Exploring Senior High School Students’ Academic Writing Difficulties: Towards an Academic Writing Model
IOER International Multidisciplinary Research Journal, Volume 2, Issue 1, March 2020
10 Pages Posted: 9 Apr 2020

Mark Joshua D. Roxas
University of Perpetual Help – Molino, Cavite, Philippines
Date Written: 2020
Undeniably, writing is an indispensable skill in different contexts of life. It is one of the pivotal components of education. With the advent of the K-12 Basic Education Curriculum, students are confronted with different academic writing tasks through the English for Academic and Professional Purposes and Practical Research courses. Despite the efforts of the educational sector to improve students’ writing skills, many students still experience difficulties in academic writing. Therefore, there is a need to fill the gap and advance an in-depth understanding of students’ academic writing difficulties. In order to satisfy the said aim, this Qualitative study grounds on Flower and Hayes’ (1981) Cognitive Process Theory of Writing. Focus group discussion of 14 purposively selected Grade 11 Senior High School students was carried out. The results expound on the different Academic Writing difficulties encountered by the participants in terms of the Task Environment, Writers’ Long-Term Memory and Writing Process. A model for teaching academic writing was formulated anchored on the identified difficulties. The model will benefit the teachers as it may serve as a guide in more effective and efficient teaching of academic writing.
Keywords: Academic writing, writing difficulties, senior high school, process writing, Philippines
Suggested Citation: Suggested Citation
Mark Joshua D. Roxas (Contact Author)
University of perpetual help – molino, cavite, philippines ( email ).
4200 Philippines
Do you have a job opening that you would like to promote on SSRN?
Paper statistics, related ejournals, pedagogy ejournal.
Subscribe to this fee journal for more curated articles on this topic
Cognitive Psychology eJournal
Developmental psychology ejournal.
Effective writing instruction for students in grades 6 to 12: a best evidence meta-analysis
- Published: 24 April 2024
Cite this article

- Steve Graham ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-6702-5865 1 ,
- Yucheng Cao 2 ,
- Young-Suk Grace Kim 3 ,
- Joongwon Lee 4 ,
- Tamara Tate 3 ,
- Penelope Collins 3 ,
- Minkyung Cho 3 ,
- Youngsun Moon 3 ,
- Huy Quoc Chung 3 &
- Carol Booth Olson 3
648 Accesses
Explore all metrics
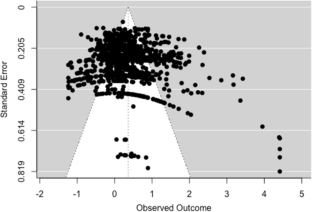
The current best evidence meta-analysis reanalyzed the data from a meta-analysis by Graham et al. (J Educ Psychol 115:1004–1027, 2023). This meta-analysis and the prior one examined if teaching writing improved the writing of students in Grades 6 to 12, examining effects from writing intervention studies employing experimental and quasi-experimental designs (with pretests). In contrast to the prior meta-analysis, we eliminated all N of 1 treatment/control comparisons, studies with an attrition rate over 20%, studies that did not control for teacher effects, and studies that did not contain at least one reliable writing measure (0.70 or greater). Any writing outcome that was not reliable was also eliminated. Across 148 independent treatment/control comparisons, yielding 1,076 writing effect sizes (ESs) involving 22,838 students, teaching writing resulted in a positive and statistically detectable impact on students’ writing (ES = 0.38). Further, six of the 10 writing treatments tested in four or more independent comparisons improved students’ performance. This included the process approach to writing (0.75), strategy instruction (0.59), transcription instruction (0.54), feedback (0.30), pre-writing activities (0.32), and peer assistance (0.59). In addition, the Self-Regulated Strategy Development model for teaching writing strategies yielded a statistically significant ES of 0.84, whereas other approaches to teaching writing strategies resulted in a statistically significant ES of 0.51. The findings from this meta-analysis and the Graham et al. (2023) review which included studies that were methodologically weaker were compared. Implications for practice, research, and theory are presented.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Similar content being viewed by others
Improving Writing Skills of Students in Turkey: a Meta-analysis of Writing Interventions

Best Practices in Writing Instruction for Students with Learning Disabilities
The effectiveness of self-regulated strategy development on improving English writing: Evidence from the last decade
References marked with an asterisk indicate studies included in the meta-analysis.
*Adams, V., (1971). A study of the effects of two methods of teaching composition to twelfth Graders [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
Aiken, L., West, S., Schwalm, D., Carroll, J., & Hsiung, S. (1998). Comparison of a randomized and two quasi-experimental designs in a single outcome evaluation. Evaluation Review, 22 , 207–244. https://doi.org/10.1177/0193841X9802200203
Article Google Scholar
*Al Shaheb, M. N. A. (n.d.). The effect of self-regulated strategy development on persuasive writing, self-efficacy, and attitude: A mixed-methods, quasi-experimental study in Grade 6 in Lebanon [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Université Saint-Joseph, Beirut, Lebanon.
Applebee, A., & Langer, J. (2011). A snapshot of writing instruction in middle schools and high schools. English Journal, 100 , 14–27.
Bangert-Drowns, R. (1993). The word processor as an instructional tool: A meta-analysis of word processing in writing instruction. Review of Educational Research, 63 , 69–93. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543063001069
Bangert-Drowns, R., Hurley, M., & Wilkinson, B. (2004). The effects of school-based writing to-learn interventions on academic achievement: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 74 (1), 29–58. https://doi.org/10.3102/00346543074001029
*Barrot, J. S. (2018). Using the sociocognitive-transformative approach in writing classrooms: Effects on L2 learners’ writing performance. Reading & Writing Quarterly, 34 (2), 187–201. https://doi.org/10.1080/10573569.2017.1387631
*Barton, H. (2018). Writing, collaborating, and cultivating: Building writing self-efficacy and skills through a student-centric, student-led writing center . Doctor of Education in Secondary Education Dissertations. 13 . https://digitalcommons.kennesaw.edu/seceddoc_etd/13
*Benson, N. L. (1979). The effects of peer feedback during the writing process on writing performance, revision behavior, and attitude toward writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of Colorado.
*Berman, R. (1994). Learners’ transfer of writing skills between languages. TESL Canada Journal, 12 (1), 29–46.
*Black, J. G. (1995). Teaching elements of written composition through use of classical music and art: the effects on high school students' writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of California, Riverside.
Bloom, B., Engelhart, M., Furst, E., Hill, W., & Krathwohl, D. (1956). Taxonomy of educational objectives: The classification of educational goals. Handbook I: Cognitive domain . David McKay Company.
*Braaksma, M. (2002). Observational learning in argumentative writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Amsterdam: University of Amsterdam.
*Braaksma, M., Rijlaarsdam, G. C. W., & van den Bergh, H. H. (2018). Effects of hypertext writing and observational learning on content knowledge acquisition, self-efficacy, and text quality: Two experimental studies exploring aptitude treatment interactions. Journal of Writing Research, 9 (3), 259–300. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2018.09.03.02
*Brantley, H., & Small, D. (1991). Effects of self evaluation on written composition skill in learning disabled children . U.S. Department of Education.
Google Scholar
*Brewer, D. (2002). Teaching writing in science through the use of a writing rubric [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Michigan-Flint.
Cheung, A., & Slavin, R. (2016). How methodological features affect effect sizes in education. Educational Researcher, 45 , 283–292. https://doi.org/10.3102/0013189X16656615
*Christensen, C. A. (2004). Relationship between orthographic-motor integration and computer use for the production of creative and well-structured written text. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 74 (4), 551–564. https://doi.org/10.1348/0007099042376373
*Chung, H. Q., Chen, V., & Olson, C. B. (2021). The impact of self-assessment, planning and goal setting, and reflection before and after revision on student self-efficacy and writing performance. Reading and Writing, 34 , 1885–1913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10186-x
*Combs, W. E. (1976). Further effects of sentence-combining practice on writing ability. Research in the Teaching of English, 10 (2), 137–149.
*Combs, W. E. (1977). Sentence-combining practice: Do gains in judgments of writing “quality” persist? The Journal of Educational Research, 70 (6), 318–321. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.1977.10885014
*Conklin, E. (2007). Concept mapping: Impact on content and organization of technical writing in science [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Walden University.
*Corey, D. R. (1990). The effects of concurrent instruction in composition and speech upon the composition writing holistic scores and sense of audience of a ninth-grade student population [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The Union for Experimenting Colleges and Universities.
Cortina, J., & Nouri, H. (2000). Effect size for ANOVA design . Sage.
Book Google Scholar
*Couzijn, M., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2004). Learning to read and write argumentative text by observation of peer learners. In Rijlaarsdam, G. (Series Ed.) & Rijlaarsdam, G., van den Bergh, H., & Couzijn, M. (Vol. 14 Eds.), Effective learning and teaching of writing , (pp. 241–258). Springer.
Couzijn, M., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2005). Learning to write instructive texts by reader observation and written feedback. In G. Rijlaarsdam, H. van den Bergh, & M. Couzijn (Eds.), Effective learning and teaching of writing (pp. 209–240). Springer.
Chapter Google Scholar
*Covill, A. E. (1996). Students' revision practices and attitudes in response to surface-related feedback as compared to content-related feedback on their writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of Washington.
*Cremin, T., Myhill, D., Eyres, I., Nash, T., Wilson, A., & Oliver, L. (2020). Teachers as writers: Learning together with others. Literacy, 54 (2), 49–59. https://doi.org/10.1111/lit.12201
*Crook, J. D. (1985). Effects of computer-assisted instruction upon seventh-grade students’ growth in writing performance [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Nebraska.
*Crossley, S. A., Roscoe, R., & McNamara, D. S. (2013). Using automated scoring models to detect changes in student writing in an intelligent tutoring system. Paper presented at Proceedings of the Twenty-sixth International Florida Artificial Intelligence Research Society Conference, Florida.
*Crossley, S. A., Varner, L. K., Roscoe, R. D., & McNamara, D. S. (2013). Using automated indices of cohesion to evaluate an intelligent tutoring system and an automated writing evaluation system. In Artificial intelligence in education: 16th international conference, AIED 2013 , Memphis, TN, USA, July 9–13, 2013. Proceedings 16 (pp. 269-278). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg.
*Dailey, E. M. (1992). The relative efficacy of cooperative learning versus individualized learning on the written performance of adolescent students with writing problems [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The Johns Hopkins University.
*Daiute, C., & Kruidenier, J. (1985). A self-questioning strategy to increase young writers’ revising processes. Applied Psycholinguistics, 6 , 307–318. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0142716400006226
*de la Paz, S., & Graham, S. (2002). Explicitly teaching strategies, skills, and knowledge: Writing instruction in middle school classrooms. Journal of Educational Psychology, 94 (4), 687. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-0663.94.4.687
*de la Paz, S., & Wissinger, D. R. (2017). Improving the historical knowledge and writing of students with or at risk for LD. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 50 (6), 658–671. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219416659444
*de la Paz, S., Wissinger, D. R., Gross, M., & Butler, C. (in press). Strategies that promote historical reasoning and contextualization: A pilot intervention with urban high school students. Reading and Writing .
*de Ment, L. (2008). The Relationship of self-evaluation, writing ability, and attitudes toward writing among gifted grade 7 language arts students [Unpublished master’s thesis] Walden University.
*de Smedt, F., & van Keer, H. (2018). Fostering writing in upper primary grades: A study into the distinct and combined impact of explicit instruction and peer assistance. Reading and Writing, 31 , 325–354. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-017-9787-4
*de Smedt, F., Graham, S., & van Keer, H. (2019). The bright and dark side of writing motivation: Effects of explicit instruction and peer assistance. The Journal of Educational Research, 112 (2), 152–167. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2018.1461598
*de Smedt, F., Graham, S., & Van Keer, H. (2020). “It takes two” : The added value of structured peer-assisted writing in explicit writing instruction. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 60 , 101835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2019.101835
Drew, S., Olinghouse, N., Luby-Faggella, M., & Welsh, M. (2017). Framework for disciplinary writing in science Grades 6–12: A national survey. Journal of Educational Psychology, 109 , 935–955. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000186
Dunnagan, K. L. (1990). Seventh grade students’ audience awareness in writing produced within and without the dramatic mode [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The Ohio State University.
*Eliason, R. G. (1994). The effect of selected word processing adjunct programs on the writing of high school students (Publication No. 0426055) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of South Florida.
*Erickson, D. K. (2009). The effects of blogs versus dialogue journals on open-response writing scores and attitudes of grade eight science students (Publication No. 3393920) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Massachusetts, Lowell. ProQuest LLC.
*Espinoza, S. F. (1992). The effects of using a word processor containing grammar and spell checkers on the composition writing of sixth graders [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Texas Tech University.
*Festas, I., Oliveira, A. L., Rebelo, J. A., Damião, M. H., Harris, K., & Graham, S. (2015). Professional development in self-regulated strategy development: Effects on the writing performance of eighth grade Portuguese students. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 40 , 17–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2014.05.004
Fisher, Z., Tipton, E., & Zhipeng, H. (2017). Package ' robumeta'. Retrieved from http://cran.uni-muenster.de/web/packages/robumeta/robumeta.pdf
*Frank, A. R. (2008). The effect of instruction in orthographic conventions and morphological features on the reading fluency and comprehension skills of high-school freshmen [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of San Francisco.
*Franzke, M., Kintsch, E., Caccamise, D., Johnson, N., & Dooley, S. (2005). Summary Street®: Computer support for comprehension and writing. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 33 (1), 53–80. https://doi.org/10.2190/DH8F-QJWM-J457-FQVB
*Frost, K. L. (2008). The effects of automated essay scoring as a high school classroom intervention (Publication No. 3352171) [Doctoral dissertation], University of Nevada, Las Vegas. ProQuest LLC.
*Galbraith, J. (2014). The effect of self-regulation writing strategies and gender on writing self-efficacy and persuasive writing achievement for secondary students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Western Connecticut State University.
*Ganong, F. L. (1974). Teaching writing through the use of a program based on the work of Donald M. Murray [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Boston University.
Goldberg, A., Russell, M., & Cook, A. (2003). The effect of computers on student writing: A meta-analysis of studies from 1992 to 2002. The Journal of Technology, Learning, and Assessment 2 (1). Retrived from https://ejournals.bc.edu/index.php/jtla/article/view/1661
*González-Lamas, J., Cuevas, I., & Mateos, M. (2016). Arguing from sources: Design and evaluation of a programme to improve written argumentation and its impact according to students’ writing beliefs. Journal for the Study of Education and Development, 39 (1), 49–83. https://doi.org/10.1080/02103702.2015.111160
*Grejda, G. F. (1988). The effects of word processing and revision patterns on the writing quality of sixth-grade students (Publication No. 8909998) [Doctoral dissertation], Pennsylvania State University.
Graham, S. (2019). Changing how writing is taught. Review of Research in Education, 43 , 277–303. https://doi.org/10.3102/0091732X18821125
Graham, S. (2018). A revised writer(s)-within-community model of writing. Educational Psychologist, 53 , 258–279. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2018.1481406
Graham, S. (2015). Inaugural editorial for the journal of educational psychology. Journal of Educational Psychology, 107 , 1–2. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000007
Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2018). Evidence-based writing practices: A meta-analysis of existing meta-analyses. In R. Fidalgo, K. R. Harris, & M. Braaksma (Eds.). Design principles for teaching effective writing: Theoretical and empirical grounded principles (pp. 13–37). Hershey, PA: Brill Editions.
Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (1997). It can be taught, but it does not develop naturally: Myths and realities in writing instruction. School Psychology Review, 26 , 414–424. https://doi.org/10.1080/02796015.1997.12085875
Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2014). Conducting high quality writing intervention research: Twelve recommendations. Journal of Writing Research 6, 89–123. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2014.06.02.1
Graham, S., & Hebert, M. (2011). Writing-to-read: A meta-analysis of the impact of writing and writing instruction on reading. Harvard Educational Review, 81, 710–744. https://doi.org/10.17763/haer.81.4.t2k0m13756113566
Graham, S., Hebert, M., & Harris, K. R. (2015). Formative assessment and writing: A meta-analysis. Elementary School Journal, 115 , 524–547. https://doi.org/10.1086/681947
Graham, S., Kim, Y., Cao, Y., Lee, W., Tate, T., Collins, T., Cho, M., Moon, Y., Chung, H., & Olson, C. (2023). A meta-analysis of writing treatments for students in Grades 6 to 12. Journal of Educational Psychology, 115 , 1004–1027. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000819
Graham, S., Kiuhara, S., & MacKay, M. (2020). The effects of writing on learning in science, social studies, and mathematics: A meta-analysis. Review of Educational Research, 90 , 179–226. https://doi.org/10.3102/0034654320914744
Graham, S., Kiuhara, S., McKeown, D., & Harris, K. R. (2012). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for students in the elementary grades. Journal of Educational Psychology, 104 , 879–896. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029185
Graham, S., & Perin, D. (2007). A meta-analysis of writing instruction for adolescent students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 99 , 445–476. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.99.3.445
Graham, S., & Rijlaarsdam, G. (2016). Writing education around the globe: Introduction and call for a new global analysis. Reading & Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 29 , 781–792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-016-9640-1
*Hamilton, H. (1960). A combined auditory-visual syllabification approach to the study of spelling [Unpublished master’s thesis]. Texas Technological College.
*Hammar, D. D. (1986). The effectiveness of computer-assisted writing instruction for juniors who have failed the Regents competency test in writing (Publication No. 8704355) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Rochester.
Harris, K. R., & Graham, S. (1992). Self-regulated strategy development: A part of the writing process. In M. Pressley, K. R. Harris, & J. Guthrie (Eds.), Promoting academic competence and literacy in school (pp. 277–309). Academic Press.
*Harville, M. L. (2001). A study of computer-assisted expository writing of middle school students with special learning needs [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University
Hedges, L. V., Tipton, E., & Johnson, M. C. (2010). Robust variance estimation in meta-regression with dependent effect size estimates. Research Synthesis Methods, 1 (1), 39–65. https://doi.org/10.1002/jrsm.5
*Hickerson, B. L. (1987). Critical thinking, reading, and writing: developing a schema for expository text through direct instruction in analysis of text structure (metacognition, webbing, mapping) [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. North Texas State University.
*Higgins, P. D. (2013). The effects of using a critical thinking graphic organizer to improve Connecticut academic performance test interdisciplinary writing assessment scores [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Western Connecticut State University.
*Hill, B. G. (1990). A comparison of the writing quality of paired and unpaired students composing at the computer [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Texas at Austin.
Hillocks, G. (2008). Writing in secondary schools. In C. Bazerman (Ed.), Handbook of research on writing: History, society, school, individual, text (pp. 311–329). Routledge.
Hillocks, G. J. (1986). Research on written composition: New directions for teaching . National Council of Teachers of English.
*Hillocks, G. (1982). The interaction of instruction, teacher comment, and revision in teaching the composing process. Research in the Teaching of English, 16 (3), 261–278.
*Hisgen, S., Barwasser, A., Wellmann, T., & Grünke, M. (2020). The effects of a multicomponent strategy instruction on the argumentative writing performance of low-achieving secondary students. Learning Disabilities: A Contemporary Journal, 18 (1), 93–110.
Higgins, J. P. T., & Green, S. (Eds.). (2011). Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions (Version 5.1.0). Retrieved from http://handbook.cochrane.org
*Holley, C. A. B. (1990). The effects of peer editing as an instructional method on the writing proficiency of selected high school students in Alabama [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Alabama.
Holliway, D., & McCutchen, D. (2004). Audience perspective in young writers’ composing and revising. In L. Allal, L. Chanquoy, & P. Largy (Eds.), Revision: Cognitive and instructional processes (pp. 87–101). Kluwer.
*Hoogeveen, M. C. E. J. (2013). Writing with peer response using genre knowledge: A classroom intervention study [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Twente.
*Hoogeveen, M., & van Gelderen, A. (2015). Effects of peer response using genre knowledge on writing quality: A randomized control trial. The Elementary School Journal, 116 (2), 265–290. https://doi.org/10.1086/684129
*Hoogeveen, M., & van Gelderen, A. (2018). Writing with peer response using different types of genre knowledge: Effects on linguistic features and revisions of sixth-grade writers. The Journal of Educational Research, 111 (1), 66–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2016.1190913
Hopewell, S., Loudon, K., Clarke, M. J., Oxman, A. D., & Dickersin, K. (2009). Publication bias in clinical trials due to statistical significance or direction of trial results. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 1 , 1–25. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.MR000006.pub3
*Iordanou, K., & Constantinou, C. P. (2015). Supporting use of evidence in argumentation through practice in argumentation and reflection in the context of SOCRATES learning environment. Science Education, 99 (2), 282–311. https://doi.org/10.1002/sce.21152
*Jacoby, K. E. (1990). Remove the dust covers and let the children play: An investigation into the effectiveness of computers in spelling drill and practice in the classroom [Unpublished master’s thesis]. University of New England.
*Jeroski, S. (1982). Competence in written expression: Interactions between instruction and individual differences among junior high school students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of British Columbia.
*Jones, J. L. (1966). Effects of spelling instruction in eighth grade biological science upon scientific spelling, vocabulary, and reading comprehension; general spelling, vocabulary and reading comprehension; science progress; and science achievement [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Maryland.
*Jones, S., Myhill, D., & Bailey, T. (2013). Grammar for writing? An investigation of the effects of contextualised grammar teaching on students’ writing. Reading and Writing, 26 (8), 1241–1263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-012-9416-1
*Kaffar, B. (1993). Exploring the effects of online instructional models on the writing achievement of high school students with and without disabilities [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Nevada.
*Kasparek, R. F. (1994). Effects of integrated writing on attitude and algebra performance of high school students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of North Carolina at Greensboro.
*Kelley, K. R. (1984). The effect of writing instruction on reading comprehension and story writing ability [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Pittsburgh.
*Kennedy, K. A. (2008). Validating FOLA: A randomized writing experiment [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Southern California.
*Kim, J. S., Olson, C. B., Scarcella, R., Kramer, J., Pearson, M., van Dyk, D., Collins, P., & Land, R. E. (2011). A randomized experiment of a cognitive strategies approach to text-based analytical writing for mainstreamed Latino English language learners in grades 6 to 12. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 4 (3), 231–263. https://doi.org/10.1080/19345747.2010.523513
Koster, M., Tribushinina, E., de Jong, P. F., & van den Bergh, H. (2015). Teaching children to write: A meta-analysis of writing intervention research. Journal of Writing Research, 7 (2), 249–274. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2015.07.02.2
*Kuscenko, D. (2018). Supporting collaborative writing in secondary Language Arts: A revision decision method intervention [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Lehigh University.
*Lane, R. A. J. (2003). “Keep cool and DECIDE”: Using discussion and writing instruction to improve the problem-solving skills of adolescent, urban students, labeled learning disabled [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University.
*Lange, A. A., Mulhern, G., & Wylie, J. (2009). Proofreading using an assistive software homophone tool. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 42 (4), 322–335. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022219408331035
*Laysears-Smith, R. R. (2005). Students' attitudes about structured journal writing and their perceptions of their self-esteem in an urban career and technical classroom [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Temple University.
*Lee, J., & Schallert, D. L. (2016). Exploring the reading-writing connection: A yearlong classroom-based experimental study of middle school students developing literacy in a new language. Reading Research Quarterly, 51 (2), 143–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/rrq.132
*Limpo, T., & Alves, R. A. (2014). Implicit theories of writing and their impact on students’ response to a SRSD intervention. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 84 (4), 571–590. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12042
Lipskey, M., & Wilson, D. (2001). Practical meta-analysis . Sage.
*López, P., Torrance, M., Rijlaarsdam, G., & Fidalgo, R. (2021). Evaluating effects of different forms of revision instruction in upper-primary students. Reading and Writing, 34 , 1741–1767. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-021-10156-3
*Lott, C. J. (1986). The effects of the microcomputer word processor on the composition skills of seventh-grade students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Montana.
*Lyons, H. L. K. (2002). The effects of technology use on student writing proficiency and student attitudes toward written assignments in a ninth-grade language arts classroom [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Idaho State University.
*Lytle, M. J. (1987). Word processors and writing: The relation of seventh grade students’ learner characteristics and revision behaviors (Publication No. 8800537) [Doctoral dissertation], University of Oregon.
Matuchniak, T., Olson, C. B., & Scarcella, R. (2014). Examining the text-based, on-demand, analytical writing of mainstreamed Latino English learners in a randomized field trial of the Pathway Project intervention. Reading and Writing, 27 , 973–994. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-013-9490-z
*Mayo, N. B. (1976). The effects of discussion and assignment questions on the quality of descriptive writing of tenth grade students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Memphis State University.
*McCarty, R. P. (2016). Leveraging historical thinking heuristics as warrants in historical argumentative writing [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Illinois at Chicago.
*McCreight, C. K. (1995). Computer-assisted process writing: A cooperative-pairs approach [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Baylor University.
*McDermott, M. A. (2009). The impact of embedding multiple modes of representation on student construction of chemistry knowledge [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of Iowa.
*McNeill, K. L., Lizotte, D. J., Krajcik, J., & Marx, R. W. (2006). Supporting students’ construction of scientific explanations by fading scaffolds in instructional materials. The Journal of the Learning Sciences, 15 (2), 153–191. https://doi.org/10.1207/s15327809jls1502_1
Morphy, P., & Graham, S. (2012). Word processing programs and weaker writers/readers: A meta-analysis of research findings. Reading and Writing: An Interdisciplinary Journal, 25 , 641–678. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-010-9292-5
*Moseley, D. S. (2003). Vocabulary instruction and its effects on writing quality [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Louisiana Tech University.
National Center for Educational Statistics (2012). The nation’s report card: Writing 2011 (NCES 2012-470). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education, Institute of Educational Sciences.
*Niemi, D., Wang, J., Steinberg, D. H., Baker, E. L., & Wang, H. (2007). Instructional sensitivity of a complex language arts performance assessment. Educational Assessment, 12 (3–4), 215–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/10627190701578271
Nunnally, J. (2017). Psychometric theory . McGraw-Hill.
*Olina, Z., & Sullivan, H. J. (2004). Student self-evaluation, teacher evaluation, and learner performance. Educational Technology Research and Development, 52 (3), 5–22. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02504672
*Olson, C. B., Kim, J. S., Scarcella, R., Kramer, J., Pearson, M., van Dyk, D. A., Collins, P., & Land, R. E. (2012). Enhancing the interpretive reading and analytical writing of mainstreamed English learners in secondary school: Results from a randomized field trial using a cognitive strategies approach. American Educational Research Journal, 49 (2), 323–355. https://doi.org/10.3102/0002831212439434
*Olson, C. B., Matuchniak, T., Chung, H. Q., Stumpf, R., & Farkas, G. (2017). Reducing achievement gaps in academic writing for Latinos and English learners in Grades 7–12. Journal of Educational Psychology, 109 (1), 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000095
*Page-Voth, V., & Graham, S. (1999). Effects of goal setting and strategy use on the writing performance and self-efficacy of students with writing and learning problems. Journal of Educational Psychology, 91 (2), 230–240. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.91.2.230
*Palumbo, D. B., & Prater, D. L. (1992). A comparison of computer-based prewriting strategies for basic ninth-grade writers. Computers in Human Behavior, 8 (1), 63–70. https://doi.org/10.1016/0747-5632(92)90019-B
*Pedersen, E. L. (1977). Improving syntactic and semantic fluency in writing of language arts students through extended practice in sentence combining [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of Minnesota.
*Pittman, R. T. (2007). Improving spelling ability among speakers of African American vernacular English: An intervention based on phonological, morphological, and orthographic principle [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Texas A&M University.
*Pivarnik, B. A. (1985). The effect of training in word processing on the writing of eleventh grade students [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. University of Connecticut.
*Prata, M. J., de Sousa, B., Festas, I., & Oliveira, A. L. (2019). Cooperative methods and self-regulated strategies development for argumentative writing. The Journal of Educational Research, 112 (1), 12–27. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2018.1427037
Pressley, M., Graham, S., & Harris, K. R. (2006). The state of educational intervention research. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 76 , 1–19. https://doi.org/10.1348/000709905x66035
*Rapanta, C. (2021). Can teachers implement a student-centered dialogical argumentation method across the curriculum? Manuscript submitted for publication.
R Core Team (2018). R: A language and environment for statistical computing. Retrieved from https://www.r-project.org/
*Reynolds, C. J., Hill, D. S., Swassing, R. H., & Ward, M. E. (1988). The effects of revision strategy instruction on the writing performance of students with learning disabilities. Journal of Learning Disabilities, 21 (9), 540–545. https://doi.org/10.1177/002221948802100904
*Reynolds, G. A., & Perin, D. (2009). A comparison of text structure and self-regulated writing strategies for composing from sources by middle school students. Reading Psychology, 30 (3), 265–300. https://doi.org/10.1080/02702710802411547
*Rice, D. P. (1968). A study of a linguistically-based spelling program in grade six [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Temple University.
*Rijlaarsdam, G., & Schoonen, R. (1988). Effects of a teaching program based on peer evaluation on written composition and some variables related to writing apprehension . SCO Cahier Nr. 47. Stichting Centrum voor Onderwijsonderzoek (SCO), Grote Bickersstraat 72, 1013 KS Amsterdam, The Netherlands.
*Rijlaarsdam, G., Couzijn, M., Janssen, T., Braaksma, M., & Kieft, M. (2006). Writing experiment manuals in science education: The impact of writing, genre, and audience. International Journal of Science Education, 28 (2–3), 203–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500690500336932
Rogers, L., & Graham, S. (2008). A meta-analysis of single subject design writing intervention research. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100 , 879–906. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.100.4.879
*Rolfe, A. B. (1991). The effects of an identify-generate-test sequence on the spelling performance of learning disabled and normally-achieving students (Publication No. 0121204) [Doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University.
*Roscoe, R. D., Allen, L. K., & McNamara, D. S. (2019). Contrasting writing practice formats in a writing strategy tutoring system. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 57 (3), 723–754. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633118763429
Roscoe, R. D., Brandon, R., Snow, E., & McNamara, D. S. (2013). Game-based writing strategy practice with the Writing Pal. In K. Pytash & R. Ferdig (Eds.), Exploring technology for writing and writing instruction (pp. 1–20). IGI Global.
*Rosenbluth, G. S., & Reed, W. M. (1992). The effects of writing-process-based instruction and word processing on remedial and accelerated 11th graders. Computers in Human Behavior, 8 , 71–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/0747-5632(92)90020-F
RStudio Team (2016). RStudio: Integrated Development for R. Retrieved from http://www.rstudio.com/ .
Sandmel, K., & Graham, S. (2011). The process writing approach: A meta-analysis. Journal of Educational Research, 104 , 396–407. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2010.488703
Schulz, K., & Grimes, D. (2002). Sample size slippages in randomized trials: Exclusions and the lost and wayward. Lancet, 359 , 781–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(02)07882-0
*Segers, E., & Verhoeven, L. (2009). Learning in a sheltered Internet environment: The use of WebQuests. Learning and Instruction, 19 , 423–432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.learninstruc.2009.02.017
Slavin, R. E., & Madden, N. A. (2011). Measures inherent to treatments in program effectiveness reviews. Journal of Research on Educational Effectiveness, 4 , 370–380. https://doi.org/10.1080/19345747.2011.558986
*Sloan, C. C. (2017). Types of feedback in peer review and the effect on student motivation and writing quality (Publication No. 10281143) [Doctoral dissertation]. Michigan State University. ProQuest LLC.
*Spilton, R. (1986). The effects of individualized language arts, sentence-combining, and traditional grammar on the syntactic maturity and quality of writing of a select group of eighth graders (Publication No. 8703964) [Doctoral dissertation]. Georgia State University.
Swanson, L., Harris, K. R., & Graham, S. (2013). Handbook of learning disabilities (Second Edition) . Guilford.
Tanner-Smith, E. E., Tipton, E., & Polanin, J. R. (2016). Handling complex meta-analytic data structures using robust variance estimates: A tutorial in R. Journal of Developmental and Life-Course Criminology, 2 (1), 85–112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40865-016-0026-5
*Tezler, E. G. (1993). The effects of modeled strategies and attributions on students' self-regulated learning and spelling achievement (Publication No. 9325155) [Doctoral dissertation]. The City University of New York.
*Thibodeau, A. E. (1964). Improving composition writing with grammar and organization exercises utilizing differentiated group patterns [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Boston University.
*Thomas, M-L. (1995). The effect of genre-specific story grammar instruction on recall, comprehension, and writing of tenth-grade English students (Publication No. 9626945) [Doctoral dissertation]. Marquette University.
Tipton, E., & Pustejovsky, J. E. (2015). Small-sample adjustments for tests of moderators and model fit using robust variance estimation in meta-regression. Journal of Educational and Behavioral Statistics, 40 (6), 604–634. https://doi.org/10.3102/1076998615606099
Tolchinsky, L. (2016). From text to language and back again: The emergence of written language. In C. A. MacArthur, S. Graham, & J. Fitzgerald (Eds.), Handbook of writing research (2nd ed., pp. 144–159). Guilford Press.
Tukey, J. W. (1977). Exploratory data analysis . Addison Wesley.
*Vahidi, A., Karimi, L., & Mahmoodi, M. H. (2016). The effect of reconstruction as a noticing strategy on Iranian female first grade high school students’ writing ability. Theory and Practice in Language Studies, 6 (2), 310–324. https://doi.org/10.17507/tpls.0602.12
*van Beuningen, C., G., de Jong, N. H., & Kuiken, F. (2012). Evidence on the effectiveness of comprehensive error correction in second language writing. Language Learning, 62 (1), 1–41. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-9922.2011.00674.x
*van Drie, J., van Boxtel, C., Erkens, G., & Kanselaar, G. (2005). Using representational tools to support historical reasoning in computer-supported collaborative learning. Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 14 (1), 25–42.
*van Drie, J., van Driel, J., & van Weijen, D. (2021). Developing students’ writing in History: Effects of a teacher-designed domain-specific writing instruction. Journal of Writing Research, 13 (2), 201–229. https://doi.org/10.17239/jowr-2021.13.02.01
*van Driel, J., van Drie, J., & van Boxtel, C. (2022). Writing about historical significance: The effects of a reading-to-write instruction. International Journal of Educational Research, 122 , 1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijer.2022.101924
*van Wagenen, D. A. (1988). Computerized prewriting activities and the writing performance of high school juniors [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The George Washington University.
*Vinson, L. L. N. (1971). The effects of two prewriting activities upon the overall quality of ninth graders’ descriptive paragraphs [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] University of South Carolina.
*Wagner, J. H. (1978). Peer teaching in spelling: An experimental study in selected Seventh-day Adventist high schools (Publication No. 7.913326) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Florida.
*Walker, R. R. (1970). A comparison of an individualized and a group-directed system for teaching spelling in the eighth grade [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Columbia University.
*Widvey, L. I. H. (1971). A study of the use of a problem-solving approach to composition in high school English [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. The University of Nebraska-Lincoln.
*Wilson, J., & Czik, A. (2016). Automated essay evaluation software in English Language Arts classrooms: Effects on teacher feedback, student motivation, and writing quality. Computers & Education, 100 , 94–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2016.05.004
*Wilson, J., & Roscoe, R. D. (2019). Automated writing evaluation and feedback: Multiple metrics of efficacy. Journal of Educational Computing Research, 58 (1), 87–125. https://doi.org/10.1177/0735633119830764
*Wise, W. G., & Slater, W. H. (1992). The effects of revision instruction on eighth graders’ persuasive writing (Publication No. 9304422) [Doctoral dissertation]. University of Maryland College Park.
*Wissinger, D. R., & de la Paz, S. (2016). Effects of critical discussions on middle school students’ written historical arguments. Journal of Educational Psychology, 108 (1), 43–59. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000043
*Wissinger, D. R., De La Paz, S., & Jackson, C. (2021). The effects of historical reading and writing strategy instruction with fourth-through sixth-grade students. Journal of Educational Psychology, 113 (1), 49–67. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000463
*Wong, B. Y. L., Hoskyn, M., Jai, D., Ellis, P., & Watson, K. (2008). The comparative efficacy of two approaches to teaching sixth graders opinion essay writing. Contemporary Educational Psychology, 33 (4), 757–784. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cedpsych.2007.12.004
*Yeh, S. S. (1998). Empowering education: Teaching argumentative writing to cultural minority middle-school students. Research in the Teaching of English, 33 (1), 49–83.
*Zellermayer, M., Salomon, G., Globerson, T., & Givon, H. (1991). Enhancing writing-related metacognitions through a computerized writing partner. American Educational Research Journal, 28 (2), 373–391. https://doi.org/10.3102/00028312028002373
Download references
Acknowledgements
The research reported here was supported by the Institute of Education Sciences, U.S. Department of Education, through Grant R305C190007 to the University of California – Irvine for the WRITE Center. The opinions expressed are those of the authors and do not represent views of the Institute or the U.S. Department of Education.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ, USA
Steve Graham
Middle Tennessee State University, Murfreesboro, TN, USA
Yucheng Cao
Changwon National University, Changwon-si, South Korea
Young-Suk Grace Kim, Tamara Tate, Penelope Collins, Minkyung Cho, Youngsun Moon, Huy Quoc Chung & Carol Booth Olson
Texas State University, San Marcos, TX, USA
Joongwon Lee
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Steve Graham .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
None of the authors have a conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions

About this article
Graham, S., Cao, Y., Kim, YS.G. et al. Effective writing instruction for students in grades 6 to 12: a best evidence meta-analysis. Read Writ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-024-10539-2
Download citation
Accepted : 19 March 2024
Published : 24 April 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-024-10539-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Instruction
- Middle school
- High school
- Meta-analysis
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
ProblemsEncountered by Grade 12 HUMSS Strand Students on their Creative Writing Subject in Bestlink College of the Philippines: Basis for Proposed Guidelines
- Hanna Ria Kempis
- Mae Enriquez
- Jessa Harochoc
- Szaira Cristine Huevia
- Sittie Aina Indad
- Midel Mirasol
Creative writing is one of the subjects in senior high school that focus on developing the students’ writing skills in terms of writing. Many students find English as the hardest subject because of the problems, struggles, and challenges that they encountered in terms of reading, writing, speaking, and grammar. The researchers assessed the students’ performance in their creative writing subject and also study the problem that they encountered on their creative writing subject to give them guidelines to improve their skills and understanding, which will help them participate in their class properly. This study used a qualitative method of research to determine the problem encountered by Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences (HUMSS) Strandstudents in Bestlink College of the Philippines. The researchers administered a survey questionnaire to gather information from Grade 12 HUMSS Strandstudents that were selected with random sampling. The research questionnaire helped to gather ideas or information easily. The personal observation and results were gathered from the survey questionnaire, and the research was conducted inside the Bestlink college of the Philippines. Results of this study showed the problem encountered by the Grade 12 HUMSS Strandstudents on their creative writing subject in Bestlink College of the Philippines. With the total of 14.95, which composed of the following: reading with the total of 11.63, with variables difficulties in reading words with the total of 3.38, difficulties in pronouncing words or sentence with the total of 3.77, and stuttering with the total In dad of 3.63; writing with a totalof 11.63, with variables difficulties to write an essay with the total of 4.0, difficulties to express idea in unity with the total of 3.9, and difficulties to create a paper works with the total of 3.72; speaking with the total of 14.96, with variables difficulties to speak in English with the total of 4.0, difficulties in communicating to others with the total of 3.60, difficulties in expressing yourself and thoughts more with the total of 3.73, having difficulties in pronouncing words with the total of 3.63; and grammar with the total of 11.53, with the variables having a hard time constructing an English sentence with the total of 3.97, having a hard time familiarizing themselves with vocabulary words with the total of 3.82, and having a hard time translating a Tagalog sentence into English with the total of 3.77. The researchers proposed guidelines on how students can improve their skills to be able to participate in their class properly.

How to Cite
- Endnote/Zotero/Mendeley (RIS)
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Dindie Grace Magana, Elizabeth Barce, Necel Ellema, Jasmin Jetajobe, Roymar Angelo Soriso, Midel Mirasol, Benefits of HUMSS Strand to Develop Self-Esteem of Grade 11 Students , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Jhunrey Mora, Camille Joy Cabarle, Maurise Silverio, Cecille Nueva, Jessica Bo, Midel Mirasol, Effects of Peer Pressure on Academic Performance of Grade 12 HUMSS Strand Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Christine Nicole Cajes, Sheila Ebrado, Monica Olaer, Rica Sarao, Queen Ahyen Tepait, Midel Mirasol, Factors Affecting Preferred College Courses of Grade 12 HUMSS Strand Students at Bestlink College of the Philippines, S.Y. 2019–2020 , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Rohaima Pulalon, Christian Paredes, Hara Mia Pastor, Aljohn Pedrosa, Edna Rejuso, Midel Mirasol, Academic Performance of Selected Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students of Bestlink College of the Philippines as Influenced by Socioeconomic Factor , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Ruth Anne Narciso, Angelika Felises, Shaene Villanueva, Divina Rocha, Clifford John Villareal, Midel Mirasol, Factors that Affect Choosing College Courses of Grade 12 HUMSS Strand Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Christian Sabado, Gilbert Atillano, Karylle Kaye Cotoner, Bob Darrel Padrino, Joel Razos Jr., Midel Mirasol, Impactsof Parent Involvement on Academic Performance of Selected Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Strand Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Krisha Valen Candeluna, Hacel Ann Garcia, Roselee An Lagrimas, Erica Morales, Joanne Rojas, Midel Mirasol, Benefits of Whole Day Class Schedule in Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Students at Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Jenny Llobrera, Arnold Bontuyan, Karen Balan, Xyreen Mae Billon, Denzel Feliciano, Midel Mirasol, Effects of Extracurricular Activities on Academic Performance of Grade 12 HUMSS Strand Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Hannah Ladrero, Angella Venus Villanueva, Midel Mirasol, Factors that Cause Low Academic Performances among Grade 12 HUMSS Strand Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Gimarie Vila, Roland Dela Cruz, Jomari Icay, Alexandra Domaoal, Patricia Mae Macaranas, Midel Mirasol, Effects of Stress on Study Habits of Grade 12 HUMSS Strand Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
Similar Articles
- Densel Dela Cruz, Alona Jen Polistico, Joven Licong, Nathaniel Chris Solayao, Christian King Contillo, Rinna Bayaborda, Improving Grammar Skills through Weekly Activity Session among Grade 11 ABM Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines, S.Y. 2019–2020 , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Richard Mark Laureano, Madine Marie Labin, John Dave Costemiano, Angeline Dela Cruz, Mark Andrew Licong, Rinna Bayaborda, Conducting Writing Contest in Improving English among Grade 12 ABM Students at Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Robert Amilda, Mar Reyes, Daniella Balmera, Leslie Ann Abesamis, Janet Solayao, Midel Mirasol, Difficulties in English Grammar of Selected Grade 12 Humanities and Social Sciences Strand Students of Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- J. Basañez, R. Delos Reyes, T. Quiliza, C. Quirona, N. Serania, Avilynne A. Tandoc, Maed, An Assessment of the Reading Comprehension Skills of the Grade VI Pupils towards a Guide at Kaligayahan E/S , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 1 No. 1 (2019): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.1, No.1, March 2019
- Nina Torogon, Rachelle Luzon, Katherine Repuela, Crissa Jean Yap, Crystel-Joy Tamon, Effectiveness of Practice Reading Sessions in Improving Reading Comprehension of Grade 12 Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Lilliann P. Abalita, May Ann S. Caroza, Jasmin A. Martillana, Ailyn E. Umali, Gladys Velasco, Dr. Amelia S. Ablen, Challenges Encountered by Grade 8 Students in Reading Comprehension Skills at Doña Rosario High School, Quezon City , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 1 No. 1 (2019): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.1, No.1, March 2019
- Nicole Munoz, Mark Calumag, Romer Riosora, Jelly Garduque, Nowellito Rivas, Geovannie Bernales Jr., Level of Effectiveness in Teaching Creative Writing as Assessed by Selected Grade 12 General Academic Strand Students in Bestlink College of the Philippines , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Melanie Legaspi, Alexis Jim Medicilo, Roldan Delos Reyes, Mark Joseph Navarro, Morrisjay Alejandro, Geovanni Bernales, Effectiveness of Reading Comprehension in Academic Achievement of Selected General Academic Strand Grade 12 Students , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Joanna Marie Villajuan, Irish Cabagtong, Zacarias Jay Aguillon, Johnrommel Tacata, Jeraldine Faustino, Crystel-Joy Tamon, Evaluation in Improving English Proficiency of Grade 12 ABM Students by Doing Research Papers in Bestlink College of the Philippines, S.Y. 2019–2020 , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
- Brilliant Bert Tee, Angela Palgan, Ma Rita Abadiano, Amalyn De Pablo, Maika Villafuerte, Crystel-Joy Tamon, Enhancing Reading Comprehension ofGrade 12 ABM Students by Reading Vocabulary Words , Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2020): Ascendens Asia Singapore – Bestlink College of the Philippines Journal of Multidisciplinary Research Abstracts, Vol.2, No1, March 2020
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 > >>
You may also start an advanced similarity search for this article.

Attitudes Toward Research and its Impact to Research Skills Development among Grade 12 students of Meycauayan National High School
- International Journal of Multidisciplinary Applied Business and Education Research 3(3)

- Department of Education of the Philippines
Discover the world's research
- 25+ million members
- 160+ million publication pages
- 2.3+ billion citations

- Can Int Educ Educ Canad Int

- Nora’asikin Abu Bakar

- T Magallanes
- M J Encarnacion
- S L Foronda
- M Christine
- Recruit researchers
- Join for free
- Login Email Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google Welcome back! Please log in. Email · Hint Tip: Most researchers use their institutional email address as their ResearchGate login Password Forgot password? Keep me logged in Log in or Continue with Google No account? Sign up
- Our Mission
5 Ways to Include Writing in Reading Intervention
Writing sometimes gets short shrift in literacy education. These strategies help foster students’ reading and writing skills in tandem.

Over the years, reading has remained in the spotlight of literacy conversations, while writing has often taken a back seat. But one of the most powerful tools we have in literacy instruction is the reciprocity between reading and writing. As Natalie Wexler shares in her article “ To Boost Learning, Weave Writing Activities Into Regular Instruction ,” we cannot write deeply about topics we do not have knowledge about.
Writing is expressive and therefore gives us a vessel for deepening our understanding of what we read. Often, in literacy intervention work, we are so focused on improving reading outcomes that we can sometimes overlook students’ writing abilities.
These five strategies offer quick ways to enhance student learning as well as develop student writing through explicit instruction and practice. You can utilize them in any intervention setting.
SENTENCE DICTATION
The first strategy is a variation on the dictated sentences that are often used in intervention work. After students read a decodable text, or even a grade-level text, sentence dictation can allow them to practice using specific vocabulary, sentence structure, or phonics patterns.
Student input can vary depending on what support is needed to craft the sentence. In this case, you, the teacher, would dictate, or say, a sentence that might include a specific phonics pattern, some words that include review patterns, a specific vocabulary word that students have studied, or a specific structure, such as a conjunction.
These instructional decisions are intentional, allowing students to not only write about their reading but practice phonics skills or develop more complex sentences that include elevated vocabulary.
SENTENCE COMPLETION
A second strategy that allows students to demonstrate comprehension of a text involves using a kernel sentence, or a stem, and then completing the sentence using the conjunctions because, but, and so .
It is important to teach students how these three conjunctions differ in the meanings they convey. A way to scaffold this strategy is to provide prewritten sentence parts and have students match them to the correct conjunction.
This strategy challenges students to take the information they learned and explain it in three different ways. For examples of this type of writing, a good resource is The Writing Revolution , by Judith Hochman and Natalie Wexler.
SENTENCE EXPANSION
Sentence expansion is another strategy that allows students to demonstrate their understanding while also developing their writing abilities. Give students a subject (the who or what) from the text, and then ask them to expand the sentence by providing the where, when, why, and how, to add details to their writing.
Each piece should demonstrate further understanding of the text while also developing students’ ability to add details, which creates a more complex and dynamic sentence.
A scaffold for this type of writing involves providing some of the details, which students can then build from. While students are adding details and expanding their sentences, they are also recalling information they learned from the text.
SENTENCE STARTERS
A fourth strategy I’ve used is sentence starters that introduce a more complex way of writing a sentence. As students become more comfortable with varying their sentence structures, they can move to crafting the entire sentence.
Some possibilities include asking them to include an appositive, or noun/pronoun that comes after a noun, to give more detail or explanation. Another option could be to start with a dependent clause. In this exercise, students are combining their content knowledge as well as developing their writing skills.
PARAGRAPH SHRINKING
One final strategy I’ve used is to have students write a sentence using paragraph shrinking or finding the gist of the text they’ve read. I ask students to find the most important who or what of the paragraph or text and then add the most important thing that happened to create a 10-to-15-word sentence that summarizes the essential information of a paragraph or text.
Literacy is a merger of reading and writing skills. Both areas need to develop in order for students to be successful. All five of these strategies can support students in demonstrating comprehension, with writing as the expressive output, in an intervention setting. You can scaffold each activity up or down, depending on the varying needs of your students.
Writing should be a part of every lesson , and using these five strategies allows us to integrate reading and writing so that both areas are woven together each time a student engages with a text.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Reading and Writing Performance of Senior High School Students

International Journal of English Language Studies
The study was conducted to determine the performance and attitudes towards reading and writing of Grade 12 students in public schools of Cabagan, Isabela. There were 244 students involved in the study. Stratified random sampling was used in selecting the participants of the study. A quantitative research method was used in the study to determine performance and attitudes towards reading and writing. Frequency counts, percentage scores, the arithmetic mean, and Kendall’s Rank Correlation Tau was used to describe and analyze the data in the study. The findings of the study revealed that students' reading and writing performance were poor. However, their attitudes toward reading and writing were positive. Hence, the study demonstrated that there is a significant correlation between students’ attitudes and their reading and writing performance. Thus, the study supports DepEd’s "SulongEdukalidad" in creating programs to enhance learners' reading mastery and sustain its ...
Related Papers
Journal of English Education
Kisno Shinoda
Good literacy ability is one of the demands in learning 21st century. The purpose of this study was to find out the correlation between students' reading literacy ability and writing visual text ability for seventh grade students of SMP Negeri 1 Pematangsiantar. 133 respondents from 200 populations were randomly selected using simple random sampling technique. This is a quantitative research method using correlation research. Data collection used tests including multiple choice and essay. Using the Pearson products moment formula, this study analyzes data from both tests. The hypothesis of this research is H1 which states that there is a correlation between reading literacy ability and writing visual text ability and H0 states that there is no correlation between reading literacy ability and writing visual text ability. The results of this study indicate the correlation coefficient between the two variables is r =0.91 It means that there is a very strong relationship between rea...
Michelle Domantay
This study looked into the English writing performance of the Grade 11 students of Malasiqui National High School, Malasiqui, Pangasinan for academic year 2017-2018. The study employed descriptive and correlational research design. Different statistical tools were used such as; frequency counts, average weighted mean, inter-rater reliability test, bivariate correlation and t-test. The data obtained were used to develop Strategic Intervention Materials that enhance students’ performance in English writing. The study revealed that of 70 res pondents, 47 or 67.1% are aged 17-19 years; in sex, 44 or 62.9% are female; 31 or 44.3% and 28 or 40% of the respondents’ fathers and mothers are high school graduates; 46 or 65.7% belong to families with below average family income; 35 or 50% of them read watt pad as their most preferred reading material ; and 68 or 97.1% of the respondents completed their Junior High School from public schools. Students have “good” performance in writing proficie...
European Journal of Foreign Language Teaching
Tessie Miralles
The purpose of this study was to determine the classroom learning environment and student writing strategy as predictors of reading competence of senior high school students. Utilizing quantitative, non-experimental design via correlational technique, data were obtained from 369 respondents of the study who are students who belong to the senior high school department, particularly Grade 12 of the national high schools under the division of Davao del Sur. The researcher utilized stratified random sampling and survey mode of data collection. The researcher also utilized the statistical tools mean, Pearson r, and multiple regression. From the results of the study, it was found that there is a high level of mean scores for all variables of classroom learning environment, student writing strategy, and reading competence of senior high school students. Also, results revealed that there are significant relationships between classroom learning environment and reading competence of senior hi...
Language and Education Journal
rekha asmara
Many researches have shown the facts that the students’ skills in writing can be improved by having a good reading habit. It was convinced that the students reading habit has great impact on the improvement of students’ writing ability. The students who read extensively will acquire more vocabularies that lead them to have greater proficiency in writing. Therefore, this study was purposed to know whether reading habit of the eighth graders of SMPN 6 Kayuagung was significantly correlated to their writing skill. By means of Purposive sampling, 124 students of the whole number of the population were selected as the sample. A correlational study was applied. A questionnaire and written test were distributed to get the data. Twenty items of a ready-made questionnaire were used to know students’ habit in reading and a writing test was administered to measure students’ writing skill. The writing test was reliable because its reliability coefficient was 0.942. In data analysis, Pearson P...
Asian Journal of Education and Social Studies
Richard Oco
Aims: Reading, Writing, and Arithmetic are three essential skills a pupil should learn and acquire. The purpose of this study was to identify factors associated with pupils’ reading; the pupils’ level of reading performance and the significant relationship between the level of reading performance and factors associated with reading performance. Study Design: The study employed Content Analysis with Descriptive Correlation. Place and Duration of Study: The study was conducted in selected schools in the division of El Salvador City during the school year: 2022. Methodology: The respondents were all the One hundred-twenty (120) Grade 3 pupils at the selected schools in El Salvador City. This study used a researcher-modified survey questionnaire that underwent validity and reliability testing. Results: The results showed that pupils’ reading performance was at a Frustration level, while factors associated with reading performance were rated as Unlikely. It was concluded that pupils'...
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences
Fatma Kırmızı
Ayu Putri Lestari
This research was aimed at investigating if there was a correlation between reading attitude and writing achievement of the eleventh grade students of SMA Muhammadiyah 6 Palembang. The writer used correlational research method to find out the relationship between students’ reading attitude and writing achievement. One hundred and ten students participated in this research with the age ranged from 15-17 years old. The writer used ready-made questionnaire used by Tullock-Rhody, Regina and Alexander, J Estill, 1980 and writing test to collect the data. The result of the test were analyzed by using Pearson Product Moment through SPSS (Statistical Package for Social and Science) 16.0. Meanwhile, to measure the correlation between the students’ reading attitude and their writing achievement, it was also referred to the interval coefficient for interpreting the correlation coefficient. From the analysis, it was showed that there was correlation between the two variables since the score of...
ANA GABRIELA
Through a previous analysis, it is possible to show that the 7th grade students of Basic General Education "A" in the Educational Unit "Camilo Gallegos Toledo", were not able to express their own ideas when developing activities related to writing, due to the lack of application of writing strategies, this study analyzed writing strategies that help to improve writing skills in students. The purpose of this work was observe the writing process that was used to acquire student´s writing strategies, to provide ideas and additional knowledge to English teachers who work with children need to encourage the writing process, it is important to correct the grammatical errors. A non-participatory observation technique was used since the researcher played a passive role; the data collection instrument was an observation guide. It was determined that, Teachers should analyze other strategies that have a greater impact on their students so that they have a better developmen...
AJHSSR Journal
This study aimed to compare the reading performance on linear and nonlinear texts of 140 Grade 11 students of President Ramon Magsaysay State University during S.Y. 2018-2019. The study was limited to the reading comprehension and analysis of ideas of students in reading and interpreting texts. The reading texts of the respondents prepared by the researcher were used in this study and the analysis of the outputs was used in the data gathering needed in this research work. The work text was evaluated by ten English Teachers, as the teacher-respondents. The study revealed that the levels of reading performance of students before the intervention were rated as "did not meet expectation" in linear text and "fairly satisfactory" in nonlinear text. The researcher developed a work text in the form of Non-Linear and Linear texts where teacherrespondents assessed it as "very valid" and "very usable" with the help of different indicators. The level of reading of students in linear and nonlinear text assessments after the intervention were both rated as "outstanding". There is a significant difference on the level of reading performance of linear text readers and non-linear text readers between the pre-test and post-test assessments. Based on the summary of the investigations conducted and the conclusions arrived at, the researcher offered the following recommendations; the use of Work text which provides more illustrations, graphic organizers, diagrams, and drawings is strongly encouraged for better academic achievement and reading performance of students; the development of work text for Non-Linear reading should be properly and carefully planned and the aesthetic principles are considered for the appreciation of the readers; an in-service training especially for English teachers for capability building across all courses in the development of work text is strongly recommended; and finally, a parallel or similar study with in-depth and wider scope so as to validate the findings obtained in the study should be conducted.
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Jurnal Ilmu Pendidikan Muhammadiyah Kramat Jati
Sherly Putri
Hady Sutris Winarlim
Register Journal
IBNU MAS'UD
Ella Mae Navarra
Didascein : Journal of English Education
Jenny Elvinna Manurung
Pancaran Pendidikan
sri sukasih
hasanul bishry
Nurul Khalisa
Journal of English Language and Pedagogy
Ahmed Zidan
Journal of Integrated Elementary Education
Jeremie Maleon
The Related Variables and the Reading Proficiency Level of Grade Six Pupils
Modern Journal of Studies in English Language Teaching and Literature
Leah Gustilo
Proceedings of the 2019 Ahmad Dahlan International Conference Series on Education & Learning, Social Science & Humanities (ADICS-ELSSH 2019)
Akmal Akmal
Science publication group
Mulugeta A S N A K E W Tadesse
Jurnal Konseling dan Pendidikan
Lamhot Naibaho
Carlo Caparas
International Journal of Educational Studies in Social Sciences (IJESSS)
Elvina Arapah
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
This study anal yzed and determined the research writing abilit y of Grade 12 Senior High . ... can implement targeted intervention programs that effectively improve students' writing skills. View.
The research skills of the students were measured using a 42-item objective type researcher-made Research Skills Test. The writing skills were evaluated through an adapted Writing Skills Test and were graded using a 20-point adapted rubric. ... Research Questions This study analyzed and determined the research writing ability of Grade 12 Senior ...
with 18 items (α = 0.952) and writing and reporting results with eight items (α = 0.918). Keywords: Research Skills, ... and Grade 12) curriculum to help students develop critical and problem-solving skills through qualitative ... development of students' research skills. The framework is descriptive, scalable, and useful for ...
The research skills of the students were measured using a 42-item objective type researcher-made Research Skills Test. The writing skills were evaluated through an adapted Writing Skills Test and were graded using a 20-point adapted rubric. The collaborative skills were assessed using a 50-item adapted and modified Collaborative Skills ...
BY GRADE 12 STUDENTS IN THESIS WRITING AT NATIONAL UNIVERSITY BULACAN INCORPORATED: A BASIS FOR DEVELOPMENT OF ... This implies that as the research skills of the Grade 12 students improve, it would greatly help them in minimizing the challenges in completing thesis writing. The researchers look forward to this study being utilized as a
The research skills of the students were measured using a 42-item objective type researcher-made Research Skills Test. The writing skills were evaluated through an adapted Writing Skills Test and ...
With the advent of the K-12 Basic Education Curriculum, students are confronted with different academic writing tasks through the English for Academic and Professional Purposes and Practical Research courses. Despite the efforts of the educational sector to improve students' writing skills, many students still experience difficulties in ...
Based on these findings, it is recommended that tailored intervention programs be implemented for Grade 11 and Grade 12 students at Lorenzo S. Sarmiento Sr. National High School to address specific areas of improvement and foster continuous enhancement of their writing skills. Keywords: GAS, Writing Skills, Intervention Program, Philippines.
A quantitative-descriptive method was used in this study with validated questionnaire as. research instrument. The study made use of 197 respondents out of 389 Grade 12 students of. Buhaynasapa ...
students' notebook as an interactive instructional helper to improve the research writing skills of Grade 12 students in Practical Research 2 in which they performed poorly. Significance of the Study Students. Learning research concepts and research writing is typically challenging to students.
The current best evidence meta-analysis reanalyzed the data from a meta-analysis by Graham et al. (J Educ Psychol 115:1004-1027, 2023). This meta-analysis and the prior one examined if teaching writing improved the writing of students in Grades 6 to 12, examining effects from writing intervention studies employing experimental and quasi-experimental designs (with pretests). In contrast to ...
INTRODUCTION Writing is known as a complex intellectual task involving many component skills which is perceived to be difficult to most students. This study aimed to determine the effectiveness of Process approach in enhancing the writing skills of grade 12 HUMSS students at Paliparan II Integrated High School. Moreover, the study is anchored on Expressivist Process Theory of Writing in which ...
research capability of Grade 12 students in the three-pioneer public secondary senior high school implementers in the Municipality of Murcia, S.Y. 2017-2018. Specifically, it sought to answer the following questions: 1. What is the level of research capability of Grade 12 students in quantitative in terms of the technical aspects, major
A total of46 students (31 females and 15 males), equivalent to 51% of the total population of Grade 12 students enrolled in the research writing course, participated in the study. The participants were all the Grade 12 students who were present in class at the time the RAT was administered.
Jigme [email protected] Phuentsholing HSS, BhutanAbstractAn action research was conducted with class 12 science students (n=15) for three months with an aim of helping students imp. ove their academic writing skill through mini revision lessons and feedback. The study was. onducted based on pre-test-intervention-post-test ...
The main objective of the research course that the Grade 12 students were taking (at the time of the study) is the development of basic research skills only (i.e., choosing a rese arch topic ...
Creative writing is one of the subjects in senior high school that focus on developing the students' writing skills in terms of writing. Many students find English as the hardest subject because of the problems, struggles, and challenges that they encountered in terms of reading, writing, speaking, and grammar. The researchers assessed the students' performance in their creative writing ...
Research 1: Qualitative, Practical Research 2: Quantitative, and Inquiries, Investigation and Immersion. Hence, EAPP aims to develop and fortify students' writing skills in different disciplines such as in the academe and in the professional field. The course introduces students to research writing skills so that they can
The primary concern of this paper was to relate how Grade 12 students of Meycauayan National High School perceived research subjects such as Practical Research 2 and how these attitudes toward ...
These strategies help foster students' reading and writing skills in tandem. By Elana Gordon. September 12, 2024. Olga Kurbatova / iStock. Over the years, reading has remained in the spotlight of literacy conversations, while writing has often taken a back seat. ... on the dictated sentences that are often used in intervention work. After ...
andy ramos. International Journal of English Language Studies. The study was conducted to determine the performance and attitudes towards reading and writing of Grade 12 students in public schools of Cabagan, Isabela. There were 244 students involved in the study. Stratified random sampling was used in selecting the participants of the study.