at work was possible, which might also have been convenient. Even though it was the factories’ first experience with implementing a promotional programme at work, which was unusual for administrators, supervisors, and workers, the overall adoption of the programme was substantial. Beyond that, the first researcher’s work experience in this workplace afforded better communication and relationships between the researcher and the factories’ staff. This experience may have contributed to the success of the programme. However, this study was conducted between February and April when there is generally not a high workload at the factories; it might have been more difficult to obtain these results in summer.
The results of the present study indicate that the Work-ProMentH is an important programme in terms of protecting workers from job stress and physical stress reactions. In the study, the programme also increased the social support and general work performance of the IG. Therefore, the hypotheses ( Workers who participate in the Work-ProMentH intervention will have decreased job stress, less severe physical symptoms, increased social support, and better job performance ) have been accepted. Moreover, the results of the study by Atlantis et al. (2004) supported this hypothesis. It was revealed that the stress, mental health, and physical function levels of the workers who received the exercise and behaviour modification programme were significantly decreased compared with those of the waiting-list group [ 11 ]. However, compared to those in the present study, the participants in that study consisted of male and female workers, some of whom performed shift work, and they were followed up for a longer time. On the other hand, there was no information about working hours and work type in that study, which are mainly accepted as common risk factors for WRS. Additionally, an intervention programme that consisted of aerobic exercise was found to be effective in women workers from various industries who had similar working hours/week to the textile women workers in the present study [ 56 ]. Beyond that, a Tai Chi intervention programme was implemented twice a week for 12 weeks to men working at ambulatory clinics who are probably more advantaged than textile women workers. Additionally, compared to the present study, in that study, the age group was older (66–71 years), which may have affected the results, but the study revealed that Tai Chi exercise had a meaningful influence on social support and stress management [ 31 ]. As seen from the example, intervention programmes with exercise have generally been found to be effective for WRS, its causes and outcomes regardless of participant sociodemographic characteristics.
The present study found no statistically significant differences between the IG and CG mental reactions. The hypothesis ( Workers who participate in the Work-ProMentH intervention will have decreased mental stress reactions ) has therefore been rejected. Mental reactions are important symptoms of WRS, but it takes time to recover from them [ 57 ]. The present study results showed that the mental reaction score at the third follow-up (end of the third month) was lower than that at the first month, indicating that this programme had significant effects on the reactions of the IG but did not result in statistically significant differences between the groups. Longer follow-up times may be necessary to see changes in mental health. Compared to WRS-related physical reactions, internal mental health improvements take longer to recover. General work absenteeism and job performance are long-term consequences of WRS, according to the model used in this study. These two components vary depending on the level of job stress and its reactions [ 58 , 59 ]. In the present study, there were meaningful differences between the work absenteeism rate of the IG and that of the CG at both post-Work-ProMentH follow-ups. The IG’s average work absenteeism score decreased, while the CG’s average score increased. For example, just three workers from the CG left their jobs due to working conditions during the third month, which could be related to the job stress level in the present study. Therefore, the hypothesis about work absenteeism has been accepted.
Cortisol hormone and IgA are important biological reactions to stress, and their levels vary according to the level of stress. For example, S-cortisol levels increase in parallel to stress. Ongoing high cortisol levels have long-term negative effects on the body’s immune system [ 9 , 10 ]. This study indicated that the Work-ProMentH had a significant effect on reducing S-cortisol levels. Therefore, the hypothesis “ Workers who participate in the Work-ProMentH intervention will have lower S-cortisol levels ” was accepted. Furthermore, it is known that cortisol concentration is influenced by circadian rhythm [ 60 ]. In the present study, the wake-up time of the workers on the cortisol collection day was not taken into consideration. It is unlikely for cortisol levels to have been influenced by the wake-up time in the present study; however, it should be noted in future studies. However, in the present study, the mean post-intervention S-IgA score of the IG was found to be meaningfully higher than that at baseline, though it was expected to be lower. S-IgA levels usually increase under acute stress as a means of coping and decrease as the stressed individual becomes relaxed [ 61 , 62 ]; in the present study, S-IgA levels were decreased after the intervention. These decreases likely may have occurred because stress, stress reactions, and work-related causes were discussed with the workers during the intervention session. The workers may have felt stress when they were expressing themselves or because the programme and process were new for them, which could explain the increased S-IgA levels. However, further long-term research is needed. In contrast to this study, research by Pawlow and Jones (2005) and Taniguchi et al. (2007) showed increased IgA levels after short relaxation exercises were initiated among female workers and students [ 63 , 64 ]. On the other hand, no significant effects on IgA levels related to exercise were found in a study conducted by Berger and O’Brien (1998) [ 65 ].
Effective coping strategies and skills play an important role in stress, and it is crucial for female workers who are trying to balance work and family. The Work-ProMentH was found to be effective in improving “seeking help for a solution,” “changing mood,” “changing one’s point of view,” “emotional expression involving others,” “active solution seeking”, and “avoidance and suppression” coping profiles among the workers. The hypothesis therefore was accepted. Working conditions, national worker rights, self-confidence, culture, and other socio-economic conditions may have effects on these coping profiles.
Limitations
Randomized sampling was used to select the study population, but the study was carried out in 2 textile factories since the intervention is considered to affect workers in the same factory. Although there was no difference between the characteristics of the two factories, a “pre-test post-test design for non-equivalent control groups” design was chosen instead of an experimental design. Additionally, the effects of the intervention programme in this study were evaluated for only 3 months.
The effect of the WRS model-based Work-ProMentH on job performance, social support, job stress, stress reactions, and work absenteeism was assessed in this study using a randomized, controlled pre-test and post-test design in stressed women workers. It was found that women workers who participated in the Work-ProMentH experienced a decreased prevalence of job stress, physical and mental stress reactions, work absenteeism, and S-cortisol levels, increased levels of social support and job performance, and improved coping profiles.
The effects of the intervention programme in this study were evaluated for only 3 months. Therefore, we suggest that researchers apply for programmes that will enable them to collect follow-up data for a longer period. Additionally, the factories were privately held, and all workers had non-permanent contracts and no union. We think that these precarious working conditions may make them feel insecure and stressed. Additionally, work-family conflicts are an important dimension among women workers, particularly in antisocial-democratic society. Therefore, we also suggest that researchers take into consideration the effect of these precarious working conditions and work-family conflicts on women workers’ mental health in upcoming studies. As a result, there is a need for more empirical studies that may support the data of the present study, but it is thought that the intervention can be maintained for the long term. We recommend that occupational health professionals at workplaces consider using this model-based cost-effective intervention, which is easy and practical to apply in real-life situations.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Work-related stress
Salivary-Immunoglobulin A
Workplace Mental Health Promotion Program
The Brief Stress Coping Profile
The Brief Job Stress Questionnaire
WHO. Occpational Health, stress at work place [Internet]: Worl Health Organization; 2019. [cited 2020 Jul 6]. Available from: https://www.who.int/occupational_health/topics/stressatwp/en/ .
Kawakami N, Haratani T, Kobayashi F, Ishizaki M, Hayashi T, Fujita O, et al. Occupational class and exposure to job stressors among employed men and women in Japan. J Epidemiol. 2004;14(6):204–11.
Article Google Scholar
Karasek J, Robert A. Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: implications for job redesign. Adm Sci Q. 1979;24(2):285–308.
Demerouti E, Bakker AB, Nachreiner F, Schaufeli WB. The job demands-resources model of burnout. J Appl Psychol. 2001;86(3):499–512.
Siegrist J. Adverse health effects of high-effort/low-reward conditions. J Occup Health Psychol. 1996;1(1):27.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Houtman I, Jettinghoff K. Raising awareness of stress at work in developing countries. Prot Work Heal Ser. 2007;(6):1–51. Available from: https://www.who.int/occupational_health/publications/raisingawarenessofstress.pdf?ua =.
Väänänen A, Anttila E, Turtiainen J, Varje P. Formulation of work stress in 1960-2000: analysis of scientific works from the perspective of historical sociology. Soc Sci Med. 2012;75(5):784–94 Available from: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2012.04.014 .
Amati M, Tomasetti M, Ciuccarelli M, Mariotti L, Tarquini LM, Bracci M, et al. Relationship of job satisfaction, Psychological Distress and Stress-Related Biological Parameters among Healthy Nurses: a Longitudinal Study. J Occup Health 2010;52:31–8.
Marchand A, Juster R-P, Durand P, Lupien SJ. Work stress models and diurnal cortisol variations: the SALVEO study. J Occup Health Psychol. 2016;21(2):182–93.
Steinisch M, Yusuf R, Li J, Stalder T, Bosch JA, Rahman O, et al. Work stress and hair cortisol levels among workers in a Bangladeshi ready-made garment factory — results from a cross-sectional study. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2014;50:20–7.
Atlantis E, Chow C-M, Kirby A, Singh MF. An effective exercise-based intervention for improving mental health and quality of life measures: a randomized controlled trial. Prev Med (Baltim). 2004;39(2):424–34.
Mayerl H, Stolz E, Waxenegger A, Rásky É, Freidl W. The role of personal and job resources in the relationship between psychosocial job demands, mental strain, and health problems. Front Psychol. 2016;7:1214.
Andrew ME, Violanti JM, Gu JK, Fekedulegn D, Li S, Hartley TA, et al. Police work stressors and cardiac vagal control. Am J Hum Biol. 2017;29(5):1–10.
Svensson T, Kitlinski M, Engström G, Melander O. Psychological stress and risk of incident atrial fibrillation in men and women with known atrial fibrillation genetic risk scores. Nat Publ Gr. 2017;14(7):42613.
Google Scholar
Becker A, Angerer P, Müller A. The prevention of musculoskeletal complaints: a randomized controlled trial on additional effects of a work-related psychosocial coaching intervention compared to physiotherapy alone. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2017;90(4):357–71.
Eskilsson T, Järvholm LS, Gavelin HM, Neely AS, Boraxbekk C-J. Aerobic training for improved memory in patients with stress-related exhaustion : a randomized controlled trial. BMC Psychiatry. 2017;17(322):1–10.
Bhui KS, Dinos S, Stansfeld SA, White PD. A Synthesis of the Evidence for Managing Stress at Work : A Review of the Reviews Reporting on Anxiety , Depression , and Absenteeism. J Environ Public Health. 2012;2012(515874):1–21.
Dalgaard VL, Aschbacher, Andersen JH, Glasscock DJ, Willert MV, Carstensen O, et al. Intervention work-focused cognitive behavioral intervention. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2017;43(5):436–46.
Holmgren K, Sandheimer C, Mårdby A, Larsson MEH, Bültmann U, Hange D, et al. Early identification in primary health care of people at risk for sick leave due to work- related stress – study protocol of a randomized controlled trial ( RCT ). BMC Public Health. 2016;16(1193):1–8.
Wada K, Sairenchi T, Haruyama Y, Taneichi H, Ishikawa Y, Muto T. Relationship between the Onset of Depression and Stress Response Measured by the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire among Japanese Employees: A Cohort Study. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56319 Lam WWT, editor.
Milzzarek M, Schneider E, Gonzalez ER. OSH in figures: stress at work — facts and figures. Luxemborg; 2009. p. 1–143. https://osha.europa.eu/en/publications/osh-figures-stress-work-facts-and-figures .
Llosa JA, Menéndez-espina S, Agulló-tomás E, Rodríguez-suárez J. Job insecurity and mental health : a meta-analytical review of the consequences of precarious work in clinical disorders. An Psicol. 2018;34(2):211–23.
Rönnblad T, Grönholm E, Jonsson J, Koranyi I, Orellana C, Kreschpaj B, et al. Precarious employment and mental health: a systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2019;45(5):429–43.
Saijo Y, Yoshioka E, Nakagi Y, Kawanishi Y, Hanley SJB, Yoshida T. Social support and its interrelationships with demand–control model factors on presenteeism and absenteeism in Japanese civil servants. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2017;90(6):539–53.
Yada H, Abe H, Omori H, Matsuo H, Masaki O. Differences in job stress experienced by female and male Japanese psychiatric nurses. Int J Ment Health Nurs. 2014;23(5):468–76.
Czabala C, Charzynska K, Mroziak B. Psychosocial interventions in workplace mental health promotion : an overview. Health Promot Int. 2011;26:70–84.
Cohidon C, Morisseau P, Derriennic F, Goldberg M, Imbernon E. Psychosocial factors at work and perceived health among agricultural meat industry workers in France. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2009;82(7):807–18.
Sein MM, Howteerakul N, Suwannaapong N, Jirachewee J. Job strain among rubber-glove-factory Workers in Central Thailand. Ind Health. 2010;48:503–10.
Böckerman P, Bryson A, Ilmakunnas P. Does high involvement management improve worker wellbeing ? J Econ Behav Organ. 2012;84(2):660–80.
Pow J, King DB, Stephenson E, DeLongis A. Does social support buffer the effects of occupational stress on sleep quality among paramedics? A daily diary study. J Occup Health Psychol. 2017;22(1):71–85.
Yeh GY, Chan CW, Wayne PM, Conboy L. The Impact of Tai Chi Exercise on Self- Efficacy , Social Support , and Empowerment in Heart Failure : Insights from a Qualitative Sub-Study from a Randomized Controlled Trial. PLoS One. 2016;11(5):1–15.
Savic I, Perski A, Osika W. MRI shows that exhaustion syndrome due to chronic occupational stress is associated with partially reversible cerebral changes. Cereb Cortex. 2017;28(3):894–906.
Peristera P, Westerlund H, Magnusson Hanson LL. Paid and unpaid working hours among Swedish men and women in relation to depressive symptom trajectories: results from four waves of the Swedish longitudinal occupational survey of health. BMJ Open. 2018;8(e017525):1–10.
ILO. World Employment And Social Outlook Trends 2020 [Internet]. International Labour Organization. Geneva: International Labour Office; 2020. Available from: https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/%2D%2D-dgreports/%2D%2D-dcomm/%2D%2D-publ/documents/publication/wcms_734455.pdf .
ILO. Global wage report 2018/19: What lies behind gender pay gaps [Internet]. 2018. Available from: https://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/%2D%2D-dgreports/%2D%2D-dcomm/%2D%2D-publ/documents/publication/wcms_650553.pdf .
Eurofound. Pay transparency in Europe: First experiences with gender pay reports and audits in four Member States [Internet]. Luxembourg; 2018. Available from: https://www.eurofound.europa.eu/sites/default/files/ef_publication/field_ef_document/ef18004en.pdf .
Bilsker D, Gilbert M, Myette TL, Stewart-Patterson C. Depression & Work Function; 2005.
Starmer AJ, Frintner MP, Matos K, Somberg C, Freed G, Byrne BJ. Gender discrepancies related to pediatrician work-life balance and household responsibilities. Pediatrics. 2019;144(4):e20182926.
Kivimäki M, Kawachi I. Work Stress as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2015;17(9):74.
Gervais R, Schneider E. New risks and trends in the safety and health of women at work. Luxembourg: European Risk Observatory A Summary of an Agency Report; 2013.
Martin A, Sanderson K, Cocker F. Meta-analysis of the effects of health promotion intervention in the workplace on depression and anxiety symptoms workplace on depression and anxiety symptoms. Scand J Work Environ Health. 2009;35(1):7–18.
Van Der Klink JJL, Blonk RWB, Schene AH, Van Dijk FJH. The benefits of interventions for work-related stress. Am J Public Health. 2001;91(2):270–6.
ILO. Women at Work: Trends 2016 [Internet], vol. 42. Geneva: International Labour Organization; 2016. Available from: http://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/%2D%2D-dgreports/%2D%2D-dcomm/%2D%2D-publ/documents/publication/wcms_457317.pdf%5Cn . http://www.ilo.org/wcmsp5/groups/public/%2D%2D-dgreports/%2D%2D-dcomm/%2D%2D-publ/documents/publication/wcms_457086.pdf .
ILO. Wages and Working Hours in the Textiles, Clothing, Leather and Footwear Industries [Internet]; 2014. p. 35. Available from: http://ilo.org/sector/activities/sectoral-meetings/WCMS_241471/lang%2D%2Den/index.htm .
Fair Wear Foundation-Turkey. FWF GENDER FACT SHEET - TURKEY FWF GENDER FACT SHEET - TURKEY [Internet]. 2019. Available from: https://api.fairwear.org/wp-content/uploads/2019/02/11.-Turkey-Gender-Fact-Sheet.pdf .
Moher D, Hopewell S, Schulz KF, Montori V, Gøtzsche PC, Devereaux PJ, et al. Original article consort 2010 explanation and elaboration : updated guidelines for reporting parallel group randomised trials. J Clin Epidemiol. 2010;63(8):e1–37.
Kessler R, Barber C, Beck A, Berglund P, Cleary P, McKenas D, et al. The World Health Organization health and work performance questionnaire (HPQ). J Occup Environ Med. 2003;45(2):156–74.
Shimomitsu T, Haratani T, Nakamura K, Kawakami N, Hayashi T, Hiro H, et al. The final development of the Brief Job Stress Questionnaire mainly used for assessment of the individuals. Ministry for Labour sponsored grant for the prevention of work-related illness: The 1999 report. Tokyo; 2000. p. 126–164.
Inoue A, Kawakami N, Shimomitsu T, Tsutsumi T, Haratani T, Yoshikawa T, et al. Development of a short questionnaire to measure an extended set of job demands, job resources, and positive health outcomes: the new brief job stress questionnaire. Ind Health. 2004;52(3):175–89.
Sato Y, Miyake H, Theriault G. Overtime work and stress response in a group of Japanese workers. Occup Med (Chic Ill). 2009;59(1):14–9.
Ornek OK, Sevim E. Work-related stress and coping profiles among Workers in Outer Garment Sector. COJ Nurs Healthc. 2018;3:1–7.
Kageyama T, Kobayashi T, Kawashima M, Kanamaru Y. Development of the Brief Scales for Coping Profile (BSCP) for workers: basic information about its reliability and validity. Sangyo Eiseigaku Zasshi. 2004;46(4):103–14.
Tomotsune Y, Sasahara S, Umeda T, Hayashi M, Usami K, Yoshino S, et al. The association of sense of coherence and coping profile with stress among research park city workers in Japan. Ind Health. 2009;47(6):664–72.
Ornek OK, Temel GY. Reliability and validity of the Turkish version of the brief scales for coping profile in textile workers. Nővér. 2018;31(2):1–8.
Cohen J. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral sciences. 2nd ed. Hillsdale: Erlbaum; 1988.
Eklöf M, Hagberg M. Are simple feedback interventions involving workplace data associated with better working environment and health? A cluster randomized controlled study among Swedish VDU workers. Appl Ergon. 2006;37(2):201–10.
McConachie DAJ, McKenzie K, Morris PG, Walley RM. Acceptance and mindfulness-based stress management for support staff caring for individuals with intellectual disabilities. Res Dev Disabil. 2014;35(6):1216–27.
Lerner D, Adler DA, Rogers WH, Chang H, Greenhill A, Cymerman E, et al. HHS public access. Psychiatr Serv. 2015;66(6):570–7.
Navidian A, Rostami Z, Rozbehani N. Effect of motivational group interviewing- based safety education on workers ’ safety behaviors in glass manufacturing. BMC Public Health. 2015;15(929):1–7.
Persson R, Garde AH, Hansen ÅM, Österberg K, Ørbæk P, Karlson B, et al. Seasonal variation in human salivary cortisol concentration. Chronobiol Int J Biol Med Rhythm Res. 2009;25(6):923–37.
Carroll D, Ring C, Winzer A. Stress and mucosal immunity. In: Fink G, editor. Encyclopedia of Stress, vol. 2. San Diego: Academic; 2000. p. 781–6.
Valdimarsdottir H, Stone A. Psychosocial factors and secretory immunoglobulin a. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med. 1997;8(4):461–74.
Pawlow LA, Jones GE. The impact of abbreviated progressive muscle relaxation on salivary cortisol and salivary immunoglobulin a (sIgA). Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback. 2005;30(4):375–87.
Taniguchi T, Hirokawa K, Tsuchiya M, Kawakami N. The immediate Eff ects of 10-minute relaxation training on salivary immunoglobulin a (s-IgA) and mood state for Japanese female medical co-workers. Acta Med Okayama. 2007;61(3):139–45.
Berger JA, O’Brien WH. Effect of a cognitive-behavioral stress management intervention on salivary IgA, self-reported levels of stress, and physical health complaints in an undergraduate population. Int J Rehabil Health. 1998;4(3):129–52.
Download references
Acknowledgments
The abstract of this study was an oral presentation under the title “ Effect of Mental Health Workplace Health Promotion Program on Work-related Stress and Coping Skills of Working Women ” at the 4th edition of International Conference on Occupational Health and Safety, May 28-29, 2018 London/The UK. We express our gratitude to the workers who participated in this study and who supported the research at the workplace.
Salivary-specific ELISA Kits, and analysis of the S-Cortisol and S-IgA in the laboratory of this study was funded by the Scientific Research Fund of Istanbul University (Project No: 50902). The funding source had no role in the design of the study and collection, and interpretation of data and in writing the manuscript. Open Access funding enabled and organized by Projekt DEAL.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Occupational and Environmental Epidemiology & NetTeaching Unit, Institute and Clinic for Occupational, Social and Environmental Medicine, University Hospital, LMU, Ziemssenstr. 1, 80336, Munich, Germany
Ozlem Koseoglu Ornek
Department of Nursing, Faculty of Health Sciences, Istanbul Bilgi University, Dolapdere Kampus, Hacıahmet Mahallesi, Pir Hüsamettin Sokak No: 20, 34440, Beyoğlu/ Istanbul, Turkey
Department of Public Health Nursing, İstanbul University-Cerrahpasa Florence Nightingale Faculty of Nursing, İstanbul Üniversitesi Florence Nightingale Hemşirelik Fakültesi, Abide-i Hürriyet Caddesi, Şişli/İstanbul, Turkey
Melek Nihal Esin
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The responsibilities and roles of the authors are as follows: OKO examines, contrives and defines the study method and strategy; collected the data; conducts the intervention program; follow-up the workers; statistical analysis, and interpretation of data; writes of the manuscript. MNE supervises the methods, statistical analysis, and interpretation of data of the study and reviews and approves its content. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ozlem Koseoglu Ornek .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
The study was approved by the Istanbul Medipol University Research Ethics Committee (approval no. 10840098–299), and oral and written permissions were obtained from the workers and factory administrations.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ornek, O.K., Esin, M.N. Effects of a work-related stress model based mental health promotion program on job stress, stress reactions and coping profiles of women workers: a control groups study. BMC Public Health 20 , 1658 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09769-0
Download citation
Received : 31 December 2019
Accepted : 26 October 2020
Published : 04 November 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-020-09769-0
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Occupational stress
- Work related stress model
- Women workers
- Coping profiles
- Immunoglobulin A
BMC Public Health
ISSN: 1471-2458
- General enquiries: [email protected]
- Tools and Resources
- Customer Services
- Affective Science
- Biological Foundations of Psychology
- Clinical Psychology: Disorders and Therapies
- Cognitive Psychology/Neuroscience
- Developmental Psychology
- Educational/School Psychology
- Forensic Psychology
- Health Psychology
- History and Systems of Psychology
- Individual Differences
- Methods and Approaches in Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational and Institutional Psychology
- Personality
- Psychology and Other Disciplines
- Social Psychology
- Sports Psychology
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Article contents
Work, stress, coping, and stress management.
- Sharon Glazer Sharon Glazer University of Baltimore
- and Cong Liu Cong Liu Hofstra University
- https://doi.org/10.1093/acrefore/9780190236557.013.30
- Published online: 26 April 2017
Work stress refers to the process of job stressors, or stimuli in the workplace, leading to strains, or negative responses or reactions. Organizational development refers to a process in which problems or opportunities in the work environment are identified, plans are made to remediate or capitalize on the stimuli, action is taken, and subsequently the results of the plans and actions are evaluated. When organizational development strategies are used to assess work stress in the workplace, the actions employed are various stress management interventions. Two key factors tying work stress and organizational development are the role of the person and the role of the environment. In order to cope with work-related stressors and manage strains, organizations must be able to identify and differentiate between factors in the environment that are potential sources of stressors and how individuals perceive those factors. Primary stress management interventions focus on preventing stressors from even presenting, such as by clearly articulating workers’ roles and providing necessary resources for employees to perform their job. Secondary stress management interventions focus on a person’s appraisal of job stressors as a threat or challenge, and the person’s ability to cope with the stressors (presuming sufficient internal resources, such as a sense of meaningfulness in life, or external resources, such as social support from a supervisor). When coping is not successful, strains may develop. Tertiary stress management interventions attempt to remediate strains, by addressing the consequence itself (e.g., diabetes management) and/or the source of the strain (e.g., reducing workload). The person and/or the organization may be the targets of the intervention. The ultimate goal of stress management interventions is to minimize problems in the work environment, intensify aspects of the work environment that create a sense of a quality work context, enable people to cope with stressors that might arise, and provide tools for employees and organizations to manage strains that might develop despite all best efforts to create a healthy workplace.
- stress management
- organization development
- organizational interventions
- stress theories and frameworks
Introduction
Work stress is a generic term that refers to work-related stimuli (aka job stressors) that may lead to physical, behavioral, or psychological consequences (i.e., strains) that affect both the health and well-being of the employee and the organization. Not all stressors lead to strains, but all strains are a result of stressors, actual or perceived. Common terms often used interchangeably with work stress are occupational stress, job stress, and work-related stress. Terms used interchangeably with job stressors include work stressors, and as the specificity of the type of stressor might include psychosocial stressor (referring to the psychological experience of work demands that have a social component, e.g., conflict between two people; Hauke, Flintrop, Brun, & Rugulies, 2011 ), hindrance stressor (i.e., a stressor that prevents goal attainment; Cavanaugh, Boswell, Roehling, & Boudreau, 2000 ), and challenge stressor (i.e., a stressor that is difficult, but attainable and possibly rewarding to attain; Cavanaugh et al., 2000 ).
Stress in the workplace continues to be a highly pervasive problem, having both direct negative effects on individuals experiencing it and companies paying for it, and indirect costs vis à vis lost productivity (Dopkeen & DuBois, 2014 ). For example, U.K. public civil servants’ work-related stress rose from 10.8% in 2006 to 22.4% in 2013 and about one-third of the workforce has taken more than 20 days of leave due to stress-related ill-health, while well over 50% are present at work when ill (French, 2015 ). These findings are consistent with a report by the International Labor Organization (ILO, 2012 ), whereby 50% to 60% of all workdays are lost due to absence attributed to factors associated with work stress.
The prevalence of work-related stress is not diminishing despite improvements in technology and employment rates. The sources of stress, such as workload, seem to exacerbate with improvements in technology (Coovert & Thompson, 2003 ). Moreover, accessibility through mobile technology and virtual computer terminals is linking people to their work more than ever before (ILO, 2012 ; Tarafdar, Tu, Ragu-Nathan, & Ragu-Nathan, 2007 ). Evidence of this kind of mobility and flexibility is further reinforced in a June 2007 survey of 4,025 email users (over 13 years of age); AOL reported that four in ten survey respondents reported planning their vacations around email accessibility and 83% checked their emails at least once a day while away (McMahon, 2007 ). Ironically, despite these mounting work-related stressors and clear financial and performance outcomes, some individuals are reporting they are less “stressed,” but only because “stress has become the new normal” (Jayson, 2012 , para. 4).
This new normal is likely the source of psychological and physiological illness. Siegrist ( 2010 ) contends that conditions in the workplace, particularly psychosocial stressors that are perceived as unfavorable relationships with others and self, and an increasingly sedentary lifestyle (reinforced with desk jobs) are increasingly contributing to cardiovascular disease. These factors together justify a need to continue on the path of helping individuals recognize and cope with deleterious stressors in the work environment and, equally important, to find ways to help organizations prevent harmful stressors over which they have control, as well as implement policies or mechanisms to help employees deal with these stressors and subsequent strains. Along with a greater focus on mitigating environmental constraints are interventions that can be used to prevent anxiety, poor attitudes toward the workplace conditions and arrangements, and subsequent cardiovascular illness, absenteeism, and poor job performance (Siegrist, 2010 ).
Even the ILO has presented guidance on how the workplace can help prevent harmful job stressors (aka hindrance stressors) or at least help workers cope with them. Consistent with the view that well-being is not the absence of stressors or strains and with the view that positive psychology offers a lens for proactively preventing stressors, the ILO promotes increasing preventative risk assessments, interventions to prevent and control stressors, transparent organizational communication, worker involvement in decision-making, networks and mechanisms for workplace social support, awareness of how working and living conditions interact, safety, health, and well-being in the organization (ILO, n.d. ). The field of industrial and organizational (IO) psychology supports the ILO’s recommendations.
IO psychology views work stress as the process of a person’s interaction with multiple aspects of the work environment, job design, and work conditions in the organization. Interventions to manage work stress, therefore, focus on the psychosocial factors of the person and his or her relationships with others and the socio-technical factors related to the work environment and work processes. Viewing work stress from the lens of the person and the environment stems from Kurt Lewin’s ( 1936 ) work that stipulates a person’s state of mental health and behaviors are a function of the person within a specific environment or situation. Aspects of the work environment that affect individuals’ mental states and behaviors include organizational hierarchy, organizational climate (including processes, policies, practices, and reward structures), resources to support a person’s ability to fulfill job duties, and management structure (including leadership). Job design refers to each contributor’s tasks and responsibilities for fulfilling goals associated with the work role. Finally, working conditions refers not only to the physical environment, but also the interpersonal relationships with other contributors.
Each of the conditions that are identified in the work environment may be perceived as potentially harmful or a threat to the person or as an opportunity. When a stressor is perceived as a threat to attaining desired goals or outcomes, the stressor may be labeled as a hindrance stressor (e.g., LePine, Podsakoff, & Lepine, 2005 ). When the stressor is perceived as an opportunity to attain a desired goal or end state, it may be labeled as a challenge stressor. According to LePine and colleagues’ ( 2005 ), both challenge (e.g., time urgency, workload) and hindrance (e.g., hassles, role ambiguity, role conflict) stressors could lead to strains (as measured by “anxiety, depersonalization, depression, emotional exhaustion, frustration, health complaints, hostility, illness, physical symptoms, and tension” [p. 767]). However, challenge stressors positively relate with motivation and performance, whereas hindrance stressors negatively relate with motivation and performance. Moreover, motivation and strains partially mediate the relationship between hindrance and challenge stressors with performance.
Figure 1. Organizational development frameworks to guide identification of work stress and interventions.
In order to (1) minimize any potential negative effects from stressors, (2) increase coping skills to deal with stressors, or (3) manage strains, organizational practitioners or consultants will devise organizational interventions geared toward prevention, coping, and/or stress management. Ultimately, toxic factors in the work environment can have deleterious effects on a person’s physical and psychological well-being, as well as on an organization’s total health. It behooves management to take stock of the organization’s health, which includes the health and well-being of its employees, if the organization wishes to thrive and be profitable. According to Page and Vella-Brodrick’s ( 2009 ) model of employee well-being, employee well-being results from subjective well-being (i.e., life satisfaction and general positive or negative affect), workplace well-being (composed of job satisfaction and work-specific positive or negative affect), and psychological well-being (e.g., self-acceptance, positive social relations, mastery, purpose in life). Job stressors that become unbearable are likely to negatively affect workplace well-being and thus overall employee well-being. Because work stress is a major organizational pain point and organizations often employ organizational consultants to help identify and remediate pain points, the focus here is on organizational development (OD) frameworks; several work stress frameworks are presented that together signal areas where organizations might focus efforts for change in employee behaviors, attitudes, and performance, as well as the organization’s performance and climate. Work stress, interventions, and several OD and stress frameworks are depicted in Figure 1 .
The goals are: (1) to conceptually define and clarify terms associated with stress and stress management, particularly focusing on organizational factors that contribute to stress and stress management, and (2) to present research that informs current knowledge and practices on workplace stress management strategies. Stressors and strains will be defined, leading OD and work stress frameworks that are used to organize and help organizations make sense of the work environment and the organization’s responsibility in stress management will be explored, and stress management will be explained as an overarching thematic label; an area of study and practice that focuses on prevention (primary) interventions, coping (secondary) interventions, and managing strains (tertiary) interventions; as well as the label typically used to denote tertiary interventions. Suggestions for future research and implications toward becoming a healthy organization are presented.
Defining Stressors and Strains
Work-related stressors or job stressors can lead to different kinds of strains individuals and organizations might experience. Various types of stress management interventions, guided by OD and work stress frameworks, may be employed to prevent or cope with job stressors and manage strains that develop(ed).
A job stressor is a stimulus external to an employee and a result of an employee’s work conditions. Example job stressors include organizational constraints, workplace mistreatments (such as abusive supervision, workplace ostracism, incivility, bullying), role stressors, workload, work-family conflicts, errors or mistakes, examinations and evaluations, and lack of structure (Jex & Beehr, 1991 ; Liu, Spector, & Shi, 2007 ; Narayanan, Menon, & Spector, 1999 ). Although stressors may be categorized as hindrances and challenges, there is not yet sufficient information to be able to propose which stress management interventions would better serve to reduce those hindrance stressors or to reduce strain-producing challenge stressors while reinforcing engagement-producing challenge stressors.
Organizational Constraints
Organizational constraints may be hindrance stressors as they prevent employees from translating their motivation and ability into high-level job performance (Peters & O’Connor, 1980 ). Peters and O’Connor ( 1988 ) defined 11 categories of organizational constraints: (1) job-related information, (2) budgetary support, (3) required support, (4) materials and supplies, (5) required services and help from others, (6) task preparation, (7) time availability, (8) the work environment, (9) scheduling of activities, (10) transportation, and (11) job-relevant authority. The inhibiting effect of organizational constraints may be due to the lack of, inadequacy of, or poor quality of these categories.
Workplace Mistreatment
Workplace mistreatment presents a cluster of interpersonal variables, such as interpersonal conflict, bullying, incivility, and workplace ostracism (Hershcovis, 2011 ; Tepper & Henle, 2011 ). Typical workplace mistreatment behaviors include gossiping, rude comments, showing favoritism, yelling, lying, and ignoring other people at work (Tepper & Henle, 2011 ). These variables relate to employees’ psychological well-being, physical well-being, work attitudes (e.g., job satisfaction and organizational commitment), and turnover intention (e.g., Hershcovis, 2011 ; Spector & Jex, 1998 ). Some researchers differentiated the source of mistreatment, such as mistreatment from one’s supervisor versus mistreatment from one’s coworker (e.g., Bruk-Lee & Spector, 2006 ; Frone, 2000 ; Liu, Liu, Spector, & Shi, 2011 ).
Role Stressors
Role stressors are demands, constraints, or opportunities a person perceives to be associated, and thus expected, with his or her work role(s) across various situations. Three commonly studied role stressors are role ambiguity, role conflict, and role overload (Glazer & Beehr, 2005 ; Kahn, Wolfe, Quinn, Snoek, & Rosenthal, 1964 ). Role ambiguity in the workplace occurs when an employee lacks clarity regarding what performance-related behaviors are expected of him or her. Role conflict refers to situations wherein an employee receives incompatible role requests from the same or different supervisors or the employee is asked to engage in work that impedes his or her performance in other work or nonwork roles or clashes with his or her values. Role overload refers to excessive demands and insufficient time (quantitative) or knowledge (qualitative) to complete the work. The construct is often used interchangeably with workload, though role overload focuses more on perceived expectations from others about one’s workload. These role stressors significantly relate to low job satisfaction, low organizational commitment, low job performance, high tension or anxiety, and high turnover intention (Abramis, 1994 ; Glazer & Beehr, 2005 ; Jackson & Schuler, 1985 ).
Excessive workload is one of the most salient stressors at work (e.g., Liu et al., 2007 ). There are two types of workload: quantitative and qualitative workload (LaRocco, Tetrick, & Meder, 1989 ; Parasuraman & Purohit, 2000 ). Quantitative workload refers to the excessive amount of work one has. In a summary of a Chartered Institute of Personnel & Development Report from 2006 , Dewe and Kompier ( 2008 ) noted that quantitative workload was one of the top three stressors workers experienced at work. Qualitative workload refers to the difficulty of work. Workload also differs by the type of the load. There are mental workload and physical workload (Dwyer & Ganster, 1991 ). Excessive physical workload may result in physical discomfort or illness. Excessive mental workload will cause psychological distress such as anxiety or frustration (Bowling & Kirkendall, 2012 ). Another factor affecting quantitative workload is interruptions (during the workday). Lin, Kain, and Fritz ( 2013 ) found that interruptions delay completion of job tasks, thus adding to the perception of workload.
Work-Family Conflict
Work-family conflict is a form of inter-role conflict in which demands from one’s work domain and one’s family domain are incompatible to some extent (Greenhaus & Beutell, 1985 ). Work can interfere with family (WIF) and/or family can interfere with work (FIW) due to time-related commitments to participating in one domain or another, incompatible behavioral expectations, or when strains in one domain carry over to the other (Greenhaus & Beutell, 1985 ). Work-family conflict significantly relates to work-related outcomes (e.g., job satisfaction, organizational commitment, turnover intention, burnout, absenteeism, job performance, job strains, career satisfaction, and organizational citizenship behaviors), family-related outcomes (e.g., marital satisfaction, family satisfaction, family-related performance, family-related strains), and domain-unspecific outcomes (e.g., life satisfaction, psychological strain, somatic or physical symptoms, depression, substance use or abuse, and anxiety; Amstad, Meier, Fasel, Elfering, & Semmer, 2011 ).
Individuals and organizations can experience work-related strains. Sometimes organizations will experience strains through the employee’s negative attitudes or strains, such as that a worker’s absence might yield lower production rates, which would roll up into an organizational metric of organizational performance. In the industrial and organizational (IO) psychology literature, organizational strains are mostly observed as macro-level indicators, such as health insurance costs, accident-free days, and pervasive problems with company morale. In contrast, individual strains, usually referred to as job strains, are internal to an employee. They are responses to work conditions and relate to health and well-being of employees. In other words, “job strains are adverse reactions employees have to job stressors” (Spector, Chen, & O’Connell, 2000 , p. 211). Job strains tend to fall into three categories: behavioral, physical, and psychological (Jex & Beehr, 1991 ).
Behavioral strains consist of actions that employees take in response to job stressors. Examples of behavioral strains include employees drinking alcohol in the workplace or intentionally calling in sick when they are not ill (Spector et al., 2000 ). Physical strains consist of health symptoms that are physiological in nature that employees contract in response to job stressors. Headaches and ulcers are examples of physical strains. Lastly, psychological strains are emotional reactions and attitudes that employees have in response to job stressors. Examples of psychological strains are job dissatisfaction, anxiety, and frustration (Spector et al., 2000 ). Interestingly, research studies that utilize self-report measures find that most job strains experienced by employees tend to be psychological strains (Spector et al., 2000 ).
Leading Frameworks
Organizations that are keen on identifying organizational pain points and remedying them through organizational campaigns or initiatives often discover the pain points are rooted in work-related stressors and strains and the initiatives have to focus on reducing workers’ stress and increasing a company’s profitability. Through organizational climate surveys, for example, companies discover that aspects of the organization’s environment, including its policies, practices, reward structures, procedures, and processes, as well as employees at all levels of the company, are contributing to the individual and organizational stress. Recent studies have even begun to examine team climates for eustress and distress assessed in terms of team members’ homogenous psychological experience of vigor, efficacy, dedication, and cynicism (e.g., Kożusznik, Rodriguez, & Peiro, 2015 ).
Each of the frameworks presented advances different aspects that need to be identified in order to understand the source and potential remedy for stressors and strains. In some models, the focus is on resources, in others on the interaction of the person and environment, and in still others on the role of the person in the workplace. Few frameworks directly examine the role of the organization, but the organization could use these frameworks to plan interventions that would minimize stressors, cope with existing stressors, and prevent and/or manage strains. One of the leading frameworks in work stress research that is used to guide organizational interventions is the person and environment (P-E) fit (French & Caplan, 1972 ). Its precursor is the University of Michigan Institute for Social Research’s (ISR) role stress model (Kahn, Wolfe, Quinn, Snoek, & Rosenthal, 1964 ) and Lewin’s Field Theory. Several other theories have since evolved from the P-E fit framework, including Karasek and Theorell’s ( 1990 ), Karasek ( 1979 ) Job Demands-Control Model (JD-C), the transactional framework (Lazarus & Folkman, 1984 ), Conservation of Resources (COR) theory (Hobfoll, 1989 ), and Siegrist’s ( 1996 ) Effort-Reward Imbalance (ERI) Model.
Field Theory
The premise of Kahn et al.’s ( 1964 ) role stress theory is Lewin’s ( 1997 ) Field Theory. Lewin purported that behavior and mental events are a dynamic function of the whole person, including a person’s beliefs, values, abilities, needs, thoughts, and feelings, within a given situation (field or environment), as well as the way a person represents his or her understanding of the field and behaves in that space. Lewin explains that work-related strains are a result of individuals’ subjective perceptions of objective factors, such as work roles, relationships with others in the workplace, as well as personality indicators, and can be used to predict people’s reactions, including illness. Thus, to make changes to an organizational system, it is necessary to understand a field and try to move that field from the current state to the desired state. Making this move necessitates identifying mechanisms influencing individuals.
Role Stress Theory
Role stress theory mostly isolates the perspective a person has about his or her work-related responsibilities and expectations to determine how those perceptions relate with a person’s work-related strains. However, those relationships have been met with somewhat varied results, which Glazer and Beehr ( 2005 ) concluded might be a function of differences in culture, an environmental factor often neglected in research. Kahn et al.’s ( 1964 ) role stress theory, coupled with Lewin’s ( 1936 ) Field Theory, serves as the foundation for the P-E fit theory. Lewin ( 1936 ) wrote, “Every psychological event depends upon the state of the person and at the same time on the environment” (p. 12). Researchers of IO psychology have narrowed the environment to the organization or work team. This narrowed view of the organizational environment is evident in French and Caplan’s ( 1972 ) P-E fit framework.
Person-Environment Fit Theory
The P-E fit framework focuses on the extent to which there is congruence between the person and a given environment, such as the organization (Caplan, 1987 ; Edwards, 2008 ). For example, does the person have the necessary skills and abilities to fulfill an organization’s demands, or does the environment support a person’s desire for autonomy (i.e., do the values align?) or fulfill a person’s needs (i.e., a person’s needs are rewarded). Theoretically and empirically, the greater the person-organization fit, the greater a person’s job satisfaction and organizational commitment, the less a person’s turnover intention and work-related stress (see meta-analyses by Assouline & Meir, 1987 ; Kristof-Brown, Zimmerman, & Johnson, 2005 ; Verquer, Beehr, & Wagner, 2003 ).

Job Demands-Control/Support (JD-C/S) and Job Demands-Resources (JD-R) Model
Focusing more closely on concrete aspects of work demands and the extent to which a person perceives he or she has control or decision latitude over those demands, Karasek ( 1979 ) developed the JD-C model. Karasek and Theorell ( 1990 ) posited that high job demands under conditions of little decision latitude or control yield high strains, which have varied implications on the health of an organization (e.g., in terms of high turnover, employee ill-health, poor organizational performance). This theory was modified slightly to address not only control, but also other resources that could protect a person from unruly job demands, including support (aka JD-C/S, Johnson & Hall, 1988 ; and JD-R, Bakker, van Veldhoven, & Xanthopoulou, 2010 ). Whether focusing on control or resources, both they and job demands are said to reflect workplace characteristics, while control and resources also represent coping strategies or tools (Siegrist, 2010 ).
Despite the glut of research testing the JD-C and JD-R, results are somewhat mixed. Testing the interaction between job demands and control, Beehr, Glaser, Canali, and Wallwey ( 2001 ) did not find empirical support for the JD-C theory. However, Dawson, O’Brien, and Beehr ( 2016 ) found that high control and high support buffered against the independent deleterious effects of interpersonal conflict, role conflict, and organizational politics (demands that were categorized as hindrance stressors) on anxiety, as well as the effects of interpersonal conflict and organizational politics on physiological symptoms, but control and support did not moderate the effects between challenge stressors and strains. Coupled with Bakker, Demerouti, and Sanz-Vergel’s ( 2014 ) note that excessive job demands are a source of strain, but increased job resources are a source of engagement, Dawson et al.’s results suggest that when an organization identifies that demands are hindrances, it can create strategies for primary (preventative) stress management interventions and attempt to remove or reduce such work demands. If the demands are challenging, though manageable, but latitude to control the challenging stressors and support are insufficient, the organization could modify practices and train employees on adopting better strategies for meeting or coping (secondary stress management intervention) with the demands. Finally, if the organization can neither afford to modify the demands or the level of control and support, it will be necessary for the organization to develop stress management (tertiary) interventions to deal with the inevitable strains.
Conservation of Resources Theory
The idea that job resources reinforce engagement in work has been propagated in Hobfoll’s ( 1989 ) Conservation of Resources (COR) theory. COR theory also draws on the foundational premise that people’s mental health is a function of the person and the environment, forwarding that how people interpret their environment (including the societal context) affects their stress levels. Hobfoll focuses on resources such as objects, personal characteristics, conditions, or energies as particularly instrumental to minimizing strains. He asserts that people do whatever they can to protect their valued resources. Thus, strains develop when resources are threatened to be taken away, actually taken away, or when additional resources are not attainable after investing in the possibility of gaining more resources (Hobfoll, 2001 ). By extension, organizations can invest in activities that would minimize resource loss and create opportunities for resource gains and thus have direct implications for devising primary and secondary stress management interventions.
Transactional Framework
Lazarus and Folkman ( 1984 ) developed the widely studied transactional framework of stress. This framework holds as a key component the cognitive appraisal process. When individuals perceive factors in the work environment as a threat (i.e., primary appraisal), they will scan the available resources (external or internal to himself or herself) to cope with the stressors (i.e., secondary appraisal). If the coping resources provide minimal relief, strains develop. Until recently, little attention has been given to the cognitive appraisal associated with different work stressors (Dewe & Kompier, 2008 ; Liu & Li, 2017 ). In a study of Polish and Spanish social care service providers, stressors appraised as a threat related positively to burnout and less engagement, but stressors perceived as challenges yielded greater engagement and less burnout (Kożusznik, Rodriguez, & Peiro, 2012 ). Similarly, Dawson et al. ( 2016 ) found that even with support and control resources, hindrance demands were more strain-producing than challenge demands, suggesting that appraisal of the stressor is important. In fact, “many people respond well to challenging work” (Beehr et al., 2001 , p. 126). Kożusznik et al. ( 2012 ) recommend training employees to change the way they view work demands in order to increase engagement, considering that part of the problem may be about how the person appraises his or her environment and, thus, copes with the stressors.
Effort-Reward Imbalance
Siegrist’s ( 1996 ) Model of Effort-Reward Imbalance (ERI) focuses on the notion of social reciprocity, such that a person fulfills required work tasks in exchange for desired rewards (Siegrist, 2010 ). ERI sheds light on how an imbalance in a person’s expectations of an organization’s rewards (e.g., pay, bonus, sense of advancement and development, job security) in exchange for a person’s efforts, that is a break in one’s work contract, leads to negative responses, including long-term ill-health (Siegrist, 2010 ; Siegrist et al., 2014 ). In fact, prolonged perception of a work contract imbalance leads to adverse health, including immunological problems and inflammation, which contribute to cardiovascular disease (Siegrist, 2010 ). The model resembles the relational and interactional psychological contract theory in that it describes an employee’s perception of the terms of the relationship between the person and the workplace, including expectations of performance, job security, training and development opportunities, career progression, salary, and bonuses (Thomas, Au, & Ravlin, 2003 ). The psychological contract, like the ERI model, focuses on social exchange. Furthermore, the psychological contract, like stress theories, are influenced by cultural factors that shape how people interpret their environments (Glazer, 2008 ; Thomas et al., 2003 ). Violations of the psychological contract will negatively affect a person’s attitudes toward the workplace and subsequent health and well-being (Siegrist, 2010 ). To remediate strain, Siegrist ( 2010 ) focuses on both the person and the environment, recognizing that the organization is particularly responsible for changing unfavorable work conditions and the person is responsible for modifying his or her reactions to such conditions.
Stress Management Interventions: Primary, Secondary, and Tertiary
Remediation of work stress and organizational development interventions are about realigning the employee’s experiences in the workplace with factors in the environment, as well as closing the gap between the current environment and the desired environment. Work stress develops when an employee perceives the work demands to exceed the person’s resources to cope and thus threatens employee well-being (Dewe & Kompier, 2008 ). Likewise, an organization’s need to change arises when forces in the environment are creating a need to change in order to survive (see Figure 1 ). Lewin’s ( 1951 ) Force Field Analysis, the foundations of which are in Field Theory, is one of the first organizational development intervention tools presented in the social science literature. The concept behind Force Field Analysis is that in order to survive, organizations must adapt to environmental forces driving a need for organizational change and remove restraining forces that create obstacles to organizational change. In order to do this, management needs to delineate the current field in which the organization is functioning, understand the driving forces for change, identify and dampen or eliminate the restraining forces against change. Several models for analyses may be applied, but most approaches are variations of organizational climate surveys.
Through organizational surveys, workers provide management with a snapshot view of how they perceive aspects of their work environment. Thus, the view of the health of an organization is a function of several factors, chief among them employees’ views (i.e., the climate) about the workplace (Lewin, 1951 ). Indeed, French and Kahn ( 1962 ) posited that well-being depends on the extent to which properties of the person and properties of the environment align in terms of what a person requires and the resources available in a given environment. Therefore, only when properties of the person and properties of the environment are sufficiently understood can plans for change be developed and implemented targeting the environment (e.g., change reporting structures to relieve, and thus prevent future, communication stressors) and/or the person (e.g., providing more autonomy, vacation days, training on new technology). In short, climate survey findings can guide consultants about the emphasis for organizational interventions: before a problem arises aka stress prevention, e.g., carefully crafting job roles), when a problem is present, but steps are taken to mitigate their consequences (aka coping, e.g., providing social support groups), and/or once strains develop (aka. stress management, e.g., healthcare management policies).
For each of the primary (prevention), secondary (coping), and tertiary (stress management) techniques the target for intervention can be the entire workforce, a subset of the workforce, or a specific person. Interventions that target the entire workforce may be considered organizational interventions, as they have direct implications on the health of all individuals and consequently the health of the organization. Several interventions categorized as primary and secondary interventions may also be implemented after strains have developed and after it has been discerned that a person or the organization did not do enough to mitigate stressors or strains (see Figure 1 ). The designation of many of the interventions as belonging to one category or another may be viewed as merely a suggestion.
Primary Interventions (Preventative Stress Management)
Before individuals begin to perceive work-related stressors, organizations engage in stress prevention strategies, such as providing people with resources (e.g., computers, printers, desk space, information about the job role, organizational reporting structures) to do their jobs. However, sometimes the institutional structures and resources are insufficient or ambiguous. Scholars and practitioners have identified several preventative stress management strategies that may be implemented.
Planning and Time Management
When employees feel quantitatively overloaded, sometimes the remedy is improving the employees’ abilities to plan and manage their time (Quick, Quick, Nelson, & Hurrell, 2003 ). Planning is a future-oriented activity that focuses on conceptual and comprehensive work goals. Time management is a behavior that focuses on organizing, prioritizing, and scheduling work activities to achieve short-term goals. Given the purpose of time management, it is considered a primary intervention, as engaging in time management helps to prevent work tasks from mounting and becoming unmanageable, which would subsequently lead to adverse outcomes. Time management comprises three fundamental components: (1) establishing goals, (2) identifying and prioritizing tasks to fulfill the goals, and (3) scheduling and monitoring progress toward goal achievement (Peeters & Rutte, 2005 ). Workers who employ time management have less role ambiguity (Macan, Shahani, Dipboye, & Philips, 1990 ), psychological stress or strain (Adams & Jex, 1999 ; Jex & Elaqua, 1999 ; Macan et al., 1990 ), and greater job satisfaction (Macan, 1994 ). However, Macan ( 1994 ) did not find a relationship between time management and performance. Still, Claessens, van Eerde, Rutte, and Roe ( 2004 ) found that perceived control of time partially mediated the relationships between planning behavior (an indicator of time management), job autonomy, and workload on one hand, and job strains, job satisfaction, and job performance on the other hand. Moreover, Peeters and Rutte ( 2005 ) observed that teachers with high work demands and low autonomy experienced more burnout when they had poor time management skills.
Person-Organization Fit
Just as it is important for organizations to find the right person for the job and organization, so is it the responsibility of a person to choose to work at the right organization—an organization that fulfills the person’s needs and upholds the values important to the individual, as much as the person fulfills the organization’s needs and adapts to its values. When people fit their employing organizations they are setting themselves up for experiencing less strain-producing stressors (Kristof-Brown et al., 2005 ). In a meta-analysis of 62 person-job fit studies and 110 person-organization fit studies, Kristof-Brown et al. ( 2005 ) found that person-job fit had a negative correlation with indicators of job strain. In fact, a primary intervention of career counseling can help to reduce stress levels (Firth-Cozens, 2003 ).
Job Redesign
The Job Demands-Control/Support (JD-C/S), Job Demands-Resources (JD-R), and transactional models all suggest that factors in the work context require modifications in order to reduce potential ill-health and poor organizational performance. Drawing on Hackman and Oldham’s ( 1980 ) Job Characteristics Model, it is possible to assess with the Job Diagnostics Survey (JDS) the current state of work characteristics related to skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback. Modifying those aspects would help create a sense of meaningfulness, sense of responsibility, and feeling of knowing how one is performing, which subsequently affects a person’s well-being as identified in assessments of motivation, satisfaction, improved performance, and reduced withdrawal intentions and behaviors. Extending this argument to the stress models, it can be deduced that reducing uncertainty or perceived unfairness that may be associated with a person’s perception of these work characteristics, as well as making changes to physical characteristics of the environment (e.g., lighting, seating, desk, air quality), nature of work (e.g., job responsibilities, roles, decision-making latitude), and organizational arrangements (e.g., reporting structure and feedback mechanisms), can help mitigate against numerous ill-health consequences and reduced organizational performance. In fact, Fried et al. ( 2013 ) showed that healthy patients of a medical clinic whose jobs were excessively low (i.e., monotonous) or excessively high (i.e., overstimulating) on job enrichment (as measured by the JDS) had greater abdominal obesity than those whose jobs were optimally enriched. By taking stock of employees’ perceptions of the current work situation, managers might think about ways to enhance employees’ coping toolkit, such as training on how to deal with difficult clients or creating stimulating opportunities when jobs have low levels of enrichment.
Participatory Action Research Interventions
Participatory action research (PAR) is an intervention wherein, through group discussions, employees help to identify and define problems in organizational structure, processes, policies, practices, and reward structures, as well as help to design, implement, and evaluate success of solutions. PAR is in itself an intervention, but its goal is to design interventions to eliminate or reduce work-related factors that are impeding performance and causing people to be unwell. An example of a successful primary intervention, utilizing principles of PAR and driven by the JD-C and JD-C/S stress frameworks is Health Circles (HCs; Aust & Ducki, 2004 ).
HCs, developed in Germany in the 1980s, were popular practices in industries, such as metal, steel, and chemical, and service. Similar to other problem-solving practices, such as quality circles, HCs were based on the assumptions that employees are the experts of their jobs. For this reason, to promote employee well-being, management and administrators solicited suggestions and ideas from the employees to improve occupational health, thereby increasing employees’ job control. HCs also promoted communication between managers and employees, which had a potential to increase social support. With more control and support, employees would experience less strains and better occupational well-being.
Employing the three-steps of (1) problem analysis (i.e., diagnosis or discovery through data generated from organizational records of absenteeism length, frequency, rate, and reason and employee survey), (2) HC meetings (6 to 10 meetings held over several months to brainstorm ideas to improve occupational safety and health concerns identified in the discovery phase), and (3) HC evaluation (to determine if desired changes were accomplished and if employees’ reports of stressors and strains changed after the course of 15 months), improvements were to be expected (Aust & Ducki, 2004 ). Aust and Ducki ( 2004 ) reviewed 11 studies presenting 81 health circles in 30 different organizations. Overall study participants had high satisfaction with the HCs practices. Most companies acted upon employees’ suggestions (e.g., improving driver’s seat and cab, reducing ticket sale during drive, team restructuring and job rotation to facilitate communication, hiring more employees during summer time, and supervisor training program to improve leadership and communication skills) to improve work conditions. Thus, HCs represent a successful theory-grounded intervention to routinely improve employees’ occupational health.
Physical Setting
The physical environment or physical workspace has an enormous impact on individuals’ well-being, attitudes, and interactions with others, as well as on the implications on innovation and well-being (Oksanen & Ståhle, 2013 ; Vischer, 2007 ). In a study of 74 new product development teams (total of 437 study respondents) in Western Europe, Chong, van Eerde, Rutte, and Chai ( 2012 ) found that when teams were faced with challenge time pressures, meaning the teams had a strong interest and desire in tackling complex, but engaging tasks, when they were working proximally close with one another, team communication improved. Chong et al. assert that their finding aligns with prior studies that have shown that physical proximity promotes increased awareness of other team members, greater tendency to initiate conversations, and greater team identification. However, they also found that when faced with hindrance time pressures, physical proximity related to low levels of team communication, but when hindrance time pressure was low, team proximity had an increasingly greater positive relationship with team communication.
In addition to considering the type of work demand teams must address, other physical workspace considerations include whether people need to work collaboratively and synchronously or independently and remotely (or a combination thereof). Consideration needs to be given to how company contributors would satisfy client needs through various modes of communication, such as email vs. telephone, and whether individuals who work by a window might need shading to block bright sunlight from glaring on their computer screens. Finally, people who have to use the telephone for extensive periods of time would benefit from earphones to prevent neck strains. Most physical stressors are rather simple to rectify. However, companies are often not aware of a problem until after a problem arises, such as when a person’s back is strained from trying to move heavy equipment. Companies then implement strategies to remediate the environmental stressor. With the help of human factors, and organizational and office design consultants, many of the physical barriers to optimal performance can be prevented (Rousseau & Aubé, 2010 ). In a study of 215 French-speaking Canadian healthcare employees, Rousseau and Aubé ( 2010 ) found that although supervisor instrumental support positively related with affective commitment to the organization, the relationship was even stronger for those who reported satisfaction with the ambient environment (i.e., temperature, lighting, sound, ventilation, and cleanliness).
Secondary Interventions (Coping)
Secondary interventions, also referred to as coping, focus on resources people can use to mitigate the risk of work-related illness or workplace injury. Resources may include properties related to social resources, behaviors, and cognitive structures. Each of these resource domains may be employed to cope with stressors. Monat and Lazarus ( 1991 ) summarize the definition of coping as “an individual’s efforts to master demands (or conditions of harm, threat, or challenge) that are appraised (or perceived) as exceeding or taxing his or her resources” (p. 5). To master demands requires use of the aforementioned resources. Secondary interventions help employees become aware of the psychological, physical, and behavioral responses that may occur from the stressors presented in their working environment. Secondary interventions help a person detect and attend to stressors and identify resources for and ways of mitigating job strains. Often, coping strategies are learned skills that have a cognitive foundation and serve important functions in improving people’s management of stressors (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 ). Coping is effortful, but with practice it becomes easier to employ. This idea is the foundation for understanding the role of resilience in coping with stressors. However, “not all adaptive processes are coping. Coping is a subset of adaptational activities that involves effort and does not include everything that we do in relating to the environment” (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 , p. 198). Furthermore, sometimes to cope with a stressor, a person may call upon social support sources to help with tangible materials or emotional comfort. People call upon support resources because they help to restructure how a person approaches or thinks about the stressor.
Most secondary interventions are aimed at helping the individual, though companies, as a policy, might require all employees to partake in training aimed at increasing employees’ awareness of and skills aimed at handling difficult situations vis à vis company channels (e.g., reporting on sexual harassment or discrimination). Furthermore, organizations might institute mentoring programs or work groups to address various work-related matters. These programs employ awareness-raising activities, stress-education, or skills training (cf., Bhagat, Segovis, & Nelson, 2012 ), which include development of skills in problem-solving, understanding emotion-focused coping, identifying and using social support, and enhancing capacity for resilience. The aim of these programs, therefore, is to help employees proactively review their perceptions of psychological, physical, and behavioral job-related strains, thereby extending their resilience, enabling them to form a personal plan to control stressors and practice coping skills (Cooper, Dewe, & O’Driscoll, 2011 ).
Often these stress management programs are instituted after an organization has observed excessive absenteeism and work-related performance problems and, therefore, are sometimes categorized as a tertiary stress management intervention or even a primary (prevention) intervention. However, the skills developed for coping with stressors also place the programs in secondary stress management interventions. Example programs that are categorized as tertiary or primary stress management interventions may also be secondary stress management interventions (see Figure 1 ), and these include lifestyle advice and planning, stress inoculation training, simple relaxation techniques, meditation, basic trainings in time management, anger management, problem-solving skills, and cognitive-behavioral therapy. Corporate wellness programs also fall under this category. In other words, some programs could be categorized as primary, secondary, or tertiary interventions depending upon when the employee (or organization) identifies the need to implement the program. For example, time management practices could be implemented as a means of preventing some stressors, as a way to cope with mounting stressors, or as a strategy to mitigate symptoms of excessive of stressors. Furthermore, these programs can be administered at the individual level or group level. As related to secondary interventions, these programs provide participants with opportunities to develop and practice skills to cognitively reappraise the stressor(s); to modify their perspectives about stressors; to take time out to breathe, stretch, meditate, relax, and/or exercise in an attempt to support better decision-making; to articulate concerns and call upon support resources; and to know how to say “no” to onslaughts of requests to complete tasks. Participants also learn how to proactively identify coping resources and solve problems.
According to Cooper, Dewe, and O’Driscoll ( 2001 ), secondary interventions are successful in helping employees modify or strengthen their ability to cope with the experience of stressors with the goal of mitigating the potential harm the job stressors may create. Secondary interventions focus on individuals’ transactions with the work environment and emphasize the fit between a person and his or her environment. However, researchers have pointed out that the underlying assumption of secondary interventions is that the responsibility for coping with the stressors of the environment lies within individuals (Quillian-Wolever & Wolever, 2003 ). If companies cannot prevent the stressors in the first place, then they are, in part, responsible for helping individuals develop coping strategies and informing employees about programs that would help them better cope with job stressors so that they are able to fulfill work assignments.
Stress management interventions that help people learn to cope with stressors focus mainly on the goals of enabling problem-resolution or expressing one’s emotions in a healthy manner. These goals are referred to as problem-focused coping and emotion-focused coping (Folkman & Lazarus, 1980 ; Pearlin & Schooler, 1978 ), and the person experiencing the stressors as potential threat is the agent for change and the recipient of the benefits of successful coping (Hobfoll, 1998 ). In addition to problem-focused and emotion-focused coping approaches, social support and resilience may be coping resources. There are many other sources for coping than there is room to present here (see e.g., Cartwright & Cooper, 2005 ); however, the current literature has primarily focused on these resources.
Problem-Focused Coping
Problem-focused or direct coping helps employees remove or reduce stressors in order to reduce their strain experiences (Bhagat et al., 2012 ). In problem-focused coping employees are responsible for working out a strategic plan in order to remove job stressors, such as setting up a set of goals and engaging in behaviors to meet these goals. Problem-focused coping is viewed as an adaptive response, though it can also be maladaptive if it creates more problems down the road, such as procrastinating getting work done or feigning illness to take time off from work. Adaptive problem-focused coping negatively relates to long-term job strains (Higgins & Endler, 1995 ). Discussion on problem-solving coping is framed from an adaptive perspective.
Problem-focused coping is featured as an extension of control, because engaging in problem-focused coping strategies requires a series of acts to keep job stressors under control (Bhagat et al., 2012 ). In the stress literature, there are generally two ways to categorize control: internal versus external locus of control, and primary versus secondary control. Locus of control refers to the extent to which people believe they have control over their own life (Rotter, 1966 ). People high in internal locus of control believe that they can control their own fate whereas people high in external locus of control believe that outside factors determine their life experience (Rotter, 1966 ). Generally, those with an external locus of control are less inclined to engage in problem-focused coping (Strentz & Auerbach, 1988 ). Primary control is the belief that people can directly influence their environment (Alloy & Abramson, 1979 ), and thus they are more likely to engage in problem-focused coping. However, when it is not feasible to exercise primary control, people search for secondary control, with which people try to adapt themselves into the objective environment (Rothbaum, Weisz, & Snyder, 1982 ).
Emotion-Focused Coping
Emotion-focused coping, sometimes referred to as palliative coping, helps employees reduce strains without the removal of job stressors. It involves cognitive or emotional efforts, such as talking about the stressor or distracting oneself from the stressor, in order to lessen emotional distress resulting from job stressors (Bhagat et al., 2012 ). Emotion-focused coping aims to reappraise and modify the perceptions of a situation or seek emotional support from friends or family. These methods do not include efforts to change the work situation or to remove the job stressors (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 ). People tend to adopt emotion-focused coping strategies when they believe that little or nothing can be done to remove the threatening, harmful, and challenging stressors (Bhagat et al., 2012 ), such as when they are the only individuals to have the skills to get a project done or they are given increased responsibilities because of the unexpected departure of a colleague. Emotion-focused coping strategies include (1) reappraisal of the stressful situation, (2) talking to friends and receiving reassurance from them, (3) focusing on one’s strength rather than weakness, (4) optimistic comparison—comparing one’s situation to others’ or one’s past situation, (5) selective ignoring—paying less attention to the unpleasant aspects of one’s job and being more focused on the positive aspects of the job, (6) restrictive expectations—restricting one’s expectations on job satisfaction but paying more attention to monetary rewards, (7) avoidance coping—not thinking about the problem, leaving the situation, distracting oneself, or using alcohol or drugs (e.g., Billings & Moos, 1981 ).
Some emotion-focused coping strategies are maladaptive. For example, avoidance coping may lead to increased level of job strains in the long run (e.g., Parasuraman & Cleek, 1984 ). Furthermore, a person’s ability to cope with the imbalance of performing work to meet organizational expectations can take a toll on the person’s health, leading to physiological consequences such as cardiovascular disease, sleep disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, and diabetes (Fried et al., 2013 ; Siegrist, 2010 ; Toker, Shirom, Melamed, & Armon, 2012 ; Willert, Thulstrup, Hertz, & Bonde, 2010 ).
Comparing Coping Strategies across Cultures
Most coping research is conducted in individualistic, Western cultures wherein emotional control is emphasized and both problem-solving focused coping and primary control are preferred (Bhagat et al., 2010 ). However, in collectivistic cultures, emotion-focused coping and use of secondary control may be preferred and may not necessarily carry a negative evaluation (Bhagat et al., 2010 ). For example, African Americans are more likely to use emotion-focused coping than non–African Americans (Knight, Silverstein, McCallum, & Fox, 2000 ), and among women who experienced sexual harassment, Anglo American women were less likely to employ emotion focused coping (i.e., avoidance coping) than Turkish women and Hispanic American women, while Hispanic women used more denial than the other two groups (Wasti & Cortina, 2002 ).
Thus, whereas problem-focused coping is venerated in Western societies, emotion-focused coping may be more effective in reducing strains in collectivistic cultures, such as China, Japan, and India (Bhagat et al., 2010 ; Narayanan, Menon, & Spector, 1999 ; Selmer, 2002 ). Indeed, Swedish participants reported more problem-focused coping than did Chinese participants (Xiao, Ottosson, & Carlsson, 2013 ), American college students engaged in more problem-focused coping behaviors than did their Japanese counterparts (Ogawa, 2009 ), and Indian (vs. Canadian) students reported more emotion-focused coping, such as seeking social support and positive reappraisal (Sinha, Willson, & Watson, 2000 ). Moreover, Glazer, Stetz, and Izso ( 2004 ) found that internal locus of control was more predominant in individualistic cultures (United Kingdom and United States), whereas external locus of control was more predominant in communal cultures (Italy and Hungary). Also, internal locus of control was associated with less job stress, but more so for nurses in the United Kingdom and United States than Italy and Hungary. Taken together, adoption of coping strategies and their effectiveness differ significantly across cultures. The extent to which a coping strategy is perceived favorably and thus selected or not selected is not only a function of culture, but also a person’s sociocultural beliefs toward the coping strategy (Morimoto, Shimada, & Ozaki, 2013 ).
Social Support
Social support refers to the aid an entity gives to a person. The source of the support can be a single person, such as a supervisor, coworker, subordinate, family member, friend, or stranger, or an organization as represented by upper-level management representing organizational practices. The type of support can be instrumental or emotional. Instrumental support, including informational support, refers to that which is tangible, such as data to help someone make a decision or colleagues’ sick days so one does not lose vital pay while recovering from illness. Emotional support, including esteem support, refers to the psychological boost given to a person who needs to express emotions and feel empathy from others or to have his or her perspective validated. Beehr and Glazer ( 2001 ) present an overview of the role of social support on the stressor-strain relationship and arguments regarding the role of culture in shaping the utility of different sources and types of support.
Meaningfulness and Resilience
Meaningfulness reflects the extent to which people believe their lives are significant, purposeful, goal-directed, and fulfilling (Glazer, Kożusznik, Meyers, & Ganai, 2014 ). When faced with stressors, people who have a strong sense of meaning in life will also try to make sense of the stressors. Maintaining a positive outlook on life stressors helps to manage emotions, which is helpful in reducing strains, particularly when some stressors cannot be problem-solved (Lazarus & Folkman, 1991 ). Lazarus and Folkman ( 1991 ) emphasize that being able to reframe threatening situations can be just as important in an adaptation as efforts to control the stressors. Having a sense of meaningfulness motivates people to behave in ways that help them overcome stressors. Thus, meaningfulness is often used in the same breath as resilience, because people who are resilient are often protecting that which is meaningful.
Resilience is a personality state that can be fortified and enhanced through varied experiences. People who perceive their lives are meaningful are more likely to find ways to face adversity and are therefore more prone to intensifying their resiliency. When people demonstrate resilience to cope with noxious stressors, their ability to be resilient against other stressors strengthens because through the experience, they develop more competencies (Glazer et al., 2014 ). Thus, fitting with Hobfoll’s ( 1989 , 2001 ) COR theory, meaningfulness and resilience are psychological resources people attempt to conserve and protect, and employ when necessary for making sense of or coping with stressors.
Tertiary Interventions (Stress Management)
Stress management refers to interventions employed to treat and repair harmful repercussions of stressors that were not coped with sufficiently. As Lazarus and Folkman ( 1991 ) noted, not all stressors “are amenable to mastery” (p. 205). Stressors that are unmanageable and lead to strains require interventions to reverse or slow down those effects. Workplace interventions might focus on the person, the organization, or both. Unfortunately, instead of looking at the whole system to include the person and the workplace, most companies focus on the person. Such a focus should not be a surprise given the results of van der Klink, Blonk, Schene, and van Dijk’s ( 2001 ) meta-analysis of 48 experimental studies conducted between 1977 and 1996 . They found that of four types of tertiary interventions, the effect size for cognitive-behavioral interventions and multimodal programs (e.g., the combination of assertive training and time management) was moderate and the effect size for relaxation techniques was small in reducing psychological complaints, but not turnover intention related to work stress. However, the effects of (the five studies that used) organization-focused interventions were not significant. Similarly, Richardson and Rothstein’s ( 2008 ) meta-analytic study, including 36 experimental studies with 55 interventions, showed a larger effect size for cognitive-behavioral interventions than relaxation, organizational, multimodal, or alternative. However, like with van der Klink et al. ( 2001 ), Richardson and Rothstein ( 2008 ) cautioned that there were few organizational intervention studies included and the impact of interventions were determined on the basis of psychological outcomes and not physiological or organizational outcomes. Van der Klink et al. ( 2001 ) further expressed concern that organizational interventions target the workplace and that changes in the individual may take longer to observe than individual interventions aimed directly at the individual.
The long-term benefits of individual focused interventions are not yet clear either. Per Giga, Cooper, and Faragher ( 2003 ), the benefits of person-directed stress management programs will be short-lived if organizational factors to reduce stressors are not addressed too. Indeed, LaMontagne, Keegel, Louie, Ostry, and Landsbergis ( 2007 ), in their meta-analysis of 90 studies on stress management interventions published between 1990 and 2005 , revealed that in relation to interventions targeting organizations only, and interventions targeting individuals only, interventions targeting both organizations and individuals (i.e. the systems approach) had the most favorable positive effects on both the organizations and the individuals. Furthermore, the organization-level interventions were effective at both the individual and organization levels, but the individual-level interventions were effective only at the individual level.
Individual-Focused Stress Management
Individual-focused interventions concentrate on improving conditions for the individual, though counseling programs emphasize that the worker is in charge of reducing “stress,” whereas role-focused interventions emphasize activities that organizations can guide to actually reduce unnecessary noxious environmental factors.
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Employee Assistance Programs
When stress become sufficiently problematic (which is individually gauged or attended to by supportive others) in a worker’s life, employees may utilize the short-term counseling services or referral services Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) provide. People who utilize the counseling services may engage in cognitive behavioral therapy aimed at changing the way people think about the stressors (e.g., as challenge opportunity over threat) and manage strains. Example topics that may be covered in these therapy sessions include time management and goal setting (prioritization), career planning and development, cognitive restructuring and mindfulness, relaxation, and anger management. In a study of healthcare workers and teachers who participated in a 2-day to 2.5-day comprehensive stress management training program (including 26 topics on identifying, coping with, and managing stressors and strains), Siu, Cooper, and Phillips ( 2013 ) found psychological and physical improvements were self-reported among the healthcare workers (for which there was no control group). However, comparing an intervention group of teachers to a control group of teachers, the extent of change was not as visible, though teachers in the intervention group engaged in more mastery recovery experiences (i.e., they purposefully chose to engage in challenging activities after work).
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Mindfulness
A popular therapy today is to train people to be more mindful, which involves helping people live in the present, reduce negative judgement of current and past experiences, and practicing patience (Birnie, Speca, & Carlson, 2010 ). Mindfulness programs usually include training on relaxation exercises, gentle yoga, and awareness of the body’s senses. In one study offered through the continuing education program at a Canadian university, 104 study participants took part in an 8-week, 90 minute per group (15–20 participants per) session mindfulness program (Birnie et al., 2010 ). In addition to body scanning, they also listened to lectures on incorporating mindfulness into one’s daily life and received a take-home booklet and compact discs that guided participants through the exercises studied in person. Two weeks after completing the program, participants’ mindfulness attendance and general positive moods increased, while physical, psychological, and behavioral strains decreased. In another study on a sample of U.K. government employees, study participants receiving three sessions of 2.5 to 3 hours each training on mindfulness, with the first two sessions occurring in consecutive weeks and the third occurring about three months later, Flaxman and Bond ( 2010 ) found that compared to the control group, the intervention group showed a decrease in distress levels from Time 1 (baseline) to Time 2 (three months after first two training sessions) and Time 1 to Time 3 (after final training session). Moreover, of the mindfulness intervention study participants who were clinically distressed, 69% experienced clinical improvement in their psychological health.
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Biofeedback/Imagery/Meditation/Deep Breathing
Biofeedback uses electronic equipment to inform users about how their body is responding to tension. With guidance from a therapist, individuals then learn to change their physiological responses so that their pulse normalizes and muscles relax (Norris, Fahrion, & Oikawa, 2007 ). The therapist’s guidance might include reminders for imagery, meditation, body scan relaxation, and deep breathing. Saunders, Driskell, Johnston, and Salas’s ( 1996 ) meta-analysis of 37 studies found that imagery helped reduce state and performance anxiety. Once people have been trained to relax, reminder triggers may be sent through smartphone push notifications (Villani et al., 2013 ).
Smartphone technology can also be used to support weight loss programs, smoking cessation programs, and medication or disease (e.g., diabetes) management compliance (Heron & Smyth, 2010 ; Kannampallil, Waicekauskas, Morrow, Kopren, & Fu, 2013 ). For example, smartphones could remind a person to take medications or test blood sugar levels or send messages about healthy behaviors and positive affirmations.
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Sleep/Rest/Respite
Workers today sleep less per night than adults did nearly 30 years ago (Luckhaupt, Tak, & Calvert, 2010 ; National Sleep Foundation, 2005 , 2013 ). In order to combat problems, such as increased anxiety and cardiovascular artery disease, associated with sleep deprivation and insufficient rest, it is imperative that people disconnect from their work at least one day per week or preferably for several weeks so that they are able to restore psychological health (Etzion, Eden, & Lapidot, 1998 ; Ragsdale, Beehr, Grebner, & Han, 2011 ). When college students engaged in relaxation-type activities, such as reading or watching television, over the weekend, they experienced less emotional exhaustion and greater general well-being than students who engaged in resources-consuming activities, such as house cleaning (Ragsdale et al., 2011 ). Additional research and future directions for research are reviewed and identified in the work of Sonnentag ( 2012 ). For example, she asks whether lack of ability to detach from work is problematic for people who find their work meaningful. In other words, are negative health consequences only among those who do not take pleasure in their work? Sonnetag also asks how teleworkers detach from their work when engaging in work from the home. Ironically, one of the ways that companies are trying to help with the challenges of high workload or increased need to be available to colleagues, clients, or vendors around the globe is by offering flexible work arrangements, whereby employees who can work from home are given the opportunity to do so. Companies that require global interactions 24-hours per day often employ this strategy, but is the solution also a source of strain (Glazer, Kożusznik, & Shargo, 2012 )?
Individual-Focused Stress Management: Role Analysis
Role analysis or role clarification aims to redefine, expressly identify, and align employees’ roles and responsibilities with their work goals. Through role negotiation, involved parties begin to develop a new formal or informal contract about expectations and define resources needed to fulfill those expectations. Glazer has used this approach in organizational consulting and, with one memorable client engagement, found that not only were the individuals whose roles required deeper re-evaluation happier at work (six months later), but so were their subordinates. Subordinates who once characterized the two partners as hostile and akin to a couple going through a bad divorce, later referred to them as a blissful pair. Schaubroeck, Ganster, Sime, and Ditman ( 1993 ) also found in a three-wave study over a two-year period that university employees’ reports of role clarity and greater satisfaction with their supervisor increased after a role clarification exercise of top managers’ roles and subordinates’ roles. However, the intervention did not have any impact on reported physical symptoms, absenteeism, or psychological well-being. Role analysis is categorized under individual-focused stress management intervention because it is usually implemented after individuals or teams begin to demonstrate poor performance and because the intervention typically focuses on a few individuals rather than an entire organization or group. In other words, the intervention treats the person’s symptoms by redefining the role so as to eliminate the stimulant causing the problem.
Organization-Focused Stress Management
At the organizational level, companies that face major declines in productivity and profitability or increased costs related to healthcare and disability might be motivated to reassess organizational factors that might be impinging on employees’ health and well-being. After all, without healthy workers, it is not possible to have a healthy organization. Companies may choose to implement practices and policies that are expected to help not only the employees, but also the organization with reduced costs associated with employee ill-health, such as medical insurance, disability payments, and unused office space. Example practices and policies that may be implemented include flexible work arrangements to ensure that employees are not on the streets in the middle of the night for work that can be done from anywhere (such as the home), diversity programs to reduce stress-induced animosity and prejudice toward others, providing only healthy food choices in cafeterias, mandating that all employees have physicals in order to receive reduced prices for insurance, company-wide closures or mandatory paid time off, and changes in organizational visioning.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Organizational-Level Occupational Health Interventions
As with job design interventions that are implemented to remediate work characteristics that were a source of unnecessary or excessive stressors, so are organizational-level occupational health (OLOH) interventions. As with many of the interventions, its placement as a primary or tertiary stress management intervention may seem arbitrary, but when considering the goal and target of change, it is clear that the intervention is implemented in response to some ailing organizational issues that need to be reversed or stopped, and because it brings in the entire organization’s workforce to address the problems, it has been placed in this category. There are several more case studies than empirical studies on the topic of whole system organizational change efforts (see example case studies presented by the United Kingdom’s Health and Safety Executive). It is possible that lack of published empirical work is not so much due to lack of attempting to gather and evaluate the data for publication, but rather because the OLOH interventions themselves never made it to the intervention stage, the interventions failed (Biron, Gatrell, & Cooper, 2010 ), or the level of evaluation was not rigorous enough to get into empirical peer-review journals. Fortunately, case studies provide some indication of the opportunities and problems associated with OLOH interventions.
One case study regarding Cardiff and Value University Health Board revealed that through focus group meetings with members of a steering group (including high-level managers and supported by top management) and facilitated by a neutral, non-judgemental organizational health consultant, ideas for change were posted on newsprint, discussed, and areas in the organization needing change were identified. The intervention for giving voice to people who initially had little already had a positive effect on the organization, as absence decreased by 2.09% and 6.9% merely 12 and 18 months, respectively, after the intervention. Translated in financial terms, the 6.9% change was equivalent to a quarterly savings of £80,000 (Health & Safety Executive, n.d. ). Thus, focusing on the context of change and how people will be involved in the change process probably helped the organization realize improvements (Biron et al., 2010 ). In a recent and rare empirical study, employing both qualitative and quantitative data collection methods, Sørensen and Holman ( 2014 ) utilized PAR in order to plan and implement an OLOH intervention over the course of 14 months. Their study aimed to examine the effectiveness of the PAR process in reducing workers’ work-related and social or interpersonal-related stressors that derive from the workplace and improving psychological, behavioral, and physiological well-being across six Danish organizations. Based on group dialogue, 30 proposals for change were proposed, all of which could be categorized as either interventions to focus on relational factors (e.g., management feedback improvement, engagement) or work processes (e.g., reduced interruptions, workload, reinforcing creativity). Of the interventions that were implemented, results showed improvements on manager relationship quality and reduced burnout, but no changes with respect to work processes (i.e., workload and work pace) perhaps because the employees already had sufficient task control and variety. These findings support Dewe and Kompier’s ( 2008 ) position that occupational health can be reinforced through organizational policies that reinforce quality jobs and work experiences.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Flexible Work Arrangements
Dewe and Kompier ( 2008 ), citing the work of Isles ( 2005 ), noted that concern over losing one’s job is a reason for why 40% of survey respondents indicated they work more hours than formally required. In an attempt to create balance and perceived fairness in one’s compensation for putting in extra work hours, employees will sometimes be legitimately or illegitimately absent. As companies become increasingly global, many people with desk jobs are finding themselves communicating with colleagues who are halfway around the globe and at all hours of the day or night (Glazer et al., 2012 ). To help minimize the strains associated with these stressors, companies might devise flexible work arrangements (FWA), though the type of FWA needs to be tailored to the cultural environment (Masuda et al., 2012 ). FWAs give employees some leverage to decide what would be the optimal work arrangement for them (e.g., part-time, flexible work hours, compressed work week, telecommuting). In other words, FWA provides employees with the choice of when to work, where to work (on-site or off-site), and how many hours to work in a day, week, or pay period (Kossek, Thompson, & Lautsch, 2015 ). However, not all employees of an organization have equal access to or equitable use of FWAs; workers in low-wage, hourly jobs are often beholden to being physically present during specific hours (Swanberg McKechnie, Ojha, & James, 2011 ). In a study of over 1,300 full-time hourly retail employees in the United States, Swanberg et al. ( 2011 ) showed that employees who have control over their work schedules and over their work hours were satisfied with their work schedules, perceived support from the supervisor, and work engagement.
Unfortunately, not all FWAs yield successful results for the individual or the organization. Being able to work from home or part-time can have problems too, as a person finds himself or herself working more hours from home than required. Sometimes telecommuting creates work-family conflict too as a person struggles to balance work and family obligations while working from home. Other drawbacks include reduced face-to-face contact between work colleagues and stakeholders, challenges shaping one’s career growth due to limited contact, perceived inequity if some have more flexibility than others, and ambiguity about work role processes for interacting with employees utilizing the FWA (Kossek et al., 2015 ). Organizations that institute FWAs must carefully weigh the benefits and drawbacks the flexibility may have on the employees using it or the employees affected by others using it, as well as the implications on the organization, including the vendors who are serving and clients served by the organization.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Diversity Programs
Employees in the workplace might experience strain due to feelings of discrimination or prejudice. Organizational climates that do not promote diversity (in terms of age, religion, physical abilities, ethnicity, nationality, sex, and other characteristics) are breeding grounds for undesirable attitudes toward the workplace, lower performance, and greater turnover intention (Bergman, Palmieri, Drasgow, & Ormerod, 2012 ; Velez, Moradi, & Brewster, 2013 ). Management is thus advised to implement programs that reinforce the value and importance of diversity, as well as manage diversity to reduce conflict and feelings of prejudice. In fact, managers who attended a leadership training program reported higher multicultural competence in dealing with stressful situations (Chrobot-Mason & Leslie, 2012 ), and managers who persevered through challenges were more dedicated to coping with difficult diversity issues (Cilliers, 2011 ). Thus, diversity programs can help to reduce strains by directly reducing stressors associated with conflict linked to diversity in the workplace and by building managers’ resilience.
Organization-Focused Stress Management: Healthcare Management Policies
Over the past few years, organizations have adopted insurance plans that implement wellness programs for the sake of managing the increasing cost of healthcare that is believed to be a result of individuals’ not managing their own health, with regular check-ups and treatment. The wellness programs require all insured employees to visit a primary care provider, complete a health risk assessment, and engage in disease management activities as specified by a physician (e.g., see frequently asked questions regarding the State of Maryland’s Wellness Program). Companies believe that requiring compliance will reduce health problems, although there is no proof that such programs save money or that people would comply. One study that does, however, boast success, was a 12-week workplace health promotion program aimed at reducing Houston airport workers’ weight (Ebunlomo, Hare-Everline, Weber, & Rich, 2015 ). The program, which included 235 volunteer participants, was deemed a success, as there was a total weight loss of 345 pounds (or 1.5 lbs per person). Given such results in Houston, it is clear why some people are also skeptical over the likely success of wellness programs, particularly as there is no clear method for evaluating their efficacy (Sinnott & Vatz, 2015 ).
Moreover, for some, such a program is too paternalistic and intrusive, as well as punishes anyone who chooses not to actively participate in disease management programs (Sinnott & Vatz, 2015 ). The programs put the onus of change on the person, though it is a response to the high costs of ill-health. The programs neglect to consider the role of the organization in reducing the barriers to healthy lifestyle, such as cloaking exempt employment as simply needing to get the work done, when it usually means working significantly more hours than a standard workweek. In fact, workplace health promotion programs did not reduce presenteeism (i.e., people going to work while unwell thereby reducing their job performance) among those who suffered from physical pain (Cancelliere, Cassidy, Ammendolia, & Côte, 2011 ). However, supervisor education, worksite exercise, lifestyle intervention through email, midday respite from repetitive work, a global stress management program, changes in lighting, and telephone interventions helped to reduce presenteeism. Thus, emphasis needs to be placed on psychosocial aspects of the organization’s structure, including managers and overall organizational climate for on-site presence, that reinforces such behavior (Cancelliere et al., 2011 ). Moreover, wellness programs are only as good as the interventions to reduce work-related stressors and improve organizational resources to enable workers to improve their overall psychological and physical health.
Concluding Remarks
Future research.
One of the areas requiring more theoretical and practical attention is that of the utility of stress frameworks to guide organizational development change interventions. Although it has been proposed that the foundation for work stress management interventions is in organizational development, and even though scholars and practitioners of organization development were also founders of research programs that focused on employee health and well-being or work stress, there are few studies or other theoretical works that link the two bodies of literature.
A second area that requires additional attention is the efficacy of stress management interventions across cultures. In examining secondary stress management interventions (i.e., coping), some cross-cultural differences in findings were described; however, there is still a dearth of literature from different countries on the utility of different prevention, coping, and stress management strategies.
A third area that has been blossoming since the start of the 21st century is the topic of hindrance and challenge stressors and the implications of both on workers’ well-being and performance. More research is needed on this topic in several areas. First, there is little consistency by which researchers label a stressor as a hindrance or a challenge. Researchers sometimes take liberties with labels, but it is not the researchers who should label a stressor but the study participants themselves who should indicate if a stressor is a source of strain. Rodríguez, Kozusznik, and Peiró ( 2013 ) developed a measure in which respondents indicate whether a stressor is a challenge or a hindrance. Just as some people may perceive demands to be challenges that they savor and that result in a psychological state of eustress (Nelson & Simmons, 2003 ), others find them to be constraints that impede goal fulfillment and thus might experience distress. Likewise, some people might perceive ambiguity as a challenge that can be overcome and others as a constraint over which he or she has little control and few or no resources with which to cope. More research on validating the measurement of challenge vs. hindrance stressors, as well as eustress vs. distress, and savoring vs. coping, is warranted. Second, at what point are challenge stressors harmful? Just because people experiencing challenge stressors continue to perform well, it does not necessarily mean that they are healthy people. A great deal of stressors are intellectually stimulating, but excessive stimulation can also take a toll on one’s physiological well-being, as evident by the droves of professionals experiencing different kinds of diseases not experienced as much a few decades ago, such as obesity (Fried et al., 2013 ). Third, which stress management interventions would better serve to reduce hindrance stressors or to reduce strain that may result from challenge stressors while reinforcing engagement-producing challenge stressors?
A fourth area that requires additional attention is that of the flexible work arrangements (FWAs). One of the reasons companies have been willing to permit employees to work from home is not so much out of concern for the employee, but out of the company’s need for the focal person to be able to communicate with a colleague working from a geographic region when it is night or early morning for the focal person. Glazer, Kożusznik, and Shargo ( 2012 ) presented several areas for future research on this topic, noting that by participating on global virtual teams, workers face additional stressors, even while given flexibility of workplace and work time. As noted earlier, more research needs to be done on the extent to which people who take advantage of FWAs are advantaged in terms of detachment from work. Can people working from home detach? Are those who find their work invigorating also likely to experience ill-health by not detaching from work?
A fifth area worthy of further research attention is workplace wellness programing. According to Page and Vella-Brodrick ( 2009 ), “subjective and psychological well-being [are] key criteria for employee mental health” (p. 442), whereby mental health focuses on wellness, rather than the absence of illness. They assert that by fostering employee mental health, organizations are supporting performance and retention. Employee well-being can be supported by ensuring that jobs are interesting and meaningful, goals are achievable, employees have control over their work, and skills are used to support organizational and individual goals (Dewe & Kompier, 2008 ). However, just as mental health is not the absence of illness, work stress is not indicative of an absence of psychological well-being. Given the perspective that employee well-being is a state of mind (Page & Vella-Brodrick, 2009 ), we suggest that employee well-being can be negatively affected by noxious job stressors that cannot be remediated, but when job stressors are preventable, employee well-being can serve to protect an employee who faces job stressors. Thus, wellness programs ought to focus on providing positive experiences by enhancing and promoting health, as well as building individual resources. These programs are termed “green cape” interventions (Pawelski, 2016 ). For example, with the growing interests in positive psychology, researchers and practitioners have suggested employing several positive psychology interventions, such as expressing gratitude, savoring experiences, and identifying one’s strengths (Tetrick & Winslow, 2015 ). Another stream of positive psychology is psychological capital, which includes four malleable functions of self-efficacy, optimism, hope, and resilience (Luthans, Youssef, & Avolio, 2007 ). Workplace interventions should include both “red cape” interventions (i.e., interventions to reduce negative experiences) and “green cape” interventions (i.e., workplace wellness programs; Polly, 2014 ).
A Healthy Organization’s Pledge
A healthy workplace requires healthy workers. Period. Among all organizations’ missions should be the focus on a healthy workforce. To maintain a healthy workforce, the company must routinely examine its own contributions in terms of how it structures itself; reinforces communications among employees, vendors, and clients; how it rewards and cares for its people (e.g., ensuring they get sufficient rest and can detach from work); and the extent to which people at the upper levels are truly connected with the people at the lower levels. As a matter of practice, management must recognize when employees are overworked, unwell, and poorly engaged. Management must also take stock of when it is doing well and right by its contributors’ and maintain and reinforce the good practices, norms, and procedures. People in the workplace make the rules; people in the workplace can change the rules. How management sees its employees and values their contribution will have a huge role in how a company takes stock of its own pain points. Providing employees with tools to manage their own reactions to work-related stressors and consequent strains is fine, but wouldn’t it be grand if organizations took better notice about what they could do to mitigate the strain-producing stressors in the first place and take ownership over how employees are treated?
- Abramis, D. J. (1994). Work role ambiguity, job satisfaction, and job performance: Meta-analyses and review. Psychological Report, 75 , 1411–1433.
- Adams, G. A. , & Jex, S. M. (1999). Relationships between time management, control, work–family conflict, and strain. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 1 , 72–77.
- Alloy, L. B. , & Abramson, L. Y. (1979). Judgment of contingency in depressed and nondepressed students: Sadder but wiser? Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 108 , 441–483.
- Amstad, F. T. , Meier, L. L. , Fasel, U. , Elfering, A. , & Semmer, N. K. (2011). A meta-analysis of work-family conflict and various outcomes with a special emphasis on cross-domain versus matching-domain relations. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 16 , 151–169.
- Assouline, M. , & Meir, E. I. (1987). Meta-analysis of the relationship between congruence and well-being measures. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 31 , 319–332.
- Aust, B. , & Ducki, A. (2004). Comprehensive health promotion interventions at the workplace: Experiences with health circles in Germany. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 9 , 258–270.
- Bakker, A. B. Demerouti, E. , Sanz-Vergel, A. I. (2014). Burnout and work engagement: The JD-R approach. Annual Review of Organizational Behavior, 1 , 389–411.
- Bakker, A. B. , van Veldhoven, M. J. P. M. , & Xanthopoulou, D. (2010). Beyond the demand-control model: Thriving on high job demands and resources. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 9 , 3–16.
- Beehr, T. A. , Glaser, K. M. , Canali, K. G. , & Wallwey, D. A. (2001). Back to basics: Re-examination of demand control theory of occupational stress. Work & Stress, 15 , 115–130.
- Beehr, T. A. , & Glazer, S. (2001). A cultural perspective of social support in relation to occupational stress. In P. Perrewé , D. C. Ganster , & J. Moran (Eds.), Research in occupational stress and well-being (pp. 97–142). Amsterdam: JAI Press.
- Bergman, M. E. , Palmieri, P. A. , Drasgow, F. , & Ormerod, A. J. (2012). Racial/ethnic harassment and discrimination, its antecedents, and its effect on job-related outcomes. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 17 , 65–78.
- Bhagat, R. S. , Krishnan, B. , Nelson, T. A. , Leonard, K. M. , Ford, D. J. , & Billing, T. K. (2010). Organizational stress, psychological strain, and work outcomes in six national contexts: A closer look at the moderating influences of coping styles and decision latitude . Cross Cultural Management, 17 , 10–29.
- Bhagat, R. S. , O’Driscoll, M. P. , Babakus, E. , Frey, L. , Chokkar, J. , Ninokumar, B. H , et al. (1994). Organizational stress and coping in seven national contexts: A cross-cultural investigation . In G. P. Keita & J. J. Hurrell (Eds.), Job stress in a changing workforce: Investigating gender, diversity, and family issues (pp. 93–105). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Bhagat, R. S. , Segovis, J. C. , & Nelson, T. A. (2012). Work stress and coping in the era of globalization . New York: Routledge.
- Billings, A. G. , & Moos, R. H. (1981). The role of coping responses and social resources in attenuating the stress of life events. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 4 , 139–157.
- Birnie, K. , Speca, M. , & Carlson, L. E. (2010). Exploring self-compassion and empathy in the context of mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR). Stress & Health, 26 , 359–371.
- Biron, C. , Gatrell, C. , & Cooper, C. L. (2010). Autopsy of a failure: Evaluating process and contextual issues in an organizational-level work stress intervention. International Journal of Stress Management, 17 , 135–158.
- Bowling, N. A. , & Kirkendall, C. (2012). Workload: A review of causes, consequences, and potential interventions. In J. Houdmont , S. Leka , & R. Sinclair (Eds.), Contemporary occupational health psychology (Vol. 2) (pp. 221–238). Chichester, U.K.: Wiley.
- Breaugh, J. A. , & Colihan, J. P. (1994). Measuring facets of job ambiguity: Construct validity evidence. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79 , 191–202.
- Bruk-Lee, V. , & Spector, P. E. (2006). The social stressors-counterproductive work behaviors link: Are conflicts with supervisors and coworkers the same? . Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 11 , 145–156.
- Cancelliere, C. , Cassidy, J. D. , Ammendolia, C. , & Côte, P. (2011). Are workplace health promotion programs effective at improving presenteeism in workers? A systematic review and best evidence synthesis of the literature. BMC Public Health, 11 , 395–406.
- Caplan, R. D. (1987). Person–environment fit in organizations: Theories, facts, and values. In A. W. Riley & S. J. Zaccaro (Eds.), Occupational stress and organizational effectiveness (pp. 103–140). New York: Praeger.
- Cartwright, S. , & Cooper, C. L. (2005). Individually targeted interventions. In J. Barling , E. K. Kelloway , & M. R. Frone (Eds.), Handbook of work stress (pp. 607–622). Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Cavanaugh, M. A. , Boswell, W. R. , Roehling, M. V. , & Boudreau, J. W. (2000). An empirical examination of self-reported work stress among U.S. managers . Journal of Applied Psychology, 85 , 65–74.
- Chong, D. S. F. , van Eerde, W. , Rutte, C. G. , & Chai, K. H. (2012). Bringing employees closer: The effect of proximity on communication when teams function under time pressure. Journal of Product Innovation Management, 29 , 205–215.
- Chrobot-Mason, D. , & Leslie, J. B. (2012). The role of multicultural competence and emotional intelligence in managing diversity. Psychologist-Manager Journal, 15 , 219–236.
- Cilliers, F. (2011). Individual diversity management and salutogenic functioning. International Review of Psychiatry, 23 , 501–507.
- Claessens, B. C. , Van Eerde, W. , Rutte, C. G. , & Roe, R. A. (2004). Planning behavior and perceived control of time at work . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 25 , 937–950.
- Cooper, C. L. , Dewe, P. D. , & O’Driscoll, M. P. (2011). Employee assistance programs: Strengths, challenges, and future roles. In J. C. Quick , L. E. Tetrick , J. C. Quick , L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of occupational health psychology (2d ed.) (pp. 337–356). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Cooper, C. L. , Dewe, P. J. , & O’Driscoll, M. P. (2001). Organizational stress: A review and critique of theory, research, and applications . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE.
- Coovert, M. D. & Thompson, L. F. (2003). Technology and workplace health. In J. C. Quick & L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of occupational health psychology (pp. 221–241). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Dawson, K. M. , O’Brien, K. E. , & Beehr, T. A. (2016). The role of hindrance stressors in the job demand-control-support model of occupational stress: A proposed theory revision . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 37 (3), 397–415.
- Dewe, P. , & Kompier, M. (2008). Foresight mental capital and wellbeing project: Wellbeing and work: Future challenges . London: The Government Office for Science.
- Dopkeen, J. C. , & DuBois, R. (2014). Stress in the workplace: A policy synthesis on its dimensions and prevalence . White paper. University of Illinois Chicago, Center for Employee Health Studies, School of Public Health.
- Dwyer, D. J. , & Ganster, D. C. (1991). The effects of job demands and control on employee attendance and satisfaction. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 12 , 595–608.
- Ebunlomo, E. O. , Hare-Everline, N. , Weber, A. , & Rich, J. (2015). Development of a comprehensive 12-week health promotion program for Houston Airport System. Texas Public Health Journal, 67 (1), 11–13.
- Edwards, J. R. (2008). Person-environment fit in organizations: An assessment of theoretical progress. The Academy of Management Annals, 2 , 167–230.
- Etzion, D. , Eden, D. , & Lapidot, Y. (1998). Relief from job stressors and burnout: Reserve service as a respite. Journal of Applied Psychology, 83 , 577–585.
- Firth-Cozens, J. (2003). Doctors, their wellbeing, and their stress: It’s time to be proactive about stress—and prevent it. British Medical Journal, 326 , 670–671.
- Flaxman, P. E. , & Bond, F. W. (2010). Worksite stress management training: Moderated effects and clinical significance. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 15 , 347–358.
- Folkman, S. , & Lazarus, R. S. (1980). An analysis of coping in a middle-aged community sample . Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 21 , 219–239.
- French, J. R. P., Jr. , & Caplan, R. D. (1972). Organizational stress and individual strain. In A. Marrow (Ed.), The failure of success . New York: AMACOM.
- French, J. R. P., Jr. , & Kahn, R. L. (1962). A programmatic approach to studying the industrial environment and mental health. Journal of Social Issues, 18 , 1–48.
- French, S. (2015, May 27). PCS workload and work-life balance survey 2013 . London: Public and Commercial Services Union.
- Fried, Y. , Laurence, G. A. , Shirom, A. , Melamed, S. , Toker, S. , Berliner, S. , & Shapira, I. (2013). The relationship between job enrichment and abdominal obesity: A longitudinal field study of apparently healthy individuals. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 18 , 458–468.
- Frone, M. R. (2000). Interpersonal conflict at work and psychological outcomes: Testing a model among young workers. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 5 , 246–255.
- Giga, S. I. , Cooper, C. L. , & Faragher, B. (2003). The development of a framework for a comprehensive approach to stress management interventions at work. International Journal of Stress Management, 10 , 280–296.
- Glazer, S. (2008). Cross-cultural issues in stress and burnout. In J. R. B. Halbesleben (Ed.), Handbook of Stress and Burnout in Health Care (pp. 79–93). Huntington, NY: Nova Science Publishers.
- Glazer, S. , & Beehr, T. A. (2005). Consistency of the implications of three role stressors across four countries. Journal of Organizational Behavior , 26 , 467–487.
- Glazer, S. , Kożusznik, M. W. , Meyers, J. H. , & Ganai, O. (2014). Cultural implications of meaningfulness as a resource to mitigate work stress. In S. Leka & R. Sinclair (Eds.), Contemporary occupational health psychology: Global perspectives on research and practice (Vol. 3) (pp. 114–130). Hoboken, NJ: Wiley.
- Glazer, S. , Kożusznik, M. W. , & Shargo, I. A. (2012). Global virtual teams: A cure for- or a cause of- stress. In P. L. Perrewé , J. Halbesleben , & C. Rosen (Eds.), Research in occupational stress and well being: The role of the economic context on occupational stress and well being (Vol. 10, pp. 213–266). Bingley, U.K.: Emerald.
- Glazer, S. , Stetz, T. A. , & Izso, L. (2004). Effects of personality on subjective job stress: A cultural analysis. Personality and Individual Differences, 37 , 645–658.
- Greenhaus, J. H. , & Beutell, N. J. (1985). Sources of conflict between work and family roles. Academy of Management Review, 10 , 76–88.
- Hackman, J. R. , & Oldham, G. R. (1980). Work Redesign . Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
- Hauke, A. , Flintrop, J. , Brun, E. , & Rugulies, R. (2011). The impact of work-related psychosocial stressors on the onset of musculoskeletal disorders in specific body regions: A review and meta-analysis of 54 longitudinal studies . Work & Stress, 25 , 243–256.
- Health & Safety Executive (n.d.). Cardiff and Value University Health Board—A stress case study .
- Heron, K. E. , & Smyth, J. M. (2010). Ecological momentary interventions: Incorporating mobile technology into psychosocial and health behaviour treatments. British Journal of Health Psychology, 15 , 1–39.
- Hershcovis, M. (2011). “Incivility, social undermining, bullying … oh my!”: A call to reconcile constructs within workplace aggression research . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32 , 499–519.
- Higgins, J. E. , & Endler, N. S. (1995). Coping, life stress, and psychological and somatic distress . European Journal of Personality, 9 , 253–270.
- Hobfoll, S. E. (1989). Conservation of resources: A new attempt at conceptualizing stress. American Psychologist, 44 , 513–524.
- Hobfoll, S. E. (1998). Stress, culture, and community: The psychology and philosophy of stress . New York: Plenum Press.
- Hobfoll, S. E. (2001). The influence of culture, community, and the nested-self in the stress process: Advancing Conservation of Resources Theory. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 50 , 337–421.
- International Labor Organization (2012, July 5). Why stress at work matters . International Labor Organization.
- International Labor Organization (n.d.). Psychosocial risks and work-related stress . International Labor Organization.
- Jackson, S. E. , & Schuler, R. S. (1985). A meta-analysis and conceptual critique of research on role ambiguity and role conflict in work settings. Organizational Behavior and Human Decision Processes, 36 , 16–78.
- Jayson, S. (2012, January 11). Yeah, we’re stressed but dealing with it; Americans report a decrease in stress for the first time in five years, maybe because it’s just the new normal . USA Today .
- Jex, S. M. , & Beehr, T. A. (1991). Emerging theoretical and methodological issues in the study of work-related stress. Research in Personnel and Human Resources Management, 9 , 311–365.
- Jex, S. M. , & Elaqua, T. C. (1999). Time management as a moderator of relations between stressors and employee strain. Work & Stress, 13 , 182–191.
- Johnson, J. V. , & Hall, E. M. (1988). Job strain, workplace social support, and cardiovascular disease: A cross-sectional study of a random sample of the Swedish working population. American Journal of Public Health, 78 , 1336–1342.
- Kahn, R. L. , Wolfe, D. M. , Quinn, R. P. , Snoek, J. D. , & Rosenthal, R. A. (1964). Organizational stress: Studies in role conflict and ambiguity . New York: Wiley.
- Kannampallil, T. G. , Waicekauskas, K. , Morrow, D. G. , Kopren, K. M. , & Fu, W. (2013). External tools for collaborative medication scheduling. Cognition, Technology & Work, 15 , 121–131.
- Karasek, R. A. (1979). Job demands, job decision latitude, and mental strain: Implications for job redesign. Administrative Science Quarterly , 24 , 285–308.
- Karasek, R. A. , & Theorell, T. (1990). Healthy work: Stress, productivity, and the reconstruction of working life . New York: Basic Books.
- van der Klink, J. J. L. , Blonk, R. W. B. , Schene, A. H. , & van Dijk, F. J. H. (2001). The benefits of interventions for work-related stress. American Journal of Public Health, 91 , 270–276.
- Knight, B. G. , Silverstein, M. , McCallum, T. J. , & Fox, L. S. (2000). A sociocultural stress and coping model for mental health outcomes among African American caregivers in southern California . The Journals of Gerontology: Series B: Psychological Sciences and Social Sciences, 55B , 142–150.
- Kossek, E. E. , Thompson, R. J. , Lautsch, B. A. (2015). Balanced workplace flexibility: Avoiding the traps. California Management Review, 57 , 5–25.
- Kożusznik, M. , Rodriguez, I. , & Peiró, J. M. (2012). Cross-national outcomes of stress appraisal. Cross Cultural Management, 19 , 507–525.
- Kożusznik, M. , Rodriguez, I. , & Peiró, J. M. (2015). Eustress and distress climates in teams: Patterns and outcomes. International Journal of Stress Management, 22 , 1–23.
- Kristof-Brown, A. L. , Zimmerman, R. D. , & Johnson, E. C. (2005). Consequences of individuals’ fit at work: A meta-analysis of person-job, person-organization, person-group, and person-supervisor fit. Personnel Psychology, 58 , 281–342.
- LaMontagne, A. D. , Keegel, T. , Louie, A. M. , Ostry, A. , & Landsbergis, P. A. (2007). A systematic review of the job-stress intervention evaluation literature, 1990–2005. International Journal of Occupational and Environmental Health, 13 , 268–280.
- LaRocco, J. M. , Tetrick, L. E. , & Meder, D. (1989). Differences in perceptions of work environment conditions, job attitudes, and health beliefs among military physicians, dentists, and nurses. Military Psychology, 1 , 135–151.
- Lazarus, R. S. , & Folkman, S. (1984). Stress, appraisal, and coping . New York: Springer.
- Lazarus, R. S. , & Folkman, S. (1991). The concept of coping. In A. Monat & R. S. Lazarus (Eds.), Stress and coping: An anthology (3d ed.) (pp. 189–206). New York: Columbia University Press.
- LePine, J. A. , Podsakoff, N. P. , & LePine, M. A. (2005). A meta-analytic test of the challenge stressor-hindrance stressor framework: An explanation for inconsistent relationships among stressors and performance. Academy of Management Journal, 48 , 764–775.
- Lewin, K. (1936). Principles of topological psychology . New York: McGraw-Hill.
- Lewin K. (1951). Field theory in social science . New York: Harper and Row.
- Lewin, K. (1997). Resolving social conflicts & Field theory in social science . Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. Previously published in 1948 and 1951.
- Lin, B. C. , Kain, J. M. , & Fritz, C. (2013). Don’t interrupt me! An examination of the relationship between intrusions at work and employee strain. International Journal of Stress Management, 20 , 77–94.
- Liu, C. , & Li, H. (2017) Stressor and stressor appraisals: The moderating effect of task efficacy . Journal of Business and Psychology , 1–14.
- Liu, C. , Liu, Y. , Spector, P. E. , Shi, L. (2011). The interaction of job autonomy and conflict with supervisor in China and the United States: A qualitative and quantitative comparison. International Journal of Stress Management, 18 , 222–245.
- Liu, C. , Spector, P. E. , & Shi, L. (2007). Cross-national job stress: A quantitative and qualitative study. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 28 , 209–239.
- Luckhaupt, S. E. , Tak, S. , Calvert, G. M. (2010). The prevalence of short sleep duration by industry and occupational in the National Health Interview Survey. Sleep, 33 , 149–159.
- Luthans, F. , Youssef, C. M. , & Avolio, B. J. (2007). Psychological capital: Developing the human competitive edge . New York: Oxford University Press.
- Macan, T. H. (1994). Time management: Test of a process model. Journal of Applied Psychology, 79 , 381–391.
- Macan, T. H. , Shahani, C. , Dipboye, R. L. , & Philips, A. P. (1990). College students’ time management: Correlations with academic performance and stress. Journal of Educational Psychology, 82 , 760–768.
- Masuda, A. D. , Poelmans, S. A. Y. , Allen, T. D. , Spector, P. E. , Lapierre, L. M. , Cooper, C. L. , et al. (2012). Flexible work arrangements availability and their relationship with work-to-family conflict, job satisfaction, and turnover intentions: A comparison of three country clusters. Applied Psychology: An International Review, 61 , 1–29.
- McMahon, M. (2007). Think you might be addicted to email? You’re not alone . AOL.
- Monat, A. , & Lazarus, R. S. (Eds.). (1991). Stress and coping: An anthology (3d ed.). New York: Columbia University Press.
- Morimoto, H. , Shimada, H. , & Ozaki, K. (2013). Does stressor evaluation mediate sociocultural influence on coping selection? An investigation using Japanese employees. International Journal of Stress Management, 20 , 1–19.
- Narayanan, L. , Menon, S. , & Spector, P. E. (1999). A cross-cultural comparison of job stressors and reactions among employees holding comparable jobs in two countries. International Journal of Stress Management, 6 , 197–212.
- National Sleep Foundation (2005). Segment profiles . National Sleep Foundation.
- National Sleep Foundation (2013). How much sleep do adults need? . National Sleep Foundation.
- Nelson, D. L. , & Simmons, B. L. (2003). Health psychology and work stress: A more positive approach. In J. C. Quick & L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of Occupational Health Psychology (pp. 97–119). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Norris, P. A. , Fahrion, S. L. , & Oikawa, L. O. (2007). Autogenic biofeedback training in psychophysiological therapy and stress management. In P. M. Lehrer , R. L. Woolfolk , & W. E. Sime (Eds.), Principles and practices of stress management (3d ed., pp. 175–205). New York: Guilford.
- Ogawa, N. (2009). Stress, coping behavior, and social support in Japan and the United States. Dissertation Abstracts International Section A , 69 , 3802.
- Oksanen, K. , & Ståhle, P. (2013). Physical environment as a source for innovation: Investigating the attributes of innovative space. Journal of Knowledge Management, 17 , 815–827.
- Page, K. M. , & Vella-Brodrick, D. A. (2009). The “what,” “why” and “how” of employee well-being: A new model. Social Indicators Research, 90 , 441–458.
- Parasuraman, S. , & Cleek, M. A. (1984). Coping behaviors and managers’ affective reactions to role stressors . Journal of Vocational Behavior, 24 , 179–193.
- Parasuraman, S. , & Purohit, Y. S. (2000). Distress and boredom among orchestra musicians: The two faces of stress. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 5 , 74–83.
- Pawelski, J. O. (2016). Defining the “positive” in positive psychology: Part II. A normative analysis . Journal of Positive Psychology, 11 , 357–365.
- Pearlin, L. I. , & Schooler, C. (1978). The structure of coping . Journal of Health and Social Behavior, 19 , 2–21.
- Peeters, M. A. G. , & Rutte, C. G. (2005). Time management behavior as a moderator for the job demand-control interaction. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology , 1 , 64–75.
- Peters, L. H. , & O’Connor, E. J. (1980). Situational constraints and work outcomes: The influence of a frequently overlooked construct. Academy of Management Review , 5, 391–397.
- Peters, L. H. , & O’Connor, E. J. (1988). Measuring work obstacles: Procedures, issues, and implications. In F. D. Schoorman & B. Schneider (Eds.), Facilitating work effectiveness (pp. 105–123). Lexington, MA: Lexington Books.
- Polly, S. (2014, July 2). Workplace well-being is not an oxymoron . Positive Psychology News Daily .
- Quick, C. J. , Quick, J. D. , Nelson, D. L. , & Hurrell, J. J. (2003). Preventive stress management in organizations . Washington, DC: APA.
- Quillian-Wolever, R. E. , & Wolever, M. E. (2003). Stress management at work . In J. C. Quick & L. E. Tetrick (Eds.), Handbook of occupational health psychology (pp. 355–375). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Ragsdale, J. M. , Beehr, T. A. , Grebner, S. , & Han, K. (2011). An integrated model of weekday stress and weekend recovery of students. International Journal of Stress Management, 18 , 153–180.
- Richardson, K. M. , & Rothstein, H. R. (2008). Effects of occupational stress management intervention programs: A meta-analysis. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 13 , 69–93.
- Rodríguez, I. , Kozusznik, M. W. , & Peiró, J. M. (2013). Development and validation of the Valencia Eustress-Distress Appraisal Scale. International Journal of Stress Management, 20 , 279–308.
- Rothbaum, F. , Weisz, J. R. , & Snyder, S. S. (1982). Changing the world and changing the self: A two-process model of perceived control. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 42 , 5–37.
- Rotter, J. B. (1966). Generalized expectancies for internal versus external control of reinforcement. Psychological Monographs, 80 , 609.
- Rousseau, V. , & Aubé, C. (2010). Social support at work and affective commitment to the organization: The moderating effect of job resource adequacy and ambient conditions. Journal of Social Psychology, 150 , 321–340.
- Saunders, T. , Driskell, J. E. , Johnston, J. , & Salas, E. (1996). The effect of stress inoculation training on anxiety and performance. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 1 , 170–186.
- Schaubroeck, J. , Ganster, D. C. , Sime, W. E. , & Ditman, D. (1993). A field experiment testing supervisory role clarification. Personnel Psychology, 46 , 1–25.
- Selmer, J. (2002). Coping strategies applied by Western vs overseas Chinese business expatriates in China. International Journal of Human Resource Management, 13 , 19–34.
- Siegrist, J. (1996). Adverse health effects of high effort/low reward conditions. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 1 , 27–41.
- Siegrist, J. (2010). Effort-reward imbalance at work and cardiovascular diseases. International Journal of Occupational Medicine and Environmental Health, 23 , 279–285.
- Siegrist, J. , Dragano, N. , Nyberg, S. T. , Lunau, T. , Alfredsson, L. , Erbel, R. , et al. (2014). Validating abbreviated measures of effort-reward imbalance at work in European cohort studies: The IPD-Work consortium. International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health, 87 , 249–256.
- Sinha, B. K. , Willson, L. R. , & Watson, D. C. (2000). Stress and coping among students in India and Canada . Canadian Journal of Behavioural Science/Revue Canadienne Des Sciences Du Comportement , 32 (4), 218–225.
- Sinnott, J. , & Vatz, R. E. (2015, March 13). Maryland doesn’t trust state employees to manage their health . Baltimore Sun .
- Siu, O. L. , Cooper, C. L. , & Phillips, D. R. (2013, July 1). Intervention studies on enhancing work well-being, reducing burnout, and improving recovery experiences among Hong Kong health care workers and teachers . International Journal of Stress Management, 21 , 69–84.
- Sonnentag, S. (2012). Psychological detachment from work during leisure time: The benefits of mentally disengaging from work. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 21 , 114–118.
- Sørensen, O. H. , & Holman, D. (2014). A participative intervention to improve employee well-being in knowledge work jobs: A mixed-methods evaluation study. Work & Stress, 28 , 67–86.
- Spector, P. E. , Chen, P. Y. , & O’Connell, B. J. (2000). A longitudinal study of relations between job stressors and job strains while controlling for prior negative affectivity and strains. Journal of Applied Psychology, 85 , 211–218.
- Spector, P. E. , & Jex, S. M. (1998). Development of four self-report measures of job stressors and strains: Interpersonal Conflict at Work Scale, Organizational Constraints Scale, Quantitative Workload Inventory, and Physical Symptoms Inventory. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 3 , 356–367.
- State of Maryland . (n.d.). Wellness program frequently asked questions . Maryland.gov.
- Strentz, T. , & Auerbach, S. M. (1988). Adjustment to the stress of simulated captivity: Effects of emotion-focused versus problem-focused preparation on hostages differing in locus of control . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 55 , 652–660.
- Swanberg, J. E. , McKechnie, S. P. , Ojha, M. U. , & James, J. B. (2011). Schedule control, supervisor support and work engagement: A winning combination for workers in hourly jobs? Journal of Vocational Behavior, 79 , 613–624.
- Tarafdar, M. , Tu, Q. , Ragu-Nathan, B. S. , & Ragu-Nathan, T. , (2007). The impact of technostress on role stress and productivity. Journal of Management Information Systems, 24 , 301–328.
- Tepper, B. J. , & Henle, C. A. (2011). A case for recognizing distinctions among constructs that capture interpersonal mistreatment in work organizations . Journal of Organizational Behavior, 32 , 487–498.
- Tetrick, L. E. , & Winslow, C. J. (2015). Workplace stress management interventions and health promotion. Annual Review of Organizational Psychology and Organizational Behavior, 2 , 583–603.
- Thomas, D. C. , Au, K. , & Ravlin, E. C. (2003). Cultural variation and the psychological contract. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 24 , 451–471.
- Toker, S. , Shirom, A. , Melamed, S. , & Armon, G. (2012). Work characteristics as predictors of diabetes incidence among apparently healthy employees. Journal of Occupational Health Psychology, 17 , 259–267.
- Velez, B. L. , Moradi, B. , & Brewster, M. E. (2013). Testing the tenets of minority stres theory in workplace contexts. Journal of Counseling Psychology, 60 , 532–542.
- Verquer, M. L. , Beehr, T. A. , & Wagner, S. H. (2003). A meta-analysis of relations between person–organization fit and work attitudes. Journal of Vocational Behavior, 63 , 473–489.
- Villani, D. , Grassi, A. , Cognetta, C. , Toniolo, D. , Cipresso, P. , & Riva, G. (2013). Self-help stress management training through mobile phones: An experience with oncology nurses. Psychological Services , 10 , 315–322.
- Vischer, J. C. (2007). The effects of the physical environment on job performance: Towards a theoretical model of workspace stress. Stress & Health, 23 , 175–184.
- Wasti, S. A. , & Cortina, L. M. (2002). Coping in context: Sociocultural determinants of responses to sexual harassment . Journal of Personality and Social Psychology , 83, 394–405.
- Willert, M. V. , Thulstrup, A. M. , Hertz, J. , & Bonde, J. P. (2010). Sleep and cognitive failures improved by a three-month stress management intervention . International Journal of Stress Management, 17 , 193–213.
- Xiao Q. , Ottosson I. , & Carlsson I. (2013). Stressors and coping strategies in Chinese and Swedish students at a Swedish university. Chinese Journal of Clinical Psychology, 21 , 309–312.
Related Articles
- Work and Family
- Organizational Climate and Culture
- Physical Activity and Stress Reactivity
- The Roles of Psychological Stress, Physical Activity, and Dietary Modifications on Cardiovascular Health Implications
- Inflammation as a Biomarker Method in Lifespan Developmental Methodology
- Stress and Coping Theory Across the Adult Lifespan
- Occupational Health Psychology
Printed from Oxford Research Encyclopedias, Psychology. Under the terms of the licence agreement, an individual user may print out a single article for personal use (for details see Privacy Policy and Legal Notice).
date: 28 August 2024
- Cookie Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
- [195.158.225.244]
- 195.158.225.244
Character limit 500 /500
A Systematic Review of Workplace Stress and Its Impact on Mental Health and Safety
- Conference paper
- First Online: 02 December 2023
- Cite this conference paper

- Gabriella Maria Schr Torres 12 ,
- Jessica Backstrom 12 &
- Vincent G. Duffy 12
Part of the book series: Lecture Notes in Computer Science ((LNCS,volume 14055))
Included in the following conference series:
- International Conference on Human-Computer Interaction
768 Accesses
4 Citations
Workplace stress and health are important subsets of the safety engineering field. Engineers need to maintain physical, emotional, and mental health to be productive and safe employees, which is beneficial to their employers through the reduction of accidents. Besides the human element, which may involve injury, death, or other lasting physical or mental consequences, accidents cost companies time, money, and valuable resources spent on extensive litigation. This paper focuses on mental health within the context of workplace stress since the globally felt adverse effects of the COVID-19 pandemic have brought high priority to research on identifying and combating mental health problems. While most mental health research focuses on healthcare professionals, our contribution is the extrapolation of this research to engineering. A systemic literature review was performed, which consisted of gathering data, using multiple bibliometric software, and providing discussion and conclusions drawn from the metadata. The software utilized for analysis included Vicinitas, Scopus, Google n-gram and Google Scholar, VOSviewer, Scite.ai, CiteSpace, BibExcel, Harzing, and MaxQDA. The original keywords included “workplace stress”, “mental health”, and “engineering,” but our analysis revealed additional trending terms of mindfulness, nursing, and COVID-19. Our findings showed that workplace stress is experienced throughout multiple industries and causes significant harm to employees and their organizations. There are practical solutions to workplace stress studied in nursing and construction that can be applied to other fields that need intervention.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Influence of psychosocial safety climate on occupational health and safety: a scoping review

Occupational stress among workers in the health service in Zimbabwe: causes, consequences and interventions

Workplace Stress and Health: Insights into Ways to Assist Healthcare Workers During COVID-19
Goetsch, D.: Chapter 11: stress and safety. In: Occupational Safety and Health for Technologists, Engineers, and Managers, Ninth, pp. 243–55. New York, Pearson (2019)
Google Scholar
Brauer, R.: Section 31–6: job stress and other stresses in chapter 31: human behavior and performance in safety. In: Safety and Health for Engineers, Third, pp. 921–24. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley (2016)
Sallinen, M., Kecklund, G.: Shift work, sleep, and sleepiness differences betwen shift schedules and systems. Scandanavian J. Work, Environ. Health 36 (2), 121–133 (2010)
Article Google Scholar
Moustafa, A.: Mental Health Effects of COVID-19. Elsevier, London (2021)
Latino, F., Cataldi, S., Fischetti, F.: Effects of an 8-week yoga-based physical exercise intervention on teachers’ burnout. Sustain. (Switzerland) 13 (4), 1–16 (2021). https://doi.org/10.3390/su13042104
Darling, E.L., et al.: A mixed-method study exploring barriers and facilitators to midwives’ mental health in ontario. BMC Women’s Health 23 (155) (2013). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-023-02309-z
Ayalp, G.G., Serter, M., Metinal, Y.B., Tel, M.Z.: Well-being of construction professionals: modelling the root factors of job-related burnout among civil engineers at contracting organisations. In: Advances in Sociology Research, vol. 40, pp. 1–38 (2023)
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH). 2022. Healthcare Workers: Work Stress & Mental Health. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. 1 Dec 2022. https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/healthcare/workstress.html
University of Maryland. 2023. Systematic Review. University Libraries. 12 April 2023. https://lib.guides.umd.edu/SR/welcome
World Health Organization (WHO). 2022. “Mental Health.” WHO Newsroom. 17 June 2022. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/mental-health-strengthening-ourresponse
Wasser, J.: NASA for Kids: Intro to Engineering. National Geographic. 27 Sept 2022. https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/nasa-kids-intro-engineering/
Borenstein, J.: 2020. Stigma, Prejudice, and Discrimination Against People with Mental Illnesses. American Psychiatric Association. Aug 2020. https://www.psychiatry.org/patients-families/stigma-and-discrimination
Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). 2021. A Brief History of the Origin of Ergonomics and Human Factors. Emergency Services Ergonomics and Wellness. 8 Feb 2021. https://www.usfa.fema.gov/a-z/health-safety-wellness/ergonomics/ch1-origin-ergonomics-human-factors.html
Bell, K.: “The Mental Health Systems Act of 1980.” Documents to the People. 2022. https://journals.ala.org/index.php/dttp/article/view/7933/11034
Bartlett, L., Lovell, P., Otahal, P., Sanderson, K.: Acceptability, feasibility, and efficacy of a workplace mindfulness program for public sector employees: a pilot randomized controlled trial with informant reports. Mindfulness 8 (3), 639–654 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-016-0643-4
Allexandre, D., Bernstein, A.M., Walker, E., Hunter, J., Roizen, M.F., Morledge, T.J.: A webbased mindfulness stress management program in a corporate call center. J. Occup. Environ. Med.up. Environ. Med. 58 (3), 254–264 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1097/JOM.0000000000000680
Larsen, R.C.: Workers’ compensation stress claims: Workplace causes and prevention. Psychiatr. Ann. 25 , 234–237 (1995). https://doi.org/10.3928/0048-5713-19950401-10
Cheung, T., Yip, P.S.F.: Depression, anxiety and symptoms of stress among Hong Kong nurses: a cross-sectional study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health (2015). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph120911072
Cheung A.T., Ho, L.L.K., Li, W.H.C., Chung, J.O.K., Smith G.D.: Psychological distress experienced by nurses amid the fifth wave of the COVID-19 pandemic in Hong Kong: a qualitative study, Front. Public Health 10 , 1023302 (2023). https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.1023302
Mansoor, A.E.R., O’Neil, C.A., McDonald, D., Fraser, V.J., Babcock, H.M., Kwon, J.H.: Knowledge, beliefs, and practices related to coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection and vaccination in healthcare personnel working at nonacute care facilities. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 44 (10), 1657–1662 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2023.45
Restauri, N., Sheridan, A.D.: Burnout and posttraumatic stress disorder in the Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: intersection, impact, and interventions. J. Am. Coll. Radiol. 17 (7), 921–926 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2020.05.021
Enshassi, A., El-Rayyes, Y., Alkilani, S.: Job stress, job burnout and safety performance in the palestinian construction industry. J. Financ. Manag. Prop. Constr. 20 (2), 170–187 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1108/JFMPC-01-2015-0004
Chen, S.W., Wang, P.C., Hsin, P.L., Oates, A., Sun, I.W., Liu, S.I.: Job stress models, depressive disorders and work performance of engineers in microelectronics industry. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Healthnt. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 84 (1), 91–103 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-010-0538-y
Saleh, S.D., Desai, K.: An empirical analysis of job stress and job satisfaction of engineers. J. Eng. Tech. Manage. 7 (1), 37–48 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1016/0923-4748(90)90024-2
Auster, E.R., Ekstein, K.L.: Professional women’s mid-career satisfaction: An empirical exploration of female engineers. Women Manag. Rev. 20 (1), 4–23 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1108/09649420510579540
National Science Foundation. SCH: Detecting and mapping stress patterns across space and time: Multimodal modeling of individuals in real-world physical and social work environments. Award Number 2204942, 22 Aug 2022
National Science Foundation. CHS: Medium: collaborative research: managing stress in the workplace: Unobtrusive Monitoring and Adaptive Interventions. Award Number 1704636, 21 June 2017
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, 47906, USA
Gabriella Maria Schr Torres, Jessica Backstrom & Vincent G. Duffy
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding authors
Correspondence to Gabriella Maria Schr Torres or Jessica Backstrom .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
Chongqing University, Chongqing, China
Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA
Vincent G. Duffy
Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH), Heraklion, Crete, Greece
Margherita Antona
University of Crete and Foundation for Research and Technology - Hellas (FORTH), Heraklion, Crete, Greece
Constantine Stephanidis
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this paper
Cite this paper.
Torres, G.M.S., Backstrom, J., Duffy, V.G. (2023). A Systematic Review of Workplace Stress and Its Impact on Mental Health and Safety. In: Gao, Q., Zhou, J., Duffy, V.G., Antona, M., Stephanidis, C. (eds) HCI International 2023 – Late Breaking Papers. HCII 2023. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 14055. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48041-6_41
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-031-48041-6_41
Published : 02 December 2023
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-031-48040-9
Online ISBN : 978-3-031-48041-6
eBook Packages : Computer Science Computer Science (R0)
Share this paper
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Work-related stress: a brief review
Affiliation.
- 1 Centre for Nursing Research and Practice Development, Faculty of Health, Canterbury Christ Church University College, Canterbury, Kent CT1 1QU, England.
- PMID: 11811093
- DOI: 10.1177/146642400112100406
Work-related stress is a serious and growing problem in the UK and as such, is regarded as a significant health and safety issue. It is vital that this issue is addressed and that action is taken to address the problems that this may create both for individuals and the organisations in which individuals work. This paper reviews the concept of work-related stress showing how its deleterious impact may exert both direct and indirect effects on the workforce thus affecting both individual and organisational effectiveness. It also shows how individual and organisational factors may contribute to the development of occupational stress. However, since not all the stress which affects people at work is caused by the workplace, the home/work interface is also considered. The paper concludes by considering how work-related stress may be managed.
PubMed Disclaimer
Similar articles
- Work-related stress: implications for the employer. Grayham DA. Grayham DA. J R Soc Health. 1997 Apr;117(2):81-7. doi: 10.1177/146642409711700204. J R Soc Health. 1997. PMID: 9223846
- The changing nature of work: workplace stress and strategies to deal with it. Cooper CL. Cooper CL. Med Lav. 2006 Mar-Apr;97(2):132-6. Med Lav. 2006. PMID: 17017336
- Increasing concern is expressed over stress in the workplace. How far should stress management be a responsibility of individuals or organizations? Wynne T. Wynne T. J Nurs Manag. 1993 Nov;1(6):293-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2834.1993.tb00230.x. J Nurs Manag. 1993. PMID: 26559036 No abstract available.
- Policy perspectives on occupational stress. O'Keefe LC, Brown KC, Christian BJ. O'Keefe LC, et al. Workplace Health Saf. 2014 Oct;62(10):432-8; quiz 439. doi: 10.3928/21650799-20140813-02. Epub 2014 Aug 20. Workplace Health Saf. 2014. PMID: 25139784 Review.
- Older women, work and health. Payne S, Doyal L. Payne S, et al. Occup Med (Lond). 2010 May;60(3):172-7. doi: 10.1093/occmed/kqq030. Occup Med (Lond). 2010. PMID: 20423947 Review.
- Effectiveness of Essence of Chicken in Improving Cognitive Function in Young People Under Work-Related Stress: A Randomized Double-Blind Trial. Chan L, Wang HM, Chen KY, Lin YC, Wu PJ, Hsieh WL, Chen YR, Liu CP, Tsai HY, Chen YR, Chang HH, Hsieh YC, Hu CJ. Chan L, et al. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 May;95(19):e3640. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003640. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27175681 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
- Effort-reward imbalance and physical health among Japanese workers in a recently downsized corporation. Irie M, Tsutsumi A, Shioji I, Kobayashi F. Irie M, et al. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2004 Aug;77(6):409-17. doi: 10.1007/s00420-004-0533-2. Epub 2004 Aug 13. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 2004. PMID: 15316792
Publication types
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
- MedlinePlus Health Information
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Med Res
- v.146(4); 2017 Oct
Workplace stress: A neglected aspect of mental health wellbeing
Pallab k. maulik.
Deputy Director and Head of Research, The George Institute for Global Health, New Delhi 110 025, India ni.gro.etutitsniegroeg@kiluamp
Workplace stress is defined by the World Health Organization as ‘the response people may have when presented with work demands and pressures that are not matched to their knowledge and abilities and which challenge their ability to cope’, and elaborated that it can be caused ‘by poor work organization (the way we design jobs and work systems, and the way we manage them), by poor work design ( e.g ., lack of control over work processes), poor management, unsatisfactory working conditions and lack of support from colleagues and supervisors’ 1 . While workplace stress, stigma and attitudes towards employees suffering from stress or mental illness have been researched and interventions developed to address them better, globally 2 , 3 , it still remains an oft-neglected aspect across different industries and countries, including India, and only a few of the learnings are actually implemented.
International laws have been in force for many decades to protect human rights of employees at workplace, and the key ones being Article 23 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights 4 , Articles 6 and 7 of the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights 5 and Article 27 of United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities 6 . However, the execution of policies is variable and often suboptimal. Moreover, low- and middle-income countries where one has the largest population in working age groups, continue to lag behind in conducting or identifying suitable interventions, and often do not have adequate policies in place to prevent discrimination against employees with mental disorders 7 .
Workplace-related stress – a reality that needs to be addressed through evidence-based interventions
Brouwers et al 8 conducted a cross-sectional study across 35 countries including India and reported that about two-third of employees who had suffered from depression either faced discrimination at work or faced discrimination while applying for new jobs. This study also found that both anticipated and perceived discrimination was more in high-income countries compared to lower-income countries. Both perceived and anticipated discrimination are major causes for people suffering silently at the workplace and not seeking proper care. This by itself can be a major issue when seeking care for mental disorders as it adds to stigma related to help-seeking and increases treatment gap - the gap in the proportion of people who suffer from mental disorders and the proportion of them who actually receive adequate mental health care. If organizations are made aware of this, and they encourage staff to seek appropriate mental health care as per need, then it will not only lead to improved care for persons with mental disorders, but also to a situation where employees are comfortable discussing their mental health issues with appropriate staff and take actions early on, so that more severe mental disorders do not manifest.
Another risk factor is that besides depression or anxiety being an outcome of stress, physical disorders such as hypertension and diabetes can also be caused due to stress. While research has established the two-way link between stress and these physical disorders 9 , 10 , organizations need to realize this and encourage staff to maintain a good work-life balance. This by itself can be a difficult task to implement given deadlines, having a competitive edge, sustaining growth and one's personal need to earn more by doing overtime. Thus, organizations need to have guidelines about working hours based on good industrial practices and take measures to enforce these routinely.
Sexual harassment and bullying at workplace is another workplace-related stress that can happen at any organization. Both genders could be affected by these, but often women and those lower in the hierarchy are at increased risk. Organizations should be cognizant of this and take active measures to ensure that workplace is a safe and secure place for every worker. In India, there are specific legal provisions to ensure safety at workplace ( http://labour.gov.in/policies/safety-health-and-environment-work-place ), and there are specific laws to prevent sexual harassment of women ( http://indiacode.nic.in/acts-in-pdf/142013.pdf ). Strict guidelines and processes are advocated, and every organization should have identified committees to handle any such issue.
While extant research has tended to focus on alleviation of symptoms and risk factors associated with workplace-related mental disorders, less emphasis has been placed on gathering evidence on how mental disorders affect performance and absenteeism and how interventions have resulted in improvement of work performance and absenteeism 3 . Thus, more research is needed to gather evidence on the cost-effectiveness of interventions and the cost of mental disorder-related loss of productivity on the larger community. This is relevant to all countries and becomes specifically significant when each employment sector tries to become more competitive and wants to increase productivity while at the same time tries to keep their cost to a minimum. In low- and middle-income countries, there are additional needs to ( i ) conduct basic epidemiological studies to understand the prevalence of workplace-related mental disorders and specific risk factors associated with different employment sectors, ( ii ) understand what kind of systems are being put in place by different sectors to manage them, and ( iii ) to what degree are existing laws being followed and implemented, and what organizational restructuring is needed to improve the situation. Current evidence suggests that no single intervention can work in isolation and it is recommended to have a package of interventions at organization level which could be accessed by those in need 3 . Some interventions that were specifically found to be useful were enhancing employee control, promoting physical activity, cognitive behaviour therapy for stress management and problem-focused return to work programmes. On the contrary, counselling and debriefing following trauma were not effective 3 and any exposure to trauma should be followed by provision of psychological first aid and formal psychological support by trained professionals. Workplace screening for mental disorders followed by access to basic mental health services has been found to be effective, but could lead to a potential increase in anxiety levels in those who are screened as false positives, so routine screening at workplace is not recommended 3 .
Guidelines to improve workplace culture and reduce stress
The World Health Organization has outlined key factors related to stress at workplace and advocated guidelines to redeem them 11 . Some factors that cause increased stress at workplace include ‘workload (both excessive and insufficient work), lack of participation and control in the workplace, monotonous or unpleasant tasks, role ambiguity or conflict, lack of recognition at work, inequity, poor interpersonal relationships, poor working conditions, poor leadership and communication and conflicting home and work demands’ 11 . This document also outlined guidelines to improve the situation and enumerated four key steps which are not only relevant to individual organizations, but to other stakeholders also, such as trade unions, employees, government and employees 11 .
Step 1 : Analyzing the mental health issues - As a first step, it is essential to have a clear understanding of not only the prevalence/incidence and risk factors associated with workplace stress, but also a better knowledge about the cost implications to an organization in terms of lost productivity. This is an exercise that can be done at individual organizations, at specific employment sector level in specific regions or across regions. This may need gathering new data through surveys or collating data available with the human resources or anonymized health records.
Step 2 : Developing the policy - A policy can be developed once the initial knowledge gained through the first step is available. The primary objective of such a policy should be to address concerns of all stakeholders and adhere to the organizations vision and mission. This should involve multiple meetings with different stakeholders to identify key components that need to be addressed. This engagement should be a continuous process throughout the development and execution of the policy.
Step 3 : Developing strategies to implement the policy - While implementing the policies, care should be taken to identify the key strategies that need to be implemented, the processes that need to be in place to implement such strategies, targets to be achieved and timelines that need to be adhered to while implementing the strategies. Finally, any additional budgetary allocations or training required to implement the policies, need to be made available.
Step 4 : Implementing and evaluating the policy - The implementation of any strategy will need collaboration and clear buy-in from all stakeholders. For some strategies, one might need to have a small demonstration project to start off, and based on the results tweak the strategies and then scale it up to a larger forum. Before implementing a policy, information should be disseminated widely either through a formal launch meeting or individual organizations’ dissemination network. For example, major government level policies that impact large number of employees or employers could have a launch meeting, whereas policies affecting only one organization with limited staff could be disseminated through office emails. This would enable everyone to be aware of the policies. One major drawback of many policies is that they lack a formal evaluation. This should be built into the system and appropriately funded from the outset. Specific guidelines about how to monitor and evaluate the policies should be in place at the time of the launch of the policies and conducted as per agreed timelines.
Role of government
The government should play a key role in ensuring that policies are in place that address workplace stress. Not only should the government identify vulnerable populations such as women, children, persons with disability at different workplaces, but also ensure that every sector has appropriate safeguards to protect the rights of all employees including vulnerable populations. The government should also monitor how different sectors are performing with respect to workplace stress and have additional strategies in place to address issues related to sectors which have specifically higher level of physical or psychological stress such as mines, factories, health sector, among others. Legal mechanisms should be in place to enforce laws and regulate them and penalize organizations which flout existing laws. The legal system should provide avenues that can be accessed both by employers and employees alike. The aim should be that workplace is seen as a fair and non-discriminatory zone as far as stress, and mental ill-health are concerned.
Workplace stress and associated mental ill-health is a fact that every employer and employee lives with on a daily basis. However, it often is the case that neither are aware of the issues fully and nor are well informed about its ramifications. Although laws are present in most countries to ensure that the rights of persons suffering from mental disorders related to workplace stress are safeguarded, often such are not executed or regulated effectively, leading to a situation where persons with mental disorders are not able to verbalize their problems and suffer silently - a situation that ultimately leads to increasing mental health-related disability that affects productivity. In this year, when workplace stress is being identified globally as a cause for concern, all stakeholders should take additional notice of its importance and see what needs to be done to improve the situation on the ground and make workplace a safer and healthier place for all.
Acknowledgment
The author is an intermediate fellow of the Wellcome Trust/DBT India Alliance.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Work-Related Stress
- Most Cited Papers
- Most Downloaded Papers
- Newest Papers
- Last »
- Films In Management Classroom Follow Following
- Organizational Effectiveness Follow Following
- Work-life issues Follow Following
- Stress and Burnout Follow Following
- Work-Family Conflict Follow Following
- Industrial/Organizational Psychology Follow Following
- Occupational Safety and Health Follow Following
- Job Search Follow Following
- Occupational Health Psychology Follow Following
- Rational Choice Theory Follow Following
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- Academia.edu Journals
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
Research on the Theory of Soil Additional Stress and Principal Stress Axis Deflection During Shield Tunneling
32 Pages Posted: 26 Aug 2024
Chenyang He
Chongqing Jiaotong University
Shield tunneling inevitably disturbs the surrounding soil, primarily causing changes in strain, stress states, and stress paths. Using Mindlin's solution from elasticity theory and the mirror method, and considering construction parameters such as face pressure, shield friction, and soil loss, a revised calculation expression for the additional stress induced in the soil during shield tunneling was derived. By calculating the additional soil stress using the parameters of the Hangzhou Metro Kanji section and comparing it with model experiments, the rationality of the calculations was validated, revealing that the surrounding soil exhibits a normal and S-shaped distribution along the tunneling direction. Additionally, using transition matrix orthogonal transformation, the three-dimensional principal stress paths and principal stress axis deflection near the vault, haunch, and invert during shield tunneling were obtained.Analysis revealed that under the combined action of three factors, the shear stress component of the additional stress is 1/3 to 1/2 of the normal stress, indicating a significant impact. During shield tunneling, the deflection angle of the principal stress axis at the vault changes between 90° and 180°, with little change in the principal stress value. The principal stress value at the invert rapidly increases from 0.25 kPa to 8 kPa, with a small degree of principal stress axis deflection. Both the principal stress variation and the principal stress axis deflection are minimal at the haunch. At the foot, the deflection angles of the major and minor principal stress axes are significant, but the principal stress value changes are minor. At the haunch, the deflection angle of the major principal stress is significant, while the value change of the minor principal stress is considerable.
Keywords: Shield tunneling, face pressure, shield friction, soil loss, stress paths, principal stress axis deflection
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Chenyang He (Contact Author)
Chongqing jiaotong university ( email ).
Xuefu Avenue Chongqing China
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, mechanical engineering ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Geophysics eJournal
Earth-surface processes ejournal, computational earth science ejournal.
Subscribe to this free journal for more curated articles on this topic
Environmental Engineering eJournal

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Abstract and Figures. Work-related stress is an ordinary reaction that occurs when the work weight progress toward becoming excessive. Occupational wellbeingimpact to the soundness of ...
Work stress and employee performance. From a psychological perspective, work stress influences employees' psychological states, which, in turn, affects their effort levels at work (Lu, 1997; Richardson and Rothstein, 2008; Lai et al., 2022 ). Employee performance is the result of the individual's efforts at work (Robbins, 2005) and thus is ...
The conceptualisation of work stress is of crucial importance when developing interventions for the workplace. Work-related stress is defined as 'a harmful reaction that people have to undue pressures and demands placed on them at work'. 1 As many as 440 000 people in the UK complain of work-related stress, depression or anxiety that makes them ill; nearly 9.9 million work days were lost ...
Work-task completion can be a source of stress, particularly under time pressure or when results impact one's reputation (Cavanaugh et al. 2000; Timotius and Octavius 2022). In such demanding ...
This review identified the types of work-related stress, its stressors and coping strategies used by. various occupations across Asia. As stipulated in the review results, most studies conducted ...
Methods. A multi-site, cross-sectional study was conducted to survey employees across four worksites participating in a WorkWell KS Well Being workshop to assess levels of stress and productivity. Stress was measured by the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) and productivity was measured by the Health and Work Questionnaire (HWQ).
While social and traditional media discussed work-related stress and burnout during the COVID-19 pandemic, there was little empirical research to examine the phenomena except for a few high-level surveys (Brynjolfsson et al., 2020; Center for National Health Statistics, 2020; CVS Health, 2020; Petterson et al., 2020).Although the quickly forced shift to working from home was brought on by ...
Aim Work is a central area of human life, and work-associated stress can affect health over a long period of time. From a health sociological perspective, it was assumed in this paper that education as a resource is able to support the management of stress(ors) and thus has a positive impact on health. Subject and methods This contribution deals with the research question of whether more ...
Based on this method, in model 4, mental health is significantly positively related to employee performance (β = 0.343, p < 0.001), and no significant correlation exists between work stress and employee performance (β = −0.016, p > 0.05). Hence, mental health fully mediates the relationship between work stress and employee performance.
Work-related stress and its detrimental effects on human health have rapidly increased during the past several years. It causes many different stress reactions, related diseases and unhealthy behavior among workers, but especially women workers. Thus, the aim of this study was to examine the effects of the work-related stress model based Workplace Mental Health Promotion Programme on the job ...
Work stress is a generic term that refers to work-related stimuli (aka job stressors) that may lead to physical, behavioral, or psychological consequences (i.e., strains) that affect both the health and well-being of the employee and the organization. Not all stressors lead to strains, but all strains are a result of stressors, actual or perceived.
Chor, Faerstein and Werneck, 2004). According to Hsieh, Huang & Su (2004), Stress means the workers' in ability to adjust to work and, as a result, includes. some natural and psychologi cal ...
In this paper, we review the role of mindfulness-based practices and of contact with nature in coping with stressful situations at work, and we propose a model of coping with work-related stress by using mindfulness in nature-based practices. Keywords: work-related stress, mindfulness, nature, review. Go to:
Studying work-related stress in organisations the Demand-Control-model (Karasek, Citation 1979; Karasek & Theorell, Citation 1990) is often used. This model depicts a broad spectrum of health-related work situations based on two factors: Demands - the work-related difficulties that the employees need to cope with. This includes physical ...
Social work is acknowledged to be a high-stress profession that involves working with people in distressing circumstances and complex life situations such as those experiencing abuse, domestic violence, substance misuse, and crime (Stanley & Mettilda, 2016).It has been observed that important sources of occupational stress for social workers include excessive workload, working overtime ...
The top terms were "stress," "work," and "covid," emphasizing the impact of the pandemic on workplace stress. "Physicians" and "medical" were also leading terms, supporting the conclusion that much of the research on workplace stress and mental health has been performed in the context of the healthcare industry (Fig. 15).
Pressure is part and parcel of all work and helps to keep us motivated. But excessive pressure can lead to stress which undermines performance, is costly to employers and can make people ill. Research reveals that many working days are lost to stress, depression and anxiety. Work-related stress costs a huge burden to the society.
The study's respondents discussed staff shortages, coworker conflict and interactions, strategies to mitigate stress, impacts of work-related stress and managing stress and burnout in the workplace. Chang noted that the study's findings suggest an urgent need for programmatic changes within health care organizations to address burnout.
Google Scholar by using key words such as ―stress‖, ―work s tress‖, ―occupational stress‖, ―job stress‖ etc. All the papers were searched from January 1993 to April 2017.
Work-related stress is a serious and growing problem in the UK and as such, is regarded as a significant health and safety issue. ... 1 Centre for Nursing Research and Practice Development, Faculty of Health, ... This paper reviews the concept of work-related stress showing how its deleterious impact may exert both direct and indirect effects ...
Guidelines to improve workplace culture and reduce stress. The World Health Organization has outlined key factors related to stress at workplace and advocated guidelines to redeem them 11.Some factors that cause increased stress at workplace include 'workload (both excessive and insufficient work), lack of participation and control in the workplace, monotonous or unpleasant tasks, role ...
Work - related Stress among Healthcare Workers in Ugep, Yakurr Local Government Area, Cross River State, Nigeria. Work Related Stress (WRS) is the harmful physical and emotional responses that occur when the requirements of job do not match the capabilities, resources, or needs of the worker in the work environment.
To verify the mediating effect of mental health on the. relationship between work stress and employee performance, we used the method introduced by Kenny et al.1998), which is described as ...
Abstract. Shield tunneling inevitably disturbs the surrounding soil, primarily causing changes in strain, stress states, and stress paths. Using Mindlin's solution from elasticity theory and the mirror method, and considering construction parameters such as face pressure, shield friction, and soil loss, a revised calculation expression for the additional stress induced in the soil during ...
The motivation behind this paper was to review workplace stress. A number of various articles, from 2010 to 2020 have been investigated. The findings of the survey reveal that work environment ...