
25 Thesis Statement Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
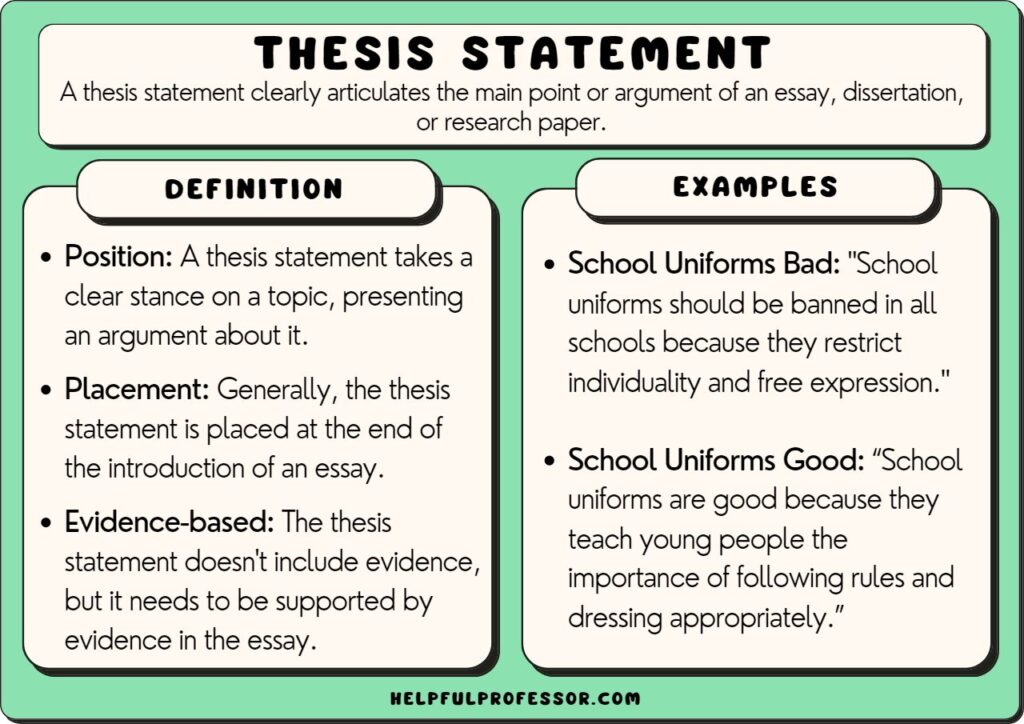
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Number Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Word Games for Kids (Free and Easy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Outdoor Games for Kids
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 50 Incentives to Give to Students
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples
Published on January 11, 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on August 15, 2023 by Eoghan Ryan.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . It usually comes near the end of your introduction .
Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you’re writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your essay should relate back to this idea.
You can write your thesis statement by following four simple steps:
- Start with a question
- Write your initial answer
- Develop your answer
- Refine your thesis statement
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is a thesis statement, placement of the thesis statement, step 1: start with a question, step 2: write your initial answer, step 3: develop your answer, step 4: refine your thesis statement, types of thesis statements, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement summarizes the central points of your essay. It is a signpost telling the reader what the essay will argue and why.
The best thesis statements are:
- Concise: A good thesis statement is short and sweet—don’t use more words than necessary. State your point clearly and directly in one or two sentences.
- Contentious: Your thesis shouldn’t be a simple statement of fact that everyone already knows. A good thesis statement is a claim that requires further evidence or analysis to back it up.
- Coherent: Everything mentioned in your thesis statement must be supported and explained in the rest of your paper.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
The thesis statement generally appears at the end of your essay introduction or research paper introduction .
The spread of the internet has had a world-changing effect, not least on the world of education. The use of the internet in academic contexts and among young people more generally is hotly debated. For many who did not grow up with this technology, its effects seem alarming and potentially harmful. This concern, while understandable, is misguided. The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education: the internet facilitates easier access to information, exposure to different perspectives, and a flexible learning environment for both students and teachers.
You should come up with an initial thesis, sometimes called a working thesis , early in the writing process . As soon as you’ve decided on your essay topic , you need to work out what you want to say about it—a clear thesis will give your essay direction and structure.
You might already have a question in your assignment, but if not, try to come up with your own. What would you like to find out or decide about your topic?
For example, you might ask:
After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process .
Receive feedback on language, structure, and formatting
Professional editors proofread and edit your paper by focusing on:
- Academic style
- Vague sentences
- Style consistency
See an example

Now you need to consider why this is your answer and how you will convince your reader to agree with you. As you read more about your topic and begin writing, your answer should get more detailed.
In your essay about the internet and education, the thesis states your position and sketches out the key arguments you’ll use to support it.
The negatives of internet use are outweighed by its many benefits for education because it facilitates easier access to information.
In your essay about braille, the thesis statement summarizes the key historical development that you’ll explain.
The invention of braille in the 19th century transformed the lives of blind people, allowing them to participate more actively in public life.
A strong thesis statement should tell the reader:
- Why you hold this position
- What they’ll learn from your essay
- The key points of your argument or narrative
The final thesis statement doesn’t just state your position, but summarizes your overall argument or the entire topic you’re going to explain. To strengthen a weak thesis statement, it can help to consider the broader context of your topic.
These examples are more specific and show that you’ll explore your topic in depth.
Your thesis statement should match the goals of your essay, which vary depending on the type of essay you’re writing:
- In an argumentative essay , your thesis statement should take a strong position. Your aim in the essay is to convince your reader of this thesis based on evidence and logical reasoning.
- In an expository essay , you’ll aim to explain the facts of a topic or process. Your thesis statement doesn’t have to include a strong opinion in this case, but it should clearly state the central point you want to make, and mention the key elements you’ll explain.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay . Everything else you write should relate to this key idea.
The thesis statement is essential in any academic essay or research paper for two main reasons:
- It gives your writing direction and focus.
- It gives the reader a concise summary of your main point.
Without a clear thesis statement, an essay can end up rambling and unfocused, leaving your reader unsure of exactly what you want to say.
Follow these four steps to come up with a thesis statement :
- Ask a question about your topic .
- Write your initial answer.
- Develop your answer by including reasons.
- Refine your answer, adding more detail and nuance.
The thesis statement should be placed at the end of your essay introduction .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, August 15). How to Write a Thesis Statement | 4 Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 12, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/thesis-statement/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write an essay introduction | 4 steps & examples, how to write topic sentences | 4 steps, examples & purpose, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Reference management. Clean and simple.
How to write a thesis statement + examples

What is a thesis statement?
Is a thesis statement a question, how do you write a good thesis statement, how do i know if my thesis statement is good, examples of thesis statements, helpful resources on how to write a thesis statement, frequently asked questions about writing a thesis statement, related articles.
A thesis statement is the main argument of your paper or thesis.
The thesis statement is one of the most important elements of any piece of academic writing . It is a brief statement of your paper’s main argument. Essentially, you are stating what you will be writing about.
You can see your thesis statement as an answer to a question. While it also contains the question, it should really give an answer to the question with new information and not just restate or reiterate it.
Your thesis statement is part of your introduction. Learn more about how to write a good thesis introduction in our introduction guide .
A thesis statement is not a question. A statement must be arguable and provable through evidence and analysis. While your thesis might stem from a research question, it should be in the form of a statement.
Tip: A thesis statement is typically 1-2 sentences. For a longer project like a thesis, the statement may be several sentences or a paragraph.
A good thesis statement needs to do the following:
- Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences.
- Answer your project’s main research question.
- Clearly state your position in relation to the topic .
- Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
Once you have written down a thesis statement, check if it fulfills the following criteria:
- Your statement needs to be provable by evidence. As an argument, a thesis statement needs to be debatable.
- Your statement needs to be precise. Do not give away too much information in the thesis statement and do not load it with unnecessary information.
- Your statement cannot say that one solution is simply right or simply wrong as a matter of fact. You should draw upon verified facts to persuade the reader of your solution, but you cannot just declare something as right or wrong.
As previously mentioned, your thesis statement should answer a question.
If the question is:
What do you think the City of New York should do to reduce traffic congestion?
A good thesis statement restates the question and answers it:
In this paper, I will argue that the City of New York should focus on providing exclusive lanes for public transport and adaptive traffic signals to reduce traffic congestion by the year 2035.
Here is another example. If the question is:
How can we end poverty?
A good thesis statement should give more than one solution to the problem in question:
In this paper, I will argue that introducing universal basic income can help reduce poverty and positively impact the way we work.
- The Writing Center of the University of North Carolina has a list of questions to ask to see if your thesis is strong .
A thesis statement is part of the introduction of your paper. It is usually found in the first or second paragraph to let the reader know your research purpose from the beginning.
In general, a thesis statement should have one or two sentences. But the length really depends on the overall length of your project. Take a look at our guide about the length of thesis statements for more insight on this topic.
Here is a list of Thesis Statement Examples that will help you understand better how to write them.
Every good essay should include a thesis statement as part of its introduction, no matter the academic level. Of course, if you are a high school student you are not expected to have the same type of thesis as a PhD student.
Here is a great YouTube tutorial showing How To Write An Essay: Thesis Statements .


Thesis Statements
What this handout is about.
This handout describes what a thesis statement is, how thesis statements work in your writing, and how you can craft or refine one for your draft.
Introduction
Writing in college often takes the form of persuasion—convincing others that you have an interesting, logical point of view on the subject you are studying. Persuasion is a skill you practice regularly in your daily life. You persuade your roommate to clean up, your parents to let you borrow the car, your friend to vote for your favorite candidate or policy. In college, course assignments often ask you to make a persuasive case in writing. You are asked to convince your reader of your point of view. This form of persuasion, often called academic argument, follows a predictable pattern in writing. After a brief introduction of your topic, you state your point of view on the topic directly and often in one sentence. This sentence is the thesis statement, and it serves as a summary of the argument you’ll make in the rest of your paper.
What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement:
- tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion.
- is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper.
- directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself. The subject, or topic, of an essay might be World War II or Moby Dick; a thesis must then offer a way to understand the war or the novel.
- makes a claim that others might dispute.
- is usually a single sentence near the beginning of your paper (most often, at the end of the first paragraph) that presents your argument to the reader. The rest of the paper, the body of the essay, gathers and organizes evidence that will persuade the reader of the logic of your interpretation.
If your assignment asks you to take a position or develop a claim about a subject, you may need to convey that position or claim in a thesis statement near the beginning of your draft. The assignment may not explicitly state that you need a thesis statement because your instructor may assume you will include one. When in doubt, ask your instructor if the assignment requires a thesis statement. When an assignment asks you to analyze, to interpret, to compare and contrast, to demonstrate cause and effect, or to take a stand on an issue, it is likely that you are being asked to develop a thesis and to support it persuasively. (Check out our handout on understanding assignments for more information.)
How do I create a thesis?
A thesis is the result of a lengthy thinking process. Formulating a thesis is not the first thing you do after reading an essay assignment. Before you develop an argument on any topic, you have to collect and organize evidence, look for possible relationships between known facts (such as surprising contrasts or similarities), and think about the significance of these relationships. Once you do this thinking, you will probably have a “working thesis” that presents a basic or main idea and an argument that you think you can support with evidence. Both the argument and your thesis are likely to need adjustment along the way.
Writers use all kinds of techniques to stimulate their thinking and to help them clarify relationships or comprehend the broader significance of a topic and arrive at a thesis statement. For more ideas on how to get started, see our handout on brainstorming .
How do I know if my thesis is strong?
If there’s time, run it by your instructor or make an appointment at the Writing Center to get some feedback. Even if you do not have time to get advice elsewhere, you can do some thesis evaluation of your own. When reviewing your first draft and its working thesis, ask yourself the following :
- Do I answer the question? Re-reading the question prompt after constructing a working thesis can help you fix an argument that misses the focus of the question. If the prompt isn’t phrased as a question, try to rephrase it. For example, “Discuss the effect of X on Y” can be rephrased as “What is the effect of X on Y?”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? If your thesis simply states facts that no one would, or even could, disagree with, it’s possible that you are simply providing a summary, rather than making an argument.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? Thesis statements that are too vague often do not have a strong argument. If your thesis contains words like “good” or “successful,” see if you could be more specific: why is something “good”; what specifically makes something “successful”?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? If a reader’s first response is likely to be “So what?” then you need to clarify, to forge a relationship, or to connect to a larger issue.
- Does my essay support my thesis specifically and without wandering? If your thesis and the body of your essay do not seem to go together, one of them has to change. It’s okay to change your working thesis to reflect things you have figured out in the course of writing your paper. Remember, always reassess and revise your writing as necessary.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? If a reader’s first response is “how?” or “why?” your thesis may be too open-ended and lack guidance for the reader. See what you can add to give the reader a better take on your position right from the beginning.
Suppose you are taking a course on contemporary communication, and the instructor hands out the following essay assignment: “Discuss the impact of social media on public awareness.” Looking back at your notes, you might start with this working thesis:
Social media impacts public awareness in both positive and negative ways.
You can use the questions above to help you revise this general statement into a stronger thesis.
- Do I answer the question? You can analyze this if you rephrase “discuss the impact” as “what is the impact?” This way, you can see that you’ve answered the question only very generally with the vague “positive and negative ways.”
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not likely. Only people who maintain that social media has a solely positive or solely negative impact could disagree.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? No. What are the positive effects? What are the negative effects?
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? No. Why are they positive? How are they positive? What are their causes? Why are they negative? How are they negative? What are their causes?
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? No. Why should anyone care about the positive and/or negative impact of social media?
After thinking about your answers to these questions, you decide to focus on the one impact you feel strongly about and have strong evidence for:
Because not every voice on social media is reliable, people have become much more critical consumers of information, and thus, more informed voters.
This version is a much stronger thesis! It answers the question, takes a specific position that others can challenge, and it gives a sense of why it matters.
Let’s try another. Suppose your literature professor hands out the following assignment in a class on the American novel: Write an analysis of some aspect of Mark Twain’s novel Huckleberry Finn. “This will be easy,” you think. “I loved Huckleberry Finn!” You grab a pad of paper and write:
Mark Twain’s Huckleberry Finn is a great American novel.
You begin to analyze your thesis:
- Do I answer the question? No. The prompt asks you to analyze some aspect of the novel. Your working thesis is a statement of general appreciation for the entire novel.
Think about aspects of the novel that are important to its structure or meaning—for example, the role of storytelling, the contrasting scenes between the shore and the river, or the relationships between adults and children. Now you write:
In Huckleberry Finn, Mark Twain develops a contrast between life on the river and life on the shore.
- Do I answer the question? Yes!
- Have I taken a position that others might challenge or oppose? Not really. This contrast is well-known and accepted.
- Is my thesis statement specific enough? It’s getting there–you have highlighted an important aspect of the novel for investigation. However, it’s still not clear what your analysis will reveal.
- Does my thesis pass the “how and why?” test? Not yet. Compare scenes from the book and see what you discover. Free write, make lists, jot down Huck’s actions and reactions and anything else that seems interesting.
- Does my thesis pass the “So what?” test? What’s the point of this contrast? What does it signify?”
After examining the evidence and considering your own insights, you write:
Through its contrasting river and shore scenes, Twain’s Huckleberry Finn suggests that to find the true expression of American democratic ideals, one must leave “civilized” society and go back to nature.
This final thesis statement presents an interpretation of a literary work based on an analysis of its content. Of course, for the essay itself to be successful, you must now present evidence from the novel that will convince the reader of your interpretation.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Anson, Chris M., and Robert A. Schwegler. 2010. The Longman Handbook for Writers and Readers , 6th ed. New York: Longman.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Ramage, John D., John C. Bean, and June Johnson. 2018. The Allyn & Bacon Guide to Writing , 8th ed. New York: Pearson.
Ruszkiewicz, John J., Christy Friend, Daniel Seward, and Maxine Hairston. 2010. The Scott, Foresman Handbook for Writers , 9th ed. Boston: Pearson Education.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Tips and Examples for Writing Thesis Statements

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Tips for Writing Your Thesis Statement
1. Determine what kind of paper you are writing:
- An analytical paper breaks down an issue or an idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents this breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- An expository (explanatory) paper explains something to the audience.
- An argumentative paper makes a claim about a topic and justifies this claim with specific evidence. The claim could be an opinion, a policy proposal, an evaluation, a cause-and-effect statement, or an interpretation. The goal of the argumentative paper is to convince the audience that the claim is true based on the evidence provided.
If you are writing a text that does not fall under these three categories (e.g., a narrative), a thesis statement somewhere in the first paragraph could still be helpful to your reader.
2. Your thesis statement should be specific—it should cover only what you will discuss in your paper and should be supported with specific evidence.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper.
4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper.
Thesis Statement Examples
Example of an analytical thesis statement:
The paper that follows should:
- Explain the analysis of the college admission process
- Explain the challenge facing admissions counselors
Example of an expository (explanatory) thesis statement:
- Explain how students spend their time studying, attending class, and socializing with peers
Example of an argumentative thesis statement:
- Present an argument and give evidence to support the claim that students should pursue community projects before entering college
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
How to Write a Strong Thesis Statement: 4 Steps + Examples

What’s Covered:
What is the purpose of a thesis statement, writing a good thesis statement: 4 steps, common pitfalls to avoid, where to get your essay edited for free.
When you set out to write an essay, there has to be some kind of point to it, right? Otherwise, your essay would just be a big jumble of word salad that makes absolutely no sense. An essay needs a central point that ties into everything else. That main point is called a thesis statement, and it’s the core of any essay or research paper.
You may hear about Master degree candidates writing a thesis, and that is an entire paper–not to be confused with the thesis statement, which is typically one sentence that contains your paper’s focus.
Read on to learn more about thesis statements and how to write them. We’ve also included some solid examples for you to reference.
Typically the last sentence of your introductory paragraph, the thesis statement serves as the roadmap for your essay. When your reader gets to the thesis statement, they should have a clear outline of your main point, as well as the information you’ll be presenting in order to either prove or support your point.
The thesis statement should not be confused for a topic sentence , which is the first sentence of every paragraph in your essay. If you need help writing topic sentences, numerous resources are available. Topic sentences should go along with your thesis statement, though.
Since the thesis statement is the most important sentence of your entire essay or paper, it’s imperative that you get this part right. Otherwise, your paper will not have a good flow and will seem disjointed. That’s why it’s vital not to rush through developing one. It’s a methodical process with steps that you need to follow in order to create the best thesis statement possible.
Step 1: Decide what kind of paper you’re writing
When you’re assigned an essay, there are several different types you may get. Argumentative essays are designed to get the reader to agree with you on a topic. Informative or expository essays present information to the reader. Analytical essays offer up a point and then expand on it by analyzing relevant information. Thesis statements can look and sound different based on the type of paper you’re writing. For example:
- Argumentative: The United States needs a viable third political party to decrease bipartisanship, increase options, and help reduce corruption in government.
- Informative: The Libertarian party has thrown off elections before by gaining enough support in states to get on the ballot and by taking away crucial votes from candidates.
- Analytical: An analysis of past presidential elections shows that while third party votes may have been the minority, they did affect the outcome of the elections in 2020, 2016, and beyond.
Step 2: Figure out what point you want to make
Once you know what type of paper you’re writing, you then need to figure out the point you want to make with your thesis statement, and subsequently, your paper. In other words, you need to decide to answer a question about something, such as:
- What impact did reality TV have on American society?
- How has the musical Hamilton affected perception of American history?
- Why do I want to major in [chosen major here]?
If you have an argumentative essay, then you will be writing about an opinion. To make it easier, you may want to choose an opinion that you feel passionate about so that you’re writing about something that interests you. For example, if you have an interest in preserving the environment, you may want to choose a topic that relates to that.
If you’re writing your college essay and they ask why you want to attend that school, you may want to have a main point and back it up with information, something along the lines of:
“Attending Harvard University would benefit me both academically and professionally, as it would give me a strong knowledge base upon which to build my career, develop my network, and hopefully give me an advantage in my chosen field.”
Step 3: Determine what information you’ll use to back up your point
Once you have the point you want to make, you need to figure out how you plan to back it up throughout the rest of your essay. Without this information, it will be hard to either prove or argue the main point of your thesis statement. If you decide to write about the Hamilton example, you may decide to address any falsehoods that the writer put into the musical, such as:
“The musical Hamilton, while accurate in many ways, leaves out key parts of American history, presents a nationalist view of founding fathers, and downplays the racism of the times.”
Once you’ve written your initial working thesis statement, you’ll then need to get information to back that up. For example, the musical completely leaves out Benjamin Franklin, portrays the founding fathers in a nationalist way that is too complimentary, and shows Hamilton as a staunch abolitionist despite the fact that his family likely did own slaves.
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing
Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and that you feel like you can truly write a paper on the topic. Once you’ve done that, you can then begin writing your paper.
When writing a thesis statement, there are some common pitfalls you should avoid so that your paper can be as solid as possible. Make sure you always edit the thesis statement before you do anything else. You also want to ensure that the thesis statement is clear and concise. Don’t make your reader hunt for your point. Finally, put your thesis statement at the end of the first paragraph and have your introduction flow toward that statement. Your reader will expect to find your statement in its traditional spot.
If you’re having trouble getting started, or need some guidance on your essay, there are tools available that can help you. CollegeVine offers a free peer essay review tool where one of your peers can read through your essay and provide you with valuable feedback. Getting essay feedback from a peer can help you wow your instructor or college admissions officer with an impactful essay that effectively illustrates your point.

Related CollegeVine Blog Posts

While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
How to Write a Solid Thesis Statement
The important sentence expresses your central assertion or argument
arabianEye / Getty Images
- Writing Research Papers
- Writing Essays
- English Grammar
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
A thesis statement provides the foundation for your entire research paper or essay. This statement is the central assertion that you want to express in your essay. A successful thesis statement is one that is made up of one or two sentences clearly laying out your central idea and expressing an informed, reasoned answer to your research question.
Usually, the thesis statement will appear at the end of the first paragraph of your paper. There are a few different types, and the content of your thesis statement will depend upon the type of paper you’re writing.
Key Takeaways: Writing a Thesis Statement
- A thesis statement gives your reader a preview of your paper's content by laying out your central idea and expressing an informed, reasoned answer to your research question.
- Thesis statements will vary depending on the type of paper you are writing, such as an expository essay, argument paper, or analytical essay.
- Before creating a thesis statement, determine whether you are defending a stance, giving an overview of an event, object, or process, or analyzing your subject
Expository Essay Thesis Statement Examples
An expository essay "exposes" the reader to a new topic; it informs the reader with details, descriptions, or explanations of a subject. If you are writing an expository essay , your thesis statement should explain to the reader what she will learn in your essay. For example:
- The United States spends more money on its military budget than all the industrialized nations combined.
- Gun-related homicides and suicides are increasing after years of decline.
- Hate crimes have increased three years in a row, according to the FBI.
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) increases the risk of stroke and arterial fibrillation (irregular heartbeat).
These statements provide a statement of fact about the topic (not just opinion) but leave the door open for you to elaborate with plenty of details. In an expository essay, you don't need to develop an argument or prove anything; you only need to understand your topic and present it in a logical manner. A good thesis statement in an expository essay always leaves the reader wanting more details.
Types of Thesis Statements
Before creating a thesis statement, it's important to ask a few basic questions, which will help you determine the kind of essay or paper you plan to create:
- Are you defending a stance in a controversial essay ?
- Are you simply giving an overview or describing an event, object, or process?
- Are you conducting an analysis of an event, object, or process?
In every thesis statement , you will give the reader a preview of your paper's content, but the message will differ a little depending on the essay type .
Argument Thesis Statement Examples
If you have been instructed to take a stance on one side of a controversial issue, you will need to write an argument essay . Your thesis statement should express the stance you are taking and may give the reader a preview or a hint of your evidence. The thesis of an argument essay could look something like the following:
- Self-driving cars are too dangerous and should be banned from the roadways.
- The exploration of outer space is a waste of money; instead, funds should go toward solving issues on Earth, such as poverty, hunger, global warming, and traffic congestion.
- The U.S. must crack down on illegal immigration.
- Street cameras and street-view maps have led to a total loss of privacy in the United States and elsewhere.
These thesis statements are effective because they offer opinions that can be supported by evidence. If you are writing an argument essay, you can craft your own thesis around the structure of the statements above.
Analytical Essay Thesis Statement Examples
In an analytical essay assignment, you will be expected to break down a topic, process, or object in order to observe and analyze your subject piece by piece. Examples of a thesis statement for an analytical essay include:
- The criminal justice reform bill passed by the U.S. Senate in late 2018 (" The First Step Act ") aims to reduce prison sentences that disproportionately fall on nonwhite criminal defendants.
- The rise in populism and nationalism in the U.S. and European democracies has coincided with the decline of moderate and centrist parties that have dominated since WWII.
- Later-start school days increase student success for a variety of reasons.
Because the role of the thesis statement is to state the central message of your entire paper, it is important to revisit (and maybe rewrite) your thesis statement after the paper is written. In fact, it is quite normal for your message to change as you construct your paper.
- The Introductory Paragraph: Start Your Paper Off Right
- Revising a Paper
- Your Personal Essay Thesis Sentence
- How to Develop a Research Paper Timeline
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- How to Narrow the Research Topic for Your Paper
- World War II Research Essay Topics
- What Is a Senior Thesis?
- How to Use Verbs Effectively in Your Research Paper
- When to Cite a Source in a Paper
- Writing an Annotated Bibliography for a Paper
- Finding Trustworthy Sources
- How to Write a 10-Page Research Paper
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- What Is an Autobiography?
- Finding Statistics and Data for Research Papers
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

What is a thesis | A Complete Guide with Examples

Table of Contents
A thesis is a comprehensive academic paper based on your original research that presents new findings, arguments, and ideas of your study. It’s typically submitted at the end of your master’s degree or as a capstone of your bachelor’s degree.
However, writing a thesis can be laborious, especially for beginners. From the initial challenge of pinpointing a compelling research topic to organizing and presenting findings, the process is filled with potential pitfalls.
Therefore, to help you, this guide talks about what is a thesis. Additionally, it offers revelations and methodologies to transform it from an overwhelming task to a manageable and rewarding academic milestone.
What is a thesis?
A thesis is an in-depth research study that identifies a particular topic of inquiry and presents a clear argument or perspective about that topic using evidence and logic.
Writing a thesis showcases your ability of critical thinking, gathering evidence, and making a compelling argument. Integral to these competencies is thorough research, which not only fortifies your propositions but also confers credibility to your entire study.
Furthermore, there's another phenomenon you might often confuse with the thesis: the ' working thesis .' However, they aren't similar and shouldn't be used interchangeably.
A working thesis, often referred to as a preliminary or tentative thesis, is an initial version of your thesis statement. It serves as a draft or a starting point that guides your research in its early stages.
As you research more and gather more evidence, your initial thesis (aka working thesis) might change. It's like a starting point that can be adjusted as you learn more. It's normal for your main topic to change a few times before you finalize it.
While a thesis identifies and provides an overarching argument, the key to clearly communicating the central point of that argument lies in writing a strong thesis statement.
What is a thesis statement?
A strong thesis statement (aka thesis sentence) is a concise summary of the main argument or claim of the paper. It serves as a critical anchor in any academic work, succinctly encapsulating the primary argument or main idea of the entire paper.
Typically found within the introductory section, a strong thesis statement acts as a roadmap of your thesis, directing readers through your arguments and findings. By delineating the core focus of your investigation, it offers readers an immediate understanding of the context and the gravity of your study.
Furthermore, an effectively crafted thesis statement can set forth the boundaries of your research, helping readers anticipate the specific areas of inquiry you are addressing.
Different types of thesis statements
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers.
Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements:
Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
Purpose : To convince the reader of a particular stance or point of view by presenting evidence and formulating a compelling argument.
Example : Reducing plastic use in daily life is essential for environmental health.
Analytical thesis statement
Purpose : To break down an idea or issue into its components and evaluate it.
Example : By examining the long-term effects, social implications, and economic impact of climate change, it becomes evident that immediate global action is necessary.
Expository (or Descriptive) thesis statement
Purpose : To explain a topic or subject to the reader.
Example : The Great Depression, spanning the 1930s, was a severe worldwide economic downturn triggered by a stock market crash, bank failures, and reduced consumer spending.
Cause and effect thesis statement
Purpose : To demonstrate a cause and its resulting effect.
Example : Overuse of smartphones can lead to impaired sleep patterns, reduced face-to-face social interactions, and increased levels of anxiety.
Compare and contrast thesis statement
Purpose : To highlight similarities and differences between two subjects.
Example : "While both novels '1984' and 'Brave New World' delve into dystopian futures, they differ in their portrayal of individual freedom, societal control, and the role of technology."
When you write a thesis statement , it's important to ensure clarity and precision, so the reader immediately understands the central focus of your work.
What is the difference between a thesis and a thesis statement?
While both terms are frequently used interchangeably, they have distinct meanings.
A thesis refers to the entire research document, encompassing all its chapters and sections. In contrast, a thesis statement is a brief assertion that encapsulates the central argument of the research.
Here’s an in-depth differentiation table of a thesis and a thesis statement.
Aspect | Thesis | Thesis Statement |
Definition | An extensive document presenting the author's research and findings, typically for a degree or professional qualification. | A concise sentence or two in an essay or research paper that outlines the main idea or argument. |
Position | It’s the entire document on its own. | Typically found at the end of the introduction of an essay, research paper, or thesis. |
Components | Introduction, methodology, results, conclusions, and bibliography or references. | Doesn't include any specific components |
Purpose | Provides detailed research, presents findings, and contributes to a field of study. | To guide the reader about the main point or argument of the paper or essay. |
Now, to craft a compelling thesis, it's crucial to adhere to a specific structure. Let’s break down these essential components that make up a thesis structure
15 components of a thesis structure
Navigating a thesis can be daunting. However, understanding its structure can make the process more manageable.
Here are the key components or different sections of a thesis structure:
Your thesis begins with the title page. It's not just a formality but the gateway to your research.

Here, you'll prominently display the necessary information about you (the author) and your institutional details.
- Title of your thesis
- Your full name
- Your department
- Your institution and degree program
- Your submission date
- Your Supervisor's name (in some cases)
- Your Department or faculty (in some cases)
- Your University's logo (in some cases)
- Your Student ID (in some cases)
In a concise manner, you'll have to summarize the critical aspects of your research in typically no more than 200-300 words.

This includes the problem statement, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. For many, the abstract will determine if they delve deeper into your work, so ensure it's clear and compelling.
Acknowledgments
Research is rarely a solitary endeavor. In the acknowledgments section, you have the chance to express gratitude to those who've supported your journey.

This might include advisors, peers, institutions, or even personal sources of inspiration and support. It's a personal touch, reflecting the humanity behind the academic rigor.
Table of contents
A roadmap for your readers, the table of contents lists the chapters, sections, and subsections of your thesis.

By providing page numbers, you allow readers to navigate your work easily, jumping to sections that pique their interest.
List of figures and tables
Research often involves data, and presenting this data visually can enhance understanding. This section provides an organized listing of all figures and tables in your thesis.

It's a visual index, ensuring that readers can quickly locate and reference your graphical data.
Introduction
Here's where you introduce your research topic, articulate the research question or objective, and outline the significance of your study.

- Present the research topic : Clearly articulate the central theme or subject of your research.
- Background information : Ground your research topic, providing any necessary context or background information your readers might need to understand the significance of your study.
- Define the scope : Clearly delineate the boundaries of your research, indicating what will and won't be covered.
- Literature review : Introduce any relevant existing research on your topic, situating your work within the broader academic conversation and highlighting where your research fits in.
- State the research Question(s) or objective(s) : Clearly articulate the primary questions or objectives your research aims to address.
- Outline the study's structure : Give a brief overview of how the subsequent sections of your work will unfold, guiding your readers through the journey ahead.
The introduction should captivate your readers, making them eager to delve deeper into your research journey.
Literature review section
Your study correlates with existing research. Therefore, in the literature review section, you'll engage in a dialogue with existing knowledge, highlighting relevant studies, theories, and findings.

It's here that you identify gaps in the current knowledge, positioning your research as a bridge to new insights.
To streamline this process, consider leveraging AI tools. For example, the SciSpace literature review tool enables you to efficiently explore and delve into research papers, simplifying your literature review journey.
Methodology
In the research methodology section, you’ll detail the tools, techniques, and processes you employed to gather and analyze data. This section will inform the readers about how you approached your research questions and ensures the reproducibility of your study.

Here's a breakdown of what it should encompass:
- Research Design : Describe the overall structure and approach of your research. Are you conducting a qualitative study with in-depth interviews? Or is it a quantitative study using statistical analysis? Perhaps it's a mixed-methods approach?
- Data Collection : Detail the methods you used to gather data. This could include surveys, experiments, observations, interviews, archival research, etc. Mention where you sourced your data, the duration of data collection, and any tools or instruments used.
- Sampling : If applicable, explain how you selected participants or data sources for your study. Discuss the size of your sample and the rationale behind choosing it.
- Data Analysis : Describe the techniques and tools you used to process and analyze the data. This could range from statistical tests in quantitative research to thematic analysis in qualitative research.
- Validity and Reliability : Address the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your findings to ensure that your results are both accurate and consistent.
- Ethical Considerations : Highlight any ethical issues related to your research and the measures you took to address them, including — informed consent, confidentiality, and data storage and protection measures.
Moreover, different research questions necessitate different types of methodologies. For instance:
- Experimental methodology : Often used in sciences, this involves a controlled experiment to discern causality.
- Qualitative methodology : Employed when exploring patterns or phenomena without numerical data. Methods can include interviews, focus groups, or content analysis.
- Quantitative methodology : Concerned with measurable data and often involves statistical analysis. Surveys and structured observations are common tools here.
- Mixed methods : As the name implies, this combines both qualitative and quantitative methodologies.
The Methodology section isn’t just about detailing the methods but also justifying why they were chosen. The appropriateness of the methods in addressing your research question can significantly impact the credibility of your findings.
Results (or Findings)
This section presents the outcomes of your research. It's crucial to note that the nature of your results may vary; they could be quantitative, qualitative, or a mix of both.

Quantitative results often present statistical data, showcasing measurable outcomes, and they benefit from tables, graphs, and figures to depict these data points.
Qualitative results , on the other hand, might delve into patterns, themes, or narratives derived from non-numerical data, such as interviews or observations.
Regardless of the nature of your results, clarity is essential. This section is purely about presenting the data without offering interpretations — that comes later in the discussion.
In the discussion section, the raw data transforms into valuable insights.
Start by revisiting your research question and contrast it with the findings. How do your results expand, constrict, or challenge current academic conversations?
Dive into the intricacies of the data, guiding the reader through its implications. Detail potential limitations transparently, signaling your awareness of the research's boundaries. This is where your academic voice should be resonant and confident.
Practical implications (Recommendation) section
Based on the insights derived from your research, this section provides actionable suggestions or proposed solutions.
Whether aimed at industry professionals or the general public, recommendations translate your academic findings into potential real-world actions. They help readers understand the practical implications of your work and how it can be applied to effect change or improvement in a given field.
When crafting recommendations, it's essential to ensure they're feasible and rooted in the evidence provided by your research. They shouldn't merely be aspirational but should offer a clear path forward, grounded in your findings.
The conclusion provides closure to your research narrative.
It's not merely a recap but a synthesis of your main findings and their broader implications. Reconnect with the research questions or hypotheses posited at the beginning, offering clear answers based on your findings.

Reflect on the broader contributions of your study, considering its impact on the academic community and potential real-world applications.
Lastly, the conclusion should leave your readers with a clear understanding of the value and impact of your study.
References (or Bibliography)
Every theory you've expounded upon, every data point you've cited, and every methodological precedent you've followed finds its acknowledgment here.

In references, it's crucial to ensure meticulous consistency in formatting, mirroring the specific guidelines of the chosen citation style .
Proper referencing helps to avoid plagiarism , gives credit to original ideas, and allows readers to explore topics of interest. Moreover, it situates your work within the continuum of academic knowledge.
To properly cite the sources used in the study, you can rely on online citation generator tools to generate accurate citations!
Here’s more on how you can cite your sources.
Often, the depth of research produces a wealth of material that, while crucial, can make the core content of the thesis cumbersome. The appendix is where you mention extra information that supports your research but isn't central to the main text.

Whether it's raw datasets, detailed procedural methodologies, extended case studies, or any other ancillary material, the appendices ensure that these elements are archived for reference without breaking the main narrative's flow.
For thorough researchers and readers keen on meticulous details, the appendices provide a treasure trove of insights.
Glossary (optional)
In academics, specialized terminologies, and jargon are inevitable. However, not every reader is versed in every term.
The glossary, while optional, is a critical tool for accessibility. It's a bridge ensuring that even readers from outside the discipline can access, understand, and appreciate your work.

By defining complex terms and providing context, you're inviting a wider audience to engage with your research, enhancing its reach and impact.
Remember, while these components provide a structured framework, the essence of your thesis lies in the originality of your ideas, the rigor of your research, and the clarity of your presentation.
As you craft each section, keep your readers in mind, ensuring that your passion and dedication shine through every page.
Thesis examples
To further elucidate the concept of a thesis, here are illustrative examples from various fields:
Example 1 (History): Abolition, Africans, and Abstraction: the Influence of the ‘Noble Savage’ on British and French Antislavery Thought, 1787-1807 by Suchait Kahlon.
Example 2 (Climate Dynamics): Influence of external forcings on abrupt millennial-scale climate changes: a statistical modelling study by Takahito Mitsui · Michel Crucifix
Checklist for your thesis evaluation
Evaluating your thesis ensures that your research meets the standards of academia. Here's an elaborate checklist to guide you through this critical process.
Content and structure
- Is the thesis statement clear, concise, and debatable?
- Does the introduction provide sufficient background and context?
- Is the literature review comprehensive, relevant, and well-organized?
- Does the methodology section clearly describe and justify the research methods?
- Are the results/findings presented clearly and logically?
- Does the discussion interpret the results in light of the research question and existing literature?
- Is the conclusion summarizing the research and suggesting future directions or implications?
Clarity and coherence
- Is the writing clear and free of jargon?
- Are ideas and sections logically connected and flowing?
- Is there a clear narrative or argument throughout the thesis?
Research quality
- Is the research question significant and relevant?
- Are the research methods appropriate for the question?
- Is the sample size (if applicable) adequate?
- Are the data analysis techniques appropriate and correctly applied?
- Are potential biases or limitations addressed?
Originality and significance
- Does the thesis contribute new knowledge or insights to the field?
- Is the research grounded in existing literature while offering fresh perspectives?
Formatting and presentation
- Is the thesis formatted according to institutional guidelines?
- Are figures, tables, and charts clear, labeled, and referenced in the text?
- Is the bibliography or reference list complete and consistently formatted?
- Are appendices relevant and appropriately referenced in the main text?
Grammar and language
- Is the thesis free of grammatical and spelling errors?
- Is the language professional, consistent, and appropriate for an academic audience?
- Are quotations and paraphrased material correctly cited?
Feedback and revision
- Have you sought feedback from peers, advisors, or experts in the field?
- Have you addressed the feedback and made the necessary revisions?
Overall assessment
- Does the thesis as a whole feel cohesive and comprehensive?
- Would the thesis be understandable and valuable to someone in your field?
Ensure to use this checklist to leave no ground for doubt or missed information in your thesis.
After writing your thesis, the next step is to discuss and defend your findings verbally in front of a knowledgeable panel. You’ve to be well prepared as your professors may grade your presentation abilities.
Preparing your thesis defense
A thesis defense, also known as "defending the thesis," is the culmination of a scholar's research journey. It's the final frontier, where you’ll present their findings and face scrutiny from a panel of experts.
Typically, the defense involves a public presentation where you’ll have to outline your study, followed by a question-and-answer session with a committee of experts. This committee assesses the validity, originality, and significance of the research.
The defense serves as a rite of passage for scholars. It's an opportunity to showcase expertise, address criticisms, and refine arguments. A successful defense not only validates the research but also establishes your authority as a researcher in your field.
Here’s how you can effectively prepare for your thesis defense .
Now, having touched upon the process of defending a thesis, it's worth noting that scholarly work can take various forms, depending on academic and regional practices.
One such form, often paralleled with the thesis, is the 'dissertation.' But what differentiates the two?
Dissertation vs. Thesis
Often used interchangeably in casual discourse, they refer to distinct research projects undertaken at different levels of higher education.
To the uninitiated, understanding their meaning might be elusive. So, let's demystify these terms and delve into their core differences.
Here's a table differentiating between the two.
Aspect | Thesis | Dissertation |
Purpose | Often for a master's degree, showcasing a grasp of existing research | Primarily for a doctoral degree, contributing new knowledge to the field |
Length | 100 pages, focusing on a specific topic or question. | 400-500 pages, involving deep research and comprehensive findings |
Research Depth | Builds upon existing research | Involves original and groundbreaking research |
Advisor's Role | Guides the research process | Acts more as a consultant, allowing the student to take the lead |
Outcome | Demonstrates understanding of the subject | Proves capability to conduct independent and original research |
Wrapping up
From understanding the foundational concept of a thesis to navigating its various components, differentiating it from a dissertation, and recognizing the importance of proper citation — this guide covers it all.
As scholars and readers, understanding these nuances not only aids in academic pursuits but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the relentless quest for knowledge that drives academia.
It’s important to remember that every thesis is a testament to curiosity, dedication, and the indomitable spirit of discovery.
Good luck with your thesis writing!
Frequently Asked Questions
A thesis typically ranges between 40-80 pages, but its length can vary based on the research topic, institution guidelines, and level of study.
A PhD thesis usually spans 200-300 pages, though this can vary based on the discipline, complexity of the research, and institutional requirements.
To identify a thesis topic, consider current trends in your field, gaps in existing literature, personal interests, and discussions with advisors or mentors. Additionally, reviewing related journals and conference proceedings can provide insights into potential areas of exploration.
The conceptual framework is often situated in the literature review or theoretical framework section of a thesis. It helps set the stage by providing the context, defining key concepts, and explaining the relationships between variables.
A thesis statement should be concise, clear, and specific. It should state the main argument or point of your research. Start by pinpointing the central question or issue your research addresses, then condense that into a single statement, ensuring it reflects the essence of your paper.
You might also like

Boosting Citations: A Comparative Analysis of Graphical Abstract vs. Video Abstract

The Impact of Visual Abstracts on Boosting Citations

Introducing SciSpace’s Citation Booster To Increase Research Visibility

Mastering the Thesis Statement: Examples and Tips for Academic Success
What is the thesis statement? When it comes to writing an essay , there are many things that we must take into consideration in order to create a well-written and respected piece of work. One such thing is the thesis statement. Every good essay should have one and it needs to be well-written and well-thought-out. In this article, we are going to be looking at exactly what a thesis statement is and what it is used for as well as looking at some examples of the thesis statement as a way to gain a greater understanding of what its function is.
A thesis statement plays a crucial role in any well-crafted essay, as it helps both the writer and the reader establish the central point of the paper. Typically found near the end of the introduction, this sentence succinctly conveys the main idea the writer intends to communicate throughout the essay. Crafting a strong thesis statement increases the likelihood that the resulting essay will be cohesive, persuasive, and engaging for the audience.
Creating an effective thesis statement can, at times, be a challenging process. One useful method is to begin by exploring examples that illustrate the various ways in which thesis statements can be constructed, depending on the type of essay or paper being written. Studying these examples can help budding writers grasp the principles behind crafting compelling thesis statements, and serve as inspiration for their own work.
What Is A Thesis Statement?
Definition and purpose.
In the most simple terms, a thesis statement is a short statement that provides insight into what the essay is going to be about. They are used to enlighten the audience on a variety of things, including:
- The main argument or point to be discussed.
- The purpose of the essay.
- The point of view of the author on a specific topic.
A thesis statement is a sentence that encapsulates the central point or main idea of a paper or essay. It is typically found near the end of the introduction and serves as a guide to the reader, outlining the writer’s stance on the topic. The thesis statement not only answers the question asked but also acts as a roadmap for the paper, indicating what the reader can expect throughout the rest of the paper.
The purpose of a thesis statement is two-fold:
- To convey a clear and concise argument or position on the topic.
- To inspire further discussion and responses from the audience.
It’s crucial for a thesis statement to be focused, specific, and arguable. A strong thesis is easy to understand and provides a solid foundation for supporting evidence within the paper.
Types of Thesis Statements
Argumentative thesis statement.
An argumentative thesis statement is a claim that takes a strong position on an issue. This type of thesis statement aims to persuade the reader to accept the writer’s viewpoint by presenting logical reasoning and supporting evidence. It is essential to have a clear and concise argumentative thesis statement to guide the rest of the essay.
For example: “ Public transportation should be free in metropolitan areas to reduce carbon emissions and economic inequalities.”
Expository Essay Thesis Statement
An expository essay thesis statement highlights a specific issue or fact that the writer will explain or analyze throughout the essay. This type of thesis should be informative and objective, without taking a strong stance on the issue.
For example: “ High-level competitive athletes face numerous physical, mental, and emotional challenges throughout their careers. ”
Persuasive Thesis Statement
A persuasive thesis statement is similar to an argumentative thesis statement, but it aims to convince the reader to take action or adopt the writer’s viewpoint through emotional appeal and relatable examples. The persuasive thesis statement should be thought-provoking and debatable.
For example: “ Animal shelters should require background checks and home visits to ensure responsible pet adoption and prevent animal abuse. ”
Compare and Contrast Thesis Statement
A compare-and-contrast thesis statement sets the stage for an essay comparing or contrasting two or more subjects. This type of thesis statement may highlight similarities, differences, or a mix of both. It is crucial to establish a basis for comparison to provide a clear focus for the essay.
For example: “ While both public and private universities offer a variety of educational opportunities, the differences in cost, class size, and campus environment directly impact a student’s experience .”
By understanding and applying these types of thesis statements, writers can effectively tailor their essays’ tone and focus to suit their specific purpose and audience.
How Is A Thesis Statement Used?
As we mentioned a thesis statement is used to point out the main argument of the essay. There are certain rules that should be followed by the thesis statement. Let’s take a look at these in a little more detail.
- A thesis statement should appear in the introduction of the essay to layout the main topic and the author’s stance on it. It should also appear in the conclusion of the essay, where the author can refer back to it.
- A thesis statement should be a short statement of only one or two sentences that delivers clear and concise information.
- The thesis statement will directly answer the main question posed by the essay, for example, if the essay question were ‘What is the biggest tourist attraction in France?’ The thesis statement might directly reply to this with ‘With over 6 million visitors each year, the Eiffel Tower is clearly the biggest tourist attraction in France.’ If the essay topic doesn’t contain a question, you can fashion one yourself.
- Many people use the ‘so what?’ technique when writing a thesis statement. If a reader is likely to think ‘so what?’ when starting your essay, you can use the thesis statement to form a relationship and a connection to the issue that will engage the reader and make them care about what is going to be talked about.
- Similarly to the above point, a thesis statement should answer why or how questions that the reader may have. Look again at the example of the Eiffel Tower, the statement clearly shows the reader why the tower is the biggest tourist attraction in France using real statistics that cannot be ignored. But in the same breath, gives the reader the chance to dispute the information. This is another key point to the thesis statement. A reader should be able to look at the thesis statement and disagree with it, this might encourage them to research the topic themselves.
- A thesis statement should agree with the body of the essay. If it does not, then it should be amended. Using the example of the French tourist attraction once again, the body of that essay would need to go into further detail about the tourist attractions in France and further prove why the Eiffel Tower is the most popular.
Creating a Strong Thesis Statement
Identifying your topic and scope.
When creating a strong thesis statement, it is essential to first identify your topic and the scope of your paper. You should consider the central idea you want to communicate and its impact on your field of study, whether it’s art, education, or environmental studies. A solid thesis statement should focus on a single aspect of your research, avoiding general terms or abstractions. Keep it clear and specific to ensure it effectively guides both you and the reader through your argument.
Forming a Debatable Claim
An argumentative thesis statement should present a debatable claim, one that reasonable people could disagree with. This means that it should not merely be a statement of fact, but rather an assertion that invites different opinions. For example, a debatable claim on nationalism could be, “Nationalism contributed to the rise of populism in the 21st century.” This claim allows for various arguments, opinions, and contextual interpretations.
Providing Evidence
A strong thesis statement should also set the stage for presenting evidence supporting your claim. In a research paper, this means providing an overview of the key elements and sources you will use to build your argument. For an argumentative essay, be prepared to provide well-researched and detailed evidence to back up your claim, whether it’s regarding renewable energy sources, the history of race and gender, or the role of nationalism in shaping global politics.
Here are some tips to help you write a strong thesis statement:
- Make sure it’s clear and concise, typically consisting of one or two sentences.
- Ensure that it’s focused and specific enough to be “proven” within the boundaries of your paper.
- Position it near the end of your essay’s introduction or within the first paragraph.
By following these guidelines and being mindful of your topic, scope, and evidence, you will be able to craft a powerful thesis statement that engages your audience and sets the stage for a successful research or argumentative paper.
Explore more: How To Write A Thesis Statement
Thesis Statement Examples
Argumentative thesis examples.
An argumentative thesis aims to establish a position and persuade the reader with evidence and reasoning. Examples include:
- Though populism may fundamentally challenge traditional political structures, its effects on social and economic policies are necessary for a more equitable society.
- Social media platforms are responsible for the increasing polarization of opinions and must adopt measures to limit the spread of misinformation.
Expository Essay Thesis Examples
An expository essay thesis presents facts, evidence, or an explanation without taking a persuasive stance. Examples include:
- The process of photosynthesis is fundamental to the survival of plants and the ecosystems they support, providing energy for growth and reproduction.
- Urbanization has led to numerous social, economic, and environmental consequences, including increased housing demand, traffic congestion, and pollution.
Persuasive Thesis Examples
A persuasive thesis seeks to convince the reader of a particular argument or opinion. Examples include:
- The benefits of implementing a universal basic income outweigh the potential drawbacks, as it can alleviate poverty and provide residents with more financial security.
- Investing in renewable energy sources is essential for combating climate change and ensuring a sustainable future for subsequent generations.

Compare and Contrast Thesis Examples
A compare and contrast thesis highlights the similarities and differences between two or more subjects. Examples include:
- While both traditional and online education offer unique advantages and challenges, the flexibility and accessibility of online learning make it a more suitable option for students juggling work and personal responsibilities.
- Despite similarities in their genre and themes, the novels “Pride and Prejudice” and “Wuthering Heights” differ significantly in their narrative styles and characterization.
Using these examples, you can create strong thesis statements tailored to your essay’s specific topic and goals. Remember to provide a clear and concise thesis that effectively showcases your argument, opinion, or comparison in a confident, knowledgeable, and neutral tone.
Thesis Statement Examples: Issues to Consider
Impact on society.
When creating a thesis statement, it’s essential to consider the potential impacts on society. The chosen topic may address issues such as education, war, and nationalism. For example, the thesis statement might analyze the effects of changing educational policies on different classes of society. This could include exploring access to education for low-income households or the impact of privatization on public schools. It is crucial to examine how the thesis topic relates to societal issues and incorporates them into the statement.
Related: Social Issues
Race, Gender, and Class
It is important to address issues related to race, gender, and class when developing thesis statements. For instance, research papers might examine inequalities in the workplace or disparities in access to resources. Such studies should think about context and historical background, comparing and contrasting the experiences of different groups. Here are some examples.
- Gender : An examination of the gender pay gap across various industries
- Race : A comparison of racial profiling incidents in law enforcement across different communities
- Class : Exploring the impact of socio-economic status on healthcare access and outcomes
Consider using tables and bullet points to help present data and findings more effectively.
Environmental Concerns
Lastly, incorporating environmental concerns into thesis statements is essential, especially in today’s world, where sustainability and environmental protection are vital. Research papers might address issues such as pollution, waste management, or the effects of climate change on marginalized communities. For example, a thesis statement could focus on exploring the consequences of a specific eco-friendly initiative in a local community, or how environmental policies have evolved over time.
Keep in mind to maintain a confident, knowledgeable, neutral, and clear tone of voice throughout the section, focusing on accurate information and avoiding exaggerated or false claims.
Examples of Thesis Statements in Different Essay Types
In a narrative essay , the thesis statement revolves around the story being told. It is typically centered on a specific event, person, or experience that had a significant impact on the writer. The thesis statement in a narrative essay serves as a brief preview of what the reader can expect. It should provide some insight into the writer’s personal connection to the topic and help set the stage for the narrative to unfold.
For example:
The moment she won the lottery, Mary’s life changed forever, teaching her the importance of cherishing every moment with her loved ones.
An analytical essay breaks down a topic into its main components and presents an evaluation or interpretation of the topic based on those components. The thesis statement in an analytical essay should clearly state the issue or idea that will be analyzed and its essential elements. This type of statement should provide enough information to guide the reader through the essay and highlight the central points of analysis.
By examining the symbolism, characterization, and theme of “The Great Gatsby,” it becomes evident that Fitzgerald uses these techniques to criticize the American Dream’s materialism and superficiality.
Argumentative
In an argumentative essay , the thesis statement takes a clear, definitive stance on a specific issue or question. This type of thesis statement aims to persuade readers of the writer’s viewpoint and provide logical and supporting evidence to back up the claim. The thesis should be concise, specific, and controversial enough to encourage debate from various perspectives.
Although some people argue that video games can be beneficial, this essay will demonstrate that excessive video gaming is linked to increased violent behavior, addiction, and social isolation, and therefore requires stricter regulation.
Cause and Effect
A cause-and-effect essay explores the relationship between certain events, actions, or conditions and their respective outcomes. The thesis statement in a cause-and-effect essay should establish the connection between the cause and the effect, asserting a causal connection between the two. This type of thesis statement should present a clear, coherent structure to guide the reader through the essay and should establish the relationship between the cause and the effect.
The widespread use of smartphones has led to increased incidents of sleep deprivation among teenagers, resulting in declining academic performance, mood disorders, and health issues.
These are examples of how thesis statements can vary based on the type of essay and showcase the importance of tailoring the thesis statement to fit the specific requirements of each essay style.
More Thesis Statement Examples
Now that we are clear on what a thesis statement is and how it can be used, we are going to take a look at some examples of strong and effective thesis statements. This will give you a better idea on what they should contain and how they function within an essay.
American Education
The American education system has been evolving, and it is essential to have a clear thesis statement when discussing the topic. Here’s an example:
The integration of technology in American schools has significantly enhanced the learning experience of students, resulting in improved academic performance.
In this example, it highlights the positive impact of technology on the education system. It also provides a concise view that can be explored and supported through research and relevant statistics.
Internet and Society
The internet has changed the way society functions in various capacities. Here is a thesis statement example that can be used to discuss the relationship between the internet and society:
The widespread use of the internet has drastically altered societal interactions, affecting the population’s ability to communicate, access information, and maintain personal privacy.
This statement outlines the primary effects of the internet on society and can be further developed through specific examples and analysis. This statement can be supported through studies, data, and real-life cases that demonstrate the impact of the internet on communication, information access, and privacy concerns.
List of Thesis Statement Examples
- Owing to the fact that many children are not being vaccinated because of illness, it is now imperative that we make it a requirement that healthy children are vaccinated in order to stop the spread of disease.
- For families on a low income, schools should provide basic equipment such as pens, calculators and laptops.
- Whilst school uniforms are expensive, they do provide security and a sense of belonging to students and for this reason, are an integral part of the school system.
- Many public libraries are closing down due to lack of interest but these are important resources within the community and we should fight to keep them open.
- With the internet becoming ever more popular and accessible to teenagers, cyber bullying is massively on the rise. A large number of cyber bullying cases end in suicide and it is down to parents and schools to tackle this growing problem.
- Cannabis is not legal in many countries and states and this is for good reason. The drug is known to diminish the brain cells and regardless of how it might relax pain and anxiety, it should not be legalised.
- Too many people are taking time of work for stress-related reasons and so it is more important than ever for workplaces to provide internal activities to combat this problem.
- Many parents do not like the idea of their children being taught sex education at an early age but unfortunately in this day and age, it is a necessity if we want to keep children safe.
Avoiding Common Mistakes
When writing a thesis statement, it is essential to avoid common mistakes that may weaken your argument or confuse your reader. In this section, we will discuss two main pitfalls to avoid: Overgeneralizing and Using Weak or Vague Language.
Overgeneralizing
Overgeneralizing refers to making broad, sweeping claims in your thesis statement without providing specific, concrete evidence to support them. To avoid overgeneralization, focus on providing a clear and concise argument, grounded in solid research and evidence. Brainstorm specific examples or points you will address in your paper that support your thesis. For example, if your thesis is about a controversial topic, make sure your argument is based on valid research and takes a clear direction, rather than making generalized statements.
To prevent overgeneralization in your thesis statement:
- Narrow the focus of your argument.
- Ensure your claim is specific and backed up by evidence.
- Be consistent with the goals and direction outlined in your paper.
Using Weak or Vague Language
Using weak or vague language in your thesis statement can result in a lack of clarity and create confusion for your reader. To maintain a strong, clear, and convincing thesis, avoid using weak or unclear terms, such as “interesting” or “might.” Instead, use assertive and definitive language that demonstrates your confidence and knowledge of the subject matter. For instance, if you are writing about a potential solution to a problem, make sure to express your stance in a strong, clear way to entice your reader and promise valuable insights.
To strengthen the language of your thesis statement:
- Avoid using vague or ambiguous terms.
- Use clear, specific language that directly communicates your argument.
- Stay focused on your main points and the direction of your paper.
Keeping these tips in mind and utilizing clear language will contribute to a stronger, more effective thesis statement.
Crafting Engaging Introductions and Conclusions
Writing a hook.
A successful introduction begins with an attention-grabbing hook. A hook is an opening statement that piques the reader’s interest and encourages them to continue reading. There are various types of hooks, such as using a quote, posing a question, or stating an intriguing fact. The hook should be relevant to the topic and set the tone for the rest of the article.
Connecting Thesis Statement to Conclusion
The conclusion of an academic paper should restate the thesis statement and summarize the main points discussed in the body paragraphs. However, it’s important to do this in a way that doesn’t merely repeat the same information, but instead provides a sense of closure and emphasizes the significance of the topic.
One way to achieve this is by connecting the thesis statement to the conclusion through the use of topic sentences and counterarguments. A well-crafted topic sentence should introduce the main idea of a body paragraph, while a counterargument addresses potential objections to the thesis statement. Utilizing these elements effectively throughout the paper creates a sense of cohesion and allows for a smooth transition from the introduction to the conclusion.
By incorporating engaging hooks and thoughtfully connecting the thesis statement to the conclusion, the reader is more likely to be drawn into the article and appreciate the depth of the content presented.
Thesis Statement Infographic

A thesis statement is made up of one or two sentences and gives the author the chance to tell the reader what the essay is going to be about as well as their stance on the topic. It should be clear and concise and should always tie in with the body paragraphs of the essay .
Whilst there are many points to consider when writing a thesis statement, a well-written one can answer a question and engage the reader in the essay. Sticking with the ‘rules’ of the thesis statement will allow the author to craft a well-written and relevant essay.
FAQs on Thesis Statement
What is a thesis statement.
A thesis statement is a sentence or two in an essay or research paper that presents the main argument or central idea of the paper. It tells the reader what to expect, guides the structure of the paper, and directly answers the question or topic being discussed.
How do I write a thesis statement?
There are four simple steps to write a thesis statement:
- Start with a question : Identify the topic or question your paper will explore.
- Write your initial answer : This should be a concise statement that provides a preliminary answer to the question.
- Develop your answer : Expand on your initial answer by considering its implications, context, and evidence.
- Refine your thesis statement : Revise and refine your statement to make it clear, specific, and arguable.
Where should the thesis statement be placed?
The placement of the thesis statement varies depending on the type of paper or essay. However, a common place for the thesis statement is at the end of the introduction paragraph, making it easier for the reader to identify the main argument early in the text.
What makes a good thesis statement?
A good thesis statement should be:
- Clear : It should communicate your main point without confusion.
- Specific : It should focus on a single topic or argument.
- Arguable : It should present a claim that people can reasonably disagree on.
- Relevant : It should relate to the purpose of the paper and contribute to its overall message.
What are the different types of thesis statements?
There are two main types of thesis statements:
- Analytical : An analytical thesis breaks down an issue or idea into its component parts, evaluates the issue or idea, and presents the breakdown and evaluation to the audience.
- Expository (explanatory) : An expository thesis explains something to the audience.
Remember, as you work on your thesis statement, keep the rest of your paper in mind to ensure that it aligns with the paper’s overall content and objective.
- How To Write An Essay
- How to Start an Essay
- Topic Sentence
- Essay Outline
- Latest Posts
- Insatiable Meaning: What Does It Mean? - January 27, 2024
- Bliss Meaning: What Does “Bliss” Mean? - January 12, 2024
- Judgement vs. Judgment: A Look at Spelling Variations - January 9, 2024
Improve your writing with the help of AI writing assistants!

- TemplateLab
Thesis Statement Templates
45 perfect thesis statement templates (+ examples).
You can create a thesis statement template for different reasons. Most commonly though, you would need this for writing essays . There are a lot of argumentative thesis statement examples, expository thesis statement examples, analytical thesis statement examples, and more available to serve as your reference for when you need to make your own. Since thesis statements are very important, it’s important for you to learn how to write one effectively.
Table of Contents
- 1 Thesis Statement Templates
- 2 What is a thesis statement?
- 3 Thesis Statement Formats
- 4 How do you create a thesis statement?
- 5 Argumentative Thesis Statement Examples
- 6 Strong qualities of a thesis statement
- 7 Expository Thesis Statement Examples
- 8 Tips for writing your thesis statement

What is a thesis statement?
A thesis statement template is an important part of an essay as you indicate your main point there. To help you understand this better, let’s define a thesis statement in the context of persuasive essays. When you write this type of essay, you must learn how to persuade others effectively.
Through the essay, you convince the readers that you have a logical and interesting point of view regarding the subject of your essay . Persuasion is an important skill we all practice in our daily lives. You persuade your children to dress up for school without making a fuss, you persuade your coworkers to help you out, and so on.
If you’re a college student , you may receive course assignments where you need to make a compelling and effective persuasive essay . To do this, you must convince the readers that your point of view is the most accurate and logical one. For this form of persuasion, which is also known as an academic argument, it follows a predictive pattern.
After writing a short introduction, you would state your main point in a single sentence. This is known as the thesis statement. Although an argumentative thesis statement example is the most common, you may also find a lot of expository thesis statement examples or analytical thesis statement examples depending on what they’re created for.
Before we go through the thesis statement format, keep in mind that your thesis statement template must:
- Tell the reader how you plan to interpret the relevance of your topic.
- Serves as the “road map” for your entire paper. Therefore, it should tell the reader what to expect from the very beginning.
- It provides a direct answer to the question your topic answers. The thesis statement is your interpretation of a subject or a question and not the subject itself. For instance, if you’re writing an essay about politics, then your thesis statement must provide the reader with a way to understand this topic.
- Make a claim which others might argue with.
- Be just one sentence which you write at the start of your document. Often, you would write your thesis statement by the end of your first paragraph and its purpose is to present your argument to the reader. From there, you can start gathering and organizing evidence which helps persuade the reader of your point of view.
If you’re assigned to develop a claim or take a side of one particular argument or subject, you should convey your main point in your thesis statement. Even if you’re not explicitly required to write a thesis statement, you must still include it. Most professors already expect this as a part of an essay.
If you’re not sure whether or not to include a thesis statement format, ask your professor about it. If your assignment requires you to interpret, to analyze, to compare, to take a stand, or to demonstrate the cause and effect of a situation, this means that you must come up with a thesis statement then support it in a persuasive way.
Thesis Statement Formats

How do you create a thesis statement?
Before you can create your thesis statement template, you must first go through a long process of thinking. Formulating your thesis statement isn’t the first thing to do in the process of writing essays. Before you can even start to come up with an argument for any topic, there are other things you must do first.
You need to gather and organize your evidence, look for any relationships like similarities or contrasts between the known facts, and consider the relevance of these relationships. After all these steps, you would have a “working thesis” in your mind which presents your main idea.
Come up with a draft of your thesis statement format along with an argument which you can support using the information you’ve gathered. Keep in mind that while you write your essay , your initial draft of the thesis statement and argument may require modifications.
Writers make use of different kinds of methods to get the ideas flowing and to help them comprehend the relevance of their topic or clarify the relationships between the facts. Only then can you arrive at your final thesis statement.
Argumentative Thesis Statement Examples

Strong qualities of a thesis statement
When you’re trying to compose your thesis statement, you must think about the thesis statement format along with other qualities. Here are the qualities you must consider to create a strong thesis statement template:
- Length You can make your thesis statement any length depending on how many points you plan to mention. Usually, though, this statement is only a short and concise sentence. It may contain two clauses but you may want to limit it to about 2 lines only.
- Position You must always place your thesis statement somewhere at the beginning of your essay, usually in the first paragraph. This is because the statement tells your reader what you’re about to talk about in the essay. But if your instructor specified where to place your thesis statement, you must follow their requirement.
- Strength Finally, you must also make your thesis statement arguable. It shouldn’t be too obvious and it shouldn’t be something that everyone will agree with. You must make it interesting and thought-provoking so your readers will continue with the rest of the content.
Composing your thesis statement may take more time, effort, and thinking compared to the other parts of your essay. But since it’s only one sentence, you shouldn’t have a problem taking this extra time to compose this statement as it directs your essay in a unique way.
Expository Thesis Statement Examples

Tips for writing your thesis statement
Each paper that you write must contain a main idea, a central message or the main point. Then any arguments you make in your document must be a reflection of this main point. In an essay, the sentence which captures your point of view is the thesis statement.
A thesis statement template focuses your arguments and ideas into a single sentence. Use it to present your essay’s topic and to share your point of view regarding the topic. The thesis statement must tell the reader about the essay, help guide your writing process, and help you focus on your arguments. Here are some tips for you:
- Determine the type of paper you want to write If your plan to write an analytical paper, you would break down an idea or issue into its basic parts. Then you would perform an evaluation. Finally, you present your breakdown and evaluation to your readers. For an expository or explanatory paper, you would provide an explanation about the main point to your readers. If you’re writing an argumentative paper, you will make a claim about a specific point then justify this claim using the evidence you’ve gathered. Here, your claim may be an evaluation, an opinion, an interpretation, a policy proposal or a cause and effect statement. The goal of this type of paper is to convince the audience of the truth of your claim based on the evidence you’ve given. Even if you’re writing any other type of paper apart from these categories, you should place the thesis statement in your first paragraph. This makes it most helpful for the reader.
- Make your thesis statement as specific as possible In this statement, you should only cover what you plan to discuss in your essay. Also, you should only include facts which you can support with evidence.
- Keep in mind that you might have to make changes in your thesis statement As you write your paper, your topic might change. Therefore, you should also make revisions to your thesis statement as needed. Otherwise, it won’t be as relevant in the end.
- Limit your thesis statement to the information you can accomplish in the specified number of pages When shaping your topic, you must make sure that you get right to the “meat” of it. The more specific you are, the more successful you can relay your message to the readers. Doing this is also more effective than just writing about general concepts which might make the readers feel confused.
- The thesis statement must also reflect your point of view Your thesis statement shouldn’t just reveal your topic. It must also announce your point of view in relation to the topic and how you will evaluate or analyze the topic.
- Come up with your own thesis statement using your own words Remember that the thesis statement is just one sentence. When composing it, use your own words. It’s not appropriate to quote others since you’re talking about your own take on the subject.

More Templates

Newspaper Templates

Essay Outline Templates

Friendly Letter Formats

Statement Of Purpose

Reflective Essay Examples

Persuasive Essay Examples

Thesis Statement

Embark on a comprehensive guide to understanding the cornerstone of any compelling essay or research paper: the thesis statement. Learn its definition, discover real-world examples, and unlock the secrets to crafting a strong thesis that captures your argument succinctly. Ideal for students, educators, and aspiring writers, this article serves as a one-stop resource for mastering the art of thesis statement creation. Boost your academic writing skills and make your arguments more persuasive with our expert tips.
What is Thesis Statement? Definition
A thesis statement is a sentence that captures the main point or claim of an essay or research paper. It serves as a roadmap, guiding the reader through the arguments that are presented in the work.
Download 120+ Thesis Statement Examples
Clear and concise, a thesis statement sets the tone and direction for the entire piece of writing.

What is the Best Example of a Thesis Statement?
A strong thesis statement is concise, specific, and sets the stage for the arguments to follow. One such example that is often cited for its effectiveness is:
Example: “Stricter plastic regulations are crucial to combat environmental damage.”
This thesis statement is considered strong for the following reasons:
- Concise : It gets straight to the point, making it easy for the reader to understand the essay’s focus.
- Specific : It clearly identifies the need for stricter regulations on plastic, providing a specific course of action.
- Arguable : The statement is not a mere fact but an arguable position that invites discussion and analysis.
- Roadmap : Though brief, it gives readers a quick idea of what the essay will argue, serving as a roadmap for the discussion that will follow.
- Relevance : The topic is timely and relevant, adding weight to the thesis statement.
This example serves as an excellent starting point for an argumentative essay, offering a clear and focused direction for both the writer and the reader.
100 Simple Thesis Statement Examples
Navigating the complexities of academic writing can be challenging, but a well-crafted thesis statement can make all the difference. Whether you’re a student, educator, or anyone interested in improving their writing skills, these 100 simple thesis statement examples will provide you with the inspiration and guidance you need. From argumentative essays to analytical papers, we’ve got you covered. Let’s dive in!
Argumentative Thesis Statements
- School uniforms should be mandatory to promote equality and reduce bullying in educational institutions.
- Social media platforms must regulate fake news to prevent the spread of misinformation.
- Animal testing is unethical and should be banned in cosmetic research.
- The death penalty is an outdated form of punishment that has no place in a civilized society.
- Climate change is a global crisis that requires immediate action from governments worldwide.
Analytical Thesis Statements
- Shakespeare’s “Hamlet” explores the complexities of human emotion through its multi-dimensional characters.
- The Great Gatsby portrays the American Dream as unattainable , offering a critical look at 1920s America.
- The symbolism in “Lord of the Flies” serves to highlight the inherent evil in human nature.
- The marketing strategies of Apple Inc. focus on emotional appeal , setting it apart from competitors.
- The rise of cryptocurrency challenges traditional financial systems , signaling a shift in how we understand money.
Expository Thesis Statements
- The benefits of exercise extend beyond physical health , including mental well-being and increased productivity.
- Remote work is becoming the new norm , offering both challenges and opportunities for businesses.
- Meditation has proven health benefits , such as reducing stress and improving focus.
- The history of the Internet traces back to military projects , but its rapid expansion has been consumer-driven.
- Renewable energy sources are essential for a sustainable future , as they reduce dependency on fossil fuels.
Compare and Contrast Thesis Statements
- While both Apple and Samsung offer high-quality smartphones , Apple’s focus on user experience sets it apart.
- Public and private schools provide different benefits and challenges , making the choice dependent on individual needs.
- Traditional and online education have distinct advantages , but online learning offers more flexibility.
- Cats and dogs make excellent pets , but cats require less maintenance and attention.
- Democracy and monarchy are contrasting forms of government , each with its own strengths and weaknesses.
Persuasive Thesis Statements
- Recycling should be made compulsory to minimize environmental impact.
- Vaccination should be mandatory for public health and safety.
- Higher education should be free for all citizens to promote economic growth and social mobility.
- Gun control laws need to be stricter to reduce the incidence of mass shootings.
- Organic farming should be subsidized to promote sustainable agriculture.
Cause and Effect Thesis Statements
- The rise in fast-food consumption has led to an increase in obesity rates among young adults.
- The advent of social media has significantly impacted mental health , leading to increased anxiety and depression.
- Global warming is causing extreme weather conditions , including more frequent and severe hurricanes.
- The decline in print journalism can be attributed to the digital revolution , which has shifted the focus to online news.
- The increase in remote work has led to a surge in demand for home office equipment , affecting the retail market.
Informative Thesis Statements
- The life cycle of a butterfly consists of four stages : egg, larva, pupa, and adult.
- The process of photosynthesis is essential for plant growth , converting sunlight into energy.
- The history of jazz music traces its roots to African and European musical traditions , blending them into a unique American art form.
- The benefits of yoga include improved flexibility, strength, and mental clarity .
- The invention of the printing press revolutionized information distribution , paving the way for the spread of knowledge.
Problem-Solution Thesis Statements
- To combat climate change, governments should invest in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
- The opioid crisis can be mitigated through stricter regulations on prescription medications and better educational programs.
- To reduce traffic congestion, cities should invest in public transportation systems like buses and subways.
- The issue of plastic waste can be addressed by implementing recycling programs and banning single-use plastics.
- To improve mental health services, there should be increased funding for research and public awareness campaigns .
Evaluation Thesis Statements
- The film “Inception” successfully combines complex storytelling with groundbreaking visual effects , making it a modern cinematic masterpiece.
- Despite its popularity, fast food is harmful to health and well-being , offering little nutritional value.
- The educational system needs a comprehensive overhaul to meet the needs of the 21st century , including a focus on STEM and vocational training.
- The novel “1984” by George Orwell offers a chilling glimpse into the dangers of totalitarianism , making it a must-read for all generations.
- The iPhone revolutionized the smartphone industry , setting new standards for design and functionality.
Definition Thesis Statements
- Success is a subjective term , defined differently by each individual based on their goals and values.
- Beauty is a complex concept , influenced by cultural, psychological, and personal factors.
- Intelligence is not solely based on IQ , but also includes emotional and social intelligence.
- Happiness is a state of well-being , influenced by external and internal factors.
- Leadership involves not just authority but also responsibility , including the ability to inspire and guide others.
Process Thesis Statements
- The process of brewing coffee involves several key steps , from bean selection to brewing technique, that influence the final flavor.
- Creating a budget involves tracking income and expenses , setting financial goals, and making adjustments as needed.
- The process of writing a novel involves planning, drafting, and revising , each stage requiring different skills and focus.
- Learning a new language involves mastering vocabulary, grammar, and cultural nuances , requiring consistent practice and immersion.
- Building a successful startup involves market research, product development, and effective marketing strategies .
Descriptive Thesis Statements
- The Grand Canyon offers breathtaking vistas , showcasing the raw beauty and power of nature.
- The Mona Lisa captivates audiences with its enigmatic expression , intricate details, and revolutionary techniques.
- New York City is a melting pot of cultures , offering a diverse range of experiences from food to entertainment.
- The Northern Lights are a natural phenomenon , characterized by vibrant colors and patterns in the night sky.
- The Amazon Rainforest is a complex ecosystem , home to a diverse range of flora and fauna.
Controversial Thesis Statements
- Genetically modified foods pose potential health risks and should be clearly labeled.
- Euthanasia should be legalized under specific conditions , to preserve the dignity and choice of terminally ill patients.
- Surveillance technology poses a threat to individual privacy , requiring stricter regulations.
- The legalization of marijuana has both pros and cons , affecting health, economy, and social issues.
- The gender pay gap is a systemic issue , requiring legislative action for equal pay.
Narrative Thesis Statements
- My journey to becoming a doctor was fueled by personal experiences , shaping my view of healthcare.
- The most impactful moment of my life was moving to a new country , which taught me resilience and adaptability.
- My passion for photography started as a hobby but evolved into a career , shaping my artistic vision.
- The experience of hiking the Appalachian Trail was transformative , offering lessons in perseverance and self-discovery.
- My year of traveling solo taught me the importance of independence and adaptability , enriching my perspective on life.
Research Thesis Statements
- The impact of climate change on coral reefs requires immediate attention , as indicated by recent scientific studies.
- The effects of video games on cognitive development are largely positive , contrary to popular belief.
- The influence of social media on body image is significant , particularly among young adults.
- The benefits of intermittent fasting are supported by scientific evidence , including improved metabolic health and longevity.
- The role of artificial intelligence in healthcare is expanding , offering promising solutions for diagnosis and treatment.
Opinion Thesis Statements
- In my opinion, remote learning is less effective than traditional classroom education , due to lack of social interaction and hands-on experience.
- I believe that mental health should be given equal importance as physical health in public healthcare systems.
- I think that electric cars are the future of transportation , offering a sustainable alternative to fossil fuels.
- I feel that organic food is worth the higher price , due to its health benefits and environmental impact.
- In my view, freelancing offers more freedom and flexibility than a 9-to-5 job , although it comes with its own set of challenges.
Proposal Thesis Statements
- I propose that schools implement mindfulness programs to improve student well-being and academic performance.
- I suggest that companies adopt a four-day workweek to increase productivity and employee satisfaction.
- I recommend that local governments invest in green infrastructure to combat the effects of climate change.
- I advocate for stricter gun control laws to reduce violence and improve public safety.
- I propose that healthcare be made universally accessible , to ensure that all citizens receive the care they need.
Reflective Thesis Statements
- Reflecting on my college experience, I realize the importance of time management in achieving academic success.
- Looking back on my career, I see the value of continuous learning in staying relevant in the job market.
- Upon reflection, my travels have broadened my understanding of cultural diversity , enriching my worldview.
- Reflecting on my relationships, I understand the importance of open communication in maintaining healthy connections.
- Looking back at my childhood, I appreciate the role of family support in shaping my values and aspirations.
Hypothetical Thesis Statements
- If renewable energy were universally adopted, it could significantly reduce carbon emissions , mitigating the effects of climate change.
- If education were made more accessible, it would lead to greater social mobility and a more equitable society.
- If healthcare were universally accessible, it would improve public health outcomes and reduce healthcare costs.
- If public transportation were more efficient, it could reduce traffic congestion and improve air quality.
- If mental health services were more widely available, it would reduce the stigma surrounding mental health issues and improve public well-being.
Future-Oriented Thesis Statements
- As technology continues to advance, ethical considerations will become increasingly important in fields like AI and biotechnology.
- As the global population grows, sustainable agriculture will become crucial in meeting the world’s food needs.
- As remote work becomes more prevalent, companies will need to adapt their management strategies to maintain productivity and employee engagement.
- As climate change intensifies, global cooperation will be essential in implementing effective mitigation strategies.
- As mental health awareness increases, the demand for qualified mental health professionals will rise , necessitating improvements in training and education.
How to Write a Thesis Statement?
Start by understanding what a thesis statement is: it’s a sentence that encapsulates your paper’s primary argument or point. The 3 parts of a thesis statement generally include the subject, the precise opinion, and the blueprint of reasons.
First, identify the subject or topic of your paper. This is the broad area that your research or essay will cover.
Next, you need to formulate a precise opinion on your chosen subject. This assertion gives your paper a unique angle and a clear direction.
Finally, the blueprint of reasons outlines the main points or arguments you will use to support your opinion. These will form the body of your essay or research paper.
Now that we’ve outlined the 3 parts, let’s talk about how to start.
- Brainstorm: Begin by brainstorming ideas related to your topic. This is a crucial step that helps in defining your precise opinion and blueprint of reasons.
- Narrow down: Based on your brainstorming, narrow down your focus to a specific aspect of your topic.
- Write a working thesis statement: Craft a working thesis statement based on your narrowed-down focus. This statement doesn’t need to be perfect yet, but it should serve as a guide for your research or writing process.
- Refine: As your research progresses, refine your thesis statement. Make sure it clearly communicates your argument and the main points that support it.
- Review and Revise: Once your essay or research paper is complete, revisit your thesis statement. Ensure it still aligns with the arguments you presented in your paper.

By following these steps, you can construct a good thesis statement that will steer your paper towards a compelling argument.
Tips for Creating Effective Thesis Statements
Here are ten straightforward tips to make your thesis statement effective and engaging.
- Focus on Detail: Your thesis statement should clearly outline your main argument. Avoid vagueness and stay precise.
- Create a Spark: Make your thesis statement thought-provoking. It should incite a reader to think about the subject in depth.
- Keep it Brief: Short, crisp sentences often make the strongest statements. Aim to keep your thesis within one or two lines.
- Locate it Right: Position your thesis statement at the end of your introduction. It provides a smooth transition into the main body.
- Use Solid Evidence: Make sure each part of your thesis can be supported with concrete evidence from your research.
- Mirror Your Structure: Your thesis should give a glimpse into how your essay or paper is organized.
- Ensure Consistency: The entire content of your paper should align with the thesis statement, reinforcing your main argument.
- Avoid Being Predictable : Stay away from cliches or commonly used structures. Let your unique voice shine through your thesis.
- Revise if Required: As you delve deeper into your topic, you may need to tweak your thesis statement to better fit your findings.
- Welcome Feedback: Constructive critique can help refine your thesis statement, making it more compelling and clear.
Thesis Statement Format
A well-structured thesis statement generally follows this format:
- Subject : This is the primary topic or subject of your research or essay.
- Claim/Position : This is your stance or claim about the subject. It’s the argument you will be supporting throughout your paper.
- Supporting Points : These are the main points or ideas that you will use to back up your claim.
Here’s an example in a simple format:
[Subject] + [Claim/Position] + [Supporting Points]
This could look like:
“Exposure to sunlight (subject) has significant health benefits (claim/position) including boosting vitamin D levels, improving mood, and regulating sleep (supporting points) .”
Remember, your thesis statement should be concise, clear, and should directly answer the question or task set in the assignment.
Blank Thesis Statement
Here’s a blank outline for a thesis statement that you can use as a starting point:
“[Your Subject] is significant because it [Your Claim/Position], due to [Your Supporting Points].”
Simply fill in the blanks with your specific details. Remember, the subject is what you’re discussing, the claim/position is your argument about the subject, and the supporting points are the reasons or evidence that back up your claim.
Examples of Good Thesis Statements
1. “Mindfulness meditation can significantly reduce stress levels due to its effects on the nervous system, promoting relaxation and emotional balance.”
2. “The implementation of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, is crucial to combat climate change and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.”
3. “Understanding cultural differences enhances international business communication by fostering mutual respect, minimizing misunderstandings, and building stronger relationships.”
4. “Maintaining a balanced diet and regular exercise routine is critical for optimal health, contributing to weight control, enhanced mood, and increased energy levels.”
5. “Education reform should focus on skills-based learning, given its potential to better prepare students for the job market, encourage critical thinking, and foster lifelong learning.”
6. “Social media plays a significant role in modern politics, shaping public opinion, promoting political engagement, and serving as a platform for activism.”
7. “Technological advancements in agriculture, including precision farming and biotechnology, can address global food security by boosting crop yields and adapting to changing climates.”
8. “Early intervention in children with developmental disorders aids in better academic performance, improved social skills, and higher quality of life in the long term.”
9. “Artificial intelligence in healthcare can enhance patient care by improving diagnosis accuracy, personalizing treatment plans, and streamlining administrative tasks.”
10. “Promoting diversity in the workplace leads to increased creativity, broader perspectives, and improved problem-solving due to the variety of experiences and backgrounds.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Research Paper
1. “The proliferation of electric vehicles can significantly curb greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to the global fight against climate change.”
2. “Exploring the therapeutic potential of psychedelic substances could revolutionize mental health treatment, offering new avenues for conditions resistant to traditional therapy.”
3. “The rise of telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic has demonstrated its viability for providing accessible and cost-effective healthcare solutions, particularly in remote areas.”
4. “Blockchain technology has transformative potential beyond cryptocurrency, with applications in supply chain transparency, digital identity verification, and secure data sharing.”
5. “Understanding the impact of microplastics on marine ecosystems is critical for developing effective environmental policies and fostering sustainable consumption habits.”
6. “The integration of AI in education can personalize learning experiences, improve student engagement, and aid teachers in instructional design and assessment.”
7. “Investigating the relationship between gut microbiota and mental health may offer insights into novel treatments for depression, anxiety, and other mental disorders.”
8. “The ethical implications of gene editing technologies like CRISPR must be addressed to balance the potential health benefits with societal and moral considerations.”
9. “Examining the role of social media in modern conflicts can help develop strategies for information management, conflict resolution, and peacebuilding efforts.”
10. “Research into sustainable farming practices can contribute to food security, environmental conservation, and the socio-economic wellbeing of farming communities.”
High School Thesis Statement Examples
1. “School uniforms should not be mandatory as they limit students’ self-expression, creativity, and individuality.”
2. “Integrating financial literacy classes in high school curriculums can better prepare students for adulthood by teaching essential skills like budgeting, investing, and debt management.”
3. “Shakespeare’s ‘Romeo and Juliet’ portrays the consequences of family feuds and impulsive decisions, demonstrating the importance of communication and reconciliation.”
4. “The use of technology in classrooms enhances the learning experience by providing interactive content, facilitating collaboration, and catering to different learning styles.”
5. “Recycling programs in high schools can foster environmental responsibility, reduce waste, and serve as a practical example of sustainability principles.”
6. “In ‘To Kill a Mockingbird’, Harper Lee uses the character of Atticus Finch to explore themes of morality, justice, and racial inequality.”
7. “School cafeterias should offer healthier food options to combat the rising rates of childhood obesity and promote better eating habits.”
8. “Participation in extracurricular activities like sports, clubs, and arts programs can enhance a high school student’s academic performance, social skills, and self-esteem.”
9. “J.D. Salinger’s ‘The Catcher in the Rye’ uses the journey of its protagonist, Holden Caulfield, to depict the struggles of adolescence and the quest for identity.”
10. “High schools should start later in the day to accommodate teenagers’ biological sleep patterns, improving students’ attention, mood, and academic performance.”
Middle School Thesis Statement Examples
1. “Keeping pets at a young age can teach children responsibility, empathy, and the importance of companionship.”
2. “In ‘Harry Potter’, J.K. Rowling explores themes of friendship, courage, and the struggle between good and evil through a magical, captivating narrative.”
3. “Recycling at school and at home helps protect the environment by reducing waste, conserving resources, and reducing pollution.”
4. “Playing a musical instrument can enhance a middle school student’s cognitive abilities, boost self-confidence, and foster discipline.”
5. “Reading is more than a school subject; it’s a gateway to learning, understanding different perspectives, and developing critical thinking skills.”
6. “Bullying in middle school should be addressed promptly and effectively to protect students’ wellbeing and create a supportive learning environment.”
7. “Outdoor education can supplement traditional classroom learning by promoting physical activity, fostering teamwork, and connecting students with nature.”
8. “In ‘The Hobbit’, J.R.R. Tolkien uses Bilbo Baggins’ journey to explore personal growth, bravery, and the importance of home.”
9. “School homework should be thoughtfully assigned, balancing the need for academic reinforcement with students’ time for extracurricular activities and relaxation.”
10. “Involving students in community service projects can foster civic responsibility, increase social awareness, and promote personal development.”
College Thesis Statement Examples
1. “Effective corporate social responsibility initiatives can enhance a company’s reputation, foster customer loyalty, and contribute to sustainable business practices.”
2. “The portrayal of mental health in modern cinema influences societal perceptions, highlighting the need for accurate and sensitive representation.”
3. “The evolution of women’s roles in Shakespeare’s plays reflects the changing societal attitudes towards gender during his time.”
4. “The rise of gig economy demonstrates a shift in employment patterns, with implications for workers’ rights, economic stability, and labor laws.”
5. “Feminism in Jane Austen’s novels subtly challenges the societal norms of her time, advocating for women’s independence and intellect.”
6. “Understanding the causes and effects of food deserts can inform public policy on nutrition, health, and urban planning.”
7. “Mandatory voting can increase political engagement, ensure representativeness, and uphold the democratic principle of political equality.”
8. “Exploring the cultural significance of hip-hop music reveals its influence on social issues, race relations, and youth culture.”
9. “Investigating the impact of climate change on global migration patterns can help formulate humanitarian and environmental policies.”
10. “The ethical considerations of artificial intelligence in healthcare encompass issues of patient privacy, algorithmic bias, and the doctor-patient relationship.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Essays
1. “The popularity of reality television reveals a societal fascination with real-life drama, celebrity culture, and the human experience under unique circumstances.”
2. “Traveling abroad can broaden one’s perspective by exposing individuals to new cultures, languages, and ways of life.”
3. “Mindful parenting promotes a healthy parent-child relationship, fostering emotional understanding, patience, and effective communication.”
4. “Sustainable fashion, though often seen as a trend, is a necessary response to the environmental and social implications of fast fashion.”
5. “Social networking platforms have revolutionized communication, but also present issues related to privacy, misinformation, and mental health.”
6. “The depiction of superheroes in comic books mirrors societal values and concerns of different eras, offering insight into cultural trends and ideologies.”
7. “Bilingual education benefits students by enhancing cognitive flexibility, promoting cultural awareness, and offering competitive advantages in the global job market.”
8. “Adopting a plant-based diet can contribute to personal health and environmental sustainability, addressing issues like animal welfare, climate change, and resource consumption.”
9. “Street art, often dismissed as vandalism, is a form of public expression that reflects societal issues, promotes dialogue, and beautifies urban spaces.”
10. “The rise of eSports challenges traditional perceptions of sports, demonstrating the importance of strategic thinking, teamwork, and digital proficiency in the modern age.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Personal Essays
1. “My volunteering experiences at the local food bank have underscored the importance of community service in alleviating poverty and promoting social unity.”
2. “Growing up in a bilingual household has enriched my cultural understanding and equipped me with effective communication skills in a multicultural world.”
3. “Overcoming adversity in my childhood has fostered resilience, empathy, and a determination to advocate for underprivileged children.”
4. “My journey in amateur photography has helped me appreciate the beauty in everyday life and taught me the power of visual storytelling.”
5. “Training for a marathon transformed not only my physical health but also taught me the values of discipline, perseverance, and goal-setting.”
6. “Navigating college as a first-generation student has been challenging yet rewarding, fostering independence, adaptability, and a strong work ethic.”
7. “The year I spent traveling solo after high school broadened my perspective, helped me understand different cultures, and instilled a sense of self-reliance.”
8. “Adopting a rescue dog changed my life, teaching me about responsibility, companionship, and the joy of giving a pet a second chance.”
9. “My passion for sustainable living, nurtured through family practices and education, has inspired me to advocate for environmental causes and green initiatives.”
10. “My experience in the school band has not only enhanced my musical skills but also instilled a deep appreciation for collaboration and shared success.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Argumentative Essay
1. “Animal testing for cosmetics should be banned due to its inhumane nature, unreliability, and the availability of alternative testing methods.”
2. “Schools should implement stricter anti-bullying policies to protect students, promote a healthy learning environment, and prevent long-term psychological effects.”
3. “Internet censorship infringes upon freedom of speech, stifles creativity and innovation, and can be used as a tool for political control.”
4. “Capital punishment should be abolished because it does not effectively deter crime, is cost-inefficient, and violates basic human rights.”
5. “Mandatory vaccination is necessary to maintain herd immunity, protect vulnerable populations, and prevent the resurgence of deadly diseases.”
6. “The government should impose stricter regulations on fast food industries to combat the obesity epidemic, improve public health, and reduce healthcare costs.”
7. “Violent video games should not be blamed for real-world violence, as there is no concrete evidence linking the two, and they can offer cognitive benefits.”
8. “Plastic bag bans are essential to reduce environmental pollution, conserve resources, and promote sustainable consumer habits.”
9. “Public funding for arts education is crucial for fostering creativity, enhancing cultural understanding, and improving academic performance in other subjects.”
10. “Telecommuting should be encouraged to reduce carbon emissions, improve work-life balance, and decrease overhead costs for businesses.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Narrative Essay
1. “My first solo trip to Europe was a whirlwind of self-discovery, independence, and an appreciation for diverse cultures.”
2. “Landing my first job taught me the values of hard work, resilience, and the joy of earning my own money.”
3. “Moving to a big city from a small town marked a significant turning point in my life, filled with challenges, adaptation, and personal growth.”
4. “The experience of surviving a hurricane emphasized the power of community, the importance of preparation, and the unpredictable force of nature.”
5. “Adopting a healthier lifestyle transformed my life, leading to a profound personal journey toward wellness, self-care, and positive change.”
6. “Learning to play the guitar during the pandemic not only developed a new skill but also provided an emotional outlet in difficult times.”
7. “My first failure in a baking contest taught me that success is a journey of continuous learning, experimentation, and embracing mistakes.”
8. “Living with a roommate for the first time was a rollercoaster ride of shared responsibilities, conflict resolution, and cherished camaraderie.”
9. “Coaching a kids’ soccer team was a rewarding experience, imparting lessons about teamwork, discipline, and the pure joy of sport.”
10. “My encounter with a humpback whale while diving in Hawaii deepened my respect for marine life and ignited a commitment to ocean conservation.”
Short Thesis Statement Examples
1. “Public libraries are indispensable resources for communities, providing access to knowledge, digital services, and learning opportunities.”
2. “Climate change is a global issue demanding immediate and collective action for mitigation and adaptation.”
3. “School uniforms restrict students’ freedom of expression and individuality.”
4. “The portrayal of women in media influences societal gender norms and expectations.”
5. “Fast food consumption contributes to obesity and other health issues.”
6. “Bilingual education fosters cognitive development and cultural appreciation.”
7. “Artificial intelligence will revolutionize the future of work.”
8. “Animal testing is unethical and often unnecessary due to technological alternatives.”
9. “Social media impacts mental health, affecting self-esteem and fostering comparison.”
10. “Music education enhances cognitive abilities, creativity, and emotional intelligence.”
Thesis Statement Examples for Short Story
1. “Through the use of vivid imagery and symbolism, the short story ‘The Necklace’ explores the consequences of pride and the pursuit of material wealth.”
2. “In the short story ‘Hills Like White Elephants,’ Ernest Hemingway skillfully portrays the complexities of communication, addressing themes of choices, power dynamics, and the implications of decision-making.”
3. “Kate Chopin’s ‘The Story of an Hour’ delves into the theme of female liberation in a patriarchal society, exemplifying the profound impact of personal freedom and societal constraints.”
4. “Through the exploration of guilt, redemption, and the complexities of human nature, Nathaniel Hawthorne’s ‘Young Goodman Brown’ unveils the dark undercurrents of Puritan society.”
5. “Alice Walker’s ‘Everyday Use’ delves into the significance of heritage and the tension between embracing cultural roots and seeking individual identity.”
6. “Anton Chekhov’s ‘The Lady with the Dog’ skillfully depicts the transformative power of love and its ability to challenge societal norms.”
7. “In ‘The Cask of Amontillado,’ Edgar Allan Poe creates a chilling atmosphere of revenge and deceit, exploring themes of betrayal, obsession, and the dark side of human nature.”
8. “Through the theme of societal conformity and individuality, Shirley Jackson’s ‘The Lottery’ raises profound questions about tradition, morality, and the dangers of blindly following rituals.”
9. “In ‘The Gift of the Magi,’ O. Henry presents a heartwarming tale of selflessness and sacrifice, emphasizing the true value of love and the spirit of giving.”
10. “Katherine Mansfield’s ‘The Garden Party’ delves into class distinctions, shedding light on the tension between privilege and empathy in a vividly portrayed social event.”
Informative Thesis Statement Examples
1. “The advancements in renewable energy technologies, such as solar and wind power, offer a promising solution to combat climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels.”
2. “The impact of social media on society is multifaceted, influencing communication patterns, shaping public opinion, and presenting both opportunities and challenges for individuals and businesses.”
3. “Understanding the principles and benefits of mindfulness meditation can help individuals reduce stress, improve mental well-being, and enhance overall quality of life.”
4. “Exploring the history and cultural significance of traditional festivals provides valuable insights into the customs, beliefs, and values of different communities around the world.”
5. “The study of genetics and genomics has revolutionized healthcare, leading to advancements in personalized medicine, disease prevention, and targeted therapies.”
6. “Investigating the effects of climate change on biodiversity reveals the interconnectedness of ecosystems, the risk of species extinction, and the urgency of conservation efforts.”
7. “Exploring the impact of technology on education reveals its transformative potential in enhancing learning experiences, promoting digital literacy, and preparing students for the future workforce.”
8. “Understanding the causes and consequences of income inequality sheds light on socioeconomic disparities, social mobility, and the implications for individuals and society as a whole.”
9. “Exploring the historical context and significance of landmark court cases provides insight into the evolution of civil rights, constitutional interpretations, and social progress.”
10. “Studying the psychological and physiological effects of exercise highlights its positive impact on mental health, physical well-being, and overall life satisfaction.”
Examples of 3 Point Thesis Statements
1. “The legalization of marijuana should be implemented nationwide due to its potential benefits in pain management, tax revenue generation, and reducing the burden on the criminal justice system.”
2. “Effective time management skills can improve academic performance by enhancing productivity, reducing stress levels, and fostering a healthy work-life balance.”
3. “Social media addiction can have detrimental effects on mental health, interpersonal relationships, and overall well-being, necessitating the need for awareness, self-regulation, and support systems.”
4. “The three main causes of climate change are industrial emissions, deforestation, and excessive fossil fuel consumption, requiring global cooperation, policy interventions, and sustainable practices for mitigation.”
5. “Gun control measures should be implemented to enhance public safety by implementing universal background checks, restricting access to high-capacity magazines, and promoting responsible firearm ownership.”
6. “The three key components of a healthy lifestyle include regular physical activity, balanced nutrition, and sufficient sleep, contributing to overall physical and mental well-being.”
7. “Online education offers advantages of flexibility, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness, making it an increasingly popular alternative to traditional classroom-based learning.”
8. “The three major effects of air pollution on human health are respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and increased risk of lung cancer, necessitating the need for stringent environmental regulations and pollution reduction strategies.”
9. “The three main benefits of cultural diversity in the workplace are increased innovation, improved problem-solving abilities, and enhanced adaptability in global markets.”
10. “The three major consequences of deforestation are loss of biodiversity, climate change acceleration, and disruption of local ecosystems, emphasizing the urgency of conservation efforts and sustainable forest management.”
What are Good Thesis Statement Sentence Starters?
“The evidence suggests that…”
“Research indicates that…”
“It is clear that…”
“The data supports the notion that…”
“A closer examination reveals that…”
“Through analysis, it becomes apparent that…”
“It is widely acknowledged that…”
“Based on the available information, it can be argued that…”
“Scholars have long debated…”
“An important aspect to consider is…”
Can a Thesis Statement Be a Question?
Yes, a thesis statement can be a question. It serves as a thought-provoking inquiry that guides the direction of the essay and prompts exploration and analysis of the topic.
How Long should a Thesis Statement Be?
A thesis statement is generally recommended to be around 40 to 60 characters or 10 to 15 words. However, the most important aspect is that it effectively conveys the main argument or point of the essay in a clear and concise manner. The length may vary depending on the complexity of the topic and the specific requirements of the assignment.
AI Generator
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting
- +44 (0) 207 391 9032
Recent Posts
- Best Colours for Your PowerPoint Presentation: How to Choose
- How to Write a Nursing Essay
- Top 5 Essential Skills You Should Build As An International Student
- How Professional Editing Services Can Take Your Writing to the Next Level
- How to Write an Effective Essay Outline
- How to Write a Law Essay: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples
- What Are the Limitations of ChatGPT?
- How to Properly Write an Essay Outline Using ChatGpt
- Why Presentation Skills Are Important for Students
- Tips on How to Make an Essay Longer
- Academic News
- Custom Essays
- Dissertation Writing
- Essay Marking
- Essay Writing
- Essay Writing Companies
- Model Essays
- Model Exam Answers
- Oxbridge Essays Updates
- PhD Writing
- Significant Academics
- Student News
- Study Skills
- University Applications
- University Essays
- University Life
- Writing Tips

How to write a thesis statement (with examples)
Since 2006, oxbridge essays has been the uk’s leading paid essay-writing and dissertation service.
We have helped 10,000s of undergraduate, Masters and PhD students to maximise their grades in essays, dissertations, model-exam answers, applications and other materials. If you would like a free chat about your project with one of our UK staff, then please just reach out on one of the methods below.
What exactly is a thesis statement?
What if I told you that one sentence in your essay or thesis could be the difference between a First and a Fail?
It may sound absurd – perhaps even unfair – but it’s true. I refer, of course, to the thesis statement. A thesis statement is your entire essay if it were condensed into a single sentence. If your essay title is a question, then your thesis statement is the one-sentence answer.
It tends to arrive near the end of the first paragraph of a thesis.
Let’s take a look at an example from a Master of Education degree thesis:
Thesis title What constitutes ‘good writing’ for GCSE students of English?
Thesis statement The examination rubric by which GCSE English writing performance is assessed, influenced by a long history of variable ‘tastes’, may now be said to describe ‘good writing’ as that which is grammatically accurate, sophisticated, and suited to purpose, genre and audience.
(The thesis statement would be located in paragraph 1, after a brief overview of the subject).
Why is a thesis statement important?
As I mentioned, the way your thesis statement is written can be the difference between a First and a Fail. But how?
To answer that, let’s think about what ‘thesis’ means. From the Greek thésis, meaning ‘proposition’, your thesis is your main argument.
It is the position you have to support and defend for the remainder of your essay. Without something clear to defend, the fortress you build will crumble and the army you deploy will run about like headless chickens.
In essence: without a clear thesis statement, you don’t have an essay.
“Establishing a clear thesis at the start of your essay is crucial for both you and your examiner. For your examiner, it’s evidence that you have answered the question. For you, it can function as an essay plan.”
For both of you, it’s a litmus test for the quality of the argument: if you can’t fit your essay’s arguments into a sentence, they are too diffuse; and if you can’t stick to your thesis statement’s focus throughout your essay, you are not focused.
A precisely focused and well-grounded essay is more worthy of a First Class grade than one with a scattergun approach.

What should a thesis statement include?
What your thesis statement includes is determined by three things:
1. The subject and topic of the essay. 2. The purpose of the essay. 3. The length of the essay.
Let’s examine each of those in more detail to see how they can help us refine our thesis statement.
The subject and topic of the essay
Look at this real-life title from an undergraduate Sports Science essay:
What are the key differences between training recommendations for maximising muscular strength and maximising muscular hypertrophy?
The first task is, of course, to determine the subject of the essay.
In this example, that would be ‘training recommendations for maximising muscular strength and training recommendations for maximising muscular hypertrophy’.
Knowing that means that I know I will need to deploy my knowledge about those two similar but distinct areas. It also means that I should be using the specialist terminology relevant to the field, such as load, isotonic and volume.
Next, I need to determine the topic.
Here it would be ‘the key differences’ between training recommendations for those two goals. That phrase ‘key differences’ is likely to be at the heart of my thesis statement, to show that I’m on track.
With that in mind, my thesis statement might look like this:
Whilst both training outcomes require resistance training centred upon isotonic contractions, it is likely that the absolute load requirements may need to be higher for strength purposes, whilst the total training volume may need to be higher for hypertrophy purposes.
It is by no means a complete essay, but it states clearly what the ‘short answer’ to the question is, whilst paving the way for the ‘long answer’ to follow.
But what if the essay isn’t just looking for the facts organised into a specific order? What if the essay is asking for analysis? Or an argument?
The purpose of the essay
Different essay purposes require different thesis statements. Fortunately, there are only three main essay purposes, and they’re pretty easy to recognise:
1. The expository essay: This is an essay type that asks for the key facts on a subject to be laid out, with explanations. The Sports Science question above is an example of this. It asks for the WHAT and HOW of something.
2. The analytical essay: This essay type asks you not only to lay out the facts, but also to analyse and deconstruct them to better understand them. It is typical in subjects such as English Literature and Fine Art. It asks for the WHY of something.
3. The argumentative essay: This type of essay asks you to use the facts available, to analyse them for value, and then to provide a point of view about the subject. It moves more quickly through the WHAT, HOW and WHY of a topic through to: WHY DOES IT MATTER?
All of the above essay types need a thesis statement that includes a proposition (a statement which answers the question or addresses the title).
Beyond that, these three essay types all require different additions.
For the expository essay , you need to add an overview of the details of the conclusion. Let’s look at an example:
Expository essay title: What are the key differences between training recommendations for maximising muscular strength and maximising muscular hypertrophy? (BSc in Sports Science)
Expository thesis statement: Whilst both training outcomes require resistance training centred upon isotonic contractions, it is likely that the absolute load requirements may need to be higher for strength purposes, whilst the total training volume may need to be higher for hypertrophy purposes. (The basic conclusion is that both approaches need isotonic resistance training; the details are teased out in bold.)
For the analytical essay , you need to add an overview of the analysis performed. Here’s an example:
Analytical essay title: Why did England and Wales vote to leave the European Union? (BA in Politics)
Analytical thesis statement: A close consideration of the voter demographics, the populist nature of political messages leading up to the referendum, and the history of Britain’s status in the EU, will demonstrate that Brexit was primarily motivated by the machinations of the Right.
(The basic conclusion is that Brexit was influenced by politicians; the analytical approach is in bold.)
For the argumentative essay , you need to add an overview of your reasoning. Another example:
Argumentative essay title: To what extent do you consider the authorship of Shakespeare’s plays to be in question? (BA in English Literature)
Argumentative thesis statement: Shakespeare’s authorship of his plays is beyond question, given both the entirely unconvincing nature of any counter-theories and the relatively unstable conception of the playwright’s identity as it stands. (The basic conclusion is that Shakespeare did write his plays; the reasoning is in bold.)
As you can see from these examples, the purpose of the essay gives a very clear demand for something beyond a simple answer.
But, there’s more!
The length of the essay
The prescribed length of the essay also defines what you need to do with your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement is a microcosm : a miniature, compressed version of your whole essay.
So, it makes sense that the length of the actual essay is going to impact upon the content of the thesis statement.
If, for example, your essay is expected to be 800 words long and on the subject of Eve in the Bible, then it would be overly ambitious for your thesis statement to say: ‘through comprehensive study of the Bible and extant criticism’. For an 800 essay, more precision will be necessary. It would be better for your thesis statement to say: ‘with due awareness of the complexity of the issue, focusing on feminist readings of Genesis .’
“Matching the scope given in your thesis statement to the depth you provide in your essay is a very effective way to ensure precision.”
Contrastingly, if your essay is expected to be 80,000 words long (a PhD thesis, for example), on the subject of stop-motion animation, it would be rather unambitious to suggest that the essay will ‘provide a visual analysis of Wallace and Gromit: The Wrong Trousers’, only. For a PhD, we would expect more content to be covered, and multiple approaches to analysis to be considered.
Indeed, matching the scope given in your thesis statement to the depth you provide in your essay is a very effective way to ensure precision.

So, to summarise, how do I write a thesis statement?
It’s a simple, three-part process:
1. Identify the question in the title (or make a question from the statement). 2. Answer that question in as few words as possible. 3. Complete the sentence by providing an overview of the foundation behind your answer.
Easy, right? It can be!
That said, there are plenty of traps that essayists can fall into with this part of the essay. Let’s look at some of these pitfalls and how to avoid them.
Pitalls to Avoid
Pitfall #1: amateurish style.
This is common throughout academic essays written by beginners. It’s not just the thesis statement that falls foul of sounding amateurish. There are plenty of ways this happens, which are beyond the scope of this argument, but the following example is a prime example: In this essay, I will explore the various pieces of evidence before concluding.
This is amateurish for a few reasons. Firstly, it doesn’t actually say anything. You could otherwise word it, ‘I will write an essay which answers the question’ – a rather wasted sentence. The next, and more forgivable issue is the use of the first-person. We want to get a sense that an individual wrote this essay, but we never want to hear them mentioned! Make sense? No? Sorry.
This should instead read more like:
This essay considers evidence from X in light of Y which ultimately reveals Z at the heart of the issue.
(It focuses on the specifics, X, Y, and Z, and is devoid of any mention of its author.)
Pitfall #2: empty phrasing
This is similar to amateurish style. However, empty phrasing is not just amateur-sounding; it’s manipulative-sounding.
Using phrases such as “in order to” instead of, simply, “to” – or “due to the fact that” instead of just “as” – look like attempts to fill up the word count with waffle rather than content. The same goes for phrases that can be substituted for one word: ‘it is evident that’ can (and should) become ‘evidently’.
Watch this thesis statement from a GCSE essay on Music go from hideous to tolerable:
Beethoven was unable to hear his work, due to the fact that he was deaf, so it is evident that he musically conceptualised the notes in order to compose. (Wordy!)
Beethoven was unable to hear his work, as he was deaf, so it is evident that he musically conceptualised the notes to compose. (Slightly less wordy.)
Beethoven’s deafness made him unable to hear his work, so evidently he musically conceptualised the notes to compose. (About as concise as such a complex sentence will get…)
Do not mistake wordiness for sophistication. Your ideas should be sophisticated; your writing should be clear.
Pitfall #3: non-standard grammar
For an examiner, the English language is not just a vehicle for your ideas. It should be, but the academic process always involves the assessment of your expression.
So, to satisfy our examiners’ prescriptive tastes, we need to adhere to the basic tenets of Standard English.
Take a look at the following thesis statement example from an A Level Sociology essay: Considering the status of BAME in Internet culture, the demonstrably racist treatment at the hands of the police, and the energy behind the BLM protests, concluding that there is hope for the future.
This sentence has no finite main verb, so it is technically not a sentence. To become a grammatical sentence, we would need to make ‘concluding’ finite: ‘it can be concluded’, or ‘we conclude’.
The writer got lost in this example because the sentence was so long!
Long sentences can also lead to a failure to make subject and verb agree, like in the next thesis statement example from a school Geography essay:
The most populous municipalities of Spain, Madrid, Barcelona, Valencia, Seville, and Zaragoza, does not rank in the top ten most dense populations of the country, with the exception of Barcelona.
Because the subject ‘municipalities’ is separated from the verb ‘does’ by eight words, it is easy to forget that they do not agree. It should, of course, be ‘do, not ‘does’.
Final words
The thesis statement, as I said at the start, can be the difference between a First and a Fail. So, take your time with it.
Write it carefully.
Then redraft and refine it several times, until it’s as good as you can make it.
The payoff is a slick, coherent thesis statement that paves the way to a great essay that really impresses your examiner.

Top 10 tips for writing a dissertation methodology

Advice for successfully writing a dissertation

How to Structure Your Dissertation in 2024
Writing services.
- Essay Plans
- Critical Reviews
- Literature Reviews
- Presentations
- Dissertation Title Creation
- Dissertation Proposals
- Dissertation Chapters
- PhD Proposals
- Journal Publication
- CV Writing Service
- Business Proofreading Services
Editing Services
- Proofreading Service
- Editing Service
- Academic Editing Service
Additional Services
- Marking Services
- Consultation Calls
- Personal Statements
- Tutoring Services
Our Company
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Become a Writer
Terms & Policies
- Fair Use Policy
- Policy for Students in England
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- [email protected]
- Contact Form
Payment Methods
Cryptocurrency payments.

Arguments and Information
Learning Objectives
- Define and explore brainstorming for argument selection
- Write a specific purpose statement
- Write effective thesis statements
When you’re preparing to speak, finding an argument, perspective, or topic can feel overwhelming. “Where should I start?” “What do I care about?” “Why should the audience care?” are all questions that you’ll likely encounter.
These are important queries, and we don’t want to downplay the difficulty in selecting an argument and formulating an idea that is worthwhile to the audience. Finding an argument that fits the context, is timely, well-reasoned, and interesting can be difficult. Oftentimes, when we sit down to think about ideas, brainstorm, and jot down some insights, our page feels oddly blank. “What should we talk about?” “Where do we start?” are common questions that race through our minds. You might experience this, too, and feel confused about how to begin selecting an argument or sorting through information to locate an interesting idea.
When you begin searching for an argument, you aren’t alone; you have tons of informational avenues that can direct you to different topics that are relevant in the world.
In fact, you’re experiencing interesting information all the time! You are constantly absorbing, sorting, and curating information and ideas. Think about your social media accounts. If you’re like us, you likely scroll through and click on articles that seem unique or insightful; you “like” or comment in response to posts that draw you in. There’s a constant flow of information (and potential speech topics).
In this chapter, we explore how to select and formulate the main argument for a speech. It’s often uncommon to snap our fingers and know exactly what our argument will be, and that’s OK! This chapter works to funnel you through brainstorming and searching toward writing a clear and narrow argument that is specific to your public speaking context. It’s our goal to encourage curiosity, and we hope that you’ll accept the challenge.
By the end of this chapter, you will have deeper critical thinking skills that lead you from broad topic ideas to specific arguments and thesis statements. Before brainstorming a topic can begin, however, you must zero in on the context.
Context is Key
Your context should always guide your preparatory process, including selecting an argument to present. The context defines why you’re there, how long you’re there for, when, and with whom.
By answering the “why” – i.e. “Why am I here?” – you can determine your general purpose for speaking: informing, persuading, or entertaining. While arguments can often be adapted to fit many purposes, it’s always important to begin any project by knowing the parameters and overarching goals – in this case, why am I speaking? For example, are you trying to:
- Solve a problem
- Reduce uncertainty
- Increase awareness
- Honor someone
Selecting a final topic before considering the context means “placing the cart before the horse,” so to speak. Your context will inform the general purpose which will guide your specific argument.
It’s important, too, to stay appraised of the other contextual factors, particularly the time. How much time you have to speak will influence how broad or narrow your argument can be. If you have 3 minutes, for example, you must have a specific and focused take-away for the audience within that short amount of time. Alternatively, a 20-minute speech provides more flexibility. There may be some ideas or arguments that aren’t feasible within certain time constraints.
As you’ll remember from Chapter 1, “context” also refers to the broader historical and cultural context. Being aware of larger cultural conversations and dialogues can assist in selecting arguments that are timely and relevant for your audience. In other words, it allows you to find information that is having an impact on your community/communities right now, and that information becomes significant to share.
If you aren’t sure how to locate such arguments, stay tuned! Below, we tackle brainstorming as a mechanism to locate potential arguments.
Brainstorming
Brainstorming is the process and practice of searching to find ideas or information. When you brainstorm, you are generating ideas to overcome a barrier or confront a problem. The problem you’re confronting is,

“What can I talk about that will sustain the audience’s attention and have an impact?” For speeches, brainstorming assists in locating and narrowing information to an accurate idea that supports the development of a well-reasoned argument.
Like we mentioned in the introduction, you are already sorting through vast amounts of information daily. We are confronted with so many ideas, research findings, memes, tweets, advertisements, and podcasts (to name a few); we develop personal strategies to find information that is meaningful and worthwhile to us.
Brainstorming is a practice that formalizes that sorting process. It asks you to make those choices more deliberately and consciously. The key to successful brainstorming is openness – you must be open to finding, locating, and narrowing down information.
Arguments are Advocacies
Topic selection and argument construction are key parts of formulating an advocacy. Speeches are meaningful and impactful communication acts. When you speak, you are supporting an idea, cause, or policy. You should approach brainstorming purposefully and intentionally with a framework in mind that “What I select matters.” Because what you select matters.
In addition, your advocacy may begin broadly, but your goal is to tailor that advocacy down to a workable argument. It’s helpful to think about your topics as orbiting an advocacy. For example, you may be interested in environmental advocacy, where environmentalism is a large and broad topic. But “environmentalism” isn’t a workable speech argument – it’s way too big! With research, critical thinking, and expertise, you’ll narrow that broad advocacy umbrella down to a workable argument – a thesis statement – and craft the remainder of your speech with that specific argument in mind.
We suggest two broad brainstorming strategies, and let’s start with the first: exploratory research.
Exploratory Research
Exploratory research encompasses brainstorming strategies that spark curiosity. When you explore, you are going on an adventure, and exploratory research is similar. You are sorting information to find broad topics or ideas (that you’ll narrow down later). Conducting a personal inventory and exploring online are two great exploratory brainstorming strategies.
Personal Inventory
An old adage states, “Write about what you know.”
To write what you know, begin by conducting a personal inventory – a process of tracking ideas, insights, or topics that you have experience with or interest in . Retail stores do regular inventories to know what is actually stocked in the business. You have much more going on in your brain and background than you can be conscious of at any one time. Being asked the right kinds of prompts can help you find ideas. Look over Table 3.1 for some prompting questions when conducting a persona inventory.
| What’s your major? | What are things that you experience that give you pause? |
| What are your hobbies? | What unique skills do you possess? |
| What online sites do commonly click through? | What social problems interest you? |
| What goals do you have? | What communities do you belong to? What have they been discussing? |
| What are barriers that you’ve experienced in working toward those goals? | What kind of values do you hold dear? |
| What’s your major? | What community problems have caught your attention? |
| What are your hobbies? | What posts do you commonly share? |
This may not be an inventory that you complete in one sitting. In fact, it’s worthwhile to jot down a few things that catch your attention throughout the day or for a series of days. Once complete, the inventory may seem long and intrusive, but digging a little deeper may help you find ideas and directions that are unique to you. Generating your list based on these questions and prompts will get you excited about your topic and talking about it to your audience.
Let’s work through a hypothetical application of the personal inventory. Imagine brainstorming for a speech, and you write the following in response to Table 3.1:
Major: Economics (for now) Goals : Complete my degree with honors; travel to Brazil; open an environmentally savvy clothing line Barriers to achieving those goals : Procrastination, assigned class schedules, expensive college and fees, problems with gaining a visa, start-up costs, competition, no regulations that incentivize environmentally-conscious clothing
As you look over these broad ideas, your next step is to highlight topics that pique your interest or are a priority. You might highlight “expensive college” as a barrier that could prohibit you from completing your economics degree on time. After all, if you are unable to afford college (or are worried about loans), you may take a semester break or drop out. Also, as an economics major, you become more interested in exploring college affordability.
As the personal inventory implies, good speech topic ideas often begin with the speaker. After all, if a speaker is intrigued by an idea, that passion is more likely to translate to an audience. But it doesn’t end there. Remember, we are just brainstorming! It’s still necessary to research and read about a topic or problem from multiple viewpoints and sources. If we only begin from ourselves, we often fail to see or learn about different perspectives, other important areas, or problems. Exploring online can help in narrowing your topic and deciding if it’s a relevant argument for your audience and community.
Explore Online
A second brainstorming technique is online exploration—searching digital information with an open mind. You can use your personal inventory as guidance or, if you’re stuck, you can read information online for ideas that spark curiosity. There are ample online locations to find an array of information, from Google News to Twitter.
When you search, look far and wide. It’s common to search and seek out information that we’re looking for, but brainstorming isn’t about finding what you already know; It’s about finding what you don’t. Use different search engines and social media platforms for help.
As you search, skim. Remember that this is an exploratory phase (we’ll talk more about searching in-depth in Chapter 4), so you don’t need to read every article that pops up on a search engine. Write down words. Write down phrases. Ask yourself questions about those words and phrases to determine how relevant and interesting they could be.
For example, if you continued brainstorming about “expensive college” – an idea on your hypothetical personal inventory—you might find a series of posts, articles, and insights that a) help you learn more and b) help narrow down the topic. You’d learn that, under the broad category of college affordability, there are a range of topics that influence students, including: student loan interest rates, textbook cost, private loans, and the depletion of Pell grants. You could attack any of these issues, of course, but some are more complicated than others. Textbooks seem like they could be a potential topic. Perhaps you recently experienced purchasing expensive college textbooks. Perhaps you loaned a friend money after their textbook bill made it difficult to pay rent. After reflecting, books seem ripe for advocacy.
Whenever you are exploring a topic online, it is important to remember that if you have one good source, you probably have several. The trick is being able to use that one good article to track down multiple sources. For example, a Vox article about textbooks, titled “The High Cost of College Textbooks, Explained,” provides opportunities for more online exploration. Below is a list of ideas or concepts to click on or research in other tabs. Look for these in every article as you brainstorm. Pretty soon, you will probably have a dozen or more tabs open, meaning you will have much more expertise and a deeper understanding of your topic.
- Hyperlinks : journalists do not cite their sources with footnotes, endnotes, or internal citations like you do for class. Instead, they hyperlink their sources to make it easier for you to track down their evidence.
- Big Ideas : You can easily Google main topics of an article to see how other people are talking about it. This will allow you to see more than one perspective on a topic and to cross-check your original article against other writers.
- People : From the author to the people they talked to or about, look up people to read their credentials and determine if they are qualified to write or talk about the relevant topic.
- Jargon: If you find any words that are unfamiliar, look them up. This will help you understand the argument better and make certain the author actually knows what they are writing about. Plus, it will give you some words to use for mind-mapping.
Before we move further into narrowing and mapping our topic, let’s conclude this section by busting a few myths about online information.
Myth # 1: Wikipedia is bad. You’ve likely heard that “you can absolutely not cite Wikipedia [in a formal essay or speech].” While, yes, Wikipedia is a collaborative encyclopedia, meaning that anyone can technically add to its content, its pages can be useful for brainstorming. We recommend using Wikipedia in two ways.
First, search Wikipedia for their internally-cited material. If you’ve used Wikipedia recently, you know that the content includes references to other sources that validate the findings. Use those! The references are helpful in locating (often) credible sources for your own research on a topic.
Second, use Wikipedia to clarify complex ideas. Because Wikipedia is a community-based and collaborative encyclopedia, technical language is commonly translated to allow better comprehension. If you aren’t sure about an idea, search Wikipedia for help (but verify the information through other sources, too).
While we don’t recommend using Wikipedia as the source, their content can direct you toward reputable research and clarify difficult concepts.
Myth #2 : Information is neutral. It’s easy to believe that, because something is published online, it’s a neutral and reputable source. Sadly, that’s not the case. In our digital information age, virtually anyone can be an author, and that’s great! But it also reduces the reliability of information that’s being posted.
You’ve likely heard about “fake news,” but we’ll use the term propaganda – biased or misleading information that promotes a particular agenda. Propaganda is junk science, and it can’t be trusted as reliable. For example, you might notice a meme that posts a Harriett Tubman quote in support of strict immigration reform. Digging deeper, you’d likely find that the quote was misrepresented or made up to support an anti-immigrant agenda.
Advertising more subtly influences information. That’s because many information sorting sites, including Google, use an algorithm that’s specific to you. If you and a friend search the same thing, your search results may differ, especially after the first page.
Does that mean you can’t use Google? Of course not. We do! But you should be aware that targeted sites may be rising to the top, and when you search, dig deep and search multiple pages.
Social Media Skepticism: You may rely on social media as an online brainstorming tool. As you scroll, videos or posts provide provocative ideas, stories, or perspectives that might spark your interest or give you an idea for a speech topic. Be weary, however, of content from influencers who may be incentivized through sponsorships and lack experience or credibility on a topic. And remember that your social media content is tailored for you by algorithms, so always triple-check what you trust from your feed!
Using a Mind Map
After conducting exploratory research to dig a little deeper, a mind map is a second brainstorming strategy to narrow and isolate a topic. A mind map is a visual tool that allows you to chart and expand key topic ideas or concepts.
As you mind map, use the following tips:
- Start with a big idea.
- Break this big concept down into smaller ideas until you can’t break them down anymore.
- Look up synonyms or like words.
- Write down any words you find during your research to tap into the larger conversation.
Figure 3.2 is an example of a mind map based on “college affordability.” You can see how the topic narrowed from college affordability to textbook costs. The mind map also includes words that were used in the Vox article, such as “open textbooks.” Jotting down ideas and language that are used in source information will provide insight into common wording used by topic experts. Keep in mind, if you do not like mind maps, make a list or develop some alternative method, but make certain to keep track of everything.
You can create a mind map using a program like Popplet , Powerpoint, Word, or Google Docs. We usually just grab a blank sheet of paper and a pencil, though.
As you expand topics through a mind map, the narrower that your argument becomes. Instead of a broad approach to “college affordability,” you now have options to explore textbook costs, open textbooks, or open educational resources.
We promise this will not be a waste of your time. Writing down your ideas and thoughts will help you identify keywords for further searching, so you won’t have to come up with words on the fly. As you search, you can easily scratch off words that fail to get you any information, mark the words that seem to get you exactly what you need, or jot down new words you stumble across as you search. All of this will save you time in the long run because it won’t leave you searching for just the right word or trying the wrong word over and over.
Formulating a Specific Purpose Statement
After identifying your general purpose (to inform, to persuade, or to entertain) and brainstorming key topic ideas, you can start to move in the direction of the specific purpose.
A specific purpose statement builds on your general purpose (such as to inform) and makes it more specific (as the name suggests). So, if you’re giving a persuasive speech, your general purpose will be to persuade your audience about, for example, the rising cost of textbooks. Written together, your specific purpose would read, “to persuade my audience to support campus solutions to rising textbook costs.”
Your general purpose and audience will influence how to write your specific purpose statement (see Table 3.3.)
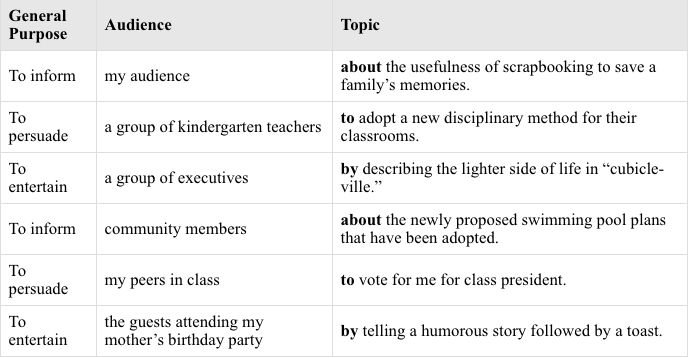
Table 3.3. (Stand Up, Speak Out).
Table 3.3 demonstrates how to move from the general purpose to the specific purpose while keeping your audience in mind.
So far, so good, right? Before moving to your thesis, be aware these common pitfalls for writing specific purpose statements.
Being Too Broad
Specific purpose statements sometimes try to cover far too much and are too broad. You are funneling a broad topic to a specific argument, so don’t stop at the topic. Instead, ask, “am I trying to do too much?”
Consider this specific purpose statement: To explain to my classmates the history of ballet.
This subject could result in a three-hour lecture, maybe even a whole course. You will probably find that your first attempt at a specific purpose statement will need refining.
These examples are much more specific and much more manageable given the limited amount of time you will have:
To explain to my classmates how ballet came to be performed and studied in the U.S. To explain to my classmates the difference between Russian and French ballet. To explain to my classmates how ballet originated as an art form in the Renaissance. To explain to my classmates the origin of the ballet dancers’ clot h ing.
Often, broadness is signaled by the use of “and,” where a specific statement is making two arguments.
These examples cover two different topics:
To explain to my audience how to swing a golf club and choose the best golf shoes. To persuade my classmates to be involved in the Special Olympics and vote to fund better classes for the intellectually disabled.
Too Specialized
The second problem with specific purpose statements is the opposite of being too broad, in that some specific purposes statements are so focused that they might only be appropriate for people who are already extremely interested in the topic or experts in a field. For example:
To inform my classmates of the life cycle of a new species of lima bean (botanists, agriculturalists). To inform my classmates about the Yellow 5 ingredient in Mountain Dew (chemists, nutritionists). To persuade my classmates that JIF Peanut Butter is better than Peter Pan. (organizational chefs in large institutions) .
Formulating a Thesis
While you will not actually say your specific purpose statement during your speech, you will need to clearly state what your focus and main points are going to be. Your specific purpose is still not your main argument. It’s part of the funnel as you move to your main argument, or thesis statement. A thesis statement is a single, declarative statement that outlines the purpose of your speech.
The point of your thesis statement is to reveal and clarify the main argument of your speech.
This part of the process is important because it’s where your topic becomes an argument. Like we mentioned in the introduction, you will funnel your advocacy down to a specific argument that fits the context and goals of your speech.
However, as you are processing your ideas and approach, you may still be working on them. Sometimes those main points will not be clear to you immediately. As much as we would like these writing processes to be straightforward, sometimes we find that we have to revise our original approach. This is why preparing a speech the night before you are giving it is a really, really bad idea. You need lots of time for the preparation and then the practice.
Sometimes you will hear the writing process referred to as “ iterative.” This word means, among other things, that a speech or document is not always written in the same order as the audience finally experiences it. You may have noticed that we have not said anything about the introduction of your speech yet. Even though that is the first thing the audience hears, it may be one of the last parts you actually compose. It is best to consider your speech flexible as you work on it, and to be willing to edit and revise. If your instructor asks you to turn the outline in before the speech, you should be clear on how much you can revise after that. Otherwise, it helps to know that you can keep editing your speech until you deliver it, especially while you practice.
Here are some examples that pair the general purpose, specific purpose statements and thesis statements.
General Purpose: To inform Specific Purpose: To demonstrate to my audience the correct method for cleaning a computer keyboard. Thesis : Your computer keyboard needs regular cleaning to function well, and you can achieve that in four easy steps.
General Purpose : To persuade Specific Purpose: To persuade my political science class that labor unions are no longer a vital political force in the U.S. Thesis : Although for decades in the twentieth century labor unions influenced local and national elections, in this speech I will point to how their influence has declined in the last thirty years.
General Purpose : To persuade Specific Purpose: To motivate my audience to oppose the policy of drug testing welfare recipients. Thesis : Many voices are calling for welfare recipients to have to go through mandatory, regular drug testing, but this pol-icy is unjust, impractical, and costly, and fair-minded Americans should actively oppose it.
General Purpose : To inform Specific Purpose: To explain to my fellow civic club members why I admire Representative John Lewis. Thesis : John Lewis has my admiration for his sacrifices during the Civil Rights movement and his service to Georgia as a leader and U.S. Representative.
Notice that in all of the above examples that neither the specific purpose nor the central idea ever exceeds one sentence. You may divide your central idea and the preview of main points into two sentences or three sentences, depending on what your instructor directs. If your central idea consists of more than three sentences, then you probably are including too much information and taking up time that is needed for the body of the speech.
For thesis statements, remember the following few guidelines:
- Do not write the statement as a question.
- Use concrete language (“I admire Beyoncé for being a talented performer and businesswoman”), and avoid subjective terms (“My speech is about why I think Beyoncé is the bomb”) or jargon and acronyms (“PLA is better than CBE for adult learners.”)
Remember that your thesis statement cements your main argument – it’s the foundation to building the speech. A clear and focused thesis statement define the speech, and we’ll continue building the research and content around your argument.
Case Studies in Specific Purposes and Thesis Statements
Case Study One : Mitchell is taking a Fundamentals of Speech course in his second year of college. As a member of the college’s tennis team, he wants to speak on his favorite subject, tennis. He is assigned an informative speech that should be seven minutes long and use four external sources (other than his own experience). He realizes off the bat that he knows a great deal about the subject as far as how to play and be good at it, but not much about the history or origins or the international impact of the sport. He brainstorms a list of topics: 1. Famous tennis players 2. Rules of tennis 3. How to start playing tennis 4. How to buy or choose equipment for tennis 5. Why tennis is a great sport 6. Tennis organizations 7. Where tennis came from 8. Dealing with tennis injuries 9. Tennis and the Olympics 10. Famous tennis tournaments—grand slam events
However, he also wants to be sure that his audience is not bored or confused. His instructor gives him a chance to get in a small group and have four of his classmates give him some ideas about the topics. He finds out no one in his group has ever played tennis but they do have questions. He knows that everyone in his class is 18-24 years old, single, no children, enrolled in college, and all have part-time jobs.
Critique Mitch’s brainstorm topics based on what you know. What should he do? Can you come up with a good starting specific purpose?
Case Study Two : Bonita is required to give a 5- to 6-minute presentation as part of a job interview. The interview is for a position as public relations and social media director of a nonprofit organization that focuses on nutrition in a five-county region near her home. There will be five people in her audience: the president of the organization, two board members, the office manager (who is also the Human Resources director), and a volunteer. She has never met these people. Bonita has a college degree in public relations, so she knows her subject. She does as much research on the organization as she can and finds out about their use of social media and the Internet for publicity, marketing, and public relations. It does have a Facebook page but is not utilizing it well. It does not have any other social media accounts.
What would you suggest for Bonita? Here are some questions to consider. Should she be persuasive, informative, or inspiring? (General purpose) What should be her specific content area? How can she answer the two questions of the value of her topic to the audience and why would the audience think she is credible?
In this chapter, we discussed best practices for brainstorming topics that funnel to an argument. Argument selection is exciting, and use these tips alongside your other creative information gathering skills. Next up: research!
Speak Out, Call In: Public Speaking as Advocacy, 2nd ed. Copyright © 2019 by Meggie Mapes is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement. Let's take a minute to first understand what ...
Placement of the thesis statement. Step 1: Start with a question. Step 2: Write your initial answer. Step 3: Develop your answer. Step 4: Refine your thesis statement. Types of thesis statements. Other interesting articles. Frequently asked questions about thesis statements.
A thesis statement is a sentence in a paper or essay (in the opening paragraph) that introduces the main topic to the reader. As one of the first things your reader sees, your thesis statement is one of the most important sentences in your entire paper—but also one of the hardest to write! In this article, we explain how to write a thesis ...
A good thesis statement needs to do the following: Condense the main idea of your thesis into one or two sentences. Answer your project's main research question. Clearly state your position in relation to the topic. Make an argument that requires support or evidence.
A thesis statement: tells the reader how you will interpret the significance of the subject matter under discussion. is a road map for the paper; in other words, it tells the reader what to expect from the rest of the paper. directly answers the question asked of you. A thesis is an interpretation of a question or subject, not the subject itself.
This thesis statement is not debatable. First, the word pollution implies that something is bad or negative in some way. Furthermore, all studies agree that pollution is a problem; they simply disagree on the impact it will have or the scope of the problem. No one could reasonably argue that pollution is unambiguously good.
3. The thesis statement usually appears at the end of the first paragraph of a paper. 4. Your topic may change as you write, so you may need to revise your thesis statement to reflect exactly what you have discussed in the paper. Thesis Statement Examples. Example of an analytical thesis statement:
Step 4: Revise and refine your thesis statement before you start writing. Read through your thesis statement several times before you begin to compose your full essay. You need to make sure the statement is ironclad, since it is the foundation of the entire paper. Edit it or have a peer review it for you to make sure everything makes sense and ...
Keep your thesis prominent in your introduction. A good, standard place for your thesis statement is at the end of an introductory paragraph, especially in shorter (5-15 page) essays. Readers are used to finding theses there, so they automatically pay more attention when they read the last sentence of your introduction.
Schools should start at a later time of day. Inspired by this sample essay about school start times. Beginning the school day at a later time would stabilize students' sleep patterns, improve students' moods, and increase students' academic success. #15. Schools should distribute birth control to teens.
Thesis. Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic. Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore ...
Examples of a thesis statement for an analytical essay include: The criminal justice reform bill passed by the U.S. Senate in late 2018 ("The First Step Act") aims to reduce prison sentences that disproportionately fall on nonwhite criminal defendants.
A good thesis statement is clear, specific, and arguable. Therefore, it is necessary for you to choose the right type of thesis statement for your academic papers. Thesis statements can be classified based on their purpose and structure. Here are the primary types of thesis statements: Argumentative (or Persuasive) thesis statement
A thesis statement is a single sentence that encapsulates your main argument. It succinctly communicates your position on the topic you're researching and provides a roadmap for the supporting evidence you'll present throughout your work. How to write a thesis statement: Crafting a powerful thesis statement: Clearly there are many ways in ...
Make sure that the thesis statement does not exceed two sentences. Avoid making obvious statements such as 'this is an essay about….' or 'the point of this paper is….'. The thesis statement should be able to convey this without using such up-front language. Write clearly and articulately.
One such thing is the thesis statement. Every good essay should have one and it needs to be well-written and well-thought-out. In this article, we are going to be looking at exactly what a thesis statement is and what it is used for as well as looking at some examples of the thesis statement as a way to gain a greater understanding of what its ...
Here's an example of a good thesis statement: "In William Shakespeare's 'Macbeth', the ambition of the main character acts as a double-edged sword, driving him to achieve power at any cost, yet simultaneously leading to his tragic downfall.". This statement provides a clear position on the role of ambition in the play, setting the ...
A thesis statement template focuses your arguments and ideas into a single sentence. Use it to present your essay's topic and to share your point of view regarding the topic. The thesis statement must tell the reader about the essay, help guide your writing process, and help you focus on your arguments.
The 3 parts of a thesis statement generally include the subject, the precise opinion, and the blueprint of reasons. First, identify the subject or topic of your paper. This is the broad area that your research or essay will cover. Next, you need to formulate a precise opinion on your chosen subject.
4. Internet addiction is a disease that requires professional intervention and treatment. 5. Social media websites are personal sites, and employers have no right to monitor employees' personal lives, reprimand them, or fire them based on personal conduct on social media websites. 6.
Master the art of creating a thesis statement! Compare good and poor thesis statement examples to find out just what a strong thesis statement should be. Dictionary ... As you can see in the thesis statement examples below, you must be very specific, summarizing points that are about to be made in your paper, and supported by specific evidence.
What your thesis statement includes is determined by three things: 1. The subject and topic of the essay. 2. The purpose of the essay. 3. The length of the essay. Let's examine each of those in more detail to see how they can help us refine our thesis statement.
A thesis statement is a statement of one's core argument, the main idea(s), and/or a concise summary of an essay, research paper, etc. [1] It is usually expressed in one or two sentences near the beginning of a paper, and may be reiterated elsewhere, such as in the conclusion. In some contexts, such as in the British educational system, a thesis statement is generally considered synonymous ...
Here are some examples that pair the general purpose, specific purpose statements and thesis statements. General Purpose: To inform Specific Purpose: To demonstrate to my audience the correct method for cleaning a computer keyboard. Thesis: Your computer keyboard needs regular cleaning to function well, and you can achieve that in four easy steps.