Top 60 Examples of Qualitative Research Topics
Table of contents
- 1.1 Align your research topic with your field of interest
- 1.2 Make sure you have all the right research on the topic
- 1.3 Follow your university guidelines!
- 2 List of qualitative research topics examples
- 3 Conclusion
Qualitative research refers to the intuitive and creative analysis of intangible information you can use for writing a top-class college paper. Due to interacting with the data before and after the collection, having the best qualitative research topics is paramount to writing a research assignment that stands above the rest.
These topics can involve gathering key data from the most relevant sources to your assignment topics and are fundamental to your effort to collect first-hand information. Some of the major fields where qualitative research is performed include:
- Anthropology
- Political science
- Business management
- Social science
The main goal of qualitative research is to help you understand the topic of your assignment by identifying the most important aspects of your topic and gathering enough information to provide an in-depth analysis of the topic at hand and provide the answers to all the related questions. This type of research aims to identify and understand the general lifestyle, issues, and problems to provide solutions to a global problem. Since doing all the research on your own can turn out to be quite daunting, you can always resort to hiring an affordable research paper writing service to get professional assistance.

Tips on how to choose good qualitative research topics
Writing a research paper or a college assignment with success solely depends on your ability to choose suitable qualitative research topics. It’s essential to carefully examine and explore the field with all the challenges before you start writing to identify the key factors and aspects of your assignment. Here are a few tips on how to do that to get good research paper ideas.
Align your research topic with your field of interest
Your assignment topic should be something that interests you deeply so that you can completely get into it and make the most out of your efforts. More importantly, your topic should allow you to develop your personal skills and learn new things.
Make sure you have all the right research on the topic
If you choose a topic that has little to no supporting research available, you’ll end up getting stuck. You must properly research the topic before you start writing. This research will also help you shortlist unrelated topics and narrow down your scope so that you can focus on the information that matches your exact needs.
Follow your university guidelines!
Consulting with your professors and going through the assessment guidelines is paramount to writing a top-class paper. Follow your university guidelines to make sure your efforts get approved by your supervisor.
List of qualitative research topics examples
- Long-term planning methods for better project management
- How to deal with issues during a project implementation program
- The best practices for dealing with tight project deadlines
- Why time management is essential for goal setting
- Flexibility in management: How to improve decision-making as a manager
- Top professional techniques for developing management skills
- Healthcare in low-income societies: How to achieve affordable medical care
- Dealing with a loss and the process of recovery
- How to make eco-friendly facemasks
- Preventing flu during cold seasons: The most effective preventative methods
- The importance of developing community-based sanitization programs
- The best practices for quitting alcohol and cigarettes
- Helping the young manage their obesity: The most effective obesity management strategies
- Promoting healthcare during COVID-19: Strategies for expanding the health sector
- Guide to collecting resources for building a centralized community
- How academic and social practices can help uplift a society
- Professional practices for building a one-on-one relationship between teachers and students
- The science behind consumer motivations and appraisals
- Reshaping the traditional form of virtual ethnography
- Are homeschooling programs as efficient as they should be?
- The importance of developing healthy eating habits
- The best strategies for getting ahead of the prospective market
- How to track the dynamics of real estate investments
- How effective are modern newsgathering technologies?
- Developing introvert behavior and its key effects
- Can sharing help an individual overcome addictions?
- Guide to creating a one-people community
- The most effective methods for dealing with cyberbullying
- The best way to bringing social equity to patriarchal societies
- How quarantine prevents the spread of infectious diseases
- The aging populations and the trends they follow
- The latest digital media trends
- Methods for mitigating communicable diseases
- How governments work on protocol observance
- Practices for preventing the spread of the coronavirus in crowded places
- Alleviating pain during childbirth
- Maternal healthcare in developing countries
- Can pop music change erratic youth behavior?
- The best therapies for recovering from brain surgery
- How alcohol changes normal behavior
- Depression management among school-going children
- Strategies for avoiding a viral disease
- Ways to influence the eating habits of children
- How and when to engage in sporting activities
- How low socioeconomic background impacts self-esteem
- The importance of parenting for shaping children’s morals
- The impact of poor market completion on supply and demand
- Do children under four years need preschool education?
- Single-gender schools vs. mixed schools
- How the world would benefit from the same education system
- How virtual reality helps reshape the world
- The hottest destinations for traveling at the moment
- How fast does the ozone layer deplete?
- Is it possible to predict natural disasters before they occur?
- The effects of digital marketing on modern businesses
- Physical learning vs. online learning
- How related are Windows and Apple products?
- Study cases of bullying in schools
- The effect of stress on human behavior
- Patient behavior and the influence of social processes
If you’re looking for the best way to choose some of the most suitable qualitative research paper topics for your college assignment, these 60 topics should help you get ahead of your task and write an engaging paper. All topics above are for your personal education and motivation. If you still need help with your assignment, our professional paper writing services are available 24/7.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on June 19, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on June 22, 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analyzing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, history, etc.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organization?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography , action research , phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasize different aims and perspectives.
| Approach | What does it involve? |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | Researchers collect rich data on a topic of interest and develop theories . |
| Researchers immerse themselves in groups or organizations to understand their cultures. | |
| Action research | Researchers and participants collaboratively link theory to practice to drive social change. |
| Phenomenological research | Researchers investigate a phenomenon or event by describing and interpreting participants’ lived experiences. |
| Narrative research | Researchers examine how stories are told to understand how participants perceive and make sense of their experiences. |
Note that qualitative research is at risk for certain research biases including the Hawthorne effect , observer bias , recall bias , and social desirability bias . While not always totally avoidable, awareness of potential biases as you collect and analyze your data can prevent them from impacting your work too much.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves “instruments” in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analyzing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organize your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorize your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analyzing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasize different concepts.
| Approach | When to use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| To describe and categorize common words, phrases, and ideas in qualitative data. | A market researcher could perform content analysis to find out what kind of language is used in descriptions of therapeutic apps. | |
| To identify and interpret patterns and themes in qualitative data. | A psychologist could apply thematic analysis to travel blogs to explore how tourism shapes self-identity. | |
| To examine the content, structure, and design of texts. | A media researcher could use textual analysis to understand how news coverage of celebrities has changed in the past decade. | |
| To study communication and how language is used to achieve effects in specific contexts. | A political scientist could use discourse analysis to study how politicians generate trust in election campaigns. |
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analyzing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analyzing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalizability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalizable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labor-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organization to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, June 22). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, qualitative vs. quantitative research | differences, examples & methods, how to do thematic analysis | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- How It Works
- PhD thesis writing
- Master thesis writing
- Bachelor thesis writing
- Dissertation writing service
- Dissertation abstract writing
- Thesis proposal writing
- Thesis editing service
- Thesis proofreading service
- Thesis formatting service
- Coursework writing service
- Research paper writing service
- Architecture thesis writing
- Computer science thesis writing
- Engineering thesis writing
- History thesis writing
- MBA thesis writing
- Nursing dissertation writing
- Psychology dissertation writing
- Sociology thesis writing
- Statistics dissertation writing
- Buy dissertation online
- Write my dissertation
- Cheap thesis
- Cheap dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help
- Pay for thesis
- Pay for dissertation
- Senior thesis
- Write my thesis
131 Interesting Qualitative Research Topics For High Scoring Thesis

Qualitative research topics are undoubtedly not easy. While statistics enthralls some students, others don’t like the subject. That’s because qualitative assignments entail cognitive analysis, which complicates them. But apart from the hardships of completing the projects, selecting topics for qualitative research papers is also a challenge.
This article presents a list of 130-plus qualitative research topic ideas to help learners that struggle to get titles for their papers. It is helpful because many learners have difficulties picking titles that will make their essays impressive to educators. But before presenting the topics, this article defines qualitative research.
What Is Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is an investigative and innovative abstract data analysis. When writing a qualitative research paper, a learner analyzes intangible data. Qualitative researchers code the data after or during collection. Therefore, having top-notch research topics is necessary for a first-class essay.
Knowing how to write a qualitative research paper is vital because it helps the student deliver a copy that provides a clear picture of an event or situation. A researcher can achieve this via practical experience, reliable reporting, and conversations. Gathering raw data is the initial step in qualitative research. A researcher can gather raw data by conducting reviews, observations, and surveys. Also, researchers can use creative methods to collect data.
Best Examples Of Qualitative Research Topics
Qualitative research covers many things. Here are examples of topics that learners can explore in their qualitative study.
- What causes stigma around some health challenges?
- Stigma facing the people living with disabilities- What is the cause?
- Can Pro Bono legal assistance improve the criminal justice system?
- How the less privileged can benefit from Pro Bono services
- The educational challenges facing rural children- Are there ways to help them?
- Child labor causes- How to mitigate the practice
- Substance and drugs- What are young people abusing more?
- How alcohol affects college students
- Can food insecurity interfere with children’s performance in school?
- Food banks intricacies- Understanding the challenge in low-income areas
- Free education- Does it have socioeconomic benefits?
- Culture and female harm- What’s the connection?
- The impact of social media on physical and social engagement among teens in urban areas
- Using medication to treat depression- What are the health benefits?
- Investigating peer educators’ efficiency in creating awareness of health and social issues
- Gender-based violence- What causes it in rural areas, and how does it affect victims?
- Sexual reproductive health challenges of child brides- Are there ways to control it?
- Investigating the causes of school dropout among teenagers
- How to address school dropout among young adults
- Investigating the deteriorating academic pursuit in Third-World countries
- Social activities- Do they have benefits for depressed people?
- Investigating cerebral palsy and the stigma that people associate with it.
- Living with disabilities- Are there social implications?
- The impact of ableism on disabled people
- Exploring the promotion and benefits of feminist values
- Why should society promote free education in all learning environments?
- What causes food insecurities among low-income earners?
- Food and housing insecurity- What are the root causes?
- What are the effects of displacement- Investigating the homeless people’s mental health
These are good examples of qualitative research topics. However, a student that picks a title in this category should research it extensively to impress the educator with their work.
Qualitative Nursing Research Topics
Professors ask students to write about qualitative topics when pursuing nursing studies. Here are issues to consider in this category.
- How does the nurse-patient relationship affect health outcomes?
- How can nurses deal with complex patients?
- How can nurses provide culturally competent care?
- How do personal beliefs affect nursing practice?
- What is the impact of spirituality on nursing care?
- How does the nurse’s role change when working with terminally ill patients?
- What challenges do nurses face when providing end-of-life care?
- How can nurses best support families whose members have serious illnesses?
- What are the unique challenges of caring for elderly patients?
- How does the nurse’s role change when working in a hospice setting?
- Health outreach programs- What are the most effective ways to execute them?
- Effective methods of curbing drug abuse
- Effective ways to help rape survivors
- How can nurses administer care to female genital mutilation victims?
- How to care for special needs individuals
- Anxiety and depression symptoms
- Methods of administering care to Dyslexia patients
- How to help individuals dealing with mental disorders
- Signs of Alzheimer’s disease in older people
- How to provide primary patient care
These are good qualitative research topics for students pursuing nursing studies. Nevertheless, learners must research any of these titles before writing their papers.
Qualitative Research Topics In Education
Most topics spring up from the education niche despite fitting other specifications. Here are examples of qualitative research topics that include the education niche.
- Are guidance and counseling essential in schools?
- How computer literacy affects education
- Why governments in developing schools should encourage adult education
- Autistic children’s education- Which learning style suits them?
- Is mental health education relevant in the modern school curriculum?
- Exploring the learning conditions for kids in third world countries
- Child education and food insecurity- What is the connection?
- The impact of virtual learning on high school students
- How does alcoholism affect a student and their education?
- Homeschooling- What are its advantages and disadvantages?
- How do teachers’ beliefs about intelligence affect their teaching?
- What is the teacher’s role in developing a student’s self-concept?
- Does race or ethnicity play a role in how teachers treat their students?
- What are the teachers’ experiences with teaching students with special needs?
- What methods do effective teachers use to motivate their students?
- What are the most effective ways to teach reading and writing?
- How does technology use affect how teachers teach, and students learn?
- What are the challenges faced by teachers in rural areas?
- What are the challenges faced by teachers in urban areas?
- How do charter schools differ from traditional public schools?
Many topics and issues in the education system allow learners to find subjects to investigate and cover in their papers quickly. And this is not an exhaustive qualitative research topic list in this field. Nevertheless, it covers the most exciting ideas to explore.
Qualitative Research Topics In Public Health
Educators ask students to write academic papers while studying the public health sector. And this provides insights into crucial and relevant aspects of this sector. Here are qualitative research topics examples in this category.
- How does the public health sector manage epidemics?
- The role of public health in disaster management
- Evaluating the effectiveness of public health campaigns
- An analysis of the factors that hinder effective public health delivery
- Access to healthcare: A study of rural and urban populations
- Health needs assessment of refugees
- Mental health support within the public health sector
- The role of technology in public health
- Understanding and addressing health disparities
- Sexual and reproductive health rights in the public health discourse
- How immunization benefits people in rural areas
- What causes water-borne diseases, and how can society mitigate them?
- Symptoms of high blood pressure among young people
- How antenatal care helps pregnant women
- How to boost breast cancer awareness
These are excellent qualitative research paper topics in the public health sector. Nevertheless, learners need sufficient time and resources to investigate their preferred titles in this category to write winning papers.
Qualitative Research Topics In Project Management
Project management writing focuses on ways to achieve results and goals while basing the achievement on the process. This subject covers planning, structuring, proffering, and controlling ways to execute plans to accomplish desired goals. Here are research topics for qualitative research in project management.
- How effective communication strategies can impact the outcome of a project
- How different leadership styles affect team productivity during a project
- The role of conflict management in ensuring successful project outcomes
- Gender differences in the perception and understanding of project risk
- The impact of organizational culture on a project’s likelihood of success
- How different project management methodologies affect its outcome
- The effect of stakeholder involvement on project success
- How to manage virtual teams effectively to ensure successful project outcomes
- What motivates project managers to achieve successful results?
- How can project managers create a positive work environment that leads to successful outcomes?
- What challenges do project managers face when trying to achieve successful outcomes?
- How can project management be used to achieve social change?
- What are the ethical implications of project management?
- What are the global impacts of project management?
- Ways to achieve sustainable development through project management
These are topics to explore in project management. Nevertheless, learners need adequate time to investigate their chosen titles and write winning essays.
Qualitative Research Topics In Political Science
Qualitative research can also cover political science. Investigating this field enables people to understand it better and can be broad. Here are sample titles to consider in for your scientific thesis .
- How do social media affect the way people engage with politics?
- What motivates people to vote?
- How does voting behavior change over time?
- What are the consequences of gerrymandering?
- How does campaign finance influence elections?
- Interest groups- What is their role in politics?
- How do the media cover politics?
- What are the effects of political scandals?
- How does public opinion influence policymakers?
- How feminism enhanced the American politics
- The adverse effects of misrepresentation
- The American democracy- A look into its dimensions
- Colorism, racism, and classism- How the American ideologies differ
- What causes an election crisis?
- Two-party system- What challenges does it face in America?
- Black women’s inclusion in the American politics
- Should America have a multi-party system?
- Why mass media matters in politics’ scrutiny and promotion
While political science is a broad field, these narrow topics help learners handle their research effectively. Pick any of these ideas to write a winning essay.
Topics For Ethnography Qualitative Research
Ethnographic research entails studying and paying attention to society and describing it. Here are topics to consider for a research paper in this field.
- Studying a subculture: Reasons people join and stay in gangs
- How does social media use vary by culture?
- An ethnographic study of a homeless shelter or soup kitchen
- Understanding the lives of sex workers through ethnography
- The impact of religion on family life
- How does parenting vary between cultures?
- How do children learn and socialize in different cultures?
- What is the effect of migration on family life?
- What are the experiences of refugees?- An explorative case study
- What is the impact of poverty on family life?
- How do people in different cultures understand and experience mental illness?
- What is the role of the family in other cultures?
- What are the end-of-life experiences and beliefs around death in different cultures?
This article has presented easy qualitative research topics. However, some need time and resources to investigate and write quality papers. Therefore, pick your paper title carefully to write an essay that will earn you an excellent grade.
Get Quality Writing Help Online
Maybe you have a title for your paper but not time for writing a unique, top-notch thesis. In that case, get the best dissertation services from our writers. We’re educated, native ENL writers with a proven track record of exceeding customers’ expectations. Our team helps university, college, and high school learners complete their writing and editing assignments. Whether writing a research paper is a requirement for a degree or a diploma course, we can help you. Contact us to get quality, custom, and cheap help from qualified experts in your study field.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Comment * Error message
Name * Error message
Email * Error message
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
As Putin continues killing civilians, bombing kindergartens, and threatening WWIII, Ukraine fights for the world's peaceful future.
Ukraine Live Updates

189+ Most Exciting Qualitative Research Topics For Students
Researchers conduct qualitative studies to gain a holistic understanding of the topic under investigation. Analyzing qualitative? Looking for the best qualitative research topics?
If yes, you are here at the right place. We are discussing here all the topics in every field. Basically, qualitative research is the most valuable approach within the fields of social sciences, humanities, and various other fields.
Qualitative research uses a wide array of methods such as interviews, focus groups, participant observation, content analysis, and case studies. Even among others, to gather and analyze non-numerical data.
In this blog, we will explore the diverse, most interesting qualitative research topics, highlighting their importance. Whether you are a student, a scholar, or a practitioner in your field, these best qualitative research ideas are most helpful for you.
Must Read: 21 Ways To Get Good Grades In College
What Is Qualitative Research?
Table of Contents
Qualitative research is a systematic and exploratory approach to research that focuses on understanding and interpreting the complexities of human experiences, behaviors, and phenomena. It aims to provide in-depth insights into the “how” and “why” of various issues by examining them in their natural settings and contexts. Unlike quantitative research, which primarily deals with numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research relies on non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, textual analysis, and participant narratives to uncover deeper meanings and patterns.
Key Characteristics of Qualitative Research
- Purpose : Qualitative research is used to delve into new or less understood areas, aiming to generate new hypotheses and theories.
- Example : Investigating the coping mechanisms of natural disaster survivors in regions where little prior research exists.
- Purpose : It seeks to understand and interpret participants’ perspectives, emotions, and experiences.
- Example : Examining how individuals with chronic pain perceive their condition and the medical care they receive.
- Purpose : Highlights the importance of context and situational factors in shaping human behavior and experiences.
- Example : Exploring how cultural backgrounds influence parenting styles in different communities.
- Purpose : Employs adaptable and open-ended data collection methods that evolve as new insights are gained.
- Example : Conducting semi-structured interviews where the researcher can ask follow-up questions based on participants’ answers.
- Purpose : Generates detailed, narrative data that offer deep insights into the studied topic, capturing the complexity of human experiences.
- Example : Collecting and analyzing detailed personal stories to understand career development and personal growth.
These characteristics enable qualitative research to provide a comprehensive, nuanced understanding of complex issues, often revealing insights that quantitative approaches might miss.
8 Great Tips On How To Choose Good Qualitative Research Topics
Here are some tips to help you select strong qualitative research topics:

1. Personal Interest and Passion: Start by considering what genuinely interests and excites you. Your enthusiasm for the topic will sustain your motivation throughout the research process.
2. Relevance: Ensure that your chosen topic is relevant to your field of study or the discipline you are working within. It should contribute to existing knowledge or address a meaningful research gap.
3. Research Gap Identification: Review relevant literature and research to identify gaps or areas where there is limited qualitative research. Look for unanswered questions or underexplored aspects of a particular subject.
4. Feasibility: Assess whether the topic is feasible within the scope of your research project. Consider factors like available time, resources, and access to potential participants or data sources.
5. Clarity and Specificity: Your research topic should be clear, specific, and well-defined. Avoid overly broad topics that are difficult to explore in depth. Narrow it down to a manageable focus.
6. Significance: Ask yourself why your research topic matters. Consider the potential implications and applications of your findings. How might your research contribute to understanding, policy, or practice?
7. Originality: Aim for a unique angle or perspective on the topic. While you can build on existing research, strive to offer a fresh viewpoint or new insights.
8. Researchable : Ensure that your topic is researchable using qualitative methods. It should allow you to collect relevant data and answer research questions effectively.
137+ Most Exciting Qualitative Research Topics For All Students
Qualitative research topics in health and medicine.
- Experiences of healthcare workers during the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Perceptions of alternative medicine among cancer patients.
- Coping mechanisms of individuals with chronic illnesses.
- The impact of telemedicine on patient-doctor relationships.
- Barriers to mental health treatment-seeking among minority populations.
- Qualitative analysis of patient experiences with organ transplantation.
- Decision-making processes of families regarding end-of-life care.
Qualitative Research Topics In Education
- The role of parental involvement in student academic achievement.
- Teacher perceptions of remote learning during a pandemic.
- Peer influence on academic motivation and performance.
- Exploring the experiences of homeschooling families.
- The impact of technology on the classroom environment.
- Factors influencing student dropout rates in higher education.
Qualitative Research Topics In Psychology and Mental Health
- Understanding the stigma associated with seeking therapy.
- Experiences of individuals living with anxiety disorders.
- Perceptions of body image among adolescents.
- Coping strategies of survivors of traumatic events.
- The impact of social support on mental health recovery.
- Narratives of individuals with eating disorders.
Qualitative Research Topics In Sociology and Culture
- Experiences of immigrants in adapting to a new culture.
- The role of social media in shaping cultural identities.
- Perceptions of police-community relations in marginalized communities.
- Gender dynamics in the workplace and career progression.
- Qualitative analysis of online dating experiences.
- Narratives of LGBTQ+ individuals coming out to their families.
Qualitative Research Topics In Technology and Society
- User experiences with augmented reality applications.
- Perceptions of online privacy and data security.
- The impact of social media on political activism.
- Ethical considerations in artificial intelligence development.
- Qualitative analysis of online gaming communities.
- Experiences of individuals participating in virtual reality environments.
Qualitative Research Topics In Environmental Studies
- Public perceptions of climate change and environmental policies.
- Experiences of individuals involved in sustainable living practices.
- Qualitative analysis of environmental activism movements.
- Community responses to natural disasters and climate change.
- Perspectives on wildlife conservation efforts.
Qualitative Research Topics In Business and Economics
- Qualitative analysis of consumer behavior and brand loyalty.
- Entrepreneurial experiences of women in male-dominated industries.
- Factors influencing small business success or failure.
- Corporate social responsibility and its impact on consumer trust.
- Experiences of employees in remote work settings.
Qualitative Research Topics In Politics and Governance
- Perceptions of voter suppression and electoral integrity.
- Experiences of political activists in grassroots movements.
- The role of social media in shaping political discourse.
- Narratives of individuals involved in civil rights movements.
- Qualitative analysis of government responses to crises.
Qualitative Research Topics In Family and Relationships
- Experiences of couples in long-distance relationships.
- Parenting styles and their impact on child development.
- Sibling dynamics and their influence on individual development.
- Narratives of individuals in arranged marriages.
- Experiences of single parents in raising their children.
Qualitative Research Topics In Art and Culture
- Qualitative analysis of the impact of art therapy on mental health.
- Experiences of artists in exploring social and political themes.
- Perceptions of cultural appropriation in the arts.
- Narratives of individuals involved in the hip-hop culture.
- The role of art in preserving cultural heritage.
Qualitative Research Topics In Crime and Justice
- Experiences of formerly incarcerated individuals reentering society.
- Perceptions of racial profiling and police violence.
- Qualitative analysis of restorative justice programs.
- Narratives of victims of cyberbullying.
- Perspectives on juvenile justice reform.
Qualitative Research Topics In Sports and Recreation
- Experiences of athletes in overcoming career-threatening injuries.
- The role of sports in building resilience among youth.
- Perceptions of performance-enhancing drugs in professional sports.
- Qualitative analysis of sports fandom and its impact on identity.
- Narratives of individuals involved in adaptive sports.
Qualitative Research Topics In History and Heritage
- Experiences of descendants of historical events or figures.
- Perceptions of cultural preservation and heritage conservation.
- Narratives of individuals connected to indigenous cultures.
- The impact of oral history on preserving traditions.
- Qualitative analysis of historical reenactment communities.
Qualitative Research Topics In Religion and Spirituality
- Experiences of individuals who have undergone religious conversion.
- Perceptions of spirituality and well-being.
- The role of religion in shaping moral values and ethics.
- Narratives of individuals who have left religious communities.
- Qualitative analysis of interfaith dialogue and cooperation.
Qualitative Research Topics In Travel and Tourism
- Experiences of solo travelers in foreign countries.
- Perceptions of sustainable tourism practices.
- Qualitative analysis of cultural immersion through travel.
- Narratives of individuals on pilgrimages or spiritual journeys.
- Experiences of individuals living in tourist destinations.
Qualitative Research Topics In Human Rights and Social Justice
- Narratives of human rights activists in advocating for change.
- Experiences of refugees and asylum seekers.
- Perceptions of income inequality and wealth distribution.
- Qualitative analysis of anti-discrimination campaigns.
- Perspectives on global efforts to combat human trafficking.
Qualitative Research Topics In Aging and Gerontology
- Experiences of individuals in assisted living facilities.
- Perceptions of aging and quality of life in older adults.
- Narratives of caregivers for elderly family members.
- The impact of intergenerational relationships on well-being.
- Qualitative analysis of end-of-life decisions and hospice care.
Qualitative Research Topics In Language and Communication
- Experiences of individuals learning a second language.
- Perceptions of non-verbal communication in cross-cultural interactions.
- Narratives of people who communicate primarily through sign language.
- The role of language in shaping identity and belonging.
- Qualitative analysis of online communication in virtual communities.
Qualitative Research Topics In Media and Entertainment
- Experiences of content creators in the digital media industry.
- Perceptions of representation in the film and television industry.
- The impact of music on emotional well-being and identity.
- Narratives of individuals involved in fan communities.
- Qualitative analysis of the effects of binge-watching on mental health.
Qualitative Research Topics In Ethics and Morality
- Experiences of individuals faced with ethical dilemmas.
- Perceptions of moral relativism and cultural differences.
- Narratives of whistleblowers in exposing corporate misconduct.
- The role of empathy in ethical decision-making.
- Qualitative analysis of the ethics of artificial intelligence.
Qualitative Research Topics In Technology and Education
- Experiences of teachers integrating technology in the classroom.
- Perceptions of online learning and its effectiveness.
- The impact of educational apps on student engagement.
- Narratives of students with disabilities using assistive technology.
- Qualitative analysis of the digital divide in education.
Qualitative Research Topics In Gender and Sexuality
- Experiences of transgender individuals in transitioning.
- Perceptions of gender roles and expectations.
- Narratives of individuals in same-sex relationships.
- The impact of intersectionality on experiences of gender and sexuality.
- Qualitative analysis of gender-based violence and advocacy.
Qualitative Research Topics In Migration and Diaspora
- Experiences of immigrants in maintaining cultural ties to their home country.
- Perceptions of identity among second-generation immigrants.
- Narratives of refugees resettling in new countries.
- The role of diaspora communities in supporting homeland causes.
- Qualitative analysis of immigration policies and their impact on families.
Qualitative Research Topics In Food and Nutrition
- Experiences of individuals with specific dietary restrictions.
- Perceptions of food sustainability and ethical consumption.
- Narratives of people with eating disorders seeking recovery.
- The role of food in cultural identity and traditions.
- Qualitative analysis of food insecurity and hunger relief efforts.
Qualitative Research Topics In Urban Studies and Community Development
- Experiences of residents in gentrifying neighborhoods.
- Perceptions of community engagement and empowerment.
- Narratives of individuals involved in urban farming initiatives.
- The impact of housing policies on homelessness.
- Qualitative analysis of neighborhood safety and crime prevention.
Qualitative Research Topics In Science and Technology Ethics
- Experiences of scientists in navigating ethical dilemmas.
- Perceptions of scientific responsibility in climate change research.
- Narratives of whistleblowers in scientific misconduct cases.
- The role of ethics in emerging technology development.
- Qualitative analysis of the ethics of genetic engineering.
Qualitative Research Topics In Social Media and Online Communities
- Experiences of individuals in online support groups.
- Perceptions of social media’s influence on self-esteem.
- Narratives of social media influencers and their impact.
- The role of online communities in social and political movements.
- Qualitative analysis of cyberbullying and online harassment.
Qualitative Research Topics in Daily Life
- The Impact of Social Media on Personal Relationships and Well-being.
- Exploring the Experience of Remote Work during the COVID-19 Pandemic.
- Perceptions of Sustainable Living Practices Among Urban Dwellers.
- Qualitative Analysis of Food Choices and Eating Habits in a Fast-paced Society.
- Understanding the Motivations and Barriers to Physical Activity Among Adults.
Qualitative Research Topics for Students
- Student Perceptions of Online Learning: Challenges and Opportunities.
- Peer Pressure and Decision-making Among Adolescents.
- Exploring the Transition from High School to College: Student Experiences.
- The Role of Extracurricular Activities in Student Development.
- Motivations and Challenges of Student Entrepreneurs in Starting Their Businesses.
Qualitative Research Topics for STEM Students
Here are some original qualitative research topic ideas for STEM students:
- Exploring the Ethical Implications of AI in Healthcare Decision-Making : Investigate healthcare professionals’ ethical perspectives and decision-making processes regarding the use of AI technologies in clinical settings.
- Gender Dynamics in STEM Education and Career Aspirations : Analyze how gender influences students’ educational experiences and career choices in STEM fields at the university level.
- Public Perception and Acceptance of Genome Editing Technologies : Conduct interviews and surveys to understand public attitudes and concerns about genome editing technologies such as CRISPR.
- Effectiveness of Online Interactive Tools in Teaching Middle School Mathematics : Explore how digital tools impact student learning and engagement in middle school mathematics education.
- Community Engagement and Impact of Renewable Energy Projects : Investigate community perceptions, concerns, and benefits related to local renewable energy initiatives like wind farms or solar installations.
- Challenges and Opportunities in Adopting Blockchain Technology in Supply Chain Management : Interview industry professionals to identify barriers and opportunities for integrating blockchain into supply chain operations.
- Decision-Making Processes in Software Development Methodologies : Explore how software engineers and development teams choose between different methodologies (e.g., Agile, Waterfall) and the factors influencing these decisions.
- Cross-Cultural Perspectives on Space Exploration : Analyze interviews with stakeholders from different cultural backgrounds to understand diverse perspectives on space exploration missions and collaborations.
- User Experience and Usability of Wearable Health Monitoring Devices : Conduct qualitative usability studies and interviews to evaluate user experiences with wearable health monitoring technologies.
- Impact of Virtual Reality on Engineering Design Processes : Study how virtual reality tools influence the design process, collaboration among engineering teams, and project outcomes.
These research topics for stem students qualitative to explore a wide range of social, ethical, cultural, and practical dimensions within their fields of study, providing opportunities for meaningful qualitative research.
Qualitative Research Titles Examples
- “Voices of Resilience: Narratives of Cancer Survivors.”
- “Exploring Cultural Identity Among Immigrant Communities.”
- “From Addiction to Recovery: Life Stories of Former Substance Abusers.”
- “Inside the Classroom: Student and Teacher Perspectives on Inclusive Education.”
- “Navigating Caregiving: Experiences of Family Members Caring for Alzheimer’s Patients.”
Qualitative Research Topics in Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Practices in Culturally Responsive Pedagogy.
- Qualitative Study of Bullying Incidents in Elementary Schools.
- Homeschooling: Parent and Student Perspectives on Alternative Education.
- Evaluating the Impact of Technology Integration in Classroom Learning.
- Parental Involvement in Early Childhood Education: A Qualitative Analysis.
Qualitative Research Topics for Nursing Students
- Patient Experiences of Chronic Illness Management.
- The Role of Empathy in Nursing Practice: A Qualitative Study.
- Qualitative Exploration of End-of-Life Care Decision-making.
- Perceptions of Nurse-Patient Communication in Intensive Care Units.
- Nursing Burnout: Causes, Consequences, and Coping Strategies.
Qualitative Research Topics for Human Studies
- Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Vulnerable Communities.
- The Role of Social Support in Mental Health Recovery.
- Experiences of First-time Homebuyers in the Real Estate Market.
- Exploring the Motivations and Challenges of Volunteering.
- Narratives of Trauma Survivors: Coping and Resilience.
Qualitative Research Topics 2023
- Emerging Trends in Remote Work: Employee Perspectives.
- The Influence of Social Media on Political Engagement in the Post-COVID-19 Era.
- Qualitative Study of Mental Health Stigma Reduction Campaigns.
- Sustainability Practices in Business: Stakeholder Perceptions and Implementation.
- Narratives of Long COVID: The Lived Experience of Survivors.
Qualitative research methods such as interviews, focus groups, participant observation, and content analysis allow researchers to delve deeply into these topics, capturing rich and detailed data that can illuminate complexities, contradictions, and underlying meanings. These methods emphasize understanding context, exploring subjective experiences, and generating nuanced insights that can inform theory-building and contribute to addressing real-world challenges.
10 Major Differences Between Qualitative And Quantitative Research
Here are the 10 best differences between qualitative and quantitative research:
| Focuses on understanding the meaning of people’s experiences | Focuses on measuring and quantifying data |
| Uses open-ended questions and interviews | Use closed-ended questions and surveys |
| Data is analyzed through interpretation and coding | Data is analyzed through statistical methods |
| Is more subjective | Is more objective |
| Is better suited for exploring new ideas and concepts | Is better suited for testing hypotheses and making predictions |
| Produces rich, detailed data | Produces more generalizable data |
| Is often used in the social sciences | Is often used in the natural sciences |
| Can be used to answer questions about why and how | Can be used to answer questions about who, what, when, and where |
| Is more time-consuming and labor-intensive | Is less time-consuming and labor-intensive |
| Is more expensive | Is less expensive |
Consequently, the selection of qualitative research topics is a critical phase in the journey of any researcher or student pursuing qualitative inquiry. The process of choosing the right topic involves a delicate balance of personal passion, research significance, feasibility, and ethical considerations.
As we’ve discussed, it’s essential to choose a topic that not only resonates with your interests but also contributes to the broader academic or practical discourse. Qualitative research offers a unique lens through which to examine the complexities of human experiences, behaviors, and phenomena.
It provides the opportunity to delve deep into the “how” and “why” of various subjects, offering nuanced insights that quantitative methods may not capture. Whether you are investigating personal narratives, cultural dynamics, educational practices, or social phenomena, qualitative research allows you to uncover the rich tapestry of human existence.
What is a good topic for qualitative research?
Self-esteem among people from low socioeconomic backgrounds. The advantages of online learning over physical learning.
What are the five topics of qualitative research?
These are biography, ethnography, phenomenology, grounded theory, and case study.
What is the easiest type of qualitative research?
Content analysis is possibly the most common and straightforward QDA method. At the simplest level, content analysis.
What are the 4 R’s of qualitative research?
Qualitative social research, whether conducted as ethnography, participant observation, or in situ interviewing, fares poorly when examined by the criteria of representativeness, reactivity, reliability, and replicability.
Similar Articles

13 Best Tips To Write An Assignment
Whenever the new semester starts, you will get a lot of assignment writing tasks. Now you enter the new academic…

How To Do Homework Fast – 11 Tips To Do Homework Fast
Homework is one of the most important parts that have to be done by students. It has been around for…
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
100+ Trending Qualitative Research Topics For College Students

Qualitative research topics are very important in college because they help students learn more about different subjects. They can think more deeply about things when they do this kind of study.
Qualitative research involves methods like interviews, observations, and case studies. It’s all about understanding human behavior, social trends, or complex issues in specific situations.
It’s also about exploring new ideas and adding to our knowledge. These topics often connect what we learn in class with real-life situations. By doing qualitative research, students improve their research skills, learn to interpret data better, and better understand the subjects they’re studying.
This article will give you 100+ Trending ideas for qualitative research topics that college students in a range of subjects can work on.
What are Qualitative Research Topics
Table of Contents
Qualitative research topics can be studied to learn more about things, understand events, or determine what they mean using qualitative methods.
Quantitative research looks at numbers and statistics, but qualitative research tries to understand people’s thoughts, feelings, behaviors, and relationships with others more deeply.
The qualitative study fields include psychology, sociology, education, anthropology, literature, etc. Some examples are looking into how social media affects their self-esteem, how teachers and students interact in multicultural classrooms, or how people from different groups feel about climate change.
Through interviews, observations, focus groups, and textual analysis, these topics try to get to deep, detailed understanding of difficult problems.
Key Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is different from counting numbers or statistics. It focuses on understanding people’s experiences and behaviors deeply. Here are its main points:
- Deep Exploration: Qualitative research deepens into understanding why people do what they do and how they experience things.
- Understanding Context: It looks at the bigger picture—like culture, society, and environment—to understand how these influence people.
- Personal Perspective: Researchers see things from their point of view and understand that everyone may have different views.
- Flexible Approach: Researchers can change how they study things as they learn more.
- Many Ways to Collect Info: They use different methods, like talking to people, watching them, or looking at things they write or make.
- Seeing the Whole Picture: Instead of focusing on one part of something, they look at everything together.
- Finding Patterns: They see what comes from what people say and do rather than deciding what to look for first.
- Researcher’s Role: People studying things is important because they talk to people and see things that shape their understanding.
- Listening to People: They care about what people say and think and focus on understanding their experiences.
- Natural Places: They often study people where they live and work to see how they act in their usual surroundings.
These things make qualitative research good at understanding why people act and think as they do.
Also Read: 170+ Creative SK Project Ideas For All Levels In 2024
Here are 100+ qualitative research topics for college students categorized into different fields of study:
Qualitative Research Topics In Education
- The impact of personalized learning on student engagement.
- Parental involvement and its effect on academic achievement.
- Perceptions of online education among students and instructors.
- Strategies for integrating technology in classroom teaching.
- Factors influencing student motivation in high school.
- Teacher-student relationships and their impact on learning outcomes.
- The effectiveness of inclusive education programs.
- Student perspectives on standardized testing.
- Challenges faced by teachers in multicultural classrooms.
- The role of mentoring programs in student success.
Qualitative Research Topics In Psychology
- Social media and its influence on self-esteem in adolescents.
- Coping mechanisms for stress among college students.
- Gender differences in coping with anxiety disorders.
- The impact of childhood trauma on adult relationships.
- Cultural variations in perceptions of mental health.
- Factors influencing decision-making processes in adolescents.
- The psychology of forgiveness and its implications for mental health.
- Body image perceptions among different cultural groups.
- The role of music therapy in treating depression.
- Attitudes towards seeking therapy in different demographic groups.
Qualitative Research Topics In Sociology
- The portrayal of gender roles in popular media.
- Social perceptions of homelessness in urban communities.
- Cultural identity among second-generation immigrants.
- The impact of social media on social movements.
- Attitudes towards LGBTQ+ rights in conservative societies.
- Factors influencing political participation among youth.
- The role of religion in shaping community values.
- Social attitudes towards interracial relationships.
- Generational differences in views on work-life balance.
- The effects of gentrification on local communities.
Qualitative Research Topics In Business and Economics
- Consumer behavior trends in the digital age.
- The role of corporate social responsibility in brand perception.
- Gender disparities in leadership positions in corporate environments.
- Factors influencing entrepreneurship among millennials.
- The impact of globalization on local businesses.
- Ethical dilemmas in business decision-making.
- Employee satisfaction and its relationship with organizational performance.
- The effectiveness of remote work policies in enhancing productivity.
- Financial literacy levels among college students.
- Sustainability practices in supply chain management.
Also Read: 40+ Interesting TensorFlow Project Ideas For All Levels In 2024
Qualitative Research Topics In Health and Wellness
- Perceptions of body image and its impact on eating disorders.
- The role of exercise in mental health maintenance.
- Cultural perspectives on alternative medicine practices.
- Factors influencing vaccine hesitancy among parents.
- The impact of social media on perceptions of beauty standards.
- Attitudes towards organ donation in different demographic groups.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based interventions in stress reduction.
- Mental health stigma among college students.
- The influence of family dynamics on adolescent substance abuse.
- Access to healthcare services among marginalized communities.
Qualitative Research Topics In Environmental Studies
- Public perceptions of climate change and its implications.
- Sustainable living practices among urban households.
- The impact of plastic waste on marine ecosystems.
- Attitudes towards renewable energy sources in rural communities.
- Conservation efforts and community involvement in local parks.
- The role of environmental education in promoting conservation behaviors.
- Urbanization and its effects on biodiversity.
- Consumer attitudes towards eco-friendly products.
- Water conservation strategies in agricultural communities.
- Environmental justice and its intersection with social inequality.
Qualitative Research Topics In Communication and Media Studies
- The influence of social media influencers on consumer behavior.
- Media portrayal of marginalized communities and its impact on public perception.
- The role of advertising in shaping cultural norms.
- Public opinion and media coverage of political campaigns.
- The evolution of digital storytelling in journalism.
- Cross-cultural communication challenges in global organizations.
- The impact of fake news on public trust in the media.
- Perceptions of privacy in the digital age.
- Gender representation in television programming.
- The effectiveness of health communication campaigns.
Qualitative Research Topics In Literature and Language Studies
- Themes of identity and belonging in contemporary literature.
- Translation strategies and cultural adaptation in literary works.
- The portrayal of mental illness in literature.
- Language acquisition and cultural integration among immigrants.
- Feminist perspectives in literary criticism.
- Historical and cultural influences on language evolution.
- Folklore and oral traditions in preserving cultural heritage.
- Literary representations of post-colonial identities.
- Narrative techniques in autobiographical literature.
- The impact of digital platforms on reading habits.
Qualitative Research Topics In History and Archaeology
- The role of archaeology in reconstructing ancient societies.
- Public perceptions of historical events and their influence on national identity.
- Archaeological ethics and the preservation of cultural heritage.
- Gender roles in ancient civilizations.
- Oral history and its contribution to understanding local communities.
- The impact of colonialism on indigenous cultures.
- Historical memory and commemoration practices.
- Technological advancements in archaeological research methods.
- The representation of history in popular culture.
- Archaeoastronomy and its implications for understanding ancient societies.
Qualitative Research Topics In Political Science and International Relations
- Youth political participation and civic engagement.
- Diplomatic negotiations and conflict resolution strategies.
- The impact of globalization on national sovereignty.
- Human rights discourse in international policymaking.
- Gender equality policies and their implementation in different countries.
- The role of international organizations in global governance.
- Migration policies and their effects on host societies.
- Environmental diplomacy and international agreements.
- Political polarization and its impact on democratic institutions.
- Peacebuilding efforts in post-conflict societies.
Qualitative Research Topics In Anthropology
- Cultural relativism and its implications for understanding diverse societies.
- Ethnographic research methods in studying community dynamics.
- Rituals and ceremonies in preserving cultural traditions.
- Indigenous knowledge systems and their relevance in modern contexts.
- Medical anthropology and cross-cultural perspectives on healthcare.
- Urbanization and its effects on traditional lifestyles.
- Food culture and identity formation.
- Gender roles in indigenous societies.
- The impact of tourism on local cultures.
- Ethical considerations in anthropological fieldwork.
These topics cover various disciplines, offering college students ample opportunities to explore qualitative research in areas that align with their academic interests and career goals.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Qualitative Research Topics For Students
When choosing a topic for qualitative research, consider these important factors to make sure your topic is a good fit:
- Interest and Passion : Pick a topic you find interesting and care about. This will keep you motivated while doing your research.
- Relevance : Make sure your topic relates to what you’re studying or learning about. It should add something new to what’s already known or fill in gaps in our understanding.
- Feasibility : Think about whether you can realistically research your topic. Consider things like access to information, resources, and available time.
- Scope : Define your topic clearly so it’s not too broad or too narrow. You want to be able to explore it deeply but still cover everything you need to.
- Research Questions : Identify specific questions your research will try to answer. These questions will guide what you do during your research, like interviews or looking at documents.
- Ethical Considerations : Consider if your research could raise any ethical issues. Think about things like keeping people’s information private, getting their permission to be part of the research, and ensuring no one gets hurt because of your research.
- Contribution : Think about how your research can help others learn more. Your topic should bring new ideas or solutions to what people are already talking about.
- Methodological Approach : Decide on the best way to do your research. You might interview people, observe them, or study documents. Pick the method that fits best with what you want to find out.
- Theoretical Framework : Think about the theories or ideas that will help explain what you find during your research. This will help you better understand your results and discuss them with others.
- Feedback and Support : Get advice from teachers or other students about your topic. They can help ensure it’s a good idea and fits what you must do for school.
Considering these factors will help you choose an interesting research topic that fits well with your studies, making your research experience successful and rewarding.
Examples of Trending Qualitative Research Topics
Qualitative research continues to evolve, addressing contemporary issues and exploring new dimensions of human experiences and societal phenomena. Here are some trending qualitative research topics:
In Social Sciences:
- Impact of Social Media on Mental Health: Investigate how social media platforms influence self-perception, relationships, and mental well-being across different age groups.
- COVID-19 Pandemic and Social Change: Study the social, economic, and psychological impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic on individuals and communities globally.
- Gender Identity and Expression: Explore the changing concepts of gender identity and expression in modern society, focusing on challenges faced by gender-nonconforming individuals.
In Education:
- Equity and Inclusion in Higher Education: Examine initiatives promoting equity and inclusion within higher education institutions, including policies, practices, and student experiences.
- Remote Learning Experiences During Crisis: Analyze the experiences of students, teachers, and parents during the shift to remote learning in emergencies like pandemics or natural disasters.
- Critical Pedagogy in Multicultural Classrooms: Investigate the application and essential effectiveness of pedagogy approaches in fostering critical thinking and cultural awareness among students.
In Health Sciences:
- Telehealth and Patient Care: Study the adoption and impact of telehealth services on patient care outcomes, provider-patient relationships, and healthcare accessibility.
- Experiences of Healthcare Workers During Crises: Explore healthcare workers’ experiences, challenges, and coping strategies during public health crises or emergencies.
- Health Disparities in Underserved Communities: Examine factors contributing to health disparities in underserved communities and explore effective strategies to address these disparities.
In Business:
- Workplace Diversity and Innovation: Investigate how diversity in organizational leadership and workforce composition influences innovation and overall organizational performance.
- Impact of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) Initiatives: Analyze perceptions and outcomes of CSR initiatives on brand reputation, consumer behavior, and stakeholder engagement.
- Entrepreneurship and Digital Transformation: Explore the role of digital technologies in shaping entrepreneurial practices, business models, and market dynamics.
In Environmental Studies:
- Community Resilience and Climate Change Adaptation: Study community responses and resilience strategies to climate change impacts, focusing on local adaptation measures and community engagement.
- Sustainable Urban Development: Investigate policies, practices, and community perceptions of sustainable urban development, including green infrastructure and smart city initiatives.
- Public Perception of Renewable Energy: Analyze public attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors towards renewable energy sources and factors influencing acceptance and adoption.
These topics represent current societal trends and issues where qualitative research is making significant contributions by providing deeper insights and contributing to positive change in various fields.
Final Words
When choosing a qualitative research topic, you should consider what interests you, how it fits into your study area, and whether or not you can do the research. You should know what questions to ask, follow moral rules, and ask others for help. What you read is interesting, and it gives us new things to think about.
If you carefully consider these things, you can start a research project that helps you learn more and makes a real difference in your studies and job. Finding the right subject is the first thing that needs to be done to make the research useful.
How do I know if a qualitative research topic suits my academic level?
Consider the complexity and depth of the topic in relation to your academic background and coursework. Ensure it aligns with your professors’ or academic institution’s expectations and requirements.
How can I ensure my chosen qualitative research topic is relevant and impactful?
Regularly engage with peers, mentors, or advisors to discuss the relevance of your topic in current academic discourse. Consider how your research can contribute new insights, address gaps, or provide practical implications within your field of study.
Related Posts

Science Fair Project Ideas For 6th Graders
When it comes to Science Fair Project Ideas For 6th Graders, the possibilities are endless! These projects not only help students develop essential skills, such…

Java Project Ideas for Beginners
Java is one of the most popular programming languages. It is used for many applications, from laptops to data centers, gaming consoles, scientific supercomputers, and…
- Privacy Policy

Home » Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Qualitative Research – Methods, Analysis Types and Guide
Table of Contents

Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations, and textual analysis.
Qualitative research aims to uncover the meaning and significance of social phenomena, and it typically involves a more flexible and iterative approach to data collection and analysis compared to quantitative research. Qualitative research is often used in fields such as sociology, anthropology, psychology, and education.
Qualitative Research Methods

Qualitative Research Methods are as follows:
One-to-One Interview
This method involves conducting an interview with a single participant to gain a detailed understanding of their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. One-to-one interviews can be conducted in-person, over the phone, or through video conferencing. The interviewer typically uses open-ended questions to encourage the participant to share their thoughts and feelings. One-to-one interviews are useful for gaining detailed insights into individual experiences.
Focus Groups
This method involves bringing together a group of people to discuss a specific topic in a structured setting. The focus group is led by a moderator who guides the discussion and encourages participants to share their thoughts and opinions. Focus groups are useful for generating ideas and insights, exploring social norms and attitudes, and understanding group dynamics.
Ethnographic Studies
This method involves immersing oneself in a culture or community to gain a deep understanding of its norms, beliefs, and practices. Ethnographic studies typically involve long-term fieldwork and observation, as well as interviews and document analysis. Ethnographic studies are useful for understanding the cultural context of social phenomena and for gaining a holistic understanding of complex social processes.
Text Analysis
This method involves analyzing written or spoken language to identify patterns and themes. Text analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative text analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Text analysis is useful for understanding media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
This method involves an in-depth examination of a single person, group, or event to gain an understanding of complex phenomena. Case studies typically involve a combination of data collection methods, such as interviews, observations, and document analysis, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the case. Case studies are useful for exploring unique or rare cases, and for generating hypotheses for further research.
Process of Observation
This method involves systematically observing and recording behaviors and interactions in natural settings. The observer may take notes, use audio or video recordings, or use other methods to document what they see. Process of observation is useful for understanding social interactions, cultural practices, and the context in which behaviors occur.
Record Keeping
This method involves keeping detailed records of observations, interviews, and other data collected during the research process. Record keeping is essential for ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the data, and for providing a basis for analysis and interpretation.
This method involves collecting data from a large sample of participants through a structured questionnaire. Surveys can be conducted in person, over the phone, through mail, or online. Surveys are useful for collecting data on attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors, and for identifying patterns and trends in a population.
Qualitative data analysis is a process of turning unstructured data into meaningful insights. It involves extracting and organizing information from sources like interviews, focus groups, and surveys. The goal is to understand people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations
Qualitative Research Analysis Methods
Qualitative Research analysis methods involve a systematic approach to interpreting and making sense of the data collected in qualitative research. Here are some common qualitative data analysis methods:
Thematic Analysis
This method involves identifying patterns or themes in the data that are relevant to the research question. The researcher reviews the data, identifies keywords or phrases, and groups them into categories or themes. Thematic analysis is useful for identifying patterns across multiple data sources and for generating new insights into the research topic.
Content Analysis
This method involves analyzing the content of written or spoken language to identify key themes or concepts. Content analysis can be quantitative or qualitative. Qualitative content analysis involves close reading and interpretation of texts to identify recurring themes, concepts, and patterns. Content analysis is useful for identifying patterns in media messages, public discourse, and cultural trends.
Discourse Analysis
This method involves analyzing language to understand how it constructs meaning and shapes social interactions. Discourse analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as conversation analysis, critical discourse analysis, and narrative analysis. Discourse analysis is useful for understanding how language shapes social interactions, cultural norms, and power relationships.
Grounded Theory Analysis
This method involves developing a theory or explanation based on the data collected. Grounded theory analysis starts with the data and uses an iterative process of coding and analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data. The theory or explanation that emerges is grounded in the data, rather than preconceived hypotheses. Grounded theory analysis is useful for understanding complex social phenomena and for generating new theoretical insights.
Narrative Analysis
This method involves analyzing the stories or narratives that participants share to gain insights into their experiences, attitudes, and beliefs. Narrative analysis can involve a variety of methods, such as structural analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. Narrative analysis is useful for understanding how individuals construct their identities, make sense of their experiences, and communicate their values and beliefs.
Phenomenological Analysis
This method involves analyzing how individuals make sense of their experiences and the meanings they attach to them. Phenomenological analysis typically involves in-depth interviews with participants to explore their experiences in detail. Phenomenological analysis is useful for understanding subjective experiences and for developing a rich understanding of human consciousness.
Comparative Analysis
This method involves comparing and contrasting data across different cases or groups to identify similarities and differences. Comparative analysis can be used to identify patterns or themes that are common across multiple cases, as well as to identify unique or distinctive features of individual cases. Comparative analysis is useful for understanding how social phenomena vary across different contexts and groups.
Applications of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research has many applications across different fields and industries. Here are some examples of how qualitative research is used:
- Market Research: Qualitative research is often used in market research to understand consumer attitudes, behaviors, and preferences. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with consumers to gather insights into their experiences and perceptions of products and services.
- Health Care: Qualitative research is used in health care to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education: Qualitative research is used in education to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. Researchers conduct classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work : Qualitative research is used in social work to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : Qualitative research is used in anthropology to understand different cultures and societies. Researchers conduct ethnographic studies and observe and interview members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : Qualitative research is used in psychology to understand human behavior and mental processes. Researchers conduct in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy : Qualitative research is used in public policy to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. Researchers conduct focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
How to Conduct Qualitative Research
Here are some general steps for conducting qualitative research:
- Identify your research question: Qualitative research starts with a research question or set of questions that you want to explore. This question should be focused and specific, but also broad enough to allow for exploration and discovery.
- Select your research design: There are different types of qualitative research designs, including ethnography, case study, grounded theory, and phenomenology. You should select a design that aligns with your research question and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Recruit participants: Once you have your research question and design, you need to recruit participants. The number of participants you need will depend on your research design and the scope of your research. You can recruit participants through advertisements, social media, or through personal networks.
- Collect data: There are different methods for collecting qualitative data, including interviews, focus groups, observation, and document analysis. You should select the method or methods that align with your research design and that will allow you to gather the data you need to answer your research question.
- Analyze data: Once you have collected your data, you need to analyze it. This involves reviewing your data, identifying patterns and themes, and developing codes to organize your data. You can use different software programs to help you analyze your data, or you can do it manually.
- Interpret data: Once you have analyzed your data, you need to interpret it. This involves making sense of the patterns and themes you have identified, and developing insights and conclusions that answer your research question. You should be guided by your research question and use your data to support your conclusions.
- Communicate results: Once you have interpreted your data, you need to communicate your results. This can be done through academic papers, presentations, or reports. You should be clear and concise in your communication, and use examples and quotes from your data to support your findings.
Examples of Qualitative Research
Here are some real-time examples of qualitative research:
- Customer Feedback: A company may conduct qualitative research to understand the feedback and experiences of its customers. This may involve conducting focus groups or one-on-one interviews with customers to gather insights into their attitudes, behaviors, and preferences.
- Healthcare : A healthcare provider may conduct qualitative research to explore patient experiences and perspectives on health and illness. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with patients and their families to gather information on their experiences with different health care providers and treatments.
- Education : An educational institution may conduct qualitative research to understand student experiences and to develop effective teaching strategies. This may involve conducting classroom observations and interviews with students and teachers to gather insights into classroom dynamics and instructional practices.
- Social Work: A social worker may conduct qualitative research to explore social problems and to develop interventions to address them. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals and families to understand their experiences with poverty, discrimination, and other social problems.
- Anthropology : An anthropologist may conduct qualitative research to understand different cultures and societies. This may involve conducting ethnographic studies and observing and interviewing members of different cultural groups to gain insights into their beliefs, practices, and social structures.
- Psychology : A psychologist may conduct qualitative research to understand human behavior and mental processes. This may involve conducting in-depth interviews with individuals to explore their thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
- Public Policy: A government agency or non-profit organization may conduct qualitative research to explore public attitudes and to inform policy decisions. This may involve conducting focus groups and one-on-one interviews with members of the public to gather insights into their perspectives on different policy issues.
Purpose of Qualitative Research
The purpose of qualitative research is to explore and understand the subjective experiences, behaviors, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Unlike quantitative research, which focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research aims to provide in-depth, descriptive information that can help researchers develop insights and theories about complex social phenomena.
Qualitative research can serve multiple purposes, including:
- Exploring new or emerging phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring new or emerging phenomena, such as new technologies or social trends. This type of research can help researchers develop a deeper understanding of these phenomena and identify potential areas for further study.
- Understanding complex social phenomena : Qualitative research can be useful for exploring complex social phenomena, such as cultural beliefs, social norms, or political processes. This type of research can help researchers develop a more nuanced understanding of these phenomena and identify factors that may influence them.
- Generating new theories or hypotheses: Qualitative research can be useful for generating new theories or hypotheses about social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data about individuals’ experiences and perspectives, researchers can develop insights that may challenge existing theories or lead to new lines of inquiry.
- Providing context for quantitative data: Qualitative research can be useful for providing context for quantitative data. By gathering qualitative data alongside quantitative data, researchers can develop a more complete understanding of complex social phenomena and identify potential explanations for quantitative findings.
When to use Qualitative Research
Here are some situations where qualitative research may be appropriate:
- Exploring a new area: If little is known about a particular topic, qualitative research can help to identify key issues, generate hypotheses, and develop new theories.
- Understanding complex phenomena: Qualitative research can be used to investigate complex social, cultural, or organizational phenomena that are difficult to measure quantitatively.
- Investigating subjective experiences: Qualitative research is particularly useful for investigating the subjective experiences of individuals or groups, such as their attitudes, beliefs, values, or emotions.
- Conducting formative research: Qualitative research can be used in the early stages of a research project to develop research questions, identify potential research participants, and refine research methods.
- Evaluating interventions or programs: Qualitative research can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or programs by collecting data on participants’ experiences, attitudes, and behaviors.
Characteristics of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is characterized by several key features, including:
- Focus on subjective experience: Qualitative research is concerned with understanding the subjective experiences, beliefs, and perspectives of individuals or groups in a particular context. Researchers aim to explore the meanings that people attach to their experiences and to understand the social and cultural factors that shape these meanings.
- Use of open-ended questions: Qualitative research relies on open-ended questions that allow participants to provide detailed, in-depth responses. Researchers seek to elicit rich, descriptive data that can provide insights into participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Sampling-based on purpose and diversity: Qualitative research often involves purposive sampling, in which participants are selected based on specific criteria related to the research question. Researchers may also seek to include participants with diverse experiences and perspectives to capture a range of viewpoints.
- Data collection through multiple methods: Qualitative research typically involves the use of multiple data collection methods, such as in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation. This allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data from multiple sources, which can provide a more complete picture of participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Inductive data analysis: Qualitative research relies on inductive data analysis, in which researchers develop theories and insights based on the data rather than testing pre-existing hypotheses. Researchers use coding and thematic analysis to identify patterns and themes in the data and to develop theories and explanations based on these patterns.
- Emphasis on researcher reflexivity: Qualitative research recognizes the importance of the researcher’s role in shaping the research process and outcomes. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their own biases and assumptions and to be transparent about their role in the research process.
Advantages of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research offers several advantages over other research methods, including:
- Depth and detail: Qualitative research allows researchers to gather rich, detailed data that provides a deeper understanding of complex social phenomena. Through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and observation, researchers can gather detailed information about participants’ experiences and perspectives that may be missed by other research methods.
- Flexibility : Qualitative research is a flexible approach that allows researchers to adapt their methods to the research question and context. Researchers can adjust their research methods in real-time to gather more information or explore unexpected findings.
- Contextual understanding: Qualitative research is well-suited to exploring the social and cultural context in which individuals or groups are situated. Researchers can gather information about cultural norms, social structures, and historical events that may influence participants’ experiences and perspectives.
- Participant perspective : Qualitative research prioritizes the perspective of participants, allowing researchers to explore subjective experiences and understand the meanings that participants attach to their experiences.
- Theory development: Qualitative research can contribute to the development of new theories and insights about complex social phenomena. By gathering rich, detailed data and using inductive data analysis, researchers can develop new theories and explanations that may challenge existing understandings.
- Validity : Qualitative research can offer high validity by using multiple data collection methods, purposive and diverse sampling, and researcher reflexivity. This can help ensure that findings are credible and trustworthy.
Limitations of Qualitative Research
Qualitative research also has some limitations, including:
- Subjectivity : Qualitative research relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers, which can introduce bias into the research process. The researcher’s perspective, beliefs, and experiences can influence the way data is collected, analyzed, and interpreted.
- Limited generalizability: Qualitative research typically involves small, purposive samples that may not be representative of larger populations. This limits the generalizability of findings to other contexts or populations.
- Time-consuming: Qualitative research can be a time-consuming process, requiring significant resources for data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
- Resource-intensive: Qualitative research may require more resources than other research methods, including specialized training for researchers, specialized software for data analysis, and transcription services.
- Limited reliability: Qualitative research may be less reliable than quantitative research, as it relies on the subjective interpretation of researchers. This can make it difficult to replicate findings or compare results across different studies.
- Ethics and confidentiality: Qualitative research involves collecting sensitive information from participants, which raises ethical concerns about confidentiality and informed consent. Researchers must take care to protect the privacy and confidentiality of participants and obtain informed consent.
Also see Research Methods
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

One-to-One Interview – Methods and Guide

Quasi-Experimental Research Design – Types...

Applied Research – Types, Methods and Examples

Case Study – Methods, Examples and Guide

Questionnaire – Definition, Types, and Examples

Exploratory Research – Types, Methods and...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples
Published on 4 April 2022 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on 30 January 2023.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analysing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research.
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research , which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis.
Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
- How does social media shape body image in teenagers?
- How do children and adults interpret healthy eating in the UK?
- What factors influence employee retention in a large organisation?
- How is anxiety experienced around the world?
- How can teachers integrate social issues into science curriculums?
Table of contents
Approaches to qualitative research, qualitative research methods, qualitative data analysis, advantages of qualitative research, disadvantages of qualitative research, frequently asked questions about qualitative research.
Qualitative research is used to understand how people experience the world. While there are many approaches to qualitative research, they tend to be flexible and focus on retaining rich meaning when interpreting data.
Common approaches include grounded theory, ethnography, action research, phenomenological research, and narrative research. They share some similarities, but emphasise different aims and perspectives.
| Approach | What does it involve? |
|---|---|
| Grounded theory | Researchers collect rich data on a topic of interest and develop theories . |
| Researchers immerse themselves in groups or organisations to understand their cultures. | |
| Researchers and participants collaboratively link theory to practice to drive social change. | |
| Phenomenological research | Researchers investigate a phenomenon or event by describing and interpreting participants’ lived experiences. |
| Narrative research | Researchers examine how stories are told to understand how participants perceive and make sense of their experiences. |
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Each of the research approaches involve using one or more data collection methods . These are some of the most common qualitative methods:
- Observations: recording what you have seen, heard, or encountered in detailed field notes.
- Interviews: personally asking people questions in one-on-one conversations.
- Focus groups: asking questions and generating discussion among a group of people.
- Surveys : distributing questionnaires with open-ended questions.
- Secondary research: collecting existing data in the form of texts, images, audio or video recordings, etc.
- You take field notes with observations and reflect on your own experiences of the company culture.
- You distribute open-ended surveys to employees across all the company’s offices by email to find out if the culture varies across locations.
- You conduct in-depth interviews with employees in your office to learn about their experiences and perspectives in greater detail.
Qualitative researchers often consider themselves ‘instruments’ in research because all observations, interpretations and analyses are filtered through their own personal lens.
For this reason, when writing up your methodology for qualitative research, it’s important to reflect on your approach and to thoroughly explain the choices you made in collecting and analysing the data.
Qualitative data can take the form of texts, photos, videos and audio. For example, you might be working with interview transcripts, survey responses, fieldnotes, or recordings from natural settings.
Most types of qualitative data analysis share the same five steps:
- Prepare and organise your data. This may mean transcribing interviews or typing up fieldnotes.
- Review and explore your data. Examine the data for patterns or repeated ideas that emerge.
- Develop a data coding system. Based on your initial ideas, establish a set of codes that you can apply to categorise your data.
- Assign codes to the data. For example, in qualitative survey analysis, this may mean going through each participant’s responses and tagging them with codes in a spreadsheet. As you go through your data, you can create new codes to add to your system if necessary.
- Identify recurring themes. Link codes together into cohesive, overarching themes.
There are several specific approaches to analysing qualitative data. Although these methods share similar processes, they emphasise different concepts.
| Approach | When to use | Example |
|---|---|---|
| To describe and categorise common words, phrases, and ideas in qualitative data. | A market researcher could perform content analysis to find out what kind of language is used in descriptions of therapeutic apps. | |
| To identify and interpret patterns and themes in qualitative data. | A psychologist could apply thematic analysis to travel blogs to explore how tourism shapes self-identity. | |
| To examine the content, structure, and design of texts. | A media researcher could use textual analysis to understand how news coverage of celebrities has changed in the past decade. | |
| To study communication and how language is used to achieve effects in specific contexts. | A political scientist could use discourse analysis to study how politicians generate trust in election campaigns. |
Qualitative research often tries to preserve the voice and perspective of participants and can be adjusted as new research questions arise. Qualitative research is good for:
- Flexibility
The data collection and analysis process can be adapted as new ideas or patterns emerge. They are not rigidly decided beforehand.
- Natural settings
Data collection occurs in real-world contexts or in naturalistic ways.
- Meaningful insights
Detailed descriptions of people’s experiences, feelings and perceptions can be used in designing, testing or improving systems or products.
- Generation of new ideas
Open-ended responses mean that researchers can uncover novel problems or opportunities that they wouldn’t have thought of otherwise.
Researchers must consider practical and theoretical limitations in analysing and interpreting their data. Qualitative research suffers from:
- Unreliability
The real-world setting often makes qualitative research unreliable because of uncontrolled factors that affect the data.
- Subjectivity
Due to the researcher’s primary role in analysing and interpreting data, qualitative research cannot be replicated . The researcher decides what is important and what is irrelevant in data analysis, so interpretations of the same data can vary greatly.
- Limited generalisability
Small samples are often used to gather detailed data about specific contexts. Despite rigorous analysis procedures, it is difficult to draw generalisable conclusions because the data may be biased and unrepresentative of the wider population .
- Labour-intensive
Although software can be used to manage and record large amounts of text, data analysis often has to be checked or performed manually.
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
There are five common approaches to qualitative research :
- Grounded theory involves collecting data in order to develop new theories.
- Ethnography involves immersing yourself in a group or organisation to understand its culture.
- Narrative research involves interpreting stories to understand how people make sense of their experiences and perceptions.
- Phenomenological research involves investigating phenomena through people’s lived experiences.
- Action research links theory and practice in several cycles to drive innovative changes.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2023, January 30). What Is Qualitative Research? | Methods & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 12 August 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/introduction-to-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Qualitative research: methods and examples
Last updated
13 April 2023
Reviewed by
Qualitative research involves gathering and evaluating non-numerical information to comprehend concepts, perspectives, and experiences. It’s also helpful for obtaining in-depth insights into a certain subject or generating new research ideas.
As a result, qualitative research is practical if you want to try anything new or produce new ideas.
There are various ways you can conduct qualitative research. In this article, you'll learn more about qualitative research methodologies, including when you should use them.
Make research less tedious
Dovetail streamlines research to help you uncover and share actionable insights
- What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a broad term describing various research types that rely on asking open-ended questions. Qualitative research investigates “how” or “why” certain phenomena occur. It is about discovering the inherent nature of something.
The primary objective of qualitative research is to understand an individual's ideas, points of view, and feelings. In this way, collecting in-depth knowledge of a specific topic is possible. Knowing your audience's feelings about a particular subject is important for making reasonable research conclusions.
Unlike quantitative research , this approach does not involve collecting numerical, objective data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is used extensively in education, sociology, health science, history, and anthropology.
- Types of qualitative research methodology
Typically, qualitative research aims at uncovering the attitudes and behavior of the target audience concerning a specific topic. For example, “How would you describe your experience as a new Dovetail user?”
Some of the methods for conducting qualitative analysis include:

Focus groups
Hosting a focus group is a popular qualitative research method. It involves obtaining qualitative data from a limited sample of participants. In a moderated version of a focus group, the moderator asks participants a series of predefined questions. They aim to interact and build a group discussion that reveals their preferences, candid thoughts, and experiences.
Unmoderated, online focus groups are increasingly popular because they eliminate the need to interact with people face to face.
Focus groups can be more cost-effective than 1:1 interviews or studying a group in a natural setting and reporting one’s observations.
Focus groups make it possible to gather multiple points of view quickly and efficiently, making them an excellent choice for testing new concepts or conducting market research on a new product.
However, there are some potential drawbacks to this method. It may be unsuitable for sensitive or controversial topics. Participants might be reluctant to disclose their true feelings or respond falsely to conform to what they believe is the socially acceptable answer (known as response bias).
Case study research
A case study is an in-depth evaluation of a specific person, incident, organization, or society. This type of qualitative research has evolved into a broadly applied research method in education, law, business, and the social sciences.
Even though case study research may appear challenging to implement, it is one of the most direct research methods. It requires detailed analysis, broad-ranging data collection methodologies, and a degree of existing knowledge about the subject area under investigation.
Historical model
The historical approach is a distinct research method that deeply examines previous events to better understand the present and forecast future occurrences of the same phenomena. Its primary goal is to evaluate the impacts of history on the present and hence discover comparable patterns in the present to predict future outcomes.
Oral history
This qualitative data collection method involves gathering verbal testimonials from individuals about their personal experiences. It is widely used in historical disciplines to offer counterpoints to established historical facts and narratives. The most common methods of gathering oral history are audio recordings, analysis of auto-biographical text, videos, and interviews.
Qualitative observation
One of the most fundamental, oldest research methods, qualitative observation , is the process through which a researcher collects data using their senses of sight, smell, hearing, etc. It is used to observe the properties of the subject being studied. For example, “What does it look like?” As research methods go, it is subjective and depends on researchers’ first-hand experiences to obtain information, so it is prone to bias. However, it is an excellent way to start a broad line of inquiry like, “What is going on here?”
Record keeping and review
Record keeping uses existing documents and relevant data sources that can be employed for future studies. It is equivalent to visiting the library and going through publications or any other reference material to gather important facts that will likely be used in the research.
Grounded theory approach
The grounded theory approach is a commonly used research method employed across a variety of different studies. It offers a unique way to gather, interpret, and analyze. With this approach, data is gathered and analyzed simultaneously. Existing analysis frames and codes are disregarded, and data is analyzed inductively, with new codes and frames generated from the research.
Ethnographic research
Ethnography is a descriptive form of a qualitative study of people and their cultures. Its primary goal is to study people's behavior in their natural environment. This method necessitates that the researcher adapts to their target audience's setting.
Thereby, you will be able to understand their motivation, lifestyle, ambitions, traditions, and culture in situ. But, the researcher must be prepared to deal with geographical constraints while collecting data i.e., audiences can’t be studied in a laboratory or research facility.
This study can last from a couple of days to several years. Thus, it is time-consuming and complicated, requiring you to have both the time to gather the relevant data as well as the expertise in analyzing, observing, and interpreting data to draw meaningful conclusions.
Narrative framework
A narrative framework is a qualitative research approach that relies on people's written text or visual images. It entails people analyzing these events or narratives to determine certain topics or issues. With this approach, you can understand how people represent themselves and their experiences to a larger audience.
Phenomenological approach
The phenomenological study seeks to investigate the experiences of a particular phenomenon within a group of individuals or communities. It analyzes a certain event through interviews with persons who have witnessed it to determine the connections between their views. Even though this method relies heavily on interviews, other data sources (recorded notes), and observations could be employed to enhance the findings.
- Qualitative research methods (tools)
Some of the instruments involved in qualitative research include:
Document research: Also known as document analysis because it involves evaluating written documents. These can include personal and non-personal materials like archives, policy publications, yearly reports, diaries, or letters.
Focus groups: This is where a researcher poses questions and generates conversation among a group of people. The major goal of focus groups is to examine participants' experiences and knowledge, including research into how and why individuals act in various ways.
Secondary study: Involves acquiring existing information from texts, images, audio, or video recordings.
Observations: This requires thorough field notes on everything you see, hear, or experience. Compared to reported conduct or opinion, this study method can assist you in getting insights into a specific situation and observable behaviors.
Structured interviews : In this approach, you will directly engage people one-on-one. Interviews are ideal for learning about a person's subjective beliefs, motivations, and encounters.
Surveys: This is when you distribute questionnaires containing open-ended questions
Free AI content analysis generator
Make sense of your research by automatically summarizing key takeaways through our free content analysis tool.
- What are common examples of qualitative research?
Everyday examples of qualitative research include:
Conducting a demographic analysis of a business
For instance, suppose you own a business such as a grocery store (or any store) and believe it caters to a broad customer base, but after conducting a demographic analysis, you discover that most of your customers are men.
You could do 1:1 interviews with female customers to learn why they don't shop at your store.
In this case, interviewing potential female customers should clarify why they don't find your shop appealing. It could be because of the products you sell or a need for greater brand awareness, among other possible reasons.
Launching or testing a new product
Suppose you are the product manager at a SaaS company looking to introduce a new product. Focus groups can be an excellent way to determine whether your product is marketable.
In this instance, you could hold a focus group with a sample group drawn from your intended audience. The group will explore the product based on its new features while you ensure adequate data on how users react to the new features. The data you collect will be key to making sales and marketing decisions.
Conducting studies to explain buyers' behaviors
You can also use qualitative research to understand existing buyer behavior better. Marketers analyze historical information linked to their businesses and industries to see when purchasers buy more.
Qualitative research can help you determine when to target new clients and peak seasons to boost sales by investigating the reason behind these behaviors.
- Qualitative research: data collection
Data collection is gathering information on predetermined variables to gain appropriate answers, test hypotheses, and analyze results. Researchers will collect non-numerical data for qualitative data collection to obtain detailed explanations and draw conclusions.
To get valid findings and achieve a conclusion in qualitative research, researchers must collect comprehensive and multifaceted data.
Qualitative data is usually gathered through interviews or focus groups with videotapes or handwritten notes. If there are recordings, they are transcribed before the data analysis process. Researchers keep separate folders for the recordings acquired from each focus group when collecting qualitative research data to categorize the data.
- Qualitative research: data analysis
Qualitative data analysis is organizing, examining, and interpreting qualitative data. Its main objective is identifying trends and patterns, responding to research questions, and recommending actions based on the findings. Textual analysis is a popular method for analyzing qualitative data.
Textual analysis differs from other qualitative research approaches in that researchers consider the social circumstances of study participants to decode their words, behaviors, and broader meaning.
Learn more about qualitative research data analysis software
- When to use qualitative research
Qualitative research is helpful in various situations, particularly when a researcher wants to capture accurate, in-depth insights.
Here are some instances when qualitative research can be valuable:
Examining your product or service to improve your marketing approach
When researching market segments, demographics, and customer service teams
Identifying client language when you want to design a quantitative survey
When attempting to comprehend your or someone else's strengths and weaknesses
Assessing feelings and beliefs about societal and public policy matters
Collecting information about a business or product's perception
Analyzing your target audience's reactions to marketing efforts
When launching a new product or coming up with a new idea
When seeking to evaluate buyers' purchasing patterns
- Qualitative research methods vs. quantitative research methods
Qualitative research examines people's ideas and what influences their perception, whereas quantitative research draws conclusions based on numbers and measurements.
Qualitative research is descriptive, and its primary goal is to comprehensively understand people's attitudes, behaviors, and ideas.
In contrast, quantitative research is more restrictive because it relies on numerical data and analyzes statistical data to make decisions. This research method assists researchers in gaining an initial grasp of the subject, which deals with numbers. For instance, the number of customers likely to purchase your products or use your services.
What is the most important feature of qualitative research?
A distinguishing feature of qualitative research is that it’s conducted in a real-world setting instead of a simulated environment. The researcher is examining actual phenomena instead of experimenting with different variables to see what outcomes (data) might result.
Can I use qualitative and quantitative approaches together in a study?
Yes, combining qualitative and quantitative research approaches happens all the time and is known as mixed methods research. For example, you could study individuals’ perceived risk in a certain scenario, such as how people rate the safety or riskiness of a given neighborhood. Simultaneously, you could analyze historical data objectively, indicating how safe or dangerous that area has been in the last year. To get the most out of mixed-method research, it’s important to understand the pros and cons of each methodology, so you can create a thoughtfully designed study that will yield compelling results.
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 18 April 2023
Last updated: 27 February 2023
Last updated: 6 February 2023
Last updated: 5 February 2023
Last updated: 16 April 2023
Last updated: 9 March 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 12 December 2023
Last updated: 11 March 2024
Last updated: 4 July 2024
Last updated: 6 March 2024
Last updated: 5 March 2024
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
300 Qualitative Research Topics For Easy Academic Victory

You are on the right page if you are looking for a perfect qualitative research topic and have difficulty finding it.
Writing a qualitative research paper is not a piece of cake. Let alone the research and writing; the first and most significant challenge is finding the qualitative research topic that is a perfect fit for you. You have to be sure about a handful of things to decide the best topic for you, and you can ace it. First and most important, you must choose a topic that you find appealing and motivating. If you are not interested in a topic, not only will it tire you, but it will make your research dull and exhausting as well. Two, choose a relevant topic that adds value to the academia. Last but not least, there must be enough data about the theme that you are about to choose. In case of any confusion, concerns, or questions, you can consult for paper writing help from Paper Perk .
Table of Contents
Qualitative Research Topics: Psych, Education, Health, Medicine & More
Wandering around the internet looking for qualitative research topics can be exhausting. We are writing this article to make it a one-stop solution for you. There is enough inspiration to come up with the most suitable topic for you, no matter your academic area.
Psychological Qualitative Research Topics
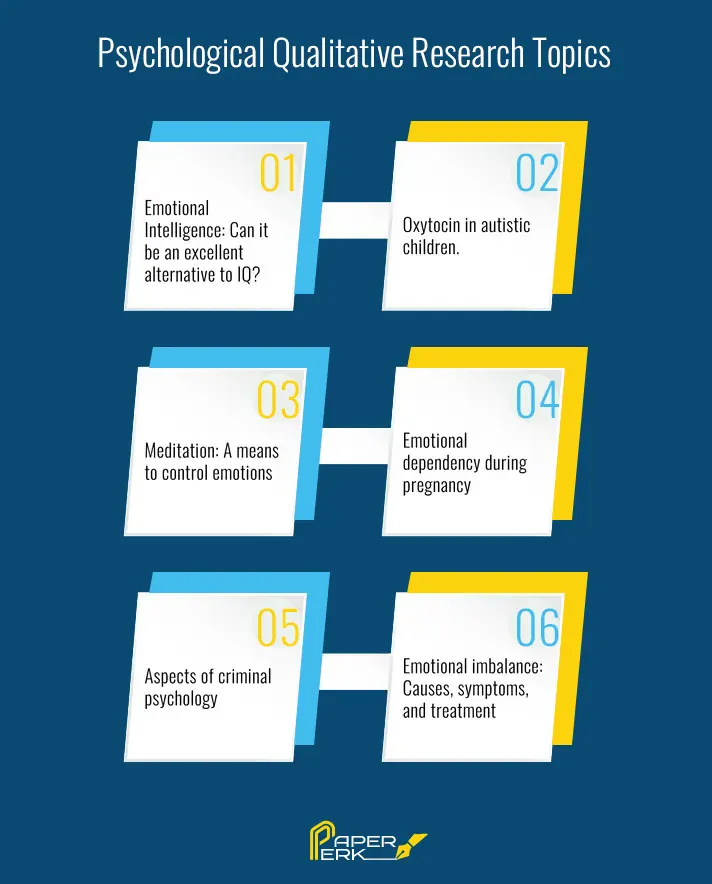
- Emotional Intelligence: Can it be an excellent alternative to IQ?
- Oxytocin in autistic children.
- Meditation: A means to control emotions
- Emotional dependency during pregnancy
- Schizophrenia: Causes and treatment
- Post-traumatic stress disorder: Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
- Psychology of physical attraction in opposite sexes
- What is a borderline personality disorder? Facts and myths
- Psychological elements in electronic media: Marketing, persuasion, and propaganda
- Psychology in public relations
- Psychology in international relations
- Causes of depression and what to do to avoid it?
- Detailed analysis of speech disorders
- Criminal psychology and the origin of serial killers
- Psychological aspects of the aging process
- The character of NGOs regarding awareness about mental health
- How to prevent child abuse with the help of psychology?
- Aspects of criminal psychology
- Emotional imbalance: Causes, symptoms, and treatment
- Memory loss? Is it a neural problem or a psychological problem?
- The secrets to well-being
- Mental disorders in teens
Read More: Psychology Research Paper Topics
Political Qualitative Research Topics

- What role did masons’ living conditions have in forming workers’ political movements ?
- How do presidential elections matter?
- Political compass: A critical analysis
- Is a representative democracy genuinely democratic?
- How has Europe evolved in terms of democracy?
- Democratic evolution in the United States in the last three centuries
- Is democracy a myth or a reality?
- Why is voter abstention a danger to democracy?
- Role of minorities in the United States politics
- Freedom of expression in developing countries
- Freedom of expression under Islamist regimes
- Misconduct on television: Awareness and Legislation
Read More: Political Science Research Topics
Qualitative Research Topics for Art and Culture

- Is history a universally shared concept?
- Can a man be indifferent to art?
- How do we articulate the link between science and technology?
- What is the purpose of art?
- What does the artist show us? Expression and symbolism
- What is an artist? What does an artist do?
- What is an artist?
- Is art always transgressive?
- Work of art: The proof of the freedom of the spirit
- Can art compete with nature?
- Does art only have the function of freeing us from our passions?
- Passion and emotion in art
- Absurd surrealism
- Grotesque surrealism
- Different movements in art
- Progress and evolution of art
- The art of the middle ages
- The art of the renaissance
- Is the work of art necessarily beautiful?
- Does art change our relationship with reality?
- Does the critic able to regard something as art or not?
- Does the experience of beauty necessarily pass through the work of art?
- Things that art teaches us, artists, as a technician
- Importance of meaning in a work of art
- Meaningless art and absurdist existentialism
- The need for a model in the production of art
- Can we conceive of a society without art?
- Different aspects of society are defined and differentiated by art
- The fear of industrial production among the artists
- Dystopian art: The ability to predict the future among artists
- Elements that distinguish the work of art from any object
- Why the artists deserve a special place in the world
- Rules and regulations in art
- Reproduction of art: Plagiarism in art and harm of repetition
- Art and escapism
- Anachronistic art and the element of satire
- Should the artist seek to please the audience
- Can we blame a work of art for not being worth anything?
- Does every human being understand and appreciate art?
- Do you think that, according to Aristotle’s formula, art is an “imitation of nature”?
- Why does what we dislike in life please us in a work of art?
- Does art seem to be a “revolt against the tyranny of desire”?
- Why do we apply the term “creation” to artistic activity?
- Sacrosanctity of art and human duty to uphold it
Read More: Music Research Topics
Qualitative Research Topics Involving Environment Issues

- Advantages and disadvantages of technology for the environment
- Benefits of environmental education in children
- Methods to make modern society aware of the environment
- Alternative energies
- Nuclear energy production: An alternative to the planet’s growing energy demand
- X degree care for the environment
- Analyze the advantages and disadvantages of the different types of renewable energy
- Need to develop environmentally friendly products
- Documentation of experience: Protection of nature
- Elements involved in environmental deterioration
- Environment and strategies for sustainability
- Environmental activism in adolescents and young people
- Sustainability and security for environmental justice
- Raising awareness about the protection of the environment through sports, literature, and culture
- Environment influenced by collective and individual actions
- Awareness of the advantages and disadvantages of the use of technologies
- Effects and causes of acid rain and groundwater
- Ways to live sustainably or focus on a specific aspect of sustainability
- Recent disasters caused by global warming
- Greenhouse effect and melting ice
- Importance of renewable energy
- Wildlife and endangered species
- Air quality and pollution
- Water quality in underdeveloped countries
- Famines caused by environmental changes
- Various recycling programs: Which one is the most effective
- Awareness to participate in the initiatives about the protection of the environment
- How deforestation has affected animals or how it is related to climate change
- Importance of the coral reef, the dangers of its destruction, or preservation strategies
Read More: Best Legal Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics on Public Relations

- Public Relations and socio-productive activity
- Organizational Communication and Public Relations
- Ethics in the practice of Public Relations
- Epistemological foundations of Public Relations.
- Factors that limit the practice of Public Relations.
- Public Relations is a strategic factor of the company.
- Relationship workers and professional practice in the United States
- Corporate image and Public Relations
- Corporate identity and Public Relations.
- Public Relations and social enterprise
- Public Relations as an integration factor.
- Profile of the teacher of Public Relations.
- Legislation of Public Relations in Europe
- The free exercise of Public Relations
- Public Relations and the labor market
- Public Relations and digital communication
- History of Public Relations in Europe
- History of Public Relations in the United States
- History of Public Relations in Canada
- Semiology and Public Relations
- Linguistics and Public Relations
- Indicators to evaluate Public Relations programs
- Planning of Public Relations in organizations
- Public Relations through radio and television
- University teaching in Public Relations
Read More: Criminal Justice Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics for High School Students

- How has technological development helped hospitals?
- Benefits of technological advances in the classroom
- Advantages and disadvantages of technology in children
- How and why are fun activities different during every stage of the educational period, Montessori, school, college, and university?
- Most dangerous challenges that must be avoided as students
- Challenges made by celebrities: How do future career choices and jobs look for you in the next decade?
- The pros and cons of viral challenges from Tiktok and reels
- How/what do social networks help?
- Disadvantages of social networks
- Problems of social network in adolescents
- What is the most suitable age for children to have a social media presence?
- Toxic behaviors accompanied by social media: Prevention and Solution
Read More: Chemistry Research Topics
Educational Qualitative Research Topics

- History of education
- How education has changed over time in one place
- Importance of sports and games in early childhood education
- Possible results of adding playtime to education
- Pros and cons of a grading system
- Most effective grading methods
- How tests affect the success or mental health of students
- Assessment methods: Such as standardized tests or open tests
- Investigate how dress codes affect student performance
- Different schools of learning
- Qualities that effective teachers possess
- Effects of teaching and lesson planning
- Different approaches of public and private schools
- Pros or cons of a charter school systems
- How class size and number of students affect student performance
- Qualities of an Effective Teacher
- The length of the school day, or the length of breaks, and how the durations affect the progress of the students
- How the start time of school affects performance
Read More: Biology Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics for Business and Economy
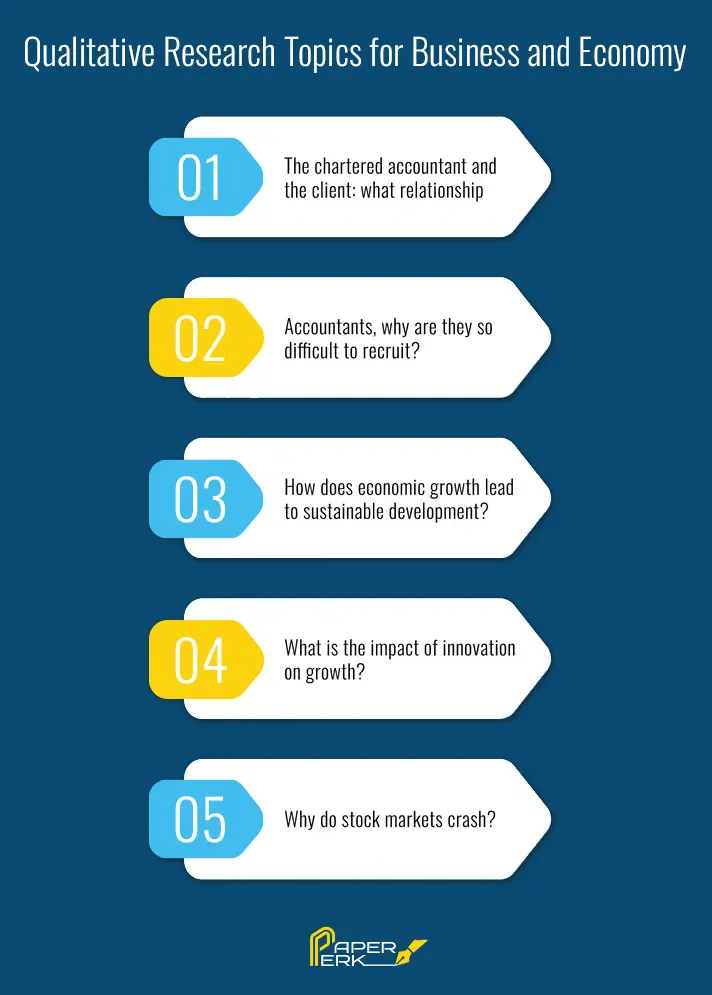
- The chartered accountant and the client: what relationship today?
- How does the arrival of the low-cost accountant change differentiation practices in accounting?
- Law and accounting: how do the new laws impact the profession of a chartered accountant?
- Accountants, why are they so difficult to recruit?
- How does accounting make it possible to assess the state of health of a company?
- Accounting and new technologies: the future or the end of the accountant?
- Can inequalities be reduced with new technologies?
- What distribution of wealth in France (or other)?
- Why do companies relocate?
- Protectionism or free trade?
- Has the organization of work changed after the pandemic?
- Do flexibility and home-working reduce unemployment?
- Should we be afraid of financial bubbles?
- Financial crises, similar cogs? Are we headed to a new recession?
- What is money, and who creates it?
- The stock market against growth?
- How does economic growth lead to sustainable development?
- What is the impact of innovation on growth?
- What role does investment play?
- What are the keys to productivity?
- Is it possible to measure economic growth?
- Why do stock markets crash?
Read More Law / Legal Research Paper Topics
Medical Qualitative Research Topics

- Current situation of palliative care in health institutions in the United States
- Complications of acute diarrheal disease in children under five years of age
- Nutritional status of surgical oncology patients and its relationship with postoperative complications
- Cost-effectiveness of cervical cancer screening strategies in California
- Thyroid cancer and risk factors in patients treated at San Jose Hospital
- Communicative processes in American ancestral medicine
- Seronegative rheumatoid arthritis in a patient with a pulmonary septic complication
- Telemedicine and Tele-health of the inhabitants of Massachusetts
- Feasibility study and technical, infrastructure and human sustainability for the implementation of the care model
- Epidemiological profile of the general surgery outpatient service
- Physical activity and sport as determinants of health
- Cost of treatment and follow-up of people with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)
- National Health System for the formal introduction of the family doctor
- How is the social security system in France unsustainable?
- Comparative study of health systems in the United States and Europe?
- Allergies and intolerances, what are the differences for lactose?
- Is gluten intolerance an actual disease?
- Social inequalities in health in rural countries
- Public health policy or health policy
- Public health at the European level, what public policies
- Public health in developing countries
- Public health and environmental issues through the prism of red meat consumption
- Communication of medicines when advertising is prohibited
Related: Medical research paper writing services
Qualitative Research Topics for Law and Crime
- Consequences of the death penalty.
- Capital offenses: Law, persecution, and penalties
- Classic methods used in the death penalty
- Arguments for or against this punishment
- The stipulation for others and the promise of a stronghold
- Consumer protection in the American Law
- The social attributions of the captain of the ship
- Recent developments in the constitutional justice
- Reframing the civil code
- Critical analysis of the scope of the principle of free justice
- Institutions of the criminal records
- Equality of the creditors in collective proceedings
- Risk management in expertise
- The repressive jurisdiction of the court of peace in the event of insufficiency of the judges
- Labor law and the rights of workers
- Secularism and labor law: Question of religion in business
- The Management of transit migration
- The legal framework of bank credit
- Legal regime of intellectual rights
- Compensation for moral damage
- Family criminal law in the relation between parents and children
- Unilateral termination of the contract
- Role of the military in public prosecution
- Critical analysis of the pre-jurisdictional procedure regarding human rights
- The fault of the administration in land matters
- The subsequent attitude of the victim and compensation for the damages
- Action for retrocession in the event of excessive liberalities
- The exploitation of child labor under Labor Law
- Reflection on the introduction of the system of the dematerialization of bearer shares
- Study on the feasibility of a structure for the amicable settlement of consumer disputes
- The life insurance contract
- Legal liability of the community pharmacist
- The legal age of marriage: legislative, jurisprudential, and doctrinal approach
- Protection of the unpaid seller in the event of insolvency of the buyer
- The renewal of the employment contract
- The regulatory framework for outdoor advertising, signs, and pre-sign
- Extra-judicial resolution of land disputes
Read More: Research Paper Topics
Qualitative Research Topics Concerning Drug Abuse

- Drug use in adolescents
- Consequences of excessive drug use
- Legal and illegal addictive substances
- Effects of drugs on the brain
- Effects of alcohol and tobacco
- Social science research on drugs
- Psychological research on drugs
- Biomedical research in the field of drugs
- Drug addiction treatment
- Cannabis in Europe: a study of social research
- Drug expectations
- Dynamics of drug cartels: Perception, politics, and markets
- Sources and uses of methamphetamine
- Sensation seeking
- Contribution of research in psychology on drugs
- Drug research: recent developments
- in the field of psychology
- Places of cannabis consumption
- Drug prevention for the most vulnerable young people
- Cannabis retail markets
- Cultivation of cannabis at home
- Cannabis Dependence and the Strength of Marijuana
- Cannabis and youth
- Cannabis and schizophrenia
Read More: Social Work Research Topics
Women Issues and Rights Qualitative Research Topics

- How to educate teens about pregnancy
- Women’s rights violations in the middle east
- Forced-Hijab conflict in Iran
- How to live a healthy pregnancy period
- Access to health is a fundamental right: what role can parliaments play in ensuring health for women and children?
- The wave of feminist movements in the Middle East
- The situation of women and children in times of conflict
- The role of women parliamentarians in the prevention of national and international terrorism and in the promotion of peace
- Promoting women’s participation and gender equality in multilateral negotiations
- The contribution of women to the establishment of a new global financial and economic model
- Feminism in Egypt
- Impact of the media on the status of women and image of women politicians in the media
- Poverty and extreme poverty: women as victims of this phenomenon and as key actors in the fight to eradicate it
- Complementarity of women’s rights and children’s rights
- Health and well-being of older people, especially women
- Women in Armed Conflict
- Feminism in the South Asian Subcontinent
- Violence against women
- Role of women in ensuring environmental protection within the framework of development
- Women in the informal economic sector and their access to microcredits
- Women in economic life and the world of work
- Impact of women on the democratic process
- Women in the political process
- Women’s rights violations in Africa
- Financing women’s electoral campaigns
- Women’s political and electoral training
- Women in political parties
- United Nations Initiatives for Women’s Education and the role of Malala Yousafzai
- Women in national parliaments
- The partnership between men and women in politics
Still feel the need to know more? It is noble to be insatiable about knowledge, so here are 402 More Research Paper Topics for you.
As we said in the beginning, writing a qualitative research paper is not a piece of cake. But after reading all these topics above, you now know that it is not rocket science either. All you need is a little commitment and a pint of inspiration potion that we have above 300 research paper topics.
If you still need professional qualitative research writing services, you can get to know our writers or contact us. We are online 24/7 with immediate responses to offer you research paper help .
Order Original Papers & Essays
Your First Custom Paper Sample is on Us!
Timely Deliveries
No Plagiarism & AI
100% Refund
Try Our Free Paper Writing Service
Related blogs.

Connections with Writers and support
Privacy and Confidentiality Guarantee
Average Quality Score

The Ultimate Guide to Qualitative Research - Part 1: The Basics

- Introduction and overview
Basics of qualitative research
Types, aspects, examples, benefits and challenges, how qualitative research complements quantitative research, how is qualitative research reported.
- What is qualitative data?
- Examples of qualitative data
- Qualitative vs. quantitative research
- Mixed methods
- Qualitative research preparation
- Theoretical perspective
- Theoretical framework
- Literature reviews
- Research question
- Conceptual framework
- Conceptual vs. theoretical framework
- Data collection
- Qualitative research methods
- Focus groups
- Observational research
- Case studies
- Ethnographical research
Ethical considerations
- Confidentiality and privacy
- Power dynamics
- Reflexivity
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is an essential approach in various academic disciplines and professional fields, as it seeks to understand and interpret the meanings, experiences, and social realities of people in their natural settings. This type of research employs an array of qualitative methods to gather and analyze non-numerical data, such as words, images, and behaviors, and aims to generate in-depth and contextualized insights into the phenomena under study.

Qualitative research is designed to address research questions that focus on understanding the "why" and "how" of human behavior, experiences, and interactions, rather than just the "what" or "how many" that quantitative methods typically seek to answer. The main purpose of qualitative research is to gain a rich and nuanced understanding of people's perspectives, emotions, beliefs, and motivations in relation to specific issues, situations, or phenomena.
Characteristics of qualitative research
Several key characteristics distinguish qualitative research from other types of research, such as quantitative research:
Naturalistic settings : Qualitative researchers collect data in the real-world settings where the phenomena of interest occur, rather than in controlled laboratory environments. This allows researchers to observe and understand the participants' behavior, experiences, and social interactions in their natural context.
Inductive approach : Unlike quantitative research, which often follows a deductive approach , qualitative research begins with the collection of data and then seeks to develop theories, concepts, or themes that emerge from the data. This inductive approach enables researchers to stay open to new insights and unexpected findings.
Holistic perspective : Qualitative research aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the phenomena under study by considering multiple dimensions, such as the social, cultural, historical, and psychological aspects that shape people's experiences and behavior.
Subjectivity and interpretation : Epistemology plays a crucial role in qualitative research. Researchers are encouraged to reflect on their biases, assumptions, and values , and to consider how these may influence their data collection, analysis, and interpretation.
Flexibility : Qualitative research methods are often flexible and adaptable, allowing researchers to refine their research questions , sampling strategies, or data collection techniques as new insights and perspectives emerge during the research process.
Key principles of qualitative research
Qualitative research is guided by several fundamental principles that shape its approach, methods, and analysis:
Empathy and reflexivity : Qualitative researchers strive to empathize with the participants and to understand their perspectives, experiences, and emotions from their viewpoint. This requires researchers to be attentive, open-minded, and sensitive to the participants' verbal and non-verbal cues. At the same, qualitative researchers critically reflect on their participants’ perspectives, experiences, and emotions to develop their findings and conclusions, instead of taking these at face value. In addition, it is important for the researcher to reflect on how their own role and viewpoint may be shaping the research.
Trustworthiness : Establishing trustworthiness in qualitative research involves demonstrating credibility, transferability, dependability, and confirmability. Researchers can enhance trustworthiness by using various strategies, such as triangulation, member checking , peer debriefing , and reflexivity .
Iterative analysis : Qualitative data analysis is an ongoing and iterative process, in which researchers continually review, compare, and revise their interpretations as they collect and analyze more data. This iterative process allows researchers to refine their understanding of the phenomena and to develop more robust and nuanced theories, concepts, or themes.
Rich description : Providing detailed, vivid, and context-sensitive descriptions of the data is essential in qualitative research. Rich descriptions help convey the complexity and nuances of the phenomena under study, and enable readers to assess the relevance and transferability of the findings to other settings or populations.

What are the common types of qualitative research?
Qualitative research is an umbrella term for various methodologies that focus on understanding and interpreting human experiences, behaviors, and social phenomena within their context. These approaches seek to gather in-depth, rich data through the analysis of language, actions, and expressions. Five common types of qualitative research are narrative research , phenomenology , grounded theory , ethnography , and case study .
Narrative research : This approach focuses on the stories and experiences of individuals, aiming to understand their lives and personal perspectives. Researchers can collect data through interviews, letters, diaries, or autobiographies, and analyze these narratives to identify recurring themes, patterns, and meanings . Narrative research can be valuable for exploring individual identities, cultural beliefs, and historical events.
Phenomenology : Phenomenology seeks to understand the essence of a particular phenomenon by analyzing the experiences and perceptions of individuals who have gone through that phenomenon . Researchers can explore participants' thoughts, feelings, and experiences through in-depth interviews, observations, or written materials. The goal is to describe the commonalities and variations in these experiences, ultimately revealing the underlying structures and meaning of the phenomenon under study.
Grounded theory : This inductive research method aims to generate new theories by systematically collecting and analyzing data. Researchers begin with an open-ended research question and gather data through observations, interviews, and document analysis . They then use a process of coding and constant comparison to identify patterns, categories, and relationships in the data. This iterative process continues until a comprehensive, grounded theory emerges that is based in the recollected data and explains the topic of interest.
Ethnography : Ethnographic research involves the in-depth study of a specific cultural or social group, focusing on understanding its members' behaviors, beliefs, and interactions. Researchers immerse themselves in the group's environment, often for extended periods, to observe and participate in daily activities. They can collect data through field notes, interviews, and document analysis, aiming to provide a holistic and nuanced understanding of the group's cultural practices and social dynamics.
Case study : A case study is an in-depth examination of a specific instance, event, organization, or individual within its real-life context. Researchers use multiple sources of data, such as interviews, observations, documents, and artifacts to build a rich, detailed understanding of the case. Case study research can be used to explore complex phenomena, generate new hypotheses , or evaluate the effectiveness of interventions or policies.
What are the purposes of qualitative research?
Qualitative research presents outcomes that emerge from the process of collecting and analyzing qualitative data. These outcomes often involve generating new theories, developing or challenging existing theories, and proposing practical implications based on actionable insights. The products of qualitative research contribute to a deeper understanding of human experiences, social phenomena, and cultural contexts. Qualitative research can also be a powerful complement to quantitative research.
Generating new theory : One of the primary goals of qualitative research is to develop new theories or conceptual frameworks that help explain previously unexplored or poorly understood phenomena. By conducting in-depth investigations and analyzing rich data, researchers can identify patterns, relationships, and underlying structures that form the basis of novel theoretical insights.
Developing or challenging existing theory : Qualitative research can also contribute to the refinement or expansion of existing theories by providing new perspectives, revealing previously unnoticed complexities, or highlighting areas where current theories may be insufficient or inaccurate. By examining the nuances and context-specific details of a phenomenon, researchers can generate evidence that supports, contradicts, or modifies existing theoretical frameworks .
Proposing practical implications : Qualitative research often yields actionable insights that can inform policy, practice, and intervention strategies. By delving into the lived experiences of individuals and communities, researchers can identify factors that contribute to or hinder the effectiveness of certain approaches, uncovering opportunities for improvement or innovation. The insights gained from qualitative research can be used to design targeted interventions, develop context-sensitive policies, or inform the professional practices of practitioners in various fields.
Enhancing understanding and empathy : Qualitative research promotes a deeper understanding of human experiences, emotions, and perspectives, fostering empathy and cultural sensitivity. By engaging with diverse voices and experiences, researchers can develop a more nuanced appreciation of the complexities of human behavior and social dynamics, ultimately contributing to more compassionate and inclusive societies.
Informing mixed-methods research : The products of qualitative research can also be used in conjunction with quantitative research, as part of a mixed-methods approach . Qualitative findings can help generate hypotheses for further testing, inform the development of survey instruments , or provide context and explanation for quantitative results. Combining the strengths of both approaches can lead to more robust and comprehensive understanding of complex research questions .
What are some examples of qualitative research?
Qualitative research can be conducted across various scientific fields, exploring diverse topics and phenomena. Here are six brief descriptions of qualitative studies that can provide researchers with ideas for their own projects:
Exploring the lived experiences of refugees : A phenomenological study could be conducted to investigate the lived experiences and coping strategies of refugees in a specific host country. By conducting in-depth interviews with refugees and analyzing their narratives , researchers can gain insights into the challenges they face, their resilience, and the factors that contribute to successful integration into their new communities.
Understanding the dynamics of online communities : An ethnographic study could be designed to explore the culture and social dynamics of a particular online community or social media platform. By immersing themselves in the virtual environment, researchers can observe patterns of interaction, communication styles, and shared values among community members, providing a nuanced understanding of the factors that influence online behavior and group dynamics.
Examining the impact of gentrification on local communities : A case study could be conducted to explore the impact of gentrification on a specific neighborhood or community. Researchers can collect data through interviews with residents, local business owners, and policymakers, as well as analyzing relevant documents and media coverage. The study can shed light on the effects of gentrification on housing affordability, social cohesion, and cultural identity, informing policy and urban planning decisions.
Studying the career trajectories of women in STEM fields : A narrative research project can be designed to investigate the career experiences and pathways of women in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields. By collecting and analyzing the stories of women at various career stages, researchers can identify factors that contribute to their success, as well as barriers and challenges they face in male-dominated fields.
Evaluating the effectiveness of a mental health intervention : A qualitative study can be conducted to evaluate the effectiveness of a specific mental health intervention, such as a mindfulness-based program for reducing stress and anxiety. Researchers can gather data through interviews and focus groups with program participants, exploring their experiences, perceived benefits, and suggestions for improvement. The findings can provide valuable insights for refining the intervention and informing future mental health initiatives.
Investigating the role of social media in political activism : A qualitative study using document analysis and visual methods could explore the role of social media in shaping political activism and public opinion during a specific social movement or election campaign. By analyzing user-generated content, such as tweets, posts, images, and videos, researchers can examine patterns of communication, mobilization, and discourse, shedding light on the ways in which social media influences political engagement and democratic processes.
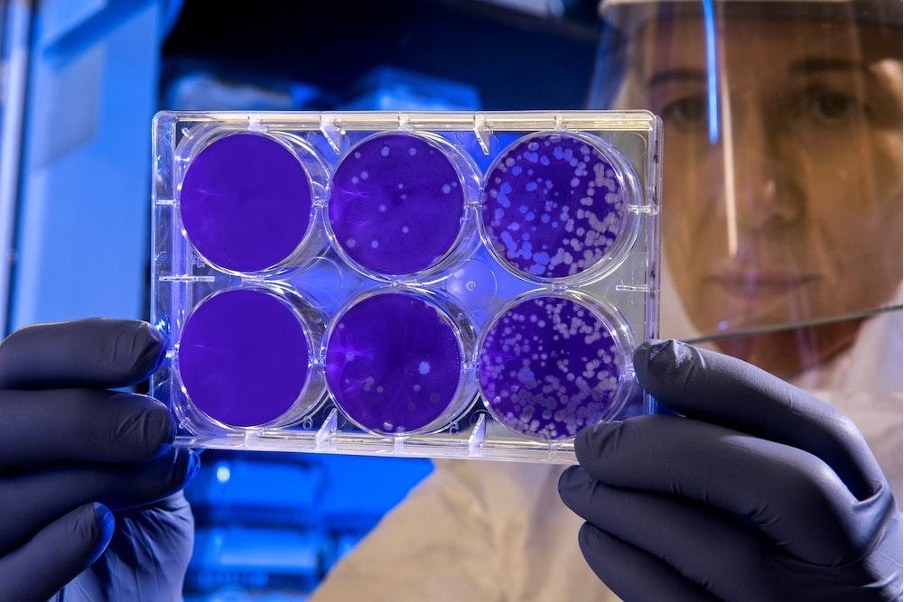
Whatever your research topic may be, ATLAS.ti makes it happen
Give a try to see how our data analysis tools can work for you.
What are common qualitative research methods?
Qualitative research methods are techniques used to collect, analyze, and interpret data in qualitative studies. These methods prioritize the exploration of meaning, context, and individual experiences. Common qualitative research methods include interviews, focus groups, observations, document analysis, and visual methods.
Interviews : Interviews involve one-on-one conversations between the researcher and the participant. They can be structured, semi-structured, or unstructured, depending on the level of guidance provided by the researcher. Interviews allow for in-depth exploration of participants' experiences, thoughts, and feelings, providing rich and detailed data for analysis.
Focus groups : Focus groups are group discussions facilitated by a researcher, usually consisting of 6-12 participants. They enable researchers to explore participants' collective perspectives, opinions, and experiences in a social setting. Focus groups can generate insights into group dynamics, cultural norms, and shared understandings, as participants interact and respond to each other's viewpoints.
Observations : Observational research involves the systematic collection of data through watching and recording people, events, or behaviors in their natural settings. Researchers can take on different roles, such as participant-observer or non-participant observer, depending on their level of involvement. Observations provide valuable information about context, social interactions, and non-verbal communication, which can help researchers understand the nuances of a particular phenomenon.
Document analysis : Document analysis is the examination of written or visual materials, such as letters, diaries, reports, newspaper articles, photographs, or videos. This method can provide insights into historical or cultural contexts, individual perspectives, and organizational processes. Researchers may use content analysis, discourse analysis, or other analytic techniques to interpret the meaning and significance of these documents.
Visual methods : Visual methods involve the use of visual materials, such as photographs, drawings, or videos, to explore and represent participants' experiences and perspectives. Techniques like photo elicitation, where participants are asked to take or select photographs related to the research topic and discuss their meaning, can encourage reflection and stimulate discussion. Visual methods can be particularly useful in capturing non-verbal information, promoting cross-cultural understanding, and engaging with hard-to-reach populations.

Importance of qualitative research and qualitative data analysis
Qualitative research and qualitative data analysis play a vital role in advancing knowledge, informing policies, and improving practices in various fields, such as education, healthcare, business, and social work. The unique insights and in-depth understanding generated through qualitative research can accomplish a number of goals.
Inform decision-making
Qualitative research helps decision-makers better understand the needs, preferences, and concerns of different stakeholders, such as customers, employees, or community members. This can lead to more effective and tailored policies, programs, or interventions that address real-world challenges.
Enhance innovation
By exploring people's experiences, motivations, and aspirations, qualitative research can uncover new ideas, opportunities, and trends that can drive innovation in products, services, or processes.
Foster empathy and cultural competence
Qualitative research can increase our empathy and understanding of diverse populations, cultures, and contexts. This can enhance our ability to communicate, collaborate, and work effectively with people from different backgrounds.
Complement quantitative research
Qualitative research can complement quantitative research by providing rich contextual information and in-depth insights into the underlying mechanisms, processes, or factors that may explain the patterns or relationships observed in quantitative data.
Facilitate social change
Qualitative research can give voice to marginalized or underrepresented groups, highlight social injustices or inequalities, and inspire actions and reforms that promote social change and well-being.
Challenges of conducting qualitative research
While qualitative research offers valuable insights and understanding of human experiences, it also presents some challenges that researchers must navigate. Acknowledging and addressing these challenges can help ensure the rigor, credibility, and relevance of qualitative research. In this section, we will discuss some common challenges that researchers may encounter when conducting qualitative research and offer suggestions on how to overcome them.
Subjectivity and bias
One of the primary challenges in qualitative research is managing subjectivity and potential biases that may arise from the researcher's personal beliefs, values, and experiences. Since qualitative research relies on the researcher's interpretation of the data , there is a risk that the researcher's subjectivity may influence the findings.
Researchers can minimize the impact of subjectivity and bias by maintaining reflexivity , or ongoing self-awareness and critical reflection on their role, assumptions, and influences in the research process. This may involve keeping a reflexive journal, engaging in peer debriefing , and discussing potential biases with research participants during member checking .
Data collection and quality
Collecting high-quality data in qualitative research can be challenging, particularly when dealing with sensitive topics, hard-to-reach populations, or complex social phenomena. Ensuring the trustworthiness of qualitative data collection is essential to producing credible and meaningful findings.
Researchers can enhance data quality by employing various strategies, such as purposive or theoretical sampling, triangulation of data sources, methods or researchers, and establishing rapport and trust with research participants.
Data analysis and interpretation
The analysis and interpretation of qualitative data can be a complex, time-consuming, and sometimes overwhelming process. Researchers must make sense of large amounts of diverse and unstructured data, while also ensuring the rigor, transparency, and consistency of their analysis.
Researchers can facilitate data analysis and interpretation by adopting systematic and well-established approaches, such as thematic analysis , grounded theory , or content analysis . Utilizing qualitative data analysis software , like ATLAS.ti, can also help manage and analyze data more efficiently and rigorously.
Qualitative research often involves exploring sensitive issues or working with vulnerable populations, which raises various ethical considerations , such as privacy, confidentiality , informed consent , and potential harm to participants.
Researchers should be familiar with the ethical guidelines and requirements of their discipline, institution, or funding agency, and should obtain ethical approval from relevant review boards or committees before conducting the research. Researchers should also maintain open communication with participants, respect their autonomy and dignity, and protect their well-being throughout the research process.
Generalizability and transferability
Qualitative research typically focuses on in-depth exploration of specific cases or contexts, which may limit the generalizability or transferability of the findings to other settings or populations. However, the goal of qualitative research is not to produce statistically generalizable results but rather to provide a rich, contextualized, and nuanced understanding of the phenomena under study.
Researchers can enhance the transferability of their findings by providing rich descriptions of the research context, participants, and methods, and by discussing the potential applicability or relevance of the findings to other settings or populations. Readers can then assess the transferability of the findings based on the similarity of their own context to the one described in the research.
By addressing these challenges and adopting rigorous and transparent research practices, qualitative researchers can contribute valuable and meaningful insights that advance knowledge, inform policies, and improve practices in various fields and contexts.
Qualitative and quantitative research approaches are often seen as distinct and even opposing paradigms. However, these two approaches can be complementary, providing a more comprehensive understanding of complex social phenomena when combined. In this section, we will discuss how qualitative research can complement quantitative research and enhance the overall depth, breadth, and rigor of research findings.
Exploring and understanding context
Quantitative research excels at identifying patterns, trends, and relationships among variables using numerical data, while qualitative research provides rich and nuanced insights into the context, meaning, and underlying processes that shape these patterns or relationships. By integrating qualitative research with quantitative research, researchers can explore not only the "what" or "how many" but also the "why" and "how" of the phenomena under study.
For example, a quantitative study in health services research might reveal a correlation between social media usage and mental health outcomes, while a qualitative study could help explain the reasons behind this correlation by exploring users' experiences, motivations, and perceptions of social media. Qualitative and quantitative data in this case complement each other to contribute to a more robust theory and more informed policy implications.
Generating and refining hypotheses
Qualitative research can inform the development and refinement of hypotheses for quantitative research by identifying new concepts, variables, or relationships that emerge from the data. This can lead to more focused, relevant, and innovative quantitative research questions and hypotheses. For instance, a qualitative study on employee motivation might uncover the importance of meaningful work and supportive relationships with supervisors as key factors influencing motivation. These findings could then be incorporated into a quantitative study to test the relationships between these factors and employee motivation.
Validating and triangulating findings
Combining qualitative and quantitative research methods can enhance the credibility and trustworthiness of research findings through validation and triangulation. Validation involves comparing the findings from different methods to assess their consistency and convergence, while triangulation involves using multiple methods, data sources, or researchers to gain a more comprehensive understanding of the phenomena under study.
For example, a researcher might use both quantitative surveys and qualitative interviews in a mixed methods research design to assess the effectiveness of a health intervention. If both methods yield similar findings, this can increase confidence in the results. If the findings differ, the researcher can further investigate the reasons for these discrepancies and refine their understanding of the intervention's effectiveness.
Enhancing communication and dissemination
Qualitative research can enhance the communication and dissemination of quantitative research findings by providing vivid narratives, case studies, or examples that bring the data to life and make it more accessible and engaging for diverse audiences, such as policymakers, practitioners, or the public.
For example, a quantitative study on the impact of a community-based program might report the percentage of participants who experienced improvements in various outcomes. By adding qualitative data, such as quotes or stories from participants, the researcher can illustrate the human impact of the program and make the findings more compelling and relatable.
In conclusion, qualitative research can complement and enrich quantitative research in various ways, leading to a more comprehensive, contextualized, and rigorous understanding of complex social phenomena. By integrating qualitative and quantitative research methods, researchers can harness the strengths of both approaches to produce more robust, relevant, and impactful findings that inform theory, policy, and practice.
Qualitative research findings are typically reported in various formats, depending on the audience, purpose, and context of the research. Common ways to report qualitative research include dissertations, journal articles, market research reports, and needs assessment reports. Each format has its own structure and emphasis, tailored to meet the expectations and requirements of its target audience.

Dissertations and theses : Doctoral,master's, or bachelor students often conduct qualitative research as part of their dissertation or thesis projects. In this format, researchers provide a comprehensive account of their research questions , methodology, data collection , data analysis , and findings. Dissertations are expected to make a significant contribution to the existing body of knowledge and demonstrate the researcher's mastery of the subject matter.
Journal articles : Researchers frequently disseminate their qualitative research findings through articles published in academic journals . These articles are typically structured in a way that includes an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, and discussion sections. In addition, articles often undergo a peer-review process before being published in the academic journal. Journal articles focus on communicating the study's purpose, methods, and findings in a concise and coherent manner, providing enough detail for other researchers to evaluate the rigor and validity of the research so that they can cite the article and build on it in their own studies.
Market research reports : Market research often employs qualitative methods to gather insights into consumer behavior, preferences, and attitudes. Market research reports present the findings of these studies to clients, typically businesses or organizations interested in understanding their target audience or market trends. These reports focus on providing actionable insights and recommendations based on the qualitative data, helping clients make informed decisions and develop effective marketing strategies.
Needs assessment reports : Needs assessment is a process used to identify gaps or areas of improvement in a specific context, such as healthcare, education, or social services. Qualitative research methods can be used to collect data on the needs, challenges, and experiences of the target population. Needs assessment reports present the findings of this research, highlighting the identified needs and providing recommendations for addressing them. These reports are used by organizations and policymakers to inform the development and implementation of targeted interventions and policies.
Other formats : In addition to the aforementioned formats, qualitative research findings can also be reported in conference presentations, white papers, policy briefs, blog posts, or multimedia presentations. The choice of format depends on the target audience and the intended purpose of the research, as well as the researcher's preferences and resources. Regardless of the format, it is important for researchers to present their findings in a clear, accurate, and engaging manner, ensuring that their work is accessible and relevant to their audience.

Analyze qualitative data with ATLAS.ti
Try out our powerful data analysis tools with a free trial.
210 Qualitative Research Topics for Students To Consider
Table of Contents
Usually, while pursuing a course, you will be either asked to conduct qualitative or quantitative research and submit a detailed thesis or dissertation on a particular topic relevant to your subject or university guidelines. But no matter whether it is quantitative or qualitative research, a good topic is needed the most for academic paper preparation. In case, you are looking for the best qualitative research topics, then this blog will be more helpful to you. Here, we have presented an overview of qualitative research along with a list of 200+ unique qualitative research paper topics and ideas on different subjects.
Explore this blog to get an amazing idea.
What is a Qualitative Research?
Qualitative research is a type of research that involves non-numerical data collection and analysis for the understanding of certain concepts, experiences, or opinions. The ultimate aim of qualitative research is to get a deep understanding of an event or a situation through firsthand experience, reliable reporting, and quotations from actual conversations. Moreover, to collect raw data for your research process, you can conduct surveys, observations, interviews, or implement any other innovative methods on your topic of study.
Qualitative Research Topics and Ideas List
As said earlier, for the preparation of a qualitative research paper, a good topic is essential. In case, you are confused about what topic to choose for your qualitative research paper, feel free to go through the list of 200+ ideas shared below and pick any topic that is convenient for you to perform qualitative research and write about.

Educational Qualitative Research Topics
- Food insecurity and child education
- Understanding adult learning
- The efficient learning style for autistic children
- The importance of computer literacy
- The importance of mental health education in the school curriculum
- The effects of alcoholism on education
- How does virtual learning affect high school students?
- Disadvantages of homeschooling
- The need to encourage adult education
- The impacts of computer literacy on education
Extra Qualitative Research Topics on Education
- Significance of school uniform to learning
- The importance of guidance and counseling in schools
- The impacts of the poor educational system
- Psychological impacts of student bullying
- The importance of research writing in schools
- Easy ways to master foreign languages for students in high school.
- The importance of social activities in schools
- How do smartphones affect students’ academic performance in the academic system?
- How to teach and improve the learning abilities of ADHD students
- The negative impacts of student loans
- What is the level of academic preparedness of university students?
- Ethnic and socioeconomic reasons for poor school attendance in developing countries
- Discuss the role of teachers in multicultural education.
- How to improve oral learning in classrooms
- The importance of reading to preschoolers
- The importance of research writing in schools.
- The effects of alcoholism on education.
- Disadvantages of homeschooling.
- Discuss the essentialities of prayers in school
Ethnography Qualitative Research Paper Topics
- Discuss the challenges transgender people undergo within and outside the LGBTQ+ community.
- The relationship that exists between political instability and migration
- Evaluating the role of parental care and the lack of it thereof in the lives of some foster kids
- Analyze the socioeconomic impacts of instability on a nation.
- How does sexual violence in rural areas affect the psychological well-being of the women and girls in such a locality?
- An insight into the primary causes of the swift migration happening from Africa to Europe.
- Explore the link between violence against women and sex trafficking.
- An overview of the rise of oral literature study in literature.
- How do social media distort the perception of reality?
- Outline some of the challenges of Muslims in Africa.
- Understanding the effects of Gender-Based Violence (GBV) in rural areas and how this negatively impacts women in such areas
- Benefits of engaging in social activities for depressed people and those struggling with certain mental health challenges
- Displacement and its accompanying effects: a look into the mental health of homeless people
- How culture contributes to female harm in the society
A Few More Qualitative Research Ideas on Ethnography
- The impacts of Westernization on human perception.
- How does male dominance breed male violence?
- How does literature contribute to changing the world?
- Understanding the effects of female genitalia mutilation in girls
- The importance of books in the lives of children in rural areas.
- How does violence breed housing and food insecurity?
- The role of the smartphone in our deteriorating attention span
- Discuss the leniency of the practice of Islam in foreign spaces.
- A study into the ways through which government enables homelessness
- A study into the importance of fraternities and sororities.
- The role of capitalism in generating food insecurity
- The place of social and academic practices in uplifting a society
- Rethinking consumer appraisals and motivations
- Transforming virtual ethnography into a modernized form.
- Observing a group of children playing.
- Observing employees in a corporate office.
- Observing medical personnel in a high-volume hospital.
- Observing an Indigenous village
- What are the long-term planning methods for efficient project management?
- Why there is a huge significance of time management for the setting of goals?
- Evaluating the levels of nursing professionals’ satisfaction in private hospitals in the US.
- Long-term planning methods for better project management.
- How to deal with issues during a project implementation program.
Qualitative Project Management Research Topics
- The impacts of financial management in the country and how it benefits citizens.
- The root causes of the lack of medical insurance and possible ways to curb it.
- Dealing with a backlash during a project implementation program.
- The importance of developing healthy customer-client relationships
- Foreign policy and its impact on developing industrial complexes.
- How to ensure effective budget planning
- Why managers should be flexible and apt in their decisions
- The role of strategy in enhancing business management.
- The efficient ways of regulating revenue distribution.
- Various means of relieving pressure for tight project deadlines.
- Analysis of the cost-effectiveness of manufacturing learning centers in urban areas.
- An investigation into the current cost of living in society and how this is propagated by capitalism.
- Design process and management of geolocators.
- The assessment of the contributing factors that lead to failed healthcare systems in rural areas
- The need to create a more inclusive healthcare system
- Plausible ways through which food insecurity can be handled within a given society.
- Design a system for building an online regulated parking system.
- How to set up an operation pest control activity in a society
- The benefits of building communication masts in rural areas
- Understanding the essence of time management in goal setting
- The best way to carry out the facility life cycle costing.
- The contemporary approaches used in project management.
Nursing Qualitative Research Paper Topics
- How do social processes influence patient behavior?
- How to identify Alzheimer’s in older patients
- Basics of patient care
- The efficacy of a particular medication to a patient
- Unique attributes of a culture that determines a patient’s success rate
- The feminist empiricism perspective of the nursing profession
- How to help patients with mental disorders
- How nurses can handle cardiovascular challenges
- Difference between workloads of ICU nurses and OR nurses
- Environmental factors that necessitate quicker patient recover
Read more: Great Nursing Research Topics for Impressive Content
Additional Qualitative Research Topics on Nursing
- Understanding how to deal with pregnant women and emergencies
- Pros & cons of Nurses’ drug prescription
- The effective ways to carry out health outreach programs
- How to take care of the elderly
- How to assist rape survivors
- Bipolar symptoms in young adults
- The role of nurses and healthcare corporations
- The benefits of immunization in rural areas
- Care for hypertensive patients with diabetes
- Why are compassion and sensitivity important for nurses?
- Patient care in psychiatric units
- First aid treatments for gun victims
- Intensive care for visually and verbally impaired patients
- Signs of Depression and anxiety in patients
- How to curb drug abuse
Qualitative Research Topics on Political Science
- Racism as a dividing factor in America
- Understanding neoliberalism and how it impacts our activities in the society
- The negative impacts of peace war in affected countries
- Dissect the causes of the election crisis
- The negative impacts of misrepresentation
- The role of feminism in enhancing American politics
- The need for a free polling system to encourage free and fair voting practices
- The role of mass media in promoting and scrutinizing politics
- The distinction between Liberalism and Conservatism and the places where they merge
- Segregation and racist laws
- The effects of capitalism on America’s health system.
- The abortion regulation bill and its effects
- Address Police Brutality in America
- Discuss the effects of American incarceration.
- The inclusion of Black women in American politics.
Qualitative Research Paper Topics on Public Health
- Preventative methods for flu during cold seasons
- Ideas for quitting cigarettes and alcohol
- How to achieve affordable healthcare in low-income societies
- Ways to create awareness about breast cancer
- Programs for community-based sanitization
- Techniques of making eco-friendly facemasks
- Effective obesity management strategies for the young
- Causes of malnutrition in young children
- The need to properly manage the source of our waste products disposal
- Poorly maintained public hospitals and their effects
- The difference between an epidemic and a pandemic
- How to properly manage to live with diabetes type II
- Barriers to clean hygiene in health centers
- The importance of safe menstrual care for girls
- Factors generating health issues in pregnant women
- Understanding the health challenges of the lack of drinkable water in a community
- The importance of post-natal to nursing mothers
- The role of finance in propagating an inclusive and efficient healthcare system.
- Control of the prevalence of drug and substance abuse
- The benefits of exercise to obese people
Best Qualitative Research Ideas
- The advantages of online learning over physical learning
- Can we detect and prevent natural disasters before they occur?
- How often should one engage in sporting activities?
- How have businesses transitioned into online digital marketing?
- The influence of pop music on erratic youth behavior
- Is it possible to have the same education system throughout the whole world?
- The impact of unhealthy market completion on supply and demand
- Evaluate the performance of mixed schools over single-gender schools.
- The effects of developing introverted behavior
- Self-esteem among people from low socioeconomic backgrounds
- Management of depression among school-going children
- Approaches to improving maternal healthcare in developing countries
- Effective strategies that can help curb the problem of cyberbullying
- Worrying trends among the aging population
- The latest newsgathering technologies and their effectiveness
- Emerging trends in digital media
- Is preschool education necessary for children under the age of four years?
- Overcoming addictions through sharing with others
- Understanding the key roles of healthy eating habits
- Working government policies on protocol observance
Read more: Excellent Case Study Topics for College Students to Think About
Trending Qualitative Research Paper Topics
- The influence of pop music on erratic youth behavior.
- How does ableism affect disabled people in our society?
- Understanding the stigma of living with disabilities
- Discuss the rate at which the ozone layer is depleting.
- How virtual reality worlds are transforming society
- Understanding the effects of Gender-Based Violence (GBV) in rural areas
- Benefits of Pro Bono services to the less privileged
- Understanding the intricacies of food banks in low-income neighborhoods
- How culture contributes to female harm in society?
- Causes of the stigma that surrounds certain health challenges
- New strategies to reduce the spread of infectious illnesses
- Explain how startup companies use digital marketing in their operations.
- Trends among the aging population that are concerning
- Quarantine’s significance in the spread of infectious illnesses
- How may patriarchal societies advance social equity?
Miscellaneous Qualitative Research Paper Ideas
- Effective measures to combat the issue of cyberbullying
- How can teachers establish a personal connection with each of their students?
- The role of academic and social activities in improving a society
- employing resources at hand to establish a centralized community
- Opportunities to develop management strategies and skills
- Discuss the importance of palliative care and EBP (evidence-based practice) for adult patients with terminal diseases
- Analysis of the Role of substance abuse and Use of illicit drugs in Teenage and College student’s life
- Explain the religious norms, laws, boundaries, and religious crimes in terms of developed and developing countries
- Discuss the way there should be different strategies primary and secondary school teachers can apply to manage children with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
- Discuss the barrier children with autism face in learning and how teachers should cater to the needs of such students in their class
- Discuss the kind of subjugation women experience in developed countries where gender-based domestic violence no longer exists
- Describe the ways to handle and manage a business by getting out of the challenges given by geographical variations in a nation
- Identify and analyze the importance of SCM (supply and chain management)and how it can be seen by applying the supply and demand theory
- Why there is an urgent need to undertake effective measures to check the growth of the emissions of CO2 and other GHG (greenhouse gas) in the environment?
- Psychology is a discipline that is very crucial for the proper development of a rational being: Explain with justifications
Engaging Qualitative Research Paper Topics
- Does free education have socioeconomic benefits?
- Explain the impact of Plato’s philosophy on mathematics.
- What are the main influences on eating habits in children?
- How to reduce violence in sports.
- Analyze the effectiveness of Apple and Windows products in the Globe.
- Write about sexual misconduct in colleges.
- What are the effective ways to resolve conflicts in the workplace?
- Discuss the application of AI in project management.
- How to eliminate corruption in developing countries.
- Why is job satisfaction important in brand management?
The above-suggested list of topics will definitely help you to write an excellent qualitative research paper. If you find it difficult to write an academic essay or research paper, then contact us immediately.

Related Post

110 Hard Words to Spell for Students and Adults

Learn How to Avoid Passive Voice in 3 Simple Steps

117 Best Greek Mythology Essay Topics For Students
About author.
Jacob Smith
I am an Academic Writer and have affection to share my knowledge through posts’. I do not feel tiredness while research and analyzing the things. Sometime, I write down hundred of research topics as per the students requirements. I want to share solution oriented content to the students.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Featured Posts
140 Unique Geology Research Topics to Focus On
200+ outstanding world history topics and ideas 2023, 190 excellent ap research topics and ideas, 150+ trending group discussion topics and ideas, 170 funny speech topics to blow the minds of audience, who invented exams learn the history of examination, how to focus on reading 15 effective tips for better concentration, what is a rhetorical analysis essay and how to write it, primary school teacher in australia- eligibility, job role, career options, and salary, 4 steps to build a flawless business letter format, get help instantly.
Raise Your Grades with Assignment Help Pro
- Write my thesis
- Thesis writers
- Buy thesis papers
- Bachelor thesis
- Master's thesis
- Thesis editing services
- Thesis proofreading services
- Buy a thesis online
- Write my dissertation
- Dissertation proposal help
- Pay for dissertation
- Custom dissertation
- Dissertation help online
- Buy dissertation online
- Cheap dissertation
- Dissertation editing services
- Write my research paper
- Buy research paper online
- Pay for research paper
- Research paper help
- Order research paper
- Custom research paper
- Cheap research paper
- Research papers for sale
- Thesis subjects
- How It Works
Qualitative Research Topics & Ideas For Students

Do you have difficulty finding a qualitative research title for your project? If you are, you need not worry because you are not alone. However, there are many unique qualitative titles you can explore for your research. You just need a few qualitative research title examples to get you started. Qualitative research is focused on data obtained through a researcher’s first-hand observations, natural setting recording, artifacts, case studies, documents, questionnaires, and interviews. The findings in qualitative research are usually non-numerical. Also, it is common in humanities and social sciences. This post provides over 100 qualitative research topics you can consider.
- The Best Qualitative Research Topics That Impress the Teacher
Exceptional Qualitative Research Topics In Social Science
Qualitative research title examples for students, fantastic examples of qualitative research titles, good topics to start for qualitative research, qualitative research topics in education, quick examples of qualitative research topics, qualitative research topics in the philippines, qualitative researches topics about humanity & social science, great choices of qualitative research title examples, qualitative research topics for students to think about, our examples of the best qualitative research topics that impress the teacher.
An excellent research topic will help you earn a good grade. Consider any example of a qualitative research title from the following options:
- The impacts of social media on physical social engagement in society
- The benefits of treating mental disorders with medication
- The effects of Gender-Based Violence on women’s social lives in rural areas
- The decline of academic pursuit in third-world countries
- Sexual workers: the stigma they experience
- How has the promotion of feminist values influenced workplaces?
- Free education: its impact in third-world countries
- What is the correlation between education and success?
- Ableism: its effects on disabled people in society
- Food insecurity in third-world nations
The topic of your research paper can influence how easily you can conduct your study and draw conclusions.
Here are fantastic examples of qualitative research titles:
- Female harm: how it is influenced by culture
- The socioeconomic impacts of free education
- The link between food insecurity and poor performance in schools
- Alcoholism among college students: a critical study
- How to mitigate child labor in our society
- The root causes of child labor in Latin America
- The stigma of living with transmissive medical conditions
- The root cause of the stigma of people living with disabilities
- How to identify depression in small children
- Signs of autism in kids below two years old
Choosing a qualitative research topic is not a task you should take lightly because it can influence your performance. Here are some noteworthy qualitative research titles examples:
- Basic patient care policies in developing nations
- The impacts of alcoholism on education
- Adult learning: what does it entail?
- Homeschooling: Is it the latest trend after the pandemic?
- Does computer literacy influence the quality of education kids enjoy?
- How to effectively teach students with learning disabilities
- The relationship between poor education systems and crime rates in third-world countries
- Student bullying: the psychological impacts
- Should high school students go through university preparedness programs?
- research writing in high schools: its significance
Are you looking for qualitative research topic examples to start your study? Below are some creative examples to consider:
- Remote tests: are they as effective as in-class tests?
- The value of social activities in academic institutions
- Why should healthcare be free in all countries?
- The implications of racist laws on society
- The reception of COVID-19 vaccines and treatments
- What is the difference between foreign policies in first-world and third-world nations?
- Racism and Colorism: what is the difference?
- Dissecting the causes of low voter turnouts in the 21 st century
- The challenges of social media on kid’s brain development
- The inclusion of black women in American politics and its impacts
When competing with several brilliant minds, a good research topic can do you greatly. The following qualitative research examples titles are a great place to start:
- Should school uniforms be discarded for high schoolers?
- The need for equal representation in global politics
- The implications of police brutality on politics
- The role of parental care in foster kids
- The distinction between Islamic values and Christian values
- The correlation between political instability and migration
- Sex trafficking and violence against women: what is the link?
- How can global governments eradicate homelessness?
- Fraternities and sororities: are they still relevant?
- The role of literature in promoting societal changes
Qualitative research is popular in the education field and other social sciences. Choose a qualitative research title example on the subject of education from the following list:
- Effectively introducing foreign languages in the high school curriculum
- How can teachers help students with disabilities improve their learning?
- The link between social activities and comprehension among students
- Research writing in high schools: is it necessary?
- How has virtual learning influenced teacher-student relationships?
- The implications of allowing smartphones in classes
- Should all schools introduce sign language lessons in their curriculum?
- Student loans: their impacts on black students
- The impacts of race on college acceptance rates
- Poverty and education: what is the link?
- Ethnic and socioeconomic causes of poor school attendance in developing worlds
- Various teaching methods and their efficiency
- Efficient teaching methods for children below two years
- Why do students perform better in humanities than in sciences?
- The difference between college acceptance and completion in most nations
- Remote learning in developing countries
- What are the best ways of approaching bullying in schools?
- How do teachers promote inequality among students?
- Does social class influence academic performance negatively or positively?
- How do teachers shape their students’ personalities?
Coming up with a qualitative research title can be hard because of the numerous subject areas and the issue of uniqueness. Therefore, we have prepared the following qualitative title examples for you:
- How to promote oral learning in classrooms
- Political instability in developing countries: its economic impacts
- The impacts of weather on social activities
- Boredom and poor-decision making: the connection
- Exploring the connection between attachment types and love languages
- Socioeconomic impacts of instability on a country
- How does social media impact the perception of reality
- Reality TV shows: are they a true reflection of reality?
- How culture applies to different age groups
- Is social media influencing the loss of cultural values?
You can base your research topic on a specific region or nation, like the Philippines. A sample qualitative research title can get you started. You can pick a sample qualitative research title from the ideas below:
- Why are so many Philippines residents migrating to America?
- The impact of politics on migration in the Philippines
- How has violence led to food insecurity in rural areas in the Philippines?
- The Philippine education system: an overview
- How cultural norms influence social activities in the Philippines
- Gender roles in the Philippines society
- How popular Filipino cultures have served as agents of social change in the nation
- The link between male dominance and GBV in the Philippines
- Barriers to clean hygiene in health centers in the Philippines
- The spread of COVID in rural areas in the Philippines
Most top performers in research subjects attribute their success to choosing the best title for qualitative research. Here are some qualitative research topics about humanities and social science to promote good performance:
- The impact of poor market rivalry on supply and demand
- The role of parents in shaping kids’ morals
- Is social media the root cause of poor societal morals?
- How does alcohol impact a person’s normal behavior?
- How often should adults engage in sporting activities?
- Children’s eating habits and their influences
- Low socioeconomic backgrounds and their impacts on self-esteem
- The effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the world’s views on viral diseases
- How can school-going kids manage depression
- Causes of mental challenges among school-going kids
Finding a good topic for qualitative research is a critical task that requires a lot of thought and research. However, we have simplified the process with the following qualitative topic ideas:
- Pop music and erratic youth behavior: is there a link?
- How do public figures influence cultures?
- Ideas for improving healthcare in developing nations
- Possible solutions for alleviating the food crisis in developing nations
- New ways of mitigating viral diseases
- Social media trends among the elderly
- Quarantine as a mitigation approach for infectious diseases
- Promoting social justice in patriarchal societies
- Worrying trends among the young population
- Emerging marketing trends in 2023
Qualitative research for college and high school students helps improve reading, writing, and intellectual skills. Here are some qualitative research examples and topic ideas for students :
- How to detect and prevent natural disasters beforehand
- Can the whole world have the same education system?
- What is the most effective therapy for patients recuperating from brain surgery?
- Possible solutions for promoting ethical practices in telehealth
- Can addicts overcome addiction without therapy?
- The latest technology trends and their impacts?
- How can global governments promote mental health awareness?
- Have smartphones caused reduced attention spans among users?
- Sexual violence in rural areas
- The introduction of Islam in African nations
We Are Here for You
Qualitative research is an investigative analysis of intangible or inexact data, mostly non-numerical. The title of qualitative research you choose will guide your entire research process and influence its conclusions. Do you need a paper or an example of a research title qualitative topic? Our expert team is ready to write it for you.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

What is Qualitative in Qualitative Research
Patrik aspers.
1 Department of Sociology, Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden
2 Seminar for Sociology, Universität St. Gallen, St. Gallen, Switzerland
3 Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger, Stavanger, Norway
What is qualitative research? If we look for a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically for one that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature is meager. In this article we systematically search, identify and analyze a sample of 89 sources using or attempting to define the term “qualitative.” Then, drawing on ideas we find scattered across existing work, and based on Becker’s classic study of marijuana consumption, we formulate and illustrate a definition that tries to capture its core elements. We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. This formulation is developed as a tool to help improve research designs while stressing that a qualitative dimension is present in quantitative work as well. Additionally, it can facilitate teaching, communication between researchers, diminish the gap between qualitative and quantitative researchers, help to address critiques of qualitative methods, and be used as a standard of evaluation of qualitative research.
If we assume that there is something called qualitative research, what exactly is this qualitative feature? And how could we evaluate qualitative research as good or not? Is it fundamentally different from quantitative research? In practice, most active qualitative researchers working with empirical material intuitively know what is involved in doing qualitative research, yet perhaps surprisingly, a clear definition addressing its key feature is still missing.
To address the question of what is qualitative we turn to the accounts of “qualitative research” in textbooks and also in empirical work. In his classic, explorative, interview study of deviance Howard Becker ( 1963 ) asks ‘How does one become a marijuana user?’ In contrast to pre-dispositional and psychological-individualistic theories of deviant behavior, Becker’s inherently social explanation contends that becoming a user of this substance is the result of a three-phase sequential learning process. First, potential users need to learn how to smoke it properly to produce the “correct” effects. If not, they are likely to stop experimenting with it. Second, they need to discover the effects associated with it; in other words, to get “high,” individuals not only have to experience what the drug does, but also to become aware that those sensations are related to using it. Third, they require learning to savor the feelings related to its consumption – to develop an acquired taste. Becker, who played music himself, gets close to the phenomenon by observing, taking part, and by talking to people consuming the drug: “half of the fifty interviews were conducted with musicians, the other half covered a wide range of people, including laborers, machinists, and people in the professions” (Becker 1963 :56).
Another central aspect derived through the common-to-all-research interplay between induction and deduction (Becker 2017 ), is that during the course of his research Becker adds scientifically meaningful new distinctions in the form of three phases—distinctions, or findings if you will, that strongly affect the course of his research: its focus, the material that he collects, and which eventually impact his findings. Each phase typically unfolds through social interaction, and often with input from experienced users in “a sequence of social experiences during which the person acquires a conception of the meaning of the behavior, and perceptions and judgments of objects and situations, all of which make the activity possible and desirable” (Becker 1963 :235). In this study the increased understanding of smoking dope is a result of a combination of the meaning of the actors, and the conceptual distinctions that Becker introduces based on the views expressed by his respondents. Understanding is the result of research and is due to an iterative process in which data, concepts and evidence are connected with one another (Becker 2017 ).
Indeed, there are many definitions of qualitative research, but if we look for a definition that addresses its distinctive feature of being “qualitative,” the literature across the broad field of social science is meager. The main reason behind this article lies in the paradox, which, to put it bluntly, is that researchers act as if they know what it is, but they cannot formulate a coherent definition. Sociologists and others will of course continue to conduct good studies that show the relevance and value of qualitative research addressing scientific and practical problems in society. However, our paper is grounded in the idea that providing a clear definition will help us improve the work that we do. Among researchers who practice qualitative research there is clearly much knowledge. We suggest that a definition makes this knowledge more explicit. If the first rationale for writing this paper refers to the “internal” aim of improving qualitative research, the second refers to the increased “external” pressure that especially many qualitative researchers feel; pressure that comes both from society as well as from other scientific approaches. There is a strong core in qualitative research, and leading researchers tend to agree on what it is and how it is done. Our critique is not directed at the practice of qualitative research, but we do claim that the type of systematic work we do has not yet been done, and that it is useful to improve the field and its status in relation to quantitative research.
The literature on the “internal” aim of improving, or at least clarifying qualitative research is large, and we do not claim to be the first to notice the vagueness of the term “qualitative” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 ). Also, others have noted that there is no single definition of it (Long and Godfrey 2004 :182), that there are many different views on qualitative research (Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11; Jovanović 2011 :3), and that more generally, we need to define its meaning (Best 2004 :54). Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ), for example, as well as Nelson et al. (1992:2 cited in Denzin and Lincoln 2003 :11), and Flick ( 2007 :ix–x), have recognized that the term is problematic: “Actually, the term ‘qualitative research’ is confusing because it can mean different things to different people” (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :10–11). Hammersley has discussed the possibility of addressing the problem, but states that “the task of providing an account of the distinctive features of qualitative research is far from straightforward” ( 2013 :2). This confusion, as he has recently further argued (Hammersley 2018 ), is also salient in relation to ethnography where different philosophical and methodological approaches lead to a lack of agreement about what it means.
Others (e.g. Hammersley 2018 ; Fine and Hancock 2017 ) have also identified the treat to qualitative research that comes from external forces, seen from the point of view of “qualitative research.” This threat can be further divided into that which comes from inside academia, such as the critique voiced by “quantitative research” and outside of academia, including, for example, New Public Management. Hammersley ( 2018 ), zooming in on one type of qualitative research, ethnography, has argued that it is under treat. Similarly to Fine ( 2003 ), and before him Gans ( 1999 ), he writes that ethnography’ has acquired a range of meanings, and comes in many different versions, these often reflecting sharply divergent epistemological orientations. And already more than twenty years ago while reviewing Denzin and Lincoln’ s Handbook of Qualitative Methods Fine argued:
While this increasing centrality [of qualitative research] might lead one to believe that consensual standards have developed, this belief would be misleading. As the methodology becomes more widely accepted, querulous challengers have raised fundamental questions that collectively have undercut the traditional models of how qualitative research is to be fashioned and presented (1995:417).
According to Hammersley, there are today “serious treats to the practice of ethnographic work, on almost any definition” ( 2018 :1). He lists five external treats: (1) that social research must be accountable and able to show its impact on society; (2) the current emphasis on “big data” and the emphasis on quantitative data and evidence; (3) the labor market pressure in academia that leaves less time for fieldwork (see also Fine and Hancock 2017 ); (4) problems of access to fields; and (5) the increased ethical scrutiny of projects, to which ethnography is particularly exposed. Hammersley discusses some more or less insufficient existing definitions of ethnography.
The current situation, as Hammersley and others note—and in relation not only to ethnography but also qualitative research in general, and as our empirical study shows—is not just unsatisfactory, it may even be harmful for the entire field of qualitative research, and does not help social science at large. We suggest that the lack of clarity of qualitative research is a real problem that must be addressed.
Towards a Definition of Qualitative Research
Seen in an historical light, what is today called qualitative, or sometimes ethnographic, interpretative research – or a number of other terms – has more or less always existed. At the time the founders of sociology – Simmel, Weber, Durkheim and, before them, Marx – were writing, and during the era of the Methodenstreit (“dispute about methods”) in which the German historical school emphasized scientific methods (cf. Swedberg 1990 ), we can at least speak of qualitative forerunners.
Perhaps the most extended discussion of what later became known as qualitative methods in a classic work is Bronisław Malinowski’s ( 1922 ) Argonauts in the Western Pacific , although even this study does not explicitly address the meaning of “qualitative.” In Weber’s ([1921–-22] 1978) work we find a tension between scientific explanations that are based on observation and quantification and interpretative research (see also Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 ).
If we look through major sociology journals like the American Sociological Review , American Journal of Sociology , or Social Forces we will not find the term qualitative sociology before the 1970s. And certainly before then much of what we consider qualitative classics in sociology, like Becker’ study ( 1963 ), had already been produced. Indeed, the Chicago School often combined qualitative and quantitative data within the same study (Fine 1995 ). Our point being that before a disciplinary self-awareness the term quantitative preceded qualitative, and the articulation of the former was a political move to claim scientific status (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ). In the US the World War II seem to have sparked a critique of sociological work, including “qualitative work,” that did not follow the scientific canon (Rawls 2018 ), which was underpinned by a scientifically oriented and value free philosophy of science. As a result the attempts and practice of integrating qualitative and quantitative sociology at Chicago lost ground to sociology that was more oriented to surveys and quantitative work at Columbia under Merton-Lazarsfeld. The quantitative tradition was also able to present textbooks (Lundberg 1951 ) that facilitated the use this approach and its “methods.” The practices of the qualitative tradition, by and large, remained tacit or was part of the mentoring transferred from the renowned masters to their students.
This glimpse into history leads us back to the lack of a coherent account condensed in a definition of qualitative research. Many of the attempts to define the term do not meet the requirements of a proper definition: A definition should be clear, avoid tautology, demarcate its domain in relation to the environment, and ideally only use words in its definiens that themselves are not in need of definition (Hempel 1966 ). A definition can enhance precision and thus clarity by identifying the core of the phenomenon. Preferably, a definition should be short. The typical definition we have found, however, is an ostensive definition, which indicates what qualitative research is about without informing us about what it actually is :
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them. Qualitative research involves the studied use and collection of a variety of empirical materials – case study, personal experience, introspective, life story, interview, observational, historical, interactional, and visual texts – that describe routine and problematic moments and meanings in individuals’ lives. (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2)
Flick claims that the label “qualitative research” is indeed used as an umbrella for a number of approaches ( 2007 :2–4; 2002 :6), and it is not difficult to identify research fitting this designation. Moreover, whatever it is, it has grown dramatically over the past five decades. In addition, courses have been developed, methods have flourished, arguments about its future have been advanced (for example, Denzin and Lincoln 1994) and criticized (for example, Snow and Morrill 1995 ), and dedicated journals and books have mushroomed. Most social scientists have a clear idea of research and how it differs from journalism, politics and other activities. But the question of what is qualitative in qualitative research is either eluded or eschewed.
We maintain that this lacuna hinders systematic knowledge production based on qualitative research. Paul Lazarsfeld noted the lack of “codification” as early as 1955 when he reviewed 100 qualitative studies in order to offer a codification of the practices (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). Since then many texts on “qualitative research” and its methods have been published, including recent attempts (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) similar to Lazarsfeld’s. These studies have tried to extract what is qualitative by looking at the large number of empirical “qualitative” studies. Our novel strategy complements these endeavors by taking another approach and looking at the attempts to codify these practices in the form of a definition, as well as to a minor extent take Becker’s study as an exemplar of what qualitative researchers actually do, and what the characteristic of being ‘qualitative’ denotes and implies. We claim that qualitative researchers, if there is such a thing as “qualitative research,” should be able to codify their practices in a condensed, yet general way expressed in language.
Lingering problems of “generalizability” and “how many cases do I need” (Small 2009 ) are blocking advancement – in this line of work qualitative approaches are said to differ considerably from quantitative ones, while some of the former unsuccessfully mimic principles related to the latter (Small 2009 ). Additionally, quantitative researchers sometimes unfairly criticize the first based on their own quality criteria. Scholars like Goertz and Mahoney ( 2012 ) have successfully focused on the different norms and practices beyond what they argue are essentially two different cultures: those working with either qualitative or quantitative methods. Instead, similarly to Becker ( 2017 ) who has recently questioned the usefulness of the distinction between qualitative and quantitative research, we focus on similarities.
The current situation also impedes both students and researchers in focusing their studies and understanding each other’s work (Lazarsfeld and Barton 1982 :239). A third consequence is providing an opening for critiques by scholars operating within different traditions (Valsiner 2000 :101). A fourth issue is that the “implicit use of methods in qualitative research makes the field far less standardized than the quantitative paradigm” (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 :9). Relatedly, the National Science Foundation in the US organized two workshops in 2004 and 2005 to address the scientific foundations of qualitative research involving strategies to improve it and to develop standards of evaluation in qualitative research. However, a specific focus on its distinguishing feature of being “qualitative” while being implicitly acknowledged, was discussed only briefly (for example, Best 2004 ).
In 2014 a theme issue was published in this journal on “Methods, Materials, and Meanings: Designing Cultural Analysis,” discussing central issues in (cultural) qualitative research (Berezin 2014 ; Biernacki 2014 ; Glaeser 2014 ; Lamont and Swidler 2014 ; Spillman 2014). We agree with many of the arguments put forward, such as the risk of methodological tribalism, and that we should not waste energy on debating methods separated from research questions. Nonetheless, a clarification of the relation to what is called “quantitative research” is of outmost importance to avoid misunderstandings and misguided debates between “qualitative” and “quantitative” researchers. Our strategy means that researchers, “qualitative” or “quantitative” they may be, in their actual practice may combine qualitative work and quantitative work.
In this article we accomplish three tasks. First, we systematically survey the literature for meanings of qualitative research by looking at how researchers have defined it. Drawing upon existing knowledge we find that the different meanings and ideas of qualitative research are not yet coherently integrated into one satisfactory definition. Next, we advance our contribution by offering a definition of qualitative research and illustrate its meaning and use partially by expanding on the brief example introduced earlier related to Becker’s work ( 1963 ). We offer a systematic analysis of central themes of what researchers consider to be the core of “qualitative,” regardless of style of work. These themes – which we summarize in terms of four keywords: distinction, process, closeness, improved understanding – constitute part of our literature review, in which each one appears, sometimes with others, but never all in the same definition. They serve as the foundation of our contribution. Our categories are overlapping. Their use is primarily to organize the large amount of definitions we have identified and analyzed, and not necessarily to draw a clear distinction between them. Finally, we continue the elaboration discussed above on the advantages of a clear definition of qualitative research.
In a hermeneutic fashion we propose that there is something meaningful that deserves to be labelled “qualitative research” (Gadamer 1990 ). To approach the question “What is qualitative in qualitative research?” we have surveyed the literature. In conducting our survey we first traced the word’s etymology in dictionaries, encyclopedias, handbooks of the social sciences and of methods and textbooks, mainly in English, which is common to methodology courses. It should be noted that we have zoomed in on sociology and its literature. This discipline has been the site of the largest debate and development of methods that can be called “qualitative,” which suggests that this field should be examined in great detail.
In an ideal situation we should expect that one good definition, or at least some common ideas, would have emerged over the years. This common core of qualitative research should be so accepted that it would appear in at least some textbooks. Since this is not what we found, we decided to pursue an inductive approach to capture maximal variation in the field of qualitative research; we searched in a selection of handbooks, textbooks, book chapters, and books, to which we added the analysis of journal articles. Our sample comprises a total of 89 references.
In practice we focused on the discipline that has had a clear discussion of methods, namely sociology. We also conducted a broad search in the JSTOR database to identify scholarly sociology articles published between 1998 and 2017 in English with a focus on defining or explaining qualitative research. We specifically zoom in on this time frame because we would have expect that this more mature period would have produced clear discussions on the meaning of qualitative research. To find these articles we combined a number of keywords to search the content and/or the title: qualitative (which was always included), definition, empirical, research, methodology, studies, fieldwork, interview and observation .
As a second phase of our research we searched within nine major sociological journals ( American Journal of Sociology , Sociological Theory , American Sociological Review , Contemporary Sociology , Sociological Forum , Sociological Theory , Qualitative Research , Qualitative Sociology and Qualitative Sociology Review ) for articles also published during the past 19 years (1998–2017) that had the term “qualitative” in the title and attempted to define qualitative research.
Lastly we picked two additional journals, Qualitative Research and Qualitative Sociology , in which we could expect to find texts addressing the notion of “qualitative.” From Qualitative Research we chose Volume 14, Issue 6, December 2014, and from Qualitative Sociology we chose Volume 36, Issue 2, June 2017. Within each of these we selected the first article; then we picked the second article of three prior issues. Again we went back another three issues and investigated article number three. Finally we went back another three issues and perused article number four. This selection criteria was used to get a manageable sample for the analysis.
The coding process of the 89 references we gathered in our selected review began soon after the first round of material was gathered, and we reduced the complexity created by our maximum variation sampling (Snow and Anderson 1993 :22) to four different categories within which questions on the nature and properties of qualitative research were discussed. We call them: Qualitative and Quantitative Research, Qualitative Research, Fieldwork, and Grounded Theory. This – which may appear as an illogical grouping – merely reflects the “context” in which the matter of “qualitative” is discussed. If the selection process of the material – books and articles – was informed by pre-knowledge, we used an inductive strategy to code the material. When studying our material, we identified four central notions related to “qualitative” that appear in various combinations in the literature which indicate what is the core of qualitative research. We have labeled them: “distinctions”, “process,” “closeness,” and “improved understanding.” During the research process the categories and notions were improved, refined, changed, and reordered. The coding ended when a sense of saturation in the material arose. In the presentation below all quotations and references come from our empirical material of texts on qualitative research.
Analysis – What is Qualitative Research?
In this section we describe the four categories we identified in the coding, how they differently discuss qualitative research, as well as their overall content. Some salient quotations are selected to represent the type of text sorted under each of the four categories. What we present are examples from the literature.
Qualitative and Quantitative
This analytic category comprises quotations comparing qualitative and quantitative research, a distinction that is frequently used (Brown 2010 :231); in effect this is a conceptual pair that structures the discussion and that may be associated with opposing interests. While the general goal of quantitative and qualitative research is the same – to understand the world better – their methodologies and focus in certain respects differ substantially (Becker 1966 :55). Quantity refers to that property of something that can be determined by measurement. In a dictionary of Statistics and Methodology we find that “(a) When referring to *variables, ‘qualitative’ is another term for *categorical or *nominal. (b) When speaking of kinds of research, ‘qualitative’ refers to studies of subjects that are hard to quantify, such as art history. Qualitative research tends to be a residual category for almost any kind of non-quantitative research” (Stiles 1998:183). But it should be obvious that one could employ a quantitative approach when studying, for example, art history.
The same dictionary states that quantitative is “said of variables or research that can be handled numerically, usually (too sharply) contrasted with *qualitative variables and research” (Stiles 1998:184). From a qualitative perspective “quantitative research” is about numbers and counting, and from a quantitative perspective qualitative research is everything that is not about numbers. But this does not say much about what is “qualitative.” If we turn to encyclopedias we find that in the 1932 edition of the Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences there is no mention of “qualitative.” In the Encyclopedia from 1968 we can read:
Qualitative Analysis. For methods of obtaining, analyzing, and describing data, see [the various entries:] CONTENT ANALYSIS; COUNTED DATA; EVALUATION RESEARCH, FIELD WORK; GRAPHIC PRESENTATION; HISTORIOGRAPHY, especially the article on THE RHETORIC OF HISTORY; INTERVIEWING; OBSERVATION; PERSONALITY MEASUREMENT; PROJECTIVE METHODS; PSYCHOANALYSIS, article on EXPERIMENTAL METHODS; SURVEY ANALYSIS, TABULAR PRESENTATION; TYPOLOGIES. (Vol. 13:225)
Some, like Alford, divide researchers into methodologists or, in his words, “quantitative and qualitative specialists” (Alford 1998 :12). Qualitative research uses a variety of methods, such as intensive interviews or in-depth analysis of historical materials, and it is concerned with a comprehensive account of some event or unit (King et al. 1994 :4). Like quantitative research it can be utilized to study a variety of issues, but it tends to focus on meanings and motivations that underlie cultural symbols, personal experiences, phenomena and detailed understanding of processes in the social world. In short, qualitative research centers on understanding processes, experiences, and the meanings people assign to things (Kalof et al. 2008 :79).
Others simply say that qualitative methods are inherently unscientific (Jovanović 2011 :19). Hood, for instance, argues that words are intrinsically less precise than numbers, and that they are therefore more prone to subjective analysis, leading to biased results (Hood 2006 :219). Qualitative methodologies have raised concerns over the limitations of quantitative templates (Brady et al. 2004 :4). Scholars such as King et al. ( 1994 ), for instance, argue that non-statistical research can produce more reliable results if researchers pay attention to the rules of scientific inference commonly stated in quantitative research. Also, researchers such as Becker ( 1966 :59; 1970 :42–43) have asserted that, if conducted properly, qualitative research and in particular ethnographic field methods, can lead to more accurate results than quantitative studies, in particular, survey research and laboratory experiments.
Some researchers, such as Kalof, Dan, and Dietz ( 2008 :79) claim that the boundaries between the two approaches are becoming blurred, and Small ( 2009 ) argues that currently much qualitative research (especially in North America) tries unsuccessfully and unnecessarily to emulate quantitative standards. For others, qualitative research tends to be more humanistic and discursive (King et al. 1994 :4). Ragin ( 1994 ), and similarly also Becker, ( 1996 :53), Marchel and Owens ( 2007 :303) think that the main distinction between the two styles is overstated and does not rest on the simple dichotomy of “numbers versus words” (Ragin 1994 :xii). Some claim that quantitative data can be utilized to discover associations, but in order to unveil cause and effect a complex research design involving the use of qualitative approaches needs to be devised (Gilbert 2009 :35). Consequently, qualitative data are useful for understanding the nuances lying beyond those processes as they unfold (Gilbert 2009 :35). Others contend that qualitative research is particularly well suited both to identify causality and to uncover fine descriptive distinctions (Fine and Hallett 2014 ; Lichterman and Isaac Reed 2014 ; Katz 2015 ).
There are other ways to separate these two traditions, including normative statements about what qualitative research should be (that is, better or worse than quantitative approaches, concerned with scientific approaches to societal change or vice versa; Snow and Morrill 1995 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2005 ), or whether it should develop falsifiable statements; Best 2004 ).
We propose that quantitative research is largely concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ); the analysis concerns the relations between variables. These categories are primarily not questioned in the study, only their frequency or degree, or the correlations between them (cf. Franzosi 2016 ). If a researcher studies wage differences between women and men, he or she works with given categories: x number of men are compared with y number of women, with a certain wage attributed to each person. The idea is not to move beyond the given categories of wage, men and women; they are the starting point as well as the end point, and undergo no “qualitative change.” Qualitative research, in contrast, investigates relations between categories that are themselves subject to change in the research process. Returning to Becker’s study ( 1963 ), we see that he questioned pre-dispositional theories of deviant behavior working with pre-determined variables such as an individual’s combination of personal qualities or emotional problems. His take, in contrast, was to understand marijuana consumption by developing “variables” as part of the investigation. Thereby he presented new variables, or as we would say today, theoretical concepts, but which are grounded in the empirical material.
Qualitative Research
This category contains quotations that refer to descriptions of qualitative research without making comparisons with quantitative research. Researchers such as Denzin and Lincoln, who have written a series of influential handbooks on qualitative methods (1994; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ; 2005 ), citing Nelson et al. (1992:4), argue that because qualitative research is “interdisciplinary, transdisciplinary, and sometimes counterdisciplinary” it is difficult to derive one single definition of it (Jovanović 2011 :3). According to them, in fact, “the field” is “many things at the same time,” involving contradictions, tensions over its focus, methods, and how to derive interpretations and findings ( 2003 : 11). Similarly, others, such as Flick ( 2007 :ix–x) contend that agreeing on an accepted definition has increasingly become problematic, and that qualitative research has possibly matured different identities. However, Best holds that “the proliferation of many sorts of activities under the label of qualitative sociology threatens to confuse our discussions” ( 2004 :54). Atkinson’s position is more definite: “the current state of qualitative research and research methods is confused” ( 2005 :3–4).
Qualitative research is about interpretation (Blumer 1969 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2003 ), or Verstehen [understanding] (Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ). It is “multi-method,” involving the collection and use of a variety of empirical materials (Denzin and Lincoln 1998; Silverman 2013 ) and approaches (Silverman 2005 ; Flick 2007 ). It focuses not only on the objective nature of behavior but also on its subjective meanings: individuals’ own accounts of their attitudes, motivations, behavior (McIntyre 2005 :127; Creswell 2009 ), events and situations (Bryman 1989) – what people say and do in specific places and institutions (Goodwin and Horowitz 2002 :35–36) in social and temporal contexts (Morrill and Fine 1997). For this reason, following Weber ([1921-22] 1978), it can be described as an interpretative science (McIntyre 2005 :127). But could quantitative research also be concerned with these questions? Also, as pointed out below, does all qualitative research focus on subjective meaning, as some scholars suggest?
Others also distinguish qualitative research by claiming that it collects data using a naturalistic approach (Denzin and Lincoln 2005 :2; Creswell 2009 ), focusing on the meaning actors ascribe to their actions. But again, does all qualitative research need to be collected in situ? And does qualitative research have to be inherently concerned with meaning? Flick ( 2007 ), referring to Denzin and Lincoln ( 2005 ), mentions conversation analysis as an example of qualitative research that is not concerned with the meanings people bring to a situation, but rather with the formal organization of talk. Still others, such as Ragin ( 1994 :85), note that qualitative research is often (especially early on in the project, we would add) less structured than other kinds of social research – a characteristic connected to its flexibility and that can lead both to potentially better, but also worse results. But is this not a feature of this type of research, rather than a defining description of its essence? Wouldn’t this comment also apply, albeit to varying degrees, to quantitative research?
In addition, Strauss ( 2003 ), along with others, such as Alvesson and Kärreman ( 2011 :10–76), argue that qualitative researchers struggle to capture and represent complex phenomena partially because they tend to collect a large amount of data. While his analysis is correct at some points – “It is necessary to do detailed, intensive, microscopic examination of the data in order to bring out the amazing complexity of what lies in, behind, and beyond those data” (Strauss 2003 :10) – much of his analysis concerns the supposed focus of qualitative research and its challenges, rather than exactly what it is about. But even in this instance we would make a weak case arguing that these are strictly the defining features of qualitative research. Some researchers seem to focus on the approach or the methods used, or even on the way material is analyzed. Several researchers stress the naturalistic assumption of investigating the world, suggesting that meaning and interpretation appear to be a core matter of qualitative research.
We can also see that in this category there is no consensus about specific qualitative methods nor about qualitative data. Many emphasize interpretation, but quantitative research, too, involves interpretation; the results of a regression analysis, for example, certainly have to be interpreted, and the form of meta-analysis that factor analysis provides indeed requires interpretation However, there is no interpretation of quantitative raw data, i.e., numbers in tables. One common thread is that qualitative researchers have to get to grips with their data in order to understand what is being studied in great detail, irrespective of the type of empirical material that is being analyzed. This observation is connected to the fact that qualitative researchers routinely make several adjustments of focus and research design as their studies progress, in many cases until the very end of the project (Kalof et al. 2008 ). If you, like Becker, do not start out with a detailed theory, adjustments such as the emergence and refinement of research questions will occur during the research process. We have thus found a number of useful reflections about qualitative research scattered across different sources, but none of them effectively describe the defining characteristics of this approach.
Although qualitative research does not appear to be defined in terms of a specific method, it is certainly common that fieldwork, i.e., research that entails that the researcher spends considerable time in the field that is studied and use the knowledge gained as data, is seen as emblematic of or even identical to qualitative research. But because we understand that fieldwork tends to focus primarily on the collection and analysis of qualitative data, we expected to find within it discussions on the meaning of “qualitative.” But, again, this was not the case.
Instead, we found material on the history of this approach (for example, Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 ; Atkinson et al. 2001), including how it has changed; for example, by adopting a more self-reflexive practice (Heyl 2001), as well as the different nomenclature that has been adopted, such as fieldwork, ethnography, qualitative research, naturalistic research, participant observation and so on (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ; Gans 1999 ).
We retrieved definitions of ethnography, such as “the study of people acting in the natural courses of their daily lives,” involving a “resocialization of the researcher” (Emerson 1988 :1) through intense immersion in others’ social worlds (see also examples in Hammersley 2018 ). This may be accomplished by direct observation and also participation (Neuman 2007 :276), although others, such as Denzin ( 1970 :185), have long recognized other types of observation, including non-participant (“fly on the wall”). In this category we have also isolated claims and opposing views, arguing that this type of research is distinguished primarily by where it is conducted (natural settings) (Hughes 1971:496), and how it is carried out (a variety of methods are applied) or, for some most importantly, by involving an active, empathetic immersion in those being studied (Emerson 1988 :2). We also retrieved descriptions of the goals it attends in relation to how it is taught (understanding subjective meanings of the people studied, primarily develop theory, or contribute to social change) (see for example, Corte and Irwin 2017 ; Frankfort-Nachmias and Nachmias 1996 :281; Trier-Bieniek 2012 :639) by collecting the richest possible data (Lofland et al. 2006 ) to derive “thick descriptions” (Geertz 1973 ), and/or to aim at theoretical statements of general scope and applicability (for example, Emerson 1988 ; Fine 2003 ). We have identified guidelines on how to evaluate it (for example Becker 1996 ; Lamont 2004 ) and have retrieved instructions on how it should be conducted (for example, Lofland et al. 2006 ). For instance, analysis should take place while the data gathering unfolds (Emerson 1988 ; Hammersley and Atkinson 2007 ; Lofland et al. 2006 ), observations should be of long duration (Becker 1970 :54; Goffman 1989 ), and data should be of high quantity (Becker 1970 :52–53), as well as other questionable distinctions between fieldwork and other methods:
Field studies differ from other methods of research in that the researcher performs the task of selecting topics, decides what questions to ask, and forges interest in the course of the research itself . This is in sharp contrast to many ‘theory-driven’ and ‘hypothesis-testing’ methods. (Lofland and Lofland 1995 :5)
But could not, for example, a strictly interview-based study be carried out with the same amount of flexibility, such as sequential interviewing (for example, Small 2009 )? Once again, are quantitative approaches really as inflexible as some qualitative researchers think? Moreover, this category stresses the role of the actors’ meaning, which requires knowledge and close interaction with people, their practices and their lifeworld.
It is clear that field studies – which are seen by some as the “gold standard” of qualitative research – are nonetheless only one way of doing qualitative research. There are other methods, but it is not clear why some are more qualitative than others, or why they are better or worse. Fieldwork is characterized by interaction with the field (the material) and understanding of the phenomenon that is being studied. In Becker’s case, he had general experience from fields in which marihuana was used, based on which he did interviews with actual users in several fields.
Grounded Theory
Another major category we identified in our sample is Grounded Theory. We found descriptions of it most clearly in Glaser and Strauss’ ([1967] 2010 ) original articulation, Strauss and Corbin ( 1998 ) and Charmaz ( 2006 ), as well as many other accounts of what it is for: generating and testing theory (Strauss 2003 :xi). We identified explanations of how this task can be accomplished – such as through two main procedures: constant comparison and theoretical sampling (Emerson 1998:96), and how using it has helped researchers to “think differently” (for example, Strauss and Corbin 1998 :1). We also read descriptions of its main traits, what it entails and fosters – for instance, an exceptional flexibility, an inductive approach (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :31–33; 1990; Esterberg 2002 :7), an ability to step back and critically analyze situations, recognize tendencies towards bias, think abstractly and be open to criticism, enhance sensitivity towards the words and actions of respondents, and develop a sense of absorption and devotion to the research process (Strauss and Corbin 1998 :5–6). Accordingly, we identified discussions of the value of triangulating different methods (both using and not using grounded theory), including quantitative ones, and theories to achieve theoretical development (most comprehensively in Denzin 1970 ; Strauss and Corbin 1998 ; Timmermans and Tavory 2012 ). We have also located arguments about how its practice helps to systematize data collection, analysis and presentation of results (Glaser and Strauss [1967] 2010 :16).
Grounded theory offers a systematic approach which requires researchers to get close to the field; closeness is a requirement of identifying questions and developing new concepts or making further distinctions with regard to old concepts. In contrast to other qualitative approaches, grounded theory emphasizes the detailed coding process, and the numerous fine-tuned distinctions that the researcher makes during the process. Within this category, too, we could not find a satisfying discussion of the meaning of qualitative research.
Defining Qualitative Research
In sum, our analysis shows that some notions reappear in the discussion of qualitative research, such as understanding, interpretation, “getting close” and making distinctions. These notions capture aspects of what we think is “qualitative.” However, a comprehensive definition that is useful and that can further develop the field is lacking, and not even a clear picture of its essential elements appears. In other words no definition emerges from our data, and in our research process we have moved back and forth between our empirical data and the attempt to present a definition. Our concrete strategy, as stated above, is to relate qualitative and quantitative research, or more specifically, qualitative and quantitative work. We use an ideal-typical notion of quantitative research which relies on taken for granted and numbered variables. This means that the data consists of variables on different scales, such as ordinal, but frequently ratio and absolute scales, and the representation of the numbers to the variables, i.e. the justification of the assignment of numbers to object or phenomenon, are not questioned, though the validity may be questioned. In this section we return to the notion of quality and try to clarify it while presenting our contribution.
Broadly, research refers to the activity performed by people trained to obtain knowledge through systematic procedures. Notions such as “objectivity” and “reflexivity,” “systematic,” “theory,” “evidence” and “openness” are here taken for granted in any type of research. Next, building on our empirical analysis we explain the four notions that we have identified as central to qualitative work: distinctions, process, closeness, and improved understanding. In discussing them, ultimately in relation to one another, we make their meaning even more precise. Our idea, in short, is that only when these ideas that we present separately for analytic purposes are brought together can we speak of qualitative research.
Distinctions
We believe that the possibility of making new distinctions is one the defining characteristics of qualitative research. It clearly sets it apart from quantitative analysis which works with taken-for-granted variables, albeit as mentioned, meta-analyses, for example, factor analysis may result in new variables. “Quality” refers essentially to distinctions, as already pointed out by Aristotle. He discusses the term “qualitative” commenting: “By a quality I mean that in virtue of which things are said to be qualified somehow” (Aristotle 1984:14). Quality is about what something is or has, which means that the distinction from its environment is crucial. We see qualitative research as a process in which significant new distinctions are made to the scholarly community; to make distinctions is a key aspect of obtaining new knowledge; a point, as we will see, that also has implications for “quantitative research.” The notion of being “significant” is paramount. New distinctions by themselves are not enough; just adding concepts only increases complexity without furthering our knowledge. The significance of new distinctions is judged against the communal knowledge of the research community. To enable this discussion and judgements central elements of rational discussion are required (cf. Habermas [1981] 1987 ; Davidsson [ 1988 ] 2001) to identify what is new and relevant scientific knowledge. Relatedly, Ragin alludes to the idea of new and useful knowledge at a more concrete level: “Qualitative methods are appropriate for in-depth examination of cases because they aid the identification of key features of cases. Most qualitative methods enhance data” (1994:79). When Becker ( 1963 ) studied deviant behavior and investigated how people became marihuana smokers, he made distinctions between the ways in which people learned how to smoke. This is a classic example of how the strategy of “getting close” to the material, for example the text, people or pictures that are subject to analysis, may enable researchers to obtain deeper insight and new knowledge by making distinctions – in this instance on the initial notion of learning how to smoke. Others have stressed the making of distinctions in relation to coding or theorizing. Emerson et al. ( 1995 ), for example, hold that “qualitative coding is a way of opening up avenues of inquiry,” meaning that the researcher identifies and develops concepts and analytic insights through close examination of and reflection on data (Emerson et al. 1995 :151). Goodwin and Horowitz highlight making distinctions in relation to theory-building writing: “Close engagement with their cases typically requires qualitative researchers to adapt existing theories or to make new conceptual distinctions or theoretical arguments to accommodate new data” ( 2002 : 37). In the ideal-typical quantitative research only existing and so to speak, given, variables would be used. If this is the case no new distinction are made. But, would not also many “quantitative” researchers make new distinctions?
Process does not merely suggest that research takes time. It mainly implies that qualitative new knowledge results from a process that involves several phases, and above all iteration. Qualitative research is about oscillation between theory and evidence, analysis and generating material, between first- and second -order constructs (Schütz 1962 :59), between getting in contact with something, finding sources, becoming deeply familiar with a topic, and then distilling and communicating some of its essential features. The main point is that the categories that the researcher uses, and perhaps takes for granted at the beginning of the research process, usually undergo qualitative changes resulting from what is found. Becker describes how he tested hypotheses and let the jargon of the users develop into theoretical concepts. This happens over time while the study is being conducted, exemplifying what we mean by process.
In the research process, a pilot-study may be used to get a first glance of, for example, the field, how to approach it, and what methods can be used, after which the method and theory are chosen or refined before the main study begins. Thus, the empirical material is often central from the start of the project and frequently leads to adjustments by the researcher. Likewise, during the main study categories are not fixed; the empirical material is seen in light of the theory used, but it is also given the opportunity to kick back, thereby resisting attempts to apply theoretical straightjackets (Becker 1970 :43). In this process, coding and analysis are interwoven, and thus are often important steps for getting closer to the phenomenon and deciding what to focus on next. Becker began his research by interviewing musicians close to him, then asking them to refer him to other musicians, and later on doubling his original sample of about 25 to include individuals in other professions (Becker 1973:46). Additionally, he made use of some participant observation, documents, and interviews with opiate users made available to him by colleagues. As his inductive theory of deviance evolved, Becker expanded his sample in order to fine tune it, and test the accuracy and generality of his hypotheses. In addition, he introduced a negative case and discussed the null hypothesis ( 1963 :44). His phasic career model is thus based on a research design that embraces processual work. Typically, process means to move between “theory” and “material” but also to deal with negative cases, and Becker ( 1998 ) describes how discovering these negative cases impacted his research design and ultimately its findings.
Obviously, all research is process-oriented to some degree. The point is that the ideal-typical quantitative process does not imply change of the data, and iteration between data, evidence, hypotheses, empirical work, and theory. The data, quantified variables, are, in most cases fixed. Merging of data, which of course can be done in a quantitative research process, does not mean new data. New hypotheses are frequently tested, but the “raw data is often the “the same.” Obviously, over time new datasets are made available and put into use.
Another characteristic that is emphasized in our sample is that qualitative researchers – and in particular ethnographers – can, or as Goffman put it, ought to ( 1989 ), get closer to the phenomenon being studied and their data than quantitative researchers (for example, Silverman 2009 :85). Put differently, essentially because of their methods qualitative researchers get into direct close contact with those being investigated and/or the material, such as texts, being analyzed. Becker started out his interview study, as we noted, by talking to those he knew in the field of music to get closer to the phenomenon he was studying. By conducting interviews he got even closer. Had he done more observations, he would undoubtedly have got even closer to the field.
Additionally, ethnographers’ design enables researchers to follow the field over time, and the research they do is almost by definition longitudinal, though the time in the field is studied obviously differs between studies. The general characteristic of closeness over time maximizes the chances of unexpected events, new data (related, for example, to archival research as additional sources, and for ethnography for situations not necessarily previously thought of as instrumental – what Mannay and Morgan ( 2015 ) term the “waiting field”), serendipity (Merton and Barber 2004 ; Åkerström 2013 ), and possibly reactivity, as well as the opportunity to observe disrupted patterns that translate into exemplars of negative cases. Two classic examples of this are Becker’s finding of what medical students call “crocks” (Becker et al. 1961 :317), and Geertz’s ( 1973 ) study of “deep play” in Balinese society.
By getting and staying so close to their data – be it pictures, text or humans interacting (Becker was himself a musician) – for a long time, as the research progressively focuses, qualitative researchers are prompted to continually test their hunches, presuppositions and hypotheses. They test them against a reality that often (but certainly not always), and practically, as well as metaphorically, talks back, whether by validating them, or disqualifying their premises – correctly, as well as incorrectly (Fine 2003 ; Becker 1970 ). This testing nonetheless often leads to new directions for the research. Becker, for example, says that he was initially reading psychological theories, but when facing the data he develops a theory that looks at, you may say, everything but psychological dispositions to explain the use of marihuana. Especially researchers involved with ethnographic methods have a fairly unique opportunity to dig up and then test (in a circular, continuous and temporal way) new research questions and findings as the research progresses, and thereby to derive previously unimagined and uncharted distinctions by getting closer to the phenomenon under study.
Let us stress that getting close is by no means restricted to ethnography. The notion of hermeneutic circle and hermeneutics as a general way of understanding implies that we must get close to the details in order to get the big picture. This also means that qualitative researchers can literally also make use of details of pictures as evidence (cf. Harper 2002). Thus, researchers may get closer both when generating the material or when analyzing it.
Quantitative research, we maintain, in the ideal-typical representation cannot get closer to the data. The data is essentially numbers in tables making up the variables (Franzosi 2016 :138). The data may originally have been “qualitative,” but once reduced to numbers there can only be a type of “hermeneutics” about what the number may stand for. The numbers themselves, however, are non-ambiguous. Thus, in quantitative research, interpretation, if done, is not about the data itself—the numbers—but what the numbers stand for. It follows that the interpretation is essentially done in a more “speculative” mode without direct empirical evidence (cf. Becker 2017 ).
Improved Understanding
While distinction, process and getting closer refer to the qualitative work of the researcher, improved understanding refers to its conditions and outcome of this work. Understanding cuts deeper than explanation, which to some may mean a causally verified correlation between variables. The notion of explanation presupposes the notion of understanding since explanation does not include an idea of how knowledge is gained (Manicas 2006 : 15). Understanding, we argue, is the core concept of what we call the outcome of the process when research has made use of all the other elements that were integrated in the research. Understanding, then, has a special status in qualitative research since it refers both to the conditions of knowledge and the outcome of the process. Understanding can to some extent be seen as the condition of explanation and occurs in a process of interpretation, which naturally refers to meaning (Gadamer 1990 ). It is fundamentally connected to knowing, and to the knowing of how to do things (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ). Conceptually the term hermeneutics is used to account for this process. Heidegger ties hermeneutics to human being and not possible to separate from the understanding of being ( 1988 ). Here we use it in a broader sense, and more connected to method in general (cf. Seiffert 1992 ). The abovementioned aspects – for example, “objectivity” and “reflexivity” – of the approach are conditions of scientific understanding. Understanding is the result of a circular process and means that the parts are understood in light of the whole, and vice versa. Understanding presupposes pre-understanding, or in other words, some knowledge of the phenomenon studied. The pre-understanding, even in the form of prejudices, are in qualitative research process, which we see as iterative, questioned, which gradually or suddenly change due to the iteration of data, evidence and concepts. However, qualitative research generates understanding in the iterative process when the researcher gets closer to the data, e.g., by going back and forth between field and analysis in a process that generates new data that changes the evidence, and, ultimately, the findings. Questioning, to ask questions, and put what one assumes—prejudices and presumption—in question, is central to understand something (Heidegger [1927] 2001 ; Gadamer 1990 :368–384). We propose that this iterative process in which the process of understanding occurs is characteristic of qualitative research.
Improved understanding means that we obtain scientific knowledge of something that we as a scholarly community did not know before, or that we get to know something better. It means that we understand more about how parts are related to one another, and to other things we already understand (see also Fine and Hallett 2014 ). Understanding is an important condition for qualitative research. It is not enough to identify correlations, make distinctions, and work in a process in which one gets close to the field or phenomena. Understanding is accomplished when the elements are integrated in an iterative process.
It is, moreover, possible to understand many things, and researchers, just like children, may come to understand new things every day as they engage with the world. This subjective condition of understanding – namely, that a person gains a better understanding of something –is easily met. To be qualified as “scientific,” the understanding must be general and useful to many; it must be public. But even this generally accessible understanding is not enough in order to speak of “scientific understanding.” Though we as a collective can increase understanding of everything in virtually all potential directions as a result also of qualitative work, we refrain from this “objective” way of understanding, which has no means of discriminating between what we gain in understanding. Scientific understanding means that it is deemed relevant from the scientific horizon (compare Schütz 1962 : 35–38, 46, 63), and that it rests on the pre-understanding that the scientists have and must have in order to understand. In other words, the understanding gained must be deemed useful by other researchers, so that they can build on it. We thus see understanding from a pragmatic, rather than a subjective or objective perspective. Improved understanding is related to the question(s) at hand. Understanding, in order to represent an improvement, must be an improvement in relation to the existing body of knowledge of the scientific community (James [ 1907 ] 1955). Scientific understanding is, by definition, collective, as expressed in Weber’s famous note on objectivity, namely that scientific work aims at truths “which … can claim, even for a Chinese, the validity appropriate to an empirical analysis” ([1904] 1949 :59). By qualifying “improved understanding” we argue that it is a general defining characteristic of qualitative research. Becker‘s ( 1966 ) study and other research of deviant behavior increased our understanding of the social learning processes of how individuals start a behavior. And it also added new knowledge about the labeling of deviant behavior as a social process. Few studies, of course, make the same large contribution as Becker’s, but are nonetheless qualitative research.
Understanding in the phenomenological sense, which is a hallmark of qualitative research, we argue, requires meaning and this meaning is derived from the context, and above all the data being analyzed. The ideal-typical quantitative research operates with given variables with different numbers. This type of material is not enough to establish meaning at the level that truly justifies understanding. In other words, many social science explanations offer ideas about correlations or even causal relations, but this does not mean that the meaning at the level of the data analyzed, is understood. This leads us to say that there are indeed many explanations that meet the criteria of understanding, for example the explanation of how one becomes a marihuana smoker presented by Becker. However, we may also understand a phenomenon without explaining it, and we may have potential explanations, or better correlations, that are not really understood.
We may speak more generally of quantitative research and its data to clarify what we see as an important distinction. The “raw data” that quantitative research—as an idealtypical activity, refers to is not available for further analysis; the numbers, once created, are not to be questioned (Franzosi 2016 : 138). If the researcher is to do “more” or “change” something, this will be done by conjectures based on theoretical knowledge or based on the researcher’s lifeworld. Both qualitative and quantitative research is based on the lifeworld, and all researchers use prejudices and pre-understanding in the research process. This idea is present in the works of Heidegger ( 2001 ) and Heisenberg (cited in Franzosi 2010 :619). Qualitative research, as we argued, involves the interaction and questioning of concepts (theory), data, and evidence.
Ragin ( 2004 :22) points out that “a good definition of qualitative research should be inclusive and should emphasize its key strengths and features, not what it lacks (for example, the use of sophisticated quantitative techniques).” We define qualitative research as an iterative process in which improved understanding to the scientific community is achieved by making new significant distinctions resulting from getting closer to the phenomenon studied. Qualitative research, as defined here, is consequently a combination of two criteria: (i) how to do things –namely, generating and analyzing empirical material, in an iterative process in which one gets closer by making distinctions, and (ii) the outcome –improved understanding novel to the scholarly community. Is our definition applicable to our own study? In this study we have closely read the empirical material that we generated, and the novel distinction of the notion “qualitative research” is the outcome of an iterative process in which both deduction and induction were involved, in which we identified the categories that we analyzed. We thus claim to meet the first criteria, “how to do things.” The second criteria cannot be judged but in a partial way by us, namely that the “outcome” —in concrete form the definition-improves our understanding to others in the scientific community.
We have defined qualitative research, or qualitative scientific work, in relation to quantitative scientific work. Given this definition, qualitative research is about questioning the pre-given (taken for granted) variables, but it is thus also about making new distinctions of any type of phenomenon, for example, by coining new concepts, including the identification of new variables. This process, as we have discussed, is carried out in relation to empirical material, previous research, and thus in relation to theory. Theory and previous research cannot be escaped or bracketed. According to hermeneutic principles all scientific work is grounded in the lifeworld, and as social scientists we can thus never fully bracket our pre-understanding.
We have proposed that quantitative research, as an idealtype, is concerned with pre-determined variables (Small 2008 ). Variables are epistemically fixed, but can vary in terms of dimensions, such as frequency or number. Age is an example; as a variable it can take on different numbers. In relation to quantitative research, qualitative research does not reduce its material to number and variables. If this is done the process of comes to a halt, the researcher gets more distanced from her data, and it makes it no longer possible to make new distinctions that increase our understanding. We have above discussed the components of our definition in relation to quantitative research. Our conclusion is that in the research that is called quantitative there are frequent and necessary qualitative elements.
Further, comparative empirical research on researchers primarily working with ”quantitative” approaches and those working with ”qualitative” approaches, we propose, would perhaps show that there are many similarities in practices of these two approaches. This is not to deny dissimilarities, or the different epistemic and ontic presuppositions that may be more or less strongly associated with the two different strands (see Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ). Our point is nonetheless that prejudices and preconceptions about researchers are unproductive, and that as other researchers have argued, differences may be exaggerated (e.g., Becker 1996 : 53, 2017 ; Marchel and Owens 2007 :303; Ragin 1994 ), and that a qualitative dimension is present in both kinds of work.
Several things follow from our findings. The most important result is the relation to quantitative research. In our analysis we have separated qualitative research from quantitative research. The point is not to label individual researchers, methods, projects, or works as either “quantitative” or “qualitative.” By analyzing, i.e., taking apart, the notions of quantitative and qualitative, we hope to have shown the elements of qualitative research. Our definition captures the elements, and how they, when combined in practice, generate understanding. As many of the quotations we have used suggest, one conclusion of our study holds that qualitative approaches are not inherently connected with a specific method. Put differently, none of the methods that are frequently labelled “qualitative,” such as interviews or participant observation, are inherently “qualitative.” What matters, given our definition, is whether one works qualitatively or quantitatively in the research process, until the results are produced. Consequently, our analysis also suggests that those researchers working with what in the literature and in jargon is often called “quantitative research” are almost bound to make use of what we have identified as qualitative elements in any research project. Our findings also suggest that many” quantitative” researchers, at least to some extent, are engaged with qualitative work, such as when research questions are developed, variables are constructed and combined, and hypotheses are formulated. Furthermore, a research project may hover between “qualitative” and “quantitative” or start out as “qualitative” and later move into a “quantitative” (a distinct strategy that is not similar to “mixed methods” or just simply combining induction and deduction). More generally speaking, the categories of “qualitative” and “quantitative,” unfortunately, often cover up practices, and it may lead to “camps” of researchers opposing one another. For example, regardless of the researcher is primarily oriented to “quantitative” or “qualitative” research, the role of theory is neglected (cf. Swedberg 2017 ). Our results open up for an interaction not characterized by differences, but by different emphasis, and similarities.
Let us take two examples to briefly indicate how qualitative elements can fruitfully be combined with quantitative. Franzosi ( 2010 ) has discussed the relations between quantitative and qualitative approaches, and more specifically the relation between words and numbers. He analyzes texts and argues that scientific meaning cannot be reduced to numbers. Put differently, the meaning of the numbers is to be understood by what is taken for granted, and what is part of the lifeworld (Schütz 1962 ). Franzosi shows how one can go about using qualitative and quantitative methods and data to address scientific questions analyzing violence in Italy at the time when fascism was rising (1919–1922). Aspers ( 2006 ) studied the meaning of fashion photographers. He uses an empirical phenomenological approach, and establishes meaning at the level of actors. In a second step this meaning, and the different ideal-typical photographers constructed as a result of participant observation and interviews, are tested using quantitative data from a database; in the first phase to verify the different ideal-types, in the second phase to use these types to establish new knowledge about the types. In both of these cases—and more examples can be found—authors move from qualitative data and try to keep the meaning established when using the quantitative data.
A second main result of our study is that a definition, and we provided one, offers a way for research to clarify, and even evaluate, what is done. Hence, our definition can guide researchers and students, informing them on how to think about concrete research problems they face, and to show what it means to get closer in a process in which new distinctions are made. The definition can also be used to evaluate the results, given that it is a standard of evaluation (cf. Hammersley 2007 ), to see whether new distinctions are made and whether this improves our understanding of what is researched, in addition to the evaluation of how the research was conducted. By making what is qualitative research explicit it becomes easier to communicate findings, and it is thereby much harder to fly under the radar with substandard research since there are standards of evaluation which make it easier to separate “good” from “not so good” qualitative research.
To conclude, our analysis, which ends with a definition of qualitative research can thus both address the “internal” issues of what is qualitative research, and the “external” critiques that make it harder to do qualitative research, to which both pressure from quantitative methods and general changes in society contribute.
Acknowledgements
Financial Support for this research is given by the European Research Council, CEV (263699). The authors are grateful to Susann Krieglsteiner for assistance in collecting the data. The paper has benefitted from the many useful comments by the three reviewers and the editor, comments by members of the Uppsala Laboratory of Economic Sociology, as well as Jukka Gronow, Sebastian Kohl, Marcin Serafin, Richard Swedberg, Anders Vassenden and Turid Rødne.
Biographies
is professor of sociology at the Department of Sociology, Uppsala University and Universität St. Gallen. His main focus is economic sociology, and in particular, markets. He has published numerous articles and books, including Orderly Fashion (Princeton University Press 2010), Markets (Polity Press 2011) and Re-Imagining Economic Sociology (edited with N. Dodd, Oxford University Press 2015). His book Ethnographic Methods (in Swedish) has already gone through several editions.
is associate professor of sociology at the Department of Media and Social Sciences, University of Stavanger. His research has been published in journals such as Social Psychology Quarterly, Sociological Theory, Teaching Sociology, and Music and Arts in Action. As an ethnographer he is working on a book on he social world of big-wave surfing.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Patrik Aspers, Email: [email protected] .
Ugo Corte, Email: [email protected] .
- Åkerström M. Curiosity and serendipity in qualitative research. Qualitative Sociology Review. 2013; 9 (2):10–18. [ Google Scholar ]
- Alford, Robert R. 1998. The craft of inquiry. Theories, methods, evidence . Oxford: Oxford University Press.
- Alvesson M, Kärreman D. Qualitative research and theory development . Mystery as method . London: SAGE Publications; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- Aspers, Patrik. 2006. Markets in Fashion, A Phenomenological Approach. London Routledge.
- Atkinson P. Qualitative research. Unity and diversity. Forum: Qualitative Social Research. 2005; 6 (3):1–15. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Outsiders. Studies in the sociology of deviance . New York: The Free Press; 1963. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Whose side are we on? Social Problems. 1966; 14 (3):239–247. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Sociological work. Method and substance. New Brunswick: Transaction Books; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. The epistemology of qualitative research. In: Richard J, Anne C, Shweder RA, editors. Ethnography and human development. Context and meaning in social inquiry. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1996. pp. 53–71. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker HS. Tricks of the trade. How to think about your research while you're doing it. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Becker, Howard S. 2017. Evidence . Chigaco: University of Chicago Press.
- Becker H, Geer B, Hughes E, Strauss A. Boys in White, student culture in medical school. New Brunswick: Transaction Publishers; 1961. [ Google Scholar ]
- Berezin M. How do we know what we mean? Epistemological dilemmas in cultural sociology. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):141–151. [ Google Scholar ]
- Best, Joel. 2004. Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , eds . Charles, Ragin, Joanne, Nagel, and Patricia White, 53-54. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf .
- Biernacki R. Humanist interpretation versus coding text samples. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):173–188. [ Google Scholar ]
- Blumer H. Symbolic interactionism: Perspective and method. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1969. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brady H, Collier D, Seawright J. Refocusing the discussion of methodology. In: Henry B, David C, editors. Rethinking social inquiry. Diverse tools, shared standards. Lanham: Rowman and Littlefield; 2004. pp. 3–22. [ Google Scholar ]
- Brown AP. Qualitative method and compromise in applied social research. Qualitative Research. 2010; 10 (2):229–248. [ Google Scholar ]
- Charmaz K. Constructing grounded theory. London: Sage; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Corte, Ugo, and Katherine Irwin. 2017. “The Form and Flow of Teaching Ethnographic Knowledge: Hands-on Approaches for Learning Epistemology” Teaching Sociology 45(3): 209-219.
- Creswell JW. Research design. Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed method approaches. 3. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Davidsson D. The myth of the subjective. In: Davidsson D, editor. Subjective, intersubjective, objective. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1988. pp. 39–52. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK. The research act: A theoretical introduction to Ssociological methods. Chicago: Aldine Publishing Company Publishers; 1970. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, editors. Collecting and interpreting qualitative materials. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2003. pp. 1–45. [ Google Scholar ]
- Denzin NK, Lincoln YS. Introduction. The discipline and practice of qualitative research. In: Denzin NK, Lincoln YS, editors. The Sage handbook of qualitative research. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications; 2005. pp. 1–32. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emerson RM, editor. Contemporary field research. A collection of readings. Prospect Heights: Waveland Press; 1988. [ Google Scholar ]
- Emerson RM, Fretz RI, Shaw LL. Writing ethnographic fieldnotes. Chicago: University of Chicago Press; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Esterberg KG. Qualitative methods in social research. Boston: McGraw-Hill; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fine, Gary Alan. 1995. Review of “handbook of qualitative research.” Contemporary Sociology 24 (3): 416–418.
- Fine, Gary Alan. 2003. “ Toward a Peopled Ethnography: Developing Theory from Group Life.” Ethnography . 4(1):41-60.
- Fine GA, Hancock BH. The new ethnographer at work. Qualitative Research. 2017; 17 (2):260–268. [ Google Scholar ]
- Fine GA, Hallett T. Stranger and stranger: Creating theory through ethnographic distance and authority. Journal of Organizational Ethnography. 2014; 3 (2):188–203. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flick U. Qualitative research. State of the art. Social Science Information. 2002; 41 (1):5–24. [ Google Scholar ]
- Flick U. Designing qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Frankfort-Nachmias C, Nachmias D. Research methods in the social sciences. 5. London: Edward Arnold; 1996. [ Google Scholar ]
- Franzosi R. Sociology, narrative, and the quality versus quantity debate (Goethe versus Newton): Can computer-assisted story grammars help us understand the rise of Italian fascism (1919- 1922)? Theory and Society. 2010; 39 (6):593–629. [ Google Scholar ]
- Franzosi R. From method and measurement to narrative and number. International journal of social research methodology. 2016; 19 (1):137–141. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gadamer, Hans-Georg. 1990. Wahrheit und Methode, Grundzüge einer philosophischen Hermeneutik . Band 1, Hermeneutik. Tübingen: J.C.B. Mohr.
- Gans H. Participant Observation in an Age of “Ethnography” Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1999; 28 (5):540–548. [ Google Scholar ]
- Geertz C. The interpretation of cultures. New York: Basic Books; 1973. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gilbert N. Researching social life. 3. London: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaeser A. Hermeneutic institutionalism: Towards a new synthesis. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 :207–241. [ Google Scholar ]
- Glaser, Barney G., and Anselm L. Strauss. [1967] 2010. The discovery of grounded theory. Strategies for qualitative research. Hawthorne: Aldine.
- Goertz G, Mahoney J. A tale of two cultures: Qualitative and quantitative research in the social sciences. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2012. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goffman E. On fieldwork. Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1989; 18 (2):123–132. [ Google Scholar ]
- Goodwin J, Horowitz R. Introduction. The methodological strengths and dilemmas of qualitative sociology. Qualitative Sociology. 2002; 25 (1):33–47. [ Google Scholar ]
- Habermas, Jürgen. [1981] 1987. The theory of communicative action . Oxford: Polity Press.
- Hammersley M. The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research & Method in Education. 2007; 30 (3):287–305. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley, Martyn. 2013. What is qualitative research? Bloomsbury Publishing.
- Hammersley M. What is ethnography? Can it survive should it? Ethnography and Education. 2018; 13 (1):1–17. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hammersley M, Atkinson P. Ethnography . Principles in practice . London: Tavistock Publications; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heidegger M. Sein und Zeit. Tübingen: Max Niemeyer Verlag; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- Heidegger, Martin. 1988. 1923. Ontologie. Hermeneutik der Faktizität, Gesamtausgabe II. Abteilung: Vorlesungen 1919-1944, Band 63, Frankfurt am Main: Vittorio Klostermann.
- Hempel CG. Philosophy of the natural sciences. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall; 1966. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hood JC. Teaching against the text. The case of qualitative methods. Teaching Sociology. 2006; 34 (3):207–223. [ Google Scholar ]
- James W. Pragmatism. New York: Meredian Books; 1907. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jovanović G. Toward a social history of qualitative research. History of the Human Sciences. 2011; 24 (2):1–27. [ Google Scholar ]
- Kalof L, Dan A, Dietz T. Essentials of social research. London: Open University Press; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Katz J. Situational evidence: Strategies for causal reasoning from observational field notes. Sociological Methods & Research. 2015; 44 (1):108–144. [ Google Scholar ]
- King G, Keohane RO, Sidney S, Verba S. Scientific inference in qualitative research. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 1994. Designing social inquiry. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamont M. Evaluating qualitative research: Some empirical findings and an agenda. In: Lamont M, White P, editors. Report from workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation; 2004. pp. 91–95. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lamont M, Swidler A. Methodological pluralism and the possibilities and limits of interviewing. Qualitative Sociology. 2014; 37 (2):153–171. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lazarsfeld P, Barton A. Some functions of qualitative analysis in social research. In: Kendall P, editor. The varied sociology of Paul Lazarsfeld. New York: Columbia University Press; 1982. pp. 239–285. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lichterman, Paul, and Isaac Reed I (2014), Theory and Contrastive Explanation in Ethnography. Sociological methods and research. Prepublished 27 October 2014; 10.1177/0049124114554458.
- Lofland J, Lofland L. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis. 3. Belmont: Wadsworth; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lofland J, Snow DA, Anderson L, Lofland LH. Analyzing social settings. A guide to qualitative observation and analysis. 4. Belmont: Wadsworth/Thomson Learning; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Long AF, Godfrey M. An evaluation tool to assess the quality of qualitative research studies. International Journal of Social Research Methodology. 2004; 7 (2):181–196. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lundberg G. Social research: A study in methods of gathering data. New York: Longmans, Green and Co.; 1951. [ Google Scholar ]
- Malinowski B. Argonauts of the Western Pacific: An account of native Enterprise and adventure in the archipelagoes of Melanesian New Guinea. London: Routledge; 1922. [ Google Scholar ]
- Manicas P. A realist philosophy of science: Explanation and understanding. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press; 2006. [ Google Scholar ]
- Marchel C, Owens S. Qualitative research in psychology. Could William James get a job? History of Psychology. 2007; 10 (4):301–324. [ PubMed ] [ Google Scholar ]
- McIntyre LJ. Need to know. Social science research methods. Boston: McGraw-Hill; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Merton RK, Barber E. The travels and adventures of serendipity . A Study in Sociological Semantics and the Sociology of Science. Princeton: Princeton University Press; 2004. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mannay D, Morgan M. Doing ethnography or applying a qualitative technique? Reflections from the ‘waiting field‘ Qualitative Research. 2015; 15 (2):166–182. [ Google Scholar ]
- Neuman LW. Basics of social research. Qualitative and quantitative approaches. 2. Boston: Pearson Education; 2007. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragin CC. Constructing social research. The unity and diversity of method. Thousand Oaks: Pine Forge Press; 1994. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ragin, Charles C. 2004. Introduction to session 1: Defining qualitative research. In Workshop on Scientific Foundations of Qualitative Research , 22, ed. Charles C. Ragin, Joane Nagel, Patricia White. http://www.nsf.gov/pubs/2004/nsf04219/nsf04219.pdf
- Rawls, Anne. 2018. The Wartime narrative in US sociology, 1940–7: Stigmatizing qualitative sociology in the name of ‘science,’ European Journal of Social Theory (Online first).
- Schütz A. Collected papers I: The problem of social reality. The Hague: Nijhoff; 1962. [ Google Scholar ]
- Seiffert H. Einführung in die Hermeneutik. Tübingen: Franke; 1992. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. Doing qualitative research. A practical handbook. 2. London: SAGE Publications; 2005. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. A very short, fairly interesting and reasonably cheap book about qualitative research. London: SAGE Publications; 2009. [ Google Scholar ]
- Silverman D. What counts as qualitative research? Some cautionary comments. Qualitative Sociology Review. 2013; 9 (2):48–55. [ Google Scholar ]
- Small ML. “How many cases do I need?” on science and the logic of case selection in field-based research. Ethnography. 2009; 10 (1):5–38. [ Google Scholar ]
- Small, Mario L 2008. Lost in translation: How not to make qualitative research more scientific. In Workshop on interdisciplinary standards for systematic qualitative research, ed in Michelle Lamont, and Patricia White, 165–171. Washington, DC: National Science Foundation.
- Snow DA, Anderson L. Down on their luck: A study of homeless street people. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1993. [ Google Scholar ]
- Snow DA, Morrill C. New ethnographies: Review symposium: A revolutionary handbook or a handbook for revolution? Journal of Contemporary Ethnography. 1995; 24 (3):341–349. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL. Qualitative analysis for social scientists. 14. Chicago: Cambridge University Press; 2003. [ Google Scholar ]
- Strauss AL, Corbin JM. Basics of qualitative research. Techniques and procedures for developing grounded theory. 2. Thousand Oaks: Sage Publications; 1998. [ Google Scholar ]
- Swedberg, Richard. 2017. Theorizing in sociological research: A new perspective, a new departure? Annual Review of Sociology 43: 189–206.
- Swedberg R. The new 'Battle of Methods'. Challenge January–February. 1990; 3 (1):33–38. [ Google Scholar ]
- Timmermans S, Tavory I. Theory construction in qualitative research: From grounded theory to abductive analysis. Sociological Theory. 2012; 30 (3):167–186. [ Google Scholar ]
- Trier-Bieniek A. Framing the telephone interview as a participant-centred tool for qualitative research. A methodological discussion. Qualitative Research. 2012; 12 (6):630–644. [ Google Scholar ]
- Valsiner J. Data as representations. Contextualizing qualitative and quantitative research strategies. Social Science Information. 2000; 39 (1):99–113. [ Google Scholar ]
- Weber, Max. 1904. 1949. Objectivity’ in social Science and social policy. Ed. Edward A. Shils and Henry A. Finch, 49–112. New York: The Free Press.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Qualitative Research Questions
Try Qualtrics for free
How to write qualitative research questions.
11 min read Here’s how to write effective qualitative research questions for your projects, and why getting it right matters so much.
What is qualitative research?
Qualitative research is a blanket term covering a wide range of research methods and theoretical framing approaches. The unifying factor in all these types of qualitative study is that they deal with data that cannot be counted. Typically this means things like people’s stories, feelings, opinions and emotions , and the meanings they ascribe to their experiences.
Qualitative study is one of two main categories of research, the other being quantitative research. Quantitative research deals with numerical data – that which can be counted and quantified, and which is mostly concerned with trends and patterns in large-scale datasets.
What are research questions?
Research questions are questions you are trying to answer with your research. To put it another way, your research question is the reason for your study, and the beginning point for your research design. There is normally only one research question per study, although if your project is very complex, you may have multiple research questions that are closely linked to one central question.
A good qualitative research question sums up your research objective. It’s a way of expressing the central question of your research, identifying your particular topic and the central issue you are examining.
Research questions are quite different from survey questions, questions used in focus groups or interview questions. A long list of questions is used in these types of study, as opposed to one central question. Additionally, interview or survey questions are asked of participants, whereas research questions are only for the researcher to maintain a clear understanding of the research design.
Research questions are used in both qualitative and quantitative research , although what makes a good research question might vary between the two.
In fact, the type of research questions you are asking can help you decide whether you need to take a quantitative or qualitative approach to your research project.
Discover the fundamentals of qualitative research
Quantitative vs. qualitative research questions
Writing research questions is very important in both qualitative and quantitative research, but the research questions that perform best in the two types of studies are quite different.
Quantitative research questions
Quantitative research questions usually relate to quantities, similarities and differences.
It might reflect the researchers’ interest in determining whether relationships between variables exist, and if so whether they are statistically significant. Or it may focus on establishing differences between things through comparison, and using statistical analysis to determine whether those differences are meaningful or due to chance.
- How much? This kind of research question is one of the simplest. It focuses on quantifying something. For example:
How many Yoruba speakers are there in the state of Maine?
- What is the connection?
This type of quantitative research question examines how one variable affects another.
For example:
How does a low level of sunlight affect the mood scores (1-10) of Antarctic explorers during winter?
- What is the difference? Quantitative research questions in this category identify two categories and measure the difference between them using numerical data.
Do white cats stay cooler than tabby cats in hot weather?
If your research question fits into one of the above categories, you’re probably going to be doing a quantitative study.
Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions focus on exploring phenomena, meanings and experiences.
Unlike quantitative research, qualitative research isn’t about finding causal relationships between variables. So although qualitative research questions might touch on topics that involve one variable influencing another, or looking at the difference between things, finding and quantifying those relationships isn’t the primary objective.
In fact, you as a qualitative researcher might end up studying a very similar topic to your colleague who is doing a quantitative study, but your areas of focus will be quite different. Your research methods will also be different – they might include focus groups, ethnography studies, and other kinds of qualitative study.
A few example qualitative research questions:
- What is it like being an Antarctic explorer during winter?
- What are the experiences of Yoruba speakers in the USA?
- How do white cat owners describe their pets?
Qualitative research question types
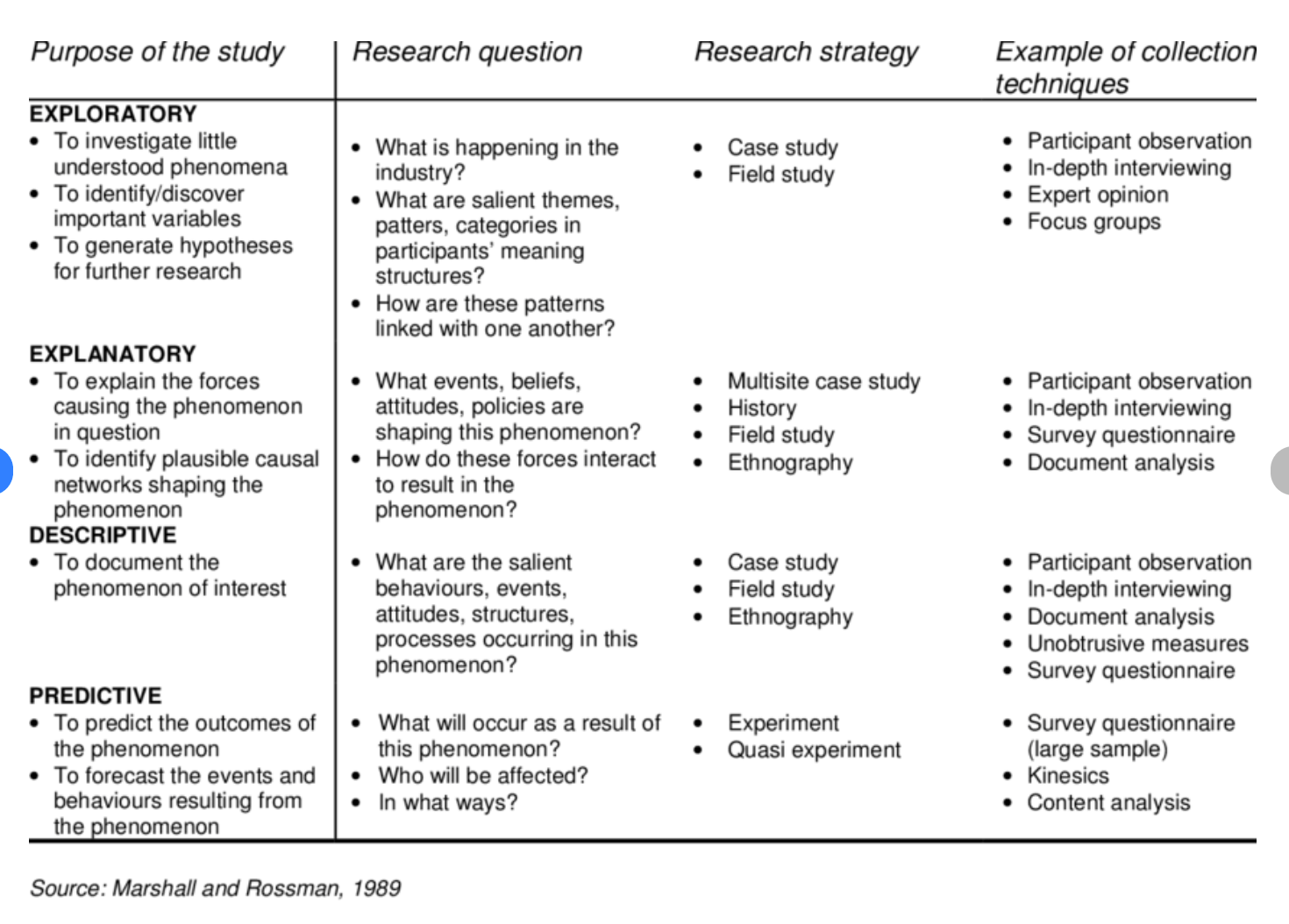
Marshall and Rossman (1989) identified 4 qualitative research question types, each with its own typical research strategy and methods.
- Exploratory questions
Exploratory questions are used when relatively little is known about the research topic. The process researchers follow when pursuing exploratory questions might involve interviewing participants, holding focus groups, or diving deep with a case study.
- Explanatory questions
With explanatory questions, the research topic is approached with a view to understanding the causes that lie behind phenomena. However, unlike a quantitative project, the focus of explanatory questions is on qualitative analysis of multiple interconnected factors that have influenced a particular group or area, rather than a provable causal link between dependent and independent variables.
- Descriptive questions
As the name suggests, descriptive questions aim to document and record what is happening. In answering descriptive questions , researchers might interact directly with participants with surveys or interviews, as well as using observational studies and ethnography studies that collect data on how participants interact with their wider environment.
- Predictive questions
Predictive questions start from the phenomena of interest and investigate what ramifications it might have in the future. Answering predictive questions may involve looking back as well as forward, with content analysis, questionnaires and studies of non-verbal communication (kinesics).
Why are good qualitative research questions important?
We know research questions are very important. But what makes them so essential? (And is that question a qualitative or quantitative one?)
Getting your qualitative research questions right has a number of benefits.
- It defines your qualitative research project Qualitative research questions definitively nail down the research population, the thing you’re examining, and what the nature of your answer will be.This means you can explain your research project to other people both inside and outside your business or organization. That could be critical when it comes to securing funding for your project, recruiting participants and members of your research team, and ultimately for publishing your results. It can also help you assess right the ethical considerations for your population of study.
- It maintains focus Good qualitative research questions help researchers to stick to the area of focus as they carry out their research. Keeping the research question in mind will help them steer away from tangents during their research or while they are carrying out qualitative research interviews. This holds true whatever the qualitative methods are, whether it’s a focus group, survey, thematic analysis or other type of inquiry.That doesn’t mean the research project can’t morph and change during its execution – sometimes this is acceptable and even welcome – but having a research question helps demarcate the starting point for the research. It can be referred back to if the scope and focus of the project does change.
- It helps make sure your outcomes are achievable
Because qualitative research questions help determine the kind of results you’re going to get, it helps make sure those results are achievable. By formulating good qualitative research questions in advance, you can make sure the things you want to know and the way you’re going to investigate them are grounded in practical reality. Otherwise, you may be at risk of taking on a research project that can’t be satisfactorily completed.
Developing good qualitative research questions
All researchers use research questions to define their parameters, keep their study on track and maintain focus on the research topic. This is especially important with qualitative questions, where there may be exploratory or inductive methods in use that introduce researchers to new and interesting areas of inquiry. Here are some tips for writing good qualitative research questions.
1. Keep it specific
Broader research questions are difficult to act on. They may also be open to interpretation, or leave some parameters undefined.
Strong example: How do Baby Boomers in the USA feel about their gender identity?
Weak example: Do people feel different about gender now?
2. Be original
Look for research questions that haven’t been widely addressed by others already.
Strong example: What are the effects of video calling on women’s experiences of work?
Weak example: Are women given less respect than men at work?
3. Make it research-worthy
Don’t ask a question that can be answered with a ‘yes’ or ‘no’, or with a quick Google search.
Strong example: What do people like and dislike about living in a highly multi-lingual country?
Weak example: What languages are spoken in India?
4. Focus your question
Don’t roll multiple topics or questions into one. Qualitative data may involve multiple topics, but your qualitative questions should be focused.
Strong example: What is the experience of disabled children and their families when using social services?
Weak example: How can we improve social services for children affected by poverty and disability?
4. Focus on your own discipline, not someone else’s
Avoid asking questions that are for the politicians, police or others to address.
Strong example: What does it feel like to be the victim of a hate crime?
Weak example: How can hate crimes be prevented?
5. Ask something researchable
Big questions, questions about hypothetical events or questions that would require vastly more resources than you have access to are not useful starting points for qualitative studies. Qualitative words or subjective ideas that lack definition are also not helpful.
Strong example: How do perceptions of physical beauty vary between today’s youth and their parents’ generation?
Weak example: Which country has the most beautiful people in it?
Related resources
Qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, business research methods 12 min read, qualitative research interviews 11 min read, market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Part 4: Using qualitative methods
17. Qualitative data and sampling
Chapter outline.
- Ethical responsibility and cultural respectfulness (7 minute read)
- Critical considerations (8 minute read)
- Find the right qualitative data to answer my research question (17 minute read)
- How to gather a qualitative sample (21 minute read)
- What should my sample look like? (9 minute read)
Content warning: examples in this chapter contain references to substance use, ageism, injustices against the Black community in research (e.g. Henrietta Lacks and Tuskegee Syphillis Study), children and their educational experiences, mental health, research bias, job loss and business closure, mobility limitations, politics, media portrayals of LatinX families, labor protests, neighborhood crime, Batten Disease (childhood disorder), transgender youth, cancer, child welfare including kinship care and foster care, Planned Parenthood, trauma and resilience, sexual health behaviors.
Now let’s change things up! In the previous chapters, we were exploring steps to create and carry out a quantitative research study. Quantitative studies are great when we want to summarize data and examine or test relationships between ideas using numbers and the power of statistics. However, qualitative research offers us a different and equally important tool. Sometimes the aim of research is to explore meaning and experience. If these are the goals of our research proposal, we are going to turn to qualitative research. Qualitative research relies on the power of human expression through words, pictures, movies, performance and other artifacts that represent these things. All of these tell stories about the human experience and we want to learn from them and have them be represented in our research. Generally speaking, qualitative research is about the gathering up of these stories, breaking them into pieces so we can examine the ideas that make them up, and putting them back together in a way that allows us to tell a common or shared story that responds to our research question. Back in Chapter 7 we talked about different paradigms.

Before plunging further into our exploration of qualitative research, I would like to suggest that we begin by thinking about some ethical, cultural and empowerment-related considerations as you plan your proposal. This is by no means a comprehensive discussion of these topics as they relate to qualitative research, but my intention is to have you think about a few issues that are relevant at each step of the qualitative process. I will begin each of our qualitative chapters with some discussion about these topics as they relate to each of these steps in the research process. These sections are specially situated at the beginning of the chapters so that you can consider how these principles apply throughout the proceeding discussion. At the end of this chapter there will be an opportunity to reflect on these areas as they apply specifically to your proposal. Now, we have already discussed research ethics back in Chapter 8 . However, as qualitative researchers we have some unique ethical commitments to participants and to the communities that they represent. Our work as qualitative researchers often requires us to represent the experiences of others, which also means that we need to be especially attentive to how culture is reflected in our research. Cultural respectfulness suggests that we approach our work and our participants with a sense of humility. This means that we maintain an open mind, a desire to learn about the cultural context of participants’ lives, and that we preserve the integrity of this context as we share our findings.
17.1 Ethical responsibility and cultural respectfulness
Learning objectives.
Learners will be able to…
- Explain how our ethical responsibilities as researchers translate into decisions regarding qualitative sampling
- Summarize how aspects of culture and identity may influence recruitment for qualitative studies
Representation
Representation reflects two important aspects of our work as qualitative researchers, who is present and how are they presented. First, we need to consider who we are including or excluding in or sample. Recruitment and sampling is especially tied to our ethical mandate as researchers to uphold the principle of justice under the Belmont Report [1] (see Chapter 6 for additional information). Within this context we need to:
- Assure there is fair distribution of risks and benefits related to our research
- Be conscientious in our recruitment efforts to support equitable representation
- Ensure that special protections to vulnerable groups involved in research activities are in place
As you plan your qualitative research study, make sure to consider who is invited and able to participate and who is not. These choices have important implications for your findings and how well your results reflect the population you are seeking to represent. There may be explicit exclusions that don’t allow certain people to participate, but there may also be unintended reasons people are excluded (e.g. transportation, language barriers, access to technology, lack of time).
The second part of representation has to do with how we disseminate our findings and how this reflects on the population we are studying. We will speak further about this aspect of representation in Chapter 21 , which is specific to qualitative research dissemination. For now, it is enough to know that we need to be thoughtful about who we attempt to recruit and how effectively our resultant sample reflects our population.
Being mindful of history
As you plan for the recruitment of your sample, be mindful of the history of how this group (and/or the individuals you may be interacting with) has been treated – not just by the research community, but by others in positions of power. As researchers, we usually represent an outside influence and the people we are seeking to recruit may have significant reservations about trusting us and being willing to participate in our study (often grounded in good historical reasons—see Chapter 6 for additional information). Because of this, be very intentional in your efforts to be transparent about the purpose of your research and what it involves, why it is important to you, as well as how it can impact the community. Also, in helping to address this history, we need to make concerted efforts to get to know the communities that we research with well, including what is important to them.
Stories as sacred: How are we requesting them?
Finally, it is worth pointing out that as qualitative researchers, we have an extra layer of ethical and cultural responsibility. While quantitative research deals with numbers, as qualitative researchers, we are generally asking people to share their stories. Stories are intimate, full of depth and meaning, and can reveal tremendous amounts about who we are and what makes us tick. Because of this, we need to take special care to treat these stories as sacred. I will come back to this point in subsequent chapters, but as we go about asking for people to share their stories, we need to do so humbly.
Key Takeaways
- As researchers, we need to consider how our participant communities have been treated historically, how we are representing them in the present through our research, and the implications this representation could have (intended and unintended) for their lives. We need to treat research participants and their stories with respect and humility.
- When conducting qualitative research, we are asking people to share their stories with us. These “data” are personal, intimate, and often reflect the very essence of who our participants are. As researchers, we need to treat research participants and their stories with respect and humility.
17.2 Critical considerations
- Assess dynamics of power in sampling design and recruitment for individual participants and participant communities
- Create opportunities for empowerment through early choice points in key research design elements
Related to the previous discussion regarding being mindful of history, we also need to consider the current dynamics of power between researcher and potential participant. While we may not always recognize or feel like we are in a position of power, as researchers we hold specialized knowledge, a particular skill set, and what we do can with the data we collect can have important implications and consequences for individuals, groups, and communities. All of these contribute to the formation of a role ascribed with power. It is important for us to consider how this power is perceived and whenever possible, how we can build opportunities for empowerment that can be built into our research design. Examples of some strategies include:
- Recruiting and meeting in spaces that are culturally acceptable
- Finding ways to build participant choice into the research process
- Working with a community advisory group during the research process (explained further in the example box below)
- Designing informative and educational materials that help to thoroughly explain the research process in meaningful ways
- Regularly checking with participants for understanding
- Asking participants what they would like to get out of their participation and what it has been like to participate in our research
- Determining if there are ways that we can contribute back to communities beyond our research (developing an ongoing commitment to collaboration and reciprocity)
While it may be beyond the scope of a student research project to address all of these considerations, I do think it is important that we start thinking about these more in our research practices. As social work researchers, we should be modeling empowerment practices in the field of social science research, but we often fail to meet this standard.
Example. A community advisory group can be a tremendous asset throughout our research process, but especially in early stages of planning, including recruitment. I was fortunate enough to have a community advisory group for one of the projects I worked on. They were incredibly helpful as I considered different perspectives I needed to include in my study, helping me to think through a respectful way to approach recruitment, and how we might make the research arrangement a bit more reciprocal so community members might benefit as well.
Intersectional identity
As qualitative researchers, we are often not looking to prove a hypothesis or uncover facts. Instead, we are generally seeking to expand our understanding of the breadth and depth of human experience. Breadth is reflected as we seek to uncover variation across participants and depth captures variation or detail within each participants’ story. Both are important for generating the fullest picture possible for our findings. For example, we might be interested in learning about people’s experience living in an assisted living facility by interviewing residents. We would want to capture a range of different residents’ experiences (breadth) and for each resident, we would seek as much detail as possible (depth). Do note, sometimes our research may only involve one person, such as in a case study . However, in these instances we are usually trying to understand many aspects or dimensions of that single case.
To capture this breadth and depth we need to remember that people are made of multiple stories formed by intersectional identities . This means that our participants never just represent one homogeneous social group. We need to consider the various aspects of our population that will help to give the most complete representation in our sample as we go about recruitment.
Identify a population you are interested in studying. This might be a population you are working with at your field placement (either directly or indirectly), a group you are especially interested in learning more about, or a community you want to serve in the future. As you formulate your question, you may draw your sample directly from clients that are being served, others in their support network, service providers that are providing services, or other stakeholders that might be invested in the well-being of this group or community. Below, list out two populations you are interested in studying and then for each one, think about two groups connected with this population that you might focus your study on.
| 1. | 1a. |
| 1b. | |
| 2. | 2a. |
| 2b. |
Next, think about what would kind of information might help you understand this group better. If you had the chance to sit down and talk with them, what kinds of things would you want to ask? What kinds of things would help you understand their perspective or their worldview more clearly? What kinds of things do we need to learn from them and their experiences that could help us to be better social workers? For each of the groups you identified above, write out something you would like to learn from their experience.
| 1 | 1a. | 1a. |
| 1b. | 1b. | |
| 2. | 2a. | 2a. |
| 2b. | 2b. |
Finally, consider how this group might perceive a request to participate. For the populations and the groups that you have identified, think about the following questions:
- How have these groups been represented in the news?
- How have these groups been represented in popular culture and popular media?
- What historical or contemporary factors might influence these group members’ opinions of research and researchers?
- In what ways have these groups been oppressed and how might research or academic institutions have contributed to this oppression?
Our impact on the qualitative process
It is important for qualitative research to thoughtfully plan for and attempt to capture our own impact on the research process. This influence that we can have on the research process represents what is known as researcher bias . This requires that we consider how we, as human beings, influence the research we conduct. This starts at the very beginning of the research process, including how we go about sampling. Our choices throughout the research process are driven by our unique values, experiences, and existing knowledge of how the world works. To help capture this contribution, qualitative researchers may plan to use tools like a reflexive journal , which is a research journal that helps the researcher to reflect on and consider their thoughts and reactions to the research process and how these may influence or shape a study (there will be more about this tool in Chapter 20 when we discuss the concept of rigor ). While this tool is not specific to the sampling process, the next few chapters will suggest reflexive journal questions to help you think through how it might be used as you develop a qualitative proposal.
Example. To help demonstrate the potential for researcher bias, consider a number of students that I work with who are placed in school systems for their field experience and choose to focus their research proposal in this area. Some are interested in understanding why parents or guardians aren’t more involved in their children’s educational experience. While this might be an interesting topic, I would encourage students to consider what kind of biases they might have around this issue.
- What expectations do they have about parenting?
- What values do they attach to education and how it should be supported in the home?
- How has their own upbringing shaped their expectations?
- What do they know about the families that the school district serves and how did they come by this information?
- How are these families’ life experiences different from their own?
The answers to these questions may unconsciously shape the early design of the study, including the research question they ask and the sources of data they seek out. For instance, their study may only focus on the behaviors and the inclinations of the families, but do little to investigate the role that the school plays in engagement and other structural barriers that might exist (e.g. language, stigma, accessibility, child-care, financial constraints, etc.).
- As researchers, we wield (sometimes subtle) power and we need to be conscientious of how we use and distribute this power.
- Qualitative study findings represent complex human experiences. As good as we may be, we are only going to capture a relatively small window into these experiences (and need to be mindful of this when discussing our findings).
In the early stages of your research process, it is a good idea to start your reflexive journal . Starting a reflexive journal is as easy as opening up a new word document, titling it and chronologically dating your entries. If you are more tactile-oriented, you can also keep your reflexive journal in paper bound journal.
To prompt your initial entry, put your thoughts down in response to the following questions:
- What led you to be interested in this topic?
- What experience(s) do you have in this area?
- What knowledge do you have about this issue and how did you come by this knowledge?
- In what ways might you be biased about this topic?
Don’t answer this last question too hastily! Our initial reaction is often—”Biased!?! Me—I don’t have a biased bone in my body! I have an open-mind about everything, toward everyone!” After all, much of our social work training directs us towards acceptance and working to understand the perspectives of others. However, WE ALL HAVE BIASES . These are conscious or subconscious preferences that lead us to favor some things over others. These preferences influence the choices we make throughout the research process. The reflexive journal helps us to reflect on these preferences, where they might stem from, and how they might be influencing our research process. For instance, I conduct research in the area of mental health. Before I became a researcher, I was a mental health clinician, and my years as a mental health practitioner created biases for me that influence my approach to research. For instance, I may be biased in perceiving mental health services as being well-intentioned and helpful. However, participants may well have very different perceptions based on their experiences or beliefs (or those of their loved ones).
17.3 Finding the right qualitative data to answer my research question
- Compare different types of qualitative data
- Begin to formulate decisions as they build their qualitative research proposal, specially in regards to selecting types of data that can effectively answer their research question
Sampling starts with deciding on the type of data you will be using. Qualitative research may use data from a variety of sources. Sources of qualitative data may come from interviews or focus groups , observations , a review of written documents, administrative data, or other forms of media, and performances. While some qualitative studies rely solely on one source of data, others incorporate a variety.
You should now be well acquainted with the term triangulation . When thinking about triangulation in qualitative research, we are often referring to our use of multiple sources of data among those listed above to help strengthen the confidence we have in our findings. Drawing on a journalism metaphor, this allows us to “fact check” our data to help ensure that we are getting the story correct. This can mean that we use one type of data (like interviews), but we intentionally plan to get a diverse range of perspectives from people we know will see things differently. In this case we are using triangulation of perspectives. In addition, we may also you a variety of different types of data, like including interviews, data from case records, and staff meeting minutes all as data sources in the same study. This reflects triangulation through types of data.
As a student conducting research, you may not always have access to vulnerable groups or communities in need, or it may be unreasonable for you to collect data from them directly due to time, resource, or knowledge constraints. Because of this, as you are reviewing the sections below, think about accessible alternative sources of data that will still allow you to answer your research question practically, and I will provide some examples along the way to get you started. In the above example, local media coverage might be a means of obtaining data that does not involve vulnerable directly collecting data from potentially vulnerable participants.

Verbal data
Perhaps the bread an d butter of t he qualitative researche r, we often rely on what people tell us as a primary source of information for qualitative studies in the form of verbal data. The researcher who schedules interviews with recipients of public assistance to capture their experience after legislation drastically changes requirements for benefits relies on the communication between the researcher and the impacted recipients of public assistance. Focus groups are another frequently used method of gathering verbal data. Focus groups bring together a group of participants to discuss their unique perspectives and explore commonalities on a given topic. One such example is a researcher who brings together a group of child welfare workers who have been in the field for one to two years to ask them questions regarding their preparation, experiences, and perceptions regarding their work.
A benefit of utilizing verbal data is that it offers an opportunity for researchers to hear directly from participants about their experiences, opinions, or understanding of a given topic. Of course, this requires that participants be willing to share this information with a researcher and that the information shared is genuine. If groups of participants are unwilling to participate in sharing verbal data or if participants share information that somehow misrepresents their feelings (perhaps because they feel intimidated by the research process), then our qualitative sample can become biased and lead to inaccurate or partially accurate findings.
As noted above, participant willingness and honesty can present challenges for qualitative researchers. You may face similar challenges as a student gathering verbal data directly from participants who have been personally affected by your research topic. Because of this, you might want to gather verbal data from other sources. Many of the students I work with are placed in schools. It is not feasible for them to interview the youth they work with directly, so frequently they will interview other professionals in the school, such as teachers, counselors, administration, and other staff. You might also consider interviewing other social work students about their perceptions or experiences working with a particular g roup.
Again, because it may be problematic or unrealistic for you to obtain verbal data directly from vulnerable groups as a student researcher, you might consider gathering verbal data from the following sources:
- Interviews and focus groups with providers, social work students, faculty, the general public, administrators, local politicians, advocacy groups
- Public blogs of people invested in your topic
- Publicly available transcripts from interviews with experts in the area or people reporting experiences in popular media
Make sure to consult with your professor to ensure that what you are planning will be realistic for the purposes of your study.

Observational data
As researcher s, we sometimes rely on our own powers of observation to gather data on a particular topic. We may observe a person’s behavior, an interaction, setting, context, and maybe even our own reactions to what we are observing (i.e. what we are thinking or feeling). When observational data is used for quantitative purposes, it involves a count, such as how many times a certain behavior occurs for a child in a classroom. However, when observational data is used for qualitative purposes, it involves the researcher providing a detailed description. For instance, a qualitative researcher may conduct observations of how mothers and children interact in child and adolescent cancer units, and take notes about where exchanges take place, topics of conversation, nonverbal information, and data about the setting itself – what the unit looks like, how it is arranged, the lighting, photos on the wall, etc.
Observational data can provide important contextual information that may not be captured when we rely solely on verbal data. However, using this form of data requires us, as researchers, to correctly observe and interpret what is going on. As we don’t have direct access to what participants may be thinking or feeling to aid us (which can lead us to misinterpret or create a biased representation of what we are observing), our take on this situation may vary drastically from that of another person observing the same thing. For instance, if we observe two people talking and one begins crying, how do we know if these are tears of joy or sorrow? When you observe someone being abrupt in a conversation, I might interpret that as the person being rude while you might perceive that the person is distracted or preoccupied with something. The point is, we can’t know for sure. Perhaps one of the most challenging aspects of gathering observational data is collecting neutral, objective observations, that are not laden with our subjective value judgments placed on them. Students often find this out in class during one of our activities. For this activity, they have to go out to public space and write down observations about what they observe. When they bring them back to class and we start discussing them together, we quickly realize how often we make (unfounded) judgments. Frequent examples from our class include determining the race/ethnicity of people they observe or the relationships between people, without any confirmational knowledge. Additionally, they often describe scenarios with adverbs and adjectives that often reflect judgments and values they are placing on their data. I’m not sharing this to call them out, in fact, they do a great job with the assignment. I just want to demonstrate that as human beings, we are often less objective than we think we are! These are great examples of research bias.
Again, gaining access to observational spaces, especially private ones, might be a challenge for you as a student. As such, you might consider if observing public spaces might be an option. If you do opt for this, make sure you are not violating anyone’s right to privacy. For instance, gathering information in a narcotics anonymous meeting or a religious celebration might be perceived as offensive, invasive or in direct opposition to values (like anonymity) of participants. When making observations in public spaces be careful not to gather any information that might identify specific individuals or organizations. Also, it is important to consider the influence your presence may have on a community, particularly if your observation makes you stand out among those typically present in that setting. Always consider the needs of the individual and the communities in formulating a plan for observing public behavior. Public spaces might include commercial spaces or events open to the public as well as municipal parks. Below we will have an expanded discussion about different varieties of non-probability sampling strategies that apply to qualitative research. Recruiting in public spaces like these may work for strategies such as convenience sampling or quota sampling , but would not be a good choice for snowball sampling or purposive sampling .
As with the cautionary note for student researchers under verbal data, you may experience restricted access to spaces in which you are able to gather observational data. However, if you do determine that observational data might be a good fit for your student proposal, you might consider the following spaces:
- Shopping malls
- Public parks or beaches
- Public meetings or rallies
- Public transportation
Artifacts (documents & other media)
Existing artifacts can also be very useful for the qualitative researcher. Examples include newspapers, blogs, websites, podcasts, television shows, movies, pictures, video recordings, artwork, and live performances. While many of these sources may provide indirect information on a topic, this information can still be quite valuable in capturing the sentiment of popular culture and thereby help researchers enhance their understanding of (dominant) societal values and opinions. Conversely, researchers can intentionally choose to seek out divergent, unique or controversial perspectives by searching for artifacts that tend to take up positions that differ from the mainstream, such as independent publications and (electronic) newsletters. While we will explore this further below, it is important to understand that data and research, in all its forms, is political. Among many other purposes, it is used to create, critique, and change policy; to engage in activism; to support and refute how organizations function; and to sway public opinion.
When utilizing documents and other media as artifacts, researchers may choose to use an entire source (such as a book or movie), or they may use a segment or portion of that artifact (such as the front-page stories from newspapers, or specific scenes in a television series). Your choice of which artifacts you choose to include will be driven by your question, and remember, you want your sample of artifacts to reflect the diversity of perspectives that may exist in the population you are interested in. For instance, perhaps I am interested in studying how various forms of media portray substance use treatment. I might intentionally include a range of liberal to conservative views that are portrayed across a number of media sources.
As qualitative researchers using artifacts, we often need to do some digging to understand the context of said artifact. We do this because data is almost always affiliated or aligned with some position (again, data is political). To help us consider this, it may be helpful to reflect on the following questions:
- Who owns the artifact or where is it housed
- What values does the owner (organization or person) hold
- How might the position or identity of the owner influence what information is shared or how it is portrayed
- What is the purpose of the artifact
- Who is the audience for which the artifact is intended
Answers to questions such as these can help us to b etter under stand and give meaning to the content of the artifacts. Content is the substance of the artifact (e.g. the wor ds, picture, scene). While c ontext is the circumstances surrounding content. Both work together to help provide meaning, and further understanding of what can be derived from an artifact. As an example to illustrate this point, let’s say that you are including meeting minutes from an organizing network as a source of data for your study. The narrative description in these minutes will certainly be important, however, they may not tell the whole story. For instance, you might not know from the text that the organization has recently voted in a new president and this has created significant division within the network. Knowing this information might help you to interpret the agenda and the discussion contained in the minutes very differently.
As student researchers, using documents and other artifacts may be a particularly appealing source of data for your study. This is because this data already exists (you aren’t creating new data) and depending on what you select, it might be relatively easy to access. Examples of utilizing existing artifacts might include studying the cultural context of movie portrayals of Latinx families or analyzing publicly available town hall meeting minutes to explore expressions of social capital. Below is a list of sources of data from documents or other media sources to consider for your student proposal:
- Movies or TV shows
- Music or music videos
- Public blogs
- Policies or other organizational documents
- Meeting minutes
- Comments in online forums
- Books, newspapers, magazines, or other print/virtual text-based materials
- Recruitment, training, or educational materials
- Musical or artistic expressions
Finally, Photovoice is a technique that merges pictures with narrative (word or voice) data that helps interpret the meaning or significance of the visual. Photovoice is often used for qualitative work that is conducted as part of Community Based Participatory Research (CBPR), wherein community members act as both participants and as co-researchers. These community members are provided with a means of capturing images that reflect their understanding of some topic, prompt or question, and then they are asked to provide a narrative description or interpretation to help give meaning to the image(s). Both the visual and n arrative information are used as qualitative data to include in the study. Dissemination of Photovoice projects often involve a public display of the works, such as through a demonstration or art exhibition to raise awareness or to produce some specific change that is desired by participants. Because this form of study is often intentionally persuasive in nature, we need to recognize that this form of data will be inherently subjective. As a student, it may be particularly challenging to implement a Photovoice project, especially due to its time-intensive nature, as well as the additional commitments of needing to engage, train, and collaborate with community partners.
| Verbal | Strengths Challenges | |
| Observational | Observations in: | Strengths Challenges |
| Documents & Other Media | Strengths Challenges |
How many kinds of data?
You will need to consider whether you will rely on one kind of data or multiple. While many qualitative studies solely use one type of data, such as interviews or focus groups, others may use multiple sources. The decision to use multiple sources is often made to help strengthen the confidence we have in our findings or to help us to produce a richer, more detailed description of our results. For instance, if we are conducting a case study of what the family experience is for a child with a very rare disorder like Batten Disease , we may use multiple sources of data. These can include observing family and community interactions, conducting interviews with family members and others connected to the family (such as service providers,) and examining journal entries families were asked to keep over the course of the study. By collecting data from a variety of sources such as this, we can more broadly represent a range of perspectives when answering our research question, which will hopefully provide a more holistic picture of the family experience. However, if we are trying to examine the decision-making processes of adult protective workers, it may make the most sense to rely on just one type of data, such as interviews with adult protective workers.
- There are numerous types of qualitative data (verbal, observational, artifacts) that we may be able to access when planning a qualitative study. As we plan, we need to consider the strengths and challenges that each possess and how well each type might answer our research question.
- The use of multiple types of qualitative data does add complexity to a study, but this complication may well be worth it to help us explore multiple dimensions of our topic and thereby enrich our findings.
Reflexive Journal Entry Prompt
For your next entry, consider responding to the following:
- What types of data appeal to you?
- Why do you think you are drawn to them?
- How well does this type of data “fit” as a means of answering your question? Why?
17.4 How to gather a qualitative sample
- Compare and contrast various non-probability sampling approaches
- Select a sampling strategy that ideologically fits the research question and is practical/actionable
Before we launch into how to plan our sample, I’m going to take a brief moment to remind us of the philosophical basis surrounding the purpose of qualitative research—not to punish you, but because it has important implications for sampling.
Nomothetic vs. idiographic
As a quick reminder, as we discussed in Chapter 8 idiographic research aims to develop a rich or deep understanding of the individual or the few. The focus is on capturing the uniqueness of a smaller sample in a comprehensive manner. For example, an idiographic study might be a good approach for a case study examining the experiences of a transgender youth and her family living in a rural Midwestern state. Data for this idiographic study would be collected from a range of sources, including interviews with family members, observations of family interactions at home and in the community, a focus group with the youth and her friend group, another focus group with the mother and her social network, etc. The aim would be to gain a very holistic picture of this family’s experiences.
On the other hand, nomothetic research is invested in trying to uncover what is ‘true’ for many. It seeks to develop a general understanding of a very specific relationship between variables. The aim is to produce generalizable findings, or findings that apply to a large group of people. This is done by gathering a large sample and looking at a limited or restricted number of aspects. A nomothetic study might involve a national survey of heath care providers in which thousands of providers are surveyed regarding their current knowledge and comp etence in treating transgender individuals. It would gather data from a very large number of people, and attempt to highlight some general findings across this population on a very focused topic.
Idiographic and nomothetic research represent two different research categories existing at opposite extremes on a continuum. Qualitative research generally exists on the idiographic end of this continuum. We are most often seeking to obtain a rich, deep, detailed understanding from a relatively small group of people.
Non-probability sampling
Non-probability sampling refers to sampling techniques for which a person’s (or event’s) likelihood of being selected for membership in the sample is unknown. Because we don’t know the likelihood of selection, we don’t know whether a sample represents a larger population or not. But that’s okay, because representing the population is not the goal of nonprobability samples. That said, the fact that nonprobability samples do not represent a larger population does not mean that they are drawn arbitrarily or without any specific purpose in mind. We typically use nonprobability samples in research projects that are qualitative in nature. We will examine several types of nonprobability samples. These include purposive samples, snowball samples, quota samples, and convenience samples.
Convenience or availability
Convenience sampling, also known as availability sampling, is a nonprobability sampling strategy that is employed by both qualitative and quantitative researchers. To draw a convenience sample, we would simply collect data from those people or other relevant elements to which we have the most convenient access. While convenience samples offer one major benefit—convenience—we should be cautious about generalizing from research that relies on convenience samples because we have no confidence that the sample is representative of a broader population. If you are a social work student who needs to conduct a research project at your field placement setting and you decide to conduct a focus group with the staff at your agency, you are using a convenience sampling approach – you are recruiting participants that are easily accessible to you. In addition, if you elect to analyze existing data that your social work program has collected as part of their graduation exit surveys, you are using data that you readily have access to for your project; again, you have a convenience sample. The vast majority of students I work with on their proposal design rely on convenience data due to time constraints and limited resources.
To draw a purposive sample, we begin with specific perspectives or purposive criteria in mind that we want to examine. We would then seek out research participants who cover that full range of perspectives. For example, if you are studying mental health supports on your campus, you may want to be sure to include not only students, but mental health practitioners and student affairs administrators as well. You might also select students who currently use mental health supports, those who dropped out of supports, and those who are waiting to receive supports. The “purposive” part of purposive sampling comes from selecting specific participants on purpose because you already know they have certain characteristics—being an administrator, dropping out of mental health supports, for example—that you need in your sample.
Note that these differ from inclusion criteria , which are more general requirements a person must possess to be a part of your sample; to be a potential participant that may or may not be sampled. For example, one of the inclusion criteria for a study of your campus’ mental health supports might be that participants had to have visited the mental health center in the past year. That differs from purposive sampling. In purposive sampling, you know characteristics of individuals and recruit them because of those characteristics. For example, I might recruit Jane because she stopped seeking supports this month, because she has worked at the center for many years, and so forth.
Also, it’s important to recognize that purposive sampling requires you to have prior information about your participants before recruiting them because you need to know their perspectives or experiences before you know whether you want them in your sample. This is a common mistake that many students make. What I often hear is, “I’m using purposive sampling because I’m recruiting people from the health center,” or something like that. That’s not purposive sampling. In most instances they really mean they are going to use convenience sampling-taking whoever they can recruit that fit the inclusion criteria (i.e. have attended the mental health center). Purposive sampling is recruiting specific people because of the various characteristics and perspectives they bring to your sample. Imagine we were creating a focus group. A purposive sample might gather clinicians, patients, administrators, staff, and former patients together so they can talk as a group. Purposive sampling would seek out people that have each of those attributes.
If you are considering using a purposive sampling approach for your research proposal, you will need to determine what your purposive criteria involves. There are a range of different purposive strategies that might be employed, including: maximum variation , typical case , extreme case , or political case , and you want to be thoughtful in thinking about which one(s) you select and why.
| Case(s) selected to represent a range of very different perspectives on a topic | You interview student leaders from the schools of social work, business, the arts, math & science, education, history & anthropology and health studies to ensure that you have the perspective of a variety of disciplines | |
| Case(s) selected to reflect a commonly held perspective. | You interview a child welfare worker specifically because many of their characteristics fit the state statistical profile for providers in that service area. | |
| Case(s) selected to represent extreme or underrepresented perspectives. | You examine websites devoted to rare cancer survivor support. | |
| Case(s) selected to represent a contemporary politicized issue | You analyze media interviews with Planned Parenthood providers, employees, and clients from 2010 to present. | |
| Case(s) selected based on specialized content knowledge or expertise | You are interested in studying resilience in trauma providers, so you research and reach out to a handful of authorities in this area. | |
| Case(s) selected based on their representation of a specific theoretical orientation or some aspect of a given theory | You are interested in studying how training methods vary by practitioner according to their theoretical orientation. You specifically reach out to a clinician who identifies as a Cognitive Behavioral clinician, one who identifies as Bowenian, and one who identifies as Structural Family. | |
| Case(s) selected based on the likelihood that the case will yield the desired information | You examine a public gaming network forum on social media to see how participants offer support to one another. |
It can be a bit tricky determining how to approach or formulate your purposive cases. Below are a couple additional resources to explore this strategy further.
For more information on purposive sampling consult this webpage from Laerd Statistics on purposive sampling and this webpage from the University of Connecticut on education research .
When using snowball sampling , we might know one or two people we’d like to include in our study but then we have to rely on those initial participants to help identify additional participants. Thus, our sample builds and grows as the study continues, much as a snowball builds and becomes larger as it rolls through the snow. Snowball sampling is an especially useful strategy when you wish to study a stigmatized group or behavior. These groups may have limited visibility and accessibility for a variety of reasons, including safety.
Malebranche and colleagues (2010) [5] were interested in studying sexual health behaviors of Black, bisexual men. Anticipating that this may be a challenging group to recruit, they utilized a snowball sampling approach. They recruited initial contacts through activities such as advertising on websites and distributing fliers strategically (e.g. barbershops, nightclubs). These initial recruits were compensated with $50 and received study information sheets and five contact cards to distribute to people in their social network that fit the study criteria. Eventually the research team was able to recruit a sample of 38 men who fit the study criteria.
Snowball sampling may present some ethical quandaries for us. Since we are essentially relying on others to help advertise for us, we are giving up some of our control over the process of recruitment. We may be worried about coercion, or having people put undue pressure to have others’ they know participate in your study. To help mitigate this, we would want to make sure that any participant we recruit understands that participation is completely voluntary and if they tell others about the studies, they should also make them aware that it is voluntary, too. In addition to coercion, we also want to make sure that people’s privacy is not violated when we take this approach. For this reason, it is good practice when using a snowball approach to provide people with our contact information as the researchers and ask that they get in touch with us, rather than the other way around. This may also help to protect again potential feelings of exploitation or feeling taken advantage of. Because we often turn to snowball sampling when our population is difficult to reach or engage, we need to be especially sensitive to why this is. It is often because they have been exploited in the past and participating in research may feel like an extension of this. To address this, we need to have a very clear and transparent informed consent process and to also think about how we can use or research to benefit the people we work in the most meaningful and tangible ways.
Quota sampling is another nonprobability sampling strategy. This type of sampling is actually employed by both qualitative and quantitative researchers, but because it is a nonprobability method, we’ll discuss it in this section. When conducting quota sampling, we identify categories that are important to our study and for which there is likely to be some variation. Subgroups are created based on each category and the researcher decides how many people (or whatever element happens to be the focus of the research) to include from each subgroup and collects data from that number for each subgroup. To demonstrate, perhaps we are interested in studying support needs for children in the foster care system. We decide that we want to examine equal numbers (seven each) of children placed in a kinship placement, a non-kinship foster placement, group home, and residential placements. We expect that the experiences and needs across these settings may differ significantly, so we want to have good representation of each one, thus setting a quota of seven for each type of placement.
| You gather data from whatever cases/people/documents happen to be convenient | |
| You seek out elements that meet specific criteria, representing different perspectives | |
| You rely on participant referrals to recruit new participants | |
| You select a designated number of cases from specified subgroups |
As you continue to plan for your proposal, below you will find some of the strengths and challenges presented by each of these types of sampling.
| Allows us to draw sample from participants who are most readily available/accessible | Sample may be biased and may represent limited or skewed diversity in characteristics of participants | |
| Ensures that specific expertise, positions, or experiences are represented in sample participants | It may be challenging to define purposive criteria or to locate cases that represent these criteria; restricts our potential sampling pool | |
| Accesses participant social network and community knowledge Can be helpful in gaining access to difficult to reach populations | May be hard to locate initial small group of participants, concerns over privacy—people might not want to share contacts, process may be slow or drawn-out | |
| Helps to ensure specific characteristics are represented and defines quantity of each | Can be challenging to fill quotas, especially for subgroups that might be more difficult to locate or reluctant to participate |
Wait a minute, we need a plan!
Both qualitative and quantitative research should be planful and systematic. We’ve actually covered a lot of ground already and before we get any further, we need to start thinking about what the plan for your qualitative research proposal will look like. This means that as you develop your research proposal, you need to consider what you will be doing each step of the way: how you will find data, how you will capture it, how you will organize it, and how you will store it. If you have multiple types of data, you need to have a plan in place for each type. The plan that you develop is your data collection protocol . If you have a team of researchers (or are part of a research team), the data collection protocol is an important communication tool, making sure that everyone is clear what is going on as the research proceeds. This plan is important to help keep you and others involved in your research consistent and accountable. Throughout this chapter and the next ( Chapter 18 —qualitative data gathering) we will walk through points you will want to include in your data collection protocol. While I’ve spent a fair amount of time talking about the importance of having a plan here, qualitative design often does embrace some degree of flexibility. This flexibility is related to the concept of emergent design that we find in qualitative studies. Emergent design is the idea that some decision in our design will be dynamic and fluid as our understanding of the research question evolves. The more we learn about the topic, the more we want to understand it thoroughly.
A research protocol is a document that not only defines your research project and its aims, but also comprehensively plans how you will carry it out. If this sounds like the function of a research proposal, you are right, they are similar. What differentiates a protocol from a proposal is the level of detail. A proposal is more conceptual; a protocol is more practical (right down to the dollars and cents!). A protocol offers explicit instructions for you and your research team, any funders that may be involved in your research, and any oversight bodies that might be responsible for overseeing your study. Not every study requires a research protocol, but what I’m suggesting here is that you consider constructing at least a limited one to help though the decisions you will need to make to construct your qualitative study.
Al-Jundi and Sakka (2016) [6] provide the following elements for a research protocol :
- What is the question? (Hypothesis) What is to be investigated?
- Why is the study important (Significance)
- Where and when will it take place?
- What is the methodology? (Procedures and methods to be used).
- How are you going to implement it? (Research design)
- What is the proposed time table and budget?
- What are the resources required (technical, scientific, and financial)?
While your research proposal in its entirety will focus on many of these areas, our attention for developing your qualitative research protocol will hone in on the two highlighted above. As we go through these next couple chapters, there will be a number of exercises that walk you though decision points that will form your qualitative research protocol.
To begin developing your qualitative research protocol:
- Select the question you have decided is the best to frame your research proposal.
- Write a brief paragraph about the aim of your study, ending it with the research question you have selected.
Here are a few additional resources on developing a research protocol:
Cameli et al., (2018) How to write a research protocol: Tips and tricks .
Ohio State University, Institutional Review Board (n.d.). Research protocol .
World Health Organization (n.d.). Recommended format for a research protocol .
Decision Point: What types of data will you be using?
- Why is this a good choice, given your research question?
- If so, provide support for this decision.
Decision Point: Which non-probability sampling strategy will you employ?
- Why is this is a good fit?
- What steps might your take to address these challenges?
Recruiting strategies
Much like quantitative research, recruitment for qualitative studies can take many different approaches. When considering how to draw your qualitative sample, it may be helpful to first consider which of these three general strategies will best fit your research question and general study design: public, targeted, or membership-based. While all will lead to a sample, the process for getting you there will look very different, depending on the strategy you select.
Taking a public approach to recruitment offers you access to the broadest swath of potential participants. With this approach, you are taking advantage of public spaces in an attempt to gain the attention of the general population of people that frequent that space so that they can learn about your study. These spaces can be in-person (e.g. libraries, coffee shops, grocery stores, health care settings, parks) or virtual (e.g. open chat forums, e-bulletin boards, news feeds). Furthermore, a public approach can be static (such as hanging a flier), or dynamic (such as talking to people and directly making requests to participate). While a public approach may offer broad coverage in that it attempts to appeal to an array of people, it may be perceived as impersonal or easily able to be overlooked, due to the potential presence of other announcements that may be featured in public spaces. Public recruitment is most likely to be associated with convenience or quota sampling and is unlikely to be used with purposive or snowball sampling, where we would need some advance knowledge of people and the characteristics they possess.
As an alternative, you may elect to take a targeted approach to recruitment. By targeting a select group, you are restricting your sampling frame to those individuals or groups who are potentially most well-suited to answer your research question. Additionally, you may be targeting specific people to help craft a diverse sample, particularly with respect to personal characteristics and/or opinions.
You can target your recruitment through the use of different strategies. First, you might consider the use of knowledgeable and well-connected community members. These are people who may possess a good amount of social capital in their community, which can aid in recruitment efforts. If you are considering the use of community members in this role, make sure to be thoughtful in your approach, as you are essentially asking them to share some of their social capital with you. This means learning about the community or group, approaching community members with a sense of humility, and making sure to demonstrate transparency and authenticity in your interactions. These community members may also be champions for the topic you are researching. A champion is someone who helps to draw the interest of a particular group of people. The champion often comes from within the group itself. As an example, let’s say you’re interested in studying the experiences of family members who have a loved one struggling with substance use. To aid in your recruitment for this study, you enlist the help of a local person who does a lot of work with Al-Anon, an organization facilitating mutual support groups for individuals and families affected by alcoholism.
A targeted approach can certainly help ensure that we are talking to people who are knowledgeable about the topic we are interested in, however, we still need to be aware of the potential for bias. If we target our recruitment based on connection to a particular person, event, or passion for the topic, these folks may share information that they think is viewed as favorable or that disproportionately reflects a particular perspective. This phenomenon is due to the fact that we often spend time with people who are like-minded or share many of our views. A targeted approach may be helpful for any type of non-probability sampling, but can be especially useful for purposive, quota, or snowball sampling, where we are trying to access people or groups of people with specific characteristics or expertise.
Membership-based
Finally, you might consider a membership-based approach . This approach is really a form of targeted recruitment, but may benefit from some individual attention. When using a membership-based approach, your sampling frame is the membership list of a particular organization or group. As you might have guessed, this organization or group must be well-suited for helping to answer your research question. You will need permission to access membership, and the identity of the person authorized to grant permission will depend on the organizational structure. When contacting members regarding recruitment, you may consider using directories, newsletters, listservs or membership meetings. When utilizing a membership-based approach, we often know that members possess specific inclusion criteria we need, however, because they are all associated with that particular group or organization, they may be homogenous or like-minded in other ways. This may limit the diversity in our sample and is something to be mindful of when interpreting our findings. Membership-based recruiting can be helpful when we have a membership group that fulfills our inclusion criteria. For instance, if you want to conduct research with social workers, you might attempt to recruit through the NASW membership distribution list (but this access will come with stipulations and a price tag). Membership-based recruitment may be helpful for any non-probability sampling approach, given that the membership criteria and study inclusion criteria are a close fit. Table 17.5 offers some additional considerations for each of these strategies with examples to help demonstrate sources that might correspond with them.
| Public | Strengths: Easier to gain access; Exposure to large numbers of people Challenges: Can be impersonal, Difficult to cultivate interest | Advertising in public events & spaces Accessing materials in local libraries or museums Finding public web-based resources and sources of data (websites, blogs, open forums)
|
| Targeted | Strengths: Prior knowledge of potential audience, More focused use of resources Challenges: May be hard to locate/access target group(s), Groups may be suspicious of/or resistant to being targeted | Working with advocacy group for issue you are studying to aid recruitment Contacting local expert (historian) to help you locate relevant documents Advertising in places that your population may frequent
|
| Membership-Based | Strengths: Shared interest (through common membership), Potentially existing infrastructure for outreach Challenges: Organization may be highly sensitive to protecting members, Members may be similar in perspectives and limit diversity of ideas | Membership newsletters Listserv or Facebook groups Advertising at membership meetings or events |
- Qualitative research predominately relies on non-probability sampling techniques. There are a number of these techniques to choose from (convenience/availability, purposive, snowball, quota), each with advantages and limitations to consider. As we consider these, we need to reflect on both our research question and the resources we have available to us in developing a sampling strategy.
- As we consider where and how we will recruit our sample, there are a range of general approaches, including public, targeted, and membership-based.
Decision Point: How will you recruit or gain access to your sample?
- If you are recruiting people, how will you identify them? If necessary (and it often is), how will gain permission to do this?
- If you are using documents or other artifacts for your study, how will you gain access to these? If necessary (and it often is), how will gain permission to do this?
17.5 What should my sample look like?
- Explain key factors that influence the makeup of a qualitative sample
- Develop and critique a sampling strategy to support their qualitative proposal
Once you have started your recruitment, you also need to know when to stop. Knowing when to stop recruiting for a qualitative research study generally involves a dynamic and reflective process. This means that you will actively be involved in a process of recruiting, collecting data, beginning to review your preliminary data, and conducting more recruitment to gather more data. You will continue this process until you have gathered enough data and included sufficient perspectives to answer your research question in rich and meaningful way.
The sample size of qualitative studies can vary significantly. For instance, case studies may involve only one participant or event, while some studies may involve hundreds of interviews or even thousands of documents. Generally speaking, when compared to quantitative research, qualitative studies have a considerably smaller sample. Your decision regarding sample size should be guided by a few considerations, described below.
Amount of data
When gathering quantitative data, the amount of data we are gathering is often specified at the start (e.g. a fixed number of questions on a survey or a set number of indicators on a tracking form). However, when gathering qualitative data, we are often asking people to expand on and explore their thoughts and reactions to certain things. This can produce A LOT of data. If you have ever had to transcribe an interview (type out the conversation while listening to an audio recorded interview), you quickly learn that a 15-minute discussion turns into many pages of dialogue. As such, each interview or focus group you conduct represents multi-page transcripts, all of which becomes your data. If you are conducting interviews or focus groups, y ou will know you have collected enough data from each interaction when you have covered all your questions and allowed the participant(s) to share any and all ideas they have related to the topic. If you are using observational data, you need to spend sufficient time making observations and capturing data to offer a genuine and holistic representation of the thing you are observing (at least to the best of your ability). When using documents and other sources of media, again, you want to ensure that diverse perspectives are represented through your artifact choices so that your data reflects a well-rounded representation of the issue you are studying. For any of these data sources, this involves a judgment call on the researcher’s part. Your judgment should be informed by what you have read in the existing literature and consultation with your professor.
As part of your analysis, you will likely eventually break these larger hunks of data apart into words or small phrases, giving you potentially thousands of pieces of data. If you are relying on documents or other artifacts, the amount of data contained in each of these pieces is determined in advance, as they already exist. However, you will need to determine how many to include. With interviews, focus groups, or other forms of data generation (e.g. taking pictures for a photovoice project), we don’t necessarily know how much data will be generated with each encounter, as it will depend on the questions that are asked, the information that is shared, and how well we capture it.
Type of study
A variety of types of qualitative studies will be discussed in greater detail in Chapter 22 . While you don’t necessarily need to have an extensive understanding of them all at this point in time, it is important that you understand which of the different design types are best for answering certain research questions. For instance, if our question involves understanding some type of experience, that is often best answered by a phenomenological design. Or, if we want to better understand some process, a grounded theory study may be best suited. While there are no hard and fast rules regarding qualitative sample size, each of these different types of designs has different guidelines for what is considered an acceptable or reasonable number to include in your sample. So drawing on the previous examples, your grounded theory study might include 45 participants because you need more people to gain a clearer picture of each step of the process, while your phenomenological study includes 20 because that provides a good representation of the experience you are interested in. Both would be reasonable targets based on the respective study design type. So as you consider your research question and which specific type of qualitative design this leads you to, you will need to do some investigation to see what size samples are recommended for that particular type of qualitative design.
Diversity of perspectives
As you consider your research question, you also may want to think about the potential variation in how your study population might view this topic. If you are conducting a case study of one person, this obviously isn’t a concern, but if you are interested in exploring a range of experiences, you want to plan to intentionally recruit so this level of diversity is reflected in your sample. The level of variation you seek will have direct implications for how big your sample might be. In the example provided above in the section on quota sampling, we wanted to ensure we had equal representation across a host of placement dispositions for children in foster care. This helped us define our target sample size: (4) settings a quota of (7) participants from each type of setting = a target sample size of (28).

In Chapter 18 , we will be talking about different approaches to data gathering, which may help to dictate the range of perspectives you want to represent. For instance, if you conduct a focus group, you want all of your participants to have some experience with the thing that you are studying, but you hope that their perspectives differ from one another. Furthermore, you may want to avoid groups of participants who know each other well in the same focus group (if possible), as this may lead to groupthink or level of familiarity that doesn’t really encourage differences being expressed. Ideally, we want to encourage a discussion where a variety of ideas are shared, offering a more complete understanding of how the topic is experienced. This is true in all forms of qualitative data, in that your findings are likely to be more well-rounded and offer a broader understanding fo the issue if you recruit a sample with diverse perspectives.
Finally, the concept of saturation has important implications for both qualitative sample size and data analysis. To understand the idea of saturation, it is first important to understand that unlike most quantitative research, with qualitative research we often at least begin the process of data analysis while we are still actively collecting data. This is called an iterative approach to data analysis. So, if you are a qualitative researcher conducting interviews, you may be aiming to complete 30 interviews. After you have completed your first five interviews, you may begin reviewing and coding (a term that refers to labeling the different ideas found in your transcripts) these interviews while you are still conducting more interviews. You go on to review each new interview that you conduct and code it for the ideas that are reflected there. Eventually, you will reach a point where conducting more interviews isn’t producing any new ideas, and this is the point of saturation. Reaching saturation is an indication that we can stop data collection. This may come before or after you hit 30, but as you can see, it is driven by the presence of new ideas or concepts in your interviews, not a specific number.
This chapter represents our transition in the text to a focus on qualitative methods in research. Throughout this chapter we have explored a number of topics including various types of qualitative data, approaches to qualitative sampling, and some considerations for recruitment and sample composition. It bears repeating that your plan for sampling should be driven by a number of things: your research question, what is feasible for you, especially as a student researcher, best practices in qualitative research. Finally, in subsequent chapters, we will continue the discussion about reflexivity as it relates to the qualitative research process that we began here.
- The composition of our qualitative sample comes with some important decisions to consider, including how large should our sample be and what level and type of diversity it should reflect. These decisions are guided by the purposes or aims of our study, as well as access to resources and our population.
- The concept of saturation is important for qualitative research. It helps us to determine when we have sufficiently collected a range of perspectives on the topic we are studying.
Decision Point(s): What should your sample look like (sample composition)?
- If so, how many?
- How was this number determined?
- OR will you use the concept of saturation to determine when to stop?
- What supports your decision in regards to the previous question?
This isn’t so much a decision point, but a chance for you to reflect on the choices you’ve made thus far in your protocol with regards to your: (1) ethical responsibility, (2) commitment to cultural humility, and (3) respect for empowerment of individuals and groups as a social work researcher. Think about each of the decisions you’ve made thus far and work across this grid to identify any important considerations that you need to take into account.
You have been prompted to make a number of choices regarding how you will proceed with gathering your qualitative sample. Based on what you have learned and what you are planning, respond to the following questions below.
- What are the strengths of your sampling plan in respect to being able to answer your qualitative research question?
- How feasible is it for you, as a student researcher, to be able to carry out your sampling plan?
- What reservations or questions do you still need to have answered to adequately plan for your sample?
- What excites you about your proposal thus far?
- What worries you about your proposal thus far?
Media Attributions
- book lights © KAROLINA GRABOWSKA is licensed under a CC BY-ND (Attribution NoDerivatives) license
- women having a conversation © Andrea Piacquadio is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- magnifying-glass-1020141_960_720 © Peggy Marco is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- content context © Cory Cummings
- idiographic vs. nomothetic © Cory Cummings
- Giant_snowball_Oxford © Kamyar Adl is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- target © bavillo13 is licensed under a CC0 (Creative Commons Zero) license
- qual data recruit process © Cory Cummings
- 7419840024_8dff7228cb_b © Free Press/Free Press Action Fund's Photostream is licensed under a CC BY-NC-SA (Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike) license
- National Commission for the Protection of Human Subjects of Biomedical and Behavioral Research. (1979). The Belmont report: Ethical principles and guidelines for the protection of human subjects of research. Retrieved from https://www.hhs.gov/ohrp/regulations-and-policy/belmont-report/read-the-belmont-report/index.html ↵
- Patel, J., Tinker, A., & Corna, L. (2018). Younger workers’ attitudes and perceptions towards older colleagues. Working with Older People, 22 (3), 129-138. ↵
- Veenstra, A. S., Iyer, N., Hossain, M. D., & Park, J. (2014). Time, place, technology: Twitter as an information source in the Wisconsin labor protests. Computers in Human Behavior, 31, 65-72. ↵
- Ohmer, M. L., & Owens, J. (2013). Using photovoice to empower youth and adults to prevent crime. Journal of Community Practice, 21 (4), 410-433. ↵
- Malebranche, D. J., Arriola, K. J., Jenkins, T. R., Dauria, E., & Patel, S. N. (2010). Exploring the “bisexual bridge”: A qualitative study of risk behavior and disclosure of same-sex behavior among Black bisexual men . American Journal of Public Health, 100( 1), 159-164. ↵
- Al-Jundi, A., & SakkA, S. (2016). Protocol writing in clinical research. Journal of Clinical and Diagnostic Research: JCDR, 10 (11), ZE10. ↵
Research that involves the use of data that represents human expression through words, pictures, movies, performance and other artifacts.
One of the three ethical principles in the Belmont Report. States that benefits and burdens of research should be distributed fairly.
Case studies are a type of qualitative research design that focus on a defined case and gathers data to provide a very rich, full understanding of that case. It usually involves gathering data from multiple different sources to get a well-rounded case description.
the various aspects or dimensions that come together in forming our identity
The unintended influence that the researcher may have on the research process.
A research journal that helps the researcher to reflect on and consider their thoughts and reactions to the research process and how it may be shaping the study
Rigor is the process through which we demonstrate, to the best of our ability, that our research is empirically sound and reflects a scientific approach to knowledge building.
A form of data gathering where researchers ask individual participants to respond to a series of (mostly open-ended) questions.
A form of data gathering where researchers ask a group of participants to respond to a series of (mostly open-ended) questions.
Observation is a tool for data gathering where researchers rely on their own senses (e.g. sight, sound) to gather information on a topic.
Triangulation of data refers to the use of multiple types, measures or sources of data in a research project to increase the confidence that we have in our findings.
sampling approaches for which a person’s likelihood of being selected for membership in the sample is unknown
A convenience sample is formed by collecting data from those people or other relevant elements to which we have the most convenient access. Essentially, we take who we can get.
A quota sample involves the researcher identifying a subgroups within a population that they want to make sure to include in their sample, and then identifies a quota or target number to recruit that represent each of these subgroups.
For a snowball sample, a few initial participants are recruited and then we rely on those initial (and successive) participants to help identify additional people to recruit. We thus rely on participants connects and knowledge of the population to aid our recruitment.
In a purposive sample, participants are intentionally or hand-selected because of their specific expertise or experience.
Content is the substance of the artifact (e.g. the words, picture, scene). It is what can actually be observed.
Context is the circumstances surrounding an artifact, event, or experience.
Photovoice is a technique that merges pictures with narrative (word or voice data that helps that interpret the meaning or significance of the visual artifact. It is often used as a tool in CBPR.
A rich, deep, detailed understanding of a unique person, small group, and/or set of circumstances.
Inclusion criteria are general requirements a person must possess to be a part of your sample.
A purposive sampling strategy where you choose cases because they represent a range of very different perspectives on a topic
A purposive sampling strategy where you select cases that represent the most common/ a commonly held perspective.
A purposive sampling strategy that selects a case(s) that represent extreme or underrepresented perspectives. It is a way of intentionally focusing on or representing voices that may not often be heard or given emphasis.
A purposive sampling strategy that focuses on selecting cases that are important in representing a contemporary politicized issue.
A plan that is developed by a researcher, prior to commencing a research project, that details how data will be collected, stored and managed during the research project.
Emergent design is the idea that some decision in our research design will be dynamic and change as our understanding of the research question evolves as we go through the research process. This is (often) evident in qualitative research, but rare in quantitative research.
approach to recruitment where participants are sought in public spaces
approach to recruitment where participants are based on some personal characteristic or group association
approach to recruitment where participants are members of an organization or social group with identified membership
To type out the text of recorded interview or focus group.
A qualitative research design that aims to capture and describe the lived experience of some event or "phenomenon" for a group of people.
A type of research design that is often used to study a process or identify a theory about how something works.
The point where gathering more data doesn't offer any new ideas or perspectives on the issue you are studying. Reaching saturation is an indication that we can stop qualitative data collection.
Graduate research methods in social work Copyright © 2021 by Matthew DeCarlo, Cory Cummings, Kate Agnelli is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Qualitative research is a methodological approach that involves gathering and analyzing non-numerical data to understand and interpret social phenomena. Unlike quantitative research, which emphasizes the collection of numerical data through surveys and experiments, qualitative research is concerned with exploring the subjective experiences ...
Qualitative research refers to the intuitive and creative analysis of intangible information you can use for writing a top-class college paper. Due to interacting with the data before and after the collection, having the best qualitative research topics is paramount to writing a research assignment that stands above the rest.
Qualitative research involves collecting and analyzing non-numerical data (e.g., text, video, or audio) to understand concepts, opinions, or experiences. It can be used to gather in-depth insights into a problem or generate new ideas for research. Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and ...
Do you need qualitative research topics for your academic papers? If so, here's a list of 130-plus interesting qualitative research topic ideas.
These research topics for stem students qualitative to explore a wide range of social, ethical, cultural, and practical dimensions within their fields of study, providing opportunities for meaningful qualitative research.
Here are 100+ qualitative research topics for college students categorized into different fields of study:
For students and novice researchers, the choice of qualitative approach and subsequent alignment among problems, research questions, data collection, and data a...
Qualitative research is a type of research methodology that focuses on exploring and understanding people's beliefs, attitudes, behaviors, and experiences through the collection and analysis of non-numerical data. It seeks to answer research questions through the examination of subjective data, such as interviews, focus groups, observations ...
This paper aims to provide an overview of the use and assessment of qualitative research methods in the health sciences. Qualitative research can be defined as the study of the nature of phenomena and is especially appropriate for answering questions ...
Qualitative research is the opposite of quantitative research, which involves collecting and analysing numerical data for statistical analysis. Qualitative research is commonly used in the humanities and social sciences, in subjects such as anthropology, sociology, education, health sciences, and history.
Qualitative research methods are designed to help reveal the behavior and perception of a target audience with reference to the topic of research.
This guide explains the focus, rigor, and relevance of qualitative research, highlighting its role in dissecting complex social phenomena and providing in-depth, human-centered insights. The guide also examines the rationale for employing qualitative methods, underscoring their critical importance. An exploration of the methodology's ...
300 Qualitative Research Topics For Easy Academic Victory You are on the right page if you are looking for a perfect qualitative research topic and have difficulty finding it.
Qualitative research is designed to address research questions that focus on understanding the "why" and "how" of human behavior, experiences, and interactions, rather than just the "what" or "how many" that quantitative methods typically seek to answer. The main purpose of qualitative research is to gain a rich and nuanced understanding of ...
Need a good topic for your qualitative research paper? Explore this blog. Here, you will get 200+ qualitative research topics and ideas.
Qualitative research is focused on data obtained through a researcher's first-hand observations, natural setting recording, artifacts, case studies, documents, questionnaires, and interviews. The findings in qualitative research are usually non-numerical. Also, it is common in humanities and social sciences. This post provides over 100 qualitative research topics you can consider.
Choosing a Qualitative Approach. Before engaging in any qualitative study, consider how your views about what is possible to study will affect your approach. Then select an appropriate approach within which to work. Alignment between the belief system underpinning the research approach, the research question, and the research approach itself is ...
Qualitative research is multimethod in focus, involving an interpretative, naturalistic approach to its subject matter. This means that qualitative researchers study things in their natural settings, attempting to make sense of, or interpret, phenomena in terms of the meanings people bring to them.
Honing in on your main research questions can make or break your research studies. Learn how to write effective qualitative research questions.
Qualitative research is defined as an exploratory method that aims to understand complex phenomena, often within their natural settings, by examining subjective experiences, beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors. Learn more about qualitative research methods, types, examples and best practices.
Sociology. Qualitative research is a type of research that aims to gather and analyse non-numerical (descriptive) data in order to gain an understanding of individuals' social reality, including understanding their attitudes, beliefs, and motivation. This type of research typically involves in-depth interviews, focus groups, or observations in ...
Qualitative research is defined as a type of research that aims to explore and understand phenomena and behaviors, focusing on the 'what', 'how', and 'why' aspects rather than quantitative measurements like 'how many' or 'how much'.
We therefore document the following: (1) Our experiences of the issues presented by undertaking qualitative research involving challenging, difficult, or sensitive topics; and (2) Practical principles devised to overcome these issues, ensuring safety and wellbeing amongst researchers engaging in these types of qualitative research.
Throughout this chapter we have explored a number of topics including various types of qualitative data, approaches to qualitative sampling, and some considerations for recruitment and sample composition.
This guide explains the focus, rigor, and relevance of qualitative research, highlighting its role in dissecting complex social phenomena and providing in-depth, human-centered insights.
Topic: Qualitative Research; Navigation . Educational Research Mini-Series. Main Menu. Topic: What is Educational Research, QI and Evaluation; ... Practical Guidance for Designing and Reporting Qualitative Research Note: Common designs in qualitative research (Timestamp: 12:45) Identify When a Research Question is Appropriate for Qualitative ...
The Research team sincerely appreciate patients, their relatives, and nurses for their cooperation in this study. The Research team also would like to thank the managerial teams of Imam Khomeini Hospital at Tehran as well as the Vice Chancellor for Research Affairs at Tehran University of Medical Sciences for helping us in conducting this research.