

How to Perform a Sales Analysis (Step-by-Step): Methods & Metrics

Want to achieve your sales goals? Then you have to kiss guesswork and intuition goodbye. Instead, get cozy with regular sales analysis to generate cold, hard data for your team.
Of course, wanting to go steady with data and actually making it happen are two different things. To make it a reality, you have to know what sales analysis is, why it's so beneficial to sales teams like yours, and how to analyze sales metrics and KPIs for your sales strategy .
Keep reading to learn everything you need to know about sales data analysis. That way, you can boost performance —for you and your team—and capture that elusive jena se qua that will turn your competitors green with envy. Let's do this!
What is Sales Analysis?
It's pretty simple: sales analysis is what happens when sales professionals monitor sales data in order to evaluate sales team performance. Doing so can uncover insights about:
- Top-performing products/services
- Underperforming products/services
- Customer behavior and retention
- New sales and market opportunities
- The future outlook of your sales team
When done right, sales analysis can help you run a more efficient and effective sales department now and in the future .
Curious about the total contract value ? Hey there, our article holds the answers.
How Often Should You Perform a Sales Analysis?
Worried you'll come off too strong? You don't want to look desperate. How much is too much? Luckily, the quickest way to sales analysis heart is to spend quality time with it.
In other words, check in regularly. How regularly depends on the sales metrics you need to track, your overall performance, and the type of sales reports you're analyzing.
Your sales goals can also impact how often you should perform sales analysis.
In general, expect to track overarching metrics like net sales and/or deal size on a monthly basis . More specific metrics, like calls or emails sent, should be tracked on a shorter-term basis. Remember to monitor seasonal changes and YoY metrics, whatever your cadence.
What is Included in a Sales Analysis?
Better said: what isn't included in a sales analysis?
Ultimately, what you decide to include in your sales analysis report will depend on your goals. Here are some ideas:
- Sales activity volume
- The ratio of new leads to qualified leads
- Information about your pricing structure
- Data on your social media campaigns
- Current sales trends
- Revenue and costs for a specific period
Along with these things, a clear sales data analytics report will show you what to do with the information. Specific action steps are a vital piece of sales analysis, meaning you can do more with the information you've gathered. Moreover, explore Google Sheets alternatives that may better suit your sales analytics needs, providing enhanced functionalities for improved data management.
What is Sales Analysis Useful For? 4 Irresistible Benefits
Why should sales managers get serious about sales analysis? Two words: the benefits!
Seriously, if you want to see how your team performs against its sales goals—throughout the entire sales cycle—you need to monitor the specific metrics that pertain to them.
They may have unmet demands that will streamline your business processes and benefit you in the long run, including outsourcing needs that cover 3PL warehouse management , manufacturing, offshore or onshore, etc. This is one of the reasons why those metrics must be monitored.
Once you do, you can make better decisions, understand market trends, boost company profits, and improve customer satisfaction. Let's take a closer look:
- Make better decisions: Sales analysis will reveal the real-time success of your sales plan . You can use this information to build a better, data-driven approach.
- Understand market trends: It doesn't matter what you're doing—launching a new product, planning inventory , etc. A sales analysis report will help you uncover hot market opportunities and must-know trends to maximize your efforts.
- Boost company profits: Top sales reps spend more time talking to high-quality leads. Sales analysis will help you identify the best prospects so your team can close more deals. It will also reveal information regarding your non-customers, which can be used to sharpen your sales pitch and personalize future marketing strategies .
- Improve customer satisfaction: Sales analysis will help you understand what customers want and why they buy. These details can be used to forge deeper bonds with your target audience, leading to more upsell and cross-sell opportunities.
Does the idea of sales analysis have you hot and bothered? Great! Now, I'll show you a proven, four-step process you can use to analyze the metrics and KPIs that matter to you.
How to Perform Sales Analysis: A 4-Step Process
You're ready to take the plunge and generate your sales analysis report—but how? Follow this four-step process, and you'll have sales analysis wrapped around your finger quickly!
Step 1: Choose the Right Sales Analysis Method
Different sales analysis methods will allow you to generate various kinds of reports. So, before you do anything else, choose a method that aligns with your sales goals.
Here are seven specific sales analysis reports you need to know about:
- Sales trend analysis: This type of sales analysis looks for patterns in sales data. Use it to track your team's progress toward its goals while understanding sales patterns in specific products, customers, and/or geographies.
- Sales performance analysis: Sales performance analysis is crucial for effective sales performance management . This type of analysis will help you gauge your sales team's performance and evaluate the overall effectiveness of your sales strategy. Utilize it to compare actual results to expected outcomes and make necessary adjustments. Implementing these changes can lead to faster closing times, increased win rates, and a significant boost in revenue growth. (Dive into the world of CRM and its pivotal role in driving revenue growth .)
- Predictive sales analysis: This type of sales analysis is designed to help you predict future risks and opportunities. Use it to create accurate sales forecasts.
- Sales pipeline analysis: This type of sales analysis will help you discover common sales activities prospects go through before they convert. As such, it will give your sales team the context to shorten sales cycles and close more deals.
- Product sales analysis: This type of analysis is perfect for large companies and/or companies with extensive product offerings. It helps them determine which products actually affect their bottom lines. Use it to understand your company's demographics better, pinpoint popular products, and the like.
- Prescriptive analysis: This type of sales analysis will empower your sales reps with knowledge, helping them determine which opportunities to pursue and which to dump like radioactive waste. Use it to increase rep success and team-wide win rates.
- Market research: This type of sales analysis may seem old-fashioned, but it's never gone out of style. To use this technique, survey your customers, research your competitors through web scraping (a technique that automates the process of extracting data from a website ) using curl proxy for greater efficiency and reliability, and read general sales statistics. Once you do, you'll better understand your customer's needs , thereby improving your sales effectiveness.
Step 2: Identify the Specific Information You Need
You've chosen the perfect sales analysis method. It just seems to get you and the sales goals you want to achieve. Congratulations! But your work is far from over…
Now, you need to identify the specific bits of information you need. For example, you might want to measure the impact of your sales training efforts. Or find the top-selling product from a recent marketing campaign. Or determine similarities between repeat customers.
When you know what information you need, you can choose metrics and KPIs to help you acquire, track, and measure it. We'll discuss this a bit more in the next section.
Before we get there, though, we need to talk about timing. What time frames should you collect data for? The answer to that question will depend on the metrics you're tracking, but weekly, monthly, quarterly, and yearly periods are common.
Remember that consistency is essential, regardless of which metrics you monitor. With that in mind, we plan to conduct an analysis more frequently during special promotions.
Step 3: Choose a Sales Analysis Tool and Analyze Your Data
Your sales analysis efforts are going strong! To keep them that way, invest in an analytics tool to help you get the most out of every metric you decide to track. Here are a few ideas:
- Spreadsheets: You gotta love the classics. A spreadsheet tool like Microsoft Excel can help you analyze and interpret your sales data. Just ensure you have sufficient quantity and quality of data before you start. If you don't, you won't be able to make informed decisions that propel your company forward. (Note: sidle up on these report templates to make spreadsheet reporting easier!)
- CRM software: Every sales organization needs a CRM. How else will you store contact information, automate email sequences, and view sales pipelines from one dashboard? Newsflash: your CRM tool can also be used for sales analysis. If you use Close , for example, you can quickly generate reports for any metric or KPI, including detailed pipeline and funnel reports, which will help you with sales forecasting .
- Sales analytics apps: Some tools are entirely dedicated to sales analysis. Chorus.ai , for example, will help you analyze sales calls and pinpoint areas of improvement. Gong.io will help you report on customer interactions and forecast future sales. And Seismic will help you calculate the effect of your sales enablement efforts.
At the end of the day, choose the sales analysis tool to help you accomplish your goals. Look for substance, not style. We all know you'll make better business decisions with the right data analytics tools in your toolbox.
Step 4: Share Your Results with Relevant Stakeholders
Last but not least, you need to present your sales data analysis to key stakeholders.
Unless you’re asked to share the process by which you arrived at your results, only show the main findings. You can use graphs and visuals to help your audience interpret the data. Additionally, employing tools like the revenue growth calculator can be instrumental in visualizing and comprehending complex sales data effectively.
For example, if you lead a sales team and want to share information regarding team performance with your CEO, you might want to include charts around your sales goals, your best-selling products, and your team's revenue and expenses.
Overall, your sales analysis presentations should share actionable insights and be easily understood. They should also end with recommendations to help accomplish this goal.
Seeking sales excellence? Discover the power of challenger selling strategies .
Choosing the Sales Analysis Metrics and KPIs That Matter
At this point, you know exactly how to perform an in-depth sales analysis—follow the four-step process above. Now, you need to choose a few KPIs to monitor.
Here are ten metrics you'll probably end up tracking at some point. This is not an exhaustive list of KPIs. If you want that, check out this article when you're done with it.
1. Monthly Sales Growth
This metric will give you the juicy details on your overall sales revenue. Is it going up, going down, or holding steady? Knowing this will help you better optimize your sales processes.
How to calculate it: (Current month’s performance - Previous month’s performance) / 100
2. Sales Opportunities
This KPI will tell you about the opportunities your sales reps create. It can be used to determine good and bad-fit prospects, which makes it useful for sales prospecting.
How to calculate it: Count the total number of opportunities your sales team creates within a specified period, such as one month, one quarter, or one year.
3. Lead Conversion Rate
This metric will help you understand why and how leads are converted . You can then use this information to design a foolproof customer acquisition plan for your company.
How to calculate it: (Number of leads that converted into opportunity in a given period) / (Number of leads created in this period)
4. Average Conversion Time
This KPI is all about productivity. Track it to determine how long leads can convert into paying customers. You can combine it with other metrics, like lead conversion rate and total sales opportunities, for a handy bird’s eye view of your company's sales pipeline.
How to calculate it: (The sum of all lead conversion times within a specified period) / (Number of lead conversion times included in that period)
5. Monthly Onboarding and Demo Calls Booked
This metric will help you understand the health of your sales funnel. Prospects who make it to the demo and/or onboarding stages of your funnel are likely to convert.
How to calculate it: Count the number of onboarding and demo calls booked in a time period
6. Pipeline Value
This KPI will tell you the revenue you can expect to generate from the sales opportunities in your department's pipeline within a specific time frame.
How to calculate it: (Value of projected sale) x (Percentage of confidence they will close.)
7. Sales Targets
This metric will share historical data regarding team performance. Want to know the amount of revenue generated or the number of product subscriptions sold? This metric will help.
8. Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
This is an extremely popular KPI —with good reason. Track it to learn how much revenue the average customer generates for your company during their lifetime based on the average deal size and how long your customers stay with you. Then, use it to predict future revenue, make informed decisions about customer acquisition , etc.
How to calculate it: (Average revenue per user) x (Average customer lifetime)
9. Calls and Emails Per Rep
This metric tells you how many calls and emails your sales team makes daily, weekly, and monthly. It can be used to evaluate productivity and identify broken sales funnels.
How to calculate it: Tally up the total number of calls/emails your sales team makes within a specified period of time.
Want to amplify your sales results? Dive into our comprehensive guide on the best sales productivity tools available.
10. New and Expansion Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
These are essential metrics for SaaS companies because they tell them how much revenue they generated this month compared to last month. Brands can then use this information to determine the effectiveness of their sales and marketing teams and help minimize churn.
How to calculate these two metrics:
New MRR = (New customers) x (MRR per new customer)
Expansion MRR = [(Expansion MRR at the end of the month – Expansion MRR at the beginning of the month) / Expansion MRR at the beginning of the month] x 100
Fall in Love with Sales Analysis
Sales analysis reports create accountability, reveal insights about one's customer base , the specific traits top-performing sales reps have… Honestly, they have the power to revolutionize your entire sales and decision-making processes, which is why they deserve your unending love and devotion.
The question is, which tool will you use to generate said reports? Here's my advice: choose Close. Our top-rated CRM platform has all the tools you need to create custom reports and monitor specific KPIs. Even better, you can try it with this 14-day free trial before buying it.
That's right, I'm not asking you to put a ring on our hand just yet. Take us out on a date, see what we offer, and then decide if you want to spend the rest of your life with us. (Or at least the rest of your sales career .) Something tells me we're a match made in heaven!
I want to try Close for free for 14 days . (Say YES!!!)
START YOUR FREE 14-DAY TRIAL

More articles from The Close Blog

Discover our latest free sales tools powered by AI
Learn from the sales pros with our free sales guides.
Sales Analysis: Learn To Zoom In & Master the Pipeline [+Types, Importance]
All companies rely on sales figures to see how they are performing. That said, looking at the revenue generated cannot help pinpoint what’s working (or not).
Without metrics to guide you, it’s hard to make educated and data-driven decisions that will benefit your company now and in the future. This is where sales analysis comes in.
In this blog post, we show you the importance of sales analysis, its types, and how to implement it into your workflows.
We’ll also show you how to ‘read between the lines’ of sales analysis reports and help you draw powerful conclusions and insights.
Table of Contents
What Is Sales Analysis?
Sales analysis assesses, analyzes, and monitors a business’s sales efforts. Sales analysis may include capturing, filtering, and analyzing sales data to evaluate past sales performance and predict future sales figures. Sales analysis aids in making strategic business decisions and developing effective sales tactics and strategies.
Sales analysis often includes the following:
- Sales trend analysis: Sales trend analysis is the process of studying sales data of a business over a specified period to determine and identify patterns, fluctuations, and trends. Trend analysis also involves the analysis of seasonal sales trends, market trend analysis, growth rates, sales forecast analysis, and performance comparisons with previous periods.
- Product performance: This sales analysis reveals the products/services that are performing well and the products/services that are not – and helps focus or redirect efforts more effectively.
- Customer behavior : This analysis helps understand your customers better, including their purchasing behavior, and helps businesses tailor their offerings to suit the customers’ needs.
- Sales channel performance: Channel analysis evaluates how effective various sales channels are – this may include direct, online, physical retail, or even social media.
- Sales force performance: Sales force analysis evaluates the performance of sales teams, regions, departments, and even individuals.
- Market comparison: This involves comparing a business’s sales performance and figures with competitors and industry benchmarks and can provide valuable insights.
Sales analysis leverages various analytical and marketing tools to help visualize complex data and monitor a business’s sales performance. This can then be used to formulate a plan of action. AI and machine learning have revolutionized sales analysis, including advanced sales forecasting, predictive analytics, and more.
It is important to note that sales analysis shouldn’t be dull numbers or dry paragraphs. You can visualize it in the form of bar graphs and charts.
Take a look at this example to see what a sample report might look like:
The above sample sales report shows a handful of metrics your company may begin tracking for your sales reps and sales team going forward.
Here are some other KPIs you need to consider:
- Regional sales
- Average purchase value
- Sales per rep
- Quote-to-close
- Cannibalization rate
- Sell-through rate
- Lead conversion rate
- Product performance
- Sales to date
- Sales opportunities
- Sales targets
- Sales growth
Read Also: 10 Top Sales Analysis Software for Small Business Owners
What Are The Different Types of Sales Analysis?
Now that you have a clearer understanding of sales analytics, let’s talk more about the different types of analysis you can perform to get valuable insight metrics.
Market Research
The first type of sales analysis we’re discussing is quite important.
It’s known as market research or market analysis , where sales professionals and sales managers survey leads and potential customers to gain insights about their behavior and affinity towards your products.
You can do this in person or through online surveys — depending on your business type.
👉Get inspired by the best sales page examples to create high-converting pages – explore our comprehensive guide now! 🌟
Prescriptive Analysis
With prescriptive analytics, you use predictive information to learn more about your potential customers.
This tells you which deals are worth chasing and which are better left behind. Also, for the deals your sales team or sales manager does decide to pursue, they’ll have a good approach ready to make the lead or prospect more receptive to the sale.
Diagnostic Analytics
Using diagnostic analytics, you can better review your company’s current and past sales data to understand less-than-stellar emerging issues.
For example, maybe your new product didn’t sell as well because it came out right before the pandemic. This sales data analysis can help you ideate better ways to reach customers and prospects.
👉Winning at sales isn’t just about closing deals. It’s about managing your leads effectively. Discover how in our comprehensive guide on sales lead management .
Sales Effectiveness Analytics
Who are your most effective sales representatives? S ales data analysis can help you pinpoint your best sales rep/sales reps (and those struggling), and can give valuable information during sales coaching.
As this dictates your company’s ability to win deals, you can use this sales data to optimize your workforce and key tasks.
Read more: Sales Blitz Definition, Example, and Sales Strategy
Product Sales Analytics
The success of your products depends on the actionable insights you gain through product sales analysis. You must conduct sales analyses for all the products you sell regularly.
If certain products have gone beyond their useful life and have underperformed for a while, you might use sales metrics here to decide whether or not to continue the said product.
Sales Pipeline Analytics
If you only had one choice, you’d have to choose this one. That’s how important sales pipeline analytics is.
By studying analytics related to your sales pipeline, you can see how many leads convert to customers, how long they remain customers, who your most qualified leads are, what their money-making potential is, and which sales team member is assigned to work with them.
Use a sales analytics software like EngageBay to streamline your sales pipelines.
Read also: 12 Powerful Sales Growth Strategies (+ Calculations)
Predictive Sales Analytics
If you’re not entirely pleased with the accuracy of your sales pipeline analysis , you may want to supplement the information with predictive sales.
These sales data analytics are automated, so your sales forecasting can give you an accurate glimpse into the future. It’s almost like having a crystal ball!
Predictive sales pipeline analysis is super helpful for companies of any size, from small businesses to Fortune 500s and anything in between.
Read also: Sales Report Template — How and Why to Create One
The Importance of Sales Analysis
Let’s look at what all good sales analysis can do for your business.
Presents Long-Term Data You Can Refer Back To
For new businesses, sales analytics is indispensable.
As you begin to experience growth in the years ahead, you can express it in specifics — with numbers and stats to back you up — instead of using general terms.
Even if your company has been around for a few years, it’s never too late to start tracking your sales analytics. Having a long-term sales data record also gives you more comparison points to consider, such as how your company performed five, 10, or even 15 years ago.
Related blog: How to Build the Perfect Sales Enablement Strategy?
Offers Deeper Understanding of Your Customers
Does sales data analysis sound too dry to you? Well, what if we refer to it as ‘Customer Analytics?’
You can see which products and services your customers like, as these will be the ones that sell the best. You can also take a closer look into your sales pipeline to review how many prospects and customers you can reach and convert.
Having a pulse on what makes your prospects and customers tick is one of the greatest tasks of any company. If you understand your audience inside and out, you’ll have more conversions and greater sales — and you can retain customers better .
Read also: Breaking the Rules — The Art of Guerrilla Marketing and Why It Works
Makes Sense of Market Trends and Data
In the last section, we mentioned market research as one of the top sales trend analysis methods.
Having good data about your audience lets you craft sales deals that become useful for your company in many ways. For example, before unveiling a new product or service, you can refer to your sales target market data to gauge receptiveness.
This lets you build awareness and create a winning sales and marketing campaign that will result in happier customers and more sales.
Fewer Missed or Lost Opportunities
Why take shots in the dark when you have sales analysis?
Without sales performance analysis, we can guarantee you’re missing out on opportunities — even if your sales team works tirelessly.
As the saying goes: ‘’Work smarter, not harder.’’ Each lost or missed opportunity is money your company loses.
Market research is crucial in reclaiming these lost opportunities. When you know your audience better, you can identify sales opportunities that weren’t otherwise apparent.
Read also: The Sales Analyst Job Description at 25 Top Companies
How to Perform a Sales Analysis Using CRM Tools
To understand your customers, continue selling goods they care about, and predict future market trends, analyze sales forecasts, your company must begin gathering sales data .
Using a customer relationship management (CRM) software like EngageBay, you can perform sales analysis without needing an expensive sales force software.
The sales process involves three simple steps:
Step 1: Determine Which Sales Data Will Go into the Report and Gather the Data
Using the metrics and types of sales analyses covered in this article, determine which sales data is most important to your company at this stage — a crucial stage of the sales process. Metrics can be anything from competitive analysis, net sales, product sale data, revenue, and even Google Analytics data to help you make informed decisions.
Ask yourself some questions during this early yet critical stage of formulating your own sales analysis report based on sales activity:
- Which of your products sells the most?
- Does one product have anything in common with the other? If so, what, and can you replicate it?
- Who are your repeat customers?
- What characteristics or traits do they have in common?
- How much time do you put into your company’s sales training?
Yes, those are a lot of questions you need to answer, but you must take the time to go through them one by one and come up with accurate, data-driven responses.
You don’t necessarily have to do this by yourself, so involve other key stakeholders in your company and your sales and marketing teams .
Once you can answer those all-important questions, you need to determine what your most relevant variables are to meet your sales goals.
Read also: What Is Sales Volume? 8 Strategies to Boost Your Revenue
Step 2: Use a CRM Tool for Evaluating Your Sales Data
Whether your CRM software requires you to manually input your information or import it over, get all the sales data loaded into the program.
You can then draw up an overview of your company’s sales (present and past sales).
Step 3: Send the Report to People Who Matter
Once you get the reports, you can let your marketing, sales, and customer service teams take a look. This can help them tremendously as it offers a roadmap to improve their sales processes.
Read also: 10 Data-driven Marketing Trends You Can’t Ignore
How Do You Analyze Sales Reports?
How do you analyze a sales report ? Here are some tips for making sense of all the information in front of you.
Determine a Relevant Range
Keep the time range in mind when creating your analysis report, so you’re not left to scale a seemingly endless mountain of numbers. Depending on what you need, you can look at quarterly data, or sales data from a year or two back to compare with current benchmarks.
Even if you went overboard in your sales reporting, you can clip the sales data range and present only the dates you want displayed, as this is most relevant to what’s happening in your company now.
👉Want to take your sales game to the next level? Understand the real meaning of strategic selling from our comprehensive guide .
Focus on Certain Sales Metrics
With a dozen or so sales metrics you can track to determine the success of your sales team, it’s easy to feel a little overwhelmed.
Again, there’s no need to present every single sales metric if your stakeholders are only interested in lead conversions or product cannibalization info.
Cherry-picking metrics is all well and good and sometimes even preferable. However, ensure you don’t fall into the trap of only pulling the sales metrics that make your company look great and sweeping the bad metrics under the rug — successful sales leaders warn against doing this.
Failing to paint the whole picture of a poor sales period can cause you to lose business partners, which is almost as bad as losing customers. It’s certainly just as costly.
Read also: Why are Startups Losing Money (& What to Do About It)?
Now that you know the importance of sales analysis for your business, it’s time to implement it.
A sales analysis tool shows both sides of the coin: On the one hand, you get to know the best-performing sales agents, segment hot leads, set up your sales goal, and identify the campaigns that bring in customers in hordes.
On the other hand, you can weed out cold leads, train struggling agents, and tweak or improve failed products or campaigns.
There are a few great CRM software in the market today. For small businesses that need a comprehensive yet affordable sales analysis software, EngageBay is an excellent choice.
Watch this testimonial from Lauraine M., a small business owner:
It’s more than a sales analysis tool, though.
You get hundreds of marketing, sales, and customer service features — all packed into affordable plans. You get all your reports in neatly organized dashboards. Oh, and you can create custom ones, too.
Sign up now, or book a 30-minute demo with our experts — we are here to help you grow your business.
About The Author
Nicole Malczan
Leave a comment cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
RESOURCE CENTRE
What is sales analysis, what is sales analysis.
Sales analysis is the art of transforming sales data into actionable insights that help boost profitability, enhance customer satisfaction, and inform data-driven decisions. An efficient sales analysis scrutinises sales data, identifies patterns, trends, and opportunities, and uses this information to streamline operations, improve sales strategies, and ultimately achieve measurable sales results too.
Sales analysis helps you identify:
- Peak sales periods
- Bestselling products
Armed with this information, you can optimise your inventory and streamline your operations for maximum efficiency.
The importance of sales analysis
Sales analysis is your strategic shield against uncertainties like market fluctuations and changing consumer preferences. Deciphering and analysing sales data uncovers vital insights. It transforms numbers into actionable strategies, serving as your GPS in the sales labyrinth, guiding you to the most profitable routes.
Elevating sales reps to peak performance
By delving into sales data, you can identify your top performers, understand their strategies, and replicate their success across the board. You will uncover areas for improvement, enabling you to provide targeted training and support. With this data-driven approach, you will turn your sales team into a powerhouse of revenue generation.
Quick tips:
- Implement a robust Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system to collect, store, and review sales data.
- Utilise analytics tools to identify top performers and understand their strategies.
- Encourage collaboration and knowledge-sharing among team members. Cross-functional alignment is the #1 tactic for driving growth and 81% of sales representatives say team selling helps them close deals ( Salesforce State of Sales Report )
- Conduct regular training sessions to share successful strategies with the entire sales team.
Boosting morale to create a culture of success
By identifying and rewarding top performers, you create a culture of healthy competition and motivation. Digging into sales analysis can help set realistic goals, giving your team a clear path to success. When your reps notice their efforts directly translating into results, job satisfaction and morale shoot through the roof. This translates into better customer interactions and, ultimately, more sales.
- Establish a formal recognition program that highlights and rewards top-performing sales reps based on key metrics such as revenue generated, conversion rates, or customer satisfaction scores.
- Set SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals with each sales rep. Analyse past performance data to establish realistic targets that motivate and challenge the team.
- Clearly communicate expectations and milestones to ensure a shared understanding of success.
- Use sales analytics to provide transparent and objective performance feedback; review and adjust goals based on performance and market dynamics.
Accelerating business growth with quick decisions
In today's fast-paced business world, quick decisions are often the difference between success and stagnation. Sales analysis offers you the gift of agility. You can rapidly respond to changing market conditions, identify trends, and pivot your strategies accordingly. No more waiting for the quarterly report – with real-time data at your fingertips, you are always a step ahead. This nimbleness helps you capitalise on opportunities and mitigate risks swiftly.
- Invest in a data analytics platform that offers real-time insights into sales performance.
- Train teams on the effective use of analytics tools to make informed, swift decisions.
- Regularly review and refine decision-making processes based on feedback and outcomes.
- Implement tools for continuous monitoring of market trends and competitor activities e.g. tools for monitoring social media, web analytics, customer feedback and review platforms, surveys and polls, etc.
Types of sales analysis
1. sales forecasting.
Sales forecasting is the practice of using historical sales data and market analysis to predict future sales accurately. This information prepares you for seasonal peaks so you can optimise inventory and ensure your business sails smoothly through market volatility.
Harness the full potential of sales forecasting with:
- Time series analysis: Use specialised forecasting software to gauge historical sales data and identify patterns and trends over time. This could involve monthly, quarterly, or yearly sales figures.
- Predictive analytics: Employ predictive modelling techniques to forecast future sales based on factors like seasonality, economic indicators, and market trends. Machine learning algorithms can be used to build predictive models for more accurate forecasts.
- Ensure that your historical data is accurate and comprehensive for meaningful forecasting.
- Work with marketing, finance, and operations teams to gather relevant data that might impact sales.
- Markets evolve, so regularly review and update your forecasting models to reflect changing conditions.
- Prepare for different scenarios by running simulations based on various market conditions.
2. Sales management
Sales management is the process of overseeing and optimising the performance of a sales team to achieve revenue goals and maximise profitability. Sales analysis in this context involves monitoring individual and team performance, identifying areas for improvement, and providing the right tools and training.
Optimise sales management using dashboards that provide real-time insights into individual and team performance, visualising key sales metrics like conversion rates, deal pipelines, and revenue generated.
3. Sales reporting
Sales reporting offers insights into what's happening within your sales department, resembling your daily news source but with data instead of headlines. It is the process of transforming sales data into comprehensible insights that guide informed business decisions.
By regularly generating and reviewing sales reports, you can track your progress, identify areas of success, and pinpoint weaknesses. This leads to informed decision-making, whether it is adjusting marketing strategies, optimising sales channels, or fine-tuning product offerings.
- Automate reporting processes to save time and ensure regular, timely updates.
- Tailor reports to focus on the most critical metrics for your business goals.
- Gather feedback on the usefulness of reports and iterate to continuously improve the reporting process.
How to use sales analysis data
Customer segmentation: tailoring the experience.
92% of companies are using data effectively to understand customer behaviour (Salesforce State of Commerce Report).
Sales analysis data allows you to categorise your customers based on demographics, purchase history, and behaviour. By understanding the unique needs and preferences of different customer segments, you can tailor your marketing strategies, product offerings, and customer service to create a personalised experience that drives loyalty and repeat-business.
Market expansion: Identifying growth opportunities
Companies wielding powerful customer analytics are 1.5 times more likely to achieve rapid sales growth, with a sales cycle capable of driving a 15–25% boost in earnings, thereby fuelling market expansion. (McKinsey Research- Future of B2B Sales)
Sales analysis data is your compass for market expansion. By identifying underperforming regions or segments with growth potential, you decide where to focus your marketing and sales efforts. Whether it is targeting new geographies or entering new customer segments, this data empowers you to expand strategically.
Pricing strategies: Maximising profit margins
Price management initiatives can increase a company’s margins by 2%- 7% in 12 months—yielding an ROI between 200%- 350% . (Deloitte’s Three-Minute Guide to Pricing Analytics)
Pricing is a critical factor in profitability. With sales analysis data, you can evaluate the performance of different price points, discounts, and promotions. You can identify the sweet spot where your products or services are competitively priced while maximising profit margins. This data-driven approach helps you make strategic pricing decisions that boost your bottom line.
Inventory optimisation: Minimising waste
Product development: meeting market needs.
Your product or service portfolio should evolve to meet changing market demands. Sales analysis data sheds light on which products are thriving and which ones need improvement or retirement. It guides you in developing new products or enhancing existing ones to stay competitive and satisfy your customers' evolving needs.
Follow these steps before you get your raw sales data ready for mining:

Top sales analysis metrics & KPIs
Your data is a gold mine, but it speaks in the language of metrics and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators). Understanding these metrics and indicators is vital to making the most out of your sales analysis data.
Here's a comprehensive list:
Revenue is the ultimate metric that reveals the financial health of your business. Tracking your total income over time helps you assess the impact of your sales strategies and marketing efforts. The goal is to ensure consistent growth and stability.
Discover: How to optimise your revenue lifecycle management
Net profit margin
Gross profit margin, customer lifetime value (ltv).
Sales do not stop at the checkout. Customer LTV measures the total revenue a customer generates throughout their relationship with your business. By understanding LTV, you can tailor your marketing strategies to retain and maximise the value of each customer.
Churn rate reveals how many customers you lose over a specific period. High churn rates can erode your revenue and profitability. By tracking and addressing churn, you can implement strategies to retain customers and boost long-term success.
Retention rate
Retaining customers is often more cost-effective than acquiring new ones. Retention rate reflects the percentage of customers who continue to do business with you over time. High retention rates are a testament to your customer-centric approach and can significantly impact your bottom line.
80% of sales reps emphasise the growing significance of post-close customer relationships. Top performers enhance customer retention through value-based communication, accountability, and proactive feedback-seeking after a sale.
How sales analysis reports help
Sales analysis reports offer a comprehensive snapshot of crucial sales data and metrics, streamlining the process of optimising your sales strategies by swiftly pinpointing strengths and weaknesses.
A typical sales analysis report has five to seven components. Here’s how each of them empowers your business.
|
|
The overview: A bird's-eye view of your sales pipeline performance | This section gives you an immediate sense of how well your business is performing and areas that need attention. |
Performance metrics | Performance metrics allow you to assess the effectiveness of your sales and marketing efforts. By comparing actual performance with goals, you can identify areas for improvement and fine-tune your operations for better results. |
Market analysis | Market analysis helps you understand customer preferences, market trends, and competitive landscapes. Armed with this knowledge, you can adjust your strategies to remain competitive and capture opportunities as they arise. |
Customer insights | Customer insights help you identify your most loyal customers, track their buying patterns, and tailor your services to meet their needs. This customer-centric approach enhances satisfaction, fosters loyalty, and translates into long-term profitability. |
Product evaluation | Product evaluation helps you identify your best-sellers and slow movers, enabling you to optimise your product mix. This section also provides valuable insights into inventory management and turnover rates. |
Sales channel breakdown | A sales channel breakdown dissects your sales sources, from online to offline, different regions, and more. By understanding where your actual sales originate, you can allocate resources efficiently to the most effective channels. It guides you in making informed decisions regarding sales and marketing strategies. |
Budget optimisation | Budget allocation examines how you are spending your resources, including marketing, advertising, and promotional expenses. It enables you to assess the efficiency of your resource allocation and helps identify areas where you can optimise costs. By ensuring resources are allocated effectively, you can improve the overall profitability of your business. |
Sales analysis tools and CRM (Customer Relationship Management)
Sales analysis tools are software or applications that empower businesses to collect, analyse, and interpret sales data and key performance metrics, enabling data-driven decisions and strategic improvements in sales and marketing strategies. Examples of sales analysis tools include business intelligence platforms, forecasting software, sales automation and management software, reporting engines to monitor sales activities, and solutions for email productivity and sales acceleration. CRM systems, on the other hand, focus on nurturing customer relationships, enhancing customer experience, and boosting loyalty.
Sales analysis tools and CRM are the dynamic duo that empowers businesses to thrive. These tools offer deep insights into sales data, helping you make data-driven decisions.
Choosing the right sales analysis tools
Scalability: Consider your business's current size and potential for growth. Ensure the tools can scale with your business.
Integration: Look for tools that can seamlessly integrate with your existing systems and software to avoid data silos.
Ease of use: User-friendliness is key. Opt for tools that your team can quickly adopt without extensive training.
Data security: Protecting customer and sales data is non-negotiable. Ensure the tools adhere to robust security standards.
Charting the course to success with Salesforce
Sales analysis tools have become indispensable for organisations seeking to enhance their sales strategies and boost overall business performance. Salesforce, a market leader in customer relationship management , offers a powerful suite of tools that can transform your sales analysis process. By leveraging Salesforce, you can gain valuable insights into your sales data, track key performance metrics, and make data-driven decisions to enhance customer engagement and satisfaction.
Unsure where to begin? Explore our free demo to kickstart your journey towards optimising your sales strategies, identifying pivotal moments of truth, and crafting a more engaging and rewarding customer experience.
Discover how Salesforce can be your trusted partner in understanding customer journeys, enhancing sales performance, and building lasting customer relationships.

Trends in Sales Operations

What Is a Sales Pipeline and How Do You Build One? A Complete Guide
More resources.

Research and Report
Trends in Generative AI for Sales

Your Sales Tech Stack Is About to Get a Whole Lot Smaller

What Is a Sales Pipeline and How Do You Build One?
Get monthly updates and fresh ideas delivered to your inbox.

- Sales CRM Software
- Application Portals
- Call Center CRM
- Mobile CRM App
- Omnichannel Communication CONVERSE
- Reporting Dashboard SIERA
- Lead Management System
- Opportunity Management
- Sales Process Automation
- Sales Tracking
- Door-to-Door Sales
- Remote Team Management
- Field Sales CRM
- Merchant Onboarding App
- App UI/UX Customizer CASA
- Outside Sales CRM
- Field Force Automation
- Collections Management
- Field Force Tracking
- Event Campaign Management
- Bancassurance Management
- Marketing Automation
- Chatbot - Website
- Chatbot - WhatsApp
- Landing Pages
- Email Campaigns
- Lead Capture Automation
- Lead Engagement
- BTL Marketing Automation
- Advanced Marketing Analytics
- Hospitals and Clinics
- Hospice and Palliative Care
- Fertility Clinics
- Dental Care
- Diagnostics Labs
- ACQUISITION
- Patient Intake Automation
- Patient Appointment Scheduling
- Healthcare Call Center Solution
- Patient Experience Management
- Self-serve Patient Portals
- EHR Integration
- Physician Empanelment
- Security and Compliance
- Patient Engagement
- Higher Education
- Pre-schools and K12
- Training Institutions
- Overseas Education
- Student Recruitment Software
- Admission Portal
- Teacher Onboarding
- Publisher Portal
- Admission Software
- Credit Unions
- Securities and Trading
- Lending CRM
- Loan Origination System
- WhatsApp Lending Bot
- Debt Recovery Automation
- Bancassurance Solution
- PAPERLESS ONBOARDING
- e-KYC Solution
- Video KYC Solution
- Merchant Onboarding
- Merchant Lifecycle Management
- Travel and Hospitality
- Agriculture
- Home Improvement
- View by Industries
- What is Sales Analytics? [Benefits, Types, and Metrics to Track]

Analytics has become an integral part of life, from finding the shortest route to work to forecasting stock market trends.
Analyzing previous trends ensures that businesses always make the right decision. And as the scale of the decision and its impact magnifies, more robust analytics need to take over. The gut feeling cannot cut it anymore.
According to McKinsey, businesses that rely on data to make decisions are 19 times more likely to be profitable. It’s no surprise that sales, a number-driven aspect of business, benefits from the right analytics. If your goal is fast and sustainable growth, your sales team must make quick and accurate decisions to improve its performance.
Sales analytics isn’t a new term. Businesses have been using it for years to optimize various steps of the sales cycle . But most of them are just at the tip of the iceberg when it comes to intelligent sales analytics.
This article aims to help you identify appropriate sales analytics to resolve business challenges.
What is Sales Analytics?
Sales analytics refers to the use of technology to collect and use sales data to derive actionable insights. It is used to identify, optimize, and forecast sales. It uses different metrics and KPIs to plan an efficient sales model that generates higher revenue for the business. Here’s how Prashant Ahlawat, Vice President – Analytics and Transformation, at LeadSquared, defines sales analytics:
“Sales analytics is a compass for your sales teams. It guides you towards growth using tools that track past data and current performance against goals. The analytics reports then help you plan targets in the future.”
Sales involves many stages with their own set of metrics. There’s always an abundance of data to track, but it’s hard to make sense of it every time.
While you may want to use data to find gaps in your sales processes, it’s next to impossible without the right tools.
One such tool is sales analytics. It can help you identify gaps and improve your sales processes.
Let’s take a closer look at it.
Benefits of Sales Analytics
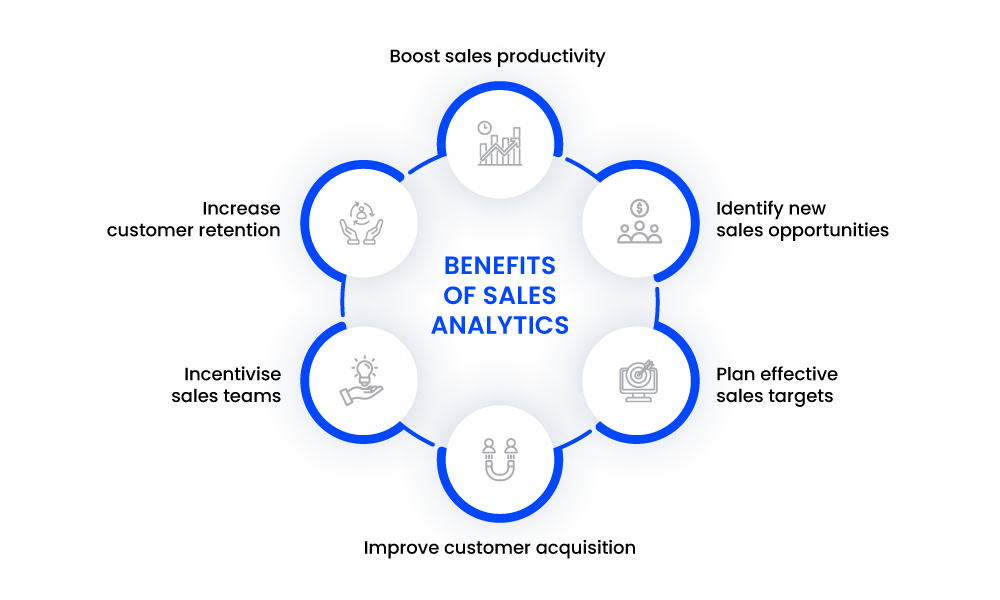
1. Boost sales productivity
Sales reps need to always be on their toes to achieve results. Sales processes are often complex. You’ll find several hurdles between lead gen to closing a sale .
Data analytics in sales help managers decrease the sales cycle length by identifying the areas of improvement. Along with an average 20% increase in sales productivity , analytics also helps salespeople decrease leakages in the sales pipeline .
2. Identify new sales opportunities
As a business grows, products evolve, new sales opportunities emerge. Tracking sales data helps enterprises understand the product fitment across industries and regions. The historical data allows salespeople to define their customer base and introduce opportunities to upsell and cross-sell .
3. Plan effective sales targets
Sales data—deals closed, qualified opportunities, length of sales cycles—captured over a year or even a quarter, can significantly improve the way businesses strategize their sales targets .
Predictive analysis helps forecast sales revenues and set individual targets based on your sales team’s performance.
4. Improve customer acquisition
Personalized customer journeys are hard to build without insights into customer behavior. The customer’s journey has multiple touchpoints , which can be improved by tracking factors like time on a certain website, tone during the call, and response rate. Customer analytics help salespeople make relevant recommendations, and over 44% of businesses use it to acquire new customers.
5. Incentivise sales teams
Incentives are the biggest motivator for sales teams. But you can’t reward their performance without accurate records.
Recording sales activities and their outcomes help businesses incentivize their sales teams fairly. Analytics simplify payroll management and help managers choose an appropriate sales commission structure .
6. Increase customer retention
Every business aims to improve their Customer Lifetime Value because acquiring a new customer is 5X more expensive than retaining one. And that’s precisely what sales analytics help you achieve! Diagnosing the possible drop-off stages and taking preventive measures brings down the number of churned accounts.
So, now you know the benefits of sales analytics. And the first step to achieve them is to use the right type of sales analytics that align with your sales goals .
7 Types of Sales Analytics [+ Metrics to Track!]
The scope of sales analysis is vast.
But it all boils down to choosing the right analytics and metrics that help you achieve your business goals.
Business analytics fall under four broad categories:
- Descriptive
- Diagnostic
- Predictive
- Prescriptive
However, sales analytics are more specific to a business’ sales process. Let’s look at the 7 essential sales analytics and relevant metrics under each type.
1. Market Research Analytics
Marketing research involves deriving data related to target customers, well-performing regions, and untapped markets. It is vital to launch a new product and begin sales in new geos.
The metrics to track are:
- Targetable customer base
- Region-wise sales
- Competitor performance and market share
- Demand for the product
- Sales performance in the previous quarter (Especially if you’re looking to ramp up sales in a certain region)
2. Product Sales Analytics
Product Sales Analytics can be highly effective for businesses with multiple or seasonal product offerings. It considers the performance of every product or service that the company offers. It helps the sales team identify the products to focus on based on the revenue and sales targets . The analytics can be tracked for a certain timeframe and demographic.
- Net Promoter Score (NPS) for the product/service (NPS score= %promoters – %detractors, where promoters rate your product 8-10 and detractors rate it 0-7 out of 10)
- The number of active users over a daily and monthly timeframe.
- Monthly recurring revenue (MRR = Average revenue per account x Total number of accounts)
- % Sales volume ((Units of individual product sold x 100) ÷ Total units of all products sold)
- Repeat buys per product (Repeat Purchase Rate = (Repeat customers x 100) ÷ Total customers)
- Minimum, maximum, and average selling price per product
Comparing these metrics across different products/services helps you ramp up sales or drop certain products.
3. Sales Effectiveness Analytics
Almost every business would want to track its sales effectiveness. The extent and type of analytics used to monitor teams vary across different industries and businesses.
Tracking productivity and sales effectiveness on a daily, monthly, and quarterly basis help in identifying your team’s scope of improvement.
The metrics to track differ as per the targets that the business has set and its sales workflow. B2Cs usually have a higher sales velocity and shorter sales cycles than B2Bs. But in general, here are a few metrics that B2Bs and B2Cs rely on.
Sales effectiveness metrics for B2B businesses
- Target achievement analytics (Your targets can be conversions or revenue dependent. For revenue dependent targets, % Achievement = (Revenue generated x 100) ÷ Target revenue). And for conversion dependent targets, % Achievement = (Number of deals closed x 100) ÷ Target conversions.))
- Number of meetings generated
- Ratio of leads to qualified meetings
- Ratio of qualified meetings to conversions
- Attrition rate (Usually calculated for team managers, Attrition Rate = (No. Of employees who left the team x 100) ÷ Average no. of team members)
- Customer feedback
- Sales and CRM hygiene
Sales effectiveness metrics for B2C businesses
- Daily talk time
- Weekly and monthly sales conversions (Conversion Rate = (Conversions x 100) ÷ Total opportunities)
- Turnaround time
- Lead to opportunity ratio
- Total revenue generated (Total Revenue = Number of products sold X Cost per unit)
- Customer feedback
- Length of the sales cycle
- Sales and CRM hygiene
4. Sales Pipeline Analytics
The journey from a qualified prospect to a customer is mapped in the sales pipeline . But each stage in the sales pipeline can turn into a drop-off point if it isn’t properly tracked and analyzed. Sales pipeline analytics help you determine what slows down the conversions and what you can do to speed it up.
The metrics to track are:
- Conversion rate by sales funnel stage
- Pipeline to conversions ratio
- Weighted value of pipeline (Weighted value = Probability of Closing x Deal Value, where the probability depends on the stage of the pipeline, such as 50% for the negotiation stage)
- Sales Pipeline Velocity (Sales Pipeline velocity= (Number of deals in pipeline x Average deal size) ÷ Average sales cycle length)
- Pipeline Coverage (Number of opportunities in pipeline for given period ÷ quota period)
- Deal Drop-off by Stage
- Sales Rep Pipeline Performance
(Also read: 32 Sales KPIs Every Manager Should Measure to learn more about the different sales performance metrics in detail)
6. Predictive Analytics for Sales Strategy
Every business aims to grow faster, witness higher conversions, and create an unmatched revenue stream. Hours of planning, strategizing, and forecasting go into realizing these goals, but there’s no guarantee they’ll be met. Creating a sales strategy using analytics can’t assure the desired results, but the chances that you will meet them shoot up. Forecasting growth while keeping all the variables in mind is highly complicated. Sales data from the past acts as a benchmark and every year the stakes are increased to ensure business growth.
Here are some of the metrics that help you set suitable targets for your teams:
- Year-over-year (YoY) growth ([(Current Year’s Revenue – Previous Year’s Revenue) x 100] ÷ Previous Year’s Revenue)
- People level analytics to assess team’s performance
- Lead Scoring , which helps you prioritize warm leads for faster conversions
- Sales Cycle length (Sum of the Number of days it took to close each deal ÷ Total Number of deals)
- Win rate (Deals closed ÷ Total Number of deals)
- Sales Linearity assesses if the progression of leads in the pipeline is as predicted
- Marketing Qualified Leads (MQL) to Sales Qualified Leads (SQL) conversion rate
7. Churn Analytics
Churned accounts can be discouraging for your sales teams. Also, it brings a steep drop in your annual revenue.
Churn analytics help you identify touchpoints with a higher drop-off rate and the accounts with a high churn probability. A lot of the churn metrics are qualitative or based on customer behavior. With this information, your salespeople can intervene to prevent churn.
The churn analytics can be divided into two categories, predictive and post-mortem. The metrics to track are interdependent for both these categories.
Metrics that predict churn:
- Low user activity
- Slow response rate
- No opportunities to upsell
- Delayed payments
Once the account is churned, it is important to evaluate the factors that caused the churn to avoid them for other accounts. It is also known as the post-mortem of the churn.
Metrics to analyze the churn:
- Lifetime Value (LTV) of a customer (LTV = Lifetime Value = Average Value of Sale × Number of Transactions × Retention Time Period)
- Churn rate ((Lost Customers ÷ Total Customers at the Start of Time Period) x 100)
- Customer and revenue churn (% Change in number of customers and annual revenue because of the churn)
8. Marketing analytics
Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs) have high intent and can be easily converted into a customer by the sales team. Employing the right marketing analytics ensure that leads keep flowing into the sales funnel .
Usually, many campaigns and marketing activities run in parallel. Figuring out which strategy generates the highest ROI and brings in the greatest number of leads is extremely important. So, analyzing your lead sources and the effectiveness of each campaign helps the marketing team restructure their budgets to improve the volume of quality leads.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) (Customer Acquisition Cost = Cost of sales and marketing ÷ number of new customers acquired)
- Lead to acquisition ratio (Lifetime Value (LTV) ÷ Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC))
- Traffic by source
- Number of Market Qualified Leads
- ROI from each Lead Source
- Lead to Demo Conversions
- Average Search Engine Results Page (SERP) Position
Now that we’ve discussed all the types of sales analysis methods, mapping them to your business analytics becomes extremely easy. This table sums it all up.

You can bookmark this page or download this Sales Analytics Guide to share with your team. Sales analytics carry the power to transform your business However, the general notion is analytics is a high-end and complicated matter that’ll take up a lot of investment.
But this isn’t true; you just need to identify what works for your business.
Getting Started with Sales Analytics
“Any business with a sales team needs sales analytics, irrespective of the industry or the complexity of your product. All KPIs that you set for your teams should be tracked and analyzed, even if you use the most basic reports.” Murali Krishna, Vice President – Sales, LeadSquared
The biggest deterrents to using advanced sales analytics tools are the cost and the need for a well-defined sales process. However, sales analysis doesn’t always need a tool.
For businesses with small teams or a short and simple sales process, people-level analytics and sales effectiveness metrics should suffice. The business can effortlessly record and analyze this data on Excel sheets.
As the size of your sales team increases, Excel sheets begin to break. The amount of data increases exponentially and only a good sales analytics software can meet the requirements.
A sales analytics software is also essential if you have multiple product offerings that need to be mapped to customers.
“While a few industries can make do without a sales analytics software, it’s a basic requirement for others such as edtech, real estate, banking and insurance, manufacturing, and e-commerce.” Pritika Khorana, Regional Sales Manager, LeadSquared
If you’re just getting started with sales analytics, the following courses and books could help!
Sales Analytics Courses:
1. LinkedIn’s Business Analytics: Sales Data 2. Sales Analytics Beginner Complete Course by Udemy 3. Wharton’s Business Analytics
Sales Analytics Books:
1. The Power of Sales Analytics by A. Zoltners, P. Sinha, and S. Lorimer 2. Predictive Analytics: The Power to Predict Who Will Click, Buy, Lie, or Die by E. Siegel 3. Business Analytics: Data Analysis & Decision Making by S. Christian Albright and Wayne L. Winston
The right sales analytics can be a game-changer for your business. That’s exactly how Tricoci University of Beauty Culture, a Chicago-based cosmetology school, increased their process efficiency by 75%.
Here’s a little peek into their sales analysis journey with LeadSquared.
How Tricoci University Increased Process Efficiency by 75%
Tricoci University has 16 campuses spread across Illinois, Wisconsin, and Indiana. The school takes pride on its people-centric approach to preparing the leading beauty professionals of tomorrow.
An absence of sales and marketing analytics made it hard for them to improve their enrolment process quickly. Here’s when they chose LeadSquared as their CRM tool to meet their enrolment goals.
| Introduce touchpoints to regularly track and store data | Digital student enrolment journeys with a detailed view of the admissions pipeline. | Real-time tracking of the lead stage, intent, and activities. |
| Generate impactful insights from sales data to improve the enrolment process. | Ability to enrolment workflows using sales and marketing data. | Improved process efficiency by |
| Improve the productivity of their enrolments team. | with various performance metrics to evaluate the team. | Highly productive sales teams. Improved remote team management. |
The sales analytics journey will be impactful only when the data trends are visualized and reported. There are a few ways to go about this. You can either integrate your sales data with a visualization and reporting tool—like Tableau, Microsoft Power BI, or Qlikview— or you can opt for a CRM with reporting tools.
Both these options work great for businesses, but a CRM with sales reporting abilities is more convenient and financially feasible. LeadSquared CRM , with its advanced reporting tools, is a one-stop solution to track and visualize sales data.
Watch our Masterclass on LeadSquared Reports & Analytics to understand the different types of reports that you can generate on the LeadSquared platform.
Every business intends to use its sales analytics software for different purposes. And there are many that you can choose from.
Key Features of a Sales Analytics Tool
A sales analytics tool tracks and analyzes sales data to make actionable improvements. But choosing the right tool for sales analysis is imperative. Here’s a checklist of the features that you should evaluate before you purchase a new sales analytics software.
1. Visualization Capabilities
The tool should be able to visualize your sales data in every way possible–charts, tables, graphs, or tables. It’s important to note that the visualization must be real-time and easy to generate and access.
2. Scalability
Can the tool handle the data when your team and the number of leads increase by 10X or 15X? If you aim to grow rapidly, it’s important for the tool to scale along with your business.
3. Platform Security
Loss of data, whether it is process-related or sensitive lead information, can affect your business negatively. The platform should be secure enough to prevent data leaks and the loss of important information.
4. Uptime of the system
Sales data is generated by the minute. So, your sales analytics software must always stay operational. The core engine should be robust enough to carry out all the calculations and handle reports even when lead volume peaks.
5. Short term and long-term data insights
The insights must help you make decisions both on a short and long term. For instance, on a daily/weekly and on a monthly/quarterly/yearly basis. So, the software must consistently record and update the data.
I hope this article helps you streamline your sales analytics strategy to resolve any business challenges you may face. To sum it up, sales analysis is all about putting your data to work to improve sales outcomes. With the right tool, sales analytics can completely transform your business.
A CRM is one such tool to track sales data, record it, and derive insights from it. If you’re looking for a CRM with advanced monitoring and reporting capabilities, you should give LeadSquared a shot!
Book a demo to know more about LeadSquared’s Sales CRM.
Sales analytics is used to identify, optimize, and forecast sales. It uses different metrics and KPIs to strategize a sales model that is efficient and generates high revenue for a business.
Sales data that is tracked on a CRM can be used to generate insightful reports. These reports help you boost sales productivity, increase customer retention , improve sales strategy and generate a high lead volume. The CRM analytics also highlight the products and markets that your sales team must focus on.
Business analytics fall under four broad categories—descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. They take both qualitative and quantitative factors into account and help your business achieve rapid growth.

Kritika is a content writer at LeadSquared. She loves reading and is trying to learn more about sales. Through her writing, she wants to make sales easier for everyone. You can connect with her on LinkedIn or write to her at [email protected].
Table of Contents
- Share on Facebook
- Share on WhatsApp
- Share on LinkedIn
Want to see LeadSquared in action?
- Customer Portal
- Performance Management
- Dev Platform LAPPS
- Help Portal
- Pricing SALES
- Pricing MARKETING
- Education CRM
- Healthcare CRM
- Insurance CRM
- Banking CRM
- Real Estate
- Marketplace CRM
- Manufacturing CRM
- What is CRM
- What is lead management
- What is vendor management
- What is sales management
- Case Studies
- Guides & Blogs
- Compare CRM
- CRM Glossary
- Sales Glossary
- Media & News
GET IN TOUCH
(+1) 732-385-3546 (US)
081-48549748 (India Sales)
080-46801265 (India Support)
62-87750-350-446 (ID)
- Legal & Compliance

Attain 100% lead capture, 75% increase in sales efficiency and 2x engagement.

What should you look for in a CRM software?
10 Important Sales Analysis Reports [+ 4 Sales Report Templates]
Published: October 28, 2022
Are you finding it difficult to hit your sales goals , unclog your sales funnel , and increase your sales velocity ? Sales reports can help.

Sales reports allow you to improve your sales process, fill knowledge gaps, and hit your quotas consistently. As a sales manager, creating a sales report also allows you to gather hard data for your colleagues or C-suite to make informed decisions quickly.
In this post, you’ll learn what sales reports are, their benefits, and how to use sales report templates.

What is a sales report?
- Benefits of Sales Reporting
How to Write a Sales Report
Types of sales analysis reports, sales report templates.
A sales report or sales analysis report is a document that shows trends impacting your sales operations within a specific period. While the content of sales reports may vary depending on your goal, they include metrics like revenue, accounts won, leads, and more. Insights from these reports help you identify the strengths and weaknesses of your sales strategy.
.png)
Free Sales Metrics Calculator
A free, interactive template to calculate your sales KPIs.
- Average Deal Size
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV)
Download Free
All fields are required.
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
The Benefits of Sales Reporting
Reporting data in a standardized way is crucial to the success of your business. Here are the common benefits of developing a sales reporting cadence.
Improving Team and Reps Performance
Sales reports provide data-driven insights about the sales performance of individual reps and your entire team. This allows you to know if underperforming reps need coaching. You can also identify who would benefit from regular one-on-one meetings to level up and hit their quotas.
The same applies to your team. If your team isn’t hitting the company’s revenue goals, you can use sales reports to find gaps to improve your sales process .
Assisting Fast Decision-making
Making informed and timely decisions is vital to the success of any sales strategy . This is where sales reporting shines.
With regular sales reporting, your C-suite or managers can quickly iterate on what drives the company's growth. You can also track and adjust sales tactics that are performing below par.
Boosting the Morale of Your Sales Team.
Creating daily sales reports may be time-consuming. But whether you do this daily, weekly, or monthly, these reports can take team morale to new heights.
Monitoring and showing the sales performance of each team member motivates them to do more. Gamifying performance results can challenge other team members to quit settling for average performance. Put another way, sales reporting can create healthy competition and push your sales team to aim for the “best” outcomes.
The goal of every sales report is to pass actionable and detailed sales information to your team. To do this, you need to know the purpose and audience of your sales report. You’ll also need to use the right data, decide on a reporting timeframe, and create engaging slides.
Here’s a breakdown of how to write an engaging sales report.
1. Know the purpose of your sales report.
Identifying your goal is the first step toward creating a winning sales report. With your goal in mind, you can easily determine the best data to include and decide on a reporting timeframe.

2. Tailor your sales report to your audience.
Metrics that interest your sales reps may not interest your CEO. Those that interest your CEO may not interest your director or VP of marketing. These folks are in the same organization as you, but they have different interests.
Sales reps may want granular details on their sales performance. Your marketing lead may only be interested in the sales reports from marketing campaigns. And your busy CEO may only want the overall results of your marketing and sales activities without the specifics of how you reached your goals. See, different strokes for different people. Tailor your sales report accordingly.
3. Determine your sales reporting timeframe.
Your reporting timeframe depends on your sales objectives and how frequently you need to update your team or management. You can do this in three ways.
Daily Sales Reporting
A daily sales report tracks the sales activities of each business day. This report increases your rep’s accountability, encourages productivity, and includes sales performance metrics like:
- Duration of each outbound call.
- Number of sales opportunities.
- Number of outbound calls.
- Number of proposals sent.
- Number of emails sent.
Weekly Sales Reporting
A weekly sales report measures the weekly sales performance of individual reps and your entire sales team. This report allows sales leaders to know which reps are on track to hit their KPIs. Weekly sales reports track metrics like:
- Call/contact volume.
- Lead-to-opportunity ratio.
- Lead conversion ratio.
- Number of appointments set.
- Number of closed deals.
- Sales volume by channel.
- Total sales by region.
Monthly Sales Reporting
A monthly sales report summarizes your sales performance for the month. This report helps you determine the effectiveness of your sales strategy so you can tweak it if necessary. Monthly sales reports track metrics like:
- Number of deals at each stage of the pipeline.
- Number of scheduled meetings.
- Length of the sales cycle.
- Average close rate.
- Average deal size.
- Sales volume.
4. Get your sales data.
Collecting and analyzing your sales data is a lot easier when you’re using a CRM. With a CRM, you can use filters to remove duplicate records and pull specific information. That’s more fun than relying on clunky spreadsheets, right? Here’s a quick video on how you can gather sales data for your reports.
You can also create custom reports if you regularly use certain sales data. Here’s how:
5. Explain key insights from your sales data.
You need to make sense of your sales data by explaining the “why” of each one.
- If there was a dip in the close rate, why?
- If there was a high lead conversion ratio, why?
- If there are more won deals in a specific region, why?
Just as the questions are endless, so are the insights you can gain by evaluating your sales data. For instance, more won deals could have resulted from a new tactic your team tried, a new channel they started using, a partner ecosystem they joined, and much more.
When you state why there’s an upward or downward trend in your data, you provide a roadmap for what your team can improve and what they can continue doing to achieve the best sales results.
Note: If possible attribute which changes to your sales data were caused by team tactics and which are attributed to the larger macro-economic environment. A spike or dip in sales may be the result of factors beyond your control. You’ll want to distinguish those factors where possible.
6. Use visuals to show vital sales trends and metrics.
Remember the popular saying, “A picture is worth a thousand words?”
It’s true, especially with sales reporting. When you create attractive visuals, your audience won’t have to wade through spreadsheets with lots of numbers. This saves their time and allows you to quickly communicate the insights in your report.
The best part? You can generate engaging visuals directly on HubSpot . Think pie charts, bar charts, line charts, and more.
Having dedicated technology to track lead and customer data makes it easy for sales leaders to analyze team performance and identify areas for improvement. But what are some essential reports every sales leader needs to track? We've listed some of the most important ones below.
- Sales Pipeline Report
- Conversion Rates Report
- Average Deal Size Report
- Average Sales Cycle Length Report
- Marketing Collateral Usage Report
- Won and Lost Deals Analysis Report
- Churned Customers Report
- Sales Call Report
- Lead Response Time Report
- Revenue Report
1. Sales Pipeline Report
A complete and accurate pipeline is a must-have. Without one, you can’t assess the sales health of your company. As a sales leader, you need to know the deals that are likely to get closed, those that may not, and how much of an impact each deal has on your bottom line.
To accurately forecast these, ensure your reps are doing their due diligence to guarantee a realistic sales pipeline .
This is an example of what a pipeline report looks like in HubSpot Sales Hub. You’ll notice each stage of the pipeline and where opportunities are within it. You can even add forecasted deal amounts to see the worth of each deal and its proximity to closing.

Image Source
Understanding the sales pipeline stages where your team excels and needs help. You can also identify the specific actions your reps should take to move prospects through each stage of your pipeline, the number of prospects in the pipeline, and how close your team is getting to their targets.
2. Conversion Rates Report
Conversion rate measures the ability of your team to turn prospects into leads and leads into customers.
By monitoring your conversion rate, you can identify where your team excels or underperforms in the sales lifecycle. If your team consistently has a high conversion rate of turning leads into opportunities, you can scale the strategies that are already working. Otherwise, you can start finding areas for improvement.
This report is also a litmus test for the strengths and weaknesses of individual reps. If a rep is performing below par, looking into their conversion rate helps you uncover why.

Revealing the efficacy of your overall sales strategy on an operational or team-wide scale. It also measures the effectiveness of your sales team at converting leads into customers.
3. Average Deal Size Report
Your average deal size helps in predicting revenue. For instance, if your revenue target is $200k per quarter and your average deal size is $20k, it means you have to land 10 deals to hit your quarterly target.
The average deal size report provides the basis for your reps' quotas and lets them know how many deals they're expected to land. It also allows you to set expectations and milestones for your sales cycle. Ultimately, it might seem like a no-brainer, but it's still worth a reminder — always monitor your average deal size because it’s vital to your sales operations.

Setting expectations for each rep, creating weekly and monthly milestones, tracking the performance of each rep, and gauging the overall success of your company’s sales strategy.
4. Average Sales Cycle Length Report
Average sales cycle length is the average time it takes a rep to close a sale. This metric shows the sales performance of individual reps and the overall efficacy of your sales process.
When considering the metric, establish an ideal timeframe to use as a benchmark. One of those benchmarks is how long it takes a rep to work through your sales cycle . If you find some reps with much longer sales cycles compared to their peers, you can evaluate their efforts and identify areas for coaching.
If all your reps can’t keep pace with your target average sales cycle length, then it's probably time to take an objective look at your operations. You might find flaws in your approach, training, or management style, and these insights can help you fix the issues. To enable your reps to see how they're performing with real-time visualization dashboards, tools like Datapine can help.

Knowing if your reps are closing deals at a similar rate as their peers. You can also create contests to foster healthy competition and unify your team to work towards a common goal.
5. Marketing Collateral Usage Report
Marketing teams expect sales reps to put the collateral they create to good use. This helps the sales reps to move prospects through the sales process quickly.
That said, some marketing collateral may be irrelevant to your rep’s prospects. With this report, you’ll know which marketing content works. Communicating this information to your marketing team gives them the insights they need to create more useful content.
Sales enablement platform SoloFire tracks how many people have used a piece of collateral, how many times they’ve interacted with it, and for how long.

Determining which marketing collateral gets the most traction with prospects and collateral that could use a refresh.
6. Won and Lost Deals Analysis Report
To understand the state of your business, you shouldn’t track only deals in progress. You should track deals you win and lose.
Perhaps prospects go crazy for specific features that you offer. Or, you notice that there’s a preference for a competitor’s product. Both trends provide an overall picture of your product’s overall strengths and weaknesses.
This is also a good way to spot under- and over-performers. For example, two reps who have the same average quota attainment could both appear to be stellar but differ wildly in actual performance.
If your data reveals that one rep spends a lot of time helping others get deals across the finish line while still maintaining high attainment, you have a great manager candidate on your hands.
On the flip side, records could reveal that a second rep has the same attainment as the first, but relies on other teammates to run demos or closing calls.
There’s always a story behind the numbers. Analyzing won and lost deals by rep will reveal it.

Evaluating performance against variables like company size, product type, sales reps, and sales teams.
7. Churned Customers Report
Every company will always experience customer churn . However, churn rates higher than your company or industry average can reveal larger problems.
There might be an issue with your pricing, service, product quality, product features, or delivery. You may also identify misalignment during the sales process, or some other aspect of the customer experience.
If your report shows higher than normal churn, speak to your customers to understand their challenges and fix them. This can improve your customer retention rate and overall customer experience.

Closely monitoring trends in churned customers so you empower your team to fix bad patterns throughout the sales process.
8. Sales Call Report
One way to measure the effectiveness of your sales reps is to track the number of calls or visits they make to prospects. You can use this report to track and find gaps in the close rate of your team.
Ideally, you want your reps to close a healthy number of deals compared to the number of prospects they meet with. If they meet with ten per day, but close none, this report will allow you to understand why and propose better closing techniques. If the opposite is true, you can find what’s working and share those tactics with the team.
The sales call report can also help you segment data. For example, if a certain industry is responding well to your products and services, you could advise your team to narrow down their call list. You can then prioritize the highest converting segment.

Identifying the most effective tactics for closing deals, setting daily call benchmarks for new hires, and iterating on your sales closing techniques.
9. Lead Response Time Report
Regardless of the length of your sales cycle, lead response time should be relatively quick. Studies show contacting prospects within the first five minutes after they become a lead increases their likelihood of converting into an opportunity.
Five minutes is short, and if you’re far from meeting this time, the best thing to do is track your progress. You won’t move from a 48-hour lead response time to five minutes overnight. But by making strategic decisions and prioritizing your team’s workload , you can attain this goal.
Here’s how a lead response time report looks in HubSpot.

Measuring the average time it takes sales reps to follow up with a lead. Plus, you can compare this metric to industry benchmarks.
10. Revenue Report
As a nice complement to the average deal size report, a revenue report can help you and your reps see how their work impacts the bottom line.

Seeing a breakdown of new business and renewals, as well as the reps who contributed to each. To get the most out of this report, you’ll want to first set your sales and revenue goals .
Many sales teams focus on identifying potential clients and closing deals, leaving little time for detailed reporting. The good news is that your team can use several powerful templates to expedite your sales reporting.
Here are four sales reporting templates we recommend.
1. Forecasted vs. Actual Sales Report Template
A forecasted vs. actual sales report can help your salespeople compare their progress against monthly and quarterly goals. These reports provide a quick way to analyze sales numbers and make adjustments as necessary.
For instance, this free sales report template from HubSpot allows you to track deals in your pipeline, know which ones to prioritize, and helps you hit your quota.

2. Reasons for Lost Deal Report Template
While every sales team strives to close as many deals as possible, some customers will inevitably say no. Understanding why your reps lose deals provides insight into why potential clients go elsewhere.
When creating this report template , you’ll want to add a column or prompt to your current sales pipeline. This allows salespeople to choose why your team lost the deal. Here are a few reasons to include in your lost deal report:
- Losing to a competitor.
- Not the right time.
- Lack of product features.
- Poor sales experience.
3. Overall Activity Report Template
For managers, having the ability to quickly view their team’s overall activity can be a great way to track productivity. It also provides information on key business development metrics, such as emails, prospect visits, and client calls.
Make sure to customize your report to include the metrics that matter most to your sales team. For instance, if your organization places a higher value on meeting prospects in person, you’ll want to include KPIs focused on visiting prospects.

4. Total Sales Report Template
Creating a custom total sales report dashboard allows your management team to quickly see how each salesperson is doing over a period. This information makes it easier to identify team members who outperform their peers and those who may need coaching.

Build Reports Your Sales Team Will Use
As a sales leader, you have a lot to keep track of. That’s where these sales reports shine. These documents provide critical insights into what’s working and what you could improve.
Here’s a key takeaway: Always track your customer and lead data. If you don’t, you'll miss out on reports that will undoubtedly help your business to drive revenue growth.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in March 2016 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

The Nature, Necessity, and Benefits of Sales Call Reporting

How to Create a Report That Displays Quarterly Sales by Territory

Why Weekly Sales Reports Need To Be Included In Your Team's Workflow

Can Big Data Really Improve Sales Effectiveness?

5 Ways to Supercharge Sales with Predictive Lead Scoring

5 Bad Sales Leaderboard Practices to Avoid at All Costs

How to Calculate Your Lead Deficit for 2015
Calculate average deal size, win-loss rate, churn rate, and more.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- Product Demos
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
- Artificial Intelligence
Market Research
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO

9 Key stages in your marketing research process
You can conduct your own marketing research. Follow these steps, add your own flair, knowledge and creativity, and you’ll have bespoke research to be proud of.
Marketing research is the term used to cover the concept, development, placement and evolution of your product or service, its growing customer base and its branding – starting with brand awareness , and progressing to (everyone hopes) brand equity . Like any research, it needs a robust process to be credible and useful.
Marketing research uses four essential key factors known as the ‘marketing mix’ , or the Four Ps of Marketing :
- Product (goods or service)
- Price ( how much the customer pays )
- Place (where the product is marketed)
- Promotion (such as advertising and PR)
These four factors need to work in harmony for a product or service to be successful in its marketplace.
The marketing research process – an overview
A typical marketing research process is as follows:
- Identify an issue, discuss alternatives and set out research objectives
- Develop a research program
- Choose a sample
- Gather information
- Gather data
- Organize and analyze information and data
- Present findings
- Make research-based decisions
- Take action based on insights
Step 1: Defining the marketing research problem
Defining a problem is the first step in the research process. In many ways, research starts with a problem facing management. This problem needs to be understood, the cause diagnosed, and solutions developed.
However, most management problems are not always easy to research, so they must first be translated into research problems. Once you approach the problem from a research angle, you can find a solution. For example, “sales are not growing” is a management problem, but translated into a research problem, it becomes “ why are sales not growing?” We can look at the expectations and experiences of several groups : potential customers, first-time buyers, and repeat purchasers. We can question whether the lack of sales is due to:
- Poor expectations that lead to a general lack of desire to buy, or
- Poor performance experience and a lack of desire to repurchase.
This, then, is the difference between a management problem and a research problem. Solving management problems focuses on actions: Do we advertise more? Do we change our advertising message? Do we change an under-performing product configuration? And if so, how?
Defining research problems, on the other hand, focus on the whys and hows, providing the insights you need to solve your management problem.
Step 2: Developing a research program: method of inquiry
The scientific method is the standard for investigation. It provides an opportunity for you to use existing knowledge as a starting point, and proceed impartially.
The scientific method includes the following steps:
- Define a problem
- Develop a hypothesis
- Make predictions based on the hypothesis
- Devise a test of the hypothesis
- Conduct the test
- Analyze the results
This terminology is similar to the stages in the research process. However, there are subtle differences in the way the steps are performed:
- the scientific research method is objective and fact-based, using quantitative research and impartial analysis
- the marketing research process can be subjective, using opinion and qualitative research, as well as personal judgment as you collect and analyze data
Step 3: Developing a research program: research method
As well as selecting a method of inquiry (objective or subjective), you must select a research method . There are two primary methodologies that can be used to answer any research question:
- Experimental research : gives you the advantage of controlling extraneous variables and manipulating one or more variables that influence the process being implemented.
- Non-experimental research : allows observation but not intervention – all you do is observe and report on your findings.
Step 4: Developing a research program: research design
Research design is a plan or framework for conducting marketing research and collecting data. It is defined as the specific methods and procedures you use to get the information you need.
There are three core types of marketing research designs: exploratory, descriptive, and causal . A thorough marketing research process incorporates elements of all of them.
Exploratory marketing research
This is a starting point for research. It’s used to reveal facts and opinions about a particular topic, and gain insight into the main points of an issue. Exploratory research is too much of a blunt instrument to base conclusive business decisions on, but it gives the foundation for more targeted study. You can use secondary research materials such as trade publications, books, journals and magazines and primary research using qualitative metrics, that can include open text surveys, interviews and focus groups.
Descriptive marketing research
This helps define the business problem or issue so that companies can make decisions, take action and monitor progress. Descriptive research is naturally quantitative – it needs to be measured and analyzed statistically , using more targeted surveys and questionnaires. You can use it to capture demographic information , evaluate a product or service for market, and monitor a target audience’s opinion and behaviors. Insights from descriptive research can inform conclusions about the market landscape and the product’s place in it.
Causal marketing research
This is useful to explore the cause and effect relationship between two or more variables. Like descriptive research , it uses quantitative methods, but it doesn’t merely report findings; it uses experiments to predict and test theories about a product or market. For example, researchers may change product packaging design or material, and measure what happens to sales as a result.
Step 5: Choose your sample
Your marketing research project will rarely examine an entire population. It’s more practical to use a sample - a smaller but accurate representation of the greater population. To design your sample, you’ll need to answer these questions:
- Which base population is the sample to be selected from? Once you’ve established who your relevant population is (your research design process will have revealed this), you have a base for your sample. This will allow you to make inferences about a larger population.
- What is the method (process) for sample selection? There are two methods of selecting a sample from a population:
1. Probability sampling : This relies on a random sampling of everyone within the larger population.
2. Non-probability sampling : This is based in part on the investigator’s judgment, and often uses convenience samples, or by other sampling methods that do not rely on probability.
- What is your sample size? This important step involves cost and accuracy decisions. Larger samples generally reduce sampling error and increase accuracy, but also increase costs. Find out your perfect sample size with our calculator .
Step 6: Gather data
Your research design will develop as you select techniques to use. There are many channels for collecting data, and it’s helpful to differentiate it into O-data (Operational) and X-data (Experience):
- O-data is your business’s hard numbers like costs, accounting, and sales. It tells you what has happened, but not why.
- X-data gives you insights into the thoughts and emotions of the people involved: employees, customers, brand advocates.
When you combine O-data with X-data, you’ll be able to build a more complete picture about success and failure - you’ll know why. Maybe you’ve seen a drop in sales (O-data) for a particular product. Maybe customer service was lacking, the product was out of stock, or advertisements weren’t impactful or different enough: X-data will reveal the reason why those sales dropped. So, while differentiating these two data sets is important, when they are combined, and work with each other, the insights become powerful.
With mobile technology, it has become easier than ever to collect data. Survey research has come a long way since market researchers conducted face-to-face, postal, or telephone surveys. You can run research through:
- Social media ( polls and listening )
Another way to collect data is by observation. Observing a customer’s or company’s past or present behavior can predict future purchasing decisions. Data collection techniques for predicting past behavior can include market segmentation , customer journey mapping and brand tracking .
Regardless of how you collect data, the process introduces another essential element to your research project: the importance of clear and constant communication .
And of course, to analyze information from survey or observation techniques, you must record your results . Gone are the days of spreadsheets. Feedback from surveys and listening channels can automatically feed into AI-powered analytics engines and produce results, in real-time, on dashboards.
Step 7: Analysis and interpretation
The words ‘ statistical analysis methods ’ aren’t usually guaranteed to set a room alight with excitement, but when you understand what they can do, the problems they can solve and the insights they can uncover, they seem a whole lot more compelling.
Statistical tests and data processing tools can reveal:
- Whether data trends you see are meaningful or are just chance results
- Your results in the context of other information you have
- Whether one thing affecting your business is more significant than others
- What your next research area should be
- Insights that lead to meaningful changes
There are several types of statistical analysis tools used for surveys. You should make sure that the ones you choose:
- Work on any platform - mobile, desktop, tablet etc.
- Integrate with your existing systems
- Are easy to use with user-friendly interfaces, straightforward menus, and automated data analysis
- Incorporate statistical analysis so you don’t just process and present your data, but refine it, and generate insights and predictions.
Here are some of the most common tools:
- Benchmarking : a way of taking outside factors into account so that you can adjust the parameters of your research. It ‘levels the playing field’ – so that your data and results are more meaningful in context. And gives you a more precise understanding of what’s happening.
- Regression analysis : this is used for working out the relationship between two (or more) variables. It is useful for identifying the precise impact of a change in an independent variable.
- T-test is used for comparing two data groups which have different mean values. For example, do women and men have different mean heights?
- Analysis of variance (ANOVA) Similar to the T-test, ANOVA is a way of testing the differences between three or more independent groups to see if they’re statistically significant.
- Cluster analysis : This organizes items into groups, or clusters, based on how closely associated they are.
- Factor analysis: This is a way of condensing many variables into just a few, so that your research data is less unwieldy to work with.
- Conjoint analysis : this will help you understand and predict why people make the choices they do. It asks people to make trade-offs when making decisions, just as they do in the real world, then analyzes the results to give the most popular outcome.
- Crosstab analysis : this is a quantitative market research tool used to analyze ‘categorical data’ - variables that are different and mutually exclusive, such as: ‘men’ and ‘women’, or ‘under 30’ and ‘over 30’.
- Text analysis and sentiment analysis : Analyzing human language and emotions is a rapidly-developing form of data processing, assigning positive, negative or neutral sentiment to customer messages and feedback.
Stats IQ can perform the most complicated statistical tests at the touch of a button using our online survey software , or data from other sources. Learn more about Stats iQ now .
Step 8: The marketing research results
Your marketing research process culminates in the research results. These should provide all the information the stakeholders and decision-makers need to understand the project.
The results will include:
- all your information
- a description of your research process
- the results
- conclusions
- recommended courses of action
They should also be presented in a form, language and graphics that are easy to understand, with a balance between completeness and conciseness, neither leaving important information out or allowing it to get so technical that it overwhelms the readers.
Traditionally, you would prepare two written reports:
- a technical report , discussing the methods, underlying assumptions and the detailed findings of the research project
- a summary report , that summarizes the research process and presents the findings and conclusions simply.
There are now more engaging ways to present your findings than the traditional PowerPoint presentations, graphs, and face-to-face reports:
- Live, interactive dashboards for sharing the most important information, as well as tracking a project in real time.
- Results-reports visualizations – tables or graphs with data visuals on a shareable slide deck
- Online presentation technology, such as Prezi
- Visual storytelling with infographics
- A single-page executive summary with key insights
- A single-page stat sheet with the top-line stats
You can also make these results shareable so that decision-makers have all the information at their fingertips.
Step 9 Turn your insights into action
Insights are one thing, but they’re worth very little unless they inform immediate, positive action. Here are a few examples of how you can do this:
- Stop customers leaving – negative sentiment among VIP customers gets picked up; the customer service team contacts the customers, resolves their issues, and avoids churn .
- Act on important employee concerns – you can set certain topics, such as safety, or diversity and inclusion to trigger an automated notification or Slack message to HR. They can rapidly act to rectify the issue.
- Address product issues – maybe deliveries are late, maybe too many products are faulty. When product feedback gets picked up through Smart Conversations, messages can be triggered to the delivery or product teams to jump on the problems immediately.
- Improve your marketing effectiveness - Understand how your marketing is being received by potential customers, so you can find ways to better meet their needs
- Grow your brand - Understand exactly what consumers are looking for, so you can make sure that you’re meeting their expectations
Free eBook: Quantitative and qualitative research design
Scott Smith
Scott Smith, Ph.D. is a contributor to the Qualtrics blog.
Related Articles
May 20, 2024
Best strategy & research books to read in 2024
May 13, 2024
Experience Management
X4 2024 Strategy & Research Showcase: Introducing the future of insights generation
November 7, 2023
Brand Experience
The 4 market research trends redefining insights in 2024
June 27, 2023
The fresh insights people: Scaling research at Woolworths Group
June 20, 2023
Bank less, delight more: How Bankwest built an engine room for customer obsession
April 1, 2023
Academic Experience
How to write great survey questions (with examples)
March 21, 2023
Sample size calculator
November 18, 2022
Statistical analysis software: your complete guide to getting started
Stay up to date with the latest xm thought leadership, tips and news., request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Revenue Hub
Accelerate revenue execution
CPQ (Configure Price Quote)
Automate quotes & subscriptions
CLM (Contract Lifecycle Management)
Streamline contract signings
Manage revenue lifecycle
Subscriptions
Unlock recurring revenue
Expert Implementation & Success
Top integrations, top features.
Revenue Operations Events
Revenue Operations Jobs
Revenue Operations Podcast
Revenue Operations Swag
Revenue Operations Terms
Trending Topics
- Infographics
- Customer Portal
- Pricing & Plans
- Feature Comparison
- Request a Demo
- Request a demo

Sales Analysis

Table of Contents
What is sales analysis.
Sales analysis is reviewing your sales data to identify trends and patterns. Sales data can help you make better decisions about your product, pricing, promotions, inventory, customer needs other aspects of your business.
Sales analysis can be as simple as reviewing your sales figures regularly. But it can also involve more complex statistical methods. Either way, the goal is to gain insights that will help you boost sales and improve your bottom line.
There are many ways to approach sales analysis. Some businesses use software that automatically crunches the numbers and produces charts and graphs. Others prefer to do things manually, using Excel or another spreadsheet program.
The most important thing is to review your sales data regularly and look for opportunities to improve your business. With sales analysis, you can make informed decisions that will help you grow your business and achieve your sales goals.
- Sales analytics
- Sales data analysis
- Sales revenue analysis
The Importance of Sales Analysis
Sales analysis is a critical tool for businesses of all sizes. By understanding revenue-driving metrics , companies can make informed decisions, from pricing and product development to sales strategies and target markets. Essential metrics to analyze are sales volume, growth, mix, and trends.
Sales volume is the total number of sales made over a specific time. This metric can help assess whether a business is growing or declining.
Sales growth is the percentage change in sales volume from one period to the next, which can help determine whether a business is growing at a healthy rate.
The sales mix is the ratio of different products and services a business sells. This metric can assess whether a company sells a diversified product and service mix.
Sales trends are changes in sales volume over time. This metric can assess whether a business is experiencing seasonal or long-term sales patterns.
Sales analysis is a critical tool for businesses of all sizes. Companies can make informed decisions about growing revenue and increasing profits by understanding these sales metrics.
Types of Sales Analysis
Sales analysis is a process that helps you to measure and manage your organization’s sales performance . The three most common types of sales analysis are:
1. Sales Forecasting
2. Sales Management
3. Sales Reporting
Sales Forecasting
Sales forecasting is the process of predicting future sales. This type of analysis is usually done internally by companies. For example, if a company wants to know how much revenue they expect to generate this year, they may forecast sales based on historical data. They might then compare those predictions with actual results to see how well they did. If their forecasts were off, they would have to take action to correct any problems in their sales processes or implement new sales enablement tools.
Sales Management
Sales management is the process of managing existing sales. Companies use sales management to ensure that they are meeting their sales targets. They also use it to identify areas where they need to improve the customer journey and accelerate the sales cycle length. For example, if they find that they are not growing revenue as expected, they could adjust prices, add new products., or enable their sales team with tools and strategies to optimize the sales process.
Sales Reporting
Sales reporting is the process of summarizing information about sales. Companies often use sales reporting to track sales progress and to communicate with investors or executives. For example, they may report monthly sales figures to shareholders so that investors can better understand how their investments are performing.
How to Use Sales Analysis Data
Sales data provides companies with a valuable source of data to make informed decisions about their sales operations and strategies.
Sales data can be used in several ways, including:
- Analyzing customer needs and preferences
- Understanding buying patterns
- Tracking competitor activity
- Analyzing the customer journey and sales cycle
- Measuring sales team performance
- Improving marketing efforts
- Targeting new customers
Top Sales Analysis Metrics & KPIs
Sales analysis is a vital part of any business. It helps you understand what’s working and what isn’t so that you can make changes to improve your sales process. Here are the top KPIs for analyzing sales performance:
The most critical metric in sales is revenue, which is the money your company makes from its products or services. To calculate revenue, multiply the number of units sold by the price per unit.
Net Profit Margin
Net profit margin measures how profitable your company is. The net profit margin, also known as net margin, indicates how much net income or profit is generated as a percentage of revenue. It’s the proportion of total profits to revenue for a firm or sector.
Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin , also known as gross margin, measures your company’s efficiency at turning orders into revenue. Gross profit margin is a financial ratio that calculates the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold. The gross profit margin ratio is important because it allows investors and analysts to see how well a company performs relative to its costs.
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)
Customer lifetime value measures how valuable your current customers are to your company. LTV is calculated by multiplying the average order size by the customer’s retention rate. The longer customers stay with your company, the more valuable they become.
The churn rate measures how often customers cancel their accounts. Churn rate is calculated by dividing the number of active users who have canceled their accounts by the total number of active users.
Retention Rate
The retention rate measures how long customers stay with your company after signing up. The retention rate is calculated by dividing active users by new users.
It’s also vital to analyze the sales pipeline to pinpoint areas where leads are not moving from one stage to the next. By tracking the correct data, you can better measure your sales pipeline performance and identify areas of improvement. Sales pipeline data to analyze include the number of leads generated, the number of qualified leads, conversion rates, average sales cycle length , average deal size , and win rates.
How Sales Analysis Reports Help
Analyzing sales reports provides valuable insights into the business’s current state and helps organizations make informed decisions about strategies to improve sales performance. Ways to use sales analysis reports include:
- Evaluate sales deal data to make informed decisions about growing revenue and improving sales performance.
- Assess overall sales trends and determine whether growth is occurring.
- Understand what customer needs are being met and where opportunities for new product development may occur.
- Determine whether prices are realistic and align with customer demand.
- Examine which channels are performing well and where there may be opportunities for improvement.
- Assess the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- Identify areas of waste or inefficiency in the sales process.
- Benchmark performance against competitors.
- Generate reports to share with key stakeholders.
Sales analysis is a critical part of running a successful business. By reviewing sales deal data regularly, companies can gain valuable insights into their performance and make informed decisions to improve sales results.
Sales Analysis Tools
Sales analysis tools come in many different shapes and sizes. Some are designed to give you a general overview of your sales data, while others focus on specific aspects or types of sales data. The most common types of sales analysis tools include:
Sales reports: These provide a high-level overview of your sales data, typically including information such as total sales, average order size, and top-selling products or services.
Sales dashboards: These provide a more detailed view of your sales data, typically including information such as customer types, geographical regions, and sales by channel.
Sales performance analysis: This type of tool is designed to help you track and improve your sales performance, typically by providing information such as win/loss ratios and conversion rates.
Sales pipeline analysis: This type of tool is designed to help you manage your sales pipeline , typically by providing information such as lead conversion rates and deal size.
Customer profile analysis: This type of tool is designed to help you understand your customers better, typically by providing information such as customer types, buying habits, and demographic information.
The right sales analysis tool for your business will depend on a number of factors, including the types of data you need to track, the level of detail you need, and your budget. Some sales tools cover many of the use-cases above, such as CRM and CPQ.
CPQ (configure price quote) software can help with sales analysis by providing accurate pricing and product configuration data. This data can be used to understand how customers are buying your products and how prices impact demand. Additionally, CPQ data can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of marketing campaigns and optimize future efforts.
Sales analysis is an important part of any sales organization. CPQ software can help make this process more efficient and accurate, resulting in better decision-making and improved sales results.
People Also Ask
Why do we do sales analysis.
There are several ways to do sales analysis, but the basic goal is always the same: to better understand your company’s sales so that you can make better decisions about how to grow your business. Sales analysis involves looking at which products are selling well, which markets are most profitable, and where you might be losing sales. In addition, it can help you make informed decisions about pricing, product development, marketing, sales operations , and other areas of your business by identifying opportunities and threats.
How do you analyze sales growth?
Sales growth can be analyzed by looking at overall sales figures, comparing sales figures to previous periods, and analyzing customer acquisition and retention rates. By understanding how sales grow, businesses can make more informed decisions about where to invest their resources. Overall sales figures can give you a broad overview of your business’s performance. You can track total revenue, average order value, and other key metrics to see how they trend over time. This can be helpful in spotting overall trends in your business. Comparing sales figures to previous periods can help you understand whether your business is growing or declining. By looking at year-over-year sales growth, month-over-month sales growth, or even day-over-day sales growth, you will see how your sales are trending, and you can make more informed decisions about how to grow your business Analyzing customer acquisition and retention rates can give insights into how well your business attracts and retains customers. For example, you can track how many new customers you acquire each period and how many existing customers you lose. This data helps identify whether your customer acquisition efforts are working and whether you’re at risk of losing customers.
What should sales analysis include?
Sales analysis evaluates sales data to make informed decisions to help sales reps win more deals , and help the company grow revenue. Some key factors to consider are: Sales volume: This is the total number of units sold over time which helps assess overall sales trends and growth. Sales mix: This refers to the types of products or services sold. This information can be useful in understanding customer needs and opportunities for new product development. Sales price: The average sale price can give insights into whether prices are realistic and align with the perceived value of the product or service. Sales expenses: This includes all costs associated with generating sales, such as advertising, commissions, and travel. Tracking sales expenses can help to identify areas where costs may be too high or where there may be opportunities for cost savings. Sales pipeline: This is a list of all potential sales that are in the process of being closed. The sales pipeline can help forecast future revenue and assess the health of the sales department.
Multistep request a demo popup
- Glossary: Organic Sales
- Glossary: Sales Analytics
- How to ignite your sales engine with data insights
How to Create a Sales Analysis Report That Can Actually Help Your Business Grow
A sales analysis report is to a business as a car dashboard is to a driver.
Without the flashing signals and the arrow pointing beyond the allowed range, a driver would have no idea something is wrong with the vehicle; exorbitant fines are on the way or the car can incur damage every mile.
Read on to find out how to create sales analysis reports, what data to collect, how to interpret resulting tables, and convert them into effective action points for your sales operations, sales team, and marketing departments.
What Is Sales Analysis?
The sales analysis report is a set of analytical data that provides an overview, trends, and particulars of a wealth of metrics pertaining to the sales process & its results, which are used by company leadership to monitor the sales dynamics and improve results.
Sales analytics is an indispensable and fundamental tool for business of any size: starting from small to medium business to big multinational corporations.
Now that we’ve discussed what a sales analysis report is, let’s deep dive into the particulars of the reporting process to improve sales performance and drive the bottom line.
Importance of Sales Analysis & Benefits of Actioning Data Timely
The rise of big data allows us to drill down as granularly as needed in any aspect of the sales process so that to better understand the efficiencies of each sales rep, the profitability of each item in stock, timely spot the underperforming units, and increase market share.
A properly established process of creation, analysis, and actioning of the sales data is vital to a company’s success and survival.
It is pretty easy to make a sales analysis report. But it takes sales acumen and entrepreneurial vision to be able to interpret it and convert the data points from the sheet into actions to enhance your business.
Sales data analysis is fundamental to gain the following benefits:
- Keep your sales team aware of the market, industry, macroeconomics, and trends. This is not TMI, no. Your team should know your market share and if the industry is on the rise. Sales Ops must advise the front liners if the global crisis is affecting the purchasing trends so your company leadership can timely regroup accordingly.
- Make sure competition and mentorship are in place within your team . Competition is the driver. Incentive plans should be public. The sales team should have team goals and individual ones. Top sellers should be up on the wall.
- Healthy competitiveness is the fuel of a proper sales team . Make sure to use your best understanding of the team’s dynamics not to hurt anyone, but using team members’ sales results in comparison is perfectly fine in the sales universe. Saying “bye” to the weakest performers is a natural business process, that should be performed regularly.
- Track your items sold, pricing, turnover, and margins. Any of those could be a problem. A well-designed sales analytical process will alarm a business owner about the items, that bring loss, items, that are under or overpriced, and items, that need better stocking.
On the large scale of things, sales data analysis reports can help your business thrive and consistently exceed your competitors with properly designed monitoring, analysis, and actioning practices in place.
Contrarily, if done improperly or left without scrutiny and unactioned, such data will lead to the early demise of your business.
Key Metrics of Sales Analytics
What needs monitoring in sales? What data points are the ones to prioritize?
The ocean of data is a great way to drown your efficiency in. How do you know what metrics need your attention to optimize the business and increase revenues?

But before we proceed with perfect KPIs to keep track of for all who are wondering how to prepare sales analysis report, let’s highlight one important axiom:
ALL REPORTING SHOULD BE STUDIED RELATIVE TO PAST, PRESENT, AND FUTURE.
Sorry for shouting, just wanted to make sure we are on the same page here. It is a prerequisite that the more data you have, the easier it is to draw flawless conclusions and create roadmaps to success based on it.
The past data shows trends and results of the applied measures, deviations of the market based on crises and seasonality, the reaction of the clients to price increases, and more. It’s your crystal ball, in fact. If you plan to do something major in your sales, check if this has been part of your history and see how it worked out.
The present is the status quo of your company’s sales is where you are with all the market knowledge and the team you have now. This is your starting point always.
However deep in the negative, you are now, there is a way out.
On the contrary, however high you climbed up in your margins, falling out in the red is always an option due to a litany of reasons. Keep your eyes peeled to spot the danger before it’s too late.
The future is where you are the king. Sales forecasts and unrealistic budgets are often a way to keep top management away from their big bonuses yet working 24/7.
Keeping realistic forecasts helps for better planning practices and a sustainable business model though. Keeping your forecast accuracy as high as possible is your ideal way forward.
KPIs and Metrics
Now let’s review the data points we need to keep in focus to keep your business competitive and kicking some butts on the market.

Product sales or product performance
- quantity sold
Based on this data, businesses can regularly perform an ABC analysis to review the inventory and exclude the items detrimental to the bottom-line.
Sales Growth or Sales Dynamics
Calculating the absolute figures and percent are both useful per period, depending on the scale of business.
Lead conversion rate
Low lead conversions at specific stages of a customer journey or disturbing valleys in the funnel may alert a team of sales ops, marketing, and sales to review the processes, content, and/or pricing.
Sales target or departmental KPIs
Ascertaining targets for your sales team is one of the major missions of sales operations and company management. The sales target can be established in the number of client calls, visits, deals won, revenue per deal, items sold, average deal check, customer retention rates, and so on. Picking the right mix of individual and team incentives is vital for any industry trendsetters.
Lead-to-Quote
This sales analysis metric allows focusing on the efficiency of your sales agents to convert leads to quote and understand reasons why the process is above/below/in line with market average or deviates from a sales rep to sales rep.
Quote-to-Close
Measuring productivity of your team from the quotation to winning of the deal allows us to spot pricing deficiencies (whether too expensive or too cheap) as well as pinpoint and address other possible failures of the sales processes.
Sales by area/segment
Whatever sales metric you are looking at – be it a revenue made, margins, or items sold, one of the granular ways of looking at it is by the region. Sales may vary in different locations for a myriad of reasons and discovering why may lead to increased efficiencies in other states.
Average check AKA average purchase value
Amazon reported that upselling and cross-selling are responsible for a whopping 35% of its revenues. Average check seems all of a sudden like even more important numbers, right?
Sales Analysis Methods & Techniques for improved efficiencies
Marketing research.
Too much is written on the importance of close collaboration of the marketing and sales team and how beneficial such unity is for a company’s bottom line, so we are keeping it short.
Marketing research and flow of information should be embedded into the daily routine of sales ops and be trickled down to every sales rep in a form of summary. Newcomers to the market, big industry M&As, pandemics , and other macro and micro-economic fluctuations may all affect your business unit. Warned means armed.
Sales performance analysis
Always make sure your targets are achievable and aligned with your overall mission and investments. Then make sure you bring your sales team leadership to pay close attention to how far away you are from reaching your monthly / quarterly / annual forecasts and budgets.
Sales trend analysis
Past trends help find cures for the present issues and engineer the most efficient roadmap to future successes.
Make sure your report has both absolute deviations and percentage-defined ones for the best perspective.
Sales pipeline analysis
Forecasting is vital for many processes, some industries more than others (like eCommerce, for example).
You base manning, purchasing, delivery, logistics, cash flow based on your forecasting. All of these business segments can be tight as a drum or all over the place, jeopardizing your company’s bottom line.
Sales effectiveness analytics
A good sales department leader is married to reporting, taking it to bed once too often. Having access to a dashboard with an overview of your sales members’ activities is paramount.
Sales-centered CRMs like Nimble offer a comprehensive overview of multiple parameters of your sales ops and sales team in a customizable dashboard. Monitor calls made, emails received and replied, the deals closed, and more in a visual graph that is easy to read and action.
How To Create A Sales Analysis Report That Actually Drives Sales
Ascertain the data points that need tracking.
If you are a small business with three sales reps and 50 items in stock, you will need a more user-friendly basic overview of the data, that focuses on growth and profitability margins. Bigger companies may use sophisticated tools and a skilled sales ops team that know how to analyze sales data based on hundreds of data points.
Establish The Regularity Of Sales Analysis
Likewise, estimate the needs of your particular business to find the perfect revision and creation of reports for optimal productivity increase.
Feed and Graph the Data
Design a report or use a ready-made template to feed your figures into for best visual representation, that highlights dips and peaks, and helps to spot the trends.
Analyze Your Results
Hire an experienced sales operations manager as quickly as you can afford one, If you have 5 sales reps on your team, it’s time to start hiring a sales rep to optimize the process and boost sales department productivity.
How To Write A Comprehensive Sales Report To Your Boss
- First of all, read all of the information on the 1 st Google page results to the inquiry “how to write a sales analysis report”. Knowing theory never hurts the results.
- Then download a few sales analysis report samples, unless your organization has an established sales report template. See which one you like most and have the info your boss is interested in.
- Fill in the data fields and check if it makes sense and all formulas are working.
- Accompany figures with notes as you interpret them.
- Pick up the highest variables and the lowest ones. Are they always the leader and the loser of your segmentation? Has it changed? Why?
- See the biggest deviations year to year or period to period in percentage . Explain the jumps and the dives. What can you do to address those highs and lows? Keep improving the good results and minimizing the damage from the bad ones.
- Estimate how far or close you are to your targets. Why are you so spot on or so far off? Can you doctor the situation going forward? How?
- Mark any big changes in the market or global aspects that impacted your performance for future reporting. If there was a big conference in the city, that changed patterns or maybe, like this year, a global pandemic changed the economic world over? Explain it in your reports so that next year or decade you can refer to this data.
Providing a monthly sales analysis report is a good practice when it comes to informing your senior management.
The sales leadership should be getting a daily overview of the dashboard and more extensive weekly sales analysis reports. Such a report distribution schedule allows them to address any potential risks timely or direct efforts and funds to just forming winning streaks and trends.
Sales Analysis Report Examples
There exist hundreds of sales analysis report examples created by professionals to aid small and medium businesses run their administrative units more efficiently.
There are paid sales analysis templates and those that are free. Make sure you request Google for a free report if you are looking for one and your company is not ready to pay for intellectual property.
The great news is that there are many websites out there providing such information that generate revenues by running Google ads on their websites and basically giving away those sheets for free.
Spreadsheets vs CRM solutions for sales reporting
A viable alternative to using spreadsheet-based reporting for small and medium businesses is using a CRM software – customer relations management system, like Nimble.
Nimble is one of the best CRMs for small business es due to its intuitive interface, the low subscription fee for users [$19-$25 depending on the plan], and all-encompassing functionality that drives growth.
Try Nimble free for 2 weeks !

About The Author
Nimble Editorial Team
Related articles.

Best Sales Role-Playing Exercises for Wedding Planning Agencies: Enhancing Client Engagement and Closing More Deals

Best Sales Pitch for Edtech

Crafting the Perfect Sales Pitch for Life Insurance: Two Detailed Examples
Marketing91
What is Sales Analysis? Why is it important?
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
For every company , Sales is the ultimate revenue generator which takes care of all costs and expenses. While Sales may be achieved easily or in some cases in a very difficult way, analysis of the Sale that has materialized is very important.
Not only the how but also the why a particular sale has happened and why not has a sale not happened along with a periodic comparison of achieved Sales is very important for the organization. This helps them to give a logical answer of Sales instead of relying on gut-feeling. That is why Sales analysis is carried out from time to time. If you have heard about Sales reviews, then it is nothing but sales analysis carried out as a timely activity.
Table of Contents
What is Sales analysis?
As the name suggests, sales analysis involves analysing the sales made by a company over a period of time. Many companies have a weekly sales analysis, a monthly sales analysis or a quarterly sales analysis. A regular sales analysis helps the company understand where they are performing better and where they need to improve.
Every company has a sales target which its salesmen have to achieve. If the target was to be achieved in a month, then on the 15th day of that month, the salesmen should know where they stand. This is where sales analysis plays it role. It helps determine where the company stands in terms of sales and then helps in sales strategy to reach a predetermined goal.
Sales analysis is done from the bottom level to the top level of the company. Even the CEO of the company does a sales analysis to understand segments where the company is gaining in sales and segments where it is dropping in sales. Such sales analysis can also help product development.
Importance of Sales Analysis

1) Missed opportunities :
Analyzing the available data can show the company where it has missed the opportunity and if or not that can be claimed. Market research will play an important role in this presenting data to compare while the field force will prove of valuable assistance in informing the practicalities of the situation.
2) Future decisions :
Sales data will help a company to take a future decision in terms of inventory management , marketing activities, schemes or offers to be rolled and changes in manufacturing processes if applicable. Based on Sales data, major decisions like continuing or discontinuing a product is taken. Those future decisions will help the external stakeholders of the company to decide whether or not to invest in the company.
3) Market Trends :
Sales analysis will also show the current market trends to the company. While the company may be preparing to launch a new product, Sales Analysis would show a drastic increase in Sales of the earlier product after an activity, showing that it was the lack of awareness which was a hindrance in realizing Sales and not the product. Also, Sales of a certain product may skyrocket during a festival or decrease seasonally.
4) Customer analysis :
Effectively, Sales Analysis is nothing but Customer Analysis . Answering why did a particular customer buy the product in a particular month may give crucial customer insights which will help with the planning of the company.
5) Detailed analysis :
A detailed Sales Analysis is broken down product wise, customer wise, year and month wise and geography wise is a source of huge information for the company.
Types of Sales Analysis:
Although many companies may use various types tailored to fit their organization, here are the few common types of Sales Analysis performed :
1) Periodic Analysis :
This can be a month on month or year on year or year till date compared to previous year till date as the need may be. This gives insight into the impact of time on sales.
2) Product wise Analysis :
Sales of products during different times in different areas can be used. This is majorly used in large-scale equipment.
3) Channel of distribution wise :
This will give the trend of where the sales are maximum and answering Why will give more insights and help the company decide whether or not to continue with the current channel of distribution .
4) Forecast vs Achievement analysis :
This gives the details of sales which were used to forecast the numbers – and inventory was arranged accordingly – and what is the actual achievement of Sales – and whether the inventory needs to refilled or schemes need to be rolled out for the liquidation of stocks.
5) Combination of above :
For more detailed analysis, the company may perform a combined analysis of above for example multinationals like Proctor and Gamble may analyze the Sales of Tide detergent in Asia Pacific region for the year 2018 and compare it with Sales of the year 2017. This involves Product as well as periodic sales.
Advantages of Sales Analysis :

1) Opportunities :
Sales analysis of own products as well as competitor products is important as analyzing sales of competitors allows insights into the market from a different perspective and may help the company to reach the missed out customers and grab the missed opportunity.
2) Decision driver :
Sales analysis, as explained above acts a decision driver for the company to make major changes in their products. If the Sales of a product are not up to the mark, the company may discontinue the product with immediate effect. For example, as the Sales of Touchscreen phones increased all the traditional button models changed their phones to touch screens. With the advent of Facebook and Twitter , earlier sites like Orkut had to be shut down because of lack of revenue and shift of audience from one platform to other.
3) Customer Service :
Knowing the reason behind why a particular sales occurred during particular time will help the companies to keep the inventory ready and help them to serve the customers better. Delighting the customers will, in turn, benefit the company by increased sales further and help to develop goodwill and establish the brand value of the company.
4) Marketing support :
Sales of a certain product may require one-time marketing support or multiple times or seasonal support. Those decisions are taken based on Sales analysis. For example, products like cough syrup would require marketing and ad campaigns just before and during winter while airline services require constant marketing support.
Disadvantages of Sales Analysis :
1) reliability :.
A lot of times, Sales Analysis might have done in a haphazard way or the reasons for the increase in sales of a particular product may go up purely on the effort of the Salespersons or offers rolled out. This may have nothing to do with customer or trends and relying on those conclusions can be problematic for the company.
2) Political factors :
12 countries in Europe introduced a single currency in 2002 which caused temporary disruption of the economy. In such cases, even though the trend may say that the Sales is supposed to increase, owing to unavailability of purchasing power of customers, the company may face a dip in sales. The following year to this incident when the economy may again stabilize, comparing previous years’ data will show askew results again since the customers are purchasing normally as per their requirement but there would be a tremendous growth in the analysis.
3) Technical knowledge :
High technical knowledge is required for Sales Analysis and not everyone may be suited to do that. Good arithmetic skills along with high market knowledge are basic requirements and those may not be fulfilled by every Salesperson.
A detailed Sales Analysis along with its interpretation is outsourced by many companies. The dedicated firms or software may be costly which the company would have to bear regularly. Also, the privacy of data would be compromised when sharing the Sales data to the third party. A Sales analysis performed by an internal employee instead of outsourcing would increase the cost of the firm in terms of salary, training the person for technical knowledge and there are chances of human error in Manual Sales Analysis.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Sales
Related posts:
- Why Sales motivation is important and what are Objectives of Sales motivation?
- What is Primary sales, Secondary sales and Tertiary sales and what factors determine them?
- Why customer reviews and recommendations are most important nowadays?
- What is the Importance of Marketing Mix and why are the 4 P’s important?
- What is Brand Activation & Why is it Important?
- Importance of Retailing – Why Retail is Important?
- Brand Strategy – Steps, Components and Why it is Important for Business
- What is Authenticity and Why it is Important?
- What are Research Skills? And Why are they Important?
- What is Service Excellence? And Why it is Important & excellent
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
Data-driven decision making via sales analytics: introduction to the special issue
- Published: 26 July 2020
- Volume 8 , pages 125–126, ( 2020 )
Cite this article

- J. Ricky Fergurson 1
4733 Accesses
3 Citations
2 Altmetric
Explore all metrics
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
Sales powers business throughout the world. While sales (and marketing) literature has spent much time exploring analytics and measurement, there seems to be a revitalized interest in sales and especially sales data and analytics. Marketing analytics powers the current wave of data-driven decision making, and leveraging strategic data remains a source of building a sustainable competitive advantage. In Volume 1, edition 1 of Journal of Marketing Analytics , Breur ( 2013 , p. 1) proclaimed in the journal’s first editorial,
We’re drowning in data. Structured data, unstructured data, ‘Big Data,’ in an increasingly digital world, we create even more data. According to an IDC report, the global growth in data volumes amounts to about 60 percent per year. That means it will grow tenfold every 5 years!.
As we stand here seven years later, the available amount of data has grown exponentially due to the increased connectivity and data availability made possible by technology increasingly permeating the sales profession. Salespeople, sales managers, and executives must quickly make sense of oceans of sales-related data. With this influx of sales data, organizations need to develop actionable insights for their sales teams and their clients. The Sales Education Foundation ( 2020 ) notes that sales-specific research is necessary for bridging the gap between academia and industry. In reinforcing this need, the Sales Education Foundation has provided more than $125,000 in grants to promote high-quality sales research since 2011. (Sales Education Foundation 2020 ).
Additionally, more universities are beginning to add sales analytics to their available sales courses. Given this increased availability of sales data and information and the apparent growing demand for sales research, I feel that reaching a better understanding of sales analytics is paramount in academic research. That is why I felt honored to be invited to edit this special issue on sales analytics.
The business world changes rapidly, and organizations must be able to help there sales teams adapt to these changes. Sales managers need the availability to quickly access published research to gain insights into best practices and solid methodology to deal with their daily challenges (Sales Education Foundation 2020 ). With the recent upheaval of industry due to the COVID-19 pandemic, the potential rise or fall of some corporations hinges on their ability to leverage sales data assets quickly and effectively. The goal of the Journal of Marketing Analytics has always been to incorporate rigorous research methods with real-world cases so that academics and industry professionals can stay on top of the latest trends and cutting-edge analytics. Measurement has always played a pivotal role in connecting theoretical concepts, and the conclusions reached about these concepts in academic research. As noted by Krishen and Petrescu ( 2018 , p. 117), “Metrics and data are empty shells without proper theories and interpretations behind them.” Hall and Lee ( 2019 ) reinforced this insight in the Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management’s special edition on “Measurement in Sales Research” by accentuating the strong links between theories, empirical data, and research conclusions.
As I set out to consider the many submissions for this special issue and extend invitations to reviewers, it was inspiring to see the high commitment level by sales scholars. The overarching goal was to meld strong theoretical and empirical analytics research in sales and sales management. The articles published in this special issue accomplish that goal and offer insightful views into each of their chosen topics. In each article, the authors’ insights and perspectives lay a foundation that should be considered for future academic research. The first two articles provide a common theme in regard to using CRM.
First, Hoyle et al. dissect how sales managers and salespeople are using the modern-day tools at their disposal to achieve accurate sales forecasting and the resulting impacts. In doing so, this article examines factors that influence the type of forecasting used and potential explanations for why. While recognizing the importance of data-driven decisions and predictive analytics in organizational success and the ability to improve day-to-day efficiencies, Hoyle et al.’s research demonstrates that there is a lack of action and follow through on these ideals among both sales managers and salespeople. This research offers several managerial contributions relating to the process of sales forecasting. It also puts forth a call for further research on forecasting, including the role of varied CRM and ERP systems, sales force automation, and other technologies to identify the diverse impacts on forecasting, planning, and goal setting.
Second, Rodriguez and Boyer integrate Technology Acceptance Model (TAM) and IS success model to explore the influence (Mobile CRM) mCRM has on sales performance. This article applies an adaptation of mCRM to salespeople in a business-to-business context. This research also helps elucidate the role mCRM plays in traditional CRM adoption.
In the other two articles, Merkle et al. use a unified theory of brand equity to explore the decline of Major League Baseball (MLB) ticket sales and game attendance within the framework of MLB brand equity. Additionally, this research examines the mediating role of attendance and local television and the moderating role of Twitter followers in the relationships between MLB marketing assets and the financial performance of the teams using secondary data from multiple sources. Additionally, Said looks at a bibliometric analysis of salesforce research from 1912–2019 to put forth a four-step procedure to merge SCOPUS and Web of Science databases when performing a bibliometric analysis. This research demonstrates that doing separate bibliometric analyses of each database does not prove a complete picture of the state of knowledge and tendencies in a field.
It was my pleasure to work with the reviewers and authors to put this special issue together. As I feel that critical research into sales analytics is still in its infancy, I hope that this special issue lays a foundation for the academic community to conduct further sales analytics research.
Breur, T. 2013. Editorial. Journal of Marketing Analytics 1: 1–2.
Article Google Scholar
Hall, Z.R., and N. Lee. 2019. Taking the measure of measurement in sales research: Introduction to the special issue. Journal of Personal Selling & Sales Management 39 (3): 201–206.
Krishen, A.S., and M. Petrescu. 2018. Marketing analytics: Delineating the field while welcoming crossover. Journal of Marketing Analytics 6: 117–119.
Sales Education Foundation. 2020. Elevating sales research . https://salesfoundation.org/elevating-sales/sales-research/ . Accessed 14 June 2020.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Scott College of Business, Indiana State University, Terre Haute, Room 215, 30 N. 7th Street, Federal Hall, IN, 47809, USA
J. Ricky Fergurson
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to J. Ricky Fergurson .
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Fergurson, J.R. Data-driven decision making via sales analytics: introduction to the special issue. J Market Anal 8 , 125–126 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41270-020-00088-2
Download citation
Published : 26 July 2020
Issue Date : September 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1057/s41270-020-00088-2
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up

- 05 Dec 2023
- Cold Call Podcast
What Founders Get Wrong about Sales and Marketing
Which sales candidate is a startup’s ideal first hire? What marketing channels are best to invest in? How aggressively should an executive team align sales with customer success? Senior Lecturer Mark Roberge discusses how early-stage founders, sales leaders, and marketing executives can address these challenges as they grow their ventures in the case, “Entrepreneurial Sales and Marketing Vignettes.”

- 22 Feb 2021
Reaching Today's Omnichannel Customer Takes a New Sales Strategy
For salespeople working harder than ever to stay ahead of customers' evolving buying habits, Frank Cespedes offers timeless advice in his new book, Sales Management That Works. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 04 May 2020
- Research & Ideas
Predictions, Prophets, and Restarting Your Business
Businesses are starting to plan their re-entry into the market, but how do they know what that market will look like? Frank V. Cespedes warns against putting too much trust in forecasters. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 22 Oct 2019
Use Artificial Intelligence to Set Sales Targets That Motivate
Setting sales targets has always been an inexact science, with serious consequences if done poorly. Using AI-based advanced analytics might be the answer, argues Doug Chung. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 30 Jun 2019
- Working Paper Summaries
The Comprehensive Effects of Sales Force Management: A Dynamic Structural Analysis of Selection, Compensation, and Training
When sales forces are well managed, firms can induce greater performance from them. For this study, the authors collaborated with a major multinational firm to develop and estimate a dynamic structural model of sales employee responses to various management instruments like compensation, training, and recruiting/termination policies.

- 22 Apr 2019
Why Salespeople Struggle at Leading
When salespeople become managers, they often do a horrible job. Four key steps can help them—and all soon-to-be managers—make the shift, says Frank V. Cespedes. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 09 Aug 2018
Two Million Fake Accounts: Sales Misconduct at Wells Fargo
Coming out of the financial crisis, Wells Fargo was one of the world’s most successful banks. But then its sales culture went wild, opening more than 2 million fake accounts. Suraj Srinivasan discusses what went wrong. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 09 Jul 2018
Overcoming the Challenges of Selling Brand New Technology (Hey, Need a 3-D Printer?)
Selling technology that is new to the market involves tricky tradeoffs around prospect targeting, channels, and tactics. Frank Cespedes makes the point with 3-D printers. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 06 Jun 2018
Cut Salaries or Cut People? The Best Way to Survive a Downturn
When times are tight, companies usually respond with employee layoffs. But what if they held on to workers and cut their salaries instead? New research by Christopher Stanton and colleagues has the answer. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 29 Apr 2018
Analyzing the Aftermath of a Compensation Reduction
This study of the effects of compensation cuts in a large sales organization provides a unique lens for analyzing the link between compensation schemes, worker performance, and turnover.
- 06 Jul 2017
Do All Your Detailing Efforts Pay Off? Dynamic Panel Data Methods Revisited
Personal selling in the form of detailing to physicians is the main go-to-market practice in the pharmaceutical industry. This paper provides a practical framework to analyze the effectiveness of detailing efforts. The method and empirical insights can help firms allocate sales-force resources more efficiently and devise optimal routes and call-pattern designs.
- 05 Apr 2017
For Women Especially, It Pays to Know What Car Repairs Should Cost
Consumers can negotiate cheaper auto repair prices by convincing service reps they know something about market rates—helping women overcome gender discrimination, according to recently published research by Ayelet Israeli and co-authors. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 22 Mar 2017
What's the Ideal Frequency for a Sales Quota?
Sales reps feed on two forms of compensation: salary, and a bonus tied to achieving a periodic quota. Would a more frequent quota incentivize better numbers? Doug Chung and Das Narayandas offer some answers. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 20 Feb 2017
Where Should We Build a Mall? The Formation of Market Structure and Its Effect on Sales
In spite of the recent surge in e-commerce, brick-and-mortar retail, specifically in the form of large-scale shopping malls, is still the dominant venue for consumer purchases in the developed world. The construction of mass-scale shopping malls has also experienced tremendous growth in newly industrialized countries such as China. This research provides a rigorous, yet practical, framework to understand and evaluate why retail stores join a shopping mall and how their decisions affect mall revenue. The model can be extended and applied to a number of settings where a decision maker must choose among alternative sites to construct a market, for example, for transportation hubs such as airports or train stations.
- 25 Jan 2017
The Effects of Quota Frequency on Sales Force Performance: Evidence from a Field Experiment
This study of different sales quotas and their effect on sales performance at a major retail chain in Sweden finds that changing from a monthly to a daily quota plan increases performance mainly for low-performing salespeople.
- 06 Dec 2016
Assortment Rotation and the Value of Concealment
Assortment rotation is the retailing practice of changing the assortment of products offered to customers throughout a selling season. It is used by both brick-and-mortar and online retailers as a strategy for gaining competitive advantage. This paper studies assortment rotation in product categories such as apparel, accessories, and toys, where consumers typically make multiple purchases during a season. The authors identify and explain a new reason for retailers to frequently rotate their assortment: Consumers may purchase more products throughout the selling season if a retailer conceals a portion of its full product catalog from consumers by rotating its assortment. Aside from its scholarly contributions, the paper provides practical insights to retailers to guide their assortment rotation strategy decisions.
- 21 Nov 2016
It Matters That Your CEO Doesn't Know Much About Sales
Sales appears to be getting short-changed in the C-suite, says Frank Cespedes. What’s needed are more links between top executives and the customer-facing side of the business. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 28 Mar 2016
Do Incentive Plans for Exemplary Employees Lead to Productive or Counterproductive Outcomes?
This study of a mobile phone retail company shows that incentive contracts that selectively incentivize exemplary employees (that is, preferential incentive plans) may be helpful when companies want to motivate employees to pursue objectively measured goals in addition to relevant tasks not explicitly written into their contracts. However, preferential incentive plans may lead to unintended consequences if they trigger perceptions of inequity.
- 08 Sep 2014
The Strategic Way To Hire a Sales Team
The equivalent of an entire sales force is replaced at many firms every four years, so it's critical that go-to-market initiatives remain tied to strategic goals. Frank Cespedes explains how in his book, Aligning Strategy and Sales. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 01 Apr 2013
First Minutes are Critical in New-Employee Orientation
Employee orientation programs ought to be less about the company and more about the employee, according to new research by Daniel M. Cable, Francesca Gino, and Bradley R. Staats. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- Technical Support
- Technical Papers
- Knowledge Base
- Question Library
Call our friendly, no-pressure support team.
Data Analytics in Marketing Research: Definition, Types, Process, and More
Data Analytics is a critical function affecting all aspects of the business. This article covers broad data analytic topics for those new to the area of data analytics. At Sawtooth Software, we focus on marketing research and primary data collection through survey research, so this article specifically calls out the use of data analytics in marketing sciences.
Before diving deep into the breadth of data analytics, let’s summarize key takeaways you will gain from this guide:
|
|
|
|---|---|
| What is Data Analytics? | Definition and significance of transforming raw data into actionable insights. |
| Data Analytics vs. Data Science | Understanding the differences and complementary roles of data analytics and data science. |
| Types of Data Analysis | Overview of descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive analytics with practical examples. |
With that introduction, let’s dive deeper into the field of Data Analytics .
Table of Contents
What Is Data Analytics?
At its core, Data Analytics involves the computational analysis of data or statistics. Data can involve numeric values, text, graphics, video or audio files. The value of data analytics lies in its ability to transform vast amounts of raw, often unstructured data into actionable insights. These insights can then guide decision-making, optimize operations, and unveil opportunities for innovation.
Consider a retail business that leverages data analytics to understand customer purchasing patterns, preferences, and behaviors. By analyzing sales data, customer feedback, social media trends, along with primary survey data, the business can tailor its product offerings, improve customer service, predict future trends, and optimize products and pricing for new or existing products. This practical application underscores the transformative power of data analytics in driving business strategy and growth.
Data Analytics vs. Data Science
While often used interchangeably, Data Analytics and Data Science involve nuanced differences, with complementary roles within an organization. Data Analytics focuses on processing and performing statistical analysis on existing datasets. In contrast, Data Science typically involves heavier programming, developing algorithms, and model-building to derive additional insights to solve complex problems and predict future outcomes. Data scientists often leverage machine learning and AI (Artificial Intelligence) in building algorithms, models, and applications.
The impact of both fields on Decision-Making is important. Data analytics provides a more immediate, focused insight primarily aimed at enhancing operational efficiency and answering specific questions. Data Science, on the other hand, dives deeper into predictive analysis, machine learning, and AI to forecast future trends and behaviors.
Marketing Research Consulting
Need help with your research study? Contact our expert consulting team for help with survey design, fielding, and interpreting survey results.
Contact Our Consulting Team
Types of Data Analysis
Data Analysis can be broadly categorized into four main types, each serving a unique purpose in the data analytics landscape. Understanding these types helps you to apply the right analytical approach to your data to derive meaningful conclusions and strategies.
Descriptive Analytics
This type of analytics focuses on the “what” and is the most basic and commonly used. For market research surveys, descriptive analytics summarizes responses to demographic, psychographic, attitudinal, brand usage data, and the like. For historical data, it aims to provide a clear picture of what has happened in the past by summarizing such things as sales data, operations data, advertising data, and website click traffic. Descriptive analytics answers the "What happened?" question by analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. For example, a business might use descriptive analytics to understand its sales trends, customer engagement levels, or production efficiencies over the past year.
Diagnostic Analytics
Moving beyond the “what” to understand the “why,” diagnostic analytics involves a deeper dive into data to examine patterns of association or correlation, with the hope to uncover root causes of attitudes, preference, events or trends. It employs techniques such as correlation analysis, t-tests, chi-square tests, key drivers analysis, and tree-based analysis (such as CART or random forests). For customer satisfaction research key drivers analysis tries to explain how overall customer satisfaction or loyalty can be improved by improving the features or elements of the product or service delivery. An organization might also leverage diagnostic analytics to identify why certain groups of respondents are more likely to be price sensitive or why customer churn increased in a specific period.
Predictive Analytics
This forward-looking analysis leverages data and models that can predict future outcomes. Conjoint analysis is a widely used predictive analytics approach for studying how changes to product features and prices affect demand. MaxDiff (best-worst scaling) is often used to assess which product claims will likely increase new product trial, or which side effects would most discourage patients from undergoing a cancer treatment therapy. Machine learning algorithms such as random forests can score a database to predict which customers are most likely to be receptive to an offer. As another example, a financial institution might use predictive analytics to assess the risk of loan default based on a customer's credit history, transaction data, and market conditions.
Prescriptive Analytics
An advanced form of analytics, prescriptive analytics, goes a step further by recommending actions you can take to affect desired outcomes. It not only predicts what will happen but also suggests various courses of action and the potential implications of each. This type of analytics is particularly valuable in complex decision-making environments. For example, a conjoint analysis market simulator leveraging optimization search routines can determine the right mix of product features and price to reach a particularly valuable market segment .
Each of these types of data analysis plays a critical role in an organization's data-driven decision-making process, enabling businesses to understand their past performance, diagnose issues, create successful products and services, predict future trends, and make informed choices that align with their strategic objectives.
Data Analytics Real-World Example
Consider the case of a data analyst working for an e-commerce platform. By analyzing customer purchase history, the analyst identifies a trend of increased sales in eco-friendly products ( descriptive analytics , the “what”). A survey is designed and conducted to dig deeper into which customers are preferring eco-friendly products, why they prefer them, and for which usage occasions ( diagnostic analytics , the “why”). Within another market research survey, a conjoint analysis or MaxDiff study is included for determining the right product claims, product features, and pricing, targeted to which market segments to develop new products for sales growth ( predictive and prescriptive analytics ).
The role of a data analyst is dynamic and impactful, bridging the gap between data and strategic decision-making. It's a role that requires not only technical skills but also curiosity, creativity, and a keen understanding of the business landscape.
The Data Analysis Process
Breaking down a data analytics process into systematic steps can demystify the journey, making it more approachable and manageable. The Data Analysis Process is a structured approach that guides data analysts from the initial phase of understanding the business problem to the final stage of delivering actionable insights.
Step 1: Defining the Question
The first and perhaps most critical step in the data analysis process is defining the question . This involves understanding the business objectives, the decisions that need to be supported by the data, and the specific questions that the analysis aims to answer. A well-defined question not only provides direction for the analysis but also ensures that the outcomes are relevant and actionable.
Step 2: Collecting Clean Data
Data collection is the next step, where data analysts gather the necessary data from various sources. This could include internal databases, secondary sources of data, customer surveys, and more. Ensuring the cleanliness of the data is paramount at this stage; hence, data cleaning and preprocessing become essential tasks. This involves removing inaccuracies, inconsistencies, handling missing values, and trimming outliers to ensure the data is reliable and accurate for analysis. For market research surveys, this also involves identifying unreliable respondents, fraudulent respondents, and records completed by survey bots.
Step 3: Data Analysis and Interpretation
With clean data in hand, analysts proceed to the heart of the process: data analysis and interpretation . This involves applying statistical methods and analytical models to the data to identify patterns, trends, and correlations. The choice of techniques varies depending on the data and the questions at hand, ranging from simple descriptive statistics to complex predictive models.
Step 4: Data Visualization and Sharing Findings
Data visualization plays a crucial role in this phase, as it transforms complex data sets into visual representations that are easier to understand and interpret. Tools like charts, graphs, and dashboards are used to illustrate the findings compellingly and intuitively.
Finally, sharing the findings with stakeholders is an integral part of the data analysis process. This involves not just presenting the data, but also providing insights, recommendations, and potential implications in a clear and persuasive manner. Effective communication is key here, as the ultimate goal is to inform decision-making and drive action based on the data insights.
For product optimization and pricing research, market simulators from conjoint analysis can be even more useful to a decision-maker than charts and graphs. They allow the manager to test thousands of potential product formulations and prices, to find the right products to best reach target market segments.
Example Scenario
Imagine a data analyst working for a healthcare provider, tasked with reducing patient wait times. By following the data analysis process, the analyst:
- Defines the question: What factors contribute to increased wait times?
- Collects and cleans data from patient records, appointment systems, and feedback surveys.
- Analyzes the data to identify patterns, such as peak times for appointments and common delays in the patient check-in process.
- Visualizes the findings using graphs that highlight peak congestion times and the factors causing delays.
- Shares the insights with the healthcare management team, recommending adjustments to appointment scheduling and check-in processes to reduce wait times.
This systematic approach not only provides actionable insights but also showcases the power of data analytics in solving real-world problems.
Understanding the data analysis process is foundational for anyone looking to delve into data analytics, providing a roadmap for transforming data into insights that can drive informed decision-making.
Tools and Techniques
The field of Data Analytics is supported by a variety of tools and techniques designed to extract, analyze, and interpret data. Market research surveys are often a key source of data. The choice of the right analytics tools and the application of specific analytical techniques can significantly impact the quality of the insights generated. In this section, we will explore some of the key data analytics techniques and highlight commonly used tools, especially for primary survey research, providing tips on how to choose the right ones for specific projects.
Key Data Analytics Techniques
Statistical Testing: When summarizing data using means (for continuous data) or percent of observations falling into different categories (for categorical or nominal data), we often want to know whether the differences we’re observing between groups of respondents, branches of a company, or time periods are statistically meaningful (that they were unlikely to occur by chance).
Correlation Analysis : A statistical approach that examines whether there is a positive, negative, or no correlation between two continuous variables. The square of the correlation coefficient indicates the percent of variance in one variable that is explained by the other.
Regression Analysis : A statistical method used to examine the relationship between dependent (outcome) and independent (predictor) variables. There are regression techniques for predicting continuous variables (ordinary least squares) as well as for categorical outcomes (logistic regression). Regression analysis is particularly useful for identifying relationships between variables, making predictions, and forecasting.
Tree-Based Analysis : These techniques are used for finding which variables tend to predict or explain some outcome, such as purchase of a product, or diagnosis with a disease. Common examples are Classification and Regression Trees (CART) and Random Forests, a combination of multiple trees that can be ensembled for a more accurate consensus prediction.
Time-Series Analysis : Focused on analyzing data points collected or recorded at specific time intervals. This technique is crucial for trend analysis, seasonal pattern identification, and forecasting.
Cluster Analysis : A family of methods used to group a set of objects (such as respondents) in such a way that objects in the same group (called a cluster) are more similar to each other than to those in other groups. It’s extensively used in market segmentation and targeting strategies. Common approaches include k-means clustering, latent class clustering, and ensemble approaches that leverage multiple techniques to achieve a more robust consensus solution.
Conjoint Analysis and MaxDiff: Discrete choice methods often used in market research and economics for assessing the importance of features, measuring price sensitivity , and predicting demand for products or services.
Quick and Intuitive Conjoint Analysis Software
Need to launch a conjoint analysis study? Get access to our free conjoint analysis tool. In just a few minutes, you can create full conjoint analysis exercises with just a few clicks of our easy-to-use interface.
Conjoint Analysis Software Tool or Request a Product Tour
Commonly Used Data Analytics Tools
Excel : A versatile tool for basic data analysis, familiar to most professionals, capable of handling various data analysis functions including pivot tables, basic statistical functions, and data visualization.
SQL : Essential for data extraction, especially from relational databases. SQL allows analysts to query specific data from large databases efficiently.
Python/R : Both are powerful programming languages favored in data analytics for their libraries and packages that support data manipulation, statistical analysis, and machine learning.
Tableau/Power BI : These tools are leaders in data visualization, providing robust platforms for creating dynamic and interactive dashboards and reports.
Sawtooth Software : Provides tools, support services, and consulting services for designing and fielding market research surveys, as well as conducting conjoint analysis, MaxDiff, and cluster analysis.
Free Survey Maker Tool
Get access to our free and intuitive survey maker. In just a few minutes, you can create powerful surveys with its easy-to-use interface.
Try our Free Survey Maker or Request a Product Tour
Choosing the Right Tools and Techniques
Selecting the appropriate tools and techniques depends on several factors:
Project Requirements : The nature of the data and the specific questions you are trying to answer will guide your choice. For instance, Python might be preferred for its machine learning capabilities, while Tableau is chosen for sophisticated visualizations.
Data Size and Complexity : Large datasets and complex analyses might require more advanced tools like Python or R, whereas Excel (limited to around 1 million rows and 16 thousand columns) could suffice for smaller, simpler datasets.
Skill Set : The proficiency of the data analyst in using these tools also plays a significant role. It’s essential to balance the choice of tool with the analyst's comfort level and expertise.
Budget and Resources : Some tools require significant investment, both in terms of licenses and training. Open-source options like Python and R offer powerful functionalities at no cost.
Example Application
Consider a retail company looking to optimize its inventory levels based on historical sales data. The data analyst might use:
- SQL to extract sales data from the company's database.
- Python for conducting time-series analysis to identify sales trends and predict future demand.
- Tableau to create visualizations that illustrate these trends and forecasts, facilitating strategic discussions on inventory management.
Through the strategic application of these tools and techniques, data analysts can uncover valuable insights that drive informed decision-making and strategic planning within organizations.
The exploration of tools and techniques underscores the versatility and power of data analytics. Whether through statistical analysis, predictive modeling, or insightful visualizations, these tools empower analysts to turn data into strategic assets.
Importance and Uses of Data Analytics
Data analytics has become a pivotal element of business strategy, influencing decisions across all levels of an organization. Its importance cannot be overstated, as it provides the insights needed for businesses to innovate, stay competitive, and improve operational efficiency. This section explores the significance of data analytics across various domains, including healthcare, product optimization and pricing, and its relevance for small enterprises and startups.
Embracing data analytics allows organizations to move from intuition-based decisions to informed strategies. As we advance, the integration of data analytics into every aspect of business operations and strategy will become more pronounced, highlighting its critical role in shaping the future of industries worldwide.
Transforming Business Success
Data analytics empowers businesses to make informed decisions by providing a deep understanding of customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. It enables companies to:
- Optimize Operations : By analyzing data, businesses can identify inefficiencies in their operations and find ways to reduce costs and improve productivity.
- Enhance Customer Experience : Data analytics allows businesses to understand their customers' preferences and behaviors, leading to improved revenues, customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Product Innovation/Optimization and Pricing : Survey research methods such as conjoint analysis and MaxDiff are especially useful for optimizing features for and pricing products/services, keeping companies at the forefront of innovation and competitiveness.
In healthcare, data analytics plays a critical role in improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. By analyzing patient data, healthcare providers can:
- Predict Outbreaks : Data analytics can help in predicting disease outbreaks, enabling healthcare systems to prepare and respond effectively.
- Personalize Treatment : Analytics (including MaxDiff and conjoint analysis) can elicit real-time preferences from patients that can lead to better personalized treatment plans, improving patient care and outcomes. Several groups of physicians and academic researchers have presented research at Sawtooth Software conferences on using these tools for facilitating better communication between patients and doctors and selecting treatment plans for diseases such as cancer to result in improved outcomes.
- Improve Operational Efficiency : Data analytics can optimize hospital operations, reducing wait times and improving patient flow.
Product Optimization and Pricing
Repositioning existing products, developing new products, and setting effective pricing strategies are vital to most any business. By using gold standard tools for survey research such as conjoint analysis and MaxDiff, businesses can:
- Find Optimal Sets of Features : Conjoint analysis can within a single survey research project evaluate 1000s of potential feature configurations, determining which feature sets will compete best relative to specific competitors.
- Identify Profitable Target Segments : Conjoint analysis or MaxDiff are excellent techniques for identifying and sizing market segments that have specific needs and are associated with different levels of price sensitivity.
- Measure Price Elasticity: Choice-Based Conjoint (CBC) analysis is particularly valuable for estimating price elasticity of demand for the firm’s brand(s), as well as assessing how changes to competitor’s prices affect quantity demanded for the firm’s brand(s) ( cross-elasticity ).
Relevance for Small Enterprises and Startups
For small enterprises and startups, data analytics offers a competitive edge, enabling them to:
- Make Informed Decisions : Even with limited resources, small businesses can use data analytics to make strategic decisions based on market trends and customer feedback.
- Identify Opportunities : Analytics can reveal market gaps and customer needs, providing startups with insights to innovate and capture new markets.
The Role of a Data Analyst
In the heart of data-driven organizations lies the Data Analyst , a professional whose responsibilities are as varied as they are critical. Understanding the role of a data analyst not only highlights the importance of data analytics in modern business but also sheds light on the skills and perspectives needed to excel in this field.
Responsibilities and Tasks
A data analyst's journey often begins with problem formulation and developing hypotheses and strategies for solving a business or organizational problem. Next often follows data collection, ensuring the quality and accuracy of the data sourced from various channels, including survey research. This foundational step is critical, as the integrity of the data directly impacts the insights derived from it. The analyst then proceeds to clean and preprocess the data, preparing it for analysis. This involves handling missing values, removing duplicates, trimming outliers, and ensuring the data is in a format suitable for analysis.
The core of a data analyst's role involves statistical analysis and data modeling to interpret the data. They employ a range of techniques, from simple descriptive statistics to more complex predictive models, to unearth trends, patterns, and correlations within the data.
However, the role extends beyond just analyzing data. Data visualization and reporting are equally important, as these allow the analyst to communicate their findings in a clear, compelling manner. Whether through dashboards, reports, or presentations, the ability to present data in an accessible way is crucial for informing decision-making processes within an organization.
Professional Insights
From the perspective of a seasoned data analyst, the job is not just about numbers and algorithms; it's about solving challenging business and organizational problems and storytelling with data. It involves translating complex datasets into actionable insights that can drive strategy and impact. An effective data analyst combines analytical skills with business acumen, understanding the broader context in which the data exists.
Career Opportunities in Data Analytics
The field of data analytics offers a dynamic career landscape, characterized by a high demand for skilled professionals capable of turning data into actionable insights. As businesses across industries continue to recognize the value of data-driven decision-making, the demand for data analysts has surged, creating a wealth of opportunities for those equipped with the right skills and knowledge. This section will explore career prospects, including job growth, and discuss the relevance of degrees and certifications in data analytics.
Job Growth and Demand
The demand for data analysts is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. According to industry reports and labor statistics, the job market for data analysts is expected to grow much faster than the average for all occupations. This growth is driven by the increasing volume of data generated by businesses and the need to analyze this data to make informed decisions.
- Projected Job Growth : Data analytics roles are expected to see one of the highest rates of job growth across all sectors.
- Industries Hiring : While technology and finance traditionally lead in hiring data analysts, healthcare, marketing, and retail are rapidly catching up, reflecting the broad applicability of data analytics skills.
Salary Ranges
Salaries for data analysts can vary widely based on experience, location, and industry. However, data analysts typically command competitive salaries, reflecting the high demand and specialized skill set required for the role.
- Entry-Level Positions : Even at entry levels, data analysts can expect salaries that are competitive, with potential for rapid growth as experience and skills develop.
- Senior Roles : Experienced data analysts, especially those with specialized skills or leadership roles, can command significantly higher salaries.
Degrees and Certifications
While a degree in data science, statistics, computer science, or a related field can provide a strong foundation, the field of data analytics also values practical experience and specialized skills.
- Relevant Degrees : Bachelors and masters degrees in relevant fields are highly valued, but not always required.
- Certifications : Certifications can supplement academic degrees and provide evidence of specialized skills in data analytics tools and methodologies. Popular certifications include Certified Analytics Professional (CAP), Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate, and various platform-specific certifications (e.g., Tableau, SAS).
Making It in Data Analytics
Success in a data analytics career is not solely determined by technical skills. Employers also value problem-solving abilities, business acumen, and the capacity to communicate complex findings in a clear and actionable manner. Continuous learning and adaptation to new tools, technologies, and methodologies are essential in this rapidly evolving field.
Get Started with Your Survey Research Today!
Ready for your next research study? Get access to our free survey research tool. In just a few minutes, you can create powerful surveys with our easy-to-use interface.
Start Survey Research for Free or Request a Product Tour
Data analytics is not just a tool but a strategic asset that can drive significant business value, enhance operational efficiency, and foster innovation across various sectors. From improving healthcare outcomes to enabling small businesses to compete more effectively, the applications of data analytics are vast and varied.
As we embrace the future, the importance of data analytics in driving business success and societal improvement will only continue to grow. For those considering a career in data analytics or looking to implement data-driven strategies in their operations, the potential is limitless. The benefits of data-driven decision-making underscore the transformative power of data analytics, making it an indispensable part of modern business and governance.
Whether you are a budding data analyst, a business leader, or simply curious about the potential of data analytics, the journey into this field is not only rewarding but essential for those looking to make an impact in the digital age.
Sawtooth Software
3210 N Canyon Rd Ste 202
Provo UT 84604-6508
United States of America
Support: [email protected]
Consulting: [email protected]
Sales: [email protected]
Products & Services
Support & Resources
9 Marketing Research Methods to Refine Your Marketing Strategy
11 min read

What are the different marketing research methods product marketing teams can use to inform their strategies?
This is the main question the article answers.
You will also learn about different types of market research and how to conduct it step by step.
Let’s dive right in.
Market research is the process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a target market, competitors, and customers.
- Its goal is to help make informed decisions about product development , marketing strategies, pricing, and customer acquisition in SaaS companies.
- Conducting market research offers numerous benefits, including a better understanding of customer needs and market trends.
- Teams can leverage the insights to guide product development for better customer satisfaction and to get ahead of competitors. They also enable targeted user engagement and improve the effectiveness of marketing campaigns.
- The main types of market research include primary research (original data collection), secondary research (using existing data), quantitative research (using measurable data), qualitative research (gathering exploratory insights), and competitor research (analyzing the competitive landscape).
Try Userpilot and Take Your Product Marketing to the Next Level
- 14 Day Trial
- No Credit Card Required

Nine effective market marketing research methods include:
- Survey research : Email and in-app surveys to collect quantitative and qualitative data.
- User interviews : One-on-one conversations for qualitative insights.
- Focus groups : Sessions leveraging group dynamics to extract diverse insights.
- Observational research : Watching users engage with the product, e.g., through session recordings.
- Social listening : Monitors what existing and prospective customers say online about you and your competitors.
- A/B testing : Testing two versions of the product or marketing collateral side-by-side.
- Heatmaps : Color-coded UI overlays indicating areas of high engagement.
- Exploratory research : Qualitative research without any pre-defined focus.
- Public databases : Secondary sources, excellent at initial research stages.
- The market research process involves defining clear goals , identifying and segmenting the target market, choosing relevant research methods, collecting data using appropriate tools, and analyzing the data to extract actionable insights .
- A wide range of tools are available for market research, including Userpilot for in-app surveys and user behavior analysis , SurveyMonkey for email surveys, Hotjar for user interviews and heatmaps, and Google Analytics for web analytics.
- Book the demo to learn how Userpilot can help your team with market research!
What is market research?
Such research helps SaaS companies make informed decisions about product development , marketing strategies, pricing, and customer acquisition.
The benefits of conducting market research
Let’s face it: market research requires time and resources. However, the investment is fully justified for a number of reasons:
- Market research helps you better understand your customers’ pain points , needs, and desires. Such insights are essential to building products that solve genuine problems and quickly achieve product-market fit .
- By understanding what your customers want, you can continuously improve your offerings and enhance customer satisfaction . This translates into higher customer retention and, ultimately, better business performance.
- Keeping a pulse on your market allows you to spot emerging trends and unmet needs. Such insights drive innovation to give you a competitive advantage.
- Understanding your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses can help you define your unique selling proposition.
- Whether you’re launching a new product or entering a new market, market research can help you test the waters before diving in and potentially save you from costly mistakes.
- With insights from market research, you can create more targeted, effective marketing campaigns that resonate with your audience.
- Market research provides solid data to back up your business decisions – so no more guesswork and acting on hunches.
Different types of market research to gather valuable insights
Market researchers rely on different kinds of research to obtain the necessary insights.
Let’s unpack the main ones.
Primary market research
Primary research is the original data you gather yourself. It’s tailor-made for your specific needs and usually involves direct interaction with your target audience , for example, through interviews or surveys .
Such research can provide up-to-date and highly relevant insights but is time-consuming and costly.
Secondary market research
Secondary research recycles information that already exists, for example, from industry benchmark reports or academic studies.
Data obtained in this way isn’t 100% relevant to your circumstances but can give you a good understanding of the trends in your niche. And it’s quicker and more cost-effective than primary market research.
Quantitative research
Quantitative market research deals with data that can be measured and statistically analyzed. In SaaS, this could be data from web and product analytics or quantitative survey questions, like NPS.
If conducted on a large enough sample, such research is very objective and allows you to identify trends and patterns over time.
However, it may not offer you the answers as to why users behave in a particular way.
Qualitative research
Qualitative market research complements quantitative insights by helping you explain the ‘why’ behind the numbers.
For practical reasons, it involves smaller customer samples than quantitative studies and uses techniques like interviews, focus groups, surveys , and session recordings.
Competitor research
Competitive research helps you understand your position in the competitive landscape.
It gives you an understanding of your competitors’ strategies, strengths, and weaknesses and allows you to identify market gaps and new opportunities.
Competitive analysis uses primary and secondary research to obtain qualitative and quantitative data.
9 marketing research methods to execute
Let’s look a bit closer at market research techniques that you can use for each type of research.
1. Customer surveys
Customer surveys are the bread and butter of market research. They’re easy to administer, and you use them to gather both quantitative and qualitative data at scale. They can help you gauge customer satisfaction , gather product feedback, or understand market trends.
When collecting feedback from existing users, in-app surveys are particularly effective and have higher response rates than email surveys.
With tools like Userpilot , you can launch an in-app survey within minutes.
Pick a template from the library, tweak the question , select the audience, and set how to send the survey. You can either pick a specific date and time or use event-based triggering to gather contextual feedback.
What if you don’t have users yet?
Tools like SurveyMonkey give you access to respondent pools you can target based on hundreds of criteria.

2. User interviews
User interviews are more time-consuming and resource-intensive, so conducting them at scale is difficult. However, nothing beats a one-to-one conversation when you’re after deep, nuanced insights .
That’s because they give you the flexibility to drill down on interviewees’ ideas.
It doesn’t mean that they’re completely unstructured.
To get the most out of the interview, they need to have a clear focus.
Here’s a template you can use to prepare for them.

How do you recruit interview participants? You can send in-app invites to your customers who meet the criteria or, again, lean into an interviewee pool available in tools like Hotjar.
3. Focus groups
A focus group brings together a small number of people, usually 6-10, from your target audience to discuss your product.
The interaction between participants can spark conversations and ideas that might not come up in individual interviews. And can reveal shared experiences, pain points , and desires that individual interviews might miss.
However, to get the most out of them, bring in a skilled moderator to guide the discussion and ensure all voices are heard and key topics are covered.
Otherwise, dominant personalities or groupthink can skew the results.
4. Observational research
Observational research involves watching how users interact with your product or service in their natural environment. This could be in-person observation or through tools like session recordings for digital products.
Why bother?
Because what people do is often more revealing than what they say. Observing customers can highlight discrepancies between reported and actual behavior or offer insights that users themselves might not be aware of or able to articulate.
This method can uncover usability issues, reveal unexpected use cases, and is particularly valuable for understanding the context in which your product is used.
Session recordings are coming to Userpilot soon to allow you to observe how users interact with your product.
5. Social listening
Social listening involves monitoring social media platforms for mentions of your brand, products, competitors, or industry. It can help you track sentiment , identify emerging trends, manage your online reputation, and even find potential customers or brand advocates .
How do you do it?
Monitor your social media accounts and review sites, and use tools like Hootsuite, Sprout Social, or Brand24 to monitor the broader expanses of the internet.
But don’t focus just on your online presence. Follow what users have to say about your competitor, too.

6. A/B testing
If you can’t decide on a version of your webpage, email, or product feature, A/B test them.
A/B testing involves comparing two options side by side to see which performs better.
This method is particularly useful for optimizing digital experiences . You can test everything from button colors to pricing structures, using real user behavior to guide your decisions.
What if you have more versions to test? Run multivariate tests .
Userpilot allows you to run both types of tests on your onboarding flows to determine if there are statistically significant differences in their performance.

7. Heatmaps
Heatmaps provide a visual representation of user behavior on your website or app. Using color coding, they show areas of high and low engagement.
They are particularly useful for understanding how users interact with your digital interfaces. It can reveal usability issues, help optimize page layouts, and show which elements are successful or unsuccessful at grabbing user attention.
With Userpilot, you can generate heatmaps of your user in-app engagement – all their clicks , hovers, and text inputs.

8. Exploratory research
When you’re venturing into new territory, exploratory research helps you establish a foothold.
This kind of research is often qualitative and can involve literature reviews, expert interviews, or case studies . It’s particularly useful in the early stages of product development or when entering new markets.
The goal is to define problems more precisely, develop hypotheses, or establish research priorities. It may not provide definitive answers but can point you in the right direction for further, more focused research.
The secret to its success?
Asking open-ended questions and being receptive to unexpected findings.
9. Public databases
Public databases, government reports, industry associations, and academic studies offer a wealth of information.
They can provide valuable context, market size estimates, demographic information, and trend data, which is a cost-effective way to get a broad overview of your market or industry.
Useful sources include:
- U.S. Census Bureau (or regional equivalents).
- Crunchbase.
- Product Hunt (to see what kinds of products get good traction).
While this data isn’t tailored to your specific needs, it can provide a solid foundation for your research and help you identify areas for further primary research.

A step-by-step process on how to conduct market research
Let’s wrap up by exploring the market research process, one step at a time.
Define your market research goals
The process starts by setting clear goals for your market research project. They will determine what data you gather and how.
The goals will differ depending on your product maturity and high-level business goals.
Early on, your goals may be to identify underserved user needs or validate a product idea . And when you’re expanding into new markets, it could be to gauge the demand and potential customers’ willingness to pay .
Whatever your focus, make your goals specific. Use a framework like SMART if you’re only starting.

Identify the target market to research on
Knowing who to research is just as important as knowing what to research. So, the next step is defining your target market as precisely as possible.
If you already have a product in place, use your current customer base for clues. Who are your best customers ? What traits do they share?
If not, start defining the target market with basic demographics like age, gender, location, and income.
Don’t stop there. Dig deeper into psychographics like interests, values, and lifestyle.
As you’re discovering more and more about your customers, segment them based on their needs and behaviors. Identifying these segments will help tailor further research and later – your products or marketing campaigns.
Use this information to create detailed customer personas .

Choose relevant market research methods
With your goals set and the target market defined, it’s time to select your research methods that are aligned with your objectives and audience.
Usually, a mix of methods provides the most comprehensive view.
For example, start with surveys and user behavior analysis and zero in on the key insights with interviews and focus groups. Or the other way round – use surveys to validate insights from an interview.
Of course, the choice of research methods depends. Balance the depth of insights you need with the resources available.
Don’t forget about your audience’s preferences. If your target audience is tech-savvy, they will happily take part in online surveys. Surveys won’t be very helpful when getting insights from my dad – a phone call might, though.
Collect data using the right tools
Time to put your research machine into motion and start collecting data using the right tools.
I’ve already mentioned a few options before, but here’s a more comprehensive list that can help you conduct effective market research:
- Email surveys: Typeform, MonkeySurvey, and HubSpot.
- In-app surveys : Userpilot.
- A/B Testing : Optimizely, VWO, and Userpilot
- Interviews: Hotjar and Fullstory.
- Heatmaps : Userpilot, Hotjar, and Mouseflow.
- Session recordings: Fullstory, Hotjar, and Userpilot soon.
- User behavior analysis: Userpilot, Google Analytics, Amplitude , and Mixpanel.
- Social listening: Hootsuite, Sprout Social, Brand24, and Mention.
Apart from the obvious things like pricing, functionality, or intuitive UI, pay attention to integrations so that you can seamlessly sync the data and analyze it in one place.

Analyze the data collected for valuable insights
Collecting market research data is only half the battle – the real value comes from analysis. The goal isn’t just to summarize what you found but to extract actionable insights that can drive business decisions.
Start by organizing your data. Clean it up, removing any duplicates or irrelevant information.
Use data visualization tools to help spot trends. Graphs, charts , and word clouds can make patterns more apparent. Leverage AI to extract insights from qualitative data, like survey responses.
In your analysis, look for patterns and trends . What common themes emerge from interviews? What correlations appear in your survey data?
Top tip: Make it a team sport. Bring in team members from different departments to get diverse perspectives on what the data might mean for your business.
The choice of market research methods isn’t as challenging as it might initially seem as long as you have a clear idea of what you want to achieve.
The success of the research process depends a lot on the tools that you have available. A well-integrated tech stack will help you collect the necessary data from the right customers and extract actionable insights.
If you’d like to learn how Userpilot can help you with your market research, book the demo!
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth,Management & Trends.
The coolest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends. Delivered fresh to your inbox, weekly.
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
You might also be interested in ...
Saffa Faisal
7 Product Advertising Examples to Inspire Your Next SaaS Campaign
Aazar Ali Shad
Product Marketing Messaging Framework: Key Elements & Examples
Wilson College Online Blog
What does a market research analyst do.
Market research is a crucial aspect of modern business that helps companies understand their customers and potential customers. Professionals such as market research analysts use data gathered through surveys, focus groups, and customer purchasing histories to gain insights into a company’s target audience and how to cater to that audience’s needs.
Market research analysts use their understanding of the customer mindset and data analysis to help companies reach their target audience. Their work is vital to the success of any product or service.
Anyone interested in a career that blends psychology and marketing should consider learning more about what a market research analyst does and how earning a bachelor’s degree can help aspiring analysts reach their career goals.
Market Research Analyst Job Description
Market research analysts help companies uncover trends in the market so that their marketing strategies may be more effective. They do research to learn what customers in different demographic groups are looking for in a particular product or service and what would make a marketing campaign successful with a specific audience. They then use software models to analyze the collected data and report their findings to marketing and sales departments to help them create data-driven strategies.
Market research analysts also gather data on their company’s competitors to learn where and how they’re succeeding or failing, incorporating these findings into their marketing recommendations.
Based on their findings and their in-depth understanding of the customer base, market research analysts’ recommendations can range from how a product should be advertised to what its price should be. Their work requires an informed interpretation of data alongside an understanding of customer psychology to predict what type of campaign will work best to achieve the company’s goals.
Market Research Analyst Job Environment
Market research is used in nearly every industry to identify what customers want from a product or service. Typical employers of market research analysts include businesses, educational institutions, and government agencies. They usually work in office settings, as most of what a market research analyst does involves using computers to analyze data and performing research. However, they may need to travel to conduct interviews or meet with focus groups.
Market Research Analyst Skills
Market research analysts need to have a firm grasp of marketing principles and customer behavior, as these skills directly relate to developing marketing strategies. Additionally, as they need to communicate their findings to other departments, they should be skilled at relaying essential information to project stakeholders.
Here are the key skills and competencies that aspiring market research analysts need to develop:
- Research skills
- Data analysis proficiency
- Marketing knowledge
- Customer psychology knowledge
- Communication skills
- Attention to detail
- Organizational skills
- Computer and software knowledge
How to Become a Market Research Analyst
Companies typically look for market research analysts with an established background in the field. The right foundational education and experience can help applicants stand out.
Most companies require candidates for marketing research positions to have a minimum of a bachelor’s degree, preferably in business, communications, or one of the social sciences, such as psychology . Psychology courses can help students learn about customer behavior and help them understand how to put purchasing habits and decisions in context. Courses that focus on interpreting research are also useful for aspiring analysts.
A bachelor’s degree is also a key requirement for graduate degree programs, which may be required for leadership positions.
Companies hiring market research analysts look for professionals with a proven track record in delivering successful strategies and big data analysis, and applicants may need to build up their resumes before becoming eligible for a position. Internships and entry-level roles such as market research assistant or data analyst can help candidates gain professional experience.
Market Research Analyst Salary and Job Outlook
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), the median annual market research analyst salary was $74,680 in 2023. Individuals’ salaries may be affected by factors such as their education, experience level, industry, and location.
The BLS projects 13% job growth for market research analysts between 2022 and 2032, significantly higher than the 3% average projected for all occupations. As companies increasingly rely on the power of customer data to provide insight into market trends, the job market for analysts will remain strong.
Take Your Next Career Step With Wilson College Online
The right education is essential to establishing the knowledge and skills core to what a market research analyst does. For those looking for a career that combines customer psychology and marketing, consider Wilson College Online’s Bachelor of Arts in Psychology degree program .
The program is designed to help students gain a firm understanding of human behavior and decision-making, which are key to success as a market research analyst or in another career. Additionally, the program teaches students how to interpret research and apply their findings in a range of different industries.
Take control of your future with Wilson College Online.
Recommended Readings
4 Types of Psychology
Online Therapy vs. In-Person Therapy
Psychology vs. Social Work: How Are These Fields Different?
Indeed, “How to Become a Market Research Analyst in 3 Steps”
Indeed, “Market Research Analyst Job Description: Top Duties and Qualifications”
Indeed, “What Is a Market Research Analyst? (With Duties and Skills)”
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, Market Research Analysts
U.S. Small Business Administration, Market Research and Competitive Analysis
Recent Articles

5 Health Psychology Careers
Wilson College
Aug 7, 2024

Feb 5, 2024

Jan 9, 2024
Learn more about the benefits of receiving your degree from Wilson College Online
- Tuition & Financial Aid
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Master’s Degrees
- Bachelor’s Degrees
- Education Degrees
- Nursing Degrees
- Business Degrees
- On Campus Programs
- Technology & Media
Russia Artificial Intelligence Market
Russia artificial intelligence market report by offering (hardware, software, services), technology (machine learning, natural language processing, context-aware computing, computer vision, and others), business function (finance, security, human resources, law, marketing and sales, and others), deployment mode (on-premises, cloud), organization size (large enterprises, small and medium-sized enterprises), end-use industry (bfsi, it/ites, telecommunication, government and defense, manufacturing, healthcare and lifesciences, retail and ecommerce, automotive, transportation and logistics, and others), and region 2024-2032.
- Report Description
- Table of Contents
- Methodology
- Request Sample
Russia Artificial Intelligence Market Overview:
The Russia artificial intelligence market is projected to exhibit a growth rate (CAGR) of 20.60% during 2024-2032 . The market is driven by increasing government support, widespread AI adoption in key economic sectors, domestic technology development, and extensive research and development (R&D) activities undertaken by both the government and non-government entities in the country.
| 2023 | |
| 20.60% |
Russia Artificial Intelligence Market Trends:
Government Support and Strategic Initiatives
Government support and strategic initiatives are crucial drivers for the AI market in Russia because they provide the necessary framework and resources for growth. The government's active role in promoting AI ensures substantial investments, creating a conducive environment for innovation and development. Regulatory incentives and funding opportunities encourage companies to adopt and integrate AI technologies, boosting the market's overall momentum. Strategic initiatives also help in setting clear goals and priorities, aligning various stakeholders towards a common vision for AI advancement. By fostering collaborations between public and private sectors, the government helps overcome barriers such as limited access to technology and skilled labor, ensuring that the AI market can expand efficiently and sustainably across the country.
According to industry reports, the government is incentivizing AI use, making state subsidies conditional on AI adoption starting in 2024. Retail is a leading sector, with AI-driven systems like BPMSoft enhancing sales, logistics, and customer service. Despite challenges like data acquisition costs and chip shortages, AI's economic potential is significant, with expectations to add RUB11.3 trillion to Russia's GDP by 2030. Additionally, in September 2023, the government held a strategic session and planned substantial investments in AI development, allocating 5.2 billion roubles from federal funds for the coming year. This funding will support research institutions to ensure that AI technologies are developed and implemented domestically.
Increasing Need to Address Labor Shortages
AI is increasingly seen as a solution to Russia's labor shortages, especially in the technology and software development sectors. Geopolitical instability and sanctions have resulted in a scarcity of skilled IT professionals. AI technologies enhance efficiency and productivity by automating tasks that traditionally required manual labor, thereby improving operational efficiency and reducing costs. These technologies, such as those used in agriculture and manufacturing, can perform complex processes with high precision and speed, ensuring that industries continue to operate smoothly despite the lack of human resources.
For instance, in April 2024, the Russian government signed a decree to update the national AI development strategy to improve productivity and address labor shortages. AI solutions like the Cognitive Agro Pilot, which enhances agricultural efficiency, are being increasingly adopted. The software development sector faces a significant brain drain, with AI already used in over a third of Russia's key economic sectors. The economic potential of AI is anticipated to reach up to $38 billion by 2028, making it the seventh globally in government support for AI development.
Russia Artificial Intelligence Market Segmentation:
IMARC Group provides an analysis of the key trends in each segment of the market, along with forecasts at the country level for 2024-2032. Our report has categorized the market based on offering, technology, business function, deployment mode, organization size, and end-use industry.
Offering Insights:
- Services
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the offering. This includes hardware, software, and services.
Technology Insights:
- Machine Learning
- Natural Language Processing
- Context-Aware Computing
- Computer Vision
- Others
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the technology have also been provided in the report. This includes machine learning, natural language processing, context-aware computing, computer vision, and others.
Business Function Insights:
- Human Resources
- Marketing and Sales
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the business function. This includes finance, security, human resources, law, marketing and sales and others.
Deployment Mode Insights:
- On-premises
- Cloud
A detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the deployment mode have also been provided in the report. This includes on-premises and cloud.
Organization Size Insights:
- Large Enterprises
- Small and Medium-sized Enterprises
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the organization size. This includes large enterprises and small and medium-sized enterprises.
End-Use Industry Insights:
- Telecommunication
- Government and Defense
- Manufacturing
- Healthcare and Lifesciences
- Retail and Ecommerce
- Transportation and Logistics
The report has provided a detailed breakup and analysis of the market based on the end-use industry. This includes BFSI, IT/ITES, telecommunication, government and defense, manufacturing, healthcare and lifesciences, retail and ecommerce, automotive, transportation and logistics, and others.
Regional Insights:
- Central District
- Volga District
- Urals District
- Northwestern District
- Siberian District
The report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of all the major regional markets, which include Central District, Volga District, Urals District, Northwestern District, Siberian District and Others.
Competitive Landscape:
The market research report has also provided a comprehensive analysis of the competitive landscape in the market. Competitive analysis such as market structure, key player positioning, top winning strategies, competitive dashboard, and company evaluation quadrant has been covered in the report. Also, detailed profiles of all major companies have been provided.
Russia Artificial Intelligence Market Report Coverage:
| Report Features | Details |
|---|---|
| Base Year of the Analysis | 2023 |
| Historical Period | 2018-2023 |
| Forecast Period | 2024-2032 |
| Units | Billion US$ |
| Scope of the Report | Exploration of Historical and Forecast Trends, Industry Catalysts and Challenges, Segment-Wise Historical and Predictive Market Assessment: |
| Offerings Covered | Hardware, Software, Services |
| Technologies Covered | Machine Learning, Natural Language Processing, Context-Aware Computing, Computer Vision, Others |
| Business Functions Covered | Finance, Security, Human Resources, Law, Marketing and Sales, Others |
| Deployment Modes Covered | On-premises, Cloud |
| Organization Sizes Covered | Large Enterprises, Small and Medium-sized Enterprises |
| End-Use Industries Covered | BFSI, IT/ITES, Telecommunication, Government and Defense, Manufacturing, Healthcare and Lifesciences, Retail and Ecommerce, Automotive, Transportation and Logistics, Others |
| Regions Covered | Central District, Volga District, Urals District, Northwestern District, Siberian District, Others |
| Customization Scope | 10% Free Customization |
| Post-Sale Analyst Support | 10-12 Weeks |
| Delivery Format | PDF and Excel through Email (We can also provide the editable version of the report in PPT/Word format on special request) |
Key Questions Answered in This Report:
- How has the Russia artificial intelligence market performed so far and how will it perform in the coming years?
- What has been the impact of COVID-19 on the Russia artificial intelligence market?
- What is the breakup of the Russia artificial intelligence market on the basis of offering?
- What is the breakup of the Russia artificial intelligence market on the basis of technology?
- What is the breakup of the Russia artificial intelligence market on the basis of business function?
- What is the breakup of the Russia artificial intelligence market on the basis of deployment mode?
- What is the breakup of the Russia artificial intelligence market on the basis of organization size?
- What is the breakup of the Russia artificial intelligence market on the basis of end use industry?
- What are the various stages in the value chain of the Russia artificial intelligence market?
- What are the key driving factors and challenges in the Russia artificial intelligence?
- What is the structure of the Russia artificial intelligence market and who are the key players?
- What is the degree of competition in the Russia artificial intelligence market?
Key Benefits for Stakeholders:
- IMARC’s industry report offers a comprehensive quantitative analysis of various market segments, historical and current market trends, market forecasts, and dynamics of the Russia artificial intelligence market from 2018-2032.
- The research report provides the latest information on the market drivers, challenges, and opportunities in the Russia artificial intelligence market.
- Porter's five forces analysis assist stakeholders in assessing the impact of new entrants, competitive rivalry, supplier power, buyer power, and the threat of substitution. It helps stakeholders to analyze the level of competition within the Russia artificial intelligence industry and its attractiveness.
- Competitive landscape allows stakeholders to understand their competitive environment and provides an insight into the current positions of key players in the market.
India Dairy Market Report Snapshots Source:
Statistics for the 2022 India Dairy market share, size and revenue growth rate, created by Mordor Intelligence™ Industry Reports.
- India Dairy Market Size Source
- --> India Dairy Market Share Source
- India Dairy Market Trends Source
- India Dairy Companies Source
Need more help?
- Speak to our experienced analysts for insights on the current market scenarios.
- Include additional segments and countries to customize the report as per your requirement.
- Gain an unparalleled competitive advantage in your domain by understanding how to utilize the report and positively impacting your operations and revenue.
- For further assistance, please connect with our analysts.
Purchase options

Benefits of Customization
Personalize this research
Triangulate with your data
Get data as per your format and definition
Gain a deeper dive into a specific application, geography, customer, or competitor
Any level of personalization
Get in Touch With Us

UNITED STATES
Phone: +1-631-791-1145

Phone: +91-120-433-0800

UNITED KINGDOM
Phone: +44-753-714-6104
Email: [email protected]
Client Testimonials

IMARC made the whole process easy. Everyone I spoke with via email was polite, easy to deal with, kept their promises regarding delivery timelines and were solutions focused. From my first contact, I was grateful for the professionalism shown by the whole IMARC team. I recommend IMARC to all that need timely, affordable information and advice. My experience with IMARC was excellent and I can not fault it.

The IMARC team was very reactive and flexible with regard to our requests. A very good overall experience. We are happy with the work that IMARC has provided, very complete and detailed. It has contributed to our business needs and provided the market visibility that we required

We were very happy with the collaboration between IMARC and Colruyt. Not only were your prices competitive, IMARC was also pretty fast in understanding the scope and our needs for this project. Even though it was not an easy task, performing a market research during the COVID-19 pandemic, you were able to get us the necessary information we needed. The IMARC team was very easy to work with and they showed us that it would go the extra mile if we needed anything extra

Last project executed by your team was as per our expectations. We also would like to associate for more assignments this year. Kudos to your team.
.webp)
We would be happy to reach out to IMARC again, if we need Market Research/Consulting/Consumer Research or any associated service. Overall experience was good, and the data points were quite helpful.

The figures of market study were very close to our assumed figures. The presentation of the study was neat and easy to analyse. The requested details of the study were fulfilled. My overall experience with the IMARC Team was satisfactory.

The overall cost of the services were within our expectations. I was happy to have good communications in a timely manner. It was a great and quick way to have the information I needed.

My questions and concerns were answered in a satisfied way. The costs of the services were within our expectations. My overall experience with the IMARC Team was very good.

I agree the report was timely delivered, meeting the key objectives of the engagement. We had some discussion on the contents, adjustments were made fast and accurate. The response time was minimum in each case. Very good. You have a satisfied customer.
.webp)
We would be happy to reach out to IMARC for more market reports in the future. The response from the account sales manager was very good. I appreciate the timely follow ups and post purchase support from the team. My overall experience with IMARC was good.

IMARC was a good solution for the data points that we really needed and couldn't find elsewhere. The team was easy to work, quick to respond, and flexible to our customization requests.
- Market Entry and Opportunity Assessment
- Competitive Intelligence and Benchmarking
- Procurement Research
- Pricing and Cost Research
- Regulatory Approvals, and Licensing
- Factory Setup
- Factory Auditing
- Company Incorporation
- Incubation Services
- Recruitment Services
- Primary Research
- Quantitative Research
- Qualitative Research
- Sourcing Partner Identification
- Distribution Partner Identification
- Contract Manufacturer Identification
- Epidemiology Intelligence
- Asset and Indication Priortiztion
- Healthcare Competitive Intelligence
- R&D Analysis
- Patient and Prescriber Insights
- Regulatory Analysis
- Report Store
Quick Links
- Press Releases
- Case Studies
- Our Customers
- Become a Publisher
United States
134 N 4th St. Brooklyn, NY 11249, USA
+1-631-791-1145
Level II & III, B-70, Sector 2, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301, India
+91-120-433-0800
United Kingdom
30 Churchill Place London E14 5EU, UK
+44-753-714-6104
Level II & III, B-70 , Sector 2, Noida, Uttar Pradesh 201301, India
+44-20-8040-3201
We use cookies, including third-party, for better services. See our Privacy Policy for more. I ACCEPT X
- Semiconductor & Electronics
- UV Sensor Market
"Electrifying your pathway to success through in-depth market research"
UV Sensor Market Size, Share, and Industry Analysis, By Product Type (Fixed UV Sensors, Portable UV Sensors, and Wearable UV Sensors); By Type (UV-A, UV-B, and UV-C); By Application (Consumer Electronics, Industrial, Automotive, Healthcare, Environmental Monitoring, and Others); By Sales Channel (Direct Sales, Distributors, and Online Channels), and Regional Forecast, 2024-2032
Region :Global | Report ID: FBI110081 | Status : Ongoing
- Request PDF Brochure
KEY MARKET INSIGHTS
- In March 2024 , STMicroelectronics introduced MEMS Studio, an integrated MEMS sensor evaluation and development tool. It is compatible with Windows, MacOS, and Linux and simplifies sensor evaluation, configuration, and programming within the STM32 microcontroller ecosystem.
Segmentation
| | | | |
Key Insights
- Micro Macro Economic Indicators
- Drivers, Restraints, Trends, and Opportunities
- Business Strategies Adopted by Key Players
- Consolidated SWOT Analysis of Key Players
Analysis By Application
Regional analysis.
To gain extensive insights into the market, Request for Customization
- In August 2023 , Vernier Science Education expanded its data-collection tools with two new wireless sensors for high school and college environmental science: the Go Direct Pyranometer and the Go Direct PAR Sensor. These sensors connect directly to student devices via the Vernier Graphical Analysis Pro app, enabling easy data collection and analysis.
- North America – 25%
- South America – 7%
- Europe – 24%
- Middle East & Africa – 12%
- Asia Pacific – 32%
- In February 2024 , ROHM developed the RPR-0720, a compact 2.0mmX1.0mm proximity sensor optimized for applications requiring proximity and attachment/detachment detection. As IoT expands, there is an increasing demand for miniaturized and functional sensor devices. ROHM's proximity sensors integrate light-emitting and receiving elements in a single package, offering versatility and widespread adoption across mobile devices and industrial equipment.
Key Players Covered
Key industry developments.
- In March 2023 , ams OSRAM introduced the OSLON UV 3535 series, mid-power UV-C LEDs offering a higher output power, longer lifetime, and easier integration. These LEDs are compact and have superior efficiency, which is ideal for water purification and air conditioning applications.
- In February 2024 , STMicroelectronics and Mobile Physics partnered to integrate a built-in optical sensor into smartphones and devices to measure household and ambient air quality accurately. Utilizing ST's multizone ranging sensors, the solution detects particulates effectively. Mobile Physics' EnviroMeter app acts as a portable environment monitor and smoke detector, providing health safety and fire protection akin to specialized monitors.
- PUBLISHING STATUS: Ongoing
- BASE YEAR: 2023
- HISTORICAL DATA: 2019-2022
Personalize this Research
- Granular Research on Specified Regions or Segments
- Companies Profiled based on User Requirement
- Broader Insights Pertaining to a Specific Segment or Region
- Breaking Down Competitive Landscape as per Your Requirement
- Other Specific Requirement on Customization

“We are quite happy with the methodology you outlined. We really appreciate the time your team has spent on this project, and the efforts of your team to answer our questions.”
“Thanks a million. The report looks great!”
“Thanks for the excellent report and the insights regarding the lactose market.”
“I liked the report; would it be possible to send me the PPT version as I want to use a few slides in an internal presentation that I am preparing.”
“This report is really well done and we really appreciate it! Again, I may have questions as we dig in deeper. Thanks again for some really good work.”
“Kudos to your team. Thank you very much for your support and agility to answer our questions.”
“We appreciate you and your team taking out time to share the report and data file with us, and we are grateful for the flexibility provided to modify the document as per request. This does help us in our business decision making. We would be pleased to work with you again, and hope to continue our business relationship long into the future.”
“I want to first congratulate you on the great work done on the Medical Platforms project. Thank you so much for all your efforts.”
“Thank you very much. I really appreciate the work your team has done. I feel very comfortable recommending your services to some of the other startups that I’m working with, and will likely establish a good long partnership with you.”
“We received the below report on the U.S. market from you. We were very satisfied with the report.”
“I just finished my first pass-through of the report. Great work! Thank you!”
“Thanks again for the great work on our last partnership. We are ramping up a new project to understand the imaging and imaging service and distribution market in the U.S.”
“We feel positive about the results. Based on the presented results, we will do strategic review of this new information and might commission a detailed study on some of the modules included in the report after end of the year. Overall we are very satisfied and please pass on the praise to the team. Thank you for the co-operation!”
“Thank you very much for the very good report. I have another requirement on cutting tools, paper crafts and decorative items.”
“We are happy with the professionalism of your in-house research team as well as the quality of your research reports. Looking forward to work together on similar projects”
“We appreciate the teamwork and efficiency for such an exhaustive and comprehensive report. The data offered to us was exactly what we were looking for. Thank you!”
“I recommend Fortune Business Insights for their honesty and flexibility. Not only that they were very responsive and dealt with all my questions very quickly but they also responded honestly and flexibly to the detailed requests from us in preparing the research report. We value them as a research company worthy of building long-term relationships.”
“Well done Fortune Business Insights! The report covered all the points and was very detailed. Looking forward to work together in the future”
“It has been a delightful experience working with you guys. Thank you Fortune Business Insights for your efforts and prompt response”
“I had a great experience working with Fortune Business Insights. The report was very accurate and as per my requirements. Very satisfied with the overall report as it has helped me to build strategies for my business”
“This is regarding the recent report I bought from Fortune Business insights. Remarkable job and great efforts by your research team. I would also like to thank the back end team for offering a continuous support and stitching together a report that is so comprehensive and exhaustive”
“Please pass on our sincere thanks to the whole team at Fortune Business Insights. This is a very good piece of work and will be very helpful to us going forward. We know where we will be getting business intelligence from in the future.”
“Thank you for sending the market report and data. It looks quite comprehensive and the data is exactly what I was looking for. I appreciate the timeliness and responsiveness of you and your team.”
+1 424 253 0390 (US)
+44 2071 939123 (UK)
+91 744 740 1245 (APAC)
[email protected]
- Request Sample
The global UV Sensor Market report covered key company as Adafruit Industries, GenUV, Apogee Instruments, Inc., Rohm Semiconductor etc.
Read More at:-
- Kreyòl Ayisyen

Cash-back Fees
Executive summary, cash-back transactions, benefits and costs to merchants.
Access to cash is a necessary component of a resilient financial system and dynamic economy. Many people rely on cash for day-to-day transactions due its privacy and reliability, and cash accessibility is particularly critical in the case of a disruption or outage of digital payment systems. While people use various means of getting cash, one common method is to get “cash back” at a store when making a purchase with a debit or prepaid card. This option may be particularly important in banking deserts and in areas where banks and ATM operators charge significant fees. Retailers are essentially filling a void in access to cash, which has historically been supplied by banks and credit unions in an affordable way.
Providing cash back is valuable to consumers and merchants. Survey data show that it is a popular method to get money via consumers’ bank debit or prepaid cards. Merchants offer cash back to attract customers and reduce their cash handling costs. In its recent engagement and market monitoring, the CFPB observed that some retailers charge a fee for this transaction.
This spotlight provides an overview of consumers’ use of cash back, the benefits and costs of such transactions to merchants, and the practices of other market actors which do not charge fees for this service. The CFPB also analyzed the cash-back fees of a sample of national retailers.
Fees for cash back may serve as a barrier and reduce people’s access to cash when they need it. The CFPB will continue to monitor developments related to the fees consumers pay for accessing cash, and the underlying failure of banks and credit unions to adequately supply cash throughout the country in an affordable manner.
Key Findings
- Cash-back fees are costing consumers millions of dollars . The CFPB found that three companies in the sample charge cash-back fees and estimates that they collect over $90 million in fees annually for people to access their cash. The CFPB also estimates that the marginal cost to merchants for processing each transaction may be a few pennies, compared to the much higher fees charged by these retailers to consumers. While there may be other costs related to cash handling, these are generally reduced by the provision of cash back, as it reduces merchants’ cash on hand.
- Three major firms charge cash-back fees even though other competitors offer it for free. Three retail companies Dollar General, Dollar Tree, and Kroger, which also operate brands such as Family Dollar, Harris Teeter, Ralph’s, and others, charge fees for this service while other national retail companies sampled by the CFPB do not charge a fee. At the two largest dollar store corporations, cash-back fees for small withdrawal amounts are the highest in the sample ($1 or more for amounts under $50). Kroger, the country’s largest grocery chain, recently expanded cash-back fees to its Harris Teeter brand (75 cents for $100 or less), higher than those in place among its other brands (50 cents for $100 or less), in addition to higher fees for larger amounts.
- Cash-back fees are levied on low pre-set cash withdrawal amounts . Many merchants pre-determine the withdrawal amount options in a single transaction, commonly between $5 and $50. The fees charged on small, constrained amounts often constitute a high percentage of the cash withdrawal and limit consumers’ ability to spread the cost of that fee over larger amounts. It may also induce repeat withdrawals, with consumers incurring a new fee each time.
- Consumers with lower incomes or fewer banking choices may be more likely to encounter cash-back fees . Dollar stores are frequently located in small rural towns, communities of color, and low-income communities. These areas are also more likely to be places where there are fewer branch locations, and communities where people are more reliant on cash for daily transactions than others.
This section summarizes the importance of cash availability and the use of cash-back as an access point for consumers.
Cash is a critical part of a resilient payment ecosystem. Surveys show people still try to have cash on hand 1 and nearly 90 percent of people used cash in the last 30 days. 2 Cash accessibility is necessary should other types of digital payment systems experience failures, 3 such as in the event of a natural disaster or some other catastrophe, 4 or a technological malfunction at a single company. 5 Additionally, some populations are more reliant on cash than others for day-to-day transactions. For example, cash is more frequently used by people with lower incomes, racial minorities, and older Americans than other populations. 6 As discussed below, cash back is a common method for obtaining cash for many consumers.
How cash back works
Consumers may obtain cash during the completion of a purchase transaction at certain stores when using a PIN-authenticated debit card or prepaid card at the register. Some merchants also provide cash back at self-service registers. Consumers typically must choose from pre-set withdrawal amount options presented at the payment terminal at the time of the transaction. In a cash-back transaction, consumers are usually limited to a maximum withdrawal amount ranging from $5 to $50, though some merchants may allow higher amounts.
Scope of usage
CFPB analysis of data from the Diary and Survey of Consumer Payment Choice (Survey) found that from 2017 to 2022, cash withdrawals at retail locations made up 17 percent of all transactions by which people got cash from their checking account, savings account, or prepaid card. As shown in Figure 1, cash withdrawals at retail are second only to ATMs (61%) and more frequently used than bank tellers (14%). The Survey and methodology are discussed in the Tables and Notes section .
Figure 1: Instances of getting cash from bank account or prepaid card, by location, 2017 to 2022, combined
Source : CFPB tabulations of the Diary and Survey of Consumer Payment Choice.
The Survey data also show that from 2017 to 2022, cash withdrawals at a retail location (restricted to those where the source of funds was the consumer’s checking, savings, or a prepaid card) had a mean withdrawal amount of $34 (median: $20). 7 By contrast, during this same timeframe, the mean ATM withdrawal among survey participants was $126 (median: $100). 8 A study by researchers at the Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta utilizing Survey data found that cash withdrawals at a retail store had the lowest average amount of cash withdrawal, and noted that “[t]he amount of cash received at a retail store is constrained by the store’s limits, so the amount of cash received in this way is not necessarily at the discretion of the consumer.” 9
Cash back may serve as a particularly important point of access in the absence of other banking services. A 2014 study by the Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond analyzed cash-back transactions from a national discount retail chain from 2010 to 2012. 10 Looking specifically at the Richmond bank’s district, the area with the highest frequency of cash-back transactions was in the southeastern region of South Carolina, an area “that has been subject to ‘persistent poverty’” and “has some of the sparsest dispersion of bank branches.” 11 The study also illustrated the lucrative nature of cash-back fees: During the course of this study period, the merchant introduced a fee for cash back. Data from this report indicates that the retailer collected approximately $21 million in cash-back fees in a year. 12
Merchants benefit from offering cash back at point-of-sale. First, the service may attract potential shoppers, either people making a purchase in order to get cash back or people who prefer one retail location over another in order to conveniently combine tasks. Second, it reduces merchants’ cash handling costs. 13 Dispensing cash to consumers, such as through cash-back transactions, reduces merchants’ supply of cash and therefore also reduces their cost of handling, transporting, and depositing excess cash.
Merchants incur costs for processing any type of payment transaction, including cash-back transactions. On any purchase using an electronic payment method, including a PIN-authorized debit-card or prepaid card, a merchant will incur a range of fees for processing that payment, such as interchange, network, and processing fees. While the merchant incurs these fees for a consumer’s purchase, there is an additional cost for providing cash back to the consumer.
To assess this additional transaction cost to the merchant for providing cash back, the CFPB modeled potential scenarios based on publicly available data and our market monitoring activities. The model incorporates estimates of merchant-incurred fees, such as interchange, network, processing, and fraud control fees. Methodology is discussed in detail in the Table and Figure Notes. The CFPB estimates that the additional marginal transactional cost to a merchant for processing a typical cash-back debit card transaction may range from a penny to about 20 cents (Table 1).
Table 1: Estimated additional merchant cost of a debit card cash-back transaction
| Example Retailer | Purchase Amount | Merchant Transaction Cost for Purchase Only | Additional Merchant Cost for $10 Cash Back | Additional Merchant Cost for $40 Cash Back |
|---|---|---|---|---|
National Discount Chain | $20 | $0.33 | $0.05 | $0.19 |
National Grocery Store | $20 | $0.33 | $0.01 | $0.02 |
Source : CFPB calculations based on public data about industry practices and averages. See Table and Figure Notes below for methodology .
This section provides an analysis of cash-back fee practices of eight national retail chains. It includes a discussion of the variation of these practices among these national chains and other actors, such as local independent grocers. The analysis is supplemented by market monitoring discussions with merchants about fees, costs, and consumer trends, both among merchants who charge cash back fees and those who do not. The CFPB also conducted consumer experience interviews and reviewed consumer complaints submitted to the CFPB. It concludes with a discussion of how these fees appear to function differently than fees for cash withdrawals at ATMs.
Current market practices
As of August 2024, there is no publicly available survey data regarding merchants’ cash-back practices or fees. To establish a baseline, the CFPB documented the fee practices of eight large retail companies. The sample consists of the two largest retail actors, measured by number of locations, across four different sectors: Dollar Stores, Grocery Stores, Drugstores, and Discount Retailers. 14 Using this approach, the eight retailers sampled are: Dollar General and Dollar Tree Inc. (Dollar Stores), Kroger Co. and Albertsons Companies (Grocery Stores), Walgreens and CVS (Drugstores), and Walmart and Target (Discount Retailers).
All retailers in our sample offer cash-back services, but only Dollar General, Dollar Tree Inc., and Kroger Co. brands charge a fee. Other retailers offer cash-back for free, even for withdrawal amounts similar to or larger than those provided by the three retailers who charge. (Table 2). Among the national chains that charge these cash-back fees, the CFPB estimates that they collect over $90 million in fees annually for people to access their cash. 15
Table 2: Cash-back fee practices, major retail companies
| Company | U.S. Stores | Fee for Cash Back | Maximum Withdrawal Amount (Per Transaction) |
|---|---|---|---|
Dollar General | 20,022 | $1 to $2.50, depending on amount and other variables | $40 |
Dollar Tree Inc. | 16,278 | Family Dollar: $1.50 | $50 |
Kroger Co. | 2,722 | Harris Teeter brand: | Harris Teeter brand: $200 |
Albertsons Brand | 2,271 | No | $200 |
Walmart | 5,214 | No | $100 |
Target | 1,956 | No | $40 |
Walgreens | 8,600 | No | $20 |
CVS | 7,500 | No | $60 |
Source : CFPB analysis of the retail cash-back market. See Table and Figure Notes for methodology .
Beyond these national chains, there are other providers offering cash back as a free service to their customers. Through its market monitoring activities, the CFPB observed that many local independent grocers offer the service, but do not charge a fee. They do not charge a fee even though they are likely to have thinner profit margins and less bargaining power than national chains to negotiate on pricing on costs they incur from wholesalers or fees for payment processors. The U.S. Postal Service also offers cash back on debit transactions, in increments of $10 up to a $50 maximum, free of charge. 16
Cash-back fees at dollar stores
Among the merchants sampled, Dollar General and Dollar Tree Inc. charge the highest fees for withdrawal amounts under $50. These fees combined with the constrained withdrawal amount may mean that the fee takes up a hefty percentage relative to the amount of cash withdrawn, and people may be less able to limit the impact of the fee by taking out more cash.
Additionally, the geographic distribution of dollar store chains and their primary consumer base raises concerns that these fees may be borne by economically vulnerable populations and those with limited banking access. Dollar stores are prevalent in rural communities, low-income communities, and communities of color – the same communities who may also face challenges in accessing banking services. 17 For example, Dollar General noted that in 2023 “approximately 80% of [its] stores are located in towns of 20,000 or fewer people,” 18 while Dollar Tree Inc. operated at least 810 dual-brand combination stores (Family Dollar and Dollar Tree in a single building) designed specifically “for small towns and rural communities…with populations of 3,000 to 4,000 residents.” 19
Though they are open to and serve consumers of all income levels, dollar stores report that they locate stores specifically to serve their core customers: lower-income consumers. 20 In urban communities, one study shows, “proximity to dollar stores is highly associated with neighborhoods of color even when controlling for other factors.” 21 These same communities may also face challenges in accessing banking services. Low-income communities and communities of color often face barriers to access to banking services, and rural communities are 10 times more likely to meet the definition of a banking desert than urban areas. 22
Though the dollar store concept existed as far back as the 1950s, it has experienced significant expansion and consolidation since the 2000s. 23 Dollar Tree Inc. acquired Family Dollar in 2015. 24 From 2018 to 2021, nearly half of all retail locations opened in the U.S. were dollar stores. 25 In research examining the impact of dollar store expansion, studies indicate that the opening of a dollar store is associated with the closure of nearby local grocery retailers. 26
Variation of fees charged
In its scan of current market practices, the CFPB found variations in fee charges among store locations and brands owned by the same company. For example, as reflected in Table 2, Dollar Tree charges consumers $1 for cash back at Dollar Tree branded stores, but $1.50 in its Family Dollar stores. Similarly, Kroger Co. has two different fee tiers for its brands. In 2019, Kroger Co. rolled out a $0.50 cash-back fee for amounts of $100 or less, and $3.50 for amounts between $100 and $300. This took effect at brands such as Kroger, Fred Meyers, Ralph’s, QFC, Pick ‘N Save, and others. At the time of the rollout, the company noted two exceptions: Electronic benefits transfer (EBT) card users would not be charged a fee, and customers using their Kroger Plus card would not be charged for amounts under $100 but would be charged $0.50 for larger amounts. Kroger Co. acquired the southern grocery chain Harris Teeter in 2014, but it did not begin charging a cash-back fee at those stores until January 2024, at $0.75 for amounts of $100 or less, and $3 for larger amounts. 27
In its engagement with stakeholders, the CFPB learned that Dollar General’s fees appeared to vary in different locations. To better understand this potential variation, in December 2022, the CFPB mystery shopped at nine locations in one state, across a mix of rural, suburban, and urban communities. The CFPB acknowledges this is a small sample and is not intended to be representative. The data collected is based on the knowledge of the store associates at the time of each interaction.
In these findings, the CFPB learned of a range of fee variations across store locations: five of the nine respondents noted that the fee varies depending on the type of card used for the transaction. When probed for the meaning of “type of card,” most noted that it is dependent on the customer’s bank, though it is not exactly clear what fees will be triggered by what card type prior to initiating the transaction. Additionally, reported fees range from $1 to $2.50, with some stores reporting a flat fee structure of $1.50 and others reporting a range that tiered up with larger withdrawal amounts (with a cap of withdrawal amounts at $40). Most stores in this sample had a range of fees between $1.00 and $1.50, although two stores located in small, completely rural counties had a higher range of fees. The store located in the smallest and most isolated county within the sample, with only about 3,600 people, had the highest reported fee amount of $2.50.
Distinction from ATM fees
One of the market dynamics likely contributing to retailers’ ability to charge these fees is the high fees also charged to consumers for using out-of-network automated teller machines (ATMs). One source estimates that the average out-of-network ATM fee is $4.77, accounting for both the surcharge fee charged by the ATM owner and the foreign fee charged by the consumer’s financial institution. 28 By comparison, a $2 fee for cash back at a retailer may appear cheaper, and usually does not trigger an additional fee by the consumers’ financial institution or prepaid card issuer. Notwithstanding the high ATM fees, there are reasons for focused attention on the consumer risk of cash-back fees charged by retailers, primarily the amount of the fee relative to the value of the cash withdrawal and the distribution of the fee burden across income groups.
In a typical ATM transaction, a consumer has a greater ability to distribute the cost of the fee across a larger amount of cash than with cash back. There may be some exceptions to this for consumers who have only $10 or $20 in their bank account, but as shown in Table 3, low-income consumers and others withdraw greater amounts at ATMs than via cash-back, on average. In cash-back transactions, lower withdrawal limits are in place, and consumers do not have that option to withdraw larger amounts. CFPB analysis of the Diary and Survey of Consumer Payment Choice from 2017 to 2022 show that even among consumers with incomes below $50,000, the amount withdrawn at an ATM is more than double the typical cash-back withdrawal amount. Additionally, for the average and median amounts, across all incomes the ATM withdrawal amounts are larger than cash-back withdrawal amounts. (Table 3).
Table 3: Average ATM and cash-back withdrawal amounts, by income, 2017 to 2022 combined
| Income | Average ATM Withdrawal | Average Cash-back Withdrawal | Median ATM Withdrawal | Median Cash-back Withdrawal |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Less than $25,000 | $144 | $45 | $65 | $20 |
$25,000 to $49,999 | $113 | $35 | $60 | $25 |
$50,000 to $74,999 | $113 | $29 | $84 | $20 |
$75,000 to $99,000 | $114 | $45 | $100 | $26 |
$100,000 or more | $146 | $33 | $100 | $20 |
|
|
|
|
|
Source: CFPB tabulations of the Diary and Survey of Consumer Payment Choice. See Table and Figure Notes for methodology .
Further, while merchants limit the amount of a single withdrawal, there is no limit on the number of withdrawals. So, if a consumer needs $100 cash at a store which limits a single withdrawal to a maximum amount of $50 with a $2 fee, the consumer would have to make two $50 withdrawals for a $4 fee plus the cost of any otherwise unwanted purchase required to access the cash-back service.
Finally, the burden of cash-back fees may be distributed differently than ATM fee burdens. The share of borrowers who pay ATM fees for cash withdrawals is relatively evenly distributed across income levels, according to a study based on the Diary and Survey of Consumer Payment Choice. 29 The study found little variation in the percentage of consumers who encountered a fee for an ATM cash withdrawal by income quintile, though the study did not look at the amount of the ATM fees paid. Analogous data are not available for cash-back fees, but a similarly even distribution across incomes is unlikely given the demographics of the consumer base served by the largest retailers which charge fees (dollar stores).
While the use of digital payment methods is on the rise, cash accessibility remains a critical component of a resilient financial infrastructure and dynamic economy. Bank mergers, branch closures, and bank fee creep have reduced the supply of free cash access points for consumers. In this void, people may be more reliant on retailers for certain financial services historically provided by banks and credit unions, such as cash access. In this context, we observe that some retailers provide cash back as a helpful service to their customers, while other retailers may be exploiting these conditions by charging fees to their consumers for accessing their cash.
This spotlight examines the presence of retailer cash-back fees and impact to consumers. Cash-back fees are being levied by just a small handful of large retail conglomerates (Dollar General, Dollar Tree Inc., and Kroger Co.) amidst a backdrop of consolidation in these segments. Meanwhile, other larger retailers continue to offer cash-back services free. The CFPB estimates cash-back fees cost consumers about $90 million a year.
The CFPB is concerned that reduced access to cash undermines the resilience of the financial system and deprives consumers of a free, reliable, and private means of engaging in day-to-day transactions. The CFPB will continue to monitor developments related to the fees consumers pay for accessing cash, and work with agencies across the federal government to ensure people have fair and meaningful access to the money that underpins our economy.
Table and Figure Notes
Notes for figure 1.
The Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta’s annual Diary and Survey of Consumer Payment Choice (Survey) tracks consumers’ self-reported payment habits over a three-day period in October using a nationally representative sample. The survey includes a question about whether and how consumers access cash, such as where they made the withdrawal, the source of the cash, and the amount of the withdrawal. Figure 1 provides a percentage of all cash-back withdrawal transactions from a bank account, checking account, or prepaid card reported between 2017 and 2022, by location (ATM, Retail point-of-sale, Bank teller, and Other). The number of observations during this time is 192 transactions. It does not include cash-back transactions made using a credit card cash advance feature or other form of credit.
Notes for Table 1
This model assumes that 80 percent of the merchant transaction cost is due to interchange fees, 15 percent due to network fees, and 5 percent due to payment acquirer fees. It also includes a $0.01 fee for fraud protection. For regulated transactions, the interchange fees are $0.22 + 0.05% of the transaction amount. Regulated transactions are those where the debit card used is issued by a bank with more than $10 billion in assets, and subject to 15 U.S.C. § 1693o-2. Exempt transactions are those not subject to this statutory cap on interchange fees. While Mastercard does not publish its fees for exempt transactions, Visa does. This model uses Visa’s published fees as of October 2023 for card-present transactions: for the National Discount Chain, the fees for Exempt Retail Debit ($0.15 + 0.80%), and for the National Grocery Chain, Exempt Supermarket Debit ($0.30 flat fee). An October 2023 Federal Reserve report on interchange fee revenue found that in 2021, the most recent data available, 56.21 percent of debit transactions were regulated and 43.79 percent were exempt. This composition is reflected in the table.
Notes for Table 2
The storefront counts for each of the retailers come from their websites, last visited on March 28, 2024, or their most recent reports to investors. Fee information was gathered either through publicly available information such as the merchant’s website, and/or verified through the CFPB’s market monitoring activities.
Dollar Tree Inc. announced on March 13, 2024 that it will close 1,000 of its Family Dollar and Dollar Tree brands stores over the course of the year. If those closures occur, Dollar Tree, Inc. will still have over 15,000 storefronts across the country.
In October 2022, Kroger Co. and Albertsons Companies announced their proposal to merge, though on February 26, 2024, the Federal Trade Commission and nine state attorneys general sued to block this proposal, alleging that the deal is anti-competitive. On April 22, 2024, Kroger Co. and Albertsons Companies announced a revised plan in which, if the merger is approved, the combined entity would divest 579 stores to C&S Wholesalers. If the divestiture occurs, the combined entity will still have over 4,400 stores across the country.
Notes for Table 3
See above notes for Figure 1 about the Diary and Survey of Consumer Payment Choice (Survey). Table 3 provides mean and median amounts of ATM and Retail point-of-sale cash withdrawal transactions by income. In the Survey, participants were asked to report the total combined income of all family members over age 15 living in the household during the past 12 months. From these responses, we constructed five income brackets – four of $25,000 each plus a fifth bin for any respondents reporting more than $100,000 in annual household income for each respondent in each year.
See e.g., Jay Lindsay, A Fatal Cash Crash? Conditions Were Ripe for It After the Pandemic Hit, but It Didn’t Happen , Fed. Rsrv. Bank of Boston (Nov. 2, 2023), https://www.bostonfed.org/news-and-events/news/2023/11/cash-crash-pandemic-increasing-credit-card-use-diary-of-consumer-payment-choice.aspx
Kevin Foster, Claire Greene, & Joanna Stavins, The 2023 Survey and Diary of Consumer Payment Choice , Fed. Rsrv Bank of Atlanta (June 2024), https://doi.org/10.29338/rdr2024-01
See e.g., Hilary Allen, Payments Failure, Boston College Law Review, Forthcoming, American University, WCL Research Paper No. 2021- 11, (Feb. 21, 2020) available at https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3539797
See e.g., Scarlett Heinbuch, Cash Is Critical in Times of Crisis , Fed. Rsrv. Bank of Atlanta (Mar. 7, 2022), https://www.atlantafed.org/blogs/take-on-payments/2022/03/07/cash-in-crisis
See e.g., Carly Page, Square Says It Has Resolved Daylong Outage , TechCrunch, (Sept. 8, 2023), https://techcrunch.com/2023/09/08/square-day-long-outage-resolved/ . See also Caroline Haskins, The Global CrowdStrike Outage Triggered a Surprise Return to Cash , Wired, (July 19, 2024), https://www.wired.com/story/microsoft-crowdstrike-outage-cash/ .
See Berhan Bayeh, Emily Cubides and Shaun O’Brien, 2024 Findings from the Diary of Consumer Payment Choice , Fed. Rsrv. (May 13, 2024), https://www.frbservices.org/binaries/content/assets/crsocms/news/research/2024-diary-of-consumer-payment-choice.pdf (findings related to low-income consumers and older Americans use of cash); Emily Cubides and Shaun O’Brian, 2023 Findings from the Diary of Consumer Payment Choice , Fed. Rsrv., (May 19, 2024), https://www.frbsf.org/cash/wp-content/uploads/sites/7/2023-Findings-from-the-Diary-of-Consumer-Payment-Choice.pdf (findings related to unbanked households use of cash), and Michelle Faviero, , More Americans are Joining the ‘Cashless’ Economy ,” Pew Rsch. Ctr, (Oct. 5, 2022), https://www.pewresearch.org/short-reads/2022/10/05/more-americans-are-joining-the-cashless-economy/ (findings related to use of cash by race and other demographics).
Similarly, the average cash-back withdrawal amount was $33 in 2012, the most recent data available from the Federal Reserve Payments Study. The study was based on self-reported information from financial institutions surveyed by the Federal Reserve. Of the reported transactions, 73 percent were debit cards with an average amount of $33 and 27 percent on general purpose prepaid cards with an average withdrawal amount of $19. 2013 Federal Reserve Payments Study: Recent and Long-Term Payment Trends in the United States: 2003 – 2012 , Fed. Rsrv. Bd. (July 2014), https://www.frbservices.org/binaries/content/assets/crsocms/news/research/2013-fed-res-paymt-study-summary-rpt.pdf
The amounts in the Survey are lower than the average ATM withdrawal amounts reported in 2022 Federal Reserve Payments study, which utilizes data from surveying financial institutions. Per this study, in 2021, the average ATM withdrawal was $198. The Federal Reserve Payments Study: 2022 Triennial Initial Data Release , Fed. Rsrv. Bd. (Apr. 21, 2023), https://www.federalreserve.gov/paymentsystems/fr-payments-study.htm
Claire Green and Oz Shy, How Consumers Get Cash: Evidence from a Diary Survey , Fed. Rsrv. Bank of Atlanta, (Apr. 2019), at 5, https://www.atlantafed.org/-/media/documents/banking/consumer-payments/research-data-reports/2019/05/08/how-consumers-get-cash-evidence-from-a-diary-survey/rdr1901.pdf (finding, “For the largest amounts of cash, respondents mostly turned to employers, with an average dollar value of cash received of $227. At bank tellers and ATMs, consumers also received average dollar values greater than the overall average: $159 and $137, respectively. Consumers received smaller amounts from family or friends ($93) and, notably, cash back at a retail store ($34). All these dollar amounts are weighted. The amount of cash received at a retail store is constrained by the store’s limits, so the amount of cash received in this way is not necessarily at the discretion of the consumer.”)
Neil Mitchell and Ann Ramage, The Second Participant in the Consumer to Business Payments Study , Fed. Rsrv. Bank of Richmond (Sept. 15, 2014), https://www.richmondfed.org/~/media/richmondfedorg/banking/payments_services/understanding_payments/pdf/psg_ck_20141118.pdf
Id. at 8, Figures 7 and 8.
See e.g., Stan Sienkiewicz, The Evolution of EFT Networks from ATMs to New On-Line Debit Payment Products , Discussion Paper, Payment Cards Ctr. of the Fed. Rsrv. Bank of Philadelphia (Apr. 2002), https://www.philadelphiafed.org/-/media/frbp/assets/consumer-finance/discussion-papers/eftnetworks_042002.pdf?la=en&hash=88302801FC98A898AB167AC2F9131CE1 (“The cash back option became popular with supermarket retailers, since store owners recognized savings as a result of less cash to count at the end of the day, a chore that represented a carrying cost to the establishment.”).
These market segments and retailers for purposes of markets analysis are similar to those used in other academic literature related to dollar store locations in the context of food access or impact on other market dynamics, such as on local grocers. See e.g., El Hadi Caoui, Brett Hollenbeck, and Matthew Osbourne, The Impact of Dollar Store Expansion on Local Market Structure and Food Access ,” (June 22, 2022), available at https://ssrn.com/abstract=4163102 (finding "In 2021, there were more of these stores operating than all the Walmarts, CVS, Walgreens, and Targets combined by a large margin.”) and Yue Cao, The Welfare Impact of Dollar Stores ,” available at https://yuecao.dev/assets/pdf/YueCaoDollarStore.pdf (last visited Aug. 23, 2024) (using the categories of dollar stores, groceries, and mass merchandise (such as Walmart) for comparisons across retail segments and noting that dollar stores regard these other segments as competitors).
Estimate based on information voluntarily provided in the CFPB's market monitoring activities.
What Forms of Payment are Accepted? U.S. Postal Serv., https://faq.usps.com/s/article/What-Forms-of-Payment-are-Accepted (last visited Aug. 23, 2024).
See generally, Stacy Mitchell, Kennedy Smith, and Susan Holmberg , The Dollar Store Invasion , Inst. for Local Self Reliance (Mar. 2023), https://cdn.ilsr.org/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/ILSR-Report-The-Dollar-Store-Invasion-2023.pdf . There is also extensive research on dollar store locations in other contexts such as food access and impact on consumer spending habits. El Hadi Caoui, Brett Hollenbeck, and Matthew Osbourne, The Impact of Dollar Store Expansion on Local Market Structure and Food Access ,” at 5, (June 22, 2022), available at https://ssrn.com/abstract=4163102
Dollar General Annual Report (Form10-K) at 7 (Mar. 25. 2024), https://investor.dollargeneral.com/websites/dollargeneral/English/310010/us-sec-filing.html?format=convpdf&secFilingId=003b8c70-dfa4-4f21-bfe7-40e6d8b26f63&shortDesc=Annual%20Report .
Dollar Tree, Inc. Annual Report (Form 10-K) at 7 (Mar. 20. 2024), https://corporate.dollartree.com/investors/sec-filings/content/0000935703-23-000016/0000935703-23-000016.pdf
See e.g., Dollar General Annual Report (Form10-K) at 7 (Mar. 25. 2024) (“We generally locate our stores and plan our merchandise selections to best serve the needs of our core customers, the low and fixed income households often underserved by other retailers, and we are focused on helping them make the most of their spending dollar.” And, Dollar Tree, Inc. Annual Report (Form 10-K) at 6 (Mar. 20. 2024), (“Family Dollar primarily serves a lower than average income customer in urban and rural locations, offering great values on everyday items.”)
Dr. Jerry Shannon, Dollar Stores, Retailer Redlining, and the Metropolitan Geographies of Precarious Consumption , Ann. of the Am. Assoc. of Geographers, Vol. 111, No. 4, 1200-1218 (2021), (analyzing over 29,000 storefront locations of Dollar General, Dollar Tree, and Family Dollar locations across the three largest MSA in each of the nine U.S. Census Bureau-defined divisions.)
Kristen Broady, Mac McComas, and Amine Ouazad, An Analysis of Financial Institutions in Black-Majority Communities: Black Borrowers and Depositors Face Considerable Challenges in Accessing Banking Services ,” Brookings Inst., (Nov. 2, 2021), https://www.brookings.edu/articles/an-analysis-of-financial-institutions-in-black-majority-communities-black-borrowers-and-depositors-face-considerable-challenges-in-accessing-banking-services/ and Drew Dahl and Michelle Franke, Banking Deserts Become a Concern as Branches Dry Up , Fed. Rsrv. Bank of St. Louis, https://www.stlouisfed.org/publications/regional-economist/second-quarter-2017/banking-deserts-become-a-concern-as-branches-dry-up (July 25, 2017).
El Hadi Caoui, Brett Hollenbeck, and Matthew Osbourne, The Impact of Dollar Store Expansion on Local Market Structure and Food Access ,” (June 22, 2022), available at https://ssrn.com/abstract=4163102 .
Dollar Tree Completes Acquisition of Family Dollar , Dollar Tree Inc., (July 6, 2015), available at https://corporate.dollartree.com/news-media/press-releases/detail/120/dollar-tree-completes-acquisition-of-family-dollar
El Hadi Caoui, Brett Hollenbeck, and Matthew Osbourne, The Impact of Dollar Store Expansion on Local Market Structure and Food Access ,” (June 22, 2022), available at https://ssrn.com/abstract=4163102 and Yue Cao, The Welfare Impact of Dollar Stores, https://yuecao.dev/assets/pdf/YueCaoDollarStore.pdf (last visited Aug. 23. 2024).
Evan Moore, Harris Teeter Introduces New Fees that Have Customers Upset. What To Know Before You’re Charged , Charlotte Observer, (Mar. 14, 2024), https://amp.charlotteobserver.com/news/business/article286627340.html
Karen Bennett and Matthew Goldberg, Survey: ATM fees Reach 26-year High While Overdraft Fees Inch Back Up , Bankrate.com (Aug. 21, 2024), https://www.bankrate.com/banking/checking/checking-account-survey/
Oz Shy and Joanna Stavins, Who Is Paying All These Fees? An Empirical Analysis of Bank Account and Credit Card Fees , Fed. Rsrv. Bank of Boston, Working Paper No. 22-18, at Table 2, (Aug. 2022), https://www.bostonfed.org/publications/research-department-working-paper/2022/who-is-paying-all-these-fees-an-empirical-analysis-of-bank-account-and-credit-card-fees .

COMMENTS
Forget guesswork and intuition: learn how to perform sales data analysis and end up with actionable results for your sales team.
Sales analysis is a method to interpret data and optimize sales strategies for business growth. Explore the significance of sales analysis.
Market research analysis is defined as the systematic process of collecting, processing, interpreting, and evaluating data related to a specific market, industry, or business environment. Learn more about market research analysis steps, benefits, and best practices.
This guide explains what a sales analysis is, why it's important, the benefits of conducting one, and how to do a sales analysis.
Learn how to do market research with this step-by-step guide, complete with templates, tools and real-world examples.
Sales analysis assesses, analyzes, and monitors a business's sales efforts. Sales analysis may include capturing, filtering, and analyzing sales data to evaluate past sales performance and predict future sales figures. Sales analysis aids in making strategic business decisions and developing effective sales tactics and strategies.
At its essence, sales analysis is the process of examining sales data to gain insights into various aspects of a company's performance. It involves analyzing metrics beyond sales volume such as sales revenue, product performance, customer behavior, and market trends to identify strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. By dissecting ...
Market research is a process of gathering, analyzing, and interpreting information about a given market. It takes into account geographic, demographic, and psychographic data about past, current, and potential customers, as well as competitive analysis to evaluate the viability of a product offer.
What is sales analysis? Sales analysis is the art of transforming sales data into actionable insights that help boost profitability, enhance customer satisfaction, and inform data-driven decisions. An efficient sales analysis scrutinises sales data, identifies patterns, trends, and opportunities, and uses this information to streamline operations, improve sales strategies, and ultimately ...
Sales analytics refers to the use of technology to collect and use sales data to derive actionable insights. It is used to identify, optimize, and forecast sales. It uses different metrics and KPIs to plan an efficient sales model that generates higher revenue for the business.
What is a sales report? A sales report or sales analysis report is a document that shows trends impacting your sales operations within a specific period. While the content of sales reports may vary depending on your goal, they include metrics like revenue, accounts won, leads, and more.
Follow these 9 key stages in the marketing research process to ensure that your research project is a successful one!
The Importance of Sales Analysis Sales analysis is a critical tool for businesses of all sizes. By understanding revenue-driving metrics, companies can make informed decisions, from pricing and product development to sales strategies and target markets. Essential metrics to analyze are sales volume, growth, mix, and trends.
What is market analysis? Market analysis is a detailed assessment of your business's target market and the competitive landscape within a specific industry. This analysis lets you project the success you can expect when you introduce your brand and its products to consumers within the market. Market analysis includes quantitative data such as the actual size of the market you want to serve ...
Read on to find out how to create sales analysis reports, what data to collect, how to interpret resulting tables, and convert them into effective action points for your sales operations, sales team, and marketing departments.
This article is part of the following collections: The Impactful Sales Research from the Journal of Marketing Theory and Practice A great deal has changed since we first accepted the invitation to write this review of sales research.
1) Opportunities : Sales analysis of own products as well as competitor products is important as analyzing sales of competitors allows insights into the market from a different perspective and may help the company to reach the missed out customers and grab the missed opportunity.
Sales powers business throughout the world. While sales (and marketing) literature has spent much time exploring analytics and measurement, there seems to be a revitalized interest in sales and especially sales data and analytics. Marketing analytics powers the current wave of data-driven decision making, and leveraging strategic data remains a source of building a sustainable competitive ...
New research on sales from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including salesforce management, perfecting the sales pitch, and the impact of incentive plans on sales productivity.
Within another market research survey, a conjoint analysis or MaxDiff study is included for determining the right product claims, product features, and pricing, targeted to which market segments to develop new products for sales growth ( The role of a data analyst is dynamic and impactful, bridging the gap between data and strategic decision ...
Market research blends consumer behavior and economic trends to confirm and improve your business idea. It's crucial to understand your consumer base from the outset. Market research lets you reduce risks even while your business is still just a gleam in your eye. Gather demographic information to better understand opportunities and ...
Marketing research methods: heatmap analysis in Userpilot. 8. Exploratory research. When you're venturing into new territory, exploratory research helps you establish a foothold. This kind of research is often qualitative and can involve literature reviews, expert interviews, or case studies. It's particularly useful in the early stages of ...
How sales and marketing come together in the pursuit of satisfying customers and achieving organizational objectives is of key concern to both academics and practitioners. Researchers have investigated many aspects of the sales-marketing interface (SMI). This paper provides a systematic literature review of the SMI domain. Based on a systematic assessment of more than 25 years of SMI research ...
Typical employers of market research analysts include businesses, educational institutions, and government agencies. They usually work in office settings, as most of what a market research analyst does involves using computers to analyze data and performing research. However, they may need to travel to conduct interviews or meet with focus groups.
Abstract Sales managers are unlikely to reap the benefits of implementing predictive analytics applications when salespeople show aversion to or lack understanding of these applications. For managers, it is essential to understand which factors mitigate or exacerbate these challenges. This article investigates these factors by studying the implementation of an application that predicts ...
Russia Artificial Intelligence Market Overview:. The Russia artificial intelligence market is projected to exhibit a growth rate (CAGR) of 20.60% during 2024-2032.The market is driven by increasing government support, widespread AI adoption in key economic sectors, domestic technology development, and extensive research and development (R&D) activities undertaken by both the government and non ...
These sensors connect directly to student devices via the Vernier Graphical Analysis Pro app, enabling easy data collection and analysis. Distribution of the Global UV Sensor Market, By Region of Origin: North America - 25%; South America - 7%; Europe - 24%; Middle East & Africa - 12%; Asia Pacific - 32%
BEV sales continue to be concentrated in the luxury category, growing to 34% of the total luxury vehicle market in the third quarter but remaining below 2% of the non-luxury vehicle market. As a share of sales within each powertrain type, vehicle sales classified as luxury accounted for 83% of all BEV sales and 13% of non-hybrid gasoline- or ...
The analysis is supplemented by market monitoring discussions with merchants about fees, costs, and consumer trends, both among merchants who charge cash back fees and those who do not. ... Dollar in 2015. 24 From 2018 to 2021, nearly half of all retail locations opened in the U.S. were dollar stores. 25 In research examining the impact of ...