Detailing the Business Model Of KFC from End-to-End

By Aditya Shastri
KFC holds a prominent position in the fast-food industry, with a presence in over 145 countries and an extensive network of 25,000 outlets, earning it the rank of the third-largest global fast-food chain. It was one of the 1st American fast-food chains to venture into international markets. As of 2023, the brand boasts a substantial estimated brand value of approximately $17,662 million.
Thus this makes us keen to know the business model of KFC. In this blog, we have listed the detailed business model of KFC which includes the value proposition, key partners, revenue model, cost structure, etc.
Before we start with its business model let us know about KFC as a company.

Colonel Harland Sanders, the founder of KFC, initially used to sell fried chicken from his roadside restaurant in Kentucky, USA. Colon Sanders, the founder of KFC kept the recipe of his trademark chicken a secret.
KFC changed the way Americans ate chicken and posed a serious threat to the existing hamburger culture. Seeing the overwhelming response, Sanders decided to expand further by adopting the franchisee business model.
Kentucky Fried Chicken ( K FC ), is a global fast-food chain that is widely known for its delicious fried chicken. Its headquarters is located in Louisville, Kentucky, in the United States. Founded by Colonel Harland Sanders in the 1930s, this brand is renowned for its secret blend of 11 herbs and spices, which makes their chicken irresistibly flavorful and crispy.
Sanders initially used to sell fried chicken from his roadside restaurant in Kentucky, USA. He kept the recipe of his trademark chicken a secret. KFC changed the way Americans ate chicken and posed a serious threat to the existing hamburger culture. Seeing the overwhelming response, Sanders decided to expand further by adopting the franchisee business model.
Today, KFC’s distinctive red-and-white logo and finger-licking good chicken have made it a beloved household name with a global presence spanning more than 25,000 locations. Since 2002, KFC has operated as a subsidiary within the “YUM!” corporate family, which also owns several other well-known restaurant chains like Taco Bell and Pizza Hut, among others.
What’s new with KFC
Check out some current news about KFC:
Big Boro Eats
The KFC Youth Foundation launched a program “Big Boro Eats” to provide food aid and education to youngsters in Middlesbrough. The major aim of this initiative was to address the pressing issue of youth deprivation, with almost a third of children living in income-deprived households. The program was conducted for seven consecutive weeks from 24th July to 8th September. It included several activities such as teaching food-related skills, budgeting, and nutrition. Through this, they successfully created a safe and inclusive space for young people to develop life skills. This was a huge step towards establishing a permanent KFC Youth Foundation center in Middlesbrough.
Partnership with Deion Sanders and his family
KFC has partnered with NFL legend and University of Colorado Boulder head football coach Deion “Prime Time” Sanders and his family to promote their latest menu innovations, including new Kentucky Fried Chicken Nuggets. The Sanders family, who are longtime KFC fans, collaborated with the brand in various promotional activities. This partnership highlights the tradition of enjoying KFC as a family during meal times, with Coach Prime and his five children appearing together in promotional content.
Drone delivery
In a recent cricket match between Australia and South Africa, a drone delivered a KFC chicken bucket to South African cricketer David Miller mid-match, creating an innovative and entertaining moment. The video was shared by the official handle of South Africa’s national cricket team. David Miller expressed his delight at the unique experience, praising KFC for their creative delivery method. The use of drones to deliver indicates a potential future trend in improving convenience and speed in food delivery services.
Target Audience of KFC
Below is a buyer persona for KFC which will help us understand the target audience.

Buyer’s Persona
Profession:
- Affordable options.
- Convenient locations.
- Diverse menu.
- Quality foods.
- Loyalty rewards.
Interest & Hobbies
- Art and craft
- Playing Guitar
- Socializing with new people
Pain Points
- Inconsistent opening hours.
- Overcrowded restaurants and slow checkout process.
- Lack of healthy options.
- Inconsistent portion sizes.
Social Media Presence
Let us now start reading in detail about the business model of KFC.
Business Model of KFC
KFC’s management cannot oversee all the operations of its outlets over the world by sitting in one city. Thus, KFC adopted the Franchise Model as its Business Model just like the other fast-food restaurant joint did.
The franchise model is used when the parent company has a unique product and gives permission through means of licenses to others to use its logo, brand name, operating methods, etc. An agreement needs to be signed where the franchisee agrees to strictly adhere to the conditions laid down by the parent company.
Let us now see step by step the different pasts under the business model of KFC.
Business Model of KFC – Value Proposition
Let us see the below-listed value proposition of KFC:
1. High-quality food
As their tagline says “Nobody does chicken like KFC”. KFC makes sure that the quality is not compromised in any manner in any franchise all over the world. All the raw material goes through thorough quality checks. The food is always clean and fresh and prepared from scratch by the cooks in the kitchen.
KFC makes sure that most of its items can be afforded by the fast-food eating population. However, the prices vary from location to location due to import duties, etc. They also have Super Meals, Buddy Meals, and Combo Meals that can fit your budget and value for money.
3. Ambiance and staff
KFC ensures that the vibe of the restaurant is very family-friendly. The layout, the decor, and the music all help to create a lively and upbeat environment that does not make you want to leave but instead makes you want to spend more time with your loved ones.
4. Variety of options
KFC is constantly trying to come up with new and innovative ways to serve its customers’ needs. Although KFC specializes in non-vegetarian food, it makes sure to add a couple of items that cater to its vegetarian audience too. They try to come up with new dishes that satisfy the local tastes of the people of that location keeping its original roots intact. Eg. Tandoori Chicken Zinger in India, Scoff EE Cup in the UK, and Porridge in China.
5. Brand name and loyalty
KFC is very popular and known worldwide for its food and services. It has created a long-standing loyalty from individual customers and families. Its iconic recipes comprising a secret blend of “11 herbs and spices” make you want to go back again and again.
Let us now see the different key partners of KFC.
Business Model of KFC – Key Partners
Handling such a huge business is not an easy job. One needs constant support on various fronts from the people specialized in that field so that the business operates smoothly and efficiently. The partners that make up the heart of the KFC Business Model are:
1. Franchise Partners
Franchise partners are very crucial to KFC’s success. Since they operate the restaurants they can make or break the brand image and identity. Thus, KFC shall make sure that it gives franchising licenses to only those food companies and private business owners whom they trust and they feel will be able to abide by the standards and rules.
2. Suppliers and Vendors
These partners supply the restaurants with raw materials, ingredients, equipment, and all those things that are necessary for the operating and day-to-day functioning of the business. It is crucial to tie up with only those suppliers that can provide good quality goods and services.
3. Marketing Partners
KFC needs to tie up with influencers on social media, celebrities, sports teams, commercial brands, advertising agencies, and other organizations that help to create a desire for the product, pique the interest of the customers , generate leads, and eventually lead to a sale.
4. Delivery and Distribution Partners
KFC needs constant support from its logistics partners, delivery agencies, home delivery services, etc that will help to streamline the process and enhance the customer experience.
Let us now see the revenue model of KFC.
Business Model of KFC – Revenue Model
KFC earns most of its revenue from the sale of food and drinks to its customers (both online and in-store). It also earns from its franchise agreement through its licensing fees. As of 2022, KFC earned around US$ 31.116 billion worth of total revenue. The annual revenue for 2022 was 6.8 billion, which was estimated to be a 3.92% growth from 2021.
Let us now see the cost structure of KFC.
Business Model of KFC – Cost Structure
KFC’s pricing cannot be the same in every country. The price depends on various factors like-
- the cost of equipment, raw materials, and ingredients
- operational costs, occupancy costs,
- payments to its various partners
- advertising costs, marketing costs, etc.
Let us now see the customer segments and marketing strategy of KFC.
Business Model of KFC – Customer Segments and Marketing Strategy
KFC targets three main customer segments.
- The Individual Customer- this customer is usually a working person who just wants something filling but it shall be quick, affordable, and accessible.
- Families- KFC is a very family-friendly place. The staff too is trained in such a way that will make families feel at home. There is also a separate play area for young children and small toys in the meals.
- Group Events- Be it a birthday party, an office get-together, or any celebration, KFC is your ultimate go-to destination.
Sander’s picture is still used today for marketing purposes. It is considered to be KFC’s international symbol of hospitality.
Business Model of KFC-Channels
KFC primarily caters to its customer base through a vast network consisting of over 25,000 outlets strategically located worldwide. This expansive network extends its reach to approximately 145 countries and territories across various continents, including North and South America, Asia, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. They have dedicated and friendly sales and service staff who are readily available to assist the customers.
In addition to this, KFC offers the convenience of online ordering through their website or app . Customers can select their preferred dishes, place orders, and even schedule a delivery at their convenience. KFC has its own team of delivery drivers to ensure that food arrives at the doorstep. This option is great for those who prefer to order from the comfort of their homes.
Let us now see the competitor analysis of KFC.
Top 5 Competitors of KFC
- McDonalds : McDonalds is the world’s largest fast-food restaurant chain. It’s widely known for its yummy burgers, crispy fries, and refreshing drinks. People love to go there for a quick and tasty meal, and they have lots of different choices on their menu. McDonald’s is a place where one can enjoy delicious food with friends and family.
- Starbucks : Starbucks is a famous coffee chain found all around the world. They are the second largest competitors of KFC and they are known for their wide range of coffee and specialty drinks, like lattes and frappuccinos. People often visit Starbucks to enjoy a cup of coffee or to work/study in a cozy environment.
- Burger King : Burger King is a fast-food restaurant chain recognized globally. They are famous for their flame-grilled burgers and a menu that includes items like the Whopper and chicken sandwiches. Burger King provides a convenient option for people looking for tasty burgers and fast meals.
- Subway : Subway is a global fast-food restaurant chain specializing in customizable sandwiches and salads. They offer a wide variety of fresh ingredients and bread choices, allowing customers to create their own sandwiches or choose from a menu of pre-designed options. Subway is known for its “Eat Fresh” slogan and is a popular choice for quick and healthy fast food options.
- Pizza Hut : Pizza Hut is a global pizza restaurant chain recognized for its diverse menu of pizza offerings. They offer a wide selection of pizzas, including classics like pepperoni. Pizza Hut often offers delivery and dine-in options, making it a convenient choice for pizza enthusiasts worldwide.
Before we conclude let us have a look at an example of a failed campaign that faced customer backlash.
Example of a Failed Campaign
The kfc coupon fiasco.
To market their newly revealed grilled chicken, KFC joined forces in 2009 with Oprah Winfrey. As a part of this business partnership, Oprah was to promote KFC’s offer of a free two-piece grilled chicken meal. Having underestimated Oprah’s influence, KFC was flabbergasted when an estimated 10 million people downloaded the coupon for the free meal online.
KFC customers felt cheated and infuriated when they were told they couldn’t receive the free chicken they were promised.
Not having enough of the product to meet the demand, KFC had to actually turn customers away and in some locations, close early. KFC was forced to drop the deal and apologize to its frustrated clientele.
Conclusion
On the overview of the business model of KFC, we have can clearly see that the company utilized its business model very well and has been growing at a wide range.
In its value proposition, it has high-quality food, affordable prices, a variety of products, and brand name and loyalty which plays a crucial role in the growth of the business. It has different partners in the market which help it grow in the market like franchise partners, suppliers and vendors, marketing partners, and distribution partners.
It has a well-distributed cost structure which constitutes the cost of equipment, raw material, and ingredients, operational costs, occupancy costs, payments to its various partner’s advertising costs, marketing costs, etc.
Wasn’t it interesting to know the business model of KFC? Learn how to grow your business using digital marketing, check out our website for more information . You can also check out Free Digital Marketing Masterclass by IIDE to understand what digital marketing is all about.
If you are interested in digital marketing and wish to be in touch with our academic counsellors then connect with them at [email protected] for a free counselling session.
Do share your thoughts about the case study in the comments below. Hope you liked this case study and found it informative and insightful!
Author's Note: My name is Aditya Shastri and I have written this case study with the help of my students from IIDE's online digital marketing courses in India . Practical assignments, case studies & simulations helped the students from this course present this analysis. Building on this practical approach, we are now introducing a new dimension for our online digital marketing course learners - the Campus Immersion Experience. If you found this case study helpful, please feel free to leave a comment below.
" * " indicates required fields

IIDE Course Recommendation

Get Syllabus
By providing your contact details, you agree to our Terms of Use & Privacy Policy
Aditya Shastri
Lead Trainer & Head of Learning & Development at IIDE
Leads the Learning & Development segment at IIDE. He is a Content Marketing Expert and has trained 6000+ students and working professionals on various topics of Digital Marketing. He has been a guest speaker at prominent colleges in India including IIMs...... [Read full bio]
Thank You for a brief and concise explanation on key points related to the KFC Business model.
Thanks, very informative. Kindly touch base on the organizational culture management of KFC stores in USA
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Related Posts

In-Depth SWOT Analysis of Jio – Market Leader of Telecommunication Industry
by Aditya Shastri | Sep 10, 2024
Quick Read The SWOT analysis of Jio highlights the company’s strengths, including...

The Zepto Business Model: A Blueprint for Quick Commerce Success
by Aditya Shastri | Sep 6, 2024
Quick Read The Zepto business model exemplifies quick commerce in India, focusing on...

Extensive SWOT Analysis of SBI – An Indian Multinational Public Sector Bank
Quick Read The blog on a detailed SWOT analysis of State Bank of India (SBI), highlighting...
I’m Interested in This Masterclass
- Kentucky Fried Chicken Firm’s Risk Management Analysis Words: 1133
- The Risk Management Process Words: 1929
- Target Engineering Company’s Risk Management Words: 3047
- HSBC: Risk Management Words: 1326
- Project Risk and Procurement Management Words: 2933
- Risk Management for Non-Financial Companies Words: 2482
- Risk Management and Its Process Words: 6034
- Supply Risk Types and Management Words: 4095
- Kentucky Fried Chicken Company’s Advertisement Words: 564
- Risk Management Technique: Risk Analysis and Evaluation Words: 2512
- Assessment and Management of Risks Words: 1380
- Tesla Company’s Corporate Risk Management Words: 2193
- The Project Risk Management: Contemporary Approaches Words: 2028
- Ethical Dilemmas in Business: KFC Company’s Case Words: 1957
- Generali Group: Strategic Risk Management Words: 1679
- Health IT Projects’ Risk Management Words: 4389
- Risk Management Strategies of Bank of America Words: 3965
- PepsiCo Inc.’s Risk Management in Purchasing Department Words: 2821
- Risk Management and Its Dimensions Words: 2072
- Risk Management in Healthcare Construction Projects Words: 1581
- Risk Management: The Project Risk Maturity Model Words: 685
- Enterprise Risk Management and Assessment Words: 1165
- Project Risk Measurement and Management Words: 2986
- Nassau Finance Corporation’s Risk Management Strategy Words: 2683
- Risk Management During Financial Crisis in the US Words: 27339
KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management
Introduction, risk assessment, analysis of the risks, measurement, reference list.
KFC is a subsidiary of YUM Brands, Inc, with about 3% own managed restaurants and 97% franchises in 131 countries worldwide, making it one of the largest restaurant chains (Uddin, 2020, p. 172). However, despite being part of one of the world’s largest companies, KFC is still vulnerable to substantial risks. Starting from the corporate model of expansion and up to the choice of meals on the menu, KFC faces numerous dilemmas, threatening its financial stability. Although the company is a corporate giant with significant marketing experience and many competitive advantages, there are still financial, strategic, and public threats that may undermine its success (Jeynes, 2009, p. 92). Understanding what constitutes the main risks to KFC’s stability is essential in ascertaining an appropriate risk response plan. Nevertheless, assessing the risk management processes of the entire corporation is quite problematic since franchises may differ in governing and the threats they face. For this reason, as a former employee of KFC Philippines, I will present a case study of the risk management processes of this franchise based on my work experience, internal information about the company’s activities, and external sources.
Risk management is an essential part of the activity of any company, regardless of its size, profit, and field of activity. In general, there are two main approaches to risk assessment, depending on the structure of the company. First, an organization may have a separate department that collects information about the activities of the entire company and is responsible for identifying risks and planning responses to them. Second, another structure assumes that each department identifies risks and prepares a response to them, but a general manager prioritizes them, draws up a final risk management plan, and allocates funds.
The information published on the official websites of KFC and their central offices, as well as other reliable sources, is limited. Consequently, one can only guess how the risk assessment process takes place in a leading company. Jeynes (2002, p. 8) noted that the larger the organization, the more it needs risk management strategies that spread from top to bottom. Thus, it is likely that KFC has a separate department for risk assessment, which determines strategies based on feedback and information provided by other departments. This structure is also confirmed by the risk management processes in the KFC franchise located in the Philippines.
As a former employee of KFC Philippines, I am familiar with the structure of the company and know how the organization approaches risk management processes. KFC Philippines is a franchise owned by the family that also has the Ramcar business group, which includes a large car battery business, Mr. Donuts, Japanese fast food Tokyo Tokyo, and Poultry Max. Since it is common in Asia to involve families in doing business, the company’s board of directors consists of family members headed by the Chairman, and the executive committee is also represented by the Chairman and his sons. While this approach may seem out of place in Western business culture, it also has its benefits since, for the owners, the reputation of the business is the honor of the family.
Risk management at KFC Philippines is somewhat complex, with Ramcar’s Poultry Max being the main chicken supplier at KFC, on which a large part of the restaurant business depends. Since the companies belong to the same group, one can define that risk management begins with the work of Poultry Max but not KFC itself. Poultry Max’s general manager reports to the executive committee twice a month on major issues to identify and prevent significant risks. These risks include the quality and cost of chicken feed, as well as animal disease, sanitation, and meat processing that affects product quality. However, the primary responsibility for risk management rests with the department called “The Office of the Chairman,” headed by the Chairman of the company. The duties of the department include monitoring all the different divisions, assessing possible risks, and creating solutions. In addition, the department must communicate and cooperate with a general manager of each division to discuss solutions and find the most effective ones.
The risk management process at KFC Philippines goes through stages that are typical and necessary for any company. These stages include defining the objectives and scope of risk management, identifying the main risks and their significance, planning a response, and managing these responses (Hillson, 1999). Each of these stages is important for the company, but the most significant is the determination of the importance and criticality of the risks since the scale of the network and the parties involved in it make it almost impossible to interfere with all threats at the same time. In addition, planning an adequate response is also a critical step because choosing the wrong strategy can be resource-intensive but not effective. For example, trying to overcome the risk of an earthquake is not possible, and the company must focus on planning a response to its consequences. For this reason, the following part will briefly describe most of the risks of KFC Philippines to identify the main ones and strategies of their management in the next section.
The first major risk the company faces is supply chain disruption. As with most fast-food restaurant chains, KFC does not normally produce the raw materials on its own but rather uses outside suppliers to prepare the ingredients for its unique meals. Subsequently, the company relies on other business entities to function. Specifically, not only do the actual food producers have to sell the processed ingredients, but these items have to be shipped from factories to restaurants. The entirety of these operations comprises a system known as a supply chain. The more third parties there are in the network, the higher the possibility of disruption and subsequent delays there will be.
Moreover, KFC faces a number of risks related to the quality of the product and its taste. Firstly, since chicken is a highly perishable food, any delays in the supply chain can lead to a decrease in quality. Consequently, if these products are used in restaurants, customers can get food poisoning. Secondly, an important aspect is the production of uniform poultry since the taste of the final product that customers expect to receive depends on the quality and taste of the meat. If changes in feed or animal care technology occur and affect the taste of the chicken, customers may be unhappy with such modifications as they visit KFC because of the unique chicken recipe.
Thirdly, the risk is also the disease of animals, which can affect both the volume and timing of deliveries, as well as the quality of the final product, if the condition is not detected in time. As a consequence, this risk can lead to a shortage of products for the operation of all restaurants in the chain or even food poisoning or illness of visitors. Fourth, one of the greatest financial risks is the provision of animal feed due to the limited local agricultural supply associated with the geography of the Philippines. Although the company uses local feed and also buys it from other countries such as Australia and Argentina, negative natural factors, even in one country, can affect yields and increase feed prices. Since the company cannot buy less feed to provide for the animals, this situation entails financial costs. Finally, there is also the risk of an allergic reaction in customers due to incorrect product labeling or accidental exposure to allergens in products that should not contain them. While it is likely that these mistakes will affect individual customers, they will damage the reputation of the company as a whole.
The second risk is the possibility of the franchise system backfiring. The primary strategy of KFC’s expansion is franchising, which means issuing licenses to local sellers to conduct commercial activities using the general brand name. It is a fast and effective way of infiltrating new markets. However, the abundance of stores that are individually managed can create issues for the franchisor, especially in foreign countries. The less control the company has over its outlets, the higher the chance of ineffective management will be. Since KFC Philippines consists of a network of sub-franchisees, this risk is also relevant for a local franchise, although it belongs to one family.
Another risk for KFC globally and the Philippines franchise is associated with personnel management. KFC has franchises and company-owned restaurants in dozens of countries around the world, employing thousands of employees. For this reason, the company constantly faces the risk of ineffective management or neglect of the rights of employees, which can harm their reputation. This problem was most clearly reflected in the work of one of the company’s main competitors when McDonald’s workers in dozens of cities organized strikes demanding an increase in wages to $ 15 per hour (Vakil, 2021). Although this issue has generally been resolved in the company-owned restaurants, there is still a problem of control of working conditions in franchises and damage to McDonald’s reputation.
At the same time, since KFC has many franchisees and sub-franchisees, the company has limited influence on its management. Consequently, even the foreseen risk of staff dissatisfaction with working conditions and taking action can lead to the destruction of the company’s image due to non-compliance with the same standards by franchises. In addition, these factors can also lead to higher employee turnover, which will affect the costs of finding and training personnel, as well as the quality of service due to their inexperience.
The third risk is the public perception of KFC and the fast-food industry in general. As the culture of healthy eating becomes more widespread, many people start to view fast-food restaurants as primary sources of unhealthy food. Nowadays, Internet users are constantly reminded of well-known products from famous brands, such as McDonald’s, Chic-fil-A, Burger King, KFC, and others, high in fats, sugar, and salt. Most of these companies, including KFC, do not deny the fact of their foods’ potential harm. As a result, the advancement of health consciousness has the capability of damaging the company’s reputation and reducing customers.
In all cases, there is the problem of weakening brand attractiveness, brand loyalty, and reduction of revenues. Baryannis et al. (2019, p. 2181) argue that KFC had already encountered complications on such a scale in 2018 when a large number of the company’s stores in the United Kingdom were closed due to the deficit of chicken. Not only did the company permanently or temporarily close half of its assets in the UK, but it also lost thousands of employees and managers. The company had to restructure its logistics to resume its services quickly. Therefore, one of the main goals of the company and its franchisees was to assess and prioritize risks to develop a timely and effective response. The results of this analysis are reflected in the measures of their management.
The company uses various tools and methods for risk analysis to evaluate issues proficiently. However, one of the most often applied tools of KFC Philippines and Poultry Max as its main suppliers is CARVER. CARVER is a tool to evaluate and prioritize risks that stand for Criticality, Accessibility, Recoverability, Vulnerability, Effect, and Recognisability (Bencie & Araboghli, 2018, p.3). In addition, this tool provides directions to develop an adequate response. All the described risks were assessed by this tool during different periods of the company’s development.
Firstly, one of the major risks is supply disruption, which also has several sub-risks or reasons for failure. The supply chain is the most critical due to the short shelf life of meat and significant sales volumes; hence, even minor disruptions will lead to temporary or permanent restaurant closures. This risk also has the highest accessibility because supply problems can arise from a number of different factors. Recoverability and vulnerability are moderate but depend on the speed of KFC’s response because short-term interruptions will reduce the number of customers but, at the same time, retain regular visitors and staff. At the same time, this problem will have a significant financial and reputational effect on local restaurants and the brand as a whole since it is the brand that receives the most attention (Madanoglu, Castrogiovanni, and Kizildag, 2019, p. 240). In addition, this risk is easy to recognize and influenced by external forces.
Moreover, KFC Philippines and its main supplier, Poultry Max, are owned by the same family; thus, The Office of the Chairman also assesses the risks associated with the supply. The most serious are the risks of delivery delays and animal diseases affecting the quality of the product. According to CARVER, they receive a higher priority since, with high criticality and accessibility, they also have a severe effect on the company’s reputation and influence recoverability and vulnerability of the company. If hundreds or thousands of customers get food poisoning, brand recovery will be very difficult or even impossible. At the same time, the risk associated with the supply of feed is low. Despite the sufficiently high criticality, it has an effect only on the financial aspect and is easily recoverable, less likely, and vulnerable.
Analysis of the risks associated with the KFC Philippines franchise and its sub-franchisees using CARVER showed that these problems are of lower priority, although they are also crucial for companies. This conclusion was also reflected in the measures taken by KFC Philippines. The criticality of the risks associated with franchises is high for KFC since the shortcomings and high-profile failures of one or several restaurants harm the image of the entire brand. This aspect is also associated with KFC Philippines, which has sub-franchisees throughout the country. In addition, the accessibility of this risk is relatively high due to the scale of KFC’s activity, and the recoverability and vulnerability are average with the adequate response and work with the media. At the same time, the problems of franchises and sub-franchisees can have significant reputational and financial effects for KFC if they are of public importance. All these parameters also characterize the problem of personnel management and the working conditions and demonstrate that the risk of franchising and sub-franchising requires the development of an adequate response.
The risk associated with the virtues of healthy eating is the lowest priority in this analysis for several reasons. First, while the criticality of a massive population transition to a healthy lifestyle is high for a chain of restaurants offering high-calorie food, the accessibility or likelihood of such a change is low. Likewise, although most people are aware of the dangers of smoking or alcohol, a significant proportion of the population consumes these products. Consequently, the vulnerability of KFC to this risk will also be low in the near future. However, if this risk is realized, it will significantly affect the reputation and profit of the company and also has a low probability of recovery. Consequently, the company needs to develop a response to mitigate the impact of an unlikely but real risk.
The CARVER tool has its advantages in assessing risks since the combination of points allows the management to accurately evaluate the priority of risks. This tool uses a five-point rating scale, in which “1” describes the least dangerous situation for each of the categories and “5” is the most dangerous. Consequently, The Office of the Chairman uses measurement data to help accurately track risks and understand their specific characteristics. In addition, although the results obtained demonstrate the priority of risks, individual categories can show directions for their management, for example, increasing chances of recovery.
However, assessing each of the categories also requires specific measurements to understand their magnitude. Risk measurement should be determined by the nature of the problem, which threatens the company’s stability. In terms of the supply chain and healthy eating tendencies, the risk is measured in quantities. Each store’s effectiveness is judged by the amount of money it has generated through sales. However, both these threats can negate these revenues partially or entirely. When the restaurants no longer receive ingredients, they cannot sell the food. When the customers stop viewing the brand as suitable for their needs, they will not buy from this retailer. Subsequently, The Office of the Chairman estimates how much losses the company will sustain if the food ingredients are not supplied.
Similarly, it is possible to calculate the approximate number of customers who will not visit the store. In both cases, the managers use the average purchase value, which will not be generated when the customers do not arrive, or the food is not sold. The resulting value constitutes KFC’s quantified financial risk. These indicators allow management to assess the criticality, recovery, and vulnerability of most risks. The same algorithm can be applied to the estimation of franchising risks, where the average purchase value is compromised by the franchisee’s incompetence. At the same time, the effectiveness of risk management will be measured by the costs of avoiding or mitigating problems and by financial losses if the risks are faced.
Having assessed the main risks, KFC Philippines has taken a number of measures to avoid described problems and their consequences. I, as a general manager, received this information while working in the company and am displaying this experience in a case study. The chosen strategies are currently demonstrating their effectiveness. One of the reasons for the choice and the possibility of implementing these strategies is also the specificity of the KFC Philippines franchise, as it is a member of the Ramsar business group run by one family.
The supply chain risks are met and controlled by management because KFC Philippines and its main chicken supplier, Poultry MAX, are owned by the same family. Consequently, risk management begins at the supplier level, which partially saves KFC from unexpected problems related to product quality. Firstly, the company overcame the risk of supplying low-quality products by introducing standards for working with live animals, farming, and product processing. All processes are uniform, and each employee is responsible for the work done, which provides consistent quality chicken to the stores at a known cost. This uniformity was achieved by building ultramodern poultry houses to control all aspects of chicken rearing, no matter the external environmental conditions. Products that do not meet the standards cannot be sold.
Secondly, the company met the second risk associated with the quality of meat due to animal diseases by building a laboratory to test animals to treat them and meat to avoid its selling in case of infection. Meat samples are constantly tested in the laboratory, as well as live animals, to prevent the spread of disease and the supply of contaminated meat. In addition, the company avoids the risk of damage to reputation due to allergic reactions of customers to restaurants’ products, noting that their products can contain allergens and disclaiming responsibility on the KFC website (“Special diets,” n.d.). Thus, while the threat of delayed delivery is only diminished, the risk of food poisoning for KFC visitors is overcome.
The risks associated with the supply of feed for animals have been overcome by using multiple sources. First, a local Feedmill was built, which ensures a constant supply of quality feed and saves on transportation costs. Secondly, the company supplies raw materials from overseas, especially wheat from Australia and soybeans from Argentina. Thus, this approach reduces the risk of feed shortages or significant cost increases because multiple sources form a safety net.
The company also eliminated the risk associated with sub-franchising by offering a unique restaurant management system. KFC Philippines invites all investors to open their own sub-franchise; however, a significant portion of the governance is vested in KFC Philippines (The Philippine Star, 2021; “Franchising,” n.d.). Thus, even inexperienced managers can open their own KFC restaurant and ensure its high income and full potential since KFC Philippines will be involved in most daily operations. This approach allows for attracting investors and developing restaurants, but at the same time, ensures that all standards of work and service of KFC are maintained. This aspect also concerns the management of personnel and the provision of decent working conditions. Consequently, KFC Philippines reduces the risk of the negative impact of the sub-franchise on the image of KFC as a brand. Moreover, the global company uses official policies that oblige its partners or third parties to provide their employees with decent work conditions and discourage the exploitation of child labor and slavery (“Modern slavery act,” 2019). However, the company is still unable to influence the activities of other franchises around the world, making it nearly impossible to manage these risks.
Finally, in terms of increasing health consciousness, KFC Philippines did not make any changes yet, since the probability of this risk is low. However, the company can change its marketing policy to mitigate the risk in the long-term perspective. Instead of emphasizing the taste and flavor, the company can accentuate nourishment. There is no such product that would be entirely harmful to health. The human body needs fats and carbohydrates as long as they are not consumed uncontrollably. Therefore, KFC can highlight the nutritional value of their products, thus making them appealing to conscious eaters. Such a change in marketing strategy will allow the company to retain its image as a crowd favorite while publicly acknowledging the problem of excess. As a result, the risk of negative public perception is controlled and minimized.
Thus, these risk management measures and the extent of their application demonstrate the priority identified in the analysis. Moreover, these examples demonstrate the different risk management strategies that are most appropriate for each situation. The choice of strategy is consistent with theoretical findings on risk management and the matrix developed for their classification (Panthi, Azhar, and Ahmed, 2007, p. 15). Risks associated with high probability and effects, such as food poisoning due to the low quality of the meat, were met with an avoidance strategy. This category of risks was overcome by building laboratories and quality standards verification centers. The risks associated with the timeliness and sufficiency of supplies and sub-franchisees management were met by a mitigation strategy. This strategy was selected because only the probability or effect of the risks is relatively high, and KFC cannot have complete control over these processes. At the same time, a strategy of transferring was applied to avoid the consequences of a customer’s allergic reaction because there is always a low probability of incidence, which can have a significant effect on the company’s reputation (Panthi, Azhar, and Ahmed, 2007, p. 15). However, KFC accepted the risk of a negative perception of the brand due to a healthy lifestyle trend since it currently has no significant effect on its activities. These facts demonstrate a qualitative assessment and prioritization of risks, as well as adequate strategies for developing a response.
Therefore, the case of KFC Philippines demonstrates an example of effective risk management that protects a company from economic losses and damage to its reputation. The main feature of KFC Philippines is that it is part of a group of businesses owned by one family. This group also includes the company that produces and supplies meat for KFC restaurants. This feature allows management, The Office of the Chairman, to assess and mitigate risks across the supply chain. The example of KFC Philippines demonstrates that risk management requires detailed and systematic assessment at each stage of identifying risks and developing a response to them. This process follows an established and critically developed plan. In the first step, The Office of the Chairman receives reports from a general manager of each department and identifies the main potential risks. In the second step, management evaluates and analyzes each risk using the CARVER tool and other supporting methods and measurements to prioritize risks and identify the aspects that require the most intervention. In the third stage, measures are developed and taken to control these risks, depending on the strategies that can benefit.
The example of KFC Philippines demonstrates that the company chooses approaches to control all parties involved in the activities if such a scenario is possible. For this reason, the main supplier of meat and one of the suppliers of animal feed is controlled by the family that owns KFC. This approach lets the company take action to mitigate the risks associated with quality and on-time delivery. At the same time, the control of KFC Philippines’s sub-franchisees helps the company mitigate the risks associated with the failure of individual restaurants, which could damage the brand’s reputation. However, assessing the risk of a negative perception of KFC due to healthy eating trends as unlikely allowed the company to avoid unnecessary costs to overcome it. Thus, this case demonstrates that the correct identification and assessment of risks is necessary for the company’s activities to prevent possible threats and effectively allocate funds for planning a response for them.
Baryannis, G. et al. (2019) ‘Supply chain risk management and artificial intelligence: state of the art and future research directions’, International Journal of Production Research, 57(7), pp.2179-2202.
Bencie, L. and Araboghli, S. (2018) ‘A 6-part tool for ranking and assessing risks’, Harvard Business Review , Web.
Franchising (n.d.) Web.
Hillson, D. (1999) ‘Developing effective risk responses’, Proceedings of the 30th Annual Project Management Institute 1999 Seminars & Symposium, October 10-16, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
Jeynes, J. (2002) Risk management: 10 principles. Oxford: Butterworth Heinemann.
Madanoglu, M., Castrogiovanni, G.J. and Kizildag, M. (2019) ‘Franchising and firm risk among restaurants’, International Journal of Hospitality Management , 83, pp.236-246.
Modern slavery act 2017/2018 (2019) Web.
Panthi, K., Ahmed, S.M. and Azhar, S. (2007) ‘Risk matrix as a guide to develop risk response strategies’, Proceedings of 43rd ASC National Annual Conference .
Special diets wizard (n.d.) Web.
The Philippine Star (2021) ‘KFC offers innovative scheme for franchising’, Philstar Global , Web.
Uddin, S. (2020) ‘Operational strategies and management of KFC: an enquiry’, EPRA International Journal of Research & Development (IJRD), 5(4), pp. 172-179.
Vakil, M. (2021) ‘What people don’t realize about the McDonald’s strikes’, Entrepreneur, Web.
Cite this paper
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2022, November 28). KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management. https://studycorgi.com/kfc-philippines-companys-risk-management/
"KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management." StudyCorgi , 28 Nov. 2022, studycorgi.com/kfc-philippines-companys-risk-management/.
StudyCorgi . (2022) 'KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management'. 28 November.
1. StudyCorgi . "KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management." November 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/kfc-philippines-companys-risk-management/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management." November 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/kfc-philippines-companys-risk-management/.
StudyCorgi . 2022. "KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management." November 28, 2022. https://studycorgi.com/kfc-philippines-companys-risk-management/.
This paper, “KFC Philippines Company’s Risk-Management”, was written and voluntary submitted to our free essay database by a straight-A student. Please ensure you properly reference the paper if you're using it to write your assignment.
Before publication, the StudyCorgi editorial team proofread and checked the paper to make sure it meets the highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, fact accuracy, copyright issues, and inclusive language. Last updated: January 12, 2023 .
If you are the author of this paper and no longer wish to have it published on StudyCorgi, request the removal . Please use the “ Donate your paper ” form to submit an essay.

Message placeholder

| Issue | 218, 2020 2020 International Symposium on Energy, Environmental Science and Engineering (ISEESE 2020) | |
|---|---|---|
| Article Number | 02005 | |
| Number of page(s) | 5 | |
| Section | New Energy Development and Energy Sustainable Development Optimization | |
| DOI | ||
| Published online | 11 December 2020 | |
Fast Food Industry in the Post-pandemic Era — A Case Study of KFC
Mushui Chen *
Dedman College of Humanities and Sciences, Southern Methodist University, Dallas, Texas, United States
The global spread of the Covid-19 pandemic exerts great influence on the global economies, and among the economic sectors which are suffering losses, the service industry, especially fast food restaurants, are greatly impacted. Before the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, the fast food restaurant benefits a lot from the process of globalization, while they lose the benefit when the pandemic causes a lot of limitations on the cross-boarder flow of commodities and people. By taking KFC as an example, based on the analysis, it is found that the reasons behind such impact include slowed globalization, customer’s reducing income and government bans. To help the fast food restaurants get through the difficulties amid pandemic, several possible solutions are proposed in this paper.
© The Authors, published by EDP Sciences, 2020

Current usage metrics show cumulative count of Article Views (full-text article views including HTML views, PDF and ePub downloads, according to the available data) and Abstracts Views on Vision4Press platform.
Data correspond to usage on the plateform after 2015. The current usage metrics is available 48-96 hours after online publication and is updated daily on week days.
Initial download of the metrics may take a while.
MBA Knowledge Base
Business • Management • Technology
Home » Management Case Studies » Case Study of KFC: Establishment of a Successful Global Business Model
Case Study of KFC: Establishment of a Successful Global Business Model
By mid 1950s, fast food franchising was still in its infancy when Harland Sanders began his cross-country travels to market “Colonel Sanders’ Recipe Kentucky Fried Chicken.” He had developed a secret chicken recipe with eleven herbs and spices. By 1963, the number of KFC franchises had crossed 300. Colonel Sanders, at 74 years of age was tired of running the daily operations and sold the business in 1964 to two Louisville businessmen — Jack Massey and John Young Brown, Jr. — for $2 million. Brown, who later became the governor of Kentucky, was named president, and Massey was named chairman. Colonel Sanders stayed in a public relations capacity.
In 1966, Massey and Brown made KFC public, and the company was enlisted on New York Stock Exchange. During late 1960s, Massey and Brown turned their attention to international markets and signed a joint venture with Mitsuoishi Shoji Kaisha Ltd. in Japan. Subsidiaries were also established in Great Britain, Hong Kong, South Africa, Australia, New Zealand, and Mexico. In the late 1970s, Brown’s desire to seek a political career led him to seek a buyer for KFC. Soon after, KFC merged with Heublein, Inc., a producer of alcoholic beverages with little restaurant experience and conflicts quickly arose between the Heublein management and Colonel Sanders, who was quite concerned about the quality control issues in restaurant cleanliness. In 1977, Heublein sent in a new management team to redirect KFC’s strategy. New unit construction was discontinued until existing restaurants could be upgraded and operating problems eliminated. The overhaul emphasised cleanliness, service, profitability, and product consistency. By 1982, KFC was again aggressively building new restaurant units.

In October 1986, KFC was sold to PepsiCo. PepsiCo had acquired Frito-Lay in 1965, Pizza Hut in 1977 with its 300 units, and Taco Bell in 1978 . PepsiCo created one of the largest consumer companies in the United States. Marketing fast food complemented PepsiCo’s consumer product orientation and followed much the same pattern as marketing soft drinks and snack foods. Pepsi soft drinks and fast food products could be marketed together in the same restaurants and through coordinated national advertising .
The Kentucky Fried Chicken acquisition gave PepsiCo the leading market share in three of the four largest and fastest growing segments in the U.S., quick-service industry. By the end of 1995, Pizza Hut held 28 per cent share of $18.5 billion, U.S pizza segment. Taco Bell held 75 per cent of $5.7 billion Mexican food segment, and KFC held 49 per cent of the $7.7 billion, U.S chicken fast food segment.
Japan, Australia, and United Kingdom accounted for the greatest share of the KFC’s international expansion during the 1970s and 1980s. During the 1990s, other markets became attractive. China with a population of over 1 billion, Europe and Latin America offered expansion opportunities. By 1996, KFC had established 158 company-owned restaurants and franchises in Mexico. In addition to Mexico, KFC was operating 220 restaurants in the Caribbean, and in the Central and South America.
Many cultures have strong culinary traditions and have not been easy to penetrate. KFC previously failed in German markets because Germans were not accustomed to take-out food or to ordering food over the counter. KFC has been more successful in the Asian markets, where chicken is a staple dish. Apart from the cultural factors, international business carries risks not present in the U.S. market. Long distances between headquarters and foreign franchises often make it difficult to control the quality of individual franchises.
In some countries of the world such as, Malaysia, Indonesia and some others, it is illegal to import poultry, a situation that has led to product shortages. Another challenge facing KFC is to adapt to foreign cultures. The company has been most successful in foreign markets when local people operate restaurants. The purpose is to think like a local, not like an American company.
As KFC entered 1996, it grappled with a number of important issues. During 1980s, consumers began demanding healthier foods, and KFC’s limited menu consisting mainly of fried foods was a difficult liability. In order to soften its fried chicken chain image, the company in 1991, changed its name and logo from Kentucky Fried Chicken to KFC. In addition, it responded to consumer demands for greater variety by introducing several new products, such as Oriental Wings, Popcorn Chicken, and Honey BBQ Chicken as alternatives to its Original Recipe fried chicken. It also introduced a dessert menu that included a variety of pies and cookies.
Soon after KFC entered India, it was greeted with protests of farmers, customers, doctors, and environmentalists. KFC had initially planned to set up 30 restaurants by 1998, but was not able to do so because its revenues did not pick. In early 1998, KFC began to investigate the whole issue more closely. The findings revealed that KFC was perceived as a restaurant serving only chicken. Indian families wanted more variety, and the impression that KFC served only one item failed to enhance its appeal. Moreover, KFC was also believed to be expensive. KFC’s failure was also attributed to certain drawbacks in the message it sent out to consumers about its positioning. It wanted to position itself as a family restaurant and not as a teenage hangout. According to analysts, the ‘family restaurant’ positioning did not come out clearly in its communications. Almost all consumers saw it as a fast food joint specializing in a chicken recipe.
KFC tried to revamp its menu in India. Cole Slaw was replaced with green fresh salads. A fierier burger called Zinger Burger was also introduced. During the Navaratri festival, KFC offered a new range of nine vegetarian products, which included Paneer burgers. Earlier, KFC offered only individual meals, but now the offerings include six individual meals, two meal combos for two people, and one family meal in the non-vegetarian category. For vegetarians, there are three meal combos for individuals, and meals for couples, and for families.
KFC also changed its positioning. Now its messages seek to attract families who look not only, for food, but also some recreation. Kids Fun Corner is a recreational area within the restaurant to serve the purpose. Games like ball pool, and Chicky Express have been introduced for kids. The company also introduced meal for kids at Rs. 60, which was served with a free gift.
Over the years, KFC had learned that opening an American fast food in many foreign markets is not easy. Cultural differences between countries result in different eating habits. For instance, people eat their main meal of the day at different times throughout the world. Different menus must also be developed for specific cultures, while still maintaining the core product — fried chicken. You can always find original recipe chicken, cole slaw, and fries at KFC outlets, but restaurants in China feature all Chinese tea and French restaurants offer more desserts. Overall, KFC emphasizes consistency and whether it is Shanghai, Paris, or India, the product basically tastes the same.
Questions For Discussion
- Analyse the case and determine the factors that have made KFC’s a success global business.
- Why are cultural factors so important to KFC’s sales success in India and China?
- Spot the cultural factors in India that go against KFC’s original recipe; KFC Fried Chicken.
- Why did Kentucky Fried Chicken change its name to KFC?
Related posts:
- Case Study of Bajaj Auto: Establishment of New Brand Identity
- Case Study: Delta Airlines Successful Business Turnaround Strategy
- Case Study: Business Model of Napster
- Case Study: MasterCard’s Business Model
- Case Study of Zara: A Better Fashion Business Model
- Case Study of Qantas Airlines: Business Model and Strategies
- Case Study of LG Electronics: Repositioning a Successful Brand
- Case Study: Nissan’s Successful Turnaround Under Carlos Ghosn
- Case Study: L’Oreal Global Branding Strategy
- Case Study of FedEx: Pioneer of Internet Business in the Global Transportation and Logistics Industry
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Philippine E-Journals
Home ⇛ ani: letran calamba research report ⇛ vol. 1 no. 1 (2011), food safety and sanitation practices of kentucky fried chicken in crossing, calamba city, laguna.
Avy Gayle A. Kanazawa | Lorenzo A. Plumares | Anthony M. Dolloso
Discipline: Hotel and Restaurant Management
The case study aimed to evaluate the food safety and sanitation practices of KFC in Crossing, Calamba City, Laguna. It also aimed to check if the actual practices of KFC personnel complied with the sanitation for food establishments as stated in P.D.856.The study adopted the evaluative research method and survey questionnaire was used to gather the needed data.
It was found out that most of the sanitation standards for food establishment in food storage were strictly implemented by the establishment. In terms of food preparation, the establishment somewhat complied with P.D.856 because of its well-organized storage area and is able to maintain it properly. In terms of personal hygiene, it complied with the standard of P.D.856 because of its existing policy strictly implemented by the management. Finally, in terms of its dining area, the establishment slightly complied with P.D.856.
In conclusion, most of the food safety and sanitation practices of KFC complied with the sanitation standards
for food establishments. However, in terms of personal hygiene and good grooming of the personnel, some of the standards were not complied upon.
The study recommended that the management should supervise the operation in the kitchen regularly. In terms of personal hygiene and good grooming of personnel, they should strictly follow the standards indicated in sanitation for food establishments (P.D.856). Moreover, employees should be re-oriented on the importance of food safety and sanitation practices through trainings. It is further suggested that further studies should be conducted in other food chains and restaurants to check the compliance to P.D.856.

Share Article:
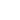
ISSN 1908-3866 (Print)
- Cite this paper
- ">Indexing metadata
- Print version
Copyright © 2024 KITE Digital Educational Solutions | Exclusively distributed by CE-Logic Terms and Conditions -->
Table of Contents
Kfc consumer profile, types of kfc marketing channels, digital marketing strategy of kfc , kfc's social media marketing , kfc marketing strategy 2024: a case study.

Committed to continuous growth, Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC) today ranks second on Forbes' list of top 10 global fast-food chains. Is it only because "it's finger-lickin' good"? No, there is more to it. The brand has always been keen to shake up its marketing strategy and engage customers more effectively. The KFC marketing strategy has been able to capture the accelerating food interests over the years spanning over 145+ countries worldwide.
Become a Certified Marketing Expert in 8 Months
KFC uses demographic segmentation to serve the target market that has both vegetarian and non-vegetarian customer segments. Its offerings cater to kids, young adults, and almost all age groups. KFC's target audience can be categorized into four groups:
- Teens and young adults
- Budget customers
Its primary customer profiles incorporate teenagers and families because most teenagers are impulsive, and they love to dine out with friends or order online to have a meal with their family. The secondary customer profile includes adults, and the tertiary customer profile has people with lower budgets.
KFC started with an undifferentiated targeting strategy as it served the same menu worldwide. However, in recent times, it has started localizing its menu for better acceptability in the market. The KFC marketing strategy incorporates two types of marketing channels: Personal and Non-personal.
Personal channels involve communicating directly with the audience, such as a KFC salesperson introducing products to a customer in person or over the telephone. Non-personal marketing channels include the use of media both online and offline, such as
- Promotion Campaigns
- PR activities
- Social Media
The KFC marketing strategy primarily includes SEO , content marketing , email marketing , social media marketing , and video marketing. However, the company pays special attention to social media marketing and uses the most popular digital marketing platforms to highlight its price and customer satisfaction.
KFC's Facebook and Twitter pages are extremely high on interactions with customers.
KFC's Facebook Pages
KFC uses Facebook as a medium to educate its customers with new offers, products, discounts, and other schemes. It also uses Facebook to address customer grievances. The brand ensures that they put across product-oriented content. It promotes online ordering facilities via social media.
KFC’s Official Facebook Page Displaying A Range of Meals
On festive occasions, the Facebook page has several animated photos that have often received tremendous responses and helped KFC connect with the audience on occasion. Their posts strike great engagement ratios, with likes soaring above 250,000 and comments reaching 5000+. On average, the total engagement level of the page is approximately 5% depicting quality interaction and engagement.
KFC's team that handles its Facebook page is extremely quick in responding to customers. They encouraged the audience to lodge a complaint of dissatisfaction at their outlets.
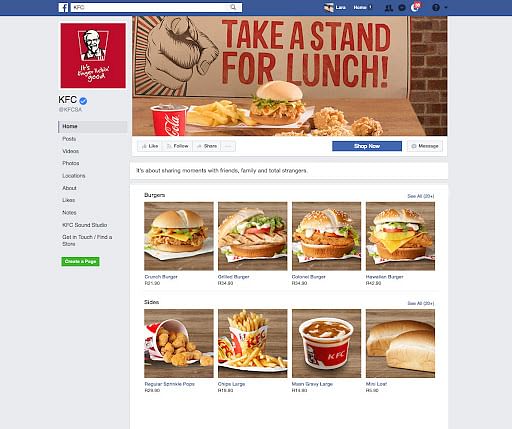
KFC's Twitter Handles
The Twitter handle of KFC is as interactive as the Facebook page. The team successfully pacifies unhappy customers and has an extremely high engagement level.
KFC’s Twitter Handle
To take interactions to the next level, the team organizes contests often integrated across Facebook and Twitter. They also promote new schemes and discounts via Twitter . Although the number of retweets or conversations on these tweets isn't quite high presently, the brand also seems focused on upscaling its business via Twitter.
KFC's Instagram Handles
KFC’s Instagram Post with the Latest Offers
KFC has several verified pages on Instagram for various countries besides its main page. It uses this digital marketing platform mainly to attract customers by posting luring images of food items on its menu. The brand also publishes posts about its present offers, new introductions, and other schemes.
KFC on Youtube
KFC India Youtube Channel Displaying Ads
Although KFC has video marketing on its list of digital marketing strategies, it uses its YouTube Channel for advertisements only. It has short videos of not more than two minutes, but the channel still has a good number of subscribers. The company uses Youtube as a secondary medium to show its ads.
KFC's Email Marketing Strategy
KFC restaurants create bulk mailings using the AMP technology to target its mobile phone users too. Its AMP emails are different from ordinary emails as these mails have interactive elements in the form of order buttons, product carousels, subscription forms, sliders, animations, an interactive showcase of meals, and more so that the emails do not get lost in the potential customer's inbox. The company also uses this strategy to segment its audience and personalize its email campaigns, targeting specific audiences. Their brand awareness campaigns lead to valuable conversions later.
Become a millennial Digital Marketer in just 6 months. Enroll now for our PGP in Digital Marketing course in collaboration with Purdue University!
The KFC marketing strategy is strong and actively uses Twitter and Facebook to attract customers, share promotions and schemes, and solve customer grievances. The potential of YouTube has still not been completely explored by them.
If you wish to formulate a stronger digital marketing strategy for your brand, enroll in Simplilearn's Post Graduate Program In Digital Marketing as the course allows you to learn from industry experts from Purdue University and Facebook. Master the digital marketing skills and take your career to the next level!
Our Digital Marketing Courses Duration And Fees
Digital Marketing Courses typically range from a few weeks to several months, with fees varying based on program and institution.
| Program Name | Duration | Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 1,699 |
| Cohort Starts: | 8 Months | € 999 |
Recommended Reads
Digital Marketing Career Guide: A Playbook to Becoming a Digital Marketing Specialist
A Case Study on Apple Marketing Strategy
Best Country to Study Abroad
Introductory Digital Marketing Guide
A Case Study on Spotify Marketing Strategy
A Complete Guide on the Types of Statistical Studies
Get Affiliated Certifications with Live Class programs
Post graduate program in digital marketing.
- Joint Purdue-Simplilearn Digital Marketer Certificate
- Become eligible to be part of the Purdue University Alumni Association
- PMP, PMI, PMBOK, CAPM, PgMP, PfMP, ACP, PBA, RMP, SP, and OPM3 are registered marks of the Project Management Institute, Inc.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Operational Strategies and Management of KFC: An Enquiry

EPRA International Journal of Research & Development (IJRD)
This is a business case report on one of the world largest fast food chain restaurants Kentucky Fried chicken (KFC) in accordance on its operation management and strategy. As the course requirement, the company has been selected on the preference of my own with a prior approval of the unit leader. The report critically analysis three operation management decision areas as design of goods and services, quality management and supply chain management of KFC with suggestions to better performance. Furthermore, it evaluates the strengths and weaknesses as well as strategies with recommendations for achieving competitive advantages. Finally, the report draws a conclusion with wrapping up the findings. KEYWORDS: Managing Quality, Supply Chain Management, SWOT Analysis, CSR
Related Papers
Piumi Tillekerathne
Critical analysis of the importance of Operations Management to the organization and how it has had an impact to the performance levels of the organization. Brief of KFC-Kentucky Fried Chicken Kentucky Fried Chicken a.k.a. KFC, is one of the leading fast food giants in the world. It is based in Louisville. It has been ranked third largest chain with more than 13000 outlets in more than 109 countries and serves approximately 12 million consumers every day. KFC is known for its original recipe for fried chicken, which is prepared using a blend of secret 11 herbs and spices (Buick, 1982). They are operating in an industry which is based on quick service and delivery to its consumers. They have managed to curtail the service time by more than 50% and improved the productivity of its employees. This helped them to outperform others and yield higher profits and sales figures (Fitzsimmons, Fitzsimmons and Bordoloi, 2014). They aim at providing continued superior service whilst non-stop improvement. It is highly crucial for them to improve the efficiently of their entire operation so as to be able to serve customers as quickly as possible. To achieve this, they have focused on all aspects, such as facility layout, quality management, total costs and infrastructure to match up with the desires and need of its consumers. i
A.M.M. Mubassher Shah
Journal of The Community Development in Asia
rivanti kawung
A fast-food restaurant, commonly known as a quick-service restaurant (QSR) in the business, is a type of eatery that specializes in fast food and offers limited table service. In the food sector, customer satisfaction and good feedback are the most important thing. Each company also has its main power source to maintain business. The goal of this study is to find how service quality can affect customer satisfaction. This study used a service quality model which is Servqual as a guide in determining customer satisfaction. The researchers chose Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC) Restaurant in Malaysia for this case study. KFC Restaurant has many competitors in the fast-food restaurant industry. The solution to these issues is to develop ways to increase service quality and customer satisfaction.
Mohamed Abdelgawwad
Emiel Sanchez
In the food industry, it is important for an organization to leverage their customer's satisfaction and this can be achieved through superior customer service. The goals of this study were to investigate the causes and problems faced by the selected restaurant and to provide suggestions on how to improve the slow customer service based on the numerous domains of operations management. A local restaurant in Kuching (M alaysia) was selected for the case study. Slow customer service has been identified as the main problem. The causes of this problem were identified and classified into four categories which involved people, environment, equipment/materials and method/procedure. This study also offered ways to improve its operational performance and overcome the problem of poor service operations. The alternatives offered include (1) Quality Function Development which helped in determining what will satisfy the customers and where to put the quality effort, (2) Total Quality M anagement (TQM), (3) process focus which uses service blueprint to strengthen the interaction between customers and the restaurant, (4) layout , (5) human resource management, (6) practice of good supply chain management , and (7) maintenance to get the most benefits and trouble-free services out of the restaurant equipment by performing regular maintenance. This paper hopes to provide relevant insights for service quality and customer satisfaction improvement for restaurant service operations.
CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research - Zenodo
Justine Beryl Ruth Gumbao
This study integrates the Kano two‐dimensional quality model and quality function deployment (QFD) to construct a systematic mechanism for food and beverage service planning and improvement. This study adopts a three stage research framework: 1. Surveying food and beverage service needs, 2. Extracting key quality factors for food and beverage service, 3. Proposing methods for improving food and beverage service. Based on the results of this research, the most five important improvement action plans are personal professional skills and knowledge, increasing the visibility of restaurant advertising, providing immediate feedback to customers, standardizing quality of ingredient purchasing, and improving time efficiency of meal preparation.
Ganesh Laulkar
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Tourism, Economics, Accounting, Management, and Social Science (TEAMS 2021)
Antonio E . L . Nyoko
Zulkifli Mohamed Udin
Rano Abryanto
Journal of Industrial Engineering and Halal Industries
RAHMA FARIZA
Shivneil Raj
The IMC Sourcebook Book: Readings and Cases in Integrated Marketing Communications
Bela Florenthal , Manar Awad
Muhammad Farooq Jan
Chenoy Ceil
Annie Gay Espino
American Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Innovation (AJMRI) ISSN: 2158-8155 (Online), 2832-4854 (Print)
Joy Dhon Chakma , Ricky Francis Rozario
DISSERTATION
Dickson Manyere
Do Quoc Viet Anh
MATEC Web of Conferences
AGUSTINA WINDARYANTI
Farida Komalasari
Prof. Nimit Chowdhary
Australasian Marketing Journal (AMJ)
Paul Patterson
International Journal of Engineering Materials and Manufacture
Abdullah Alrashidi
SHAIRA ISMAIL
IJSRP Journal
Scientific Bulletin – Economic Sciences
Dr. Waqar Badshah
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

COMMENTS
It also earns from its franchise agreement through its licensing fees. As of 2022, KFC earned around US$ 31.116 billion worth of total revenue. The annual revenue for 2022 was 6.8 billion, which was estimated to be a 3.92% growth from 2021. Let us now see the cost structure of KFC.
Case Studies C24.1. Joll ibee Food s Corpora tion. Leonar do R. Garci a Jr., Chr istopher Lovelock, and Jo chen Wirtz. A Philippine fast food company has achieved market dominance in three ...
The case of KFC Philippines demonstrates an example of effective risk management that protects a company from economic losses and damage to its reputation. ... as a former employee of KFC Philippines, I will present a case study of the risk management processes of this franchise based on my work experience, internal information about the ...
Nov 22, 2018. KFC: A very fcking clever campaign. CASE STUDY: The inside story on how the brand and its agency, Mother, dragged victory from the jaws of potentially disastrous supply issues in the UK. It was the calamity that had the UK choking on its chicken. When KFC's "#ChickenCrisis" became international news in February 2018, after the ...
3 CASE STUDY OF KFC. KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken) is a fast food company affiliated to Parkson Retail Group, and its company business mainly include providing eat-in services, and the impact of the pandemic on Yum Brands continues to expand. Following shutting down one third of global restaurants, it is reported that, Yum Brands has temporally ...
Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC) is the world's well-known global brand of fast food that has more than 26,000 restaurants in over 150 countries and territories around the world.
KFC-CASE-STUDY - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. This document discusses a case study of a KFC branch in Cubao, Quezon City, Philippines that was experiencing long wait times for customers due to staffing issues. Specifically, staff scheduling was not optimized, with shifts planned only a short time in advance, excluding long ...
This is a business case report on one of the world largest fast food chain restaurants Kentucky Fried chicken (KFC) in accordance on its operation management and strategy. As the course ...
This study used a service quality model which is Servqual as a guide in determining customer satisfaction. The researchers chose Kentucky Fried Chicken (KFC) Restaurant in Malaysia for this case study. KFC Restaurant has many competitors in the fast-food restaurant industry.
Before the outbreak of the Covid-19 pandemic, the fast food restaurant benefits a lot from the process of globalization, while they lose the benefit when the pandemic causes a lot of limitations on the cross-boarder flow of commodities and people. By taking KFC as an example, based on the analysis, it is found that the reasons behind such ...
By 1963, the number of KFC franchises had crossed 300. Colonel Sanders, at 74 years of age was tired of running the daily operations and sold the business in 1964 to two Louisville businessmen — Jack Massey and John Young Brown, Jr. — for $2 million. Brown, who later became the governor of Kentucky, was named president, and Massey was named ...
<p>The case study aimed to evaluate the food safety and sanitation practices of KFC in Crossing, Calamba City, Laguna. It also aimed to check if the actual practices of KFC personnel complied with the sanitation for food establishments as stated in P.D.856.The study adopted the evaluative research method and survey questionnaire was used to gather the needed data.</p> <p>It was found out that ...
673 Quirino Highway, San Bartolome, Novaliches, Quezon City College of Engineering Industrial Engineering Department Delineates the scope of the system This study focuses on the customers of the fast-food chain - KFC - from the branch of Cubao, Quezon City, Philippines. This case is designed to have a thorough knowledge of problems between ...
Case study . 2.1 KFC . 2.1.1 Profile . ... It mainly sells fried chicken hamburgers, French fries, soft drinks and other Western fast food. KFC belongs to the world's biggest food group Parkson restaurants group- It . has more than 3.3 chain stores and 840000 employees, in its more than 100 countries
ORCID ID: 0000-0002-2501-1019. ABSTRA CT. The purpose of this study is to examine consumer satisfaction towards Kentucky Fried. Chicken Corporation (KFC). This pa per is presenting what are the ...
The KFC marketing strategy incorporates two types of marketing channels: Personal and Non-personal. Personal channels involve communicating directly with the audience, such as a KFC salesperson introducing products to a customer in person or over the telephone. Non-personal marketing channels include the use of media both online and offline ...
This is a business case report on one of the world largest fast food chain restaurants Kentucky Fried chicken (KFC) in accordance on its operation management and strategy. As the course requirement, the company has been selected on the preference of my own with a prior approval of the unit leader. The report critically analysis three operation ...
Financial Statement Analysis of KFC. Saree Abdullah Brake. Abu Dhabi University, Email: [email protected]. Supervised by: Professor Haitham Nobanee. Abstract. Financial ratios derived ...
CASE STUDY ABOUT KFC CONTROVERSY KENTUCKY FRIED CHICKEN (KFC) KENTUCKY FRIED CHICKEN BRANCH BANGALORE, INDIA. Name of the company : ... In 1967 the Philippines open the first store in KFC With the rise of delicious and new food creations came growth of the business in numbers. Filipinos from all over the country craved KFC so much so that on ...