- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer

Additional menu
Khan Academy Blog
Free Math Worksheets — Over 100k free practice problems on Khan Academy
Looking for free math worksheets.
You’ve found something even better!
That’s because Khan Academy has over 100,000 free practice questions. And they’re even better than traditional math worksheets – more instantaneous, more interactive, and more fun!
Just choose your grade level or topic to get access to 100% free practice questions:
Kindergarten, basic geometry, pre-algebra, algebra basics, high school geometry.
- Trigonometry
Statistics and probability
High school statistics, ap®︎/college statistics, precalculus, differential calculus, integral calculus, ap®︎/college calculus ab, ap®︎/college calculus bc, multivariable calculus, differential equations, linear algebra.
- Addition and subtraction
- Place value (tens and hundreds)
- Addition and subtraction within 20
- Addition and subtraction within 100
- Addition and subtraction within 1000
- Measurement and data
- Counting and place value
- Measurement and geometry
- Place value
- Measurement, data, and geometry
- Add and subtract within 20
- Add and subtract within 100
- Add and subtract within 1,000
- Money and time
- Measurement
- Intro to multiplication
- 1-digit multiplication
- Addition, subtraction, and estimation
- Intro to division
- Understand fractions
- Equivalent fractions and comparing fractions
- More with multiplication and division
- Arithmetic patterns and problem solving
- Quadrilaterals
- Represent and interpret data
- Multiply by 1-digit numbers
- Multiply by 2-digit numbers
- Factors, multiples and patterns
- Add and subtract fractions
- Multiply fractions
- Understand decimals
- Plane figures
- Measuring angles
- Area and perimeter
- Units of measurement
- Decimal place value
- Add decimals
- Subtract decimals
- Multi-digit multiplication and division
- Divide fractions
- Multiply decimals
- Divide decimals
- Powers of ten
- Coordinate plane
- Algebraic thinking
- Converting units of measure
- Properties of shapes
- Ratios, rates, & percentages
- Arithmetic operations
- Negative numbers
- Properties of numbers
- Variables & expressions
- Equations & inequalities introduction
- Data and statistics
- Negative numbers: addition and subtraction
- Negative numbers: multiplication and division
- Fractions, decimals, & percentages
- Rates & proportional relationships
- Expressions, equations, & inequalities
- Numbers and operations
- Solving equations with one unknown
- Linear equations and functions
- Systems of equations
- Geometric transformations
- Data and modeling
- Volume and surface area
- Pythagorean theorem
- Transformations, congruence, and similarity
- Arithmetic properties
- Factors and multiples
- Reading and interpreting data
- Negative numbers and coordinate plane
- Ratios, rates, proportions
- Equations, expressions, and inequalities
- Exponents, radicals, and scientific notation
- Foundations
- Algebraic expressions
- Linear equations and inequalities
- Graphing lines and slope
- Expressions with exponents
- Quadratics and polynomials
- Equations and geometry
- Algebra foundations
- Solving equations & inequalities
- Working with units
- Linear equations & graphs
- Forms of linear equations
- Inequalities (systems & graphs)
- Absolute value & piecewise functions
- Exponents & radicals
- Exponential growth & decay
- Quadratics: Multiplying & factoring
- Quadratic functions & equations
- Irrational numbers
- Performing transformations
- Transformation properties and proofs
- Right triangles & trigonometry
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry (Advanced)
- Analytic geometry
- Conic sections
- Solid geometry
- Polynomial arithmetic
- Complex numbers
- Polynomial factorization
- Polynomial division
- Polynomial graphs
- Rational exponents and radicals
- Exponential models
- Transformations of functions
- Rational functions
- Trigonometric functions
- Non-right triangles & trigonometry
- Trigonometric equations and identities
- Analyzing categorical data
- Displaying and comparing quantitative data
- Summarizing quantitative data
- Modeling data distributions
- Exploring bivariate numerical data
- Study design
- Probability
- Counting, permutations, and combinations
- Random variables
- Sampling distributions
- Confidence intervals
- Significance tests (hypothesis testing)
- Two-sample inference for the difference between groups
- Inference for categorical data (chi-square tests)
- Advanced regression (inference and transforming)
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- Scatterplots
- Data distributions
- Two-way tables
- Binomial probability
- Normal distributions
- Displaying and describing quantitative data
- Inference comparing two groups or populations
- Chi-square tests for categorical data
- More on regression
- Prepare for the 2020 AP®︎ Statistics Exam
- AP®︎ Statistics Standards mappings
- Polynomials
- Composite functions
- Probability and combinatorics
- Limits and continuity
- Derivatives: definition and basic rules
- Derivatives: chain rule and other advanced topics
- Applications of derivatives
- Analyzing functions
- Parametric equations, polar coordinates, and vector-valued functions
- Applications of integrals
- Differentiation: definition and basic derivative rules
- Differentiation: composite, implicit, and inverse functions
- Contextual applications of differentiation
- Applying derivatives to analyze functions
- Integration and accumulation of change
- Applications of integration
- AP Calculus AB solved free response questions from past exams
- AP®︎ Calculus AB Standards mappings
- Infinite sequences and series
- AP Calculus BC solved exams
- AP®︎ Calculus BC Standards mappings
- Integrals review
- Integration techniques
- Thinking about multivariable functions
- Derivatives of multivariable functions
- Applications of multivariable derivatives
- Integrating multivariable functions
- Green’s, Stokes’, and the divergence theorems
- First order differential equations
- Second order linear equations
- Laplace transform
- Vectors and spaces
- Matrix transformations
- Alternate coordinate systems (bases)
Frequently Asked Questions about Khan Academy and Math Worksheets
Why is khan academy even better than traditional math worksheets.
Khan Academy’s 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don’t need to be graded, and don’t require a printer.
| Math Worksheets | Khan Academy |
|---|---|
| Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet | Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus |
| Math worksheets can vary in quality from site to site | Every Khan Academy question was written by a math expert with a strong education background |
| Math worksheets can have ads or cost money | Khan Academy is a nonprofit whose resources are always free to teachers and learners – no ads, no subscriptions |
| Printing math worksheets use up a significant amount of paper and are hard to distribute during virtual learning | Khan Academy practice requires no paper and can be distributed whether your students are in-person or online |
| Math worksheets can lead to cheating or a lack of differentiation since every student works on the same questions | Khan Academy has a full question bank to draw from, ensuring that each student works on different questions – and at their perfect skill level |
| Math worksheets can slow down student learning since they need to wait for feedback | Khan Academy gives instant feedback after every answer – including hints and video support if students are stuck |
| Math worksheets take up time to collect and take up valuable planning time to grade | Khan Academy questions are graded instantly and automatically for you |
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets look like?
Here’s an example:
What are teachers saying about Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets?
“My students love Khan Academy because they can immediately learn from their mistakes, unlike traditional worksheets.”
Is Khan Academy free?
Khan Academy’s practice questions are 100% free—with no ads or subscriptions.
What do Khan Academy’s interactive math worksheets cover?
Our 100,000+ practice questions cover every math topic from arithmetic to calculus, as well as ELA, Science, Social Studies, and more.
Is Khan Academy a company?
Khan Academy is a nonprofit with a mission to provide a free, world-class education to anyone, anywhere.
Want to get even more out of Khan Academy?
Then be sure to check out our teacher tools . They’ll help you assign the perfect practice for each student from our full math curriculum and track your students’ progress across the year. Plus, they’re also 100% free — with no subscriptions and no ads.
Get Khanmigo
The best way to learn and teach with AI is here. Ace the school year with our AI-powered guide, Khanmigo.
For learners For teachers For parents
In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask you enter in the text you see in the image below so we can confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
© 2003 - 2024 All other trademarks and copyrights are the property of their respective owners. All rights reserved.
Free Algebra Questions and Problems with Answers
Free intermediate and college algebra questions and problems are presented along with answers and explanations. Free worksheets to download are also included.
Intermediate Algebra Questions with Answers
- sample 1 .(student generated solutions). Also included are the solutions with full explanations .
- sample 2 .(True / False type). Also included are the solutions with full explanations .
- sample 3 .(student generated solutions). solutions with full explanations are included.
- sample 4 .(True / False type). solutions with full explanations included.
- sample 5 .(Multiple choice questions type). Also included are the solutions with full explanations .
- sample 6 .(True / False type). solutions with full explanations included.
Intermediate Algebra Problems with Detailed Solutions
- Algebra Problems .
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 1 : equations, system of equations, percent problems, relations and functions.
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 2 :Find equation of line, domain and range from graph, midpoint and distance of line segments, slopes of perpendicular and parallel lines.
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 3 : equations and system of equations, quadratic equations, function given by a table, intersections of lines, problems.
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 4 . Functions, domain, range, zeros.
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 5 . Scientific Notation
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 6 . Equations of Lines
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 7 . Slopes of Lines
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 8 . Absolute Value Expressions
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 9 . Solve Absolute Value Equations
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 10 . Solve Absolute Value Inequalities
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 11 . Simplify Algebraic Expressions by Removing Brackets
- Intermediate Algebra Problems With Answers - sample 12 . Simplify Algebraic Expressions with Exponents
Intermediate Algebra Worksheets
- Worksheet (1) .
- Worksheet (2) .
- Worksheet (3) .
- Worksheet (4) .
- Worksheet (5) .
- Worksheet (6) .
College Algebra Questions with Answers
- sample 1 .(multiple choice questions). Also Detailed solutions with full explanations are included
- sample 2 . (multiple choice questions)
College Algebra Problems with Answers
- sample 1: Quadratic Functions .
- sample 2: Composite and Inverse Functions .
- sample 3: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions .
- sample 4: Graphs of Functions .
- sample 5: Find Domain and Range of Functions .
- sample 6: Problems on Polynomials : Graphs, Factoring, Finding, Multiplying, Dividing, Factor theorem, Zeros
- sample 7: Equation of Circle : Finding equations, center, radius of circles
- sample 8: Equation of Ellipse : Finding equations, foci, center, vertices of ellipses
- sample 9: Equation of Parabola : Finding equations, focus, vertex, axis, directrix of parabola.
- sample 10: Equation of Hyperbola : Finding equations, foci, center and vertices of hyperbola.
College Algebra Worksheets
- Worksheet (1): Graphs of Basic Functions .
- Worksheet (2): Exponential Growth and Decay Problems .
- Worksheet (3): Graphing Exponential Functions .
- Worksheet (4): Graphing Logarithmic Functions .
- Worksheet (5): Solve Exponential Equations .
- Worksheet (6): Solve Logarithmic Equations .
- Worksheet (7): Multiple Choice Questions on Polynomials and Solutions
- Worksheet (8): Multiple Choice Questions on Rational Functions and Solutions .
- Worksheet (9): Graphing Inverse Functions .

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
Complete List of FREE SAT Math Practice Problems

Need to study for the SAT Math section but don't know where to start? On a budget, too? Not to worry! In this article, we've put together a comprehensive list of all the best (and free!) SAT Math study materials and guides currently available online.
Note: For info on the best SAT study materials you have to pay for, check out our picks for top SAT prep books.
Feature Image: Alan O'Rourke /Flickr
The Importance of Using High-Quality SAT Math Materials
It is incredibly important to get your study materials from the right places. The SAT is a very specific kind of test, and there are many (many!) websites and programs out there that, sadly, offer only poor-quality SAT resources.
If you study using mainly inferior SAT materials, you won't get a clear sense as to how you'll do on test day. Test prep is about assessing and improving upon your current level, but you won't be able to do this if you get a false sense of your skills based on poor study materials. Ultimately, products and test questions that don't accurately reflect the SAT are a waste of time.
Therefore, it's best to prioritize official SAT materials. The SAT is designed by the College Board, and their free materials are by far the best place to start studying. From here, you can branch off into programs and materials that use (or closely resemble) official SAT material.
Now, let's look at the best resources you can use for free official SAT Math practice questions.

Top 5 Free Resources for Quality SAT Math Practice
In this section, we go over the top five free resources you can use for quality SAT Math prep.
#1: The College Board
As the creator and issuer of the SAT, the College Board is the best place to begin for collecting your free SAT Math study materials. The official website offers full-length SAT practice tests and practice questions for all sections.
The closest you can get to taking the actual SAT is the free, full-length practice exams in Bluebook , College Board’s online testing platform. The six available practice tests provide you with a sneak peek of the interface, format, and scoring of the online test, so they’re a useful tool as you prepare for the digital format.
In addition to full-length exams, Bluebook also offers previews of individual questions from the actual SAT. Even these are useful as you’re trying out the digital interface and learning what kinds of math problems to expect.
Note that if you have testing accommodations that allow you to take the test on paper, you'll want to practice on the the official, printable practice tests created for the digital SAT.
Old Official Full-Length SAT Practice Tests
While the newest practice tests will be most useful for your prep, you can also use these old (pre-digital) SAT practice tests, though keep in mind there will be differences
There are 10 official practice tests from the 2016-2023 version of the SAT. Each test comes with an answer key and in-depth answer explanations to help you understand why you got questions wrong.
Although the general format of these tests is quite different, the individual math questions will be fairly similar to what you'll see on the digital SAT. Just keep in mind that they should be used for practicing skills and concepts rather than estimating your score.
#2: Khan Academy
Khan Academy is a nonprofit and partner of the College Board that offers a free online SAT prep program and practice questions.
While most of the questions come from official SAT practice materials (such as those linked above), others have been created or adapted with approval from or in tandem with the College Board itself.
Sign up for a free Khan Academy account to get access to SAT study questions and materials, complete with guides and explanation videos to aid your studying.
#3: PrepScholar SAT Blog
Here at PrepScholar, we offer tons of free resources, including detailed guides on every SAT math topic and a complete collection of our best SAT Math articles . All our guides include definitions and explanations, examples of how you'll see the topic on the test, and real SAT practice questions with detailed answer explanations.
Browse our SAT Math guides below to get started! All guides are arranged by topic.
Integers (Basic)
Integers (Advanced)
Fractions, Ratios, and Proportions
Statistics (Mean, Median, Mode)
Probability
Single Variable Equations
Systems of Equations
- Completing the Square
Coordinate Geometry
Lines and Slopes
Reflections, Translations, and Rotations
Plane and Solid Geometry
Lines and Angles
Solid Geometry
- Trigonometry
The 28 Critical SAT Math Formulas You MUST Know
In addition, we have strategy guides that will help you solve numerous SAT Math problems across the board:
Plugging in Answers
Plugging in Numbers
If you find our guides and quizzes helpful, you can also sign up for a free five-day trial to our test prep program. Our program assesses your current strengths and weaknesses and adapts based on your progress. It gives you practice questions tailored to your areas of needed improvement and provides answer explanations for all questions.
All our questions are based off real SAT test questions and, though the full program is not free, we guarantee your money back if you do not improve by 160 points.
#4: CrackSAT.net
CrackSAT is a free, unofficial SAT website offering PDFs of official SAT practice tests and an array of both official and unofficial SAT Math questions.
Many of the questions on CrackSAT come from SAT prep books by well-known test-prep companies including The Princeton Review and Kaplan. Though generally solid, unofficial SAT questions can vary wildly in quality, so don't rely on only these to give you a sense of your math abilities. Rather, it's best to use this website after you've exhausted all the official SAT resources above.
What's especially nice about this website is its organization: math questions are available in both multiple-choice and grid-in categories to give you the full range of math practice. You can also browse problems by concept (e.g., linear functions , exponents and radicals , etc.).

You've gathered all your study material ... so now what?
How to Use SAT Math Study Materials Effectively: 6 Tips
It's just as important to know how to best utilize your SAT study materials as it is to know how to access them. These six tips will help you achieve your highest SAT Math score on test day.
#1: Take a Full Practice Test in One Sitting
You're probably most concerned about your SAT Math score, but it's still important to take a full SAT practice test so you can see how you'll fare on test day. Although answering one or two Math questions might not be too much of a challenge for you, in truth the SAT is a marathon—and if you aren't prepared, you'll likely be exhausted by the end of it. And exhaustion can lead anyone to make mistakes!
So before you dedicate your focus to the SAT Math section, take an official SAT practice test on the Bluebook app to see how your Math score fits into the larger test-taking picture. Make sure to take the whole test in one sitting; this will help you build endurance for test day.
#2: Use Proper Timing and Pace Yourself
As you take SAT practice tests and any Math-specific sections, be sure to use the same time limits you'll have on test day.
The chart below shows how much time you'll have on each SAT section as well as how much time you should (approximately) spend per question. Note that each section is split into two modules of equal lengths.
| Reading and Writing | 64 minutes | 54 | 71 seconds |
You'll have about 9 5 seconds per SAT Math question. Some questions might take you less or more time, but keep practicing so that you're not consistently spending too long on a single math question.
Remember that accuracy is only half the battle—you have to actually finish the questions within the time limits if you want to get a high Math score!
That said, don't worry if you run out of time while taking your first SAT practice test. This is completely normal and gives you a starting point from which you can later improve.
#3: Review Your Mistakes
It's one thing to take an SAT Math test, but you also need to look over your results and identify any patterns in your correct and incorrect answers. Do you tend to get the last few questions wrong on each Math section? Do function questions just seem to throw you for a loop?
First, figure out what went wrong. Then, see how you can pick up some easy points and diligently target those areas in your prep. (Remember that each Math question, no matter its difficulty, is worth the same number of points!)
#4: Target Your Biggest Weaknesses
Once you've pinpointed patterns in the errors you make, it's time to dig deeper and examine your biggest weaknesses. Your ultimate goal will be to tailor your studying so that you can focus on improving the areas you struggle with the most.
Since your overall objective is to answer as many questions as accurately as possible, you'll want to dedicate the majority of your study time to improving your weaknesses, rather than to reviewing material you already know well.
Refreshing your known material again and again might make you feel productive and confident, but it doesn't do a whole lot to improve your score. Your best bet is to focus on your problem areas by practicing and expanding your knowledge base.
#5: Set a Study Schedule
Don't be tempted to cram right before the test . You might have a busy schedule and feel as if your only option is to cram for the SAT, but improvement really happens over time. We generally advise giving yourself at least three to six months to study for the SAT.
If you don't have a lot of time left before test day, however, don't give up! No matter how much time you've got for studying, it is possible to come up with a balanced SAT study plan .
First, calculate the amount of time you have before your test date . (For example, say you've got a month before your test .)
Next, assign yourself at least three full practice tests (in addition to your normal study materials) and spread them out over the course of your study schedule. If you only have a week or so before test day, this probably won't be possible. In this case, try to fit in at least one or two practice tests wherever you can.
Nothing else replicates the SAT experience like a full practice test does, so don't underestimate its importance in your prep!
#6: Not Seeing Any Improvement? Get Additional Prep Help
Some students prefer to do all of their SAT studying by themselves, but others work better with a little guidance.
If the SAT subject matter just isn't making sense to you or you need help prioritizing your time, an SAT tutor or prep program (or both!) are excellent options to try. Both can give you that final push you need to stay focused and maximize your SAT Math score.
At PrepScholar, we offer expert SAT tutoring services in addition to a fully customizable SAT prep program . For more info, read our guides on how to find the best SAT tutor for you and how much you should spend on tutoring .

Targeted and careful practice, rest, and confidence: the perfect recipe for SAT success.
What's Next?
Don't know where to start? Take a look at our list of all math topics on the SAT Math section , and target your weaknesses with our individual SAT Math guides .
Want to know what the hardest SAT Math questions are? We've compiled a list of the 13 most challenging SAT Math questions , along with answer explanations for each.
Bitten by the procrastination bug? Time running out until test day? Check out how to beat the urge to procrastinate , and learn how to balance time for your studies.
Looking to get a perfect SAT Math score? Dig into our guide to getting a perfect 800 on SAT Math , written by a perfect scorer!
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Courtney scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT in high school and went on to graduate from Stanford University with a degree in Cultural and Social Anthropology. She is passionate about bringing education and the tools to succeed to students from all backgrounds and walks of life, as she believes open education is one of the great societal equalizers. She has years of tutoring experience and writes creative works in her free time.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Math Word Problems
Welcome to the math word problems worksheets page at Math-Drills.com! On this page, you will find Math word and story problems worksheets with single- and multi-step solutions on a variety of math topics including addition, multiplication, subtraction, division and other math topics. It is usually a good idea to ensure students already have a strategy or two in place to complete the math operations involved in a particular question. For example, students may need a way to figure out what 7 × 8 is or have previously memorized the answer before you give them a word problem that involves finding the answer to 7 × 8.
There are a number of strategies used in solving math word problems; if you don't have a favorite, try the Math-Drills.com problem-solving strategy:
- Question : Understand what the question is asking. What operation or operations do you need to use to solve this question? Ask for help to understand the question if you can't do it on your own.
- Estimate : Use an estimation strategy, so you can check your answer for reasonableness in the evaluate step. Try underestimating and overestimating, so you know what range the answer is supposed to be in. Be flexible in rounding numbers if it will make your estimate easier.
- Strategize : Choose a strategy to solve the problem. Will you use mental math, manipulatives, or pencil and paper? Use a strategy that works for you. Save the calculator until the evaluate stage.
- Calculate : Use your strategy to solve the problem.
- Evaluate : Compare your answer to your estimate. If you under and overestimated, is the answer in the correct range. If you rounded up or down, does the answer make sense (e.g. is it a little less or a little more than the estimate). Also check with a calculator.
Most Popular Math Word Problems this Week

Arithmetic Word Problems

- Addition Word Problems One-Step Addition Word Problems Using Single-Digit Numbers One-Step Addition Word Problems Using Two-Digit Numbers
- Subtraction Word Problems Subtraction Facts Word Problems With Differences from 5 to 12
- Multiplication Word Problems One-Step Multiplication Word Problems up to 10 × 10
- Division Word Problems Division Facts Word Problems with Quotients from 5 to 12
- Multi-Step Word Problems Easy Multi-Step Word Problems
Copyright © 2005-2024 Math-Drills.com You may use the math worksheets on this website according to our Terms of Use to help students learn math.
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Tests and Exams
How to Do Well on Multiple Choice Questions
Last Updated: January 31, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Ted Dorsey, MA . Ted Dorsey is a Test Prep Tutor, author, and founder of Tutor Ted, an SAT and ACT tutoring service based in Southern California. Ted earned a perfect score on the SAT (1600) and PSAT (240) in high school. Since then, he has earned perfect scores on the ACT (36), SAT Subject Test in Literature (800), and SAT Subject Test in Math Level 2 (800). He has a BA in English from Princeton University and a MA in Education from the University of California, Los Angeles. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 304,664 times.
Multiple choice exams are popular among educators, as they test a student’s critical thinking and problem solving skills. You may struggle with multiple choice exams and not know how to do well on them. To get a good grade on a multiple choice exam, start by analyzing the questions. Then, answer the questions effectively by working through them strategically. You can also prepare for the exam so you do well and get a high mark.
Analyzing the Questions

- You can also read the question more than once to ensure you understand it. Take your time and do not rush through the question.

- You should also analyze the question for any phrasing that asks for multiple answers to the question, such as “Choose more than one answer” or “Choose two of the four options.”

- Doing this can help you think of an answer before you look at the multiple choice options. Chances are, the answer you come up with is one of the options for the question.
- If you can’t come up with your own answer, don’t fret. You can use the answers provided to come up with the right answer for the question.
- Indications of time: before, after, while, always, never
- Superlatives: most, least, most common, fastest, the best, the only
- Conditionals: each time X happens, if X happens, unless X, assuming X
Answering the Questions Effectively

- Take your time and read over each possible answer. Do not skim or skip over any possible answers. This will ensure you make an informed decision about the correct answer to the question.

- Look for possible answers that have “always,” “never,” and “none of the above” in them, as they are usually incorrect.
- When you go over the answers, avoid thinking that your instructor is trying to trip you up with sneaky or confusing options. Most instructors won't give you "trick" answers like this.

- For example, you may be torn between two answers for the question. Try out both answers for the question. Read the question to yourself and place each answer at the end of the question. Pick the one that appears the most correct to you.

- If you get stuck on one question, try to work through it slowly. If you are really stumped, put a star or mark next to it so you know to come back to it at the very end of the exam.

- When in doubt on an answer to a difficult question on the exam, go with your best judgement and choose the best answer you can identify from the list of options.
Preparing For a Multiple Choice Exam

- Cramming for the exam will cause you a lot of stress and anxiety. You may not retain information well if you cram the night before the exam, leading to a poor grade.

- Use the old exams and example questions to prepare for the test. Study the structure of the questions as well as the provided answers. Take several practice tests to get better at multiple choice style exams.
- If the instructor will not give you past exams, join a study group so you can study with others. You can also get a study tutor to help you study for the exam.

- Make sure you have a good breakfast high in protein, vitamins, and nutrients, like eggs, toast, and fruit, or yogurt and granola.

- 5 Study with trusted friends, and keep out of distractions, such as parties. This can cause to fail, distract you from the test you are studying. [15] X Research source
Community Q&A
- Don't assume that there will be a logic behind the order of correct answers. For example, just because you've already answered C three times in a row, doesn't mean that the next question can't also have C as its answer. Likewise, if you notice that you haven't answered D in a while, that doesn't mean that the next questions are more like to have D for an answer. Treat every question independently of the answers to the other questions. Thanks Helpful 7 Not Helpful 1
- Give yourself enough time to transfer your final answers to the official exam sheet (like a Scantron). About 5 minutes for every 10 questions is a good rule of thumb. Thanks Helpful 5 Not Helpful 1

You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.butte.edu/departments/cas/tipsheets/studystrategies/multiple_choice.html
- ↑ https://www.educationcorner.com/multiple-choice-tests.html
- ↑ https://student.unsw.edu.au/multiple-choice-exams
- ↑ https://umanitoba.ca/student/academiclearning/media/Tips_on_Taking_Multiple_Choice_Exams_NEW.pdf
- ↑ https://www.dmu.edu/wp-content/uploads/MULTIPLE-CHOICE-TEST-TAKING-STRATEGIES.pdf
- ↑ https://www.socialpsychology.org/testtips.htm
- ↑ Ted Dorsey, MA. Academic Tutor. Expert Interview. 11 December 2019.
- ↑ https://learningcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/studying-101-study-smarter-not-harder/
- ↑ Ted Coopersmith, MBA. Academic Tutor. Expert Interview. 10 July 2020.
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Raghav Datta
Oct 28, 2017
Did this article help you?

Jun 5, 2017
Mar 27, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Develop the tech skills you need for work and life
Multi-Step Equations Exercises
Multi-step equations practice problems with answers.
For this exercise, I have prepared seven (7) multi-step equations for you to practice. If you feel the need to review the techniques involved in solving multi-step equations, take a short detour to review my other lesson about it. Click the link below to take you there!
Solving Multi-Step Equations
1) Solve the multi-step equation for [latex]\large{c}[/latex].
[latex]c – 20 = 4 – 3c[/latex]
Add both sides by [latex]20[/latex]. Next, add [latex]3c[/latex] to both sides. Finally, divide both sides by the coefficient of [latex]4c[/latex] which is [latex]4[/latex] to get [latex]c=6[/latex].
2) Solve the multi-step equation for [latex]\large{n}[/latex].
[latex] – \,4\left( { – 3n – 8} \right) = 10n + 20[/latex]
- Remember to always perform the same operation on both sides of the equation.
- Subtract by [latex]32[/latex].
- Subtract by [latex]10n[/latex].
- Divide by [latex]2[/latex]
- The final solution is [latex]n=-6[/latex].
3) Solve the multi-step equation for [latex]\large{y}[/latex].
[latex]2\left( {4 – y} \right) – 3\left( {y + 3} \right) = – 11[/latex]
Apply twice the Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition to the left side of the equation. Then combine like terms . Add both sides by [latex]1[/latex] followed by dividing both sides of the equation by [latex]-5[/latex].
4) Solve the multi-step equation for [latex]\large{k}[/latex].
[latex]{\Large{{6k + 4} \over 2}} = 2k – 11[/latex]
Multiply both sides by [latex]2[/latex]. Next, subtract [latex]4[/latex] to both sides. Then, subtract [latex]4k[/latex]. Finally, divide by [latex]2[/latex] to obtain the value of [latex]k[/latex] which is [latex]-13[/latex].
5) Solve the multi-step equation for [latex]\large{x}[/latex].
[latex] – \left( { – 8 – 3x} \right) = – 2\left( {1 – x} \right) + 6x[/latex]
Apply the Distributive Property on both sides of the equation. Be careful when multiplying expressions with the same or different signs . Next, add [latex]2[/latex] to both sides, then subtract [latex]3x[/latex], and finally finish it off by dividing [latex]5[/latex] to both sides.
6) Solve the multi-step equation for [latex]\large{m}[/latex].
[latex]{\large{3 \over 4}}m – 2\left( {m – 1} \right) = {\large{1 \over 4}}m + 5[/latex]
7) Solve the multi-step equation for [latex]\large{x}[/latex].
[latex]3\left( {3x – 8} \right) – 5\left( {3x – 8} \right) = 4\left( {x – 2} \right) – 6\left( {x – 2} \right)[/latex]
You might also like these tutorials:
- Two-Step Equations Practice Problems with Answers

Word Problem Practice Questions with Answer Key
- Posted by Brian Stocker
- Date February 13, 2019
- Comments 11 comments
Problem Solving – Word Problems
Word problems are mathematical problems using everyday language and real-world situations. Some information is given and one or more pieces or information (variables) are missing. You must understand the given information, identify the mathematical operations necessary to solve the problem, and then carry out those operations to obtain the missing information or variables.
The Biggest Tip!
Tackling word problems is much easier if you have a systematic approach which we outline below.
Here is the biggest tip for word problems practice. Practice regularly and systematically. Sounds simple and easy right? Yes it is, and yes it really does work. Word problems are a way of thinking and require you to translate a real world problem into mathematical terms.
Some math instructors go so far as to say that learning how to think mathematically is the main reason for teaching word problems. So what do we mean by Practice regularly and systematically? Studying word problems and math in general requires a logical and mathematical frame of mind. The only way that you can get this is by practicing regularly, which means everyday.
How to Solve Word Problems
Types of Word Problems
Most Common Word Problem Mistakes on a Test
It is critical that you practice word problems everyday for the 5 days before the exam as a bare minimum. If you practice and miss a day, you have lost the mathematical frame of mind and the benefit of your previous practice is pretty much gone. Anyone who has done any number of math tests will agree – you have to practice everyday.
See Also Algebra Word Problems
Effective problem-solving skills are essential in many areas of life, from academia to the workplace and beyond. Developing the ability to solve word problems requires practice and patience, as well as a strong understanding of basic mathematical concepts and operations.
Video Version
Try a FREE Quiz
Word problem practice questions.
1. A box contains 7 black pencils and 28 blue ones. What is the ratio between the black and blue pens?
a. 1:4 b. 2:7 c. 1:8 d. 1:9
2. The manager of a weaving factory estimates that if 10 machines run at 100% efficiency for 8 hours, they will produce 1450 meters of cloth. Due to some tech¬nical problems, 4 machines run of 95% efficiency and the remaining 6 at 90% efficiency. How many meters of cloth can these machines will produce in 8 hours?
a. 1334 meters b. 1310 meters c. 1300 meters d. 1285 meters
3. In a local election at polling station A, 945 voters cast their vote out of 1270 registered voters. At poll¬ing station B, 860 cast their vote out of 1050 regis¬tered voters and at station C, 1210 cast their vote out of 1440 registered voters. What is the total turnout from all three polling stations?
a. 70% b. 74% c. 76% d. 80%
4. If Lynn can type a page in p minutes, what portion of the page can she do in 5 minutes?
a. p/5 b. p – 5 c. p + 5 d. 5/p
5. If Sally can paint a house in 4 hours, and John can paint the same house in 6 hours, how long will it take for both to paint a house?
a. 2 hours and 24 minutes b. 3 hours and 12 minutes c. 3 hours and 44 minutes d. 4 hours and 10 minutes
6. Employees of a discount appliance store receive an additional 20% off the lowest price on any item. If an employee purchases a dishwasher during a 15% off sale, how much will he pay if the dishwasher originally cost $450?
a. $280.90 b. $287.00 c. $292.50 d. $306.00
7. The sale price of a car is $12,590, which is 20% off the original price. What is the original price?
a. $14,310.40 b. $14,990.90 c. $15,108.00 d. $15,737.50
8. Richard gives ‘s’ amount of salary to each of his ‘n’ employees weekly. If he has ‘x’ amount of money, how many days he can employ these ‘n’ employees.
a. sx/7n b. 7x/nx c. nx/7s d. 7x/ns
9. A distributor purchased 550 kilograms of potatoes for $165. He distributed these at a rate of $6.4 per 20 kilograms to 15 shops, $3.4 per 10 kilograms to 12 shops and the remainder at $1.8 per 5 kilo¬grams. If his total distribution cost is $10, what will his profit be?
a. $10.40 b. $8.60 c. $14.90 d. $23.40
10. How much pay does Mr. Johnson receive if he gives half of his pay to his family, $250 to his land¬lord, and has exactly 3/7 of his pay left over?
a. $3600 b. $3500 c. $2800 d. $175042
11. The cost of waterproofing canvas is .50 a square yard. What’s the total cost for waterproofing a canvas truck cover that is 15’ x 24’?
a. $18.00 b. $6.67 c. $180.00 d. $20.00
1. A The ratio between black and blue pens is 7 to 28 or 7:28. Bring to the lowest terms by dividing both sides by 7 gives 1:4.
2. A At 100% efficiency 1 machine produces 1450/10 = 145 m of cloth. At 95% efficiency, 4 machines produce 4 * 145 * 95/100 = 551 m of cloth. At 90% efficiency, 6 machines produce 6 * 145 * 90/100 = 783 m of cloth. Total cloth produced by all 10 machines = 551 + 783 = 1334 m Since the information provided and the question are based on 8 hours, we did not need to use time to reach the answer.
The turnout at polling station A is 945 out of 1270 registered voters. So, the percentage turnout at station A is:
(945/1270) × 100% = 74.41%
The turnout at polling station B is 860 out of 1050 registered voters. So, the percentage turnout at station B is:
(860/1050) × 100% = 81.90%
The turnout at polling station C is 1210 out of 1440 registered voters. So, the percentage turnout at station C is:
(1210/1440) × 100% = 84.03%
To find the total turnout from all three polling stations, we need to add up the total number of voters and the total number of registered voters from all three stations:
Total number of voters = 945 + 860 + 1210 = 3015
Total number of registered voters = 1270 + 1050 + 1440 = 3760
The overall percentage turnout is:
(3015/3760) × 100% = 80.12%
Therefore, the total turnout from all three polling stations is 80.12% — rounding to 80%.
Video Solution
4. D This is a simple direct proportion problem: If Lynn can type 1 page in p minutes, then she can type x pages in 5 minutes We do cross multiplication: x * p = 5 * 1 Then, x = 5/p
5. A This is an inverse ratio problem. 1/x = 1/a + 1/b where a is the time Sally can paint a house, b is the time John can paint a house, x is the time Sally and John can together paint a house. So, 1/x = 1/4 + 1/6 … We use the least common multiple in the denominator that is 24: 1/x = 6/24 + 4/24 1/x = 10/24 x = 24/10 x = 2.4 hours. In other words; 2 hours + 0.4 hours = 2 hours + 0.4•60 minutes = 2 hours 24 minutes
The original price of the dishwasher is $450. During a 15% off sale, the price of the dishwasher will be reduced by:
15% of $450 = 0.15 x $450 = $67.50
So the sale price of the dishwasher will be:
$450 – $67.50 = $382.50
As an employee, the person receives an additional 20% off the lowest price, which is $382.50. We can calculate the additional discount as:
20% of $382.50 = 0.20 x $382.50 = $76.50
So the final price that the employee will pay for the dishwasher is:
$382.50 – $76.50 = $306.00
Therefore, the employee will pay $306.00 for the dishwasher.
7. D Original price = x, 80/100 = 12590/X, 80X = 1259000, X = 15,737.50.
8. D We are given that each of the n employees earns s amount of salary weekly. This means that one employee earns s salary weekly. So; Richard has ‘ns’ amount of money to employ n employees for a week. We are asked to find the number of days n employees can be employed with x amount of money. We can do simple direct proportion: If Richard can employ n employees for 7 days with ‘ns’ amount of money, Richard can employ n employees for y days with x amount of money … y is the number of days we need to find. We can do cross multiplication: y = (x * 7)/(ns) y = 7x/ns
9. B The distribution is done at three different rates and in three different amounts: $6.4 per 20 kilograms to 15 shops … 20•15 = 300 kilograms distributed $3.4 per 10 kilograms to 12 shops … 10•12 = 120 kilograms distributed 550 – (300 + 120) = 550 – 420 = 130 kilograms left. This 50 amount is distributed in 5 kilogram portions. So, this means that there are 130/5 = 26 shops. $1.8 per 130 kilograms. We need to find the amount he earned overall these distributions. $6.4 per 20 kilograms : 6.4•15 = $96 for 300 kilograms $3.4 per 10 kilograms : 3.4 *12 = $40.8 for 120 kilograms $1.8 per 5 kilograms : 1.8 * 26 = $46.8 for 130 kilograms So, he earned 96 + 40.8 + 46.8 = $ 183.6 The total distribution cost is given as $10 The profit is found by: Money earned – money spent … It is important to remember that he bought 550 kilograms of potatoes for $165 at the beginning: Profit = 183.6 – 10 – 165 = $8.6
10. B We check the fractions taking place in the question. We see that there is a “half” (that is 1/2) and 3/7. So, we multiply the denominators of these fractions to decide how to name the total money. We say that Mr. Johnson has 14x at the beginning; he gives half of this, meaning 7x, to his family. $250 to his landlord. He has 3/7 of his money left. 3/7 of 14x is equal to: 14x * (3/7) = 6x So, Spent money is: 7x + 250 Unspent money is: 6×51 Total money is: 14x Write an equation: total money = spent money + unspent money 14x = 7x + 250 + 6x 14x – 7x – 6x = 250 x = 250 We are asked to find the total money that is 14x: 14x = 14 * 250 = $3500
11. D First calculate total square feet, which is 15 * 24 = 360 ft 2 . Next, convert this value to square yards, (1 yards 2 = 9 ft 2 ) which is 360/9 = 40 yards 2 . At $0.50 per square yard, the total cost is 40 * 0.50 = $20.
- Not reading the problem carefully and thoroughly, so that you either misunderstand or solve the problem incorrectly.
- Not identifying the important information in the problem, such as the quantities, units, and the operation to be performed.
- Not translating the information in the problem into mathematical language and equations.
- Not checking the units of measure and making sure they match your final answer.
- Not double-checking the answer to ensure it makes sense.
- Not understanding the underlying mathematical concept or operation the problem is asking for.
- Not using estimation or approximations as a tool to check the reasonableness of your answer.
Try a FREE Math Quiz
Got a Question? Email me anytime - [email protected]
Previous post
Pythagorean Geometry - Tutorial and Practice Questions
Calculate the slope of a line - practice questions, you may also like.

Basic Math Video Tutorials
How to answer basic math multiple choice, how to solve linear inequalities – quick review and practice.
Basic linear inequalities have one of the following forms: ax + b > 0 ax + b < 0 ax + b > 0 ax + b < 0 where a and b are some real numbers. Our solution to …
11 Comments
Will we need to know units and their conversions such as yards to feet? Should we memorise those?
are we allowed to use a calculator? To expect someone to complete these in their head is absurd especially with a time limit. The second question requires multiplication by decimals, which would be okay if you got a whole number but you dont, you get a fraction and the only way to get it to 551 is by then multiplying that number by 4. Doubt anyone would be required to do these kind of calculations in a real world scenario especially unaided and under time constraints.
Hi Depends on the test – what test are you studying for?
is this preparation for the CAAT level C???
These questions vary in subject and difficulty level to give students practice on different types of questions for different types of tests. They are not specific to one test or one level.
Yes the LEAST common multiple of 6 and 4 is 12 – i did it with 24 – it will give the same answer no matter which way you do it. Good point though – perhaps for simplicity sake 12 would be better.
Are these questions appeared on the Cbest?
The are the same TYPE of questions – not exactly
sorry for the message above, i like your site and i have won 1st place in an exam due to this site
I used Chat GPT. Solved every one…. perfectly. I’m still dumb as a rock though.
Oh Really? You may want to check that again!! It gave me wrong answers and weird steps to calculate for 2 of them!
Leave A Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Have an account?
Suggestions for you See more

Stress Busters
Professional development , day and night, 57.6k plays, digital electronics, university , blooms taxonomy, human resources management, entrepreneurship, 12th - university , general knowledge trivia, first impression.

Problem Solving Techniques
Professional development.

12 questions

Introducing new Paper mode
No student devices needed. Know more
The absolute first step of problem solving is ...
to be sure you know the answer
to be sure you've got the right cause
to be sure you are you
to be sure you've read the question
What's the most common reason for getting the wrong cause?
A problem might not have a cause at all
Fixing the symptomps will be enough
A problem might be it's own cause
There can be a common cause for two problems so we think one problem is causing the other.
What is the best type of thinking when solving a problem?
Use the logical part of your brain first, then the creative part.
Generate lots of ideas and then choose the best one.
Tap your intuition by running with the first idea that you think of. It will be the best.
Think inside the box.
When brainstorming, you should adopt this practice for the results.
Collect all the ideas, including the bad ones.
Throw out the bad ideas as you go along.
Separate the ideas generation from the judging process.
Use the same people for the idea generation and for the judging.
What should an effective problem solver keep in mind when thinking about creativity?
There are just three effective ways to increase creativity.
Creativity can help you identify a problem but not solve it.
Creativity is fixed -- you either have it or you don't
Creativity can be increased via many different techniques.
A problem can be:
An obstacle
The solution
A difficulty
The first step in solving a problem is:
Develop a solution
Reflect and review
Understand the problem
Investigate and research the problem
The solution to a problem is the
Steps you take to define the problem.
Steps you take to solve the problem.
Steps you take to make the problem worst.
Who would you ask to help you solve a problem?
Someone who solved the problem before.
Someone who failed at solving the problem.
Someone who has never experienced the problem before.
The final step to solving a problem is:
Investigate and research the problem.
Reflect and Review.
Develop a solution.
Understanding the problem means:
Figuring out the problem.
Checking to see if the problem worked.
Writing the steps to solve the problem.
Thinking of solutions.
Preparing to solve the problem might include brainstorming.
Explore all questions with a free account

Continue with email
Continue with phone

- Request new password
- Create a new account
Essential Psychology
Student resources, multiple choice questions.
1. The Tower of London problem-solving task was developed by
- Shackleton (1982)
- Shallice (1982)
- Sheriff (1982)
- Sherrington (1982)
2. The process of breaking down goals into subgoals is termed
- means–ends analysis
- initial-desired state analysis
- subgoal appropriation
- subgoal potentiation
3. According to Newell and Simon, a problem-solver
- analyzes all possible solutions before beginning
- attempts to resolve differences between problem states
- works backwards from the goal state
- prioritizes subgoals
4. What computer programme did Newell and Simon create to validate their theory?
- general purpose solution
- general problem solver
- enigma machine
5. A challenge to Newell and Simon’s problem-solving theory is that
- experts mostly use means–ends analysis
- novices mostly use means–ends analysis
- experts do not always use means–ends analysis
- novices do not always use means–ends analysis
6. Answers that appear out of the blue to solve problems are
7. Difficulty seeing the solution to a problem is
- means analysis
8. Which is NOT a type of reasoning?
- probabilistic
9. Bayes’ theorem can be used to calculate
- possibility
- probability
- information criterion
- means–ends differences
10. A heuristic is
- a rule of thumb
For Solo Learner Computer science
Fundamentals of algorithms and problem-solving mcqs.
Home » Computer Science MCQs Sets » Computer Basics MCQs » Fundamentals of Algorithms and problem-solving MCQs
PRACTICE IT NOW TO SHARPEN YOUR CONCEPT AND KNOWLEDGE
1. Which graph algorithm can be used to find the longest path in a directed acyclic graph (DAG)?
- Depth-first search (DFS)
- Breadth-first search (BFS)
- Topological sort
- Dijkstra's algorithm
Topological sort can be used to find the longest path in a directed acyclic graph (DAG).
2. What does "brute force" mean in the context of problem-solving?
- Using the most complex approach to solve a problem
- Trying all possible solutions without optimization
- Solving problems without a plan
- Applying advanced mathematics to solve a problem
"Brute force" in problem-solving means trying all possible solutions without optimization.
3. What is "trial and error" as a problem-solving strategy?
- A systematic approach to problem-solving
- Randomly trying different solutions until one works
- A method used only in mathematics
- A formal proof technique
"Trial and error" as a problem-solving strategy involves randomly trying different solutions until one succeeds.
4. What is "divide and conquer" as a problem-solving technique?
- A strategy that avoids breaking problems into smaller subproblems
- A strategy that involves solving the largest subproblem first
- A strategy that breaks a problem into smaller subproblems and solves them independently
- A strategy that only works for small-scale problems
"Divide and conquer" is a problem-solving technique that breaks a problem into smaller subproblems and solves them independently.
5. In problem-solving, what is a "heuristic"?
- An optimal solution to a problem
- A rule of thumb or a practical approach to find a solution
- A random choice among multiple solutions
A heuristic is a rule of thumb or a practical approach used to find a solution in problem-solving.
6. What is "trial division" as a technique in number theory and prime factorization?
- A method to find the smallest prime number
- A method to verify if a number is prime by dividing it by smaller primes
- A method to find the largest prime number
- A method to add prime numbers
"Trial division" is a technique in number theory and prime factorization used to verify if a number is prime by dividing it by smaller primes.
7. What is the primary purpose of "backtracking" in problem-solving?
- To find the optimal solution
- To explore all possible solutions systematically
- To avoid exploring all possible solutions
- To simplify the problem
The primary purpose of "backtracking" in problem-solving is to explore all possible solutions systematically, typically in a recursive manner.
8. What is an algorithm?
- A data structure used to store information
- A sequence of steps to solve a problem
- A programming language
- A type of computer hardware
An algorithm is a sequence of steps or instructions designed to solve a specific problem or perform a task.
9. What is the primary goal of algorithm analysis?
- To design algorithms
- To implement algorithms
- To compare algorithms and evaluate their efficiency
- To debug algorithms
The primary goal of algorithm analysis is to compare algorithms and evaluate their efficiency.
10. Which of the following is NOT a characteristic of a good algorithm?
- Clarity and simplicity
- Efficiency in terms of time and space
- The use of complex data structures
- Correctness
A good algorithm is characterized by clarity, simplicity, efficiency, and correctness. Complex data structures may be used if necessary, but simplicity is preferred.

11. What is the purpose of pseudocode in algorithm development?
- To hide the algorithm's logic
- To provide a step-by-step implementation guide
- To obfuscate the algorithm
- To prevent others from understanding the algorithm
Pseudocode is used to provide a step-by-step implementation guide for an algorithm, making it easier to understand and develop.
12. Which algorithm design technique involves breaking a problem into smaller subproblems and solving each subproblem recursively?
- Divide and conquer
- Dynamic programming
- Greedy algorithm
- Backtracking
The "divide and conquer" algorithm design technique involves breaking a problem into smaller subproblems and solving each subproblem recursively.
13. What is the time complexity of an algorithm?
- The number of steps required to execute the algorithm
- The amount of memory used by the algorithm
- The analysis of the algorithm's efficiency in terms of input size
- The number of loops in the algorithm
Time complexity is the analysis of an algorithm's efficiency in terms of input size.
14. What is the "Big O notation" used for in algorithm analysis?
- To measure the algorithm's popularity
- To describe the algorithm's internal details
- To express the upper bound of an algorithm's time complexity
- To provide pseudocode for the algorithm
The Big O notation is used to express the upper bound of an algorithm's time complexity.
15. Which of the following time complexities represents the most efficient algorithm?
O(1) represents constant time complexity, which is the most efficient algorithm in terms of time.
16. What is the space complexity of an algorithm?
- The analysis of the algorithm's efficiency in terms of output size
Space complexity is the amount of memory used by the algorithm.
17. What does "optimization" refer to in the context of algorithms?
- The process of making an algorithm more complex
- The process of making an algorithm run slower
- The process of improving an algorithm's efficiency
- The process of making an algorithm more obscure
Optimization in the context of algorithms refers to the process of improving an algorithm's efficiency.
18. Which searching algorithm works by repeatedly dividing the search range in half until the target element is found?
- Linear search
- Binary search
- Quick search
- Merge search
Binary search works by repeatedly dividing the search range in half until the target element is found.
19. Which sorting algorithm has an average time complexity of O(n log n) and is often used for large datasets?
- Bubble sort
- Insertion sort
- Selection sort
Merge sort has an average time complexity of O(n log n) and is efficient for large datasets.
20. What is the primary advantage of quicksort over some other sorting algorithms like bubble sort and insertion sort?
- Quicksort always has a time complexity of O(1).
- Quicksort is a stable sorting algorithm.
- Quicksort has an average time complexity of O(n log n).
- Quicksort uses fewer comparisons.
Quicksort has an average time complexity of O(n log n), which is more efficient than the average case time complexity of bubble sort and insertion sort.
21. Which sorting algorithm repeatedly selects the smallest element from the unsorted part of the array and places it at the beginning of the sorted part?
Selection sort repeatedly selects the smallest element from the unsorted part and places it at the beginning of the sorted part.
22. What is the time complexity of the bubble sort algorithm in the worst-case scenario?
The worst-case time complexity of the bubble sort algorithm is O(n^2).
23. What data structure represents a collection of nodes connected by edges, where each edge has a direction?
- Linked list
A graph represents a collection of nodes connected by edges, where edges can have directions.
24. In a binary tree, how many children can each node have at most?
In a binary tree, each node can have at most two children: a left child and a right child.
25. What is the root node in a tree data structure?
- The node with the highest value
- The first node in the tree
- The node with the lowest value
- The topmost node from which all other nodes descend
The root node in a tree data structure is the topmost node from which all other nodes descend.
26. Which traversal method starts from the root node and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking?
- Inorder traversal
- Preorder traversal
- Postorder traversal
- Depth-first traversal
Preorder traversal starts from the root node and explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking.
27. What is a common application of breadth-first search (BFS) in graph algorithms?
- Finding the shortest path between two nodes
- Sorting the nodes in a graph
- Calculating the depth of a tree
- Traversing a tree in preorder
A common application of breadth-first search (BFS) is finding the shortest path between two nodes in a graph.
28. What is dynamic programming commonly used for in algorithm design?
- Solving problems that cannot be solved by algorithms
- Solving problems by breaking them into smaller subproblems and caching their solutions
- Creating algorithms without any optimization
- Generating random solutions to problems
Dynamic programming is commonly used for solving problems by breaking them into smaller subproblems and caching their solutions to avoid redundant computation.
29. What is memoization in the context of dynamic programming?
- A technique for generating random numbers
- A method for optimizing algorithms using parallel processing
- Caching and reusing previously computed results to avoid redundant calculations
- A type of sorting algorithm
Memoization in dynamic programming involves caching and reusing previously computed results to avoid redundant calculations.
30. Which dynamic programming technique typically uses a table to store and retrieve solutions to subproblems?
- Memoization
Tabulation is a dynamic programming technique that typically uses a table to store and retrieve solutions to subproblems.
31. In dynamic programming, what does "optimal substructure" mean?
- The process of finding the best algorithm
- The property that the optimal solution to a problem can be constructed from the optimal solutions of its subproblems
- The use of greedy algorithms
- The analysis of algorithm efficiency
Optimal substructure is the property that the optimal solution to a problem can be constructed from the optimal solutions of its subproblems.
32. What is the primary advantage of dynamic programming over brute-force methods?
- Dynamic programming always produces the correct result.
- Dynamic programming is faster.
- Dynamic programming requires less memory.
- Dynamic programming optimally solves all problems.
The primary advantage of dynamic programming is that it is often faster than brute-force methods because it avoids redundant computations.
33. What is a greedy algorithm in algorithm design?
- An algorithm that always selects the largest available option
- An algorithm that makes a series of choices, each one being the best decision at the moment
- An algorithm that never backtracks
- An algorithm that solves problems by brute force
A greedy algorithm makes a series of choices, each being the best decision at the moment, with the hope of finding a globally optimal solution.
34. In the context of greedy algorithms, what is a "greedy choice property"?
- The property that a locally optimal choice leads to a globally optimal solution
- The property that a greedy algorithm is always the best choice
- The property that a greedy algorithm never makes a mistake
- The property that a greedy algorithm selects the largest option first
The greedy choice property states that a locally optimal choice in a greedy algorithm leads to a globally optimal solution.
35. Which classic greedy algorithm is used to solve the problem of finding the minimum number of coins needed to make change for a given amount of money?
- Kruskal's algorithm
- Huffman coding
- Coin change algorithm
The coin change algorithm is used to find the minimum number of coins needed to make change for a given amount of money.
36. What is the primary drawback of greedy algorithms?
- They are slow and inefficient.
- They can sometimes lead to suboptimal solutions.
- They require a lot of memory.
- They are difficult to implement.
The primary drawback of greedy algorithms is that they can sometimes lead to suboptimal solutions because they make locally optimal choices at each step.
37. What is a "cycle" in a directed graph?
- A path that visits every node exactly once
- A path that visits the same node twice or more, starting and ending at the same node
- A path that visits every node in the graph
- A path that visits all leaf nodes
In a directed graph, a cycle is a path that visits the same node twice or more, starting and ending at the same node.
38. Which algorithm is commonly used to find the shortest path between nodes in a weighted graph?
Dijkstra's algorithm is commonly used to find the shortest path between nodes in a weighted graph.
39. What is a "topological sort" of a directed acyclic graph (DAG)?
- An arrangement of nodes in ascending order based on their values
- An arrangement of nodes in descending order based on their values
- A linear ordering of nodes such that for every directed edge (u, v), node u comes before node v
- A linear ordering of nodes that connects all nodes in a graph
A topological sort of a directed acyclic graph (DAG) is a linear ordering of nodes such that for every directed edge (u, v), node u comes before node v.
40. What is a "spanning tree" of a graph?
- A tree that includes all nodes of the graph
- A tree with the fewest number of nodes
- A tree with the most number of nodes
- A tree with no nodes
A spanning tree of a graph is a tree that includes all nodes of the graph.
41. In dynamic programming, what is "bottom-up" or "tabulation" approach?
- Starting with the largest subproblems and solving them first
- Starting with the smallest subproblems and solving them first
- Starting with the middle-sized subproblems and solving them first
- Starting with the most complex subproblems and solving them first
The "bottom-up" or "tabulation" approach in dynamic programming starts with the smallest subproblems and solves them first, building up to the larger problem.
42. In dynamic programming, what is the "optimal substructure" property?
- The property that an algorithm always produces the optimal solution
- The property that an algorithm never uses subproblems
- The property that the optimal solution can be constructed from optimal solutions of subproblems
- The property that subproblems cannot be solved independently
The "optimal substructure" property in dynamic programming states that the optimal solution can be constructed from optimal solutions of subproblems.
43. What is the purpose of a "memoization table" in dynamic programming?
- To store the algorithm's pseudocode
- To store the names of subproblems
- To cache and retrieve previously computed results of subproblems
- To store debugging information
A memoization table in dynamic programming is used to cache and retrieve previously computed results of subproblems to avoid redundant calculations.
44. What is the "overlap" property in dynamic programming?
- The property that two subproblems share a common solution
- The property that subproblems do not share any common elements
- The property that all subproblems have identical solutions
The "overlap" property in dynamic programming refers to the property that two or more subproblems share a common solution, leading to the need for memoization.
45. In the context of dynamic programming, what is "pruning"?
- The process of removing nodes from a graph
- The process of reducing the complexity of an algorithm
- The process of removing unnecessary branches from a search
- The process of rearranging data structures
In dynamic programming, pruning is the process of removing unnecessary branches from a search to reduce computational effort.
46. Which dynamic programming technique uses a bottom-up approach and fills a table iteratively to solve problems?
- Greedy approach
The tabulation technique in dynamic programming uses a bottom-up approach and fills a table iteratively to solve problems.
47. What is a "weighted graph" in graph theory?
- A graph with no edges
- A graph in which each edge has a numerical weight or cost
- A graph with a large number of nodes
- A directed graph
A weighted graph is a graph in which each edge has a numerical weight or cost associated with it.
48. Which graph algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree of a weighted, connected graph?
- Bellman-Ford algorithm
Kruskal's algorithm is used to find the minimum spanning tree of a weighted, connected graph.
49. What is a "strongly connected component" in a directed graph?
- A component that contains only one node
- A component in which any two nodes are connected by a single edge
- A component in which there is a directed path from any node to any other node
- A component with the fewest edges
A strongly connected component in a directed graph is a component in which there is a directed path from any node to any other node within the component.
50. What is a "cycle detection" algorithm used for in graph theory?
- Detecting loops or cycles in a graph
- Finding the maximum flow in a network
A cycle detection algorithm is used to detect loops or cycles in a graph.
Looking for more? Check out the below resources.
Copyright © 2024 | ExamRadar. | Contact Us | Copyright || Terms of Use || Privacy Policy
Math quiz helps us to increase our knowledge. Online math quizzes will take 5 minutes of your time to complete a set of questions on math test quiz which will help you to know how much you know about math quizzes and how much time you need to complete a set of math questions. If you want you can also take printable math quizzes from your home printers and share the questions with your friends.
In set VIII let’s complete 10 easy multiple choice questions on math quizzes.
| = 169 / / / |
Math quiz 1 Math quiz 2 Math quiz 3 Math quiz 4 Math quiz 5 Math quiz 6 Math quiz 7 Math quiz 8 Math quiz 9 Math quiz 10 Math quiz 11 Math quiz 12 Math quiz 13 Math quiz 14 Math quiz 15 Math quiz 16 Math quiz 17 Math quiz 18
Online Math Quiz From Math Quiz to HOME PAGE
Didn't find what you were looking for? Or want to know more information about Math Only Math . Use this Google Search to find what you need.
New! Comments
Share this page: What’s this?
- Preschool Activities
- Kindergarten Math
- 1st Grade Math
- 2nd Grade Math
- 3rd Grade Math
- 4th Grade Math
- 5th Grade Math
- 6th Grade Math
- 7th Grade Math
- 8th Grade Math
- 9th Grade Math
- 10th Grade Math
- 11 & 12 Grade Math
- Concepts of Sets
- Probability
- Boolean Algebra
- Math Coloring Pages
- Multiplication Table
- Cool Maths Games
- Math Flash Cards
- Online Math Quiz
- Math Puzzles
- Binary System
- Math Dictionary
- Conversion Chart
- Homework Sheets
- Math Problem Ans
- Free Math Answers
- Printable Math Sheet
- Funny Math Answers
- Employment Test
- Math Patterns
- Link Partners
- Privacy Policy
| E-mail Address | |
| First Name | |
| to send you Math Only Math. |
Recent Articles
5th grade math problems | table of contents | worksheets |free answers.
Aug 19, 24 02:00 AM
Construction of Perpendicular Lines by Using a Protractor, Set-square
Aug 18, 24 02:47 PM

Constructing a Line Segment |Construction of Line Segment|Constructing
Aug 16, 24 04:35 PM

Construction of a Circle | Working Rules | Step-by-step Explanation |
Aug 13, 24 01:27 AM
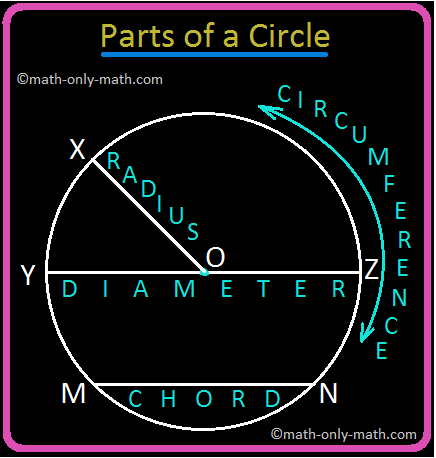
Practical Geometry | Ruler | Set-Squares | Protractor |Compass|Divider
Aug 12, 24 03:20 PM
© and ™ math-only-math.com. All Rights Reserved. 2010 - 2024.
Artificial Intelligence MCQ – Problem-Solving Agents
Here are 25 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to Artificial Intelligence, focusing specifically on Problem-Solving Agents. Each question includes four options, the correct answer, and a brief explanation. These MCQ questions cover various aspects of AI problem-solving agents, including algorithms, search strategies, optimization techniques, and problem-solving methods, providing a comprehensive overview of this area in AI.
1. What is the primary objective of a problem-solving agent in AI?
Explanation:.
A problem-solving agent is designed to find a sequence of actions that leads from the initial state to a goal state, solving a specific problem or achieving a set goal.
2. In AI, a heuristic function is used in problem-solving to:
A heuristic function is used to guide the search process by providing an educated guess about the cost to reach the goal from each node, thus helping to efficiently reduce the search space.
3. Which algorithm is commonly used for pathfinding in AI?
The A* Algorithm is widely used for pathfinding and graph traversal. It efficiently finds the shortest path between two nodes in a graph, combining the features of uniform-cost search and greedy best-first search.
4. What is "backtracking" in AI problem-solving?
Backtracking involves going back to previous states and trying different actions when the current path does not lead to a solution, allowing for exploring alternative solutions.
5. The "branch and bound" technique in AI is used to:
Branch and bound is an algorithmic technique used for solving various optimization problems. It systematically enumerates candidate solutions by branching and then uses a bounding function to eliminate suboptimal solutions.
6. Which of the following is a characteristic of a depth-first search algorithm?
Depth-first search explores as far as possible along each branch before backtracking, going deep into a search tree before exploring siblings of earlier nodes.
7. In AI, "constraint satisfaction problems" are typically solved using:
Constraint satisfaction problems, where a set of constraints must be met, are commonly solved using backtracking algorithms, which incrementally build candidates to the solutions and abandon candidates as soon as they determine that the candidate cannot possibly be completed to a valid solution.
8. The primary goal of "minimax" algorithm in AI is:
The minimax algorithm is used in decision-making and game theory to minimize the possible loss for a worst-case scenario. When dealing with gains, it seeks to maximize the minimum gain.
9. What is "state space" in AI problem-solving?
The state space in AI problem-solving refers to the set of all possible states that can be reached from the initial state by applying a sequence of actions. It is often represented as a graph.
10. In AI, "pruning" in the context of search algorithms refers to:
Pruning in search algorithms involves eliminating paths that are unlikely to lead to the goal or are less optimal, thus reducing the search space and improving efficiency.
11. The "traveling salesman problem" in AI is an example of:
The traveling salesman problem is a classic optimization problem in AI and computer science, where the goal is to find the shortest possible route that visits a set of locations and returns to the origin.
12. "Greedy best-first search" in AI prioritizes:
Greedy best-first search is a search algorithm that prioritizes nodes that seem to be leading to a solution the quickest, often using a heuristic to estimate the cost from the current node to the goal.
13. In AI, "dynamic programming" is used to:
Dynamic programming is a method for solving complex problems by breaking them down into simpler subproblems. It is used when the subproblems are overlapping and the problem exhibits the properties of optimal substructure.
14. The "Monte Carlo Tree Search" algorithm in AI is widely used in:
Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS) is an algorithm used for making decisions in some kinds of game-playing, particularly where it is impractical to search all possible moves due to the complexity of the game.
15. What does an "admissible heuristic" in AI guarantee?
An admissible heuristic is one that never overestimates the cost to reach the goal. In heuristic search algorithms, using an admissible heuristic guarantees finding an optimal solution.
16. The concept of "hill climbing" in AI problem solving is similar to:
Hill climbing in AI is a mathematical optimization technique which belongs to the family of local search. It is used to solve computational problems by continuously moving in the direction of increasing elevation or value.
17. The "no free lunch theorem" in AI implies that:
The "no free lunch" theorem states that no one algorithm works best for every problem. It implies that each problem needs to be approached uniquely and that there's no universally superior method.
18. In AI, "means-ends analysis" is a technique used in:
Means-ends analysis is a problem-solving technique used in AI that involves breaking down the difference between the current state and the goal state into smaller and smaller differences, then achieving those smaller goals.
19. The "Pigeonhole principle" in AI is used to:
In AI and mathematics, the Pigeonhole principle is used to prove that a solution exists under certain conditions. It states that if n items are put into m containers, with n > m, then at least one container must contain more than one item.
20. "Simulated annealing" in AI is inspired by:
Simulated annealing is an optimization algorithm that mimics the process of annealing in metallurgy. It involves heating and controlled cooling of a material to increase the size of its crystals and reduce their defects.
21. In AI, the "Bellman-Ford algorithm" is used for:
The Bellman-Ford algorithm is an algorithm that computes shortest paths from a single source vertex to all of the other vertices in a weighted graph. It's particularly useful for graphs where edge weights may be negative.
22. What is the primary function of "Alpha-Beta pruning" in AI?
Alpha-Beta pruning is a search algorithm that seeks to decrease the number of nodes that are evaluated by the minimax algorithm in its search tree. It is used in game playing to prune away branches that cannot possibly influence the final decision.
23. The "Hungarian algorithm" in AI is best suited for solving:
The Hungarian algorithm, a combinatorial optimization algorithm, is used for solving assignment problems where the goal is to assign resources or tasks to agents in the most effective way.
24. In problem-solving, "depth-limited search" is used to:
Depth-limited search is a modification of depth-first search, where the search is limited to a specific depth. This prevents the algorithm from going down infinitely deep paths and helps manage the use of memory.
25. "Bidirectional search" in AI problem solving is used to:
Bidirectional search is an efficient search strategy that runs two simultaneous searches: one forward from the initial state and the other backward from the goal, stopping when the two meet. This approach can drastically reduce the amount of required exploration.
Related MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) :
Artificial intelligence mcq – agents, artificial intelligence mcq – natural language processing, artificial intelligence mcq – partial order planning, artificial intelligence mcq – expert systems, artificial intelligence mcq – fuzzy logic, artificial intelligence mcq – neural networks, artificial intelligence mcq – robotics, artificial intelligence mcq – rule-based system, artificial intelligence mcq – semantic networks, artificial intelligence mcq – bayesian networks, artificial intelligence mcq – alpha beta pruning, artificial intelligence mcq – text mining, leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Artificial Intelligence Questions and Answers – Problem Solving
This set of Artificial Intelligence Multiple Choice Questions & Answers (MCQs) focuses on “Problem Solving”.
Sanfoundry Global Education & Learning Series – Artificial Intelligence.
- Practice Computer Science MCQs
- Check Artificial Intelligence Books
- Apply for Computer Science Internship
- Check Computer Science Books
Recommended Articles:
- Artificial Intelligence Questions & Answers – Agents
- Artificial Intelligence Questions and Answers – Artificial Intelligence Algorithms
- Artificial Intelligence Questions and Answers – Game Theory
- Artificial Intelligence Questions & Answers – State Space Search
- Artificial Intelligence Questions and Answers – Artificial Intelligence Agents
- Artificial Intelligence Questions and Answers – Uncertain Knowledge and Reasoning
- Artificial Intelligence Questions and Answers – Intelligent Agents and Environment
- Artificial Intelligence Questions and Answers – Partial Order Planning
- Artificial Intelligence Questions & Answers – Online Search Agent
- Artificial Intelligence Questions & Answers – Agent Architecture
- Artificial Intelligence MCQ Questions
- Automata Theory MCQ Questions
- C++ Algorithm Library
- Searching and Sorting Algorithms in C
- Basic Chemical Engineering MCQ Questions
- Event Handling in Java with Examples
- Engineering Chemistry II MCQ Questions
- Unit Processes MCQ Questions
- Engineering Mechanics MCQ Questions
- Aircraft Performance MCQ Questions

PERMUTATION PRACTICE PROBLEMS WITH ANSWERS
Problem 1 :
Determine the number of permutations of the letters of the word SIMPLE if all are taken at a time?
Number of letters in the word "SIMPLE" = 6
All are unique letters.
Number of permutation = 6 P 6 = 6!
= 6 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1
= 720
Hence total number of permutation is 720.
Problem 2 :
A test consists of 10 multiple choice questions. In how many ways can the test be answered if
(i) Each question has four choices?
(ii) The first four questions have three choices and the remaining have five choices?
(iii) Question number n has n + 1 choices?
Number of ways to answer 1 st question = 4
Number of ways to answer 2 nd question = 4
Number of ways to answer 3 rd question = 4
............................
Number of ways = 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 4
= 4 10
Hence the total number of ways = 4 10
Number of ways to answer 1 st question = 3
Number of ways to answer 2 nd question = 3
Number of ways to answer 3 rd question = 3
Number of ways to answer 4 th question = 3
Number of ways to answer 5 th question = 5
Number of ways to answer 6 th question = 5
..............................
Number of ways = 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 5
= 3 4 ⋅ 5 6
Hence the total number of ways is 3 4 ⋅ 5 6 .
Number of ways to answer 1 st question = 2
Number of ways to answer 2 nd question = 3
Number of ways to answer 4 th question = 5
...................
Number of ways to answer 10 th question = 11
Number of ways = 1 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 6 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 8 ⋅ 9 ⋅ 10 ⋅ 11
= 11!
Hence the total number of ways is 11!.
Kindly mail your feedback to [email protected]
We always appreciate your feedback.
© All rights reserved. onlinemath4all.com
- Sat Math Practice
- SAT Math Worksheets
- PEMDAS Rule
- BODMAS rule
- GEMDAS Order of Operations
- Math Calculators
- Transformations of Functions
- Order of rotational symmetry
- Lines of symmetry
- Compound Angles
- Quantitative Aptitude Tricks
- Trigonometric ratio table
- Word Problems
- Times Table Shortcuts
- 10th CBSE solution
- PSAT Math Preparation
- Privacy Policy
- Laws of Exponents
Recent Articles
Digital sat math problems and solutions (part - 30).
Aug 19, 24 08:09 AM
SAT Math Resources (Videos, Concepts, Worksheets and More)
Aug 19, 24 08:07 AM
Solving Exponential Equations Problems and Solutions (Part -2)
Aug 18, 24 11:16 PM
Multiples Questions

Multiples questions are provided here with their solutions to help students practice and understand the concept of factors and multiples . Practising these questions will be beneficial for students in lower grades. We recommend students to practice these questions within a time limit this will increase their solving speed.
Also, Check Factors and Multiples Worksheets .
Multiples of any number are the product of the given number with natural numbers. For example, the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, … In other words, we can say multiples of a number are those numbers which come in times table of that number.
Multiples Questions with Solution
Let us solve some questions based on multiples of a number.
Question 1: List the first 10 multiples of the following numbers:
(i) The first 10 multiples of 12 are
| 12 × 1 | 12 |
| 12 × 2 | 24 |
| 12 × 3 | 36 |
| 12 × 4 | 48 |
| 12 × 5 | 60 |
| 12 × 6 | 72 |
| 12 × 7 | 84 |
| 12 × 8 | 96 |
| 12 × 9 | 108 |
| 12 × 10 | 120 |
(ii) The first 10 multiples of 52 are
| 52 × 1 | 52 |
| 52 × 2 | 104 |
| 52 × 3 | 156 |
| 52 × 4 | 208 |
| 52 × 5 | 260 |
| 52 × 6 | 312 |
| 52 × 7 | 364 |
| 52 × 8 | 416 |
| 52 × 9 | 468 |
| 52 × 10 | 520 |
(iii) The first 10 multiples of 9 are
| 9 × 1 | 9 |
| 9 × 2 | 18 |
| 9 × 3 | 27 |
| 9 × 4 | 36 |
| 9 × 5 | 45 |
| 9 × 6 | 54 |
| 9 × 7 | 63 |
| 9 × 8 | 72 |
| 9 × 9 | 81 |
| 9 × 10 | 90 |
Question 2: Find the first three common multiples of 2 and 14.
Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14 , 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26, 28 , 30, 32, 34, 36, 38, 40, 42 , …
Multiples of 14: 14 , 28 , 42 , 56, 70, 84, 98, …
Therefore, the first three common multiples of 2 and 14 are 14, 28 and 42.
|
As there is an infinite number of multiples of a number, so it is not possible to find all the common multiples of a number, but we can find the least common multiple of two or more numbers. For example, in the above question the LCM(2, 14) = 14. Thus, 14 is the lowest number which both 2 and 14 can divide. Learn more about . |
- HCF of Numbers
- Prime Factorization and Division Method for LCM and HCF
- Prime Factorization
Question 3: Find the smallest number whose factors are 2, 3 and 7.
The smallest number whose factors are 2,3 and 7 is the LCM(2, 3, 7)
Now, LCM (2, 3, 7) = 2 × 3 × 7 = 42
∴ 42 is the smallest number whose factors are 2, 3 and 7.
Question 4: There are 62 students in a classroom. If 310 notebooks are to be distributed among them, find how many notebooks each student gets.
Total number of students = 62
Total number of notebooks = 310
We observe that 310 is the 5th multiple of 62, that is, 62 × 5 = 310.
∴ each student gets 5 notebooks.
Question 5: How many complete weeks are there in a leap year?
Number of days in a week = 7
Number of days in a leap year = 366
Now, 7 × 52 = 364 and 7 × 53 = 371 such that 364 < 366 < 371
Therefore, there are 52 complete weeks are there in a leap year.
Question 6: Is 111 divisible by 3?
Now 3 × 37 = 111, that is 111 is a multiple of 3.
∴ 111 is divisible by 3.
Question 7: If there are 20 mangoes in a basket. How many mangoes will be there in 30 such baskets?
Number of mangoes in one basket = 20
Number of baskets = 30
Total number of mangoes in 30 baskets = 20 × 30 = 600.
Therefore, there are 600 mangoes in 30 baskets.
Question 8: Which of the following is not a multiple of 23?
Now, 23 × 6 = 138, 23 × 8 = 184 and 23 × 11 = 253, so clearly 254 is not a multiple of 23.
(c) is the answer.
Question 9: 72 books are kept on a bookshelf with 8 shelves. If each shelf has the same number of books. Find the number of books on each shelf.
Total number of books = 72
Number of shelves = 8
Now, 8 × 9 = 72
Therefore, there are 9 books on each shelf.
Question 10: Arifa daily practices 5 maths sums. How many sums did she solve in the month of July?
Number of questions she daily solves = 5
Number of days in July = 31
Total number of questions = 31 × 5 = 155
Therefore, she solved 155 questions in the month of July.
Video Lesson on Common Multiples and Its Applications
|
|
|
|
|
|
Practice Questions on Multiples
1. Find the first five multiples of 13.
2. Find the first three common multiples of 6 and 18.
3. Find the lowest common multiple of 2, 14, and 16.
4. Niya ate 4 chocolates every day for a week. How many total chocolates did she eat?
5. List all the numbers whose multiple is 286.
Keep visiting BYJU’S to get more such study materials explained in an easy and concise way. Also, register now and get access to 1000+ hours of video lessons on different topics.
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
- Data Science
- Trending Now
- Data Structures
- System Design
- Foundational Courses
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- Data Science Using Python
- Web Development
- Web Browser
- Design Patterns
- Software Development
- Product Management
- Programming
Top 50 Algorithms MCQs with Answers
External entities in DFD are shown by:-
What is the time complexity of Floyd–Warshall algorithm to calculate all pair shortest path in a graph with n vertices?
O(n 2log(n) )
Theta(n 2log(n) )
Theta(n 4 )
Theta(n 3 )
The following statement is valid. log(n!) = [Tex]\\theta [/Tex](n log n).
Which of the following is not true about comparison-based sorting algorithms?
The minimum possible time complexity of a comparison-based sorting algorithm is O(n(log(n)) for a random input array
Any comparison based sorting algorithm can be made stable by using position as a criteria when two elements are compared
Counting Sort is not a comparison based sorting algorithm
Heap Sort is not a comparison based sorting algorithm.
Which of the following is not O(n 2 )?
n 3 /(sqrt(n))
- Selection sort
- Bubble sort
- Insertion sort
- Greedy method
- Backtracking
- Dynamic programming
- Divide and Conquer
If we use Radix Sort to sort n integers in the range (n k/2 ,n k ], for some k>0 which is independent of n, the time taken would be?
Quick sort is run on 2 inputs shown below to sort in ascending order
Let C1 and C2 be the number of comparisons made for A and B respectively. Then
C1 < C2
Cannot say anything for arbitrary n
Question 10
Assume that we use Bubble Sort to sort n distinct elements in ascending order. When does the best case of Bubble Sort occur?
When elements are sorted in ascending order
When elements are sorted in descending order
When elements are not sorted by any order
There is no best case for Bubble Sort. It always takes O(n*n) time
There are 50 questions to complete.
1000+ Problem Solving MCQ Questions and Answers - 1
- engineering-questions
Question: 1
The maximum length of the data variable can hold is called
(A) header file
(B) length of a variable
(C) field width of a variable
(D) width of a variable
field width of a variable
Question: 2
The program created with the help of an editor is called
(A) source program or source code
(B) linking
(C) source program
(D) object program
source program or source code
Question: 3
Which of the following is easier to be transformed into a computer program?
(A) algorithm
(B) flow chart
(C) pseudo code
(D) none of these
pseudo code
Question: 4
The function printf() is used to print any combination of
(A) character
(C) string, number and character
string, number and character
Question: 5
The use of structure tags allow the structure to be
(A) separate from the constant declaration
(B) separate from the constant declaration
(C) separate from the variable declaration
(D) with the variable declaration
separate from the variable declaration
Model MCQ Online Test
Error Report!
- advanced communication
- 1000+ Problem Solving MCQ Questions and Answers
- 1000+ Problem Solving Quiz Questions and Answers Pdf
REGISTER TO GET FREE UPDATES
2024 © MeritNotes

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Get Problem Solving Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ Quiz) with answers and detailed solutions. ... Problem Solving Question 5: Recently you are appointed as the head of a department that looks after conserving trees in the area and prevention of illegal transport of logs. While traveling by public bus you got a chance to hear a conversation ...
Khan Academy's 100,000+ free practice questions give instant feedback, don't need to be graded, and don't require a printer. Math Worksheets. Khan Academy. Math worksheets take forever to hunt down across the internet. Khan Academy is your one-stop-shop for practice from arithmetic to calculus. Math worksheets can vary in quality from ...
Answer ALL questions (or only a few at a time), then use the BUTTON at the BOTTOM of the page to check your answers. If you are told that an answer is incorrect, go back and redo that question and CHECK ANSWERS again. You may CHECK ANSWERS at any time. You may use your graphing calculator when working on these problems.
1. The answer is b) 2/3. To solve, your child must reduce the fraction 8/12. Divide the numerator and denominator by four, which is 2/3. 2. The solution is c) 30 because 10 x 3 = 30. 3. For this question, the answer is d) 1:4. For this problem, your child may get the wrong answer if he doesn't read carefully.
College Algebra Questions with Answers. sample 1.(multiple choice questions). Also Detailed solutions with full explanations are included sample 2. (multiple choice questions) College Algebra Problems with Answers. sample 1: Quadratic Functions. sample 2: Composite and Inverse Functions. sample 3: Exponential and Logarithmic Functions
Free Basic Math Practice test questions including- Long & Short Division, Multiplication, Decimals, Fractions, and Percent ... decimals, percent, exponents word problems and more! Test your math skills! Also includes tutorials! Get Started. Answer Key. 1. A 2. B 3. C 4. C 5. A 6. D 7. C 8. A 9. A 10. C. ... How to Answer Basic Math Multiple ...
Two-Step Equations Exercises. Hone your skills in solving two-step equations because it will serve as your foundation when solving multi-step equations. I prepared eight (8) two-step equations problems with complete solutions to get you rolling. My advice is for you to solve them by hand using a pencil or pen and paper.
There are 10 official practice tests from the 2016-2023 version of the SAT. Each test comes with an answer key and in-depth answer explanations to help you understand why you got questions wrong. Practice Test 1: Questions | Answers | Answer Explanations. Practice Test 2: Questions | Answers | Answer Explanations.
Welcome to the math word problems worksheets page at Math-Drills.com! On this page, you will find Math word and story problems worksheets with single- and multi-step solutions on a variety of math topics including addition, multiplication, subtraction, division and other math topics. It is usually a good idea to ensure students already have a strategy or two in place to complete the math ...
Download Article. 1. Study in advance for the exam. To do well on a multiple choice exam, you should make a point of studying ahead of your exam date. Make a study schedule for the exam and set aside the necessary time for studying. [11] Study in the week leading up to the exam or several days beforehand.
Multi-Step Equations Practice Problems with Answers. For this exercise, I have prepared seven (7) multi-step equations for you to practice. If you feel the need to review the techniques involved in solving multi-step equations, take a short detour to review my other lesson about it. Click the link below to take you there!
Answer Key. 5. This is an inverse ratio problem. 1/x = 1/a + 1/b where a is the time Sally can paint a house, b is the time John can paint a house, x is the time Sally and John can together paint a house. So, 1/x = 1/4 + 1/6 …. We use the least common multiple in the denominator that is 24: 1/x = 6/24 + 4/24. 1/x = 10/24.
Creativity can help you identify a problem but not solve it. Creativity is fixed -- you either have it or you don't. Creativity can be increased via many different techniques. Someone who has never experienced the problem before. Preparing to solve the problem might include brainstorming.
The Mathematics multiple-choice questions test your ability to solve mathematical problems involving arithmetic, algebra I and II, geometry, data interpretation, basic statistics and probability, and word problems by using problem-solving insight, logic, and the application of basic skills. You should have a total of about 42 to 46 multiple ...
The Tower of London problem-solving task was developed byShackleton (1982)Shallice (1982)Sheriff (1982)Sherrington (1982)Answer: B2. The process of breaking down goals into subgoals is termed Multiple Choice Questions | Online Resources
Here are 50 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) on the fundamentals of algorithms and problem-solving, along with their answers and explanations.These questions continue to cover various aspects of algorithms, graph theory, problem-solving strategies, and their applications,providing a comprehensive overview of these fundamental concepts.
Math quiz helps us to increase our knowledge. Online math quizzes will take 5 minutes of your time to complete a set of questions on math test quiz which will help you to know how much you know about math quizzes and how much time you need to complete a set of math questions. If you want you can also take printable math quizzes from your home ...
Here are 25 multiple-choice questions (MCQs) related to Artificial Intelligence, focusing specifically on Problem-Solving Agents. Each question includes four options, the correct answer, and a brief explanation. These MCQ questions cover various aspects of AI problem-solving agents, including algorithms, search strategies, optimization ...
A solution to a problem is a path from the initial state to a goal state. Solution quality is measured by the path cost function, and an optimal solution has the highest path cost among all solutions. a) True. b) False. View Answer. 8. The process of removing detail from a given state representation is called ______.
Problem 1 : Determine the number of permutations of the letters of the word SIMPLE if all are taken at a time? Solution : Number of letters in the word "SIMPLE" = 6. All are unique letters. Number of permutation = 6 P 6 = 6! = 6 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 4 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 1. = 720. Hence total number of permutation is 720.
Multiples Questions with Solution. Let us solve some questions based on multiples of a number. Question 1: List the first 10 multiples of the following numbers: (i) 12. (ii) 52. (ii) 9. Solution: (i) The first 10 multiples of 12 are. 12 × 1.
Top 50 Algorithms MCQs with Answers Quiz will help you to test and validate your DSA Quiz knowledge. It covers a variety of questions, from basic to advanced. The quiz contains 50 questions. You just have to assess all the given options and click on the correct answer.
GATE Problem Solving MCQ, Quiz, Objective Type, Multiple Choice, Online Test, Question Bank, Mock Test Questions and Answers Pdf Free Download for various Interviews, Competitive Exams and Entrance Test. - 1