

Steps for Writing a History Paper
Writing a history paper is a process. Successful papers are not completed in a single moment of genius or inspiration, but are developed over a series of steps. When you first read a paper prompt, you might feel overwhelmed or intimidated. If you think of writing as a process and break it down into smaller steps, you will find that paper-writing is manageable, less daunting, and even enjoyable. Writing a history paper is your opportunity to do the real work of historians, to roll up your sleeves and dig deep into the past.
What is a History paper?
History papers are driven by arguments. In a history class, even if you are not writing a paper based on outside research, you are still writing a paper that requires some form of argument. For example, suppose your professor has asked you to write a paper discussing the differences between colonial New England and colonial Virginia. It might seem like this paper is straightforward and does not require an argument, that it is simply a matter of finding the “right answer.” However, even here you need to construct a paper guided by a larger argument. You might argue that the main differences between colonial New England and Virginia were grounded in contrasting visions of colonization. Or you might argue that the differences resulted from accidents of geography or from extant alliances between regional Indian groups. Or you might make an argument that draws on all of these factors. Regardless, when you make these types of assertions, you are making an argument that requires historical evidence. Any history paper you write will be driven by an argument demanding evidence from sources.
History writing assignments can vary widely–and you should always follow your professor’s specific instructions–but the following steps are designed to help no matter what kind of history paper you are writing. Remember that the staff of the History Writing Center is here to assist you at any stage of the writing process.
- Sometimes professors distribute prompts with several sub-questions surrounding the main question they want you to write about. The sub-questions are designed to help you think about the topic. They offer ideas you might consider, but they are not, usually, the key question or questions you need to answer in your paper. Make sure you distinguish the key questions from the sub-questions. Otherwise, your paper may sound like a laundry list of short-answer essays rather than a cohesive argument. A helpful way to hone in on the key question is to look for action verbs, such as “analyze” or “investigate” or “formulate.” Find such words in the paper prompt and circle them. Then, carefully consider what you are being asked to do. Write out the key question at the top of your draft and return to it often, using it to guide you in the writing process. Also, be sure that you are responding to every part of the prompt. Prompts will often have several questions you need to address in your paper. If you do not cover all aspects, then you are not responding fully to the assignment. For more information, visit our section, “Understanding Paper Prompts.”
- Before you even start researching or drafting, take a few minutes to consider what you already know about the topic. Make a list of ideas or draw a cluster diagram, using circles and arrows to connect ideas–whatever method works for you. At this point in the process, it is helpful to write down all of your ideas without stopping to judge or analyze each one in depth. You want to think big and bring in everything you know or suspect about the topic. After you have finished, read over what you have created. Look for patterns or trends or questions that keep coming up. Based on what you have brainstormed, what do you still need to learn about the topic? Do you have a tentative argument or response to the paper prompt? Use this information to guide you as you start your research and develop a thesis.
- Depending on the paper prompt, you may be required to do outside research or you may be using only the readings you have done in class. Either way, start by rereading the relevant materials from class. Find the parts from the textbook, from the primary source readings, and from your notes that relate to the prompt. If you need to do outside research, the UCLA library system offers plenty of resources. You can begin by plugging key words into the online library catalog. This process will likely involve some trial and error. You will want to use search terms that are specific enough to address your topic without being so narrow that you get no results. If your keywords are too general, you may receive thousands of results and feel overwhelmed. To help you narrow your search, go back to the key questions in the essay prompt that you wrote down in Step 1. Think about which terms would help you respond to the prompt. Also, look at the language your professor used in the prompt. You might be able to use some of those same words as search terms. Notice that the library website has different databases you can search depending on what type of material you need (such as scholarly articles, newspapers, books) and what subject and time period you are researching (such as eighteenth-century England or ancient Rome). Searching the database most relevant to your topic will yield the best results. Visit the library’s History Research Guide for tips on the research process and on using library resources. You can also schedule an appointment with a librarian to talk specifically about your research project. Or, make an appointment with staff at the History Writing Center for research help. Visit our section about using electronic resources as well.
- By this point, you know what the prompt is asking, you have brainstormed possible responses, and you have done some research. Now you need to step back, look at the material you have, and develop your argument. Based on the reading and research you have done, how might you answer the question(s) in the prompt? What arguments do your sources allow you to make? Draft a thesis statement in which you clearly and succinctly make an argument that addresses the prompt. If you find writing a thesis daunting, remember that whatever you draft now is not set in stone. Your thesis will change. As you do more research, reread your sources, and write your paper, you will learn more about the topic and your argument. For now, produce a “working thesis,” meaning, a thesis that represents your thinking up to this point. Remember it will almost certainly change as you move through the writing process. For more information, visit our section about thesis statements. Once you have a thesis, you may find that you need to do more research targeted to your specific argument. Revisit some of the tips from Step 3.
- Now that you have a working thesis, look back over your sources and identify which ones are most critical to you–the ones you will be grappling with most directly in order to make your argument. Then, annotate them. Annotating sources means writing a paragraph that summarizes the main idea of the source as well as shows how you will use the source in your paper. Think about what the source does for you. Does it provide evidence in support of your argument? Does it offer a counterpoint that you can then refute, based on your research? Does it provide critical historical background that you need in order to make a point? For more information about annotating sources, visit our section on annotated bibliographies. While it might seem like this step creates more work for you by having to do more writing, it in fact serves two critical purposes: it helps you refine your working thesis by distilling exactly what your sources are saying, and it helps smooth your writing process. Having dissected your sources and articulated your ideas about them, you can more easily draw upon them when constructing your paper. Even if you do not have to do outside research and are limited to working with the readings you have done in class, annotating sources is still very useful. Write down exactly how a particular section in the textbook or in a primary source reader will contribute to your paper.
- An outline is helpful in giving you a sense of the overall structure of your paper and how best to organize your ideas. You need to decide how to arrange your argument in a way that will make the most sense to your reader. Perhaps you decide that your argument is most clear when presented chronologically, or perhaps you find that it works best with a thematic approach. There is no one right way to organize a history paper; it depends entirely on the prompt, on your sources, and on what you think would be most clear to someone reading it. An effective outline includes the following components: the research question from the prompt (that you wrote down in Step 1), your working thesis, the main idea of each body paragraph, and the evidence (from both primary and secondary sources) you will use to support each body paragraph. Be as detailed as you can when putting together your outline.
If you have trouble getting started or are feeling overwhelmed, try free writing. Free writing is a low-stakes writing exercise to help you get past the blank page. Set a timer for five or ten minutes and write down everything you know about your paper: your argument, your sources, counterarguments, everything. Do not edit or judge what you are writing as you write; just keep writing until the timer goes off. You may be surprised to find out how much you knew about your topic. Of course, this writing will not be polished, so do not be tempted to leave it as it is. Remember that this draft is your first one, and you will be revising it.
A particularly helpful exercise for global-level revision is to make a reverse outline, which will help you look at your paper as a whole and strengthen the way you have organized and substantiated your argument. Print out your draft and number each of the paragraphs. Then, on a separate piece of paper, write down each paragraph number and, next to it, summarize in a phrase or a sentence the main idea of that paragraph. As you produce this list, notice if any paragraphs attempt to make more than one point: mark those for revision. Once you have compiled the list, read it over carefully. Study the order in which you have sequenced your ideas. Notice if there are ideas that seem out of order or repetitive. Look for any gaps in your logic. Does the argument flow and make sense?
When revising at the local level, check that you are using strong topic sentences and transitions, that you have adequately integrated and analyzed quotations, and that your paper is free from grammar and spelling errors that might distract the reader or even impede your ability to communicate your point. One helpful exercise for revising on the local level is to read your paper out loud. Hearing your paper will help you catch grammatical errors and awkward sentences.
Here is a checklist of questions to ask yourself while revising on both the global and local levels:
– Does my thesis clearly state my argument and its significance?
– Does the main argument in each body paragraph support my thesis?
– Do I have enough evidence within each body paragraph to make my point?
– Have I properly introduced, analyzed, and cited every quotation I use?
– Do my topic sentences effectively introduce the main point of each paragraph?
– Do I have transitions between paragraphs?
– Is my paper free of grammar and spelling errors?
- Congratulate yourself. You have written a history paper!
Download as PDF

6265 Bunche Hall Box 951473 University of California, Los Angeles Los Angeles, CA 90095-1473 Phone: (310) 825-4601
Other Resources
- UCLA Library
- Faculty Intranet
- Department Forms
- Office 365 Email
- Remote Help
Campus Resources
- Maps, Directions, Parking
- Academic Calendar
- University of California
- Terms of Use
Social Sciences Division Departments
- Aerospace Studies
- African American Studies
- American Indian Studies
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Asian American Studies
- César E. Chávez Department of Chicana & Chicano Studies
- Communication
- Conservation
- Gender Studies
- Military Science
- Naval Science
- Political Science

Writing a history essay

An essay is a piece of sustained writing in response to a question, topic or issue. Essays are commonly used for assessing and evaluating student progress in history. History essays test a range of skills including historical understanding, interpretation and analysis, planning, research and writing.
To write an effective essay, students should examine the question, understand its focus and requirements, acquire information and evidence through research, then construct a clear and well-organised response. Writing a good history essay should be rigorous and challenging, even for stronger students. As with other skills, essay writing develops and improves over time. Each essay you complete helps you become more competent and confident in exercising these skills.
Study the question
This is an obvious tip but one sadly neglected by some students. The first step to writing a good essay, whatever the subject or topic, is to give plenty of thought to the question.
An essay question will set some kind of task or challenge. It might ask you to explain the causes and/or effects of a particular event or situation. It might ask if you agree or disagree with a statement. It might ask you to describe and analyse the causes and/or effects of a particular action or event. Or it might ask you to evaluate the relative significance of a person, group or event.
You should begin by reading the essay question several times. Underline, highlight or annotate keywords or terms in the text of the question. Think about what it requires you to do. Who or what does it want you to concentrate on? Does it state or imply a particular timeframe? What problem or issue does it want you to address?
Begin with a plan
Every essay should begin with a written plan. Start constructing a plan as soon as you have received your essay question and given it some thought.
Prepare for research by brainstorming and jotting down your thoughts and ideas. What are your initial responses or thoughts about the question? What topics, events, people or issues are connected with the question? Do any additional questions or issues flow from the question? What topics or events do you need to learn more about? What historians or sources might be useful?
If you encounter a mental ‘brick wall’ or are uncertain about how to approach the question, don’t hesitate to discuss it with someone else. Consult your teacher, a capable classmate or someone you trust. Bear in mind too that once you start researching, your plan may change as you locate new information.
Start researching
After studying the question and developing an initial plan, start to gather information and evidence.
Most will start by reading an overview of the topic or issue, usually in some reliable secondary sources. This will refresh or build your existing understanding of the topic and provide a basis for further questions or investigation.
Your research should take shape from here, guided by the essay question and your own planning. Identify terms or concepts you do not know and find out what they mean. As you locate information, ask yourself if it is relevant or useful for addressing the question. Be creative with your research, looking in a variety of places.
If you have difficulty locating information, seek advice from your teacher or someone you trust.
Develop a contention
All good history essays have a clear and strong contention. A contention is the main idea or argument of your essay. It serves both as an answer to the question and the focal point of your writing.
Ideally, you should be able to express your contention as a single sentence. For example, the following contention might form the basis of an essay question on the rise of the Nazis:
Q. Why did the Nazi Party win 37 per cent of the vote in July 1932? A. The Nazi Party’s electoral success of 1932 was a result of economic suffering caused by the Great Depression, public dissatisfaction with the Weimar Republic’s democratic political system and mainstream parties, and Nazi propaganda that promised a return to traditional social, political and economic values.
An essay using this contention would then go on to explain and justify these statements in greater detail. It will also support the contention with argument and evidence.
At some point in your research, you should begin thinking about a contention for your essay. Remember, you should be able to express it briefly as if addressing the essay question in a single sentence, or summing up in a debate.
Try to frame your contention so that is strong, authoritative and convincing. It should sound like the voice of someone well informed about the subject and confident about their answer.
Plan an essay structure

Once most of your research is complete and you have a strong contention, start jotting down a possible essay structure. This need not be complicated, a few lines or dot points is ample.
Every essay must have an introduction, a body of several paragraphs and a conclusion. Your paragraphs should be well organised and follow a logical sequence.
You can organise paragraphs in two ways: chronologically (covering events or topics in the order they occurred) or thematically (covering events or topics based on their relevance or significance). Every paragraph should be clearly signposted in the topic sentence.
Once you have finalised a plan for your essay, commence your draft.
Write a compelling introduction
Many consider the introduction to be the most important part of an essay. It is important for several reasons. It is the reader’s first experience of your essay. It is where you first address the question and express your contention. It is also where you lay out or ‘signpost’ the direction your essay will take.
Aim for an introduction that is clear, confident and punchy. Get straight to the point – do not waste time with a rambling or storytelling introduction.
Start by providing a little context, then address the question, articulate your contention and indicate what direction your essay will take.
Write fully formed paragraphs
Many history students fall into the trap of writing short paragraphs, sometimes containing as little as one or two sentences. A good history essay contains paragraphs that are themselves ‘mini-essays’, usually between 100-200 words each.
A paragraph should focus on one topic or issue only – but it should contain a thorough exploration of that topic or issue.
A good paragraph will begin with an effective opening sentence, sometimes called a topic sentence or signposting sentence. This sentence introduces the paragraph topic and briefly explains its significance to the question and your contention. Good paragraphs also contain thorough explanations, some analysis and evidence, and perhaps a quotation or two.
Finish with an effective conclusion
The conclusion is the final paragraph of your essay. A good conclusion should do two things. First, it should reiterate or restate the contention of your essay. Second, it should close off your essay, ideally with a polished ending that is not abrupt or awkward.
One effective way to do this is with a brief summary of ‘what happened next’. For example, an essay discussing Hitler’s rise to power in 1933 might close with a couple of sentences about how he consolidated and strengthened his power in 1934-35.
Your conclusion need not be as long or as developed as your body paragraphs. You should avoid introducing new information or evidence in the conclusion.
Reference and cite your sources
A history essay is only likely to succeed if it is appropriately referenced. Your essay should support its information, ideas and arguments with citations or references to reliable sources.
Referencing not only acknowledges the work of others, but it also gives authority to your writing and provides the teacher or assessor with an insight into your research. More information on referencing a piece of history writing can be found here .
Proofread, edit and seek feedback
Every essay should be proofread, edited and, if necessary, re-drafted before being submitted for assessment. Essays should ideally be completed well before their due date then put aside for a day or two before proofreading.
When proofreading, look first for spelling and grammatical errors, typographical mistakes, incorrect dates or other errors of fact.
Think then about how you can improve the clarity, tone and structure of your essay. Does your essay follow a logical structure or sequence? Is the signposting in your essay clear and effective? Are some sentences too long or ‘rambling’? Do you repeat yourself? Do paragraphs need to be expanded, fine-tuned or strengthened with more evidence?
Read your essay aloud, either to yourself or another person. Seek feedback and advice from a good writer or someone you trust (they need not have expertise in history, only in effective writing).
Some general tips on writing
- Always write in the third person . Never refer to yourself personally, using phrases like “I think…” or “It is my contention…”. Good history essays should adopt the perspective of an informed and objective third party. They should sound rational and factual – not like an individual expressing their opinion.
- Always write in the past tense . An obvious tip for a history essay is to write in the past tense. Always be careful about your use of tense. Watch out for mixed tenses when proofreading your work. One exception to the rule about past tense is when writing about the work of modern historians (for example, “Kershaw writes…” sounds better than “Kershaw wrote…” or “Kershaw has written…”).
- Avoid generalisations . Generalisation is a problem in all essays but it is particularly common in history essays. Generalisation occurs when you form general conclusions from one or more specific examples. In history, this most commonly occurs when students study the experiences of a particular group, then assume their experiences applied to a much larger group – for example, “All the peasants were outraged”, “Women rallied to oppose conscription” or “Germans supported the Nazi Party”. Both history and human society, however, are never this clear cut or simple. Always try to avoid generalisation and be on the lookout for generalised statements when proofreading.
- Write short, sharp and punchy . Good writers vary their sentence length but as a rule of thumb, most of your sentences should be short and punchy. The longer a sentence becomes, the greater the risk of it becoming long-winded or confusing. Long sentences can easily become disjointed, confused or rambling. Try not to overuse long sentences and pay close attention to sentence length when proofreading.
- Write in an active voice . In history writing, the active voice is preferable to the passive voice. In the active voice, the subject completes the action (e.g. “Hitler [the subject] initiated the Beer Hall putsch [the action] to seize control of the Bavarian government”). In the passive voice, the action is completed by the subject (“The Beer Hall putsch [the action] was initiated by Hitler [the subject] to seize control of the Bavarian government”). The active voice also helps prevent sentences from becoming long, wordy and unclear.
You may also find our page on writing for history useful.
Citation information Title : ‘Writing a history essay’ Authors : Jennifer Llewellyn, Steve Thompson Publisher : Alpha History URL : https://alphahistory.com/writing-a-history-essay/ Date published : April 13, 2020 Date updated : December 20, 2022 Date accessed : Today’s date Copyright : The content on this page may not be republished without our express permission. For more information on usage, please refer to our Terms of Use.

- Written Essays
How to write source-based history essays

The biggest assessment task you will be required to complete is a written research essay which develops an argument and uses a range of sources.
All types of assessment tasks will need you to use essay-writing skills in some form, but their fundamental structure and purpose remains the same.
Therefore, learning how to write essays well is central to achieving high marks in History.
What is an 'essay'?
A History essay is a structured argument that provides historical evidence to substantiate its points.
To achieve the correct structure for your argument, it is crucial to understand the separate parts that make up a written essay.
If you understand how each part works and fits into the overall essay, you are well on the way to creating a great assessment piece.
Most essays will require you to write:
- 1 Introduction Paragraph
- 3 Body Paragraphs
- 1 Concluding Paragraph
Explanations for how to structure and write each of these paragraphs can be found below, along with examples of each:
Essay paragraph writing advice

How to write an Introductory Paragraph
This page explains the purpose of an introduction, how to structure one and provides examples for you to read.

How to write Body Paragraphs
This page explains the purpose of body paragraphs, how to structure them and provides examples for you to read.

How to write a Conclusion
This page explains the purpose of conclusions, how to structure them and provides examples for you to read.
More essay resources
What do you need help with, download ready-to-use digital learning resources.

Copyright © History Skills 2014-2024.
Contact via email
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a History Essay
Last Updated: December 27, 2022 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a Private Tutor and Life Coach in Santa Cruz, California. In 2018, she founded Mindful & Well, a natural healing and wellness coaching service. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. Emily also received her Wellness Coach Certificate from Cornell University and completed the Mindfulness Training by Mindful Schools. There are 8 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 246,121 times.
Writing a history essay requires you to include a lot of details and historical information within a given number of words or required pages. It's important to provide all the needed information, but also to present it in a cohesive, intelligent way. Know how to write a history essay that demonstrates your writing skills and your understanding of the material.
Preparing to Write Your Essay

- The key words will often need to be defined at the start of your essay, and will serve as its boundaries. [2] X Research source
- For example, if the question was "To what extent was the First World War a Total War?", the key terms are "First World War", and "Total War".
- Do this before you begin conducting your research to ensure that your reading is closely focussed to the question and you don't waste time.

- Explain: provide an explanation of why something happened or didn't happen.
- Interpret: analyse information within a larger framework to contextualise it.
- Evaluate: present and support a value-judgement.
- Argue: take a clear position on a debate and justify it. [3] X Research source

- Your thesis statement should clearly address the essay prompt and provide supporting arguments. These supporting arguments will become body paragraphs in your essay, where you’ll elaborate and provide concrete evidence. [4] X Trustworthy Source Purdue Online Writing Lab Trusted resource for writing and citation guidelines Go to source
- Your argument may change or become more nuanced as your write your essay, but having a clear thesis statement which you can refer back to is very helpful.
- For example, your summary could be something like "The First World War was a 'total war' because civilian populations were mobilized both in the battlefield and on the home front".

- Pick out some key quotes that make your argument precisely and persuasively. [5] X Research source
- When writing your plan, you should already be thinking about how your essay will flow, and how each point will connect together.
Doing Your Research

- Primary source material refers to any texts, films, pictures, or any other kind of evidence that was produced in the historical period, or by someone who participated in the events of the period, that you are writing about.
- Secondary material is the work by historians or other writers analysing events in the past. The body of historical work on a period or event is known as the historiography.
- It is not unusual to write a literature review or historiographical essay which does not directly draw on primary material.
- Typically a research essay would need significant primary material.

- Start with the core texts in your reading list or course bibliography. Your teacher will have carefully selected these so you should start there.
- Look in footnotes and bibliographies. When you are reading be sure to pay attention to the footnotes and bibliographies which can guide you to further sources a give you a clear picture of the important texts.
- Use the library. If you have access to a library at your school or college, be sure to make the most of it. Search online catalogues and speak to librarians.
- Access online journal databases. If you are in college it is likely that you will have access to academic journals online. These are an excellent and easy to navigate resources.
- Use online sources with discretion. Try using free scholarly databases, like Google Scholar, which offer quality academic sources, but avoid using the non-trustworthy websites that come up when you simply search your topic online.
- Avoid using crowd-sourced sites like Wikipedia as sources. However, you can look at the sources cited on a Wikipedia page and use them instead, if they seem credible.

- Who is the author? Is it written by an academic with a position at a University? Search for the author online.
- Who is the publisher? Is the book published by an established academic press? Look in the cover to check the publisher, if it is published by a University Press that is a good sign.
- If it's an article, where is published? If you are using an article check that it has been published in an academic journal. [8] X Research source
- If the article is online, what is the URL? Government sources with .gov addresses are good sources, as are .edu sites.

- Ask yourself why the author is making this argument. Evaluate the text by placing it into a broader intellectual context. Is it part of a certain tradition in historiography? Is it a response to a particular idea?
- Consider where there are weaknesses and limitations to the argument. Always keep a critical mindset and try to identify areas where you think the argument is overly stretched or the evidence doesn't match the author's claims. [9] X Research source

- Label all your notes with the page numbers and precise bibliographic information on the source.
- If you have a quote but can't remember where you found it, imagine trying to skip back through everything you have read to find that one line.
- If you use something and don't reference it fully you risk plagiarism. [10] X Research source
Writing the Introduction

- For example you could start by saying "In the First World War new technologies and the mass mobilization of populations meant that the war was not fought solely by standing armies".
- This first sentences introduces the topic of your essay in a broad way which you can start focus to in on more.

- This will lead to an outline of the structure of your essay and your argument.
- Here you will explain the particular approach you have taken to the essay.
- For example, if you are using case studies you should explain this and give a brief overview of which case studies you will be using and why.

Writing the Essay

- Try to include a sentence that concludes each paragraph and links it to the next paragraph.
- When you are organising your essay think of each paragraph as addressing one element of the essay question.
- Keeping a close focus like this will also help you avoid drifting away from the topic of the essay and will encourage you to write in precise and concise prose.
- Don't forget to write in the past tense when referring to something that has already happened.

- Don't drop a quote from a primary source into your prose without introducing it and discussing it, and try to avoid long quotations. Use only the quotes that best illustrate your point.
- If you are referring to a secondary source, you can usually summarise in your own words rather than quoting directly.
- Be sure to fully cite anything you refer to, including if you do not quote it directly.

- Think about the first and last sentence in every paragraph and how they connect to the previous and next paragraph.
- Try to avoid beginning paragraphs with simple phrases that make your essay appear more like a list. For example, limit your use of words like: "Additionally", "Moreover", "Furthermore".
- Give an indication of where your essay is going and how you are building on what you have already said. [15] X Research source

- Briefly outline the implications of your argument and it's significance in relation to the historiography, but avoid grand sweeping statements. [16] X Research source
- A conclusion also provides the opportunity to point to areas beyond the scope of your essay where the research could be developed in the future.
Proofreading and Evaluating Your Essay

- Try to cut down any overly long sentences or run-on sentences. Instead, try to write clear and accurate prose and avoid unnecessary words.
- Concentrate on developing a clear, simple and highly readable prose style first before you think about developing your writing further. [17] X Research source
- Reading your essay out load can help you get a clearer picture of awkward phrasing and overly long sentences. [18] X Research source

- When you read through your essay look at each paragraph and ask yourself, "what point this paragraph is making".
- You might have produced a nice piece of narrative writing, but if you are not directly answering the question it is not going to help your grade.

- A bibliography will typically have primary sources first, followed by secondary sources. [19] X Research source
- Double and triple check that you have included all the necessary references in the text. If you forgot to include a reference you risk being reported for plagiarism.
Sample Essay

Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.historytoday.com/robert-pearce/how-write-good-history-essay
- ↑ https://www.hamilton.edu/academics/centers/writing/writing-resources/writing-a-good-history-paper
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/thesis_statement_tips.html
- ↑ http://history.rutgers.edu/component/content/article?id=106:writing-historical-essays-a-guide-for-undergraduates
- ↑ https://guides.lib.uw.edu/c.php?g=344285&p=2580599
- ↑ http://www.hamilton.edu/documents/writing-center/WritingGoodHistoryPaper.pdf
- ↑ http://www.bowdoin.edu/writing-guides/
- ↑ https://www.wgtn.ac.nz/hppi/publications/Writing-History-Essays.pdf
About This Article

To write a history essay, read the essay question carefully and use source materials to research the topic, taking thorough notes as you go. Next, formulate a thesis statement that summarizes your key argument in 1-2 concise sentences and create a structured outline to help you stay on topic. Open with a strong introduction that introduces your thesis, present your argument, and back it up with sourced material. Then, end with a succinct conclusion that restates and summarizes your position! For more tips on creating a thesis statement, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lea Fernandez
Nov 23, 2017
Did this article help you?

Matthew Sayers
Mar 31, 2019
Millie Jenkerinx
Nov 11, 2017
Oct 18, 2019
Shannon Harper
Mar 9, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Writing a Good History Paper
- Top Ten Reasons for Negative Comments
- Making Sure your Paper has Substance
Common Marginal Remarks on Style, Clarity, Grammar, and Syntax
Word and phrase usage problems, analyzing a historical document, writing a book review, writing a term paper or senior thesis, top ten reasons for negative comments on history papers.
(Drawn from a survey of the History Department ) 10. You engage in cheap, anachronistic moralizing . 9. You are sloppy with the chronology . 8. You quote excessively or improperly . 7. You have written a careless “one-draft wonder.” (See revise and proofread) 6. You are vague or have empty, unsupported generalizations . 5. You write too much in the passive voice. 4. You use inappropriate sources . 3. You use evidence uncritically. 2. You are wordy . 1. You have no clear thesis and little analysis.
Making Sure your History Paper has Substance
Get off to a good start..
Avoid pretentious, vapid beginnings. If you are writing a paper on, say, British responses to the rebellion in India in 1857, don't open with a statement like this: “Throughout human history people in all cultures everywhere in the world have engaged in many and long-running conflicts about numerous aspects of government policy and diplomatic issues, which have much interested historians and generated historical theories in many areas.” This is pure garbage, bores the reader, and is a sure sign that you have nothing substantive to say. Get to the point. Here’s a better start: “The rebellion in 1857 compelled the British to rethink their colonial administration in India.” This sentence tells the reader what your paper is actually about and clears the way for you to state your thesis in the rest of the opening paragraph. For example, you might go on to argue that greater British sensitivity to Indian customs was hypocritical.
State a clear thesis.
Whether you are writing an exam essay or a senior thesis, you need to have a thesis. Don’t just repeat the assignment or start writing down everything that you know about the subject. Ask yourself, “What exactly am I trying to prove?” Your thesis is your take on the subject, your perspective, your explanation—that is, the case that you’re going to argue. “Famine struck Ireland in the 1840s” is a true statement, but it is not a thesis. “The English were responsible for famine in Ireland in the 1840s” is a thesis (whether defensible or not is another matter). A good thesis answers an important research question about how or why something happened. (“Who was responsible for the famine in Ireland in the 1840s?”) Once you have laid out your thesis, don’t forget about it. Develop your thesis logically from paragraph to paragraph. Your reader should always know where your argument has come from, where it is now, and where it is going.
Be sure to analyze.
Students are often puzzled when their professors mark them down for summarizing or merely narrating rather than analyzing. What does it mean to analyze? In the narrow sense, to analyze means to break down into parts and to study the interrelationships of those parts. If you analyze water, you break it down into hydrogen and oxygen. In a broader sense, historical analysis explains the origins and significance of events. Historical analysis digs beneath the surface to see relationships or distinctions that are not immediately obvious. Historical analysis is critical; it evaluates sources, assigns significance to causes, and weighs competing explanations. Don’t push the distinction too far, but you might think of summary and analysis this way: Who, what, when, and where are the stuff of summary; how, why, and to what effect are the stuff of analysis. Many students think that they have to give a long summary (to show the professor that they know the facts) before they get to their analysis. Try instead to begin your analysis as soon as possible, sometimes without any summary at all. The facts will “shine through” a good analysis. You can't do an analysis unless you know the facts, but you can summarize the facts without being able to do an analysis. Summary is easier and less sophisticated than analysis—that’s why summary alone never earns an “A.”
Use evidence critically.
Like good detectives, historians are critical of their sources and cross-check them for reliability. You wouldn't think much of a detective who relied solely on a suspect’s archenemy to check an alibi. Likewise, you wouldn't think much of a historian who relied solely on the French to explain the origins of World War I. Consider the following two statements on the origin of World War I: 1) “For the catastrophe of 1914 the Germans are responsible. Only a professional liar would deny this...” 2) “It is not true that Germany is guilty of having caused this war. Neither the people, the government, nor the Kaiser wanted war....” They can’t both be right, so you have to do some detective work. As always, the best approach is to ask: Who wrote the source? Why? When? Under what circumstances? For whom? The first statement comes from a book by the French politician Georges Clemenceau, which he wrote in 1929 at the very end of his life. In 1871, Clemenceau had vowed revenge against Germany for its defeat of France in the Franco-Prussian War. As premier of France from 1917 to 1920, he represented France at the Paris Peace Conference in 1919. He was obviously not a disinterested observer. The second statement comes from a manifesto published by ninety-three prominent German intellectuals in the fall of 1914. They were defending Germany against charges of aggression and brutality. They too were obviously not disinterested observers. Now, rarely do you encounter such extreme bias and passionate disagreement, but the principle of criticizing and cross-checking sources always applies. In general, the more sources you can use, and the more varied they are, the more likely you are to make a sound historical judgment, especially when passions and self-interests are engaged. You don’t need to be cynical as a historian (self-interest does not explain everything), but you do need to be critical and skeptical. Competent historians may offer different interpretations of the same evidence or choose to stress different evidence. You will not find a single historical Truth with a capital “T” on any matter of significance. You can, however, learn to discriminate among conflicting interpretations, not all of which are created equal. (See also: Analyzing a Historical Document )
Be precise.
Vague statements and empty generalizations suggest that you haven't put in the time to learn the material. Consider these two sentences: “During the French Revolution, the government was overthrown by the people. The Revolution is important because it shows that people need freedom.” What people? Landless peasants? Urban journeymen? Wealthy lawyers? Which government? When? How? Who exactly needed freedom, and what did they mean by freedom? Here is a more precise statement about the French Revolution: “Threatened by rising prices and food shortages in 1793, the Parisian sans-culottes pressured the Convention to institute price controls.” This statement is more limited than the grandiose generalizations about the Revolution, but unlike them, it can open the door to a real analysis of the Revolution. Be careful when you use grand abstractions like people, society, freedom, and government, especially when you further distance yourself from the concrete by using these words as the apparent antecedents for the pronouns they and it. Always pay attention to cause and effect. Abstractions do not cause or need anything; particular people or particular groups of people cause or need things. Avoid grandiose trans-historical generalizations that you can’t support. When in doubt about the appropriate level of precision or detail, err on the side of adding “too much” precision and detail.
Watch the chronology.
Anchor your thesis in a clear chronological framework and don't jump around confusingly. Take care to avoid both anachronisms and vagueness about dates. If you write, “Napoleon abandoned his Grand Army in Russia and caught the redeye back to Paris,” the problem is obvious. If you write, “Despite the Watergate scandal, Nixon easily won reelection in 1972,” the problem is more subtle, but still serious. (The scandal did not become public until after the election.) If you write, “The revolution in China finally succeeded in the twentieth century,” your professor may suspect that you haven’t studied. Which revolution? When in the twentieth century? Remember that chronology is the backbone of history. What would you think of a biographer who wrote that you graduated from Hamilton in the 1950s?
Cite sources carefully.
Your professor may allow parenthetical citations in a short paper with one or two sources, but you should use footnotes for any research paper in history. Parenthetical citations are unaesthetic; they scar the text and break the flow of reading. Worse still, they are simply inadequate to capture the richness of historical sources. Historians take justifiable pride in the immense variety of their sources. Parenthetical citations such as (Jones 1994) may be fine for most of the social sciences and humanities, where the source base is usually limited to recent books and articles in English. Historians, however, need the flexibility of the full footnote. Try to imagine this typical footnote (pulled at random from a classic work of German history) squeezed into parentheses in the body of the text: DZA Potsdam, RdI, Frieden 5, Erzgebiet von Longwy-Briey, Bd. I, Nr. 19305, gedruckte Denkschrift für OHL und Reichsleitung, Dezember 1917, und in RWA, Frieden Frankreich Nr. 1883. The abbreviations are already in this footnote; its information cannot be further reduced. For footnotes and bibliography, historians usually use Chicago style. (The Chicago Manual of Style. 15th edition. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2003.) On the Writing Center’s website you can find a useful summary of Chicago citation style prepared by a former history major, Elizabeth Rabe ’04 ( Footnotes ). RefWorks (on the library’s website) will convert your citations to Chicago style. Don’t hesitate to ask one of the reference librarians for help if you have trouble getting started on RefWorks.
Use primary sources.
Use as many primary sources as possible in your paper. A primary source is one produced by a participant in or witness of the events you are writing about. A primary source allows the historian to see the past through the eyes of direct participants. Some common primary sources are letters, diaries, memoirs, speeches, church records, newspaper articles, and government documents of all kinds. The capacious genre “government records” is probably the single richest trove for the historian and includes everything from criminal court records, to tax lists, to census data, to parliamentary debates, to international treaties—indeed, any records generated by governments. If you’re writing about culture, primary sources may include works of art or literature, as well as philosophical tracts or scientific treatises—anything that comes under the broad rubric of culture. Not all primary sources are written. Buildings, monuments, clothes, home furnishings, photographs, religious relics, musical recordings, or oral reminiscences can all be primary sources if you use them as historical clues. The interests of historians are so broad that virtually anything can be a primary source. (See also: Analyzing a Historical Document )
Use scholarly secondary sources.
A secondary source is one written by a later historian who had no part in what he or she is writing about. (In the rare cases when the historian was a participant in the events, then the work—or at least part of it—is a primary source.) Historians read secondary sources to learn about how scholars have interpreted the past. Just as you must be critical of primary sources, so too you must be critical of secondary sources. You must be especially careful to distinguish between scholarly and non-scholarly secondary sources. Unlike, say, nuclear physics, history attracts many amateurs. Books and articles about war, great individuals, and everyday material life dominate popular history. Some professional historians disparage popular history and may even discourage their colleagues from trying their hand at it. You need not share their snobbishness; some popular history is excellent. But—and this is a big but—as a rule, you should avoid popular works in your research, because they are usually not scholarly. Popular history seeks to inform and entertain a large general audience. In popular history, dramatic storytelling often prevails over analysis, style over substance, simplicity over complexity, and grand generalization over careful qualification. Popular history is usually based largely or exclusively on secondary sources. Strictly speaking, most popular histories might better be called tertiary, not secondary, sources. Scholarly history, in contrast, seeks to discover new knowledge or to reinterpret existing knowledge. Good scholars wish to write clearly and simply, and they may spin a compelling yarn, but they do not shun depth, analysis, complexity, or qualification. Scholarly history draws on as many primary sources as practical. Now, your goal as a student is to come as close as possible to the scholarly ideal, so you need to develop a nose for distinguishing the scholarly from the non-scholarly. Here are a few questions you might ask of your secondary sources (bear in mind that the popular/scholarly distinction is not absolute, and that some scholarly work may be poor scholarship). Who is the author? Most scholarly works are written by professional historians (usually professors) who have advanced training in the area they are writing about. If the author is a journalist or someone with no special historical training, be careful. Who publishes the work? Scholarly books come from university presses and from a handful of commercial presses (for example, Norton, Routledge, Palgrave, Penguin, Rowman & Littlefield, Knopf, and HarperCollins). If it’s an article, where does it appear? Is it in a journal subscribed to by our library, listed on JSTOR , or published by a university press? Is the editorial board staffed by professors? Oddly enough, the word journal in the title is usually a sign that the periodical is scholarly. What do the notes and bibliography look like? If they are thin or nonexistent, be careful. If they are all secondary sources, be careful. If the work is about a non-English-speaking area, and all the sources are in English, then it's almost by definition not scholarly. Can you find reviews of the book in the data base Academic Search Premier? If the book was published within the last few decades, and it’s not in there, that’s a bad sign. With a little practice, you can develop confidence in your judgment—and you’re on your way to being a historian. If you are unsure whether a work qualifies as scholarly, ask your professor. (See also: Writing a Book Review )
Avoid abusing your sources.
Many potentially valuable sources are easy to abuse. Be especially alert for these five abuses: Web abuse. The Web is a wonderful and improving resource for indexes and catalogs. But as a source for primary and secondary material for the historian, the Web is of limited value. Anyone with the right software can post something on the Web without having to get past trained editors, peer reviewers, or librarians. As a result, there is a great deal of garbage on the Web. If you use a primary source from the Web, make sure that a respected intellectual institution stands behind the site. Be especially wary of secondary articles on the Web, unless they appear in electronic versions of established print journals (e.g., The Journal of Asian Studies in JSTOR). Many articles on the Web are little more than third-rate encyclopedia entries. When in doubt, check with your professor. With a few rare exceptions, you will not find scholarly monographs in history (even recent ones) on the Web. You may have heard of Google’s plans to digitize the entire collections of some of the world’s major libraries and to make those collections available on the Web. Don’t hold your breath. Your days at Hamilton will be long over by the time the project is finished. Besides, your training as a historian should give you a healthy skepticism of the giddy claims of technophiles. Most of the time and effort of doing history goes into reading, note-taking, pondering, and writing. Finding a chapter of a book on the Web (as opposed to getting the physical book through interlibrary loan) might be a convenience, but it doesn’t change the basics for the historian. Moreover, there is a subtle, but serious, drawback with digitized old books: They break the historian’s sensual link to the past. And of course, virtually none of the literally trillions of pages of archival material is available on the Web. For the foreseeable future, the library and the archive will remain the natural habitats of the historian. Thesaurus abuse. How tempting it is to ask your computer’s thesaurus to suggest a more erudite-sounding word for the common one that popped into your mind! Resist the temptation. Consider this example (admittedly, a bit heavy-handed, but it drives the point home): You’re writing about the EPA’s programs to clean up impure water supplies. Impure seems too simple and boring a word, so you bring up your thesaurus, which offers you everything from incontinent to meretricious. “How about meretricious water?” you think to yourself. “That will impress the professor.” The problem is that you don’t know exactly what meretricious means, so you don’t realize that meretricious is absurdly inappropriate in this context and makes you look foolish and immature. Use only those words that come to you naturally. Don’t try to write beyond your vocabulary. Don’t try to impress with big words. Use a thesaurus only for those annoying tip-of-the-tongue problems (you know the word and will recognize it instantly when you see it, but at the moment you just can’t think of it). Quotation book abuse. This is similar to thesaurus abuse. Let’s say you are writing a paper on Alexander Hamilton’s banking policies, and you want to get off to a snappy start that will make you seem effortlessly learned. How about a quotation on money? You click on the index of Bartlett’s Familiar Quotations , and before you know it, you’ve begun your paper with, “As Samuel Butler wrote in Hudibras , ‘For what is worth in anything/ But so much money as ’t will bring?’” Face it, you’re faking it. You don’t know who Samuel Butler is, and you’ve certainly never heard of Hudibras , let alone read it. Your professor is not fooled. You sound like an insecure after-dinner speaker. Forget Bartlett’s, unless you're confirming the wording of a quotation that came to you spontaneously and relates to your paper. Encyclopedia abuse. General encyclopedias like Britannica are useful for checking facts (“Wait a sec, am I right about which countries sent troops to crush the Boxer Rebellion in China? Better check.”). But if you are footnoting encyclopedias in your papers, you are not doing college-level research.
Dictionary Abuse. The dictionary is your friend. Keep it by your side as you write, but do not abuse it by starting papers with a definition. You may be most tempted to start this way when you are writing on a complex, controversial, or elusive subject. (“According to Webster’s Collegiate Dictionary , liberalism is defined as...”). Actually, the dictionary does you little good in such cases and makes you sound like a conscientious but dull high-school student. Save in the rare case that competing dictionary definitions are the subject at hand, keep dictionary quotations out of your paper.
Quote sparingly
Avoid quoting a secondary source and then simply rewording or summarizing the quotation, either above or below the quotation. It is rarely necessary to quote secondary sources at length, unless your essay focuses on a critical analysis of the author’s argument. (See also: Writing a Book Review ) Your professor wants to see your ability to analyze and to understand the secondary sources. Do not quote unless the quotation clarifies or enriches your analysis. When in doubt, do not quote; instead, integrate the author’s argument into your own (though be sure to acknowledge ideas from your sources, even when you are paraphrasing). If you use a lot of quotations from secondary sources, you are probably writing a poor paper. An analysis of a primary source, such as a political tract or philosophical essay, might require lengthy quotations, often in block format. In such cases, you might need to briefly repeat key points or passages as a means to introduce the author’s ideas, but your analysis and interpretation of the text’s meaning should remain the most important aim. (See also: Using primary sources and Use scholarly secondary sources .)
Know your audience
Unless instructed otherwise, you should assume that your audience consists of educated, intelligent, nonspecialists. In fact, your professor will usually be your only reader, but if you write directly to your professor, you may become cryptic or sloppy (oh well, she’ll know what I’m talking about). Explaining your ideas to someone who doesn't know what you mean forces you to be clear and complete. Now, finding the right amount of detail can, admittedly, be tricky (how much do I put in about the Edict of Nantes, the Embargo Act, or President Wilson’s background?). When in doubt, err on the side of putting in extra details. You’ll get some leeway here if you avoid the extremes (my reader’s an ignoramus/my reader knows everything).
Avoid cheap, anachronistic moralizing
Many of the people and institutions of the past appear unenlightened, ignorant, misguided, or bigoted by today’s values. Resist the temptation to condemn or to get self-righteous. (“Martin Luther was blind to the sexism and class prejudice of sixteenth-century German society.”) Like you, people in the past were creatures of their time; like you, they deserve to be judged by the standards of their time. If you judge the past by today’s standards (an error historians call “presentism”), you will never understand why people thought or acted as they did. Yes, Hitler was a bad guy, but he was bad not only by today’s standards, but also by the commonly accepted standards of his own time. Someday you’re going to look pretty foolish and ignorant yourself. (“Early twenty-first century Hamilton students failed to see the shocking inderdosherism [that’s right, you don’t recognize the concept because it doesn’t yet exist] implicit in their career plans.”)
Have a strong conclusion
Obviously, you should not just stop abruptly as though you have run out of time or ideas. Your conclusion should conclude something. If you merely restate briefly what you have said in your paper, you give the impression that you are unsure of the significance of what you have written. A weak conclusion leaves the reader unsatisfied and bewildered, wondering why your paper was worth reading. A strong conclusion adds something to what you said in your introduction. A strong conclusion explains the importance and significance of what you have written. A strong conclusion leaves your reader caring about what you have said and pondering the larger implications of your thesis. Don’t leave your reader asking, “So what?”
Revise and proofread
Your professor can spot a “one-draft wonder,” so don't try to do your paper at the last moment. Leave plenty of time for revising and proofreading. Show your draft to a writing tutor or other good writer. Reading the draft aloud may also help. Of course, everyone makes mistakes, and a few may slip through no matter how meticulous you are. But beware of lots of mistakes. The failure to proofread carefully suggests that you devoted little time and effort to the assignment. Tip: Proofread your text both on the screen and on a printed copy. Your eyes see the two differently. Don’t rely on your spell checker to catch all of your misspellings. (If ewe ken reed this ewe kin sea that a computer wood nut all ways help ewe spill or rite reel good.)
Note: The Writing Center suggests standard abbreviations for noting some of these problems. You should familiarize yourself with those abbreviations, but your professor may not use them.
Remarks on Style and Clarity
Wordy/verbose/repetitive..
Try your hand at fixing this sentence: “Due to the fact that these aspects of the issue of personal survival have been raised by recently transpired problematic conflicts, it is at the present time paramount that the ultimate psychological end of suicide be contemplated by this individual.” If you get it down to “To be or not to be, that is the question,” you’ve done well. You may not match Shakespeare, but you can learn to cut the fat out of your prose. The chances are that the five pages you’ve written for your history paper do not really contain five pages’ worth of ideas.
Misuse of the passive voice.
Write in the active voice. The passive voice encourages vagueness and dullness; it enfeebles verbs; and it conceals agency, which is the very stuff of history. You know all of this almost instinctively. What would you think of a lover who sighed in your ear, “My darling, you are loved by me!”? At its worst, the passive voice—like its kin, bureaucratic language and jargon—is a medium for the dishonesty and evasion of responsibility that pervade contemporary American culture. (“Mistakes were made; I was given false information.” Now notice the difference: “I screwed up; Smith and Jones lied to me; I neglected to check the facts.”) On history papers the passive voice usually signals a less toxic version of the same unwillingness to take charge, to commit yourself, and to say forthrightly what is really going on, and who is doing what to whom. Suppose you write, “In 1935 Ethiopia was invaded.” This sentence is a disaster. Who invaded? Your professor will assume that you don't know. Adding “by Italy” to the end of the sentence helps a bit, but the sentence is still flat and misleading. Italy was an aggressive actor, and your passive construction conceals that salient fact by putting the actor in the syntactically weakest position—at the end of the sentence as the object of a preposition. Notice how you add vigor and clarity to the sentence when you recast it in the active voice: "In 1935 Italy invaded Ethiopia." I n a few cases , you may violate the no-passive-voice rule. The passive voice may be preferable if the agent is either obvious (“Kennedy was elected in 1960”), irrelevant (“Theodore Roosevelt became president when McKinley was assassinated”), or unknown (“King Harold was killed at the Battle of Hastings”). Note that in all three of these sample sentences the passive voice focuses the reader on the receiver of the action rather than on the doer (on Kennedy, not on American voters; on McKinley, not on his assassin; on King Harold, not on the unknown Norman archer). Historians usually wish to focus on the doer, so you should stay with the active voice—unless you can make a compelling case for an exception.
Abuse of the verb to be.
The verb to be is the most common and most important verb in English, but too many verbs to be suck the life out of your prose and lead to wordiness. Enliven your prose with as many action verbs as possible. ( “In Brown v. Board of Education it was the opinion of the Supreme Court that the doctrine of ‘separate but equal’ was in violation of the Fourteenth Amendment.”) Rewrite as “ In Brown v. Board of Education the Supreme Court ruled that the doctrine of ‘separate but equal’ violated the Fourteenth ”
Explain/what’s your point?/unclear/huh?
You may (or may not) know what you’re talking about, but if you see these marginal comments, you have confused your reader. You may have introduced a non sequitur ; gotten off the subject; drifted into abstraction; assumed something that you have not told the reader; failed to explain how the material relates to your argument; garbled your syntax; or simply failed to proofread carefully. If possible, have a good writer read your paper and point out the muddled parts. Reading your paper aloud may help too.
Paragraph goes nowhere/has no point or unity.
Paragraphs are the building blocks of your paper. If your paragraphs are weak, your paper cannot be strong. Try underlining the topic sentence of every paragraph. If your topic sentences are vague, strength and precision—the hallmarks of good writing—are unlikely to follow. Consider this topic sentence (from a paper on Ivan the Terrible): “From 1538 to 1547, there are many different arguments about the nature of what happened.” Disaster looms. The reader has no way of knowing when the arguing takes place, who’s arguing, or even what the arguing is about. And how does the “nature of what happened” differ from plain “what happened”? Perhaps the writer means the following: “The childhood of Ivan the Terrible has provoked controversy among scholars of Russian history.” That's hardly deathless prose, but it does orient the reader and make the writer accountable for what follows in the paragraph. Once you have a good topic sentence, make sure that everything in the paragraph supports that sentence, and that cumulatively the support is persuasive. Make sure that each sentence follows logically from the previous one, adding detail in a coherent order. Move, delete, or add material as appropriate. To avoid confusing the reader, limit each paragraph to one central idea. (If you have a series of supporting points starting with first, you must follow with a second, third , etc.) A paragraph that runs more than a printed page is probably too long. Err on the side of shorter paragraphs.
Inappropriate use of first person.
Most historians write in the third person, which focuses the reader on the subject. If you write in the first person singular, you shift the focus to yourself. You give the impression that you want to break in and say, “Enough about the Haitian revolution [or whatever], now let’s talk about me!” Also avoid the first person plural (“We believe...”). It suggests committees, editorial boards, or royalty. None of those should have had a hand in writing your paper. And don’t refer to yourself lamely as “this writer.” Who else could possibly be writing the paper?
Tense inconsistency.
Stay consistently in the past tense when you are writing about what took place in the past. (“Truman’s defeat of Dewey in 1948 caught the pollsters by surprise.”) Note that the context may require a shift into the past perfect. (“The pollsters had not realized [past perfect] that voter opinion had been [past perfect] changing rapidly in the days before the election.”) Unfortunately, the tense problem can get a bit more complicated. Most historians shift into the present tense when describing or commenting on a book, document, or evidence that still exists and is in front of them (or in their mind) as they write. (“de Beauvoir published [past tense] The Second Sex in 1949. In the book she contends [present tense] that woman....”) If you’re confused, think of it this way: History is about the past, so historians write in the past tense, unless they are discussing effects of the past that still exist and thus are in the present. When in doubt, use the past tense and stay consistent.
Ill-fitted quotation.
This is a common problem, though not noted in stylebooks. When you quote someone, make sure that the quotation fits grammatically into your sentence. Note carefully the mismatch between the start of the following sentence and the quotation that follows: “In order to understand the Vikings, writes Marc Bloch, it is necessary, ‘To conceive of the Viking expeditions as religious warfare inspired by the ardour of an implacable pagan fanaticism—an explanation that has sometimes been at least suggested—conflicts too much with what we know of minds disposed to respect magic of every kind.’” At first, the transition into the quotation from Bloch seems fine. The infinitive (to conceive) fits. But then the reader comes to the verb (conflicts) in Bloch’s sentence, and things no longer make sense. The writer is saying, in effect, “it is necessary conflicts.” The wordy lead-in and the complex syntax of the quotation have tripped the writer and confused the reader. If you wish to use the whole sentence, rewrite as “Marc Bloch writes in Feudal Society , ‘To conceive of...’” Better yet, use your own words or only part of the quotation in your sentence. Remember that good writers quote infrequently, but when they do need to quote, they use carefully phrased lead-ins that fit the grammatical construction of the quotation.
Free-floating quotation.
Do not suddenly drop quotations into your prose. (“The spirit of the Progressive era is best understood if one remembers that the United States is ‘the only country in the world that began with perfection and aspired to progress.’”) You have probably chosen the quotation because it is finely wrought and says exactly what you want to say. Fine, but first you inconvenience the reader, who must go to the footnote to learn that the quotation comes from The Age of Reform by historian Richard Hofstadter. And then you puzzle the reader. Did Hofstadter write the line about perfection and progress, or is he quoting someone from the Progressive era? If, as you claim, you are going to help the reader to judge the “spirit of the Progressive era,” you need to clarify. Rewrite as “As historian Richard Hofstadter writes in the Age of Reform , the United States is ‘the only country in the world...’” Now the reader knows immediately that the line is Hofstadter’s.
Who’s speaking here?/your view?
Always be clear about whether you’re giving your opinion or that of the author or historical actor you are discussing. Let’s say that your essay is about Martin Luther’s social views. You write, “The German peasants who revolted in 1525 were brutes and deserved to be crushed mercilessly.” That’s what Luther thought, but do you agree? You may know, but your reader is not a mind reader. When in doubt, err on the side of being overly clear.
Jargon/pretentious theory.
Historians value plain English. Academic jargon and pretentious theory will make your prose turgid, ridiculous, and downright irritating. Your professor will suspect that you are trying to conceal that you have little to say. Of course, historians can’t get along without some theory; even those who profess to have no theory actually do—it’s called naïve realism. And sometimes you need a technical term, be it ontological argument or ecological fallacy. When you use theory or technical terms, make sure that they are intelligible and do real intellectual lifting. Please, no sentences like this: “By means of a neo-Althusserian, post-feminist hermeneutics, this essay will de/construct the logo/phallo/centrism imbricated in the marginalizing post-colonial gendered gaze, thereby proliferating the subjectivities that will re/present the de/stabilization of the essentializing habitus of post-Fordist capitalism.”
Informal language/slang.
You don’t need to be stuffy, but stay with formal English prose of the kind that will still be comprehensible to future generations. Columbus did not “push the envelope in the Atlantic.” Henry VIII was not “looking for his inner child when he broke with the Church.” Prime Minister Cavour of Piedmont was not “trying to play in the major leagues diplomatic wise.” Wilson did not “almost veg out” at the end of his second term. President Hindenburg did not appoint Hitler in a “senior moment.” Prime Minister Chamberlain did not tell the Czechs to “chill out” after the Munich Conference, and Gandhi was not an “awesome dude.”
Try to keep your prose fresh. Avoid cliches. When you proofread, watch out for sentences like these: “Voltaire always gave 110 percent and thought outside the box. His bottom line was that as people went forward into the future, they would, at the end of the day, step up to the plate and realize that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.” Ugh. Rewrite as “Voltaire tried to persuade people that the Jesuits were cony, step up to the plate and realize that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.” Ugh. Rewrite as “Voltaire tried to persuade people that the Jesuits were conniving perverts.”
Intensifier abuse/exaggeration.
Avoid inflating your prose with unsustainable claims of size, importance, uniqueness, certainty, or intensity. Such claims mark you as an inexperienced writer trying to impress the reader. Your statement is probably not certain ; your subject probably not unique , the biggest, the best, or the most important. Also, the adverb very will rarely strengthen your sentence. Strike it. (“President Truman was very determined to stop the spread of communism in Greece.”) Rewrite as “President Truman resolved to stop the spread of communism in Greece.”
Mixed image.
Once you have chosen an image, you must stay with language compatible with that image. In the following example, note that the chain, the boiling, and the igniting are all incompatible with the image of the cold, rolling, enlarging snowball: “A snowballing chain of events boiled over, igniting the powder keg of war in 1914.” Well chosen images can enliven your prose, but if you catch yourself mixing images a lot, you're probably trying to write beyond your ability. Pull back. Be more literal.
Clumsy transition.
If your reader feels a jolt or gets disoriented at the beginning of a new paragraph, your paper probably lacks unity. In a good paper, each paragraph is woven seamlessly into the next. If you find yourself beginning your paragraphs with phrases such as “Another aspect of this problem...,” then you are probably “stacking note cards” rather than developing a thesis.
Unnecessary relative clause.
If you don’t need to restrict the meaning of your sentence’s subject, then don’t. (“Napoleon was a man who tried to conquer Europe.”) Here the relative clause adds nothing. Rewrite as “Napoleon tried to conquer Europe.” Unnecessary relative clauses are a classic form of wordiness.
Distancing or demeaning quotation marks.
If you believe that a frequently used word or phrase distorts historical reality, don’t put it in dismissive, sneering quotation marks to make your point (“the communist ‘threat’ to the ‘free’ world during the Cold War”). Many readers find this practice arrogant, obnoxious, and precious, and they may dismiss your arguments out of hand. If you believe that the communist threat was bogus or exaggerated, or that the free world was not really free, then simply explain what you mean.
Remarks on Grammar and Syntax
Ideally, your professor will help you to improve your writing by specifying exactly what is wrong with a particular passage, but sometimes you may find a simple awk in the margin. This all-purpose negative comment usually suggests that the sentence is clumsy because you have misused words or compounded several errors. Consider this sentence from a book review:
“However, many falsehoods lie in Goldhagen’s claims and these will be explored.”
What is your long-suffering professor to do with this sentence? The however contributes nothing; the phrase falsehoods lie is an unintended pun that distracts the reader; the comma is missing between the independent clauses; the these has no clear antecedent ( falsehoods? claims? ); the second clause is in the passive voice and contributes nothing anyway; the whole sentence is wordy and screams hasty, last-minute composition. In weary frustration, your professor scrawls awk in the margin and moves on. Buried under the twelve-word sentence lies a three-word idea: “Goldhagen often errs.” When you see awk, check for the common errors in this list. If you don’t understand what’s wrong, ask.
Unclear antecedent.
All pronouns must refer clearly to antecedents and must agree with them in number. The reader usually assumes that the antecedent is the immediately preceding noun. Do not confuse the reader by having several possible antecedents. Consider these two sentences:
“Pope Gregory VII forced Emperor Henry IV to wait three days in the snow at Canossa before granting him an audience. It was a symbolic act.”
To what does the it refer? Forcing the Emperor to wait? The waiting itself? The granting of the audience? The audience itself? The whole previous sentence? You are most likely to get into antecedent trouble when you begin a paragraph with this or it , referring vaguely back to the general import of the previous paragraph. When in doubt, take this test: Circle the pronoun and the antecedent and connect the two with a line. Then ask yourself if your reader could instantly make the same diagram without your help. If the line is long, or if the circle around the antecedent is large, encompassing huge gobs of text, then your reader probably will be confused. Rewrite. Repetition is better than ambiguity and confusion.
Faulty parallelism.
You confuse your reader if you change the grammatical construction from one element to the next in a series. Consider this sentence:
“King Frederick the Great sought to expand Prussia, to rationalize agriculture, and that the state support education.”
The reader expects another infinitive, but instead trips over the that . Rewrite the last clause as “and to promote state-supported education.” Sentences using neither/nor frequently present parallelism problems. Note the two parts of this sentence:
“After 1870 the cavalry charge was neither an effective tactic, nor did armies use it frequently.”
The sentence jars because the neither is followed by a noun, the nor by a verb. Keep the parts parallel.
Rewrite as “After 1870 the cavalry charge was neither effective nor frequently used.”
Sentences with not only/but also are another pitfall for many students. (“Mussolini attacked not only liberalism, but he also advocated militarism.”) Here the reader is set up to expect a noun in the second clause, but stumbles over a verb. Make the parts parallel by putting the verb attacked after the not only .
Misplaced modifier/dangling element.
Do not confuse the reader with a phrase or clause that refers illogically or absurdly to other words in the sentence. (“Summarized on the back cover of the American paperback edition, the publishers claim that...”) The publishers are not summarized on the back cover. (“Upon finishing the book, many questions remain.”) Who finished the book? Questions can’t read. Avoid following an introductory participial clause with the expletives it or there . Expletives are by definition filler words; they can’t be agents. (“Having examined the origins of the Meiji Restoration in Japan, it is apparent that...”) Apparent to whom? The expletive it didn’t do the examining. (“After going on the Long March, there was greater support for the Communists in China.”) Who went on the Long March? There didn’t go on the Long March. Always pay attention to who’s doing what in your sentences.
Run-on sentence.
Run-on sentences string together improperly joined independent clauses. Consider these three sentences:
“Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved privately he maintained his convictions.” “Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved, privately he maintained his convictions.” “Galileo recanted his teaching that the earth moved, however, privately he maintained his convictions.”
The first fuses two independent clauses with neither a comma nor a coordinating conjunction; the second uses a comma but omits the coordinating conjunction; and the third also omits the coordinating conjunction (however is not a coordinating conjunction). To solve the problem, separate the two clauses with a comma and the coordinating conjunction but. You could also divide the clauses with a semicolon or make separate sentences. Remember that there are only seven coordinating conjunctions ( and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet ).
Sentence fragment.
Write in sentences. A sentence has to have a subject and a predicate. If you string together a lot of words, you may lose control of the syntax and end up with a sentence fragment. Note that the following is not a sentence:
“While in Western Europe railroad building proceeded rapidly in the nineteenth century, and in Russia there was less progress.”
Here you have a long compound introductory clause followed by no subject and no verb, and thus you have a fragment. You may have noticed exceptions to the no-fragments rule. Skilful writers do sometimes intentionally use a fragment to achieve a certain effect. Leave the rule-breaking to the experts.
Confusion of restrictive and nonrestrictive clauses.
Consider these two versions of the same sentence:
1. “World War I, which raged from 1914-1918, killed millions of Europeans.” 2. “World War I that raged from 1914-1918 killed millions of Europeans.”
The first sentence has a nonrestrictive relative clause; the dates are included almost as parenthetical information. But something seems amiss with the second sentence. It has a restrictive relative clause that limits the subject (World War I) to the World War I fought between 1914 and 1918, thus implying that there were other wars called World War I, and that we need to distinguish among them. Both sentences are grammatically correct, but the writer of the second sentence appears foolish. Note carefully the distinction between that (for use in restrictive clauses, with no comma) and which (for use in nonrestrictive clauses, with a comma).
Confusion about who’s doing what.
Remember—history is about what people do, so you need to be vigilant about agency. Proofread your sentences carefully, asking yourself, “Have I said exactly who is doing or thinking what, or have I inadvertently attributed an action or belief to the wrong person or group?” Unfortunately, there are many ways to go wrong here, but faulty punctuation is among the most common. Here’s a sentence about Frantz Fanon, the great critic of European imperialism. Focus on the punctuation and its effect on agency: “Instead of a hierarchy based on class, Fanon suggests the imperialists establish a hierarchy based on race.” As punctuated, the sentence says something absurd: that Fanon is advising the imperialists about the proper kind of hierarchy to establish in the colonies. Surely, the writer meant to say that, in his analysis of imperialism, Fanon distinguishes between two kinds of hierarchy. A comma after suggests fixes the immediate problem. Now look at the revised sentence. It still needs work. Better diction and syntax would sharpen it. Fanon does not suggest (with connotations of both hinting and advocating); he states outright. What’s more, the comparison of the two kinds of hierarchy gets blurred by too many intervening words. The key point of the sentence is, in effect, “instead of A, we have B.” Clarity demands that B follow A as closely as possible, and that the two elements be grammatically parallel. But between the elements A and B, the writer inserts Fanon (a proper noun), suggests (a verb), imperialists (a noun), and establish (a verb). Try the sentence this way: “Fanon says that the imperialists establish a hierarchy based on race rather than class.” Now the agency is clear: We know what Fanon does, and we know what the imperialists do. Notice that errors and infelicities have a way of clustering. If you find one problem in a sentence, look for others.
Confusion about the objects of prepositions.
Here’s another one of those common problems that does not receive the attention it merits. Discipline your prepositional phrases; make sure you know where they end. Notice the mess in this sentence: “Hitler accused Jewish people of engaging in incest and stating that Vienna was the ‘personification of incest.’” The reader thinks that both engaging and stating are objects of the preposition of. Yet the writer intends only the first to be the object of the preposition. Hitler is accusing the Jews of engaging , but not of stating ; he is the one doing the stating . Rewrite as “Hitler accused the Jews of incest; he stated that Vienna was the ‘personification of incest.’” Note that the wordiness of the original encouraged the syntactical mess. Simplify. It can’t be said too many times: Always pay attention to who’s doing what in your sentences.
Misuse of the comparative.
There are two common problems here. The first might be called the “floating comparative.” You use the comparative, but you don’t say what you are comparing. (“Lincoln was more upset by the dissolution of the union.”) More upset than by what? More upset than who? The other problem, which is more common and takes many forms, is the unintended (and sometimes comical) comparison of unlike elements. Consider these attempts to compare President Clinton to President George H. W. Bush. Often the trouble starts with a possessive:
“President Clinton’s sexual appetite was more voracious than President Bush.”
You mean to compare appetites, but you've forgotten about your possessive, so you absurdly compare an appetite to a man. Rewrite as “more voracious than President Bush’s.” A variation of this problem is the unintended comparison resulting from the omission of a verb:
“President Clinton liked women more than President Bush.”
Re-write as “more than did President Bush.”
A misplaced modifier may also cause comparison trouble: “Unlike the Bush administration, sexual scandal nearly destroyed the Clinton administration.” Rewrite as “Unlike the Bush administration, the Clinton administration was nearly destroyed by sexual scandal.” Here the passive voice is better than the misplaced modifier, but you could rewrite as “The Bush administration had been free of sexual scandal, which nearly destroyed the Clinton administration.”
Misuse of apostrophe.
Get control of your apostrophes. Use the apostrophe to form singular or plural possessives (Washington’s soldiers; the colonies’ soldiers) or to form contractions (don’t; it’s). Do not use the apostrophe to form plurals. (“The communists [not communists’] defeated the nationalists [not nationalists’] in China.”)
Comma after although.
This is a new error, probably a carryover from the common conversational habit of pausing dramatically after although . ( “Although , coffee consumption rose in eighteenth-century Europe, tea remained far more popular.”) Delete the comma after although . Remember that although is not a synonym for the word however , so you cannot solve the problem in the sentence by putting a period after Europe . A clause beginning with although cannot stand alone as a sentence.
Comma between subject and verb.
This is a strange new error. (“Hitler and Stalin, agreed to a pact in August 1939.”) Delete the comma after Stalin. Finally, two hints: If your word-processing program underlines something and suggests changes, be careful. When it comes to grammar and syntax, your computer is a moron. Not only does it fail to recognize some gross errors, it also falsely identifies some correct passages as errors. Do not cede control of your writing decisions to your computer. Make the suggested changes only if you are positive that they are correct. If you are having trouble with your writing, try simplifying. Write short sentences and read them aloud to test for clarity. Start with the subject and follow it quickly with an active verb. Limit the number of relative clauses, participial phrases, adjectives, adverbs, and prepositional phrases. You will win no prizes for eloquence, but at least you will be clear. Add complexity only when you have learned to handle it.
An historical/an historian.
The consonant “H” is not silent in historical and historian , so the proper form of the indefinite article is “A.”
Avoid the common solecism of using feel as a synonym for think, believe, say, state, assert, contend, argue, conclude, or write. (“Marx felt that the bourgeoisie exploited the proletariat.” “Emmeline Pankhurst felt that British women should be able to vote.”) The use of feel in these sentences demeans the agents by suggesting undisciplined sentiment rather than carefully formulated conviction. Concentrate on what your historical actors said and did; leave their feelings to speculative chapters of their biographies. As for your own feelings, keep them out of your papers. (“I feel that Lincoln should have freed the slaves earlier.”) Your professor will be delighted that the material engages both your head and your heart, but your feelings cannot be graded. If you believe that Lincoln should have acted earlier, then explain, giving cogent historical reasons.
The fact that.
This is a clumsy, unnecessary construction. ( “The fact that Nixon resigned in disgrace damaged the Republican Party.”) Re-word as “Nixon resigned in disgrace, damaging the Republican Party.” Never use the hideous phrase due to the fact that.
In terms of.
This phrase is filler. Get rid of it. (“Bismarck was a success in terms of uniting Germany.) Rewrite as “Bismarck successfully united Germany.”
Attend carefully to the placement of this limiting word. Note, for example, these three sentences:
“The government only interred Japanese Americans during World War II.” “The government interred only Japanese Americans during World War II.” “The government interred Japanese Americans only during World War II.”
The first limits the action to interring (as opposed to, say, killing); the second limits the group interred (i.e., not Italian Americans); the third limits the time of interring (i.e., not during other wars).
Thus and therefore.
More than likely, you have not earned these words and are implying that you have said more than you actually have. Use them sparingly, only when you are concluding a substantial argument with a significant conclusion.
Misuse of instead.
Instead is an adverb, not a conjunction. Consider this sentence: “Charles Beard argued that the framers of the constitution were not idealists, instead they promoted their economic interests.” Revise as “The framers of the constitution, Charles Beard argued, did not uphold ideals; instead , they promoted their economic interests.” Now the instead appears properly as an adverb. (Note also that the two clauses are now parallel—both contain transitive verbs.)
Essentially and basically.
These are usually either filler words (the written equivalent of “uh” or “um”) or weasel words that merely call attention to your vagueness, lack of conviction, or lazy unwillingness to qualify precisely. (“ Essentially , Churchill believed that Nazi Germany presented a grave danger to Britain.”) Delete essentially and basically unless you are writing about essences or bases.
Both share or both agree.
These are redundant. If two people share or agree , they are both involved by definition. (“Stalin and Mao both agreed that capitalism belonged in the dustbin of history.”) Delete both .
This word means one of a kind. It is an absolute. Something cannot be very unique, more unique, or somewhat unique.
Incredible.
In casual conversation incredible often means extraordinary, astonishing, or impressive (“Yesterday’s storm was incredible.”). To avoid confusion in historical prose, you should stick with the original meaning of incredible : not believable. If you write that “William Jennings Bryan gave incredible speeches,” you’re saying that you don’t believe his speeches, or that his audiences didn’t believe them at the time—in other words, that he appeared to be lying or mistaken. You probably mean that he gave great speeches. If you write that “It’s incredible that Japan attacked Pearl Harbor,” you’re calling into question the very existence of a historical event. You probably mean that the Japanese attack was unwise or reckless. English is rich with adjectives. Finding the best one forces you to think about what you really mean.
As a synonym for subject matter, bone of contention, reservation, or almost anything else vaguely associated with what you are discussing, the word issue has lost its meaning through overuse. (“There were many issues involved with Truman’s decision to use the atomic bomb, and some historians have issues with his decision.”) Stop talking about issues and get to the point.
Beware of the word literally . It’s commonly misused, and you almost never need it in historical prose. Literally means actually, factually, exactly, directly, without metaphor. The careful writer would never say, “Roosevelt literally swamped Landon in the election of 1936.” One imagines Roosevelt (in his wheelchair no less!) dumping the hapless Landon off a pier in the Everglades on election night. The swamping was figurative, strictly a figure of speech. The adverb literally may also cause you trouble by falsely generalizing the coverage of your verb. “London was literally destroyed by the blitz.” This suggests that the whole city was destroyed, when, in fact, only parts were destroyed. Rewrite as “The blitz destroyed parts of London.” Now you’ve qualified properly (and gotten rid of the passive).
When you’re tempted to use this word, resist. Like issue , involve tells the reader too little. (“Erasmus was involved in the Renaissance.”) This statement could mean virtually anything. Delete it and discuss specifically what Erasmus said or did.
This is a fine old word with many precise meanings, but as an overused synonym for feature, side, or part, it is usually a sign of insipid prose (“Another aspect of the issues in this area is the fact that...”). Just get directly to the point.
Most good writers frown on the use of this word as a verb.(“Eisenhower’s military background impacted his foreign policy.”) Affected, influenced, or shaped would be better here. Impacted suggests painfully blocked wisdom teeth or feces. Had an impact is better than impacted , but is still awkward because impact implies a collision.
Here is another beloved but vapid word. (“Many factors led to the Reformation.”) Such a sentence usually opens a vague, boring, weaseling paragraph. If you believe (quite reasonably) that the Reformation had many causes, then start evaluating them.
Meaningful.
Overuse has drained the meaning from meaningful . (“Peter the Great took meaningful steps to westernize Russia.”) Just get to the point.
Interesting.
The adjective interesting is vague, overused, and does not earn its keep. (“Burckhardt had an interesting perspective on the Renaissance.”) This sentence is filler. Delete it and explain and analyze his perspective.
The events that transpired.
Your professor will gag on this one. Events take place or happen by definition, so the relative clause is redundant. Furthermore, most good writers do not accept transpire as a synonym for happen. Again, follow the old rule of thumb: Get right to the point, say what happened, and explain its significance. You don’t need any filler about events and transpiring .
The reason is because.
This phrase is awkward and redundant. Replace it with the reason is, or better still, simply delete it and get right to your reason.
For all intensive purposes.
The phrase is for all intents and purposes , and few good writers use it in formal prose anyway.
Take for granite.
This is an illiteracy. The phrase is “ take for granted .”
Should of/could of.
You mean should have or could have .
Center around.
Good writers frown on this phrase because it’s illogical and jarring. Use center on or center in. Attention to a small detail like this indicates that you’re thinking carefully about what you’re saying, so when the big problems confront you, you’ll be disciplined and ready.
Begs the question.
Recently, many people have started to use this phrase to mean raises, invites, or brings up the question. (“Stalin’s purges beg the question of whether he was paranoid.”) Actually, begging the question is the common logical fallacy of assuming your conclusion as part of your argument. (“In the late nineteenth century, many Americans moved to the cities because of urbanization.”) Note that the use of abstractions (e.g., urbanization) encourages begging the question . Understanding this fallacy is central to your education. The formal Latin term, petitio principii, is too fancy to catch on, so you need to preserve the simple English phrase. If something raises a question, just say so.
Historic/historical confusion.
Everything in the past or relating to the past is historical. Resist the media-driven hype that elevates the ordinary to the historic . (“A three-alarm fire last night destroyed the historic site of the first Portuguese-owned dry cleaners in Cleveland.”) Reserve the word historic for the genuinely important events, persons, or objects of the past. The Norman invasion of England in 1066 was indeed historic . Historically , historians have gathered annually for a historical convention; so far, none of the conventions has been historic .
Affect/effect confusion.
The chances are that the verb you want is affect , which means to have an influence on (“The Iranian hostage crisis affected [not effected] the presidential election of 1980”). Effect as a verb means to bring about or cause to exist ( effect change). Effect as a noun means result or consequence (“The effect of the Iranian hostage crisis on the election...”).
While/whereas confusion.
If you’re stressing contrast, the word you want is whereas . While stresses simultaneity. “Hobbes had a dismal view of human nature, whereas [not while] Rousseau believed that man had a natural sense of pity.”
It’s/its confusion.
This is the classic bonehead error. Note that the spell checker won’t help you. And remember— its’ is not a word at all.
Reign/rein confusion.
A queen reigns during her reign. You rein in a horse with reins.
Their/there/they’re confusion.
You do know the difference. Pay attention.
Everyday/every day confusion.
As an adjective, everyday (one word) means routine. If you wish to say that something happened on every successive day, then you need two words, the adjective every and the noun day . Note the difference in these two sentences: “Kant was famous for going on the same constitutional at the same time every day . For Kant, exercise and thinking were everyday activities.”
Refer/allude confusion.
To allude means to refer to indirectly or to hint at. The word you probably want in historical prose is refer , which means to mention or call direct attention to. “In the first sentence of the ‘Gettysburg Address’ Lincoln refers [not alludes ] to the fathers of the nation [he mentions them directly]; he alludes to the ‘Declaration of Independence’ [the document of four score and seven years earlier that comes to the reader’s mind, but that Lincoln doesn’t directly mention].”
Novel/book confusion.
Novel is not a synonym for book. A novel is a long work of fiction in prose. A historical monograph is not a novel —unless the historian is making everything up.
Than/then confusion.
This is an appalling new error. If you are making a comparison, you use the conjunction than . (“President Kennedy’s health was worse than [not then ] the public realized.”)
Lead/led confusion.
The past tense of the verb to lead is led (not lead ). “Sherman led [not lead ] a march to the sea.”
Lose/loose confusion.
The opposite of win is lose , not loose . “Supporters of the Equal Rights Amendment suspected that they would lose [not loose ] the battle to amend the constitution.”
However/but confusion.
However may not substitute for the coordinating conjunction but. (“Mussolini began his career as a socialist, but [not however ] he later abandoned socialism for fascism.”) The word however has many proper uses; however , [note the semicolon and comma] graceful writers use it sparingly.
Cite/site/sight confusion.
You cited a source for your paper; ancient Britons sited Stonehenge on a plain; Columbus’s lookout sighted land.
Conscience/conscious confusion.
When you wake up in the morning you are conscious , though your conscience may bother you if you’ve neglected to write your history paper.
Tenet/tenant confusion.
Your religion, ideology, or worldview all have tenets —propositions you hold or believe in. Tenants rent from landlords.
All are not/not all are confusion.
If you write, “ All the colonists did not want to break with Britain in 1776,” the chances are you really mean, “ Not all the colonists wanted to break with Britain in 1776.” The first sentence is a clumsy way of saying that no colonists wanted to break with Britain (and is clearly false). The second sentence says that some colonists did not want to break with Britain (and is clearly true, though you should go on to be more precise).
Nineteenth-century/nineteenth century confusion.
Historians talk a lot about centuries, so you need to know when to hyphenate them. Follow the standard rule: If you combine two words to form a compound adjective, use a hyphen, unless the first word ends in ly. (“ Nineteenth-century [hyphenated] steamships cut the travel time across the Atlantic.”) Leave out the hyphen if you’re just using the ordinal number to modify the noun century. (“In the nineteenth century [no hyphen] steamships cut the travel time across the Atlantic.”) By the way, while you have centuries in mind, don’t forget that the nineteenth century is the 1800s, not the 1900s. The same rule for hyphenating applies to middle-class and middle class —a group that historians like to talk about.
Bourgeois/bourgeoisie confusion.
Bourgeois is usually an adjective, meaning characteristic of the middle class and its values or habits. Occasionally, bourgeois is a noun, meaning a single member of the middle class. Bourgeoisie is a noun, meaning the middle class collectively. (“Marx believed that the bourgeoisie oppressed the proletariat; he argued that bourgeois values like freedom and individualism were hypocritical.”)
Your professor may ask you to analyze a primary document. Here are some questions you might ask of your document. You will note a common theme—read critically with sensitivity to the context. This list is not a suggested outline for a paper; the wording of the assignment and the nature of the document itself should determine your organization and which of the questions are most relevant. Of course, you can ask these same questions of any document you encounter in your research.
- What exactly is the document (e.g., diary, king’s decree, opera score, bureaucratic memorandum, parliamentary minutes, newspaper article, peace treaty)?
- Are you dealing with the original or with a copy? If it is a copy, how remote is it from the original (e.g., photocopy of the original, reformatted version in a book, translation)? How might deviations from the original affect your interpretation?
- What is the date of the document?
- Is there any reason to believe that the document is not genuine or not exactly what it appears to be?
- Who is the author, and what stake does the author have in the matters discussed? If the document is unsigned, what can you infer about the author or authors?
- What sort of biases or blind spots might the author have? For example, is an educated bureaucrat writing with third-hand knowledge of rural hunger riots?
- Where, why, and under what circumstances did the author write the document?
- How might the circumstances (e.g., fear of censorship, the desire to curry favor or evade blame) have influenced the content, style, or tone of the document?
- Has the document been published? If so, did the author intend it to be published?
- If the document was not published, how has it been preserved? In a public archive? In a private collection? Can you learn anything from the way it has been preserved? For example, has it been treated as important or as a minor scrap of paper?
- Does the document have a boilerplate format or style, suggesting that it is a routine sample of a standardized genre, or does it appear out of the ordinary, even unique?
- Who is the intended audience for the document?
- What exactly does the document say? Does it imply something different?
- If the document represents more than one viewpoint, have you carefully distinguished between the author’s viewpoint and those viewpoints the author presents only to criticize or refute?
- In what ways are you, the historian, reading the document differently than its intended audience would have read it (assuming that future historians were not the intended audience)?
- What does the document leave out that you might have expected it to discuss?
- What does the document assume that the reader already knows about the subject (e.g., personal conflicts among the Bolsheviks in 1910, the details of tax farming in eighteenth-century Normandy, secret negotiations to end the Vietnam war)?
- What additional information might help you better interpret the document?
- Do you know (or are you able to infer) the effects or influences, if any, of the document?
- What does the document tell you about the period you are studying?
- If your document is part of an edited collection, why do you suppose the editor chose it? How might the editing have changed the way you perceive the document? For example, have parts been omitted? Has it been translated? (If so, when, by whom, and in what style?) Has the editor placed the document in a suggestive context among other documents, or in some other way led you to a particular interpretation?
Your professor may ask you to write a book review, probably of a scholarly historical monograph. Here are some questions you might ask of the book. Remember that a good review is critical, but critical does not necessarily mean negative. This list is not meant to be exhaustive, nor is it a suggested outline. Of course, you can ask these same questions of any secondary historical work, even if you’re not writing a review.
- Who is the author, and what are his or her qualifications? Has the author written other books on the subject?
- When was the book written, and how does it fit into the scholarly debate on the subject? For example, is Smith writing to refute that idiot Jones; to qualify the work of the competent but unimaginative Johnson; or to add humbly to the evidence presented by the redoubtable Brown’s classic study? Be sure not to confuse the author’s argument with those arguments he or she presents only to criticize later.
- What is the book’s basic argument? (Getting this right is the foundation of your review.)
- What is the author’s method? For example, does the author rely strictly on narrative and anecdotes, or is the book analytical in some way?
- What kinds of evidence does the author use? For example, what is the balance of primary and secondary sources? Has the author done archival work? Is the source base substantial, or does it look thin? Is the author up-to-date in the scholarly literature?
- How skillfully and imaginatively has the author used the evidence?
- Does the author actually use all of the material in the bibliography, or is some of it there for display?
- What sorts of explicit or implicit ideological or methodological assumptions does the author bring to the study? For example, does he or she profess bland objectivity? A Whig view of history? Marxism?
- How persuasive is the author’s argument?
- Is the argument new, or is it old wine in new bottles?
- Is the argument important, with wide-ranging implications, or is it narrow and trivial?
- Is the book well organized and skillfully written?
- What is your overall critical assessment of the book?
- What is the general significance, if any, of the book? (Make sure that you are judging the book that the author actually wrote, not complaining that the author should have written a different book.)
Here are some tips for those long, intimidating term papers or senior theses:
- Start early. If you don’t, none of these tips will matter. Big trouble is looming if you don’t have a specific topic by the end of the first week. You should be delving into the sources during the second week.
- Keep in mind all of the dos and don’ts in this booklet.
- Work closely with your professor to assure that your topic is neither too broad nor too narrow.
- Set up a schedule with your professor and check his or her policy about reading rough drafts or parts of rough drafts. Then keep your professor informed about what you’re doing. You don’t want any unpleasant surprises. You certainly don’t want to hear, “I haven’t seen you for weeks, and it sounds like you’re way off base. How can you possibly get this done with only two weeks left in the semester?”
- Make an appointment with Kristin Strohmeyer, the history reference librarian in Burke Library. She will help you to find and use the appropriate catalogs and indexes.
- Use your imagination in compiling a bibliography. Think of all of the possible key words and subjects that may lead you to material. If you find something really good, check the subjects under which it is cataloged. Comb the notes and bibliographies of books and articles you’ve already found.
- Much of what you need will not be in our library, so get to know the friendly folks in the Interlibrary Loan department.
- Start early. This can’t be said too often.
- Use as many primary sources as you can.
- Jot down your ideas as they come to you. You may not remember them later.
- Take careful notes on your reading. Label your notes completely and precisely. Distinguish meticulously and systematically between what you are directly quoting and what you are summarizing in your own words. Unintended plagiarism is still plagiarism. Stay clean as a hound’s tooth. Write down not just the page of the quotation or idea, but also the whole run of pages where the matter is discussed. Reread all of your notes periodically to make sure that you still understand them and are compiling what you will need to write your paper. Err on the side of writing down more than you think you will need. Copious, precise notes won’t come back to haunt you; skimpy, vague notes will. Just accept that there is something anal about good note-taking.
- If you take notes directly into your computer, they will be easy to index and pull up, but there are a couple of downsides. You will not be able to see all of them simultaneously, as you can note cards laid out on a big table. What you gain in ease of access may come at the price of losing the big picture. Also, if your notes are in your computer, you may be tempted to save time and thought by pasting many of them directly into your paper. Note cards encourage you to rethink and to rework your ideas into a unified whole.
- Don’t start to write until you have a good outline.
- Make sure that your paper has a thesis. (See the entry State a clear thesis. )
- Check and recheck your facts.
- Footnote properly. (See the entry Cite sources carefully .)
- Save plenty of time to proofread.
- Start early.
Top Ten Signs that you may be Writing a Weak History Paper
10. You’re overjoyed to find that you can fill the required pages by widening all margins.
9. You haven’t mentioned any facts or cited any sources for several paragraphs.
8. You find yourself using the phrase “throughout history mankind has...”
7. You just pasted in another 100 words of quotations.
6. You haven’t a clue about the content of your next paragraph.
5. You’re constantly clicking on The Britannica, Webster’s, and Bartlett’s.
4. Your writing tutor sneaks another look at her watch as she reminds you for the third time to clarify your thesis.
3. Your main historical actors are this, it, they, the people, and society, and they are all involved with factors, aspects, impacts, and issues.
2. You just realize that you don’t understand the assignment, but it’s 3:00 A.M, the paper is due at 9:00, and you don’t dare call your professor.
1. You’re relieved that the paper counts for only 20 percent of the course grade.
Final Advice
You guessed it — start early.
Studying History at Hamilton
Students will learn to use interdisciplinary methods from the humanities and social sciences to probe the sources of the past for answers to present questions. They will learn to draw comparisons and connections among diverse societies across a range of historical eras. They will further learn to convey their findings through writing that is clearly structured, precise, and persuasive.
Tutor Appointments
Peer tutor and consultant appointments are managed through TracCloud (login required). Find resources and more information about the ALEX centers using the following links.
Office / Department Name
Nesbitt-Johnston Writing Center
Contact Name
Jennifer Ambrose
Writing Center Director

Help us provide an accessible education, offer innovative resources and programs, and foster intellectual exploration.
Site Search
How to Write a History Essay?
04 August, 2020
10 minutes read
Author: Tomas White
There are so many types of essays. It can be hard to know where to start. History papers aren’t just limited to history classes. These tasks can be assigned to examine any important historical event or a person. While they’re more common in history classes, you can find this type of assignment in sociology or political science course syllabus, or just get a history essay task for your scholarship. This is Handmadewriting History Essay Guide - let's start!

Purpose of a History Essay
Wondering how to write a history essay? First of all, it helps to understand its purpose. Secondly, this essay aims to examine the influences that lead to a historical event. Thirdly, it can explore the importance of an individual’s impact on history.
However, the goal isn’t to stay in the past. Specifically, a well-written history essay should discuss the relevance of the event or person to the “now”. After finishing this essay, a reader should have a fuller understanding of the lasting impact of an event or individual.
Need basic essay guidance? Find out what is an essay with this 101 essay guide: What is an Essay?
Elements for Success
Indeed, understanding how to write a history essay is crucial in creating a successful paper. Notably, these essays should never only outline successful historic events or list an individual’s achievements. Instead, they should focus on examining questions beginning with what , how , and why . Here’s a pro tip in how to write a history essay: brainstorm questions. Once you’ve got questions, you have an excellent starting point.
Preparing to Write

Evidently, a typical history essay format requires the writer to provide background on the event or person, examine major influences, and discuss the importance of the forces both then and now. In addition, when preparing to write, it’s helpful to organize the information you need to research into questions. For example:
- Who were the major contributors to this event?
- Who opposed or fought against this event?
- Who gained or lost from this event?
- Who benefits from this event today?
- What factors led up to this event?
- What changes occurred because of this event?
- What lasting impacts occurred locally, nationally, globally due to this event?
- What lessons (if any) were learned?
- Why did this event occur?
- Why did certain populations support it?
- Why did certain populations oppose it?
These questions exist as samples. Therefore, generate questions specific to your topic. Once you have a list of questions, it’s time to evaluate them.
Evaluating the Question

Seasoned writers approach writing history by examining the historic event or individual. Specifically, the goal is to assess the impact then and now. Accordingly, the writer needs to evaluate the importance of the main essay guiding the paper. For example, if the essay’s topic is the rise of American prohibition, a proper question may be “How did societal factors influence the rise of American prohibition during the 1920s? ”
This question is open-ended since it allows for insightful analysis, and limits the research to societal factors. Additionally, work to identify key terms in the question. In the example, key terms would be “societal factors” and “prohibition”.
Summarizing the Argument
The argument should answer the question. Use the thesis statement to clarify the argument and outline how you plan to make your case. In other words. the thesis should be sharp, clear, and multi-faceted. Consider the following tips when summarizing the case:
- The thesis should be a single sentence
- It should include a concise argument and a roadmap
- It’s always okay to revise the thesis as the paper develops
- Conduct a bit of research to ensure you have enough support for the ideas within the paper
Outlining a History Essay Plan

Once you’ve refined your argument, it’s time to outline. Notably, many skip this step to regret it then. Nonetheless, the outline is a map that shows where you need to arrive historically and when. Specifically, taking the time to plan, placing the strongest argument last, and identifying your sources of research is a good use of time. When you’re ready to outline, do the following:
- Consider the necessary background the reader should know in the introduction paragraph
- Define any important terms and vocabulary
- Determine which ideas will need the cited support
- Identify how each idea supports the main argument
- Brainstorm key points to review in the conclusion
Gathering Sources
As a rule, history essays require both primary and secondary sources . Primary resources are those that were created during the historical period being analyzed. Secondary resources are those created by historians and scholars about the topic. It’s a good idea to know if the professor requires a specific number of sources, and what kind he or she prefers. Specifically, most tutors prefer primary over secondary sources.
Where to find sources? Great question! Check out bibliographies included in required class readings. In addition, ask a campus Librarian. Peruse online journal databases; In addition, most colleges provide students with free access. When in doubt, make an appointment and ask the professor for guidance.

Writing the Essay
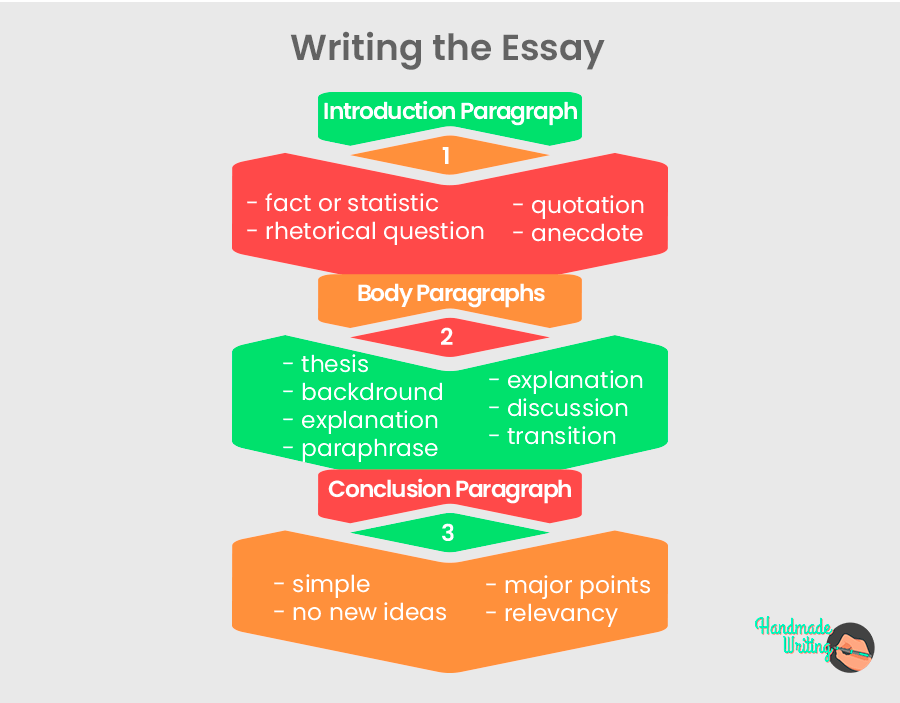
Now that you have prepared your questions, ideas, and arguments; composed the outline ; and gathered sources – it’s time to write your first draft. In particular, each section of your history essay must serve its purpose. Here is what you should include in essay paragraphs.
Introduction Paragraph
Unsure of how to start a history essay? Well, like most essays, the introduction should include an attention-getter (or hook):
- Relevant fact or statistic
- Rhetorical Question
- Interesting quotation
- Application anecdote if appropriate
Once you’ve captured the reader’s interest, introduce the topic. Similarly, present critical historic context. Namely, it is necessary to introduce any key individuals or events that will be discussed later in the essay. At last, end with a strong thesis which acts as a transition to the first argument.
Body Paragraphs
Indeed, each body paragraph should offer a single idea to support the argument. Then, after writing a strong topic sentence, the topic should be supported with correctly cited research. Consequently, a typical body paragraph is arranged as follows:
- Topic sentence linking to the thesis
- Background of the topic
- Research quotation or paraphrase #1
- Explanation and analysis of research
- Research quotation or paraphrase #2
- Transition to the next paragraph
Equally, the point of body paragraphs is to build the argument. Hence, present the weakest support first and end with the strongest. Admittedly, doing so leaves the reader with the best possible evidence.
Conclusion Paragraph
You’re almost there! Eventually, conclusion paragraphs should review the most important points in the paper. In them, you should prove that you’ve supported the argument proposed in the thesis. When writing a conclusion paragraph keep these tips in mind:
- Keep it simple
- Avoid introducing new information
- Review major points
- Discuss the relevance to today
Problems with writing Your History essay ? Try our Essay Writer Service!

Proofreading Your Essay
Once the draft is ready and polished, it’s time to proceed to final editing. What does this process imply? Specifically, it’s about removing impurities and making the essay look just perfect. Here’s what you need to do to improve the quality of your paper:
- Double check the content. In the first place, it’s recommended to get rid of long sentences, correct vague words. Also, make sure that all your paragrahps contain accurate sentences with transparent meaning.
- Pay attention to style. To make the process of digesting your essay easier, focus on crafting a paper with readable style, the one that is known to readers. Above all, the main mission here is to facilitate the perception of your essay. So, don’t forget about style accuracy.
- Practice reading the essay. Of course, the best practice before passing the paper is to read it out loud. Hence, this exercise will help you notice fragments that require rewriting or a complete removal.
History Essay Example
Did you want a history essay example? Take a look at one of our history essay papers.
Make it Shine
An A-level essay takes planning and revision, but it’s achievable. Firstly, avoid procrastination and start early. Secondly, leave yourself plenty of time to brainstorm, outline, research and write. Finally, follow these five tips to make your history essay shine:
- Write a substantial introduction. Particularly, it’s the first impression the professor will have of the paper.
- State a clear thesis. A strong thesis is easier to support.
- Incorporate evidence critically. If while researching you find opposing arguments, include them and discuss their flaws.
- Cite all the research. Whether direct quotations or paraphrases, citing evidence is crucial to avoiding plagiarism, which can have serious academic consequences.
- Include primary and secondary resources. While primary resources may be harder to find, the professor will expect them—this is, after all, a history essay.
History Essay Sample
Ready to tackle the history essay format? Great! Check out this history essay sample from an upper-level history class. While the essay isn’t perfect, the professor points out its many strengths.
Remember: start early and revise, revise, revise . We can’t revise history, but you can revise your ideas until they’re perfect.

A life lesson in Romeo and Juliet taught by death
Due to human nature, we draw conclusions only when life gives us a lesson since the experience of others is not so effective and powerful. Therefore, when analyzing and sorting out common problems we face, we may trace a parallel with well-known book characters or real historical figures. Moreover, we often compare our situations with […]

Ethical Research Paper Topics
Writing a research paper on ethics is not an easy task, especially if you do not possess excellent writing skills and do not like to contemplate controversial questions. But an ethics course is obligatory in all higher education institutions, and students have to look for a way out and be creative. When you find an […]

Art Research Paper Topics
Students obtaining degrees in fine art and art & design programs most commonly need to write a paper on art topics. However, this subject is becoming more popular in educational institutions for expanding students’ horizons. Thus, both groups of receivers of education: those who are into arts and those who only get acquainted with art […]
The Writing Place
Resources – historical writing essentials, introduction to the topic.
Are you taking your first history class at Northwestern and struggling to write that 4-6 page argumentative essay that your professor just assigned you? Or maybe you are a seasoned history major and just need a refresher on how to write an extended research paper? Don’t fret—anyone can learn the essentials of good history writing. I’ve collected the wisdom of four Northwestern history professors (Ed Muir, Brodwyn Fischer, Amy Stanley, and Daniel Immerwahr) and a history PhD student (Joel Penning). I’ve synthesized their wisdom into the following ten essentials of good history writing.
The following quotations are from email messages from these scholars; December 11, 2012.
*Note: This text and its corrected version are not meant to convey historically true information
10 Essentials of Writing a Good History Paper
1. argument.
Though essential to most academic writing, good history writing always contains a strong argument. According to professor Muir, history writing isn’t about coming up with an opinion; instead, “what matters is proving a provable thesis.” An argument isn’t an argument unless you can disagree with it. Professor Fischer adds, “In the best papers, the argument will also be creative, and make me think about the material in a new way.” Oftentimes students try to be overly comprehensive in their response to a prompt. Their argument may be a list of historically true things, but a “list is not an argument,” says professor Stanley. A prompt may ask you to discuss why the colonists rebelled against Britain in the 1770s. You should not say, “The colonists rebelled against Britain in the 1770s because they favored republican government, did not like Britain’s taxation policies, and were outraged at oppressive events like the Boston Massacre.” While most historians consider these three items true, this statement is not a sufficient historical argument because it does not explain how these three items relate to one another. Joel Penning, a grad student in history, says, “don’t be afraid to go out on a limb.” It’s better to say something with which many people will disagree than something that does not really capture anyone’s attention.
2. Counter-arguments
A good argumentative history paper must address counter-arguments. According to professor Immerwahr, “The claim that X happened is rarely interesting. By contrast, X happened, when we might have expected Y to happen , is rarely not interesting.”
3. Evidence
Because good history writing makes an argument, you must have relevant evidence to back up your argument. Penning puts it well in saying that “every paragraph must contain both assertions and evidence which supports them. A paragraph with only assertions is bad scholarship. A paragraph with only evidence is boring.” Referencing good evidence does not mean that you should write about every fact relating to your topic; instead, only use the evidence that supports your argument. Immerwahr goes even further and says that the evidence must provide an “intellectual pathway that the reader must follow to be convinced of the thesis.” Thus, the formula is not argument+supporting evidence=good history writing . Each piece of evidence should ideally relate to what comes before and what comes next.
4. Avoid Generalizations
Penning puts it well: “For the most part, historians don’t care about whether dictatorship always leads to corruption, or if government intervention helps or hinders the economy. So students writing papers for historians shouldn’t care either. Comparison is becoming an increasingly important part of the discipline, but generally historians are interested in specific cases. Do talk about whether Mussolini’s dictatorship led to corruption, or how much the New Deal helped or hurt Depression-era America. For almost anything you write at Northwestern, you won’t have the evidence to say anything broader than that, whether it’s true or not. If you want to talk about universal rules of dictatorship, you’d probably like political science or sociology better.”
5. Conclude Well
In a history paper, your last paragraph should just restate your argument and your evidence, albeit in a different way, right? Wrong. Writing a solid conclusion may be the most overlooked aspect of good history writing. Professor Stanley suggests, “use your conclusion to make one final, elegant point, or point out an irony, or direct the reader to look at the implications of your argument for the next historical period, or suggest some additional avenues for exploration.” Summary isn’t bad, of course, but provide your reader with something interesting to leave him or her feeling good about your paper!
6. No Passive Voice!
Along with having a good argument, any history professor will tell you not to use the passive voice in your history writing. Using the active voice is a good practice in general in your writing, but history seeks to be precise with agency—that is, it seeks to discover what happened and who did it. The passive voice often overlooks this precision. Take, for example, the following sentence written in passive voice: “President Bob was killed on Tuesday.” This sentence says nothing about who killed Bob, which may be essential to your historical argument. The following sentence in active voice reveals more information: “Senator Joe killed President Bob on Tuesday.” In editing your history paper, keep a close look out for passive verbs.
7. Avoid Excessive Use of "To Be" Verbs
Do you find yourself using “was” and “were” too much in your history paper? There’s nothing grammatically wrong with using these past tense forms of “to be,” but your writing may be weak if you do. Instead, use stronger verbs that more descriptively capture what you are trying to say. You could say, “In Boston in 1776, the colonists were angry with British taxation policy.” It’s better to say, “In Boston in 1776, the colonists revolted against British taxation policy.” “Revolted” is stronger and describes more accurately what happened than “were angry.”
8. Past Tense
This should be self-explanatory. In your history paper, your task is to talk about something that happened in the past, so talk about it as if it happened in the past.
9. Wordiness
Have you ever struggled to reach those 6 pages and make up for it by repeating some phrases and adding unnecessary words to make your sentences a little bit longer? History professors know the temptation, and you won’t fool them. Professor Stanley warns, “If you find yourself adding words because you’re worried about making the minimum, that’s a bad sign. You need a new idea to add to your analysis; you don’t need wordier or repetitive sentences.” Instead of saying, “At the end of the eighteenth century, the people who identified themselves as colonists sought to rebel against the British rule of government in 1776,” say, “The colonists rebelled against the British in 1776.”
10. Write Out What Century You Are Referring To
This last history essential may seem small, but not incorporating it into your writing won’t make a good impression on your professor or TA. Always write out the century. Don’t say “the 18 th century.” Instead say, “the eighteenth century.” Moreover use the following grammatical convention when you want to talk about the early, mid, or late part of a century: “the mid-eighteenth century” or “the late-eighteenth century.”
Exercise: Finding Mistakes in a Sample Passage
Practice: diagnosing mistakes.
With practice, you can incorporate these ten essentials of good history writing into your own writing. In the meantime, review the following writing excerpt and see if you can diagnose the mistakes it is making.
Sample Excerpt: Suburban Development
Suburbs were established extensively in the United States in the 20 th century. Suburban expansion was result of rich people wanting to move away from inner cities for new work opportunities, the development of rail lines, the automobile, and new jobs away from inner cities. Suburbs now make up a large part of metropolitan areas.
In the early 1900s, rich people who previously lived in inner cities sought out to move to the suburbs because they thought through the ramifications of potentially losing their jobs if they stayed in the inner cities. Paul Johnson said, “I think it’s really fascinating that in 1925 people moved from downtown Chicago to new suburbs like Naperville and Wilmette.”[1] In addition, “the automobile clearly helped people who had previously lived in inner cities commute to work everyday from their suburban homes.”[2] Cars were manufactured and driven very often from suburbs to the cities. One can assume from all of this that economic decisions and transportation opportunities helped people move to the suburbs.
In conclusion, the suburb was the development of several factors. There were rich people wanting to move away from the city, new railroads were constructed that extended into the outer periphery of the city in places that we now can suburbs, automobile production was greatly expanded, and new jobs rose up in cities for these rich people. It is clear that suburbs have led to the democratization of the United States .
Commentary on the Sample Excerpt
Suburbs were established extensively in the United States in the 20 th century. (Passive voice. “Were established” is passive. Hypothetically, this sentence could say, “Business and government leaders established…” In addition, “20 th century” should be twentieth century.) Suburban expansion was result of rich people wanting to move away from inner cities for new work opportunities, the development of rail lines, the automobile, and new jobs away from inner cities. (Argumentation. This sentence, intended to be the thesis statement, merely lists a variety of factors that led to the rise of suburbs; it does not contain a coherent argument. A revised thesis statement could be the following: “New economic opportunities in city peripheries, coupled with new transportation developments, sparked the growth of suburbs.”) Suburbs now make up a large part of metropolitan areas. (Argumentation. This sentence is slightly out of place; if it were intended to be the argument, it would not suffice as you can’t really argue with it.)
In the early 1900s, rich people who previously lived in inner cities sought out to move to the suburbs because they thought through the ramifications of potentially losing their jobs if they stayed in the inner cities. (Wordiness. This sentence is too wordy; here is a more condensed version: “In the early 1900s, wealthy people moved to suburbs because they feared losing their jobs in the inner cities.”) Paul Johnson said, “I think it’s really fascinating that in 1925 people moved from downtown Chicago to new suburbs like Naperville and Wilmette.” (Evidence. Who is Paul Johnson, and how does this quote relate to the overall point?) In addition, “the automobile clearly helped people who had previously lived in inner cities commute to work everyday from their suburban homes.” (Evidence. This quote seems to introduce a new idea—one about automobiles—that seems out of place; also, it’s not clear if this quote comes from a different source.) Cars were manufactured and driven very often from suburbs to the cities. (Passive Voice. Here’s a corrected version: “Companies such as Ford and Oldsmobile manufactured cars, and suburban dwellers drove these cars very often.”) One can assume from all of this that economic decisions and transportation opportunities help people move to the suburbs. (Past tense. This sentences breaks out of the past tense.)
In conclusion, the rise of the suburb was the development of several factors. (Past tense of “to be.” Pick a stronger verb than “was” that is more descriptive.) There were rich people wanting to move away from the city, new railroads were constructed that extended into the outer periphery of the city in places that we now can suburbs, automobile production was greatly expanded, and new jobs rose up in cities for these rich people. (Conclusion. This conclusion merely restates the introduction paragraph; in addition, the passive voice appears several times.) It is clear that suburbs have led to the democratization of the United States. (Generalization.)
(Counter-argument: In general, this excerpt did not address any counter-arguments, thus weakening its already weak argument.)
-Developed by Adam Dominik for The Writing Place at Northwestern University.
Printable version of this resource , click here to return to the “writing place resources” main page..
945 History Topics: Best Historical Events to Write about
History is full of events that defined our world for generations. If people want to understand current events, they have to study history. Many historical occurrences impacted and shaped the world we live in today.
The best way to understand history is to write about it. For such purposes, you must dive into details, examine political and economic factors. You have to explore every aspect that made the event possible. It makes writing about a historical event thrilling. The trouble is, where to start?
Start your paper with a historical topic and instructions on source research. For this article, we found the best historical events to write about. Each event was chosen due to its fertile base for analysis and discussion.
This is why Essay writing on any historical topic is a popular school and college assignment. Our experts have provided 322 interesting titles for you to analyze and discuss.
💹 Top 10 Historical Topics to Write about
🏆 best history topic ideas & essay examples, 🥇 good essay topics on history, ✍️ simple & easy history essay titles, 💡 interesting topics to write about history, 📑 good research topics about history, 📌 most interesting history topics to write about, ❓ how to choose a history essay topic, 🕶️ cool ideas for essays on historical topics, 🔎 most interesting historical events to write about.
- ☝️ Essay Questions
- 💬 Presentation Ideas
- 👨🎓 Term Paper Ideas
- 📜 Thesis Topics
- 📚 Dissertation Ideas
- 🌍 World History
- 👨🚀 US History
- 🍁 Canadian History
- 🎩 European History
- 🏖️ African History
- 🌿 Indian History
- 🏺 Ancient History
- 🗡️ Medieval History
- 📺 Modern History
❓ Research Questions About History
👀 how to find sources for an essay on historical topics.
- The building of Taj Mahal.
- Boston Tea Party.
- The Meiji era in Japan.
- American Indian Wars.
- The reign of Alexander the Great.
- Ancient Chinese philosophers.
- The Roaring Twenties.
- Evolution of Black History Month.
- Famous Civil War generals.
- 20th century colonization of Africa.
- The Effects of Colonialism in Africa Cause and Effect Essay The cutting down of trees contributed greatly to negative impacts of the climate in the Africa continent. This has resulted to the wide spread of HIV/AIDs in African States.
- The History of Elizabethan Drama Era The early Elizabethan dramas were not performed in permanent theaters. In most cases, traveling troupes performed these plays in the courtyards.
- Land Transport – History, Evolution, and Development Essay The combination of the horse and the wheel made transportation system simple as it facilitated exchange of crops. This was the origin of movement of a large number of people in the 18th century.
- The Survival of the Sotho Under Moshoeshoe The survival of this group of people is attributed to the strong leadership of their king Moshoeshoe the Great that was necessitated by frequent cattle raids.
- Impact of Apartheid on Education in South Africa One of the bleak outcomes of European settlement in South Africa was the adoption of the apartheid. This was because of the policy of “separate development” in the field of education which was encouraged by […]
- Privatization of Education: History, Causes, Implementation, and Effects Hence, for the purpose of this paper, one may define privatisation of education as the transfer of educational services from public to private domain via the variety of policies and approaches accompanied by increasing marketization […]
- Michael Jackson: His Life and Career His father was a guitarist and he wanted his children to succeed in the music industry that served as an inspiration to the young Michael.
- How the Puritans Differed from the Pilgrims The most significant difference between the two groups is that while the Pilgrims desired a separation of church and state, the Puritans only wanted to purify the Church of England from within.
- Significance of the Event – The Labor Day Carnival The main event is the parade along the Eastern Parkway and is the highlight of the day that ends at exactly six in the evening.
- History and Development of Dance The art of dancing was connected by Greeks to the idea of harmony and perfection of human body: therefore, dancing ultimately had to be graceful in order to emphasize and not to destroy the natural […]
- Why Is Studying History Important for Our Present and Future? The history of the US proves that people understand themselves and the others learning and interpreting historical events of the past.
- Violence in Sports: History and Causes This paper discusses the issue of violence in sports by first looking at the history of sports as associated to violence, causes of sports violence and violence as a whole.
- Judaism Essay: Summary of Judaism, Its Origin and History The construction of the first great temple by Solomon made the Jews to focus the worship of God in the temple.
- Mesopotamian Civilization The history of this great land can be traced through looking at the history of different people who occupied it who included the Sumerians, the Akkadians, the Amorites, the Hitites, the Kassites, the Assyrians, and […]
- Influential People of American History between 1492 to 1865 In 1801 he was elected as the third President of the United States. In 1861 he was elected as the 16th President of the United States.
- The Importance of Studying History The fall of Saddam Hussein as the ruler of Iraq is eerily analogous to the situation that befell the Balkans following the death of communist dictator Marshall Tito.
- Leonardo Da Vinci The other great work by Leonardo is the Mona Lisa, which he painted in the 1500s, and it is arguably one of the most famous paintings in the world to date.
- Advantages & Disadvatages of Biography or Memoir as a Source Memoirs have subsequently been used in recording of past accounts as Fowale points out.[1] Memoirs express the truth in history due to the fact that they are primary sources of evidence and as such the […]
- The History of India Since 1900 In the beginning of 1919, there was implementation of the Government of India Act and this helped in introduction of national parliament.
- Apartheid in South Africa This essay gives a detailed coverage of the issue of apartheid in South Africa and its impact to the economy, politics and social life of South Africans.
- Napoleon: A Child and Destroyer of the Revolution The fathers of the revolution wanted to make the people free by destroying the “absolute monarchy” in the country. Napoleon supported the same idea by established new policies to safeguard the needs of the people.”He […]
- The History of Cars The next natural thing that the inventors of the wheel did was to design the axle so that it could fit into the hole made in the centre of the wooden wheel.
- Pakistan History and Current Affairs The Aryans society established the beginning of the modern Hinduism. The rule of the dynasty was indubitable in the 16th and 17th centuries.
- Khalid Ibn Al Walid He was a wealthy chief of one of the villages in Makkah and a trader of the Bani Makhzum clan which was among the three noblest and leading clans of the Quraish People.
- The History Civilization of China The prominent dynasties that had significance in the social and the political phases of China included the Shang dynasty and the Ch’in the Chou dynasty.
- History of Algebra Brief Overview Algebra is a mathematical concept that basically involves the applications of operations and relations, and the concepts that are as a result of the combination of the two.
- Role Model: Nelson Mandela Through the African National Congress party, Mandela was determined to undergo any form of suffering for the sake of the South Africans blacks who were facing a lot of suffering at the hand of apartheid.
- Importance of History and Evolution of Businesses to Managers Business managers are expected to organize, plan, control and oversee the implementation of business plans and strategies with the ultimate aim of accomplishing the goals and objectives of the firm.
- Isaac Newton, Mathematician and Scientist Through his private studies Newton was able to discover numerous theories the primary ones being calculus, optics, the foundation of the theory of light and color, and the law of gravitation.
- Susie Guillory Phipps and Racial Identity in Modern-Day America The war was not only important because it was fought for the future of the Union but also because of a side-story, the abolition of slavery in America.
- The Life and Work of Mother Teresa The purpose of this essay is to consider the life and contribution of the most inspiring women of all times, Mother Teresa.
- Mahatma Gandhi’s Leadership This report is an analysis of the behaviour and leadership style of Ghandi, the transactional and transformative aspects of his leadership and the way he used the power he had to help India gain Independence.
- Architecture: History of the Angkor Wat In the main body of the paper, different aspects are discussed including the materials, tools, and methods used to construct the temple.
- Cleopatra and Her Influence on the Ptolemaic Dynasty C and he left the will that he allowed Cleopatra and Ptolemy XIII, her younger brother, to rule the kingdom and Cleopatra was directed to wed her brother and deputy ruler because of the Egyptians’ […]
- The Stone Age Period and Its Evolution Therefore, the term is associated with the tools and the equipments that the ancient people made from the stones. In the Neolithic age, there was development of weaving, pottery and metal weapons and tools began […]
- Historical Schools of Thought They are sure that it is impossible to describe truth with the help of language, which presupposes that historical facts can also be questioned.
- The Role of the Church in the Life of the Middle Ages The church was thus an inseparable part of the medieval times, and anyone researching the history of the middle ages, must come across the role played by the church during this time.
- Early Greek, Roman, and Christian Historiography The historiography context of the Romans is quite distinct from the Greek one The Greek historiography began with oral tradition whereas that of the Romans was based on annals and pontifex maximus which were recorded.
- Egypt’s History, Culture, Religion, and Economy Over the next three millennia, Egypt would see the rise and fall of several civilizations, including the Old Kingdom, the Middle Kingdom, and the New Kingdom.
- “The Cold War: A New History” by John Lewis Gaddis In Chapter 1 “Return of Fear”, Gaddis states that the Cold War was caused due to the competing and divergent ideologies of the United States and the Soviet Union.
- The Great Wall of China The construction is claimed to have began during the dynasty of Emperor Qin Shi Huangi who ruled the country in the early 200 BC to the 16th century during the Ming dynasty.
- Pakistan: Culture and History Pakistan, officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan, is a large culturally diverse country located at the crossroads of the strategically significant expanses of South Asia, Central Asia and Western Asia, and borders Afghanistan and Iran […]
- Frederick Douglass Leadership Personality Traits Report (Assessment) The book was so humorous that he feared that he would be enslaved again for the weaknesses that he portrayed in the American lifestyle and how he was able to trick them with the attire […]
- “History of the NCO 1700: Valley Forge”: Case Study Analysis The American Revolution is one of the most pivotal moments in the history of the United States of America. One of the solutions to the problem of unsanitary conditions and the spread of diseases among […]
- Umbrella History, Design and Usage Third, some people tend to assume that the use of umbrellas as fashion accessories is just a fantasy because it is cumbersome to carry an umbrella around, especially during normal weather conditions.
- The Catholic Church and the Black Death in the 14th Century Therefore, the essence of this research paper is to investigate the role of Catholic Church during the Black Death, specifically paying attention to the steps the church used to prevent the disease, the Flagellants and […]
- History of Christianity At that time the development of Christianity was based on the common idea of the virtue and compassion which united the people and gave them the hope for the achievement of happiness and freedom.”Traditional Christian […]
- United States of America Apart from the impact of these varied opportunities, many significant aspects in the American history such as industrialization and formation of the initial states would also take place in the course of this period, making […]
- The History of Print Media and Its Competition With the Internet Print media remain one of the areas within the media industry that have undergone considerable suffering due to the emergence of the internet.
- The History of Indus and Chinese Civilizations Interaction Almost a thousand years later, along the Yellow River sprang another civilization in the plains of North China; one that would go on to become the largest and most prosperous in the region.
- Alan Taylor: American Colonies The author is successful in relating the 1680 and 1696 revolts in Northern America against the Spanish to natives’ dissatisfactions of the religions and economic systems of colonizers.
- The History of Yoga This is one of the issues that can be identified. This is one of the main aspects that can be identified.
- War, Its Definition, History and Aspects It should be known that there are a lot of moral theories that revolve around war and this is something that the society needs to understand.
- Colonialism in “Manifesto to Certain Filipinos” by Jose Rizal It must be noted that towards the latter part of his essay Rizal mentions the need for reform and education, research into the 333 years of Spanish colonial rule in the Philippines shows that while […]
- History of Children’s Literature in Western Culture Plato, one of the most notable rulers of the time, held it that story-telling sessions should take the form of a play and he insisted that professional storytellers and poets be the ones in charge […]
- Criteria of Significance in History Studies In order to appreciate and contextualize the importance of the past, it is crucial to consider how deeply people were affected by an event.
- Strawberries History They are the most famous and trendiest fruits in the planet. Strawberries are also used as ingredients in strawberry tiramisu which substitutes the coffee flavor for tasty and colorful strawberry effect.
- Christopher Columbus: Life, Discoveries, and Contributions Christopher Columbus was born in the Republic of Genoa in the middle of the 15th century. It led to the development of market relationships and the emergence of new items in Europe.
- Pornography’s History and Societal Effects In addition to this, the internet increased the supply of pornography by allowing consumers to be producers of the material at the same time.
- Papyrus: Its Invention and Impact on the World The invention of papyrus paper by the Egyptians changed the scene since papyrus-paper proved to be the ideal writing material of the time.
- Literature: Development Throughout History With the evolution of language and the written word, the capacity of people to create stories also changed and developed, being responsible for the creation of new literary genres, traditions and customs.
- Pablo Escobar Is a Robin Hood or a Villain Specifically, the paper focuses on Pablo Escobar as a noble bandit who retaliates against the Colombian and American government through his involvement in the trafficking of cocaine and how he uses his wealth to benefit […]
- Peace and Justice Revolving around a prominent hotel in Kigali, George features Don Cheadle as the manager of the hotel and a representative of the majority Hutus, the wealthy tribe that enjoys majority of the country’s resources.
- The Kaaba Structure: History and Description According to the Quran, the Kaaba was the primary building that was constructed for people to worship. In the reign of the prophet Muhammad, the Kaaba was damaged by floods and the prophet helped in […]
- Turning Points in the History of Christianity by Noll The introductory part presents a cogent argument for the book’s organization of the turning points in church history and an admission of the possibility of failing to capture certain milestones.
- Ancient Rome: The Birthplace of Modern Sports The popularity of sporting competition in the modern society reflects that of the ancient Roman Empire’s vision for its society. Chariot racing was one of the most popular sports in ancient Rome, it later spread […]
- Reflecting the Horrors of War People learn more about the horrors of war through literature but do not infer from experience they gain; the only way they apply the knowledge about the war is the development of more sophisticated weapon […]
- The Three Cs of History: Change, Comparison, Conversion What made their journey necessary was the big change of the Mongols and the peace in the transcontinental kingdom. As he traversed different places, he was in the company of some Islam merchants, and together, […]
- Stenography Concept, History and Usage Some people who were held hostage in some parts of the world have also used stenography to communicate a form of coded messages to the outer world. The Morse code is one of the codes […]
- The Salt March in India Therefore, the salt march movement contributed to the independence movement of India and the replication of similar non-violent movements around the world.
- 10,000 B.C.: The Pivotal Turning Point in Mankind’s History From the various examples presented in this paper it can be seen that the various developments that started from 10,000 B.C.were pivotal in mankind’s history since not only did they necessitate the creation of modern […]
- The Impacts of British Imperialism in India In order to ease the transportation of raw material from the remote areas to the ports and finished goods from the ports to various destinations in India, the British government started the railway network.
- History and Criminal Actions of the Yamaguchi-Gumi Yakuza Organization According to Howard Abadinsky, the Yamaguchi-Gumi Yakuza organization accounts for more than 50 percent of all the members of organized crime in Japan.
- “Long Walk to Freedom” by Nelson Mandela In the fast developing world, advances and progress move countries and nations forward but at the same time, some things are left behind and become a burden for the people and evolution to better life […]
- Post-Cold War Challenges At the time when strained relations between the US and the Soviet Union ended, the financial systems of several countries, particularly those in Eastern Europe, were in the process of collapsing.
- History of Aviation The idea of the airscrews, propellers and parachutes contributed to great heights in the aviation industry. Kites were used in testing aerodynamics and the stability of the flight.
- Innovation in History: How Guns Changed the World During a long period of time, guns have changed the world considerably: they help to defend oneself; they make it easier and faster to kill and injure people, very often, innocent people; and they obliterate […]
- The Zulu Nation’s History and Culture The Zulu people live on the continent of Africa, in the southern part of it, which is known as KwaZulu-Natal. In this family, the husband stands for the chief, and institution of marriage is hallowed.
- Abraham Lincoln’s Speech “The Gettysburg Address” The brief analyses has shown major characteristics of the speech and it is easy to understand what it means for me and why.
- History of Computers: From Abacus to Modern PC Calculators were among the early machines and an example of this is the Harvard Mark 1 Early man was in need of a way to count and do calculations.
- History of the Telescope This was not to be end of the journey in terms of improvement of the telescope. This kind of telescope solved the problem of chromatic aberration that was witnessed in the Keplerian telescopes.
- Modernization of Japan This was because by the time the industrial revolution was taking root, Japan was under the Edo period of isolation and was therefore not allowed to take part in the revolution.
- The 18th Century Children’s Clothing in England With that background in mind, this paper shall discus the characteristics of girls’ and boys’ dresses in the eighteenth century as well as the similarities between the dresses of both sexes.
- Gaza-Israel Conflict: History and Portents The Gaza-Israel conflict took a new dimension following the election of the Hamas Party in 2005. The topic “History of the Gaza-Israel Conflict” will focus on the issues surrounding the conflict experienced in Gaza.
- Impact of the Black Death An obvious social impact of the plague is the fact that the Black Death led to a significant reduction in the human population of the affected areas.
- History of Management Managers and management students need to study the history of management critically so that they can know where the profession is headed to in the future.
- Slavery in the Roman Empire The elite were the rich people, and majority of the population that comprised of the common farmers, artisans, and merchants known as the plebeians occupied the low status.
- Pastoral Care: History and Foundations For instance, the origin of the pastoral church has been traced to the eastern churches of Europe and the western church.
- Freedom and equality According to Liliuokalani of Hawaii, the conquest contravened the basic rights and freedoms of the natives and their constitution by undermining the power of their local leaders.
- The P-57 Mustang: The Most Important Aircraft in History The author assumes that the P-57 Mustang aircraft did not play a significant role in the Allies’ success and considers the contribution of P-47Cs and the P-38 Lightning aircraft in the war effort.
- A Closer Look at the Life of Princess Diana The humble Diana was to later be the talk of the century after she walked down the aisle with her prince in a colorful wedding.
- The 20th to 21st Century History The 20th century was the beginning of many social changes across the globe and several worldwide war conflicts that affected both Western and non-Western countries.
- The Ancient Mayan Civilization The political-social organization of the Maya was hierarchical with a king, nobles and priests on top and the common people and slaves on the bottom.
- Joseph Stalin Foreign Policies Furthermore, Stalin also was able to develop a strong and capable military defense which he invested heavily in order to safeguard the interest of the Soviet State.
- Narrative of the Life of Fredrick Douglass – An American Slave Another evidence of beatings perpetrated on slaves is seen when Douglass is taken to the custody of Mr. The effect of this can be seen when Douglass was taken to Mr.
- History: Role of Knowing the Past The present is a myriad of events in the past. As a historian, the study of these preserved artifacts is important in knowing about the past.
- Personality of Julius Caesar and His Effect on Rome Caesar’s role in the play is not immense, though he dominates the play, even after his demise in the third act of the play.
- Timeline of gangs in America The arrival of half a million people in the United States between 1941 and 1945 led to the increase in population of main towns like New York leading to the emergence of new gangs.
- The Maps’ Importance in Human History In fact Akerman praises the American road map of the twentieth century to be one of the greatest inventions at the benefit of the public.
- Language in the Study of History Apart from this type of classification, we also have philosophy of history “which is the theory aspect of the discipline of academic history, and deals with questions such as the nature of historical evidence, the […]
- Herodotus: The Father of History He proceeded on tour to Athena, Egypt, the Black Sea, and the East of Europe, demonstrating the knowledge and was eventually referred to as “The Father of History”.
- Muhammad Ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi Bagdad brightened the world at that time with its brilliance, and the intellectual dominance of the Arab civilization influenced the Western Europe to a great extent.
- Heroes – Nelson Mandela Instead, Mandela chose to remain behind the bars for the rest of his life and by putting his feet down in defense of his people’s rights, his long struggle would finally grant South Africans their […]
- A History of Romantic Love The paper examines the history of love starting from the ancient times then to the medieval chivalry and finally the contemporary period.
- Gucci Brand History and Development The positioning of the brand was the combination of aristocratic esthetics and Italian craftsmanship. The emergence of Gucci was originally associated with the need for a luxury brand in Tuscany.
- History of Modern South Africa Began With the Discovery of Diamonds and Gold Evidently the perception of South Africa as an overseas investment saw the exclusion of the locals in the participation of the mining business.
- “A Brief History of the Human Race” by Michael Cook Michael Cook’s “A Brief History of the Human Race” portrays the general outline of global human history over the past 10,000 years.
- Javanese Music, Its History and Aspects Specifically, the gamelan music style uses metallic idiophones and drums, which are the unique features of Javanese music. Two tuning systems are used in the Javanese music, viz.the Sandro and pelog.
- Desmond Tutu, South African Theologian In the year 1975, Tutu was given the position of the dean and he served in this capacity in St. Tutu immediately realized the lack of willingness of the South Africa’s white government to engage […]
- Chinese Influence on Korea: Compare and Contrast the Silla and Tang Dynasties It is imperative to note that the Tang Dynasty was also influenced by the cultures and civilizations of the trading partners.
- Pythagorean Theorem: History, Formula, and Proof It is used not only to simply solve the missing side of a right-angled triangle but also more extensively to solve Reasoning and Application problems and also can be used to solve many higher mathematics […]
- The History of the English Language Chapter 3 and 4 of Gelderen’s book looks at the analysis of how the English language evolved from the eras of prehistory to the modern English period.
- American Paradox Arguably, elements of oppression and slavery were dominant features in the American history, an idea that is well supported by the American paradox.
- Julius Caesar an Iconic Roman This was highly unexpected, as Caesar, a declared dictator, had the support of all the people of Rome, and his death resulted in administrative imbalances.
- History of Art and Design Styles such as still life painting advanced from the use of pencils in the past to the use of colors in the present.
- How Did Religion Affect the Pattern of Colonization in America and Life in Those Colonies? When the Europeans begun their exploration and subsequent colonization in North America, their religious beliefs and practices were a significant tool in how they conquered and approached the local natives, although majority of them already […]
- What Makes Airplanes Fly? The Industrial Revolution It was the Industrial Revolution that saw the invention of the steam engine, which was used to power ships, trains and motor vehicles.
- The Comparison of Roman and Mongol Empires Silk road supported the economy of the whole empire and was important in the transportation of porcelain, silk and tea to the outside world.
- World History: “Empire: A Very Short Introduction” by Stephen Howe It is irrefutable that the first chapter of the book is a vivid discussion of ancient territories and their influence in the development of modern empires.
- The Gunpowder Invention and Its Impacts on the World In the present times, the production of gunpowder still goes on as a continuation of the works of the ancient alchemists from China.
- The Russian Revolution by Sheila Fitzpatrick The author of this book defines the following frames: “The timespan of the Russian Revolution runs from February 1917 to the Great Purge of 1937-8. The first theme is the Bolsheviks’ vision of the revolution […]
- The History of Rice in Japan Towards the end of the 1930s, the government took control of the rice markets and licensed all the brokers as well as rice dealers.
- Positive and Negative Effects of WW1 on Canada Nonetheless, the war led to great negative impacts such as loss of lives, economic downtrend, and the generation of tensions involving the Francophones and Anglophones who disagreed after the emergence of the notion of conscription.
- Queens Midtown Tunnel: Construction History Besides, the time the engineers spent working in the Holland tunnel was three years longer than it took them to create the Queens Midtown tunnel, this is one of the advantages of the experience received […]
- Personalistic and Naturalistic Approach in the History of Psychology Therefore, changes and progress occur due to the goals and charisma of individuals who changed the course of history. In contrast, naturalistic theory implies that social, intellectual, and cultural development depends on the Zeitgeist, the […]
- The Life of Imam al-Bukhari The memorizing capability was very important to him, and it is said that during his early years of acquiring knowledge he committed over three thousand hadithas to his memory.
- Who was Pedro Calosa? This Church was also referred to as the church of poor Filipinos as well as the oppressed. The revolt was known as Tayug Colorum and deplored the feudal system for poor land tenure without success.
- Comparison and Contrast of Art History Daniel Strobel, Jr.and Her Son, George is one from the pair of neoclassical portraits of the Strobel family Daniel Strobel, the American Diplomat in France, and his wife, Anna Church, the daughter of the first […]
- Map Making History and Development Globalization has made the world interconnected at a level that was unprecedented in the past resulting in people thinking of the world and the various countries and societies within it in a way that is […]
- American Cowboy: Myth vs Reality The paper shall then explore the reality of the cowboy so as to reinforce the fact the image of the cowboy that most people have is an invention of myth and not reality.
- Industrial Revolution’ Process and Challenges In this case there was a shift from the use of human labor to the use of machines and modern tools.
- Fatima bint Muhammad, the Daughter of a Prophet Her position in Islam was reaffirmed by the Prophet who considered Fatima as one of the most significant women in Islam alongside the Pharaoh’s wife Asiya, Mary the mother of Jesus, and the Prophet’s wife, […]
- History: Plutarch’s Vision of Alexander the Great One of the greatest strengths of Alexander’s character is his vision, ambition, and thirst to succeed. The same corruption leads to Philotus disrespecting the king by claiming that he is enjoying the fruits of his […]
- The Age of Exploration However, the exploration, or the settlement of the Viking Norsemen, had little effects on the lives of the Native Americans because these explorers soon sailed back across the Atlantic and to Europe.
- History of Nokia Over a period o f time, the usefulness of Nokianvirta River led to the origin of the company name, Nokia. Nokia continued to conquer the world with new GSM handsets and in 1994, experts managed […]
- Cause and Effects of The Great Depression The economic devastation of the 1920s led to the Great Depression and brought a tragedy for the whole society. Crash of stock market The crash of the stock market in 1929 ushered in the Great […]
- How Geography Has Impacted the Development of Ancient Cultures They include: the Gobi and Taklamakan Deserts, the Yellow and Yangtze Rivers, and The Himalayas. To the Egyptians, the Nile River was also a source of transport, facilitating the movements of the people up and […]
- History of the Internet In the late 1960s, some proponents of the internet conducted research to find out the likelihood of interconnection between systems using the ARPANET.
- Geography and History in the Classroom Their main purpose is to increase the cultural background of a child and to enhance their knowledge of the surrounding world.
- Hospitality History in “Hotel” by Arthur Hailey The author fulfilled the purpose of the book and the needs of the audience, as he described realistic events, created a down-to-earth hero and made the plot thrilling.
- Martin Luther King’s Speech: A Summary King noted that the constitution and the Declaration of Independence guaranteed the freedom and equality of all the citizens of the country.
- How the Romans built the Aqueducts and how it led to the collapse of Rome A thorough consideration of factors, ranging from the location of the main source of the water to the magnitude and span of the expected aqueduct, preceded the construction process.
- Factors That Influenced Development on Human Civilization Some of the ancient trading activities included the exchange of food crops which led to development of agriculture in various territories.”Ideas also spread and developed through trading activities”. At this time many people were concerned […]
- Political and Cultural Impact of Alexander the Great’s Conquests Due to many territories that he conquered, the dominion that Alexander the Great had was regarded as one of the greatest in the history of the world.
- A Brief History of Punishments The following are some of the most common forms of punishments used in those early days; This was a common practice in England where the heads off criminals would be completely cut off using swords […]
- Indira Gandhi: Autocratic Leader of India She was assassinated in 1984 by her Sikh bodyguard in revenge for her ordering the invasion of the Golden temple, which was a Sikh holy place to flush out separists hiding in the temple.
- Rosa Parks’ Life and Influences Nevertheless, Parks’ heroic act in the evening of December 1, 1955 in a bus in Montgomery Alabama brought a revolution that led to the famous Montgomery bus boycott and the subsequent birth of numerous human […]
- “Burying the White Gods: New Perspectives on the Conquest of Mexico” by Camilla Townsend Camilla Townsend endeavors to establish the true foundation of the origin of the thought that the Spaniards were gods and to dispel the wrong belief by arguing that that the Indians regarded the Spaniards as […]
- Marriage and Adultery Laws of Emperor Augustus The laws were enacted to deal with marriage avoidance, the preference for childless unions, marriage of lower class women by the Roman elite, and adultery, all of which threatened the continuity of the Roman aristocracy.
- Bill Gates: Life and Contributions To have a clear indication of what the other part of the world needed, the couple toured Africa in 1995, and they resolved to donate part of their wealth to help the poor Africans.
- Lessons from Fredrick Douglass’s Life Douglass believed that the greatness of the master could not be transferred to the slaves. Education would empower the people to fight for their rights and overcome any form of slavery.
- Encounter with the Indians At the same time, Ross lists the obstacles facing him in the removal of the Cherokee people to the West, chief among others being the scantiness of the food ration provided to the native people.
- Thanksgiving History and Significance This holiday is celebrated with a lot of merrymaking and communal Thanksgiving as it is the day celebrated with an aim of showing gratitude for all the great things that life has given to a […]
- Impressionism History Impressionism, an art movement, was born in France in the 19th century specifically in the period between 1860 and 1880 with its major goal being to popularize the impressionist art style, which was a deviation […]
- Women Empowerment in Modern Society In view of the process that led to women empowerment, it is evident that people have the ability to shape their culture and traditions through social, religious, political, and economic changes in their environment.
- The History of Architecture and It Changes It is also important to note that, the use of arched and vaulted forms in architecture has occasioned the development of several new technologies in materials, structure, plan, and building forms as discussed hereby.
- The History of Drought in Cape Town About 63% of the water is used for domestic and industrial use, and the rest for agriculture and other uses. Drought and cities running out of water is a scenario that many cities would face […]
- Achievements of Nelson Mandela During these elections, the Africa National Congress won with a landslide and, as the leader of the party, Nelson Mandela was installed as South Africa’s first Black President on 10 May 1994.
- Angelina Jolie, Her Life and Behavior Since the two separated when the actress was still a youth and the mother decided to migrate to New York and stay with her, she learnt a lot from her mother about relationships and it […]
- Egyptian Pyramid’s Importance in Egypt’s Society The construction of Pyramids in Egypt started with the third dynasty under the rule of Netjerikhet Djoser, the 2nd King of Egypt.
- Learning History Through the Past to the Future
- History: Cultural Exchanges in the Medieval Period
- The Expulsion of the Acadians
- The Pyramids of Giza
- Why were Lewis and Clark Ever Hungry? Or How Can You Starve in a Sushi Bar?
- Napoleon Bonaparte, His Rise and Fall
- Atoms: History, Structure and Application
- Patty Smith Hill and Her Contribution to Education
- Soujourner Truth: “Ain’t I a Woman?” Speech
- The Renaissance and Its Cultural, Political and Economic Influence
- The Creation of Narrative Films: History and Factors
- TomTom Company: History, Development and Analysis
- Ballistics Evidence of John F. Kennedy’s Assassination
- The NVIDIA Company’s History, Products, Challenges
- History of Multicultural America by Ronald Takaki
- New York City Gangs and Their History
- Special Education, Its History and Current Issues
- Ronald Takaki’s “The Tempest in the Wilderness”
- “Oroonoko” by Aphra Behn: Main Character Analysis
- Meaning of History
- Management History and Its Key Milestones
- ”The History of God” by Karen Armstrong: An Overview of the History of Judaism, Islam, Christianity, Buddhism, and Hinduism
- Short-Term and Long-Term Consequences of Removals for the Indigenous Children
- History of Interior Design
- What is Middle East?
- History of Stone Harbor New Jersey
- Diogenes and Alexander
- Nursing History and Theory Evolution
- United States History to 1877: The Climax of the Developments That Transformed the Country Forever
- Narrative: History, Functions, and Features
- Liz Claiborne Inc.’s History and Future Growth
- Arab-Israeli Conflict
- “Band of Brothers” by Stephen Ambrose
- Compare and Contrast the Totalitarian Regimes of Germany and the Soviet Union
- The French Revolution: Romanticism Period
- The History of Mambo Music
- The Role of Women in Business From the Past Century to Today
- American History: The Civil War (1861-1865)
- Diversity Issue Through History and Humanities Lenses
- History of Nursing in the Last 100 Years
- Borderline Personality Disorder: History, Causes, Treatment
- Aviation Industry: Past and Present
- George Washington: Life and Achievements
- American History’s Events in the Period from 1492 to 1865
- Communism and Capitalism Through the History
- History of the Independence Day
- Arc de Triomphe. History. Construction
- Mechanical Engineering: Description and History
- The Collapse of the Greatest World Civilizations: the Maya, the Aztec, and the Inca Civilizations
- Compare and contrast the Virginia and New Jersey plans presented at the Constitutional Convention
- Sojourner Truth
- Critical Research on “The idea on Latin America” by Walter Mignolo
- History of French Revolution
- “A History of the World in 6 Glasses” by Tom Standage
- The Ottoman Empire History: the Rise and Fall
- Mandela’s Leadership
- Egyptian Economy: History and Views
- “Declaration of the Rights of Man and the Citizen” and “Declaration of the rights of woman and the female citizen”
- The Western Culture in the Early 21st Century
- The Rise of Hitler to Power
- Napoleon Bonaparte and Its Revolutions
- The Connection of History and Photography
- Oceania Cruises’ History and Marketing Strategies
- The Sikhism Religion History and Development
- Treaty of Paris
- Role of Cricket in Australia During the 1930s
- Some of the most significant innovations of the 20th Century
- Socrates: His Life, Philosophy, & Death
- History of Cryptography
- History of Rock Music: The Influence and Importance of Bon Jovi
- The History of Welding
- Political Science and History: The Influence of Interests on Policy Change
- History: Yali’s Question and Diamond’s Objections
- A Brief History of the Conflict Between India and Pakistan
- Civil Rights-Black Power Movement
- The British East India Company
- Historical Methodologies
- Rape in Ancient Societies
- History of Coca Cola
- The Major Point in Lies My Teacher Told Me: Everything Your American History Textbook Got Wrong
- The Mona Lisa Painting’s History and Influence on Art
- Korean Culture: History and Principles
- The American Dandies and Fops History: Men With a Great Passion for Fashion, Style, and Art
- Indonesia Overview: History, Politics, Economy, Culture, and Foreign Policy
- Nike: Brief History and Business Description
- Heroification in American History
- World History: The Roman Empire
- History: Ancient Greek Olympics
- Principal Causes and Consequences of the Spanish-American War
- British Colonialism in Malaysia and its Effects on Modern Malaysia
- Postmodernism and Education
- Alcoholism and the Impact Colonization Has Had on Aboriginals
- Gary Okihiro’s arguments regarding the writing of American history
- Bob Marley and Fela Anikulapo-Kuti
- The Tragical History of the Life and Death of Dr. Faustus
- Sports Cards, Their History and Culture
- History of the Napoleonic Code for the Establishment of the Civil Laws
- UTi Worldwide Company’s History
- Native American Indian Arrowheads
- The History of Housing in Abu Dhabi and Dubai
- The Cellphone: The History and Technology of the Gadget that Changed the World
- Jamie Oliver and Leadership in the Food Industry
- Julius Caesar and Rome
- The Conditions of Hindu and Islamic Women in Medieval India
- Voices of Freedom
- History of the Networking Technology
- 9/11 Reminder That History Is Always Incomplete
- The U.S. Navy Ranks: History and Background
- Deuteronomistic History and Martin Noth’s Works
- The Life and Legacy of John Wesley
- Almarai Company Profile: Performance & History
- The History of Catapults Technology Before 1850
- Critical review of The perils of prosperity 1914-32 by William E. Leuchtenburg
- Analysis of the History of Biological Psychology and Its Relationship With Other Psychology Branches
- The History of Jamaicans Immigration to Canada
- Perseus: A Hero of Greek Mythology
- Queen Elizabeth I Speech Before Her Troops Analytical Essay
- History of the Multiculturalism Movement in 1980
- The Cheesecake Factory’s History and Mission
- Australia History of Country Known for Its Unusual Nature and Beautiful Sights
- The History of Mass Communication: New Opportunities and Challenges for Society
- History of Westward Expansion
- The Mind-Body Problem in the History of Psychology
- The Middle East: A Brief History of Conquest
- Benazir Bhutto: A Female Leader in a Muslim Nation
- Reasons for the Collapse of the Ming Dynasty
- Character type of Sun Wukong
- Ned Kelly as an Iconic Figure
- Critics of Modern Civilization in India
- Effects of the Industrial Revolution in Relation to World War I
- Human Interaction and Cultural Exchange in the Sixteenth Century
- What were pilgrims, puritans, separatists, antinomians, and quakers? How did these groups come together in the formation of new england?
- The compromise of 1850
- Life of a Japanese Warlord: Oda Nobunaga
- Letter by Galileo to a Friend
- Alexander the Great: A Pioneer of Western Civilization
- Brief Summary of the History of Christianity
- Civilization in Ancient Egypt
- William Bradford’s personality
- History of Ancient Greek
- Rothschilds: History of Rothschild and the Spread of Rothschild Empire
- Color History and Spirituality
- Pumps Concepts and History
- Apple Company History and Competitors
- First Generations: Women in Colonial America
- History of Feudal System
- Chinese Manhua History Development
- The Marxist Theory on Class Struggle: The History of Human Relations has been one of Class Struggle
- History Of Biotechnology
- Overview of the Scientific Revolution Periods
- The Rise and fall of Napoleon and The Cause of Revolution
- The Salem Witch Trials History
- The Role of Women in the American Society of the 17th Century
- Plague Disease Through the History
- Definition and History of Fundamentalism
- History of Western Europe in the 17th -18th Century
- The Agricultural Revolution: From the Neolithic Age to a New Era of Agricultural Growth
- Single Parenthood: History and Economic Implication
- Overview of Taj Mahal: History
- History of the Arabian Gulf: The Al-Qasimi Dynasty
- The History of Bricks Making
- A History of the World in Six Glasses
- The Colosseum: History and Design
- History of Radio and Guglielmo Marconi
- History of Sanitary Pad in Ancient Period
- Sciences and Technology Role in History
- Target Corporation History and Current Situation
- The Trojan War: A New History by Barry Strauss
- The Medieval and Renaissance Periods Description
- What Made Pericles an Outstanding Leader in Athens
- File Transfer Protocol History and Development
- Julius Caesar’ Desire for Power
- The Process of Production
- The Achievements of Cyrus the Great
- History and Evolution of the Guitar Instrument
- The Heartbreaking Story of Pocahontas Life
- Napoleon’s Strategy and Tactics
- Causes of Revolutionary War in America
- Alexander the Great and the Hellenistic Legacy
- Alexander the Great: Western Civilization
- Multicultural Roman Empire History
- Sushi: History, Origin and the Cultural Landscape
- Vietnam War: History and Facts of War That Began in 1959
- History and Everyday Life of Nanticoke Tribe
- History of Byzantine Art: The Late Roman Mediterranean Civic Culture
- Music Sampling: Concept and History
- Santeria Religion: History and Rituals
- The History of Ancient India Analysis
- Revolutions’ History and Definition
- History of the Arabian Gulf
- The Movie “Into the Storm”
- The Life of Shaykh Abd al-Aziz Bin Baz
- The Critical Journal: Scotts’s “The Onondaga Madonna” and Veracini’s “Settler Colonialism and Decolonization”
- Effect of Gunpowder on the Mongolian Invasion of the Europe before 1850
- James Madison’s Leadership Qualities
- “Islam, A Short History” by Karen Armstrong
- History of the Great Chicago Fire
- History of Communication Technology
- The History of the British rule, the British and the Dutch East India Companies.
- Political Cooperation Through History
- NUCOR’s History and Development
- History of the Dalit Theology in India
- Analyzing the Political Cartoons of Dr. Seuss
- A Brief History of Chili
- Fashion History’s Understanding
- The Impact of Genocide on the Modern Society
- The History and the Nature of Human Societies
- Ancient History of Mesopotamia and Egypt
- Labor Racketeering: Definition and History
- The Nile Delta: Impact on History and Culture
- The History of Computer Storage
- Bhutan’s History, Geography, Politics, and Economy
- Porsche Company’s History, 4Ps, Competitors
- Chromolithography Peculiarities in the History of Art
- Technologies: History of Telephone
- Social Darwinism Through the History
- The Dark Ages as the Golden Ages of European History
- Sheikh Zayed bin Sultan Al Nahyan: The Great Man
- Hiroshima: Rising from the Ashes of Nuclear Destruction
- History of Empires in Past and Modern World
- The third of May, 1808: by Francisco Goya – 1814
- Women’s Education and its Implications in Pre-modern China
- How could King be more upset with moderate whites than violent extremists like clansmen?
- The History of the Romanticism Period
- Structure of Harappa and Mohenjo Daro
- Haiti History and Culture
- The Impact of the Great Depression on Canada
- The American Revolution and Its Effects
- Steve Jobs’ Impacts on the World
- Factors behind The economic and social development of UAE
- Impacts of English Civil War
- Peloponnesian War: Summary, Causes, & Effects
- Concepts of the Rise and Fall of the Babylonian and Egyptian Empires
- Air Rights in New York City: Definition and History
- American History: Bacon’s Rebellion & King Phillip’s War
- Depression in the Lens of History and Humanities
- The Gynecologic Health History and Its Importance
- Human Rights History and Approaches
- Koprince’s “Baseball as History and Myth in August Wilson’s Fences”
- Yahoo! Company History
- Space Exploration History and Prospects
- The Dhofar War: Background and History
- The History of New York and the Role of Robert Moses
- The Role of Historians Work for Studying History
- American History: Reconstruction, 1865 -1877
- Slavery History: Letters Analysis
- “The US: A Narrative History Volume 1” by James Davidson
- Asian History: The Battle of Long Tan
- Money and Its Value Throughout the World History
- “Day of Empire” by Amy Chua: Dominant Cultures in History
- The Progressive Era History
- Agamemnon as a Leader – Ancient History
- Native Americans in the United States
- “History and Topography of Ireland” by Gerald of Wales
- History of British Empire
- Cultural Theory: Uses and Disadvantages of History for Life
- Community Development: History, Themes and Issues
- Miroslava Chavez-Garcia’s book “Negotiating Conquest: Gender and Power in California, 1770s-1880s”
- Japanese War Crimes
- The Early Modern Age and Today’s World
- Unfinished Migrations: African Diaspora Notion
- The Picture of Arabic Feminist
- History of Brothels and Red Light District
- Maya, Aztec and Inca Collapse
- Gorbachev’s Ideas: Communist Society and Economy
- Revolution in Physics and Chemistry
- “The Conquest of Toledo (1085)” and “The Siege of Lisbon (1147)”
- The Battle of the Alamo
- History of Easter Sunday
- Relationship Between Law and History
- King’s Life: Alexander the Great
- American Imperialism
- The Watergate Scandal
- The Serfs in Poland
- Overview on the World’s History
- Loss of RMS Titanic (1912): Significant Events of the 20th Century
- Nelson Mandela “Freedom in Africa”
- Art History: Female Figures in Ancient Greek Sculpture
- Institution of Marriage and Its History
- The History of Body Art
- History of Ethical Principles in Psychology
- The History and Diversity of Turkish Cuisine
- Indigenous Australian Culture, History, Importance
- McDonald’s Company: History and Overview
- The Republic of Venice History: Rise and Fall
- Understanding the Biography and History Link
- British Military Catering System’s History and Future
- Vanilla: History, Culture and Production
- The History of the Vehicle Industry
- Puritan Religion beliefs: History and Origin
- History of Hollywood, California
- Muslim Civilisation: The Mechanical Water Clock of Ibn Al-Haytham
- Ethiopia: Historical Background and Modern Issues
- The Life and Times of Sir Francis Walsingham
- Otto von Bismarck: Life and Significance
- Women, Development and Disabilities
- Ten Hours Act of 1847: History and Implications
- The Life of John Pierpont Morgan
- Moses History
- Omar Khayyam: Life and Contributions
- Civilization in Mesopotamia and Egypt
- History of Nigeria
- Narrative of the Life of Frederick Douglass
- The City of Khor Fakkan: History and Tourism
- Events in the Geomorphic History of the Seal Rocks
- History of Baseball and Its Impact on American History
- Negro Spirituals’ History and Origins
- Deuteronomistic History: The Rise and Fall of Israelite Monarchy
- Understanding Culture and Tradition as an Effective Way of Teaching Indigenous History
- The Silk Road Trade and Its History
- History of Spanish Empire 1500-1700
- Art History: Art and Medicine of the Ancient Egypt
- History of Agriculture in the American West
- Turkish History Since 1900 B.C.
- The History and Nowadays of Somali Pirates
- Emblazoned on History: The Fleur de Lis
- Chauri Chaura Incident in History and Memory
- Art History During Twentieth-Century
- Health History in the Genogram Presentation
- Liberalism: History, Ideologies, Justification
- The Private Security’ History and Evolution
- Victims of Crime Act: History and Development
- The Three Rs of the New Deal in the United States History
- Waitangi Treaty History: Intentions, Expected and Results
- The Black Americans Ideologies and Stereotypes
- Eli Whitney Life and Influence
- History of Psychological Assessment: Wundt’s Laboratory
- History of General Motors
- European Colonization Impacts on the Native American Population
- Americas Rise to Become a Super Power
- Dr. Maya Angelou and Her Leadership Abilities
- Barack Obama’s Family History
- Historical Facts of Australia
- Education in Taiwan under Japanese Rule
- Concept of Studying History
- History of Linux
- Chinese History
- Capital and Labor in the Age of Enterprise 1877-1900
- Choral Music History
- Chinese Art’s Definition, Influence and History
- Christopher Hill “The World Turned Upside Down”
- Childhood Evolution and History
- O’Connor and Sabato: “The Constitution” Chapter
- Martin Luther’s Address to the Christian Nobility of the German Nation as a Historical Document
- Women in Roman Society
- History of Mexican Festival
- Impact of Civil Rights Movement
- History of Catholic Church
- Women in the United Arab Emirates
- The Aftermath of World War I for Germany
- The Peace Pipe and Mi’kmaq
- Columbus Discovered America in 1492 and How It Impacted the History of America
- History of Tectonic Formations of Texas
- History of the Christianity Contributions to the Western World
- Yusuf ibn-Ayyub Salah-al-Din
- Nelson Mandela’s Use of Power
- East Meets West: Culture Differences
- The Boxer Rebellion
- Why the Story of Beowulf Focuses on the History of the Main Character as a Hero Rather Than a King
- Should the United States Have Annexed the Philippines?
- History of the Production Processes
- Schönbrunn Palace Vienna, Austria
- Why the Reconstruction After the Civil War Was a Failure
- Citizenship History and Development
- Oscar Wilde and His Influence on the History of Europe and America
- Globalization in Latin American Countries
- Women’s Education: A Comparison of Selected Works by Adrienne Rich and Virginia Woolf
- The Chicano Movement
- Comparisons of Early Greek and Early Roman Cultures
- Justice Through the Lenses of Social Science and History
- Civilized Nations vs. Barbarians in History
- History of SoHo: Famous District of New York
- The US History During the 1800s and Early 1900s
- American Airlines’ History, Economy, and Structure
- The Concept of Dualism in the History of Philosophy
- The Role of the Olive in Human History and Lives
- Oduduwa in the Yoruba History and Traditions
- Gravitation: Definition and History of Discovery
- “History of Ocean Basins” by Hess
- Muslim Culture: History, Values, Notions
- The Trujillo Era in the Dominican Republic’s History
- Studying the History of Indigenous Peoples
- Diesel Generator, Its History and Future
- The History of China: Sun Yat-Sen as One of the Most Respected Revolutionary Leaders
- The History of Queen Lydia Liliuokalani: The Last Monarch of the Kingdom of Hawaii
- NBA Live 08 by EA Sports: History and Gameplay
- British History: The Victorian England
- Contributions of the Barbarians to Modern World History
- The Navajo Tribe History Review: One of the Largest Tribes of North American Indians
- The History of Jainism in India
- Ancient History of Babylon and Mohenjo-Daro Cities
- History in Social Context and the Curriculum
- Electrical Engineering Career: History and Future
- Marcus Furius Camillus in the History of Rome
- Paper Money and Its Role Throughout History
- American Food, Its History and Global Distribution
- Water Resources: History and Potential Impacts
- The Boxer Rebellion in China: History and Impacts
- Garamond Font Stylistics: History and Modern Usage
- Richard Nixon’s Presidency
- Greek City-States – Ancient History
- The History of the Mongol Empire
- Ireland History and Development
- Women’s Rights in the 21st Century: Education and Politics
- History of Christopher Columbus’ Voyage
- Alexander the Great – the King of Macedonia
- History: Women in Hinduism and Buddhism
- History of Easter Bunny in Canada
- Summary of Aung San Suu Kyi’s Biography
- Indian Boarding Schools
- MySpace History and Development
- History of Fashion Merchandising
- HR Management at British Airways: The Hardest Times of the History of Airlines Industry
- Candy Evolution Through the History
- Women in World War II
- History of Hockey in Canada
- Philosophers and Their Works
- International Olympic Committee: History, Culture and Social Theory
- The First World War and the Russian Revolution
- Fischer on Historical Fallacies
- The Atlantic Slave Trade
- Post Traumatic Stress Disorder: History and Symptoms
- Honey’s History and Trade
- Nationalism in World War II
- Review of Colin Powell: My American Journey
- The Magnetic Tape Recorder, Its History and Technological Advancements
- Astronomy History: Past, Present, and Future
- Colonization: Why Africa Suffers
- Political Impacts of Julius Caesar
- Man and Monster: The Life of Adolf Hitler
- The Hijab, Stereotyping and Cultural Differences Among American and Arab Muslim Women
- History of the Nile River
- Prohibition and the Rise of Organized Crime
- Cleopatra’s Life, From Her Ascension to the Throne to Solemn Death
- The Epic of Sundiata
- American West, 1860-1900
- Black Americans In The Westward Movement: The Key Figures
- French Revolution: Liberal and Radical Portions
Choosing a history topic can prove to be a difficult task. The amount of great historical events is overwhelming. However, there are reliable ways of finding the idea right just for you. Follow these pieces of advice to choose a good idea.
- Determine a general historical field that engages you. Choose a quite broad one and be ready to narrow it down. Make your topic about some specific subject to do actual research. A general retelling of history is never a good idea.
- Start researching the area. It will help you to understand what subject you’re ready to explore in detail. Plus, you’ll see how you can specify your idea.

- Think outside of the box. Find an event and try to come up with a unique perspective on it. Challenge conventional ideas and beliefs. This way, you’ll make a creative topic out of almost any historical event.
- Find out whether there are sources available on the idea of interest.
In a history paper, you should rely on trustworthy sources. Fact-checking is the key for you. If you’re sure that your topic doesn’t interfere with the factual data, you can write a paper on it.
With so many engaging events in history, picking one becomes a real challenge. Here you will find several cool history topics to write about . Also, there are plenty of cool US history topics that can be interesting for you.
- Wars of the Diadochi. Explain why Alexander’s Successors were in constant conflict.
- What played a crucial role in Rome’s dominance over other Italian tribes?
- Spartacus Rebellion – Roman Servile Wars. Analyze why Spartacus’ Rebellion made such an impact on Roman society.
- How the Gallic wars reshaped the Roman Republic?
- Battle of Alesia: the pinnacle of Caesar’s military genius.
- Christianization of Northern Europe and Scandinavia.
- Battle of Poitiers: the final halt to Arab expansion. Talk about how the Arabs were able to reach southern France and tactics of the battle.
- Battle of Hastings and its influence on England’s history.
- Why were the Crusades largely unsuccessful during the late Middle Ages?
- Most important artworks that defined the Italian Renaissance.
- The rise of the Swiss Guard as a leading military unit. Discuss the military innovations used by the Swiss Guard and their influence of the Papacy.
- Ottoman-Venetian wars of the Renaissance and their influence on the European market.
- The American Revolutionary War. Why did it become a precursor to the British expansion in India?
- The creation of National Parks in the United States.

- The stock market crash and the Great Depression in the United States.
- Korean War of 1950-1953: the first battle of the superpowers. Analyze how the Korean War became the first proxy war between the United States and the USSR.
- The impact of the chairman’s Mao Cultural Revolution in China.
- Iran-Iraq War: the first war in the Persian Gulf.
- The 2008 stock market crash and its influence on the 2010s.
Even if you pick any random history topic, it can prove to be interesting. History is full of amusing events that are worthy of a detailed analysis. Here you will find the most interesting historical events to write about.
- The architecture and purpose of a ziggurat.
- Why is the Nile river called the Cradle of Civilization?
- Child Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt. Talk about the children who became rulers of an entire country at an early age. Elaborate on their mental struggles and complications.
- The role of the Roman Empire in ancient history.
- The life of an average Roman legionary off and on duty.
- Impact of the Great Schism on world history.
- The engineering solutions behind cathedrals’ construction.
- Silk Road as a primary route of the Black Plague. Discuss how the Silk Road became the main route of disease to the West. Analyze how nations dealt with the outbreak.
- The principles of Feudalism. Comment on many aspects of Feudalism. Why did it become the leading legal, economic, and military custom in medieval Europe?
- Europe’s trade and the Slave Triangle.
- The role of segregation policies in American history.
- The hidden story behind the creation of Central Park.
⭐ Creative Historical Topics for Research Papers
Historical ideas can be useful in many ways. In school, there are specific tasks for the history class, like an internal assessment or a historical project. Some university programs involve history courses. Our topics for a history paper will help to brainstorm a topic for a historical investigation.
☝️ History Essay Questions
- What is the history of standardized testing in the United States?
- The topic for an Extended Essay: How did the Six-Day War of 1967 end? What did contribute to the victory of Israel?
- What are the essential similarities between Hitler and Mussolini’s coming to power?
- How did Mexico gain independence from Spain?
- What was the impact of Karl Marx’s Materialist Conception Of History on the world?
- Why did the Mesopotamian civilization cease to exist?
- Who are the most influential women in Western art history?
- How did the crusades affect Mediterranean history?

- What contributed to the decline and fall of the Roman empire?
- How did the Tudor dynasty affect the Parliament of England?
- Why did Cambodia become a communist country?
- What was the impact of Hollywood on American society?
- The topic for an Extended Essay: How did Mao Zedong propose to solve China’s problems?
- How did the US and Mexico change their politics after the Mexican-American war?
- What are the similar traits of Aztec and Maya empires?
- How did the Spanish Inquisition come to an end?
- What was peculiar about the labor structure in ancient Egypt?
- How did the Industrial Revolution influence Christianity?
- Why did Susan B Anthony go to jail?
- What is the impact of Indian art on other cultures?
For more specific historical questions , transform the topics above. Add more details, limit the time period, etc. It will ensure the singularity of your idea.
💬 Historical Topics for Presentation
- What are the key accomplishments of the Progressive Era in the United States?
- Explore its history and the changes it brought in the country.
- 19th-century European imperialism. Identify and explain its political, economic, and social causes. Compare European imperialism to the American one during the same period.
- Independence movements of the Muslims in Pakistan.
- The history of the fast-food industry. How its role for the US and the world changed over the years.
- Italian mafia history: its origins, influence on the country’s economy and politics.

- How the GoodBye, Lenin movie altered historical facts and events.
- The history of imperialism, the extension, or rule by one government in Africa. Analyze the western influence on the continent and the impact of colonization.
- 1960s women in American society: a sudden revolution on a way of thinking.
- Teddy Roosevelt and his role in the Progressive Era in American History.
- What is the history behind the kiwi fruit? Its origins and benefits.
- The fear of communism in the US. Use this American history presentation topic to analyze the background of the fear. Elaborate on the impact of the US politicians and media, and the effects of such propaganda.
- Sports history related to gender: stereotypes and the start of women’s sports.
- The history of the democrats in Congress in the US.
- The California Gold Rush. Prepare an oral presentation on the history of the phenomenon, its effects, and its impact on the country.
- Treating mental illness in the 1800s. Define and comment on the main methods.
- Is the Bible a trustworthy source of history?
- Who discovered frogs? The frogs’ evolution and misconceptions about them.
- The history of Babylonian mathematics, its key aspects, and its impact on modern days.
- How did the world wars affect American society? A study of the significant changes brought by the global armed conflicts.
- Jewish Americans during the progressive era. The theory of John R. Commons and anti-semitism.
👨🎓 Term Paper History Topics
- The history of Punjab State of Sikh religion situated in the north of India and east of Pakistan.
- How did the Chinese fast-food chain industry develop in China? An overview and historical analysis of the phenomenon
- The Era of Good Feeling. Explore the period between the years 1815 and 1825 in the history of the United States of America.
- Environmental issues and solutions before the 20th century.
- The background of Chinese immigration to Canada and the US.
- Exploring the purpose and evolution of homeland security over the years
- How Versailles treaties affected the world after World War I and led to definitive changes in global politics.
- The hippies’ movement: the origination of the hippies, their evolution through time and influence on society.
- Finding the source of unhappiness in France: when and why it covered the major part of the society.

- The history of public health in the world. Compare the origins and public health organizations in various countries.
- How bolshevism impacted the Russian orthodox church and altered its position in the country.
- Cuban music culture: what influenced the music, how, and when it appeared.
- Origins and evolution of E-Commerce in Bangladesh.
- The background and effects of the Long-Term Care Security Act.
- North Korean propaganda: the history, evolution, and effects of information dissemination.
- The history of humanitarian missions to Africa. Advantages and disadvantages of such practices.
- Flash mobs, their variety, and status in the world over the years.
- Analyzing, comparing, and contrasting the major causes of revolutions in Asia, Europe, and America.
- The US vs. the UK political systems: the origins and differences. What similar changes did the systems undergo?
- How did the attitudes towards people with mental illness evolve?
📜 History Thesis Topics
- The history of the death penalty in the Philippines. How did capital punishment impact the country?
- The role of the minorities in the French Revolution.
- Viking invasions: the background and their impact on other cultures over the 8th, 9th, and 10th centuries.
- Ancient architecture and whether the construction styles accurately represent artistic work.
- How did Mormons contribute to banishing Native Americans from the indigenous land?
- The history of Caribbean culture in Central America and pirates’ involvement in its development.
- Modern art’s evolution: how it changed people’s perception of art in the late 19th-early 20th century.
- Analyze the most popular and influential dictators in the world. Compare and contrast the way their rule started and ended.
- Why hasn’t the War in Afghanistan ended since 2001?
- The role of the British Crown in the slave trade over the centuries.
- Sumerian culture: what unique traditions were hidden from general history for a long time.
- How did the Roman conquest change the course of British history?
- Significant consequences of the Brazilian industrialization.
- The history of Hispanic Americans in US politics.
- World’s largest universities: what are the significant similarities of their foundation and reputation?
📚 History Dissertation Ideas
- Natural philosophy: origins and disputes. How the philosophy of nature contributed to modern science.
- The Russian Empire from the western point of view over the years.
- Ancient Chinese civilization. Explore the old Chinese world, lifestyle, and social norms. Compare and contrast with the modern state of affairs in China.
- The pedagogy and education reforms in 17th-century central Europe.
- Russian History dissertation: how was Christianity introduced to people and absorbed by the culture.
- How did the public react to animal experimentation when it first appeared? The controversy surrounding the dissection and vivisection of animals for scientific purposes.
- Language and ethnic diversity in Northern Ireland. The history of migrations and biases.

- Napoleon and Josephine. How did Napoleon’s wife and friend affect his decisions during the Napoleonic Wars?
- Italian Unification in the 19th century. How did Garibaldi and Mazzini influence Italy becoming one nation?
- Irish History Dissertation: analyze the Anglo-Irish conflicts in the 20th century.
- Myths and misconceptions about the Nuremberg Main Trial.
- The Soviet influence on Ethiopia. What new concepts were introduced to Ethiopia in the second half of the 20th century?
- The history of the birthday celebration. Examine who introduced the tradition, how it evolved over the centuries. Does it differ from society to society?
- Ancient History Dissertation: the concept of immortality in the ancient world. Compare and contrast how different cultures interpreted eternal life.
- How did the Cold War change Cuba? The issue of Sovietization and americanization.
👍 History Essay Topics on Territory
People usually associate an event in history with a place where it happened. The connection between history and civilization shifts across the territory is direct.
Discussing countries, you can talk about its internal affairs. Or elaborate on external ones and analyze other states occupying neighboring territory.
🌍 World History Topics
- First Jewish tribes of Palestine.
- Buddhism in Ancient China: influences and notable preachers.
- Great Exodus: deciphering myths from facts. Talk about the Biblical event that created the Jewish people.
- Cult of Isis in Ancient Egypt and its spread to other cultures of Antiquity.
- Marriage and adultery laws of emperor Augustus .
- Pandemics that shaped history. Talk about the most deadly pandemics that altered the course of history.
- Medicine in Umayyad and Abbasid Caliphates.
- Islamization of the Silk Road .
- The expedition of Marco Polo to China.

- The Christian Commonwealth of Byzantium .
- How the Mongols conquered most of Eurasia?
- The siege of Constantinople of 1453: tactical analysis. Analyze tactical and strategic decisions of Mehmed the Conqueror that led to the capture of Constantinople in 1453.
- The Mayan Civilization .
- The bloody conquest of South America by the Spanish and Portuguese. Discuss the means of Spanish and Portuguese conquests of South American people. How did it lead to a native’s demographic disaster?
- Industrial revolution history .
- Seven Years War: the first world war in European history.
- New York and Bombay history from 1500 to the XX century .
- Ireland’s history and development .
- China and the issue of Opium Wars. Analyze British influence on Chinese economy politics in the XIXth century.
- China in World War II.
- The political struggle of French Indochina. Talk about the causes and events of the struggle for independence among Cambodians, Laotians, and the Vietnamese. For more world history topics, you can check another list of ideas or find a title in the news.
👨🚀 US History Topics
- The Mayflower and the first settlers in America. Discuss and analyze the struggles of the first American colonists and their life in the New World.
- Servants treatment in Colonial Virginia.
- African communities in America .
- The personality of George Washington: a critical analysis.
- The War of 1812 and its impact on the United States.
- Reasons behind the abolition of slavery in the United States.
- The legacy of the US Civil War.
- Casualties of the US Civil War: a numerical analysis. Analyze the casualties of the US Civil War and why they were so immense.
- Waves of immigration to the United States .
- The expansion of federal bureaucracy during WWI .
- The interwar economy of the United States.
- History of Hollywood, California .
- The fate of Japanese Americans in World War II.
- America in the Vietnam War: a strategic analysis. Analyze the long-term solution plans of the United States in the Vietnam War and why they were ineffective. American history is full of memorable events and historical figures, so finding the perfect US topic shouldn’t be a problem.
🍁 Canadian History Topics
You may lack knowledge about Canada, even though it’s the world’s second-largest country. Start with searching for the more popular events for your essay on this list. Then, you can dive deeper into Canadian history .
- The first colonies in Canada. Talk about the first colonists of Hudson Bay.
- History: the first nations in Canada .
- History of Ontario and Quebec.
- The role of British Canada in the War of 1812.
- Canadian social democracy historical evolution .
- History of World War I: positive and negative effect on Canada .
- Canada’s foreign relations in the interwar period.
- History: “The Invisibles: migrant workers in Canada.”
- Women’s rights and the suffrage movement in Canada.
- The effect of the Great Depression on Canada .
- Canada’s participation in World War II and the postwar economic boost.

- The development of bilingual identity in Canada.
- Canada’s road to independence and national identity.
- Prime minister Pierre Trudeau and his policies. Analyze Pierre Trudeau’s term as Canada’s prime minister. Examine his policies in every social, political, and economic aspect of the country.
🎩 European History Topics
To interpret the development of western civilization, you need to understand European history. Here we separated the territory into West and East Europe. They are quite different in both culture and events that defined their identities.
So, enjoy interesting European history topics:
Western Europe
- The Neanderthals: who were they, and why they went extinct?
- The political system of the Roman Republic.
- The Age of Vikings in the early Middle Ages. Discuss how kingdoms of Scandinavia united and conquered much of North Sea territories.
- The Holy Crusades: a logistical analysis.
- The reasons behind the sack of Constantinople in 1204.
- Spanish Reconquista of the Iberian Peninsula.
- Hussite Wars as the first example of widespread firearms usage.
- The French wars of religion, 1562-1598 .
- The Protestant Reformation and Martin Luther’s role in it.
- The role of Spanish Inquisition in European history.
- Parlement of Paris under Louis XV .
- Analysis of the 18th-century European Enlightenment.
- History of the British Empire .
- French Revolution and Napoleon’s role in it.
- Napoleon’s Egyptian campaign and its effects on the Arab World.
- The Battle of Waterloo: tactical analysis.
- Controversial history topic: would Napoleon’s rule benefit France and Europe in the long term?
- The Revolution of 1848 in France .
- Franco-Prussian war of 1870-1871: a historical analysis. Analyze how Prussia united German lands and defeated one of the biggest empires of the XIXth century.
- The coming of the Third Reich .
- World War II and the tragedy of the Jewish people in Europe.
Eastern Europe
- Eastern European tribes of Antiquity. Talk about the tribes of East Europe that we know about from Greek and Roman sources. Discuss the traditions and customs of these tribes.
- History of Ancient Scythians. Their political, economic, and social system.
- Rule of Olga and the expeditions of Svyatoslav into Byzantium.
- Historical and theological context of Byzantine Iconoclasm .
- Historical event topic: Christianization of Rus and its rise in the European theatre.
- Unification of Eastern Slavic people around Kyiv. Creation of Kievan Rus.
- The Kingdom of Bohemia as a part of the Holy Roman Empire. Examine how Bohemia became one of the most prominent kingdoms in the HRE. Remember to talk about their social and military structure.
- Conquests of Batu Khan into Rus and Eastern Europe.

- The creation of the Teutonic Order. Its political, economic, and cultural system.
- Motifs behind Eastern European Crusades. The Battle of Grunwald.
- The personality of Sofia Paleologos and her alliance with Ivan III of Russia. Describe Sofia Paleologos’ character and her cultural activities in Russia.
- Livonian War of the 16th century: its goals and consequences.
- Trade relations between Russia and England of the 16th century.
- Polish expansion to Moscow. Time of Troubles in Russia.
- Westernization of Russia by Peter I and the Great Northern War.
- Russian art and culture during the reign of Catherine the Great.
- Spread of Russian influence on Eastern Europe under Catherine the Great.
- Economic relations between Russian and British empires in the early XIXth century. Discuss in detail the trade relations between Russia and Great Britain. Explain how it became the catalyst for Russia’s conflict with Napoleonic France.
- The reaction of European countries on Russia’s westward expansion. Crimean War.
- Wars for Balkan independence from the Ottoman Empire.
- The serfs in Poland .
- Economic dependency of Greece from European bankers.
- The Russian working-class movement .
- The First World War and the Russian Revolution .
- Joseph Stalin foreign policies .
- Soviet military innovations in the Second World War. Discuss and analyze technical and logistical changes that occurred in the Red Army during WWII.
- Totalitarianism and Soviet Russia .’
- Causes of the breakup of the former Yugoslavia .
- Modern European history topic: cultural and political Soviet heritage in Eastern Europe.
🏖️ African History Topics
- Global migrations of first humans from Africa: a historical analysis.
- Ancient Egypt: the first superpower of North Africa
- Phoenician colonies in North Africa.
- Roman presence in North Africa. A historical analysis.
- North African reaction to Arab conquests and Islamization.
- Arab slave trade in Africa. Discuss how the Arabs utilized the African continent for trading with Europeans.
- Mali Empire: cultural and social aspects.
- West African slave trade and commercial relations with early European colonists.
- Ethiopia and the Bible. Talk about remarks on Ethiopia in the Bible.
- History of Ethiopian Jews. From King Solomon to modern times.
- Kingdoms of West Africa and their relations with colonial empires.
- Western influence on Mohammed Ali’s Egypt.

- South African history: a struggle for independence and formation of national identity.
- History of Cape town. Strategic and economic importance of the city to the British Empire.
- Black history: from the first African slaves in America to modern times.
- African-American studies: the Great Migration’s causes .
- Interesting African history topic. History of modern South Africa began with the discovery of diamonds and gold .
- History of Christianity in Africa.
- African history essay question. How would nations have developed on the African continent if the colonization never happened?
- History of slavery in western Africa.
🌿 Indian History Topics
- Tribes of the Indus valley civilization in the Bronze Age.
- The social, political, and economic structure of Vedic Aryans.
- Development of religion after the Vedic period. Talk about the development of Buddhism and Jainism.
- Persian and Greek invasions to India. Ancient sources on the history of India.
- Ancient Indian history: Mauryan Empire and its impact on the Indian subcontinent.
- Development of ancient South India: culture, religion, art, and architecture.
- The social, political, and economic structure of the Gupta Empire. The feudal system of the post-Gupta period.
- Expansion of Islam into northern India and aspects of its coexistence with other religions.
- Project idea: social, political, and cultural structure of the Delhi Sultanate.
- Mamluk dynasty of the Delhi Sultanate; Muhammad of Ghor’s biography.
- Indian history research paper: Akbar the Great of Mughal Empire in detail. Explore Akbar’s personality and his efforts to strengthen the Mughal Empire.
- History of the Indian castes .
- First European powers in India and their trade relations.

- British East India Company and their first conquests in India.
- Modern Indian history: impact of the British rule in India.
- The origin and course of the Indian Revolt of 1857 .
- Indian soldiers of WWI and WWII.
- India’s post-war struggle for independence and the formation of the Indian National Congress.
- Political aspects of Mahatma Gandhi’s campaign.
- Partition of India. Origins of the India-Pakistan conflict.
- Introduction of mutual funds in India and their impact on the country’s economy.
- Best Indian history project topic: Curry: the history of Indian cuisine.
✨ Historical Topics on Time Period
It’s convenient to talk about historical articles and papers in the context of a single period. Understanding its boundaries make your historical analysis and investigation logical. It’ll help you to make comparisons with other periods and trace the development of any phenomenon.
🏺 Ancient History Topics
- Research paper: Rise and fall of the Minoan civilization.
- Ancient history: the Epic of Gilgamesh by Sumerians .
- Ancient history: the Great Pyramid of Giza .
- Ancient Greek Olympics .
- The societies of Ancient Mesoamerica .
- History of Athenian democracy .
- The city-state of Sparta in Ancient Greece. Explore and analyze one of the ancient civilizations of Sparta in Ancient Greece. Comment on their social and military structure and wars with Persians.
- The kings of Ancient Egypt .
- The city of Rome. A historical analysis. Talk about the foundation of one of the oldest cities in the world. Explain how and why conquered neighboring Italic tribes.
- Concepts of Ancient Greek culture .
- The kings of Ancient Rome.
- The daily life of the ancient Maya .
- Rape in ancient societies .
- Egyptian art and culture in the Ptolemaic Kingdom.
- Cleopatra – the last ruler of Egypt. Talk about Cleopatra’s personality and political games with the Roman Republic.
- The Aqueduct – Rome’s greatest invention? Discuss Roman engineering solutions to improve the conditions of its citizens. Analyze the idea of an aqueduct and its impact on humanity.
- Crisis of the Third Century. A critical analysis. Analyze the crisis of the Third Century in the Roman Empire and how it almost collapsed. Talk about the role of the Praetorian Guard during the crisis.
- Barbarian invasions of the Western Roman Empire and their impact on Roman society.
🗡️ Medieval History Topics
- Dark Ages and cultural regression. Was the cultural decline an issue outside of Europe, and why?
- Bubonic Plague: its origin, history, and impact on British society.
- Who was Nicholas of Cusa, and what did he discover?

- Elaborate on the role of religion in medieval Europe. Speculate on the reasons why it became significant during the Dark Ages.
- Why did feudalism flourish during the Medieval Ages?
- Crimes and punishment: how the criminals were punished for various offenses during the Middle Ages.
- Who were troubadours in the medieval world? Describe their role in society, their lives, and work.
- Explore a peasant’s life and work in Europe during the Middle Ages. How did the Black Death change it?
- What impact did the Quran have on medieval Europe?
- Games and entertainment: the different ways nobles and peasants had fun.
- Early medieval monastic education and how it developed over the years.
- Comment on the most significant historical events in the medieval period outside of Europe.
- What was hygiene like for nobles and peasants in the Medieval Ages?
- Health care in the Medieval Ages: what myths and superstition were most common during this time.
- The history of knighthood during the Middle Ages.3

📺 Modern History Topics
- The history of socialism in the 20th century and the countries that tried it.
- Current events in Nepal: how did the Nepalese royal massacre affect the country’s politics?
- What led to the collapse of the British Empire? Elaborate on the event’s historical background and immediate effects.
- Trade Union movements in North America: their background and impact on the US.
- Explore how Gandhi contributed to India’s independence and his lasting effect on the country’s society.
- The history of China in 1912-1949: the rise and fall of the Republic of China.
- What were the most crucial military alliances in the first half of the 1900s? Why?
- How did events of the 20th century impact Jamaica?
- The instances of genocide in modern world history and its impact on future generations.
- Examine astrology’s role in modern European History and how it changed.
- The history of modern mathematical theory.
- How did human rights evolve over the 20th century? Focus on the key events that changed the discourse.
- What is the American dream in modern society?
- The Graffiti Art: the history of the movement and why some people consider it as vandalism.
- The background of the democratic movement in Hong Kong.
- Analyze how the Cold War influences current events in the US.
- Did Religion Impact American History?
- Does Oppression and Identity Define Black History?
- Does Technology Drive History?
- What Role, According to Legend, Did Amaterasu Play in Japanese History?
- How Cancer Has Caused Much Misery throughout History?
- How British Cultural History Influenced JK Rowling’s “Harry Potter” Series?
- How Did Nationalism Arise in Southeast Asia History?
- How Did the Minoans Influence the Mycenaean Civilization History?
- How Does Hegel Perceive the Idea of Time in History?
- How Does the Rhetorical Use the Retelling of History?
- How Does Pablo Picasso Art Represent the History and Society?
- How Fashion Professionals Are Inspired by History and Culture?
- How Gender Roles Have Played a Big Part of the History?
- How Has Religion Affected History and Literature?
- Why the Communist Manifesto Is Important to European History?
- Why Did Human History Unfold Differently on Different Continents?
- Why Did Buddhism Become So Powerful in Ancient History?
- Why African American History Is Important for Contemporary Americans?
- How Has Literature Taught Us about History?
- What Was the Mayflower Compact and What Is Its Significance in American History?
- What Was the Western Influence on History of Japanese Empire?
- Why Do Jewish People Link Their History to Their System of Morality?
- What Humanistic Ideas Lead to the Two Reforms in Europe History?
- How the Amendments Made American History?
- How the Nuclear Agenda Influenced American Popular Culture and History?
Finding the right sources for any academic paper is critical. You need them to prove the legitimacy of your work. Good sources provide you with information and improve your critical thinking.

There are two types of sources: primary and secondary.
Primary sources are materials, which were made during the time of a studied subject. They include literature written by the participants of events. It can be personal (correspondence, diaries) or more official (interviews, newspapers, official statements.)
Secondary sources are materials written post-factum by non-participants. Usually, they analyze the issue and use evidence from primary sources. The most common secondary sources are scholarship works.
To detect a good history source, you have to ask a few questions:
- Who created the source? Is this an accredited author?
- When and where was it created? Is it outdated? Are there any other similar sources produced during this time? Is it a product that relies on the place or time context of its creation?
- For whom did they produce this source? What is the target audience? What purposes does the source serve?
- How does this source compare to other sources? Do they overlap or contradict each other? Does it contribute anything to your research?

Thank you for reading this article. We hope it will assist you in choosing and researching your historical topic. Share it with other people who might need some guidance for their studies.
- 100 Good Research Paper Topics for History Class: Jule Romans, Owlcation
- Types of Sources and Where to Find Them, Primary Sources: History, Philosophy, and Newspaper Library, University of Illinois Library
- History Research Guide: Giovale Library, Westminster
- Internet Modern History Sourcebook: the History Department of Fordham University, New York
- Research & Writing Guide: Mark Brilliant, Department of History, Berkeley University of California
- Six Simple Steps for Writing a Research Paper: Potsdam State University of New York
- How to Write a Research Paper: David R. Caprette, Rice University
- How to Write a Thesis: Kim Kastens, Stephanie Pfirman, Martin Stute, Bill Hahn, Dallas Abbott, and Chris Scholz
- The Methodology, Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper: Research Guides at University of Southern California
- A Comprehensive Guide for Writing Research Papers, Humanities Edition: Megan Betancourt, Southwestern University
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines: Harvard College Writing Center
- Modern World History: Infobase
- How To Write A Dissertation: Purdue University
- African History Essay Topics: Bartleby
- AP European History: AP Students, College Board
- Major Topics in Ancient Greek History: N.S. Gill, ThoughtCo
- Middle Ages Facts, Worksheets, Events, Culture & Traditions For Kids: KidsKonnect
- Environment Research Topics
- Crime Ideas
- Commerce Research Ideas
- Immigration Titles
- Culture Topics
- Population Titles
- Industrialization Topics
- Economic Growth Research Ideas
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2024, February 29). 945 History Topics: Best Historical Events to Write about. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/history-essay-topics/
"945 History Topics: Best Historical Events to Write about." IvyPanda , 29 Feb. 2024, ivypanda.com/essays/topic/history-essay-topics/.
IvyPanda . (2024) '945 History Topics: Best Historical Events to Write about'. 29 February.
IvyPanda . 2024. "945 History Topics: Best Historical Events to Write about." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/history-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "945 History Topics: Best Historical Events to Write about." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/history-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "945 History Topics: Best Historical Events to Write about." February 29, 2024. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/history-essay-topics/.
Writing a Thesis and Making an Argument
Almost every assignment you complete for a history course will ask you to make an argument. Your instructors will often call this your "thesis"– your position on a subject.
What is an Argument?
An argument takes a stand on an issue. It seeks to persuade an audience of a point of view in much the same way that a lawyer argues a case in a court of law. It is NOT a description or a summary.
- This is an argument: "This paper argues that the movie JFK is inaccurate in its portrayal of President Kennedy."
- This is not an argument: "In this paper, I will describe the portrayal of President Kennedy that is shown in the movie JFK."
What is a Thesis?
A thesis statement is a sentence in which you state an argument about a topic and then describe, briefly, how you will prove your argument.
- This is an argument, but not yet a thesis: "The movie ‘JFK’ inaccurately portrays President Kennedy."
- This is a thesis: "The movie ‘JFK’ inaccurately portrays President Kennedy because of the way it ignores Kennedy’s youth, his relationship with his father, and the findings of the Warren Commission."
A thesis makes a specific statement to the reader about what you will be trying to argue. Your thesis can be a few sentences long, but should not be longer than a paragraph. Do not begin to state evidence or use examples in your thesis paragraph.
A Thesis Helps You and Your Reader
Your blueprint for writing:
- Helps you determine your focus and clarify your ideas.
- Provides a "hook" on which you can "hang" your topic sentences.
- Can (and should) be revised as you further refine your evidence and arguments. New evidence often requires you to change your thesis.
- Gives your paper a unified structure and point.
Your reader’s blueprint for reading:
- Serves as a "map" to follow through your paper.
- Keeps the reader focused on your argument.
- Signals to the reader your main points.
- Engages the reader in your argument.
Tips for Writing a Good Thesis
- Find a Focus: Choose a thesis that explores an aspect of your topic that is important to you, or that allows you to say something new about your topic. For example, if your paper topic asks you to analyze women’s domestic labor during the early nineteenth century, you might decide to focus on the products they made from scratch at home.
- Look for Pattern: After determining a general focus, go back and look more closely at your evidence. As you re-examine your evidence and identify patterns, you will develop your argument and some conclusions. For example, you might find that as industrialization increased, women made fewer textiles at home, but retained their butter and soap making tasks.
Strategies for Developing a Thesis Statement
Idea 1. If your paper assignment asks you to answer a specific question, turn the question into an assertion and give reasons for your opinion.
Assignment: How did domestic labor change between 1820 and 1860? Why were the changes in their work important for the growth of the United States?
Beginning thesis: Between 1820 and 1860 women's domestic labor changed as women stopped producing home-made fabric, although they continued to sew their families' clothes, as well as to produce butter and soap. With the cash women earned from the sale of their butter and soap they purchased ready-made cloth, which in turn, helped increase industrial production in the United States before the Civil War.
Idea 2. Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main Idea: Women's labor in their homes during the first half of the nineteenth century contributed to the growth of the national economy.
Idea 3. Spend time "mulling over" your topic. Make a list of the ideas you want to include in the essay, then think about how to group them under several different headings. Often, you will see an organizational plan emerge from the sorting process.
Idea 4. Use a formula to develop a working thesis statement (which you will need to revise later). Here are a few examples:
- Although most readers of ______ have argued that ______, closer examination shows that ______.
- ______ uses ______ and ______ to prove that ______.
- Phenomenon X is a result of the combination of ______, ______, and ______.
These formulas share two characteristics all thesis statements should have: they state an argument and they reveal how you will make that argument. They are not specific enough, however, and require more work.
As you work on your essay, your ideas will change and so will your thesis. Here are examples of weak and strong thesis statements.
- Unspecific thesis: "Eleanor Roosevelt was a strong leader as First Lady." This thesis lacks an argument. Why was Eleanor Roosevelt a strong leader?
- Specific thesis: "Eleanor Roosevelt recreated the role of the First Lady by her active political leadership in the Democratic Party, by lobbying for national legislation, and by fostering women’s leadership in the Democratic Party." The second thesis has an argument: Eleanor Roosevelt "recreated" the position of First Lady, and a three-part structure with which to demonstrate just how she remade the job.
- Unspecific thesis: "At the end of the nineteenth century French women lawyers experienced difficulty when they attempted to enter the legal profession." No historian could argue with this general statement and uninteresting thesis.
- Specific thesis: "At the end of the nineteenth century French women lawyers experienced misogynist attacks from male lawyers when they attempted to enter the legal profession because male lawyers wanted to keep women out of judgeships." This thesis statement asserts that French male lawyers attacked French women lawyers because they feared women as judges, an intriguing and controversial point.
Making an Argument – Every Thesis Deserves Its Day in Court
You are the best (and only!) advocate for your thesis. Your thesis is defenseless without you to prove that its argument holds up under scrutiny. The jury (i.e., your reader) will expect you, as a good lawyer, to provide evidence to prove your thesis. To prove thesis statements on historical topics, what evidence can an able young lawyer use?
- Primary sources: letters, diaries, government documents, an organization’s meeting minutes, newspapers.
- Secondary sources: articles and books from your class that explain and interpret the historical event or person you are writing about, lecture notes, films or documentaries.
How can you use this evidence?
- Make sure the examples you select from your available evidence address your thesis.
- Use evidence that your reader will believe is credible. This means sifting and sorting your sources, looking for the clearest and fairest. Be sure to identify the biases and shortcomings of each piece of evidence for your reader.
- Use evidence to avoid generalizations. If you assert that all women have been oppressed, what evidence can you use to support this? Using evidence works to check over-general statements.
- Use evidence to address an opposing point of view. How do your sources give examples that refute another historian’s interpretation?
Remember -- if in doubt, talk to your instructor.
Thanks to the web page of the University of Wisconsin at Madison’s Writing Center for information used on this page. See writing.wisc.edu/handbook for further information.
HIST 290 Historical Methods & Theory
- Thinking Like a Historian
- Finding Books & Videos
- Finding Articles
What is a Historiographical Essay?
Historiographical essays, evaluating secondary sources, acknowledgement.
- Citing Sources This link opens in a new window
- Need Help? Ask a Librarian This link opens in a new window
A historiographical essay:
- Is based on a broad, less focused topic or theme, e.g., Reconstruction in the United States)
- Critically examines secondary sources written by historians
- Puts emphasis on the historian, the historian's bias and how the writing of a particular topic has changed over the years
- Examines and compares other historians' arguments in opposition to each other
The purpose of an historiographic essay is threefold:
- To allow you to view an historical event or issue from multiple perspectives by engaging multiple sources;
- To display your mastery over those sources and over the event or issue itself; and
- To develop your critical reading skills as you seek to answer why your sources disagree, and what their disagreement tells you about the event or issue and the very nature of history itself.
Selected Titles About Historiography
- What information is given about the author? Is the author an historian?
- Can you identify the historian's school of thought?
- Read the table of contents, preface and other introductry material. Does the author set up his/her thesis (or point of view) in these sections? Who is the intended audience? Is it written for historians or for a general audience?
- What is the date of publication? If the book or article is old, it will not highlight recent scholarship. Is this important? Is it a reflection of the histories of the time or does it deviate from the norm?
- What primary source material does the author use? What primary source material may have been available to the author at the time?
- Consider the bibliography. Do the sources listed indicate serious works that are relevant to your topic? You may want to consult works used by the author.
All materials from: Historiography: Ramapo College, https://libguides.ramapo.edu/HIST201rice
- << Previous: Finding Articles
- Next: Citing Sources >>
- Last Updated: Aug 28, 2024 3:23 PM
- URL: https://library.mcla.edu/historiography
Today's hours:
See all library hours »
- Ask a Librarian
- Find, Borrow, Request
- Libraries & Collections
- Using the Libraries
- Search Library Website
- Take our survey!
HIST 300: Guide for History Thesis Writers
- Starting your thesis project
- More on finding sources
- Important resources and services
- Reflection questions
Ask a Vassar Librarian

Attribution
This guide was created by Carollynn Costella, Vassar's History and Multidisciplinary Librarian 2006-2024. Carollynn passed away in July 2024 and is greatly missed by the Vassar community. Her colleagues in the Academic Engagement department hope to build on her excellent work in order to support this year's History majors.
Refine your topic
In consultation with your faculty thesis advisor, you will articulate a broad beginning of a thesis topic. Through your initial research in preparation for submitting your thesis proposal and preliminary bibliography, you will begin to focus your thesis topic to an appropriate scope.
Consider the following questions:
What did you discuss with your advisor about the feasibility of your topic?
Did your advisor suggest any sources that could be essential?
What other sources did they suggest you look into?
What would your “dream” sources be? (e.g., I hope ____’s papers are published. I wonder if there was a trial about _____. I'd like to read newspaper coverage of ___ event from _____ perspective.)
What sources may be easiest or hardest to attain? What sources will be easier or harder to read and work with and how? What opportunities and risks could a digital version of a particular source present? Where are there gaps or silences in the archives related to your topic, and how might you address these?
Where would you locate your topic in the bigger picture? One way to approach that is in terms of its position within social, economic, or political conditions.
What scholarly conversations are relevant to your topic? Identify the scholars, ideas, and debates that are essential to your topic. How does your thesis fit into these conversations?
Identify key secondary sources
Secondary sources help to situate your thesis in the framework of larger scholarly conversations. Identify scholars whose work you will engage with early on in your research process.
As you search through library catalogs and databases, take note (literally, make lists) of the keywords and terms that you find useful, as well as the Library of Congress Subject Headings associated with your topic. The subject headings will be the same in other library catalogs and databases, and that language provides crucial keyword searching terms.
When you are searching in library catalogs for book length studies about your topic, remember to search broader than your topic as well as in narrower related sub-topics. Many book-length secondary sources will not require reading in entirety. Use tables of contents and indexes effectively to identify crucial chapters and passages.
Peruse the bibliographies and footnotes in your secondary sources; this will help you find additional relevant secondary sources and may direct you to primary sources in archives, published sourcebooks, databases of primary source collections, and elsewhere. Also take note of dates/events, organization names, personal names, names of particular policies, laws or initiatives etc.; all of these are potential keywords for finding primary sources.
- Library Search (Vassar's catalog)
- WorldCat WorldCat is the union catalog for all the libraries that participate in Interlibrary Loan.
- Historical Abstracts Index to scholarship about world history after 1450 excluding U.S. and Canada
- America: History and Life Index to scholarship on U.S. and Canadian history
- Databases at Vassar Browse Vassar's databases in other disciplines to find scholarly indexes (e.g., Index Islamicus, ABSEES, HAPI, ITER) that are likely to include citations relevant to your thesis.
Confirm your primary source base
Before you begin searching for primary sources, ask yourself: What types of sources are most likely to contribute perspective on my topic?
Some examples of primary sources include: newspapers and magazines, personal narrative sources like memoirs and letters, government documents, the papers of organizations, and scholarly journals of the historical period. You will search for different types of sources using different techniques.
Use the Advanced Search screen in Library Search to:
- place limits on your search by location, language, or material type.
- do subject searches. A subject search will look for keywords ONLY in the subject fields of catalog records. Knowing the vocabulary used in the subject searches will help you do effective searches of library collections. For example, Library of Congress Subject Headings use the following keywords to indicate primary sources: sources, letters, interviews, speeches, personal narratives, diaries, correspondence, sermons, notebooks, sketches, description and travel, treaties, pamphlets, biography (includes memoirs), newspapers, periodicals, pictorial works, art, architecture, portraits, caricatures and cartoons, cookery, decorative arts, furniture, material culture, guide books, maps, fiction, poetry, periodicals, newspapers, bibliography, early works to 1800. It's not a perfect system, but an effective technique. Example search: (united states women) AND (sources or correspon dence)
- find reference sources like encyclopedias and historical dictionaries. Never underestimate how helpful these sources are in establishing historical context, suggesting keywords, identifying related people/events/places for your topic and providing bibliographies of important primary or secondary sources.
- identify digital collections of primary sources. Some of the digital primary sources that appear in our catalog are from unique databases that are more effectively searched in their native interface. If you find digital sources in our catalog that you are interested in finding more of, ask a librarian .
- WorldCat WorldCat is the union catalog for all the libraries that participate in InterLibrary Loan. Use Library of Congress Subject Headings to search for material. If an item is not available through ILL, use the "Libraries worldwide that own item" link to determine if you can travel there to look at the source in person. ALWAYS CALL AHEAD and speak to a librarian to confirm you will be allowed access to the library and to the sources you want to see.
- Center for Research Libraries Center for Research Libraries is an actual library in Chicago that Vassar Library pays membership dues to so our campus can access items in CRL's collection through ILL. EVERYTHING in CRL's catalog is available through ILL. Indicate the OCLC # on an ILL form in addition to all the other citation information when you make a request.
- Databases at Vassar Electronic databases of primary sources require some specialized techniques for thesis level research. Browse in various "Content Type" categories of Vassar's databases page and consult with a librarian about the most effective way to navigate the databases you are interested in.
- New York Public Library The NYPL system includes specialized Research Libraries (Stephen A. Schwarzman Building and Schomburg Center for Research in Black Culture) that have invaluable resources available and are only a train ride away.
- HathiTrust HathiTrust is a partnership of academic & research institutions, offering a collection of millions of titles digitized from libraries around the world.
Meet with librarians and thesis advisors
Some tips for effective meetings with librarians and thesis advisors:
- Bring a working bibliography with you. Even if you're not sure about many of the sources on there, it will give us an idea of what work you are doing and what direction you are going in.
- If you're looking for a particular source you found cited somewhere else, show your librarian the original source you found the citation in.
- It helps to have an idea about the types of sources you are interested in finding. Is it a personal narrative, a foreign newspaper, a magazine written from a particular political perspective? Do you have secondary sources addressing the relevant "layers" for your thesis questions? Do you need sources that contextualize your topic, provide historical background, or help you understand the historiography of your topic?
- Next: More on finding sources >>
- Last Updated: Sep 10, 2024 11:50 AM
- URL: https://library.vassar.edu/hist300

Exploring 250 Essay Topics in Biographies: From Autobiographies to Cultural and Ethnic Stories
Welcome to our comprehensive guide exploring 25 essay topics in various branches of historical inquiry. History is a multidimensional field of study that encompasses a wide range of disciplines, methodologies, and perspectives. In this article, we will delve into different branches of historical research, providing you with thought-provoking essay topics to ignite your curiosity and inspire your academic exploration.
Whether you are a history student, a researcher, or simply an enthusiast seeking to deepen your understanding of the past, these essay topics will offer you a starting point to explore and analyze significant themes and concepts within each field. From the examination of historical schools of thought to the exploration of diverse histories such as gender, culture, and postcolonialism, this collection of essay topics aims to engage with the complexity and richness of historical scholarship.
Historical Schools of Thought
Historical schools of thought refer to different theoretical frameworks and approaches used by historians to interpret and understand the past. These schools of thought offer distinct perspectives on how history should be studied, emphasizing different aspects such as political, social, economic, cultural, or intellectual factors. They provide a foundation for historical analysis and contribute to the ongoing debates and interpretations within the field of history.
Historical Schools of Thought Essay Topics
- The Enlightenment and its impact on modern political thought
- The Renaissance: A rebirth of art, science, and humanism
- The Industrial Revolution and its effects on social and economic thought
- The rise of Marxism and its influence on socialist movements
- The impact of Freudian psychoanalysis on psychology and the study of the mind
- The contributions of ancient Greek philosophers to Western philosophical thought
- The development of existentialism and its impact on philosophy and literature
- The role of the Scientific Revolution in challenging traditional religious beliefs
- The influence of the Bauhaus movement on modern architecture and design
- The feminist movement and its contribution to gender studies and social thought
- The development of the Civil Rights Movement and its impact on racial equality
- The emergence of the Romantic movement and its influence on art and literature
- The impact of the French Revolution on political ideologies and systems
- The rise of nationalism and its effects on the formation of modern nation-states
- The development of the human rights movement and its global impact
- The role of Confucianism in shaping East Asian social and ethical thought
- The Enlightenment and the birth of modern science and the scientific method
- The contributions of African-American intellectuals to the Civil Rights Movement
- The impact of Darwin's theory of evolution on religious and scientific thought
- The emergence of postmodernism and its critique of traditional knowledge systems
- The influence of the Harlem Renaissance on African-American art and literature
- The rise of colonialism and its effects on indigenous cultures and thought
- The philosophical underpinnings of the American Revolution and the founding of the United States
- The development of feminist literary criticism and its impact on literary studies
- The impact of the Enlightenment on educational systems and the spread of knowledge.
Comparative History
Comparative history involves the study and analysis of historical events, processes, or phenomena across different regions, societies, or time periods. By comparing similarities and differences, comparative historians aim to identify patterns, relationships, and causal factors that shape historical developments. This approach allows for a broader understanding of historical phenomena and offers insights into the diversity of human experiences and societies.
Comparative History Essay Topics
- A Comparative Study of Ancient Civilizations: Egypt, Mesopotamia, and Indus Valley
- Comparative Analysis of Ancient Greek and Roman Democracy
- Comparing the Byzantine and Islamic Empires: Religion, Politics, and Culture
- A Comparative Study of Feudalism in Europe and Japan
- The French Revolution and the American Revolution: A Comparative Analysis
- Comparative Examination of Colonialism in Africa and Asia
- The Industrial Revolution in Britain and Germany: A Comparative Perspective
- Comparative Study of the Bolshevik Revolution in Russia and the Chinese Communist Revolution
- Comparative Analysis of the Civil Rights Movements in the United States and South Africa
- A Comparative Study of the Women's Suffrage Movements in the United States and Britain
- Comparing the Renaissance in Italy and the Northern European Countries
- Comparative Study of Imperialism in the British and Ottoman Empires
- The Cold War: A Comparative Analysis of the United States and Soviet Union
- Comparative Analysis of the Mayan and Inca Civilizations in the Americas
- A Comparative Study of the Age of Exploration: European and Chinese Voyages
- Comparative Analysis of the Mughal Empire in India and the Ottoman Empire in the Middle East
- Comparative Study of the Protestant Reformation and the Counter-Reformation
- A Comparative Analysis of the Russian Revolution and the Iranian Revolution
- Comparative Study of Ancient Law Codes: Hammurabi's Code and the Twelve Tables
- Comparing the Reformation in England and Germany: Henry VIII and Martin Luther
- Comparative Analysis of the Mongol Empires: Genghis Khan and Kublai Khan
- A Comparative Study of the American Civil War and the Spanish Civil War
- Comparative Analysis of the Cultural Revolutions in China and Iran
- Comparative Study of the Indian National Congress and African National Congress
- A Comparative Analysis of the American Great Depression and the Global Financial Crisis of 2008
Oral History
Oral history is a research method that involves gathering and analyzing firsthand accounts and personal narratives of individuals who have lived through particular historical events or periods. It emphasizes the importance of capturing and preserving the voices of those often excluded from written records, providing valuable insights into their experiences, perspectives, and memories. Oral history enhances our understanding of the lived realities of individuals and communities, offering a more nuanced and inclusive historical narrative.
Oral History Essay Topics
- The Importance of Oral History: Preserving Personal and Collective Narratives
- Oral History as a Tool for Indigenous Perspectives and Decolonization
- Ethics and Challenges in Conducting Oral History Interviews
- Oral History and Memory: Examining the Reliability and Subjectivity of Oral Accounts
- Oral History and Social Change: Amplifying Marginalized Voices
- Oral History and Family Narratives: Exploring Intergenerational Transmission of Memory
- Gender and Oral History: Uncovering Women's Experiences and Perspectives
- Oral History and War: Examining the Impact of Conflicts through Personal Testimonies
- Oral History and Migration: Capturing Stories of Displacement and Identity
- Oral History and Oral Traditions: Analyzing Cultural Continuity and Change
- Oral History and Community Engagement: Empowering Local Narratives
- Oral History and Labor Movements: Documenting Worker Experiences and Activism
- Oral History and LGBTQ+ Narratives: Archiving Queer Lives and Histories
- Oral History and Holocaust Studies: Bearing Witness to Survivors' Testimonies
- Indigenous Oral Histories: Resilience, Cultural Identity, and Land Rights
- Oral History and Environmental History: Narratives of Ecological Change
- Oral History and Urban History: Capturing Urban Transformations and Neighborhood Stories
- Oral History and Civil Rights Movements: Amplifying Voices of Activism and Resistance
- Oral History and Aging: Exploring Life Stories and Perspectives on Aging
- Oral History and Disability Studies: Challenging Stereotypes and Promoting Inclusion
- Oral History and Medicine: Exploring Patient Narratives and Healthcare Experiences
- Oral History and Genocide Studies: Preserving Stories of Survival and Loss
- Oral History and Indigenous Language Revitalization: Connecting Language and Culture
- Oral History and Folklore: Uncovering Legends, Myths, and Traditional Knowledge
- Oral History and the Digital Age: Opportunities and Challenges in Archiving and Sharing Stories
Archival Research
Archival research involves the investigation and analysis of primary source materials that are preserved in archives, such as documents, letters, diaries, photographs, maps, and other records. Historians rely on archival research to access and interpret original sources that provide direct evidence of past events and activities. It enables researchers to delve into specific historical contexts, uncover hidden or neglected histories, and construct detailed and accurate narratives based on authentic documentation.
Archival Research Essay Topics
- The Importance of Archival Research in Historical Scholarship
- Exploring the Role of Archival Research in Uncovering Hidden or Neglected Histories
- The Challenges and Opportunities of Conducting Archival Research
- Comparative Analysis of Traditional and Digital Archival Research Methods
- Archival Research and the Preservation of Cultural Heritage
- The Ethics of Access and Use in Archival Research
- Archival Research and the Reconstruction of Historical Narratives
- Archival Research and the Study of Material Culture
- Archival Research in Genealogy and Family History
- Archival Research and the Study of Linguistics and Dialects
- Archival Research and the Documentation of Oral Histories
- Archival Research and the Reconstruction of Historical Landscapes
- Archival Research and the Study of Economic History and Business Records
- Archival Research and the Study of Political History and Government Documents
- Archival Research and the Examination of Social Movements and Activism
- Archival Research and the Study of Gender and Sexuality History
- Archival Research and the Exploration of Colonialism and Post-Colonial Studies
- Archival Research and the Study of Diplomatic Relations and International Affairs
- Archival Research and the Examination of Literary and Artistic Works
- Archival Research and the Study of Science and Technology History
- Archival Research and the Analysis of Environmental History
- Archival Research and the Study of Medical History and Health Records
- Archival Research and the Exploration of Religious and Spiritual Traditions
- Archival Research and the Study of Education History and School Records
- Archival Research and the Investigation of Legal History and Court Records
Quantitative History
Quantitative history employs quantitative methods and statistical analysis to study historical phenomena. It involves the collection and analysis of numerical data, such as demographic records, economic indicators, voting patterns, or crime statistics. By quantifying historical data, historians can identify patterns, trends, and correlations, enabling them to make empirical claims about historical events and processes. Quantitative history complements qualitative approaches and provides a more systematic and quantitative understanding of the past.
Quantitative History Essay Topics
- The Rise of Quantitative History: Methodological Approaches and Contributions
- Quantitative History and Demographic Analysis: Exploring Population Dynamics
- Quantitative Analysis of Economic History: Patterns, Trends, and Growth
- Quantitative Approaches to Social Inequality and Class Structure
- Quantitative History and the Study of Migration and Mobility
- Statistical Analysis of Political History: Voting Patterns and Electoral Behavior
- Quantitative Methods in Studying War and Conflict: Casualties, Strategies, and Outcomes
- Quantitative Approaches to the Study of Disease and Public Health
- Quantitative Analysis of Urbanization and Urban Development
- Quantitative History and the Study of Colonialism and Imperialism
- Quantitative Methods in Exploring Environmental History and Climate Change
- Quantitative Analysis of Technological Change and Innovation
- Quantitative Approaches to the Study of Education and Literacy
- Quantitative History and the Analysis of Cultural and Intellectual Trends
- Quantitative Methods in Studying Long-Term Trends and Historical Cycles
- Quantitative Approaches to the Study of Gender and Women's History
- Quantitative Analysis of Social Networks and Community Dynamics
- Quantitative History and the Exploration of Religious and Spiritual Practices
- Quantitative Methods in Studying Legal History and Crime Patterns
- Quantitative Approaches to the Study of Material Culture and Consumer Behavior
- Quantitative Analysis of Diplomatic Relations and International Relations
- Quantitative History and the Examination of Media and Communication
- Quantitative Methods in Exploring Family and Household Structures
- Quantitative Approaches to the Study of Intellectual Property and Copyright
- Quantitative History and the Analysis of Historical Memory and Commemoration.
Postcolonial History
Postcolonial history examines the legacies, impacts, and consequences of colonialism and imperialism on societies and cultures. It explores the experiences of colonized peoples, their struggles for independence, and the processes of decolonization. Postcolonial historians challenge Eurocentric perspectives, centering marginalized voices, and engaging with issues of power, identity, resistance, cultural hybridity, and the ongoing effects of colonial domination.
Postcolonial History Essay Topics
- Postcolonial History: Defining the Field and Key Concepts
- Decolonization and the Birth of Postcolonial Nations
- The Impact of Colonialism on Indigenous Peoples: Continuities and Disruptions
- Postcolonial Identities: Hybridity, Resistance, and Cultural Expression
- Postcolonial Feminism: Intersectionality and Gender in the Global South
- Nationalism and Anti-Colonial Movements: Case Studies from Africa, Asia, and the Americas
- Economic Legacies of Colonialism: Dependency, Exploitation, and Unequal Development
- Language and Literature in Postcolonial Contexts: Rewriting History and Reclaiming Narratives
- Postcolonialism and Environmental Justice: Ecological Consequences of Colonial Exploitation
- Postcolonial Approaches to Education: Decolonizing Curricula and Pedagogies
- Postcolonial Cities: Urban Space, Power, and Marginalization
- Postcolonial Memory and Commemoration: Remembering and Reckoning with the Colonial Past
- Postcolonialism and Global Health: Colonial Medicine, Biopower, and Health Inequalities
- Postcolonial Legal Systems: Legal Pluralism, Human Rights, and Indigenous Justice
- Postcolonial Borders: Migration, Citizenship, and Identity
- Postcolonial Resistance and Social Movements: Solidarity, Anti-Imperialism, and Liberation
- Postcolonial Media and Popular Culture: Representation, Subversion, and Stereotypes
- Postcolonial Urbanism: Infrastructure, Displacement, and Gentrification
- Postcolonial Tourism: Authenticity, Exoticism, and Power Dynamics
- Postcolonial Intellectuals: Theorizing and Critiquing the Legacy of Empire
- Postcolonial Trauma and Healing: Addressing Historical Wounds and Collective Memory
- Postcolonial Science and Technology: Knowledge Production, Appropriation, and Resistance
- Postcolonial Ecocriticism: Nature, Land, and Environmental Justice
- Postcolonialism and Global Capitalism: Neocolonialism, Dependency, and Resistance
- Postcolonial Perspectives on International Relations: Global South, Diplomacy, and Power Dynamics
Gender History
Gender history explores the ways in which gender has shaped societies, institutions, and individuals throughout history. It examines how gender roles, identities, and power dynamics have influenced social, political, economic, and cultural developments. Gender historians explore issues such as gendered labor, family dynamics, sexuality, masculinity, femininity, and the intersections of gender with other social categories such as race, class, and ethnicity.
Gender History Essay Topics
- Gender History: Exploring the Intersections of Gender, Power, and Identity
- Gendered Perspectives on Historical Methodologies and Approaches
- Gender and the Construction of Sexuality: Challenging Norms and Categories
- Gendered Experiences of Colonialism: Agency, Resistance, and Subjugation
- Gender and the Evolution of Feminism: Waves, Debates, and Transnational Movements
- Gendered Labor and Work: From the Home to the Factory and Beyond
- Masculinity Studies and the Reconstruction of Male Identity
- Gender, Religion, and Spirituality: Roles, Rituals, and Challenges to Patriarchy
- Gender and the Politics of Reproduction: Birth Control, Abortion, and Family Planning
- Gendered Violence and the Struggle for Justice: Historical Perspectives
- Gender and Education: Access, Exclusion, and the Strive for Equality
- Gender and Health: Medicalization, Reproductive Health, and Sexuality
- Transgender History: Narratives of Identity, Activism, and Resistance
- Gender and Resistance Movements: Women's Suffrage, Civil Rights, and LGBTQ+ Activism
- Gender and War: Women's Roles, Military Masculinity, and Post-Conflict Reconstruction
- Gender and Popular Culture: Representations, Stereotypes, and Subversion
- Gender and the Body: Beauty Standards, Body Politics, and Embodiment
- Gendered Spaces: Public/Private Divide, Urbanization, and Domesticity
- Intersectionality and Gender: Race, Class, and Sexuality in Historical Context
- Gender and Technology: Women's Contributions, Technological Shifts, and Digital Divide
- Gender and Resistance to Colonial Rule: Indigenous Perspectives and Movements
- Gendered Perspectives on Immigration and Diaspora: Identity, Assimilation, and Transnationalism
- Gender and Intellectual History: Contributions, Exclusions, and Challenges
- Gender and Sport: Athletics, Competitions, and Breaking Gender Barriers
- Gender and the Law: Legal Rights, Discrimination, and Activism for Equality
Social History
Social history focuses on the everyday lives, experiences, and social structures of ordinary people. It examines aspects such as social classes, labor relations, family dynamics, social institutions, and cultural practices. Social historians aim to understand the lived experiences of individuals and groups within specific historical contexts, shedding light on social relationships, power dynamics, and societal changes over time.
Social History Essay Topics
- Social History: Tracing the Lives and Experiences of Everyday People
- Social Class and Inequality: Exploring Social Stratification in Historical Context
- Family and Kinship: Changing Dynamics and Structures in Social History
- Urbanization and Social Change: Impact on Communities and Everyday Life
- Social Movements and Activism: Grassroots Organizing for Change
- Gender and Sexuality in Social History: Norms, Expectations, and Subversion
- Race and Ethnicity in Social History: Identity, Discrimination, and Intersectionality
- Religion and Society: Influence, Conflict, and Rituals in Social History
- Work and Labor: From Agrarian to Industrial to Post-Industrial Eras
- Education and Intellectual Culture: Access, Systems, and Ideals in Social History
- Health and Medicine in Social History: Public Health, Disease, and Well-being
- Social Networks and Communities: Bonds, Networks, and Social Capital
- Consumption and Consumer Culture: Materialism, Advertising, and Social Change
- Leisure and Recreation: Entertainment, Sports, and Social Identity
- Migration and Mobility: Impacts on Society and Cultural Exchange
- The Family in Social History: Changing Roles, Structures, and Dynamics
- Youth Culture: Rebellion, Identity Formation, and Countercultures
- Crime and Deviance: Social Control, Law Enforcement, and Punishment
- Social Welfare and Assistance: Evolution of Support Systems and Safety Nets
- Social History of Technology: Impact on Daily Life, Communication, and Industry
- Social History and Environmental Perspectives: Human Interactions with Nature
- Social History of Childhood: Child Labor, Education, and Changing Concepts
- Social History of Aging: Elder Care, Retirement, and Intergenerational Relationships
- Housing and the Built Environment: Architecture, Neighborhoods, and Social Cohesion
- Social History of Food and Eating: Dietary Habits, Class, and Cultural Significance
Cultural History
Cultural history investigates the beliefs, values, practices, and cultural expressions of past societies. It examines art, literature, music, rituals, symbols, and popular culture to understand how cultural ideas and practices shape and are shaped by historical contexts. Cultural historians explore the ways in which cultural dynamics intersect with social, political, economic, and intellectual dimensions, contributing to a deeper understanding of human experiences and identities.
Cultural History Essay Topics
- Cultural History: Interpreting and Analyzing the Meaning of Cultural Expressions
- Cultural Encounters and Cross-Cultural Exchanges: Exploring Cultural Interactions and Influences
- Cultural Identity and Nationalism: Constructing and Negotiating Collective Belonging
- Cultural Icons and Symbols: Analyzing the Significance and Evolution of Cultural Representations
- Popular Culture and Everyday Life: Examining Cultural Practices and Consumption Patterns
- Material Culture and Cultural Artifacts: Uncovering the Meanings and Histories of Objects
- Cultural Memory and Commemoration: Remembering and Preserving Collective Histories
- Cultural Movements and Countercultures: Subversion, Resistance, and Social Change
- Cultural Appropriation and Cultural Heritage: Debates and Ethical Considerations
- Cultural Landscapes and Urban Spaces: Tracing the Impact of Culture on Built Environments
- Cultural Performance and Ritual: Exploring the Role of Rituals and Performances in Society
- Cultural Revivals and Cultural Preservation: The Politics of Heritage and Identity
- Gender and Cultural History: Analyzing the Role of Gender in Cultural Practices and Representations
- Ethnicity and Cultural Expression: Examining the Interplay between Culture and Ethnic Identity
- Cultural History of Language and Linguistic Practices: Communication and Cultural Identity
- Cultural Responses to War and Conflict: Art, Literature, and Popular Culture
- Cultural History of Food and Cuisine: Culinary Traditions, Identity, and Globalization
- Cultural Perspectives on Religion and Spirituality: Beliefs, Practices, and Symbolism
- Cultural History of Music and Dance: Sound, Movement, and Cultural Expression
- Cultural Representations in Visual Arts: Paintings, Sculptures, and Photography
- Cultural History of Technology: Technological Innovations and Cultural Transformations
- Cultural History of Fashion: Clothing, Style, and Cultural Significance
- Cultural History of Literature: Analyzing Literary Works as Reflections of Culture and Society
- Cultural Responses to Globalization: Hybridity, Localization, and Transnationalism
- Cultural History of Sports: Sports as Social and Cultural Phenomena
Revisionist History
Revisionist history refers to the reexamination and reinterpretation of historical events, narratives, and perspectives. It involves challenging established interpretations and seeking alternative viewpoints to provide a more nuanced and accurate understanding of the past. Revisionist historians critically analyze traditional accounts of history, question prevailing assumptions, and incorporate new evidence or perspectives that may have been marginalized or overlooked. By revisiting and reevaluating historical narratives, revisionist history contributes to ongoing debates, expands our knowledge, and offers fresh insights into the complexities of the past. It encourages a more comprehensive and inclusive understanding of history by addressing biases, filling gaps in existing knowledge, and shedding light on previously marginalized voices and perspectives.
Revisionist History Essay Topics
- The Concept of Revisionist History: Exploring Its Definition and Purpose
- Revisionist History and the Reinterpretation of Historical Events
- The Role of Revisionist History in Challenging Dominant Narratives
- Revisionist Approaches to Political History: Reassessing Leaders, Movements, and Ideologies
- Revisionist Perspectives on Social History: Reevaluating Power Structures and Marginalized Groups
- Revisionist History and the Reassessment of Historical Figures: Heroes, Villains, and Complicated Legacies
- Revisionist Approaches to Cultural History: Rethinking Art, Literature, and Popular Culture
- Revisionist History and the Reinterpretation of Historical Documents and Sources
- Revisionist Perspectives on Colonial History: Decentering European Narratives
- Revisionist History and the Examination of Gender and Sexuality: Challenging Traditional Assumptions
- Revisionist Approaches to Military History: Rethinking Strategies, Tactics, and Consequences
- Revisionist History and the Reassessment of Economic Systems and Inequalities
- Revisionist Perspectives on Diplomatic History: Rethinking Alliances, Treaties, and Conflicts
- Revisionist History and the Study of Science and Technology: Examining Alternative Narratives
- Revisionist Approaches to Environmental History: Rethinking Human-Environment Interactions
- Revisionist History and the Reevaluation of Indigenous Perspectives and Histories
- Revisionist Perspectives on Medical History: Challenging Biomedical Assumptions and Practices
- Revisionist History and the Examination of Intellectual Movements and Ideas
- Revisionist Approaches to Legal History: Rethinking Laws, Justice, and Rights
- Revisionist History and the Reassessment of Historical Periodizations and Boundaries
- Revisionist Perspectives on Migration and Diaspora: Rethinking Identity, Belonging, and Borders
- Revisionist History and the Examination of Religion and Spirituality: Challenging Established Beliefs
- Revisionist Approaches to Educational History: Rethinking Pedagogies and Knowledge Transmission
- Revisionist History and the Reassessment of Historical Trauma and Memory
- Revisionist Perspectives on Global History: Rethinking Eurocentrism and Multiple Modernities
As we conclude our journey through these 25 essay topics across various branches of historical inquiry, we hope that they have sparked your interest and provided you with a glimpse into the diverse and fascinating realms of historical research. Each field offers its unique perspective, methodologies, and critical questions, inviting scholars and students alike to delve deeper into the complexities of the past.
By exploring historical schools of thought, comparative history, oral history, archival research, quantitative history, postcolonial history, gender history, social history, cultural history, and revisionist history, we have encountered a myriad of lenses through which we can view and interpret the past. These essay topics encourage us to challenge conventional narratives, explore untold stories, and engage with the diverse experiences of individuals, communities, and societies across time.
The study of history is an ever-evolving endeavor, as new evidence, methodologies, and perspectives continually shape our understanding of the past. We encourage you to seize the opportunity to engage with these essay topics, conduct further research, and embark on your own intellectual exploration of the vast tapestry of human history. Through critical analysis, empathy, and an open mind, we can contribute to the ongoing conversations that shape our collective understanding of the past and its significance for the present and future.
Department of History
Historiography essay titles, note: the exam format for 2018 will change. there will be no longer a,b,c sections..
Also, remember that it is a 'seen' exame which means you will receive the exam questions a week in advance.
But you are still welcome to use the questions below for any formative/assessed essay.
Questions on Specific Text/Historian for Essays
- What was the impact of the Enlightenment on History-writing in Europe?
- Would James Mill have written a better history of India if he had known Indian languages?
- Describe historical thinking in colonial era India.
- Assess the significance of style in Ranke’s historical writing.
- If Ranke ‘rejected Sir Walter Scott’, what was he rejecting?
- Was Leopold von Ranke a Romantic?
- Describe von Ranke’s ‘Ideal of Universal History’. Discuss its relationship to the local and the universal in the historical thinking of EITHER Karl Marx OR Max Weber.
- Describe Iggers’ and Wang’s ‘history of Leopold von Ranke in the world’. Account for any deficiencies in their argument.
- What did Karl Marx mean when he asserted that ‘the social revolution of the nineteenth century can only create its poetry from the future, not from the past’? (Eighteenth Brumaire , Section 1).
- How was The Eighteenth Brumaire revisited on its 150th birthday?
- ‘Where Hegel started with philosophy, Marx started with people’s experiences’. Discuss.
- ‘Simplicity supplies the key to the secret of the unchangeableness of Asiatic societies’ (Marx, Capital , Vol.1, xiv, s. 4). How typical was Marx’s historiography of India?
- Discuss the ‘Marxism’ of any twentieth-century historian or theorist of history [state the person clearly in the title].
- Why is Walter Benjamin’s ‘On the Concept of History’ still regarded as an important text?
- Can Walter Benjamin’s understanding of History be described as Marxist?
- What is a 'historical fact'?
- What is class consciousness for Marx?
- Was Weber anti-Marx?
- How did Weber approach the problem of causation in history?
- What does Weber understand by rational capitalism and how does it differ from Marx's ideas?
- What does Gramsci mean by hegemony? How does it work?
- ‘The science of men in time’ is how Marc Bloch described the practice of history. What did he mean?
- ‘With their examination of mentalité the Annalist historians furnished the historical profession with a new mode of reconstructing the past’. Discuss.
- ‘It is undeniable that a science [like the historical science] will always seem to us somehow incomplete if it cannot, sooner or later, in one way or another, aid us to live better’. (Bloch, Historian’s Craft ) Discuss Bloch’s view of the historical enterprise within society.
- There are many English-language educational and media websites devoted to the work of Annales historians. Make a selection of them, and give an account of the ways in which a twentieth-century ‘historical school’ is presented to twenty-first century reading publics.
- The Making of the English Working Class ‘has come to be seen as the single most influential work of English history of the post-war period’ (John Rule, DNB entry for E. P. Thompson). Why?
- Drawing on the resources of advanced options and special subjects, discuss whether or not there is still ‘a Thompsonian legacy’ in historical studies.
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of micro-history.
- Discuss any historical case-study you have read. Is the case-study approach the same as the micro-historical approach?
- What was cultural about ‘the New Cultural History’?
- Is Foucault's still disturbing for readers today as it was for readers in the 1970s and 1980s?
- What does Foucault mean by biopower?
- Is Foucault still valuable today?
- ‘A challenge to the conventional Western interpretation of the non-Western world’. Is this an adequate description of the impact of Said’s work on historical scholarship?
- Describe ‘the reception of Edward Said’ by historians and others.
- What – if anything – was original about Subaltern Studies?
- To what extent is it possible to hear the voice of the subalter.
- ‘It is now men (and masculinity) that are truly hidden from history’. Discuss.
- Discuss the view that Judy Walkowitz’s City of Dreadful Delight is ‘about stories, not about history’.
Part B-style general questions
(note: you should answer such questions comparatively, not focusing on just one historian or thinker.)
- Why study historiography?
- What is a ‘historian’?
- Is history a ‘science’?
- History is closer to literature than to science.‟ Discuss.
- Is History primarily about the past or the present?
- What are the implications of E. H. Carr's claim that ‘only the future can provide the key to the interpretation of the past’?
- Is total or holistic history possible or desirable?
- Describe and discuss the historical enterprise of any one society, past or present, that you have studied during your degree course.
- What counts as a historical source?
- Is there any difference between a historical ‘fact’ and historical ‘evidence’?
- ‘The idea of what is considered “valid historical evidence” has changed considerably over the past two centuries.’ Discuss.
- ‘The science of men in time’ is how Marc Bloch characterised history. What did he mean? Introduce other historians’ conceptions of time in answering this question.
- ‘The writing of history tells us more about the historian than about the past.’ Do you agree?‘
- “Time” has no agreed meaning for historians.’ Discuss.
- ‘History from below invariably romanticises popular culture.’ Discuss.
- Is history, as it is written, inevitably relativistic?
- Is it true, as George Orwell claimed, that those with power in the present control the past?
- Has history ended, as Francis Fukuyma claimed?
- Can the writing of history be politically neutral?
- Does political history have a future?
- How and why has cultural history become so important?
- ‘Modern history can only be conceived in relationship to the nation state’.’ Discuss.
- ‘Since the early nineteenth century, historians have been engaged in a continuing debate with the heritage of the Enlightenment.’ Discuss.
- How should history be taught in schools?
- Why should governments fund historical research?
- What is the value of popular history? (You may answer this in terms of television history, film or drama.)
- Why has family history become so popular in modern Britain?
- Why was Marxist theory central to twentieth-century historical scholarship?
- Has the historical writing influenced by Marx been good history?
- To what extent has gender as a category of analysis changed the way historians conceptualise identity and experience?
- ‘History as a discipline has been and is highly Eurocentric.’ Is this true?
- ‘Postcolonialism forces us to re-evaluate the whole history of Britain in modern times.’ Discuss.
- How important has the history of the non-Western world been to the shaping of Western historiography?
- Are postmodernist views of history plausible?
- Was postmodernism a serious ‘challenge to history’ in the late twentieth century?
- Has the linguistic turn produced good history writing
- Visucal and material culture is important to history writing. Discuss.
Neuroscience can help us to write better history. Discuss.
- Did you think the material and visual turn enrich history writing?
- 'Historians should stick to literary sources. They are the only way to access the past objectively'. Discuss.
History Essay Examples

Top History Essay Examples To Get Inspired By
Published on: May 4, 2023
Last updated on: Jan 31, 2024

Share this article
History essays are a crucial component of many academic programs, helping students to develop their critical thinking, research, and writing skills.
However, writing a great history essay is not always easy, especially when you are struggling to find the right approach. This is where history essay examples come in handy.
By reading and examining samples of successful history essays, you can gain inspiration, learn new ways to approach your topic. Moreover, you can develop a better understanding of what makes a great history essay.
In this blog, you will find a range of history essay examples that showcase the best practices in history essay writing.
Read on to find useful examples.
On This Page On This Page -->
Sample History Essays
Explore our collection of excellent history paper examples about various topics. Download the pdf examples for free and read to get inspiration for your own essay.
History Essay Samples for Middle School
The Impact of Ancient Civilizations on Modern Society
The Rise and Fall of the Roman Empire
The Causes and Consequences of the American Revolution
History Writing Samples for High School Students
The Impact of the Industrial Revolution on Society
Grade 10 History Essay Example: World War 1 Causes and Effects
Grade 12 History Essay Example: The Impact of Technology on World War II
Ancient History Essay Examples
The Societal and Political Structures of the Maya Civilization
The Role of Phoenicians in the Development of Ancient Mediterranean World
The Contributions of the Indus Civilization
Medieval History Essay Examples
The Crusades Motivations and Consequences
The Beginning of Islamic Golden Age
The Black Death
Modern History Essay Examples
The Suez Crisis and the End of British Dominance
The Rise of China as an Economic Powerhouse
World History Essay Examples
The Role of the Silk Road in Shaping Global Trade and Culture
The Rise and Fall of the Ottoman Empire
The Legacy of Ancient Greek Philosophy and Thought

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That's our Job!
American History Essay Examples
The Civil Rights Movement and its Impact on American Society
The American Civil War and its Aftermath
The Role of Women in American Society Throughout History
African History Essay Examples
The Impact of Colonialism on African Societies
The Rise and Fall of the Mali Empire
European History Essay Examples
The Protestant Reformation and the Rise of Protestantism in Europe
The French Revolution and its Impact on European Politics and Society
The Cold War and the Division of Europe
Argumentative History Essay Examples
Was the US Civil War Primarily About Slavery or States
The Effects of British Colonization on Colonies
Art History Essay Examples
The Influence of Greek and Roman Art on Neoclassicism
The Depiction of Women in Art Throughout History
The Role of Art in the Propaganda of Fascist Regimes
How to Use History Essay Examples
History essay examples are a valuable tool for students looking for inspiration and guidance on how to approach their own essays.
By analyzing successful essays, you can learn effective writing techniques that can be expected in a high-quality history essay.
Here are some tips that will help you take full advantage of the samples above.
Tips for Effectively Using History Essay Examples
- Analyze the Structure:
Pay close attention to how the essay is organized, including the introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Look for how the author transitions between paragraphs and the use of evidence to support their argument.
- Study the Thesis Statement:
The thesis statement is the backbone of any successful history essay. Analyze how the author crafted their thesis statement, and consider how you can apply this to your own writing.
- Take Note of the Evidence:
Effective history essays rely on using strong evidence to support their arguments. Take note of the sources and types of evidence used in the essay. Consider how you can apply similar evidence to support your own arguments.
- Pay Attention to the Formatting and Other Academic Formalities:
The sample essays also demonstrate how you can incorporate academic formalities and standards while keeping the essay engaging. See how these essays fulfill academic standards and try to follow them in your own writing.
- Practice Writing:
While analyzing history essay examples can be helpful, it is important to also practice writing your own essays. Use the examples as inspiration, but try to craft your own unique approach to your topic.
History essays are an essential aspect of learning and understanding the past. By using history essay examples, students can gain inspiration on how to develop their history essays effectively.
Furthermore, following the tips outlined in this blog, students can effectively analyze these essay samples and learn from them.
However, writing a history essay can still be challenging.
Looking for an online essay writing service that specializes in history essays? Look no further!
Our history essay writing service is your go-to source for well-researched and expertly crafted papers.
And for an extra edge in your academic journey, explore our AI essay writing tool . Make history with your grades by choosing our online essay writing service and harnessing the potential of our AI essay writing tool.
Get started today!
Cathy A. (Law, Marketing)
For more than five years now, Cathy has been one of our most hardworking authors on the platform. With a Masters degree in mass communication, she knows the ins and outs of professional writing. Clients often leave her glowing reviews for being an amazing writer who takes her work very seriously.
Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!

Legal & Policies
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Terms of Use
- Refunds & Cancellations
- Our Writers
- Success Stories
- Our Guarantees
- Affiliate Program
- Referral Program
- AI Essay Writer
Disclaimer: All client orders are completed by our team of highly qualified human writers. The essays and papers provided by us are not to be used for submission but rather as learning models only.
278 Interesting History Essay Topics and Events to Write about
A history class can become a jumble of years, dates, odd moments, and names of people who have been dead for centuries. Despite this, you’ll still need to find history topics to write about. You may have no choice!
But once in a while, your instructor may let you pick a history essay topic. Are you clueless about where to start? If you are, don’t worry. You’ve come to the right place! In this article, you’ll see 278 cool historical events to write about. You’ll also discover some sources for good research on our ideas.
Before you read further:
Review the professional writing services offered by our academic experts. They can surely help you with essay writing or any other assignments.
Top 10 History Essay Topics
- The US’s role in World War I.
- Child labor during the Puritan era.
- Religion during the Aztec times.
- Causes of the Battle of Germantown.
- The economic impact of the Titanic ’s sinking.
- The economic effect of the Bracero Program.
- Cultural impact of the Spanish-American War.
- Industrial Revolution’s impact on the environment.
- The goal of Protestors at the 1968 Democratic Convention.
- Women’s employment during the Great Depression.
How to Pick the Best History Essay Topic
Most of this article is devoted to listing history topics that are ideal for essays, but first, it’s important to have a simple process for using a list of possible essay topics like this.
- Before you start writing, brainstorm. Read this list. Scan lists of history essay prompts. Maybe even skim a history essay example or 2 (or 10, or 25). When you find a topic you like even a bit, write it down in your personal list. Add any other topics that come to your mind.
- Pick a topic that will satisfy your instructor and you can write well about. After you have a long list, review the assignment instructions. Then, eliminate the most inappropriate topics from your list. Lastly, reread the remaining topics. At this point, decide the topics you know enough about to write about wisely.
This 2-step process will make sure you get started on the right foot, but don’t forget the basics of sound writing. Remember these two rules. First, always plan your essay by using an outline. Second, stick to a well-structured essay with an introduction, body, and conclusion (use a 5-paragraph essay if it’s suitable).
Here’s one further tip that is notably helpful for history essays. Use Wikipedia to explore historical events that you don’t understand well. (But of course use primary sources if you are writing a true research paper.) Alternatively, if you have some keywords in mind, you can find a random topic generator for writing and see what it can offer you.
Here’s the list of history essay prompts that you’ve been waiting for.
The Ultimate List of Historical Events to Write about
- An Industrial Revolution in England essay is an excellent Industrial Revolution essay. Use this essay to explain some Industrial Revolution effects. Or perhaps give a brief but analytical overview of the Industrial Revolution timeline.
- Alternatively, you could write an Industrial Revolution in Europe essay . England was the first nation to industrialize. But it wasn’t the last. In this Industrial Revolution essay, perhaps discuss differences among European nations in industrialization. (This kind of comparative approach yields an especially fine Industrial Revolution research paper as well.)
- Or use a markedly different topic by writing a Martin Luther King essay . This key historical figure still shapes how we think about race, social justice, and the power of nonviolent protest. His death was tragic.
- One way to avoid making your essay a Martin Luther King biography is to focus on a specific event or impact of this man’s life. For example, your Martin Luther King essay could be about a specific Martin Luther King speech or quote . (But if you’re going to write about King’s famous “I Have a Dream” speech, make sure you have something unique to say!)
- Instead, you could write a broader Civil Rights Movement essay . In this, you must go beyond a basic Civil Rights Movement summary and focus on the meaning of this period over time or some specific change caused by it. (Again, don’t let your Civil Rights Movement essay become a Civil Rights Movement research paper.)
- You could write about another period of dramatic change in a French Revolution essay . This violent revolution filled with imprisonments, trials, and beheadings was caused by immense suffering by the poorest people in France. As such, when writing this essay, provide only a brief French Revolution summary, and focus on the impact and triggers of specific events.

- Similarly, you could write an American Revolution essay . Both events involved overthrowing a monarch, but unlike a French Revolution essay, an American Revolution essay is effectively about a war, the build up to war, and the recovery from a war.
- Perhaps your historical essay could focus on a person who was instrumental to the American Revolution. For example, consider Ben Franklin , a famous early American statesman, diplomat, scientist, and inventor.
- The War of 1812 was the conflict between America and Britain directly following the American Revolutionary War. It’s a fine essay topic for those seeking to understand early American history.
- Wars make notable topics for historical essay, but the aftermath can be even more interesting. The Weimar Republic was the terribly failed German government created after World War I. A critique of this government could be a superb essay subject.
- In contrast, post-war Vietnam has been a relative success story. The nation reunified following the defeat of South Vietnam. The modern Vietnamese people possess a higher quality of life than citizens of many nearby nations.
- You could also write about the Post-World War II 1950s . During this time, America exhibited surprising growth and prosperity. However, the United States began to wage a deadly Cold War with the USSR.
- Another quite related topic is the messy late 21 st century American foreign policy . You could focus on the rise of terrorism after America’s invasion of Iraq, the worldwide US military bases, or any number of military dictators that the US has supported. These are all very provocative topics.
- Or you could focus on a more specific military event, such as the Battle of Hastings . This battle shaped the whole history of England, as kings from continental Europe invaded English.

- The time of the Battle of Hastings was also characterized by the heavy influence of knights and feudal law in daily life. Knights were more than heavily armed warriors. They were also lords that controlled the land and subjugated peasants. This was a major cause of uprisings such as the French Revolution.
- Many medieval knights were also involved in the Crusades . This invasion of the Holy Land by European kingdoms represented a violent period. During these conquests, European nobility pillaged sacred sites and artifacts; with the goal of controlling the birthplace of their Christian faith.
- Following this time, Europe entered a period of Renaissance Humanism . Humans began to think about their humanity a bit more deeply. In doing so, many works of fine art, such as the first realistic paintings and sculptures, were produced.
- Your essay could focus on slightly later events, such as the fall of great empires . At various times in the past, nations such as Rome, China, Portugal, England, and the Holy Roman Empire controlled huge areas of our globe. Your essay could survey the implosion of these once great powers.
- The abolition of slavery is a fascinating and important historical essay topic. You may focus on this process within a single country, or you can write a comparative essay in which you compare and contrast the process of abolition across the globe or between two societies.
- Another highly relevant topic is the impact of Karl Marx . Few historical figures have had as huge an impact on society as Marx. Accordingly, you can consider how his writings were used (or abused) in a variety of nominally communist parties, movements, uprisings, and nations.
- Of course, you should always consider writing an integrative history essay . You can’t pick just one topic? Why not pick two or more! This is a nice approach for selecting compare and contrast essay topics . In this type of essay, you compare or contrast, people, events, or countries. In choosing this path, you make it possible to write a totally unique essay. The sky is the limit!
- A more human-focused approach could be an interesting hook for the paper. A paper based on the writing of the soldiers in World War I could outline what war was like at the beginning of the 20th century.

- A personal look at World War II could be just as interesting and with more available documents.
- One of the possible hooks for such papers may be the plight of the African American soldiers who fought in World War I and II .
- Another topic may be dedicated to soldiers from India who fought for the British in World War I .
- The economics of Europe after World War I may show the causes and effects that led to further conflict.
- You may dedicate your project may to the changes in fashion in the 20th century .
- More obscure topics like the Canadian history of film can make for an interesting thesis.
- American art of the 20th century is a big topic that has many interesting examples.
- History of math can show the timeline of math’s evolution.
- The conclusion of the British rule in India caused many positive and negative effects on the country which can make for an interesting project.
- The history of Roman sport provides fascinating examples of contests through the ages.
- History of architecture during renaissance can show the differences between the eras.
- Life before the invention of photography could be a topic that outlines how people preserved images back in the day.
- You can compare and contrast the history of Roman and British empires .
- Examples of music created for political causes could be an interesting hook for a music history essay.
- T he history of medicine can provide some striking facts about the bizarre antique cures.
- “What are the events that led to the fall of Roman Empire?” is one of the more common history essay questions.
- Summary of the achievements of the American civil rights movement can provide an impression of what a dream of one man could do.
- An argumentative essay topic about the value of public communication can be chosen and created by using examples from the world history.
- A paper on the music of ancient civilizations can shine a light on prehistoric cultures.
- Your project can be about the anti-fascist activists in the US before WW II .
- It is possible for high school students to write about the events of the year when they were born .
- A thematic paper answering the question “ what started the worst wars in world history? ” could compare and contrast different wars to find similar causes and effects.
- The hippie culture of the 1960s can be presented as a response to the events of the era.
- Also, the fashion of hippies can be explored in your project with examples of real clothing.
- The New Wave movement in cinema was revolutionary for its time and can be an interesting essay topic.
- The same could be said about the New Wave genre of music that became popular in the 1980s.

- Another music genre that captured the imagination of the public can be explored in an essay on the history of rock music .
- History of propaganda in films can help explore some pivotal moments in world history.
- Canadian history of sport is an interesting topic to explain why hockey is so popular in the Great White North.
- Economics of sport throughout history may also interest the reader due to the massive commercial expansion of sport in recent decades.
- Education during the renaissance was booming and could serve as a great topic for an essay.
- Education during the middle ages was rare and could contrast the previous topic.
- The justifications that the US used for the drop of the nuclear bombs during World War II is a controversial topic but an interesting one.
- American involvement in the Korean War is an often overlooked topic, but it deserves attention.
- To show how turbulent history of a single country may be, the causes and effects of the military coups in Nigeria could be fascinating.
- The war between Iran and Iraq could be seen as one of the most critical proxy wars of the modern history.
- The space race was an iconic element of the Cold War, and it is related to many history essay topics.
- Events that led to the rise of the Saudi Arabia can show how fast a country can develop when money is not an issue.
- The British music invasion into the US market has had a significant effect on American music and can be an interesting topic.
- History of American worker unions could serve as a topical essay in today’s political climate.
- The process of reparations for the Maori people in New Zealand in a rare success story of an ex-British colonial country making up for the discrimination its natives endured.
- Roman graffiti is a lighthearted topic that describes a less discussed aspect of Roman culture.
- The gender roles of Roman society can be compared and contrasted with the gender roles of the people of Gaul that often fought each other.
- The prominent figures of the American Revolution include a great variety of people who would later compose the most important documents of the US.
- A compare and contrast essay about the similarities of American and Bolshevik revolutions can show how the most prominent opponents of the Cold War had similar beginnings.
- The history of Japanese isolationism could be interesting to explore as a unique moment in world history.
- The Millerites believed that the world would end on a specific date, but it only led to the events known as “The Great Disappointment” which could make for a great history topic.
- The Carnation Revolution of 1974 was an almost bloodless coup and represents one of the few examples of peaceful transitions to democracy.
- The golden age of piracy is an interesting topic about an era that is often glamorized in fiction.
- The Copper Country Strike was one of the most tragic cases of death due to anti-strike action, and its events are still discussed today.
- The St. Valentine’s Day Massacre was a gruesome murder committed in broad daylight and emblematic of the gangster activity of the era.
- The Yalta Conference was one of the most important events of World War II with British, Soviet, and American leaders discussing post-war plans.
- British colonization of Africa was one of the most tragic; the causes and effects of it could be interesting to examine.

- A paper on the evolution of flight could provide a timeline of marvelous engineering throughout history.
- Operation Paperclip was a secret plan to integrate scientists of Nazi Germany after the end of World War II which events lead to the beginning of the space race.
- Historical events that were predicted in fiction can be one of the more exciting history essay topics.
- African-American music history can be explored to show how oppression influenced culture.
- Biography of Julius Caesar is filled with dramatic events and is one of the most exciting history essay topics.
- Aztec life before the arrival of the colonists was filled with horrible sacrifices and deserves examination.
- The causes and effects of Manifest Destiny are bizarre and tragic by modern standards but were considered righteous in their day.
- You could compare and contrast the life of the Roman leader Julius Caesar and Nicholas II of Russia because they were almost mirrored images of each other.
- The actions of Churchill led to some of the worst defeats for the British forces during World War I , but are overshadowed by his later leadership.
- The transition from the 50s to 60s fashion can be explored to show the drastic change in the culture of those years.
- The events that led to the emergence of teenage culture after World War II can be outlined.
- The economics of international trade during the Renaissance period can be described to show the complex relationships of Europe.
- American Revolution in film rarely receives accurate portrayals. A look at its depictions can be interesting.
- A paper on the causes and effects of Cold War paranoia could show how quickly people can be overwhelmed by fear.
- Ronald Reagan’s policy of a winnable nuclear war launched a chain of events that could end the world.
- The diversity of the Roman Empire is a rarely explored topic and could lead to an interesting paper.
- Medieval medicine is a fascinating topic. It combines the ideas from Ancient Greece and Rome, pagan medicine, and many religious superstitions.
- Another interesting history topic is the history of dystopian art . In turbulent times, it may be especially fascinating to trace the development of dystopian art and see what shaped the ideas of dystopian worlds in different eras. Moreover, you may find it interesting to see the predictions about the modern era in dystopian literature and cinema.
- Medicine in the early XX century is an excellent topic for an essay. At the turn of the century, there was a major change in the way people treated medical technology, hygiene, and chemistry. Groundbreaking achievements, such as the discovery of X-rays and penicillin, shaped modern medicine as we know it.
- The history of video games is an exciting essay topic. See how video games developed from the most primitive forms into the glorious, hyper-realistic works of art that we enjoy now.
- The history of quantum mechanics is a history topic that can teach us a lot about the world around us. You can write about the groundbreaking experiments that changed the way we think about nature, and learn about great minds who were not afraid to question even the most fundamental laws of physics.
- Alternatively, you can write about the development of astronomy . Another fascinating scientific field that can show us how people in different eras were discovering the beauty and complexity of the Universe .
- Similarly, you can write about the history of evolutionary theory. All ancient cultures had their ideas about the origin of life. See how Darwin’s idea of natural selection revolutionized not just science, but human thought in general.
- Another outstanding example of a revolution of human thought is the history of psychology. From the ancient idea of spirits and possession to the groundbreaking ideas of Freud and the discovery of conditioning – see how the cultural perception of the human psyche changed over time.
- A topic closely related to the current issues, pandemics that changed history can be explored to see the effects of epidemics on nature, science, and society as a whole. It may also be interesting to write about how viral infections spread around the world.
- The history of transport is a fascinating topic. Starting from the earliest of times, humans are continually developing new ways of traveling as far and safe as possible. See how technology evolved from the discovery of a wheel to rocket science, and how it changed history and the world around us.
- The history of the punk subculture is an excellent topic for presentation. Show how punk philosophy, fashion, and music changed the culture in the U.K. and around the world.
- Another interesting research topic for high school students is the Great Depression . Learn what caused the severe economic crisis, and what socio-economic effects it had on countries all around the world.
- From the first settlements built by ex-convicts to the outbreaks of smallpox and aboriginal resistance – the history of Australia is full of dramatic events and stories that we can learn a lot from.
- Or you can choose the exploration of Africa as the subject of your history essay. The story of two extraordinary individuals in search of a path into the heart of the continent inspired the novel Heart of Darkness.
- Historical figures in Shakespeare’s plays is a great history research paper topic. You could compare the lives of real historical figures, such as Julius Caesar and Henry V, to those of their fictional counterparts.
- Voyages of Christopher Columbus is one of the most critical events in history before 1500. While the discovery of the New World had an enormous influence on the colonization era, Columbus’s legacy remains controversial.
- Or you can write an essay on Hernán Cortés , a pivotal figure in the colonization of South America. His actions against native civilizations are highly controversial, and his life story is full of myths and mysteries.
- The Civil War was the defining event in the U.S. history before 1877. It had an enormous impact on American society and led to major changes in the Constitution.
- One of the world history topics that everyone needs to know about is the culture and society of ancient Greece . Incredible art, philosophy, politics, and scientific ideas of the ancient Greeks continue to inspire us today.
- Similarly, an essay on the Greek Dark Ages can shine a light on the fall of the great civilization. It is also the period during which Homer’s famous poems Odyssey and Iliad were composed.
- Chivalry in the Middle Ages is an interesting history topic, and it is often romanticized. Learn about the chivalric code, tournaments, and epic legends about famous Medieval knights.
- Also, it may be interesting to write a world history essay on King Arthur . Explore the real events that inspired stories about the legendary British leader and the Knights of the Round Table.
- The history of Easter Island is a very intriguing history topic. You can talk about the mysteries surrounding the culture, language, and the eventual demise of the inhabitants of one of the world’s most isolated islands.
- The history of nuclear weapons is an excellent controversial topic for an essay and a discussion. The stories of research, development, and the use of atomic bombs can be used as cautionary tales for people today.
- From cave paintings and letters to telephone and the Internet – the history of communication is one of the best topics for a research paper. See how the means of communication evolved throughout human history.
- Also, the history of the Internet can be explored in your research paper. What was initially created for research and military use became one of the defining elements of modern life.
- The history of animation is an interesting topic for high school students. Learn about the evolution of animation – from the ancient Egyptian murals depicting motion to the first CGI cartoons and everything in-between.
- The history of museums has many exciting twists and turns. Discover how people of different eras were preserving art and other extraordinary objects. Also, it may be interesting to learn about the most significant art thefts in history.
- The history of cosmetics is an excellent topic for a research paper with a presentation. See how makeup was used in different eras, what it was made of, and how historical figures influenced makeup trends of the past epochs.
- Amelia Earhart is a wonderful role model whose life you can research in your history essay. She was an aviator pioneer and a best-selling author. Her disappearance in 1937 remains a mystery.
- History of Eurovision song contest is a lighthearted topic with serious political undertones. It was originally intended to unite all countries of post-war Europe in one song contest, broadcast live on television.
- The history of theater is a fascinating subject for a research paper. Theater first appeared in Ancient Greece, went through significant changes during the Renaissance, and it remains a popular art form that covers many genres.
- The history of the death penalty is an interesting topic for an essay that you can have a discussion about. The death penalty has a fascinating and gruesome history and remains a controversial subject even today.
- You can write an outstanding research paper on the history of whaling . People have been hunting whales since prehistoric times for various reasons, including perfume and candle manufacturing.
- Another exciting world history topic is Gold Rush . While the California Gold Rush is by far the most famous, there were many other cases throughout history, dating as far back as ancient Egypt.
- One of the more mysterious history topics that you can write about is Stonehenge . This majestic stone structure has been for a long time associated with druids. The latest discoveries suggest that it was used as an observatory.
- Maybe an even more mysterious history research paper topic is the Pyramids of Egypt . The only surviving Wonder of the Ancient World, they are some of the largest structures ever built, and their history remains intriguing.
- Or you can choose to write about all the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World ! They are remarkable buildings and constructions, all but one of which are entirely destroyed, and some are speculated to have never existed.
- Similarly, you can write a paper on other beautiful buildings, such as the picturesque Machu Picchu. An iconic citadel of the Inca civilization, it is now considered one of the New Seven Wonders of the World.
- A paper on Joan of Arc can show how one extraordinary individual is capable of changing the course of history. Her life is surrounded by many legends, and she remains a popular subject in art.
- Similarly, you can write about Abraham Lincoln’s Gettysburg Address and what impact it had on the entire American nation. Delivered during the Civil War, it is considered to be the greatest speech ever.
- A history research paper on feminism could provide a timeline of the fight for equality. Closely connected to the current issues, this topic covers everything from the women’s suffrage movement to the modern Women’s Marches.
- One of the most exciting history topics that everyone needs to know about is the Minoan Civilization – the first highly advanced society in Europe. You can talk about its discovery in the late XIX, the incredible art of Knossos, and its numerous legends, including the famous Labyrinth.
- You can choose to write an essay on history of Indigenous Australians . The timeline of first humans populating Australia is full of mysteries, and their culture remains fascinating.
- An interesting essay can be written on the earliest universities. They were founded long before 1500 in Asia and Africa for educating government officials, and are a fascinating subject to explore.
- You can write an exciting research paper on Alexandria – a city in Egypt founded by Alexander the Great. In ancient times, it was a city like no other, and had an enormous influence on the Mediterranean culture.
- Middle Ages are full of interesting history topics – for example, you can choose to write about medieval magic. From alchemy and astrology to inquisition and witch trials, it’s an existing subject to explore.
- One of the best topics on the history of explorations is the North Pole expeditions . It is full of dramatic events, and it took numerous failed attempts until the North Pole was finally reached in the XX century.
- The first English settlements in America are among the essential parts of the U.S. history before 1877. It includes stories of hardships of the first settlers, bad weather, hunger, and conflicts with native inhabitants.
- Napoleon is an incredibly interesting historical figure. You can write a stunning paper on the rise and fall of his empire.

- You can focus on a specific era in your essay – for example, Victorian England. This period of history, both fascinating and terrifying, still inspires countless novels, movies, and T.V. series.
- Titanic is an excellent topic for an essay and a discussion. A cautionary tale about a luxurious ship that sank due to criminal negligence.
- Death of the Romanovs is an interesting history topic that is still being investigated. This gruesome story inspired many myths, including that of the survival of Anastasia.
- Similarly, you can choose an essay on the assassination of J.F. Kennedy . Learn about what caused it and what long-term effects it had on the American nation.
- Similarly, the assassination of Martin Luther King was an enormous tragedy for the whole country. The circumstances of this event are still not entirely clear, and there are several different theories as to what happened.
- Chernobyl disaster is a fascinating topic that is very popular today. See what led to the tragedy, and what long-term consequences it had on nature and society.
- The fall of the Berlin Wall is a crucial event in modern history. You can write about life in GDR and FRG prior to the fall of the Wall and compare it to what happened afterward.
- Another history topic that you can choose for your essay is the history of berserkers. These Old Norse warriors were fighting in what’s often described as a trans-like state, and their name became synonymous with uncontrolled rage.
- Education in the modern world. The new opportunities of the globalized world influence quality and expectations towards studying. A historical essay can analyze the significant inventions that impacted education. For example, you may focus on the Internet.
- South African Apartheid . The racial segregation regime threw South Africa into poverty and conflicts. Your essay might discuss the historical events that led it. Or you can trace the Apartheid’s timeline from setting to abolishment.
- The founding of the United Nations . The organization’s support of equal human rights is crucial for modern society. The history of the UN is a broad topic with many key events. You may also study the influence of countries such as the USSR on its establishment.
- Cultural trends during World War II. Music, fashion, and art reflected humanity’s hopes and fears of the world. They also supported people when life was tough. In a research paper, you can choose and describe specific examples. Discuss the impact of entertainment during that period, or compare it to World War I.
- The creation of the United States’ Constitution is an interesting US history essay topic. The road to the first national frame of government includes many events. You can analyze the contents of the original Constitution articles based on their drafts.
- Changes in European economies following the discovery of America. After Columbus’ return from his journey, the most powerful empires started to occupy new lands. Later, economic progress led the world to its current conditions. An essay that highlights these milestones can be fascinating!
- Fight against terrorism. After September 11, 2001, the world enforced its war on terrorism. Governments applied measures such as peacemaking interventions to unstable areas. A historical assignment might include the most significant attacks. You can also discuss the UN’s campaigns against terrorism under this topic.
- Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945. The attacks were crucial events that finished World War II . Your essay might address the events that led to the attacks. Discuss if there could have been other ways of stopping Japan’s aggression.
- Urbanization in the US is an interesting essay topic. The most significant change took place in the 19th century. The railroads connected the whole country, and trading opportunities grew. Discuss why people moved from rural areas to cities and the consequences of it.
- History of railroads in the United States. Broad territories were the major obstacles to American economic development. In 1827, the first railway journey took place in the US. The roads were rapidly built during the following century. A discussion these events is a fun historical assignment topic.
- Immigration and scientific progress in the 20th century. Back then, thousands of Europeans were forced to migrate to the US. Many of them were responsible for important discoveries and inventions. Discuss its effect of immigration on science and technology in a historical essay.
- The three most important inventions of the 19th century. The 1800s are full of creations that changed humanity’s history. Typewriters, bicycles, and telephones were first made in that period. For an essay, you can pick the inventions based on their historical value.
- The stock market crash in 1929 was the worst experience for the industrialized world at the time. Entertainment during the Great Depression played an essential role in supporting America. It is also an interesting historical topic to write about.
- The history behind today’s foreign affairs . Despite prolonged peace, governments still have political disagreements. Choose two conflicting countries and identify the events that led to the current situation.
- The history of the LGBTQ community in the United States. Modern American society praises equity and respects the rights of minority groups. However, it wasn’t always like this. LGBTQ is a broad discussion topic influenced by past events. It might also be interesting to compare the US community to the European one.
- The global financial crisis of 2008 is a great modern history essay topic . An economy can crash for multiple reasons. If it happens worldwide, the effects are severe. An argumentative essay can be a basis for analyzing the causes of the crisis. Compare it to other economic disasters such as the Great Depression.
- Cultural progress led humanity to important social developments. One of them is the legalization of same-sex marriages . Historical analysis can include a timeline of such marriages. Social activism related to the topic is an excellent basis for an essay.
- The Holocaust. One of the darkest events in the 20th century’s history is the European Jews’ genocide. Analyze the chain of events leading to it in a historical essay. How did it impact human rights enforcement during the post-war period?
- Space exploration in the 21st century is a historical topic that develops right now. Jeff Bezos’ Blue Origin was founded in 2000, and Elon Musk started SpaceX in 2002. An essay can highlight the milestones of space exploration after the Cold War.
- The history of Thanksgiving. Pilgrims established the holiday based on celebrating the harvest. Discuss the tradition’s roots and the impact of English colonists on American culture. An essay can also describe similar feasts around the world.
- Another good history essay topic is Antarctica. The impactful exploration of ice lands only began in the late 19th century. Today, scientists study Antarctica’s land, resources, and animals. Trace the past events and discoveries of the region in your historical essay.
- The history of infections. Our lives have changed in 2020 during the COVID-19 pandemic. There were similar events in the past, where plague and flu diseases killed millions of people. A comparison can help you learn about the development of today’s healthcare practices.
- Women’s suffrage . In August 1920, the US Congress ratified the 19th Amendment that gave women the right to vote. Many campaigns and protests preceded the event. The perception of women by society started transforming since then. An essay might describe the challenges leading to these changes.
- History of the Olympic Games is a fascinating topic for middle school . The legacy of ancient Greece was revived only in the 19th century. Study the events that took place throughout the Olympic Games’ history.
- If you need a world history essay topic, try writing about the International Red Cross . In 1863, Swiss businessman Henry Dunant established the Red Cross. He was influenced by the terrifying experience of seeing thousands of wounded men at war. A persuasive essay can highlight the organization’s historical importance.
- Weapon development during World War II. Military weapons contributed to technological progress in the 20th century. A research paper might focus on the weapons invented during the War. You can also discuss the impact of military innovations on post-war life.
- An essay on Korean history can analyze how one nation can change if divided into separate regimes. North and South Korea started making peace only in 2018. Try and determine the reasons for the 1948 separation and political instability.
- Ku Klux Klan as a resistance movement is an important topic. Four million citizens nationwide joined the group in the 1920s. Such popularity revealed the demand for change. Your historical essay might include crucial outcomes of Klan’s activities. A comparison to the medieval inquisition might lead to interesting conclusions.
- Globalization is another excellent history essay topic for high school students. The world has never had so many cultural and economic connections as it does today. Your essay can go through historical events that caused globalization. Or, you may analyze its benefits and downsides.
- History of climate change . In 2009, the UN Climate Change Conference stated that the world is in danger due to human impact on climate. A historical essay can focus on the environmental factors of the topic. Alternatively, you may trace the discoveries and studies about climate change.
- Labor Day is a national holiday first celebrated in the industrial era. It originated in the 19th century when workers spent 12 hours daily to earn the minimum wage. In your historical essay, describe the events that led to the holiday’s creation.
- The history of the American presidency is a broad topic to write about. More than 40 people ruled the country and impacted all facets of America. For example, you may choose to evaluate education under different presidents. You can also compare democrats and republicans as presidents.
- Gutenberg’s printing press invention changed the world. It was as significant in the 15th century as the Internet was for modern history. An essay can reconstruct the events before and after the invention of printing. Its impact on education and the economy are interesting points for discussion.
- The European Union has deep historical roots since the Empire period. An essay about it might cover the timeline of democracy established in Europe. You can highlight the changes that took place in the countries that joined the Union. Alternatively, compare the organization and its aims to other historical alliances.
- Modern religions are an intriguing subject for an essay. Historical events often shape peoples’ beliefs. Discuss why people started updating the main religions in recent decades.
- Population resettlement took place multiple times in human history. For example, thousands of Serbian Albanians were forced to flee Kosovo during the 1999 conflict. An essay that describes a migration can include the reasons for it. Compare it to similar occurrences, and discuss its outcomes.
- Ancient architecture is the most incredible legacy cherished by generations. Design patterns and colors of creations reflect the periods they were built in. For your essay, choose specific examples and mention the events associated with them. Research can include ancient European, Asian, or American architecture.
- Socialism as a political regime significantly impacted world history. Socialist movements took place in Europe and the United States. The Soviet Union was established under its conditions. Choose this interesting 20th-century essay topic and describe a country affected by socialism. For example, China is still ruled by that regime.
- History of democracy in Africa . African history includes centuries of foreign occupation. Yet, its countries have recently started getting deserved independence. Algeria, Morocco, Namibia, and Zimbabwe only got their democratic government in the last 60 years. Historical research can analyze the influence of ex-colonizers on Africa. Or, you may choose a country to describe its journey from a colony to a democracy.
- History of South American countries. Colonizers occupied the regions in South America after Columbus’ journey. You can discuss the conflicts between the land’s native inhabitants and migrants. A research paper may also reveal how the nations were formed by combing two different populations.
- The history behind the petroleum industry is an interesting basis for an essay. Oil defines the UAE and Russia’s economies and has significant influence in politics. Study the formation of the world’s oil industry, or choose one country to explore.
- History of Native American tribes. More than 500 groups of Indigenous Americans lived in the US territories. Each had its own culture and policies. For your essay, gather information about conflicts between the natives and migrants.
- History of vaccination. The development of this practice is an interesting essay topic. You can review the timeline, starting from the 1798 smallpox vaccine.
- History of China. Write an essay that explores the most significant events of the country’s history. An interesting idea is to compare it to other major countries. Moreover, you can discuss the Chinese presence in the World Wars by analyzing its strategies.
- Events that affected the environment. There are many examples of history playing against nature. Think of nuclear bomb explosions, rapid industrialization of the 19th century, and deforestation. Your essay might analyze several such events and provide lessons for the future.
- The history behind popular foods . Migration and global trading helped humanity discover chocolate , potatoes, and coffee . A historical essay can focus on one product and describe what made it famous.
- The Vikings played a significant role in European history. Scandinavians still cherish their traditions and unique culture. Your research might be about their settlements in Scotland, France, and Ireland. Also, you can describe the unique worldview of the Vikings.
- Ancient piracy covers many themes that you can mention in an essay. The first pirates were the Sea Peoples in the 14th century BC. Today, the pirates still exist in politically unstable regions such as Somalia. Your historical paper can include the most significant acts of piracy in ancient times.
- History of money . People have been exchanging goods throughout history. Yet in 770s BC, the Chinese invented the ultimate trading product — money. The historical timeline of the financial systems is an excellent topic for an essay.
Other History Essay Topics
- European motives for expansion & colonization in New World
- “Birth of Modernity” of Renaissance
- Racial tensions and immigration in California
- Gandhi’s innovative renovation of tradition explained
- Colonists’ actions in the pre-revolutionary era
- The French Revolution an outcome of Enlightenment ideas
- The autobiography of St. Ignatius
- Land disputes between native American groups and the United States
- The 1930s generation of Soviet spies and operatives
- The Tea Act and the Coercive Acts: Britain and the colonies
- The Middle Ages as the “Dark Ages”
- The making of the modern Middle East: term definition
- The uniqueness of World War One
- Social structure and lifestyles of the 1960s counterculture
- Depression period and new deal legislation
- United States’ policy of isolationism since the 19th century
- History: Abraham Lincoln’s address in Gettysburg
- The use of armed forces by the United States and its effect
- Radical republicans during the Reconstruction era
- Lincoln’s vs. Davis’ administrations during the war
- Civil War’s impact on Northern and Southern economies
- Consumerism critique in the 1950s-70s
- Lincoln’s plan for Reconstruction and opposition to it
- Women and blacks’ participation in the Civil War
- War of 1812: reasons and outcomes for native communities
- The causes of the Protestant reformation
- Palestinian Liberation Organization’s history
- Ethnographic sketch of Brazilians
- British colonization of America and its results
- What was the purpose of Lee’s plan on Gettysburg?
- The leaders of command for the modern war in 1864
- What did George Washington Thanksgiving proclamation state?
- Post-WWII events that caused loss of faith in American way
- European groups’ motives to migrate to America
- Industrial economics and its social impact on Britain
- Refugee definition development in the 20th century
- Positive things to learn from Medieval culture
- Scientific revolution in Western European civilization
- The Spanish-American war: definition and facts
- The role of violence in the America’s expansion
- Protestant Reformation leaders & Catholic Church’s response
- Asian studies: Takahashi Mutsuo’s “The Snow of Memory”
- Colonization of freedmen: arguments for and against
- Major milestones of the Kyoto treaty and Montreal Protocol
- Progressive Era & New Deal outsiders and corporate ownership
- American progressive movement and its participants
- Steel industry & American history changes in the 1890-1920s
- Anarchist & socialist movements and terrorism
- What is the Third Estate? What role did it play in Revolution?
- The Islamic revolution of 1979 and its main causes
- Conservatism in American life from 1968 to the present
- African American Civil Rights Movement in 1950-1980
- Second World War and the end of colonial rule in Africa
- The main reasons of the American Civil War
- Alexander Graham Bell’s most important day
- History of gangs in America and Utah
- Civil Rights vs. Black Lives Matter movement
- Latin America: national issues
- American ancient people and Skull Wars
- Historical events in history of white people of America
- Reasons of Confederacy’s defeat during Civil War
- Tombs Egypt during the period of 3200 BC to 1200 BC
- Republican Reconstruction and its achievements
- Christians-Rome relationship: persons and events
- Lincoln’s answer to the Emancipation question
- US women’s rights movements in 1850-1900
- The Eighteenth Amendment and Volstead Act
- Japan, China, and the Ottoman Empire during the 19th century
- Capital punishment and African Americans
- Industrial growth during the last 100 years in the US
These are a tiny handful of the wide array of topics that you can write about for history class. When in doubt, always solicit opinions from your professor. (The worst case scenario is that they say no.)

Most importantly:
Remember, the analysis of historical events is subjective. Two scholars may have vastly unique explanations for a series of historical events unfolding the way they did. Accordingly, try to write from the perspective that your instructors most likely hold. And if you’re unsure, ask them to review a first draft of your essay, or at least talk to them about your thesis statement!
You might also be interested in:
- A List of History Websites for a Perfect Research
- World War 2 Essay Example + Argumentative Topics
- Essay on India after Independence: How-to Guide and Prompts
- 497 Interesting History Topics to Research
- A List of 212 Brilliant Research Proposal Topics to Investigate
- 350 Powerful Feminism & Women’s Rights Topics [2024]
- 430 Philosophy Topics & Questions for Your Essay
- 229 Good Dissertation Topics and Thesis Ideas for Ph.D. & Masters
Historical Essay FAQ
Students are often asked to write on historical topics. Such an essay can be:
1. A description of a persona; 2. An analysis of historical events; 3. An overview of the context of the whole epoch, etc.
In any case, a historical essay deals with a retrospective and requires looking into history.
There are countless interesting topics for essays and research projects. You can look into any epoch from the ancient times up to the present days. Choose something that genuinely fascinates you. You might prefer a controversial issue as it is more exciting to study.
For any research paper, it is essential to create an outline first. Once you’ve identified some key aspects that you want to focus on, write them as bullet points. They will become the Body of your research paper. Don’t forget to add an introduction and a conclusion.
Whether you write about the World, the civil, the cold, the Vietnam, or any other war, be sure to stay as objective as possible. It is a very emotionally charged topic, but you need to refrain from opinionated judgments. Do not resort to direct accusations.
- Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started – Outlining: University of Maryland Global Campus
- Understanding the Subjective Nature of History
- Writing Cause and Effect Papers
- One Hundred Good Research Paper Topics for History Class
- History Topics
- Modern History Resources
- Research Paper Topics About United States History
- The Importance of History Essay
- The Foundation of History
- What is History Essay Examples
- Index: American History
- World History: Encyclopedia Britannica
- Historical Topics: Library of Congress
- American History: Smithsonian Institution
- Political History: Historians.org
- Primary Sources on History: Gale
- History of the UN: United Nations
- Ancient History Encyclopedia: Index
- Share to Facebook
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email
![title for historical essay 150 Argumentative Research Paper Topics [2024 Upd.]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/close-up-magnifier-glass-yellow-background-284x153.jpg)
Argumentative research paper topics are a lot easier to find than to come up with. We always try to make your life easier. That’s why you should feel free to check out this list of the hottest and most controversial argumentative essay topics for 2024. In the article prepared by...

One of the greatest problems of the scholarly world is the lack of funny topics. So why not jazz it up? How about creating one of those humorous speeches the public is always so delighted to listen to? Making a couple of funny informative speech topics or coming up with...
![title for historical essay Gun Control Argumentative Essay: 160 Topics + How-to Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/bullets-gun-black-velvet-desk-284x153.jpg)
After the recent heartbreaking mass shootings, the gun control debate has reached its boiling point. Do we need stricter gun control laws? Should everyone get a weapon to oppose crime? Or should guns be banned overall? You have the opportunity to air your opinion in a gun control argumentative essay....
![title for historical essay Best Childhood Memories Essay Ideas: 94 Narrative Topics [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/child-working-in-cambodia-284x153.jpg)
Many people believe that childhood is the happiest period in a person’s life. It’s not hard to see why. Kids have nothing to care or worry about, have almost no duties or problems, and can hang out with their friends all day long. An essay about childhood gives an opportunity...
![title for historical essay A List of 272 Informative Speech Topics: Pick Only Awesome Ideas! [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/meeting-room-professional-meeting-284x153.jpg)
Just when you think you’re way past the question “How to write an essay?” another one comes. That’s the thing students desperately Google: “What is an informative speech?” And our custom writing experts are here to help you sort this out. Informative speaking is a speech on a completely new issue....
![title for historical essay 435 Literary Analysis Essay Topics and Prompts [2024 Upd]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/girl-having-idea-with-copy-space-284x153.jpg)
Literature courses are about two things: reading and writing about what you’ve read. For most students, it’s hard enough to understand great pieces of literature, never mind analyzing them. And with so many books and stories out there, choosing one to write about can be a chore. But you’re in...
![title for historical essay A List of 580 Interesting Research Topics [2024 Edition]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Fotolia_141866189_S-284x153.jpg)
In school and college, you will be required to write research papers. Yes — papers in the plural. And that’s the first reason you may want to turn to Custom Writing and seek help with research projects. When assigned a paper, the very first undertaking is to choose from a...
![title for historical essay 335 Unique Essay Topics for College Students [2024 Update]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/smiling-students-walking-after-lessons1-284x153.jpg)
The success of any college essay depends on the topic choice. If you want to impress your instructors, your essay needs to be interesting and unique. Don’t know what to write about? We are here to help you! In this article by our Custom-Writing.org team, you will find 335 interesting...

Social studies is an integrated research field. It includes a range of topics on social science and humanities, such as history, culture, geography, sociology, education, etc. A social studies essay might be assigned to any middle school, high school, or college student. It might seem like a daunting task, but...

Looking for a good argumentative essay topic? In need of a persuasive idea for a research paper? You’ve found the right page! Academic writing is never easy, whether it is for middle school or college. That’s why there are numerous educational materials on composing an argumentative and persuasive essay, for...

Persuasive speech is the art of convincing the audience to understand and trust your opinion. Are you ready to persuade someone in your view? Our list of sports persuasive speech topics will help you find a position to take and defend. If you need more options quick, apart from contents...

When you look for a good research paper topic, you can easily become the severest critic of any proposed idea. Some topics do not interest you at the very least, while others might shock your teachers. Where is the golden mean? Check out this list of top 100 research paper...
This was decent.
No words can express how I appreciate the work you do! Your posts are real salvation to when I don’t know how to write this or that paper. This post on Industrial Revolution essay writing gives many brilliant ideas!
Hi! I’m Ivan. I just wanted to thank you for your post on Industrial Revolution essay writing! I helped me greatly with my essay writing on this topic. THXZZZ!

75 Interesting History Essay Topics
Do you wonder how ancient civilizations functioned and evolved through the years of inventions and innovation? History indeed teaches us so much about the people and communities that created an impact back then. While literary essay topics help you explore the nuanced writing forms, history essay topics are meant to nurture your research skills. The thirst to discover stories of war, victories of freedom fighters, and the smuggling of arms can be quenched by engaging in essay writing.
History is vast, ranging from states to nations, from forts to ports and so much more. In such a case, you simply cannot be studying it all or exploring topics all of a sudden. Hence, it is important to know that history can be categorized into different types wherein you can choose the one that interests you the most. Writing history essays empowers critical thinking skills and builds a problem-solving mindset in everyday life. This article will take you through different history essay topics motivating you to discover varied perspectives, ideas, and ideologies of the past.
Engaging History Essay Topics
Various creative writing topics for high schoolers tap into building their imagination skills and enhancing their thinking abilities. However, along with history websites , interesting history essay Topics enable students to dive deeper into the ancient world and discover evolution. It is important to provide students with the right topic that interests them thereby inspiring them to research and find facts. The below-mentioned topics are a combination of various parts of history that help teachers offer a comprehensive learning environment.
1. General History Essay Topics
- The reasons behind the fall of the Roman Empire and its effects.
- The effects of the printing press on the Renaissance’s dissemination of knowledge.
- Propaganda’s function in World War II and its impact on public opinion.
- The historical contributions of ancient African civilizations.
- The Silk Road’s importance in promoting trade and cultural exchange between East and West.
- The elements that led to the Byzantine Empire’s rise and demise.
- How the Scientific Revolution affected the growth of modern science.
- Analyzing the social and cultural backdrop of the frenzy during the Salem Witch Trials.
- The Louisiana Purchase’s importance in influencing American expansion.
- The effects of the Spanish Inquisition on freedom and toleration of religion.
- The impact of Enlightenment thought on the French and American Revolutions.
- How the Mongol invasions affected the economies and societies of Eurasian countries.
- The consequences of the Protestant Reformation on politics and society in Europe.
- The artistic and governmental achievements of the ancient Persian Empire.
- The reasons for and effects of the Chinese and British opium wars.
2. Essay Topics on Ancient History
- The pharaohs’ achievements offer a glimpse into the growth and fall of Egyptian civilization.
- The legacy of ancient Mesopotamia is the contributions it made to early human cultures and culture.
- What can we infer about the Indus Valley Civilization, a prehistoric culture, and its significance?
- The causes behind the rise, expansion, and ultimate destruction of the Roman Empire.
- The construction of China’s Great Wall and its significance.
- Ancient Rome’s aqueducts, roadways, and structures are feats of engineering.
- The development and significance of early scripts like cuneiform and hieroglyphics.
- Symbolism and purpose in the art and architecture of ancient civilizations.
- The impact of mummification methods on ancient Egyptian ideas about the afterlife.
- Beginnings and religious practices of ancient civilizations: A comparison.
- The importance of the ancient Olympic Games in promoting peace and harmony between city-states.
- Legendary stories’ cultural value to ancient cultures.
- Influence of the Persian Empire on regional trade and cultural exchange.
- Investigating the Mayan civilization’s triumphs and demise.
- Early Indian mathematicians’ contributions to mathematics.
3. Essay Topics on World History
- How Europe’s intellectual and cultural development was fueled by the Renaissance.
- The effects of the Cuban Missile Crisis on the Cold War and world politics.
- The effect of the Mongol invasions on how medieval Eurasia developed.
- The legacy of ancient civilizations: Contrasting and comparing the contributions of the civilizations of Mesopotamia, Egypt, and the Indus Valley.
- Gender rights and the position of women during the French Revolution.
- The causes of the Roman Empire’s collapse during its ascent and fall.
- The reasons for and effects of the 1917 Russian Revolution.
- The importance of the Silk Road in fostering commercial exchange.
- The contribution of the Enlightenment to world upheavals and reformations.
- China’s connections with the West after the Opium Wars.
- The effect of the Spanish Conquistadors on the Americas’ indigenous cultures.
- The causes of the Byzantine Empire’s collapse and its historical repercussions throughout Europe.
- Political and religious changes in Europe as a result of the Protestant Reformation.
- The emergence of empires in prehistoric Mesopotamia and their historical consequences.
- The Declaration of Independence’s importance in molding American history.
4. Essay Topics on Black History
- The influence of the Harlem Renaissance on African-American culture.
- The importance of the Underground Railroad in aiding slaves’ freedom-related escapes.
- African-American participation in the Civil War and their struggle for freedom.
- The racial equality campaigns carried out by the Black Panthers.
- African-American aviators in World War II as the Tuskegee Airmen.
- The integration process of the first African American pupils into previously all-white schools.
- The history of Black History Month and its importance.
- The Civil Rights Act of 1964’s legacy and ongoing effects.
- The battle for desegregation by the Little Rock Nine.
- Black Lives Matter: Its Background and Importance
- The fight for voting rights and electoral participation by African Americans.
- Historically Black colleges and universities (HBCUs’): Background and Influence.
- Importance of the March on Washington for Jobs and Freedom.
- The Black Arts Movement’s influence on culture during the 1960s and 1970s.
- The National Association for the Advancement of Coloured People’s (NAACP): Background and Significance.
5. Argumentative Essay Topics on History
- Was the American Revolution a true revolution or was it merely a fight for independence?
- Social and economic effects of the Industrial Revolution on the working class.
- Women’s participation and contributions to the war effort during World War II.
- The Mongol Empire’s legacy: Did it make a positive or detrimental impact on world history?
- The Declaration of Independence’s importance in influencing American values and administration.
- The benefits and drawbacks of imperialism.
- The effects of the Treaty of Versailles on post-World War I stability in Europe.
- The Black Death’s consequences on medieval society and how they affected Europe in the long run.
- The reasons behind the French Revolution and its effects.
- The reasons behind and effects of the Cold War’s Cuban Missile Crisis.
- Analyzing the civil rights movement’s effects on society and determining its effectiveness.
- The importance of ancient Greek and Roman culture in forming contemporary Western culture.
- The discussion around the use of atomic bombs in Hiroshima and Nagasaki.
- The function of propaganda in World Wars I and II.
- Nelson Mandela’s contribution to the end of apartheid in South Africa.
Final Words
Drafting your thoughts about different history topics helps you explore a world of possibilities. Essay writing helps develop control grammar and language skills thereby strengthening communication.
With the above-mentioned history essay topics, you can choose the one that interests you the most. Ensure to pen down your thoughts and add new perspectives to the stories of the past. Students can also explore and play online history games to learn more about history and practice the same.

Sananda Bhattacharya, Chief Editor of TheHighSchooler, is dedicated to enhancing operations and growth. With degrees in Literature and Asian Studies from Presidency University, Kolkata, she leverages her educational and innovative background to shape TheHighSchooler into a pivotal resource hub. Providing valuable insights, practical activities, and guidance on school life, graduation, scholarships, and more, Sananda’s leadership enriches the journey of high school students.
Explore a plethora of invaluable resources and insights tailored for high schoolers at TheHighSchooler, under the guidance of Sananda Bhattacharya’s expertise. You can follow her on Linkedin
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Home / Essay Samples / History
Free History Essays
The world’s history is our collective memory about the past, it is a record of our successes and failures, aspirations, temptations, suffering, strengths and weaknesses, inventiveness. A history essay typically evokes and analyzes important events from the past or even tries to predict the future by analyzing our past.
History also contains valuable information about human nature and typical mistakes that individuals, communities, or societies tend to make – while every age has its own specific circumstances, at the very core, there are great similarities between various events or processes. Hence, learning history is not only important for the sake of knowing our origins, but also for safeguarding ourselves against future mistakes and for learning to detect perils in advance.
Ancient Egypt: Analysis of Political and Cultural Life
Ancient Egypt, with its rich history spanning thousands of years along the banks of the Nile River, remains a source of fascination and wonder. In this essay, we delve into the political and cultural aspects of ancient Egypt, examining its dynastic rulers, societal structure, religious...
Why is Black History Important Nowadays
Black history is an integral part of the broader human narrative, yet it has often been marginalized and overlooked. This essay explores the profound importance of black history, shedding light on its contributions, struggles, and lessons that resonate far beyond the African American community. Understanding...
The Jim Crow Laws: a Legacy of Slavery
The Jim Crow Laws, a system of racial segregation and discrimination that prevailed in the United States from the late 19th century to the mid-20th century, are inextricably linked to the history of slavery. This essay explores the historical context, development, and impact of Jim...
The Fall of Rome: Causes and Impact on History
The fall of the Roman Empire, a vast and powerful civilization, is a pivotal event in history that continues to captivate scholars and enthusiasts alike. This essay explores the causes behind the fall of Rome and its profound impact on subsequent historical developments. The decline...
Martin Luther King Jr.: a Legacy of Civil Rights and Social Justice
Martin Luther King Jr. is an iconic figure in American history, celebrated for his tireless efforts in advancing civil rights and social justice. His life and work continue to inspire and resonate with people around the world. This essay delves into the remarkable journey of...
Black History: a Reflection on Resilience and Triumph
Black history is a tapestry woven with the threads of resilience, courage, and triumph. It is a chronicle of struggle against oppression and a testament to the indomitable spirit of Black individuals throughout history. This essay delves into the rich tapestry of Black history, exploring...
The Tragic Hero in "Julius Caesar": an Analysis
William Shakespeare's play "Julius Caesar" is a classic tragedy that raises the question of who among its characters can be considered the tragic hero. The term "tragic hero" refers to a character of noble stature who possesses a fatal flaw leading to their downfall, and...
Westward Expansion as a Cause of the Civil War
The American Civil War, a defining moment in U.S. history, was a complex and multifaceted conflict with a range of underlying causes. While slavery is often identified as the primary cause of the war, westward expansion played a significant and intertwined role in escalating tensions...
Exploring the Main Areas of Historiographical Research
Historiographical research is a fundamental aspect of the field of history. It involves the study of how historical events and topics have been interpreted, analyzed, and written about over time. This essay provides an in-depth examination of the main areas of historiographical research, highlighting the...
Causes of the American Revolution: Political, Economic, and Ideological
The American Revolution, an epochal event that forever altered the course of history, was underpinned by a complex web of causes that encompassed political, economic, and ideological factors. This essay embarks on a comprehensive exploration of these causes, aiming to provide a detailed analysis of...
Trying to find an excellent essay sample but no results?
Don’t waste your time and get a professional writer to help!
- Ancient Greece
- British Empire
- Colonialism
- Contemporary History
- Historical Figures
- History of China
- History of The United States
- Medieval Europe
- Mesoamerica
- Mesopotamia
- Nazi Germany
- Roman Empire
- Russian Empire
- Daedalus and Icarus
- Mother Teresa
- Harriet Tubman
- Alexander Hamilton
- John Proctor
- Eleanor Roosevelt
- Great Depression
- Civil Rights Movement
- Industrial Revolution
- American Revolution
- The Progressive Era
- Salem Witch Trials
- Hurricane Katrina
- Louisiana Purchase
- Trail of Tears
- French Revolution
- Imperialism
- Romanticism
- Julius Caesar
- Cesar Chavez
- Frederick Douglass
- Human Trafficking
- Christopher Columbus
- African Diaspora
- Mahatma Gandhi
- Historiography
- Ancient Civilizations
- Crucible Conflict
- Historical Criticism
- Oral History
- Polish History
- South Sudan
- Tokugawa Shogunate
- Treaty of Waitangi
- What Is History
- World History
samplius.com uses cookies to offer you the best service possible.By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .--> -->