Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- Review Article
- Open access
- Published: 01 September 2024

Utilisation of rondavel space by amaXhosa people: a case of Mbhashe local municipality, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa
- Africa Ndude 1 &
- Sinenhlanhla Memela 1
Humanities and Social Sciences Communications volume 11 , Article number: 1122 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
- Anthropology
Traditional rondavel building patterns, designs and materials have changed due to urbanisation, economic status, globalisation, and modernisation. There is limited understanding of how the architectural change has impacted the utilisation of rondavel space. This study uses the concept of habitus to understand whether the changing design of traditional rondavels has influenced their utilisation, based on a case study of the Mbhashe Local Municipality in the Eastern Cape province, South Africa. The data was collected using semi-structured interviews. The findings reveal the habitus of the AmaXhosa people on how they utilise traditional rondavels (family house) for childbirth, placing a deceased’s coffin, sleeping, seating, food preparation, serving and storage, keeping the spear, hosting ceremonies, communicating with ancestors, and interacting with the living. While the influence of contemporary architecture has changed the construction of rondavels, the inhabitants have not resisted changes to the architecture or cultural values as they have found different ways to adapt. Certain old dispositions are adaptable to contemporary structures, but some people are uninterested in adapting elements to the contemporary rondavel. Some habits of utilising traditional rondavels cannot be adapted to the contemporary rondavel because of health and medical innovations.
Similar content being viewed by others

Architectural characteristics of accommodation buildings within the context of sustainable ecotourism in Cyprus: evaluation and recommendations
New insights on commemoration of the dead through mortuary and architectural use of pigments at Neolithic Çatalhöyük, Turkey
Discovering the meaning of contemporary urban squares for its users—a case study of Poznan, Poland
Introduction.
Based on archaeological evidence, rondavels have existed since pre-colonial times as a prime settlement form in homesteads in much of South Africa and other African countries, including Botswana, Kenya, Lesotho and Eswatini (Schoenauer 2000 ; Steyn 2006 ). The rondavel is considered as a vernacular architecture: it is built using locally sourced material and forms part of a region’s culture and heritage (OpenHeritage 2016 ). Steyn ( 2006 :1) describes the rondavel as a “drum”, often built with mud and grass-thatched roofs (Fig. 1A ). They are popular indigenous settlements which are still prevalent in the rural areas. While most households have more than one rondavels (Fig. 1B ), some indigenous settlements are now roofed with zinc materials (Fig. 1B ). Going forward, this article refers to indigenous settlements as traditional rondavels.

A traditional rondavel with grass-thatched roof and ( B ) household two rondavels with zinc roof.
Traditional rondavels were used for dwelling and hosting important customary rituals and celebrations in Africa (Steyn 2006 ). Modern day rondavels exist with flat-roofed rectangular buildings or structures built using cement and zinc roofs, which will be referred to as contemporary rondavel design henceforth (Van Vuuren 2017 ).
Steyn ( 2006 ) argues that the change is a result of urbanisation and economic status because people admire urban architecture and can afford their desired building materials. A study by Aikpehae et al. ( 2016 ) reveals that globalisation, urbanisation and modernisation transformed building patterns, designs and materials used for construction. They illustrate how Nigerian building patterns and housing have transformed because of the influence of colonisation (Aikpehae et al. 2016 ). Guerrieri ( 2020 ) adds that migration has allowed the export of architecture and urban planning models from one country to another; hence, we see the same style across countries. The global intercultural contact led to the change in dwellings in southern Africa (Frescura 1981 , 2015 ) where traditional dwellings were constructed using mud, wattle and thatch grass. Missionaries introduced contemporary building constructed using sun brick and mortar with corrugated iron sheet for roofing as well as highveld and parapet housing styles, the contemporary building is illustrated in Fig. 2 .
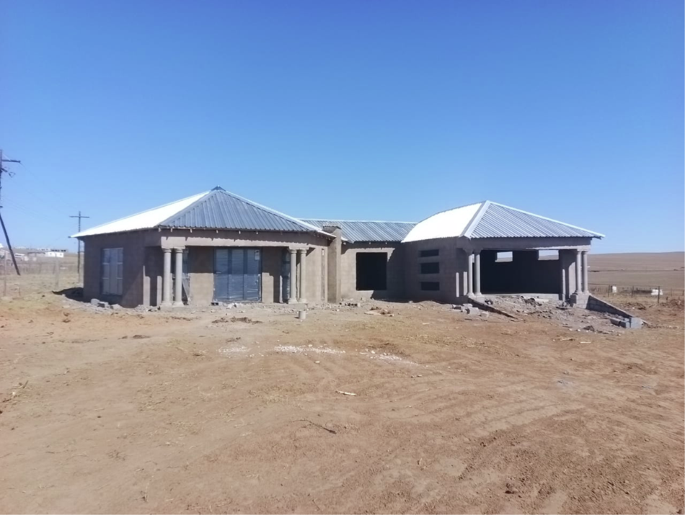

Illustration of the contemporary building under construction.
Tapiero et al. ( 2024 ) indicates that in Montesinho Natural Park, north-east of Portugal, residents had vernacular buildings constructed using locally available wood, slate stone tiles, lime mortar, schist and granite. The availability of industrialised material and decreasing traditional labour posed a threat vernacular buildings.
The following section discusses the evolution of the traditional and modern rondavel followed by the utilisation of rondavels by amaXhosa people, detailing the study area, research methods, results, discussion and conclusion.
Traditional and modern rondavel evolution
Early African dwellings were caves, stone-walled iron shelters or houses quickly erected and dismantled as nomadic societies followed herds of animals (Frescura, 1981 ; Moremoholo, 2021 ). Frescura ( 1981 ) explains the historical development of dwelling types, presented in Fig. 3 . The earliest traditional dwelling was a beehive hut also known as ngqu-phantsi . It was made up of stakes organised in a circle with their tops arched inward to a point. The stakes were then bound together by hoops and the frame was insulated with thatched grass (Walton, 1949 ). It is possible that the need for more living space resulted in the rondavel, which is a cone-on-cylinder rondavel with a wall and roof. Although its doorway was raised higher compared to the beehive hut, it was still lower than the height of a man. The material used to construct traditional rondavel was either a thatch roof with stones and mud bricks or sticks mixed clay and dung mortar or mud and wattle (Walton 1949 ; Frescura 1981 ; Oliver 2006 ; Moremoholo 2021 ; Onyejegbu et al. 2023 ). These vernacular dwellings were constructed using locally available materials (Tapiero et al. 2024 ).
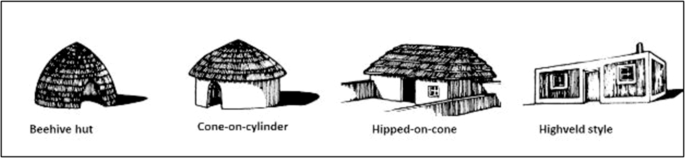
This figure is covered by Creative Commons licence.
The third iteration of dwelling development was influenced by Western ideas of hipped-on-cone, which had a linear floor plan, rooms divided into rows and triangulation of the thatch roof. The fourth dwelling type was an introduction of the highveld style with iron-sheet roofing and sun brick (Frescura 1981 ).
Western ideas influenced the cone-on-cylinder rondavel design and materials used which included the use of iron-sheet roofing and sun brick. Despite the Western influences, the traditional rondavel still exists while others have modernised (Moremoholo 2021 ; Onyejegbu et al. 2023 ). Vellinga ( 2006 ) notes that the traditional vernacular architecture has not vanished, but has rather merged with modern styles to suit the current circumstances. Tapiero et al. ( 2024 ) argue that the use of modern materials in construction does not compromise the values of the dwelling in the community. They also note that conserving vernacular architecture plays an essential role in the preservation of culture and sustainable practises by optimising energy usage (Tapiero et al. 2024 ). Onyejegbu et al. ( 2023 ) argue that some Nigerian households still have traditional mud huts that were built by their forefathers in commemoration of their culture, tradition and prowess.
Moremoholo ( 2021 ) used a case study of the Sotho community in Makgabeng, a rural area in Limpopo to investigate how indigenous values have been incorporated or retained on houses built using brick and mortar. The findings show that both traditional rondavel and modern dwellings exist and residents were able to adapt values of indigenous rondavel to modern dwellings, including practising ancestral ceremonies.
Smith ( 2022 ) suggests that the modernisation of the traditional rondavel design into contemporary sensibilities reflects the development of awareness of the diverse heritage that connects South Africa to the rest of the African continent and its people. Thus, the integration and adaptation of indigenous values into modernisation promotes self-definition for many South Africans. Moreover, it encourages a deeper appreciation of the connections between South Africa and the rest of the world. Bianco ( 2022 ) states that this hybrid form of building reflects the evolution of local culture and ways of life so that one can imagine new development aspects entrenched in the culture and environment (Bianco 2022 ). Thus, currently, vernacular architecture can be understood as the foundation of the contemporary architectural type that is rooted in integrating local building traditions (Naude 2010 ; Bianco 2022 ). The current study focuses on the amaXhosa people and intends to understand whether the changing design of traditional rondavels has influenced their utilisation.
The utilisation of rondavels by amaXhosa people
The amaXhosa people are predominantly located in the Eastern Cape province (Nyamende 1994 ; Mokhoathi 2021 ). A rondavel in a Xhosa home ( umzi ) typically exists in a cluster of other structures. Umzi , plural imizi , is a collection of physical, social and organic elements constituting a settlement component known as homestead. It typically comprises several rondavels or huts (the family house, with middle huts reserved for children and visitors as well as a traditional dispensary and consultation), an adjacent garden and a kraal with tools and equipment often used in various ways (Perry 2013 ).
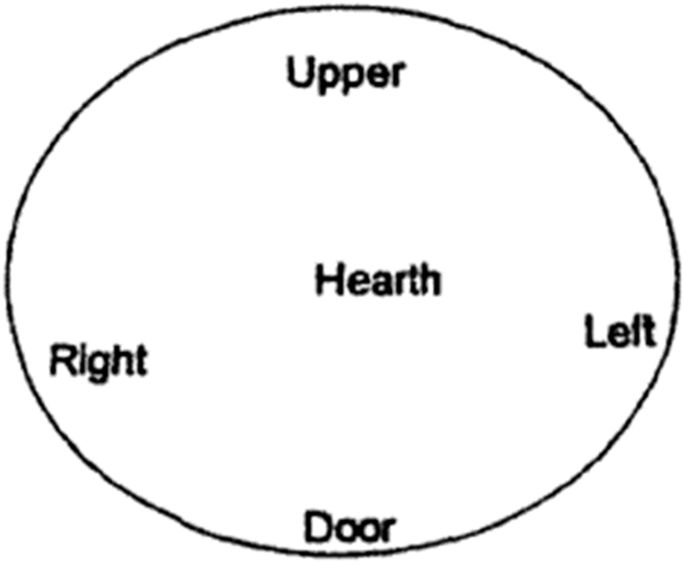
The family house ( indlu enkulu ) is the main hut where everyone meets to socialise and prepare, store and eat food (McAllister 2004 ). It is a space where all rituals take place and people communicate with their ancestors (McAllister 2004 ; Mlisa 2009 ). In the past, following the birth of a child in the family house, children and men were prohibited from using the space (Kobo 2016 ). McAllister ( 2004 ) illustrates how the family house is divided, as shown in Fig. 4 .
This figure was reproduced with permission: Ethnology, Department of Anthropology at the University of Pittsburgh.
The upper part, called entla , is associated with ancestors; an appointed person will commune with the ancestors, and it serves a storage space for meat and beer if there is a ritual planned (McAllister 2004 ; Reeve 2011 ). The right side is the sitting area for men while the left is reserved women. Older people sit next to the door on either side, while the youngest generation often sits next to the upper part of the rondavel (McAllister 2004 ). At the centre is a hearth ( eziko ), where they make fire for cooking (McAllister, 2004 ; Brocious 2021 ). Kobo ( 2016 ) identifies the hearth as a pedagogical space for the girl child to learn food preparation. The way the amaXhosa people utilise the traditional family house can be purported as a gendered space.
A gendered space is “…more attractive for women than for men; men and women use the same space in different ways: some spaces give feelings of comfort and belonging to men, while women feel excluded; in some spaces, women have authority, while other spaces are under male authority” (Fortuijn et al. 2004 : 215). This is a gendered space because of how a spatial order of seating and gender roles in the utilisation of the space is enforced (McAllister 2004 ; Kobo 2016 ).
It should be noted that the number of rondavels in a homestead depends on the family’s needs. In addition to the family house, a rondavel may be reserved as a bedroom for younger family members and to accommodate visitors (Mlisa 2009 ). Moreover, a rondavel may be used by traditional healers for consultations and storing dispensary (umrawule) items. Certain people are often excluded from using such a space. Menstruating women are prohibited from accessing this space while on their cycle because of a belief that they will defile the herbs (Mlisa, 2009 ). The dispensary is only built once a rondavel has been revealed to a potential traditional healer in a dream, and a ritual is performed to officially open the rondavel and the dispensary prior to consultations being held (Mlisa, 2009 ).
Literature is ambiguous as to whether the recorded rondavel uses are performed in traditional or contemporary rondavels and whether the uses are adaptable to current rondavel designs (McAllister 2004 ; Mlisa 2009 ; Perry 2013 ; Kobo 2016 ; Brocious 2021 ). The available literature focuses on understanding traditional rondavel architecture, its utilisation, history and the changes in the design and structure (Schoenauer 2000 ; Steyn 2006 ). Vellinga ( 2006 ) also notes that publications on vernacular architecture are rarely featured and those that are available focus on drawings, forms and material. The impact of changing building designs and structures in traditional space utilisation is inadequately understood. It is against this backdrop that this study uses the concept of habitus to understand whether the changing design and structure of rondavels has influenced the traditional utilisation of rondavel spaces, based on a case study of the Mbhashe Local Municipality in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa.
Pierre Bourdieu, a French sociologist who was concerned with what motivates social action and behaviour (Navarro 2006 ), developed the concept of habitus, which refers to the norms, values, habits, dispositions and behaviour of a particular group. Each society has its own habitus. Habitus can then guide how a particular group feels, thinks, acts and uses the space (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). Habitus can be a product of past experiences and practices learned from parents, family experiences, and society (Hong and Zhao 2015 ). It is created and reproduced by the structures and practices of society (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). People with similar backgrounds (social class, religion, nationality, ethnicity, education and profession) usually share habitus which shapes how individuals perceive or receive the world. It is not fixed; it changes due to circumstances (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). However, when change occurs, some within the group may resist the change while others adapt to a new style of doing things. Often, others combine the traits of new and old habitus. Therefore, the theory seeks to provide an in-depth understanding of how people adapt in a changing world and circumstances resulting to change.
Bourdieu used this concept to study how the Algerian habitus changed during the liberation struggle in the 1950s (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). He analysed their norms, values, habits, dispositions and behaviour before and after colonisation. He defined Algerian peasantry as a traditional society which believed in:
the importance of group solidarity;
kinship based on patriarchal and patrilineal relationships;
patriarchal division of labour;
marriage as the primary concern of the family; and
an economy governed by pre-capitalist methods such as
subsistence farming,
products not sold but shared by the community
goods exchanged for social capital (i.e. a neighbour will lend you an ox in exchange for fresh produce).
The economy was governed by strict reciprocity and non-payment. The blacksmith was expected to provide each peasantry with all repairs in exchange for goods and services (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). Their habitus was passed from generation to generation. As determined by Bourdieu, habitus changes over time due to circumstances. The change in the Algerian habitus was a result of French colonial imposition which introduced a capitalist economy leading to a decline in agricultural activities and the establishment of factories in urban areas (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). Due to this increased urbanisation, people started working for wages, which resulted in the development of social classes (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). Subsequently, women were granted access to receiving an education and earning a living. Likewise, society was introduced to the concept of bachelorhood, with marriage being an individual choice. Communal living with neighbours sharing their fresh produce evolved into neighbours selling their produce for cash (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). Ultimately, the culture of group solidarity was destroyed, and the focus was on individualism.
Bourdieu argues that change can be adopted or resisted, as evidenced in Algeria (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). Certain Algerian norms, values, habits, dispositions and behaviours were influenced by innate traditions of peasantry and colonial imposition (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). Most older people resisted the change and continued to be trapped in the old way of life.
This study focuses on the traditional family house rondavel with the users’ social activities derived from the norms, values, habits, dispositions and behaviours of amaXhosa. Premised on the concept of habitus used by Bourdieu et al. ( 2000 ) and Navarro ( 2006 ) in the analysis of Algerian peasantry, this study unpacks the utilisation of the traditional family house rondavel before the introduction of contemporary architecture and design changes. Before the introduction of the contemporary architecture, the traditional family house rondavel was spatially divided based on gender and used for childbirth, communicating with ancestors and hosting rituals, serving and storing food and igniting a fire for warmth (McAllister 2004 ; Kobo 2016 ; Brocious 2021 ). This paper intends to understand whether the changing design and structure of rondavels has influenced its utilisation, using the case of Mbhashe Local Municipality.
Mbhashe local municipality
The Mbhashe Local Municipality extends over a geographic area of over 3200 km² and is situated within the Amathole District Municipality in the Eastern Cape Province, South Africa (Mbhashe Local Municipality IDP, 2016 ; 2023 a). The municipality is named after the Mbhashe River, which tracks between the municipality’s major urban regions of Willowvale (Gatyane), Xhorha and Dutywa, the latter being the administrative centre or municipal headquarters. The municipality has a total population of approximately 240 020 people (Municipalities of South Africa 2023 ), 94% of whom speak the isiXhosa language (Mbhashe Local Municipality IDP, 2016 ; 2023 b). It is a rural region facing various challenges, including poor road infrastructure, high unemployment and inadequate access to essential services such as water and electricity (Mbhashe Local Municipality IDP, 2016 ; 2023 a). It finds significant economic leverage from tourism nodes through coastal, inland and historic or heritage site attractions.
Rondavel structures are prominent in every homestead. Over 66% of households in the municipality are traditional dwellings Footnote 1 , followed by 21 and 5% of households living in brick or concrete block structures and flat blocks, respectively (Mbhashe Local Municipality IDP, 2021 ). However, some households have a modernised rondavel and, more commonly, an octagonal-shape veranda structure, sometimes with an attached garage. Others tend not to have a rondavel at all albeit infrequently. In rural areas, the process of domestic building is not influenced by planning schemes and policies (Oliver 2006 ). Instead, rural architecture is enriched by the surrounding natural environment, local economy and livelihood of villagers (Pirzad and Moghaddam 2023 ). This offers villagers free will to build the type and design of house they desire.
Figure 5 represents the spatial location and geographical extent of Mbhashe Local Municipality in the Amathole District Municipality, with reference to the Eastern Cape Province and South Africa, respectively. The points of interest indicated in the map are examples of homesteads and places across the municipality where:
contemporary rondavels at the Village Lodge in the Dutywa urban region,
rondavel clusters in the homestead of Nqadu great place (Komkhulu ) in rural Willowvale,
Emanzothweni , a multitype dwelling homestead in Bende location, rural Dutywa (Photo: Lilitha Breakfast), and
Kwa-Nonyameko, a multitype dwelling homestead in the Mbhangcolo administration area in rural Willowvale (Photo: Luyanda Ndude).
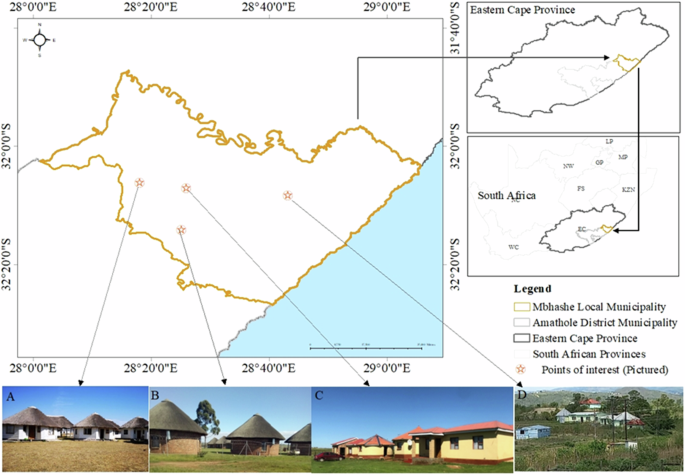
A map representing a study area—Mbhashe Local Municipality.
Methodology
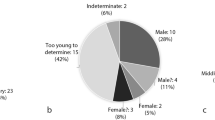
Ethical clearance was received from Rhodes University. Purposive sampling was used to select a sample population, which included participants of amaXhosa descent with a rondavel structure in their homesteads and residing within the Mbhashe Local Municipality. Ten participants, aged 24–48 years old, were interviewed; they are referred to as Participants 1 to 10 (P01–P10).
Data was collected using participatory mapping and semi-structured interviews consisting of open-ended questions. The interview schedule was developed with a purpose of obtaining an in-depth understanding of the utilisation of rondavels and changes that occurred over time because of the new architectural style. The interviews were conducted face-to-face at the participants’ residences. The participants were also given a rondavel diagram to illustrate the spatial ordering of how the rondavel family house was utilised in the Mbhashe Local Municipality. The results are presented in Fig. 6 .
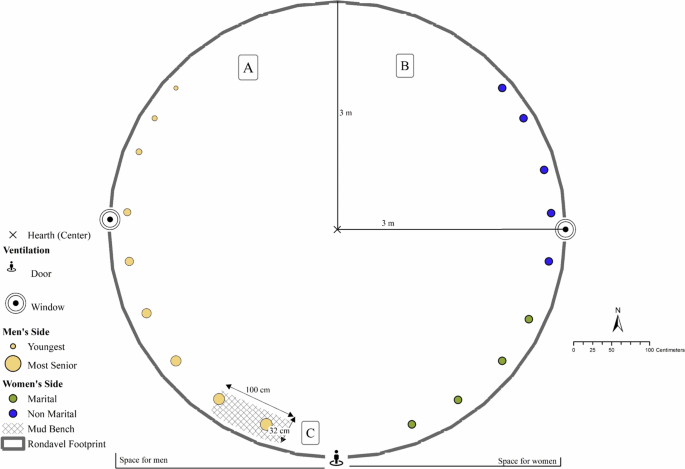
Spatial ordering of how the amaXhosa family house rondavel was utilized in the Mbhashe Municipality.
The information from the participants' drawings were then used to create Fig. 6 diagram, which was constructed using ArcMap 10.7.1 software for visualisation of the activities undertaken in the family house. The circle represents a typical rondavel floorplan with a diameter of 6 m (3 m radius). The diameter of the rondavel intersects the doorway and therefore dictates the gendered sides. The points in the diagram do not represent actual geometric values, instead they are ordinal representations of circular living in the AmaXhosa family house. Data was analysed and presented using thematic analysis. The concept of habitus guided the development of the themes presented. The first theme related to the amaXhosa habitus and the utilisation of traditional rondavels in the Mbhashe Local Municipality and the second was the amaXhosa habitus and the changing rondavel design in the Mbhashe Local Municipality
In both themes, specialised quotations to highlight some pertinent statements and demonstrate how the participants make sense of the rondavels and their utilisation, using their exact words.
amaXhosa habitus and the utilisation of traditional rondavel in the Mbhashe municipality
The section of findings only focus on the traditional family house rondavel before the introduction of the contemporary architecture. Adapted from McAllister ( 2004 ), the participants were given a circle to explain the use of each space and its purpose. They also revealed some uses that were not presented in earlier sections. First, the spatial division of the family house based on gender was discussed, followed by how the Mbhashe people utilised the family house. Figure 6 illustrates the spatial division between men (right) and women (left) inside the family house. Women married into the family ( makoti ) are forbidden to access the men’s side. The mud bench, known as soze , is built on the men’s side by the door for seating.
Women sit on the floor on handcrafted mats woven from reeds or grass known as ikhukho . Behind the door on the women’s side is a place for childbirth. The participants also alluded to the statement made by Kobo ( 2016 ) that during the birthing process, children and men are prohibited from using the space. They revealed that there was no cultural significance in giving birth at home. Instead, the inaccessibility of health facilities necessitated home births. Booysen ( 2003 ) argues that, in South African rural areas, women give birth at home because health facilities are located remotely to the homesteads and they do not have the means to access them.
Regarding funeral rites, the deceased’s coffin will arrive at the homestead the day before the funeral and a night vigil – a ceremony to honour the deceased—will be held in the family house. The coffin is usually placed on the women’s side and senior women will gather to sleep next to the coffin until the funeral. An elderly family member will burn impepho (incense) and request the ancestors to welcome the deceased. It is believed that if this ritual is not performed, the deceased will not rest in peace.
In households that use the family house for sleeping, designated spaces will be allocated for men and women. A handcrafted mat is used as a base for the foam mattress on both sides. The seating arrangement in the family house is based on seniority, with younger members of the household placed toward the upper layer, as noted by McAllister ( 2004 ). The participants further explained that seniority was not based on age: married women were regarded as senior and women who were not related by blood or matrimony would occupy the upper end of the women’s side. Men’s seating arrangements depend on when one was initiated, with the youngest (the last to go to the bush) towards the upper layer.
McAllister ( 2004 ) and Reeve ( 2011 ) reveal that an appointed person will commune with the ancestors, and store meat and beer in the upper part of the rondavel if there is a ritual. Their findings concur with how the Mbhashe people utilise the space, further indicating that the upper layer is divided into A and B, as shown in Fig. 6 . On the right (men’s side) is where slaughtered meat and beer is stored. It is the responsibility of the men to serve both the meat and beer; hence, it is located on their side. Section B in Fig. 6 is a space in the uppermost end of the rondavel on the women’s side. It contains domestic essentials such as a table and cupboard, crockery, and cutlery and ilitye lokuguba , which is a flat rock which is used to grind food.
In the centre of the family house is a hearth. Kobo ( 2016 ) argues that this is where women are taught to prepare food. The findings of this study also reveal that men also use the space to roast corn. So, there are no gender-based restrictions on the use of this space. The centre also has a pole called intsika , which supports the roof structure. The door is positioned in the lower part of the family house. Section C, illustrated in Fig. 6 , is where the spear ( umkhonto) is kept by sticking it on the roof above the doorway on the men’s side. The spear is used for the slaughter of traditional animals if there is a ritual or ceremony. The spear is believed to obstruct lightning during a storm and is placed in the doorway.
The participants also utilised the rondavel for interacting with each other and the ancestors. Interaction takes place through song and dance during ceremonies. People also interact through spoken word to communicate with or appease ancestors, to socialize with each other by telling stories of love, horror, fiction, and the past, and to play games. The study’s participants expressed clearly how the family house is used which they learned from growing up in rural areas and passed from generation to generation. They have the duty to continue passing this information to the younger members of the family.
amaXhosa habitus and the changing rondavel design in the Mbhashe local municipality
People in the rural areas of the Mbhashe Local Municipality were inclined to architectural change and desire contemporary architecture and luxury, including those who did not currently own it. The contemporary rondavel design was considered progressive, cognisant of the times and, for that matter, the contemporary way of life to which there was a strong inclination to conform: “I too [wish to have a modern house] because these are the houses that are built nowadays, and they make the home beautiful” (P 01).
Notwithstanding, there was a strong consensus to preserve conventional ways of using space and adapt to the contemporary design, including the structure and shape (multi-room), the material used (no longer a thatched roof or mud walls), or hard surfaces (tiles/concrete). The respondents preferred contemporary structures because of their aesthetic and convenience: “…contemporary houses have better aesthetical value, spacious and are functional (e.g., energy consumption, natural lighting)” ( P 09).
Other uses were not adopted in the contemporary house design such as utilising the family house for childbirth because modern women mostly give birth in hospitals and clinics. Statistics South Africa ( 2020 ) revealed that the number of home deliveries has decreased from 14% in 1998 to 4% in 2016 while health facility deliveries have increased from 83.4% in 1998 to 96.7% in 2016 (Statistics South Africa 2020 ). Both 1998 and 2016 home deliveries statistics are indicative of the national level (Statistics South Africa 2020 ).
Placing the deceased’s coffin in the upper part of the family house (section B in Fig. 6 ) was adopted in contemporary rondavel utilisation until the Covid-19 pandemic when people became sceptical of disease transmission. Before the pandemic, the deceased’s body would arrive at home a day before burial, and people would gather for a final ceremony the night before the funeral (night vigil) inside the family house to honour the deceased (Bambalele 2020 ). A South African Covid-19 restriction prohibited corpses being sent home prior to the funeral and the hosting of night vigils (Bambalele 2020 ). This practice has continued since Covid-19 restrictions were relaxed, while others have stopped. However, once the deceased’s coffin arrives on the funeral day, it is taken to the upper part of the family house and a ritual will still be performed where incense is burnt and a request is made to the ancestors to welcome the deceased. Therefore, the cultural significance of the whole process does not rest with the placement of the deceased’s body a day before the funeral but the performance of the ritual.
The presence of mud benches on the men’s side no longer exists. Although the traditional rondavel structure is diminishing in the physical environment, modernisation has certainly swayed people’s sense of feeling, thinking, acting and their use of space. Admittedly, modernisation has not entirely appropriated the Xhosa people’s habitus. Some people were uninterested in adapting to some elements of the contemporary rondavel and house design: “A traditional rondavel must be present in a home. You can make fire, but it is difficult to do that on floor tiles. Still, you perform customs in traditional rondavel” (P 03).
These people continue to use traditional rondavels for the above purposes while also adapting the contemporary rondavel or house design for other uses such as sleeping, unless there is a ceremony when there is no space: “ People do not want to sleep on the floor in the rondavel, and there is no privacy and tile, or cemented floor is cold” (P 04).
While other participants preferred to continue performing traditional ceremonies and communicating with ancestors in the traditional rondavel structure, there were respondents who were open to communicating with ancestors and interacting with the living, and divide space based on gender in the contemporary rondavel – as indicated in Fig. 6 . The cultural strongholds continued to be practiced regardless of the house structure. Therefore, in the absence of a traditional rondavel structure in a homestead, any other house design such as butterfly or flat-roof corner houses can be used for traditional ceremonies: “any house structure can be used as a rondavel; it does not change the culture. It is the same” (P01).
Regarding food preparation, serving and storage, some people used the contemporary rondavel with slight changes for cooking. For example, food is prepared in the family house’s upper part (B section in Fig. 6 ) using a gas or electric stove instead of a hearth at the centre. Others will prepare food and store it in the kitchen of the main house, but people will be served in the contemporary rondavel.
This paper used the concept of habitus to understand whether the changing design and structure of rondavels has influenced its utilisation. Habitus refers to the norms, values, habits, dispositions and behaviours of a particular group, which can then guide how they feel, think, act, and use the space. Habitus can be a product of past experiences and practices learned from parents, family experiences, and society (Hong and Zhao 2015 ). It is created and reproduced by structures and practices of society; it is not fixed and changes over time due to particular circumstances (Bourdieu et al. 2000 ; Navarro 2006 ). The study discussed the amaXhosa people’s habitus on the utilisation of the traditional family house rondavel and how it has been influenced by the introduction of contemporary architectural designs. It is noted that architectural change brought by society does not change cultural norms, values, habits, dispositions and behaviours attached to rondavels but results in finding ways to accommodate and preserve its utilisation in new architectural developments and selectively choosing ideas to be transmitted to the contemporary house design. The cultural norms, values, habits, dispositions, and behaviours attached to rondavels have also been influenced by advancements in health and medical innovation, as well as Covid-19.
The findings revealed the habitus of the amaXhosa people at the Mbhashe Local Municipality. The utilisation of the traditional family house rondavel includes childbirth, placement of the deceased’s coffin, sleeping, seating, food preparation, serving and storage, keeping the spear, hosting ceremonies, communicating with ancestors, and interacting with the living. The amaXhosa habitus is acquired by growing up in the Xhosa society, being taught by parents, and observing how things are done, which has been passed down from generation to generation. The influence of contemporary architecture brought changes in the construction of rondavel.
Home births are no longer practised because of advancements in health and medicine. The placement of the deceased’s coffin in the upper part of the rondavel a day prior to the funeral has been adopted in the use of a contemporary rondavel; however, it is no longer prevalent because of the Covid-19 restrictions. However, on the day of the funeral, the deceased’s coffin is placed in the upper part of the rondavel for a shorter period and a ritual burning incense and asking the ancestors to welcome the deceased is performed because it is a critical cultural practice.
People also do not opt to sleep on the floor unless there is a ceremony. The preparation of food, its serving and storage differs in that there is no hearth in the new contemporary house; so food is prepared in the main house or the upper part of the rondavel. The gendered division of space, hosting ceremonies, communicating and interacting with ancestors has been adopted in contemporary houses too. However, some still prefer to host ceremonies and communicate with the ancestors in traditional rondavels instead.
People have not resisted new architectural designs or changing cultural norms, values, habits, dispositions and behaviours but have found ways to adapt. Certain old dispositions are adaptable to contemporary structures. Also, a study conducted by Moremoholo ( 2021 ) reveals that some indigenous values such as practising ancestral ceremonies can be incorporated or retained in modern house structure. However, some people are not interested in adapting elements to the contemporary rondavel. They would rather have two structures – the current rondavel design and a traditional rondavel to be utilised for uses that cannot be adapted to the contemporary rondavel. The presence of traditional rondavel in modern times is also witnessed even in Nigeria (Onyejegbu et al. 2023 ).
Some cultural norms, values, old habits, dispositions, and behaviours of utilising traditional rondavels were not adapted to the contemporary rondavel because of health and medical innovations such as childbirth and placing the deceased’s coffin in the rondavel. Clearly, some amaXhosa cultural practices are modified but not completely forgotten.
Future studies can focus on profiling architectural designs found in the Mbhashe Local Municipality and investigate their origins and influencing factors. Others could also focus on rondavels utilised by traditional healers to understand how they have been impacted by architectural changes to space utilisation. It will be also interesting to understand why people still opt for traditional rondavels despite the existence of beautiful modern buildings.
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article and additional information is available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
A traditional dwelling has walls made of less durable material, such as dried clay, sun-dried bricks, bamboo or latticework, with the roof made of reeds, palm fronds or straw (World bank, 2018).
Aikpehae AM, Isiwele AJ, Adamolekun MO (2016) Globalisation, urbanisation and modernisation influence on housing and building architecture in Nigeria. Int J Serv Sci, Manag Eng 3(2):6–13
Google Scholar
Bambalele P (2020) Lockdown has Offended African Burial Rites. [Online]. Accessed on 13 November 2023 from https://www.sowetanlive.co.za/news/south-africa/2020-05-19-lockdown-has-offended-african-burial-rites/
Bianco CD (2022) Imagining New Forms of Urban Development through the Enhancement of the Local Culture of Living: The Pemba Case Study in Mozambique. In Vawda, S and Denison, E (eds). Modern Heritage of Africa conference proceedings, 22 – 24 September 2021, University of Cape Town. [retrieved 16 May 2024]. https://www.ucl.ac.uk/bartlett/architecture/sites/bartlett_architecture/files/mohoa_2021_final_proceedings.pdf
Bourdieu P, Nice R, Wacquant L (2000) Making the economic habitus: Algerian workers revisited. Ethnography 1(1):17–41
Article Google Scholar
Booysen F (2003) Urban–rural inequalities in health care delivery in South Africa. Dev South Afr 20(5):659–673
Brocious JM (2021) Lesotho and the sani pass: A 4-wheel-drive adventure to the Kingdom in the Sky. [Online]. Accessed 17 July 2023 from https://rtwin30days.com/lesotho-sani-pass/
Fortuijn JD, Horn A, Ostendorf W (2004) Gendered spaces in urban and rural contexts: An introduction. GeoJournal 61(3):215–217
Frescura F (2015) A case of hopeless failure: The role of missionaries in the transition of Southern Africa’s indigenous architecture. J Study Relig 22:64–68
Frescura F (1981) Rural Shelter in Southern Africa. Raven Press, Johannesburg
Guerrieri PM (2020) Migration, translation, and transformation of western urban planning models. City, Territory Architecture 7(1):1–9
Article MathSciNet Google Scholar
Hong Y, Zhao Y (2015) From capital to habitus: Class differentiation of family educational patterns in Urban China. J Chin Sociol 2(18):1–18
Kobo F (2016) Umfazi akangeni ebuhlanti emzini . A Womanist Dialogue with Black Theology of Liberation in the 21st Century. HTS Teologiese Stud/Theological Stud 72(1):1–6
Mbhashe Local Municipality (2023a) Mbhashe Local Municipality Integrated Development Plan (IDP) 2023-2024. [Online]. Accessed 6 July 2023 from https://www.mbhashemun.gov.za/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Final-Reviewed-2023-24-IDP-Adopted-31-May-2023.pdf
Mbhashe Local Municipality (2023b) Mbhashe Local Municipality Integrated Development Plan (IDP) 2020-2021. [Online]. Accessed 6 July 2023 from https://www.cogta.gov.za/cgta_2016/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/MBHASHE-LOCAL-M-2020-2021.pdf
Mbhashe Local Municipality (2016) Mbhashe Local Municipality Integrated Development Plan (IDP) 2020–2021. [Online]. Accessed 28 August 2024 from https://www.ecsecc.org/documentrepository/informationcentre/2015-2016-idp-final-10-06-15_00518.pdf
Mbhashe Local Municipality (2021) Mbhashe Local Municipality Integrated Development Plan (IDP) 2020–2021. [Online]. Accessed 28 August 2024 from https://www.cogta.gov.za/cgta_2016/wp-content/uploads/2021/02/MBHASHE-LOCAL-M-2020-2021.pdf
McAllister PXR (2004) Domestic space, habitus. Ethnology 43(2):117–135
Mlisa LRN (2009) Ukuthwasa Initiation of Amagqirha: Identity Construction and the Training of Xhosa Women as Traditional Healers (Doctoral dissertation, University of the Free State)
Mokhoathi J (2021) Christianity in Transformation: The Rise of African Christianity among the AmaXhosa of the Eastern Cape. Acta Theologica 41(32):149–164
Moremoholo M (2021) Retaining Indigenous Values of Built Heritage: A Case of Makgabeng, Limpopo Province, South Africa. Doctoral Dissertation, Faculty of Science, University of the Witwatersrand, Johannesburg, South Africa
Municipalities of South Africa (2023) Mbhashe Local Municipality (EC121). [Online]. Accesses 17 November 2023 from https://municipalities.co.za/demographic/1006/mbhashe-local-municipality
Naude M (2010) Circular structures and buildings associated with vernacular farm architecture and folk engineering. SAJAH 25(2):1–28
Navarro Z (2006) In search of a cultural interpretation of power: The Contribution of Pierre Bourdieu. IDS Bull 37(6):11–21
Nyamende, A. (1994). Regional variation in Xhosa. Stellenbosch Papers in Linguistics Plus, 26, 202–217
Oliver P (2006) Built to Meet Needs: Cultural Issues in Vernacular Architecture. Architectural Press, Jordan Hill, Oxford
Onyejegbu MN, Okonkwo UU, David-Ojukwu I (2023) Traditional architectural mud huts in Africa: Forms, aesthetics, history and preservation in South-Eastern Nigeria. Cogent Arts Humanities 10(1):2188781
OpenHeritage (2016) Vernacular Architecture of the Eastern Cape. Accessed 16 May 2024 from https://www.openheritage.org.za/sites/default/files/docs/attacheddocs/2016/12/07/VernacularArchitecture_EasternCape_Doc_FINAL4.pdf
Perry AF (2013) Ethnographic insights on rural sustainability: homestead design and permaculture of eastern cape Settlements in South Africa. Africanus 43(1):115–125
Pirzad A, Moghaddam SR (2023) A survey for relationship between ecological rural architecture and rural economic (in moderate-humid regions and hot-dry areas). Hist Persian Art Islamic Period 1(1):189–214
Reeve ZRLP (2011) Staged Authenticities an Exploration of the Representations of AmaXhosa Culture within the Main Programme of the National Arts Festival, 2009. Master of Arts, Rhodes University
Schoenauer N (2000) 6 000 Years of Housing (revised and expanded edition). New York: Norton
Smith ET (2022) Rondavels: From Mamelodi to the Presidential Library and Archives. South Afr J Cultural Hist 36(1):111–132. https://doi.org/10.54272/sach.2022.v36n1a6
Statistics South Africa (2020) Maternal Health Care in SA Shows Signs of Improvement. [Online]. Accessed on 13 November 2023 from
Steyn G (2006) The Indigenous Rondavel – A Case for Conservation. South Afr J Art Hist 1(1):21–38
Tapiero JCA, Graus S, Khei S, Silva D, Conde O, Ferreira TM, Ortega J, Luso E, Rodrigues H, Vasconcelos G (2024) An ICT-enhanced methodology for the characterization of vernacular built heritage at the regional scale. Int J Architectural Heritage, 1–20. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583058.2024.2320862
Van Vuuren CJ (2017) The heritage of the cone-on-cylinder dwelling of the Ndebele of South Africa. South Afr J Art Hist 31(1):120–136
Vellinga M (2006) Engaging the Future: Vernacular architecture studies in the twenty-first century. In Asquith and Vellinga (eds.), Vernacular Architecture in the Twenty-first Century: Theory, Education and Practice . Oxon: Taylor & Francis
Walton J (1949) South African peasant architecture: Nguni Folk building. Afr Stud 8(2):70–79. https://doi.org/10.1080/00020184908706785
World Bank (2018) Modern/traditional dwelling definitions. [Online]. Accessed on 13 November 2023 from http://pubdocs.worldbank.org/en/118361539796472136/pdf/ICP-TF-HOU03-PT-S06-Housing-Dwelling-Definitions.pdf
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Rhodes University, Makhanda, South Africa
Africa Ndude & Sinenhlanhla Memela
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
The authors contributed equally to the writing of this paper.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Sinenhlanhla Memela .
Ethics declarations
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval
The research involves human participants, so Rhodes University has given ethical clearance to this research project. You can request to see the clearance certificate by contacting the Ethics Coordinator ([email protected]). All procedures performed involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Rhodes University Ethical Standards Committee, reference number 2023-7347-7994.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individuals who participated in the study. Participants had to sign an informed consent declaration form, which provided information about the nature and purpose of the study, the benefits and risks, and how data is collected, managed, analysed, presented, and stored. The study uses the concept of habitus to understand whether the changing design of traditional rondavels has influenced their utilisation, based on a case study of the Mbhashe Local Municipality in the Eastern Cape province, South Africa. Participating in this research project contributes to the sustainability and preservation of memory. Participants answered questions from the interview schedule. Participation was entirely voluntary, and they were made aware that they could withdraw at any stage without any negative consequences and would not be compensated for participating. Participants were also notified that some use of space might trigger bad experiences and be sensitive or hurtful; should they feel triggered, they can withdraw or not talk about such experiences. Confidentiality and anonymity of records were maintained when presenting the results. The data collected is stored securely, and only used for publication of this journal, if any data collected is to be used by the Researcher for any further study, the participants will be informed in writing. Participants have a right to receive feedback about this research unless they elect not to receive this feedback.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Transcribed data, rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License, which permits any non-commercial use, sharing, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if you modified the licensed material. You do not have permission under this licence to share adapted material derived from this article or parts of it. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Ndude, A., Memela, S. Utilisation of rondavel space by amaXhosa people: a case of Mbhashe local municipality, Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. Humanit Soc Sci Commun 11 , 1122 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03649-3
Download citation
Received : 13 February 2024
Accepted : 21 August 2024
Published : 01 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-024-03649-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
IEEE Account
- Change Username/Password
- Update Address
Purchase Details
- Payment Options
- Order History
- View Purchased Documents
Profile Information
- Communications Preferences
- Profession and Education
- Technical Interests
- US & Canada: +1 800 678 4333
- Worldwide: +1 732 981 0060
- Contact & Support
- About IEEE Xplore
- Accessibility
- Terms of Use
- Nondiscrimination Policy
- Privacy & Opting Out of Cookies
A not-for-profit organization, IEEE is the world's largest technical professional organization dedicated to advancing technology for the benefit of humanity. © Copyright 2024 IEEE - All rights reserved. Use of this web site signifies your agreement to the terms and conditions.

- Search term Advanced Search Citation Search
- Individual login
- Institutional login
- IFT Members, log in to access Journal of Food Science
- IFT Members, log in to access Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety

Blockchain implementation for food safety in supply chain: A review
Corresponding Author
V. Sri Vigna Hema
- [email protected]
School of Engineering, University of Guelph, Guelph, Ontario, Canada
Correspondence
Sri Vigna Hema V, School of Engineering, University of Guelph, 2401, Thornbrough Building, 50 Stone Road East, Guelph, ON, Canada N1G 2W1.
Email: [email protected]
Annamalai Manickavasagan, School of Engineering, University of Guelph, 2401, Thornbrough Building, 50 Stone Road East, Guelph, ON, Canada N1G 2W1.
Contribution: Conceptualization, Investigation, Writing - original draft, Methodology, Validation, Writing - review & editing, Data curation, Formal analysis
Annamalai Manickavasagan
- orcid.org/0000-0003-2562-9772
Contribution: Conceptualization, Funding acquisition, Writing - review & editing, Supervision
Food safety has emerged as the topmost priority in the current fast-paced food industry era. According to the World Health Organization, around 600 million people, approximately 1 in 10 individuals worldwide, experience illness due to contaminated food consumption, resulting in nearly 0.42 million fatalities annually. The recent development in software and hardware sectors has created opportunities to improve the safety concerns in the food supply chain. The objective of this review is to explain the fundamentals of blockchain and its integration into the supply chain of various food commodities to enhance food safety. This paper presents the analysis of 31 conceptual works, 10 implementation works, 39 case studies, and other investigations in blockchain-based food supply chain from a total of 80 published papers. In this paper, the significance of adapting conceptual ideas into practical applications for effectively tracing food commodities throughout the supply chain has been discussed. This paper also describes the transformative role of blockchain platforms in the food industry, providing a decentralized and transparent ledger to access real-time and immutable records of a product's journey. In addition, both the positive impacts and challenges associated with implementing blockchain technology in the food supply chain have been evaluated. In summary, the blockchain-based food supply chains offer greater transparency, traceability, and trust, ultimately resulting in higher standards of food safety and quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, consumers are eager to know not only about the ingredients and food processing methods but also about the origin, nutritional content, and broader environmental and social implications of the food products they consume (Tandon et al., 2020).
Moreover, the global food supply chain has become increasingly interconnected. This transformation has had a significant impact on food production and consumption worldwide in recent decades. Consumers now recognize food products that originate from different regions of the world. For example, when you order a Caramel Macchiato, have you ever stopped to consider where the primary ingredients come from? The espresso beans may be sourced from South America, the milk from local dairy farms, the vanilla syrup from Madagascar, and the caramel sauce from a specialty producer. These ingredients come together from various regions, each contributing its own unique flavor, resulting in the creamy and indulgent taste of your favorite coffee shop's Caramel Macchiato. This serves as a small glimpse into the current landscape of the food industry.
Due to the globalization of the food industry, the number of actors increases with extended transportation of perishable goods, and heightened variability in information across food supply chains. This has led to a more complex food system, making it harder to address problems within food supply chains. The intricacy of food supply chains results in challenges, including food safety issues, food waste, food loss, and cost issues at each stage. Recently, the United Nations Environment Programme ( 2024 ) reported that approximately 13% of food is lost during production and transportation before reaching consumers, whereas inefficiencies at the manufacturing and retail levels result in about 30% of food in grocery stores being discarded. Owing to this, unethical practices and transparency issues have created serious problems, such as food recalls and food fraud. Moreover, food recalls have led to substantial costs in the supply chain and damaged trust in consumers. Therefore, trust issues among consumers may be worsened by the absence of transparency, that is, to track food products as well as to understand environmental impact in the food supply chain, thus featuring the vital need for innovative solutions (Duan et al., 2020 ).
Blockchain technology has emerged as a transformative force in the food supply chain and acts as a promising solution to overcome food safety issues by enabling real-time tracking of food products from farm to table (Patel et al., 2023). In the food supply chain, blockchain operates without a central authority by distributing information across multiple computers (nodes), wherein, each transaction is added to a “block,” which links to the previous one, forming a “chain” (as in Figure 1 ). This decentralized approach ensures no single entity controls or manipulates the data, promoting transparency and trust among participants (Thangamayan et al., 2023 ).

In a food supply chain network, operations typically follow a three-layer architecture (as in Figure 2 ), wherein the “data layer” serves as the foundation for information exchange among various stakeholders, such as farmers, processors, distributors, retailers, and customers, enabling them to read and write data. The “blockchain layer” acts as the core, incorporating essential components like trading and delivery event records, smart contracts for automating processes, a reputation system for evaluating participant trustworthiness, and a traceability chain to maintain transparency with an immutable record of events and transactions. This layer enhances transparency through decentralized storage using the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), provides security by making transactions tamper-proof, fosters trust with immutable records, reduces fraud by verifying product authenticity, and increases efficiency by streamlining processes. Finally, the “storage layer” at the top, represented by a network of nodes in IPFS, ensures secure and decentralized data storage. It maintains accessibility even if individual nodes go offline, thus complementing the blockchain layer with a reliable storage solution, without needing a centralized manager (Gad et al., 2022 ).

- How can blockchain features address existing issues in food supply chains?
- In what ways can blockchain enhance the traceability and management of commodity groups within the food supply chain?
- Which active blockchain platforms are most effective in the food industry?
- What are the primary advantages and challenges to adopting blockchain technology in food supply chains, and how can they be overcome?
Therefore, the objective of this review was to investigate the blockchain parameters and blockchain platforms for each food commodity type based on papers that were published as concept-based, implementation-based, or case studies.
The rest of the paper is systematized as follows: Section 2 investigates several studies with the application of blockchain technology in various commodity groups in food supply chains, particularly focusing on enhancing food safety. Section 3 describes the transformative role of blockchain platforms in the food industry. In Section 4 , both positive impacts and challenges while implementing blockchain in the food supply chains are discussed. Finally, Section 5 concludes with a conclusion and further research directions.
2 REVIEW ON BLOCKCHAIN-BASED FOOD SUPPLY CHAINS
Several researchers have used blockchain and other cutting-edge technologies, such as the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, artificial intelligence (AI), data science, and machine learning, to enhance the safety and traceability in the food supply chain. Figure 3 depicts the steps involved in the review process.

2.1 Conceptual works
Conceptual work refers to theoretical or abstract intellectual endeavors that involve the development, analysis, or exploration of ideas, concepts, or theories. It often involves synthesizing existing knowledge, proposing new frameworks or models, and discussing hypothetical scenarios or possibilities. Table 1 represents the summary of blockchain-based conceptual works in food supply chains.
| S. no | Tech used | Country | Commodity | Focus | Blockchain parameters | Pros | Cons | Findings | References | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | DC | DS | DT | SC | Tc | Tr | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |||||||
| 1 | BC and IoT | China | Fruits | Fruit quality monitoring | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y. Zhang et al. ( ) | |
| 2 | BC and IoT | Malaysia | Fruits | Data storage | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Miraz et al. ( ) | |
| 3 | BC | China | Herbs | Data fraudulence | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Yik et al. ( ) | |
| 4 | BC | China | Herbs | Data storage and safety | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Liu et al. ( ) | |
| 5 | BC | Nepal | Herbs | Trade trust and security | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Thapa et al. ( ) | |
| 6 | BC | China | Rice | Planting records | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Q. Tao, Iftekhar et al. ( ) | |
| 7 | BC | Pakistan | Rice | Pest information | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Peng et al. ( ) | |
| 8 | BC and IoT | India | Wheat | Food waste (wheat) | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Rathore et al. ( ) | |
| 9 | BC | Pakistan | Wheat | Wheat price control | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Rafiq et al. ( ) | |
| 10 | BC and IoT | India | Dairy—milk, cheese, and butter | Adulteration | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Khanna et al. ( ) | |
| 11 | BC, IoT, and I4.0 | Greece | Dairy—milk, yogurt, and cheese | Quality control | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Casino et al. ( ) | |
| 12 | BC | Italy | Dairy—cheese | Cheese immutability | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Varavallo et al. ( ) | |
| 13 | BC | Switzerland | Dairy—milk | Milk price and quality | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Niya et al. ( ) | |
| 14 | BC | The United States | Dairy—milk | Milk process | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Kasten ( ) | |
| 15 | BC and IoT | Vietnam | Dairy—milk | Milk adulteration and fraud | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Tan and Ngan ( ) | |
| 16 | BC | Turkey | Dairy—milk | Societal impact | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Mangla et al. ( ) | |
| 17 | BC and IoT | The USA | Dairy | Ecosystem | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Fang and Stone ( ) | |
| 18 | BC and IoT | Italy | Bakery—bread | Hygiene control | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Cocco et al. ( ) | |
| 19 | BC and IoT | India | Beverage—water | Anomaly detection | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Maouriyan and Krishna ( ) | |
| 20 | BC | Pakistan | Beverage—soft drinks | Traceability | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Bilal and Kamran ( ) | |
| 21 | BC | China | Chicken | Data sharing | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y. Feng et al. ( ) | |
| 22 | BC | Indonesia | Chicken | Slaughter | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Akbar et al. ( )BC | |
| 23 | BC and IoT | Hungary | Beef | Visibility | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Rejeb ( ) | |
| 24 | BC and IoT | India | Fish | App-based livelihood | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Sengupta et al. ( ) | |
| 25 | BC | Indonesia | Fish | Rotten fish tracking | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Larissa and Parung ( ) | |
| 26 | BC | Portugal | Fish | Value chain | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Cruz and da Cruz ( ) | |
| 27 | BC | Indonesia | Beef | Business process flow | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Meidayanti et al. ( ) | |
| 28 | BC | Australia | Beef | Prototype testing | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Cao et al. ( ) | |
| 29 | BC | The USA | Beef cattle | Anonymity | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Ferdousi et al. ( ) | |
| 30 | BC | Australia | Beef | Dependability level | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | Natanelov et al. ( ) | |
| 31 | BC | Indonesia | Beef | Halal certification | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Hidayati et al. ( ) | |
- Abbreviations: Au, authenticity; BC, blockchain; BD, big data; C1, technical complexity; C2, governance issue; C3, lack in regulations; C4, cost issue; C5, alertness and learning; DC, decentralization; Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT), distributed ledger technology; DS, data security; DT, digitalized transaction; I4.0, Industry 4.0; ICT, information and communication technology; IoT, Internet of Things; N, no; P1, food safety; P2, food quality; P3, decrease in transaction time; P4, decrease in transaction cost; P5, revenue improvement; P6, performance enhancement; P7, sustainability upgrade; SC, smart contract; Tc, traceability; Tr, transparency; Y, yes.
2.1.1 Fresh produces
Zang et al. presented a blockchain technology–based fresh fruit supply chain system that collects reliable data from picking to consumption via IoT technologies. The encrypted and verified data are shared on a P2P network, balancing supply-demand tensions, bringing financial benefits, and simplifying supervision. Despite its advantages, challenges include architectural integration difficulties, dependence on IoT, undeveloped fruit preservation methodology, legal uncertainties, limited reference cases, and practical vulnerabilities (Y. Zhang et al., 2022 ). Miraz et al. ( 2023 ) developed an end-to-end fruit traceability system, which improves trust among customers as well as suppliers. Yik et al. ( 2021 ) established HerBChain from the open-source blockchain and prioritized information records without asset transactions. Hosted on at least three cloud servers, it ensures quick data access and scalability. Utilizing cryptographic algorithms and a decentralized network, HerBChain ensures data integrity, security, and privacy as it requires a specific mobile app for decoding QR codes to access stored information. Liu et al. ( 2021 ) considered a traceability system for herbal medicine to involve a double-chain structure. The system utilizes the efficiency of a private blockchain and the consortium blockchain extensibility. Information from each process is stored in the IPFS with hash values recorded in the private blockchain. To enhance safety and reliability, the hash value of the final sales stage is linked to the consortium blockchain for transaction and tamper-proof verification. Thapa et al. ( 2021 ) introduced a groundbreaking solution for the intermittent challenges in the Nepal–India ginger supply chain. Although the focus is on ginger, the concept's versatility extends to improving any agricultural supply chain, ensuring comprehensive tracking from origin to final products. By storing transactions in a tamper-proof manner, blockchain technology addresses trust deficits between nations, presenting a theoretical framework applicable to various trade scenarios.
2.1.2 Grains and cereals
Tao, Iftekhar et al. ( 2021 ) proposed a blockchain-based rice traceability scheme, enhancing transparency and providing real quality information to both enterprises and consumers for safe and healthy food purchasing. Peng et al. ( 2022a ) presented a dynamic supervision model that is anticipated for rice supply chains to ensure data integrity, interconnectivity, and dynamic monitoring throughout the supply chain by presenting a practical solution to enhance food industry digitization, crop supervision, and overall food security. Rathore et al. evaluated the blockchain adoption in the wheat supply chain in India and highlighted its potential benefits such as increased transparency and traceability. Despite the promising impact on supply chain flows and reduced food waste, challenges remain, including cost considerations and the evolving nature of blockchain technology. The practical application of blockchain-enabled supply chains provides concrete insights, indicating moderate feasibility and a growing interest among food end-users, albeit with ongoing financial and deployment complexities (Rathore et al., 2022). Rafiq et al. aimed to develop a web-based application to empower farmers by ensuring fair payment and transparency in transactions. By providing a platform for direct selling at market prices, the application addresses issues of exploitation by intermediaries and promotes accountability in the supply chain. The successful realization of the project's objectives underscores its commitment to supporting farmers and nurturing equitable compensation for their efforts (Rafiq et al., 2021 ).
2.1.3 Beverages, dairy, and bakery products
Khanna et al. ( 2022 ) addressed the existing problems in Indian dairy commerce and developed a solution by utilizing blockchain and machine learning to minimize wastage by preventing overproduction. A blockchain-based framework is presented by Casino et al. ( 2021 ) for food supply chain traceability by utilizing smart contracts for automation and delegating a real-world dairy firm case scenario with implementation details on a local private blockchain. Varavallo et al. proposed an Algorand blockchain–based traceability platform for the supply chain. With a green blockchain approach for sustainability and cost-effectiveness, the platform minimizes transaction costs by batching data collection and transmission (Varavallo et al., 2022 ). The NUTRIA project by Niya et al. ( 2021 ) employed blockchain technology in the Swiss dairy supply chain, in which the decentralized application is designed to automate data collection with increased consumer trust through immutable information availability.
Kasten ( 2019 ) outlined a blockchain-based system that guarantees the integrity of dairy product testing data, provides immutable confirmation for regulators, enhances inspection efficiency, is potentially applicable to milk-producing countries and other agricultural industries, and offers heightened food chain visibility at minimal cost to stakeholders. Tan and Ngan ( 2020 ) developed a traceability solution using blockchain for addressing food fraud and safety issues in the Vietnamese dairy industry, recognizing challenges of adulteration, contamination, and counterfeiting with potential benefits for supply chain actors in terms of operational effectiveness, cost, time, and human resources. Mangla et al. ( 2021 ) aimed to map milk supply chains for enhanced traceability and assessed societal impacts by gathering data from a Turkish agricultural cooperative and evaluating the effects of blockchain on farmers, communities, and animals, considering various parameters for meeting sustainable development goals. Fang and Stone ( 2021 ) introduced a novel blockchain-based dairy logistic supply network to ensure the products with reasonable costs. Cocco et al. ( 2021 ) designed the decentralized application by integrating radio-frequency identification (RFID) and near field communication devices with blockchain in the bread supply chain. Maouriyan and Krishna ( 2019 ) proposed an aquachain that incorporates IoT and DLTs for water traceability with the high reliability of Ethereum.
2.1.4 Meat, poultry, and sea food
Y. Feng et al. ( 2022 ) proposed a consortium blockchain–based system for secure tracking management and trustworthy packing and distribution of trace data for chicken products. Akbar et al. ( 2022 ) designed a framework for a chicken-slaughtering factory in Indonesia, which was tested with 46 cases, demonstrating its effectiveness in tracing halal food supply chains and offering faster transparent processing compared to paper-based systems. Rejeb ( 2018 ) introduced a decentralized traceability system combining blockchain and IoT technologies to address the issues faced by the meat supply chain and enhance safety using RFID and sensors to promote visibility. Sengupta et al. employed disruptive technology, including satellite imagery and blockchain, to address challenges in food supply chains in developing markets. Further, a framework is proposed for supply chain resilience amidst global pandemics and unorganized sectors, emphasizing the significance of positive deviance in overcoming contextual bottlenecks (Sengupta et al., 2021 ).
Larissa and Parung ( 2021 ) offered insights into the definition, applications, and new supply chain models of blockchain as well as emphasized economic benefits and implementation costs in the fishery supply chain. Cruz and da Cruz implemented a smart contract on the Ethereum blockchain to integrate all operators in the fish value chain. The suitability of blockchain for traceability enables collaboration among operators without complete trust, requiring memory-saving strategies and user-friendly tools for accessing stored information (Cruz & da Cruz, 2020 ). Meidayanti et al. ( 2019 ) examined the requirements for implementing blockchain in the beef supply chain and focused on the potential for a transparent supply chain facilitated by data sharing capabilities of blockchain amidst regulatory threats and commercial opportunities.
Cao et al. ( 2021 ), initially, necessitated the essentials for automated data integration via IoT for the beef supply chain. Ferdousi et al. ( 2020 ) presented a blockchain-based supply chain management framework tailored for the US beef cattle industry to isolate private data and offer owners control over data visibility. Natanelov et al. ( 2022 ) investigated the impact of integrating blockchain and smart contract technologies on supply chain finance, which in terms demonstrates their effectiveness in minimizing risk and reducing cash flow cycles in traditional finance models in the Australia–China beef supply chain.
2.2 Real-time implementations
Real-time implementations refer to the practical application or execution of systems, or processes. Table 2 shows the summary of blockchain-based real-time implementations in food supply chains.
| S. no | Tech used | Country | Commodity | Focus | Blockchain parameters | Pros | Cons | Findings | References | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | DC | DS | DT | SC | Tc | Tr | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |||||||
| 1 | BC, BD, and IoT | China | Fruits and vegetables | Data storage | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Yang et al. ( ) | |
| 2 | BC | Indonesia | Vegetables | Data authenticity | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Suroso et al. ( ) | |
| 3 | BC | China | Rice | Supervision reliability | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | J. Wang et al. ( ) | |
| 4 | BC | Pakistan | Rice | Commercial transactions | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Yakubu et al. ( ) | |
| 5 | BC | China | Rice | Data storage | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Peng et al. ( ) | |
| 6 | BC | China | Rice | Data testing and trustworthiness | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Peng et al. ( ) | |
| 7 | BC and IoT | China | Rice | Data transmission | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Peng, Zhang, Wang, Xu et al. ( ) | |
| 8 | BC | China | Rice | Rice price control | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Farooq et al. ( ) | |
| 9 | BC | Indonesia | Chicken | Web-based traceability | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Susanty et al. ( ) | |
| 10 | BC | Abu Dhabi | Fish | Fish fraud and malpractice | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Patro et al. ( ) | |
- Abbreviations: Au, authenticity; BC, blockchain; BD, big data; C1, technical complexity; C2, governance issue; C3, lack in regulations; C4, cost issue; C5, alertness and learning; DC, decentralization; DLT, distributed ledger technology; DS, data security; DT, digitalized transaction; I4.0, Industry 4.0; ICT, information and communication technology; IoT, Internet of Things; N, no; P1, food safety; P2, food quality; P3, decrease in transaction time; P4, decrease in transaction cost; P5, revenue improvement; P6, performance enhancement; P7, sustainability upgrade; SC, smart contract; Tc, traceability; Tr, transparency; Y, yes.
2.2.1 Fresh produces
Based on the non-tampering features of blockchain, Yang et al. ( 2021 ) implemented the fruits and vegetables traceability system. To address the challenges of high data load and security issues in blockchain traceability, a hybrid (i.e., database and blockchain) approach is designed. Public information for consumers is stored locally in the supply chain database, with its hash value uploaded to the blockchain. However, private information is encrypted and stored directly in the blockchain for sharing with relevant entities. This method optimizes data load on the blockchain while ensuring the security of private information and enabling effective public supervision of supply chain data. Suroso et al. designed a traceability system for manufacturers to guarantee product authenticity and transparency by allowing actors to input supply chain data. Once created, the records become immutable and accessible through QR code scanning, which empowers consumers to verify product authenticity. This blockchain-based traceability system not only expedites decision support but also adds value and innovation, mitigating errors associated with manual systems for enhanced food safety as well as transparency in the supply chain (Suroso et al., 2021 ).
2.2.2 Grains and cereals
Wang et al. analyzed quality and safety information across each rice supply chain link, establishing a comprehensive classification table. Moreover, introducing hierarchical data encryption and a scoring mechanism within the blockchain network enhances data security, privacy, and consensus efficiency, thereby bolstering supply chain supervision reliability (J. Wang et al., 2022 ). Yakubu et al. presented a functional prototype that evaluates the viability of the blockchain in the rice supply chain, offering security and cost assessments. Besides, the system is developed on a private Ethereum blockchain, and the framework ensures visibility, transparency, and security, fostering trust among users. Customizable to diverse company needs, the solution facilitates efficient tracing and monitoring of rice supply chains, enhancing regulatory compliance and reducing food contamination risks through sensor-based monitoring (Yakubu et al., 2022 ). Farooq et al. ( 2023 ) proposed a blockchain-based framework for the Binance Smart Chain network, ensuring transparency, traceability, and price control in the rice crop supply chain while enhancing security and reliability in transactions using the Rice Coin and IPFS storage.
Peng et al. ( 2022c ) presented three types of research pertinent to the rice supply chain: Initially, a cross-chain model based on blockchain is employed, where smart contracts enhance rice supply chain supervision, ensuring transparency and real-time data exchange across various stakeholders, thereby fortifying trust and cohesion in the entire rice supply chain. Second, a rice supply chain information management and control model is introduced for utilizing multi-chain collaboration and trusted chaining mechanisms that offer a robust framework for data supervision, storage, and cross-chain communication. Moreover, it addresses the complexities of agricultural information management and enhances food security measures (Peng et al., 2022b ). Third, the multi-blockchain architecture proposed for rice supply chain regulation demonstrates innovation in utilizing next-generation information technology, enabling precise data supervision, sustainable development, and economic feasibility, albeit with certain limitations regarding manual data entry security and extension to other food crops (Peng, Zhang, Wang, Xu, et al., 2022 ).
2.2.3 Meat, poultry, and sea food
Susanty et al. presented a Halal chicken meat–based food traceability system using blockchain, featuring essential components and testing for successful halal assurance throughout the supply chain. The system also enhances halal integrity and consumer awareness promotions (Susanty et al., 2023 ). Patro et al. ( 2022 ) introduced a blockchain-based solution for transparent and secure tracing of fish products in the supply chain with deployment on the Ethereum network and employed five smart contracts to prevent fraud compared to existing solutions.
2.3 Case studies
Various case studies are considered by the researchers: Stranieri et al. ( 2021 ) proposed an integrated conceptual framework based on a case study that assesses the influence of blockchain technology on food supply chains, which comprised a comprehensive set of performance dimensions. Semi-structured interview methods were adopted (A. Sharma et al., 2024 ) to improve the efficiency of the agri-food supply chain. Kshetri and DeFranco ( 2020 ) provided numerous examples to elucidate the economic aspects of blockchain in food supply chains. Compagnucci et al. ( 2022 ) investigated and examined the blockchain implementations in two agri-food organizations. The investigation (Yontar, 2023 ) focused on critical success factors for implementing blockchain in a cyclical approach to reduce resource waste, particularly in the agri-food sector. The study aimed to address the challenges associated with excessive food consumption, a significant concern arising from population growth. Longo et al. ( 2019 ) explored the potential influence of blockchain in the milk processing industry using a case study. The factors influencing the adoption of blockchain technology and their impact on the behavioral intentions of stakeholders within the agri-food supply chain are explored (A. Sharma et al., 2023 ). Additionally, the research endeavors to formulate a comprehensive framework to improve the intellectual capacity of blockchain adoption in the agri-food supply chain and to elucidate stakeholders’ motivations for embracing blockchain solutions. Chen et al. ( 2021 ) employed qualitative thematic examination to explore the procedures, welfare, and challenges associated with the adoption of blockchain in food supply chains. Duan et al. ( 2020 ) conducted content-investigation-based works on blockchain implementation within food supply chains, discussing various welfare and possible challenges. Table 3 shows the blockchain-based case studies in food supply chains.
| S. no | Tech used | Country | Commodity | Focus | Blockchain parameters | Pros | Cons | Findings | References | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | DC | DS | DT | SC | Tc | Tr | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P5 | P6 | P7 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 | |||||||
| 1 | BC and I4.0 | The UK | Food | Design | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Sunmola and Burgess ( ) | |
| 2 | BC | Netherlands | Dairy | Boundary condition | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | Behnke and Janssen ( ) | |
| 3 | BC and IoT | The United States | Egg | Use cases | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | Bumblauskas et al. ( ) | |
| 4 | BC | China | Food | Thematic investigation | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Chen et al. ( ) | |
| 5 | BC | Greece | Agri | Traceability | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Demestichas et al. ( ) | |
| 6 | BC and IoT | China | Food | Challenges | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Duan et al. ( ) | |
| 7 | BC and IoT | China | Food | Traceability | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | H. Feng et al. ( ) | |
| 8 | BC, IoT, and BD | China | Food | Use cases | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Fu et al. ( ) | |
| 9 | BC | Spain | Food | Traceability | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | Galvez et al. ( ) | |
| 10 | BC | Australia | Food | Safety | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Johnson ( ) | |
| 11 | BC | Spain | Agri-food | Regulatory | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Kamilaris et al. ( ) | |
| 12 | BC | Denmark | Food | Challenges | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | Katsikouli et al. ( ) | |
| 13 | BC | Denmark | Food | Trust | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Köhler and Pizzol ( ) | |
| 14 | BC | Germany | Agri-food | Impacts | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Kramer et al. ( ) | |
| 15 | BC | The USA | Food | Safety | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Kshetri ( ) | |
| 16 | BC | The USA | Food | Safety | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Kshetri and DeFranco ( ) | |
| 17 | BC | The USA | Food | Challenges | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Kumar et al. ( ) | |
| 18 | BC | The USA | Food | Platforms | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Li et al. ( ) | |
| 19 | BC and IoT | China | Organic food | Traceability | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Lin et al. ( ) | |
| 20 | BC | Italy | Fresh milk | Processing | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | Y | Longo et al. ( ) | |
| 21 | BC | Italy | Food | Traceability | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Mirabelli and Solina ( ) | |
| 22 | BC, IoT, and DLT | Austria | Food | Sustainability | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Nurgazina et al. ( ) | |
| 23 | BC and DLT | The UK | Food | Robustness | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Pearson et al. ( ) | |
| 24 | AI and BC | China | Food | Traceability | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Qian et al. ( ) | |
| 25 | BC and DLT | Italy | Agri-food | Sustainability | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | Rana et al. ( ) | |
| 26 | BC | The UK | Food | Visibility | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Rogerson and Parry ( ) | |
| 27 | BC and ICT | India | Grape wine | Traceability | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Saurabh and Dey ( ) | |
| 28 | BC | The United States | Food | Economy | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Schahczenski and Schahczenski ( ) | |
| 29 | BC | Italy | Agri-food | Flexibility | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | Stranieri et al. ( ) | |
| 30 | BC and IoT | Malaysia | Halal | Traceability | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | Tan et al. ( ) | |
| 31 | BC | India | Food | Transparency | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | N | Y | N | N | N | N | Tayal et al. ( ) | |
| 32 | BC | Italy | Agri-food | Sustainability | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Tiscini et al. ( ) | |
| 33 | BC | India | Agri | Security | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Yadav et al. ( ) | |
| 34 | BC, I4.0, and IoT | The UK | Agri-food | Traceability | Y | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Zhao et al. ( ) | |
| 35 | BC and IoT | India | Dairy | Short-review | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Shingh et al. ( ) | |
| 36 | BC and I4.0 | Malaysia | Halal | Sustainable production | Y | Y | N | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Ali et al. ( ) | |
| 37 | BC | Vietnam | Pork | Food safety | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | Pham et al. ( ) | |
| 38 | BC | Australia | Beef | Transparency | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | Y | Y | Y | N | Cao et al. ( ) | |
| 39 | BC | Netherlands | Meat | Transparency | N | N | N | N | N | Y | Y | N | N | N | N | N | Y | N | Y | Y | Y | Y | N | Sander et al. ( ) | |
- Abbreviations: AI, artificial intelligence; Au, authenticity; BC, blockchain; BD, big data; C1, technical complexity; C2, governance issue; C3, lack in regulations; C4, cost issue; C5, alertness and learning; DC, decentralization; DLT, distributed ledger technology; DS, data security; DT, digitalized transaction; I4.0, Industry 4.0; ICT, information and communication technology; IoT, Internet of Things; N, no; P1, food safety; P2, food quality; P3, decrease in transaction time; P4, decrease in transaction cost; P5, revenue improvement; P6, performance enhancement; P7, sustainability upgrade; SC, smart contract; Tc, traceability; Tr, transparency; Y, yes.
The absence of traceability poses a significant challenge in food supply chains, wherein blockchain technology emerges as a potential solution. Y. Zhang, Wu et al. ( 2023 ) introduced a novel approach combining blockchain and machine learning to enhance the authenticity and reliability of traceability data in the grain-and-oil food supply chain. The implemented Hyperledger Fabric–based traceability system showcases significant advancements in multi-source data handling, lightweight storage, and traceability, contributing to the safety assurance of grain-and-oil food in China. H. Feng et al. ( 2020 ) conducted a review of the features and functionalities of blockchain technology and explored blockchain-based solutions for addressing food traceability issues. The study contributes by proposing an architecture design framework and application analysis flowchart for blockchain-based food traceability systems, providing valuable guidance to enhance food traceability and sustainability through the implementation of blockchain technology. Galvez et al. ( 2018 ) assessed the innovative perspective of blockchain for ensuring traceability and authenticity in the food supply chain, particularly focusing on enhancing the quality of data acquisition and management in the analytical processes.
Casino et al. ( 2021 ) introduced a secure and trustless design for food supply chain traceability, demonstrated through a case study from a dairy firm. The feasibility is assessed, showcasing wholly functional smart contracts and an indigenous private blockchain, with discussions on managerial implications and potential areas for future research. Tayal et al. ( 2021 ) presented a unique three-stage methodology to integrate blockchain with the food supply chain. The methodology, incorporating data analysis and hierarchical categorization, identified nine key critical success factors, addressing various blockchain parameters. It integrates blockchain with operational management to offer a solution for enhancing efficiency and effectiveness in the food supply chain. Guo et al. ( 2021 ) addressed the food quality issues and proposed a traceability system for agricultural products based on blockchain and IoT. The detailed system architecture leverages a consortium blockchain to enhance reliability and trustworthiness in tracking agricultural products. Demestichas et al. ( 2020 ) offered a comprehensive overview of applying blockchain technologies for traceability in the agri-food sector. The broad literature assessment delves into the integration of blockchain into traceability systems, examining commercial applications, addressing challenges, and outlining prospects in the agri-food supply chain. Qian et al. ( 2020 ) compared the traceability system developments in Europe and China, whereas Lin et al. ( 2021 ) studied the intention of consumers to adopt a blockchain food traceability system for organic products using survey data. Bumblauskas et al. ( 2020 ) presented a case study employing blockchain to track eggs from farm to consumer, capturing traceability and engagement data. Tan et al. ( 2022 ) addressed the traceability challenges in the Malaysian food supply chain, proposing a blockchain-based traceability framework. Behnke and Janssen ( 2020 ) emphasized that although technology is crucial, standardization of interior and exterior traceability processes and master data is essential for achieving transparency across the entire supply chain.
2.4 Research gaps and its blockchain solutions
Supply chain traceability: Traditional supply chains often have slow and error-prone traceability due to manual processes. This issue can be overcome by blockchain that enables end-to-end traceability by recording every transaction and movement of food products on an immutable ledger (Patel et al., 2023 ).
Preventing fraud and counterfeiting: In existing food supply chain systems, there is a high risk of fraud due to manual record-keeping and the difficulty of verifying product authenticity, leading to potential for counterfeit goods entering the supply chain. The transparency and immutability of blockchain make it an effective tool in preventing fraud and counterfeiting (Chandan et al., 2023 ). By providing consumers with real-time access to the origin and journey of products, blockchain offers confidence and ensures the authenticity of food items.
Quality assurance: In existing food supply chains, quality assurance is often inconsistent due to manual checks and varying standards across different stages, leading to delays in detecting issues. This inconsistency, coupled with fragmented data, makes it difficult to pinpoint where quality lapses occur, resulting in limited accountability. In contrast, blockchain-based supply chains offer automated, real-time monitoring that ensures consistent quality checks throughout the process. Immediate alerts for any deviations allow for swift corrective actions, whereas the transparent and immutable records provide a clear audit trail, enhancing accountability and overall quality assurance (Thangamayan et al., 2023 ).
Faster and more accurate recalls: In existing food supply chains, recalls are often slow and inefficient due to fragmented data and manual processes, which can delay identifying affected products and increase risk to consumers. However, blockchain enables rapid and accurate identification of affected products. This significantly reduces the time required for recalls, minimizes the impact on consumers, and enhances overall food safety management (Kravenkit & So-In, 2022 ).
Collaboration in the supply chain: Traditional food supply chains face barriers to effective communication and coordination among stakeholders, whereas blockchain fosters collaboration among stakeholders in the food supply chain (Akhavan & Philsoophian, 2022 ). By providing a shared platform for data exchange, it enhances communication, builds trust, and streamlines processes, ultimately contributing to improved food safety practices.
Table 4 provides a comparison between existing food supply chains and blockchain-based food supply chains, highlighting differences in transparency, traceability, data security, efficiency, cost, trust, response to issues, quality assurance, and auditability.
| Features | Existing food supply chain | Blockchain-based food supply chain |
|---|---|---|
| Transparency | Limited | High |
| Traceability | Slow and error-prone | Real-time and accurate |
| Data security | Vulnerable to tampering | Immutable and secure |
| Efficiency | Manual processes and slower | Automated and faster |
| Cost | Higher due to intermediaries | Reduced by eliminating redundancies |
| Trust | Dependent on third parties | Decentralized verification |
| Response to issue | Delayed | Immediate |
| Quality assurance | Inconsistent and manual check | Consistent quality check |
| Auditability | Complex and time-consuming | Simplified and instantaneous |
Overall, addressing these research gaps could advance the understanding and adoption of blockchain technology in food supply chains. This, in turn, would lead to improved transparency, efficiency, and sustainability across the entire supply network.
3 ROLE OF BLOCKCHAIN PLATFORMS IN FOOD SUPPLY CHAINS
Digital advancements have transformed conventional supply chains by introducing a plethora of online platforms that offer on-demand goods and services (J. Tao, Dai, et al., 2021 ). The emergence of information and communication technologies, combined with e-business solutions, has prompted food supply chains to leverage online platforms to enhance the efficiency of food production, storage, processing, distribution, and accessibility (Ivanov et al., 2019 ). Various blockchain-based and other platforms exist (as shown in Figure 4 ), facilitating the delivery of products, services, and information throughout the entire food supply chain (i.e., from farm to fork) (Gharehgozli et al., 2017 ).

The blockchain platform has been categorized into four main groups—food production and sharing, food delivery, grocery delivery, and food leftover distribution. These platforms serve diverse players within the food supply chain. Although the first category encompasses up- and downstream participants, the latter categories are more consumer-centric, aiming to enhance food accessibility. Notably, food and grocery delivery platforms come in two types: supermarket (or restaurant)-to-customer delivery and platform-to-consumer delivery, with the latter acting as an intermediary for on-demand grocery and food delivery between customers and restaurants or grocery stores. Table 5 depicts the key feature comparisons of various platforms for the food supply chain in the food sector. The significance of food delivery platforms has notably increased, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic, as highlighted in Hobbs ( 2020 ).
| Platform | Blockchain features | Key findings | References | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BI | Tc | Ts | SC | DS | DC | |||
| AgriDigital | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Xu et al. ( ) | |
| Ambrosus | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Hellani et al. ( ) | |
| BlockGrain | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Hellani ( ) | |
| Costco | ✗ | ↓ | ↓ | ✗ | ↓ | ✗ | Persaud ( ) | |
| FreshDirect | ✗ | ↓ | ↓ | ✗ | ↓ | ✗ | Chua and Yoo ( ) | |
| HEB | ✗ | ↓ | ↓ | ✗ | ↓ | ✗ | Stewart ( ) | |
| IBM Food Trust | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Nguyen and Do ( ) | |
| Instacart | ✗ | ↓ | ↓ | ✗ | ↓ | ✗ | Busse and Springer ( ) | |
| Kroger | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Harriman et al. ( ) | |
| OpenSC | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Howson ( ) | |
| Peapod | ✗ | ↓ | ↓ | ✗ | ↓ | ✗ | Caltagirone and Psrkinson ( ) | |
| Provenance | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Provenance ( ) | |
| Ripe.io | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Jin and Saucier ( ) | |
| Sam's Club | ✗ | ↓ | ↓ | ✗ | ↓ | ✗ | Courtemanche and Carden ( ) | |
| Shipt | ✗ | ↓ | ↓ | ✗ | ↓ | ✗ | Dillahunt et al. ( ) | |
| TE-Food | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | Köhler and Pizzol ( ) | |
| Walmart | ✓ | ↑ | ↑ | ✓ | ↑ | ✓ | M. Sharma and Kumar ( ) | |
- Note : ↑, high; ↓, low; ✗, no; ✓, yes.
- Abbreviations: BI, blockchain integration; DC, decentralization; DS, data security; SC, smart contracts; Tc, traceability; Ts, transparency.
3.1 Transparency in food production and supply
The emphasis within food supply chains has shifted toward the development of blockchain-based platforms, specifically in the domain of food production, from providers to distribution to customers (Köhler & Pizzol, 2020 ). Examples of these blockchain-based platforms include: (a) AgriBlockIoT—an utterly decentralized traceability solution for the agri-food supply chain, based on blockchain technology, capable of effortlessly incorporating IoT devices that generate and utilize digital data throughout the entire chain (Caro et al., 2018 ); (b) FairChain—this farming ensures that farmers, as well as workers, achieve sustainable incomes by overseeing profitable farms. Moreover, it is engaging in value-added activities, ultimately enhancing livelihoods and contributing to the betterment of communities (C. Zhang, Gong, et al., 2023 ); (c) FoodTrail—this blockchain meticulously archives and monitors the traceability of food products in the supply chain (Hayati & Nugraha, 2018 ); (d) IBM Food Trust—a blockchain-based modular solution designed to enhance the safety, intelligence, and sustainability of the entire food ecosystem, delivering benefits to all participants within the network (Kawaguchi, 2019 ); (e) OpenSC—an unprecedented prospect for producers at the initial stages of the value chain to establish a seamless connection with end consumers. Furthermore, the data captured by OpenSC positions us at the forefront of advanced fisheries management and efficient supply chain operations (Howson, 2020 ); (f) TE-Food—a blockchain-powered farm-to-table food traceability solution committed to enhancing trust and efficiency in the food industry (Champion et al., 2018 ; Fahmi et al., 2023 ); (g) Water Ledger—it stands as the pioneering license-centric secure platform that is empowered by blockchain technology as well as revolutionizing the management of water licenses. This transformation ensures sustainability and fosters trust in the process (Samanta & Sarkar, 2023 ); and (h) World Wide Fund Pilot—implementing digital technology within the fresh and frozen tuna sectors of the western and central Pacific region, the blockchain supply chain traceability project enhances supply chain management by tracking fish from the vessel to the supermarket (Xiao et al., 2024 ). Although these platforms are still in their early stages, they have proven advantageous for food supply chains by mitigating food waste and enhancing the efficacy of food production and supply processes.
3.2 Transparency in grocery shopping
Grocery shopping experiences can differ in terms of transparency, traceability, efficiency, and trust. Deprived of blockchain technology, conventional grocery shopping platforms have limited transparency as they rely on trust in the information provided by the retailer. Consumers may not have access to detailed information about the origin, handling, or quality of products. Moreover, it has manual traceability of products and relies on traditional methods, making it challenging for consumers to verify the authenticity of claims regarding organic, local, or sustainable sourcing. The supply chain involves various intermediaries, such as distributors and wholesalers. This complexity can make it harder to pinpoint the exact journey of a product from the producer to the consumer. Subsequently, record-keeping in the supply chain may still be paper-based or rely on centralized databases, which can be susceptible to errors, manipulation, or a lack of real-time updates. Some examples of grocery shopping platforms are Costco, Deliv, FreshDirect, HEB, Instacart, Kroger, Meijer, Out of Milk, Peapod, Sam's Club, Shipt, Target, and Walmart+ (Esper, 2021 ; Hays et al., 2005 ; Huo & Rui, 2021 ; Michelson et al., 2018 ).
Furthermore, blockchain-based platforms provide a decentralized and transparent ledger for consumers to access real-time, immutable records of a product's journey, including details about its origin, processing, and transportation. IBM Food Trust is the preeminent instance for streamlining the grocery supply chain and decreasing food wastage (Tiwari, 2020 ). Each step in the supply chain is recorded on the blockchain, which enables end-to-end traceability, allowing consumers to verify claims made by retailers regarding the authenticity and quality of products. Herein, smart contracts automate various processes, including payments, quality checks, and delivery. This automation reduces the need for intermediaries, streamlining the supply chain and potentially lowering costs. Data on the blockchain are decentralized and secured through cryptography; thus, it reduces the risk of a single point of failure and makes it more challenging for malicious actors to tamper with information. Consumers have more control and empowerment as they can make informed decisions based on verified information. They can choose products based on factors like ethical sourcing, sustainability, and adherence to specific standards. With blockchain, updates to the supply chain are recorded in real time, ensuring that consumers have the latest and most accurate information about the products they are purchasing. Although the adoption of blockchain in grocery shopping is still evolving, it holds the potential to transform the industry by providing a higher level of transparency, trust, and efficiency in the supply chain (Rai et al., 2021 ).
3.3 Transparency in food delivery
Blockchain platforms are increasingly gaining traction in the food delivery industry, offering innovative solutions to enhance overall efficiency. Companies are exploring these platforms to address challenges related to food safety, authentication, and supply chain integrity. One notable example is the collaboration between major retailers and IBM Food Trust (Kamath, 2018 ). Walmart, for instance, has leveraged IBM Food Trust (Eletter et al., 2022 ) to improve traceability in its supply chain, including aspects of food delivery. This blockchain-based system allows for real-time tracking of products from source to destination, providing consumers with verifiable information about the origin and handling of food items. Provenance is another blockchain platform that has been applied to trace the journey of products and authorize transparency in the delivery process. It allows consumers to access verified information about the products they purchase, embracing trust in the supply chain. Some other potential platforms in food delivery are FoodChain, DeliverChain by Walmart, VeChainThor with Foodgates, Deliveroo, DoorDash, Grubhub, Just Eat, Pizza Hut, Postmates, Seamless Dominos, and Uber Eats (Folha et al., 2022 ; Kshetri, 2023 ). Companies in the food industry are increasingly recognizing the potential benefits of blockchain for guaranteeing transparency, reducing fraud, and enhancing overall efficiency in the delivery process.
3.4 Transparency in food leftover distribution
Blockchain platforms in food leftover distribution leverage innovative approaches to address the global challenge of food waste while promoting transparency and efficiency. One prominent example is Food Trax, a platform that harnesses blockchain technology to trace the entire journey of surplus food items, creating an immutable and transparent ledger (Srivastava et al., 2021 ). This ensures that each step, from donation by food providers to the destination with recipients, is recorded, providing an auditable history of the surplus food's distribution. The utilization of blockchain enhances traceability, instills trust, and facilitates the reliable redirection of surplus food to individuals and communities in need. In a similar vein, FoodChain exemplifies the application of smart contracts within the blockchain to automate critical processes in surplus food management (Folha et al., 2022 ). Smart contracts execute predefined conditions, such as identification of surplus food, coordination for pickups, and timely distribution. This automation streamlines logistics, reducing manual efforts and contributing to the efficient redistribution of surplus food. Platforms like ShareEat further emphasize the decentralization aspect of blockchain by employing decentralized databases. This approach enhances the reliability and accessibility of real-time data related to surplus food, creating a distributed network that ensures information accuracy. The collaborative effort of ReFood is another noteworthy example, emphasizing transparency through blockchain's transparent records. By fostering collaboration among food donors, nonprofits, and distribution partners, ReFood ensures a seamless and accountable surplus food redistribution process (Dani, 2021 ). These platforms collectively showcase the transformative potential of blockchain in revolutionizing surplus food distribution, promoting sustainability, and combating food waste on a global scale.
4 POSITIVE IMPACTS AND CHALLENGES WHILE INTEGRATING BLOCKCHAIN INTO FOOD SUPPLY CHAINS
This section evaluates the positive impacts and challenges associated with implementing blockchain technology in the food supply chain.
4.1 Positive impacts
4.1.1 guaranteed food safety and quality standards.
- Traceability enhancement: The transparency and immutability of blockchain records prevent the loss of traceability, enhancing accountability and reducing the risk of fraud or contamination (Singh et al., 2023 ). The decentralized and transparent ledger ensures an unbroken chain of custody for each food product. From the origin at the farm to every touchpoint in the supply chain, every transaction is recorded and time-stamped. This heightened traceability helps in quickly identifying and isolating any contaminated or compromised products, facilitating targeted recalls, and minimizing potential health risks (Kampan et al., 2022 ).
- Prevention of food adulteration: Tamper-resistant nature of blockchain significantly reduces the risk of food adulteration. The immutable records on the blockchain provide a secure and verifiable history of each product, ensuring that the information related to ingredients, processing, and quality certifications remains intact. This dispirits fraudulent activities and promotes the authenticity of food items. Smart contracts in blockchain can trigger alerts in case of any tampering or unauthorized changes in the product composition. Correspondingly, a decentralized ledger verifies the authenticity of food products, providing a secure and unalterable record of each ingredient and its source (Leung et al., 2021 ).
- Efficient food recall processes: In the occurrence of a food safety concern or contamination, the traceability features of blockchain enable rapid and precise recalls. Identifying the exact source and distribution path of affected products becomes a streamlined process, allowing for targeted recalls. This efficiency not only reduces the impact on consumers but also minimizes financial losses for businesses by isolating affected batches (Leow, 2023 ).
- Mitigation of food waste: Real-time visibility into the supply chain helps prevent overstocking and enables the timely distribution of perishable goods. By reducing delays and inefficiencies in the distribution process, businesses can better match supply with demand, minimizing overstock situations that often lead to food wastage. This, in turn, contributes to a more sustainable and economically viable food supply chain. With blockchain, the entire history of a food product is accessible instantly, facilitating targeted and swift recalls in case of contamination or safety concerns (Dey et al., 2022 ).
4.1.2 Improved efficiency through operational characteristics
- Decrease in transaction time: The streamlined, peer-to-peer approach significantly decreases transaction times. Smart contracts, a key component of blockchain, enable self-executing agreements, eliminating manual processing delays. As a result, operational processes, such as supply chain transactions or financial settlements, experience notable efficiency gains, leading to faster and more responsive business operations (Swan, 2015 ).
- Decrease in transaction cost: Blockchain offers a notable advantage in reducing transaction costs by eliminating intermediaries and associated fees. In traditional systems, financial transactions, especially across borders, involve banks, payment processors, and other intermediaries, each charging a fee. With decentralization and peer-to-peer systems, transactions occur directly among parties, minimizing or eliminating intermediary fees. This cost reduction is particularly significant in sectors such as cross-border payments and supply chain finance. Overall, businesses leveraging blockchain can achieve significant cost savings in their operational transactions (Narayanan et al., 2021 ).
- Revenue improvement: The impact of blockchain on revenue improvement is evident through increased transparency, reduced fraud, and enhanced trust among participants. Transparency and immutability of blockchain ledgers ensure trust in financial transactions, reducing the risk of fraudulent activities. This increased trust, coupled with transparent supply chain practices enabled by blockchain, can enhance a company's reputation and customer loyalty, ultimately leading to revenue improvement (Tapscott & Tapscott, 2016 ).
- Performance enhancement: The distributed and decentralized architecture of the blockchain enhances overall system performance. The elimination of a central authority and the use of consensus mechanisms improve system resilience and reduce the risk of a single point of failure. This decentralized approach also enhances data integrity and security, ensuring that records are tamper-proof and reliable. As a result, businesses experience improved overall performance, from increased data accuracy to more resilient and robust operational processes (Antonopoulos & Harding, 2023 ).
These operational advantages illustrate the potential of blockchain technology to revolutionize the food industry, making processes more efficient, cost-effective, and transparent. Real-life examples include companies utilizing blockchain for supply chain management, such as Walmart's application of blockchain to trace the source of certain food products, ensuring quality and safety throughout the supply chain (Bhat & Dubey, 2023 ).
4.1.3 Improved robustness through viability characteristics
- Environment viability: Blockchain technology contributes to environmental viability by promoting sustainability initiatives. Decentralization reduces the need for intermediaries and traditional paper-based processes, leading to a significant reduction in paper usage. Smart contracts, integral to the blockchain, facilitate automated and digitized agreements, minimizing the reliance on physical documentation. This shift toward a paperless and more efficient system aligns with environmental conservation efforts. Additionally, blockchain's transparency can enhance supply chain traceability, allowing businesses to monitor and reduce their environmental impact. This aligns with global environmental goals and sustainable business practices (Saurabh & Dey, 2021 ).
- Economic viability: Blockchain enhances economic viability by reducing transaction costs, minimizing the risk of fraud, and streamlining financial processes. Through decentralized ledgers and smart contracts, blockchain eliminates the need for intermediaries in various transactions, leading to cost savings. The increased transparency and security provided by blockchain also mitigates the risk of fraud, contributing to the economic viability. Furthermore, the efficiency and transparency of blockchain can attract investments, fostering economic growth and sustainability (Kshetri & DeFranco, 2020 ).
- Sustainability: Blockchain technology promotes sustainability through transparent and traceable supply chains, ensuring ethical sourcing and production practices. By providing a decentralized and immutable ledger, blockchain enables consumers to make informed choices about sustainable products. This transparency extends to verifying the authenticity of certifications related to sustainability. Additionally, blockchain can facilitate the creation of tokenized assets that represent real-world sustainable initiatives, allowing for investment in environmentally friendly projects (Schahczenski & Schahczenski, 2020 ).
Overall, blockchain-based viability advantages contribute to a more environmentally friendly, economically efficient, and socially responsible food industry. Real-life examples include major retailers collaborating with blockchain platforms to enhance sustainability practices and provide consumers with transparent information about the environmental and ethical aspects of the products they purchase (Chandan et al., 2023 ).
4.2 Challenges
Numerous actors in the food supply chain have expressed keen interest in integrating blockchain technology, leading to the initiation of several experimental projects worldwide. Notably, Walmart has conducted successful blockchain trials focusing on food traceability as well as transparency in the pork supply chain (in China) and the mango supply chain (in America). Additionally, a Singapore-based wine company has introduced a secure blockchain platform, enabling consumers to purchase wines via digital tokens while gaining access to comprehensive information regarding the origin, quality, and realism of the wines. Despite these developments, the widespread implementation of blockchain faces uncertainties attributed to the early stage of technology and the myriad challenges it currently confronts (Li et al., 2023 ).
One of the prominent environmental challenges associated with blockchain technology is its substantial energy consumption. Blockchain networks, especially those that use proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, need a significant amount of computational power to validate transactions and ensure network security. This process consumes a significant amount of electricity, leading to higher carbon emissions and a negative environmental impact. To address this issue and improve the environmental impact of blockchain, it is essential to adopt energy-efficient consensus mechanisms such as proof-of-stake, make use of renewable energy sources, and implement Layer 2 solutions to reduce computational demands. Additionally, optimizing protocols and supporting green initiatives can further enhance sustainability.
- Technical complexity: Implementing blockchain in the food supply chain involves technological complexities, including interoperability issues, scalability concerns, and integration with existing systems. Ensuring seamless communication between diverse stakeholders and technologies poses a significant challenge.
- Cost issue: The initial investment required for adopting blockchain technology, including development, integration, and maintenance costs, can be substantial. Small and medium enterprises may find it challenging to bear these costs, hindering widespread adoption.
- Governance issue: Establishing effective governance models for decentralized blockchain networks is critical. Determining decision-making processes, and protocols, and ensuring consensus among network participants present governance challenges that require careful consideration.
- Lack of regulations: The regulatory landscape for blockchain in the food industry is evolving. Navigating and complying with miscellaneous regulations across regions poses challenges. Regulatory uncertainties can impact the adoption rate as stakeholders seek clarity on compliance requirements.
- Alertness and learning: Lack of awareness and understanding about blockchain technology within the food industry can impede adoption. Stakeholders may be hesitant due to a limited understanding of the benefits and processes associated with blockchain, emphasizing the need for educational initiatives.
| Challenge | Explanation | Impact | Mitigation strategy | Resource requirement | Stakeholder involvement | Timeline for resolution | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technical complexity | High | Developers and tech experts | Short term | Chang et al. ( ) | |||
| Cost issue | Moderate | Financial experts | Medium term | Wang et al. ( ) | |||
| Governance issue | Moderate | Governance experts | Medium term | Fu et al. ( ) | |||
| Lack in regulations | Moderate | Regulatory experts | Long term | Duan et al. ( ) | |||
| Alertness and learning | Low | Educational experts | Short-to-medium term | Queiroz et al. ( ) |
5 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE DIRECTIONS
The integration of blockchain technology into food supply chains represents a pivotal step in addressing the current issue of food safety. Through the analysis of numerous studies and case studies, it is evident that blockchain offers immense potential in enhancing transparency, traceability, and trust within the food industry. By utilizing blockchain platforms, stakeholders can access real-time and immutable records of food products, thereby minimizing risks associated with contamination and ensuring higher standards of food quality. However, although the benefits of blockchain are substantial, it is essential to acknowledge and address the challenges associated with its implementation. Furthermore, continued research and collaboration are vital to further optimize and scale blockchain-based solutions, ultimately safeguarding the health and well-being of consumers worldwide.
Moreover, future research should prioritize the refinement of existing blockchain frameworks, the resolution of any additional challenges, and the exploration of innovative applications within the food supply chain. For example, the integration of AI with blockchain technology can significantly enhance efficiency and decision-making by rapidly analyzing large data sets, predicting trends, automating tasks, and identifying patterns or anomalies. When utilized in a blockchain-based food supply chain, AI improves traceability, optimizes resource allocation, ensures quality, and detects fraudulent activities. Ultimately, this results in heightened transparency and sustainability.
Furthermore, collaborative efforts across industry stakeholders, policymakers, and researchers are vital to overcome potential hurdles and ensure the seamless integration of blockchain technology. The future direction of blockchain in the safe food supply chain involves investigating deeper into socio-economic impacts, understanding consumer perceptions, and fostering a standardized approach to ensure interoperability among various blockchain platforms. Additionally, exploring the scalability and sustainability of blockchain solutions in diverse global contexts will be paramount for their widespread adoption. As technology develops, it is essential to emphasize educational initiatives to enhance awareness and understanding of blockchain among industry professionals. This will foster a conducive environment for the acceptance and implementation of blockchain-based solutions, ultimately contributing to the creation of a more resilient, transparent, and trustworthy food supply chain.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
V Sri Vigna Hema : Conceptualization; investigation; writing—original draft; methodology; validation; writing—review and editing; data curation; formal analysis. Annamalai Manickavasagan : Conceptualization; funding acquisition; writing—review and editing; supervision.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by Food from Thought—Canada First Research Excellence Fund.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
- Akbar, A. , Rakhmawati, N. A. , & Vanany, I. ( 2022 ). Halal blockchain application for a chicken slaughtering factory . International Journal on Food System Dynamics , 13 ( 3 ), 321 – 334 . Google Scholar
- Akhavan, P. , & Philsoophian, M. ( 2022 ). Improving of supply chain collaboration and performance by using block chain technology as a mediating role and resilience as a moderating variable . Journal of the Knowledge Economy , 14 , 4561 – 4582 . 10.1007/s13132-022-01085-9 Google Scholar
- Ali, M. H. , Chung, L. , Kumar, A. , Zailani, S. , & Tan, K. H. ( 2021 ). A sustainable Blockchain framework for the halal food supply chain: Lessons from Malaysia . Technological Forecasting and Social Change , 170 , 120870. 10.1016/j.techfore.2021.120870 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Antonopoulos, A. M. , & Harding, D. A. ( 2023 ). Mastering bitcoin . O'Reilly Media, Inc. Google Scholar
- Behnke, K. , & Janssen, M. F. W. H. A. ( 2020 ). Boundary conditions for traceability in food supply chains using blockchain technology . International Journal of Information Management , 52 , 101969. 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.05.025 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Bhat, M. S. , & Dubey, S. ( 2023 ). An overview of the effects of blockchain technology in food chain supply: A case study on Walmart . The Online Journal of Distance Education and e-Learning , 11 ( 2 ), 1205 – 1209 . Google Scholar
- Bilal, M. , & Kamran, M. U. ( 2023 ). Blockchain-based soft drinks supply chain traceability by using hash algorithm . Journal of NCBAE , 2 ( 2 ), 42 – 58 . Google Scholar
- Bumblauskas, D. , Mann, A. , Dugan, B. , & Rittmer, J. ( 2020 ). A blockchain use case in food distribution: Do you know where your food has been? International Journal of Information Management , 52 , 102008. 10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2019.09.004 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Busse, M. , & Springer, S. ( 2023 ). Grocery delivery in the united states: Trying to bag profits . Kellogg School of Management. Google Scholar
- Caltagirone, J. A. , & Psrkinson, T. ( 2000 ). Peapod on supply chain: H ow e-commerce changed the traditional logistics model [Conference presentation]. The Council of Logistics Management Fall Meeting, Council of Logistics Management, New Orleans, LA. Google Scholar
- Cao, S. , Foth, M. , Powell, W. , Miller, T. , & Li, M. ( 2022 ). A blockchain-based multisignature approach for supply chain governance: A use case from the Australian beef industry . Blockchain: Research and Applications , 3 ( 4 ), 100091. 10.1016/j.bcra.2022.100091 Google Scholar
- Cao, S. , Powell, W. , Foth, M. , Natanelov, V. , Miller, T. , & Dulleck, U. ( 2021 ). Strengthening consumer trust in beef supply chain traceability with a blockchain-based human-machine reconcile mechanism . Computers and Electronics in Agriculture , 180 , 105886. 10.1016/j.compag.2020.105886 Google Scholar
- Caro, M. P. , Ali, M. S. , Vecchio, M. , & Giaffreda, R. ( 2018 ). Blockchain-based traceability in agri-foo d supply chain management: A practical implementation [Conference presentation]. The 2018 IoT Vertical and Topical Summit on Agriculture-Tuscany (IOT Tuscany), Tuscany, Italy. Google Scholar
- Casino, F. , Kanakaris, V. , Dasaklis, T. K. , Moschuris, S. , Stachtiaris, S. , Pagoni, M. , & Rachaniotis, N. P. ( 2021 ). Blockchain-based food supply chain traceability: A case study in the dairy sector . International Journal of Production Research , 59 ( 19 ), 5758 – 5770 . 10.1080/00207543.2020.1789238 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Champion, D. , Stevens, B. , Ward, R. , & Kerridge, A. ( 2018 ). Can the ‘blockchain’ contribute to achieving global food security? A report for the Science and Technology Facilities Council, UK Research and Innovation . 1 – 62 . Google Scholar
- Chandan, A. , John, M. , & Potdar, V. ( 2023 ). Achieving UN SDGs in food supply chain using blockchain technology . Sustainability , 15 ( 3 ), 2109 . 10.3390/su15032109 Google Scholar
- Chang, Y. , Iakovou, E. , & Shi, W. ( 2020 ). Blockchain in global supply chains and cross border trade: A critical synthesis of the state-of-the-art, challenges and opportunities . International Journal of Production Research , 58 ( 7 ), 2082 – 2099 . 10.1080/00207543.2019.1651946 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Chen, S. , Liu, X. , Yan, J. , Hu, G. , & Shi, Y. ( 2021 ). Processes, benefits, and challenges for adoption of blockchain technologies in food supply chains: A thematic analysis . Information Systems and e-Business Management , 19 , 909 – 935 . 10.1007/s10257-020-00467-3 Google Scholar
- Chua, C. S. , & Yoo, C. A. ( 2018 ). Future of grocery retail shopping: Challenges and opportunities in e-commerce grocery shopping . Massachusetts Institute of Technology. Google Scholar
- Cocco, L. , Mannaro, K. , Tonelli, R. , Mariani, L. , Lodi, M. B. , Melis, A. , Simone, M. , & Fanti, A. ( 2021 ). A blockchain-based traceability system in agri-food SME: Case study of a traditional bakery . IEEE Access , 9 , 62899 – 62915 . 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3074874 Google Scholar
- Compagnucci, L. , Lepore, D. , Spigarelli, F. , Frontoni, E. , Baldi, M. , & Di Berardino, L. ( 2022 ). Uncovering the potential of blockchain in the agri-food supply chain: An interdisciplinary case study . Journal of Engineering and Technology Management , 65 , 101700. 10.1016/j.jengtecman.2022.101700 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Courtemanche, C. , & Carden, A. ( 2014 ). Competing with Costco and Sam's Club: Warehouse club entry and grocery prices . Southern Economic Journal , 80 ( 3 ), 565 – 585 . 10.4284/0038-4038-2012.135 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Cruz, E. F. , & da Cruz, A. M. R. ( 2020 ). Using blockchain to implement traceability on fishery value chain . ICSOFT , 1195 , 501 – 508 . Google Scholar
- Dani, S. ( 2021 ). Food supply chain management and logistics: Understanding the challenges of production, operation and sustainability in the food industry . Kogan Page Publishers. Google Scholar
- Demestichas, K. , Peppes, N. , Alexakis, T. , & Adamopoulou, E. ( 2020 ). Blockchain in agriculture traceability systems: A review . Applied Sciences , 10 ( 12 ), 4113 . 10.3390/app10124113 CAS Google Scholar
- Dey, S. , Saha, S. , Singh, A. , & McDonald-Maier, K. ( 2022 ). SmartNoshWaste: Using blockchain, machine learning, cloud computing and QR code to reduce food waste in decentralized web 3.0 enabled smart cities . Smart Cities , 5 , 162 – 176 . 10.3390/smartcities5010011 Google Scholar
- Dillahunt, T. R. , Simioni, S. , & Xu, X. ( 2019 ). Online grocery delivery services: An opportunity to address food disparities in transportation-scarce areas [Conference presentation]. the Proceedings of the 2019 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Glasgow, UK, Article 4, 1 – 15 . https://doi.org/10.1145/3290605.3300879 10.1145/3290605.3300879 Google Scholar
- Duan, J. , Zhang, C. , Gong, Y. , Brown, S. , & Li, Z. ( 2020 ). A content-analysis based literature review in blockchain adoption within food supply chain . International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 17 ( 5 ), 1784 . 10.3390/ijerph17051784 PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Eletter, S. F. , Elrefae, G. A. , Yasmin, T. , Qasem, A. , Alshehadeh, A. R. , & Belarbi, A. ( 2022 ). Leveraging blockchain-based smart contracts in the management of supply chai n: Evidence from Carrefour UAE [Conference presentation]. The 2022 International Arab Conference on Information Technology (ACIT), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates. Google Scholar
- Esper, T. L. ( 2021 ). Supply chain management amid the coronavirus pandemic . Journal of Public Policy & Marketing , 40 ( 1 ), 101 – 102 . 10.1177/0743915620932150 Google Scholar
- Fahmi, A. , Maqbool, Z. , Amin, F. , & Aslam, M. ( 2023 ). Blockchain knowledge selection under the trapezoidal fermatean fuzzy number . Soft Computing , 27 ( 7 ), 3601 – 3621 . 10.1007/s00500-022-07611-w PubMed Google Scholar
- Fang, C. , & Stone, W. Z. ( 2021 ). An ecosystem for the dairy logistics supply chain with blockchain technology [Conference presentation]. The 2021 International Conference on Electrical, Computer, Communications and Mechatronics Engineering (ICECCME), Mauritius, Mauritius. Google Scholar
- Farooq, M. S. , Riaz, S. , Rehman, I. U. , Khan, M. A. , & Hassan, B. ( 2023 ). A blockchain-based framework to make the rice crop supply chain transparent and reliable in agriculture . Systems , 11 ( 9 ), 476 . 10.3390/systems11090476 Google Scholar
- Feng, H. , Wang, X. , Duan, Y. , Zhang, J. , & Zhang, X. ( 2020 ). Applying blockchain technology to improve agri-food traceability: A review of development methods, benefits and challenges . Journal of Cleaner Production , 260 , 121031. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121031 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Feng, Y. , Yan, W. , Zuo, M. , & Zhang, Q. ( 2022 ). Consortium blockchains based traceability system for chicken product supply chain [Conference presentation]. The MATEC Web of Conferences. 355, 02037. https://doi.org/10.1051/matecconf/202235502037 10.1051/matecconf/202235502037 Google Scholar
- Ferdousi, T. , Gruenbacher, D. , & Scoglio, C. M. ( 2020 ). A permissioned distributed ledger for the US beef cattle supply chain . IEEE Access , 8 , 154833 – 154847 . 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3019000 Google Scholar
- Folha, R. , Times, V. , Carvalho, A. , Araújo, A. , Couto, H. , & Viana, F. ( 2022 ). FoodChain: A food delivery platform based on blockchain for keeping data privacy [Conference presentation]. The International Conference on Database Systems for Advanced Applications (pp. 500 – 504 ). Springer. Google Scholar
- Fu, H. , Zhao, C. , Cheng, C. , & Ma, H. ( 2020 ). Blockchain-based agri-food supply chain management: Case study in China . International Food and Agribusiness Management Review , 23 ( 5 ), 667 – 680 . 10.22434/IFAMR2019.0152 Google Scholar
- Gad, A. G. , Mosa, D. T. , Abualigah, L. , & Abohany, A. A. ( 2022 ). Emerging trends in blockchain technology and applications: A review and outlook . Journal of King Saud University-Computer and Information Sciences , 34 ( 9 ), 6719 – 6742 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.03.007 10.1016/j.jksuci.2022.03.007 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Galvez, J. F. , Mejuto, J. C. , & Simal-Gandara, J. ( 2018 ). Future challenges on the use of blockchain for food traceability analysis . TrAC Trends in Analytical Chemistry , 107 , 222 – 232 . 10.1016/j.trac.2018.08.011 CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Gharehgozli, A. , Iakovou, E. , Chang, Y. , & Swaney, R. ( 2017 ). Trends in global E-food supply chain and implications for transport: Literature review and research directions . Research in Transportation Business & Management , 25 , 2 – 14 . 10.1016/j.rtbm.2017.10.002 Google Scholar
- González-Puetate, I. , Marín Tello, C. L. , & Reyes Pineda, H. ( 2022 ). Agri-food safety optimized by blockchain technology . Revista Facultad Nacional De Agronomía Medellín , 75 ( 1 ), 9839 – 9851 . Google Scholar
- Guo, J. , Cengiz, K. , & Tomar, R. ( 2021 ). An IOT and Blockchain approach for food traceability system in agriculture . Scalable Computing: Practice and Experience , 22 ( 2 ), 127 – 137 . 10.12694/scpe.v22i2.1876 Google Scholar
- Harriman, C. , Diaz-Infante, M. , Loayza, T. , Lee, S. , Detwiler, K. , & Awwad, M. ( 2020 ). Effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the grocery retail supply chains [Conference presentation]. The 5th International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Operations Management, IEOM Society, Michigan, USA. Google Scholar
- Hayati, H. , & Nugraha, I. G. B. B. ( 2018 ). Blockchain based traceability system in food supply chain [Conference presentation]. The 2018 International Seminar on Research of Information Technology and Intelligent Systems (ISRITI), Yogyakarta, Indonesia. Google Scholar
- Hays, T. , Keskinocak, P. , & De López, V. M. ( 2005 ). Strategies and challenges of internet grocery retailing logistics . Applications of supply chain management and e-commerce research (pp. 217 – 252 ). Springer. 10.1007/0-387-23392-X_8 Google Scholar
- Hellani, H. ( 2022 ). Reliable platform using distributed ledger technology for IoT-based industrial environment . Université de Pau et des Pays de l'Adour. Google Scholar
- Hellani, H. , Sliman, L. , Samhat, A. E. , & Exposito, E. ( 2021 ). On blockchain integration with supply chain: Overview on data transparency . Logistics , 5 ( 3 ), 46 . 10.3390/logistics5030046 Google Scholar
- Hidayati, J. , Vamelia, R. , Hammami, J. , & Endri, E. ( 2023 ). Transparent distribution system design of halal beef supply chain . Uncertain Supply Chain Management , 11 ( 1 ), 31 – 40 . 10.5267/j.uscm.2022.12.003 Google Scholar
- Hobbs, J. E. ( 2020 ). Food supply chains during the COVID-19 pandemic . Canadian Journal of Agricultural Economics/Revue Canadienne D'agroeconomie , 68 ( 2 ), 171 – 176 . 10.1111/cjag.12237 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Howson, P. ( 2020 ). Building trust and equity in marine conservation and fisheries supply chain management with blockchain . Marine Policy , 115 , 103873. 10.1016/j.marpol.2020.103873 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Huo, H. , & Rui, Y. ( 2021 ). The assessment of Co stco management strategy in Chinese market based on supply cha in [Conference presentation]. The 2021 International Conference on E-Commerce and E-Management (ICECEM), Dalian, China. Google Scholar
- Ivanov, D. , Dolgui, A. , & Sokolov, B. ( 2019 ). The impact of digital technology and Industry 4.0 on the ripple effect and supply chain risk analytics . International Journal of Production Research , 57 ( 3 ), 829 – 846 . 10.1080/00207543.2018.1488086 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Jin, N. , & Saucier, C. ( 2016 ). ripe.io: Reconnecting the food supply chain . Google Scholar
- Johnson, W. G. ( 2019 ). Blockchain meets genomics: Governance considerations for promoting food safety and public health . Journal of Food Law & Policy , 15 , 74 . Google Scholar
- Kamath, R. ( 2018 ). Food traceability on blockchain: Walmart's pork and mango pilots with IBM . The Journal of the British Blockchain Association , 1 ( 1 ), 1 – 12 . 10.31585/jbba-1-1-(10)2018 Google Scholar
- Kamilaris, A. , Fonts, A. , & Prenafeta-Boldύ, F. X. ( 2019 ). The rise of blockchain technology in agriculture and food supply chains . Trends in Food Science & Technology , 91 , 640 – 652 . 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.07.034 CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Kampan, K. , Tsusaka, T. W. , & Anal, A. K. ( 2022 ). Adoption of blockchain technology for enhanced traceability of livestock-based products . Sustainability , 14 ( 20 ), 13148. 10.3390/su142013148 Google Scholar
- Kasten, J. ( 2019 ). Blockchain application: The dairy supply chain . Journal of Supply Chain Management Systems , 8 ( 1 ), 45 – 54 . Google Scholar
- Katsikouli, P. , Wilde, A. S. , Dragoni, N. , & Høgh-Jensen, H. ( 2021 ). On the benefits and challenges of blockchains for managing food supply chains . Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture , 101 ( 6 ), 2175 – 2181 . 10.1002/jsfa.10883 CAS PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Kawaguchi, N. ( 2019 ). Application of blockchain to supply chain: Flexible blockchain technology . Procedia Computer Science , 164 , 143 – 148 . 10.1016/j.procs.2019.12.166 Google Scholar
- Khanna, A. , Jain, S. , Burgio, A. , Bolshev, V. , & Panchenko, V. ( 2022 ). Blockchain-enabled supply chain platform for Indian dairy industry: Safety and traceability . Foods , 11 ( 17 ), 2716 . 10.3390/foods11172716 CAS PubMed Google Scholar
- Köhler, S. , & Pizzol, M. ( 2020 ). Technology assessment of blockchain-based technologies in the food supply chain . Journal of Cleaner Production , 269 , 122193. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.122193 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Kramer, M. P. , Bitsch, L. , & Hanf, J. ( 2021 ). Blockchain and its impacts on agri-food supply chain network management . Sustainability , 13 ( 4 ), 2168 . 10.3390/su13042168 Google Scholar
- Kravenkit, S. , & So-In, C. ( 2022 ). Blockchain-based traceability system for product recall . IEEE Access , 10 , 95132 – 95150 . 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3204750 Google Scholar
- Kshetri, N. ( 2019 ). Blockchain and the economics of food safety . IEEE IT Professional , 21 ( 3 ), 63 – 66 . 10.1109/MITP.2019.2906761 Google Scholar
- Kshetri, N. ( 2023 ). Blockchains with Chinese characteristics . Blockchain in the global south: Opportunities and challenges for businesses and societies (pp. 83 – 111 ). Springer. 10.1007/978-3-031-33944-8_4 Google Scholar
- Kshetri, N. , & Defranco, J. ( 2020 ). The economics behind food supply blockchains . Computer , 53 ( 12 ), 106 – 110 . 10.1109/MC.2020.3021549 Google Scholar
- Kumar, A. , Liu, R. , & Shan, Z. ( 2020 ). Is blockchain a silver bullet for supply chain management? Technical challenges and research opportunities . Decision Sciences , 51 ( 1 ), 8 – 37 . 10.1111/deci.12396 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Larissa, S. , & Parung, J. ( 2021 ). Designing supply chain models with blockchain technology in the fishing industry in Indonesia . The IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering , 1072 , 012020. 10.1088/1757-899X/1072/1/012020 Google Scholar
- Leow, P. Y. ( 2023 ). Ingredients tracing using blockchain for rapid product recall . UTAR. Google Scholar
- Leung, H. W. , Chapman, A. , & Fadhel, N. F. ( 2021 ). Identifying food fraud using blockchain . The IoTBDS (pp. 185 – 192 ). SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. Google Scholar
- Li, K. , Lee, J.-Y. , & Gharehgozli, A. ( 2023 ). Blockchain in food supply chains: A literature review and synthesis analysis of platforms, benefits and challenges . International Journal of Production Research , 61 ( 11 ), 3527 – 3546 . 10.1080/00207543.2021.1970849 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Lin, X. , Chang, S.-C. , Chou, T.-H. , Chen, S.-C. , & Ruangkanjanases, A. ( 2021 ). Consumers’ intention to adopt blockchain food traceability technology towards organic food products . International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , 18 ( 3 ), 912 . 10.3390/ijerph18030912 PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Liu, H. , Dong, J. , & Ge, S. ( 2021 ). Traceability system for rare Chinese herbal medicines based on blockchain str ucture [Conference presentation]. The 2021 3rd International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Advanced Manufacture (AIAM), Manchester, United Kingdom. Google Scholar
- Longo, F. , Nicoletti, L. , & Padovano, A. ( 2019 ). Estimating the impact of blockchain adoption in the food processing industry and supply chain . International Journal of Food Engineering , 16 ( 5–6 ), 20190109. 10.1515/ijfe-2019-0109 Google Scholar
- Mangla, S. K. , Kazancoglu, Y. , Ekinci, E. , Liu, M. , Özbiltekin, M. , & Sezer, M. D. ( 2021 ). Using system dynamics to analyze the societal impacts of blockchain technology in milk supply chainsrefer . Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review , 149 , 102289. 10.1016/j.tre.2021.102289 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Maouriyan, N. , & Krishna, A. A. ( 2019 ). Notice of v iolation of IEEE publication pri nciples: AQUACHAIN- water supply-chain management using distributed ledger techn ology [Conference presentation]. The 2019 3rd International Conference on Computing and Communications Technologies (ICCCT), Chennai, India. Google Scholar
- Meidayanti, K. , & Arkeman, Y. , & Sugiarto ( 2019 ). Analysis and design of beef supply chain traceability system based on blockchain technology . The IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science , 335 , 012012. 10.1088/1755-1315/335/1/012012 Google Scholar
- Michelson, H. , Boucher, S. , Cheng, X. , Huang, J. , & Jia, X. ( 2018 ). Connecting supermarkets and farms: The role of intermediaries in Walmart China's fresh produce supply chains . Renewable Agriculture and Food Systems , 33 ( 1 ), 47 – 59 . 10.1017/S174217051600051X Google Scholar
- Mirabelli, G. , & Solina, V. ( 2020 ). Blockchain and agricultural supply chains traceability: Research trends and future challenges . Procedia Manufacturing , 42 , 414 – 421 . 10.1016/j.promfg.2020.02.054 Google Scholar
- Miraz, M. H. , Gazi, M. A. I. , & Hasan, M. T. ( 2023 ). Fruits supply chain management using blockchain: A theoretic operation . Journal of Survey in Fisheries Sciences , 10 ( 1S ), 5438 – 5450 . Google Scholar
- Narayanan, A. , Bonneau, J. , Felten, E. , Miller, A. , & Goldfeder, S. ( 2021 ). Bitcoin and cryptocurrency technologies . Curso Elaborado Pela , 1 ( 1 ), 1 – 308 . Google Scholar
- Natanelov, V. , Cao, S. , Foth, M. , & Dulleck, U. ( 2022 ). Blockchain smart contracts for supply chain finance: Mapping the innovation potential in Australia-China beef supply chains . Journal of Industrial Information Integration , 30 , 100389. 10.1016/j.jii.2022.100389 Google Scholar
- Nguyen, H. , & Do, L. ( 2018 ). The adoption of blockchain in food retail supply chain: Case: IBM food trust blockchain and the food retail supply chain in Malta, Autumn , 1 – 158 . Google Scholar
- Niya, S. R. , Dordevic, D. , Hurschler, M. , Grossenbacher, S. , & Stiller, B. ( 2021 ). A blockchain-based supply chain tracing for the Swiss dairy use cas e [Conference presentation]. The 2020 2nd International Conference on Societal Automation (SA), Funchal, Portugal. Google Scholar
- Nurgazina, J. , Pakdeetrakulwong, U. , Moser, T. , & Reiner, G. ( 2021 ). Distributed ledger technology applications in food supply chains: A review of challenges and future research directions . Sustainability , 13 ( 8 ), 4206 . 10.3390/su13084206 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Patel, A. S. , Brahmbhatt, M. N. , Bariya, A. R. , Nayak, J. B. , & Singh, V. K. ( 2023 ). Blockchain technology in food safety and traceability concern to livestock products . Heliyon , 9 ( 6 ), e16526. 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16526 CAS PubMed Google Scholar
- Patro, P. K. , Jayaraman, R. , Salah, K. , & Yaqoob, I. ( 2022 ). Blockchain-based traceability for the fishery supply chain . IEEE Access , 10 , 81134 – 81154 . 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3196162 Google Scholar
- Pearson, S. , May, D. , Leontidis, G. , Swainson, M. , Brewer, S. , Bidaut, L. , Frey, J. G. , Parr, G. , Maull, R. , & Zisman, A. ( 2019 ). Are distributed ledger technologies the panacea for food traceability? Global Food Security , 20 , 145 – 149 . 10.1016/j.gfs.2019.02.002 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Peng, X. , Zhang, X. , Wang, X. , Li, H. , Xu, J. , & Zhao, Z. ( 2022a ). Construction of rice supply chain supervision model driven by blockchain smart contract . Scientific Reports , 12 ( 1 ), 20984. 10.1038/s41598-022-25559-7 CAS PubMed Google Scholar
- Peng, X. , Zhang, X. , Wang, X. , Li, H. , Xu, J. , & Zhao, Z. ( 2022b ). Multi-chain collaboration-based information management and control for the rice supply chain . Agriculture , 12 ( 5 ), 689 . 10.3390/agriculture12050689 Google Scholar
- Peng, X. , Zhang, X. , Wang, X. , Li, H. , Xu, J. , Zhao, Z. , & Wang, Y. ( 2022c ). Research on the cross-chain model of rice supply chain supervision based on parallel blockchain and smart contracts . Foods , 11 ( 9 ), 1269 . 10.3390/foods11091269 CAS PubMed Google Scholar
- Peng, X. , Zhang, X. , Wang, X. , Xu, J. , Li, H. , Zhao, Z. , & Qi, Z. ( 2022 ). A refined supervision model of rice supply chain based on multi-blockchain . Foods , 11 ( 18 ), 2785 . 10.3390/foods11182785 PubMed Google Scholar
- Persaud, T. ( 2022 ). Analyzing Costco's supply chain responsiveness through lean and agile strategies, Major research papers 2021-2022, YorkSpace, York University's Institutional Repository , 1 – 49 . Google Scholar
- Pham, C. , Nguyen, T.-T. , Adamopoulos, A. , & Tait, E. ( 2022 ). Blockchain-enabled traceability in sustainable food supply chains: A case study of the pork industry in Vietnam . Information systems research in Vietnam: A shared vision and new frontiers (pp. 65 – 81 ). Springer. Google Scholar
- Provenance . ( 2024 ). Drive growth with sustainability claims shoppers can trust . https://www.provenance.org/ Google Scholar
- Qian, J. , Ruiz-Garcia, L. , Fan, B. , Villalba, J. I. R. , McCarthy, U. , Zhang, B. , Yu, Q. , & Wu, W. ( 2020 ). Food traceability system from governmental, corporate, and consumer perspectives in the European Union and China: A comparative review . Trends in Food Science & Technology , 99 , 402 – 412 . 10.1016/j.tifs.2020.03.025 CAS Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Queiroz, M. M. , Fosso Wamba, S. , De Bourmont, M. , & Telles, R. ( 2021 ). Blockchain adoption in operations and supply chain management: Empirical evidence from an emerging economy . International Journal of Production Research , 59 ( 20 ), 1 – 17 . 10.1080/00207543.2020.1803511 Google Scholar
- Rafiq, A. , Younus, M. U. , Ali, A. , Hamza, M. , & Ahmed, U. ( 2021 ). Web-based wheat tracker system using blockchain in agriculture . Journal of Agricultural Research , 59 ( 4 ), 389 . Google Scholar
- Rai, A. , Shaikh, S. , & Vishwakarma, R. ( 2021 ). Secure grocery recommendation system using blockchain . Journal on Software Engineering , 16 ( 1 ), 23 . Google Scholar
- Rana, R. L. , Tricase, C. , & De Cesare, L. ( 2021 ). Blockchain technology for a sustainable agri-food supply chain . British Food Journal , 123 ( 11 ), 3471 – 3485 . 10.1108/BFJ-09-2020-0832 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Rathore, S. , Gupta, N. , Rathore, A. S. , & Soni, G. ( 2022 ). Blockchain-based smart wheat supply chain model in Indian context . Agri-food 4.0 (Vol. 27 , pp. 77 – 96 ). Emerald Publishing Limited. 10.1108/S1877-636120220000027006 Google Scholar
- Rejeb, A. ( 2018 ). Halal meat supply chain traceability based on HACCP, blockchain and internet of things . Acta Technica Jaurinensis , 11 ( 1 ), 218 – 247 . 10.14513/actatechjaur.v11.n4.467 Google Scholar
- Rogerson, M. , & Parry, G. C. ( 2020 ). Blockchain: Case studies in food supply chain visibility . Supply Chain Management: An International Journal , 25 ( 5 ), 601 – 614 . 10.1108/SCM-08-2019-0300 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Samanta, S. , & Sarkar, A. ( 2023 ). IoT and blockchain for smart water quality management in future cities: A hyperledger fabric framework for smart water quality management and distribution . Research Square , 1 – 28 . https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3727101/v1 10.21203/rs.3.rs-3727101/v1 Google Scholar
- Sander, F. , Semeijn, J. , & Mahr, D. ( 2018 ). The acceptance of blockchain technology in meat traceability and transparency . British Food Journal , 120 ( 9 ), 2066 – 2079 . 10.1108/BFJ-07-2017-0365 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Saurabh, S. , & Dey, K. ( 2021 ). Blockchain technology adoption, architecture, and sustainable agri-food supply chains . Journal of Cleaner Production , 284 , 124731. 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.124731 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Schahczenski, J. , & Schahczenski, C. ( 2020 ). Blockchain and the resurrection of consumer sovereignty in a sustainable food economy . Journal of Agriculture, Food Systems, and Community Development , 9 ( 3 ), 79 – 84 . Google Scholar
- Sengupta, T. , Narayanamurthy, G. , Moser, R. , Pereira, V. , & Bhattacharjee, D. ( 2021 ). Disruptive technologies for achieving supply chain resilience in COVID-19 era: An implementation case study of satellite imagery and blockchain technologies in fish supply chain . Information Systems Frontiers , 24 , 1107 – 1123 . 10.1007/s10796-021-10228-3 PubMed Google Scholar
- Sharma, A. , Bhatia, T. , Singh, R. K. , & Sharma, A. ( 2024 ). Developing the framework of blockchain-enabled agri-food supply chain . Business Process Management Journal , 30 , 291 – 316 . 10.1108/BPMJ-01-2023-0035 Google Scholar
- Sharma, A. , Sharma, A. , Singh, R. K. , & Bhatia, T. ( 2023 ). Blockchain adoption in agri-food supply chain management: An empirical study of the main drivers using extended UTAUT . Business Process Management Journal , 29 ( 3 ), 737 – 756 . 10.1108/BPMJ-10-2022-0543 Google Scholar
- Sharma, M. , & Kumar, P. ( 2021 ). Adoption of blockchain technology: A case study of Walmart . Blockchain technology and applications for digital marketing (pp. 210 – 225 ). IGI Global. 10.4018/978-1-7998-8081-3.ch013 Google Scholar
- Shingh, S. , Kamalvanshi, V. , Ghimire, S. , & Basyal, S. ( 2020 ). Dairy supply chain system based on blockchain technology . Asian Journal of Economics, Business and Accounting , 14 ( 2 ), 13 – 19 . 10.9734/ajeba/2020/v14i230189 Google Scholar
- Singh, A. , Gutub, A. , Nayyar, A. , & Khan, M. K. ( 2023 ). Redefining food safety traceability system through blockchain: Findings, challenges and open issues . Multimedia Tools and Applications , 82 ( 14 ), 21243 – 21277 . 10.1007/s11042-022-14006-4 PubMed Google Scholar
- Srivastava, A. , Dubey, V. , & Hazela, B. ( 2021 ). Delivering green supply chain using blockchain technology for sustainable environment: A survey . The Emerging Technologies in Data Mining and Information Security: Proceedings of IEMIS 2020 (Vol. 1 , pp. 759 – 768 ). Springer. Google Scholar
- Stewart, B. L. ( 2021 ). Pandemic panic and retail reconfiguration: Consumer and supply chain responses to COVID-19 . Journal of Family & Consumer Sciences , 113 ( 1 ), 7 – 16 . 10.14307/JFCS113.1.7 Google Scholar
- Stranieri, S. , Riccardi, F. , Meuwissen, M. P. M. , & Soregaroli, C. ( 2021 ). Exploring the impact of blockchain on the performance of agri-food supply chains . Food Control , 119 , 107495. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107495 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Sunmola, F. , & Burgess, P. ( 2023 ). Transparency by design for blockchain-based supply chains . Procedia Computer Science , 217 , 1256 – 1265 . 10.1016/j.procs.2022.12.324 Google Scholar
- Suroso, A. I. , Rifai, B. , & Hasanah, N. ( 2021 ). Traceability system in hydroponic vegetables supply chain using blockchain technology . International Journal of Information & Management Sciences , 32 ( 4 ), 347 – 361 . Google Scholar
- Susanty, A. , Puspitasari, N. B. , Rosyada, Z. F. , Pratama, M. A. , & Kurniawan, E. ( 2023 ). Design of blockchain-based halal traceability system applications for halal chicken meat-based food supply chain . International Journal of Information Technology , 16 , 1449 – 1473 . 10.1007/s41870-023-01650-8 Google Scholar
- Swan, M. ( 2015 ). Blockchain: Blueprint for a new economy . O'Reilly Media, Inc. Google Scholar
- Tan, A. , Gligor, D. , & Ngah, A. ( 2022 ). Applying blockchain for halal food traceability . International Journal of Logistics Research and Applications , 25 ( 6 ), 947 – 964 . 10.1080/13675567.2020.1825653 Google Scholar
- Tan, A. , & Ngan, P. T. ( 2020 ). A proposed framework model for dairy supply chain traceability . Sustainable Futures , 2 , 100034. 10.1016/j.sftr.2020.100034 Google Scholar
- Tandon, A. , Dhir, A. , Kaur, P. , Kushwah, S. , & Salo, J. ( 2020 ). Why do people buy organic food? The moderating role of environmental concerns and trust . Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services , 57 , 102247. 10.1016/j.jretconser.2020.102247 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Tao, J. , Dai, H. , Jiang, H. , & Chen, W. ( 2021 ). Dispatch optimisation in O2O on-demand service with crowd-sourced and in-house drivers . International Journal of Production Research , 59 ( 20 ), 6054 – 6068 . 10.1080/00207543.2020.1800120 Google Scholar
- Tao, Q. , Iftekhar, A. , Cai, Z. , & Cui, X. ( 2021 ). Blockchain-based rice supply chain traceability to ensure rice quality and food safety . Preprints.org , 1 – 10 . https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202106.0223.v1 10.20944/preprints202106.0223.v1 Google Scholar
- Tapscott, D. , & Tapscott, A. ( 2016 ). Blockchain revolution: How the technology behind bitcoin is changing money, business, and the world . Penguin. Google Scholar
- Tayal, A. , Solanki, A. , Kondal, R. , Nayyar, A. , Tanwar, S. , & Kumar, N. ( 2021 ). Blockchain-based efficient communication for food supply chain industry: Transparency and traceability analysis for sustainable business . International Journal of Communication Systems , 34 ( 4 ), e4696. 10.1002/dac.4696 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Thangamayan, S. , Pradhan, K. , Loganathan, G. B. , Sitender, S. , Sivamani, S. , & Tesema, M. ( 2023 ). Blockchain-based secure traceable scheme for food supply chain . Journal of Food Quality , 2023 , 1 – 11 . 10.1155/2023/4728840 Google Scholar
- Thapa, S. , Piras, G. , Thapa, S. , Rimal, P. , Thapa, A. , & Adhikari, K. ( 2021 ). Blockchain-based secured traceability system for the agriculture supply chain of ginger in Nepal: A case study . Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science , 6 , 391 – 396 . 10.26832/24566632.2021.0603020 Google Scholar
- Tiscini, R. , Testarmata, S. , Ciaburri, M. , & Ferrari, E. ( 2020 ). The blockchain as a sustainable business model innovation . Management Decision , 58 ( 8 ), 1621 – 1642 . 10.1108/MD-09-2019-1281 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Tiwari, U. ( 2020 ). Application of blockchain in agri-food supply chain . Britain International of Exact Sciences (BIoEx) Journal , 2 ( 2 ), 574 – 589 . 10.33258/bioex.v2i2.233 Google Scholar
- United Nations Environment Programme . ( 2024 ). The United Nations Environment Programme's (UNEP) 2024 food waste index report . https://www.biocycle.net/2024-food-waste-index/ Google Scholar
- Varavallo, G. , Caragnano, G. , Bertone, F. , Vernetti-Prot, L. , & Terzo, O. ( 2022 ). Traceability platform based on green blockchain: An application case study in dairy supply chain . Sustainability , 14 ( 6 ), 3321 . 10.3390/su14063321 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Wang, J. , Zhang, X. , Xu, J. , Wang, X. , Li, H. , Zhao, Z. , & Kong, J. ( 2022 ). Blockchain-based information supervision model for rice supply chains . Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience , 2022 , 2914571. 10.1155/2022/2914571 PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Wang, Y. , Chen, C. H. , & Zghari-Sales, A. ( 2021 ). Designing a blockchain enabled supply chain . International Journal of Production Research , 59 ( 5 ), 1450 – 1475 . 10.1080/00207543.2020.1824086 Google Scholar
- Xiao, G. , Samian, N. , Faizal, M. F. M. , As'ad, M. A. Z. M. , Fadzil, M. F. M. , Abdullah, A. , Seah, W. K. G. , Ishak, M. , & Hermadi, I. ( 2024 ). A framework for blockchain and internet of things integration in improving food security in the food supply chain . Journal of Advanced Research in Applied Sciences and Engineering Technology , 34 ( 1 ), 24 – 37 . 10.37934/araset.34.1.2437 Google Scholar
- Xu, X. , Weber, I. , Staples, M. , Xu, X. , Weber, I. , & Staples, M. ( 2019 ). Case study: AgriDigital: Blockchain technology in the trade and finance of agriculture supply chains . Architecture for blockchain ap plications (pp. 239 – 255 ). Springer. 10.1007/978-3-030-03035-3_12 Google Scholar
- Yadav, V. S. , Singh, A. R. , Raut, R. D. , & Govindarajan, U. H. ( 2020 ). Blockchain technology adoption barriers in the Indian agricultural supply chain: An integrated approach . Resources, Conservation and Recycling , 161 , 104877. 10.1016/j.resconrec.2020.104877 Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Yakubu, B. M. , Latif, R. , Yakubu, A. , Khan, M. I. , & Magashi, A. I. ( 2022 ). RiceChain: Secure and traceable rice supply chain framework using blockchain technology . PeerJ Computer Science , 8 , e801. 10.7717/peerj-cs.801 PubMed Google Scholar
- Yang, X. , Li, M. , Yu, H. , Wang, M. , Xu, D. , & Sun, C. ( 2021 ). A trusted blockchain-based traceability system for fruit and vegetable agricultural products . IEEE Access , 9 , 36282 – 36293 . 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3062845 Google Scholar
- Yik, M. H.-Y. , Wong, V. C.-W. T. , Wong, T.-H. , & Shaw, P.-C. ( 2021 ). HerBChain, a blockchain-based informative platform for quality assurance and quality control of herbal products . Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine , 11 ( 6 ), 598 – 600 . 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.07.005 CAS PubMed Google Scholar
- Yontar, E. ( 2023 ). Critical success factor analysis of blockchain technology in agri-food supply chain management: A circular economy perspective . Journal of Environmental Management , 330 , 117173. 10.1016/j.jenvman.2022.117173 PubMed Web of Science® Google Scholar
- Zhang, C. , Gong, Y. , & Brown, S. ( 2023 ). Case analysis: FairChain . Blockchain applications in food supply chain management: Case studies and implications (pp. 175 – 211 ). Springer. 10.1007/978-3-031-27054-3_6 Google Scholar
- Zhang, Y. , Chen, L. , Battino, M. , Farag, M. A. , Xiao, J. , Simal-Gandara, J. , Gao, H. , & Jiang, W. ( 2022 ). Blockchain: An emerging novel technology to upgrade the current fresh fruit supply chain . Trends in Food Science & Technology , 124 , 1 – 12 . 10.1016/j.tifs.2022.03.030 CAS Google Scholar
- Zhang, Y. , Wu, X. , Ge, H. , Jiang, Y. , Sun, Z. , Ji, X. , Jia, Z. , & Cui, G. ( 2023 ). A blockchain-based traceability model for grain and oil food supply chain . Foods , 12 ( 17 ), 3235 . 10.3390/foods12173235 PubMed Google Scholar
- Zhao, G. , Liu, S. , Lopez, C. , Lu, H. , Elgueta, S. , Chen, H. , & Boshkoska, B. M. ( 2019 ). Blockchain technology in agri-food value chain management: A synthesis of applications, challenges and future research directions . Computers in Industry , 109 , 83 – 99 . 10.1016/j.compind.2019.04.002 Web of Science® Google Scholar

Volume 23 , Issue 5
September 2024
Information

Log in to Wiley Online Library
Ift members, log in to access: journal of food science, comprehensive reviews in food science and food safety, change password, your password must have 10 characters or more:.
- a lower case character,
- an upper case character,
- a special character
Password Changed Successfully
Your password has been changed
Create a new account
Forgot your password.
Enter your email address below.
Please check your email for instructions on resetting your password. If you do not receive an email within 10 minutes, your email address may not be registered, and you may need to create a new Wiley Online Library account.
Request Username
Can't sign in? Forgot your username?
Enter your email address below and we will send you your username
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to retrieve your username
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on May 8, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyze the case, other interesting articles.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
TipIf your research is more practical in nature and aims to simultaneously investigate an issue as you solve it, consider conducting action research instead.
Unlike quantitative or experimental research , a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
Example of an outlying case studyIn the 1960s the town of Roseto, Pennsylvania was discovered to have extremely low rates of heart disease compared to the US average. It became an important case study for understanding previously neglected causes of heart disease.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience or phenomenon.
Example of a representative case studyIn the 1920s, two sociologists used Muncie, Indiana as a case study of a typical American city that supposedly exemplified the changing culture of the US at the time.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews , observations , and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data.
Example of a mixed methods case studyFor a case study of a wind farm development in a rural area, you could collect quantitative data on employment rates and business revenue, collect qualitative data on local people’s perceptions and experiences, and analyze local and national media coverage of the development.
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis , with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyze its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Normal distribution
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Ecological validity
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Case Study? | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved September 2, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/case-study/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, primary vs. secondary sources | difference & examples, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is action research | definition & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
What Is a Case Study?
Weighing the pros and cons of this method of research
Verywell / Colleen Tighe
- Pros and Cons
What Types of Case Studies Are Out There?
Where do you find data for a case study, how do i write a psychology case study.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
The point of a case study is to learn as much as possible about an individual or group so that the information can be generalized to many others. Unfortunately, case studies tend to be highly subjective, and it is sometimes difficult to generalize results to a larger population.
While case studies focus on a single individual or group, they follow a format similar to other types of psychology writing. If you are writing a case study, we got you—here are some rules of APA format to reference.
At a Glance
A case study, or an in-depth study of a person, group, or event, can be a useful research tool when used wisely. In many cases, case studies are best used in situations where it would be difficult or impossible for you to conduct an experiment. They are helpful for looking at unique situations and allow researchers to gather a lot of˜ information about a specific individual or group of people. However, it's important to be cautious of any bias we draw from them as they are highly subjective.
What Are the Benefits and Limitations of Case Studies?
A case study can have its strengths and weaknesses. Researchers must consider these pros and cons before deciding if this type of study is appropriate for their needs.
One of the greatest advantages of a case study is that it allows researchers to investigate things that are often difficult or impossible to replicate in a lab. Some other benefits of a case study:
- Allows researchers to capture information on the 'how,' 'what,' and 'why,' of something that's implemented
- Gives researchers the chance to collect information on why one strategy might be chosen over another
- Permits researchers to develop hypotheses that can be explored in experimental research
On the other hand, a case study can have some drawbacks:
- It cannot necessarily be generalized to the larger population
- Cannot demonstrate cause and effect
- It may not be scientifically rigorous
- It can lead to bias
Researchers may choose to perform a case study if they want to explore a unique or recently discovered phenomenon. Through their insights, researchers develop additional ideas and study questions that might be explored in future studies.
It's important to remember that the insights from case studies cannot be used to determine cause-and-effect relationships between variables. However, case studies may be used to develop hypotheses that can then be addressed in experimental research.
Case Study Examples
There have been a number of notable case studies in the history of psychology. Much of Freud's work and theories were developed through individual case studies. Some great examples of case studies in psychology include:
- Anna O : Anna O. was a pseudonym of a woman named Bertha Pappenheim, a patient of a physician named Josef Breuer. While she was never a patient of Freud's, Freud and Breuer discussed her case extensively. The woman was experiencing symptoms of a condition that was then known as hysteria and found that talking about her problems helped relieve her symptoms. Her case played an important part in the development of talk therapy as an approach to mental health treatment.
- Phineas Gage : Phineas Gage was a railroad employee who experienced a terrible accident in which an explosion sent a metal rod through his skull, damaging important portions of his brain. Gage recovered from his accident but was left with serious changes in both personality and behavior.
- Genie : Genie was a young girl subjected to horrific abuse and isolation. The case study of Genie allowed researchers to study whether language learning was possible, even after missing critical periods for language development. Her case also served as an example of how scientific research may interfere with treatment and lead to further abuse of vulnerable individuals.
Such cases demonstrate how case research can be used to study things that researchers could not replicate in experimental settings. In Genie's case, her horrific abuse denied her the opportunity to learn a language at critical points in her development.
This is clearly not something researchers could ethically replicate, but conducting a case study on Genie allowed researchers to study phenomena that are otherwise impossible to reproduce.
There are a few different types of case studies that psychologists and other researchers might use:
- Collective case studies : These involve studying a group of individuals. Researchers might study a group of people in a certain setting or look at an entire community. For example, psychologists might explore how access to resources in a community has affected the collective mental well-being of those who live there.
- Descriptive case studies : These involve starting with a descriptive theory. The subjects are then observed, and the information gathered is compared to the pre-existing theory.
- Explanatory case studies : These are often used to do causal investigations. In other words, researchers are interested in looking at factors that may have caused certain things to occur.
- Exploratory case studies : These are sometimes used as a prelude to further, more in-depth research. This allows researchers to gather more information before developing their research questions and hypotheses .
- Instrumental case studies : These occur when the individual or group allows researchers to understand more than what is initially obvious to observers.
- Intrinsic case studies : This type of case study is when the researcher has a personal interest in the case. Jean Piaget's observations of his own children are good examples of how an intrinsic case study can contribute to the development of a psychological theory.
The three main case study types often used are intrinsic, instrumental, and collective. Intrinsic case studies are useful for learning about unique cases. Instrumental case studies help look at an individual to learn more about a broader issue. A collective case study can be useful for looking at several cases simultaneously.
The type of case study that psychology researchers use depends on the unique characteristics of the situation and the case itself.
There are a number of different sources and methods that researchers can use to gather information about an individual or group. Six major sources that have been identified by researchers are:
- Archival records : Census records, survey records, and name lists are examples of archival records.
- Direct observation : This strategy involves observing the subject, often in a natural setting . While an individual observer is sometimes used, it is more common to utilize a group of observers.
- Documents : Letters, newspaper articles, administrative records, etc., are the types of documents often used as sources.
- Interviews : Interviews are one of the most important methods for gathering information in case studies. An interview can involve structured survey questions or more open-ended questions.
- Participant observation : When the researcher serves as a participant in events and observes the actions and outcomes, it is called participant observation.
- Physical artifacts : Tools, objects, instruments, and other artifacts are often observed during a direct observation of the subject.
If you have been directed to write a case study for a psychology course, be sure to check with your instructor for any specific guidelines you need to follow. If you are writing your case study for a professional publication, check with the publisher for their specific guidelines for submitting a case study.
Here is a general outline of what should be included in a case study.
Section 1: A Case History
This section will have the following structure and content:
Background information : The first section of your paper will present your client's background. Include factors such as age, gender, work, health status, family mental health history, family and social relationships, drug and alcohol history, life difficulties, goals, and coping skills and weaknesses.
Description of the presenting problem : In the next section of your case study, you will describe the problem or symptoms that the client presented with.
Describe any physical, emotional, or sensory symptoms reported by the client. Thoughts, feelings, and perceptions related to the symptoms should also be noted. Any screening or diagnostic assessments that are used should also be described in detail and all scores reported.
Your diagnosis : Provide your diagnosis and give the appropriate Diagnostic and Statistical Manual code. Explain how you reached your diagnosis, how the client's symptoms fit the diagnostic criteria for the disorder(s), or any possible difficulties in reaching a diagnosis.
Section 2: Treatment Plan
This portion of the paper will address the chosen treatment for the condition. This might also include the theoretical basis for the chosen treatment or any other evidence that might exist to support why this approach was chosen.
- Cognitive behavioral approach : Explain how a cognitive behavioral therapist would approach treatment. Offer background information on cognitive behavioral therapy and describe the treatment sessions, client response, and outcome of this type of treatment. Make note of any difficulties or successes encountered by your client during treatment.
- Humanistic approach : Describe a humanistic approach that could be used to treat your client, such as client-centered therapy . Provide information on the type of treatment you chose, the client's reaction to the treatment, and the end result of this approach. Explain why the treatment was successful or unsuccessful.
- Psychoanalytic approach : Describe how a psychoanalytic therapist would view the client's problem. Provide some background on the psychoanalytic approach and cite relevant references. Explain how psychoanalytic therapy would be used to treat the client, how the client would respond to therapy, and the effectiveness of this treatment approach.
- Pharmacological approach : If treatment primarily involves the use of medications, explain which medications were used and why. Provide background on the effectiveness of these medications and how monotherapy may compare with an approach that combines medications with therapy or other treatments.
This section of a case study should also include information about the treatment goals, process, and outcomes.
When you are writing a case study, you should also include a section where you discuss the case study itself, including the strengths and limitiations of the study. You should note how the findings of your case study might support previous research.
In your discussion section, you should also describe some of the implications of your case study. What ideas or findings might require further exploration? How might researchers go about exploring some of these questions in additional studies?
Need More Tips?
Here are a few additional pointers to keep in mind when formatting your case study:
- Never refer to the subject of your case study as "the client." Instead, use their name or a pseudonym.
- Read examples of case studies to gain an idea about the style and format.
- Remember to use APA format when citing references .
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011;11:100.
Crowe S, Cresswell K, Robertson A, Huby G, Avery A, Sheikh A. The case study approach . BMC Med Res Methodol . 2011 Jun 27;11:100. doi:10.1186/1471-2288-11-100
Gagnon, Yves-Chantal. The Case Study as Research Method: A Practical Handbook . Canada, Chicago Review Press Incorporated DBA Independent Pub Group, 2010.
Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research and Applications: Design and Methods . United States, SAGE Publications, 2017.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
How to Write a Case Study: Bookmarkable Guide & Template
Published: July 18, 2024
Earning the trust of prospective customers can be a major challenge. Before you can expect to earn their business, you’ll need to demonstrate your ability to deliver on the promises of your product or service. The best way to win new business is with cold, hard proof.

A great way to prove your worth is through a compelling case study. HubSpot’s 2024 State of Marketing report found that case studies are so captivating that they were the fifth most commonly used type of content that marketers relied on.
That statistic still holds true in Forbes Advisor’s 2024 study, which adds that 78% of B2B businesses report using case studies and customer stories because they are “ crucial for demonstrating real-world value. ”
Having written these ever more frequently over the past ten years, I hope to serve as your guide through a process that can feel daunting, but I promise is worth the effort. Below, I'll walk you through what a case study is, how to prepare for writing one, what to include in it, and how it can be an effective tactic.
Table of Contents
Case Study Definition
- Why Write a Case Study?
- How Long Should a Case Study Be?
Case Study Templates
How to write a case study, case study format, business case study examples.

Free Case Study Templates
Showcase your company's success using these three free case study templates.
- Data-Driven Case Study Template
- Product-Specific Case Study Template
- General Case Study Template
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
A case study is coverage of a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc.
In professional settings, it‘s common for a case study to tell the story of a successful business partnership between a vendor and a client.
Perhaps the success you’re highlighting is in the number of leads your client generated, customers closed, or revenue gained. Any one of these key performance indicators (KPIs) are examples of your company's services in action.
When done correctly, these examples of your work can chronicle the positive impact your business has on existing or previous customers, helping you attract new clients.
Why write a case study?
I know, it sounds like a huge endeavor — is it really worth it?
The truth is that while case studies are a huge undertaking, they are powerful marketing tools that allow you to demonstrate the value of your product to potential customers using real-world examples.
Here are a few reasons why you should write case studies.
1. Explain complex topics or concepts.
Case studies give you the space to break down complex concepts, ideas, and strategies, showing how they can be applied in a practical way.
You can use real-world examples, like an existing client, and use their story to create a compelling narrative that demonstrates how your product solved their issue. Most importantly, it explains how those strategies can be repeated to help other customers get similar, successful results.
2. Show expertise.
Case studies are a great way to demonstrate your knowledge and expertise on a given topic or industry. This is where you get the opportunity to show off your problem-solving skills and how you’ve generated successful outcomes for clients you’ve worked with.
3. Build trust and credibility.
In addition to showing off the attributes above, case studies are an excellent way to build credibility. They’re often filled with data and thoroughly researched, which shows readers you’ve done your homework.
A robust case study instills confidence in the solutions you present because the reader has now vicariously experienced the problem — and they followed, step-by-step, what it took to solve it. These elements work together, enabling you to build trust with potential customers.
4. Create social proof.
Using existing clients that have seen success working with your brand builds social proof .
People are more likely to choose your brand if they know that others have found success working with you. Case studies do just that — put your success on display for potential customers to see.
All of these attributes play together like an orchestra to help you gain more clients. Afterward, the case study acts as a reference. You can pull quotes from customers that were featured in these studies to repurpose them in other marketing content.
How long should a case study be?
Now that you’re more acquainted with the benefits of producing a case study, let’s explore how long these documents should be.
The length of a case study will vary depending on the complexity of the project or topic discussed. However, as a general guideline, case studies typically range from 500 to 1,500 words.
Whatever length you choose, it should provide a clear understanding of the challenge, the solution you implemented, and the results achieved.
This may be easier said than done, but it‘s important to strike a balance between providing enough detail to make the case study informative and concise enough to keep the reader’s interest.
The primary goal here is to effectively communicate the key points and takeaways of the case study. It’s worth noting that this shouldn’t be a wall of text. Make it attractive to dive into by using headings, subheadings, bullet points, charts, and other graphics to break up the content and make it more scannable for readers.
I’ve also seen more and more brands incorporate video elements into case studies listed on their site for a more engaging experience, which is highly recommended given that video is currently the best performing marketing content format.
In terms of the interview structure, I recommend categorizing the questions in a way that the answers flow into six specific sections that will mirror a successful case study format. Combined, they'll allow you to gather enough information to put together a rich, comprehensive study.
Open with the customer's business.
The goal of this section is to generate a better understanding of the company's current challenges and goals, plus how they fit into the landscape of their industry. Sample questions might include:
- How long have you been in business?
- How many employees do you have?
- What are some of the objectives of your department at this time?
Cite a problem or pain point.
To tell a compelling story, you need context that helps match the customer's needs with your solution. Sample questions might include:
- What challenges and objectives led you to look for a solution?
- What might have happened if you did not identify a solution?
- Did you explore other solutions before this that did not work out? If so, what happened?
Discuss the decision process.
Exploring how the customer decided to work with you helps to guide potential customers through their own decision-making processes.
Sample questions might include:
- How did you hear about our product or service?
- Who was involved in the selection process?
- What was most important to you when evaluating your options?
Explain how a solution was implemented.
The focus here should be placed on the customer's experience during the onboarding process. Sample questions might include:
- How long did it take to get up and running?
- Did that meet your expectations?
- Who was involved in the process?
Explain how the solution works.
The goal of this section is to better understand how the customer is using your product or service. Sample questions might include:
- Is there a particular aspect of the product or service that you rely on most?
- Who is using the product or service?
End with the results.
In this section, you want to uncover impressive measurable outcomes — the more numbers, the better. Sample questions might include:
- How is the product or service helping you save time and increase productivity?
- In what ways does that enhance your competitive advantage?
- How much have you increased metrics X, Y, and Z?
It’s a smart idea to send a copy of your interview questions to your subject ahead of time so they can prepare strong answers and collect the numerical data you need from them.
10. Lay out your case study format.
When it comes time to take all of the information you‘ve collected and actually turn it into something useful, it’s easy to feel overwhelmed. I always do, but I also know that it works out in the end, so I just jump on in and work it through.
So where should you start? What should you include? What's the best way to structure it?
It‘s important to first understand that there is no one-size-fits-all when it comes to the ways you can present a case study.
They can be very visual, which you’ll see in some of the examples we've included below, and can sometimes be communicated through video or photos with a bit of accompanying text.
Here are the sections I’d suggest, and I'll cover these in more detail after #11 below:
- Title. Keep it short. Develop a succinct but interesting project name you can give the work you did with your subject.
- Subtitle. Use this copy to briefly elaborate on the accomplishment. What was done? The case study itself will explain how you got there.
- Executive Summary . A 2-4 sentence summary of the entire story. You'll want to follow it with 2-3 bullet points that display metrics showcasing success.
- About the Subject. An introduction to the person or company you served, which can be pulled from a LinkedIn Business profile or client website.
- Challenges and Objectives. A 2-3 paragraph description of the customer's challenges, before using your product or service. This section should also include the goals or objectives the customer set out to achieve.
- How Product/Service Helped. A 2-3 paragraph section that describes how your product or service provided a solution to their problem.
- Results. A 2-3 paragraph testimonial that proves how your product or service specifically benefited the person or company and helped achieve its goals. Include numbers to quantify your contributions.
- Supporting Visuals or Quotes. Pick one or two powerful quotes that you would feature at the bottom of the sections above, as well as a visual that supports the story you are telling.
- Future Plans. Everyone likes an epilogue. Comment on what's ahead for your case study subject, whether or not those plans involve you.
- Call-to-Action (CTA). Not every case study needs a CTA, but putting a passive one at the end of your case study can encourage your readers to take an action on your website after learning about the work you've done.
When laying out your case study, focus on conveying the information you've gathered in the most clear and concise way possible.
Make it easy to scan and comprehend, and be sure to provide an attractive call-to-action at the bottom — that should provide readers an opportunity to learn more about your product or service.
11. Publish and promote your case study.
Once you‘ve completed your case study, it’s time to publish and promote it.
Some case study formats have pretty obvious promotional outlets — a video case study can go on YouTube, just as an infographic case study can go on Pinterest.
But there are still other ways to publish and promote your case study. Here are a couple of ideas.
Lead Gen in a Blog Post
As stated earlier, written case studies make terrific lead-generators if you convert them into a downloadable format, like a PDF.
To generate leads from your case study, consider writing a blog post that tells an abbreviated story of your client‘s success and asking readers to fill out a form with their name and email address if they’d like to read the rest in your PDF.
Then, promote this blog post on social media, through a Facebook post or a tweet.
Published as a Page on Your Website
As a growing business, you might need to display your case study out in the open to gain the trust of your target audience.
Rather than gating it behind a landing page, publish your case study to its own page on your website, and direct people to it from your homepage with a “Case Studies” or “Testimonials” button along your homepage's top navigation bar.
The traditional case study format includes the following parts: a title and subtitle, a client profile, a summary of the customer’s challenges and objectives, an account of how your solution helped, and a description of the results. You might also want to include supporting visuals and quotes, future plans, and calls-to-action.

27 Case Study Examples Every Marketer Should See
![case study plan definition 7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]](https://knowledge.hubspot.com/hubfs/contenttypes.webp)
7 Pieces of Content Your Audience Really Wants to See [New Data]

How to Market an Ebook: 21 Ways to Promote Your Content Offers
![case study plan definition How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]](https://www.hubspot.com/hubfs/listicle-1.jpg)
How to Write a Listicle [+ Examples and Ideas]
![case study plan definition What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]](https://53.fs1.hubspotusercontent-na1.net/hubfs/53/business%20whitepaper.jpg)
What Is a White Paper? [FAQs]

What is an Advertorial? 8 Examples to Help You Write One

How to Create Marketing Offers That Don't Fall Flat

20 Creative Ways To Repurpose Content

16 Important Ways to Use Case Studies in Your Marketing

11 Ways to Make Your Blog Post Interactive
Showcase your company's success using these free case study templates.
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
- What is qualitative research?
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
What is a case study?
Applications for case study research, what is a good case study, process of case study design, benefits and limitations of case studies.
- Ethnographical research
- Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
Case studies
Case studies are essential to qualitative research , offering a lens through which researchers can investigate complex phenomena within their real-life contexts. This chapter explores the concept, purpose, applications, examples, and types of case studies and provides guidance on how to conduct case study research effectively.

Whereas quantitative methods look at phenomena at scale, case study research looks at a concept or phenomenon in considerable detail. While analyzing a single case can help understand one perspective regarding the object of research inquiry, analyzing multiple cases can help obtain a more holistic sense of the topic or issue. Let's provide a basic definition of a case study, then explore its characteristics and role in the qualitative research process.
Definition of a case study
A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods of research. The specific case or cases being studied can be a single person, group, or organization – demarcating what constitutes a relevant case worth studying depends on the researcher and their research question .
Among qualitative research methods , a case study relies on multiple sources of evidence, such as documents, artifacts, interviews , or observations , to present a complete and nuanced understanding of the phenomenon under investigation. The objective is to illuminate the readers' understanding of the phenomenon beyond its abstract statistical or theoretical explanations.
Characteristics of case studies
Case studies typically possess a number of distinct characteristics that set them apart from other research methods. These characteristics include a focus on holistic description and explanation, flexibility in the design and data collection methods, reliance on multiple sources of evidence, and emphasis on the context in which the phenomenon occurs.
Furthermore, case studies can often involve a longitudinal examination of the case, meaning they study the case over a period of time. These characteristics allow case studies to yield comprehensive, in-depth, and richly contextualized insights about the phenomenon of interest.
The role of case studies in research
Case studies hold a unique position in the broader landscape of research methods aimed at theory development. They are instrumental when the primary research interest is to gain an intensive, detailed understanding of a phenomenon in its real-life context.
In addition, case studies can serve different purposes within research - they can be used for exploratory, descriptive, or explanatory purposes, depending on the research question and objectives. This flexibility and depth make case studies a valuable tool in the toolkit of qualitative researchers.
Remember, a well-conducted case study can offer a rich, insightful contribution to both academic and practical knowledge through theory development or theory verification, thus enhancing our understanding of complex phenomena in their real-world contexts.
What is the purpose of a case study?
Case study research aims for a more comprehensive understanding of phenomena, requiring various research methods to gather information for qualitative analysis . Ultimately, a case study can allow the researcher to gain insight into a particular object of inquiry and develop a theoretical framework relevant to the research inquiry.
Why use case studies in qualitative research?
Using case studies as a research strategy depends mainly on the nature of the research question and the researcher's access to the data.
Conducting case study research provides a level of detail and contextual richness that other research methods might not offer. They are beneficial when there's a need to understand complex social phenomena within their natural contexts.
The explanatory, exploratory, and descriptive roles of case studies
Case studies can take on various roles depending on the research objectives. They can be exploratory when the research aims to discover new phenomena or define new research questions; they are descriptive when the objective is to depict a phenomenon within its context in a detailed manner; and they can be explanatory if the goal is to understand specific relationships within the studied context. Thus, the versatility of case studies allows researchers to approach their topic from different angles, offering multiple ways to uncover and interpret the data .
The impact of case studies on knowledge development
Case studies play a significant role in knowledge development across various disciplines. Analysis of cases provides an avenue for researchers to explore phenomena within their context based on the collected data.

This can result in the production of rich, practical insights that can be instrumental in both theory-building and practice. Case studies allow researchers to delve into the intricacies and complexities of real-life situations, uncovering insights that might otherwise remain hidden.
Types of case studies
In qualitative research , a case study is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Depending on the nature of the research question and the specific objectives of the study, researchers might choose to use different types of case studies. These types differ in their focus, methodology, and the level of detail they provide about the phenomenon under investigation.
Understanding these types is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach for your research project and effectively achieving your research goals. Let's briefly look at the main types of case studies.
Exploratory case studies
Exploratory case studies are typically conducted to develop a theory or framework around an understudied phenomenon. They can also serve as a precursor to a larger-scale research project. Exploratory case studies are useful when a researcher wants to identify the key issues or questions which can spur more extensive study or be used to develop propositions for further research. These case studies are characterized by flexibility, allowing researchers to explore various aspects of a phenomenon as they emerge, which can also form the foundation for subsequent studies.

Descriptive case studies
Descriptive case studies aim to provide a complete and accurate representation of a phenomenon or event within its context. These case studies are often based on an established theoretical framework, which guides how data is collected and analyzed. The researcher is concerned with describing the phenomenon in detail, as it occurs naturally, without trying to influence or manipulate it.
Explanatory case studies
Explanatory case studies are focused on explanation - they seek to clarify how or why certain phenomena occur. Often used in complex, real-life situations, they can be particularly valuable in clarifying causal relationships among concepts and understanding the interplay between different factors within a specific context.

Intrinsic, instrumental, and collective case studies
These three categories of case studies focus on the nature and purpose of the study. An intrinsic case study is conducted when a researcher has an inherent interest in the case itself. Instrumental case studies are employed when the case is used to provide insight into a particular issue or phenomenon. A collective case study, on the other hand, involves studying multiple cases simultaneously to investigate some general phenomena.
Each type of case study serves a different purpose and has its own strengths and challenges. The selection of the type should be guided by the research question and objectives, as well as the context and constraints of the research.
The flexibility, depth, and contextual richness offered by case studies make this approach an excellent research method for various fields of study. They enable researchers to investigate real-world phenomena within their specific contexts, capturing nuances that other research methods might miss. Across numerous fields, case studies provide valuable insights into complex issues.
Critical information systems research
Case studies provide a detailed understanding of the role and impact of information systems in different contexts. They offer a platform to explore how information systems are designed, implemented, and used and how they interact with various social, economic, and political factors. Case studies in this field often focus on examining the intricate relationship between technology, organizational processes, and user behavior, helping to uncover insights that can inform better system design and implementation.
Health research
Health research is another field where case studies are highly valuable. They offer a way to explore patient experiences, healthcare delivery processes, and the impact of various interventions in a real-world context.

Case studies can provide a deep understanding of a patient's journey, giving insights into the intricacies of disease progression, treatment effects, and the psychosocial aspects of health and illness.
Asthma research studies
Specifically within medical research, studies on asthma often employ case studies to explore the individual and environmental factors that influence asthma development, management, and outcomes. A case study can provide rich, detailed data about individual patients' experiences, from the triggers and symptoms they experience to the effectiveness of various management strategies. This can be crucial for developing patient-centered asthma care approaches.
Other fields
Apart from the fields mentioned, case studies are also extensively used in business and management research, education research, and political sciences, among many others. They provide an opportunity to delve into the intricacies of real-world situations, allowing for a comprehensive understanding of various phenomena.
Case studies, with their depth and contextual focus, offer unique insights across these varied fields. They allow researchers to illuminate the complexities of real-life situations, contributing to both theory and practice.
Whatever field you're in, ATLAS.ti puts your data to work for you
Download a free trial of ATLAS.ti to turn your data into insights.
Understanding the key elements of case study design is crucial for conducting rigorous and impactful case study research. A well-structured design guides the researcher through the process, ensuring that the study is methodologically sound and its findings are reliable and valid. The main elements of case study design include the research question , propositions, units of analysis, and the logic linking the data to the propositions.
The research question is the foundation of any research study. A good research question guides the direction of the study and informs the selection of the case, the methods of collecting data, and the analysis techniques. A well-formulated research question in case study research is typically clear, focused, and complex enough to merit further detailed examination of the relevant case(s).
Propositions
Propositions, though not necessary in every case study, provide a direction by stating what we might expect to find in the data collected. They guide how data is collected and analyzed by helping researchers focus on specific aspects of the case. They are particularly important in explanatory case studies, which seek to understand the relationships among concepts within the studied phenomenon.
Units of analysis
The unit of analysis refers to the case, or the main entity or entities that are being analyzed in the study. In case study research, the unit of analysis can be an individual, a group, an organization, a decision, an event, or even a time period. It's crucial to clearly define the unit of analysis, as it shapes the qualitative data analysis process by allowing the researcher to analyze a particular case and synthesize analysis across multiple case studies to draw conclusions.
Argumentation
This refers to the inferential model that allows researchers to draw conclusions from the data. The researcher needs to ensure that there is a clear link between the data, the propositions (if any), and the conclusions drawn. This argumentation is what enables the researcher to make valid and credible inferences about the phenomenon under study.
Understanding and carefully considering these elements in the design phase of a case study can significantly enhance the quality of the research. It can help ensure that the study is methodologically sound and its findings contribute meaningful insights about the case.
Ready to jumpstart your research with ATLAS.ti?
Conceptualize your research project with our intuitive data analysis interface. Download a free trial today.
Conducting a case study involves several steps, from defining the research question and selecting the case to collecting and analyzing data . This section outlines these key stages, providing a practical guide on how to conduct case study research.
Defining the research question
The first step in case study research is defining a clear, focused research question. This question should guide the entire research process, from case selection to analysis. It's crucial to ensure that the research question is suitable for a case study approach. Typically, such questions are exploratory or descriptive in nature and focus on understanding a phenomenon within its real-life context.
Selecting and defining the case
The selection of the case should be based on the research question and the objectives of the study. It involves choosing a unique example or a set of examples that provide rich, in-depth data about the phenomenon under investigation. After selecting the case, it's crucial to define it clearly, setting the boundaries of the case, including the time period and the specific context.
Previous research can help guide the case study design. When considering a case study, an example of a case could be taken from previous case study research and used to define cases in a new research inquiry. Considering recently published examples can help understand how to select and define cases effectively.
Developing a detailed case study protocol
A case study protocol outlines the procedures and general rules to be followed during the case study. This includes the data collection methods to be used, the sources of data, and the procedures for analysis. Having a detailed case study protocol ensures consistency and reliability in the study.
The protocol should also consider how to work with the people involved in the research context to grant the research team access to collecting data. As mentioned in previous sections of this guide, establishing rapport is an essential component of qualitative research as it shapes the overall potential for collecting and analyzing data.
Collecting data
Gathering data in case study research often involves multiple sources of evidence, including documents, archival records, interviews, observations, and physical artifacts. This allows for a comprehensive understanding of the case. The process for gathering data should be systematic and carefully documented to ensure the reliability and validity of the study.
Analyzing and interpreting data
The next step is analyzing the data. This involves organizing the data , categorizing it into themes or patterns , and interpreting these patterns to answer the research question. The analysis might also involve comparing the findings with prior research or theoretical propositions.
Writing the case study report
The final step is writing the case study report . This should provide a detailed description of the case, the data, the analysis process, and the findings. The report should be clear, organized, and carefully written to ensure that the reader can understand the case and the conclusions drawn from it.
Each of these steps is crucial in ensuring that the case study research is rigorous, reliable, and provides valuable insights about the case.
The type, depth, and quality of data in your study can significantly influence the validity and utility of the study. In case study research, data is usually collected from multiple sources to provide a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case. This section will outline the various methods of collecting data used in case study research and discuss considerations for ensuring the quality of the data.
Interviews are a common method of gathering data in case study research. They can provide rich, in-depth data about the perspectives, experiences, and interpretations of the individuals involved in the case. Interviews can be structured , semi-structured , or unstructured , depending on the research question and the degree of flexibility needed.
Observations
Observations involve the researcher observing the case in its natural setting, providing first-hand information about the case and its context. Observations can provide data that might not be revealed in interviews or documents, such as non-verbal cues or contextual information.
Documents and artifacts
Documents and archival records provide a valuable source of data in case study research. They can include reports, letters, memos, meeting minutes, email correspondence, and various public and private documents related to the case.

These records can provide historical context, corroborate evidence from other sources, and offer insights into the case that might not be apparent from interviews or observations.
Physical artifacts refer to any physical evidence related to the case, such as tools, products, or physical environments. These artifacts can provide tangible insights into the case, complementing the data gathered from other sources.
Ensuring the quality of data collection
Determining the quality of data in case study research requires careful planning and execution. It's crucial to ensure that the data is reliable, accurate, and relevant to the research question. This involves selecting appropriate methods of collecting data, properly training interviewers or observers, and systematically recording and storing the data. It also includes considering ethical issues related to collecting and handling data, such as obtaining informed consent and ensuring the privacy and confidentiality of the participants.
Data analysis
Analyzing case study research involves making sense of the rich, detailed data to answer the research question. This process can be challenging due to the volume and complexity of case study data. However, a systematic and rigorous approach to analysis can ensure that the findings are credible and meaningful. This section outlines the main steps and considerations in analyzing data in case study research.
Organizing the data
The first step in the analysis is organizing the data. This involves sorting the data into manageable sections, often according to the data source or the theme. This step can also involve transcribing interviews, digitizing physical artifacts, or organizing observational data.
Categorizing and coding the data
Once the data is organized, the next step is to categorize or code the data. This involves identifying common themes, patterns, or concepts in the data and assigning codes to relevant data segments. Coding can be done manually or with the help of software tools, and in either case, qualitative analysis software can greatly facilitate the entire coding process. Coding helps to reduce the data to a set of themes or categories that can be more easily analyzed.
Identifying patterns and themes
After coding the data, the researcher looks for patterns or themes in the coded data. This involves comparing and contrasting the codes and looking for relationships or patterns among them. The identified patterns and themes should help answer the research question.
Interpreting the data
Once patterns and themes have been identified, the next step is to interpret these findings. This involves explaining what the patterns or themes mean in the context of the research question and the case. This interpretation should be grounded in the data, but it can also involve drawing on theoretical concepts or prior research.
Verification of the data
The last step in the analysis is verification. This involves checking the accuracy and consistency of the analysis process and confirming that the findings are supported by the data. This can involve re-checking the original data, checking the consistency of codes, or seeking feedback from research participants or peers.
Like any research method , case study research has its strengths and limitations. Researchers must be aware of these, as they can influence the design, conduct, and interpretation of the study.
Understanding the strengths and limitations of case study research can also guide researchers in deciding whether this approach is suitable for their research question . This section outlines some of the key strengths and limitations of case study research.
Benefits include the following:
- Rich, detailed data: One of the main strengths of case study research is that it can generate rich, detailed data about the case. This can provide a deep understanding of the case and its context, which can be valuable in exploring complex phenomena.
- Flexibility: Case study research is flexible in terms of design , data collection , and analysis . A sufficient degree of flexibility allows the researcher to adapt the study according to the case and the emerging findings.
- Real-world context: Case study research involves studying the case in its real-world context, which can provide valuable insights into the interplay between the case and its context.
- Multiple sources of evidence: Case study research often involves collecting data from multiple sources , which can enhance the robustness and validity of the findings.
On the other hand, researchers should consider the following limitations:
- Generalizability: A common criticism of case study research is that its findings might not be generalizable to other cases due to the specificity and uniqueness of each case.
- Time and resource intensive: Case study research can be time and resource intensive due to the depth of the investigation and the amount of collected data.
- Complexity of analysis: The rich, detailed data generated in case study research can make analyzing the data challenging.
- Subjectivity: Given the nature of case study research, there may be a higher degree of subjectivity in interpreting the data , so researchers need to reflect on this and transparently convey to audiences how the research was conducted.
Being aware of these strengths and limitations can help researchers design and conduct case study research effectively and interpret and report the findings appropriately.

Ready to analyze your data with ATLAS.ti?
See how our intuitive software can draw key insights from your data with a free trial today.
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Assignments
- Annotated Bibliography
- Analyzing a Scholarly Journal Article
- Group Presentations
- Dealing with Nervousness
- Using Visual Aids
- Grading Someone Else's Paper
- Types of Structured Group Activities
- Group Project Survival Skills
- Leading a Class Discussion
- Multiple Book Review Essay
- Reviewing Collected Works
- Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Writing a Case Study
- About Informed Consent
- Writing Field Notes
- Writing a Policy Memo
- Writing a Reflective Paper
- Writing a Research Proposal
- Generative AI and Writing
- Acknowledgments
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity. A case study research paper usually examines a single subject of analysis, but case study papers can also be designed as a comparative investigation that shows relationships between two or more subjects. The methods used to study a case can rest within a quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-method investigative paradigm.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010 ; “What is a Case Study?” In Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London: SAGE, 2010.
How to Approach Writing a Case Study Research Paper
General information about how to choose a topic to investigate can be found under the " Choosing a Research Problem " tab in the Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper writing guide. Review this page because it may help you identify a subject of analysis that can be investigated using a case study design.
However, identifying a case to investigate involves more than choosing the research problem . A case study encompasses a problem contextualized around the application of in-depth analysis, interpretation, and discussion, often resulting in specific recommendations for action or for improving existing conditions. As Seawright and Gerring note, practical considerations such as time and access to information can influence case selection, but these issues should not be the sole factors used in describing the methodological justification for identifying a particular case to study. Given this, selecting a case includes considering the following:
- The case represents an unusual or atypical example of a research problem that requires more in-depth analysis? Cases often represent a topic that rests on the fringes of prior investigations because the case may provide new ways of understanding the research problem. For example, if the research problem is to identify strategies to improve policies that support girl's access to secondary education in predominantly Muslim nations, you could consider using Azerbaijan as a case study rather than selecting a more obvious nation in the Middle East. Doing so may reveal important new insights into recommending how governments in other predominantly Muslim nations can formulate policies that support improved access to education for girls.
- The case provides important insight or illuminate a previously hidden problem? In-depth analysis of a case can be based on the hypothesis that the case study will reveal trends or issues that have not been exposed in prior research or will reveal new and important implications for practice. For example, anecdotal evidence may suggest drug use among homeless veterans is related to their patterns of travel throughout the day. Assuming prior studies have not looked at individual travel choices as a way to study access to illicit drug use, a case study that observes a homeless veteran could reveal how issues of personal mobility choices facilitate regular access to illicit drugs. Note that it is important to conduct a thorough literature review to ensure that your assumption about the need to reveal new insights or previously hidden problems is valid and evidence-based.
- The case challenges and offers a counter-point to prevailing assumptions? Over time, research on any given topic can fall into a trap of developing assumptions based on outdated studies that are still applied to new or changing conditions or the idea that something should simply be accepted as "common sense," even though the issue has not been thoroughly tested in current practice. A case study analysis may offer an opportunity to gather evidence that challenges prevailing assumptions about a research problem and provide a new set of recommendations applied to practice that have not been tested previously. For example, perhaps there has been a long practice among scholars to apply a particular theory in explaining the relationship between two subjects of analysis. Your case could challenge this assumption by applying an innovative theoretical framework [perhaps borrowed from another discipline] to explore whether this approach offers new ways of understanding the research problem. Taking a contrarian stance is one of the most important ways that new knowledge and understanding develops from existing literature.
- The case provides an opportunity to pursue action leading to the resolution of a problem? Another way to think about choosing a case to study is to consider how the results from investigating a particular case may result in findings that reveal ways in which to resolve an existing or emerging problem. For example, studying the case of an unforeseen incident, such as a fatal accident at a railroad crossing, can reveal hidden issues that could be applied to preventative measures that contribute to reducing the chance of accidents in the future. In this example, a case study investigating the accident could lead to a better understanding of where to strategically locate additional signals at other railroad crossings so as to better warn drivers of an approaching train, particularly when visibility is hindered by heavy rain, fog, or at night.
- The case offers a new direction in future research? A case study can be used as a tool for an exploratory investigation that highlights the need for further research about the problem. A case can be used when there are few studies that help predict an outcome or that establish a clear understanding about how best to proceed in addressing a problem. For example, after conducting a thorough literature review [very important!], you discover that little research exists showing the ways in which women contribute to promoting water conservation in rural communities of east central Africa. A case study of how women contribute to saving water in a rural village of Uganda can lay the foundation for understanding the need for more thorough research that documents how women in their roles as cooks and family caregivers think about water as a valuable resource within their community. This example of a case study could also point to the need for scholars to build new theoretical frameworks around the topic [e.g., applying feminist theories of work and family to the issue of water conservation].
Eisenhardt, Kathleen M. “Building Theories from Case Study Research.” Academy of Management Review 14 (October 1989): 532-550; Emmel, Nick. Sampling and Choosing Cases in Qualitative Research: A Realist Approach . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2013; Gerring, John. “What Is a Case Study and What Is It Good for?” American Political Science Review 98 (May 2004): 341-354; Mills, Albert J. , Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Seawright, Jason and John Gerring. "Case Selection Techniques in Case Study Research." Political Research Quarterly 61 (June 2008): 294-308.
Structure and Writing Style
The purpose of a paper in the social sciences designed around a case study is to thoroughly investigate a subject of analysis in order to reveal a new understanding about the research problem and, in so doing, contributing new knowledge to what is already known from previous studies. In applied social sciences disciplines [e.g., education, social work, public administration, etc.], case studies may also be used to reveal best practices, highlight key programs, or investigate interesting aspects of professional work.
In general, the structure of a case study research paper is not all that different from a standard college-level research paper. However, there are subtle differences you should be aware of. Here are the key elements to organizing and writing a case study research paper.
I. Introduction
As with any research paper, your introduction should serve as a roadmap for your readers to ascertain the scope and purpose of your study . The introduction to a case study research paper, however, should not only describe the research problem and its significance, but you should also succinctly describe why the case is being used and how it relates to addressing the problem. The two elements should be linked. With this in mind, a good introduction answers these four questions:
- What is being studied? Describe the research problem and describe the subject of analysis [the case] you have chosen to address the problem. Explain how they are linked and what elements of the case will help to expand knowledge and understanding about the problem.
- Why is this topic important to investigate? Describe the significance of the research problem and state why a case study design and the subject of analysis that the paper is designed around is appropriate in addressing the problem.
- What did we know about this topic before I did this study? Provide background that helps lead the reader into the more in-depth literature review to follow. If applicable, summarize prior case study research applied to the research problem and why it fails to adequately address the problem. Describe why your case will be useful. If no prior case studies have been used to address the research problem, explain why you have selected this subject of analysis.
- How will this study advance new knowledge or new ways of understanding? Explain why your case study will be suitable in helping to expand knowledge and understanding about the research problem.
Each of these questions should be addressed in no more than a few paragraphs. Exceptions to this can be when you are addressing a complex research problem or subject of analysis that requires more in-depth background information.
II. Literature Review
The literature review for a case study research paper is generally structured the same as it is for any college-level research paper. The difference, however, is that the literature review is focused on providing background information and enabling historical interpretation of the subject of analysis in relation to the research problem the case is intended to address . This includes synthesizing studies that help to:
- Place relevant works in the context of their contribution to understanding the case study being investigated . This would involve summarizing studies that have used a similar subject of analysis to investigate the research problem. If there is literature using the same or a very similar case to study, you need to explain why duplicating past research is important [e.g., conditions have changed; prior studies were conducted long ago, etc.].
- Describe the relationship each work has to the others under consideration that informs the reader why this case is applicable . Your literature review should include a description of any works that support using the case to investigate the research problem and the underlying research questions.
- Identify new ways to interpret prior research using the case study . If applicable, review any research that has examined the research problem using a different research design. Explain how your use of a case study design may reveal new knowledge or a new perspective or that can redirect research in an important new direction.
- Resolve conflicts amongst seemingly contradictory previous studies . This refers to synthesizing any literature that points to unresolved issues of concern about the research problem and describing how the subject of analysis that forms the case study can help resolve these existing contradictions.
- Point the way in fulfilling a need for additional research . Your review should examine any literature that lays a foundation for understanding why your case study design and the subject of analysis around which you have designed your study may reveal a new way of approaching the research problem or offer a perspective that points to the need for additional research.
- Expose any gaps that exist in the literature that the case study could help to fill . Summarize any literature that not only shows how your subject of analysis contributes to understanding the research problem, but how your case contributes to a new way of understanding the problem that prior research has failed to do.
- Locate your own research within the context of existing literature [very important!] . Collectively, your literature review should always place your case study within the larger domain of prior research about the problem. The overarching purpose of reviewing pertinent literature in a case study paper is to demonstrate that you have thoroughly identified and synthesized prior studies in relation to explaining the relevance of the case in addressing the research problem.
III. Method
In this section, you explain why you selected a particular case [i.e., subject of analysis] and the strategy you used to identify and ultimately decide that your case was appropriate in addressing the research problem. The way you describe the methods used varies depending on the type of subject of analysis that constitutes your case study.
If your subject of analysis is an incident or event . In the social and behavioral sciences, the event or incident that represents the case to be studied is usually bounded by time and place, with a clear beginning and end and with an identifiable location or position relative to its surroundings. The subject of analysis can be a rare or critical event or it can focus on a typical or regular event. The purpose of studying a rare event is to illuminate new ways of thinking about the broader research problem or to test a hypothesis. Critical incident case studies must describe the method by which you identified the event and explain the process by which you determined the validity of this case to inform broader perspectives about the research problem or to reveal new findings. However, the event does not have to be a rare or uniquely significant to support new thinking about the research problem or to challenge an existing hypothesis. For example, Walo, Bull, and Breen conducted a case study to identify and evaluate the direct and indirect economic benefits and costs of a local sports event in the City of Lismore, New South Wales, Australia. The purpose of their study was to provide new insights from measuring the impact of a typical local sports event that prior studies could not measure well because they focused on large "mega-events." Whether the event is rare or not, the methods section should include an explanation of the following characteristics of the event: a) when did it take place; b) what were the underlying circumstances leading to the event; and, c) what were the consequences of the event in relation to the research problem.
If your subject of analysis is a person. Explain why you selected this particular individual to be studied and describe what experiences they have had that provide an opportunity to advance new understandings about the research problem. Mention any background about this person which might help the reader understand the significance of their experiences that make them worthy of study. This includes describing the relationships this person has had with other people, institutions, and/or events that support using them as the subject for a case study research paper. It is particularly important to differentiate the person as the subject of analysis from others and to succinctly explain how the person relates to examining the research problem [e.g., why is one politician in a particular local election used to show an increase in voter turnout from any other candidate running in the election]. Note that these issues apply to a specific group of people used as a case study unit of analysis [e.g., a classroom of students].
If your subject of analysis is a place. In general, a case study that investigates a place suggests a subject of analysis that is unique or special in some way and that this uniqueness can be used to build new understanding or knowledge about the research problem. A case study of a place must not only describe its various attributes relevant to the research problem [e.g., physical, social, historical, cultural, economic, political], but you must state the method by which you determined that this place will illuminate new understandings about the research problem. It is also important to articulate why a particular place as the case for study is being used if similar places also exist [i.e., if you are studying patterns of homeless encampments of veterans in open spaces, explain why you are studying Echo Park in Los Angeles rather than Griffith Park?]. If applicable, describe what type of human activity involving this place makes it a good choice to study [e.g., prior research suggests Echo Park has more homeless veterans].
If your subject of analysis is a phenomenon. A phenomenon refers to a fact, occurrence, or circumstance that can be studied or observed but with the cause or explanation to be in question. In this sense, a phenomenon that forms your subject of analysis can encompass anything that can be observed or presumed to exist but is not fully understood. In the social and behavioral sciences, the case usually focuses on human interaction within a complex physical, social, economic, cultural, or political system. For example, the phenomenon could be the observation that many vehicles used by ISIS fighters are small trucks with English language advertisements on them. The research problem could be that ISIS fighters are difficult to combat because they are highly mobile. The research questions could be how and by what means are these vehicles used by ISIS being supplied to the militants and how might supply lines to these vehicles be cut off? How might knowing the suppliers of these trucks reveal larger networks of collaborators and financial support? A case study of a phenomenon most often encompasses an in-depth analysis of a cause and effect that is grounded in an interactive relationship between people and their environment in some way.
NOTE: The choice of the case or set of cases to study cannot appear random. Evidence that supports the method by which you identified and chose your subject of analysis should clearly support investigation of the research problem and linked to key findings from your literature review. Be sure to cite any studies that helped you determine that the case you chose was appropriate for examining the problem.
IV. Discussion
The main elements of your discussion section are generally the same as any research paper, but centered around interpreting and drawing conclusions about the key findings from your analysis of the case study. Note that a general social sciences research paper may contain a separate section to report findings. However, in a paper designed around a case study, it is common to combine a description of the results with the discussion about their implications. The objectives of your discussion section should include the following:
Reiterate the Research Problem/State the Major Findings Briefly reiterate the research problem you are investigating and explain why the subject of analysis around which you designed the case study were used. You should then describe the findings revealed from your study of the case using direct, declarative, and succinct proclamation of the study results. Highlight any findings that were unexpected or especially profound.
Explain the Meaning of the Findings and Why They are Important Systematically explain the meaning of your case study findings and why you believe they are important. Begin this part of the section by repeating what you consider to be your most important or surprising finding first, then systematically review each finding. Be sure to thoroughly extrapolate what your analysis of the case can tell the reader about situations or conditions beyond the actual case that was studied while, at the same time, being careful not to misconstrue or conflate a finding that undermines the external validity of your conclusions.
Relate the Findings to Similar Studies No study in the social sciences is so novel or possesses such a restricted focus that it has absolutely no relation to previously published research. The discussion section should relate your case study results to those found in other studies, particularly if questions raised from prior studies served as the motivation for choosing your subject of analysis. This is important because comparing and contrasting the findings of other studies helps support the overall importance of your results and it highlights how and in what ways your case study design and the subject of analysis differs from prior research about the topic.
Consider Alternative Explanations of the Findings Remember that the purpose of social science research is to discover and not to prove. When writing the discussion section, you should carefully consider all possible explanations revealed by the case study results, rather than just those that fit your hypothesis or prior assumptions and biases. Be alert to what the in-depth analysis of the case may reveal about the research problem, including offering a contrarian perspective to what scholars have stated in prior research if that is how the findings can be interpreted from your case.
Acknowledge the Study's Limitations You can state the study's limitations in the conclusion section of your paper but describing the limitations of your subject of analysis in the discussion section provides an opportunity to identify the limitations and explain why they are not significant. This part of the discussion section should also note any unanswered questions or issues your case study could not address. More detailed information about how to document any limitations to your research can be found here .
Suggest Areas for Further Research Although your case study may offer important insights about the research problem, there are likely additional questions related to the problem that remain unanswered or findings that unexpectedly revealed themselves as a result of your in-depth analysis of the case. Be sure that the recommendations for further research are linked to the research problem and that you explain why your recommendations are valid in other contexts and based on the original assumptions of your study.
V. Conclusion
As with any research paper, you should summarize your conclusion in clear, simple language; emphasize how the findings from your case study differs from or supports prior research and why. Do not simply reiterate the discussion section. Provide a synthesis of key findings presented in the paper to show how these converge to address the research problem. If you haven't already done so in the discussion section, be sure to document the limitations of your case study and any need for further research.
The function of your paper's conclusion is to: 1) reiterate the main argument supported by the findings from your case study; 2) state clearly the context, background, and necessity of pursuing the research problem using a case study design in relation to an issue, controversy, or a gap found from reviewing the literature; and, 3) provide a place to persuasively and succinctly restate the significance of your research problem, given that the reader has now been presented with in-depth information about the topic.
Consider the following points to help ensure your conclusion is appropriate:
- If the argument or purpose of your paper is complex, you may need to summarize these points for your reader.
- If prior to your conclusion, you have not yet explained the significance of your findings or if you are proceeding inductively, use the conclusion of your paper to describe your main points and explain their significance.
- Move from a detailed to a general level of consideration of the case study's findings that returns the topic to the context provided by the introduction or within a new context that emerges from your case study findings.
Note that, depending on the discipline you are writing in or the preferences of your professor, the concluding paragraph may contain your final reflections on the evidence presented as it applies to practice or on the essay's central research problem. However, the nature of being introspective about the subject of analysis you have investigated will depend on whether you are explicitly asked to express your observations in this way.
Problems to Avoid
Overgeneralization One of the goals of a case study is to lay a foundation for understanding broader trends and issues applied to similar circumstances. However, be careful when drawing conclusions from your case study. They must be evidence-based and grounded in the results of the study; otherwise, it is merely speculation. Looking at a prior example, it would be incorrect to state that a factor in improving girls access to education in Azerbaijan and the policy implications this may have for improving access in other Muslim nations is due to girls access to social media if there is no documentary evidence from your case study to indicate this. There may be anecdotal evidence that retention rates were better for girls who were engaged with social media, but this observation would only point to the need for further research and would not be a definitive finding if this was not a part of your original research agenda.
Failure to Document Limitations No case is going to reveal all that needs to be understood about a research problem. Therefore, just as you have to clearly state the limitations of a general research study , you must describe the specific limitations inherent in the subject of analysis. For example, the case of studying how women conceptualize the need for water conservation in a village in Uganda could have limited application in other cultural contexts or in areas where fresh water from rivers or lakes is plentiful and, therefore, conservation is understood more in terms of managing access rather than preserving access to a scarce resource.
Failure to Extrapolate All Possible Implications Just as you don't want to over-generalize from your case study findings, you also have to be thorough in the consideration of all possible outcomes or recommendations derived from your findings. If you do not, your reader may question the validity of your analysis, particularly if you failed to document an obvious outcome from your case study research. For example, in the case of studying the accident at the railroad crossing to evaluate where and what types of warning signals should be located, you failed to take into consideration speed limit signage as well as warning signals. When designing your case study, be sure you have thoroughly addressed all aspects of the problem and do not leave gaps in your analysis that leave the reader questioning the results.
Case Studies. Writing@CSU. Colorado State University; Gerring, John. Case Study Research: Principles and Practices . New York: Cambridge University Press, 2007; Merriam, Sharan B. Qualitative Research and Case Study Applications in Education . Rev. ed. San Francisco, CA: Jossey-Bass, 1998; Miller, Lisa L. “The Use of Case Studies in Law and Social Science Research.” Annual Review of Law and Social Science 14 (2018): TBD; Mills, Albert J., Gabrielle Durepos, and Eiden Wiebe, editors. Encyclopedia of Case Study Research . Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010; Putney, LeAnn Grogan. "Case Study." In Encyclopedia of Research Design , Neil J. Salkind, editor. (Thousand Oaks, CA: SAGE Publications, 2010), pp. 116-120; Simons, Helen. Case Study Research in Practice . London: SAGE Publications, 2009; Kratochwill, Thomas R. and Joel R. Levin, editors. Single-Case Research Design and Analysis: New Development for Psychology and Education . Hilldsale, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 1992; Swanborn, Peter G. Case Study Research: What, Why and How? London : SAGE, 2010; Yin, Robert K. Case Study Research: Design and Methods . 6th edition. Los Angeles, CA, SAGE Publications, 2014; Walo, Maree, Adrian Bull, and Helen Breen. “Achieving Economic Benefits at Local Events: A Case Study of a Local Sports Event.” Festival Management and Event Tourism 4 (1996): 95-106.
Writing Tip
At Least Five Misconceptions about Case Study Research
Social science case studies are often perceived as limited in their ability to create new knowledge because they are not randomly selected and findings cannot be generalized to larger populations. Flyvbjerg examines five misunderstandings about case study research and systematically "corrects" each one. To quote, these are:
Misunderstanding 1 : General, theoretical [context-independent] knowledge is more valuable than concrete, practical [context-dependent] knowledge. Misunderstanding 2 : One cannot generalize on the basis of an individual case; therefore, the case study cannot contribute to scientific development. Misunderstanding 3 : The case study is most useful for generating hypotheses; that is, in the first stage of a total research process, whereas other methods are more suitable for hypotheses testing and theory building. Misunderstanding 4 : The case study contains a bias toward verification, that is, a tendency to confirm the researcher’s preconceived notions. Misunderstanding 5 : It is often difficult to summarize and develop general propositions and theories on the basis of specific case studies [p. 221].
While writing your paper, think introspectively about how you addressed these misconceptions because to do so can help you strengthen the validity and reliability of your research by clarifying issues of case selection, the testing and challenging of existing assumptions, the interpretation of key findings, and the summation of case outcomes. Think of a case study research paper as a complete, in-depth narrative about the specific properties and key characteristics of your subject of analysis applied to the research problem.
Flyvbjerg, Bent. “Five Misunderstandings About Case-Study Research.” Qualitative Inquiry 12 (April 2006): 219-245.
- << Previous: Writing a Case Analysis Paper
- Next: Writing a Field Report >>
- Last Updated: Jun 3, 2024 9:44 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/assignments
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods
Published on 5 May 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 30 January 2023.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organisation, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research.
A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods , but quantitative methods are sometimes also used. Case studies are good for describing , comparing, evaluating, and understanding different aspects of a research problem .
Table of contents
When to do a case study, step 1: select a case, step 2: build a theoretical framework, step 3: collect your data, step 4: describe and analyse the case.
A case study is an appropriate research design when you want to gain concrete, contextual, in-depth knowledge about a specific real-world subject. It allows you to explore the key characteristics, meanings, and implications of the case.
Case studies are often a good choice in a thesis or dissertation . They keep your project focused and manageable when you don’t have the time or resources to do large-scale research.
You might use just one complex case study where you explore a single subject in depth, or conduct multiple case studies to compare and illuminate different aspects of your research problem.
| Research question | Case study |
|---|---|
| What are the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction? | Case study of wolf reintroduction in Yellowstone National Park in the US |
| How do populist politicians use narratives about history to gain support? | Case studies of Hungarian prime minister Viktor Orbán and US president Donald Trump |
| How can teachers implement active learning strategies in mixed-level classrooms? | Case study of a local school that promotes active learning |
| What are the main advantages and disadvantages of wind farms for rural communities? | Case studies of three rural wind farm development projects in different parts of the country |
| How are viral marketing strategies changing the relationship between companies and consumers? | Case study of the iPhone X marketing campaign |
| How do experiences of work in the gig economy differ by gender, race, and age? | Case studies of Deliveroo and Uber drivers in London |
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Once you have developed your problem statement and research questions , you should be ready to choose the specific case that you want to focus on. A good case study should have the potential to:
- Provide new or unexpected insights into the subject
- Challenge or complicate existing assumptions and theories
- Propose practical courses of action to resolve a problem
- Open up new directions for future research
Unlike quantitative or experimental research, a strong case study does not require a random or representative sample. In fact, case studies often deliberately focus on unusual, neglected, or outlying cases which may shed new light on the research problem.
If you find yourself aiming to simultaneously investigate and solve an issue, consider conducting action research . As its name suggests, action research conducts research and takes action at the same time, and is highly iterative and flexible.
However, you can also choose a more common or representative case to exemplify a particular category, experience, or phenomenon.
While case studies focus more on concrete details than general theories, they should usually have some connection with theory in the field. This way the case study is not just an isolated description, but is integrated into existing knowledge about the topic. It might aim to:
- Exemplify a theory by showing how it explains the case under investigation
- Expand on a theory by uncovering new concepts and ideas that need to be incorporated
- Challenge a theory by exploring an outlier case that doesn’t fit with established assumptions
To ensure that your analysis of the case has a solid academic grounding, you should conduct a literature review of sources related to the topic and develop a theoretical framework . This means identifying key concepts and theories to guide your analysis and interpretation.
There are many different research methods you can use to collect data on your subject. Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data .
The aim is to gain as thorough an understanding as possible of the case and its context.
In writing up the case study, you need to bring together all the relevant aspects to give as complete a picture as possible of the subject.
How you report your findings depends on the type of research you are doing. Some case studies are structured like a standard scientific paper or thesis, with separate sections or chapters for the methods , results , and discussion .
Others are written in a more narrative style, aiming to explore the case from various angles and analyse its meanings and implications (for example, by using textual analysis or discourse analysis ).
In all cases, though, make sure to give contextual details about the case, connect it back to the literature and theory, and discuss how it fits into wider patterns or debates.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, January 30). Case Study | Definition, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 2 September 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/case-studies/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, correlational research | guide, design & examples, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, descriptive research design | definition, methods & examples.
How to Write a Case Conceptualization: 10 Examples (+ PDF)

Such understanding can be developed by reading relevant records, meeting with clients face to face, and using assessments such as a mental status examination.
As you proceed, you are forming a guiding concept of who this client is, how they became who they are, and where their personal journey might be heading.
Such a guiding concept, which will shape any needed interventions, is called a case conceptualization, and we will examine various examples in this article.
Before you continue, we thought you might like to download our three Positive CBT Exercises for free . These science-based exercises will provide you with detailed insight into positive Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT) and give you the tools to apply it in your therapy or coaching.
This Article Contains:
What is a case conceptualization or formulation, 4 things to include in your case formulation, a helpful example & model, 3 samples of case formulations, 6 templates and worksheets for counselors, relevant resources from positivepsychology.com, a take-home message.
In psychology and related fields, a case conceptualization summarizes the key facts and findings from an evaluation to provide guidance for recommendations.
This is typically the evaluation of an individual, although you can extend the concept of case conceptualization to summarizing findings about a group or organization.
Based on the case conceptualization, recommendations can be made to improve a client’s self-care , mental status, job performance, etc (Sperry & Sperry, 2020).

- Summary of the client’s identifying information, referral questions, and timeline of important events or factors in their life . A timeline can be especially helpful in understanding how the client’s strengths and limitations have evolved.
- Statement of the client’s core strengths . Identifying core strengths in the client’s life should help guide any recommendations, including how strengths might be used to offset limitations.
- Statement concerning a client’s limitations or weaknesses . This will also help guide any recommendations. If a weakness is worth mentioning in a case conceptualization, it is worth writing a recommendation about it.
Note: As with mental status examinations , observations in this context concerning weaknesses are not value judgments, about whether the client is a good person, etc. The observations are clinical judgments meant to guide recommendations.
- A summary of how the strengths, limitations, and other key information about a client inform diagnosis and prognosis .
You should briefly clarify how you arrived at a given diagnosis. For example, why do you believe a personality disorder is primary, rather than a major depressive disorder?
Many clinicians provide diagnoses in formal psychiatric terms, per the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) or Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5). Some clinicians will state a diagnosis in less formal terms that do not coincide exactly with ICD-10 or DSM-5 codes. What is arguably more important is that a diagnostic impression, formal or not, gives a clear sense of who the person is and the support they need to reach their goals.
Prognosis is a forecast about whether the client’s condition can be expected to improve, worsen, or remain stable. Prognosis can be difficult, as it often depends on unforeseeable factors. However, this should not keep you from offering a conservative opinion on a client’s expected course, provided treatment recommendations are followed.

Download 3 Free Positive CBT Exercises (PDF)
These detailed, science-based exercises will equip you or your clients with tools to find new pathways to reduce suffering and more effectively cope with life stressors.
Download 3 Free Positive CBT Tools Pack (PDF)
By filling out your name and email address below.
Based on the pointers for writing a case conceptualization above, an example for summarizing an adolescent case (in this instance, a counseling case for relieving depression and improving social skills) might read as follows.
Background and referral information
This is a 15-year-old Haitian–American youth, referred by his mother for concerns about self-isolation, depression, and poor social skills. He reportedly moved with his mother to the United States three years ago.
He reportedly misses his life and friends in Haiti. The mother states he has had difficulty adjusting socially in the United States, especially with peers. He has become increasingly self-isolating, appears sad and irritable, and has started to refuse to go to school.
His mother is very supportive and aware of his emotional–behavioral needs. The youth has been enrolled in a social skills group at school and has attended three sessions, with some reported benefit. He is agreeable to start individual counseling. He reportedly does well in school academically when he applies himself.
Limitations
Behavioral form completed by his mother shows elevated depression scale (T score = 80). There is a milder elevation on the inattention scale (T score = 60), which suggests depression is more acute than inattention and might drive it.
He is also elevated on a scale measuring social skills and involvement (T score = 65). Here too, it is reasonable to assume that depression is driving social isolation and difficulty relating to peers, especially since while living in Haiti, he was reportedly quite social with peers.
Diagnostic impressions, treatment guidance, prognosis
This youth’s history, presentation on interview, and results of emotional–behavioral forms suggest some difficulty with depression, likely contributing to social isolation. As he has no prior reported history of depression, this is most likely a reaction to missing his former home and difficulty adjusting to his new school and peers.
Treatments should include individual counseling with an evidence-based approach such as Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT). His counselor should consider emotional processing and social skills building as well.
Prognosis is favorable, with anticipated benefit apparent within 12 sessions of CBT.
How to write a case conceptualization: An outline
The following outline is necessarily general. It can be modified as needed, with points excluded or added, depending on the case.
- Client’s gender, age, level of education, vocational status, marital status
- Referred by whom, why, and for what type of service (e.g., testing, counseling, coaching)
- In the spirit of strengths-based assessment, consider listing the client’s strengths first, before any limitations.
- Consider the full range of positive factors supporting the client.
- Physical health
- Family support
- Financial resources
- Capacity to work
- Resilience or other positive personality traits
- Emotional stability
- Cognitive strengths, per history and testing
- The client’s limitations or relative weaknesses should be described in a way that highlights those most needing attention or treatment.
- Medical conditions affecting daily functioning
- Lack of family or other social support
- Limited financial resources
- Inability to find or hold suitable employment
- Substance abuse or dependence
- Proneness to interpersonal conflict
- Emotional–behavioral problems, including anxious or depressive symptoms
- Cognitive deficits, per history and testing
- Diagnoses that are warranted can be given in either DSM-5 or ICD-10 terms.
- There can be more than one diagnosis given. If that’s the case, consider describing these in terms of primary diagnosis, secondary diagnosis, etc.
- The primary diagnosis should best encompass the client’s key symptoms or traits, best explain their behavior, or most need treatment.
- Take care to avoid over-assigning multiple and potentially overlapping diagnoses.
When writing a case conceptualization, always keep in mind the timeline of significant events or factors in the examinee’s life.
- Decide which events or factors are significant enough to include in a case conceptualization.
- When these points are placed in a timeline, they help you understand how the person has evolved to become who they are now.
- A good timeline can also help you understand which factors in a person’s life might be causative for others. For example, if a person has suffered a frontal head injury in the past year, this might help explain their changeable moods, presence of depressive disorder, etc.

Sample #1: Conceptualization for CBT case
This is a 35-year-old Caucasian man referred by his physician for treatment of generalized anxiety.
Strengths/supports in his case include willingness to engage in treatment, high average intelligence per recent cognitive testing, supportive family, and regular physical exercise (running).
Limiting factors include relatively low stress coping skills, frequent migraines (likely stress related), and relative social isolation (partly due to some anxiety about social skills).
The client’s presentation on interview and review of medical/psychiatric records show a history of chronic worry, including frequent worries about his wife’s health and his finances. He meets criteria for DSM-5 generalized anxiety disorder. He has also described occasional panic-type episodes, which do not currently meet full criteria for panic disorder but could develop into such without preventive therapy.
Treatments should include CBT for generalized anxiety, including keeping a worry journal; regular assessment of anxiety levels with Penn State Worry Questionnaire and/or Beck Anxiety Inventory; cognitive restructuring around negative beliefs that reinforce anxiety; and practice of relaxation techniques, such as progressive muscle relaxation and diaphragmatic breathing .
Prognosis is good, given the evidence for efficacy of CBT for anxiety disorders generally (Hofmann, Asnaani, Vonk, Sawyer, & Fang, 2012).

World’s Largest Positive Psychology Resource
The Positive Psychology Toolkit© is a groundbreaking practitioner resource containing over 500 science-based exercises , activities, interventions, questionnaires, and assessments created by experts using the latest positive psychology research.
Updated monthly. 100% Science-based.
“The best positive psychology resource out there!” — Emiliya Zhivotovskaya , Flourishing Center CEO
Sample #2: Conceptualization for DBT case
This 51-year-old Haitian–American woman is self-referred for depressive symptoms, including reported moods of “rage,” “sadness,” and “emptiness.” She says that many of her difficulties involve family, friends, and coworkers who regularly “disrespect” her and “plot against her behind her back.”
Her current psychiatrist has diagnosed her with personality disorder with borderline features, but she doubts the accuracy of this diagnosis.
Strengths/supports include a willingness to engage in treatment, highly developed and marketable computer programming skills, and engagement in leisure activities such as playing backgammon with friends.
Limiting factors include low stress coping skills, mild difficulties with attention and recent memory (likely due in part to depressive affect), and a tendency to self-medicate with alcohol when feeling depressed.
The client’s presentation on interview, review of medical/psychiatric records, and results of MMPI-2 personality inventory corroborate her psychiatrist’s diagnosis of borderline personality disorder.
The diagnosis is supported by a longstanding history of unstable identity, volatile personal relationships with fear of being abandoned, feelings of emptiness, reactive depressive disorder with suicidal gestures, and lack of insight into interpersonal difficulties that have resulted in her often stressed and depressive state.
Treatments should emphasize a DBT group that her psychiatrist has encouraged her to attend but to which she has not yet gone. There should also be regular individual counseling emphasizing DBT skills including mindfulness or present moment focus, building interpersonal skills, emotional regulation, and distress tolerance. There should be a counseling element for limiting alcohol use. Cognitive exercises are also recommended.
Of note, DBT is the only evidence-based treatment for borderline personality disorder (May, Richardi, & Barth, 2016). Prognosis is guardedly optimistic, provided she engages in both group and individual DBT treatments on a weekly basis, and these treatments continue without interruption for at least three months, with refresher sessions as needed.
Sample #3: Conceptualization in a family therapy case
This 45-year-old African-American woman was initially referred for individual therapy for “rapid mood swings” and a tendency to become embroiled in family conflicts. Several sessions of family therapy also appear indicated, and her psychiatrist concurs.
The client’s husband (50 years old) and son (25 years old, living with parents) were interviewed separately and together. When interviewed separately, her husband and son each indicated the client’s alcohol intake was “out of control,” and that she was consuming about six alcoholic beverages throughout the day, sometimes more.
Her husband and son each said the client was often too tired for household duties by the evening and often had rapid shifts in mood from happy to angry to “crying in her room.”
On individual interview, the client stated that her husband and son were each drinking about as much as she, that neither ever offered to help her with household duties, and that her son appeared unable to keep a job, which left him home most of the day, making demands on her for meals, etc.
On interview with the three family members, each acknowledged that the instances above were occurring at home, although father and son tended to blame most of the problems, including son’s difficulty maintaining employment, on the client and her drinking.
Strengths/supports in the family include a willingness of each member to engage in family sessions, awareness of supportive resources such as assistance for son’s job search, and a willingness by all to examine and reduce alcohol use by all family members as needed.
Limiting factors in this case include apparent tendency of all household members to drink to some excess, lack of insight by one or more family members as to how alcohol consumption is contributing to communication and other problems in the household, and a tendency by husband and son to make this client the family scapegoat.
The family dynamic can be conceptualized in this case through a DBT lens.
From this perspective, problems develop within the family when the environment is experienced by one or more members as invalidating and unsupportive. DBT skills with a nonjudgmental focus, active listening to others, reflecting each other’s feelings, and tolerance of distress in the moment should help to develop an environment that supports all family members and facilitates effective communication.
It appears that all family members in this case would benefit from engaging in the above DBT skills, to support and communicate with one another.
Prognosis is guardedly optimistic if family will engage in therapy with DBT elements for at least six sessions (with refresher sessions as needed).
Introduction to case conceptualization – Thomas Field
The following worksheets can be used for case conceptualization and planning.
- Case Conceptualization Worksheet: Individual Counseling helps counselors develop a case conceptualization for individual clients.
- Case Conceptualization Worksheet: Couples Counseling helps counselors develop a case conceptualization for couples.
- Case Conceptualization Worksheet: Family Counseling helps counselors develop a case conceptualization for families.
- Case Conceptualization and Action Plan: Individual Counseling helps clients facilitate conceptualization of their own case, at approximately six weeks into counseling and thereafter at appropriate intervals.
- Case Conceptualization and Action Plan: Couples Counseling helps couples facilitate conceptualization of their own case, at approximately six weeks into counseling and thereafter at appropriate intervals.
- Case Conceptualization and Action Plan: Family Counseling helps families facilitate conceptualization of their own case, at approximately six weeks into counseling and thereafter at appropriate intervals.

17 Science-Based Ways To Apply Positive CBT
These 17 Positive CBT & Cognitive Therapy Exercises [PDF] include our top-rated, ready-made templates for helping others develop more helpful thoughts and behaviors in response to challenges, while broadening the scope of traditional CBT.
Created by Experts. 100% Science-based.
The following resources can be found in the Positive Psychology Toolkit© , and their full versions can be accessed by a subscription.
Analyzing Strengths Use in Different Life Domains can help clients understand their notable strengths and which strengths can be used to more advantage in new contexts.
Family Strength Spotting is another relevant resource. Each family member fills out a worksheet detailing notable strengths of other family members. In reviewing all worksheets, each family member can gain a greater appreciation for other members’ strengths, note common or unique strengths, and determine how best to use these combined strengths to achieve family goals.
Four Front Assessment is another resource designed to help counselors conceptualize a case based on a client’s personal and environmental strengths and weaknesses. The idea behind this tool is that environmental factors in the broad sense, such as a supportive/unsupportive family, are too often overlooked in conceptualizing a case.
If you’re looking for more science-based ways to help others through CBT, check out this collection of 17 validated positive CBT tools for practitioners. Use them to help others overcome unhelpful thoughts and feelings and develop more positive behaviors.
In helping professions, success in working with clients depends first and foremost on how well you understand them.
This understanding is crystallized in a case conceptualization.
Case conceptualization helps answer key questions. Who is this client? How did they become who they are? What supports do they need to reach their goals?
The conceptualization itself depends on gathering all pertinent data on a given case, through record review, interview, behavioral observation, questionnaires completed by the client, etc.
Once the data is assembled, the counselor, coach, or other involved professional can focus on enumerating the client’s strengths, weaknesses, and limitations.
It is also often helpful to put the client’s strengths and limitations in a timeline so you can see how they have evolved and which factors might have contributed to the emergence of others.
Based on this in-depth understanding of the client, you can then tailor specific recommendations for enhancing their strengths, overcoming their weaknesses, and reaching their particular goals.
We hope you have enjoyed this discussion of how to conceptualize cases in the helping professions and that you will find some tools for doing so useful.
We hope you enjoyed reading this article. For more information, don’t forget to download our three Positive CBT Exercises for free .
- Hofmann, S. G., Asnaani, A., Vonk, I. J., Sawyer, A. T., & Fang, A. (2012). The efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy: A review of meta-analyses. Cognitive Therapy and Research , 36 (5), 427–440.
- May, J. M., Richardi, T. M., & Barth, K. S. (2016). Dialectical behavior therapy as treatment for borderline personality disorder. The Mental Health Clinician , 6 (2), 62–67.
- Sperry, L., & Sperry, J. (2020). Case conceptualization: Mastering this competency with ease and confidence . Routledge.
Share this article:
Article feedback
What our readers think.
I want the toolkit! This article was very helpful. I enjoyed the different examples of the case studies and how each therapy was utilized in their treatments.
I found this very helpful and MORE understanding. I think I will often visit this page.
Let us know your thoughts Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related articles

Youth Counseling: 17 Courses & Activities for Helping Teens
From a maturing body and brain to developing life skills and values, the teen years can be challenging, and mental health concerns may arise. Teens [...]

How To Plan Your Counseling Session: 6 Examples
Planning is crucial in a counseling session to ensure that time inside–and outside–therapy sessions is well spent, with the client achieving a successful outcome within [...]

65+ Counseling Methods & Techniques to Apply With Your Clients
Counselors have found it challenging to settle on a single definition of their profession or agree on the best counseling methods and techniques to treat [...]
Read other articles by their category
- Body & Brain (52)
- Coaching & Application (39)
- Compassion (23)
- Counseling (40)
- Emotional Intelligence (21)
- Gratitude (18)
- Grief & Bereavement (18)
- Happiness & SWB (40)
- Meaning & Values (26)
- Meditation (16)
- Mindfulness (40)
- Motivation & Goals (41)
- Optimism & Mindset (29)
- Positive CBT (28)
- Positive Communication (23)
- Positive Education (36)
- Positive Emotions (32)
- Positive Leadership (16)
- Positive Parenting (14)
- Positive Psychology (21)
- Positive Workplace (35)
- Productivity (16)
- Relationships (46)
- Resilience & Coping (38)
- Self Awareness (20)
- Self Esteem (37)
- Strengths & Virtues (29)
- Stress & Burnout Prevention (33)
- Theory & Books (42)
- Therapy Exercises (37)
- Types of Therapy (54)
- Privacy Policy

Home » Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide
Table of Contents

A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation.
It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied. Case studies typically involve multiple sources of data, including interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts, which are analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, and grounded theory. The findings of a case study are often used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Types of Case Study
Types and Methods of Case Study are as follows:
Single-Case Study
A single-case study is an in-depth analysis of a single case. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand a specific phenomenon in detail.
For Example , A researcher might conduct a single-case study on a particular individual to understand their experiences with a particular health condition or a specific organization to explore their management practices. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a single-case study are often used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Multiple-Case Study
A multiple-case study involves the analysis of several cases that are similar in nature. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to identify similarities and differences between the cases.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a multiple-case study on several companies to explore the factors that contribute to their success or failure. The researcher collects data from each case, compares and contrasts the findings, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as comparative analysis or pattern-matching. The findings of a multiple-case study can be used to develop theories, inform policy or practice, or generate new research questions.
Exploratory Case Study
An exploratory case study is used to explore a new or understudied phenomenon. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to generate hypotheses or theories about the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an exploratory case study on a new technology to understand its potential impact on society. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as grounded theory or content analysis. The findings of an exploratory case study can be used to generate new research questions, develop theories, or inform policy or practice.
Descriptive Case Study
A descriptive case study is used to describe a particular phenomenon in detail. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to provide a comprehensive account of the phenomenon.
For Example, a researcher might conduct a descriptive case study on a particular community to understand its social and economic characteristics. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of a descriptive case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Instrumental Case Study
An instrumental case study is used to understand a particular phenomenon that is instrumental in achieving a particular goal. This type of case study is useful when the researcher wants to understand the role of the phenomenon in achieving the goal.
For Example, a researcher might conduct an instrumental case study on a particular policy to understand its impact on achieving a particular goal, such as reducing poverty. The researcher collects data from multiple sources, such as interviews, observations, and documents, and uses various techniques to analyze the data, such as content analysis or thematic analysis. The findings of an instrumental case study can be used to inform policy or practice or generate new research questions.
Case Study Data Collection Methods
Here are some common data collection methods for case studies:
Interviews involve asking questions to individuals who have knowledge or experience relevant to the case study. Interviews can be structured (where the same questions are asked to all participants) or unstructured (where the interviewer follows up on the responses with further questions). Interviews can be conducted in person, over the phone, or through video conferencing.
Observations
Observations involve watching and recording the behavior and activities of individuals or groups relevant to the case study. Observations can be participant (where the researcher actively participates in the activities) or non-participant (where the researcher observes from a distance). Observations can be recorded using notes, audio or video recordings, or photographs.
Documents can be used as a source of information for case studies. Documents can include reports, memos, emails, letters, and other written materials related to the case study. Documents can be collected from the case study participants or from public sources.
Surveys involve asking a set of questions to a sample of individuals relevant to the case study. Surveys can be administered in person, over the phone, through mail or email, or online. Surveys can be used to gather information on attitudes, opinions, or behaviors related to the case study.
Artifacts are physical objects relevant to the case study. Artifacts can include tools, equipment, products, or other objects that provide insights into the case study phenomenon.
How to conduct Case Study Research
Conducting a case study research involves several steps that need to be followed to ensure the quality and rigor of the study. Here are the steps to conduct case study research:
- Define the research questions: The first step in conducting a case study research is to define the research questions. The research questions should be specific, measurable, and relevant to the case study phenomenon under investigation.
- Select the case: The next step is to select the case or cases to be studied. The case should be relevant to the research questions and should provide rich and diverse data that can be used to answer the research questions.
- Collect data: Data can be collected using various methods, such as interviews, observations, documents, surveys, and artifacts. The data collection method should be selected based on the research questions and the nature of the case study phenomenon.
- Analyze the data: The data collected from the case study should be analyzed using various techniques, such as content analysis, thematic analysis, or grounded theory. The analysis should be guided by the research questions and should aim to provide insights and conclusions relevant to the research questions.
- Draw conclusions: The conclusions drawn from the case study should be based on the data analysis and should be relevant to the research questions. The conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clearly stated.
- Validate the findings: The findings of the case study should be validated by reviewing the data and the analysis with participants or other experts in the field. This helps to ensure the validity and reliability of the findings.
- Write the report: The final step is to write the report of the case study research. The report should provide a clear description of the case study phenomenon, the research questions, the data collection methods, the data analysis, the findings, and the conclusions. The report should be written in a clear and concise manner and should follow the guidelines for academic writing.
Examples of Case Study
Here are some examples of case study research:
- The Hawthorne Studies : Conducted between 1924 and 1932, the Hawthorne Studies were a series of case studies conducted by Elton Mayo and his colleagues to examine the impact of work environment on employee productivity. The studies were conducted at the Hawthorne Works plant of the Western Electric Company in Chicago and included interviews, observations, and experiments.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment: Conducted in 1971, the Stanford Prison Experiment was a case study conducted by Philip Zimbardo to examine the psychological effects of power and authority. The study involved simulating a prison environment and assigning participants to the role of guards or prisoners. The study was controversial due to the ethical issues it raised.
- The Challenger Disaster: The Challenger Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Space Shuttle Challenger explosion in 1986. The study included interviews, observations, and analysis of data to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
- The Enron Scandal: The Enron Scandal was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the Enron Corporation’s bankruptcy in 2001. The study included interviews, analysis of financial data, and review of documents to identify the accounting practices, corporate culture, and ethical issues that led to the company’s downfall.
- The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster : The Fukushima Nuclear Disaster was a case study conducted to examine the causes of the nuclear accident that occurred at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant in Japan in 2011. The study included interviews, analysis of data, and review of documents to identify the technical, organizational, and cultural factors that contributed to the disaster.
Application of Case Study
Case studies have a wide range of applications across various fields and industries. Here are some examples:
Business and Management
Case studies are widely used in business and management to examine real-life situations and develop problem-solving skills. Case studies can help students and professionals to develop a deep understanding of business concepts, theories, and best practices.
Case studies are used in healthcare to examine patient care, treatment options, and outcomes. Case studies can help healthcare professionals to develop critical thinking skills, diagnose complex medical conditions, and develop effective treatment plans.
Case studies are used in education to examine teaching and learning practices. Case studies can help educators to develop effective teaching strategies, evaluate student progress, and identify areas for improvement.
Social Sciences
Case studies are widely used in social sciences to examine human behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. Case studies can help researchers to develop theories, test hypotheses, and gain insights into complex social issues.
Law and Ethics
Case studies are used in law and ethics to examine legal and ethical dilemmas. Case studies can help lawyers, policymakers, and ethical professionals to develop critical thinking skills, analyze complex cases, and make informed decisions.
Purpose of Case Study
The purpose of a case study is to provide a detailed analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. A case study is a qualitative research method that involves the in-depth exploration and analysis of a particular case, which can be an individual, group, organization, event, or community.
The primary purpose of a case study is to generate a comprehensive and nuanced understanding of the case, including its history, context, and dynamics. Case studies can help researchers to identify and examine the underlying factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and detailed understanding of the case, which can inform future research, practice, or policy.
Case studies can also serve other purposes, including:
- Illustrating a theory or concept: Case studies can be used to illustrate and explain theoretical concepts and frameworks, providing concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Developing hypotheses: Case studies can help to generate hypotheses about the causal relationships between different factors and outcomes, which can be tested through further research.
- Providing insight into complex issues: Case studies can provide insights into complex and multifaceted issues, which may be difficult to understand through other research methods.
- Informing practice or policy: Case studies can be used to inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
Advantages of Case Study Research
There are several advantages of case study research, including:
- In-depth exploration: Case study research allows for a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific phenomenon, issue, or problem in its real-life context. This can provide a comprehensive understanding of the case and its dynamics, which may not be possible through other research methods.
- Rich data: Case study research can generate rich and detailed data, including qualitative data such as interviews, observations, and documents. This can provide a nuanced understanding of the case and its complexity.
- Holistic perspective: Case study research allows for a holistic perspective of the case, taking into account the various factors, processes, and mechanisms that contribute to the case and its outcomes. This can help to develop a more accurate and comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Theory development: Case study research can help to develop and refine theories and concepts by providing empirical evidence and concrete examples of how they can be applied in real-life situations.
- Practical application: Case study research can inform practice or policy by identifying best practices, lessons learned, or areas for improvement.
- Contextualization: Case study research takes into account the specific context in which the case is situated, which can help to understand how the case is influenced by the social, cultural, and historical factors of its environment.
Limitations of Case Study Research
There are several limitations of case study research, including:
- Limited generalizability : Case studies are typically focused on a single case or a small number of cases, which limits the generalizability of the findings. The unique characteristics of the case may not be applicable to other contexts or populations, which may limit the external validity of the research.
- Biased sampling: Case studies may rely on purposive or convenience sampling, which can introduce bias into the sample selection process. This may limit the representativeness of the sample and the generalizability of the findings.
- Subjectivity: Case studies rely on the interpretation of the researcher, which can introduce subjectivity into the analysis. The researcher’s own biases, assumptions, and perspectives may influence the findings, which may limit the objectivity of the research.
- Limited control: Case studies are typically conducted in naturalistic settings, which limits the control that the researcher has over the environment and the variables being studied. This may limit the ability to establish causal relationships between variables.
- Time-consuming: Case studies can be time-consuming to conduct, as they typically involve a detailed exploration and analysis of a specific case. This may limit the feasibility of conducting multiple case studies or conducting case studies in a timely manner.
- Resource-intensive: Case studies may require significant resources, including time, funding, and expertise. This may limit the ability of researchers to conduct case studies in resource-constrained settings.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...

Correlational Research – Methods, Types and...

Research Methods – Types, Examples and Guide

Basic Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Experimental Design – Types, Methods, Guide

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples
AI Detector
What is a Case Study?: Definition, Examples, & Methods
Published on July 9th, 2024

I. What is a Case Study?: Introduction
Case study definition.
A case study is a research method involving an in-depth examination of a single subject, group, event, or phenomenon within its real-world context. Widely used across various disciplines such as social sciences, business, law, medicine, and education, case studies provide comprehensive insights into complex issues that broader surveys or experimental research cannot capture. The essence of a case study is to explore and analyze real-life situations to uncover patterns, identify causes, and propose practical solutions. Case study examples illustrate how theoretical knowledge can be applied to practical scenarios, making them invaluable for both academic research and problem-solving.
Importance in Research and Business
Case studies are crucial in both research and business due to their ability to provide detailed and nuanced insights. In academic research, case studies enable in-depth analysis of complex issues, helping researchers understand the how and why of phenomena, and leading to the development of new theories or the refinement of existing ones. In business, case studies help understand market dynamics, consumer behavior, and the effectiveness of strategies. They showcase successes and failures, offering valuable lessons for future projects. In education, especially in business schools, case studies help students develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills by analyzing real-world scenarios.
Brief History of Case Study Methodology
The case study methodology has a rich history, originating in the early 20th century in sociology. The Chicago School of Sociology used case studies to explore urban life and social issues. This approach was later adopted in psychology by figures like Sigmund Freud, who used detailed case studies to develop his theories on psychoanalysis. By the mid-20th century, Harvard Business School had popularized case studies as a teaching tool, encouraging students to analyze real-world business scenarios. Over the years, standardized templates have been developed to ensure consistency in data collection and analysis.
In modern times, case studies have adapted to the digital age with advanced data analysis software and AI tools, which ensures the originality and accuracy of case study content. This evolution highlights the adaptability and enduring relevance of case studies as a powerful tool for gaining in-depth understanding and generating valuable insights across various fields.
II. Types of Case Studies
Let’s learn about the different types of case studies that help researchers choose the appropriate method to gain deep insights into their subject.
A. Explanatory Case Studies
Explanatory case studies are designed to explore cause-and-effect relationships. They aim to explain how and why certain events occur and what factors influence these outcomes. This type of case study is often used in social sciences, business, and policy research to test theories and develop new insights. For example, an explanatory case study might investigate how a specific business strategy led to increased market share or how a new policy affected public health outcomes. By focusing on detailed and comprehensive analysis, explanatory case studies help researchers define case study contexts and understand complex phenomena.
B. Exploratory Case Studies
Exploratory case studies are used to explore a topic or issue when there are no clear outcomes or established theories. They serve as a preliminary step that can help to identify research questions and hypotheses for further study. This type of case study is particularly useful when the subject matter is new or not well understood. For instance, researchers might conduct an exploratory case study to investigate the impact of emerging technologies on consumer behavior. Exploratory case studies are flexible and open-ended, allowing researchers to gather rich, qualitative data that can guide future research directions.
C. Descriptive Case Studies
Descriptive case studies provide a detailed account of a specific subject, event, or phenomenon. They aim to describe the context, characteristics, and outcomes without necessarily investigating causal relationships. This type of case study is useful for documenting and understanding the particulars of a situation. For example, a descriptive case study might provide an in-depth look at a company's organizational structure and culture. By offering a comprehensive overview, descriptive case studies help to illustrate and contextualize complex issues, making them easier to understand and analyze.
D. Multiple-Case Studies
Multiple-case studies, also known as comparative case studies, involve the analysis of several cases to understand similarities and differences. This type of case study allows researchers to compare and contrast different instances of a phenomenon, which can lead to more robust and generalizable findings. For example, a multiple-case study might examine several companies that have implemented similar business strategies to identify common factors that contribute to success. By analyzing multiple cases, researchers can draw broader conclusions and develop more nuanced insights.
E. Intrinsic Case Studies
Intrinsic case studies focus on a specific case because it is unique or interesting in its own right. The primary aim is to gain a deeper understanding of the case itself, rather than to generalize findings to other contexts. This type of case study is often used when the case has particular significance or offers unique insights. For example, an intrinsic case study might investigate a rare medical condition to understand its characteristics and implications. By delving deeply into the specifics of the case, intrinsic case studies provide valuable, detailed knowledge that can inform practice and theory.
F. Instrumental Case Studies
Instrumental case studies use a specific case to gain insights into a broader issue or to refine a theoretical concept. The case itself is of secondary interest; it serves as a means to understand something else. For example, a researcher might use an instrumental case study of a particular organization to explore general principles of organizational behavior. This type of case study is useful for developing and testing theories, as it allows researchers to apply and examine theoretical frameworks in real-world contexts.
G. Collective Case Studies
Collective case studies, also known as multiple-case studies, involve studying a group of cases simultaneously or sequentially. This approach aims to investigate a phenomenon, population, or general condition by analyzing multiple instances. Collective case studies are valuable for identifying patterns and trends across different cases. For instance, a collective case study might examine several educational programs across different schools to understand common factors that contribute to student success. By studying multiple cases, researchers can enhance the reliability and validity of their findings and develop a more comprehensive understanding of the topic.
Each type of case study offers unique advantages and serves different research purposes. Whether researchers aim to explain causal relationships, explore new topics, provide detailed descriptions, compare multiple instances, or gain insights into broader issues, case studies are versatile tools that can be tailored to fit various research needs. Using tools like case study templates and following a structured case study format can help ensure that the research is thorough and well-organized. By understanding the different types of case studies, researchers can choose the most appropriate method to achieve their objectives and generate meaningful insights.
Also read: Uncover the power of our recruitment automation through customer stories, read our customer stories .
III. The Structure of a Case Study
A well-structured case study is essential for effectively communicating the research findings and insights, ensuring clarity and comprehensiveness.
Title and Abstract : The title should be clear, concise, and reflective of the main focus of the case study. The abstract provides a summary, usually between 150-250 words, outlining the purpose, methodology, key findings, and conclusions of the study. This section helps readers quickly understand the essence of the case study.
B. Background Information
Background Information : This section sets the context for the case study by providing relevant information about the subject being studied. It includes details about the history, environment, and circumstances surrounding the case. For example, if the case study is about a business, the background information might cover the company’s history, industry context, and market conditions.
C. Introduction and Problem Statement
Introduction and Problem Statement : The introduction offers an overview of the case study’s purpose and scope. The problem statement clearly defines the specific issue or research question that the case study aims to address. This section explains why the problem is significant and warrants investigation. For example, a problem statement might highlight a decline in customer satisfaction at a company and the need to understand the underlying causes.
D. Methodology
Methodology : The methodology section details the research design and approach used to conduct the study. It includes the methods and procedures for data collection and analysis. This section should provide enough detail to allow replication of the study. Common methodologies include qualitative methods like interviews and observations, quantitative methods like surveys and statistical analysis, or a combination of both.
E. Data Collection and Analysis
Data Collection and Analysis : This section describes the specific techniques used to gather data and the process of analyzing it. It includes information on data sources, sampling methods, and data collection instruments. The analysis part explains how the data was processed and interpreted to arrive at the findings. For example, in a business case study, data collection might involve employee interviews and customer surveys, while analysis might involve thematic coding and statistical correlation.
F. Findings and Analysis
Findings and Analysis : The findings section presents the results of the study, detailing what the data revealed about the problem. The analysis interprets these findings, explaining their significance and implications. This section should be organized logically, often using headings and subheadings to guide the reader through different aspects of the findings. For instance, findings might show a correlation between employee training and customer satisfaction, with the analysis explaining how training improves service quality.
G. Proposed Solutions and Recommendations
Proposed Solutions and Recommendations : Based on the findings, this section suggests practical actions or strategies to address the identified problems. It outlines specific steps that stakeholders can take to implement these solutions. Recommendations should be feasible, backed by the data, and aligned with the study’s goals. For example, recommendations might include implementing a new training program for employees or adopting new customer service policies.
H. Conclusion
Conclusion : The conclusion summarizes the main findings and their implications. It reinforces the significance of the study and may suggest areas for further research. This section ties together the entire case study, providing a final perspective on the problem and the proposed solutions. The conclusion should leave the reader with a clear understanding of what was learned and why it matters.
I. References and Appendices
References and Appendices : The references section lists all the sources cited in the case study, following a standard citation format (e.g., APA, MLA). This ensures proper attribution and allows readers to locate the original sources. The appendices include supplementary materials that support the case study, such as raw data, detailed tables, questionnaires, or interview transcripts. These materials provide additional context and evidence for the study’s findings and conclusions.
By adhering to this comprehensive structure, researchers can ensure their case studies are thorough, and well-organized, and effectively communicate their findings and insights to the audience.
IV. The Case Study Process
The process of conducting a case study involves several systematic steps that ensure thorough and credible research.
A. Identifying the Research Question
The first step in the case study process is to define a clear and focused research question. This question should address a specific issue or problem that the case study aims to explore. The research question guides the entire study, helping to determine the scope and objectives. For instance, a business case study might pose the question, "How does employee training impact customer satisfaction in retail settings?"
B. Selecting the Case and Determining Data-Gathering Techniques
Once the research question is established, the next step is to select a case that provides the best opportunity to explore this question. The case can be an individual, group, organization, event, or phenomenon. The selection should be purposeful and based on specific criteria relevant to the research question. Additionally, researchers must determine the most appropriate data-gathering techniques, such as interviews, surveys, observations, or document analysis, to collect the necessary information.
C. Preparing to Collect Data
Before data collection begins, researchers must develop a detailed plan outlining the procedures and tools to be used. This preparation includes creating data collection instruments (e.g., interview guides, and survey questionnaires), obtaining necessary permissions and ethical approvals, and ensuring logistical arrangements are in place. Proper preparation ensures that data collection is systematic and consistent, minimizing potential biases and errors.
D. Collecting Data in the Field
Data collection involves gathering information directly from the selected case using predetermined techniques. This phase requires careful attention to detail and adherence to the planned methods. For example, conducting interviews requires skilled questioning and active listening, while observations necessitate systematic note-taking. Ensuring data quality and integrity is crucial during this phase to maintain the credibility of the study.
E. Evaluating and Analyzing the Data
After data collection, researchers must evaluate and analyze the gathered information to draw meaningful conclusions. This process involves organizing the data, coding for themes and patterns, and using analytical techniques to interpret the findings. Qualitative data might be analyzed through thematic analysis, while quantitative data could be subjected to statistical analysis. The goal is to identify key insights that address the research question and provide a deeper understanding of the case.
F. Reporting the Findings
The final step in the case study process is to compile the findings into a comprehensive report. This report should follow a structured format, including sections such as the introduction, methodology, findings, analysis, proposed solutions, and conclusion. The report should clearly communicate the research question, the process followed, the data collected, and the insights gained. Visual aids like charts, graphs, and tables can enhance the presentation of data. Additionally, the report should provide actionable recommendations based on the findings, and it should be tailored to the intended audience, whether academic, professional, or general readers.
By following these steps, researchers can ensure a rigorous and systematic approach to conducting case studies, resulting in credible and valuable insights that contribute to knowledge and practice in their respective fields.
V. Benefits of Case Studies
Case studies offer numerous benefits that make them a valuable research method in various fields.
A. In-depth Analysis of Complex Issues
In-depth Analysis of Complex Issues : Case studies allow researchers to conduct a thorough and detailed examination of complex issues. This method provides a deep understanding of the subject matter by exploring multiple facets and perspectives. For instance, a case study on a company’s turnaround strategy can delve into the financial, operational, and cultural changes that contributed to its success. This in-depth analysis is often impossible to achieve through other research methods that provide more generalized data.
B. Real-world Application of Theories
Real-world Application of Theories : Case studies bridge the gap between theory and practice by applying theoretical concepts to real-world scenarios. They demonstrate how abstract theories can be implemented and tested in practical situations. For example, a case study on leadership styles in crisis management can show how different theoretical approaches to leadership are applied in real-life crises, providing valuable insights for both academics and practitioners.
C. Generation of New Hypotheses
Generation of New Hypotheses : Through detailed investigation and observation, case studies often reveal new insights and patterns that can lead to the generation of new hypotheses. These hypotheses can then be tested in future research, contributing to the advancement of knowledge in the field. For example, a case study on consumer behavior might uncover new trends or factors influencing purchasing decisions, prompting further research into these areas.
D. Versatility Across Various Fields
Versatility Across Various Fields : Case studies are a versatile research method that can be applied in various fields, including business, education, medicine, law, and social sciences. They can be used to study a wide range of topics, from individual behaviors to organizational practices and societal phenomena. This versatility makes case studies a popular choice for researchers seeking to understand diverse and complex issues.
VI. Challenges in Conducting Case Studies
Despite their benefits, conducting case studies also presents several challenges that researchers need to be aware of and address.
A. Potential for Researcher Bias
Potential for Researcher Bias : One of the primary challenges of case studies is the potential for researcher bias. Since case studies often involve close interaction between the researcher and the subject, there is a risk that the researcher’s perspectives and preconceptions may influence the findings. To mitigate this, researchers must strive for objectivity, use multiple sources of evidence, and employ techniques like triangulation to validate their findings.
B. Limited Generalizability
Limited Generalizability : Case studies typically focus on a single case or a small number of cases, which can limit the generalizability of the findings. The insights gained from a specific case may not necessarily apply to other contexts or populations. To address this limitation, researchers should clearly define the scope of their study and acknowledge the extent to which their findings can be generalized.
C. Time-consuming Nature
Time-consuming Nature : Conducting a thorough case study can be time-consuming, requiring extensive data collection, analysis, and reporting. This can be a significant drawback, especially for researchers with limited time and resources. To manage this challenge, researchers should plan their study carefully, set realistic timelines, and ensure they have the necessary resources to complete the study effectively.
D. Ethical Considerations
Ethical Considerations : Case studies often involve collecting detailed information about individuals or organizations, which raises important ethical considerations. Researchers must ensure that they obtain informed consent from participants, protect their privacy and confidentiality, and avoid any potential harm. Adhering to ethical guidelines and obtaining necessary approvals from ethics committees are crucial steps in conducting ethical case study research.
By understanding and addressing these challenges, researchers can enhance the reliability and credibility of their case studies, ensuring that their findings provide valuable contributions to their respective fields.
VII. Case Studies in Different Fields
Case studies are a versatile research method that can be applied across a wide range of fields, each benefiting from the in-depth analysis and practical insights they provide.
Business and Management : In the field of business and management, case studies are widely used to analyze organizational strategies, market dynamics, leadership practices, and operational processes. They offer detailed insights into how companies address challenges, implement changes, and achieve success.
For example, a business case study might explore how a company successfully navigated a financial crisis, providing lessons on crisis management, financial planning, and leadership. These case studies are valuable for both academic purposes and practical applications, helping managers and executives learn from real-world examples.
Psychology and Social Sciences : Case studies in psychology and social sciences provide an in-depth examination of individual or group behavior, social phenomena, and cultural practices. They are particularly useful for exploring complex psychological conditions, social interactions, and cultural contexts.
For instance, a psychological case study might investigate the development and treatment of a specific mental health disorder in a patient, offering insights into therapeutic approaches and patient experiences. In social sciences, case studies can explore social issues such as poverty, education, and community development, contributing to a deeper understanding of societal challenges and potential solutions.
Medicine and Healthcare : In medicine and healthcare, case studies are essential for understanding unique medical conditions, treatment outcomes, and healthcare practices. They provide detailed accounts of patient histories, diagnoses, treatments, and responses, contributing to medical knowledge and practice.
For example, a medical case study might document a rare disease, detailing the symptoms, diagnostic process, treatment plan, and patient recovery. These studies are valuable for medical education, helping practitioners learn from specific cases and improve patient care. They also play a crucial role in advancing medical research by highlighting unusual cases that can lead to new discoveries.
Law and Criminal Justice : Case studies in law and criminal justice offer comprehensive analyses of legal cases, criminal behavior, law enforcement practices, and judicial decisions. They help understand the intricacies of legal principles, the application of laws, and the effectiveness of criminal justice policies.
For instance, a legal case study might analyze a landmark Supreme Court decision, examining the legal arguments, judicial reasoning, and broader implications for society. In criminal justice, case studies can explore crime patterns, investigative techniques, and rehabilitation programs, providing valuable insights for law enforcement and policy-making.
Education : In the field of education, case studies are used to explore teaching methods, learning outcomes, educational policies, and institutional practices. They provide detailed examinations of specific educational settings, programs, and student experiences.
For example, an educational case study might investigate the implementation of a new teaching strategy in a classroom, analyzing its impact on student engagement and academic performance. These studies are valuable for educators, administrators, and policymakers, offering practical insights into effective educational practices and innovations. Case studies in education help identify best practices, address challenges, and improve the overall quality of education.
VIII. Tools and Techniques for Case Study Research
The effectiveness of case study research often hinges on the tools and techniques used for data collection and analysis. Here are some key methods and tools that enhance the quality and depth of case study research.
Interviews and Surveys :
Interviews and surveys are fundamental techniques for gathering qualitative and quantitative data in case studies. Interviews allow for in-depth exploration of subjects' experiences, perspectives, and insights. They can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, depending on the research goals. Surveys, on the other hand, provide a means to collect data from a larger sample, offering quantifiable insights that can complement qualitative findings. For example, in a business case study, interviews with key stakeholders can reveal detailed insights into organizational culture, while surveys can gauge employee satisfaction across the company.
Observation Methods :
Observation involves systematically recording behaviors, events, and interactions as they occur naturally. This method is particularly useful for understanding the context and dynamics of the case under study. Participant observation, where the researcher becomes part of the group being studied, and non-participant observation, where the researcher observes from a distance, are common techniques. For instance, in an educational case study, observing classroom interactions can provide valuable data on teaching methods and student engagement.
Document Analysis :
Document analysis involves reviewing and interpreting existing documents related to the case. These documents can include reports, memos, letters, emails, meeting minutes, policy documents, and other records. Analyzing these documents can provide insights into the historical context, organizational processes, and key events relevant to the case. For example, in a legal case study, analyzing court documents, legal briefs, and case law can help understand the legal arguments and judicial decisions.
Data Analysis Software :
Data analysis software helps researchers organize, code, and analyze qualitative and quantitative data efficiently. Tools like NVivo, ATLAS.ti, and MAXQDA are commonly used for qualitative data analysis, enabling researchers to code text, identify themes, and visualize relationships. For quantitative data, software like SPSS, Stata, and R can perform statistical analysis, providing detailed insights into data patterns and correlations. These tools enhance the rigor and reliability of the analysis, making it easier to manage large volumes of data and derive meaningful conclusions.
AI Tools like HireQuotient's AI Detector :
HireQuotient's AI Detector is an advanced tool designed to ensure the originality and integrity of written content. It uses artificial intelligence to detect plagiarism, analyze text for unique patterns, and verify the authenticity of research material.
How It Can Be Used in Case Study Research : In case study research, HireQuotient's AI Detector can be used to check the originality of the case study report, ensuring that the content is free from plagiarism. This tool can also help in verifying the authenticity of sources and data used in the case study, providing an additional layer of validation. By analyzing text for unique patterns, the AI Detector can assist researchers in maintaining the quality and credibility of their work.
Benefits of Using AI in Case Study Analysis : Using AI tools like HireQuotient's AI Detector in case study analysis offers several benefits. First, it enhances the credibility and reliability of the research by ensuring that all content is original and properly cited. Second, it saves time and effort in manually checking for plagiarism and verifying sources, allowing researchers to focus on more critical aspects of the study. Third, AI tools can process large volumes of data quickly and accurately, identifying patterns and insights that might be missed through manual analysis. Overall, integrating AI into case study research improves the efficiency, accuracy, and integrity of the research process.
By leveraging these tools and techniques, researchers can conduct comprehensive and rigorous case studies that provide valuable insights and contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields.
IX. Writing and Presenting Case Studies
Effectively writing and presenting case studies is crucial for conveying research findings in a clear and impactful manner. Here are key considerations for each aspect of this process.
A. Choosing a Compelling Narrative Style
The narrative style chosen for a case study can significantly influence its readability and engagement. A compelling narrative weaves facts and analysis into a cohesive story that captures the reader’s attention. Depending on the audience and purpose, the narrative style can be:
- Descriptive : Providing a detailed account of events and contexts, often used for educational purposes.
- Analytical : Focusing on the interpretation and implications of the findings, suitable for academic and research audiences.
- Persuasive : Aiming to convince the reader of a particular viewpoint or course of action, commonly used in business and policy-making contexts.
- Reflective : Incorporating personal insights and reflections, which can be effective in educational and professional development settings.
Selecting a narrative style that aligns with the objectives of the case study and the preferences of the target audience helps ensure that the message is conveyed effectively.
B. Structuring the Case Study Report
A well-structured case study report enhances clarity and coherence, making it easier for readers to follow the research process and understand the findings. A typical structure includes:
- Title and Abstract : Concise summary of the study’s focus and key findings.
- Introduction : Overview of the research question, objectives, and significance of the study.
- Background Information : Contextual information about the subject or case being studied.
- Problem Statement : Clear definition of the problem or issue addressed by the study.
- Methodology : Detailed description of the research methods and procedures used for data collection and analysis.
- Findings and Analysis : Presentation and interpretation of the research results.
- Proposed Solutions and Recommendations : Practical suggestions based on the findings.
- Conclusion : Summary of the main insights and their implications.
- References and Appendices : List of sources cited and supplementary materials.
Using headings and subheadings to organize these sections helps guide the reader through the report and ensures all key components are covered.
C. Using Visuals and Data Representation
Visual aids such as charts, graphs, tables, and diagrams can significantly enhance the presentation of data and findings in a case study. Effective use of visuals can:
- Clarify Complex Information : Simplifying complex data and relationships.
- Highlight Key Points : Drawing attention to important findings and trends.
- Enhance Engagement : Making the report more visually appealing and easier to digest.
When using visuals, it’s important to ensure they are clearly labeled, accurately represent the data, and are integrated seamlessly into the narrative. Visuals should complement and reinforce the textual content rather than distract from it.
D. Tailoring the Presentation to the Audience
The presentation of a case study should be tailored to the specific needs and preferences of the intended audience. Consider the following:
- Academic Audience : Focus on methodological rigor, theoretical contributions, and detailed analysis. Use formal language and provide extensive references.
- Business Audience : Emphasize practical implications, actionable recommendations, and real-world applications. Use clear, concise language and highlight key insights and solutions.
- General Audience : Make the content accessible and engaging by using simple language, storytelling techniques, and relatable examples. Avoid jargon and technical terms that may be unfamiliar.
By paying careful attention to narrative style, report structure, use of visuals, and audience tailoring, researchers can create compelling and impactful case studies that effectively convey their findings and insights.
X. Case Studies vs. Other Research Methods
Experimental research involves manipulating one or more variables to observe the effect on another variable, typically in a controlled environment. This method is highly effective for establishing cause-and-effect relationships and testing hypotheses. In contrast, case studies focus on the in-depth exploration of a single subject or small group within its real-life context. While experiments prioritize control and generalizability, case studies emphasize detailed understanding and contextual relevance. Case studies are particularly valuable when the research question requires exploring complex phenomena that cannot be easily isolated in an experimental setting.
Surveys and questionnaires are quantitative research methods designed to gather data from a large population, often through structured questions with predefined response options. These methods are useful for identifying trends, measuring attitudes, and making statistical generalizations. In contrast, case studies employ qualitative methods such as interviews and observations to provide rich, detailed insights into a specific case. While surveys and questionnaires offer breadth, case studies provide depth, allowing researchers to uncover nuanced information and develop a comprehensive understanding of the subject.
Ethnographic studies involve immersive, long-term fieldwork where researchers observe and interact with participants in their natural environment to understand cultural practices and social behaviors. Both ethnographic studies and case studies prioritize in-depth, qualitative analysis and contextual understanding. However, ethnography typically focuses on entire communities or cultures, while case studies concentrate on specific individuals, groups, or events. Case studies may use ethnographic techniques but are usually narrower in scope and duration.
Mixed methods research combines qualitative and quantitative approaches to provide a more comprehensive understanding of the research problem. Case studies can be an integral part of mixed methods research by incorporating both qualitative data (e.g., interviews, observations) and quantitative data (e.g., surveys, statistical analysis). This integration allows researchers to explore the case in detail while also quantifying certain aspects, enhancing the robustness and validity of the findings. Mixed methods research benefits from the detailed insights of case studies and the generalizability of quantitative data.
XI. The Future of Case Study Research
Technological Advancements in Data Collection and Analysis : Advances in technology are revolutionizing the way data is collected and analyzed in case study research. Tools such as mobile apps, online surveys, and digital recording devices facilitate efficient and accurate data collection. Data analysis software like NVivo and ATLAS.ti enables researchers to organize, code, and interpret large volumes of qualitative data. Additionally, big data analytics and machine learning algorithms offer new possibilities for identifying patterns and insights from complex datasets, enhancing the depth and precision of case study analysis.
Increasing Focus on Cross-Cultural Case Studies : Globalization and interconnectedness have heightened the importance of understanding cultural differences and similarities. Cross-cultural case studies are gaining prominence as researchers seek to compare and contrast cases from different cultural contexts. These studies provide valuable insights into how cultural factors influence behaviors, practices, and outcomes. By examining cases from diverse settings, researchers can develop more comprehensive and culturally sensitive theories and solutions.
The Role of AI and Machine Learning in Case Study Research : AI and machine learning are transforming case study research by automating data analysis and enhancing accuracy. Tools like HireQuotient's AI Detector help ensure the originality and integrity of case study content by detecting plagiarism and verifying sources. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets quickly, identifying patterns and correlations that may be overlooked by human researchers. These technologies enable more efficient data processing, allowing researchers to focus on interpreting and applying the findings.
Emerging Trends in Case Study Methodology : New trends in case study methodology are shaping the future of research. One trend is the increasing use of digital ethnography, where researchers study online communities and virtual environments. Another trend is the emphasis on participatory case studies, involving stakeholders in the research process to ensure their perspectives are represented. Additionally, there is a growing interest in longitudinal case studies that track changes over time, providing deeper insights into dynamic processes and long-term outcomes.
XII. Conclusion
Case studies are a versatile and valuable research method that offers in-depth analysis, real-world applications, and the ability to generate new hypotheses. They differ from other research methods in their focus on detailed, contextual understanding.
Thus, undertake your own case studies, leveraging the tools and techniques discussed to explore complex issues and contribute to their fields. With advancements in technology and methodology, conducting case studies is more accessible and impactful than ever. Whether for academic research, business analysis, or personal interest, case studies offer a powerful means to gain deep, actionable insights.

Soujanya Varada
As a technical content writer and social media strategist, Soujanya develops and manages strategies at HireQuotient. With strong technical background and years of experience in content management, she looks for opportunities to flourish in the digital space. Soujanya is also a dance fanatic and believes in spreading light!

Hire the best without stress

Never Miss The Updates
We cover all recruitment, talent analytics, L&D, DEI, pre-employment, candidate screening, and hiring tools. Join our force & subscribe now!
Stay On Top Of Everything In HR
- Case Reports
Qualitative Case Study Methodology: Study Design and Implementation for Novice Researchers
- January 2010
- The Qualitative Report 13(4)

- McMaster University

Abstract and Figures

Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations
- Saleha Haris Kayani
- Muhammad Arif Saleem
- Raja Mazhar Hameed

- J ACAD LIBR
- TELECOMMUN POLICY
- Henning Schoenenberger
- Kai Jun Chew
- Holly M. Matusovich

- Bob Algozzine

- B J Breitmayer
- Y.S. Lincoln
- ADV NURS SCI
- Margarete Sandelowski

- John W. Scheib
- Robert E. Stake
- Thomas J. Richards

- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- Usability testing
Run remote usability tests on any digital product to deep dive into your key user flows
- Product analytics
Learn how users are behaving on your website in real time and uncover points of frustration
- Research repository
A tool for collaborative analysis of qualitative data and for building your research repository and database.
- Trymata Blog
How-to articles, expert tips, and the latest news in user testing & user experience
- Knowledge Hub
Detailed explainers of Trymata’s features & plans, and UX research terms & topics
- Plans & Pricing
Get paid to test
- User Experience (UX) testing
- User Interface (UI) testing
- Ecommerce testing
- Remote usability testing
- Plans & Pricing
- Customer Stories
How do you want to use Trymata?
Conduct user testing, desktop usability video.
You’re on a business trip in Oakland, CA. You've been working late in downtown and now you're looking for a place nearby to grab a late dinner. You decided to check Zomato to try and find somewhere to eat. (Don't begin searching yet).
- Look around on the home page. Does anything seem interesting to you?
- How would you go about finding a place to eat near you in Downtown Oakland? You want something kind of quick, open late, not too expensive, and with a good rating.
- What do the reviews say about the restaurant you've chosen?
- What was the most important factor for you in choosing this spot?
- You're currently close to the 19th St Bart station, and it's 9PM. How would you get to this restaurant? Do you think you'll be able to make it before closing time?
- Your friend recommended you to check out a place called Belly while you're in Oakland. Try to find where it is, when it's open, and what kind of food options they have.
- Now go to any restaurant's page and try to leave a review (don't actually submit it).
What was the worst thing about your experience?
It was hard to find the bart station. The collections not being able to be sorted was a bit of a bummer
What other aspects of the experience could be improved?
Feedback from the owners would be nice
What did you like about the website?
The flow was good, lots of bright photos
What other comments do you have for the owner of the website?
I like that you can sort by what you are looking for and i like the idea of collections
You're going on a vacation to Italy next month, and you want to learn some basic Italian for getting around while there. You decided to try Duolingo.
- Please begin by downloading the app to your device.
- Choose Italian and get started with the first lesson (stop once you reach the first question).
- Now go all the way through the rest of the first lesson, describing your thoughts as you go.
- Get your profile set up, then view your account page. What information and options are there? Do you feel that these are useful? Why or why not?
- After a week in Italy, you're going to spend a few days in Austria. How would you take German lessons on Duolingo?
- What other languages does the app offer? Do any of them interest you?
I felt like there could have been a little more of an instructional component to the lesson.
It would be cool if there were some feature that could allow two learners studying the same language to take lessons together. I imagine that their screens would be synced and they could go through lessons together and chat along the way.
Overall, the app was very intuitive to use and visually appealing. I also liked the option to connect with others.
Overall, the app seemed very helpful and easy to use. I feel like it makes learning a new language fun and almost like a game. It would be nice, however, if it contained more of an instructional portion.
All accounts, tests, and data have been migrated to our new & improved system!
Use the same email and password to log in:
Legacy login: Our legacy system is still available in view-only mode, login here >
What’s the new system about? Read more about our transition & what it-->
What is a Case Study? Definition, Research Methods, Sampling and Examples
Conduct End-to-End User Testing & Research
What is a Case Study?
A case study is defined as an in-depth analysis of a particular subject, often a real-world situation, individual, group, or organization.
It is a research method that involves the comprehensive examination of a specific instance to gain a better understanding of its complexities, dynamics, and context.
Case studies are commonly used in various fields such as business, psychology, medicine, and education to explore and illustrate phenomena, theories, or practical applications.
In a typical case study, researchers collect and analyze a rich array of qualitative and/or quantitative data, including interviews, observations, documents, and other relevant sources. The goal is to provide a nuanced and holistic perspective on the subject under investigation.
The information gathered here is used to generate insights, draw conclusions, and often to inform broader theories or practices within the respective field.
Case studies offer a valuable method for researchers to explore real-world phenomena in their natural settings, providing an opportunity to delve deeply into the intricacies of a particular case. They are particularly useful when studying complex, multifaceted situations where various factors interact.
Additionally, case studies can be instrumental in generating hypotheses, testing theories, and offering practical insights that can be applied to similar situations. Overall, the comprehensive nature of case studies makes them a powerful tool for gaining a thorough understanding of specific instances within the broader context of academic and professional inquiry.
Key Characteristics of Case Study
Case studies are characterized by several key features that distinguish them from other research methods. Here are some essential characteristics of case studies:
- In-depth Exploration: Case studies involve a thorough and detailed examination of a specific case or instance. Researchers aim to explore the complexities and nuances of the subject under investigation, often using multiple data sources and methods to gather comprehensive information.
- Contextual Analysis: Case studies emphasize the importance of understanding the context in which the case unfolds. Researchers seek to examine the unique circumstances, background, and environmental factors that contribute to the dynamics of the case. Contextual analysis is crucial for drawing meaningful conclusions and generalizing findings to similar situations.
- Holistic Perspective: Rather than focusing on isolated variables, case studies take a holistic approach to studying a phenomenon. Researchers consider a wide range of factors and their interrelationships, aiming to capture the richness and complexity of the case. This holistic perspective helps in providing a more complete understanding of the subject.
- Qualitative and/or Quantitative Data: Case studies can incorporate both qualitative and quantitative data, depending on the research question and objectives. Qualitative data often include interviews, observations, and document analysis, while quantitative data may involve statistical measures or numerical information. The combination of these data types enhances the depth and validity of the study.
- Longitudinal or Retrospective Design: Case studies can be designed as longitudinal studies, where the researcher follows the case over an extended period, or retrospective studies, where the focus is on examining past events. This temporal dimension allows researchers to capture changes and developments within the case.
- Unique and Unpredictable Nature: Each case study is unique, and the findings may not be easily generalized to other situations. The unpredictable nature of real-world cases adds a layer of authenticity to the study, making it an effective method for exploring complex and dynamic phenomena.
- Theory Building or Testing: Case studies can serve different purposes, including theory building or theory testing. In some cases, researchers use case studies to develop new theories or refine existing ones. In others, they may test existing theories by applying them to real-world situations and assessing their explanatory power.
Understanding these key characteristics is essential for researchers and practitioners using case studies as a methodological approach, as it helps guide the design, implementation, and analysis of the study.
Key Components of a Case Study
A well-constructed case study typically consists of several key components that collectively provide a comprehensive understanding of the subject under investigation. Here are the key components of a case study:
- Provide an overview of the context and background information relevant to the case. This may include the history, industry, or setting in which the case is situated.
- Clearly state the purpose and objectives of the case study. Define what the study aims to achieve and the questions it seeks to answer.
- Clearly identify the subject of the case study. This could be an individual, a group, an organization, or a specific event.
- Define the boundaries and scope of the case study. Specify what aspects will be included and excluded from the investigation.
- Provide a brief review of relevant theories or concepts that will guide the analysis. This helps place the case study within the broader theoretical context.
- Summarize existing literature related to the subject, highlighting key findings and gaps in knowledge. This establishes the context for the current case study.
- Describe the research design chosen for the case study (e.g., exploratory, explanatory, descriptive). Justify why this design is appropriate for the research objectives.
- Specify the methods used to gather data, whether through interviews, observations, document analysis, surveys, or a combination of these. Detail the procedures followed to ensure data validity and reliability.
- Explain the criteria for selecting the case and any sampling considerations. Discuss why the chosen case is representative or relevant to the research questions.
- Describe how the collected data will be coded and categorized. Discuss the analytical framework or approach used to identify patterns, themes, or trends.
- If multiple data sources or methods are used, explain how they complement each other to enhance the credibility and validity of the findings.
- Present the key findings in a clear and organized manner. Use tables, charts, or quotes from participants to illustrate the results.
- Interpret the results in the context of the research objectives and theoretical framework. Discuss any unexpected findings and their implications.
- Provide a thorough interpretation of the results, connecting them to the research questions and relevant literature.
- Acknowledge the limitations of the study, such as constraints in data collection, sample size, or generalizability.
- Highlight the contributions of the case study to the existing body of knowledge and identify potential avenues for future research.
- Summarize the key findings and their significance in relation to the research objectives.
- Conclude with a concise summary of the case study, its implications, and potential practical applications.
- Provide a complete list of all the sources cited in the case study, following a consistent citation style.
- Include any additional materials or supplementary information, such as interview transcripts, survey instruments, or supporting documents.
By including these key components, a case study becomes a comprehensive and well-rounded exploration of a specific subject, offering valuable insights and contributing to the body of knowledge in the respective field.
Sampling in a Case Study Research
Sampling in case study research involves selecting a subset of cases or individuals from a larger population to study in depth. Unlike quantitative research where random sampling is often employed, case study sampling is typically purposeful and driven by the specific objectives of the study. Here are some key considerations for sampling in case study research:
- Criterion Sampling: Cases are selected based on specific criteria relevant to the research questions. For example, if studying successful business strategies, cases may be selected based on their demonstrated success.
- Maximum Variation Sampling: Cases are chosen to represent a broad range of variations related to key characteristics. This approach helps capture diversity within the sample.
- Selecting Cases with Rich Information: Researchers aim to choose cases that are information-rich and provide insights into the phenomenon under investigation. These cases should offer a depth of detail and variation relevant to the research objectives.
- Single Case vs. Multiple Cases: Decide whether the study will focus on a single case (single-case study) or multiple cases (multiple-case study). The choice depends on the research objectives, the complexity of the phenomenon, and the depth of understanding required.
- Emergent Nature of Sampling: In some case studies, the sampling strategy may evolve as the study progresses. This is known as theoretical sampling, where new cases are selected based on emerging findings and theoretical insights from earlier analysis.
- Data Saturation: Sampling may continue until data saturation is achieved, meaning that collecting additional cases or data does not yield new insights or information. Saturation indicates that the researcher has adequately explored the phenomenon.
- Defining Case Boundaries: Clearly define the boundaries of the case to ensure consistency and avoid ambiguity. Consider what is included and excluded from the case study, and justify these decisions.
- Practical Considerations: Assess the feasibility of accessing the selected cases. Consider factors such as availability, willingness to participate, and the practicality of data collection methods.
- Informed Consent: Obtain informed consent from participants, ensuring that they understand the purpose of the study and the ways in which their information will be used. Protect the confidentiality and anonymity of participants as needed.
- Pilot Testing the Sampling Strategy: Before conducting the full study, consider pilot testing the sampling strategy to identify potential challenges and refine the approach. This can help ensure the effectiveness of the sampling method.
- Transparent Reporting: Clearly document the sampling process in the research methodology section. Provide a rationale for the chosen sampling strategy and discuss any adjustments made during the study.
Sampling in case study research is a critical step that influences the depth and richness of the study’s findings. By carefully selecting cases based on specific criteria and considering the unique characteristics of the phenomenon under investigation, researchers can enhance the relevance and validity of their case study.
Case Study Research Methods With Examples
- Interviews:
- Interviews involve engaging with participants to gather detailed information, opinions, and insights. In a case study, interviews are often semi-structured, allowing flexibility in questioning.
- Example: A case study on workplace culture might involve conducting interviews with employees at different levels to understand their perceptions, experiences, and attitudes.
- Observations:
- Observations entail direct examination and recording of behavior, activities, or events in their natural setting. This method is valuable for understanding behaviors in context.
- Example: A case study investigating customer interactions at a retail store may involve observing and documenting customer behavior, staff interactions, and overall dynamics.
- Document Analysis:
- Document analysis involves reviewing and interpreting written or recorded materials, such as reports, memos, emails, and other relevant documents.
- Example: In a case study on organizational change, researchers may analyze internal documents, such as communication memos or strategic plans, to trace the evolution of the change process.
- Surveys and Questionnaires:
- Surveys and questionnaires collect structured data from a sample of participants. While less common in case studies, they can be used to supplement other methods.
- Example: A case study on the impact of a health intervention might include a survey to gather quantitative data on participants’ health outcomes.
- Focus Groups:
- Focus groups involve a facilitated discussion among a group of participants to explore their perceptions, attitudes, and experiences.
- Example: In a case study on community development, a focus group might be conducted with residents to discuss their views on recent initiatives and their impact.
- Archival Research:
- Archival research involves examining existing records, historical documents, or artifacts to gain insights into a particular phenomenon.
- Example: A case study on the history of a landmark building may involve archival research, exploring construction records, historical photos, and maintenance logs.
- Longitudinal Studies:
- Longitudinal studies involve the collection of data over an extended period to observe changes and developments.
- Example: A case study tracking the career progression of employees in a company may involve longitudinal interviews and document analysis over several years.
- Cross-Case Analysis:
- Cross-case analysis compares and contrasts multiple cases to identify patterns, similarities, and differences.
- Example: A comparative case study of different educational institutions may involve analyzing common challenges and successful strategies across various cases.
- Ethnography:
- Ethnography involves immersive, in-depth exploration within a cultural or social setting to understand the behaviors and perspectives of participants.
- Example: A case study using ethnographic methods might involve spending an extended period within a community to understand its social dynamics and cultural practices.
- Experimental Designs (Rare):
- While less common, experimental designs involve manipulating variables to observe their effects. In case studies, this might be applied in specific contexts.
- Example: A case study exploring the impact of a new teaching method might involve implementing the method in one classroom while comparing it to a traditional method in another.
These case study research methods offer a versatile toolkit for researchers to investigate and gain insights into complex phenomena across various disciplines. The choice of methods depends on the research questions, the nature of the case, and the desired depth of understanding.
Best Practices for a Case Study in 2024
Creating a high-quality case study involves adhering to best practices that ensure rigor, relevance, and credibility. Here are some key best practices for conducting and presenting a case study:
- Clearly articulate the purpose and objectives of the case study. Define the research questions or problems you aim to address, ensuring a focused and purposeful approach.
- Choose a case that aligns with the research objectives and provides the depth and richness needed for the study. Consider the uniqueness of the case and its relevance to the research questions.
- Develop a robust research design that aligns with the nature of the case study (single-case or multiple-case) and integrates appropriate research methods. Ensure the chosen design is suitable for exploring the complexities of the phenomenon.
- Use a variety of data sources to enhance the validity and reliability of the study. Combine methods such as interviews, observations, document analysis, and surveys to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case.
- Clearly document and describe the procedures for data collection to enhance transparency. Include details on participant selection, sampling strategy, and data collection methods to facilitate replication and evaluation.
- Implement measures to ensure the validity and reliability of the data. Triangulate information from different sources to cross-verify findings and strengthen the credibility of the study.
- Clearly define the boundaries of the case to avoid scope creep and maintain focus. Specify what is included and excluded from the study, providing a clear framework for analysis.
- Include perspectives from various stakeholders within the case to capture a holistic view. This might involve interviewing individuals at different organizational levels, customers, or community members, depending on the context.
- Adhere to ethical principles in research, including obtaining informed consent from participants, ensuring confidentiality, and addressing any potential conflicts of interest.
- Conduct a rigorous analysis of the data, using appropriate analytical techniques. Interpret the findings in the context of the research questions, theoretical framework, and relevant literature.
- Offer detailed and rich descriptions of the case, including the context, key events, and participant perspectives. This helps readers understand the intricacies of the case and supports the generalization of findings.
- Communicate findings in a clear and accessible manner. Avoid jargon and technical language that may hinder understanding. Use visuals, such as charts or graphs, to enhance clarity.
- Seek feedback from colleagues or experts in the field through peer review. This helps ensure the rigor and credibility of the case study and provides valuable insights for improvement.
- Connect the case study findings to existing theories or concepts, contributing to the theoretical understanding of the phenomenon. Discuss practical implications and potential applications in relevant contexts.
- Recognize that case study research is often an iterative process. Be open to revisiting and refining research questions, methods, or analysis as the study progresses. Practice reflexivity by acknowledging and addressing potential biases or preconceptions.
By incorporating these best practices, researchers can enhance the quality and impact of their case studies, making valuable contributions to the academic and practical understanding of complex phenomena.
Interested in learning more about the fields of product, research, and design? Search our articles here for helpful information spanning a wide range of topics!
What are the Types of Software Testing and Techniques?
Top 14 usability testing tools for enhancing experience, cx testing: methods, challenges & best practices for success, 15 user acceptance testing tools for quality & satisfaction.

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
The case study creation process
Types of case studies, benefits and limitations.

- Where was science invented?
- When did science begin?

Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Academia - Case Study
- Verywell Mind - What is a Case Study?
- Simply Psychology - Case Study Research Method in Psychology
- CORE - Case study as a research method
- National Center for Biotechnology Information - PubMed Central - The case study approach
- BMC Journals - Evidence-Based Nursing - What is a case study?
- Table Of Contents
case study , detailed description and assessment of a specific situation in the real world created for the purpose of deriving generalizations and other insights from it. A case study can be about an individual, a group of people, an organization, or an event, among other subjects.
By focusing on a specific subject in its natural setting, a case study can help improve understanding of the broader features and processes at work. Case studies are a research method used in multiple fields, including business, criminology , education , medicine and other forms of health care, anthropology , political science , psychology , and social work . Data in case studies can be both qualitative and quantitative. Unlike experiments, where researchers control and manipulate situations, case studies are considered to be “naturalistic” because subjects are studied in their natural context . ( See also natural experiment .)
The creation of a case study typically involves the following steps:
- The research question to be studied is defined, informed by existing literature and previous research. Researchers should clearly define the scope of the case, and they should compile a list of evidence to be collected as well as identify the nature of insights that they expect to gain from the case study.
- Once the case is identified, the research team is given access to the individual, organization, or situation being studied. Individuals are informed of risks associated with participation and must provide their consent , which may involve signing confidentiality or anonymity agreements.
- Researchers then collect evidence using multiple methods, which may include qualitative techniques, such as interviews, focus groups , and direct observations, as well as quantitative methods, such as surveys, questionnaires, and data audits. The collection procedures need to be well defined to ensure the relevance and accuracy of the evidence.
- The collected evidence is analyzed to come up with insights. Each data source must be reviewed carefully by itself and in the larger context of the case study so as to ensure continued relevance. At the same time, care must be taken not to force the analysis to fit (potentially preconceived) conclusions. While the eventual case study may serve as the basis for generalizations, these generalizations must be made cautiously to ensure that specific nuances are not lost in the averages.
- Finally, the case study is packaged for larger groups and publication. At this stage some information may be withheld, as in business case studies, to allow readers to draw their own conclusions. In scientific fields, the completed case study needs to be a coherent whole, with all findings and statistical relationships clearly documented.

Case studies have been used as a research method across multiple fields. They are particularly popular in the fields of law, business, and employee training; they typically focus on a problem that an individual or organization is facing. The situation is presented in considerable detail, often with supporting data, to discussion participants, who are asked to make recommendations that will solve the stated problem. The business case study as a method of instruction was made popular in the 1920s by instructors at Harvard Business School who adapted an approach used at Harvard Law School in which real-world cases were used in classroom discussions. Other business and law schools started compiling case studies as teaching aids for students. In a business school case study, students are not provided with the complete list of facts pertaining to the topic and are thus forced to discuss and compare their perspectives with those of their peers to recommend solutions.
In criminology , case studies typically focus on the lives of an individual or a group of individuals. These studies can provide particularly valuable insight into the personalities and motives of individual criminals, but they may suffer from a lack of objectivity on the part of the researchers (typically because of the researchers’ biases when working with people with a criminal history), and their findings may be difficult to generalize.
In sociology , the case-study method was developed by Frédéric Le Play in France during the 19th century. This approach involves a field worker staying with a family for a period of time, gathering data on the family members’ attitudes and interactions and on their income, expenditures, and physical possessions. Similar approaches have been used in anthropology . Such studies can sometimes continue for many years.

Case studies provide insight into situations that involve a specific entity or set of circumstances. They can be beneficial in helping to explain the causal relationships between quantitative indicators in a field of study, such as what drives a company’s market share. By introducing real-world examples, they also plunge the reader into an actual, concrete situation and make the concepts real rather than theoretical. They also help people study rare situations that they might not otherwise experience.
Because case studies are in a “naturalistic” environment , they are limited in terms of research design: researchers lack control over what they are studying, which means that the results often cannot be reproduced. Also, care must be taken to stay within the bounds of the research question on which the case study is focusing. Other limitations to case studies revolve around the data collected. It may be difficult, for instance, for researchers to organize the large volume of data that can emerge from the study, and their analysis of the data must be carefully thought through to produce scientifically valid insights. The research methodology used to generate these insights is as important as the insights themselves, for the latter need to be seen in the proper context. Taken out of context, they may lead to erroneous conclusions. Like all scientific studies, case studies need to be approached objectively; personal bias or opinion may skew the research methods as well as the results. ( See also confirmation bias .)
Business case studies in particular have been criticized for approaching a problem or situation from a narrow perspective. Students are expected to come up with solutions for a problem based on the data provided. However, in real life, the situation is typically reversed: business managers face a problem and must then look for data to help them solve it.

Research Writing and Analysis
- NVivo Group and Study Sessions
- SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Statistical Analysis Group sessions
- Using Qualtrics
- Dissertation and Data Analysis Group Sessions
- Defense Schedule - Commons Calendar This link opens in a new window
- Research Process Flow Chart
- Research Alignment Chapter 1 This link opens in a new window
- Step 1: Seek Out Evidence
- Step 2: Explain
- Step 3: The Big Picture
- Step 4: Own It
- Step 5: Illustrate
- Annotated Bibliography
- Seminal Authors
- Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses
- How to Synthesize and Analyze
- Synthesis and Analysis Practice
- Synthesis and Analysis Group Sessions
- Problem Statement
- Purpose Statement
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical Framework
- Locating Theoretical and Conceptual Frameworks This link opens in a new window
- Quantitative Research Questions
- Qualitative Research Questions
- Trustworthiness of Qualitative Data
- Analysis and Coding Example- Qualitative Data
- Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Dissertation to Journal Article This link opens in a new window
- International Journal of Online Graduate Education (IJOGE) This link opens in a new window
- Journal of Research in Innovative Teaching & Learning (JRIT&L) This link opens in a new window
Writing a Case Study

What is a case study?

A Case study is:
- An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology.
- Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research.
- Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event.
- Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
What are the different types of case studies?

| Descriptive | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How has the implementation and use of the instructional coaching intervention for elementary teachers impacted students’ attitudes toward reading? |
| Explanatory | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | Why do differences exist when implementing the same online reading curriculum in three elementary classrooms? |
| Exploratory | This type of case study allows the researcher to:
| What are potential barriers to student’s reading success when middle school teachers implement the Ready Reader curriculum online? |
| Multiple Case Studies or Collective Case Study | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How are individual school districts addressing student engagement in an online classroom? |
| Intrinsic | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How does a student’s familial background influence a teacher’s ability to provide meaningful instruction? |
| Instrumental | This type of case study allows the researcher to: | How a rural school district’s integration of a reward system maximized student engagement? |
Note: These are the primary case studies. As you continue to research and learn
about case studies you will begin to find a robust list of different types.
Who are your case study participants?

|
|
This type of study is implemented to understand an individual by developing a detailed explanation of the individual’s lived experiences or perceptions.
|
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore a particular group of people’s perceptions. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore the perspectives of people who work for or had interaction with a specific organization or company. |
|
| This type of study is implemented to explore participant’s perceptions of an event. |
What is triangulation ?
Validity and credibility are an essential part of the case study. Therefore, the researcher should include triangulation to ensure trustworthiness while accurately reflecting what the researcher seeks to investigate.

How to write a Case Study?
When developing a case study, there are different ways you could present the information, but remember to include the five parts for your case study.

|
|
|
|
|
|

Was this resource helpful?
- << Previous: Thematic Data Analysis in Qualitative Design
- Next: Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS) >>
- Last Updated: Aug 30, 2024 8:27 AM
- URL: https://resources.nu.edu/researchtools


Designing and Conducting Case Studies
This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of records, and collections of writing samples. Starting with a definition of the case study, the guide moves to a brief history of this research method. Using several well documented case studies, the guide then looks at applications and methods including data collection and analysis. A discussion of ways to handle validity, reliability, and generalizability follows, with special attention to case studies as they are applied to composition studies. Finally, this guide examines the strengths and weaknesses of case studies.
Definition and Overview
Case study refers to the collection and presentation of detailed information about a particular participant or small group, frequently including the accounts of subjects themselves. A form of qualitative descriptive research, the case study looks intensely at an individual or small participant pool, drawing conclusions only about that participant or group and only in that specific context. Researchers do not focus on the discovery of a universal, generalizable truth, nor do they typically look for cause-effect relationships; instead, emphasis is placed on exploration and description.
Case studies typically examine the interplay of all variables in order to provide as complete an understanding of an event or situation as possible. This type of comprehensive understanding is arrived at through a process known as thick description, which involves an in-depth description of the entity being evaluated, the circumstances under which it is used, the characteristics of the people involved in it, and the nature of the community in which it is located. Thick description also involves interpreting the meaning of demographic and descriptive data such as cultural norms and mores, community values, ingrained attitudes, and motives.
Unlike quantitative methods of research, like the survey, which focus on the questions of who, what, where, how much, and how many, and archival analysis, which often situates the participant in some form of historical context, case studies are the preferred strategy when how or why questions are asked. Likewise, they are the preferred method when the researcher has little control over the events, and when there is a contemporary focus within a real life context. In addition, unlike more specifically directed experiments, case studies require a problem that seeks a holistic understanding of the event or situation in question using inductive logic--reasoning from specific to more general terms.
In scholarly circles, case studies are frequently discussed within the context of qualitative research and naturalistic inquiry. Case studies are often referred to interchangeably with ethnography, field study, and participant observation. The underlying philosophical assumptions in the case are similar to these types of qualitative research because each takes place in a natural setting (such as a classroom, neighborhood, or private home), and strives for a more holistic interpretation of the event or situation under study.
Unlike more statistically-based studies which search for quantifiable data, the goal of a case study is to offer new variables and questions for further research. F.H. Giddings, a sociologist in the early part of the century, compares statistical methods to the case study on the basis that the former are concerned with the distribution of a particular trait, or a small number of traits, in a population, whereas the case study is concerned with the whole variety of traits to be found in a particular instance" (Hammersley 95).
Case studies are not a new form of research; naturalistic inquiry was the primary research tool until the development of the scientific method. The fields of sociology and anthropology are credited with the primary shaping of the concept as we know it today. However, case study research has drawn from a number of other areas as well: the clinical methods of doctors; the casework technique being developed by social workers; the methods of historians and anthropologists, plus the qualitative descriptions provided by quantitative researchers like LePlay; and, in the case of Robert Park, the techniques of newspaper reporters and novelists.
Park was an ex-newspaper reporter and editor who became very influential in developing sociological case studies at the University of Chicago in the 1920s. As a newspaper professional he coined the term "scientific" or "depth" reporting: the description of local events in a way that pointed to major social trends. Park viewed the sociologist as "merely a more accurate, responsible, and scientific reporter." Park stressed the variety and value of human experience. He believed that sociology sought to arrive at natural, but fluid, laws and generalizations in regard to human nature and society. These laws weren't static laws of the kind sought by many positivists and natural law theorists, but rather, they were laws of becoming--with a constant possibility of change. Park encouraged students to get out of the library, to quit looking at papers and books, and to view the constant experiment of human experience. He writes, "Go and sit in the lounges of the luxury hotels and on the doorsteps of the flophouses; sit on the Gold Coast settees and on the slum shakedowns; sit in the Orchestra Hall and in the Star and Garter Burlesque. In short, gentlemen [sic], go get the seats of your pants dirty in real research."
But over the years, case studies have drawn their share of criticism. In fact, the method had its detractors from the start. In the 1920s, the debate between pro-qualitative and pro-quantitative became quite heated. Case studies, when compared to statistics, were considered by many to be unscientific. From the 1930's on, the rise of positivism had a growing influence on quantitative methods in sociology. People wanted static, generalizable laws in science. The sociological positivists were looking for stable laws of social phenomena. They criticized case study research because it failed to provide evidence of inter subjective agreement. Also, they condemned it because of the few number of cases studied and that the under-standardized character of their descriptions made generalization impossible. By the 1950s, quantitative methods, in the form of survey research, had become the dominant sociological approach and case study had become a minority practice.
Educational Applications
The 1950's marked the dawning of a new era in case study research, namely that of the utilization of the case study as a teaching method. "Instituted at Harvard Business School in the 1950s as a primary method of teaching, cases have since been used in classrooms and lecture halls alike, either as part of a course of study or as the main focus of the course to which other teaching material is added" (Armisted 1984). The basic purpose of instituting the case method as a teaching strategy was "to transfer much of the responsibility for learning from the teacher on to the student, whose role, as a result, shifts away from passive absorption toward active construction" (Boehrer 1990). Through careful examination and discussion of various cases, "students learn to identify actual problems, to recognize key players and their agendas, and to become aware of those aspects of the situation that contribute to the problem" (Merseth 1991). In addition, students are encouraged to "generate their own analysis of the problems under consideration, to develop their own solutions, and to practically apply their own knowledge of theory to these problems" (Boyce 1993). Along the way, students also develop "the power to analyze and to master a tangled circumstance by identifying and delineating important factors; the ability to utilize ideas, to test them against facts, and to throw them into fresh combinations" (Merseth 1991).
In addition to the practical application and testing of scholarly knowledge, case discussions can also help students prepare for real-world problems, situations and crises by providing an approximation of various professional environments (i.e. classroom, board room, courtroom, or hospital). Thus, through the examination of specific cases, students are given the opportunity to work out their own professional issues through the trials, tribulations, experiences, and research findings of others. An obvious advantage to this mode of instruction is that it allows students the exposure to settings and contexts that they might not otherwise experience. For example, a student interested in studying the effects of poverty on minority secondary student's grade point averages and S.A.T. scores could access and analyze information from schools as geographically diverse as Los Angeles, New York City, Miami, and New Mexico without ever having to leave the classroom.
The case study method also incorporates the idea that students can learn from one another "by engaging with each other and with each other's ideas, by asserting something and then having it questioned, challenged and thrown back at them so that they can reflect on what they hear, and then refine what they say" (Boehrer 1990). In summary, students can direct their own learning by formulating questions and taking responsibility for the study.
Types and Design Concerns
Researchers use multiple methods and approaches to conduct case studies.
Types of Case Studies
Under the more generalized category of case study exist several subdivisions, each of which is custom selected for use depending upon the goals and/or objectives of the investigator. These types of case study include the following:
Illustrative Case Studies These are primarily descriptive studies. They typically utilize one or two instances of an event to show what a situation is like. Illustrative case studies serve primarily to make the unfamiliar familiar and to give readers a common language about the topic in question.
Exploratory (or pilot) Case Studies These are condensed case studies performed before implementing a large scale investigation. Their basic function is to help identify questions and select types of measurement prior to the main investigation. The primary pitfall of this type of study is that initial findings may seem convincing enough to be released prematurely as conclusions.
Cumulative Case Studies These serve to aggregate information from several sites collected at different times. The idea behind these studies is the collection of past studies will allow for greater generalization without additional cost or time being expended on new, possibly repetitive studies.
Critical Instance Case Studies These examine one or more sites for either the purpose of examining a situation of unique interest with little to no interest in generalizability, or to call into question or challenge a highly generalized or universal assertion. This method is useful for answering cause and effect questions.
Identifying a Theoretical Perspective
Much of the case study's design is inherently determined for researchers, depending on the field from which they are working. In composition studies, researchers are typically working from a qualitative, descriptive standpoint. In contrast, physicists will approach their research from a more quantitative perspective. Still, in designing the study, researchers need to make explicit the questions to be explored and the theoretical perspective from which they will approach the case. The three most commonly adopted theories are listed below:
Individual Theories These focus primarily on the individual development, cognitive behavior, personality, learning and disability, and interpersonal interactions of a particular subject.
Organizational Theories These focus on bureaucracies, institutions, organizational structure and functions, or excellence in organizational performance.
Social Theories These focus on urban development, group behavior, cultural institutions, or marketplace functions.
Two examples of case studies are used consistently throughout this chapter. The first, a study produced by Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988), looks at a first year graduate student's initiation into an academic writing program. The study uses participant-observer and linguistic data collecting techniques to assess the student's knowledge of appropriate discourse conventions. Using the pseudonym Nate to refer to the subject, the study sought to illuminate the particular experience rather than to generalize about the experience of fledgling academic writers collectively.
For example, in Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman's (1988) study we are told that the researchers are interested in disciplinary communities. In the first paragraph, they ask what constitutes membership in a disciplinary community and how achieving membership might affect a writer's understanding and production of texts. In the third paragraph they state that researchers must negotiate their claims "within the context of his sub specialty's accepted knowledge and methodology." In the next paragraph they ask, "How is literacy acquired? What is the process through which novices gain community membership? And what factors either aid or hinder students learning the requisite linguistic behaviors?" This introductory section ends with a paragraph in which the study's authors claim that during the course of the study, the subject, Nate, successfully makes the transition from "skilled novice" to become an initiated member of the academic discourse community and that his texts exhibit linguistic changes which indicate this transition. In the next section the authors make explicit the sociolinguistic theoretical and methodological assumptions on which the study is based (1988). Thus the reader has a good understanding of the authors' theoretical background and purpose in conducting the study even before it is explicitly stated on the fourth page of the study. "Our purpose was to examine the effects of the educational context on one graduate student's production of texts as he wrote in different courses and for different faculty members over the academic year 1984-85." The goal of the study then, was to explore the idea that writers must be initiated into a writing community, and that this initiation will change the way one writes.
The second example is Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of a group of twelfth graders. In this study, Emig seeks to answer the question of what happens to the self as a result educational stimuli in terms of academic writing. The case study used methods such as protocol analysis, tape-recorded interviews, and discourse analysis.
In the case of Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composing process of eight twelfth graders, four specific hypotheses were made:
- Twelfth grade writers engage in two modes of composing: reflexive and extensive.
- These differences can be ascertained and characterized through having the writers compose aloud their composition process.
- A set of implied stylistic principles governs the writing process.
- For twelfth grade writers, extensive writing occurs chiefly as a school-sponsored activity, or reflexive, as a self-sponsored activity.
In this study, the chief distinction is between the two dominant modes of composing among older, secondary school students. The distinctions are:
- The reflexive mode, which focuses on the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- The extensive mode, which focuses on conveying a message.
Emig also outlines the specific questions which guided the research in the opening pages of her Review of Literature , preceding the report.
Designing a Case Study
After considering the different sub categories of case study and identifying a theoretical perspective, researchers can begin to design their study. Research design is the string of logic that ultimately links the data to be collected and the conclusions to be drawn to the initial questions of the study. Typically, research designs deal with at least four problems:
- What questions to study
- What data are relevant
- What data to collect
- How to analyze that data
In other words, a research design is basically a blueprint for getting from the beginning to the end of a study. The beginning is an initial set of questions to be answered, and the end is some set of conclusions about those questions.
Because case studies are conducted on topics as diverse as Anglo-Saxon Literature (Thrane 1986) and AIDS prevention (Van Vugt 1994), it is virtually impossible to outline any strict or universal method or design for conducting the case study. However, Robert K. Yin (1993) does offer five basic components of a research design:
- A study's questions.
- A study's propositions (if any).
- A study's units of analysis.
- The logic that links the data to the propositions.
- The criteria for interpreting the findings.
In addition to these five basic components, Yin also stresses the importance of clearly articulating one's theoretical perspective, determining the goals of the study, selecting one's subject(s), selecting the appropriate method(s) of collecting data, and providing some considerations to the composition of the final report.
Conducting Case Studies
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of approaches and methods. These approaches, methods, and related issues are discussed in depth in this section.
Method: Single or Multi-modal?
To obtain as complete a picture of the participant as possible, case study researchers can employ a variety of methods. Some common methods include interviews , protocol analyses, field studies, and participant-observations. Emig (1971) chose to use several methods of data collection. Her sources included conversations with the students, protocol analysis, discrete observations of actual composition, writing samples from each student, and school records (Lauer and Asher 1988).
Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) collected data by observing classrooms, conducting faculty and student interviews, collecting self reports from the subject, and by looking at the subject's written work.
A study that was criticized for using a single method model was done by Flower and Hayes (1984). In this study that explores the ways in which writers use different forms of knowing to create space, the authors used only protocol analysis to gather data. The study came under heavy fire because of their decision to use only one method.
Participant Selection
Case studies can use one participant, or a small group of participants. However, it is important that the participant pool remain relatively small. The participants can represent a diverse cross section of society, but this isn't necessary.
For example, the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study looked at just one participant, Nate. By contrast, in Janet Emig's (1971) study of the composition process of twelfth graders, eight participants were selected representing a diverse cross section of the community, with volunteers from an all-white upper-middle-class suburban school, an all-black inner-city school, a racially mixed lower-middle-class school, an economically and racially mixed school, and a university school.
Often, a brief "case history" is done on the participants of the study in order to provide researchers with a clearer understanding of their participants, as well as some insight as to how their own personal histories might affect the outcome of the study. For instance, in Emig's study, the investigator had access to the school records of five of the participants, and to standardized test scores for the remaining three. Also made available to the researcher was the information that three of the eight students were selected as NCTE Achievement Award winners. These personal histories can be useful in later stages of the study when data are being analyzed and conclusions drawn.
Data Collection
There are six types of data collected in case studies:
- Archival records.
- Interviews.
- Direct observation.
- Participant observation.
In the field of composition research, these six sources might be:
- A writer's drafts.
- School records of student writers.
- Transcripts of interviews with a writer.
- Transcripts of conversations between writers (and protocols).
- Videotapes and notes from direct field observations.
- Hard copies of a writer's work on computer.
Depending on whether researchers have chosen to use a single or multi-modal approach for the case study, they may choose to collect data from one or any combination of these sources.
Protocols, that is, transcriptions of participants talking aloud about what they are doing as they do it, have been particularly common in composition case studies. For example, in Emig's (1971) study, the students were asked, in four different sessions, to give oral autobiographies of their writing experiences and to compose aloud three themes in the presence of a tape recorder and the investigator.
In some studies, only one method of data collection is conducted. For example, the Flower and Hayes (1981) report on the cognitive process theory of writing depends on protocol analysis alone. However, using multiple sources of evidence to increase the reliability and validity of the data can be advantageous.
Case studies are likely to be much more convincing and accurate if they are based on several different sources of information, following a corroborating mode. This conclusion is echoed among many composition researchers. For example, in her study of predrafting processes of high and low-apprehensive writers, Cynthia Selfe (1985) argues that because "methods of indirect observation provide only an incomplete reflection of the complex set of processes involved in composing, a combination of several such methods should be used to gather data in any one study." Thus, in this study, Selfe collected her data from protocols, observations of students role playing their writing processes, audio taped interviews with the students, and videotaped observations of the students in the process of composing.
It can be said then, that cross checking data from multiple sources can help provide a multidimensional profile of composing activities in a particular setting. Sharan Merriam (1985) suggests "checking, verifying, testing, probing, and confirming collected data as you go, arguing that this process will follow in a funnel-like design resulting in less data gathering in later phases of the study along with a congruent increase in analysis checking, verifying, and confirming."
It is important to note that in case studies, as in any qualitative descriptive research, while researchers begin their studies with one or several questions driving the inquiry (which influence the key factors the researcher will be looking for during data collection), a researcher may find new key factors emerging during data collection. These might be unexpected patterns or linguistic features which become evident only during the course of the research. While not bearing directly on the researcher's guiding questions, these variables may become the basis for new questions asked at the end of the report, thus linking to the possibility of further research.
Data Analysis
As the information is collected, researchers strive to make sense of their data. Generally, researchers interpret their data in one of two ways: holistically or through coding. Holistic analysis does not attempt to break the evidence into parts, but rather to draw conclusions based on the text as a whole. Flower and Hayes (1981), for example, make inferences from entire sections of their students' protocols, rather than searching through the transcripts to look for isolatable characteristics.
However, composition researchers commonly interpret their data by coding, that is by systematically searching data to identify and/or categorize specific observable actions or characteristics. These observable actions then become the key variables in the study. Sharan Merriam (1988) suggests seven analytic frameworks for the organization and presentation of data:
- The role of participants.
- The network analysis of formal and informal exchanges among groups.
- Historical.
- Thematical.
- Ritual and symbolism.
- Critical incidents that challenge or reinforce fundamental beliefs, practices, and values.
There are two purposes of these frameworks: to look for patterns among the data and to look for patterns that give meaning to the case study.
As stated above, while most researchers begin their case studies expecting to look for particular observable characteristics, it is not unusual for key variables to emerge during data collection. Typical variables coded in case studies of writers include pauses writers make in the production of a text, the use of specific linguistic units (such as nouns or verbs), and writing processes (planning, drafting, revising, and editing). In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, researchers coded the participant's texts for use of connectives, discourse demonstratives, average sentence length, off-register words, use of the first person pronoun, and the ratio of definite articles to indefinite articles.
Since coding is inherently subjective, more than one coder is usually employed. In the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study, for example, three rhetoricians were employed to code the participant's texts for off-register phrases. The researchers established the agreement among the coders before concluding that the participant used fewer off-register words as the graduate program progressed.
Composing the Case Study Report
In the many forms it can take, "a case study is generically a story; it presents the concrete narrative detail of actual, or at least realistic events, it has a plot, exposition, characters, and sometimes even dialogue" (Boehrer 1990). Generally, case study reports are extensively descriptive, with "the most problematic issue often referred to as being the determination of the right combination of description and analysis" (1990). Typically, authors address each step of the research process, and attempt to give the reader as much context as possible for the decisions made in the research design and for the conclusions drawn.
This contextualization usually includes a detailed explanation of the researchers' theoretical positions, of how those theories drove the inquiry or led to the guiding research questions, of the participants' backgrounds, of the processes of data collection, of the training and limitations of the coders, along with a strong attempt to make connections between the data and the conclusions evident.
Although the Berkenkotter, Huckin, and Ackerman (1988) study does not, case study reports often include the reactions of the participants to the study or to the researchers' conclusions. Because case studies tend to be exploratory, most end with implications for further study. Here researchers may identify significant variables that emerged during the research and suggest studies related to these, or the authors may suggest further general questions that their case study generated.
For example, Emig's (1971) study concludes with a section dedicated solely to the topic of implications for further research, in which she suggests several means by which this particular study could have been improved, as well as questions and ideas raised by this study which other researchers might like to address, such as: is there a correlation between a certain personality and a certain composing process profile (e.g. is there a positive correlation between ego strength and persistence in revising)?
Also included in Emig's study is a section dedicated to implications for teaching, which outlines the pedagogical ramifications of the study's findings for teachers currently involved in high school writing programs.
Sharan Merriam (1985) also offers several suggestions for alternative presentations of data:
- Prepare specialized condensations for appropriate groups.
- Replace narrative sections with a series of answers to open-ended questions.
- Present "skimmer's" summaries at beginning of each section.
- Incorporate headlines that encapsulate information from text.
- Prepare analytic summaries with supporting data appendixes.
- Present data in colorful and/or unique graphic representations.
Issues of Validity and Reliability
Once key variables have been identified, they can be analyzed. Reliability becomes a key concern at this stage, and many case study researchers go to great lengths to ensure that their interpretations of the data will be both reliable and valid. Because issues of validity and reliability are an important part of any study in the social sciences, it is important to identify some ways of dealing with results.
Multi-modal case study researchers often balance the results of their coding with data from interviews or writer's reflections upon their own work. Consequently, the researchers' conclusions become highly contextualized. For example, in a case study which looked at the time spent in different stages of the writing process, Berkenkotter concluded that her participant, Donald Murray, spent more time planning his essays than in other writing stages. The report of this case study is followed by Murray's reply, wherein he agrees with some of Berkenkotter's conclusions and disagrees with others.
As is the case with other research methodologies, issues of external validity, construct validity, and reliability need to be carefully considered.
Commentary on Case Studies
Researchers often debate the relative merits of particular methods, among them case study. In this section, we comment on two key issues. To read the commentaries, choose any of the items below:
Strengths and Weaknesses of Case Studies
Most case study advocates point out that case studies produce much more detailed information than what is available through a statistical analysis. Advocates will also hold that while statistical methods might be able to deal with situations where behavior is homogeneous and routine, case studies are needed to deal with creativity, innovation, and context. Detractors argue that case studies are difficult to generalize because of inherent subjectivity and because they are based on qualitative subjective data, generalizable only to a particular context.
Flexibility
The case study approach is a comparatively flexible method of scientific research. Because its project designs seem to emphasize exploration rather than prescription or prediction, researchers are comparatively freer to discover and address issues as they arise in their experiments. In addition, the looser format of case studies allows researchers to begin with broad questions and narrow their focus as their experiment progresses rather than attempt to predict every possible outcome before the experiment is conducted.
Emphasis on Context
By seeking to understand as much as possible about a single subject or small group of subjects, case studies specialize in "deep data," or "thick description"--information based on particular contexts that can give research results a more human face. This emphasis can help bridge the gap between abstract research and concrete practice by allowing researchers to compare their firsthand observations with the quantitative results obtained through other methods of research.
Inherent Subjectivity
"The case study has long been stereotyped as the weak sibling among social science methods," and is often criticized as being too subjective and even pseudo-scientific. Likewise, "investigators who do case studies are often regarded as having deviated from their academic disciplines, and their investigations as having insufficient precision (that is, quantification), objectivity and rigor" (Yin 1989). Opponents cite opportunities for subjectivity in the implementation, presentation, and evaluation of case study research. The approach relies on personal interpretation of data and inferences. Results may not be generalizable, are difficult to test for validity, and rarely offer a problem-solving prescription. Simply put, relying on one or a few subjects as a basis for cognitive extrapolations runs the risk of inferring too much from what might be circumstance.
High Investment
Case studies can involve learning more about the subjects being tested than most researchers would care to know--their educational background, emotional background, perceptions of themselves and their surroundings, their likes, dislikes, and so on. Because of its emphasis on "deep data," the case study is out of reach for many large-scale research projects which look at a subject pool in the tens of thousands. A budget request of $10,000 to examine 200 subjects sounds more efficient than a similar request to examine four subjects.
Ethical Considerations
Researchers conducting case studies should consider certain ethical issues. For example, many educational case studies are often financed by people who have, either directly or indirectly, power over both those being studied and those conducting the investigation (1985). This conflict of interests can hinder the credibility of the study.
The personal integrity, sensitivity, and possible prejudices and/or biases of the investigators need to be taken into consideration as well. Personal biases can creep into how the research is conducted, alternative research methods used, and the preparation of surveys and questionnaires.
A common complaint in case study research is that investigators change direction during the course of the study unaware that their original research design was inadequate for the revised investigation. Thus, the researchers leave unknown gaps and biases in the study. To avoid this, researchers should report preliminary findings so that the likelihood of bias will be reduced.
Concerns about Reliability, Validity, and Generalizability
Merriam (1985) offers several suggestions for how case study researchers might actively combat the popular attacks on the validity, reliability, and generalizability of case studies:
- Prolong the Processes of Data Gathering on Site: This will help to insure the accuracy of the findings by providing the researcher with more concrete information upon which to formulate interpretations.
- Employ the Process of "Triangulation": Use a variety of data sources as opposed to relying solely upon one avenue of observation. One example of such a data check would be what McClintock, Brannon, and Maynard (1985) refer to as a "case cluster method," that is, when a single unit within a larger case is randomly sampled, and that data treated quantitatively." For instance, in Emig's (1971) study, the case cluster method was employed, singling out the productivity of a single student named Lynn. This cluster profile included an advanced case history of the subject, specific examination and analysis of individual compositions and protocols, and extensive interview sessions. The seven remaining students were then compared with the case of Lynn, to ascertain if there are any shared, or unique dimensions to the composing process engaged in by these eight students.
- Conduct Member Checks: Initiate and maintain an active corroboration on the interpretation of data between the researcher and those who provided the data. In other words, talk to your subjects.
- Collect Referential Materials: Complement the file of materials from the actual site with additional document support. For example, Emig (1971) supports her initial propositions with historical accounts by writers such as T.S. Eliot, James Joyce, and D.H. Lawrence. Emig also cites examples of theoretical research done with regards to the creative process, as well as examples of empirical research dealing with the writing of adolescents. Specific attention is then given to the four stages description of the composing process delineated by Helmoltz, Wallas, and Cowley, as it serves as the focal point in this study.
- Engage in Peer Consultation: Prior to composing the final draft of the report, researchers should consult with colleagues in order to establish validity through pooled judgment.
Although little can be done to combat challenges concerning the generalizability of case studies, "most writers suggest that qualitative research should be judged as credible and confirmable as opposed to valid and reliable" (Merriam 1985). Likewise, it has been argued that "rather than transplanting statistical, quantitative notions of generalizability and thus finding qualitative research inadequate, it makes more sense to develop an understanding of generalization that is congruent with the basic characteristics of qualitative inquiry" (1985). After all, criticizing the case study method for being ungeneralizable is comparable to criticizing a washing machine for not being able to tell the correct time. In other words, it is unjust to criticize a method for not being able to do something which it was never originally designed to do in the first place.
Annotated Bibliography
Armisted, C. (1984). How Useful are Case Studies. Training and Development Journal, 38 (2), 75-77.
This article looks at eight types of case studies, offers pros and cons of using case studies in the classroom, and gives suggestions for successfully writing and using case studies.
Bardovi-Harlig, K. (1997). Beyond Methods: Components of Second Language Teacher Education . New York: McGraw-Hill.
A compilation of various research essays which address issues of language teacher education. Essays included are: "Non-native reading research and theory" by Lee, "The case for Psycholinguistics" by VanPatten, and "Assessment and Second Language Teaching" by Gradman and Reed.
Bartlett, L. (1989). A Question of Good Judgment; Interpretation Theory and Qualitative Enquiry Address. 70th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. San Francisco.
Bartlett selected "quasi-historical" methodology, which focuses on the "truth" found in case records, as one that will provide "good judgments" in educational inquiry. He argues that although the method is not comprehensive, it can try to connect theory with practice.
Baydere, S. et. al. (1993). Multimedia conferencing as a tool for collaborative writing: a case study in Computer Supported Collaborative Writing. New York: Springer-Verlag.
The case study by Baydere et. al. is just one of the many essays in this book found in the series "Computer Supported Cooperative Work." Denley, Witefield and May explore similar issues in their essay, "A case study in task analysis for the design of a collaborative document production system."
Berkenkotter, C., Huckin, T., N., & Ackerman J. (1988). Conventions, Conversations, and the Writer: Case Study of a Student in a Rhetoric Ph.D. Program. Research in the Teaching of English, 22, 9-44.
The authors focused on how the writing of their subject, Nate or Ackerman, changed as he became more acquainted or familiar with his field's discourse community.
Berninger, V., W., and Gans, B., M. (1986). Language Profiles in Nonspeaking Individuals of Normal Intelligence with Severe Cerebral Palsy. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 2, 45-50.
Argues that generalizations about language abilities in patients with severe cerebral palsy (CP) should be avoided. Standardized tests of different levels of processing oral language, of processing written language, and of producing written language were administered to 3 male participants (aged 9, 16, and 40 yrs).
Bockman, J., R., and Couture, B. (1984). The Case Method in Technical Communication: Theory and Models. Texas: Association of Teachers of Technical Writing.
Examines the study and teaching of technical writing, communication of technical information, and the case method in terms of those applications.
Boehrer, J. (1990). Teaching With Cases: Learning to Question. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 42 41-57.
This article discusses the origins of the case method, looks at the question of what is a case, gives ideas about learning in case teaching, the purposes it can serve in the classroom, the ground rules for the case discussion, including the role of the question, and new directions for case teaching.
Bowman, W. R. (1993). Evaluating JTPA Programs for Economically Disadvantaged Adults: A Case Study of Utah and General Findings . Washington: National Commission for Employment Policy.
"To encourage state-level evaluations of JTPA, the Commission and the State of Utah co-sponsored this report on the effectiveness of JTPA Title II programs for adults in Utah. The technique used is non-experimental and the comparison group was selected from registrants with Utah's Employment Security. In a step-by-step approach, the report documents how non-experimental techniques can be applied and several specific technical issues can be addressed."
Boyce, A. (1993) The Case Study Approach for Pedagogists. Annual Meeting of the American Alliance for Health, Physical Education, Recreation and Dance. (Address). Washington DC.
This paper addresses how case studies 1) bridge the gap between teaching theory and application, 2) enable students to analyze problems and develop solutions for situations that will be encountered in the real world of teaching, and 3) helps students to evaluate the feasibility of alternatives and to understand the ramifications of a particular course of action.
Carson, J. (1993) The Case Study: Ideal Home of WAC Quantitative and Qualitative Data. Annual Meeting of the Conference on College Composition and Communication. (Address). San Diego.
"Increasingly, one of the most pressing questions for WAC advocates is how to keep [WAC] programs going in the face of numerous difficulties. Case histories offer the best chance for fashioning rhetorical arguments to keep WAC programs going because they offer the opportunity to provide a coherent narrative that contextualizes all documents and data, including what is generally considered scientific data. A case study of the WAC program, . . . at Robert Morris College in Pittsburgh demonstrates the advantages of this research method. Such studies are ideal homes for both naturalistic and positivistic data as well as both quantitative and qualitative information."
---. (1991). A Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. College Composition and Communication. 32. 365-87.
No abstract available.
Cromer, R. (1994) A Case Study of Dissociations Between Language and Cognition. Constraints on Language Acquisition: Studies of Atypical Children . Hillsdale: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, 141-153.
Crossley, M. (1983) Case Study in Comparative and International Education: An Approach to Bridging the Theory-Practice Gap. Proceedings of the 11th Annual Conference of the Australian Comparative and International Education Society. Hamilton, NZ.
Case study research, as presented here, helps bridge the theory-practice gap in comparative and international research studies of education because it focuses on the practical, day-to-day context rather than on the national arena. The paper asserts that the case study method can be valuable at all levels of research, formation, and verification of theories in education.
Daillak, R., H., and Alkin, M., C. (1982). Qualitative Studies in Context: Reflections on the CSE Studies of Evaluation Use . California: EDRS
The report shows how the Center of the Study of Evaluation (CSE) applied qualitative techniques to a study of evaluation information use in local, Los Angeles schools. It critiques the effectiveness and the limitations of using case study, evaluation, field study, and user interview survey methodologies.
Davey, L. (1991). The Application of Case Study Evaluations. ERIC/TM Digest.
This article examines six types of case studies, the type of evaluation questions that can be answered, the functions served, some design features, and some pitfalls of the method.
Deutch, C. E. (1996). A course in research ethics for graduate students. College Teaching, 44, 2, 56-60.
This article describes a one-credit discussion course in research ethics for graduate students in biology. Case studies are focused on within the four parts of the course: 1) major issues, 2 )practical issues in scholarly work, 3) ownership of research results, and 4) training and personal decisions.
DeVoss, G. (1981). Ethics in Fieldwork Research. RIE 27p. (ERIC)
This article examines four of the ethical problems that can happen when conducting case study research: acquiring permission to do research, knowing when to stop digging, the pitfalls of doing collaborative research, and preserving the integrity of the participants.
Driscoll, A. (1985). Case Study of a Research Intervention: the University of Utah’s Collaborative Approach . San Francisco: Far West Library for Educational Research Development.
Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Association of Colleges of Teacher Education, Denver, CO, March 1985. Offers information of in-service training, specifically case studies application.
Ellram, L. M. (1996). The Use of the Case Study Method in Logistics Research. Journal of Business Logistics, 17, 2, 93.
This article discusses the increased use of case study in business research, and the lack of understanding of when and how to use case study methodology in business.
Emig, J. (1971) The Composing Processes of Twelfth Graders . Urbana: NTCE.
This case study uses observation, tape recordings, writing samples, and school records to show that writing in reflexive and extensive situations caused different lengths of discourse and different clusterings of the components of the writing process.
Feagin, J. R. (1991). A Case For the Case Study . Chapel Hill: The University of North Carolina Press.
This book discusses the nature, characteristics, and basic methodological issues of the case study as a research method.
Feldman, H., Holland, A., & Keefe, K. (1989) Language Abilities after Left Hemisphere Brain Injury: A Case Study of Twins. Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 9, 32-47.
"Describes the language abilities of 2 twin pairs in which 1 twin (the experimental) suffered brain injury to the left cerebral hemisphere around the time of birth and1 twin (the control) did not. One pair of twins was initially assessed at age 23 mo. and the other at about 30 mo.; they were subsequently evaluated in their homes 3 times at about 6-mo intervals."
Fidel, R. (1984). The Case Study Method: A Case Study. Library and Information Science Research, 6.
The article describes the use of case study methodology to systematically develop a model of online searching behavior in which study design is flexible, subject manner determines data gathering and analyses, and procedures adapt to the study's progressive change.
Flower, L., & Hayes, J. R. (1984). Images, Plans and Prose: The Representation of Meaning in Writing. Written Communication, 1, 120-160.
Explores the ways in which writers actually use different forms of knowing to create prose.
Frey, L. R. (1992). Interpreting Communication Research: A Case Study Approach Englewood Cliffs, N.J.: Prentice Hall.
The book discusses research methodologies in the Communication field. It focuses on how case studies bridge the gap between communication research, theory, and practice.
Gilbert, V. K. (1981). The Case Study as a Research Methodology: Difficulties and Advantages of Integrating the Positivistic, Phenomenological and Grounded Theory Approaches . The Annual Meeting of the Canadian Association for the Study of Educational Administration. (Address) Halifax, NS, Can.
This study on an innovative secondary school in England shows how a "low-profile" participant-observer case study was crucial to the initial observation, the testing of hypotheses, the interpretive approach, and the grounded theory.
Gilgun, J. F. (1994). A Case for Case Studies in Social Work Research. Social Work, 39, 4, 371-381.
This article defines case study research, presents guidelines for evaluation of case studies, and shows the relevance of case studies to social work research. It also looks at issues such as evaluation and interpretations of case studies.
Glennan, S. L., Sharp-Bittner, M. A. & Tullos, D. C. (1991). Augmentative and Alternative Communication Training with a Nonspeaking Adult: Lessons from MH. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 7, 240-7.
"A response-guided case study documented changes in a nonspeaking 36-yr-old man's ability to communicate using 3 trained augmentative communication modes. . . . Data were collected in videotaped interaction sessions between the nonspeaking adult and a series of adult speaking."
Graves, D. (1981). An Examination of the Writing Processes of Seven Year Old Children. Research in the Teaching of English, 15, 113-134.
Hamel, J. (1993). Case Study Methods . Newbury Park: Sage. .
"In a most economical fashion, Hamel provides a practical guide for producing theoretically sharp and empirically sound sociological case studies. A central idea put forth by Hamel is that case studies must "locate the global in the local" thus making the careful selection of the research site the most critical decision in the analytic process."
Karthigesu, R. (1986, July). Television as a Tool for Nation-Building in the Third World: A Post-Colonial Pattern, Using Malaysia as a Case-Study. International Television Studies Conference. (Address). London, 10-12.
"The extent to which Television Malaysia, as a national mass media organization, has been able to play a role in nation building in the post-colonial period is . . . studied in two parts: how the choice of a model of nation building determines the character of the organization; and how the character of the organization influences the output of the organization."
Kenny, R. (1984). Making the Case for the Case Study. Journal of Curriculum Studies, 16, (1), 37-51.
The article looks at how and why the case study is justified as a viable and valuable approach to educational research and program evaluation.
Knirk, F. (1991). Case Materials: Research and Practice. Performance Improvement Quarterly, 4 (1 ), 73-81.
The article addresses the effectiveness of case studies, subject areas where case studies are commonly used, recent examples of their use, and case study design considerations.
Klos, D. (1976). Students as Case Writers. Teaching of Psychology, 3.2, 63-66.
This article reviews a course in which students gather data for an original case study of another person. The task requires the students to design the study, collect the data, write the narrative, and interpret the findings.
Leftwich, A. (1981). The Politics of Case Study: Problems of Innovation in University Education. Higher Education Review, 13.2, 38-64.
The article discusses the use of case studies as a teaching method. Emphasis is on the instructional materials, interdisciplinarity, and the complex relationships within the university that help or hinder the method.
Mabrito, M. (1991, Oct.). Electronic Mail as a Vehicle for Peer Response: Conversations of High and Low Apprehensive Writers. Written Communication, 509-32.
McCarthy, S., J. (1955). The Influence of Classroom Discourse on Student Texts: The Case of Ella . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
A look at how students of color become marginalized within traditional classroom discourse. The essay follows the struggles of one black student: Ella.
Matsuhashi, A., ed. (1987). Writing in Real Time: Modeling Production Processes Norwood, NJ: Ablex Publishing Corporation.
Investigates how writers plan to produce discourse for different purposes to report, to generalize, and to persuade, as well as how writers plan for sentence level units of language. To learn about planning, an observational measure of pause time was used" (ERIC).
Merriam, S. B. (1985). The Case Study in Educational Research: A Review of Selected Literature. Journal of Educational Thought, 19.3, 204-17.
The article examines the characteristics of, philosophical assumptions underlying the case study, the mechanics of conducting a case study, and the concerns about the reliability, validity, and generalizability of the method.
---. (1988). Case Study Research in Education: A Qualitative Approach San Francisco: Jossey Bass.
Merry, S. E., & Milner, N. eds. (1993). The Possibility of Popular Justice: A Case Study of Community Mediation in the United States . Ann Arbor: U of Michigan.
". . . this volume presents a case study of one experiment in popular justice, the San Francisco Community Boards. This program has made an explicit claim to create an alternative justice, or new justice, in the midst of a society ordered by state law. The contributors to this volume explore the history and experience of the program and compare it to other versions of popular justice in the United States, Europe, and the Third World."
Merseth, K. K. (1991). The Case for Cases in Teacher Education. RIE. 42p. (ERIC).
This monograph argues that the case method of instruction offers unique potential for revitalizing the field of teacher education.
Michaels, S. (1987). Text and Context: A New Approach to the Study of Classroom Writing. Discourse Processes, 10, 321-346.
"This paper argues for and illustrates an approach to the study of writing that integrates ethnographic analysis of classroom interaction with linguistic analysis of written texts and teacher/student conversational exchanges. The approach is illustrated through a case study of writing in a single sixth grade classroom during a single writing assignment."
Milburn, G. (1995). Deciphering a Code or Unraveling a Riddle: A Case Study in the Application of a Humanistic Metaphor to the Reporting of Social Studies Teaching. Theory and Research in Education, 13.
This citation serves as an example of how case studies document learning procedures in a senior-level economics course.
Milley, J. E. (1979). An Investigation of Case Study as an Approach to Program Evaluation. 19th Annual Forum of the Association for Institutional Research. (Address). San Diego.
The case study method merged a narrative report focusing on the evaluator as participant-observer with document review, interview, content analysis, attitude questionnaire survey, and sociogram analysis. Milley argues that case study program evaluation has great potential for widespread use.
Minnis, J. R. (1985, Sept.). Ethnography, Case Study, Grounded Theory, and Distance Education Research. Distance Education, 6.2.
This article describes and defines the strengths and weaknesses of ethnography, case study, and grounded theory.
Nunan, D. (1992). Collaborative language learning and teaching . New York: Cambridge University Press.
Included in this series of essays is Peter Sturman’s "Team Teaching: a case study from Japan" and David Nunan’s own "Toward a collaborative approach to curriculum development: a case study."
Nystrand, M., ed. (1982). What Writers Know: The Language, Process, and Structure of Written Discourse . New York: Academic Press.
Owenby, P. H. (1992). Making Case Studies Come Alive. Training, 29, (1), 43-46. (ERIC)
This article provides tips for writing more effective case studies.
---. (1981). Pausing and Planning: The Tempo of Writer Discourse Production. Research in the Teaching of English, 15 (2),113-34.
Perl, S. (1979). The Composing Processes of Unskilled College Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 13, 317-336.
"Summarizes a study of five unskilled college writers, focusing especially on one of the five, and discusses the findings in light of current pedagogical practice and research design."
Pilcher J. and A. Coffey. eds. (1996). Gender and Qualitative Research . Brookfield: Aldershot, Hants, England.
This book provides a series of essays which look at gender identity research, qualitative research and applications of case study to questions of gendered pedagogy.
Pirie, B. S. (1993). The Case of Morty: A Four Year Study. Gifted Education International, 9 (2), 105-109.
This case study describes a boy from kindergarten through third grade with above average intelligence but difficulty in learning to read, write, and spell.
Popkewitz, T. (1993). Changing Patterns of Power: Social Regulation and Teacher Education Reform. Albany: SUNY Press.
Popkewitz edits this series of essays that address case studies on educational change and the training of teachers. The essays vary in terms of discipline and scope. Also, several authors include case studies of educational practices in countries other than the United States.
---. (1984). The Predrafting Processes of Four High- and Four Low Apprehensive Writers. Research in the Teaching of English, 18, (1), 45-64.
Rasmussen, P. (1985, March) A Case Study on the Evaluation of Research at the Technical University of Denmark. International Journal of Institutional Management in Higher Education, 9 (1).
This is an example of a case study methodology used to evaluate the chemistry and chemical engineering departments at the University of Denmark.
Roth, K. J. (1986). Curriculum Materials, Teacher Talk, and Student Learning: Case Studies in Fifth-Grade Science Teaching . East Lansing: Institute for Research on Teaching.
Roth offers case studies on elementary teachers, elementary school teaching, science studies and teaching, and verbal learning.
Selfe, C. L. (1985). An Apprehensive Writer Composes. When a Writer Can't Write: Studies in Writer's Block and Other Composing-Process Problems . (pp. 83-95). Ed. Mike Rose. NMY: Guilford.
Smith-Lewis, M., R. and Ford, A. (1987). A User's Perspective on Augmentative Communication. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 3, 12-7.
"During a series of in-depth interviews, a 25-yr-old woman with cerebral palsy who utilized augmentative communication reflected on the effectiveness of the devices designed for her during her school career."
St. Pierre, R., G. (1980, April). Follow Through: A Case Study in Metaevaluation Research . 64th Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association. (Address).
The three approaches to metaevaluation are evaluation of primary evaluations, integrative meta-analysis with combined primary evaluation results, and re-analysis of the raw data from a primary evaluation.
Stahler, T., M. (1996, Feb.) Early Field Experiences: A Model That Worked. ERIC.
"This case study of a field and theory class examines a model designed to provide meaningful field experiences for preservice teachers while remaining consistent with the instructor's beliefs about the role of teacher education in preparing teachers for the classroom."
Stake, R. E. (1995). The Art of Case Study Research. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications.
This book examines case study research in education and case study methodology.
Stiegelbauer, S. (1984) Community, Context, and Co-curriculum: Situational Factors Influencing School Improvements in a Study of High Schools. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association, New Orleans, LA.
Discussion of several case studies: one looking at high school environments, another examining educational innovations.
Stolovitch, H. (1990). Case Study Method. Performance And Instruction, 29, (9), 35-37.
This article describes the case study method as a form of simulation and presents guidelines for their use in professional training situations.
Thaller, E. (1994). Bibliography for the Case Method: Using Case Studies in Teacher Education. RIE. 37 p.
This bibliography presents approximately 450 citations on the use of case studies in teacher education from 1921-1993.
Thrane, T. (1986). On Delimiting the Senses of Near-Synonyms in Historical Semantics: A Case Study of Adjectives of 'Moral Sufficiency' in the Old English Andreas. Linguistics Across Historical and Geographical Boundaries: In Honor of Jacek Fisiak on the Occasion of his Fiftieth Birthday . Berlin: Mouton de Gruyter.
United Nations. (1975). Food and Agriculture Organization. Report on the FAO/UNFPA Seminar on Methodology, Research and Country: Case Studies on Population, Employment and Productivity . Rome: United Nations.
This example case study shows how the methodology can be used in a demographic and psychographic evaluation. At the same time, it discusses the formation and instigation of the case study methodology itself.
Van Vugt, J. P., ed. (1994). Aids Prevention and Services: Community Based Research . Westport: Bergin and Garvey.
"This volume has been five years in the making. In the process, some of the policy applications called for have met with limited success, such as free needle exchange programs in a limited number of American cities, providing condoms to prison inmates, and advertisements that depict same-sex couples. Rather than dating our chapters that deal with such subjects, such policy applications are verifications of the type of research demonstrated here. Furthermore, they indicate the critical need to continue community based research in the various communities threatened by acquired immuno-deficiency syndrome (AIDS) . . . "
Welch, W., ed. (1981, May). Case Study Methodology in Educational Evaluation. Proceedings of the Minnesota Evaluation Conference. Minnesota. (Address).
The four papers in these proceedings provide a comprehensive picture of the rationale, methodology, strengths, and limitations of case studies.
Williams, G. (1987). The Case Method: An Approach to Teaching and Learning in Educational Administration. RIE, 31p.
This paper examines the viability of the case method as a teaching and learning strategy in instructional systems geared toward the training of personnel of the administration of various aspects of educational systems.
Yin, R. K. (1993). Advancing Rigorous Methodologies: A Review of 'Towards Rigor in Reviews of Multivocal Literatures.' Review of Educational Research, 61, (3).
"R. T. Ogawa and B. Malen's article does not meet its own recommended standards for rigorous testing and presentation of its own conclusions. Use of the exploratory case study to analyze multivocal literatures is not supported, and the claim of grounded theory to analyze multivocal literatures may be stronger."
---. (1989). Case Study Research: Design and Methods. London: Sage Publications Inc.
This book discusses in great detail, the entire design process of the case study, including entire chapters on collecting evidence, analyzing evidence, composing the case study report, and designing single and multiple case studies.
Related Links
Consider the following list of related Web sites for more information on the topic of case study research. Note: although many of the links cover the general category of qualitative research, all have sections that address issues of case studies.
- Sage Publications on Qualitative Methodology: Search here for a comprehensive list of new books being published about "Qualitative Methodology" http://www.sagepub.co.uk/
- The International Journal of Qualitative Studies in Education: An on-line journal "to enhance the theory and practice of qualitative research in education." On-line submissions are welcome. http://www.tandf.co.uk/journals/tf/09518398.html
- Qualitative Research Resources on the Internet: From syllabi to home pages to bibliographies. All links relate somehow to qualitative research. http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/qualres.html
Becker, Bronwyn, Patrick Dawson, Karen Devine, Carla Hannum, Steve Hill, Jon Leydens, Debbie Matuskevich, Carol Traver, & Mike Palmquist. (2005). Case Studies. Writing@CSU . Colorado State University. https://writing.colostate.edu/guides/guide.cfm?guideid=60

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The study uses the concept of habitus to understand whether the changing design of traditional rondavels has influenced their utilisation, based on a case study of the Mbhashe Local Municipality ...
Quantum computing, with its potential to expedite specific tasks, requires a more precise definition of its benefits in early research. This paper introduces the Quantum DNA Encoder (QDE), a novel approach for encoding genetic information efficiently and effectively. Utilizing a simple circuit suitable for a 4-qubit system, QDE surpasses One-Hot Encoding (OHE) in creating better class ...
The integration of blockchain technology into food supply chains represents a pivotal step in addressing the current issue of food safety. Through the analysis of numerous studies and case studies, it is evident that blockchain offers immense potential in enhancing transparency, traceability, and trust within the food industry.
A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are sometimes also used.
A case study is an in-depth study of one person, group, or event. In a case study, nearly every aspect of the subject's life and history is analyzed to seek patterns and causes of behavior. Case studies can be used in many different fields, including psychology, medicine, education, anthropology, political science, and social work.
Case Study Definition. A case study is coverage of a specific challenge a business has faced, and the solution they've chosen to solve it. Case studies can vary greatly in length and focus on several details related to the initial challenge and applied solution, and can be presented in various forms like a video, white paper, blog post, etc ...
Definition of a case study. A case study in qualitative research is a strategy of inquiry that involves an in-depth investigation of a phenomenon within its real-world context. It provides researchers with the opportunity to acquire an in-depth understanding of intricate details that might not be as apparent or accessible through other methods ...
Rather than discussing case study in general, a targeted step-by-step plan with real-time research examples to conduct a case study is given. VanWynsberghe, R., & Khan, S. (2007). ... In this paper the authors propose a more precise and encompassing definition of case study than is usually found. They support their definition by clarifying that ...
A case study is one of the most commonly used methodologies of social research. This article attempts to look into the various dimensions of a case study research strategy, the different epistemological strands which determine the particular case study type and approach adopted in the field, discusses the factors which can enhance the effectiveness of a case study research, and the debate ...
Case study examples. While templates are helpful, seeing a case study in action can also be a great way to learn. Here are some examples of how Adobe customers have experienced success. Juniper Networks. One example is the Adobe and Juniper Networks case study, which puts the reader in the customer's shoes.
Rather than discussing case study in general, a targeted step-by-step plan with real-time research examples to conduct a case study is given. Introduction In recent years, a great increase in the number of students working on their final dissertation across business and management disciplines has been noticed ( Lee & Saunders, 2017 ).
A case study is a document that focuses on a business problem and provides a clear solution. Marketers use case studies to tell a story about a customer's journey or how a product or service solves a specific issue. Case studies can be used in all levels of business and in many industries. A thorough case study often uses metrics, such as key ...
A case study research paper examines a person, place, event, condition, phenomenon, or other type of subject of analysis in order to extrapolate key themes and results that help predict future trends, illuminate previously hidden issues that can be applied to practice, and/or provide a means for understanding an important research problem with greater clarity.
Case studies tend to focus on qualitative data using methods such as interviews, observations, and analysis of primary and secondary sources (e.g., newspaper articles, photographs, official records). Sometimes a case study will also collect quantitative data. Example: Mixed methods case study. For a case study of a wind farm development in a ...
This case work and case planning social work guide has been published to equip social workers to empower individuals and promote positive change through social casework. We will explore what is social case work, the models and theories of social case work, social work case studies, and real-life social work case examples, providing a ...
Sample #3: Conceptualization in a family therapy case. This 45-year-old African-American woman was initially referred for individual therapy for "rapid mood swings" and a tendency to become embroiled in family conflicts. Several sessions of family therapy also appear indicated, and her psychiatrist concurs.
A case study is a research method that involves an in-depth examination and analysis of a particular phenomenon or case, such as an individual, organization, community, event, or situation. It is a qualitative research approach that aims to provide a detailed and comprehensive understanding of the case being studied.
A case study is an in-depth, detailed examination of a particular case (or cases) within a real-world context. [1] [2] For example, case studies in medicine may focus on an individual patient or ailment; case studies in business might cover a particular firm's strategy or a broader market; similarly, case studies in politics can range from a narrow happening over time like the operations of a ...
Case Study Definition. A case study is a research method involving an in-depth examination of a single subject, group, event, or phenomenon within its real-world context. Widely used across various disciplines such as social sciences, business, law, medicine, and education, case studies provide comprehensive insights into complex issues that ...
Researchers, economists, and others frequently use case studies to answer questions across a wide spectrum of disciplines, from analyzing decades of climate data for conservation efforts to developing new theoretical frameworks in psychology. Learn about the different types of case studies, their benefits, and examples of successful case studies.
The definition above is an example of an all-inclusive descriptive definition of case study research represented by Yin (2003).According to the definition of case study research, there is no doubt that this research strategy is one of the most powerful methods used by researchers to realize both practical and theoretical aims.
McMaster University, West Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. Qualitative case study methodology prov ides tools for researchers to study. complex phenomena within their contexts. When the approach is ...
A case study is defined as an in-depth analysis of a particular subject, often a real-world situation, individual, group, or organization. It is a research method that involves the comprehensive examination of a specific instance to gain a better understanding of its complexities, dynamics, and context.
A case study is a detailed description and assessment of a specific situation in the real world, often for the purpose of deriving generalizations and other insights about the subject of the case study. Case studies can be about an individual, a group of people, an organization, or an event, and they are used in multiple fields, including business, health care, anthropology, political science ...
A Case study is: An in-depth research design that primarily uses a qualitative methodology but sometimes includes quantitative methodology. Used to examine an identifiable problem confirmed through research. Used to investigate an individual, group of people, organization, or event. Used to mostly answer "how" and "why" questions.
Designing and Conducting Case Studies. This guide examines case studies, a form of qualitative descriptive research that is used to look at individuals, a small group of participants, or a group as a whole. Researchers collect data about participants using participant and direct observations, interviews, protocols, tests, examinations of ...