Rubric Best Practices, Examples, and Templates
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
Rubrics can help instructors communicate expectations to students and assess student work fairly, consistently and efficiently. Rubrics can provide students with informative feedback on their strengths and weaknesses so that they can reflect on their performance and work on areas that need improvement.

How to Get Started
Best practices, moodle how-to guides.
- Workshop Recording (Spring 2024)
- Workshop Registration
Step 1: Analyze the assignment
The first step in the rubric creation process is to analyze the assignment or assessment for which you are creating a rubric. To do this, consider the following questions:
- What is the purpose of the assignment and your feedback? What do you want students to demonstrate through the completion of this assignment (i.e. what are the learning objectives measured by it)? Is it a summative assessment, or will students use the feedback to create an improved product?
- Does the assignment break down into different or smaller tasks? Are these tasks equally important as the main assignment?
- What would an “excellent” assignment look like? An “acceptable” assignment? One that still needs major work?
- How detailed do you want the feedback you give students to be? Do you want/need to give them a grade?
Step 2: Decide what kind of rubric you will use
Types of rubrics: holistic, analytic/descriptive, single-point
Holistic Rubric. A holistic rubric includes all the criteria (such as clarity, organization, mechanics, etc.) to be considered together and included in a single evaluation. With a holistic rubric, the rater or grader assigns a single score based on an overall judgment of the student’s work, using descriptions of each performance level to assign the score.
Advantages of holistic rubrics:
- Can p lace an emphasis on what learners can demonstrate rather than what they cannot
- Save grader time by minimizing the number of evaluations to be made for each student
- Can be used consistently across raters, provided they have all been trained
Disadvantages of holistic rubrics:
- Provide less specific feedback than analytic/descriptive rubrics
- Can be difficult to choose a score when a student’s work is at varying levels across the criteria
- Any weighting of c riteria cannot be indicated in the rubric
Analytic/Descriptive Rubric . An analytic or descriptive rubric often takes the form of a table with the criteria listed in the left column and with levels of performance listed across the top row. Each cell contains a description of what the specified criterion looks like at a given level of performance. Each of the criteria is scored individually.
Advantages of analytic rubrics:
- Provide detailed feedback on areas of strength or weakness
- Each criterion can be weighted to reflect its relative importance
Disadvantages of analytic rubrics:
- More time-consuming to create and use than a holistic rubric
- May not be used consistently across raters unless the cells are well defined
- May result in giving less personalized feedback
Single-Point Rubric . A single-point rubric is breaks down the components of an assignment into different criteria, but instead of describing different levels of performance, only the “proficient” level is described. Feedback space is provided for instructors to give individualized comments to help students improve and/or show where they excelled beyond the proficiency descriptors.
Advantages of single-point rubrics:
- Easier to create than an analytic/descriptive rubric
- Perhaps more likely that students will read the descriptors
- Areas of concern and excellence are open-ended
- May removes a focus on the grade/points
- May increase student creativity in project-based assignments
Disadvantage of analytic rubrics: Requires more work for instructors writing feedback
Step 3 (Optional): Look for templates and examples.
You might Google, “Rubric for persuasive essay at the college level” and see if there are any publicly available examples to start from. Ask your colleagues if they have used a rubric for a similar assignment. Some examples are also available at the end of this article. These rubrics can be a great starting point for you, but consider steps 3, 4, and 5 below to ensure that the rubric matches your assignment description, learning objectives and expectations.
Step 4: Define the assignment criteria
Make a list of the knowledge and skills are you measuring with the assignment/assessment Refer to your stated learning objectives, the assignment instructions, past examples of student work, etc. for help.
Helpful strategies for defining grading criteria:
- Collaborate with co-instructors, teaching assistants, and other colleagues
- Brainstorm and discuss with students
- Can they be observed and measured?
- Are they important and essential?
- Are they distinct from other criteria?
- Are they phrased in precise, unambiguous language?
- Revise the criteria as needed
- Consider whether some are more important than others, and how you will weight them.
Step 5: Design the rating scale
Most ratings scales include between 3 and 5 levels. Consider the following questions when designing your rating scale:
- Given what students are able to demonstrate in this assignment/assessment, what are the possible levels of achievement?
- How many levels would you like to include (more levels means more detailed descriptions)
- Will you use numbers and/or descriptive labels for each level of performance? (for example 5, 4, 3, 2, 1 and/or Exceeds expectations, Accomplished, Proficient, Developing, Beginning, etc.)
- Don’t use too many columns, and recognize that some criteria can have more columns that others . The rubric needs to be comprehensible and organized. Pick the right amount of columns so that the criteria flow logically and naturally across levels.
Step 6: Write descriptions for each level of the rating scale
Artificial Intelligence tools like Chat GPT have proven to be useful tools for creating a rubric. You will want to engineer your prompt that you provide the AI assistant to ensure you get what you want. For example, you might provide the assignment description, the criteria you feel are important, and the number of levels of performance you want in your prompt. Use the results as a starting point, and adjust the descriptions as needed.
Building a rubric from scratch
For a single-point rubric , describe what would be considered “proficient,” i.e. B-level work, and provide that description. You might also include suggestions for students outside of the actual rubric about how they might surpass proficient-level work.
For analytic and holistic rubrics , c reate statements of expected performance at each level of the rubric.
- Consider what descriptor is appropriate for each criteria, e.g., presence vs absence, complete vs incomplete, many vs none, major vs minor, consistent vs inconsistent, always vs never. If you have an indicator described in one level, it will need to be described in each level.
- You might start with the top/exemplary level. What does it look like when a student has achieved excellence for each/every criterion? Then, look at the “bottom” level. What does it look like when a student has not achieved the learning goals in any way? Then, complete the in-between levels.
- For an analytic rubric , do this for each particular criterion of the rubric so that every cell in the table is filled. These descriptions help students understand your expectations and their performance in regard to those expectations.
Well-written descriptions:
- Describe observable and measurable behavior
- Use parallel language across the scale
- Indicate the degree to which the standards are met
Step 7: Create your rubric
Create your rubric in a table or spreadsheet in Word, Google Docs, Sheets, etc., and then transfer it by typing it into Moodle. You can also use online tools to create the rubric, but you will still have to type the criteria, indicators, levels, etc., into Moodle. Rubric creators: Rubistar , iRubric
Step 8: Pilot-test your rubric
Prior to implementing your rubric on a live course, obtain feedback from:
- Teacher assistants
Try out your new rubric on a sample of student work. After you pilot-test your rubric, analyze the results to consider its effectiveness and revise accordingly.
- Limit the rubric to a single page for reading and grading ease
- Use parallel language . Use similar language and syntax/wording from column to column. Make sure that the rubric can be easily read from left to right or vice versa.
- Use student-friendly language . Make sure the language is learning-level appropriate. If you use academic language or concepts, you will need to teach those concepts.
- Share and discuss the rubric with your students . Students should understand that the rubric is there to help them learn, reflect, and self-assess. If students use a rubric, they will understand the expectations and their relevance to learning.
- Consider scalability and reusability of rubrics. Create rubric templates that you can alter as needed for multiple assignments.
- Maximize the descriptiveness of your language. Avoid words like “good” and “excellent.” For example, instead of saying, “uses excellent sources,” you might describe what makes a resource excellent so that students will know. You might also consider reducing the reliance on quantity, such as a number of allowable misspelled words. Focus instead, for example, on how distracting any spelling errors are.
Example of an analytic rubric for a final paper
| Above Average (4) | Sufficient (3) | Developing (2) | Needs improvement (1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| (Thesis supported by relevant information and ideas | The central purpose of the student work is clear and supporting ideas always are always well-focused. Details are relevant, enrich the work. | The central purpose of the student work is clear and ideas are almost always focused in a way that supports the thesis. Relevant details illustrate the author’s ideas. | The central purpose of the student work is identified. Ideas are mostly focused in a way that supports the thesis. | The purpose of the student work is not well-defined. A number of central ideas do not support the thesis. Thoughts appear disconnected. |
| (Sequencing of elements/ ideas) | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which flows naturally and is engaging to the audience. | Information and ideas are presented in a logical sequence which is followed by the reader with little or no difficulty. | Information and ideas are presented in an order that the audience can mostly follow. | Information and ideas are poorly sequenced. The audience has difficulty following the thread of thought. |
| (Correctness of grammar and spelling) | Minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. | The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by spelling and/or grammatical errors. | Grammatical and/or spelling errors distract from the work. | The readability of the work is seriously hampered by spelling and/or grammatical errors. |
Example of a holistic rubric for a final paper
| The audience is able to easily identify the central message of the work and is engaged by the paper’s clear focus and relevant details. Information is presented logically and naturally. There are minimal to no distracting errors in grammar and spelling. : The audience is easily able to identify the focus of the student work which is supported by relevant ideas and supporting details. Information is presented in a logical manner that is easily followed. The readability of the work is only slightly interrupted by errors. : The audience can identify the central purpose of the student work without little difficulty and supporting ideas are present and clear. The information is presented in an orderly fashion that can be followed with little difficulty. Grammatical and spelling errors distract from the work. : The audience cannot clearly or easily identify the central ideas or purpose of the student work. Information is presented in a disorganized fashion causing the audience to have difficulty following the author’s ideas. The readability of the work is seriously hampered by errors. |
Single-Point Rubric
| Advanced (evidence of exceeding standards) | Criteria described a proficient level | Concerns (things that need work) |
|---|---|---|
| Criteria #1: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #2: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #3: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| Criteria #4: Description reflecting achievement of proficient level of performance | ||
| 90-100 points | 80-90 points | <80 points |
More examples:
- Single Point Rubric Template ( variation )
- Analytic Rubric Template make a copy to edit
- A Rubric for Rubrics
- Bank of Online Discussion Rubrics in different formats
- Mathematical Presentations Descriptive Rubric
- Math Proof Assessment Rubric
- Kansas State Sample Rubrics
- Design Single Point Rubric
Technology Tools: Rubrics in Moodle
- Moodle Docs: Rubrics
- Moodle Docs: Grading Guide (use for single-point rubrics)
Tools with rubrics (other than Moodle)
- Google Assignments
- Turnitin Assignments: Rubric or Grading Form
Other resources
- DePaul University (n.d.). Rubrics .
- Gonzalez, J. (2014). Know your terms: Holistic, Analytic, and Single-Point Rubrics . Cult of Pedagogy.
- Goodrich, H. (1996). Understanding rubrics . Teaching for Authentic Student Performance, 54 (4), 14-17. Retrieved from
- Miller, A. (2012). Tame the beast: tips for designing and using rubrics.
- Ragupathi, K., Lee, A. (2020). Beyond Fairness and Consistency in Grading: The Role of Rubrics in Higher Education. In: Sanger, C., Gleason, N. (eds) Diversity and Inclusion in Global Higher Education. Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore.
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
Free printable to elevate your AI game 🤖
15 Helpful Scoring Rubric Examples for All Grades and Subjects
In the end, they actually make grading easier.

When it comes to student assessment and evaluation, there are a lot of methods to consider. In some cases, testing is the best way to assess a student’s knowledge, and the answers are either right or wrong. But often, assessing a student’s performance is much less clear-cut. In these situations, a scoring rubric is often the way to go, especially if you’re using standards-based grading . Here’s what you need to know about this useful tool, along with lots of rubric examples to get you started.
What is a scoring rubric?
In the United States, a rubric is a guide that lays out the performance expectations for an assignment. It helps students understand what’s required of them, and guides teachers through the evaluation process. (Note that in other countries, the term “rubric” may instead refer to the set of instructions at the beginning of an exam. To avoid confusion, some people use the term “scoring rubric” instead.)
A rubric generally has three parts:
- Performance criteria: These are the various aspects on which the assignment will be evaluated. They should align with the desired learning outcomes for the assignment.
- Rating scale: This could be a number system (often 1 to 4) or words like “exceeds expectations, meets expectations, below expectations,” etc.
- Indicators: These describe the qualities needed to earn a specific rating for each of the performance criteria. The level of detail may vary depending on the assignment and the purpose of the rubric itself.
Rubrics take more time to develop up front, but they help ensure more consistent assessment, especially when the skills being assessed are more subjective. A well-developed rubric can actually save teachers a lot of time when it comes to grading. What’s more, sharing your scoring rubric with students in advance often helps improve performance . This way, students have a clear picture of what’s expected of them and what they need to do to achieve a specific grade or performance rating.
Learn more about why and how to use a rubric here.
Types of Rubric
There are three basic rubric categories, each with its own purpose.
Holistic Rubric

Source: Cambrian College
This type of rubric combines all the scoring criteria in a single scale. They’re quick to create and use, but they have drawbacks. If a student’s work spans different levels, it can be difficult to decide which score to assign. They also make it harder to provide feedback on specific aspects.
Traditional letter grades are a type of holistic rubric. So are the popular “hamburger rubric” and “ cupcake rubric ” examples. Learn more about holistic rubrics here.
Analytic Rubric
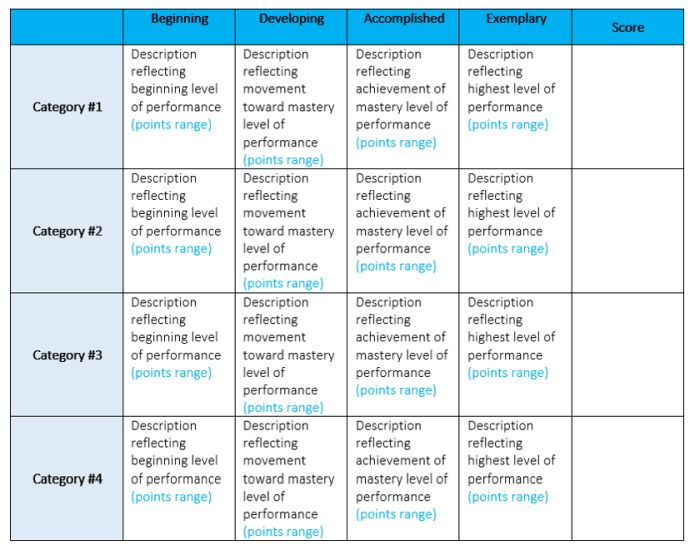
Source: University of Nebraska
Analytic rubrics are much more complex and generally take a great deal more time up front to design. They include specific details of the expected learning outcomes, and descriptions of what criteria are required to meet various performance ratings in each. Each rating is assigned a point value, and the total number of points earned determines the overall grade for the assignment.
Though they’re more time-intensive to create, analytic rubrics actually save time while grading. Teachers can simply circle or highlight any relevant phrases in each rating, and add a comment or two if needed. They also help ensure consistency in grading, and make it much easier for students to understand what’s expected of them.
Learn more about analytic rubrics here.
Developmental Rubric
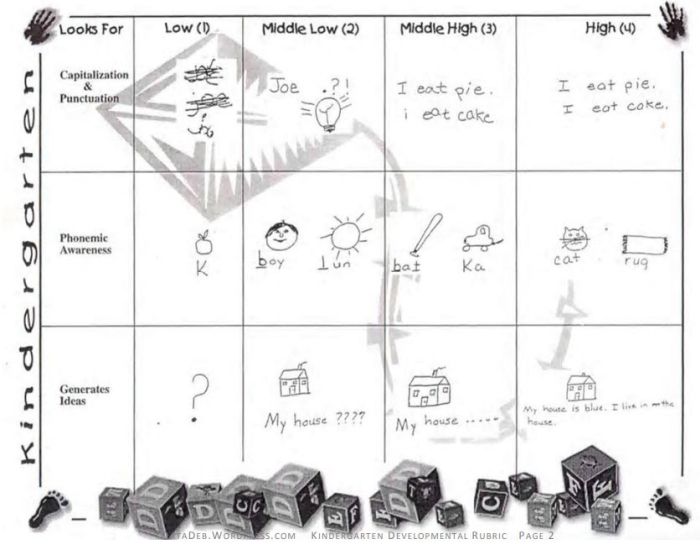
Source: Deb’s Data Digest
A developmental rubric is a type of analytic rubric, but it’s used to assess progress along the way rather than determining a final score on an assignment. The details in these rubrics help students understand their achievements, as well as highlight the specific skills they still need to improve.
Developmental rubrics are essentially a subset of analytic rubrics. They leave off the point values, though, and focus instead on giving feedback using the criteria and indicators of performance.
Learn how to use developmental rubrics here.
Ready to create your own rubrics? Find general tips on designing rubrics here. Then, check out these examples across all grades and subjects to inspire you.
Elementary School Rubric Examples
These elementary school rubric examples come from real teachers who use them with their students. Adapt them to fit your needs and grade level.
Reading Fluency Rubric
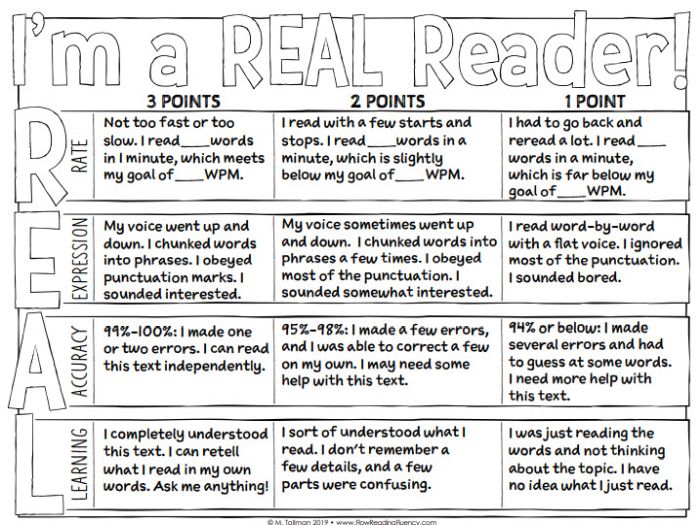
You can use this one as an analytic rubric by counting up points to earn a final score, or just to provide developmental feedback. There’s a second rubric page available specifically to assess prosody (reading with expression).
Learn more: Teacher Thrive
Reading Comprehension Rubric
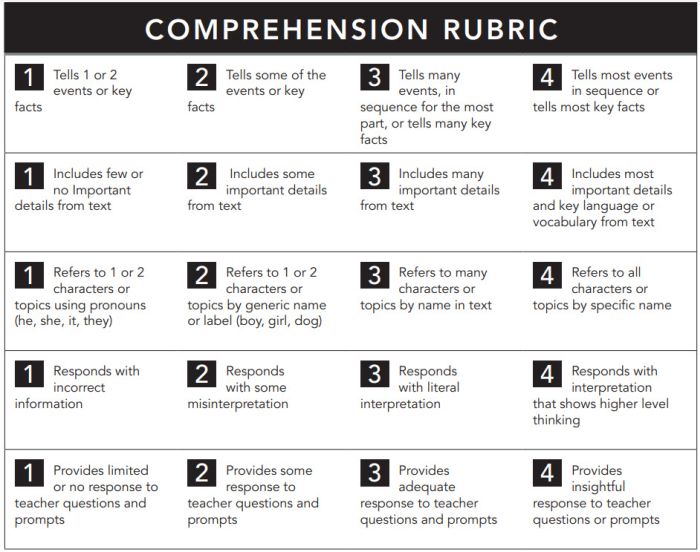
The nice thing about this rubric is that you can use it at any grade level, for any text. If you like this style, you can get a reading fluency rubric here too.
Learn more: Pawprints Resource Center
Written Response Rubric

Rubrics aren’t just for huge projects. They can also help kids work on very specific skills, like this one for improving written responses on assessments.
Learn more: Dianna Radcliffe: Teaching Upper Elementary and More
Interactive Notebook Rubric
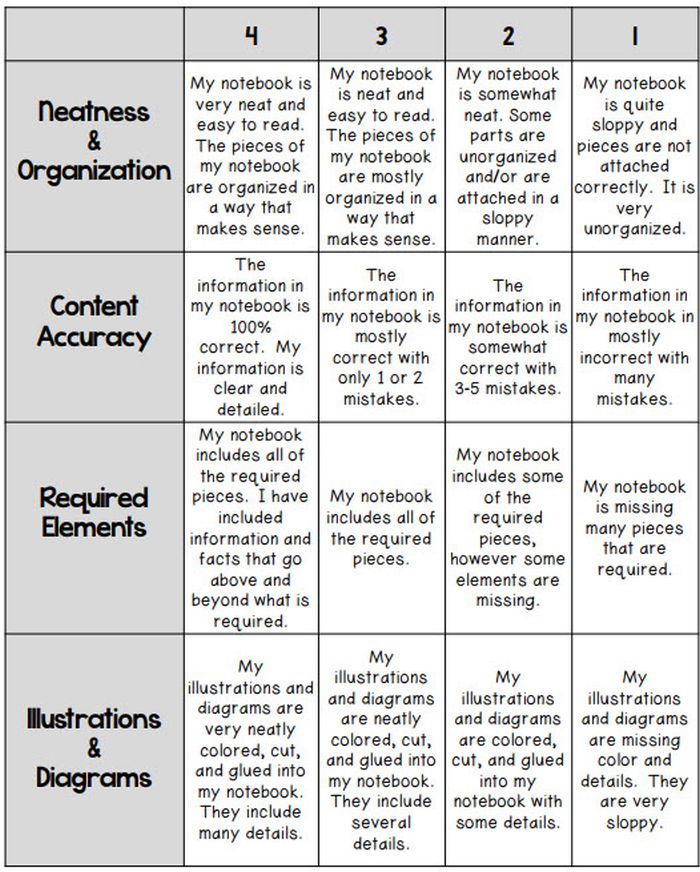
If you use interactive notebooks as a learning tool , this rubric can help kids stay on track and meet your expectations.
Learn more: Classroom Nook
Project Rubric
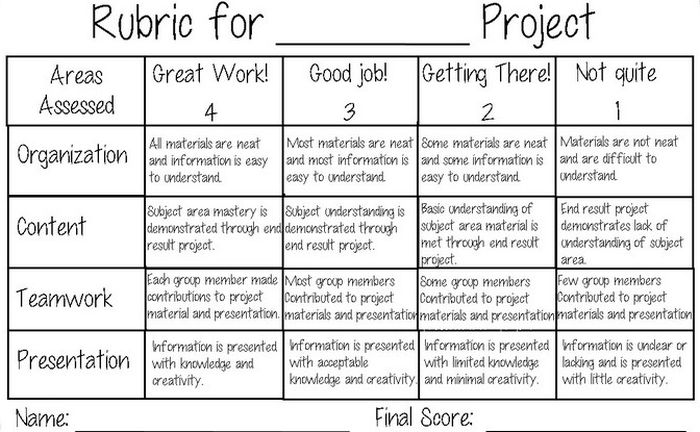
Use this simple rubric as it is, or tweak it to include more specific indicators for the project you have in mind.
Learn more: Tales of a Title One Teacher
Behavior Rubric
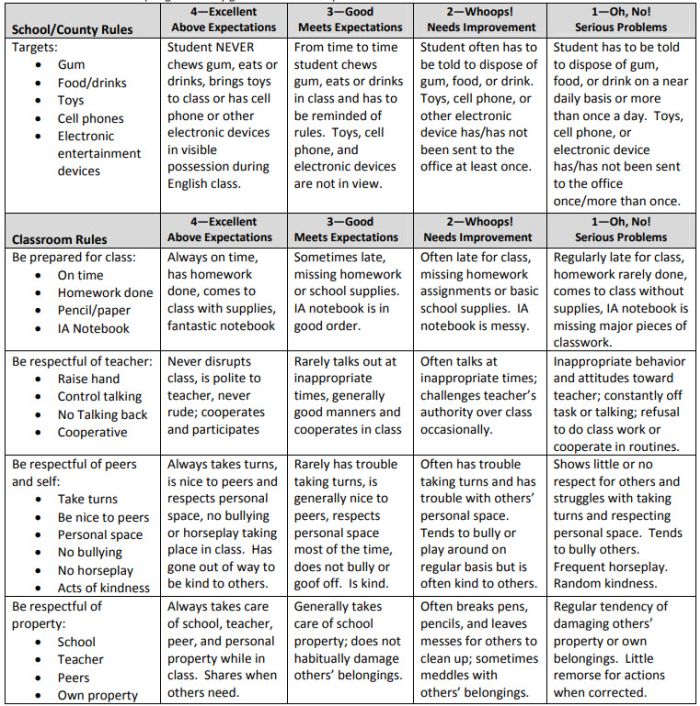
Developmental rubrics are perfect for assessing behavior and helping students identify opportunities for improvement. Send these home regularly to keep parents in the loop.
Learn more: Teachers.net Gazette
Middle School Rubric Examples
In middle school, use rubrics to offer detailed feedback on projects, presentations, and more. Be sure to share them with students in advance, and encourage them to use them as they work so they’ll know if they’re meeting expectations.
Argumentative Writing Rubric
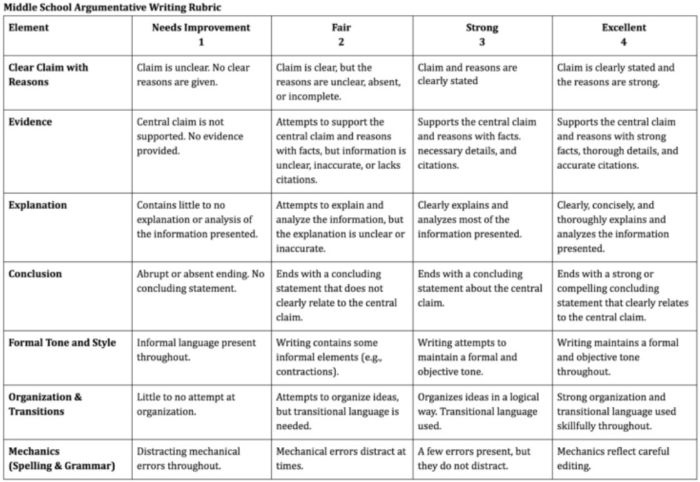
Argumentative writing is a part of language arts, social studies, science, and more. That makes this rubric especially useful.
Learn more: Dr. Caitlyn Tucker
Role-Play Rubric
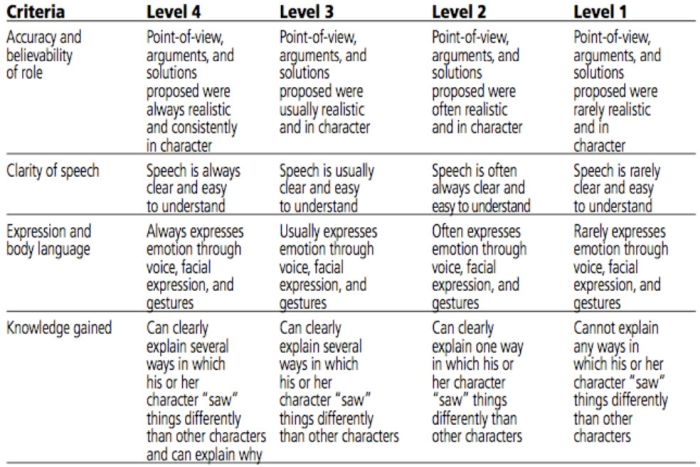
Role-plays can be really useful when teaching social and critical thinking skills, but it’s hard to assess them. Try a rubric like this one to evaluate and provide useful feedback.
Learn more: A Question of Influence
Art Project Rubric
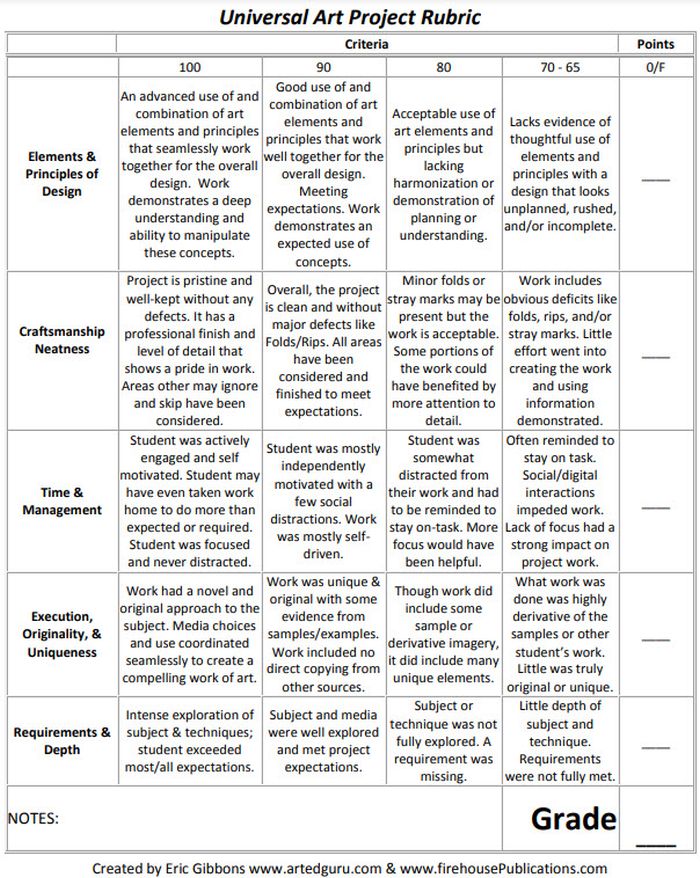
Art is one of those subjects where grading can feel very subjective. Bring some objectivity to the process with a rubric like this.
Source: Art Ed Guru
Diorama Project Rubric
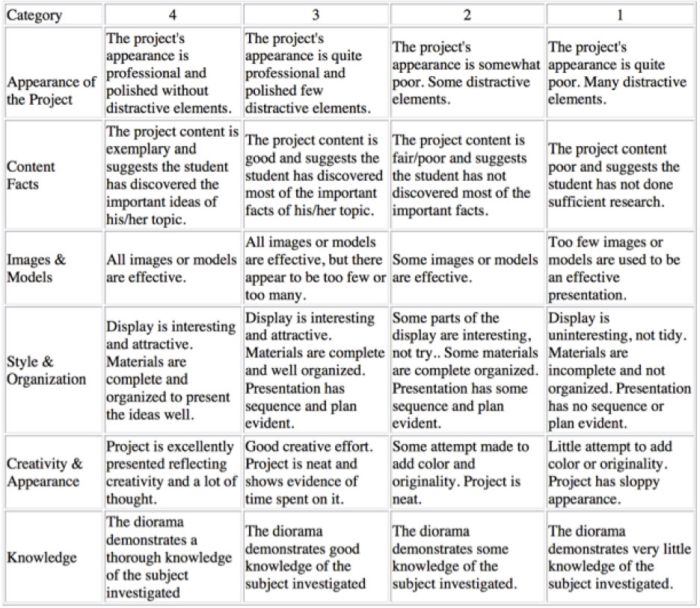
You can use diorama projects in almost any subject, and they’re a great chance to encourage creativity. Simplify the grading process and help kids know how to make their projects shine with this scoring rubric.
Learn more: Historyourstory.com
Oral Presentation Rubric
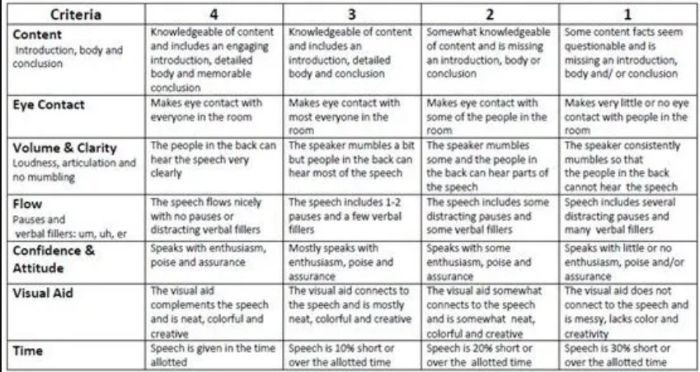
Rubrics are terrific for grading presentations, since you can include a variety of skills and other criteria. Consider letting students use a rubric like this to offer peer feedback too.
Learn more: Bright Hub Education
High School Rubric Examples
In high school, it’s important to include your grading rubrics when you give assignments like presentations, research projects, or essays. Kids who go on to college will definitely encounter rubrics, so helping them become familiar with them now will help in the future.
Presentation Rubric
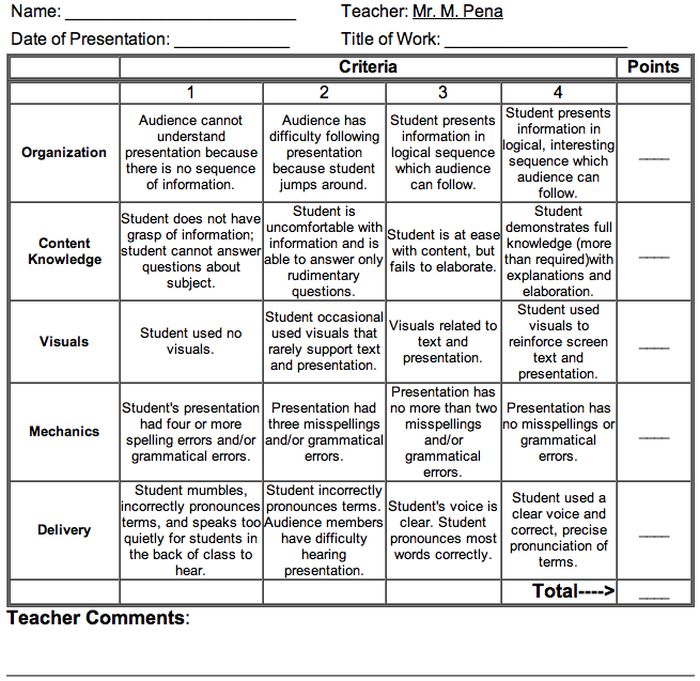
Analyze a student’s presentation both for content and communication skills with a rubric like this one. If needed, create a separate one for content knowledge with even more criteria and indicators.
Learn more: Michael A. Pena Jr.
Debate Rubric
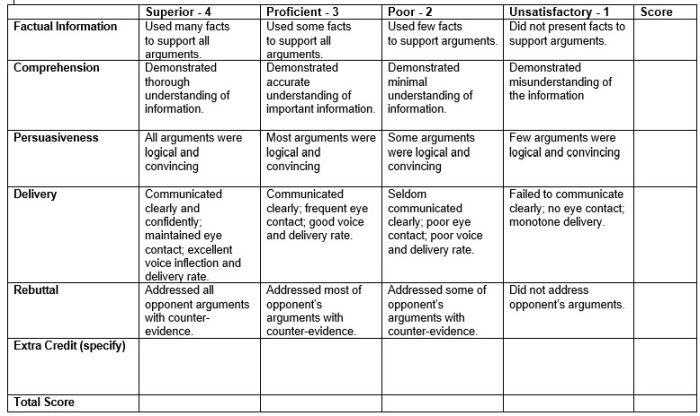
Debate is a valuable learning tool that encourages critical thinking and oral communication skills. This rubric can help you assess those skills objectively.
Learn more: Education World
Project-Based Learning Rubric
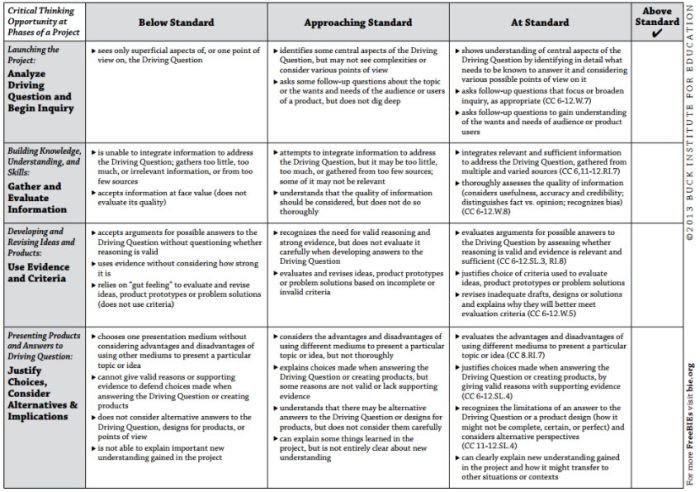
Implementing project-based learning can be time-intensive, but the payoffs are worth it. Try this rubric to make student expectations clear and end-of-project assessment easier.
Learn more: Free Technology for Teachers
100-Point Essay Rubric
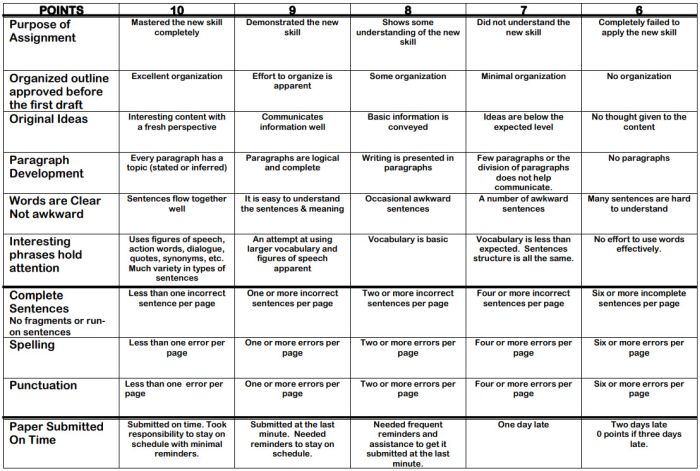
Need an easy way to convert a scoring rubric to a letter grade? This example for essay writing earns students a final score out of 100 points.
Learn more: Learn for Your Life
Drama Performance Rubric
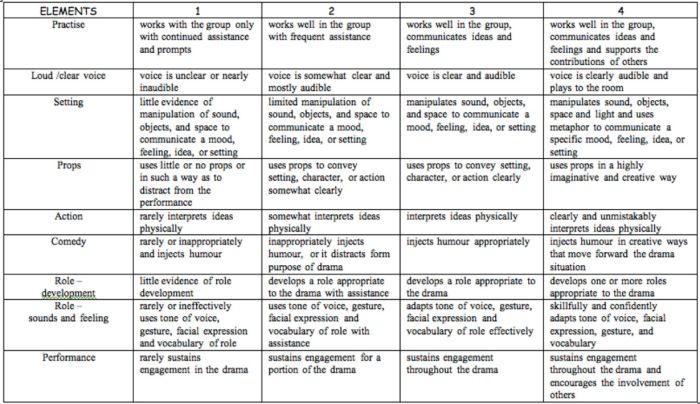
If you’re unsure how to grade a student’s participation and performance in drama class, consider this example. It offers lots of objective criteria and indicators to evaluate.
Learn more: Chase March
How do you use rubrics in your classroom? Come share your thoughts and exchange ideas in the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook .
Plus, 25 of the best alternative assessment ideas ..


You Might Also Like
What Is Project-Based Learning and How Can I Use It With My Students?
There's a difference between regular projects and true-project based learning. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Grading Rubrics
Rubrics represent criteria used to grade a variety of assignments and other classroom activities in a way that provides transparency to learners. Specifically, some of the benefits of grading rubrics to learners include:
- clearer assignments expectations
- more objective grading that is aligned with learning objectives
- improved fairness and consistency in grading among learners
- reducing learners' anxiety about the subjectivity of grading
There are also benefits to instructors which include:
- a more objective evaluation process by viewing learner performance through previously identified and expressed standards
- more efficient and effective grading
- improved clarity of assignment/activity development and instructions to learners
- enhanced constructive written feedback
- reduced learner complaints about perceived subjectivity of grading and associated grade challenges
While it is considered a best practice to use grading rubrics and explicit grading criteria for these reasons, the associated rating scales don't always provide the level of detailed feedback that will allow the learner to know how to improve. Therefore, it is important to remember that rubrics should not be used in isolation. Rather, they can also serve as a guide to provide critical feedback to learners that elaborates on strengths and areas of growth. Below are some resources for developing grading rubrics for various courses and assignments.
Different assignments require different grading rubrics. Review these various grading rubric sample scales to determine what works best for your context. You can then use online tools to create your own grading rubric.
Review this CFDE resource on Creating and Using Assignment Rubrics .
Peer evaluation can vary depending on the target of the evaluation. The Johns Hopkins University Center for Teaching and Learning offers this list of sample peer evaluation rubrics for presentations, individual or group projects, analytic papers, and other assignments. Peer evaluation rubrics can easily be collected by using Qualtrics or Google Forms. Contact [email protected] to set up a Qualtrics account.
For synchronous online courses, here is a sample online discussion rubric . For asynchronous online courses with required discussion posts, you may consider asking learners to complete their own self-assessment rubric .
You can also create a rubric in Canvas . These can be saved in Speedgrader and posted directly in the grade book.
Rubrics for Use in Assessments in Healthcare Education

In healthcare education, evaluation of student progress is essential for producing competent future healthcare workers. Faculty often use assessment rubrics as helpful tools for producing reliable and relevant assessment results. Rubrics provide a structured framework for evaluating various aspects of student work, from written assignments to clinical skills.
Let’s consider the benefits of using rubrics for assessments and how they can be used in a healthcare education setting.
Benefits of Rubrics for Assessments
Rubrics are favored in healthcare education for several reasons:
- Transparency and Clarity: They clearly communicate the criteria and expectations for assignments or assessments to students. This transparency promotes fairness and helps students understand what is expected of them.
- Consistency: They provide uniformity in grades when several instructors evaluate the same work. This is especially important in healthcare education, where students are often asked to exhibit and perform certain skills and competencies
- Objective Assessment: Rubrics encourage objective evaluation by breaking down complex tasks into specific components. This minimizes bias in grading and helps faculty and students focus on learning.
- Feedback: They facilitate constructive feedback. Faculty can provide specific comments based on the rubric criteria, aiding students in understanding their strengths and areas needing improvement.
- Continuous Improvement: With rubrics, faculty can analyze assessment data to identify areas where curriculum or teaching methods may need adjustments. Rubrics also show students what their next steps should be, so the repeated use of rubrics promotes a growth mindset for them.
Using Rubrics in Healthcare Education
Though rubrics can be used for nearly all aspects of healthcare education, there are some components that are easier to assess with rubrics.
- Objective Structured Clinical Examinations (OSCEs): Rubrics make it relatively easy to collect information, from patient interaction to diagnosis and treatment. And with a detailed rubric you can also assess criteria for professionalism.
- Clinical Rotations/Clerkships: Rubrics help in clerkship or clinical assessments. At some point, students in every health science discipline will participate in clinical experiences. In this phase of their education, students are evaluated in multiple ways where rubrics can offer an objective framework.
- Problem-based or Team-based learning: Rubrics are also great tools for assessing scenarios where students might be working in small groups, such as team-based learning .
- Case Presentations: Rubrics make it easier to assess the understanding, analysis, and even research components of case presentations.
- Peer and Self-Evaluations: It's crucial to emphasize the importance of using rubrics as a means to encourage self-reflection. Rubrics are also a great way for students to assess their peers.
Rubrics can be powerful tools in healthcare education assessments. Leo, our healthcare education-specific enterprise software platform, gives you the same transparency , making it easier to assess students and track their progress. To learn more about how Leo can help you, your students, and your program, contact us today .
OTHER RESOURCES

510 Meadowmont Village Circle #129 Chapel Hill, NC 27517 (919) 694-7498
View privacy policy
DAVINCI EDUCATION MANAGEMENT SYSTEM®, ACADEMIC PORTRAIT®, and LEO® are the registered trademarks of DaVinci Education, Inc.
- Patient Care
College of Public Health
Quick links, educational technology and assessment, rubric tutorial, creating a rubric: tutorial, introduction.
This tutorial will guide you through the basic steps to create a grading rubric for evaluating student performances. In this tutorial we will cover the following topics:
What is a Rubric?
Why use a rubric.
- Steps to Create a Rubric
At the end of the tutorial you will find a series of templates you can use for your own grading rubrics. They were created using Microsoft Word, and can be modified to meet your needs. Should you have any questions about this tutorial, or would like additional information about the use of grading rubrics, please contact [email protected]
In education, rubrics are a tool developed by instructors to assess the performances of their students. This assessment tool lists the dimensions (tasks) of the performance to be evaluated, and the specific criteria used to evaluate each dimension. It is different than a simple checklist since it also describes the gradations of quality (levels) for each dimension of the performance to be evaluated, and assigns a point value to each gradation of quality.
An example of a template for a rubric with 4 dimensions and 3 levels of quality:
| Lowest Quality (1pt) | Average Quality (2pts) | Best Quality (3pts) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 Dimension/Task | |||
| 2 Dimension/Task | |||
| 3 Dimension/Task | |||
| 4 Dimension/Task |
Rubrics are typically used with assessments that are subjective (presentations, papers, discussions, portfolios, essays, projects) rather than objective assessments (multiple choice, true/false or fill-in-the-blank tests.)
Rubrics are used for many reasons, some of which include:
- Rubrics make the instructor’s expectations clear to the students
- Rubrics show students how to meet the instructor’s expectations i.e. what they need to do to be successful
- Rubrics help students evaluate the quality of their own work
- Rubrics identify the specific elements an instructor uses to differentiate between the qualities of performances. i.e. it helps the student answer the question ‘why did I get a point taken off?’
- If more than one person is evaluating the performance, it improves the consistency and objectivity (standardization) of grading
- It may reduce the time it takes to grade if there are similarities among comments made to students regarding flaws or excellence in a performance
How to Create a Rubric
Creating a rubric is easy once you have taken to time to evaluate the dimensions/tasks which make up the students performance, and the criterion you will use to evaluate it. That being said, let’s begin with the steps to create a rubric.*
The steps to create a rubric are listed in sequential order, however they can be performed in any order as long as the rubric contains the following:
- Performance Objective
- List of dimensions to be evaluated
- Levels of gradation of quality
- Criterion and points for each level of quality
We have divided the task of creating a grading rubric into 6 steps:
- Record the performance objective
- Identify the dimensions/tasks comprising the performance
- Identify the potential gradations of quality
- Assign a point value to each gradation, and a total point value for the assessment
- Identify the criteria for each level of quality within a dimension/task
- Create the rubric table
Record/write the performance objective.
Performance Objectives (also known as learning objectives) are statements which identify the specific knowledge, skill, or attitude the learner should gain and display as a result of the instructional activity.
Performance objectives should consist of 3 elements:
- Student Performance
The Student performance is the observable behavior that a student will do to demonstrate that the lesson is learned. The conditions are the tools, resources and enviroment where the performance will take place. The criteria is the accuracy level assigned to the performance. As mentioned above, the rubric is the written document communicating the criteria to the student.
Below is an example of a performance statement without the criteria. (The criteria will be written in the form of a rubric.)
Project 1 Objective: Given a choice of a public health topic, Excel software, access to the USF library and internet, create the research question, present proposed sources for literature review, identify the objectives, identify the proposed methods, present a discussion of the proposed results, and present a suggested conclusion.
Total points achievable for this project: 21 points.
You do not have to list the conditions for the student when writing the performance statement. However, if you identify them when you are creating your course it will help you preplan the resources you may need to generate for this performance.
Identify the dimensions/tasks comprising the performance.
Step 2: Identify the dimensions/tasks comprising the performance. Dimensions are the broad concepts or specific tasks the student should demonstrate when performing the activity. Dimensions can be specific tasks or they can address a variety of intellectual or cognitive competencies that target a specific academic discipline or involve multiple disciplines. The dimensions you use may also be defined by National Standards, degreed programs, or job-related competencies.
Examples of dimensions for a group exercise analyzing a case study may include:
- Contribute to the group discussion
- Take responsibility for required work
- Value others viewpoints
- Analyze the study cooperatively
- Present the outcome in a given format
Here are a few more examples: Example of dimensions which are specific tasks for a written project Example of dimensions which are broad concepts for an online discussion Example of dimensions which are broad concepts and tasks for a presentation
Identify the potential gradations of quality.
Gradations are the descriptive levels of quality starting with the worst quality up to the best quality.
- Example of a 3 level gradation: poor, average, excellent
- Example of a 4 level gradation: beginning, developing, accomplished, exemplary
- Example of a 5 level gradation: poor, fair, average, very good, excellent
The gradations of quality may or may not be listed on the actual rubric. You can have different gradations for the dimensions listed, but this may be confusing to the student.
Assign a point value to each gradation, and a total point value for the assessment.
Assign a point value to each gradation of quality, and identify the total point value for the assessment.
If you already know the total number of points for this assessment... Divide the total number of points by the number of dimensions to get the maximum point value for achieving the highest gradation for a dimension. For example, if the assessment is worth 15 points, and there are 5 dimensions, the highest gradation will be worth 3 points. Each gradation below this highest level should be valued at less than the 3 points.
If you do not have a total number of points for this assessment... Identify the maximum number of points for achieving the highest level of quality. Assign a number to each of the lower levels of quality. Typically, the gradations are in increments of 1 point. Multiply the maximum point value by the total number of dimensions. This is the total point value for the assessment. For example, if you have 3 levels (poor, average, excellent) the highest level is worth 3 points, the middle level is worth 2 points and the lowest level is worth 1 point. If there are 7 dimensions, the total point value for this assessment is 21 points.
See an example of a rubric with points assigned to the 3 levels of quality
Although most rubrics have at least 1 point for the lowest value, you can have a zero for the lowest gradation.
Identify the criteria for each level of quality within a dimension/task.
Start with the best quality of each dimension. Simply list the specific expectations you have for the student. Then, for each level below the best quality, identify the flaws or missing elements which will cause the student to lose points off the best quality performance.
View a rubric with criteria for a written research proposal project View a rubric with criteria for an online discussion View a rubric with criteria for an oral presentation
Avoid negative language when listing the criteria. Instead try to identify the specific criteria which is missing, or flaw so they know why they were assessed with a lower quality performance.
Create the rubric table.
Your rubric will be a table. Each dimension should be in a separate row, and each gradation of quality should be in a separate column. Provide a place at the top of the rubric for your performance statement, an extra row for the header, and a column on the left to list the dimensions. If you plan to use this rubric as a method of feedback to the students. Create an additional column on the right side of the page where you can place the point values earned for each dimension. We have created a few templates as a starting point.
Download a template with 3 gradations of quality Download a template with 4 gradations of quality Download a template with 5 gradations of quality
Note: You can modify these templates to meet your needs.
You do not have to list the descriptive words for each quality degradation, only the points they will earn if they meet this level of quality.
- help_outline help
iRubric: Comprehensive Health Assessment rubric
| Rubric Code: By Ready to use Public Rubric Subject: Type: Grade Levels: Undergraduate |
| Comprehensive Health Assessment | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
| | ||||||
Nursing Education Network

Writing Exceptional Rubrics for Nursing
Journal Club Article: Stanley, D., Coman, S., Murdoch, D., & Stanley, K. (2020). Writing exceptional (specific, student and criterion-focused) rubrics for nursing studies. Nurse Education in Practice , 102851.[ Abstract ]
What are Rubrics? ‘a scoring guide used to evaluate the quality of students’ constructed responses.
Effective Assessment: “Rubrics can effectively communicate unit learning outcomes to students and may contribute towards the academic rigour of nursing courses, when assessment criteria are articulated clearly and consistently to both students and educators/academics.”
Valid and reliable rubrics standardise the grading of assignments and assessments.
“Ensuring assessment tasks are clear, transparent and consistent helps both educators/academics and students to minimise stress, manage their workload and reach expectations in terms of addressing learning outcomes.”
They set the goals for the assignment, guide students and keep them on task, link the assignment and learning outcomes for the unit, module or subject and they provide a shorthand approach to providing effective and timely feedback
- Set the goals for the assignment (specific)
- guide students and keep them on task (student focused)
- link the assignment and learning outcomes for the unit, module or subject (criterion-focused
- provide a shorthand approach to providing effective and timely feedback
Components of a Rubric: Analytic and Specific . These include the criteria (based on the Intended Learning Outcomes) and standards (use of taxonomy such as Bloom’s or SOLO), the marking grid and the weighting for each criterion/standard. Be clear on what the ‘pass’ criteria is, ensure the criteria and pass standard are identical.
Standardising Assessment: Benchmarking is required when a group of assessors are conducting grading assessments or assignments.

Nursing Education Network. (2016). Intended Learning Outcomes (ILO’s) .
Nursing Education Network. (2019). Intended Learning Outcomes .
Nursing Education Network. (2020). Learning Needs Assessment .
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
Leave a Reply Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Learning Environments
- Teaching, learning and assessment
Assessment rubrics
An assessment rubric is a criteria-based marking tool. Rubrics give students clarity on what is expected and build students’ self-efficacy.
What is it?
Assessment rubrics are criteria-based marking tools that support consistency in marking practices and provide opportunities for effective formative assessment. Analytic rubrics are most common and supported by many learning technologies; they dissect an assessment task into different criteria, each of which is graded on a scale and accompanied with descriptions for different levels of performance. Analytic rubrics give students clarity on what is expected and ensure that their work is marked in line with a consistent set of criteria. In addition, analytic rubrics can offer an effective way to facilitate formative assessment and self-regulation. For example, using assessment rubrics for self-assessment and/or peer review will help students’ track their progress towards achievement of intended learning outcomes and increase self-confidence in their ability to complete the task. Regular rubric-based exercises will develop students’ evaluative judgement and understanding of academic quality – the core attributes of a life-long learner.
Why is it useful?
Benefits for students.
- Supplements assessment guidelines by providing clarity on what is expected at different levels of achievement
- Promotes independent learning by giving students a device to self-assess and understand their progress
- Engages students in metacognition and facilitates the development of evaluative judgement
- Supports formative feedback provision in preparation for a summative assessment.
Benefits for educators
- Facilitates consistent marking across your teaching team
- Supports implementation of effective formative assessment.
How do I implement it?
To implement assessment rubrics in your teaching, try these strategies:
- Provide clarity and consistency through a clear and concise articulation of different levels of achievement. For example, use adjectives and adverbs consistently across different criteria to prompt consistency in their application.
- Support reliability and validity in assessment by aligning assessment criteria with intended learning outcomes and test rubrics before release. For example, you can get different members of your teaching team to use the rubric to mark a sample of past papers. This will ensure agreement among different markers and consistent interpretation of the rubric criteria. Testing a newly written rubric on past assignments also allows you to check if the rating descriptions are applied consistently and that they capture distinct levels of student achievement.
- Encourage student interactions with the rubric by making it available well before the assessment task is due. This will give students adequate time to seek clarification. It will also allow you to create purposeful interactions between the students and the rubric. For example, you can give students time in class to assess their own – or their peers’ – drafts against the rubric. Rubric-based self-assessment and peer-review exercises give students a chance to not only understand how they are progressing towards the completion of the task but also engage them in metacognition and develop their evaluative judgement.
- Co-create rubrics with students to enhance students’ self-regulation. In some teaching contexts, it may be appropriate and feasible to involve students in writing rubrics together with the teaching staff. The process of co-design will make students internalise the assessment criteria, which, in turn, can help with goal setting and activation of appropriate learning strategies. Students can participate in the design of rubrics through in-class brainstorming exercises. Following the brainstorming session with students, collate their contributions and use them to build a rubric.
Supporting technologies
- LMS rubrics can be attached to any assignment, including LMS Quizzes and Discussions, and used for marking students’ submissions via the SpeedGrader. LMS rubrics can have either a point value or a point range attached to each criterion. You can also remove the points to create a qualitative rubric or choose to write free-form comments on each criterion when marking students’ submissions in the SpeedGrader.
- FeedbackFruits can facilitate rubric-based peer review, self-assessment, and group member evaluation. In FeedbackFruits, you can set up feedback criteria through rubrics, scale ratings or free-form comments or use a combination of these tools within a single assessment task. Criteria you create within one assessment task can be reused in your future FeedbackFruits activities.
- PebblePad ATLAS allows you to add rubrics using the feedback template functionality, or the score card functionality. You can use lists of criteria or analytic rubrics. ATLAS can pass numeric marks back to the LMS Gradebook; however, the details of the rubric and any written feedback would stay in PebblePad.
- Gradescope allows you to build and refine rubrics while marking. This gives you a chance to capture a wide range of students’ responses and makes rubrics an effective feedback device. The changes will apply to all assignments, including those already marked.
- Cadmus can facilitate marking via the Turnitin Feedback Studio . If you already have a rubric in .xls, .xlsc or .rbc file, you can upload that to the Turnitin Feedback Studio. Once the rubric is uploaded, it can be edited in the Rubric Manager on Turnitin. Turnitin QuickMarks (i.e., in-text comments) can be associated with a specific criterion within the rubric. You can also create a library of QuickMarks to be reused across different assessment tasks.
- Cadmus. Marking with Turnitin Feedback Studio .
- Cadmus. Using Turnitin rubrics and Grading forms .
- Fraile, J., Panadero, E., & Pardo, R. (2017). Co-creating rubrics: The effects on self-regulated learning, self-efficacy and performance of establishing assessment criteria with students . Studies in Educational Evaluation, 53, 69-76.
- Instructure Community. How do I add a rubric to an assignment?
- Instructure Community. How do I add a rubric to a graded discussion?
- Instructure Community. How do I add a rubric to a quiz?
- Instructure Community. How do I manage rubrics in a subject?
- Jonsson, A. (2014). Rubrics as a way of providing transparency in assessment . Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education , 39 (7), 840-852.
- Tomas, C., Whitt, E., Lavelle-Hill, R., & Severn, K. (2019). Modeling holistic marks with analytic rubrics . Frontiers in Education, 4.
- Turnitin. Uploading rubric scorecards .
- University of Melbourne. (2020, August). LMS Rubrics .
- University of Melbourne. (2021, April). Creating and using rubrics for assessment?
- University of Melbourne. Gradescope .
- University of Melbourne. PebblePad .
This page was last updated on 11 Apr 2024.
Please report any errors on this page to our website maintainers
Support centre
Login to the lms.
Assessment Rubrics
A rubric is commonly defined as a tool that articulates the expectations for an assignment by listing criteria, and for each criteria, describing levels of quality (Andrade, 2000; Arter & Chappuis, 2007; Stiggins, 2001). Criteria are used in determining the level at which student work meets expectations. Markers of quality give students a clear idea about what must be done to demonstrate a certain level of mastery, understanding, or proficiency (i.e., "Exceeds Expectations" does xyz, "Meets Expectations" does only xy or yz, "Developing" does only x or y or z). Rubrics can be used for any assignment in a course, or for any way in which students are asked to demonstrate what they've learned. They can also be used to facilitate self and peer-reviews of student work.
Rubrics aren't just for summative evaluation. They can be used as a teaching tool as well. When used as part of a formative assessment, they can help students understand both the holistic nature and/or specific analytics of learning expected, the level of learning expected, and then make decisions about their current level of learning to inform revision and improvement (Reddy & Andrade, 2010).
Why use rubrics?
Rubrics help instructors:
Provide students with feedback that is clear, directed and focused on ways to improve learning.
Demystify assignment expectations so students can focus on the work instead of guessing "what the instructor wants."
Reduce time spent on grading and develop consistency in how you evaluate student learning across students and throughout a class.
Rubrics help students:
Focus their efforts on completing assignments in line with clearly set expectations.
Self and Peer-reflect on their learning, making informed changes to achieve the desired learning level.
Developing a Rubric
During the process of developing a rubric, instructors might:
Select an assignment for your course - ideally one you identify as time intensive to grade, or students report as having unclear expectations.
Decide what you want students to demonstrate about their learning through that assignment. These are your criteria.
Identify the markers of quality on which you feel comfortable evaluating students’ level of learning - often along with a numerical scale (i.e., "Accomplished," "Emerging," "Beginning" for a developmental approach).
Give students the rubric ahead of time. Advise them to use it in guiding their completion of the assignment.
It can be overwhelming to create a rubric for every assignment in a class at once, so start by creating one rubric for one assignment. See how it goes and develop more from there! Also, do not reinvent the wheel. Rubric templates and examples exist all over the Internet, or consider asking colleagues if they have developed rubrics for similar assignments.
Sample Rubrics
Examples of holistic and analytic rubrics : see Tables 2 & 3 in “Rubrics: Tools for Making Learning Goals and Evaluation Criteria Explicit for Both Teachers and Learners” (Allen & Tanner, 2006)
Examples across assessment types : see “Creating and Using Rubrics,” Carnegie Mellon Eberly Center for Teaching Excellence and & Educational Innovation
“VALUE Rubrics” : see the Association of American Colleges and Universities set of free, downloadable rubrics, with foci including creative thinking, problem solving, and information literacy.
Andrade, H. 2000. Using rubrics to promote thinking and learning. Educational Leadership 57, no. 5: 13–18. Arter, J., and J. Chappuis. 2007. Creating and recognizing quality rubrics. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson/Merrill Prentice Hall. Stiggins, R.J. 2001. Student-involved classroom assessment. 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall. Reddy, Y., & Andrade, H. (2010). A review of rubric use in higher education. Assessment & Evaluation In Higher Education, 35(4), 435-448.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Microbiol Biol Educ
- v.23(3); 2022 Dec

Using a One Health Assignment as a Final Project in a Microbiology Course
Jennifer r. huddleston.
a Department of Biology, Abilene Christian University, Abilene, Texas, USA
Associated Data
The One Health initiative is a comprehensive strategy that seeks to understand the balance between the human, animal, environmental domains and how each affects the health of the others. A One Health project is presented here that can be used as a final formative and summative assignment for undergraduate students enrolled in a microbiology course. Students learn about the initiative and then choose topics of relevance. They then synthesize concepts learned throughout the course and new information about the One Health initiative. An assessment rubric is provided that can be modified to a variety of different project types, not just papers, as described here. This One Health assignment helps students learn the importance of the microbiology concepts addressed in the course and also their real-world implications.
INTRODUCTION
Globalization has led to a high degree of interconnectedness among all inhabitants of the earth and has served as the impetus for the One Health initiative. This initiative is a strategic program aimed at understanding the intersecting health of humans, animals, and the environment ( https://cdc.gov/onehealth ). The One Health initiative is supported by the CDC, the American Veterinary Medical Association, and the American Medical Association, and was originally adopted as a collaboration in 2007 ( 1 ). Its primary focus is on the zoonotic diseases that can wreak havoc on both animal and human populations. It is for this reason that One Health should be an initiative of utmost relevance and importance to undergraduate students learning microbiology.
A few undergraduate classroom activities have previously addressed One Health ( 2 , 3 ), but most students are introduced to the concept in graduate, veterinary, or medical school. However, there is a movement to introduce One Health to students earlier in their educational careers ( 4 ). The assignment described here is given as a final project in an undergraduate microbiology course. It serves as both formative and summative in learning about specific aspects of One Health, integrating this knowledge, and addressing all of the objectives of AAAS Vision and Change and American Society for Microbiology (ASM) Curriculum Guidelines ( 5 , 6 ). The objectives are listed in Table 1 . This assignment gives students an opportunity to demonstrate knowledge while integrating it into a One Health framework, focusing heavily on the ASM guidelines related to scientific thinking (guidelines 30, 30a, 30b, 31, 31a) ( 6 ).
TABLE 1
Unique learning objectives for the One Health assignment
| One Health assignment | ASM guidelines |
|---|---|
| Demonstrate understanding of basic microbiology knowledge and terminology | Cell structure and function (8, 9, 10) Metabolic pathways (12, 13) Information flow and genetics (15, 16, 17, 18, 19) |
| Apply basic microbiology knowledge and tools to problem-solving in the context of the One Health initiatives | Evolution (3) Microbial systems (23) Impact of microorganisms (24, 27) |
| Analyze sources for currency, relevance, authority, accuracy, and purpose | Scientific thinking (30b) |
| Synthesize information found in sources to educate and challenge the audience of the final project | Scientific thinking (30b) |
| Judge, evaluate, and select best solutions to the microbiological problem based on evidence from peer-reviewed sources | Scientific thinking (31a) |
| Communicate findings in an effective manner through written and oral communication through a variety of formats | Scientific thinking (30a) |
At the beginning of the 3-week unit, students are introduced to the One Health initiative through a series of formative assignments that are also scaffolding assignments for the final submission (see Appendix S1 and S2 in the supplemental material). The students learn about the initiative through a series of videos and the CDC website. They choose three topics which are given peer and instructor feedback, followed by a final topic decision. Three primary sources are chosen to learn source selection and proper citation style. The students then submit an annotated bibliography with at least 10 peer-reviewed sources, followed by an outline and part of a rough draft. Finally, they submit their projects (see Appendix S3) through an originality program in the course management system, which allows multiple resubmissions before the deadline and reinforces proper paraphrasing as students see their mistakes highlighted and have a chance for correction. The students then give an oral presentation summarizing their topic to classmates. This allows all students to learn about an array of different problems addressed by One Health. Students are evaluated with a single-point rubric ( Table 2 ) that gives transparent expectations of the project and efficient individualized feedback. The project comprises 10% of the final course grade (see Appendix S4).
TABLE 2
Single-point rubric for assessment of One Health assignment
| Criterion | Points possible |
|---|---|
| Microbiological in scope Any microorganism found in any domain is allowed as a topic of the project. This also includes viruses. Topics of direct microbiological importance, such as antibiotic resistance, are also allowed. | 5 |
| Natural history of the microbe or history of the problem The student clearly and completely explains what is known about this microbe (or problem), what kind of microbe it is, where is it normally found, etc. | 10 |
| One Health The project must explicitly address all of the ways that the topic relates to the initiatives of One Health. | 15 |
| Problem The problem is explained from several perspectives, not just the biological perspective. | 15 |
| Solutions Proposed solutions are discussed, with critiques and advantages. | 15 |
| Mechanics of the project The student exhibits excellent command of standard English that skillfully communicates meaning to the audience with clarity and fluency and is virtually error-free. | 15 |
| Ethical and appropriate use of sources There must be a minimum of 10 peer-reviewed, relevant references. These sources must be from legitimate science journals and must have an impact factor. The final reference list should not be annotated. Correctly implement all four of the following strategies: 1. Select critical sources. 2. Adhere to the citation and reference style indicated by the instructor. 3. Paraphrase or summarize in ways that are true to the original context. 4. Distinguish between common knowledge and ideas requiring attribution; practice ethical and legal restrictions on the use of published, confidential, and/or proprietary information. | 15 |
| Presentation The student clearly communicates the main concept of the project in a 10- to 15-min oral presentation, using visual aids that are helpful and engaging for the audience; the student is prepared to answer questions. | 10 |
| Total | 100 |
Students may change their topic at any point. Sometimes students realize there is not enough information on their topic, or their topic is causing them emotional trauma (e.g., SARS-CoV-2 and a COVID-19 death in the family). Other than potential emotional trauma, there are no safety issues with this assignment.
This assignment has been used with four semesters of microbiology students ( n = 73) who have participated in informal conversations. The students appreciate writing a paper about a self-chosen topic over studying for a comprehensive exam. The most common challenge is learning how to discern primary peer-reviewed sources and how to paraphrase with integrity. Student feedback has led to improved transparency of the rubric (to expand types of topics, clarify length, etc.) and to a knowledge of how to direct students toward more achievable topics. Topics that have been successfully developed include Middle Eastern respiratory syndrome, antibiotic usage in agriculture, Rift Valley fever, Lyme disease, coral bleaching, and others.
Initially, this assignment was intended to allow for a variety of different types of projects, such as movies, not just papers. However, the students chose the paper format because of lack of rubric clarity for other types of projects, but with a modification, this assignment could allow for different project types.
The concepts in the One Health initiative are imperative for all citizens to understand, but they are especially important for microbiology students as future health care providers, veterinarians, teachers, researchers, and voting citizens. This assignment allows them to think critically and delve deeper into crises that our world is facing.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
I thank all of the students in the microbiology courses who worked on One Health assignments and provided feedback on their experience and who asked questions when the assignment was not transparent. I declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Supplemental material is available online only.
Supplemental file 1
Appendices S1 to S4. Download jmbe.00077-22-s0001.pdf, PDF file, 0.1 MB
Yekaterinburg
| and the from | |
| Show map of Russia Show map of Sverdlovsk Oblast | |
| Coordinates: 60°36′46″E / 56.83556°N 60.61278°E / 56.83556; 60.61278 | |
| Country | |
| Founded | 18 November 1723 |
| City status since | 1781 |
| Government | |
| • Body | |
| • Head | Alexey Orlov |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,111 km (429 sq mi) |
| Elevation | 237 m (778 ft) |
| Population ( Census) | |
| • Total | 1,349,772 |
| • Estimate | 1,536,183 |
| • Rank | in 2010 |
| • Density | 1,200/km (3,100/sq mi) |
| • Subordinated to | of Yekaterinburg |
| • of | , City of Yekaterinburg |
| • Urban okrug | Yekaterinburg Urban Okrug |
| • of | Yekaterinburg Urban Okrug |
| ( ) | |
| +7 343 | |
| ID | 65701000001 |
| City Day | 3rd Saturday of August |
| Website | |
Yekaterinburg [lower-alpha 1] is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District , Russia. The city is located on the Iset River between the Volga-Ural region and Siberia , with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, [14] up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in the Ural Federal District, and one of Russia's main cultural and industrial centres. Yekaterinburg has been dubbed the "Third capital of Russia", as it is ranked third by the size of its economy, culture, transportation and tourism. [15] [16] [17] [18]
Imperial era
Contemporary era, demographics, administrative districts, administration, living costs and the labor market, finance and business, retail and services, transportation, public transit, media and telecommunications, life and culture, architecture, international relations, bric summit, twin towns – sister cities, notable people, bibliography, external links.
Yekaterinburg was founded on 18 November 1723 and named after the Orthodox name of Catherine I (born Marta Helena Skowrońska), the wife of Russian Emperor Peter the Great . The city served as the mining capital of the Russian Empire as well as a strategic connection between Europe and Asia. In 1781, Catherine the Great gave Yekaterinburg the status of a district town of Perm Province , and built the historical Siberian Route through the city. [3] Yekaterinburg became a key city to Siberia, which had rich resources. In the late 19th century, Yekaterinburg became one of the centres of revolutionary movements in the Urals. In 1924, after the Russian SFSR founded the Soviet Union , the city was renamed Sverdlovsk after the Bolshevik leader Yakov Sverdlov . During the Soviet era, Sverdlovsk was turned into an industrial and administrative powerhouse. On 23 September 1991 the city returned to its historical name.
Yekaterinburg is one of Russia's most important economic centres and was one of the host cities of the 2018 FIFA World Cup . The city is currently experiencing an economic and population boom, which resulted in some of the tallest skyscrapers of Russia being located in the city. Yekaterinburg is home to the headquarters of the Central Military District of the Russian Armed Forces , as well as the presidium of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences .
Yekaterinburg is famous for its constructivist architecture [19] [20] [21] and is also considered the "Russian capital of street art ". [22] [23] [24]

The area was settled in prehistory. The earliest settlements date to 8000–7000 BC, in the Mesolithic period . The Isetskoe Pravoberezhnoye I archaeological site contains a Neolithic settlement dated to 6000–5000 BC. It includes stone processing workshops with artefacts such as grinding plates, anvils, clumps of rock, tools, and finished products. Over 50 different types of rock and minerals were used in tool making, indicating extensive knowledge of the region's natural resources. The Gamayun peninsula (left bank of the Verkh-Isetsky Pond) has archaeological findings from the Chalcolithic Period : workshops for producing stone tools (upper area) and two dwellings of the Ayat culture (lower area). There are also traces of the Koptyak culture from 2000 BC: dishes decorated with bird images and evidence of metallurgical production. The Tent I site contains the only Koptyak culture burials discovered in the Ural Mountains . In the Bronze Age , the people of Gamayun culture lived in the area. They left fragments of ceramics, weapons, and ornaments. [25] [26] [27]
Archaeological artifacts in the vicinity of Yekaterinburg were first discovered during railway construction, at the end of the 19th century. Excavation and research began in the 20th century. Artifacts are held at the Sverdlovsk Regional Museum of Local Lore , at the Hermitage , at the Museum of Anthropology and Ethnography of the Academy of Sciences, and at other museums. [26]

The first Russian settlements within the boundaries of modern Yekaterinburg appeared in the second half of the 17th century — in 1672, an Old Believers village arose in the area of Shartash lake [28] (this fact is disputed by historians, since no evidence of the founding of the village at that time was found in the sources), [29] and in 1680 – 1682, the villages of Nizhny and Verkhny Uktus appeared on the banks of Uktus River (now the territory of the Chkalovsky district of the city). [30] In 1702, by the initiative of the head of Sibirskiy prikaz Andrew Vinius , the Uktus state ironwork plant was founded near Nizhny Uktus — the first ironworks within the boundaries of modern Yekaterinburg. [31] In 1704, the Shuvakish ironworks was built (now the territory of the Zheleznodorozhny district of the city). [28] With the beginning of active construction of factories in the Urals in the 18th century, relations with their southern neighbors, the Bashkirs , became strained. As a result of the Bashkir raid in 1709, the village of Verkhny Uktus was devastated, all buildings, including the wooden church and chapel, were burned, the residents fled to the protection of the Uktus plant fortifications. [30] On the night of 5 April 1718, a fire destroyed all the factory buildings of the Uktus plant, except for the dam, and the plant was restored only by 1720 under the supervision of Timofey Burtsev. [32] However, the plant did not receive further development due to the lack of water in Uktus river.
In 1720, by decree of Peter I , a delegation led by mining specialist Johann Blüher and statesman Vasily Tatishchev was sent to the Urals . [33] They were entrusted with managing the mining industry, identifying the causes of the collapse and reduction of production at state-owned factories. [33] On 29 December 1720, [33] Tatishchev and Blüher arrive at the Uktus plant, which became their main residence in the Urals. As a result of familiarizing himself with the state of nearby state-owned factories, Tatishchev came to the conclusion that on the basis of these factories, even if they were reconstructed and expanded, it would not be possible to quickly increase the production of iron, and it would be more profitable to build a new large plant. After inspecting the immediate area, together with the commissary of the Uktus plant, Timofey Burtsev, a place rich in ore and forest was chosen on the banks of the more full-flowing Iset River , 7 versts from Uktus. [33] On 6 February 1721, Tatishchev sent a message to the Collegium of Mining , in which he asked permission to begin construction of the plant, with detailed explanations and justification for this project. [33] On 1 March 1721, without waiting for a response from the Collegium, Tatishchev began construction of the new plant, [28] but he failed to convince Collegium, and by the Collegium decree of 10 December 1721, he was removed from the leadership of mining affairs in the Urals. [28] In 1722, by decree of Peter the Great, a mining engineer, Major General Georg Wilhelm de Gennin , was sent to the Urals in place of Tatishchev. Having studied all the circumstances, de Gennin fully supported Tatishchev’s project, and on 12 March 1723, construction of the plant on Iset resumed. [28]

Russian historian Vasily Tatishchev and Russian engineer Georg Wilhelm de Gennin founded Yekaterinburg with the construction of a massive iron-making plant under the decree of Russian emperor Peter the Great in 1723. [34] They named the city after the emperor's wife, Yekaterina, who later became empress regnant Catherine I . [2] Officially, the city's founding date is 18 November 1723, when the shops carried out a test run of the bloomery for trip hammers. [2] The plant was commissioned 6 days later, on 24 November. [35] 1723 also saw the establishment of Yekaterinburg fortress , which would encompass many of the settlement's earliest buildings. Dmitry Mamin-Sibiryak very vividly described the beginning of the construction of a mining plant and a fortress: "Imagine completely deserted banks of the Iset river, covered with forest. In the spring of 1723, soldiers from Tobolsk, peasants of the assigned settlements, hired craftsmen appeared, and everything around came to life, as if by the dictates of a fairy tale. They dropped the forest, prepared a place for the dam, laid blast furnaces, raised the rampart, set up barracks and houses for the authorities... ". [36]
In 1722–1726 the Verkhne-Uktussky mining plant was built, [37] which was officially called the plant of the princess Elizabeth (the future village of Elizabeth, or Elizavetinskoe) and became a part of modern Yekaterinburg in 1934. [38] In 1726, Wilhelm de Gennin founded an auxiliary Verkh-Isetsky plant with a working settlement 2 versts from Yekaterinburg upstream ('verkh' in Russian) the Iset River. [39] The plant's dam formed the Verkh-Isetsky pond. Colloquially called by the Russian acronym VIZ, it was a satellite town until in 1926, with a population of over 20,000 people by this time, it was incorporated into Yekaterinburg as the core of the Verkh-Isetsky district. [39]

Yekaterinburg was one of the industrial cities of Russia prompted at the beginning of the 18th century by decrees of Tsar Peter the Great which demanded the development of the metalworking industry. With extensive use of iron, the city was built to a regular square plan with ironworks and residential buildings at the centre. These were surrounded by fortified walls so that Yekaterinburg was at the same time both a manufacturing centre and a fortress at the frontier between Europe and Asia. It, therefore, found itself at the heart of Russia's strategy for further development of the entire Ural region. The so-called Siberian Route became operational in 1763 and placed the city on an increasingly important transit route, which led to its development as a focus of trade and commerce between east and west, and gave rise to the description of the city as the "window to Asia". With the growth in trade and the city's administrative importance, the ironworks became less critical, and the more important buildings were increasingly built using expensive stone. Small manufacturing and trading businesses proliferated. In 1781 Russia's empress, Catherine the Great, granted Yekaterinburg town status and nominated it as the administrative centre for the wider region within Perm Governorate . [3] In 1807, the role of the capital of the mining and smelting region was confirmed by assigning it the status of the only "mountain city" in Russia. Until 1863, Yekaterinburg remained subordinate to the head of the mining plants of the Ural ridge , the minister of finance and personally to the emperor, and enjoyed considerable freedom from the governor's power. Since the 1830s, mountainous Yekaterinburg has become the center of mechanical engineering. [36]

In 1820–1845, 45% of the world's gold was mined in Yekaterinburg. This is the first ever "Gold Rush". [40] Until 1876, 80% of the coins in circulation in the Russian Empire were produced at the Yekaterinburg mint. [41]
Following the October Revolution , the family of deposed Tsar Nicholas II was sent to internal exile in Yekaterinburg where they were imprisoned in the Ipatiev House in the city. In July 1918, the Czechoslovak Legions were closing on Yekaterinburg. In the early hours of the morning of 17 July, the deposed Tsar, his wife Alexandra , and their children Grand Duchesses Olga , Tatiana , Maria , Anastasia , and Tsarevich Alexei were murdered by the Bolsheviks at the Ipatiev House. Other members of the Romanov family were killed at Alapayevsk later the same day. The Legions arrived less than a week later and captured the city. [42] [43] The city remained under the control of the White movement in which a provisional government was established. The Red Army took back the city and restored Soviet authority on 14 July 1919. [44] [45]

In the years following the Russian Revolution and the Russian Civil War , political authority of the Urals was transferred from Perm to Yekaterinburg. On 19 October 1920, Yekaterinburg established its first university, the Ural State University , as well as polytechnic, pedagogical, and medical institutions under the decree of Soviet leader Vladimir Lenin . Enterprises in the city ravaged by the war were nationalised, including: the Metalist (formerly Yates) Plant, the Verkh-Isetsky (formerly Yakovleva) Plant, and the Lenin flax-spinning factory (formerly Makarov). In 1924, the city of Yekaterinburg was renamed Sverdlovsk after the Bolshevik leader Yakov Sverdlov . [46] [28] [44]
By the 1934, following a series of administrative reforms carried by the early Soviet government, the earliest Russian settlements which predated Yekaterinburg and laid the basis of its founding, were incorporated into the city proper. [38] [47]
During the reign of Stalin, Sverdlovsk was one of several places developed by the Soviet government as a centre of heavy industry. Old factories were reconstructed and new large factories were built, especially those specialised in machine-building and metalworking. These plants included Magnitogorsk and the Chelyabinsk Tractor Plant in Chelyabinsk oblast , and Uralmash in Sverdlovsk. During this time, the population of Sverdlovsk tripled in size, and it became one of the fastest-growing cities of the Soviet Union. At that time, very large powers were given to the regional authorities. By the end of the 1930s, there were 140 industrial enterprises, 25 research institutes, and 12 higher education institutions in Sverdlovsk. [48] [49]
During World War II, the city became the headquarters of the Ural Military District on the basis of which more than 500 different military units and formations were formed, including the 22nd Army and the Ural Volunteer Tank Corps. Uralmash became the main production site for armoured vehicles. Many state technical institutions and whole factories were relocated to Sverdlovsk away from cities affected by war (mostly Moscow), with many of them staying in Sverdlovsk after the victory. The Hermitage Museum collections were also partly evacuated from Leningrad to Sverdlovsk in July 1941 and remained there until October 1945. [50] In the postwar years, new industrial and agricultural enterprises were put into operation and massive housing construction began. [51] [44] The lookalike five-story apartment blocks that remain today in Kirovsky, Chkalovsky, and other residential areas of Sverdlovsk sprang up in the 1960s, under the direction of Nikita Khrushchev 's government. [52] In 1977, Ipatiev House was demolished by order of Boris Yeltsin in accordance to a resolution from the Politburo in order to prevent it from being used as a rallying location for monarchists . Yeltsin later became the first President of Russia and represented the people at the funeral of the former Tsar in 1998. [53] There was an anthrax outbreak in Sverdlovsk in April and May 1979, which was attributed to a release from the Sverdlovsk-19 military facility . [54]
During the 1991 coup d'état attempt , Sverdlovsk, the home city of President Boris Yeltsin, was selected by him as a temporary reserve capital for the Russian Federation, in case Moscow became too dangerous for the Russian government. A reserve cabinet headed by Oleg Lobov was sent to the city, where Yeltsin enjoyed strong popular support at that time. [55] Shortly after the failure of the coup and subsequent dissolution of the Soviet Union, the city regained its historical name of Yekaterinburg on 23 September 1991. However, Sverdlovsk Oblast, of which Yekaterinburg is the administrative centre, kept its name. [56] [57]
In the 2000s, an intensive growth of trade, business, and tourism began in Yekaterinburg. In 2003, Russian President Vladimir Putin and German Chancellor Gerhard Schröder negotiated in Yekaterinburg. On 15–17 June 2009, the SCO and BRIC summits were held in Yekaterinburg, which greatly improved the economic, cultural, and tourist situation in the city. On 13–16 July 2010, a meeting between Russian President Dmitry Medvedev and German Chancellor Angela Merkel took place in the city. [58]
In 2018, Yekaterinburg hosted four matches of the 2018 FIFA World Cup and hosted the inaugural University International Sports Festival in 2023. [59]

Geographically, Yekaterinburg is in North Asia, close to the Ural Mountains (which divide Europe from Asia), 1,667 km (1,036 mi) east of the nation's capital Moscow.
The city has a total area of 1,111 km 2 (429 sq mi) .
Yekaterinburg is on the eastern side of the Urals. The city is surrounded by wooded hills, partially cultivated for agricultural purposes. Yekaterinburg is located on a natural watershed, so there would be many bodies of water close and in the city. The city is bisected by the Iset River , which flows from the Urals into the Tobol River . There are two lakes in the city, Lake Shuvakish and Lake Shartash. The city borders Verkh-Isetskiy Pond, through which the Iset River flows. Lake Isetskoye and Lake Baltym are both near the city, with Lake Isetskoye located near Sredneuralsk , and Lake Baltym located near the towns of Sanatornyy and Baltym.
Yekaterinburg uses the Yekaterinburg Time, which is five hours ahead of UTC (UTC+5), and two hours ahead of Moscow Time . [60]
The city possesses a humid continental climate ( Dfb ) under the Köppen climate classification . [61] It is characterised by sharp variability in weather conditions, with well-marked seasons. The Ural Mountains, despite their insignificant height, block air from the west, from the European part of Russia. As a result, the Central Urals are open to the invasion of cold arctic air and continental air from the West Siberian Plain. Equally, warm air masses from the Caspian Sea and the deserts of Central Asia can freely penetrate from the south. Therefore, the weather in Yekaterinburg is characterised by sharp temperature fluctuations and weather anomalies: in winter, from frost at −40 °C to thaw and rain; in summer, from frosts to temperatures above 35 °C (95 °F) . [61]

The distribution of precipitation is determined by the circulation of air masses, relief, and air temperatures. The main part of the precipitation is brought by cyclones with a western air mass transfer, that is, from the European part of Russia, while their average annual amount is 601 mm. The maximum falls on a warm season, during which about 60–70% of the annual amount falls. For the winter period is characterized by snow cover with an average capacity of 40–50 cm. The coefficient of moistening(the ratio of yearly precipitation and potential evaporation ) – 1. [61]
- The average temperature in January is −12.6 °C (9.3 °F) . The record minimum temperature is −44.6 °C (−48.3 °F) (6 January 1915);
- The average July temperature is 18.9 °C (66.0 °F) . The record maximum temperature is 40.0 °C (104.0 °F) (11 July 2023);
- The average annual temperature is 2.1 °C (35.8 °F) ;
- The average annual wind speed is 2.9 m/s (10 km/h; 6.5 mph) ;
- The average annual humidity is 75%;
- The average annual precipitation is 534 mm (21.0 in) ;
| Climate data for Yekaterinburg (1991–2020, extremes 1831–present) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 5.6 (42.1) | 9.4 (48.9) | 18.1 (64.6) | 28.8 (83.8) | 34.7 (94.5) | 36.4 (97.5) | 40.0 (104.0) | 37.2 (99.0) | 31.9 (89.4) | 24.7 (76.5) | 13.5 (56.3) | 5.9 (42.6) | 40.0 (104.0) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | −9.3 (15.3) | −6.6 (20.1) | 0.9 (33.6) | 10.1 (50.2) | 18.3 (64.9) | 22.6 (72.7) | 24.3 (75.7) | 21.4 (70.5) | 15.0 (59.0) | 6.9 (44.4) | −2.6 (27.3) | −7.8 (18.0) | 7.8 (46.0) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | −12.6 (9.3) | −10.8 (12.6) | −3.6 (25.5) | 4.7 (40.5) | 12.2 (54.0) | 16.9 (62.4) | 18.9 (66.0) | 16.2 (61.2) | 10.4 (50.7) | 3.6 (38.5) | −5.4 (22.3) | −10.7 (12.7) | 3.3 (37.9) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | −15.5 (4.1) | −14.1 (6.6) | −7.3 (18.9) | 0.3 (32.5) | 6.9 (44.4) | 12.0 (53.6) | 14.4 (57.9) | 12.2 (54.0) | 6.8 (44.2) | 1.0 (33.8) | −7.8 (18.0) | −13.3 (8.1) | −0.4 (31.3) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −44.6 (−48.3) | −42.4 (−44.3) | −39.2 (−38.6) | −21.8 (−7.2) | −13.5 (7.7) | −5.3 (22.5) | 1.5 (34.7) | −2.2 (28.0) | −9.0 (15.8) | −22.0 (−7.6) | −39.2 (−38.6) | −44.0 (−47.2) | −44.6 (−48.3) |
| Average mm (inches) | 25 (1.0) | 19 (0.7) | 25 (1.0) | 31 (1.2) | 47 (1.9) | 73 (2.9) | 93 (3.7) | 75 (3.0) | 45 (1.8) | 41 (1.6) | 33 (1.3) | 28 (1.1) | 534 (21.0) |
| Average extreme snow depth cm (inches) | 33 (13) | 42 (17) | 38 (15) | 5 (2.0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1 (0.4) | 8 (3.1) | 21 (8.3) | 42 (17) |
| Average rainy days | 1 | 1 | 5 | 13 | 20 | 20 | 19 | 22 | 22 | 17 | 6 | 1 | 147 |
| Average snowy days | 26 | 23 | 18 | 10 | 4 | 0.4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 13 | 23 | 25 | 144 |
| Average (%) | 79 | 75 | 68 | 60 | 58 | 63 | 68 | 73 | 75 | 75 | 78 | 79 | 71 |
| Mean monthly | 47 | 94 | 164 | 206 | 256 | 272 | 269 | 217 | 143 | 78 | 51 | 37 | 1,834 |
| Source 1: Pogoda.ru | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: NOAA (sun 1961–1990) | |||||||||||||
| Year | ||
|---|---|---|
| 1897 | 37,399 | — |
| 1926 | 134,831 | +260.5% |
| 1939 | 425,533 | +215.6% |
| 1959 | 778,602 | +83.0% |
| 1970 | 1,025,045 | +31.7% |
| 1979 | 1,211,172 | +18.2% |
| 1989 | 1,364,621 | +12.7% |
| 2002 | 1,293,537 | −5.2% |
| 2010 | 1,349,772 | +4.3% |
| 2021 | 1,544,376 | +14.4% |
According to the results of the 2021 Census , the population of Yekaterinburg was 1,544,376 ; [64] up from 1,349,772 recorded in the 2010 Census . [7]
As of 2021, the ethnic composition of Yekaterinburg was: [65]
| Ethnicity | Population | Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| 1,172,704 | 91.0% | |
| 27,431 | 2.1% | |
| 13,102 | 1.0% | |
| 8,769 | 0.7% | |
| 6,121 | 0.5% | |
| 4,987 | 0.4% | |
| 4,755 | 0.4% | |
| 4,307 | 0.3% | |
| 4,014 | 0.3% | |
| Others | 42,033 | 3.3% |

Christianity is the predominant religion in the city, of which most are adherents to the Russian Orthodox Church. The Yekaterinburg and Verkhotursky diocese is located in the Holy Trinity Cathedral in the city. Other religions practised in Yekaterinburg include Islam , Old Believers , Catholicism , Protestantism , and Judaism .
Yekaterinburg has a significant Muslim community, but it suffers from a lack of worship space: there are only two small mosques . Another mosque was built in the nearby city of Verkhnyaya Pyshma . On 24 November 2007, the first stone was laid in the construction of a large Cathedral Mosque with four minarets , and space for 2,500 parishioners in the immediate vicinity of the cathedral and a synagogue , thus forming the "area of the three religions". [66] The mosque was planned to be built for the SCO summit, but due to funding problems, construction did not move from zero and is now frozen.
Construction of a Methodist church started in 1992, and with the help of American donations, finished in 2001. [67] A synagogue was opened in 2005, on the same place a 19th-century synagogue was demolished in 1962.
Most of the city's religious buildings were destroyed during the Soviet era, in addition to the synagogue, the three largest Orthodox churches in Yekaterinburg were demolished – the Epiphany Cathedral, the Ekaterininsky Cathedral, and the Great Zlatoust Church . Other Christian churches such as the Lutheran Church of Yekaterinburg and the Roman Catholic Church of St. Anne (a new Catholic St. Anne's Church was built in 2000) were demolished as well. Other churches were used as warehouses and industrial sites. The only religious building in Yekaterinburg in the Soviet era was the Cathedral of St. John the Baptist. Recently, some churches are being rebuilt. Since 2006, according to the surviving drawings, the Great Zlatoust Church was restored in 2012. On 17 April 2010, the city was visited by Patriarch Kirill . [68]
Yekaterinburg is the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast . [1] Within the framework of the administrative divisions , it is, together with twenty-nine rural localities , incorporated as the City of Yekaterinburg, [9] an administrative unit with the status equal to that of the districts . [1] As a municipal division, the City of Yekaterinburg is incorporated as Yekaterinburg Urban Okrug. [10]
| Administrative districts of Yekaterinburg | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label | Name | Area (2019) | Population (2019) | Founded | Head | Website | Dialing code(s) | Subdivisions | |||
| 1 | Akademicheskiy | 81,000 | 2020 | Smirnyagin Nikolai Sergeevich | +7 3432, +7 3433 | 3 | |||||
| 2 | Verkh-Isetsky | 240 square kilometres (93 sq mi) | 221,207 | 1919 | Morozov Andrey Mikhailovich | 1 December 2021 at the | +7 3432, +7 3433 | 5 | |||
| 3 | Zheleznodorozhnyy | 126.3 square kilometres (48.8 sq mi) | 221,207 | 1938 | Pershin Vitaly Pavlovich | 1 March 2022 at the | +7 343 | 8 | |||
| 4 | Kirovsky | 72 square kilometres (28 sq mi) | 228,864 | 1943 | Bolikov Vladimir Yurievich | 15 March 2022 at the | +7 343 | 7 | |||
| 5 | Leninsky | 25 square kilometres (9.7 sq mi) | 156,723 | 1934 | Beruashvili Elena Zauryevna | 15 March 2022 at the | +7 343 | 3 | |||
| 6 | Oktyabrsky | 157 square kilometres (61 sq mi) | 148,981 | 1934 | Kostenko Igor Vitalievich | 10 November 2021 at the | +7 3432 | 11 | |||
| 7 | Ordzhonikidzevsky | 102 square kilometres (39 sq mi) | 286,482 | 1934 | Kravchenko Roman Gennadievich | 16 March 2022 at the | +7 3433 | 6 | |||
| 8 | Chkalovsky | 402 square kilometres (155 sq mi) | 275,571 | 1943 | Shipitsyn Evgeny Viktorovich | 9 May 2019 at the | +7 3432 | 10 | |||
Each district is not a municipal formation, and the historical centre of the city is divided into five inner-city districts (except Chkalovsky and Ordzhonikidzevsky).
A district named Akademicheskiy was formed from the parts of Leninsky and Verkh-Isetsky districts on 3 January 2020. [70] On 1 October 2021, more settlements were transferred from Verkh-Isetsky to Akademicheskiy district. [71]

The Charter of Yekaterinburg establishes a four-link system for the organisation of local authorities, which includes: the Head of Yekaterinburg, who serves as the chairman of the Yekaterinburg City Duma, the Yekaterinburg City Duma, the Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg, and the Chamber of Accounts. [74]
According to the charter of Yekaterinburg, the highest official of the municipal formation is the mayor of Yekaterinburg. The mayor is elected by universal suffrage, but since 3 April 2018, the procedure for direct elections of the mayor of the City of Yekaterinburg was abolished. The mayor of the city is endowed with representative powers and powers to organize activities and guide the activities of the City Duma. In addition, the mayor of the city exercises other powers such as concluding a contract with the head of the city administration and ensuring compliance with the Russian Constitution, Russian legislation, the city charter, and other normative acts. [75] [76]
In the event of a temporary absence of the mayor of Yekaterinburg, his authority under his written order is exercised by the deputy mayor of Yekaterinburg. [77]
The representative body of the municipal formation is the Yekaterinburg City Duma, which represents the city's entire population. The membership of the Duma is 36 deputies (18 deputies were elected in single-mandate constituencies and 18 in a single electoral district). Residents of the city elect deputies on the basis of universal suffrage for a period of 5 years. [74]
The executive and administrative body of the municipal formation is the Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg, led by the head of the Administration, currently held by Aleksandr Yacob. The administration is endowed with its own powers to resolve issues of local importance, but it is under the control and accountable to the Yekaterinburg City Duma. The building of the Administration of Yekaterinburg is located on 1905 Square . [76]
The Chamber of Accounts is a permanently operating body of external municipal financial control. The Chamber is formed by the apparatus of the City Duma and is accountable to it. The Chamber consists of the chairman, deputy chairman, auditors and staff. The structure and number of staff of the chamber, including the number of auditors, is determined by the decision of the City Duma. The term of office of the Chamber staff is 5 years. The Chamber of Accounts is a legal entity. [77]

In accordance with the regional charter, Yekaterinburg is the administrative centre of the Sverdlovsk Oblast. [1] The executive power is exercised by the governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast, the legislative power by the legislative assembly of Sverdlovsk Oblast, and the judicial power by the Sverdlovsk Regional Court, located in the building of the Palace of Justice. [78] The building serving the regional government is the White House and the building serving the legislative assembly is located next to it on October Square. The ministries of the Sverdlovsk Region are located in the building of the regional government, as well as in other separate buildings of the city. [79]

Yekaterinburg serves as the centre of the Ural Federal District. As a result, it serves as the residence of the presidential envoy , the highest official of the district and part of the administration of the President of Russia. The residence is located the building of the regional government on October Square near the Iset River embankment.

In addition, Yekaterinburg serves as the centre of the Central Military District and more than 30 territorial branches of the federal executive bodies, whose jurisdiction extends not only to Sverdlovsk Oblast, but also to other regions in the Ural Mountains, Siberia, and the Volga Region.
According to the results of the September 2013 elections, the mayor of the city was Yevgeny Roizman , nominated by the Civil Platform party. Out of the 36 seats in the City Duma, 21 belong to United Russia , 7 to A Just Russia , 3 to the Civil Platform, 2 to the Communist Party and 1 seat to the LDPR . The turnout in the mayoral elections was 33.57%. [80]
| 78,289 | 38.4% | ||||
| 31,288 | 15.4% | ||||
| 25,869 | 12.7% | ||||
| 22,293 | 10.9% | ||||
| 11,340 | 5.6% | ||||
| Party | Candidate | Votes | % | ±% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
It was the last popular vote in Yekaterinburg. Since 2018, there have been no elections, but a vote in the Municipal Duma. On 25 September 2018 the majority of the representatives in the Duma voted in favour of the Vice-Governor of Sverdlovsk oblast, Alexander Vysokinskiy.
Yekaterinburg is one of the largest economic centres in Russia. It is included in the City-600 list (it unites the 600 largest cities in the world that produce 60% of global GDP), compiled by the McKinsey Global Institute, a research organisation. In 2010, the consulting company estimated the gross product of Yekaterinburg to be about $19 billion (according to the calculations of the company, it should grow to $40 billion by 2025). [82] [83]
By volume of the economy, Yekaterinburg ranks third in the country, after Moscow and St. Petersburg. According to a research of the Institute for Urban Economics, in the ranking of the largest cities and regional capital cities according to economic standards for 2015, Yekaterinburg ranked third. The city's gross urban product (GVP) was 898 billion rubles. Per capita GDP was 621.0 thousand rubles (18th place). [84] In 2015, the gross urban product of the Yekaterinburg metropolitan area amounted to 50.7 billion international dollars (the fourth place in the country) or 25.4 thousand international dollars in terms of per inhabitant of the metropolitan area. [85]
In the Soviet era, Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) was a purely industrial city, with a share of industry in the economy of 90% (of which 90% were in defense production). With Chelyabinsk and Perm, the three cities formed what to be the Urals industrial hub. [86]
The former head of Yekaterinburg, Arkady Chernetsky, has set the goal of diversifying the city's economy, which has resulted in the development of sectors such as warehousing, transportation, logistics, telecommunications, financial sector, wholesale and retail trade, etc. in Yekaterinburg. [86] Economist-geographer Natalia Zubarevich points out that at the present stage, Yekaterinburg has practically lost its industrial specialisation. [87]

The standard of living in Yekaterinburg exceeds the average standard across Russia. According to the Department of Sociology of the Financial University under the Government of the Russian Federation, it is among the top ten cities with the highest standard of living. Compared to other Russian cities with a population of around or over one million, in 2015, Yekaterinburg held a leading position in terms of average monthly wages and retail turnover, in terms of the total volume of investments in fourth place of fixed assets, and second place in housing placement. [88] [89]

The average monthly wage in Yekaterinburg following the results of 2019 was 54,976 rubles. This is the first place among the millionth municipalities of the Russian Federation. [90] There are on average 440,300 people employed by large and middle-sized organisations and companies. The unemployment rate at the end of 2015 was 0.83% of the total economically active population. Locals labelled the main problems of the city such the current state of the healthcare system, housing system, and transportation system. [89] [91]
The budget of Yekaterinburg in 2015 was executed on income in the amount of 32,063.6 million rubles, for expenses in the amount of 32,745.8 million rubles. Among the budget expenditures: 17 billion rubles were spent on education, over 1 billion rubles on culture, and about 900 million rubles on health. The main part of the revenue of the city treasury was its own tax and non-tax revenues (more than 18 billion rubles). The revenues from the regional and federal budgets were at the lowest level in 10 years. Specialists noted a decrease in tax revenues and an increase in tax debt (exceeded 2 billion rubles). [89] [92]
The main budget expenditures are the development of the economy (which accounts for 19% of expenditures) and the social security of the townspeople (11% of expenditures go). Cities such as Perm, Kazan and Ufa, spend for these purposes in a smaller percentage of costs (from 2 to 6%). Also, a fairly strict budgetary discipline is noted—the budget deficit is kept at the level of 2% of its volume. [93]

Yekaterinburg is one of the largest financial and business centres in Russia, with offices of multinational corporations, representative offices of foreign companies, and a large number of federal and regional financial and credit organisations. The financial market of Yekaterinburg is characterised by stability and independence, based both on the broad presence of large foreign and Moscow credit organisations and on the availability of large and stable local financial holdings. [94]
The financial sector of Yekaterinburg has more than 100 banks, including 11 foreign banks. The list of the largest Russian banks for assets for 2016 included 10 banks registered in Yekaterinburg, including but not all: Ural Bank for Reconstruction and Development, SKB-Bank, Uraltransbank, and UM Bank. [95] [96]
IT "SKB Kontur" from Yekaterinburg – the largest software manufacturer in Russia – first place according to the RAEX rating [97]
Also in Yekaterinburg is the Ural headquarters of the Central Bank of Russia. Since 7 August 2017, by order of the Bank of Russia, the branches of the Siberian, Far Eastern and part of the Prevolzhsky Federal Districts have been transferred to the control of the Ural Megaregal Directorate. Thus, this is one of the three main departments of the Mega-regulator in the territory of Russia. [98]
A major role in the formation of Yekaterinburg as a business centre has its infrastructural potential, which is growing at a high rate: transport accessibility for Russian and foreign economic entities, the availability of hotels, advanced communication services, business related services (consulting, exhibition activities, etc.). [94] Yekaterinburg has its own central business district, Yekaterinburg City. [99]

Yekaterinburg has been a major industrial centre since its foundation. In the 18th century, the main branches were smelting and processing of metal. Since the beginning of the 19th century, machine building appeared, and in the second half of the 19th century, light and food (especially milling) industry was widely spread. A new stage in the development of production occurred during the period of industrialisation – at this time in the city, factories were built, which determined the industry specialisation of heavy engineering. During World War II, Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) hosted about sixty enterprises evacuated from Central Russia and Ukraine. As a result, there was a sharp increase in the production capacity of existing plants and the emergence of new branches of the Urals industry.
At present, more than 220 large and medium-sized enterprises are registered in Yekaterinburg, 197 of them in manufacturing industries. [94] In 2015, they shipped 323,288 million rubles worth of own-produced goods. Production by industry was divided accordingly: metallurgical production and metalworking 20.9%, food production 13.3%, production of electrical equipment, electronic and optical equipment 9.2%, production of vehicles 8.4%, production of machinery and equipment 6.4%, chemical production 5.5%, production of other nonmetallic mineral products 3.7%, production of rubber and plastic products 2.8%, pulp and paper production, publishing and printing 0.5%, and other 29.3%. [100]
Several headquarters of large Russian industrial companies are located in the city: IDGC of Urals, Enel Russia, Steel-Industrial Company, Russian Copper Company, Kalina, NLMK-Sort, VIZ-Stal, Sinara Group, Uralelectrotyazhmash, Automation Association named after academician NA Semikhatov, Ural Heavy Machinery Plant (Uralmash), Fat Plant, Fores, confectionery association Sladko, Machine Building Plant named after M.I. Kalinin, Ural Turbine Plant, Uralkhimmash and others. [101]

Yekaterinburg ranks first in retail trade of the Russian Federation per capita, ahead of Moscow. [102] The consumer market contributes significantly to Yekaterinburg's economy. Revenue of retail stores in 2015 amounted to 725.9 billion rubles, and the number of retailers totaled 4,290. [103] As of 1 January 2016, 36 shopping centers operate in the city, taking up a total area of which was 1,502,700 m 2 (16,175,000 sq ft) . The availability of shopping centres per 1,000 inhabitants increased to 597.2 m 2 (6,428 sq ft) . [104]
Retail areas amounted to 2,019,000 m 2 (21,730,000 sq ft) , with the availability of retail space reached 1,366.3 m 2 (14,707 sq ft) per 1,000 inhabitants. According to these statistics, Yekaterinburg holds leading positions among other major cities of Russia. In the consumer market of Yekaterinburg, 1041 network operators are represented. The number of wholesale enterprises totalled 1,435. Among the Federal construction stores represented in the city, you can select: Leroy Merlin, [105] Castorama, [106] Domostroy, [107] Maxidom, [108] OBI, [109] Sdvor. [110] Yekaterinburg has an agricultural market named Shartashsky. [104] [111]
The revenue of catering in 2015 totalled 38.6 billion rubles. The network of catering enterprises in Yekaterinburg is presented as follows: 153 restaurants, 210 bars, 445 cafes, 100 coffee houses, 582 dining rooms, 189 eateries, 173 fast-food establishments, 10 tea shops, 319 other types of institutions (buffets, cafeterias, catering companies). 82.6% of catering enterprises provide additional services to consumers. [112]
The revenue of the services industry in 2015 totalled 74.9 billion rubles. The fastest pace in the city is developing hairdressing services, sewing and knitting atelier services, pawnshop services, fitness centre services. The network of public service enterprises in Yekaterinburg includes 5,185 facilities. In 2015, the provision of service areas for service enterprises totaled 382.1 m 2 (4,113 sq ft) per 1,000 citizens. The highest concentration of household services is observed in the Verkh-Isetsky, Oktyabrsky and Leninsky districts. [113]
Greenwich Shopping Center, as of 2021, is the largest shopping center in Europe. [114]
The largest store in the world by area is Sima-Land. [115]
Yekaterinburg is a major centre for the Russian tourist industry. In 2015, the city was one of the top five most visited Russian cities (others being Moscow, St. Petersburg, Novosibirsk , and Vladivostok ) according to the Global Destinations Cities Index, which represents the payment system Mastercard . [116] In recent years, a lot of work has been done to create a positive image of Yekaterinburg as a centre for international tourism, including holding of summits for the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) in 2008 and 2009 and the international exhibition Innoprom in 2009 and 2010. [117] In 2014, Yekaterinburg ranked third among Russian cities in popularity among foreign tourists after Moscow and St. Petersburg. [118]
In 2015, the total flow of inbound tourism grew by 10% compared to the previous year and amounted to 2.1 million people. [119] In recent years, there has been a tendency to reduce the role of business tourism in the overall flow: if in 2013 about 80% of trips were business, in 2015 their number was already 67%. Most tourists go to "bow to the memory of the last [czar] and his family." In addition, new tourist ideas are developing such as the Bazhov theme, the geological and mineralogical theme, industrial tourism, and the event calendar. [120]
Yekaterinburg is the third largest transport hub of Russia, behind Moscow and St. Petersburg. The city has 6 federal highways, 7 main railway lines, and an international airport. The location of Yekaterinburg in the central part of the region allows for 7 to 10 hours to get from it to any large city of the Urals. [121] The formation of Yekaterinburg as an important transportation hub is largely due to the city's favourable geographical location on a low stretch of the Ural Mountains, through which it was convenient to lay the main roads connecting the European and Eastern parts of Russia. [122]

Yekaterinburg is one of the ten Russian megacities with the largest car fleet (0.437 megacars were registered in the city in 2014), which has been intensively increasing in recent years (by 6–14% annually). [123] [124] The level of car ownership in 2015 has reached 410 cars per 1,000 people. [125] Its pace in the past few years has seriously exceeded the pace of development and the capacity of the road infrastructure. For the first time, transport problems started to appear in Yekaterinburg in the 1980s and though it did not seem threatening at first, the situation gets worse every year. Studies have shown that as early as 2005, the capacity limit for the road network was reached, which has now led to permanent congestion. [126] To increase the capacity of the street-road network, stage-by-stage reconstruction of streets is being carried out, as well as multi-level interchanges being built. In order to reduce the transit traffic, the Sverdlovsk Oblast administration announced two road projects in 2014: the Yekaterinburg Ring Road (EKAD) and an overpass road on Sovetskaya Street. The Yekaterinburg Ring Road would surround the largest municipalities of Yekaterinburg. Its purpose would be to help the city's economy and reduce traffic on the Middle Ring Road of the city, making it easier for civilians to commute around the city than going through the city's traffic congestion. Eventually, the Ring Road would connect to other federal roads in order for easier access between other Russian cities. Construction of the road started in the same year. The projects were assigned to the Ministry of Transport and Communications since the projects were crucial to the city's economy. Officials hope the road projects will build environments more conducive to improving local quality of life and outside investments. Completing these major inter-regional roads will increase productive traffic by 50% to 100%, improving the local economy with its ease of access to industries. [127]
Since 2014, the project for the introduction of paid parking in the central part of Yekaterinburg is being implemented. The project is implemented in parallel with the increase in the number of intercepting parking lots and the construction of parking lots. At the end of 2015, in the central part of the city there were 2,307 paid parking places. [125]
The total length of the road network in Yekaterinburg is 1,311.5 km (814.9 mi) , of which 929.8 km (577.8 mi) is cobbled carriageways, 880 km (550 mi) is with upgraded coverage, 632 km (393 mi) is backbone networks, of which 155 km (96 mi) are on the citywide backbone network movement. 20 interchanges have been constructed at different levels within the city limits, including 11 on the EKAD and 9 on the middle ring. 74 transport facilities (27 bridges across the Iset River, Patrushikha, Mostovka, Istok Rivers, 13 dams on the Iset, Patrushikha, Istok, Olkhovka, Warm, Shilovka Rivers, 23 road overpasses , and 18 out-of-the-way pedestrian crossings) were built as well. [128]
Yekaterinburg is served by the following highways: [129]

Yekaterinburg uses almost all types of public transport. The largest transportation services—the Municipal Association of Bus Enterprises, the Tram-Trolleybus Office, and the Yekaterinburg Metro —transported 207.4 million people in 2015. [130] The total volume of passenger transportation by all land transport modes decreases annually. If the annual passenger traffic of municipal transport was 647.1 million people in 2002, and according to this index the city occupied the third place in the country with a wide margin, then in 2008 this figure would be 412 million people (the fourth place in Russia). [131] [132]

Since 1991, the city operates the sixth metro in Russia and the thirteenth in the CIS . At the moment there is one line with 9 stations. In 2015 49.9 million passengers were transported; according to this metric the Yekaterinburg Metro is the fourth in Russia, behind the Moscow Metro, Saint Petersburg Metro, and Novosibirsk Metro . [133] Although the metro is the second most popular type of public transport, in recent years significant problems have appeared in its work: loss-making, obsolete rolling stock, and a shortage of funds for modernisation. [134] The tram network was established in 1929 and currently [ when? ] plays a leading role in the urban transport system. The volume of passengers carried for 2013 is 127.8 million, [135] but this declines every year (245 million people in 2013 [136] ). In 2016 there were 30 routes operating 459 cars. The total length of the tracks is 185.5 km. As of 2016 [ update ] , the construction of a tram line "Ekaterinburg-Verkhnyaya Pyshma" was planned. [137]

There are 93 bus routes operating in Yekaterinburg, including 30 municipal ones (EMUP "MOAP"). [138] In 2007, 114.5 million passengers were transported by municipal intercity buses (124.6 million in 2006). [139] The decrease in volume is due to the increasing role of the fixed-route taxis in the urban transport system of Yekaterinburg, as well as the high cost of travel. However, the city bus transport network provides significant employment for the people of Ekaterinburg, including the formidable babushkas who collect passenger fares. In the park of EMPU, there are 537 buses. [140] In 2013, there are 19 routes, which employ 250 trolleybuses. The total length of trolleybus lines is 168.4 km. The number of passengers transported by trolleybus in 2007 amounted to 78.4 million (84.3 million in 2006). [139]
In addition, the city operates an electric train route linking the north-western and the southern parts of Yekaterinburg, from Sem' Klyuchey to Elizavet.

Yekaterinburg is a major railway junction. In the Yekaterinburg node, 7 main lines converge (to Perm , Tyumen , Kazan , Nizhny Tagil , Chelyabinsk , Kurgan , and Tavda ). The Sverdlovsk Railway Administration is located in the city, which serves trains on the territory of the Sverdlovsk and Tyumen Regions, the Perm Territory, the Khanty-Mansiysk and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Districts, as well as parts of the Omsk Region, and there is a single road traffic control centre. The Perm–Yekaterinburg–Tyumen section is now part of the main route of the Trans-Siberian Railway .

Yekaterinburg is served by two primary airports: Koltsovo International Airport (SVX) and the smaller Yekaterinburg Aramil Airport . Koltsovo Airport is one of the largest airports in the country, serving 5.404 million passengers (including 3.485 million serviced by domestic airlines, 1.919 million at international flights) in 2017, making it the sixth busiest airport in Russia . [141]

Yekaterinburg has an extensive network of municipal, regional and federal health facilities. There are 54 hospitals, designed at a capacity of 18,200 beds, [142] 272 ambulatory polyclinics, and 156 dental clinics and offices. [143] Some health facilities are based on medical research institutes such as the Research Institute of Phthisiopulmonology, [144] the Research Institute of Dermatology and Immunopathology, [145] and the Ural State Medical University, as well as others.
In clean areas of the city, there is the Yekaterinburg Medical Centre, which includes the Sverdlovsk Regional Clinical Hospital No. 1 (also includes a polyclinic and a boarding house), Central City Hospital No. 40 (polyclinic, therapeutic building, surgical building, infectious body, neuro-surgical building, maternity hospital), Regional Cardiology Centre, Centre for Prevention and Control of AIDS, and MNTK Eye Microsurgery. [146]
Other large medical centres are the Uralmash Health Centre (Hospital No. 14), the Hospital of veterans of the Great Patriotic War, the district hospital of the Ministry of Internal Affairs, the district military hospital, the Oncology Centre, the Sverdlovsk Oblast Psychiatric Hospital, the Disaster Medicine Centre, the Sanguis Blood Transfusion Centre, children's versatile hospital No. 9, and the regional rehabilitation centre on Chusovsky lake. There are about 300 pharmacies in the city. [143] The number of doctors in public medical institutions is 11,339 people (83.9 per 10,000 people) and the number of nurses is 16,795 (124 per 10,000 people).
Private medical institutions also operate in the city. [147]

Yekaterinburg's education system includes institutions of all grades and conditions: preschool, general, special (correctional), and vocational (secondary and higher education), as well as others. Today, the city is one of the largest educational centres of Russia, with Yekaterinburg considered to be the leading educational and scientific centre of the Urals . [148]

There are 164 educational institutions in Yekaterinburg: 160 of them operate in the morning and the other 4 in the evening. In 2015, 133,800 people were enrolled in general education institutions, which holds a capacity of 173,161 people. [149] Yekaterinburg's education system also includes state pre-school educational institutions, non-state pre-school institutions, out-of-town health camps, and municipal city health facilities with a one-day stay. [150] Five educational institutions of the city: SUNC UrFU, Gymnasium No. 2, Gymnasium No. 9, Gymnasium No. 35, and Lyceum No. 135, were included in the rating of the five hundred best schools in the country by the Moscow Center for Continuous Mathematical Education and the Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation . [151]
On 16 July 1914, the Ural Mining Institute of Emperor Nicholas II (now the Ural State Mining University ) was established as Yekaterinburg's first educational institution. [152] In 1930, the Sverdlovsk Power Engineering College (now the Ural Technical Institute of Communications and Informatics) was opened to train specialists in the field of communications. The Alexei Maximovich Gorky Ural State University (now the Ural Federal University ) became the first university in Yekaterinburg by decree of the Council of People's Commissars of the RSFSR , signed by Vladimir Lenin on 19 October 1920. The Sverdlovsk Engineering and Pedagogical Institute (today the Russian State Vocational and Pedagogical University) became the first university of the USSR for the training of engineering and pedagogical personnel when it was opened in 1979.

In terms of the level of qualification of the graduates, Yekaterinburg's universities are among the leading in Russia, in particular in terms of the number of graduates representing the current managing elite of the country, Yekaterinburg universities are second only to the educational institutions of Moscow and Saint Petersburg. [153] [154] Currently, there are 20 state universities in the city, which currently holds a total of 140,000 students. [155] In addition, there are 14 non-state institutions of higher education in the city, such as the Yekaterinburg Academy of Contemporary Art and the Yekaterinburg Theological Seminary. The prestigious architecture school, the Ural State Academy of Architecture and Arts , is also located within the city limits. Other institutions of higher education Ural State Pedagogical University, Ural State University of Forestry, Ural State University of Railway Transport, Ural State University of Economics, Military Institute of Artillery, Ural State Conservatory , Ural State Agricultural Academy, Ural State Law Academy , Ural State Medical University, Ural State Academy of Performing Arts, Ural Academy of Public Service, and Institute of International Relations .
In May 2011, the Ural State University and Ural State Technical University merged to form the Boris N. Yeltsin Ural Federal University , making it the largest university in the Urals and the largest university in Russia. As of 1 January 2016, the university had 35,300 students and 2,950 teachers. The university's budget in 2015 totalled 9,1 billion rubles and the volume of research and development work totalled 1,6 billion rubles. [156] As of 2021, UrFU is the largest university in Russia in terms of the number of students, being on the 351st place in the QS World University Rankings. [157] [158] The number of publications of the university in the Web of Science database is about a thousand per year. [159]
There are many branches of non-resident universities in the city, including the Ural branch of the Siberian State University of Telecommunications and Informatics, the Ural branch of the Russian Academy of Private Law, the Yekaterinburg branch of the Plekhanov Russian Economic Academy, the Yekaterinburg branch of the University of the Russian Academy of Education, the Yekaterinburg branch of the Moscow State University, and Sholokhov Humanitarian University, as well as others.

In Yekaterinburg, a large number of print publications are published: about 200 newspapers, the most read being the Ural Worker , Vecherny Yekaterinburg , Oblastnaya Gazeta , and For Change! , and 70 magazines, with most read being Red Burda and I'm Buying . [160] [161]
A television studio was built in Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) in 1955 and on 6 November of the same year, the first telecast appeared. Coloured television later appeared in 1976. [162] Now the television is broadcast by 19 companies, including but not all: STRC Ural, Channel Four, 41 Home, Channel 10, OTV, Union (Orthodox), and UFO 24. Broadcasting is carried out from the TV tower on Lunacharsky street (television studio GTRK Ural), the TV tower on the Moskovskiy Hill, and from the TV tower (radio relay tower) on Blyukher Street. In 1981, construction of a new television tower was started, which was to become the second tallest in Russia after the Ostankino Tower and cover the territory of most of the Sverdlovsk region, but economic difficulties postponed construction. As a result, the television tower was the tallest uncompleted structure in the world. On 24 March 2018, the television tower was demolished by detonation for the city's beautification in preparation of the 2018 FIFA World Cup . [163] The Shartash radio mast, which broadcasts, is the tallest structure in the city, with a height of 263 meters. [164] In addition, several dozens of national and local news agencies are broadcast in Yekaterinburg, with the most watched being ITAR-TASS Ural, RUIA-Ural, and Interfax-Ural.
At the moment [ when? ] , there are 26 internet providers and 6 cellular operators in the city. [165] According to Yekaterinburg News , the city has signed a cooperative agreement with the Russian mobile operator Vimpelcom , working under the Beeline brand. The partnership will involve cooperation on investment projects and social programmes focused on increasing access to mobile services in the city. Beeline has launched an initiative to provide Wi-Fi services in 500 public trams and trolley buses in Yekaterinburg. [166]
| Generation | Mobile communication standard | Operators |
|---|---|---|
| , , , , Motive | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia, Motive | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia, Motive | ||
| , | MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia | |
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, Tele2 Russia, Motive, | ||
| MTS, MegaFon, Beeline, |

Yekaterinburg is a multipurpose cultural centre of the Urals Federal District. [148] There are about fifty libraries in the city. The largest library organisations are the Sverdlovsk Oblast Universal Scientific Library, the V.G. Belinsky Scientific Library, which is the largest public library in Sverdlovsk Oblast, and the Municipal Library Association, which is composed of 41 libraries throughout the city, including the AI Herzen Central City Library. [167]
There are about 50 different museums in the city. [168] Yekaterinburg has unique museum collections, such as the collections of Russian paintings in the Yekaterinburg Museum of Fine Arts and the Nevyansk icons in the Nevyansk Icon Museum , with more than 300 icons representing the eighteenth through the twentieth centuries on display. There is also a unique exhibit, the Kaslinsky cast iron pavilion, which received main awards at the 1900 World Exhibition in Paris. The Kasli Pavilion was registered by UNESCO as the only cast-iron architectural structure in the world, which is in the museum collection. [169] Museums of the city also have collections of jewellery and stone ornaments. The United Museum of Writers of the Urals presents exhibitions in memory of writers such as Dmitry Mamin-Sibiryak and Pavel Bazhov . It also is the home of the Shigirskaya Kladovaya ( Шигирская кладовая ), or Shigir Collection, which includes the oldest known wooden sculpture in the world. The sculpture was found near Nevyansk and originally estimated to have been made approximately 9,500 years ago, but now is estimated to have been made 11,500 years ago. [170] Yekaterinburg museums annually participate in the international event Long Night of Museums .
Yekaterinburg has the third most theatres in Russia. [171] The influence of theatrical life of the city was made by the Moscow Art Academic Theater and the Central Theater of the Soviet Army when they evacuated to Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk) during World War II, and they had their own theater in the city. [172] Notable theatres that operate in the city are Academic Theater of Musical Comedy, Drama Theater, Kolyada-Theater , the youth theatre, and the puppet theatre, as well as others. The Yekaterinburg Opera and Ballet Theater received four awards at the Golden Mask 2020 Festival in Moscow, including the main Golden Mask for the Best Opera Performance [173]
In 2014, the city showcased its education, literary, art, and theatre culture through the Russian Year of Culture Programme. [174]
The city has a well-developed film industry. Opened back in 1909, Laurage was the first cinema in Yekaterinburg. In 1943, the Sverdlovsk Film Studio was opened and produced its first feature film Silva a year later. After the Second World War, the studio produced up to ten feature films a year. There are more than 20 cinemas in Yekaterinburg, the oldest of which is the Salyut, while the most capacious is the Cosmos spacecraft. [175] [176] There are also chains of movie theatres such as Premier-Zal, Kinomaks, and Kinoplex, which usually open in shopping and entertainment centres.
A number of popular Russian rock bands, such as Urfin Dzhyus, Chaif , Chicherina , Nautilus Pompilius , Nastya, Trek, Agata Kristi , Slaughter to Prevail and Smyslovye Gallyutsinatsii , were originally formed in Yekaterinburg ( Ural Rock is often considered as a particular variety of rock music. Yekaterinburg and St. Petersburg are actually considered to be the main centres of the genre in Russia). Also, opera singers like Boris Shtokolov , Yuri Gulyayev , Vera Bayeva graduated from the Urals State Conservatory. The Ural Philharmonic Orchestra (currently conducted by Dmitry Liss ), founded by Mark Paverman and located in Yekaterinburg, is also very popular in Russia and in Europe, as well as the Ural Academic Popular Chorus, a folk-singing and dance ensemble. [ citation needed ]

Yekaterinburg V. I. Filatov State Circus is located in the centre of the city, on the western bank of the Iset River. In 2012, the Yekaterinburg Circus was nominated "Best Circus of the Year" for the circus show Sharivari by the Rosgoscirk and the Ministry of Culture . [177]
The Presidential Center named after Boris Yeltsin was built in Yekaterinburg in 2015. It is considered to be a public, cultural and educational center. Center has its art gallery, library, museum equipped with the newest multimedia technologies that help to present the documents, video materials and archive photos. In 2017, the Yeltsin Center was recognized as the best museum in Europe by the Council of Europe, the first of the museums in Russia. [178]
The Urals Society of Natural Science Lovers pushed Yekaterinburg to have a zoo. Currently, the zoo has more than 1,000 animals that belong to more than 350 species. The zoo covers an area of 2.7 hectares.
On 18 June 2011, Yekaterinburg launched Red Line as a pedestrian tourist route for self-guided tours by residents and visitors to go to 34 landmarks in the historical section of the city. [179]

Many buildings of Yekaterinburg are ranged from a different number of architectural styles. The city had a regular layout, based on the fortresses of the Renaissance and by the principles of French town planning during the 17th century. By the 18th century, the Baroque movement was not that influential in Yekaterinburg, with the style being seen in churches which later declined [180]
In the first half of the 19th century, neoclassicism grew influential in the Yekaterinburg's architecture. The estates were built in the neoclassic style, including the main house, wings, services, and often an English-style park. This style's influence in Yekaterinburg is mostly due to the contributions of architect Michael Malakhov, who worked in the city from 1815 to 1842. He designed the assemblies of the Verkhne-Isetsky factory as well as the Novo-Tikhvinsky Monastery. [180]
At the beginning of the 20th century, eclecticism became a dominant influence in Yekaterinburg's architecture. Buildings such as the Opera House and Yekaterinburg railway station were built in this style. During the 1920s and the 1930s, constructivism took effect, influencing residential complexes, industrial buildings, stadiums, etc. Architects Moses Ginzburg, Jacob Kornfeld, the Vesnina brothers, Daniel Friedman, and Sigismund Dombrovsky contributed greatly to the constructivism in the city. More than 140 structures in Yekaterinburg are designed through the constructivist style. [181]

During the 1930s to 1950s, there was a turn back to neoclassicism, with much attention paid to public buildings and monuments. Notable examples include the buildings of the Ural Industrial Institute on Lenin Avenue, the City Party Committee and the City Council Executive Committee building (now the City Administrative building), the District Officers' House, and the House of Defense complex. Cultural buildings are built in the squares in orderly composition. In these years, architects Golubev, K. T. Babykin, Valenkov worked fruitfully in Yekaterinburg with this style. In the 1960s, changes in the approach to construction led to widespread distribution of apartment blocks common in the Khrushchev era . Buildings built by individuals were rare, among them being: KKT "Kosmos", the Palace of Youth, and DK UZTM. [182]
From the 1960s to the 1980s, as industrial development grew in Yekaterinburg, so did rationalism . The situation changed in the 1990s when Russia transferred into a market economy. At that time, older buildings were restored, giving the urban area a new environment such as: the Cosmos Concert Hall, the Puppet Theater, the children's ballet theatre The Nutcracker, the Palace of Justice, the Cathedral of the Blood, and the Church of the Transfiguration . At the same time, the construction of new buildings was accompanied by the demolition of historical buildings, leading to the development of the "facade" phenomenon, where the facades of historic buildings are preserved while adjacent modern buildings are built. [183]
The centre of Yekaterinburg became the centre of new construction, where banks, business centres, hotels, luxury residential complexes, and sports and shopping centres were built. High-tech architecture grew influential, with buildings such as the Center for Railway Transportation Management, the Summit business centre, the Aquamarine residential complex, and the retail strip at Vaynera Street being notable examples. Along with this, postmodernism revived interest in the older architectural styles of Yekaterinburg, growing more emphasis on historicalism and contextualism. In the late 1990s, architects grew interested in regionalism . [183]
At the beginning of the 21st century, Yekaterinburg architects turned back to the Soviet-based avant-garde, and influence future city buildings with the neoconstructivist style. The practice of attracting large foreign investors to projects has become popular. In 2007, the construction of the Central business district started, being headed by the French architect Jean Pistre. [183] In 2010, Yekaterinburg became one of the largest centers for the construction of High-rise buildings. In the city, 1,189 high-rise buildings were built, including 20 skyscrapers, the tallest of which is the Iset Tower , with a height of 209 meters. [184]
Yekaterinburg is also a leading sports centre in Russia. A large number of well-known athletes, both world and Olympics champions, are associated with the city. Since 1952, Yekaterinburg athletes have won 137 medals at the Olympic Games (46 gold, 60 silver and 31 bronze). In the 2008 Summer Olympics , 8 residents of Yekaterinburg returned with medals (1 gold, 3 silver and 4 bronze). [185]

In 1965, Yekaterinburg (as Sverdlovsk), along with a number of Russian cities, hosted the Bandy World Championship . In 2018, Yekaterinburg was one of the 11 Russian cities that hosted the 2018 FIFA World Cup. The matches were played on the upgraded Yekaterinburg Arena (called Central Stadium before the World Cup). [186]
Yekaterinburg has a total of 1728 sports facilities, including 16 stadiums with stands, 440 indoor gyms and 45 swimming pools. There are 38 sports children's and youth schools for reserves for the Olympic Games, in which more than 30,000 people are participating. [187]
Sport clubs
Yekaterinburg has many professional sports clubs in sports such as volleyball, basketball, futsal , bandy , and ice hockey for both women and men. Bandy club SKA-Sverdlovsk , women's volleyball club VC Uralochka-NTMK , women's basketball club UMMC Yekaterinburg , and futsal club MFK Sinara Yekaterinburg were among the best teams in Russia and Europe.
| Club | Sport | Founded | Current League | League Tier | Stadium |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1930 | 1st | ||||
| 2006 | 1st | ||||
| Avto Yekaterinburg | 2009 | Jr. 1st | |||
| Spartak-Merkury | 1992 | Women's Hockey Championship | 1st | Sports Palace Snezhinka | |
| 1937 | 1st | ||||
| 1935 | 2nd | ||||
| 2006 | 2nd | ||||
| 1938 | 1st | ||||
| Lokomotiv-Izumrud Yekaterinburg | 1945 | 2nd | |||
| 1966 | Women's Volleyball Superleague | 1st | Metallurg-Forum | ||
| 1992 | 1st |
2018 FIFA World Cup

Yekaterinburg hosted four matches of the 2018 FIFA World Cup [59] Yekaterinburg is one of the 11 Russian cities that hosted the 2018 FIFA World Cup. The matches were played on the upgraded Yekaterinburg Arena . [186]
For the World Cup 2018, from 7 October 2015 to 29 December 2017, the Central Stadium was upgraded to bring it into compliance with FIFA requirements for the World Cup and was renamed Yekaterinburg Arena. The architectural concept of the new stadium is built on a combination of historical walls and the built-in core of the modern arena. During the reconstruction of the sports facility, which is a monument of history and culture, the facades are carefully preserved, and the arena itself is equipped with the latest technical achievements of the sports industry. Temporary stands extending outside the stadium's original perimeter were erected to comply with the FIFA requirement of seating for 35,000 spectators. They can hold a total of 12,000 spectators, but the seating will be removed after the World Cup, decreasing the seating capacity back to 23,000. [188] [189]
The FIFA Fan Fest in Yekaterinburg is located in the Mayakovsky Central Park of Entertainment and Culture. Located just outside the city centre in a popular and well-known amusement park, it will have a capacity to hold 17,000 people. [190]
Koltsovo Airport was also reconstructed and had a second runway built. In addition, work was done to prepare another passenger terminal, modernize the technical infrastructure, and launch the business aviation hangar. The airport's capacity in preparation for the World Cup has increased to two thousand people per hour. The street and road network was also upgraded. [191]
The United States, [192] United Kingdom, [193] Germany, [194] France, [195] China [196] and several other countries have consulates in Yekaterinburg.
The BRIC countries met for their first official summit on 16 June 2009, in Yekaterinburg, [197] with Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva , Dmitry Medvedev , Manmohan Singh , and Hu Jintao , the respective leaders of Brazil, Russia, India and China, all attending.
The foreign ministers of the BRIC countries had also met in Yekaterinburg previously on 16 May 2008.
In June 2013, at the 153rd General Assembly of the Bureau of International Expositions held in Paris, representatives from Yekaterinburg presented the city's bid to host the 2020 World Expo . Yekaterinburg's concept for the upcoming exhibition relates to the impact of globalisation on the modern world.
Russian President Vladimir Putin confirmed during a televised statement in English to earmark the required funds to build an exhibition complex large enough to receive the estimated 30 million visitors from more than 150 countries. [198]
Yekaterinburg later bid for the Expo 2025 . Yekaterinburg's concept for the bid exhibition relates to the technologies to make people happy by changing the world with innovation and quality of life. The host was announced on 23 November 2018 and Yekaterinburg lost out to Osaka, Japan.
Yekaterinburg hosted the Global Summit on Manufacturing and Industrialization (GMIS — 2019) GMIS under the auspices of the United Nations. [199] The annual INNOPROM exhibition is among the five largest industrial exhibitions in the world. [200]
Yekaterinburg is twinned with: [201]
- Anton Bakov , Leader of the Monarchist Party
- Irina Antonenko , Miss Russia 2010
- Aleksei Balabanov , film director, screenwriter, producer
- Vera Bazarova , pairs figure skater
- Pavel Bazhov , folklorist and children's author
- Old Man Bukashkin , artist and poet
- Pavel Datsyuk , ice hockey player
- Nikolay Durakov , bandy legend
- Chiang Fang-liang , former first lady of Taiwan
- Aleksey Fedorchenko , film director, producer
- Denis Galimzyanov , sprinter cyclist
- Anna Gavrilenko , Group rhythmic gymnast Olympic Gold medalist
- Nikolay Karpol , national women volleyball team coach
- Nikolai Khabibulin , ice hockey player
- Alexei Yashin , ice hockey player
- Alexei Khvostenko , avant-garde poet, singer-songwriter, artist, and sculptor
- Nikolay Kolyada , actor, director, writer, playwright, and playwriting teacher
- Ilya Kormiltsev , poet, translator, publisher
- Olga Kotlyarova , Olympic runner
- Maxim Kovtun , figure skater
- Vladislav Krapivin , children's author
- Valeria Savinykh , WTA Professional player
- Nikolay Krasovsky , mathematician
- Yulia Lipnitskaya , figure skater
- Iskander Makhmudov , businessman
- Vladimir Malakhov , ice hockey player
- Gennady Mesyats , vice-president of the Russian Academy of Sciences
- Maxim Miroshkin , pairs figure skater
- Vladimir Mulyavin (1941 – 2003), Belarusian musician and the founder of the folk-rock band Pesniary [202]
- Alfia Nazmutdinova , rhythmic gymnast
- Ernst Neizvestny , sculptor
- Oleg Platonov , writer, historian, and economist
- Daria Pridannikova , rhythmic gymnast
- Eduard Rossel , ex-governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast
- Boris Ryzhy , poet
- Mikhail Shchennikov , race walker
- Vera Sessina , rhythmic gymnast
- Georgy Shishkin , painter
- Vassily Sigarev , playwright, screenwriter, film director
- Anastasiia Tatareva , Group rhythmic gymnast Olympic Gold medalist
- Sergei Tchepikov , Olympic biathlon competitor
- Vladimir Tretyakov , ex-rector of the Ural State University
- Lev Vainshtein , Olympic shooter
- Sergei Vonsovsky , physicist
- Alexander Dudoladov , writer
- Alexander Malinin , singer
- Petr Yan , Former UFC Bantamweight Champion
- A ballistic missile submarine of the Project 667BDRM Delfin class ( NATO reporting name: Delta IV ) is named Ekaterinburg (K-84/"807") in honour of the city.
- The asteroid 27736 Ekaterinburg was named in the city's honour on 1 June 2007.
Related Research Articles
Sverdlovsk Oblast is a federal subject of Russia located in the Ural Federal District. Its administrative center is the city of Yekaterinburg, formerly known as Sverdlovsk. Its population is 4,268,998.

Irbit is a town in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located 203 kilometers (126 mi) from Yekaterinburg by train or 250 kilometers (160 mi) by car, on the right bank of the Nitsa. Population: 37,009 (2021 Census) ; 38,357 (2010 Census) ; 43,318 (2002 Census) ; 51,708 (1989 Soviet census) .

Koltsovo International Airport is the international airport serving Yekaterinburg, Russia, located 16 km (10 mi) southeast of the city. Being the largest airport in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Koltsovo also serves nearby towns such as Aramil, Sysert, and Polevskoy. In general, the airport is responsible for serving approximately 4,290,000 people yearly. The airport is a hub for Ural Airlines, RusLine and Aviacon Zitotrans. Due to its location in the center of Russia, Yekaterinburg's airport is included in the "Priority Airports" list of Russia's Federal Air Transport Agency (Rosaviatsia).

Serov is a mining and commercial town in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the eastern foothills of the Ural Mountains, on the left bank of the Kakva River, about 350 kilometers (220 mi) north of Yekaterinburg. Population: 99,373 (2010 Census) ; 99,804 (2002 Census) ; 104,158 (1989 Soviet census) .

Pervouralsk is a city in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the Chusovaya River 39 kilometers (24 mi) west of Yekaterinburg, the administrative center of the oblast. Population: 124,528 (2010 Census) ; 132,277 (2002 Census) ; 142,193 (1989 Soviet census) ; 122,000 (1974); 90,000 (1959); 44,000 (1939).

Sredneuralsk is a town under the administrative jurisdiction of the Town of Verkhnyaya Pyshma in Sverdlovsk Oblast, Russia, located on the shore of Iset Lake, at the head of the Iset River, 25 kilometers (16 mi) north of Yekaterinburg. Population: 20,449 (2010 Census) ; 19,555 ; 18,786 (1989 Soviet census) .

Anton Alekseyevich Bakov is a Russian businessman, monarchist politician, traveler, writer and human rights activist. He is the chairman of the Russian Monarchist Party, was a member of the 4th convocation of the State Duma of Russia from 2003 to 2007 and was a candidate at 2018 Russian presidential election. Due to being known for a long series of unusual political projects such as Ural franc, the writer Alexei Ivanov coined him a "political Leonardo".

Alexander Sergeevich Misharin is the former governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast, a region in Russia. He was appointed in 2009 after resignation of the previous governor, Eduard Rossel and resigned on May 14, 2012. Prior to his governorship, he made a career in the railway industry, rising to Russia's Deputy Railway Minister. He was appointed first vice-president of Russian Railways and head of Skorostniye Magistrali, the Russian high-speed rail developer and operator on November 28, 2012.

Isetsky District is an administrative district (raion), one of the twenty-two in Tyumen Oblast, Russia. As a municipal division, it is incorporated as Isetsky Municipal District . It is located in the west of the oblast. The area of the district is 2,751 square kilometers (1,062 sq mi). Its administrative center is the rural locality of Isetskoye. Population: 26,061 ; 26,565 (2002 Census) ; 25,862 (1989 Soviet census) . The population of Isetskoye accounts for 28.7% of the district's total population.

Gostiny Dvor – is a shopping (merchant) center in the historical center of Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

The Men's College building is a mansion in the historical center of Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Zyryanov manor house is located in the historical center of Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Church of the Intercession of the Most Holy Mother of God - is an Orthodox church in Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Ural Aluminum Smelter Proletarian's Group of Houses is a complex of residential buildings in Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

The Rail Bridge over the Iset River - is an experimental bridge over the Iset River is a unique engineering structure made according to the advanced technology of the late 1930s in Kamensk-Uralsky, Sverdlovsk oblast.

Boris Yeltsin Street is a street in Yekaterinburg, Russia.
The coat of arms of Yekaterinburg is the official municipal coat of arms of Yekaterinburg, Russia. The current symbol was adopted on 23 May 2008 and consists of a French shield divided horizontally into two fields, with a white mine shaft and a white furnace within the top field, which is green, and a blue wavy bend within the bottom field, which is gold. A gold bear and gold sable are located to the left and right of the shield, respectively. A gold crown with a gold laurel wreath is located above the shield and a gold ribbon is located below the shield. A grey druse is located at the bottom center of the shield.

Yevgeny Vladmirovich Kuyvashev is a Russian politician serving as Governor of Sverdlovsk Oblast since 29 May 2012. He served as the acting governor from 14 May 2012 to 29 May 2012, and again from 17 April 2017 to 18 September 2017.

Alexander Leonidovich Burkov is a Russian politician who served as governor of Omsk Oblast from 2017 to 2023. He is a member of the Central Council of A Just Russia — For Truth party.
The 2022 Sverdlovsk Oblast gubernatorial election took place on 11 September 2022, on common election day. Governor Yevgeny Kuyvashev was re-elected for a third term.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Law #30-OZ
- 1 2 3 Haywood, A. J. (2010). Siberia: A Cultural History , Oxford University Press, p. 32
- ↑ Charter of Yekaterinburg, Article 24.1
- ↑ Official website of Yekaterinburg. Alexander Edmundovich Yakob, Head of Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg Archived 12 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine (in Russian)
- ↑ "Проект о внесении изменений в Генеральный план развития городского округа – муниципального образования «город Екатеринбург» на период до 2025 года" (in Russian). p. 168. [ permanent dead link ]
- 1 2 Federal State Statistics Service (21 May 2004). Численность населения России, субъектов Российской Федерации в составе федеральных округов, районов, городских поселений, сельских населённых пунктов – районных центров и сельских населённых пунктов с населением 3 тысячи и более человек [ Population of Russia, Its Federal Districts, Federal Subjects, Districts, Urban Localities, Rural Localities—Administrative Centers, and Rural Localities with Population of Over 3,000 ] (XLS) . Всероссийская перепись населения 2002 года [All-Russia Population Census of 2002] (in Russian).
- ↑ "Federal State Statistic Service" . Government of Russia. 1 January 2024 . Retrieved 6 June 2024 .
- 1 2 Государственный комитет Российской Федерации по статистике. Комитет Российской Федерации по стандартизации, метрологии и сертификации. №ОК 019-95 1 января 1997 г. « Общероссийский классификатор объектов административно-территориального деления. Код 65 401 », в ред. изменения №278/2015 от 1 января 2016 г.. (State Statistics Committee of the Russian Federation. Committee of the Russian Federation on Standardization, Metrology, and Certification. # OK 019-95 January 1, 1997 Russian Classification of Objects of Administrative Division (OKATO). Code 65 401 , as amended by the Amendment # 278/2015 of January 1, 2016. ).
- 1 2 3 Law #85-OZ
- ↑ "Об исчислении времени" . Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации (in Russian). 3 June 2011 . Retrieved 19 January 2019 .
- 1 2 "Срок регистрации домена закончился" . www.ekaterinburg.com . Archived from the original on 21 January 2013 . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ Upton, Clive ; Kretzschmar, William A. Jr. (2017). The Routledge Dictionary of Pronunciation for Current English (2nd ed.). Routledge. p. 1552. ISBN 978-1-138-12566-7 .
- ↑ "RUSSIA: Ural'skij Federal'nyj Okrug: Ural Federal District" . City Population.de . 4 August 2020 . Retrieved 2 October 2020 .
- ↑ "Рейтинг столичных городов России от Фонда "Институт экономики города" " . Urbaneconomics.ru .
- ↑ Kolossov, Vladimir; Eckert, Denis (1 January 2007). "Russian regional capitals as new international actors: the case of Yekaterinburg and Rostov" . Belgeo (1): 115–132. doi : 10.4000/belgeo.11686 .
- ↑ "Central Asian Chapter by Eurasian Respiratory and Allergy Consortium" . Era-cac.org . Archived from the original on 12 June 2018 . Retrieved 1 June 2018 .
- ↑ "Yekaterinburg - Entertainment - Russia.com" . Russia.com .
- ↑ "Конструктивизм. Жемчужина архитектуры Екатеринбурга" . www.e1.ru (in Russian). 16 January 2018 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Как Екатеринбург за 10 лет стал столицей конструктивизма" . Strelka Mag (in Russian). Archived from the original on 5 March 2021 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ Урал, Наш (19 May 2016). "Советская утопия: эпоха конструктивизма в Екатеринбурге" . Наш Урал (in Russian) . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Все кругом храпят, а Екатеринбург — пробужденный Когда уральский город объявил себя российской столицей стрит-арта, многие смеялись. А потом он стал ею" . Meduza (in Russian) . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Как Екатеринбург становится столицей стрит-арта" . Российская газета (in Russian). 16 April 2019 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Екатеринбург – столица стрит-арта. Часть первая" . www.uralweb.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 3 March 2021 . Retrieved 21 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Памятникик археологии" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "1.2. Палкинские каменные палатки. Проект 1. | "Образование Урала" " . uraledu.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 5 April 2012 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ ГАМАЮНСКАЯ КУЛЬТУРА – Уральская Историческая Энциклопедия . ural.ru (in Russian). Archived from the original on 22 July 2014 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Екатеринбург" . Геральдика Свердловской области . Официальный сайт областной думы законодательного собрания. Archived from the original on 8 March 2013 . Retrieved 6 December 2009 .
- ↑ Юрий, Коновалов (26 March 2004). "Первые русские поселения на реке Уктус" . www.okorneva.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 7 June 2024 .
- 1 2 Кулешов, Николай (2001). "Горных заводов щит" . Домострой (4).
- ↑ Архипова, Нина (2001). "Тайны "превысочайшего Камня" ". Родина (11).
- ↑ Корепанов Н. С. Уктус — исток Екатеринбурга — Екатеринбург: Грачёв и партнёры, 2012. — 40 экз. — ISBN 978-5-91256-129-0
- 1 2 3 4 5 Юхт, Александр (1985). Государственная деятельность В. Н. Татищева в 20-е — начале 30-х годов XVIII века (in Russian). Moscow: Наука .
- ↑ "Библиотека истории: Ремесло историка в России – Бердинских В.А." history-library.com . Archived from the original on 1 April 2019 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Завод-крепость – История основания Екатеринбурга – Информационный портал Екатеринбурга . ekburg.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "Основание Екатеринбурга" . Histrf.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ Металлургические заводы Урала XVII—XX вв.: Энциклопедия / глав. ред. В. В. Алексеев. — Екатеринбург : Издательство «Академкнига», 2001.
- 1 2 ipravo.info. "О ликвидации Баженовского и Сысертского районов Уральской области и о расширении городской черты и пригородной зоны города Свердловска – Российский Правовой Портал" (in Russian). ipravo.info. Archived from the original on 19 June 2018 . Retrieved 19 June 2018 .
- 1 2 "History of the Verkh-Isetsky district" . Administration of Verkh-Isetsky district . Archived from the original on 16 December 2021 . Retrieved 7 June 2024 .
- ↑ "Золотой век Екатеринбурга" . Уралнаш. Интересно о Екатеринбурге . 9 October 2019. Archived from the original on 14 August 2021 . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ "50 интересных фактов об Екатеринбурге — Общенет" . obshe.net . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ Massie, Robert K. (22 February 2012). The Romanovs: The Final Chapter . Random House Publishing Group. ISBN 9780307873866 .
- ↑ "FSU News" . fsu.edu . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 История Екатеринбурга – Информационный портал Екатеринбурга . ekburg.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Временное Областное Правительство Урала – Энциклопедия Екатеринбурга – Энциклопедии & Словари" . enc-dic.com . Archived from the original on 20 May 2018 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Главная: НОВОСТИ . familii.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Справочник по административно-территориальному делению Свердловской области" (PDF) . ГАСО (State Archive of the Sverdlovsk oblast). p. 37. Archived from the original (PDF) on 22 February 2017 . Retrieved 2 February 2013 .
- ↑ Rappaport, Helen (1999). Joseph Stalin: A Biographical Companion . ABC-CLIO. ISBN 978-1-57607-084-0 .
- ↑ Беркович Артём. "Пермь и Екатеринбург: история соперничества" . Муниципальный музей истории Екатеринбурга. Archived from the original on 25 May 2013 . Retrieved 16 December 2009 .
- ↑ In the name of Victory. Sverdlovsk-Yekaterinburg during the Great Patriotic War of 1941–1945 . 2005 – via Ekaterinburg: Institute of History and Archeology of the Ural Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences.
- ↑ "Свердловск – 1983 год" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Интервью – АПИ-Урал" . apiural.ru . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- ↑ "President Yeltsin speaks about Tsar Murder" . BBC News . 17 July 1998 . Retrieved 4 April 2012 .
- ↑ Matthew S. Meselson, et al., "The Sverdlovsk Anthrax Outbreak of 1979", Science 266:5188 (18 November 1994): 1202–1208.
- ↑ Martin McCauley, "Who's who in Russia since 1900", Routledge , 1997: p.133.
- ↑ Ровно 18 лет назад Свердловск снова стал Екатеринбургом . Официальный портал Екатеринбурга (in Russian). Archived from the original on 16 April 2013 . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- ↑ "О возвращении городу Свердловску его исторического названия Екатеринбург, Указ Президиума Верховного Совета РСФСР от 23 сентября 1991 года №1674-1" . docs.cntd.ru . Retrieved 15 May 2018 .
- ↑ (www.dw.com), Deutsche Welle. "First BRIC summit concludes | DW | 16 June 2009" . DW.COM . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 FIFA.com. "2018 FIFA World Cup Russia" . fifa.com . Archived from the original on 12 April 2014 . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Russia moves to year-round winter time" . BBC News . 22 July 2014 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 Грязнов Олег Николаевич; Гуляев Александр Николаевич; Рубан Наталья Валентиновна (2015). "Факторы инженерно-геологических условий города Екатеринбурга" . Izvestiia Uralʹskogo Gorno-Geologicheskoĭ Akademii (журнал) (3) (Известия Уральского государственного горного университета ed.). Екатеринбург: Федеральное государственное бюджетное образовательное учреждение высшего образования "Уральский государственный горный университет": 5–21. ISSN 2307-2091 .
- ↑ Погода и Климат – Климат Екатеринбург [ Weather and Climate – The Climate of Yekaterinburg ] (in Russian). Weather and Climate (Погода и климат) . Retrieved 8 November 2021 .
- ↑ "WMO Climate Normals for Sverdlovsk 1961–1990" . National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration . Retrieved 29 October 2021 .
- ↑ Russian Federal State Statistics Service. Всероссийская перепись населения 2020 года. Том 1 [ 2020 All-Russian Population Census, vol. 1 ] (XLS) (in Russian). Federal State Statistics Service .
- ↑ "Национальный состав населения" (PDF) . Территориальный орган Федеральной службы государственной статистики по Свердловской области и Курганской области . Retrieved 7 June 2023 .
- ↑ "В Екатеринбурге заложили первый камень в основание соборной мечети – Уральская палата недвижимости" . upn.ru . Archived from the original on 10 October 2012 . Retrieved 5 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Четвертый канал" . channel4.ru . Archived from the original on 20 December 2010 . Retrieved 5 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Встреча Святейшего Патриарха Кирилла с общественностью Уральского федерального округа / Видеоматериалы / Патриархия.ru" . Патриархия.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Устав Свердловской области (с изменениями на 7 декабря 2017 года), Устав Свердловской области от 23 декабря 2010 года №105-ОЗ, Закон Свердловской области от 23 декабря 2010 года №105-ОЗ" . docs.cntd.ru . Retrieved 2 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "Закон Свердловской области Губернатора Свердловской области № 141-ОЗ" . www.pravo.gov66.ru . Retrieved 12 March 2022 .
- 1 2 "Закон Свердловской области от 18.02.2021 № 9-ОЗ ∙ Официальное опубликование правовых актов ∙ Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации" . publication.pravo.gov.ru . Archived from the original on 12 March 2022 . Retrieved 12 March 2022 .
- 1 2 The population of the Russian Federation for municipalities as of 1 January 2019 Archived 16 October 2019 at the Wayback Machine (2 May 2019)
- ↑ "К 2023 году население Академического района вырастет до 120 тысяч человек" . Новый День (in Russian). 27 March 2019 . Retrieved 12 March 2022 .
- 1 2 "Chapter IV. Bodies and officials of local self-government of the municipality "city of Yekaterinburg" " . екатеринбург.рф . 25 July 2017. Archived from the original on 26 June 2016 . Retrieved 19 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Официальный интернет-портал правовой информации" . publication.pravo.gov.ru .
- 1 2 "Вы точно человек?" . КиберЛенинка . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "О внесении изменений в Устав муниципального образования "город Екатеринбург", Решение Екатеринбургской городской Думы Свердловской области от 12 октября 2010 года №62/29" . docs.cntd.ru .
- ↑ Article 42 of the Charter of Sverdlovsk Oblast
- ↑ "О ПРЕОБРАЗОВАНИИ И РЕОРГАНИЗАЦИИ АДМИНИСТРАЦИИ СВЕРДЛОВСКОЙ ОБЛАСТИ (с изменениями на: 06.02.1997), Постановление Правительства Свердловской области от 27 сентября 1995 года №13-П" . docs.cntd.ru .
- ↑ "Сведения о проводящихся выборах и референдумах" . sverdlovsk.vybory.izbirkom.ru . Archived from the original on 22 September 2013 . Retrieved 21 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Voting results for the Federal Electoral District – Election of Deputies of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation of the Seventh Convocation – September 18, 2016" . CEC. Archived from the original on 28 December 2016 . Retrieved 21 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Российские города отстают в развитии" . НИУ ВШЭ . 28 August 2014. Archived from the original on 5 February 2017 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ "Urban world: Mapping the economic power of cities" . McKinsey Global Institute . March 2011. Archived from the original on 2 April 2024 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ "Рейтинг столичных городов России от Фонда "Институт экономики города" | Институт экономики города" . urbaneconomics.ru . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Economics of Russian cities and urban agglomeration , Institute for Urban Economics
- 1 2 Алексей Белоусов, Орнат Валентина. (13 October 2015). "Екатеринбург – глобальный город" . Мегаполис. Archived from the original on 27 August 2016 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ Зубаревич Н.В. (2013). "Крупные города России: лидеры и аутсайдеры" (PDF) . Demoskop Weekly (журнал) (551–552) (Демоскоп Weekly ed.). М.: НИУ ВШЭ: 1–17. ISSN 1726-2887 .
- ↑ "Екатеринбург вошел в топ-10 городов с самым высоким уровнем жизни" . JustMedia . 17 December 2014 . Retrieved 14 May 2018 .
- 1 2 3 "Results of social and economic development of the municipal formation "city of Yekaterinburg" in 2015" . 2016. p. 202 – via Ekaterinburg: Department of Economics of the Administration of the City of Yekaterinburg.
- ↑ "Итоги социально-экономического развития Екатеринбурга" . Archived from the original on 2 December 2020 . Retrieved 19 October 2022 .
- ↑ Дарья Воронина. (19 June 2013). "Главными проблемами Екатеринбурга назвали медицину, ЖКХ и дороги" . Российская газета . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ Юлия Позднякова. (22 April 2016). "Расходы бюджета Екатеринбурга за 2015 год составили почти 33 млрд рублей" . Коммерсантъ . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- ↑ Полина Путякова. (30 August 2016). "Меряемся бюджетами: Откуда города берут деньги и на что тратят" . zvzda.ru. Archived from the original on 2 September 2016 . Retrieved 7 July 2016 .
- 1 2 3 Kachanova E.A. Strategic Priorities for the formation of finance for municipalities in the context of reforming the budgetary system Archived 15 December 2017 at the Wayback Machine , – Moscow: Russian Academy of National Economy and State Service under the President of the Russian Federation, 2013. – 354 p.
- ↑ Vyacheslav, Kostyuk (12 December 2014). "His alien" . The Ural Worker . Archived from the original on 10 April 2018 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Крупнейшие банки России по капиталу" . Журнал "Коммерсантъ Деньги" . 25 July 2016. p. 60 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Крупнейшие производители ПО" .
- ↑ "О распределении обязанностей по контролю и надзору за соблюдением законодательства Российской Федерации организациями, осуществляющими профессиональную деятельность на рынке ценных бумаг, деятельность центрального депозитария, деятельность по проведению организованных торгов, клиринговую деятельность и деятельность центрального контрагента, репозитарную деятельность, а также деятельность саморегулируемых организаций в сфере финансового рынка, объединяющих профессиональных участников рынка ценных бумаг, и об отмене отдельных распорядительных актов Банка России, Приказ Банка России от 07 августа 2017 года №ОД-2228" . docs.cntd.ru .
- ↑ "Падающие пиксели и огромный шар: как может выглядеть "Екатеринбург-Сити" " . РБК Недвижимость . 13 September 2016 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 76
- ↑ "ТОП-100 крупнейших предприятий Свердловской области Екатеринбург" . Деловой квартал. 11 October 2011 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ "ИТОГИ социально-экономического развития муниципального образования «город Екатеринбург» в 2019 году" . Archived from the original on 29 November 2020 . Retrieved 19 October 2022 .
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , p. 127–128
- 1 2 Development results, 2016 , p. 129
- ↑ "Леруа Мерлен" . Archived from the original on 18 October 2021 . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ↑ "Castorama – строительный гипермаркет: купить товары для дома, дачи и ремонта" . Castorama.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Домострой" . Archived from the original on 30 July 2019 . Retrieved 27 April 2020 .
- ↑ "Максидом - интернет-магазин товаров для дома" . www.maxidom.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ "ОБИ строительный гипермаркет: товары для дачи, сада, дома и ремонта: каталог ОБИ" . Obi.ru . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Строительный Двор – интернет-магазин стройматериалов, купить с доставкой строительные материалы в магазинах сети" . Sdvor.com . Archived from the original on 13 May 2020 . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 130
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 131–132
- ↑ Development results, 2016 , pg 133–135
- ↑ "Топ-20 самых больших торговых центров РФ" . marketmedia.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 11 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Сима-Ленд" . 20 October 2016.
- ↑ Вячеславовна, Логунцова Ирина (2015). "Специфика и перспективы Российской индустрии туризма на современном этапе" . Государственное управление. Электронный вестник (52): 259–278.
- ↑ Геннадьевич, Шеломенцев Андрей; Сергеевна, Головина Анна (2011). "Индустрия туризма региона в контексте принципов саморегулирования региональных социально-экономических систем" . Экономика региона (1): 166–170. ISSN 2072-6414 .
- ↑ Екатеринбург поднялся на третье место в топе российских городов по популярности среди иностранных туристов . URBC.RU – новости экономики (in Russian) . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Число посетивших Екатеринбург туристов выросло в 2015 году на 10%" . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Туристический мастер-класс" . expert.ru . Archived from the original on 13 September 2016 . Retrieved 20 May 2018 .
- ↑ Маренков Г.В. (2012). "Транспортная инфраструктура Свердловской области – связующее звено между Европой и Азией" (PDF) . Инфраструктура России (Том 1 ed.). М.: Центр стратегического партнёрства. pp. 254–260. Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2018 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ Мальцева Ю.; Волкова М.В. (2015). "Изучение возможности постройки современного экологического жилья в Свердловской области" (PDF) (сборник трудов IX заочной международной научно-практической конференции (Екатеринбург, 30–31 мая 2015 г.)) (Система управления экологической безопасностью ed.). Екатеринбург: УрФУ. pp. 138–141.
- ↑ Ведомости (10 March 2015). "Автопарк России увеличился в 2014 году на 1 млн легковых машин" . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Вы точно человек?" . КиберЛенинка . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- 1 2 "ИТОГИ социально-экономического развития муниципального образования в 2015 году" . 2016. Archived from the original on 16 August 2021 . Retrieved 7 July 2022 .
- ↑ Цариков А.А.; Обухова Н.А.; Оглы Мирзоев Н.З. (2015). "Эволюция системы заторов на улично-дорожной сети города Екатеринбурга" (PDF) (журнал) (Эксплуатация автомобильного транспорта ed.). Екатеринбург: Общероссийская общественная организация "Российская академия транспорта". pp. 74–86. ISSN 2311-164X . Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2016 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ Reports, Yekaterinburg News. "Sverdlovsk focusing on two road projects" . Archived from the original on 6 October 2017 . Retrieved 14 June 2017 .
- ↑ Крицкий В.П. (2009). "Дорожное хозяйство Екатеринбурга" (PDF) . Дороги России-2009. Информационно-аналитический каталог (Издание второе, подготовлено к IХ Международной выставке-форуму "Дороги России XXI века" и Дню работников дорожного хозяйства 3000 экз ed.). Екатеринбург: Информационно-издательский холдинг "Реал-Медиа". pp. 204–205, 302. ISBN 978-5-98266-061-9 . Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 July 2018 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Google Maps" . Google Maps . Retrieved 1 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Скандальный бывший МУП Мирошника лидер сферы общественного транспорта Екатеринбурга? По данным мэрии, именно трамваи перевезли больше всего горожан за 2015 год" . Ведомости-Урал. 18 March 2016. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ "БГД" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 20 May 2016 . Retrieved 17 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Города Свердловской области" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 10 July 2009 . Retrieved 8 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Основные технико-эксплуатационные характеристики метрополитенов за 2015 год" (PDF) . asmetro.ru. Archived from the original (PDF) on 8 August 2016 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ Дмитрий Ольшванг. (18 March 2016). "Проблемы екатеринбургского метро: убытки, снижение пассажиропотока! Общественник Беззуб: "Если учитывать стоимость строительства станций, то цена билета на метро должна быть 144 рубля"..." Ведомости-Урал. Archived from the original on 15 September 2016 . Retrieved 14 June 2016 .
- ↑ "Шины для трамваев, бензин для поездов. Документы: на что транспортные МУПы Екатеринбурга тратят деньги" . uralpolit.ru . Retrieved 13 March 2014 .
- ↑ "Города Свердловской области" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 30 June 2013 . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Строительство трамвайной линии Екатеринбург – Верхняя Пышма начнут в 2016 году" . Портал 66.ru. 22 July 2015 . Retrieved 22 July 2015 .
- ↑ "Официальный портал Екатеринбурга" . Официальный портал Екатеринбурга . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- 1 2 "Города Свердловской области" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 10 July 2009 . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ Автобусный парк Екатеринбурга утепляют к зиме . УралИнформБюро (in Russian) . Retrieved 18 October 2017 .
- ↑ "Более 5,4 миллионов пассажиров обслужил аэропорт Кольцово в 2017 году (АвиаПорт)" . АвиаПорт.Ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 1 May 2018 .
- ↑ "БГД" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 15 June 2009 . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- 1 2 According to the city directory Dubl.
- ↑ Уральский научно-исследовательский институт фтизиопульмонологии – филиал ФГБУ "НМИЦ ФПИ" Минздрава России . urniif.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Официальный сайт ГБУ СО "Уральский научно-исследовательский институт дерматовенерологии и иммунопатологии" " . urniidvi.ru . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ Екатеринбургский центр МНТК "Микрохирургия глаза" . eyeclinic.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ Открытие второго центра МРТ-диагностики в городе Екатеринбурге! . ekaterinburg.ldc.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- 1 2 М.м, Рогалёва (2014). "Екатеринбург как современный мегаполис" . Человек в мире культуры (4): 14–17. ISSN 2227-9857 .
- ↑ Report of the head of the Yekaterinburg administration, 2016 Archived 5 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine , p. 14.
- ↑ Report of the head of the Yekaterinburg administration, 2016 Archived 5 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine , p. 13, 15.
- ↑ Лучшие школы России-2015 . РИА Новости (in Russian). 12 October 2015 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Общие сведения об университете – ФГБОУ ВО "Уральский государственный горный университет" " . about.ursmu.ru . Archived from the original on 7 July 2016 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ The second business rating of higher education Archived 29 September 2018 at the Wayback Machine – Federal Portal Russian Education, 22 May 2018
- ↑ Formation of the state elite 2008 Archived 5 February 2017 at the Wayback Machine – Federal Portal Russian Education, 22 May 2018
- ↑ "Российская академия наук намерена готовить кадры самостоятельно | Новости образования | Обучение Екатеринбург" . uchim66.ru . Archived from the original on 4 March 2016 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "УрФУ перестраивается в школы" . Коммерсантъ (Екатеринбург) . 22 April 2016 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "По количеству бюджетных мест мы уже обошли МГУ" . 7 April 2021.
- ↑ "Ural Federal University – UrFU" .
- ↑ Case study: Ural Federal University as a basic university of industry in the region Archived 1 April 2019 at the Wayback Machine . – Ekaterinburg: Ural Federal University, 2016. – p. 2, 9–10.
- ↑ "Гильдия издателей периодической печати" . 18 September 2011. Archived from the original on 18 September 2011 . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Welcome media-atlas.ru - BlueHost.com" . www.media-atlas.ru . Archived from the original on 15 June 2018 . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ Официальный сайт "Вести Урал" – Официальный сайт "Вести Урал" . Официальный сайт "Вести Урал" (in Russian). Archived from the original on 16 July 2012 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ Вальханская, Наталья (24 March 2018). Взрыв и обрушение: снос телебашни в Екатеринбурге на видео очевидцев . Телеканал "Звезда" (in Russian) . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Тёмная башня" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Uralnets" . uralnets.ru . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ Fletcher, Martin. "Yekaterinburg signs cooperative agreement with Vimpelcom under Beeline brand" Archived 22 July 2013 at archive.today , Yekateringburg News , 19 July 2013. (Retrieved 22 July 2013).
- ↑ "WiseCms – troubles..." culture.ekburg.ru . Archived from the original on 11 July 2012 . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ "WiseCms – troubles..." Culture.ekburg.ru . Archived from the original on 19 January 2011 . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Триумф России на Всемирной выставке в Париже 1900 года – Новости РуАН" . новости-россии.ru-an.info . Retrieved 20 February 2022 .
- ↑ Lykova TR Cultural and historical centres of the Sverdlovsk region Archived 11 October 2016 at the Wayback Machine // method. instructions for studying the course "Cultural and Historical Centres of the Urals" for full-time or part-time students, direction 100400 – Tourism. – Ekaterinburg: UGLTU, 2014. – P. 15-16 .
- ↑ "Главная страница - АПИ-Урал" . www.apiural.ru . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Архитектура и планировка социалистического Свердловска. Часть 2" . 1723.ru . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ Вейн, Инна (10 November 2020). "Уральские актеры и режиссеры привезли домой сразу четыре "Золотые маски" " . Ekb.dk.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ Fletcher, Martin. "Yekaterinburg to showcase city’s cultural achievements during Year of Culture" Archived 13 February 2014 at archive.today . Yekaterinburg News . 13 February 2014. (Retrieved 13 Feb 2014).
- ↑ Pozdnyakova, Julia (27 May 2016). "Sverdlovsk Oblast was in the picture" . Kommersant . Retrieved 24 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Интервью - АПИ-Урал" . www.apiural.ru . Retrieved 26 February 2022 .
- ↑ "Премией "Шаривари" отметили лучших деятелей циркового искусства – В МИРЕ ЦИРКА И ЭСТРАДЫ" . ruscircus.ru . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Ельцин Центр признали «лучшим европейским музеем 2017 года»" . The Village (in Russian) . Retrieved 15 August 2021 .
- ↑ Самые популярные достопримечательности Екатеринбурга соединит красная линия на тротуаре . Interfax-Russia.ru (in Russian). 17 June 2011 . Retrieved 25 May 2018 .
- 1 2 Yekaterinburg Encyclopedia (PDF) . Yekaterinburg: "Akademkniga". 2002. p. 30. ISBN 5-93472-068-6 – via PDF.
- ↑ Yekaterinburg Encyclopedia (PDF) . Yekaterinburg: "Akademkniga". 2002. pp. 30–31. ISBN 5-93472-068-6 – via PDF.
- ↑ Yekaterinburg Encyclopedia (PDF) . Yekaterinburg: "Akademkniga". 2002. p. 31. ISBN 5-93472-068-6 – via PDF.
- 1 2 3 Shvets, A. V. (2016). "Domestic architecture of the late XX – early XXI century" (PDF) . New Ideas of the New Century: Scientific. Compilation . 2 . Khabarovsk: Pacific State University: 355–362. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2016 . Retrieved 8 June 2018 – via PDF.
- ↑ GmbH, Emporis. "Yekaterinburg | Buildings | EMPORIS" . Emporis . Archived from the original on 8 April 2015 . Retrieved 8 June 2018 . {{ cite web }} : CS1 maint: unfit URL ( link )
- ↑ "Официальный портал Екатеринбурга" . Официальный портал Екатеринбурга . Archived from the original on 8 August 2010 . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- 1 2 "The announcement ceremony of the host cities of the 2018 World Cup united the whole of Russia" . ru.fifa.com . Archived from the original on 3 September 2014 . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ "База данных показателей муниципальных образований" . gks.ru . Archived from the original on 14 August 2009 . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ sport, Guardian (4 October 2017). "Outer space: the Russia World Cup stadium with a novel seating extension" . the Guardian . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Construction: Tsentralnyj Stadion Yekaterinburg – StadiumDB.com" . stadiumdb.com . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ FIFA.com. "2018 FIFA World Cup Russia - News - FIFA Fan Fest venues announced for 2018 FIFA World Cup Russia" . fifa.com . Retrieved 23 May 2018 .
- ↑ Azmukhanov, Alexander (3 May 2018). "The three most expensive projects of the region for the World Cup" . Oblastnaya Gazeta . Retrieved 22 May 2018 .
- ↑ "Official website of the U.S. Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Archived from the original on 8 April 2012 . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Official website of the British Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Archived from the original on 3 January 2012 . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Official website of the German Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Official website of the French Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Archived from the original on 29 April 2012 . Retrieved 19 April 2012 .
- ↑ "Chinese Consulate General in Yekaterinburg" . Retrieved 7 September 2013 .
- ↑ "First summit for emerging giants" . BBC News . 16 June 2009 . Retrieved 16 June 2009 .
- ↑ Hamilton, Louis (18 June 2013). "Yekaterinburg presents city's bid for 2020 World Expo" . Yekaterinburg News. Archived from the original on 27 November 2013 . Retrieved 20 June 2013 .
- ↑ "Глобальный саммит по производству и индустриализации (GMIS – 2019)" . Росконгресс . Retrieved 12 December 2021 .
- ↑ КИРЯГИН, Кирилл (22 July 2015). "ИННОПРОМ – в пятёрке крупнейших промышленных выставок мира" . ural.aif.ru (in Russian) . Retrieved 12 December 2021 .
- ↑ "Побратимы и тезки Екатеринбурга" . ekb-room.ru (in Russian). The Ekb Room. 20 October 2014. Archived from the original on 18 November 2018 . Retrieved 22 December 2020 .
- ↑ "Museum Vladimir Mulyavin in Belarusian State Philharmonic" . Retrieved 22 April 2022 .
- Екатеринбургская городская Дума. Решение №8/1 от 30 июня 2005 г. «О принятии Устава муниципального образования "Город Екатеринбург"», в ред. Решения №1/27 от 27 января 2015 г. «О внесении изменений в Устав муниципального образования "Город Екатеринбург"». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Вестник Екатеринбургской городской Думы", №95, 15 июля 2005 г. (Yekaterinburg City Duma. Decision # 8/1 of June 30, 2005 On the Adoption of the Charter of the Municipal Formation of the "City of Yekaterinburg" , as amended by the Decision # 1/27 of January 27, 2015 On Amending the Charter of the Municipal Formation of the "City of Yekaterinburg" . Effective as of the day of the official publication.).
- Областная Дума Законодательного Собрания Свердловской области. Областной закон №30-ОЗ от 20 мая 1997 г. «Об административно-территориальном устройстве Свердловской области», в ред. Закона №32-ОЗ от 25 апреля 2012 г. «О внесении изменений в Областной закон "Об административно-территориальном устройстве Свердловской области"». Вступил в силу со дня официального опубликования за исключением отдельных положений, вступающих в силу в иные сроки. Опубликован: "Областная газета", №81, 3 июня 1997 г. (Oblast Duma of the Legislative Assembly of Sverdlovsk Oblast. Oblast Law # 30-OZ of May 20, 1997 On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Sverdlovsk Oblast , as amended by the Law # 32-OZ of April 25, 2012 On Amending the Oblast Law "On the Administrative-Territorial Structure of Sverdlovsk Oblast" . Effective as of the day of the official publication with the exception of several clauses which take effect on a different date.).
- Областная Дума Законодательного Собрания Свердловской области. Закон №85-ОЗ от 12 июля 2007 г. «О границах муниципальных образований, расположенных на территории Свердловской области», в ред. Закона №107-ОЗ от 29 октября 2013 г. «Об упразднении отдельных населённых пунктов, расположенных на территории города Ивделя, и о внесении изменений в Приложение 39 к Закону Свердловской области "О границах муниципальных образований, расположенных на территории Свердловской области"». Вступил в силу через 10 дней после официального опубликования. Опубликован: "Областная газета", №232–249, 17 июля 2007 г. (Oblast Duma of the Legislative Assembly of Sverdlovsk Oblast. Law # 85-OZ of July 12, 2007 On the Borders of the Municipal Formations on the Territory of Sverdlovsk Oblast , as amended by the Law # 107-OZ of October 29, 2013 On Abolishing Several Inhabited Localities on the Territory of the Town of Ivdul and on Amending the Law of Sverdlovsk Oblast "On the Borders of the Municipal Formations on the Territory of Sverdlovsk Oblast" . Effective as of the day which is 10 days after the official publication.).
- Official website of Yekaterinburg (in Russian)
| : • | |
| Administrative districts | |
| Cities and towns | |

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Developed by Teaching, Learning, and Scholarship, School of Medicine & Health Sciences, University of North Dakota (2020) Build a Rubric for Scoring Papers and Projects Rubrics provide a standardized format for feedback and assessment of projects and papers that are more difficult to assess than traditional measures like multiple-choice tests.
A rubric is a scoring tool that identifies the different criteria relevant to an assignment, assessment, or learning outcome and states the possible levels of achievement in a specific, clear, and objective way. Use rubrics to assess project-based student work including essays, group projects, creative endeavors, and oral presentations.
15 Helpful Scoring Rubric Examples for All Grades and Subjects. In the end, they actually make grading easier. By Jill Staake, B.S., Secondary ELA Education. Jun 16, 2023. When it comes to student assessment and evaluation, there are a lot of methods to consider. In some cases, testing is the best way to assess a student's knowledge, and the ...
Grading Rubrics. Rubrics represent criteria used to grade a variety of assignments and other classroom activities in a way that provides transparency to learners. Specifically, some of the benefits of grading rubrics to learners include: clearer assignments expectations. more objective grading that is aligned with learning objectives.
Rubrics are favored in healthcare education for several reasons: Transparency and Clarity: They clearly communicate the criteria and expectations for assignments or assessments to students. This transparency promotes fairness and helps students understand what is expected of them. Consistency: They provide uniformity in grades when several ...
Example 1 - Research Paper Rubric. Characteristics to note in the rubric: Language is descriptive, not evaluative. Labels for degrees of success are descriptive ("Expert" "Proficient", etc.); by avoiding the use of letters representing grades or numbers representing points, there is no implied contract that qualities of the paper will ...
Health History and Physical Assessment. Comprehensive Health Assessment. Rubric for writing up a Comprehensive Health Assessment. Rubric Code: Y928CW. By Reviswjr. Ready to use. Public Rubric. Subject: Nursing. Type: Assignment.
Health Assignment Rubric 2011- 2012 Criteria 3 2 1 Concepts Question #1 Student accurately summarizes all concepts with details Student identifies only part of the concept (s) or indentifies with some errors Fails to identify any concepts Data/Statistics Question #2 Student lists all data/stats ...
The steps to create a rubric are listed in sequential order, however they can be performed in any order as long as the rubric contains the following: We have divided the task of creating a grading rubric into 6 steps: Identify the dimensions/tasks comprising the performance. Assign a point value to each gradation, and a total point value for ...
Comprehensive Health Assessment. Includes all pertinent objective data. Student provides 3 to to 7 items of biographical data. Student includes all nine elements of biographical data. Provides a focused clearly written statement regarding the patient reason for seeking care. Places reason in quotations.
Set the goals for the assignment (specific) guide students and keep them on task (student focused) link the assignment and learning outcomes for the unit, module or subject (criterion-focused; provide a shorthand approach to providing effective and timely feedback; Components of a Rubric: Analytic and Specific.
This was an assignment created for grade 5 Health and Phys Ed. This download outlines the entire task and the rubric for assessment, all based on Ontario Curriculum guidelines. It specifically fits into the Fitness unit. The assignment is for students to create an aerobics routine in groups. 4 th - 6 th.
This study examined the use of rubrics in scoring a performance-based assessment. After receiving a health lesson of ways to have a healthy brain, fifth grade students were given an assignment to illustrate and write a booklet that demonstrated their knowledge of the topic. From students' responses the researchers constructed four sample
Physical Education 10Unit#2 Lesson# 20STD Health AssignmentLesson PlanBy the end of the lesson, students will know more about STI's, discuss ways to prevent their spread, become
Descriptions of key items are clear and concise. Summarizes the evaluation at the level of detail needed for an executive summary. Introduction, key items: Program rationale and magnitude of problem. Program description. Public health relevance. Summary of evaluation design and measures. Confusing or absent rationale or problem statement.
LMS rubrics can be attached to any assignment, including LMS Quizzes and Discussions, and used for marking students' submissions via the SpeedGrader. LMS rubrics can have either a point value or a point range attached to each criterion. You can also remove the points to create a qualitative rubric or choose to write free-form comments on each ...
Assessment Rubrics. A rubric is commonly defined as a tool that articulates the expectations for an assignment by listing criteria, and for each criteria, describing levels of quality (Andrade, 2000; Arter & Chappuis, 2007; Stiggins, 2001). Criteria are used in determining the level at which student work meets expectations.
Health Promotion Assignment: Description, Grading Rubric, and Template Assignment Purpose Use the nursing process to develop a health promotion plan of care for a community client in one of the following age groups: infant (1 month to one year); toddler (1-3 years); preschooler (3-6 years); school age (6-12 years); older adult (>60 years).
An assessment rubric is provided that can be modified to a variety of different project types, not just papers, as described here. This One Health assignment helps students learn the importance of the microbiology concepts addressed in the course and also their real-world implications.
APU School of Nursing GNRS 578 - Health Assessment. The Complete Health History Assignment. The purpose of the health history is to collect subjective data, which is what the person says about himself or herself.. DIRECTIONS You will practice your interviewing skills by taking a health history on an adult family member or friend who is the "patient."
Ontrak Health Demonstrates Significant Improvement in Members' Quality of Life from ReQoL Mental Health Assessment. Ontrak, Inc. (NASDAQ: OTRK), a leading AI-powered and technology-enabled ...
Yekaterinburg [lower-alpha 1] is a city and the administrative centre of Sverdlovsk Oblast and the Ural Federal District, Russia.The city is located on the Iset River between the Volga-Ural region and Siberia, with a population of roughly 1.5 million residents, [14] up to 2.2 million residents in the urban agglomeration. Yekaterinburg is the fourth-largest city in Russia, the largest city in ...
1)国家政府机构和地方市政机构的正式文件,包括法律、其他法律文本、司法决定、其他具有立法、行政和司法性质的材料、国际组织的正式文件及其正式译文;. 2)国家象征和标志 (旗帜、标志、命令、钞票等)以及市政组织的符号和标志;. 3)没有具体作者的民间 ...
Prospective students considering higher education at the Ural State Medical University shall fulfill certain criteria in order to secure their admission, these are: Are 17 years or older before 31st December of the admission year. Must have passed 10+2 from a recognized board or university with at least 50% marks in Physics, Chemistry, and Biology.