

Concept Papers in Research: Deciphering the blueprint of brilliance
Concept papers hold significant importance as a precursor to a full-fledged research proposal in academia and research. Understanding the nuances and significance of a concept paper is essential for any researcher aiming to lay a strong foundation for their investigation.
Table of Contents
What Is Concept Paper
A concept paper can be defined as a concise document which outlines the fundamental aspects of a grant proposal. It outlines the initial ideas, objectives, and theoretical framework of a proposed research project. It is usually two to three-page long overview of the proposal. However, they differ from both research proposal and original research paper in lacking a detailed plan and methodology for a specific study as in research proposal provides and exclusion of the findings and analysis of a completed research project as in an original research paper. A concept paper primarily focuses on introducing the basic idea, intended research question, and the framework that will guide the research.
Purpose of a Concept Paper
A concept paper serves as an initial document, commonly required by private organizations before a formal proposal submission. It offers a preliminary overview of a project or research’s purpose, method, and implementation. It acts as a roadmap, providing clarity and coherence in research direction. Additionally, it also acts as a tool for receiving informal input. The paper is used for internal decision-making, seeking approval from the board, and securing commitment from partners. It promotes cohesive communication and serves as a professional and respectful tool in collaboration.
These papers aid in focusing on the core objectives, theoretical underpinnings, and potential methodology of the research, enabling researchers to gain initial feedback and refine their ideas before delving into detailed research.
Key Elements of a Concept Paper
Key elements of a concept paper include the title page , background , literature review , problem statement , methodology, timeline, and references. It’s crucial for researchers seeking grants as it helps evaluators assess the relevance and feasibility of the proposed research.
Writing an effective concept paper in academic research involves understanding and incorporating essential elements:

How to Write a Concept Paper?
To ensure an effective concept paper, it’s recommended to select a compelling research topic, pose numerous research questions and incorporate data and numbers to support the project’s rationale. The document must be concise (around five pages) after tailoring the content and following the formatting requirements. Additionally, infographics and scientific illustrations can enhance the document’s impact and engagement with the audience. The steps to write a concept paper are as follows:
1. Write a Crisp Title:
Choose a clear, descriptive title that encapsulates the main idea. The title should express the paper’s content. It should serve as a preview for the reader.
2. Provide a Background Information:
Give a background information about the issue or topic. Define the key terminologies or concepts. Review existing literature to identify the gaps your concept paper aims to fill.
3. Outline Contents in the Introduction:
Introduce the concept paper with a brief overview of the problem or idea you’re addressing. Explain its significance. Identify the specific knowledge gaps your research aims to address and mention any contradictory theories related to your research question.
4. Define a Mission Statement:
The mission statement follows a clear problem statement that defines the problem or concept that need to be addressed. Write a concise mission statement that engages your research purpose and explains why gaining the reader’s approval will benefit your field.
5. Explain the Research Aim and Objectives:
Explain why your research is important and the specific questions you aim to answer through your research. State the specific goals and objectives your concept intends to achieve. Provide a detailed explanation of your concept. What is it, how does it work, and what makes it unique?
6. Detail the Methodology:
Discuss the research methods you plan to use, such as surveys, experiments, case studies, interviews, and observations. Mention any ethical concerns related to your research.
7. Outline Proposed Methods and Potential Impact:
Provide detailed information on how you will conduct your research, including any specialized equipment or collaborations. Discuss the expected results or impacts of implementing the concept. Highlight the potential benefits, whether social, economic, or otherwise.
8. Mention the Feasibility
Discuss the resources necessary for the concept’s execution. Mention the expected duration of the research and specific milestones. Outline a proposed timeline for implementing the concept.
9. Include a Support Section:
Include a section that breaks down the project’s budget, explaining the overall cost and individual expenses to demonstrate how the allocated funds will be used.
10. Provide a Conclusion:
Summarize the key points and restate the importance of the concept. If necessary, include a call to action or next steps.
Although the structure and elements of a concept paper may vary depending on the specific requirements, you can tailor your document based on the guidelines or instructions you’ve been given.
Here are some tips to write a concept paper:

Example of a Concept Paper
Here is an example of a concept paper. Please note, this is a generalized example. Your concept paper should align with the specific requirements, guidelines, and objectives you aim to achieve in your proposal. Tailor it accordingly to the needs and context of the initiative you are proposing.
Download Now!
Importance of a Concept Paper
Concept papers serve various fields, influencing the direction and potential of research in science, social sciences, technology, and more. They contribute to the formulation of groundbreaking studies and novel ideas that can impact societal, economic, and academic spheres.
A concept paper serves several crucial purposes in various fields:

In summary, a well-crafted concept paper is essential in outlining a clear, concise, and structured framework for new ideas or proposals. It helps in assessing the feasibility, viability, and potential impact of the concept before investing significant resources into its implementation.
How well do you understand concept papers? Test your understanding now!
Fill the Details to Check Your Score

Role of AI in Writing Concept Papers
The increasing use of AI, particularly generative models, has facilitated the writing process for concept papers. Responsible use involves leveraging AI to assist in ideation, organization, and language refinement while ensuring that the originality and ethical standards of research are maintained.
AI plays a significant role in aiding the creation and development of concept papers in several ways:
1. Idea Generation and Organization
AI tools can assist in brainstorming initial ideas for concept papers based on key concepts. They can help in organizing information, creating outlines, and structuring the content effectively.
2. Summarizing Research and Data Analysis
AI-powered tools can assist in conducting comprehensive literature reviews, helping writers to gather and synthesize relevant information. AI algorithms can process and analyze vast amounts of data, providing insights and statistics to support the concept presented in the paper.
3. Language and Style Enhancement
AI grammar checker tools can help writers by offering grammar, style, and tone suggestions, ensuring professionalism. It can also facilitate translation, in case a global collaboration.
4. Collaboration and Feedback
AI platforms offer collaborative features that enable multiple authors to work simultaneously on a concept paper, allowing for real-time contributions and edits.
5. Customization and Personalization
AI algorithms can provide personalized recommendations based on the specific requirements or context of the concept paper. They can assist in tailoring the concept paper according to the target audience or specific guidelines.
6. Automation and Efficiency
AI can automate certain tasks, such as citation formatting, bibliography creation, or reference checking, saving time for the writer.
7. Analytics and Prediction
AI models can predict potential outcomes or impacts based on the information provided, helping writers anticipate the possible consequences of the proposed concept.
8. Real-Time Assistance
AI-driven chat-bots can provide real-time support and answers to specific questions related to the concept paper writing process.
AI’s role in writing concept papers significantly streamlines the writing process, enhances the quality of the content, and provides valuable assistance in various stages of development, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the final document.
Concept papers serve as the stepping stone in the research journey, aiding in the crystallization of ideas and the formulation of robust research proposals. It the cornerstone for translating ideas into impactful realities. Their significance spans diverse domains, from academia to business, enabling stakeholders to evaluate, invest, and realize the potential of groundbreaking concepts.
Frequently Asked Questions
A concept paper can be defined as a concise document outlining the fundamental aspects of a grant proposal such as the initial ideas, objectives, and theoretical framework of a proposed research project.
A good concept paper should offer a clear and comprehensive overview of the proposed research. It should demonstrate a strong understanding of the subject matter and outline a structured plan for its execution.
Concept paper is important to develop and clarify ideas, develop and evaluate proposal, inviting collaboration and collecting feedback, presenting proposals for academic and research initiatives and allocating resources.
I got wonderful idea
It helps a lot for my concept paper.
Information is key to the guidelines of a concept paper
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Career Corner
Academic Webinars: Transforming knowledge dissemination in the digital age
Digitization has transformed several areas of our lives, including the teaching and learning process. During…

- Manuscripts & Grants
- Reporting Research
Mastering Research Grant Writing in 2024: Navigating new policies and funder demands
Entering the world of grants and government funding can leave you confused; especially when trying…

How to Create a Poster That Stands Out: Tips for a smooth poster presentation
It was the conference season. Judy was excited to present her first poster! She had…

Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
![concept paper thesis What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- AI in Academia
- Promoting Research
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

In your opinion, what is the most effective way to improve integrity in the peer review process?
How To Write a Concept Paper for Academic Research: An Ultimate Guide

A concept paper is one of the first steps in helping you fully realize your research project. Because of this, some schools opt to teach students how to write concept papers as early as high school. In college, professors sometimes require their students to submit concept papers before suggesting their research projects to serve as the foundations for their theses.
If you’re reading this right now, you’ve probably been assigned by your teacher or professor to write a concept paper. To help you get started, we’ve prepared a comprehensive guide on how to write a proper concept paper.
Related: How to Write Significance of the Study (with Examples)
Table of Contents
What is the concept paper, 1. academic research concept papers, 2. advertising concept papers, 3. research grant concept papers, concept paper vs. research proposal, tips for finding your research topic, 2. think of research questions that you want to answer in your project, 3. formulate your research hypothesis, 4. plan out how you will achieve, analyze, and present your data, 2. introduction, 3. purpose of the study, 4. preliminary literature review, 5. objectives of the study, 6. research questions and hypotheses, 7. proposed methodology, 8. proposed research timeline, 9. references, sample concept paper for research proposal (pdf), tips for writing your concept paper.
Generally, a concept paper is a summary of everything related to your proposed project or topic. A concept paper indicates what the project is all about, why it’s important, and how and when you plan to conduct your project.
Different Types of the Concept Paper and Their Uses

This type of concept paper is the most common type and the one most people are familiar with. Concept papers for academic research are used by students to provide an outline for their prospective research topics.
These concept papers are used to help students flesh out all the information and ideas related to their topic so that they may arrive at a more specific research hypothesis.
Since this is the most common type of concept paper, it will be the main focus of this article.
Advertising concept papers are usually written by the creative and concept teams in advertising and marketing agencies.
Through a concept paper, the foundation or theme for an advertising campaign or strategy is formed. The concept paper can also serve as a bulletin board for ideas that the creative and concept teams can add to or develop.
This type of concept paper usually discusses who the target audience of the campaign is, what approach of the campaign will be, how the campaign will be implemented, and the projected benefits and impact of the campaign to the company’s sales, consumer base, and other aspects of the company.
This type of concept paper is most common in the academe and business world. Alongside proving why your research project should be conducted, a research grant concept paper must also appeal to the company or funding agency on why they should be granted funds.
The paper should indicate a proposed timeline and budget for the entire project. It should also be able to persuade the company or funding agency on the benefits of your research project– whether it be an increase in sales or productivity or for the benefit of the general public.
It’s important to discuss the differences between the two because a lot of people often use these terms interchangeably.
A concept paper is one of the first steps in conducting a research project. It is during this process that ideas and relevant information to the research topic are gathered to produce the research hypothesis. Thus, a concept paper should always precede the research proposal.
A research proposal is a more in-depth outline of a more fleshed-out research project. This is the final step before a researcher can conduct their research project. Although both have similar elements and structures, a research proposal is more specific when it comes to how the entire research project will be conducted.
Getting Started on Your Concept Paper
1. find a research topic you are interested in.
When choosing a research topic, make sure that it is something you are passionate about or want to learn more about. If you are writing one for school, make sure it is still relevant to the subject of your class. Choosing a topic you aren’t invested in may cause you to lose interest in your project later on, which may lower the quality of the research you’ll produce.
A research project may last for months and even years, so it’s important that you will never lose interest in your topic.
- Look for inspiration everywhere. Take a walk outside, read books, or go on your computer. Look around you and try to brainstorm ideas about everything you see. Try to remember any questions you might have asked yourself before like why something is the way it is or why can’t this be done instead of that .
- Think big. If you’re having trouble thinking up a specific topic to base your research project on, choosing a broad topic and then working your way down should help.
- Is it achievable? A lot of students make the mistake of choosing a topic that is hard to achieve in terms of materials, data, and/or funding available. Before you decide on a research topic, make sure you consider these aspects. Doing so will save you time, money, and effort later on.
- Be as specific as can be. Another common mistake that students make is that they sometimes choose a research topic that is too broad. This results in extra effort and wasted time while conducting their research project. For example: Instead of “The Effects of Bananas on Hungry Monkeys” , you could specify it to “The Effects of Cavendish Bananas on Potassium-deficiency in Hungry Philippine Long-tailed Macaques in Palawan, Philippines”.
Now that you have a general idea of the topic of your research project, you now need to formulate research questions based on your project. These questions will serve as the basis for what your project aims to answer. Like your research topic, make sure these are specific and answerable.
Following the earlier example, possible research questions could be:
- Do Cavendish bananas produce more visible effects on K-deficiency than other bananas?
- How susceptible are Philippine long-tailed macaques to K-deficiency?
- What are the effects of K-deficiency in Philippine long-tailed macaques?
After formulating the research questions, you should also provide your hypothesis for each question. A research hypothesis is a tentative answer to the research problem. You must provide educated answers to the questions based on your existing knowledge of the topic before you conduct your research project.
After conducting research and collecting all of the data into the final research paper, you will then have to approve or disprove these hypotheses based on the outcome of the project.
Prepare a plan on how to acquire the data you will need for your research project. Take note of the different types of analysis you will need to perform on your data to get the desired results. Determine the nature of the relationship between different variables in your research.
Also, make sure that you are able to present your data in a clear and readable manner for those who will read your concept paper. You can achieve this by using tables, charts, graphs, and other visual aids.
Related: How to Make Conceptual Framework (with Examples and Templates)
Generalized Structure of a Concept Paper
Since concept papers are just summaries of your research project, they are usually short and no longer than 5 pages. However, for big research projects, concept papers can reach up to more than 20 pages.
Your teacher or professor may give you a certain format for your concept papers. Generally, most concept papers are double-spaced and are less than 500 words in length.
Even though there are different types of concept papers, we’ve provided you with a generalized structure that contains elements that can be found in any type of concept paper.

The title for your paper must be able to effectively summarize what your research is all about. Use simple words so that people who read the title of your research will know what it’s all about even without reading the entire paper.
The introduction should give the reader a brief background of the research topic and state the main objective that your project aims to achieve. This section should also include a short overview of the benefits of the research project to persuade the reader to acknowledge the need for the project.
The Purpose of the Study should be written in a way that convinces the reader of the need to address the existing problem or gap in knowledge that the research project aims to resolve. In this section, you have to go into more detail about the benefits and value of your project for the target audience/s.
This section features related studies and papers that will support your research topic. Use this section to analyze the results and methodologies of previous studies and address any gaps in knowledge or questions that your research project aims to answer. You may also use the data to assert the importance of conducting your research.
When choosing which papers and studies you should include in the Preliminary Literature Review, make sure to choose relevant and reliable sources. Reliable sources include academic journals, credible news outlets, government websites, and others. Also, take note of the authors for the papers as you will need to cite them in the References section.
Simply state the main objectives that your research is trying to achieve. The objectives should be able to indicate the direction of the study for both the reader and the researcher. As with other elements in the paper, the objectives should be specific and clearly defined.
Gather the research questions and equivalent research hypotheses you formulated in the earlier step and list them down in this section.
In this section, you should be able to guide the reader through the process of how you will conduct the research project. Make sure to state the purpose for each step of the process, as well as the type of data to be collected and the target population.
Depending on the nature of your research project, the length of the entire process can vary significantly. What’s important is that you are able to provide a reasonable and achievable timeline for your project.
Make sure the time you will allot for each component of your research won’t be too excessive or too insufficient so that the quality of your research won’t suffer.
Ensure that you will give credit to all the authors of the sources you used in your paper. Depending on your area of study or the instructions of your professor, you may need to use a certain style of citation.
There are three main citation styles: the American Psychological Association (APA), Modern Language Association (MLA), and the Chicago style.
The APA style is mostly used for papers related to education, psychology, and the sciences. The APA citation style usually follows this format:

The MLA citation style is the format used by papers and manuscripts in disciplines related to the arts and humanities. The MLA citation style follows this format:

The Chicago citation style is usually used for papers related to business, history, and the fine arts. It follows this citation format:

This is a concept paper sample provided by Dr. Bernard Lango from the Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology (modified for use in this article). Simply click the link above the download the PDF file.
- Use simple, concise language. Minimize the use of flowery language and always try to use simple and easy-to-understand language. Too many technical or difficult words in your paper may alienate your readers and make your paper hard to read.
- Choose your sources wisely. When scouring the Internet for sources to use, you should always be wary and double-check the authenticity of your source. Doing this will increase the authenticity of your research project’s claims and ensure better data gathered during the process.
- Follow the specified format, if any. Make sure to follow any specified format when writing your concept paper. This is very important, especially if you’re writing your concept paper for class. Failure to follow the format will usually result in point deductions and delays because of multiple revisions needed.
- Proofread often. Make it a point to reread different sections of your concept paper after you write them. Another way you can do this is by taking a break for a few days and then coming back to proofread your writing. You may notice certain areas you’d like to revise or mistakes you’d like to fix. Make proofreading a habit to increase the quality of your paper.
Written by Ruth Raganit
in Career and Education , Juander How
Ruth Raganit
Ruth Raganit obtained her Bachelor of Science degree in Geology from the University of the Philippines – Diliman. Her love affair with Earth sciences began when she saw a pretty rock and wondered how it came to be. She also likes playing video games, doing digital art, and reading manga.
Browse all articles written by Ruth Raganit
Copyright Notice
All materials contained on this site are protected by the Republic of the Philippines copyright law and may not be reproduced, distributed, transmitted, displayed, published, or broadcast without the prior written permission of filipiknow.net or in the case of third party materials, the owner of that content. You may not alter or remove any trademark, copyright, or other notice from copies of the content. Be warned that we have already reported and helped terminate several websites and YouTube channels for blatantly stealing our content. If you wish to use filipiknow.net content for commercial purposes, such as for content syndication, etc., please contact us at legal(at)filipiknow(dot)net

Community Blog
Keep up-to-date on postgraduate related issues with our quick reads written by students, postdocs, professors and industry leaders.
What is a Concept Paper and How do You Write One?
- By DiscoverPhDs
- August 26, 2020

What is a Concept Paper?
A concept paper is a short document written by a researcher before starting their research project, with the purpose of explaining what the study is about, why it is important and the methods that will be used.
The concept paper will include your proposed research title, a brief introduction to the subject, the aim of the study, the research questions you intend to answer, the type of data you will collect and how you will collect it. A concept paper can also be referred to as a research proposal.
What is the Purpose of a Concept Paper?
The primary aim of a research concept paper is to convince the reader that the proposed research project is worth doing. This means that the reader should first agree that the research study is novel and interesting. They should be convinced that there is a need for this research and that the research aims and questions are appropriate.
Finally, they should be satisfied that the methods for data collection proposed are feasible, are likely to work and can be performed within the specific time period allocated for this project.
The three main scenarios in which you may need to write a concept paper are if you are:
- A final year undergraduate or master’s student preparing to start a research project with a supervisor.
- A student submitting a research proposal to pursue a PhD project under the supervision of a professor.
- A principal investigator submitting a proposal to a funding body to secure financial support for a research project.
How Long is a Concept Paper?
The concept paper format is usually between 2 and 3 pages in length for students writing proposals for undergraduate, master’s or PhD projects. Concept papers written as part of funding applications may be over 20 pages in length.
How do you Write a Concept Paper?
There are 6 important aspects to consider when writing a concept paper or research proposal:
- 1. The wording of the title page, which is best presented as a question for this type of document. At this study concept stage, you can write the title a bit catchier, for example “Are 3D Printed Engine Parts Safe for Use in Aircraft?”.
- A brief introduction and review of relevant existing literature published within the subject area and identification of where the gaps in knowledge are. This last bit is particularly important as it guides you in defining the statement of the problem. The concept paper should provide a succinct summary of ‘the problem’, which is usually related to what is unknown or poorly understood about your research topic . By the end of the concept paper, the reader should be clear on how your research idea will provide a ‘solution’ to this problem.
- The overarching research aim of your proposed study and the objectives and/or questions you will address to achieve this aim. Align all of these with the problem statement; i.e. write each research question as a clear response to addressing the limitations and gaps identified from previous literature. Also give a clear description of your primary hypothesis.
- The specific data outputs that you plan to capture. For example, will this be qualitative or quantitative data? Do you plan to capture data at specific time points or at other defined intervals? Do you need to repeat data capture to asses any repeatability and reproducibility questions?
- The research methodology you will use to capture this data, including any specific measurement or analysis equipment and software you will use, and a consideration of statistical tests to help interpret the data. If your research requires the use of questionnaires, how will these be prepared and validated? In what sort of time frame would you plan to collect this data?
- Finally, include a statement of the significance of the study , explaining why your research is important and impactful. This can be in the form of a concluding paragraph that reiterate the statement of the problem, clarifies how your research will address this and explains who will benefit from your research and how.
You may need to include a short summary of the timeline for completing the research project. Defining milestones of the time points at which you intend to complete certain tasks can help to show that you’ve considered the practicalities of running this study. It also shows that what you have proposed is feasible in order to achieve your research goal.
If you’re pitching your proposed project to a funder, they may allocate a proportion of the money based on the satisfactory outcome of each milestone. These stakeholders may also be motivated by knowing that you intend to convert your dissertation into an article for journal publication; this level of dissemination is of high importance to them.
Additionally, you may be asked to provide a brief summary of the projected costs of running the study. For a PhD project this could be the bench fees associated with consumables and the cost of any travel if required.
Make sure to include references and cite all other literature and previous research that you discuss in your concept paper.
This guide gave you an overview of the key elements you need to know about when writing concept papers. The purpose of these are first to convey to the reader what your project’s purpose is and why your research topic is important; this is based on the development of a problem statement using evidence from your literature review.
Explain how it may positively impact your research field and if your proposed research design is appropriate and your planned research method achievable.

Reference management software solutions offer a powerful way for you to track and manage your academic references. Read our blog post to learn more about what they are and how to use them.

Are you always finding yourself working on sections of your research tasks right up until your deadlines? Are you still finding yourself distracted the moment

Choosing a good PhD supervisor will be paramount to your success as a PhD student, but what qualities should you be looking for? Read our post to find out.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.

Browse PhDs Now

PhD stress is real. Learn how to combat it with these 5 tips.

Tenure is a permanent position awarded to professors showing excellence in research and teaching. Find out more about the competitive position!

Dr Roberts gained her PhD from Duke University in 2014 in the field of biomedical engineering. She now runs her own business named Personal Finance for PhDs.

Dr Day gained her PhD Physical Chemistry at the University of Nottingham in 2000. She is now a Science & Fiction writer, an Associate Editor at PseudoPod.org and runs the blog ‘The Chronicle Flask’ about all things chemistry.
Join Thousands of Students
How to Write a Concept Paper
How do you write a concept paper? Why is there a need to write one before writing a full-blown thesis proposal? How do you write a concept paper?
This article explains why a concept paper is important before writing a full-blown research paper. It also provides a step-by-step approach on how to write it.
I once browsed the internet to look for information on how to write a concept paper. It took me some time to find the information I wanted. I did find some, but I am not entirely satisfied with those explanations. The explanation and discussion are either too short or vaguely explain the concept paper.
I remembered once again when a colleague asked me the other day to explain a concept paper and how to write it. He needs this information because students have been asking him how to write it.
To him and his students, I dedicate this article.
What is a Concept Paper and Why Do You Need It?
Before going into the details on how to write a concept paper, let me explain what a concept paper is and why you need it.
A concept paper serves as a prelude to writing a full-blown manuscript.
What do you consider a full-blown write-up? It could be a thesis, a program, a project, or anything that will require a longer time to prepare.
In essence, a concept paper embodies your ideas on a particular topic or item of interest. The concept paper saves time because your thesis or review panel may say that your concept is not worth pursuing.
A concept paper should consist only of 1 or 2 pages. Alternatively, if you want to deal with complex issues that require expounding on the ideas, it can go up to 5 pages.
For example, as a student, you will be asked to prepare your concept paper before writing your thesis proposal. This task means that you need to develop an idea and express it for others to understand. The central idea of that concept paper is your thesis statement .
You may glean from either your experience or from your literature review. Of course, your topic should be within your respective area of specialization. It makes sense to be an expert in your field.
If you are a computer science student, you might want to study the behavior of wi-fi signals bounced to different kinds of material . Alternatively, maybe you wish to create a simple gadget to concentrate signals for a portable USB wi-fi connection to improve its performance.
How Do You Write a Concept Paper?
The ultimate goal is for you to be able to express your intention. What do you want to do or achieve?
1. A Rationale
What prompted you to prepare the concept paper? Why is the issue of such importance? What should you be able to produce out of your intended study?
2. A Conceptual Framework
A conceptual framework serves as your guide in working on your idea. It is like a map to follow to arrive at your destination.
A mind map is simply a list of keywords that you can connect to clarify an individual issue. It is our subconscious’ way of analyzing things. We tend to associate things with other things. This tendency relates to how we recall past experiences.
In the field of computers, we have the so-called “links” that connect commands in a computer module to make an application program work.
How does mind mapping work?
The following video explains how to build a mind map using XMind, my favorite mind mapping tool.
3. Your Hypothesis
Once you have identified the specific variables you would like to study, ask yourself the following questions:
A quick review of relevant and updated literature will help you identify which variables matter.
Example of Hypotheses
1. There is no significant difference in wi-fi signal behavior between wood and metal.
If you find this discussion worthwhile, or you would like to clarify further the discussion above, your feedback is welcome.
© 2012 October 31 P. A. Regoniel | Updated: 12/5/21
Related Posts
Data accuracy, reliability and triangulation in qualitative research, five tips on how to discuss the results of your study, understanding rotc from the perspective of millennial students: exploring their perception and engagement, about the author, patrick regoniel, 69 comments.
thank you very much… i have an idea now what to do… still preparing a concept paper for my dissertation…
Thanks a lot for your article on how to write a concept paper……………….such a great help for me!
Thanks alot. This really helped me as i had to write a concept note as part of the process of applying for a Masters Degree programme in my institution of choice.
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy
What exactly is a Concept Paper, and how do you write one?
Learn why a concept paper is important, what the main elements of a research concept paper are, and how to create an excellent one.
Prior to submitting a formal proposal (business proposal, product, or research proposal), many private organizations have historically asked for the submission of a concept paper for review.
Recently, organizations have begun to advocate for the usage of concept papers as a way for applicants to obtain informal input on their ideas and projects before submitting a proposal. Several of these organizations now demand a concept paper as part of the official application process.
Simply described, a concept paper is a preliminary document that explains the purpose of research, why it is being conducted, and how it will be performed. It examines a concept or idea and offers an outline of the topic that a researcher wants to pursue. Continue reading to learn more about concept papers and how to create a good one.
What a concept paper is and its purpose
A concept paper is a brief paper that outlines the important components of a research or project before it is carried out. Its purpose is to offer an overview. Entrepreneurs working on a business idea or product, as well as students and researchers, frequently write concept papers .
Researchers may be required to prepare a concept paper when submitting a project proposal to a funding authority to acquire the required grants.
As a consequence, the importance is based on the fact that it should help the examiner determine whether the research is relevant, practicable, and useful .
If not, they may suggest looking into a different research area. It also allows the examiner to assess your comprehension of the research and, as a result, if you are likely to require assistance in completing the research.
Illustrate your Concept Paper with infographics
Infographics are very useful to explain complex subjects in a very short time. Use Mind the Graph to create beautiful infographics for your Concept Paper with scientifically accurate illustrations, icons, arrows and many other design tools.
Concept paper’s elements for an academic research
To produce an effective concept paper, you must first comprehend the essential elements of academic research:
- Title page: Mention the applicant’s name, institution, project title, and submission date.
- Background for the research: The second section should be the purpose section, which should be able to clear out what has already been stated about the subject, any gaps in information that need to be filled or problems to be solved, as well as the reason why you wish to examine the issue.
- Literature review: In this section, you should provide a theoretical basis and supporting material for your chosen subject.
- State the problem and your goals: Describe the overall problems, including the research questions and objectives. State your research’s unique and original aspects, concentrate on providing and clearly discussing your goals towards the problem.
- Methodology : Provide the data analysis system to be utilized, data collecting method, tools to be used, and research participants in this section.
- Timeline: Include a realistic timeline estimate that is defined in months and years.
- References: Add a list of all sources cited in your concept paper , such as books, journals, and other resources.
Tips on writing an effective concept paper
A concept paper is extremely crucial for a project or research, especially if it requires funding. Check out these simple tips to ensure your concept paper is successful and simple.
- Choose a research topic that truly piques your curiosity
- Create a list of research questions. The more, the merrier.
- When describing the project’s reasoning, use data and numbers.
- Use no more than 5 single-spaced pages.
- Tailor your speech to the appropriate audience.
- Make certain that the basic format elements, such as page numbers, are included.
- Spend additional time on your timeline as this section is critical for funding.
- Give specific examples of how you plan to measure your progress toward your goals.
- Provide an initial budget when seeking funds. Sponsors will want to obtain an idea of how much funds are required.
Start creating infographics and scientific illustrations
Use the power of infographics and scientific illustrations to your advantage. Including graphic assets in your work may increase your authority and highlight all of the most valuable information, ensuring that your audience is engaged and completely comprehensive of the information you are providing.
Related Articles

Subscribe to our newsletter
Exclusive high quality content about effective visual communication in science.
Sign Up for Free
Try the best infographic maker and promote your research with scientifically-accurate beautiful figures
no credit card required
About Jessica Abbadia
Jessica Abbadia is a lawyer that has been working in Digital Marketing since 2020, improving organic performance for apps and websites in various regions through ASO and SEO. Currently developing scientific and intellectual knowledge for the community's benefit. Jessica is an animal rights activist who enjoys reading and drinking strong coffee.
Content tags
How to Write a Concept Paper Easily with Our Guide

Did you know that some of the most revolutionary ideas in history started with a simple concept paper? From scientific breakthroughs to groundbreaking inventions, the power of well-crafted concept papers cannot be underestimated.
In this article, experts at our academic essay writing service will demystify the process of writing a concept paper, offering straightforward tips and guidance to help you articulate your ideas effectively. Whether you're a researcher, entrepreneur, or student, you'll lay the foundation for your next big endeavor effortlessly.
Defining What is a Concept Paper
A concept paper is a starting point for any major project or research endeavor. When you're asked to write one, what your teachers or professors are really asking for is a clear, concise summary of what you plan to explore or investigate. It's your chance to explain your idea, why it matters, and how you're going to tackle it.
Imagine you're pitching your idea to someone who doesn't know anything about it. You want to grab their attention and get them excited about what you're planning to do. That's what a concept paper is all about – setting the stage for your project or research in a way that makes people want to learn more.
Don't Delay Your Scholarly Pursuits!
Our team is here to nurture your concepts! Seize this opportunity to lay the groundwork for your academic exploration.
Why Does a Concept Paper Matter
So, why does knowing how to write a concept paper for academic research matter? First off, it helps you clarify your thoughts and organize your ideas. Writing down your concept forces you to think through the details of your project, which can be super helpful, especially when things start to get overwhelming.
Secondly, it's a way to get feedback early on. By sharing your concept paper with your teachers, advisors, or classmates, you can get valuable input that can help you refine your idea and make it even better.
Plus, it shows that you're serious about your project. Taking the time to write a concept paper demonstrates to your instructors that you've put thought and effort into your work, which can earn you some serious brownie points.
Understanding How Long is a Concept Paper
When it comes to the length of a concept paper, think quality over quantity. It's not about hitting a specific word count; it's about conveying your ideas clearly and concisely. In general, a concept paper is meant to be short and to the point. You want to give enough detail to explain your idea thoroughly, but you don't want to overwhelm your reader with unnecessary information.
As a rule of thumb, most concept papers range from 1 to 3 pages. However, this can vary depending on your specific assignment or the requirements of the project you're proposing.
The key is to focus on the essentials. Include a brief introduction to your topic, a clear statement of your purpose or objective, an overview of your methodology or approach, and a summary of the potential impact or significance of your project. And if you ever need further help, simply ask us - write my research paper for the professionally crafted project.
Concept Paper Vs. Research Paper
While both concept papers and research papers are common in academia, they serve different purposes and have distinct formats.
.webp)
A concept paper, as we've discussed, is a concise document that outlines the basic idea or proposal for a project. It's like the blueprint or roadmap for your research endeavor. The focus here is on articulating the central concept, defining the objectives, and outlining the methodology. Think of writing a concept paper as laying the groundwork before diving into the detailed work of a research project.
On the other hand, a research paper is a more comprehensive and in-depth exploration of a topic or question. It involves conducting original research, analyzing data, and presenting findings in a formal written format. Research papers typically follow a structured format, including an introduction, literature review, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
How to Write a Concept Paper in 8 Steps
Alright, getting into the nitty-gritty of writing your concept paper format might seem a bit overwhelming at first, but don't worry! We've got your back. By breaking down the process into eight manageable steps, we'll guide you through each stage with clarity and confidence.
.webp)
Define the Study Title and Its Objectives
The first crucial step in crafting your concept paper is to clearly define the study title and its objectives. This sets the foundation for your entire paper and helps guide your research direction.
Begin by crafting a clear and concise title that effectively communicates the essence of your study. Your title should be descriptive yet succinct, giving readers a glimpse into the focus of your research.
Next, outline the objectives of your study. What specific goals do you aim to achieve through your research? Be precise and realistic in outlining these objectives, ensuring they are achievable within the scope of your study.
Explain the Study's Context and Extent
After defining the title and objectives, it's essential to provide context and define the extent of your study. This step of how to write a concept paper for college helps readers understand the background and scope of your research.
Start by providing background information on the topic of your study. Discuss relevant theories, concepts, or existing research that contextualizes your work and highlights its importance.
Next, define the extent of your study by outlining its boundaries and limitations. What specific aspects of the topic will you focus on, and what areas will you exclude? Clarifying these boundaries helps ensure that your research remains focused and manageable.
Additionally, consider discussing the significance of your study within the broader field. How does your research contribute to existing knowledge, and what potential impact does it have?
Identify the Issue
This is where you clearly articulate the core challenge or question that your research seeks to explore. Start by providing a concise overview of the issue at hand. What is the specific problem or question that motivates your research? Why is it important or relevant within your field of study?
Next, consider providing context or background information that helps readers understand the significance of the issue. This could include discussing relevant trends, statistics, or real-world examples that highlight the importance of addressing the problem.
Finally, be sure to articulate the significance of the issue within the broader context of your field. Why is it important to study this particular issue, and what potential impact could your research have on addressing it?
List Goals and Objectives
In this step, you'll make a concept paper outline of the specific goals and objectives of your study. Goals represent the broader aims of your research, while objectives provide clear, measurable steps toward achieving those goals.
Start by defining your overarching goals. What do you hope to accomplish through your research? Think about the broader outcomes or changes you aim to bring about in your field or community.
Next, break down these goals into smaller, achievable objectives. Objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART). They should outline the concrete steps you will take to accomplish your goals.
Consider organizing your goals and objectives into a hierarchical structure, with broader goals at the top and more specific objectives underneath. Even if you'd rather buy essay from our pros, this step will help you provide clarity and coherence to your research plan.
Approach and Methodology
In this step, you'll detail the approach and methodology you'll use to conduct your research. According to our expert thesis writing services , this section is crucial as it outlines the methods you'll employ to address your research question and achieve your objectives.
Start by explaining your overall approach to research. Will you be conducting qualitative or quantitative research, or perhaps a combination of both? Describe the rationale behind your chosen approach and how it aligns with your research goals.
Next, outline the specific methodologies you'll use to collect and analyze data. This may include methods such as surveys, interviews, experiments, or literature reviews. Provide justification for why each method is appropriate for addressing your research question and objectives.
Be sure to consider any ethical considerations or limitations associated with your chosen methodologies and outline how you plan to address them.
Finally, discuss your data analysis plan. How will you analyze the data you collect to draw meaningful conclusions? Will you use statistical analysis, thematic coding, or another method?
Overview of Planned Methods and Expected Outcomes
In this step of how to write a concept paper for research, you'll provide an overview of the specific methods you plan to use and outline the expected outcomes or results.
Start by summarizing the methods you'll employ to collect data. This may include qualitative methods such as interviews or focus groups, quantitative methods such as surveys or experiments, or a combination of both. Briefly explain why you've chosen these methods and how they align with your research goals.
Next, outline the planned steps for implementing each method. Describe the procedures you'll follow to collect and analyze data, including any tools or instruments you'll use.
After detailing your methods, discuss the expected outcomes or results of your research. What do you hope to learn or discover through your study? How will your findings contribute to existing knowledge in your field?
Be realistic in your expectations and consider potential challenges or limitations that may affect your results. By acknowledging these factors upfront, you demonstrate a thoughtful and nuanced understanding of your research process.
Include Supporting Details
Here, you'll enrich your concept paper by incorporating supporting details that bolster your argument and provide additional context for your research.
Start by providing relevant background information or literature reviews that support your research topic. This could include citing key studies, theories, or concepts that inform your understanding of the issue.
Next, consider including any relevant data, statistics, or examples that illustrate the significance of your research topic. This could involve presenting findings from previous studies, real-world examples, or case studies that highlight the need for further investigation.
Additionally, discuss any theoretical frameworks or conceptual models that underpin your research approach. How do these frameworks help guide your study and shape your research questions?
Finally, be sure to cite your sources properly using the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA). This demonstrates academic integrity and allows readers to verify the information you've presented.
Wrap Up with a Summary
In this final step, you'll bring your concept paper to a close by summarizing the key points and reinforcing the significance of your research.
If you're uncertain how to write a conclusion for an essay , start by briefly recapping the main elements of your concept paper, including the research topic, objectives, methodology, and expected outcomes. This helps reinforce the central message of your paper and reminds readers of the key insights you've presented.
Next, reiterate the importance of your research topic and its potential impact within your field. Emphasize how your study fills a gap in existing knowledge or addresses a pressing issue, highlighting the relevance and significance of your research.
Finally, conclude with a call to action or a thought-provoking statement that encourages further reflection or discussion. This could involve suggesting avenues for future research, proposing practical implications for policymakers or practitioners, or inviting readers to consider the broader implications of your findings.
Tips for Writing a Concept Paper
Now that you've got a solid understanding of how to write a concept paper, let's explore some invaluable tips to help you navigate the writing process with finesse.
- Be Specific in Your Objectives : Clearly define your objectives with measurable outcomes. Avoid vague language and ensure each objective is actionable and achievable within the scope of your study. Specific objectives provide clarity and help guide your research effectively.
- Provide Contextual Background : Offer sufficient background information to contextualize your research topic. This includes explaining relevant theories, historical context, or existing literature related to your study. Providing context in your concept paper helps readers understand the significance of your research and its relevance within the broader field.
- Justify Your Methodological Choices : Explain why you've chosen specific research methods and justify their appropriateness for your study. Consider factors such as feasibility, ethical considerations, and alignment with your research objectives. Providing a rationale for your methodological choices adds credibility to your research approach.
- Anticipate and Address Limitations : Acknowledge potential limitations or challenges associated with your study and discuss how you plan to mitigate them. This demonstrates a thoughtful approach to your research and shows that you've considered the broader implications of your study. Being transparent about limitations also helps manage expectations and build trust with your audience.
Concept Paper Example
Now that we've explored the steps and tips for writing a concept paper let's put theory into practice. In this section, we'll provide you with a concept paper example to illustrate how these principles can be applied in a real-world scenario.
Eager to See Your Ideas Leap Off the Page?
Don't wait any longer—bring your concepts to life with our expertly crafted concept papers.
Concept Paper Topics
In this section, we'll provide you with a range of thought-provoking concept paper ideas spanning various disciplines and interests. Whether you're passionate about social issues, scientific advancements, or want to learn how to research a topic on cultural phenomena, you're sure to find inspiration here.
- The Influence of Instagram Fitness Influencers on Body Image Perception Among Adolescent Girls
- Implementing Bicycle-Sharing Programs to Reduce Carbon Emissions in Downtown Metropolitan Areas
- Analyzing the Effectiveness of Food Pantry Programs in Alleviating Food Insecurity Among Undergraduate Students at Urban Universities
- Assessing the Accuracy and Efficiency of Machine Learning Algorithms in Early Detection of Breast Cancer Using Medical Imaging Data
- Strategies for Increasing Female Representation in Computer Science and Engineering Programs at Universities
- Investigating the Impact of Workplace Mindfulness Programs on Employee Burnout Rates in High-stress Industries
- Barriers to Accessing Mental Health Services in Rural Appalachia: A Case Study
- The Ecological Impact of Microplastic Contamination on Coral Reef Ecosystems in the Caribbean
- Addressing Online Harassment and Cyberbullying Among Middle School Students Through Digital Literacy Education Programs
- The Relationship Between Proximity to Parks and Greenspaces and Mental Health Outcomes in Urban Dwellers: A Cross-sectional Study
- Virtual Reality Rehabilitation for Upper Limb Motor Recovery After Stroke: A Comparative Analysis of Traditional Therapy Methods
- Evaluating the Economic Viability and Environmental Sustainability of Indoor Vertical Farming Systems in Urban Settings
- Psychological Profiles of Adolescent Online Gamers: A Longitudinal Study on Risk Factors for Gaming Addiction
- Peer Mentoring Interventions for Improving Academic Performance and Retention Rates Among First-generation College Students in STEM Majors
- Universal Basic Income Pilot Programs: Assessing Socioeconomic Impacts and Policy Implications in Scandinavian Countries.
And there you have it - you've journeyed through the ins and outs of concept paper writing! You've learned the ropes, discovered valuable tips, explored an example, and got a bunch of topic ideas to fuel your creativity.
Now armed with the know-how, it's time to dive in and start crafting your concept paper. Remember to keep it focused, stay organized, and don't forget to let your passion shine through. With your enthusiasm and newfound skills, there's no doubt you'll create a paper that grabs attention and makes a real impact in your field.

Daniel Parker
is a seasoned educational writer focusing on scholarship guidance, research papers, and various forms of academic essays including reflective and narrative essays. His expertise also extends to detailed case studies. A scholar with a background in English Literature and Education, Daniel’s work on EssayPro blog aims to support students in achieving academic excellence and securing scholarships. His hobbies include reading classic literature and participating in academic forums.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.
.webp)
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Finance and Business
- Business Skills
- Business Writing
How to Write a Concept Paper
Last Updated: March 20, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Anar Kazimov . Anar Kazimov is a Digital Marketing Expert based in Vancouver, Canada. He is the Owner and Marketing Director of Pixel Prodigies, a company created to help business owners achieve more sales by revamping their digital portfolio. He has helped the NIH, IBM, Canadian film studios, Rolex dealerships, and many other firms in their marketing campaigns. He previously had a career in the IT industry and worked at Freelancer.com. He received a BS in Computer Science from the University of Victoria. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,630,286 times.
If you’ve got a great idea for a new product, program, or service, writing a concept paper is one way to seek funding for it. Concept papers describe the purpose and projected outcomes of the project, and are delivered to potential sponsors. To create a successful one, use clear, passionate language that expresses why your project matters, and who will benefit from it. Above all, show the sponsor that the goals of your project match up with the kinds of initiatives they want to support.
Sample Concept Papers

Establishing the Purpose

- For instance, you could start off your paper with an attention-grabbing statistic related to your project: “Every year, 10.5 million pounds of food go to waste due to one common pest: rats.”
- Giving your concept paper a descriptive title, like “Lock the Rat Box: Humane, Hands-Free Rodent Control,” is another good way to grab their attention.

- Try something like: “The Savco Foundation has long been committed to funding projects that foster healthy communities. We have developed Lock the Rat Box as an easy, cost-effective means to lower illness rates and sanitation costs in municipalities, and are seeking your support for the project.”

- For instance, your concept paper could include a statement like: “Rats are a nuisance, but also a serious vector of diseases such as rabies and the bubonic plague. Municipalities across the United States spend upwards of twenty million dollars a year combating these issues.”
- Include references to verify any data you cite.
Explaining How your Concept Works

- For instance, your project may involve building a prototype device to humanely trap rats.
- Your methods might also involve activities. For instance, you may propose advertising programs to educate communities about rat problems, or sending investigators to study the extent of the issue in various communities.

- Try using statements like: “While previous governmental services have explained rat infestations via poster, radio, and television campaigns, they have not taken advantage of social media as a means of connecting with community members. Our project fills that gap.”

- For example: “February 2018: sign a lease for a workshop space. Late February 2018: purchase materials for Lock the Rat Box prototype. March 2018: conduct preliminary tests of the prototype.”

- Other assessment tools could include things like surveys to gauge customer satisfaction, community involvement, or other metrics.

- Personnel, including any assistants
- Equipment and supplies
- Consultants you may need to bring in
- Space (rent, for example)

Reviewing the Draft

- If the application requests a particular format, follow the directions exactly.
- Otherwise, type your paper in a standard font at a readable size (12 point is good), number your pages, and use reasonable margins (1 inch all around is fine).

- For instance, avoid statements like “We believe that our product, Lock the Rat Box, could potentially help certain municipalities at least control rat infestations.”
- A stronger statement would be: “Lock the Rat Box will curtail rat infestations in any mid-sized municipality, and completely eradicate them in many cases.”

- If you are writing for a general, non-expert audience, ask someone unfamiliar with your project to read your concept paper and tell you if there were any parts they did not understand.

- Have someone who has not previously read your concept paper take a look at the final draft before you submit it. They’ll be more likely to catch any lingering errors.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.aub.edu.lb/ogc/Documents/Writing_Concept_Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://ovpr.uconn.edu/wp-content/uploads/sites/2557/2018/09/How-to-Write-a-Concept-Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://www.ias.edu/sites/default/files/media-assets/Guidance%20Doc_Concept%20Paper.pdf
- ↑ https://www.umass.edu/cfr/grant-writing/guidelines-letter-intent
About This Article

To write a concept paper for a new product, program, or service, start with a descriptive, attention-grabbing title. Then, explain why you’re approaching the sponsor by describing what your project goals have in common with their company mission. Next, describe the problem you want to solve, and the methods you’ll use in order to solve it. Additionally, include a timeline for implementing your methods, and a preliminary budget with a list of the estimated costs. Finally, end your paper with a short summary reiterating your project’s purpose. For more advice, including how to make your paper stand out with proper formatting and action-oriented language, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Kathryn Torres
Jul 17, 2020

Did this article help you?
Ongole Churchill
Jun 17, 2016
Ruth Denson
Mar 6, 2020
Naseem Khan
Apr 4, 2019
Kumudham Sandrasegaran
Oct 5, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

How to Write a PhD Concept Paper

A concept paper – or concept note – is one of the initial requirements of a PhD programme. It is normally written during the PhD application process as well as early on in the programme once a student has been admitted.
A concept paper is basically a shorter version of a research proposal – in most cases between 2,000 and 2,500 words – that expresses the research ideas of the potential PhD student.
Besides being short, it should be concise yet have adequate details to convince the Department the student is applying to that he/she is worth being admitted to the programme.
Example of a title with a sub-title
References/bibliography, why do phd programmes require applicants to submit a concept paper.
A concept paper serves four main purposes:
- It gives the Department the student is applying to an idea of the student’s research interests.
- Based on point one, it informs the Department whether the student will be a good fit to the Department or not. To be a good fit, the research interests of the applicant should match those of the Department’s faculty.
- Based on the two points above, it enables the Department to offer support to the student throughout his/her PhD studies in the form of supervision and mentorship.
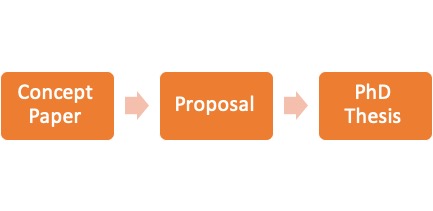
- Because the concept paper is written – and must be accepted – before the full proposal, it saves the student time and effort that would otherwise be spent on topics that may end up being rejected by the Department. A concept paper is therefore the first step to writing the PhD thesis/dissertation (see the figure below).
Format of a PhD Concept Paper
The format of a concept paper might vary from one university to another. A PhD student should therefore read the guidelines provided by his/her University of interest before writing a concept paper.
In general, the following is a common format of a concept paper:
Title of proposed study
The title of the proposed study is the first element of a concept paper.
The title should describe what the study is about by highlighting the variables of the study and the relationship between the variables if applicable.
The title should be short and specific: it is best to have a title that is not more than 15 words’ long.
Example of a title:
Use of Mobile Phone Applications for Weight Management in the United States
In order to add more specificity to the title, you can add a subtitle to the main title. The title and subtitle should be separated by a full colon.
Use of Mobile Phone Applications for Weight Management in the United States:
A Behavioural Economics’ Analysis
Background to the study
The background to the study contains the following elements:
- The history of the topic, both globally and in the proposed location of your study.
- What other researchers have found out from their own studies.
- What the gaps in the existing literature are, that is, what the other researchers have not addressed.
- What your study will contribute towards filling the identified gaps.
The implication of the above is that one must have conducted some literature review prior to writing the background to the study.
Statement of the problem
The statement of the problem is a clear description of the issue that the study will address, the relevance of the issue, the importance (benefits) of addressing the issue, and the method the researcher will use to address the issue.
Goal and objectives of the study
Once you have identified the problem of your study, the next step is to write the goal and objectives of the study. There is a difference between these two:
The goal of the study is a broad statement of what the researcher hopes to accomplish at the end of the study. The goal should also be related to the problem statement.
Any given project should have one goal because having many goals would lead to confusion. However, that one goal can have multiple elements in it, which would be accomplished through the project’s objectives.
The objectives of the study, on the other hand, are specific and detailed statements of how the researcher will go about accomplishing the stated goal.
The objectives should:
- Support the accomplishment of the goal.
- Follow a sequence, that is, like a step-by-step order. This will help you frame the activities needed to be undertaken in a logical manner so that the goal is achieved.
- Be stated using action verbs, for instance, “to identify”, “to create”, “to establish”, “to measure”, etc.
- Be about 3-4: having too few of objectives will limit the scope of your PhD dissertation, while having too many objectives may complicate the dissertation.
- Be SMART, that is, Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound.
The video below clearly explains how to set SMART goals and objectives:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MAhs-m6cNzY
Important tip 1: depending on your PhD programme, you may be required to have at least 3 journal papers to qualify for graduation. Each of your objectives can be converted into a separate journal paper on its own.
Research questions and hypotheses
Every PhD dissertation needs research questions. Research questions will help the student stay focused on his/her research.
The aim of the research is to provide answers to the research questions. The answers to the questions will form the thesis statement.
Examples of research questions:
In the title example given earlier about use of mobile phone applications for weight management in the United States, a student may be interested in the following questions:
- To what extent do adults in the United States use mobile phone applications to manage their weight?
- Is there any gender disparity in the use of mobile phone apps for weight management in the United States?
- How effective are mobile apps for weight management in the United States?
Good research questions are those that can be explored deeply and widely as well as defended using evidence. Questions with ‘yes” or “no” responses are not academic-worthy.
When developing research questions, you also need to think about the data that will be required to answer the questions. Do you have access to that data? If no, will your time and financial resources allow you to collect that data?
Important tip 2: Your PhD study is time-limited therefore data requirement issues need to be thought through at the initial stages of your concept paper writing so that you don’t waste too much time either collecting the data in the future or trying to access the data if it already exists elsewhere.
Preliminary literature review
At the concept paper stage, a preliminary literature review serves three main purposes:
- It shows whether you have knowledge of the current state of debate about your chosen topic.
- It shows whether you are familiar with the experts in your chosen topic.
- It also helps you identify the research gaps.
Proposed research design, methods and procedures
This sections provides a brief overview of the research methodology that you will adopt in your study. Some issues to consider include:
- Will your study use quantitative, qualitative or mixed-methods approach?
- Will you use secondary or primary data?
- What will be the sources of your data? Will you need any ethical clearance from your university before collecting data?
- Will the data sources be readily accessible?
- Will you use external assistance for data collection? Or will you do all the data collection yourself?
- How will the data be analysed? Which softwares will you use? Are you competent in those softwares?
While the above issues are important to think through, please note that the research design and methods will be informed by your research objectives and research questions. As an illustration:
A research question that aims to measure the effect of one (or more) variable(s) on another variable will definitely require quantitative research methods.
On the other hand, a research question that aims to explain the existence of a phenomenon will render itself to the use of qualitative research methods.
Contribution to knowledge
This is perhaps the most important aspect of a PhD dissertation. Your concept note needs to briefly highlight how your project will add value to knowledge.
Making significant contribution to knowledge at the PhD level does not mean a Nobel prize standard of knowledge (this you can do after your PhD when you’ll have all the time in the world to do so). You can achieve this in various ways:
- New applications of existing ideas.
- New interpretations of previous ideas.
- Investigating an existing issue in a new location.
- Development of a new theory.
- Coming up with a new technique, among others.
The last section of the concept paper is the reference list or bibliography. This is the section that lists the literatures that you have reviewed and cited in your paper.
There is a slight difference between a reference list and a bibliography:
A reference list includes all those studies that have been directly cited in the paper.
A bibliography, on the other hand, includes all those studies that have been directly cited in the paper as well as those that were reviewed and consulted but not cited in the paper.
When creating the reference list/bibliography, one should be mindful of the referencing style that is required by their PhD department (that is, whether APA, MLA, Chicago, Havard, etc).
Final Thoughts on Writing a PhD Concept Paper
The concept paper is the first step to writing the PhD dissertation. Once accepted, the student will proceed to writing the proposal, which will then be defended before proceeding with writing the full dissertation.
The concept paper is a mini-proposal and has most of the components expected in the proposal.
However, the concept paper should be short and precise while at the same time have adequate information to enable the PhD Committee of the PhD Programme the student is applying to judge if the student will be a good fit to the programme or not.
Related posts
How To Choose a Research Topic For Your PhD Thesis (7 Key Factors to Consider)
Comprehensive Guidelines for Writing a PhD Thesis Proposal (+ free checklist for PhD Students)
Grace Njeri-Otieno
Grace Njeri-Otieno is a Kenyan, a wife, a mom, and currently a PhD student, among many other balls she juggles. She holds a Bachelors' and Masters' degrees in Economics and has more than 7 years' experience with an INGO. She was inspired to start this site so as to share the lessons learned throughout her PhD journey with other PhD students. Her vision for this site is "to become a go-to resource center for PhD students in all their spheres of learning."
Recent Content
SPSS Tutorial #12: Partial Correlation Analysis in SPSS
Partial correlation is almost similar to Pearson product-moment correlation only that it accounts for the influence of another variable, which is thought to be correlated with the two variables of...
SPSS Tutorial #11: Correlation Analysis in SPSS
In this post, I discuss what correlation is, the two most common types of correlation statistics used (Pearson and Spearman), and how to conduct correlation analysis in SPSS. What is correlation...
Essay Papers Writing Online
Master the art of crafting a concept essay and perfect your writing skills.

Every great work of literature begins with a spark of inspiration, a kernel of an idea that germinates within the writer’s mind. It is this concept, this central theme, that serves as the foundation of the entire writing process, guiding the writer along the creative journey. In the realm of academic writing, the concept essay holds a special place, as it requires the writer to explore abstract ideas, dissect complex theories, and present their understanding of a particular concept.
Unlike traditional essays where arguments are made, and evidence is provided, concept essays delve into the intangible realm of ideas, taking the reader on a captivating exploration of abstract concepts. These essays challenge the writer to convey their understanding of a concept without relying on concrete evidence or facts. Instead, they rely on the writer’s ability to provide clear definitions, logical explanations, and compelling examples that elucidate the intricacies of the concept at hand.
Effectively crafting a concept essay requires skillful mastery of language and an astute understanding of how ideas interconnect. It is a delicate dance between the power of words and the depth of thought, where metaphors and analogies can breathe life into otherwise elusive notions. The successful concept essay requires more than merely stating definitions or describing the concept; it necessitates the writer’s ability to engage and captivate the reader, transporting them into the realm of ideas where the abstract becomes clear and tangible.
Mastering the Art of Crafting a Conceptual Essay: Indispensable Suggestions and Instructions
Embarking on the journey of composing a conceptual essay necessitates an astute understanding of the complexities involved. This particular form of written expression empowers individuals to delve deeply into abstract concepts, unravel their intricacies, and articulate their findings in a clear and coherent manner. To accomplish this task with finesse, it is imperative to familiarize oneself with indispensable suggestions and instructions that pave the way to success.
1. Explore Profusely:
- Investigate, scrutinize, and immerse yourself in the vast realm of ideas, allowing your mind to explore a myriad of perspectives.
- Delve into diverse disciplines and subjects, sourcing inspiration and insight from a wide array of sources such as literature, art, philosophy, science, and history.
- Be cognizant of the fact that the more extensive your exploration, the richer your conceptual essay will be.
2. Define Your Focus:
- Once you have gathered an abundant collection of ideas, narrow down your focus to a specific concept that captivates your interest.
- Choose a concept that is both intriguing and stimulating, as this will fuel your motivation throughout the writing process.
- Strive to select a concept that possesses a level of complexity, rendering it ripe for analysis and interpretation.
3. Establish a Clear Structure:
- Prior to commencing the writing process, create a well-structured outline that delineates the key sections and points you wish to convey in your essay.
- Ensure that your essay possesses a clear introduction, body paragraphs that expound upon your chosen concept, and a comprehensive conclusion that ties together your arguments.
- Organize your thoughts in a logical manner, employing effective transitions that allow your essay to flow seamlessly.
4. Support your Claims:
- Avoid presenting mere conjecture or personal opinions; instead, bolster your arguments with credible evidence and examples.
- Cite reputable sources, such as scholarly articles, books, or studies, to lend credibility and authority to your assertions.
- Engage critically with the works of other esteemed thinkers, analyzing their viewpoints and incorporating them into your own exploration of the concept.
5. Polish and Perfect:
- Once you have crafted the initial draft of your conceptual essay, allocate ample time for revision and refinement.
- Engage in meticulous proofreading to eliminate any errors in grammar, punctuation, or syntax that may detract from the overall impact of your work.
- Solicit feedback from trusted peers or mentors, incorporating their suggestions into your final version.
In conclusion, mastering the art of crafting a conceptual essay demands diligent exploration, focused attention, and a commitment to delivering a well-structured and thought-provoking piece of writing. By following these essential tips and guidelines, you can navigate the intricacies of this unique form of expression and develop an essay that both captivates and informs its readers.
Understanding the Purpose of a Concept Essay
Having a clear understanding of the purpose behind writing a concept essay is crucial for creating a successful piece of writing. Concept essays aim to explore and explain abstract ideas, theories, or concepts in a way that is accessible and engaging to readers.
Although concept essays may vary in subject matter, their main objective is to break down complex ideas and make them understandable to a wider audience. These essays often require deep analysis and critical thinking to present the chosen concept in a comprehensive and enlightening manner.
A concept essay goes beyond simply defining a concept but delves deeper into the underlying principles and implications. It requires the writer to provide insight, examples, and evidence to support their claims and demonstrate a thorough understanding of the concept being discussed.
Concept essays also provide an opportunity for writers to explore new and innovative ideas and present them in a thought-provoking way. They allow for personal interpretation and creativity, encouraging writers to examine a concept from different angles and offer unique perspectives.
Furthermore, concept essays can be used as a tool for education and learning, helping readers expand their knowledge and gain a deeper understanding of various concepts. By breaking down complex ideas into more digestible forms, these essays enable readers to grasp abstract concepts and apply them to real-world situations.
In conclusion, the purpose of a concept essay is to convey abstract ideas or concepts in a clear and engaging manner, utilizing critical thinking and analysis. By presenting complex ideas in a comprehensive way, concept essays facilitate understanding and encourage readers to explore and expand their knowledge in the chosen subject area.
Choosing a Strong and Specific Concept
When it comes to crafting a well-written piece of work, selecting a compelling and precise concept is crucial. The concept you choose will serve as the foundation for your essay, shaping the content, tone, and direction of your writing.
Before diving into the process of choosing a concept, it’s important to understand what exactly a concept is. In this context, a concept can be defined as a broad idea or theme that encapsulates a particular subject or topic. It is the main point or central idea that you want to convey to your readers through your essay.
An effective concept should be strong, meaning it should be able to capture the attention and interest of your readers. It should be something that has depth and substance, allowing for exploration and analysis. A strong concept will engage your audience and motivate them to continue reading.
In addition to being strong, your concept should also be specific. It should be focused and clearly defined, narrowing down your topic to a specific aspect or angle. A specific concept will help you maintain a clear direction in your writing and prevent your essay from becoming too broad or unfocused.
To choose a strong and specific concept, start by brainstorming ideas related to your topic. Think about the main themes or issues you want to address in your essay. Consider what aspects of the topic interest you the most and which ones you feel are worth exploring further.
Once you have a list of potential concepts, evaluate each one based on its strength and specificity. Ask yourself whether the concept captures your interest and whether it has the potential to captivate your audience. Consider whether it is specific enough to guide your writing and provide a clear focus for your essay.
By choosing a strong and specific concept, you will set yourself up for success in writing your concept essay. Remember to select a concept that is compelling, focused, and meaningful to you and your readers. With a well-chosen concept, you will be able to create a thought-provoking and engaging essay that effectively conveys your ideas.
Developing a Clear and Coherent Thesis Statement
When crafting an effective essay, one of the most important elements to consider is the development of a clear and coherent thesis statement. The thesis statement acts as the central theme or main argument of your essay, providing a roadmap for your readers to understand the purpose and direction of your writing.
A well-developed thesis statement not only states your main argument but also provides a clear focus for your essay. It helps you organize your thoughts and ensures that your essay remains cohesive and logical. A strong thesis statement sets the tone for your entire essay and guides the reader through your main ideas.
To develop a clear and coherent thesis statement, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the topic you are writing about. Conducting research and gathering relevant information will help you form a solid foundation for your thesis statement. Make sure to analyze different perspectives on the topic and consider any counterarguments that may arise.
Once you have a good understanding of the topic, you can begin brainstorming and drafting your thesis statement. Start by considering the main idea or argument you want to communicate to your readers. Your thesis statement should be concise and specific, clearly conveying your main point. Avoid vague or general statements that lack focus.
In addition to being clear and concise, your thesis statement should also be arguable. It should present a debatable claim that can be supported with evidence and logical reasoning. This allows you to engage your readers and encourages them to consider different perspectives on the topic.
After drafting your thesis statement, it is important to review and revise it as needed. Make sure it accurately reflects the content and direction of your essay. Consider seeking feedback from peers or instructors to ensure that your thesis statement is clear, coherent, and effectively conveys your main argument.
In conclusion, developing a clear and coherent thesis statement is essential for writing an effective essay. It sets the tone for your entire essay, provides a clear focus, and guides the reader through your main ideas. By thoroughly understanding the topic, brainstorming and drafting a concise and arguable thesis statement, and revising as needed, you can ensure that your essay is well-structured and persuasive.
Structuring Your Concept Essay Effectively

Creating a well-organized structure is vital when it comes to conveying your ideas effectively in a concept essay. By carefully structuring your essay, you can ensure that your audience understands your concept and its various aspects clearly. In this section, we will explore some essential guidelines for structuring your concept essay.
1. Introduction: Begin your essay with an engaging introduction that captures the reader’s attention. This section should provide a brief overview of the concept you will be discussing and its significance. You can use an anecdote, a rhetorical question, or a thought-provoking statement to make your introduction compelling.
2. Definition: After the introduction, it is crucial to provide a clear definition of the concept you will be exploring in your essay. Define the concept in your own words and highlight its key characteristics. You may also include any relevant background information or historical context to enhance the reader’s understanding.
3. Explanation: In this section, you will delve deeper into the concept and explain its various elements, components, or features. Use examples, analogies, or real-life situations to illustrate your points and make them more relatable to the reader. Break down complex ideas into simpler terms and highlight the connections between different aspects of the concept.
4. Analysis: Once you have provided a thorough explanation of the concept, it is time to analyze it critically. Discuss different perspectives or interpretations of the concept and evaluate their strengths and weaknesses. Consider any controversies or debates surrounding the concept and present a balanced view by weighing different arguments.
5. Examples and Case Studies: To further support your arguments and enhance the reader’s understanding, include relevant examples and case studies. These examples can be from real-life situations, historical events, or fictional scenarios. Analyze how the concept has been applied or manifested in these examples and discuss their implications.
6. Conclusion: Conclude your concept essay by summarizing your main points and restating the significance of the concept. Reflect on the insights gained from your analysis and offer any recommendations or suggestions for further exploration. End your essay on a thought-provoking note that leaves the reader with a lasting impression.
By structuring your concept essay effectively, you can ensure that your ideas are presented coherently and persuasively. Remember to use clear and concise language, provide logical transitions between sections, and support your arguments with evidence. With a well-structured essay, you can effectively communicate your understanding of the concept to your audience.
Using Concrete Examples to Illustrate Your Concept
One effective way to clarify and reinforce your concept in a concept essay is by using concrete examples. By providing specific and tangible instances, you can help your readers grasp the abstract and theoretical nature of your concept. Concrete examples bring your concept to life, making it easier for your audience to understand and relate to.
Instead of relying solely on abstract theories, you can support your concept with real-life scenarios, research studies, or personal anecdotes. These examples add depth and relevance to your essay, making it more engaging and meaningful.
When choosing examples to illustrate your concept, it is important to select ones that accurately represent the core elements of your concept. Look for examples that exhibit the underlying principles, attributes, or behaviors that are associated with your concept.
For instance, if your concept is “leadership,” you can provide examples of influential leaders from history or modern-day society. These examples can demonstrate the qualities that define effective leadership, such as integrity, communication skills, and the ability to inspire and motivate others.
Additionally, when presenting concrete examples, ensure that they are relevant and relatable to your target audience. Consider the background and interests of your readers and choose examples that they can easily comprehend and connect with. This will enhance the effectiveness of your essay and create a stronger impact.
In conclusion, using concrete examples is a powerful technique for illustrating your concept in a concept essay. By incorporating specific instances, you can bring clarity, relevance, and authenticity to your writing. This approach allows your readers to grasp your concept more easily and appreciate its practical application in real-life scenarios.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
- How It Works
- Prices & Discounts
How to Write a Concept Paper for a PhD: A 10-Step Guide
Table of contents
Share this article
Achieve Academic Success with Expert Assistance!
Crafted from Scratch for You.
Ensuring Your Work’s Originality.
Transform Your Draft into Excellence.
Perfecting Your Paper’s Grammar, Style, and Format (APA, MLA, etc.).
Calculate the cost of your paper
Get ideas for your essay

Concept Essay Paper
Concept essay generator.

Every writer has his/her own way of presenting a topic or an idea to the readers. Some of them wants to stir imaginations and make you create characters and places of your own. Others want to provoke your emotions and indulge you into the story. While others want to simply demonstrate a subject.
Essay writing is considered a talent. It requires a creative mind to be able to present thoughts and emotions and put them into writing. And the most difficult part is how to make it appealing to the readers. Knowing how to start an essay is even more difficult because you have to find the right inspiration to write.
What is Concept Essay? A concept essay is a piece writing that is used to present an idea or a topic with the sole purpose of providing a clear definition and explanation. Their usual content are those topics that may have previously been presented but were not given with full emphasis. Others are controversial and timely issues that raises questions but are not given full answers. What is Concept Paper? A concept paper is a brief document written to provide an overview of a project, research, or idea. It outlines the main goals, objectives, and methods of the intended project, serving as a preliminary proposal. Concept papers are often used to seek approval or funding, presenting the project’s significance, potential impact, and feasibility in a concise manner. This document helps stakeholders, such as sponsors or academic committees, understand the essence of the proposed work and decide whether to support it further.
Concept Paper Writing Topics & Ideas
In conceptual writing, the central focus lies on the idea or concept driving the work, positioning it as the cornerstone of the narrative. This approach dictates that all planning and critical decisions are determined in advance, rendering the actual writing process secondary. Essentially, the concept acts as a blueprint, guiding the creation of the text in a manner that is almost mechanical. Through this method, the initial idea transforms into an engine that propels the development of the written piece, underscoring the precedence of thought over the act of writing itself. Below are the topics and ideas of concept writing
- The Evolution of Digital Privacy
- The Psychology Behind Social Media Addiction
- The Impact of Remote Work on Urban Development
- Sustainability in Fashion: A New Trend
- The Future of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Cultural Identity in a Globalized World
- The Ethics of Genetic Editing
- The Role of Cryptocurrency in Modern Finance
- Mental Health Awareness in the Workplace
- The Influence of Music on Cognitive Development
- Climate Change and Its Effects on Biodiversity
- The Philosophy of Minimalism and Its Life Benefits
- The Rise of E-Learning and Its Educational Impacts
- Urban Farming: Solutions for Food Security
- Virtual Reality: Transforming Entertainment and Education
- The Gig Economy and Its Impact on Traditional Employment
- Social Entrepreneurship: Business for Social Good
- The Intersection of Art and Technology
- Cybersecurity in the Age of Internet of Things
- The Role of Nutrition in Preventing Chronic Diseases
Concept Essay Paper Format
Introduction.
Hook : Start with an engaging sentence to capture the reader’s interest. Background Information : Provide a brief context for the concept you are going to explore. Thesis Statement : Clearly state the concept or idea you will discuss, outlining the main point or argument of your essay.
Body Paragraphs
Each paragraph should focus on a specific aspect of the concept or idea.
Topic Sentence : Introduce the main idea of the paragraph that supports your thesis. Explanation : Offer a detailed explanation of the idea, including definitions, descriptions, and relevant information. Examples and Evidence : Use specific examples, illustrations, or evidence to support your explanations and arguments. This could include statistics, quotes from experts, or real-life scenarios. Analysis : Analyze how the example or evidence supports your topic sentence and thesis, explaining its significance. Transition : Conclude the paragraph with a sentence that smoothly transitions to the next point or paragraph.
Summary of Main Points : Briefly recap the key arguments or explanations presented in your essay. Restatement of Thesis : Reiterate your thesis statement, highlighting how it has been supported through your discussion. Final Thoughts : Offer closing remarks that leave a lasting impression on the reader. This could include implications, future prospects, or a call to action related to the concept.
Concept Paper Example
Enhancing Digital Literacy in Rural Communities: A Pathway to Bridging the Digital Divide The rapid advancement of digital technologies has significantly transformed the way we live, work, and communicate. However, this digital revolution has also led to a widening gap between urban and rural areas in terms of access to technology and digital skills. This concept paper proposes a comprehensive project aimed at enhancing digital literacy in rural communities as a fundamental step toward bridging the digital divide. By equipping rural populations with the necessary digital skills, the project seeks to empower individuals, improve educational outcomes, and unlock economic opportunities. The purpose of this initiative is to develop and implement a scalable digital literacy program tailored to the needs of rural communities. This program will focus on basic computer skills, internet navigation, online safety, and the use of digital tools for education and entrepreneurship. The significance of this project lies in its potential to transform the lives of rural residents, providing them with the skills required to participate fully in the digital world. Objectives of the project include: Assessing the current level of digital literacy in targeted rural areas. Developing a comprehensive digital literacy curriculum that addresses identified needs. Delivering digital literacy training to residents of rural communities through workshops and online modules. Establishing community-based digital hubs equipped with internet access and computing resources. Evaluating the impact of the program on participants’ digital skills, economic opportunities, and educational outcomes. The methodology will encompass a needs assessment to identify specific digital literacy gaps, followed by the development of a curriculum that incorporates both theoretical knowledge and practical skills. Training will be delivered through a combination of in-person workshops and online modules, ensuring broad access. Pre- and post-program assessments will measure the effectiveness of the training. Expected outcomes include improved digital literacy rates among rural populations, increased access to educational and economic opportunities, and enhanced participation in the digital economy. The project aims to establish a model for digital literacy training that can be replicated and scaled in other rural areas. In conclusion, enhancing digital literacy in rural communities presents a critical opportunity to bridge the digital divide and foster equitable access to the benefits of the digital age. This concept paper outlines a clear and actionable plan to empower rural residents with the digital skills necessary for success in a rapidly evolving world.
Concept Essay Outline Sample

penandthepad.com
Concept Essay on Love

professays.com
Concept on Success

nicoletaylor13.weebly.com
Self Concept Essay Example

bestessayhelp.com
Cultural Concept Essay Sample

missouriwestern.edu
Concept Analysis

bristolcc.edu
Concept Essay Format

Business Concept Essay Example

Free Concept Essay

What Are the Steps to Writing a Concept Essay?
One of the things to consider in essay writing is to know how to start an essay. In addition to that, you have to come up with the steps on how to write an effective one.
- Choose a topic. An effective essay is one that presents a more relevant topic. You need to choose the right topic first before you start writing.
- Do your research. You have to back up your claims with factual information from reliable sources. Present at least three to four points for reference.
- Create your outline. The essay outline of your concept essay because readers will consider how your ideas are presented.
Key Elements of Concept Paper
A concept paper outlines a project or idea, presenting its purpose, significance, methodology, expected outcomes, and, if applicable, budget and timeline. It serves to introduce and justify the project, aiming to secure interest or support by succinctly detailing its goals and potential impact.
The key elements are:
How to Make/ Create Concept Paper
1. choose your topic wisely.
Select a topic that is both interesting to you and relevant to your audience or potential funders. It should address a specific problem, need, or question.
2. Conduct Preliminary Research
Gather information on your topic to ensure there’s enough background material to support your concept. This research will help refine your idea and identify gaps your project could fill.
3. Write the Introduction
Start with a strong introduction that captures the essence of your concept. Include a brief overview of the problem or issue your project intends to address, its significance, and why it is worth exploring or implementing.
4. State the Purpose or Objective
Clearly articulate the purpose or objectives of your project or research. What do you aim to achieve? Be specific about the outcomes you anticipate.
5. Provide Background Information
Offer a detailed background that gives context to your concept. This section should include any relevant research, current findings, and a justification for your project or study.
6. Describe the Project or Research Design
Outline how you plan to achieve your objectives. This includes your methodology, the steps you will take, and the resources you will need. For research projects, specify your research questions, hypothesis, and the methods for data collection and analysis.
7. Discuss the Significance
Explain the potential impact of your project or research. How will it contribute to the field, benefit a specific group, or solve a problem? This section is crucial for persuading readers of the value of your concept.
8. Outline the Budget (if applicable)
If your concept paper is for a project requiring funding, provide an estimate of the budget. Break down the costs involved, including materials, personnel, and any other resources.
9. Set a Timeline
Include a proposed timeline for your project or research. This demonstrates planning and feasibility and helps funders understand the project’s scope.
10. Conclude Your Paper
Summarize the key points of your concept paper, reinforcing the importance and feasibility of your project or research. End with a call to action or a statement of next steps.
Importance of Concept Essay
As we go along the path of discovering new and better ideas that could feed our minds with more useful information, we also need to pause and make sure that these concepts are well explained.
The main importance of a concept analytical essay is to provide a more vivid evaluation as well as explanation of the ideas that may seem ambiguous. We cannot just live in a world where we are fed with information that we are supposed to accept. Remember that we have the freedom to accept what is true and decline what is not. With a concept essay, we can dig deeper into things and find out its true essence.
When do you need a concept paper?
A concept paper is needed when initiating a project, seeking funding, or proposing an idea to stakeholders. It serves as a preliminary outline, presenting the project’s rationale, goals, and methodology in a concise format to gauge interest or secure support.
How is a concept paper different from a research paper?
A concept paper differs from a research paper in its purpose and scope. While a concept paper outlines a project idea, seeking approval or funding with a focus on potential impact and methodology, a research paper presents detailed findings from completed research, including analysis and results.
What is the purpose of a concept essay?
The purpose of a concept essay is to explore and clarify a specific idea or concept. It aims to deepen understanding and stimulate thought by examining the concept from various angles, using examples, definitions, and personal insights to articulate its significance and implications.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Explore the concept essay of happiness: what does it mean and how is it achieved?
Discuss in a concept essay the idea of freedom in the modern world.
- Translation
Concept Paper vs. Research Proposal – and when to use each
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 08 March, 2022
On the surface, concept papers sound like they do the same job as a research proposal – and essentially, they do. Both are designed to communicate the rationale, methodology and outcomes of a proposed piece of work. The difference between the two lies mostly in the level of detail and the potential audience, based on which your approach towards writing each will vary. In this article, we dig deeper into these and recommend when to use which.
Concept paper: Putting your idea to paper
- What : A concept paper verbalises an idea and puts it to paper for the first time. Here, an overall rationale is presented, with a focus on the essential idea and potential impact of the expected outcome(s). However, what you would not include here is much in-depth detail.
- When : Writing a concept paper is most useful when an initial expression of interest is made to either a collaborator or funder – provided the funder has mechanisms for you to do this, like an open call.
- Why : The aim of your concept paper will be to win your audience over with your idea and its potential ramifications.
(For more on concept papers, read: Understanding and developing a concept paper )
Research proposal: Showing how things will get done
Let’s say that through your concept paper, you find funding and collaborators for your proposed research project. You will now get into the nitty gritty of the project with a research proposal, while still keeping it “consumable” enough for a broader audience.
- What : A research proposal builds on a concept paper by now including aspects like key deliverables, milestones and specific outcomes, as well as how you plan to achieve these.
- When : You will typically send a research proposal to sources of funding of an open nature, i.e. those that do not require a standardised form to be filled in, as is often the case with institutional internal funding or private investors.
- Why : It is not necessary for you to first send someone a concept paper and follow it up with a proposal. However, you may often need to follow this sequence in order to provide only ‘need to know’ material depending on the stage of your relationship with potential partners.
( For more on research proposals, read: Writing a successful research proposal )
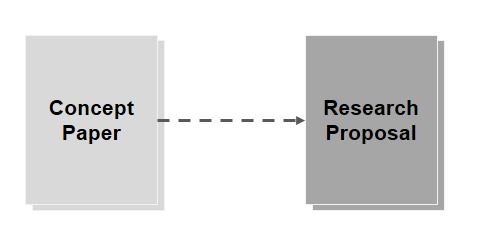
When both are needed, a concept paper precedes a research proposal
Deciding between a concept paper and a research proposal
Whether you send someone a concept paper or a research proposal depends entirely on two things:
- Your existing relationship with whomever you are reaching out to
- What you are trying to achieve
If you are emailing an organisation or individual for the first time, you are more likely to receive a response by attaching a brief, snappy concept paper that is easily read by a multitude of people. On the other hand, some larger organisations, such as pharmaceutical companies, are very used to seeing full-fledged research proposals and may have a portal on their website where you would need to upload one, enabling them to skip the preliminary step of vetting your work through a concept paper.
Our recommendation : Given how pressed many people are for time these days, it would be prudent to send concept papers more frequently than research proposals. If more information is required, you will be asked for it.
Concept papers and research proposals do very similar things, but set out and achieve very different aims. They are often sent in sequence – the concept paper first, followed by the research proposal. The need for a research proposal arises when the concept paper has achieved its mark – when, for example, more information is required for a funding decision to be reached, or due diligence is to be performed, as a result of your concept paper gaining preliminary acceptance. Following up with a research proposal fills in the gaps and will aid in answering questions arising from the concept paper.
Read previous (second) in series: Writing a successful Research Proposal
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Charlesworth Author Services, a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928.
To know more about our services, visit: Our Services
Share with your colleagues
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction
Published on September 7, 2022 by Tegan George and Shona McCombes. Revised on November 21, 2023.
The introduction is the first section of your thesis or dissertation , appearing right after the table of contents . Your introduction draws your reader in, setting the stage for your research with a clear focus, purpose, and direction on a relevant topic .
Your introduction should include:
- Your topic, in context: what does your reader need to know to understand your thesis dissertation?
- Your focus and scope: what specific aspect of the topic will you address?
- The relevance of your research: how does your work fit into existing studies on your topic?
- Your questions and objectives: what does your research aim to find out, and how?
- An overview of your structure: what does each section contribute to the overall aim?
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to start your introduction, topic and context, focus and scope, relevance and importance, questions and objectives, overview of the structure, thesis introduction example, introduction checklist, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about introductions.
Although your introduction kicks off your dissertation, it doesn’t have to be the first thing you write — in fact, it’s often one of the very last parts to be completed (just before your abstract ).
It’s a good idea to write a rough draft of your introduction as you begin your research, to help guide you. If you wrote a research proposal , consider using this as a template, as it contains many of the same elements. However, be sure to revise your introduction throughout the writing process, making sure it matches the content of your ensuing sections.
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Begin by introducing your dissertation topic and giving any necessary background information. It’s important to contextualize your research and generate interest. Aim to show why your topic is timely or important. You may want to mention a relevant news item, academic debate, or practical problem.
After a brief introduction to your general area of interest, narrow your focus and define the scope of your research.
You can narrow this down in many ways, such as by:
- Geographical area
- Time period
- Demographics or communities
- Themes or aspects of the topic
It’s essential to share your motivation for doing this research, as well as how it relates to existing work on your topic. Further, you should also mention what new insights you expect it will contribute.
Start by giving a brief overview of the current state of research. You should definitely cite the most relevant literature, but remember that you will conduct a more in-depth survey of relevant sources in the literature review section, so there’s no need to go too in-depth in the introduction.
Depending on your field, the importance of your research might focus on its practical application (e.g., in policy or management) or on advancing scholarly understanding of the topic (e.g., by developing theories or adding new empirical data). In many cases, it will do both.
Ultimately, your introduction should explain how your thesis or dissertation:
- Helps solve a practical or theoretical problem
- Addresses a gap in the literature
- Builds on existing research
- Proposes a new understanding of your topic
Perhaps the most important part of your introduction is your questions and objectives, as it sets up the expectations for the rest of your thesis or dissertation. How you formulate your research questions and research objectives will depend on your discipline, topic, and focus, but you should always clearly state the central aim of your research.
If your research aims to test hypotheses , you can formulate them here. Your introduction is also a good place for a conceptual framework that suggests relationships between variables .
- Conduct surveys to collect data on students’ levels of knowledge, understanding, and positive/negative perceptions of government policy.
- Determine whether attitudes to climate policy are associated with variables such as age, gender, region, and social class.
- Conduct interviews to gain qualitative insights into students’ perspectives and actions in relation to climate policy.
To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
I. Introduction
Human language consists of a set of vowels and consonants which are combined to form words. During the speech production process, thoughts are converted into spoken utterances to convey a message. The appropriate words and their meanings are selected in the mental lexicon (Dell & Burger, 1997). This pre-verbal message is then grammatically coded, during which a syntactic representation of the utterance is built.
Speech, language, and voice disorders affect the vocal cords, nerves, muscles, and brain structures, which result in a distorted language reception or speech production (Sataloff & Hawkshaw, 2014). The symptoms vary from adding superfluous words and taking pauses to hoarseness of the voice, depending on the type of disorder (Dodd, 2005). However, distortions of the speech may also occur as a result of a disease that seems unrelated to speech, such as multiple sclerosis or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
This study aims to determine which acoustic parameters are suitable for the automatic detection of exacerbations in patients suffering from chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) by investigating which aspects of speech differ between COPD patients and healthy speakers and which aspects differ between COPD patients in exacerbation and stable COPD patients.
Checklist: Introduction
I have introduced my research topic in an engaging way.
I have provided necessary context to help the reader understand my topic.
I have clearly specified the focus of my research.
I have shown the relevance and importance of the dissertation topic .
I have clearly stated the problem or question that my research addresses.
I have outlined the specific objectives of the research .
I have provided an overview of the dissertation’s structure .
You've written a strong introduction for your thesis or dissertation. Use the other checklists to continue improving your dissertation.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
Scope of research is determined at the beginning of your research process , prior to the data collection stage. Sometimes called “scope of study,” your scope delineates what will and will not be covered in your project. It helps you focus your work and your time, ensuring that you’ll be able to achieve your goals and outcomes.
Defining a scope can be very useful in any research project, from a research proposal to a thesis or dissertation . A scope is needed for all types of research: quantitative , qualitative , and mixed methods .
To define your scope of research, consider the following:
- Budget constraints or any specifics of grant funding
- Your proposed timeline and duration
- Specifics about your population of study, your proposed sample size , and the research methodology you’ll pursue
- Any inclusion and exclusion criteria
- Any anticipated control , extraneous , or confounding variables that could bias your research if not accounted for properly.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. & McCombes, S. (2023, November 21). How to Write a Thesis or Dissertation Introduction. Scribbr. Retrieved August 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/introduction-structure/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to choose a dissertation topic | 8 steps to follow, how to write an abstract | steps & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
Developing a Thesis Statement
Many papers you write require developing a thesis statement. In this section you’ll learn what a thesis statement is and how to write one.
Keep in mind that not all papers require thesis statements . If in doubt, please consult your instructor for assistance.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement . . .
- Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic.
- Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper.
- Is focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Is generally located near the end of the introduction ; sometimes, in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or in an entire paragraph.
- Identifies the relationships between the pieces of evidence that you are using to support your argument.
Not all papers require thesis statements! Ask your instructor if you’re in doubt whether you need one.
Identify a topic
Your topic is the subject about which you will write. Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic; or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper.
Consider what your assignment asks you to do
Inform yourself about your topic, focus on one aspect of your topic, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts, generate a topic from an assignment.
Below are some possible topics based on sample assignments.
Sample assignment 1
Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II.
Identified topic
Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis
This topic avoids generalities such as “Spain” and “World War II,” addressing instead on Franco’s role (a specific aspect of “Spain”) and the diplomatic relations between the Allies and Axis (a specific aspect of World War II).
Sample assignment 2
Analyze one of Homer’s epic similes in the Iliad.
The relationship between the portrayal of warfare and the epic simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64.
This topic focuses on a single simile and relates it to a single aspect of the Iliad ( warfare being a major theme in that work).
Developing a Thesis Statement–Additional information
Your assignment may suggest several ways of looking at a topic, or it may name a fairly general concept that you will explore or analyze in your paper. You’ll want to read your assignment carefully, looking for key terms that you can use to focus your topic.
Sample assignment: Analyze Spain’s neutrality in World War II Key terms: analyze, Spain’s neutrality, World War II
After you’ve identified the key words in your topic, the next step is to read about them in several sources, or generate as much information as possible through an analysis of your topic. Obviously, the more material or knowledge you have, the more possibilities will be available for a strong argument. For the sample assignment above, you’ll want to look at books and articles on World War II in general, and Spain’s neutrality in particular.
As you consider your options, you must decide to focus on one aspect of your topic. This means that you cannot include everything you’ve learned about your topic, nor should you go off in several directions. If you end up covering too many different aspects of a topic, your paper will sprawl and be unconvincing in its argument, and it most likely will not fulfull the assignment requirements.
For the sample assignment above, both Spain’s neutrality and World War II are topics far too broad to explore in a paper. You may instead decide to focus on Franco’s role in the diplomatic relationships between the Allies and the Axis , which narrows down what aspects of Spain’s neutrality and World War II you want to discuss, as well as establishes a specific link between those two aspects.
Before you go too far, however, ask yourself whether your topic is worthy of your efforts. Try to avoid topics that already have too much written about them (i.e., “eating disorders and body image among adolescent women”) or that simply are not important (i.e. “why I like ice cream”). These topics may lead to a thesis that is either dry fact or a weird claim that cannot be supported. A good thesis falls somewhere between the two extremes. To arrive at this point, ask yourself what is new, interesting, contestable, or controversial about your topic.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times . Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Derive a main point from topic
Once you have a topic, you will have to decide what the main point of your paper will be. This point, the “controlling idea,” becomes the core of your argument (thesis statement) and it is the unifying idea to which you will relate all your sub-theses. You can then turn this “controlling idea” into a purpose statement about what you intend to do in your paper.
Look for patterns in your evidence
Compose a purpose statement.
Consult the examples below for suggestions on how to look for patterns in your evidence and construct a purpose statement.
- Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis
- Franco turned to the Allies when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from the Axis
Possible conclusion:
Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: Franco’s desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power.
Purpose statement
This paper will analyze Franco’s diplomacy during World War II to see how it contributed to Spain’s neutrality.
- The simile compares Simoisius to a tree, which is a peaceful, natural image.
- The tree in the simile is chopped down to make wheels for a chariot, which is an object used in warfare.
At first, the simile seems to take the reader away from the world of warfare, but we end up back in that world by the end.
This paper will analyze the way the simile about Simoisius at 4.547-64 moves in and out of the world of warfare.
Derive purpose statement from topic
To find out what your “controlling idea” is, you have to examine and evaluate your evidence . As you consider your evidence, you may notice patterns emerging, data repeated in more than one source, or facts that favor one view more than another. These patterns or data may then lead you to some conclusions about your topic and suggest that you can successfully argue for one idea better than another.
For instance, you might find out that Franco first tried to negotiate with the Axis, but when he couldn’t get some concessions that he wanted from them, he turned to the Allies. As you read more about Franco’s decisions, you may conclude that Spain’s neutrality in WWII occurred for an entirely personal reason: his desire to preserve his own (and Spain’s) power. Based on this conclusion, you can then write a trial thesis statement to help you decide what material belongs in your paper.
Sometimes you won’t be able to find a focus or identify your “spin” or specific argument immediately. Like some writers, you might begin with a purpose statement just to get yourself going. A purpose statement is one or more sentences that announce your topic and indicate the structure of the paper but do not state the conclusions you have drawn . Thus, you might begin with something like this:
- This paper will look at modern language to see if it reflects male dominance or female oppression.
- I plan to analyze anger and derision in offensive language to see if they represent a challenge of society’s authority.
At some point, you can turn a purpose statement into a thesis statement. As you think and write about your topic, you can restrict, clarify, and refine your argument, crafting your thesis statement to reflect your thinking.
As you work on your thesis, remember to keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Sometimes your thesis needs to evolve as you develop new insights, find new evidence, or take a different approach to your topic.
Compose a draft thesis statement
If you are writing a paper that will have an argumentative thesis and are having trouble getting started, the techniques in the table below may help you develop a temporary or “working” thesis statement.
Begin with a purpose statement that you will later turn into a thesis statement.
Assignment: Discuss the history of the Reform Party and explain its influence on the 1990 presidential and Congressional election.
Purpose Statement: This paper briefly sketches the history of the grassroots, conservative, Perot-led Reform Party and analyzes how it influenced the economic and social ideologies of the two mainstream parties.
Question-to-Assertion
If your assignment asks a specific question(s), turn the question(s) into an assertion and give reasons why it is true or reasons for your opinion.
Assignment : What do Aylmer and Rappaccini have to be proud of? Why aren’t they satisfied with these things? How does pride, as demonstrated in “The Birthmark” and “Rappaccini’s Daughter,” lead to unexpected problems?
Beginning thesis statement: Alymer and Rappaccinni are proud of their great knowledge; however, they are also very greedy and are driven to use their knowledge to alter some aspect of nature as a test of their ability. Evil results when they try to “play God.”
Write a sentence that summarizes the main idea of the essay you plan to write.
Main idea: The reason some toys succeed in the market is that they appeal to the consumers’ sense of the ridiculous and their basic desire to laugh at themselves.
Make a list of the ideas that you want to include; consider the ideas and try to group them.
- nature = peaceful
- war matériel = violent (competes with 1?)
- need for time and space to mourn the dead
- war is inescapable (competes with 3?)
Use a formula to arrive at a working thesis statement (you will revise this later).
- although most readers of _______ have argued that _______, closer examination shows that _______.
- _______ uses _______ and _____ to prove that ________.
- phenomenon x is a result of the combination of __________, __________, and _________.
What to keep in mind as you draft an initial thesis statement
Beginning statements obtained through the methods illustrated above can serve as a framework for planning or drafting your paper, but remember they’re not yet the specific, argumentative thesis you want for the final version of your paper. In fact, in its first stages, a thesis statement usually is ill-formed or rough and serves only as a planning tool.
As you write, you may discover evidence that does not fit your temporary or “working” thesis. Or you may reach deeper insights about your topic as you do more research, and you will find that your thesis statement has to be more complicated to match the evidence that you want to use.
You must be willing to reject or omit some evidence in order to keep your paper cohesive and your reader focused. Or you may have to revise your thesis to match the evidence and insights that you want to discuss. Read your draft carefully, noting the conclusions you have drawn and the major ideas which support or prove those conclusions. These will be the elements of your final thesis statement.
Sometimes you will not be able to identify these elements in your early drafts, but as you consider how your argument is developing and how your evidence supports your main idea, ask yourself, “ What is the main point that I want to prove/discuss? ” and “ How will I convince the reader that this is true? ” When you can answer these questions, then you can begin to refine the thesis statement.
Refine and polish the thesis statement
To get to your final thesis, you’ll need to refine your draft thesis so that it’s specific and arguable.
- Ask if your draft thesis addresses the assignment
- Question each part of your draft thesis
- Clarify vague phrases and assertions
- Investigate alternatives to your draft thesis
Consult the example below for suggestions on how to refine your draft thesis statement.
Sample Assignment
Choose an activity and define it as a symbol of American culture. Your essay should cause the reader to think critically about the society which produces and enjoys that activity.
- Ask The phenomenon of drive-in facilities is an interesting symbol of american culture, and these facilities demonstrate significant characteristics of our society.This statement does not fulfill the assignment because it does not require the reader to think critically about society.
Drive-ins are an interesting symbol of American culture because they represent Americans’ significant creativity and business ingenuity.
Among the types of drive-in facilities familiar during the twentieth century, drive-in movie theaters best represent American creativity, not merely because they were the forerunner of later drive-ins and drive-throughs, but because of their impact on our culture: they changed our relationship to the automobile, changed the way people experienced movies, and changed movie-going into a family activity.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast-food establishments, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize America’s economic ingenuity, they also have affected our personal standards.
While drive-in facilities such as those at fast- food restaurants, banks, pharmacies, and dry cleaners symbolize (1) Americans’ business ingenuity, they also have contributed (2) to an increasing homogenization of our culture, (3) a willingness to depersonalize relationships with others, and (4) a tendency to sacrifice quality for convenience.
This statement is now specific and fulfills all parts of the assignment. This version, like any good thesis, is not self-evident; its points, 1-4, will have to be proven with evidence in the body of the paper. The numbers in this statement indicate the order in which the points will be presented. Depending on the length of the paper, there could be one paragraph for each numbered item or there could be blocks of paragraph for even pages for each one.
Complete the final thesis statement
The bottom line.
As you move through the process of crafting a thesis, you’ll need to remember four things:
- Context matters! Think about your course materials and lectures. Try to relate your thesis to the ideas your instructor is discussing.
- As you go through the process described in this section, always keep your assignment in mind . You will be more successful when your thesis (and paper) responds to the assignment than if it argues a semi-related idea.
- Your thesis statement should be precise, focused, and contestable ; it should predict the sub-theses or blocks of information that you will use to prove your argument.
- Make sure that you keep the rest of your paper in mind at all times. Change your thesis as your paper evolves, because you do not want your thesis to promise more than your paper actually delivers.
In the beginning, the thesis statement was a tool to help you sharpen your focus, limit material and establish the paper’s purpose. When your paper is finished, however, the thesis statement becomes a tool for your reader. It tells the reader what you have learned about your topic and what evidence led you to your conclusion. It keeps the reader on track–well able to understand and appreciate your argument.

Writing Process and Structure
This is an accordion element with a series of buttons that open and close related content panels.
Getting Started with Your Paper
Interpreting Writing Assignments from Your Courses
Generating Ideas for
Creating an Argument
Thesis vs. Purpose Statements
Architecture of Arguments
Working with Sources
Quoting and Paraphrasing Sources
Using Literary Quotations
Citing Sources in Your Paper
Drafting Your Paper
Generating Ideas for Your Paper
Introductions
Paragraphing
Developing Strategic Transitions
Conclusions
Revising Your Paper
Peer Reviews
Reverse Outlines
Revising an Argumentative Paper
Revision Strategies for Longer Projects
Finishing Your Paper
Twelve Common Errors: An Editing Checklist
How to Proofread your Paper
Writing Collaboratively
Collaborative and Group Writing

IMAGES
COMMENTS
follow these steps: 1. Concept paper title. Every pa per must have a title and concept paper is not left out as one needs to have a title that. summarizes what the paper is about. The title should ...
Write to your audience. A concept paper is a piece of academic writing, so use a professional tone. Avoid colloquialisms, slang, and other conversational language. Your concept paper should use the same tone and style as your accompanying research paper. Write according to your reader's familiarity with the subject of your concept paper.
Additionally, infographics and scientific illustrations can enhance the document's impact and engagement with the audience. The steps to write a concept paper are as follows: 1. Write a Crisp Title: Choose a clear, descriptive title that encapsulates the main idea. The title should express the paper's content.
Concept Paper vs. Research Proposal. Getting Started on Your Concept Paper. 1. Find a research topic you are interested in. Tips for finding your research topic. 2. Think of research questions that you want to answer in your project. 3. Formulate your research hypothesis.
A concept paper is a short document written by a researcher before starting their research project, with the purpose of explaining what the study is about, why it is important and the methods that will be used. The concept paper will include your proposed research title, a brief introduction to the subject, the aim of the study, the research ...
Funders that request concept papers often provide a template or format. If templates or formats are not provided, the following can serve as a useful concept paper structure. THE FIVE ELEMENTS OF A CONCEPT PAPER 1. The first section, the Introduction, identifies how and where the applicant's mission and the funder's mission intersect or align.
1. To explore and expand an idea: Researchers can use concept papers to transform an incipient research idea into a focused, high-quality study proposal. The paper is also a means to obtain feedback that can be used to strengthen a detailed proposal at a later stage. 2. To draw the interest of funding agencies: Through an effective concept ...
A pre-proposal or white paper is. a concise, authoritative document that presents a summary of the proposed research, methodology, team, and an estimated budget. Unlike proposals, which include more extensive information, white papers offer a brief overview of. a research project in a way that explores why it would be important to a funder.
The concept paper saves time because your thesis or review panel may say that your concept is not worth pursuing. A concept paper should consist only of 1 or 2 pages. Alternatively, if you want to deal with complex issues that require expounding on the ideas, it can go up to 5 pages.
A concept paper is a brief paper that outlines the important components of a research or project before it is carried out. Its purpose is to offer an overview. Entrepreneurs working on a business idea or product, as well as students and researchers, frequently write concept papers. Researchers may be required to prepare a concept paper when ...
A concept paper, as we've discussed, is a concise document that outlines the basic idea or proposal for a project. It's like the blueprint or roadmap for your research endeavor. The focus here is on articulating the central concept, defining the objectives, and outlining the methodology. ... research papers, and various forms of academic essays ...
Otherwise, type your paper in a standard font at a readable size (12 point is good), number your pages, and use reasonable margins (1 inch all around is fine). 2. Check that the language of your concept paper is action-oriented. Sponsors are looking for projects that are well-thought out and doable.
The title of the proposed study is the first element of a concept paper. The title should describe what the study is about by highlighting the variables of the study and the relationship between the variables if applicable. The title should be short and specific: it is best to have a title that is not more than 15 words' long.
Ensure that your essay possesses a clear introduction, body paragraphs that expound upon your chosen concept, and a comprehensive conclusion that ties together your arguments. Organize your thoughts in a logical manner, employing effective transitions that allow your essay to flow seamlessly. 4. Support your Claims:
A concept paper for a Ph.D. is a written statement outlining the objectives and concepts of a proposed research study. It acts as an introduction to your dissertation or full thesis. It is also an important part of the application process for Ph.D. programs and helps the admissions committee evaluate a student's research potential.
Conceptual frameworks are often represented in a visual format and illustrate cause-and-effect relationships. You can start conceptualizing this as you determine your relevant paper, thesis, or dissertation topic. Keep reading for a step-by-step guide to help you construct your own conceptual framework.
A concept paper is a brief document written to provide an overview of a project, research, or idea. It outlines the main goals, objectives, and methods of the intended project, serving as a preliminary proposal. Concept papers are often used to seek approval or funding, presenting the project's significance, potential impact, and feasibility ...
08 March, 2022. On the surface, concept papers sound like they do the same job as a research proposal - and essentially, they do. Both are designed to communicate the rationale, methodology and outcomes of a proposed piece of work. The difference between the two lies mostly in the level of detail and the potential audience, based on which ...
Revised on April 16, 2024. A thesis is a type of research paper based on your original research. It is usually submitted as the final step of a master's program or a capstone to a bachelor's degree. Writing a thesis can be a daunting experience. Other than a dissertation, it is one of the longest pieces of writing students typically complete.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
A thesis statement makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of the paper. It summarizes the conclusions that the writer has reached about the topic. A thesis statement is generally located near the end of the introduction. Sometimes in a long paper, the thesis will be expressed in several sentences or an entire ...
Overview of the structure. To help guide your reader, end your introduction with an outline of the structure of the thesis or dissertation to follow. Share a brief summary of each chapter, clearly showing how each contributes to your central aims. However, be careful to keep this overview concise: 1-2 sentences should be enough.
A thesis statement . . . Makes an argumentative assertion about a topic; it states the conclusions that you have reached about your topic. Makes a promise to the reader about the scope, purpose, and direction of your paper. Is focused and specific enough to be "proven" within the boundaries of your paper. Is generally located near the end ...