
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Chapter 11: Presenting Your Research

Writing a Research Report in American Psychological Association (APA) Style
Learning Objectives
- Identify the major sections of an APA-style research report and the basic contents of each section.
- Plan and write an effective APA-style research report.
In this section, we look at how to write an APA-style empirical research report , an article that presents the results of one or more new studies. Recall that the standard sections of an empirical research report provide a kind of outline. Here we consider each of these sections in detail, including what information it contains, how that information is formatted and organized, and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles.
Sections of a Research Report
Title page and abstract.
An APA-style research report begins with a title page . The title is centred in the upper half of the page, with each important word capitalized. The title should clearly and concisely (in about 12 words or fewer) communicate the primary variables and research questions. This sometimes requires a main title followed by a subtitle that elaborates on the main title, in which case the main title and subtitle are separated by a colon. Here are some titles from recent issues of professional journals published by the American Psychological Association.
- Sex Differences in Coping Styles and Implications for Depressed Mood
- Effects of Aging and Divided Attention on Memory for Items and Their Contexts
- Computer-Assisted Cognitive Behavioural Therapy for Child Anxiety: Results of a Randomized Clinical Trial
- Virtual Driving and Risk Taking: Do Racing Games Increase Risk-Taking Cognitions, Affect, and Behaviour?
Below the title are the authors’ names and, on the next line, their institutional affiliation—the university or other institution where the authors worked when they conducted the research. As we have already seen, the authors are listed in an order that reflects their contribution to the research. When multiple authors have made equal contributions to the research, they often list their names alphabetically or in a randomly determined order.
In some areas of psychology, the titles of many empirical research reports are informal in a way that is perhaps best described as “cute.” They usually take the form of a play on words or a well-known expression that relates to the topic under study. Here are some examples from recent issues of the Journal Psychological Science .
- “Smells Like Clean Spirit: Nonconscious Effects of Scent on Cognition and Behavior”
- “Time Crawls: The Temporal Resolution of Infants’ Visual Attention”
- “Scent of a Woman: Men’s Testosterone Responses to Olfactory Ovulation Cues”
- “Apocalypse Soon?: Dire Messages Reduce Belief in Global Warming by Contradicting Just-World Beliefs”
- “Serial vs. Parallel Processing: Sometimes They Look Like Tweedledum and Tweedledee but They Can (and Should) Be Distinguished”
- “How Do I Love Thee? Let Me Count the Words: The Social Effects of Expressive Writing”
Individual researchers differ quite a bit in their preference for such titles. Some use them regularly, while others never use them. What might be some of the pros and cons of using cute article titles?
For articles that are being submitted for publication, the title page also includes an author note that lists the authors’ full institutional affiliations, any acknowledgments the authors wish to make to agencies that funded the research or to colleagues who commented on it, and contact information for the authors. For student papers that are not being submitted for publication—including theses—author notes are generally not necessary.
The abstract is a summary of the study. It is the second page of the manuscript and is headed with the word Abstract . The first line is not indented. The abstract presents the research question, a summary of the method, the basic results, and the most important conclusions. Because the abstract is usually limited to about 200 words, it can be a challenge to write a good one.
Introduction
The introduction begins on the third page of the manuscript. The heading at the top of this page is the full title of the manuscript, with each important word capitalized as on the title page. The introduction includes three distinct subsections, although these are typically not identified by separate headings. The opening introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting, the literature review discusses relevant previous research, and the closing restates the research question and comments on the method used to answer it.
The Opening
The opening , which is usually a paragraph or two in length, introduces the research question and explains why it is interesting. To capture the reader’s attention, researcher Daryl Bem recommends starting with general observations about the topic under study, expressed in ordinary language (not technical jargon)—observations that are about people and their behaviour (not about researchers or their research; Bem, 2003 [1] ). Concrete examples are often very useful here. According to Bem, this would be a poor way to begin a research report:
Festinger’s theory of cognitive dissonance received a great deal of attention during the latter part of the 20th century (p. 191)
The following would be much better:
The individual who holds two beliefs that are inconsistent with one another may feel uncomfortable. For example, the person who knows that he or she enjoys smoking but believes it to be unhealthy may experience discomfort arising from the inconsistency or disharmony between these two thoughts or cognitions. This feeling of discomfort was called cognitive dissonance by social psychologist Leon Festinger (1957), who suggested that individuals will be motivated to remove this dissonance in whatever way they can (p. 191).
After capturing the reader’s attention, the opening should go on to introduce the research question and explain why it is interesting. Will the answer fill a gap in the literature? Will it provide a test of an important theory? Does it have practical implications? Giving readers a clear sense of what the research is about and why they should care about it will motivate them to continue reading the literature review—and will help them make sense of it.
Breaking the Rules
Researcher Larry Jacoby reported several studies showing that a word that people see or hear repeatedly can seem more familiar even when they do not recall the repetitions—and that this tendency is especially pronounced among older adults. He opened his article with the following humourous anecdote:
A friend whose mother is suffering symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) tells the story of taking her mother to visit a nursing home, preliminary to her mother’s moving there. During an orientation meeting at the nursing home, the rules and regulations were explained, one of which regarded the dining room. The dining room was described as similar to a fine restaurant except that tipping was not required. The absence of tipping was a central theme in the orientation lecture, mentioned frequently to emphasize the quality of care along with the advantages of having paid in advance. At the end of the meeting, the friend’s mother was asked whether she had any questions. She replied that she only had one question: “Should I tip?” (Jacoby, 1999, p. 3)
Although both humour and personal anecdotes are generally discouraged in APA-style writing, this example is a highly effective way to start because it both engages the reader and provides an excellent real-world example of the topic under study.
The Literature Review
Immediately after the opening comes the literature review , which describes relevant previous research on the topic and can be anywhere from several paragraphs to several pages in length. However, the literature review is not simply a list of past studies. Instead, it constitutes a kind of argument for why the research question is worth addressing. By the end of the literature review, readers should be convinced that the research question makes sense and that the present study is a logical next step in the ongoing research process.
Like any effective argument, the literature review must have some kind of structure. For example, it might begin by describing a phenomenon in a general way along with several studies that demonstrate it, then describing two or more competing theories of the phenomenon, and finally presenting a hypothesis to test one or more of the theories. Or it might describe one phenomenon, then describe another phenomenon that seems inconsistent with the first one, then propose a theory that resolves the inconsistency, and finally present a hypothesis to test that theory. In applied research, it might describe a phenomenon or theory, then describe how that phenomenon or theory applies to some important real-world situation, and finally suggest a way to test whether it does, in fact, apply to that situation.
Looking at the literature review in this way emphasizes a few things. First, it is extremely important to start with an outline of the main points that you want to make, organized in the order that you want to make them. The basic structure of your argument, then, should be apparent from the outline itself. Second, it is important to emphasize the structure of your argument in your writing. One way to do this is to begin the literature review by summarizing your argument even before you begin to make it. “In this article, I will describe two apparently contradictory phenomena, present a new theory that has the potential to resolve the apparent contradiction, and finally present a novel hypothesis to test the theory.” Another way is to open each paragraph with a sentence that summarizes the main point of the paragraph and links it to the preceding points. These opening sentences provide the “transitions” that many beginning researchers have difficulty with. Instead of beginning a paragraph by launching into a description of a previous study, such as “Williams (2004) found that…,” it is better to start by indicating something about why you are describing this particular study. Here are some simple examples:
Another example of this phenomenon comes from the work of Williams (2004).
Williams (2004) offers one explanation of this phenomenon.
An alternative perspective has been provided by Williams (2004).
We used a method based on the one used by Williams (2004).
Finally, remember that your goal is to construct an argument for why your research question is interesting and worth addressing—not necessarily why your favourite answer to it is correct. In other words, your literature review must be balanced. If you want to emphasize the generality of a phenomenon, then of course you should discuss various studies that have demonstrated it. However, if there are other studies that have failed to demonstrate it, you should discuss them too. Or if you are proposing a new theory, then of course you should discuss findings that are consistent with that theory. However, if there are other findings that are inconsistent with it, again, you should discuss them too. It is acceptable to argue that the balance of the research supports the existence of a phenomenon or is consistent with a theory (and that is usually the best that researchers in psychology can hope for), but it is not acceptable to ignore contradictory evidence. Besides, a large part of what makes a research question interesting is uncertainty about its answer.
The Closing
The closing of the introduction—typically the final paragraph or two—usually includes two important elements. The first is a clear statement of the main research question or hypothesis. This statement tends to be more formal and precise than in the opening and is often expressed in terms of operational definitions of the key variables. The second is a brief overview of the method and some comment on its appropriateness. Here, for example, is how Darley and Latané (1968) [2] concluded the introduction to their classic article on the bystander effect:
These considerations lead to the hypothesis that the more bystanders to an emergency, the less likely, or the more slowly, any one bystander will intervene to provide aid. To test this proposition it would be necessary to create a situation in which a realistic “emergency” could plausibly occur. Each subject should also be blocked from communicating with others to prevent his getting information about their behaviour during the emergency. Finally, the experimental situation should allow for the assessment of the speed and frequency of the subjects’ reaction to the emergency. The experiment reported below attempted to fulfill these conditions. (p. 378)
Thus the introduction leads smoothly into the next major section of the article—the method section.
The method section is where you describe how you conducted your study. An important principle for writing a method section is that it should be clear and detailed enough that other researchers could replicate the study by following your “recipe.” This means that it must describe all the important elements of the study—basic demographic characteristics of the participants, how they were recruited, whether they were randomly assigned, how the variables were manipulated or measured, how counterbalancing was accomplished, and so on. At the same time, it should avoid irrelevant details such as the fact that the study was conducted in Classroom 37B of the Industrial Technology Building or that the questionnaire was double-sided and completed using pencils.
The method section begins immediately after the introduction ends with the heading “Method” (not “Methods”) centred on the page. Immediately after this is the subheading “Participants,” left justified and in italics. The participants subsection indicates how many participants there were, the number of women and men, some indication of their age, other demographics that may be relevant to the study, and how they were recruited, including any incentives given for participation.
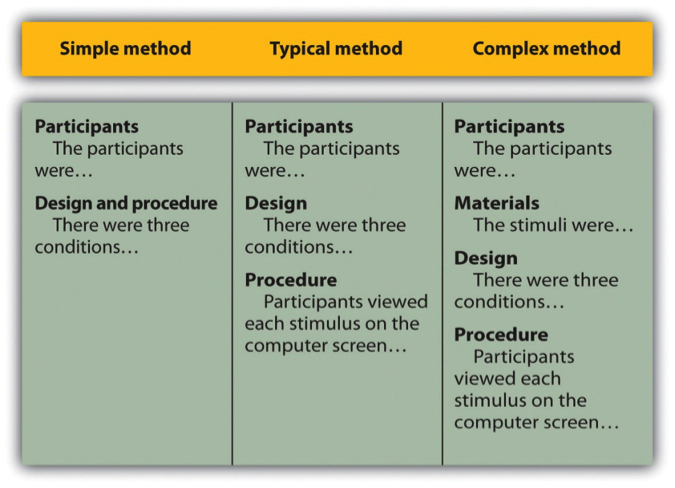
After the participants section, the structure can vary a bit. Figure 11.1 shows three common approaches. In the first, the participants section is followed by a design and procedure subsection, which describes the rest of the method. This works well for methods that are relatively simple and can be described adequately in a few paragraphs. In the second approach, the participants section is followed by separate design and procedure subsections. This works well when both the design and the procedure are relatively complicated and each requires multiple paragraphs.
What is the difference between design and procedure? The design of a study is its overall structure. What were the independent and dependent variables? Was the independent variable manipulated, and if so, was it manipulated between or within subjects? How were the variables operationally defined? The procedure is how the study was carried out. It often works well to describe the procedure in terms of what the participants did rather than what the researchers did. For example, the participants gave their informed consent, read a set of instructions, completed a block of four practice trials, completed a block of 20 test trials, completed two questionnaires, and were debriefed and excused.
In the third basic way to organize a method section, the participants subsection is followed by a materials subsection before the design and procedure subsections. This works well when there are complicated materials to describe. This might mean multiple questionnaires, written vignettes that participants read and respond to, perceptual stimuli, and so on. The heading of this subsection can be modified to reflect its content. Instead of “Materials,” it can be “Questionnaires,” “Stimuli,” and so on.
The results section is where you present the main results of the study, including the results of the statistical analyses. Although it does not include the raw data—individual participants’ responses or scores—researchers should save their raw data and make them available to other researchers who request them. Several journals now encourage the open sharing of raw data online.
Although there are no standard subsections, it is still important for the results section to be logically organized. Typically it begins with certain preliminary issues. One is whether any participants or responses were excluded from the analyses and why. The rationale for excluding data should be described clearly so that other researchers can decide whether it is appropriate. A second preliminary issue is how multiple responses were combined to produce the primary variables in the analyses. For example, if participants rated the attractiveness of 20 stimulus people, you might have to explain that you began by computing the mean attractiveness rating for each participant. Or if they recalled as many items as they could from study list of 20 words, did you count the number correctly recalled, compute the percentage correctly recalled, or perhaps compute the number correct minus the number incorrect? A third preliminary issue is the reliability of the measures. This is where you would present test-retest correlations, Cronbach’s α, or other statistics to show that the measures are consistent across time and across items. A final preliminary issue is whether the manipulation was successful. This is where you would report the results of any manipulation checks.
The results section should then tackle the primary research questions, one at a time. Again, there should be a clear organization. One approach would be to answer the most general questions and then proceed to answer more specific ones. Another would be to answer the main question first and then to answer secondary ones. Regardless, Bem (2003) [3] suggests the following basic structure for discussing each new result:
- Remind the reader of the research question.
- Give the answer to the research question in words.
- Present the relevant statistics.
- Qualify the answer if necessary.
- Summarize the result.
Notice that only Step 3 necessarily involves numbers. The rest of the steps involve presenting the research question and the answer to it in words. In fact, the basic results should be clear even to a reader who skips over the numbers.
The discussion is the last major section of the research report. Discussions usually consist of some combination of the following elements:
- Summary of the research
- Theoretical implications
- Practical implications
- Limitations
- Suggestions for future research
The discussion typically begins with a summary of the study that provides a clear answer to the research question. In a short report with a single study, this might require no more than a sentence. In a longer report with multiple studies, it might require a paragraph or even two. The summary is often followed by a discussion of the theoretical implications of the research. Do the results provide support for any existing theories? If not, how can they be explained? Although you do not have to provide a definitive explanation or detailed theory for your results, you at least need to outline one or more possible explanations. In applied research—and often in basic research—there is also some discussion of the practical implications of the research. How can the results be used, and by whom, to accomplish some real-world goal?
The theoretical and practical implications are often followed by a discussion of the study’s limitations. Perhaps there are problems with its internal or external validity. Perhaps the manipulation was not very effective or the measures not very reliable. Perhaps there is some evidence that participants did not fully understand their task or that they were suspicious of the intent of the researchers. Now is the time to discuss these issues and how they might have affected the results. But do not overdo it. All studies have limitations, and most readers will understand that a different sample or different measures might have produced different results. Unless there is good reason to think they would have, however, there is no reason to mention these routine issues. Instead, pick two or three limitations that seem like they could have influenced the results, explain how they could have influenced the results, and suggest ways to deal with them.
Most discussions end with some suggestions for future research. If the study did not satisfactorily answer the original research question, what will it take to do so? What new research questions has the study raised? This part of the discussion, however, is not just a list of new questions. It is a discussion of two or three of the most important unresolved issues. This means identifying and clarifying each question, suggesting some alternative answers, and even suggesting ways they could be studied.
Finally, some researchers are quite good at ending their articles with a sweeping or thought-provoking conclusion. Darley and Latané (1968) [4] , for example, ended their article on the bystander effect by discussing the idea that whether people help others may depend more on the situation than on their personalities. Their final sentence is, “If people understand the situational forces that can make them hesitate to intervene, they may better overcome them” (p. 383). However, this kind of ending can be difficult to pull off. It can sound overreaching or just banal and end up detracting from the overall impact of the article. It is often better simply to end when you have made your final point (although you should avoid ending on a limitation).
The references section begins on a new page with the heading “References” centred at the top of the page. All references cited in the text are then listed in the format presented earlier. They are listed alphabetically by the last name of the first author. If two sources have the same first author, they are listed alphabetically by the last name of the second author. If all the authors are the same, then they are listed chronologically by the year of publication. Everything in the reference list is double-spaced both within and between references.
Appendices, Tables, and Figures
Appendices, tables, and figures come after the references. An appendix is appropriate for supplemental material that would interrupt the flow of the research report if it were presented within any of the major sections. An appendix could be used to present lists of stimulus words, questionnaire items, detailed descriptions of special equipment or unusual statistical analyses, or references to the studies that are included in a meta-analysis. Each appendix begins on a new page. If there is only one, the heading is “Appendix,” centred at the top of the page. If there is more than one, the headings are “Appendix A,” “Appendix B,” and so on, and they appear in the order they were first mentioned in the text of the report.
After any appendices come tables and then figures. Tables and figures are both used to present results. Figures can also be used to illustrate theories (e.g., in the form of a flowchart), display stimuli, outline procedures, and present many other kinds of information. Each table and figure appears on its own page. Tables are numbered in the order that they are first mentioned in the text (“Table 1,” “Table 2,” and so on). Figures are numbered the same way (“Figure 1,” “Figure 2,” and so on). A brief explanatory title, with the important words capitalized, appears above each table. Each figure is given a brief explanatory caption, where (aside from proper nouns or names) only the first word of each sentence is capitalized. More details on preparing APA-style tables and figures are presented later in the book.
Sample APA-Style Research Report
Figures 11.2, 11.3, 11.4, and 11.5 show some sample pages from an APA-style empirical research report originally written by undergraduate student Tomoe Suyama at California State University, Fresno. The main purpose of these figures is to illustrate the basic organization and formatting of an APA-style empirical research report, although many high-level and low-level style conventions can be seen here too.

Key Takeaways
- An APA-style empirical research report consists of several standard sections. The main ones are the abstract, introduction, method, results, discussion, and references.
- The introduction consists of an opening that presents the research question, a literature review that describes previous research on the topic, and a closing that restates the research question and comments on the method. The literature review constitutes an argument for why the current study is worth doing.
- The method section describes the method in enough detail that another researcher could replicate the study. At a minimum, it consists of a participants subsection and a design and procedure subsection.
- The results section describes the results in an organized fashion. Each primary result is presented in terms of statistical results but also explained in words.
- The discussion typically summarizes the study, discusses theoretical and practical implications and limitations of the study, and offers suggestions for further research.
- Practice: Look through an issue of a general interest professional journal (e.g., Psychological Science ). Read the opening of the first five articles and rate the effectiveness of each one from 1 ( very ineffective ) to 5 ( very effective ). Write a sentence or two explaining each rating.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and identify where the opening, literature review, and closing of the introduction begin and end.
- Practice: Find a recent article in a professional journal and highlight in a different colour each of the following elements in the discussion: summary, theoretical implications, practical implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
Long Descriptions
Figure 11.1 long description: Table showing three ways of organizing an APA-style method section.
In the simple method, there are two subheadings: “Participants” (which might begin “The participants were…”) and “Design and procedure” (which might begin “There were three conditions…”).
In the typical method, there are three subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”).
In the complex method, there are four subheadings: “Participants” (“The participants were…”), “Materials” (“The stimuli were…”), “Design” (“There were three conditions…”), and “Procedure” (“Participants viewed each stimulus on the computer screen…”). [Return to Figure 11.1]
- Bem, D. J. (2003). Writing the empirical journal article. In J. M. Darley, M. P. Zanna, & H. R. Roediger III (Eds.), The compleat academic: A practical guide for the beginning social scientist (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association. ↵
- Darley, J. M., & Latané, B. (1968). Bystander intervention in emergencies: Diffusion of responsibility. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 4 , 377–383. ↵
A type of research article which describes one or more new empirical studies conducted by the authors.
The page at the beginning of an APA-style research report containing the title of the article, the authors’ names, and their institutional affiliation.
A summary of a research study.
The third page of a manuscript containing the research question, the literature review, and comments about how to answer the research question.
An introduction to the research question and explanation for why this question is interesting.
A description of relevant previous research on the topic being discusses and an argument for why the research is worth addressing.
The end of the introduction, where the research question is reiterated and the method is commented upon.
The section of a research report where the method used to conduct the study is described.
The main results of the study, including the results from statistical analyses, are presented in a research article.
Section of a research report that summarizes the study's results and interprets them by referring back to the study's theoretical background.
Part of a research report which contains supplemental material.
Research Methods in Psychology - 2nd Canadian Edition Copyright © 2015 by Paul C. Price, Rajiv Jhangiani, & I-Chant A. Chiang is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
- Academic and Writing Resources
Writing Research Papers
- Research Paper Structure
Whether you are writing a B.S. Degree Research Paper or completing a research report for a Psychology course, it is highly likely that you will need to organize your research paper in accordance with American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines. Here we discuss the structure of research papers according to APA style.
Major Sections of a Research Paper in APA Style
A complete research paper in APA style that is reporting on experimental research will typically contain a Title page, Abstract, Introduction, Methods, Results, Discussion, and References sections. 1 Many will also contain Figures and Tables and some will have an Appendix or Appendices. These sections are detailed as follows (for a more in-depth guide, please refer to " How to Write a Research Paper in APA Style ”, a comprehensive guide developed by Prof. Emma Geller). 2
What is this paper called and who wrote it? – the first page of the paper; this includes the name of the paper, a “running head”, authors, and institutional affiliation of the authors. The institutional affiliation is usually listed in an Author Note that is placed towards the bottom of the title page. In some cases, the Author Note also contains an acknowledgment of any funding support and of any individuals that assisted with the research project.
One-paragraph summary of the entire study – typically no more than 250 words in length (and in many cases it is well shorter than that), the Abstract provides an overview of the study.
Introduction
What is the topic and why is it worth studying? – the first major section of text in the paper, the Introduction commonly describes the topic under investigation, summarizes or discusses relevant prior research (for related details, please see the Writing Literature Reviews section of this website), identifies unresolved issues that the current research will address, and provides an overview of the research that is to be described in greater detail in the sections to follow.
What did you do? – a section which details how the research was performed. It typically features a description of the participants/subjects that were involved, the study design, the materials that were used, and the study procedure. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Methods section. A rule of thumb is that the Methods section should be sufficiently detailed for another researcher to duplicate your research.
What did you find? – a section which describes the data that was collected and the results of any statistical tests that were performed. It may also be prefaced by a description of the analysis procedure that was used. If there were multiple experiments, then each experiment may require a separate Results section.
What is the significance of your results? – the final major section of text in the paper. The Discussion commonly features a summary of the results that were obtained in the study, describes how those results address the topic under investigation and/or the issues that the research was designed to address, and may expand upon the implications of those findings. Limitations and directions for future research are also commonly addressed.
List of articles and any books cited – an alphabetized list of the sources that are cited in the paper (by last name of the first author of each source). Each reference should follow specific APA guidelines regarding author names, dates, article titles, journal titles, journal volume numbers, page numbers, book publishers, publisher locations, websites, and so on (for more information, please see the Citing References in APA Style page of this website).
Tables and Figures
Graphs and data (optional in some cases) – depending on the type of research being performed, there may be Tables and/or Figures (however, in some cases, there may be neither). In APA style, each Table and each Figure is placed on a separate page and all Tables and Figures are included after the References. Tables are included first, followed by Figures. However, for some journals and undergraduate research papers (such as the B.S. Research Paper or Honors Thesis), Tables and Figures may be embedded in the text (depending on the instructor’s or editor’s policies; for more details, see "Deviations from APA Style" below).
Supplementary information (optional) – in some cases, additional information that is not critical to understanding the research paper, such as a list of experiment stimuli, details of a secondary analysis, or programming code, is provided. This is often placed in an Appendix.
Variations of Research Papers in APA Style
Although the major sections described above are common to most research papers written in APA style, there are variations on that pattern. These variations include:
- Literature reviews – when a paper is reviewing prior published research and not presenting new empirical research itself (such as in a review article, and particularly a qualitative review), then the authors may forgo any Methods and Results sections. Instead, there is a different structure such as an Introduction section followed by sections for each of the different aspects of the body of research being reviewed, and then perhaps a Discussion section.
- Multi-experiment papers – when there are multiple experiments, it is common to follow the Introduction with an Experiment 1 section, itself containing Methods, Results, and Discussion subsections. Then there is an Experiment 2 section with a similar structure, an Experiment 3 section with a similar structure, and so on until all experiments are covered. Towards the end of the paper there is a General Discussion section followed by References. Additionally, in multi-experiment papers, it is common for the Results and Discussion subsections for individual experiments to be combined into single “Results and Discussion” sections.
Departures from APA Style
In some cases, official APA style might not be followed (however, be sure to check with your editor, instructor, or other sources before deviating from standards of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association). Such deviations may include:
- Placement of Tables and Figures – in some cases, to make reading through the paper easier, Tables and/or Figures are embedded in the text (for example, having a bar graph placed in the relevant Results section). The embedding of Tables and/or Figures in the text is one of the most common deviations from APA style (and is commonly allowed in B.S. Degree Research Papers and Honors Theses; however you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first).
- Incomplete research – sometimes a B.S. Degree Research Paper in this department is written about research that is currently being planned or is in progress. In those circumstances, sometimes only an Introduction and Methods section, followed by References, is included (that is, in cases where the research itself has not formally begun). In other cases, preliminary results are presented and noted as such in the Results section (such as in cases where the study is underway but not complete), and the Discussion section includes caveats about the in-progress nature of the research. Again, you should check with your instructor, supervisor, or editor first.
- Class assignments – in some classes in this department, an assignment must be written in APA style but is not exactly a traditional research paper (for instance, a student asked to write about an article that they read, and to write that report in APA style). In that case, the structure of the paper might approximate the typical sections of a research paper in APA style, but not entirely. You should check with your instructor for further guidelines.
Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of the process of writing research papers, please consider attending this department’s “Writing Research Papers” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
Downloadable Resources
- How to Write APA Style Research Papers (a comprehensive guide) [ PDF ]
- Tips for Writing APA Style Research Papers (a brief summary) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – empirical research) [ PDF ]
- Example APA Style Research Paper (for B.S. Degree – literature review) [ PDF ]
Further Resources
How-To Videos
- Writing Research Paper Videos
APA Journal Article Reporting Guidelines
- Appelbaum, M., Cooper, H., Kline, R. B., Mayo-Wilson, E., Nezu, A. M., & Rao, S. M. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for quantitative research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 3.
- Levitt, H. M., Bamberg, M., Creswell, J. W., Frost, D. M., Josselson, R., & Suárez-Orozco, C. (2018). Journal article reporting standards for qualitative primary, qualitative meta-analytic, and mixed methods research in psychology: The APA Publications and Communications Board task force report . American Psychologist , 73 (1), 26.
External Resources
- Formatting APA Style Papers in Microsoft Word
- How to Write an APA Style Research Paper from Hamilton University
- WikiHow Guide to Writing APA Research Papers
- Sample APA Formatted Paper with Comments
- Sample APA Formatted Paper
- Tips for Writing a Paper in APA Style
1 VandenBos, G. R. (Ed). (2010). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (6th ed.) (pp. 41-60). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
2 geller, e. (2018). how to write an apa-style research report . [instructional materials]. , prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology.
Back to top
- Formatting Research Papers
- Using Databases and Finding References
- What Types of References Are Appropriate?
- Evaluating References and Taking Notes
- Citing References
- Writing a Literature Review
- Writing Process and Revising
- Improving Scientific Writing
- Academic Integrity and Avoiding Plagiarism
- Writing Research Papers Videos

Sample Papers
This page contains sample papers formatted in seventh edition APA Style. The sample papers show the format that authors should use to submit a manuscript for publication in a professional journal and that students should use to submit a paper to an instructor for a course assignment. You can download the Word files to use as templates and edit them as needed for the purposes of your own papers.
Most guidelines in the Publication Manual apply to both professional manuscripts and student papers. However, there are specific guidelines for professional papers versus student papers, including professional and student title page formats. All authors should check with the person or entity to whom they are submitting their paper (e.g., publisher or instructor) for guidelines that are different from or in addition to those specified by APA Style.
Sample papers from the Publication Manual
The following two sample papers were published in annotated form in the Publication Manual and are reproduced here as PDFs for your ease of use. The annotations draw attention to content and formatting and provide the relevant sections of the Publication Manual (7th ed.) to consult for more information.
- Student sample paper with annotations (PDF, 5MB)
- Professional sample paper with annotations (PDF, 2.7MB)
We also offer these sample papers in Microsoft Word (.docx) format with the annotations as comments to the text.
- Student sample paper with annotations as comments (DOCX, 42KB)
- Professional sample paper with annotations as comments (DOCX, 103KB)
Finally, we offer these sample papers in Microsoft Word (.docx) format without the annotations.
- Student sample paper without annotations (DOCX, 36KB)
- Professional sample paper without annotations (DOCX, 96KB)
Sample professional paper templates by paper type
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different professional paper types. Professional papers can contain many different elements depending on the nature of the work. Authors seeking publication should refer to the journal’s instructions for authors or manuscript submission guidelines for specific requirements and/or sections to include.
- Literature review professional paper template (DOCX, 47KB)
- Mixed methods professional paper template (DOCX, 68KB)
- Qualitative professional paper template (DOCX, 72KB)
- Quantitative professional paper template (DOCX, 77KB)
- Review professional paper template (DOCX, 112KB)
Sample papers are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 2 and the Concise Guide Chapter 1
Related handouts
- Heading Levels Template: Student Paper (PDF, 257KB)
- Heading Levels Template: Professional Paper (PDF, 213KB)
Other instructional aids
- Journal Article Reporting Standards (JARS)
- APA Style Tutorials and Webinars
- Handouts and Guides
- Paper Format
View all instructional aids
Sample student paper templates by paper type
These sample papers demonstrate APA Style formatting standards for different student paper types. Students may write the same types of papers as professional authors (e.g., quantitative studies, literature reviews) or other types of papers for course assignments (e.g., reaction or response papers, discussion posts), dissertations, and theses.
APA does not set formal requirements for the nature or contents of an APA Style student paper. Students should follow the guidelines and requirements of their instructor, department, and/or institution when writing papers. For instance, an abstract and keywords are not required for APA Style student papers, although an instructor may request them in student papers that are longer or more complex. Specific questions about a paper being written for a course assignment should be directed to the instructor or institution assigning the paper.
- Discussion post student paper template (DOCX, 31KB)
- Literature review student paper template (DOCX, 37KB)
- Quantitative study student paper template (DOCX, 53KB)
Sample papers in real life
Although published articles differ in format from manuscripts submitted for publication or student papers (e.g., different line spacing, font, margins, and column format), articles published in APA journals provide excellent demonstrations of APA Style in action.
APA journals began publishing papers in seventh edition APA Style in 2020. Professional authors should check the author submission guidelines for the journal to which they want to submit their paper for any journal-specific style requirements.
Credits for sample professional paper templates
Quantitative professional paper template: Adapted from “Fake News, Fast and Slow: Deliberation Reduces Belief in False (but Not True) News Headlines,” by B. Bago, D. G. Rand, and G. Pennycook, 2020, Journal of Experimental Psychology: General , 149 (8), pp. 1608–1613 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/xge0000729 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Qualitative professional paper template: Adapted from “‘My Smartphone Is an Extension of Myself’: A Holistic Qualitative Exploration of the Impact of Using a Smartphone,” by L. J. Harkin and D. Kuss, 2020, Psychology of Popular Media , 10 (1), pp. 28–38 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000278 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Mixed methods professional paper template: Adapted from “‘I Am a Change Agent’: A Mixed Methods Analysis of Students’ Social Justice Value Orientation in an Undergraduate Community Psychology Course,” by D. X. Henderson, A. T. Majors, and M. Wright, 2019, Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology , 7 (1), 68–80. ( https://doi.org/10.1037/stl0000171 ). Copyright 2019 by the American Psychological Association.
Literature review professional paper template: Adapted from “Rethinking Emotions in the Context of Infants’ Prosocial Behavior: The Role of Interest and Positive Emotions,” by S. I. Hammond and J. K. Drummond, 2019, Developmental Psychology , 55 (9), pp. 1882–1888 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/dev0000685 ). Copyright 2019 by the American Psychological Association.
Review professional paper template: Adapted from “Joining the Conversation: Teaching Students to Think and Communicate Like Scholars,” by E. L. Parks, 2022, Scholarship of Teaching and Learning in Psychology , 8 (1), pp. 70–78 ( https://doi.org/10.1037/stl0000193 ). Copyright 2020 by the American Psychological Association.
Credits for sample student paper templates
These papers came from real students who gave their permission to have them edited and posted by APA.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Sweepstakes
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
50+ Research Topics for Psychology Papers
How to Find Psychology Research Topics for Your Student Paper
- Specific Branches of Psychology
- Topics Involving a Disorder or Type of Therapy
- Human Cognition
- Human Development
- Critique of Publications
- Famous Experiments
- Historical Figures
- Specific Careers
- Case Studies
- Literature Reviews
- Your Own Study/Experiment
Are you searching for a great topic for your psychology paper ? Sometimes it seems like coming up with topics of psychology research is more challenging than the actual research and writing. Fortunately, there are plenty of great places to find inspiration and the following list contains just a few ideas to help get you started.
Finding a solid topic is one of the most important steps when writing any type of paper. It can be particularly important when you are writing a psychology research paper or essay. Psychology is such a broad topic, so you want to find a topic that allows you to adequately cover the subject without becoming overwhelmed with information.
I can always tell when a student really cares about the topic they chose; it comes through in the writing. My advice is to choose a topic that genuinely interests you, so you’ll be more motivated to do thorough research.
In some cases, such as in a general psychology class, you might have the option to select any topic from within psychology's broad reach. Other instances, such as in an abnormal psychology course, might require you to write your paper on a specific subject such as a psychological disorder.
As you begin your search for a topic for your psychology paper, it is first important to consider the guidelines established by your instructor.
Research Topics Within Specific Branches of Psychology
The key to selecting a good topic for your psychology paper is to select something that is narrow enough to allow you to really focus on the subject, but not so narrow that it is difficult to find sources or information to write about.
One approach is to narrow your focus down to a subject within a specific branch of psychology. For example, you might start by deciding that you want to write a paper on some sort of social psychology topic. Next, you might narrow your focus down to how persuasion can be used to influence behavior .
Other social psychology topics you might consider include:
- Prejudice and discrimination (i.e., homophobia, sexism, racism)
- Social cognition
- Person perception
- Social control and cults
- Persuasion, propaganda, and marketing
- Attraction, romance, and love
- Nonverbal communication
- Prosocial behavior
Psychology Research Topics Involving a Disorder or Type of Therapy
Exploring a psychological disorder or a specific treatment modality can also be a good topic for a psychology paper. Some potential abnormal psychology topics include specific psychological disorders or particular treatment modalities, including:
- Eating disorders
- Borderline personality disorder
- Seasonal affective disorder
- Schizophrenia
- Antisocial personality disorder
- Profile a type of therapy (i.e., cognitive-behavioral therapy, group therapy, psychoanalytic therapy)
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Cognition
Some of the possible topics you might explore in this area include thinking, language, intelligence, and decision-making. Other ideas might include:
- False memories
- Speech disorders
- Problem-solving
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Human Development
In this area, you might opt to focus on issues pertinent to early childhood such as language development, social learning, or childhood attachment or you might instead opt to concentrate on issues that affect older adults such as dementia or Alzheimer's disease.
Some other topics you might consider include:
- Language acquisition
- Media violence and children
- Learning disabilities
- Gender roles
- Child abuse
- Prenatal development
- Parenting styles
- Aspects of the aging process
Do a Critique of Publications Involving Psychology Research Topics
One option is to consider writing a critique paper of a published psychology book or academic journal article. For example, you might write a critical analysis of Sigmund Freud's Interpretation of Dreams or you might evaluate a more recent book such as Philip Zimbardo's The Lucifer Effect: Understanding How Good People Turn Evil .
Professional and academic journals are also great places to find materials for a critique paper. Browse through the collection at your university library to find titles devoted to the subject that you are most interested in, then look through recent articles until you find one that grabs your attention.
Topics of Psychology Research Related to Famous Experiments
There have been many fascinating and groundbreaking experiments throughout the history of psychology, providing ample material for students looking for an interesting term paper topic. In your paper, you might choose to summarize the experiment, analyze the ethics of the research, or evaluate the implications of the study. Possible experiments that you might consider include:
- The Milgram Obedience Experiment
- The Stanford Prison Experiment
- The Little Albert Experiment
- Pavlov's Conditioning Experiments
- The Asch Conformity Experiment
- Harlow's Rhesus Monkey Experiments
Topics of Psychology Research About Historical Figures
One of the simplest ways to find a great topic is to choose an interesting person in the history of psychology and write a paper about them. Your paper might focus on many different elements of the individual's life, such as their biography, professional history, theories, or influence on psychology.
While this type of paper may be historical in nature, there is no need for this assignment to be dry or boring. Psychology is full of fascinating figures rife with intriguing stories and anecdotes. Consider such famous individuals as Sigmund Freud, B.F. Skinner, Harry Harlow, or one of the many other eminent psychologists .
Psychology Research Topics About a Specific Career
Another possible topic, depending on the course in which you are enrolled, is to write about specific career paths within the field of psychology . This type of paper is especially appropriate if you are exploring different subtopics or considering which area interests you the most.
In your paper, you might opt to explore the typical duties of a psychologist, how much people working in these fields typically earn, and the different employment options that are available.
Topics of Psychology Research Involving Case Studies
One potentially interesting idea is to write a psychology case study of a particular individual or group of people. In this type of paper, you will provide an in-depth analysis of your subject, including a thorough biography.
Generally, you will also assess the person, often using a major psychological theory such as Piaget's stages of cognitive development or Erikson's eight-stage theory of human development . It is also important to note that your paper doesn't necessarily have to be about someone you know personally.
In fact, many professors encourage students to write case studies on historical figures or fictional characters from books, television programs, or films.
Psychology Research Topics Involving Literature Reviews
Another possibility that would work well for a number of psychology courses is to do a literature review of a specific topic within psychology. A literature review involves finding a variety of sources on a particular subject, then summarizing and reporting on what these sources have to say about the topic.
Literature reviews are generally found in the introduction of journal articles and other psychology papers , but this type of analysis also works well for a full-scale psychology term paper.
Topics of Psychology Research Based on Your Own Study or Experiment
Many psychology courses require students to design an actual psychological study or perform some type of experiment. In some cases, students simply devise the study and then imagine the possible results that might occur. In other situations, you may actually have the opportunity to collect data, analyze your findings, and write up your results.
Finding a topic for your study can be difficult, but there are plenty of great ways to come up with intriguing ideas. Start by considering your own interests as well as subjects you have studied in the past.
Online sources, newspaper articles, books , journal articles, and even your own class textbook are all great places to start searching for topics for your experiments and psychology term papers. Before you begin, learn more about how to conduct a psychology experiment .
What This Means For You
After looking at this brief list of possible topics for psychology papers, it is easy to see that psychology is a very broad and diverse subject. While this variety makes it possible to find a topic that really catches your interest, it can sometimes make it very difficult for some students to select a good topic.
If you are still stumped by your assignment, ask your instructor for suggestions and consider a few from this list for inspiration.
- Hockenbury, SE & Nolan, SA. Psychology. New York: Worth Publishers; 2014.
- Santrock, JW. A Topical Approach to Lifespan Development. New York: McGraw-Hill Education; 2016.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Sample Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper
This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication). These differences mostly extend to the title page and running head. Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper.
However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style.
Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples. Those authored by [AF] denote explanations of formatting and [AWC] denote directions for writing and citing in APA 7.
APA 7 Student Paper:
Apa 7 professional paper:.

Psychology Research Paper

This sample psychology research paper features: 6000 words (approx. 20 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 32 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
History of Psychology
Every day, psychologists make history. It can be in an act as small as sending an e-mail or as large as winning a Nobel Prize. What remains of these acts and the contexts in which they occur are the data of history. When transformed by historians of psychology to produce narrative, these data represent our best attempts to make meaning of our science and profession.
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, more psychology research papers:.
- Aggression Research Paper
- Artificial Intelligence Research Paper
- Discrimination Research Paper
- Early Childhood Education Research Paper
- Environmental Psychology Research Paper
- Learning Disabilities Research Paper
- Social Cognition Research Paper
The meaning that is derived from the data of history is most often made available to students of psychology through a course in the history of psychology. For a variety of reasons, the history of psychology has maintained a strong presence in the psychology curriculum at both the undergraduate and graduate levels for as long as there has been a psychology curriculum in America (Fuchs & Viney, 2002; Hilgard, Leary, & McGuire, 1991). As a result, most students will have some exposure to the subject matter and some sense of its importance.
Why are psychologists so interested in their own history? In trying to answer this question, consider the following quotations from two eminent British historians. One, Robin Collingwood (1946), wrote that the “proper object of historical study.. .is the human mind, or more properly the activities of the human mind” (p. 215). And the other, Edward H. Carr (1961), proposed that “the historian is not really interested in the unique, but what is general in the unique” and that “the study of history is a study of causes.. .the historian.. .continuously asks the question: Why?” (pp. 80, 113). Thus, according to these historians, to study history is to study the human mind, to be able to generalize beyond the characteristics of a single individual or single event to other individuals and other events, and to be able to answer the “why” of human behavior in terms of motivation, personality, past experience, expectations, and so forth. Historians are not satisfied, for example, with a mere description of the events of May 4, 1970, in which national guard troops killed four unarmed students on a college campus in Ohio. Description is useful, but it is not the scholarly end product that is sought. By itself, description is unlikely to answer the questions that historians want to answer. They want to understand an event, like the shootings at Kent State University, so completely that they can explain why it happened.
Collingwood (1946) has described history as “the science of human nature” (p. 206). In defining history in that way, Collingwood has usurped psychology’s definition for itself. One can certainly argue about the scientific nature of history and thus his use of the term science in his definition. Whereas historians do not do experimental work, they are engaged in empirical work, and they approach their questions in much the same way that psychologists do, by generating hypotheses and then seeking evidence that will confirm or disconfirm those hypotheses. Thus the intellectual pursuits of the historian and the psychologist are not really very different. And so as psychologists or students of psychology, we are not moving very far from our own field of interest when we study the history of psychology.
Historians of psychology seek to understand the development of the discipline by examining the confluence of people, places, and events within larger social, economic, and political contexts. Over the last forty years the history of psychology has become a recognized area of research and scholarship in psychology. Improvements in the tools, methods, and training of historians of psychology have created a substantial body of research that contributes to conversations about our shared past, the meaning of our present divergence, and the promise of our future. In this research-paper you will learn about the theory and practice of research on the history of psychology.
Historiography refers to the philosophy and methods of doing history. Psychology is certainly guided by underlying philosophies and a diversity of research methods. A behaviorist, for example, has certain assumptions about the influence of previous experience, in terms of a history of punishment and reinforcement, on current behavior. And the methods of study take those assumptions into account in the design and conduct of experiments. A psychoanalytic psychologist, on the other hand, has a very different philosophy and methodology in investigating the questions of interest, for example, believing in the influence of unconscious motives and using techniques such as free association or analysis of latent dream content to understand those motives. Historical research is guided in the same way. It will help you understand history by knowing something about its philosophy and methods as well.
The historical point of view is highly compatible with our notions of our science. Psychologists tend to view individuals in developmental terms, and historians of psychology extend this point of view to encompass the developmental life of the discipline. Like any area of inquiry in psychology, historians of psychology modify their theories, principles, and practices with the accumulation of knowledge, the passage of time, and available technology. One simply needs to compare E. G. Boring’s epic 1929 tome, A History of Experimental Psychology, with Duane and Sydney Ellen Schultz’s 2004 text, A History of Modern Psychology, to see the difference that 75 years can make.
Approaches to history have changed dramatically over the last 75 years. Indeed much of the early research and scholarship in the history of psychology was ceremonial and celebratory. Most often it was not written by historians. It was, and in some circles remains, a reflexive view of history—great people cause great change. Such a view is naive and simplistic. Psychological theories, research practices, and applications are all bound in a context, and it is this dynamic and fluid model that is the trend in historical research today. Just as inferential statistics have advanced from simple regression analysis to structural equation modeling, so too has historical research embraced a notion of multiple determinants and estimates of their relative impact on historical construction. In 1989 historian of psychology Laurel Furumoto christened this “the new history,” a signifier denoting that historic research should strive to be more contextual and less internal.
Postmodern, deconstructionist, and social constructionist perspectives all share an emphasis on context, and have influenced historical research in psychology. The postmodern approach embraces a more critical and questioning attitude toward the enterprise of science (Anderson, 1998). The rise of science studies has led to what some have dubbed the “science wars” and to contentious arguments between those who see science as an honest attempt at objective and dispassionate fact-finding and those who see science (psychological and otherwise) as a political exercise subject to disorder, bias, control, and authority mongering. It is an issue that is present in today’s history of psychology (for examples and discussions see Popplestone, 2004; Zammito, 2004).
Perhaps the largest growth in scholarship on the history of psychology has been in the area of intellectual history. As mentioned earlier, the construction of narrative in these works tends to eschew the older, more ceremonial, and internal histories in favor of a point of view that is more external and contextual. Rather than merely providing a combination of dates and achievements, modern historical scholarship in psychology tends to illuminate. The value of this point of view is in its contributions to our ongoing discussions of the meanings and directions of our field. The ever-expanding universe that psychology occupies and the ongoing debates of the unity of psychology are sufficient to warrant consideration and discussion of how our science and practice have evolved and developed. Historical analysis offers insight into personal, professional, and situational variables that impact and influence the field.
There is also a growing interest in what can be termed the material culture of psychology. The objects and artifacts that occupy psychological laboratories and aid our assessment of mind and behavior are becoming objects of study in their own right (Robinson, 2001; Sturm & Ash, 2005). For example, we continue to study reaction time and memory but we no longer use Hipp chronoscopes or mechanical memory drums. Changes in technology bring changes in methodologies and a host of other variables that are of interest to the historian of psychology.
Another area of increased interest and attention is the impact that racism and discrimination have had on the field. Traditionally underrepresented groups in psychology have often been made invisible by the historical record, but recent scholarship seeks to illuminate the people, places, and practices that have been part of both the problem and the solution to some of the 20th century’s most vexing questions on race, gender, and religion (for examples see Philogène, 2004; Winston, 2004).
Psychologists typically study contemporary events (behaviors and mental processes), whereas historians study events of the distant past. Both might be interested in the same behavior, but the time frame and the methods are usually distinct. Psychologists are interested in marriage, for example, and they might study marriage using surveys, ex post facto methods, or quasi-experimental designs using a sample of married couples (or perhaps divorced couples). Historians, on the other hand, would be likely to look at marriage, for example, as an institution in Victorian England, and they would be unable to use any of the methods listed previously as part of the arsenal of the psychologist. The questions on marriage that would interest psychologists and historians might be similar—how are mates selected in marriage, at what age do people marry, what roles do wives and husbands play in these marriages, what causes marriages to end? But again, the methods of research and the time frame for the events would be different.
History, then, is the branch of knowledge that attempts to analyze and explain events of the past. The explanatory product is a narrative of those events, a story. Central to telling any historical story is the accumulation of facts. We typically think of facts as some kind of demonstrable truth, some real event whose occurrence cannot be disputed. Yet facts are more elusive, as evidenced in the typical dictionary definition, which notes that a fact is information that is “presented” as objectively real. Historians present as fact, for example, that an atomic bomb was dropped on the Japanese city of Hiroshima on August 6, 1945. Because of detailed records of that event, as well as many eyewitness accounts, that fact seems indisputable; however, there are other kinds of facts.
In addition to the date of the bombing of Hiroshima, historians have also presented a number of facts relevant to the decision made by the United States government to drop that bomb. Not surprisingly, those facts are more debatable. Thus facts differ in terms of their certainty. Sometimes that is because evidence is incomplete and much inference has to be made, sometimes it is because evidence is contradictory, and sometimes it is because of bias introduced in the observation or in the interpretation of these events. Flawed though they may be, facts are the basis of history. It is the job of the historian to uncover these items of the past and to piece them together in an account that is as accurate as can be constructed.
In contemporary historiography, the researcher must always be alert to bias in the selection and interpretation of facts. Objectivity is a critical goal for the historian. Carr (1961) has argued that objectivity is indeed only a dream: “The emphasis on the role of the historian in the making of history tends, if pressed to its logical conclusion, to rule out any objective history at all: history is what the historian makes” (p. 29).
Like psychologists, historians are human too, and they bring to their task a bundle of prejudices, preconceptions, penchants, predispositions, premises, and predilections. Such baggage does not mean that they abandon their hope for objectivity, nor does it mean that their histories are hopelessly flawed. Good historians know their biases.
They use their understanding of them to search for evidence in places where they might not otherwise look or to ask questions that they would not ordinarily ask. When this searching and questioning causes them to confront facts contrary to their own views, they must deal with those facts as they would with facts that are more consistent with their biases.
Bias in history begins at the beginning: “The historian displays a bias through the mere choice of a subject…” (Gilderhus, 1992, p. 80). There are an infinite number of historical subjects to pursue. The historian selects from among those, often selecting one of paramount personal interest. The search within that subject begins with a question or questions that the historian hopes to answer, and likely the historian starts with some definite ideas about the answers to those questions.
Bias is evident too in the data of history. It can occur in primary source material—for example, census records or other government documents—even though such sources are often regarded as quite accurate. Yet such sources are inherently biased by the philosophies underlying the construction of the instruments themselves and the ways in which those instruments are used. Secondary sources too are flawed. Their errors occur in transcription, translation, selection, and interpretation.
Oral histories are subject to the biases of the interviewer and the interviewee. Some questions are asked, while others are not. Some are answered, and others are avoided. And memories of events long past are often unreliable. Manuscript collections, the substance of modern archives, are selective and incomplete. They contain the documents that someone decided were worth saving, and they are devoid of those documents that were discarded or lost for a host of reasons, perhaps known only to the discarder.
After they have selected a topic of study and gathered the facts, historians must assemble them into a narrative that can also be subject to biases. Leahey (1986) reviews some of the pitfalls that modern historians of science want to avoid. These include Whig history, presentism, internalist history, and Great Man theories. Whig history refers to historical narrative that views history as a steady movement toward progress in an orderly fashion. Presentism is the tendency to view the past in terms of current values and beliefs. Internalist history focuses solely on developments within a field and fails to acknowledge the larger social, political, and economic contexts in which events and individual actions unfold. Great Man theories credit single, unique individuals (most often white males) as makers of history without regard for the impact that the spirit of the times (often referred to as the zeitgeist) has on the achievements of individuals. Avoiding these errors of interpretation calls for a different approach, which Stocking (1965) has labeled “historicism”: an understanding of the past in its own context and for its own sake. Such an approach requires historians to immerse themselves in the context of the times they are studying.
These are just some of the hurdles that the historian faces in striving for objectivity. They are not described here to suggest that the historian’s task is a hopeless one; instead, they are meant to show the forces against which historians must struggle in attempts at accuracy and objectivity. Carr (1961) has characterized the striving for this ideal as follows:
When we call a historian objective, we mean, I think, two things. First of all, we mean that he has the capacity to rise above the limited vision of his own situation in society and in history… .Secondly, we mean that he has the capacity to project his vision into the future in such a way as to give him a more profound and lasting insight into the past than can be attained by those historians whose outlook is entirely bounded by their own immediate situation. (p. 163)
In summary, history is a product of selection and interpretation. Knowing that helps us understand why books are usually titled “A History…” and not “The History….” There are many histories of psychology, and it would be surprising to find any historians so arrogant as to presume that their individual narratives constituted “The History of Psychology.”
History research is often like detective work: the search for one piece of evidence leads to the search for another and another. One has to follow all leads, some of which produce no useful information. When all of the leads have been exhausted, then you can analyze the facts to see if they are sufficient for telling the story. The leads or the data of history are most often found in original source material. The published record provides access to original source material through monographs and serials that are widely circulated and available in most academic libraries (including reference works such as indexes, encyclopedias, and hand-books). Hard-to-find and out-of-print material (newspapers, newsletters) are now much more easily available thanks to the proliferation of electronic resources. Too often valuable sources of information (obituaries, departmental histories and records, and oral histories) that are vital to maintaining the historical record are not always catalogued and indexed in ways that make them readily available and visible. The most important of all sources of data are archival repositories. Within such repositories one can find records of individuals (referred to as manuscript collections) and organizations (termed archival collections). Manuscript collections preserve and provide access to unique documents such as correspondence, lab notes, drafts of manuscripts, grant proposals, and case records. Archival collections of organizations contain materials such as membership records, minutes of meetings, convention programs, and the like. Archival repositories provide, in essence, the “inside story,” free of editorial revision or censure and marked by the currency of time as opposed to suffering the losses and distortion of later recall. In much the same way, still images, film footage, and artifacts such as apparatus and instrumentation aid in the process of historical discovery.
There are literally thousands of collections of letters of individuals, most of them famous, but some not. And in those historically significant collections are millions of stories waiting to be told. Michael Hill (1993) has described the joys of archival research in this way:
Archival work appears bookish and commonplace to the uninitiated, but this mundane simplicity is deceptive. It bears repeating that events and materials in archives are not always what they seem on the surface. There are perpetual surprises, intrigues, and apprehensions. Suffice it to say that it is a rare treat to visit an archive, to hold in one’s hand the priceless and irreplaceable documents of our unfolding human drama. Each new box of archival material presents opportunities for discovery as well as obligations to treat the subjects of your… research with candor, theoretical sophistication, and a sense of fair play. Each archival visit is a journey into an unknown realm that rewards its visitors with challenging puzzles and unexpected revelations. (pp. 6-7)
“Surprise, intrigue, apprehension, puzzles, and discovery”—those are characteristics of detective work, and historical research is very much about detective work.
The papers of important psychologists are spread among archives and libraries all over the world. In the United States you will find the papers of William James and B. F. Skinner in the collections at Harvard University. The papers of Hugo Munsterberg, a pioneer in the application of psychology to business, can be found at the Boston Public Library. The papers of Mary Whiton Calkins and Christine Ladd-Franklin, important early contributors to experimental psychology, can be found at Wellesley College and at Vassar College and Columbia University, respectively. The Library of Congress includes the papers of James McKeen Cattell and Kenneth B. Clark. Cattell was one of the founders of American psychology and a leader among American scientists in general, and Clark, an African American psychologist, earned fame when his research on self-esteem in black children was cited prominently in the U.S. Supreme Court decision that made school segregation illegal (Brown v. Board of Education, 1954).
The single largest collection of archival materials on psychology anywhere in the world can be found at the Archives of the History of American Psychology (AHAP) at the University of Akron in Akron, Ohio. Founded by psychologists John A. Popplestone and Marion White McPherson in 1965, its purpose is to collect and preserve the historical record of psychology in America (Baker, 2004). Central to this mission is the preservation of personal papers, artifacts, and media that tell the story of psychology in America. In archival terms, “papers” refers to one-of-a-kind (unique) items. Papers can include such things as correspondence (both personal and professional), lecture notes, diaries, and lab journals. Recently named a Smithsonian Affiliate, the AHAP houses more than 1,000 objects and artifacts that offer unique insights into the science and practice of psychology. Instruments from the brass-and-glass era of the late 19th century share space alongside such significant 20th century objects as the simulated shock generator used by Stanley Milgram in his famous studies of obedience and conformity, the flags of the Eagles and Rattlers of the Robbers Cave experiment by Muzafir and Carolyn Sherif, and the props that supported Phillip Zimbardo’s well-known Stanford University prison studies.
Currently, the AHAP houses the personal papers of over 700 psychologists. There are papers of those representing experimental psychology (Leo and Dorothea Hurvich, Kenneth Spence, Ward Halstead, Mary Ainsworth, Frank Beach, Knight Dunlap, Dorothy Rethlingshafer, and Hans Lukas-Tuber), professional psychology (David Shakow, Edgar Doll, Leta Hollingworth, Herbert Freudenberger, Sidney Pressey, Joseph Zubin, Erika Fromm, Jack Bardon, Robert Waldrop, Marie Crissey, and Morris Viteles), and just about everything in between. Also included are the records of more than 50 psychological organizations, including the American Group Psychotherapy Association, the Association for Women in Psychology, Psi Chi, Psi Beta, the Association for Humanistic Psychology, the International Council of Psychologists, and the Psychonomic Society. State and regional association records that can be found at the AHAP include those of the Midwestern Psychological Association, the Ohio Psychological Association, and the Western Psychological Association. The test collection includes more than 8,000 tests and records. There are more than 15,000 photographs and 6,000 reels of film, including home movies of Freud, footage of Pavlov’s research institute, and research film from Arnold Gesell and the Yale Child Study Center. All of these materials serve as trace elements of people, places, and events to which we no longer have access. These archival elements are less fallible than human memory, and if properly preserved, are available to all for review and interpretation. Because an in-person visit to the Archives of the History of American Psychology is not always possible, the AHAP is seeking to make more of its collection available online ( https://www.uakron.edu/ahap ). Indeed, with the advent of the information age, material that was once available only by visitation to an archival repository can now be scanned, digitized, and otherwise rendered into an electronic format. From the diaries and correspondence of women during the civil war to archival collections of animation movies, the digital movement is revolutionizing access to original source material. More information on electronic resources in the history of psychology can be found in the annotated bibliography at the end of this research-paper.
All archives have a set of finding aids to help the researcher locate relevant materials. Some finding aids are more comprehensive than others. Finding aids are organized around a defined set of characteristics that typically include the following:
- Collection dates (date range of the material)
- Size of collection (expressed in linear feet)
- Provenance (place of origin of a collection, previous ownership)
- Access (if any part of the collection is restricted)
- Finding aid preparer name and date of preparation
- Biographical/historical note (a short, succinct note about the collection’s creator)
- Scope and content note (general description and highlights of the collection)
- Series descriptions (headings used to organize records of a similar nature)
- Inventory (description and location of contents of a collection)
Even if an on-site review of the contents of a collection is not possible, reviewing finding aids can still be useful because of the wealth of information they provide.
Applications
In the mid-1960s, a critical mass of sorts was achieved for those interested in teaching, research, and scholarship in the history of psychology. Within the span of a few years, two major organizations appeared: Cheiron: The International Society for the History of the Social and Behavioral Sciences, and Division 26 (Society for the History of Psychology) of the American Psychological Association (APA). Both sponsor annual meetings, and both are affiliated with scholarly journals (Cheiron is represented by the Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences and the Society for the History of Psychology by History of Psychology) that provide an outlet for original research. Two doctoral training programs in the history of psychology exist in North America. One is at York University in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, and the other is at the University of New Hampshire.
For most students in psychology, the closest encounter with historical research comes in the form of a project or paper as part of a requirement for a class on the history of psychology. Using the types of resources that we have described in this research-paper, it should be possible to construct a narrative on any number of topical issues in psychology.
For example, the ascendancy of professional psychology with its concomitant focus on mental health is a topic of interest to historians of psychology and of considerable importance to many students who wish to pursue graduate training in professional psychology. Using archival materials, original published material, secondary sources, and government documents, a brief example of a historical narrative is provided.
World War II and the Rise of Professional Psychology
America’s entrance into World War II greatly expanded the services that American psychologists offered, especially in the area of mental health. Rates of psychiatric illness among recruits were surprisingly high, the majority of discharges from service were for psychiatric reasons, and psychiatric casualties occupied over half of all beds in Veterans Administration hospitals. Not only was this cause for concern among the military, it also alerted federal authorities to the issue among the general population. At the time, the available supply of trained personnel met a fraction of the need. In a response that was fast and sweeping, the federal government passed the National Mental Health Act of 1946, legislation that has been a major determinant in the growth of the mental health profession in America (Pickren & Schneider, 2004). The purpose of the act was clear:
The improvement of the mental health of the people of the United States through the conducting of researches, investigations, experiments, and demonstrations relating to the cause, diagnosis, and treatment of psychiatric disorders; assisting and fostering such research activities by public and private agencies, and promoting the coordination of all such researches and activities and the useful application of their results; training personnel in matters relating to mental health; and developing, and assisting States in the use of the most effective methods of prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of psychiatric disorders. (Public Law 487, 1946, p. 421)
The act provided for a massive program of federal assistance to address research, training, and service in the identification, treatment, and prevention of mental illness.
It created the National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) and provided broad support to psychiatry, psychiatric social work, psychiatric nursing, and psychology for the training of mental health professionals (Rubens tein, 1975). Through the joint efforts of the United States Public Health Service and the Veterans Administration, funds were made available to psychology departments willing to train professional psychologists. Never before had such large sums of money been available to academic psychology. The grants and stipends available from the federal government allowed universities to hire clinical faculty to teach graduate students, whose education and training was often supported by generous stipends. It was these funds that subsidized the Boulder Conference on Graduate Education in Clinical Psychology in 1949 (Baker & Benjamin, 2000).
The chief architect of the Boulder model was David Shakow (1901-1981). At the time, there was no other person in American psychology who had more responsibility and influence in defining standards of training for clinical psychologists. In 1947, Shakow crafted a report on the training of doctoral students in clinical psychology that became the working document for the Boulder Conference of 1949 (APA, 1947; Benjamin & Baker, 2004; Felix, 1947).
By the 1950s, professional psychologists achieved identities that served their members, served their various publics, attracted students and faculty, and ensured survival by maintaining the mechanisms necessary for professional accreditation and later for certification and licensure. In the free-market economy, many trained for public service have found greener pastures in private practice.
The training model inaugurated by the NIMH in 1949 has continued unabated for five decades, planned and supported largely through the auspices of the American Psychological Association. The exigencies that called for the creation of a competent mental health work force have changed, yet the professional psychologist engineered at mid-century has endured, as has the uneasy alliance between science and practice.
This brief historical analysis shows how archival elements can be gathered from a host of sources and used to illuminate the contextual factors that contributed to a significant development in modern American psychology. This story could not be told without access to a number of original sources. For example, the inner workings of the two-week Boulder conference are told in the surviving papers of conference participants, including the personal papers of David Shakow that are located at Akron in the Archives of the History of American Psychology. Papers relevant to the Mental Health Act of 1946 can be found in the National Archives in Washington, DC. Information about the role of the Veterans Administration in contributing to the development of the profession of clinical psychology can be found in the oral history collection available at the archives of the APA. Such analysis also offers an opportunity for reflection and evaluation, and tells us some of the story of the bifurcation of science and practice that has resulted in American psychology. We believe that historical analysis provides a perspective that can contribute to our understanding of current debates and aid in the consideration of alternatives.
Indeed, almost any contemporary topic that a student of psychology is interested in has a history that can be traced. Topics in cognition, emotions, forensics, group therapy, parenting, sexuality, memory, and animal learning, to name but a very few, can be researched. Archival resources are often more readily available than most might think. Local and regional archives and university library special collections all are sources of original material. For example, students can do interesting research on the history of their own psychology departments (Benjamin, 1990). University archives can offer minutes of faculty meetings, personnel records (those that are public), college yearbooks (which often show faculty members, student groups, etc.), course catalogues, building plans, and many more items. Interviews can be conducted with retired faculty and department staff, and local newspapers can be researched for related stories. The work can be informative, instructive, and very enjoyable.
In the end we are left with an important question: So what? What is the importance of the history of psychology? What do we gain? The history of psychology is not likely to serve as an empirically valid treatment for anxiety, nor is it likely to offer a model of how memory works. But that is not the point. It is easily argued that the history of psychology offers some instrumental benefits. The examination of psychology’s past provides not only a more meaningful understanding of that past, but a more informed and enriched appreciation of our present, and the best crystal ball available in making predictions about our field’s future. It aids critical thinking by providing a compendium of the trials, tribulations, and advances that accrue from the enormous questions we ask of our science and profession, and it offers the opportunity to reduce the interpersonal drift we seem to experience. In recent years, psychologists have become estranged from one another in ways that were unknown not all that long ago. Yet we share a connection, however tenuous, and it is found in our shared history.
At the risk of being labeled Whiggish, we would add that the history of psychology, professional and otherwise, has contributed to a corpus of knowledge that is real, tangible, and capable of improving the quality of life of all living things, including our planet. There are few secrets; we know how to encourage recycling, we understand effective ways of treating drug addiction, we have methods for alleviating some of the suffering of mental illness, we can provide tools to improve reading skills, we can design good foster homes—the list could get quite long.
Our knowledge is a powerful tool that has developed over time and is a narrative worth knowing. Like any good story, it has its heroes and its villains, it is set in a time and place, and it offers us a message we can all hear and use.
Bibliography:
- American Psychological Association, Committee on Training in Clinical Psychology. (1947). Recommended graduate training program in clinical psychology. American Psychologist, 2, 539-558.
- Anderson, P. (1998). The origins of postmodernity. London: Verso. Archives of the History of American Psychology. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.uakron.edu/ahap
- Baker, D. B. (2004). Thirty-five years of archival achievement. In D. Baker (Ed.), Thick description and fine texture: Studies in the history of psychology (pp. vii-x). Akron, OH: The University of Akron Press.
- Baker, D. B., & Benjamin, L. T., Jr. (2000). The affirmation of the scientist-practitioner: A look back at Boulder. American Psychologist, 55, 241-247.
- Benjamin, L. T., Jr. (1990). Involving students and faculty in preparing a departmental history. Teaching of Psychology, 17, 97-100.
- Benjamin, L. T., Jr. (2006). A history of psychology in letters (2nd ed.). Malden, MA: Blackwell.
- Benjamin, L. T., Jr., & Baker, D. B. (2004). From séance to science: A history of the profession of psychology in America. Belmont, CA: Thomson/Wadsworth.
- Boring, E. G. (1929). A history of experimental psychology. New York: Century Co.
- Carr, E. H. (1961). What is history? New York: Random House.
- Collingwood, R. G. (1946). The idea of history. London: Oxford University Press.
- Fancher, R. E. (2004). A tale of two institutions: York University’s history of psychology program and the Archives of the History of American Psychology. In D. Baker (Ed.), Thick description and fine texture: Studies in the history of psychology (pp. 162-173). Akron, OH: The University of Akron Press.
- Felix, R. H. (1947, December 12). Memo to National Advisory Health Council. (Shakow Papers, M1375). Akron, OH: The University of Akron, Archives of the History of American Psychology.
- Freedheim, D. K. (Ed.). (2003). History of psychology. In I. B. Weiner (Series Ed.), Handbook of psychology (Vol. 1, pp. 492-495). New York: Wiley.
- Fuchs, A. H., & Viney, W. (2002). The course in the history of psychology: Present status and future concerns. History of Psychology, 5, 3-15.
- Furumoto, L. (1989). The new history of psychology. In I. S. Cohen (Ed.), G. Stanley Hall lecture series (Vol. 9, pp. 534). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Gilderhus, M. T. (1992). History and historians: A historiographical introduction (2nd ed.). Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
- Green, C. D. (n.d.). Classics in the history of psychology. Retrieved from http://psychclassics.yorku.ca/
- Green, C. D. (n.d.). This week in the history of psychology. Retrieved from https://www.yorku.ca/christo/podcasts/
- Guthrie, R. V. (2003) Even the rat was white: A historical view of psychology (2nd ed.). Boston: Allyn & Bacon.
- Hilgard, E. R., Leary, D. E., & McGuire, G. R. (1991). The history of psychology: A survey and critical assessment. Annual Review of Psychology, 42, 79-107.
- Hill, M. R. (1993). Archival strategies and techniques. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
- Leahey, T. H. (1986). History without the past. Contemporary Psychology, 31, 648-650.
- Philogene, G. (Ed.). (2004). Racial identity in context: The legacy of Kenneth B. Clark. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Pickren, W. E., & Dewsbury, D. A. (Eds.). (2002). Evolving perspectives on the history of psychology. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Pickren, W. E., & Schneider, S. F. (2004). Psychology and the National Institute of Mental Health: A historical analysis of science, practice, and policy. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Popplestone, J. A. (2004). Reinventing the past through interpretation: Reflections on the history of psychology—35 years in the trenches. In T. C. Dalton & R. B. Evans (Eds.), The life cycle of psychological ideas: Understanding prominence and the dynamics of intellectual change (pp. 59-81). New York: Kluwer.
- Robinson, D. K. (2001). Reaction-time experiments in Wundt’s institute and beyond. In R. Rieber & D. K. Robinson (Eds.), Wilhelm Wundt in history: The making of a scientific psychology (pp. 161-204). New York: Kluwer.
- Rubenstein, E. A. (1975). Unpublished interview with Robert Felix. Available from the archives of the American Psychological Association.
- Schultz, D. P., & Schultz, S. E. (2004). A history of modern psychology (8th ed.). Belmont, CA: Wadsworth/Thompson.
- Stocking, G. W., Jr. (1965). On the limits of ‘presentism’ and ‘historicism’ in the historiography of the behavioral sciences. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences, 1, 211-218.
- Sturm, T., & Ash, M. (2005). Roles of instruments in psychological research. History of Psychology, 8, 3-34.
- Winston, A. S. (Ed.). (2004). Defining difference: Race and racism in the history of psychology. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
- Zammito, J. H. (2004). A nice derangement of epistemes: Post-positivism in the study of science from Quine to Latour. Chicago: University of Chicago.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- How to write an APA results section
Reporting Research Results in APA Style | Tips & Examples
Published on December 21, 2020 by Pritha Bhandari . Revised on January 17, 2024.
The results section of a quantitative research paper is where you summarize your data and report the findings of any relevant statistical analyses.
The APA manual provides rigorous guidelines for what to report in quantitative research papers in the fields of psychology, education, and other social sciences.
Use these standards to answer your research questions and report your data analyses in a complete and transparent way.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What goes in your results section, introduce your data, summarize your data, report statistical results, presenting numbers effectively, what doesn’t belong in your results section, frequently asked questions about results in apa.
In APA style, the results section includes preliminary information about the participants and data, descriptive and inferential statistics, and the results of any exploratory analyses.
Include these in your results section:
- Participant flow and recruitment period. Report the number of participants at every stage of the study, as well as the dates when recruitment took place.
- Missing data . Identify the proportion of data that wasn’t included in your final analysis and state the reasons.
- Any adverse events. Make sure to report any unexpected events or side effects (for clinical studies).
- Descriptive statistics . Summarize the primary and secondary outcomes of the study.
- Inferential statistics , including confidence intervals and effect sizes. Address the primary and secondary research questions by reporting the detailed results of your main analyses.
- Results of subgroup or exploratory analyses, if applicable. Place detailed results in supplementary materials.
Write up the results in the past tense because you’re describing the outcomes of a completed research study.
Are your APA in-text citations flawless?
The AI-powered APA Citation Checker points out every error, tells you exactly what’s wrong, and explains how to fix it. Say goodbye to losing marks on your assignment!
Get started!

Before diving into your research findings, first describe the flow of participants at every stage of your study and whether any data were excluded from the final analysis.
Participant flow and recruitment period
It’s necessary to report any attrition, which is the decline in participants at every sequential stage of a study. That’s because an uneven number of participants across groups sometimes threatens internal validity and makes it difficult to compare groups. Be sure to also state all reasons for attrition.
If your study has multiple stages (e.g., pre-test, intervention, and post-test) and groups (e.g., experimental and control groups), a flow chart is the best way to report the number of participants in each group per stage and reasons for attrition.
Also report the dates for when you recruited participants or performed follow-up sessions.
Missing data
Another key issue is the completeness of your dataset. It’s necessary to report both the amount and reasons for data that was missing or excluded.
Data can become unusable due to equipment malfunctions, improper storage, unexpected events, participant ineligibility, and so on. For each case, state the reason why the data were unusable.
Some data points may be removed from the final analysis because they are outliers—but you must be able to justify how you decided what to exclude.
If you applied any techniques for overcoming or compensating for lost data, report those as well.
Adverse events
For clinical studies, report all events with serious consequences or any side effects that occured.
Descriptive statistics summarize your data for the reader. Present descriptive statistics for each primary, secondary, and subgroup analysis.
Don’t provide formulas or citations for commonly used statistics (e.g., standard deviation) – but do provide them for new or rare equations.
Descriptive statistics
The exact descriptive statistics that you report depends on the types of data in your study. Categorical variables can be reported using proportions, while quantitative data can be reported using means and standard deviations . For a large set of numbers, a table is the most effective presentation format.
Include sample sizes (overall and for each group) as well as appropriate measures of central tendency and variability for the outcomes in your results section. For every point estimate , add a clearly labelled measure of variability as well.
Be sure to note how you combined data to come up with variables of interest. For every variable of interest, explain how you operationalized it.
According to APA journal standards, it’s necessary to report all relevant hypothesis tests performed, estimates of effect sizes, and confidence intervals.
When reporting statistical results, you should first address primary research questions before moving onto secondary research questions and any exploratory or subgroup analyses.
Present the results of tests in the order that you performed them—report the outcomes of main tests before post-hoc tests, for example. Don’t leave out any relevant results, even if they don’t support your hypothesis.
Inferential statistics
For each statistical test performed, first restate the hypothesis , then state whether your hypothesis was supported and provide the outcomes that led you to that conclusion.
Report the following for each hypothesis test:
- the test statistic value,
- the degrees of freedom ,
- the exact p- value (unless it is less than 0.001),
- the magnitude and direction of the effect.
When reporting complex data analyses, such as factor analysis or multivariate analysis, present the models estimated in detail, and state the statistical software used. Make sure to report any violations of statistical assumptions or problems with estimation.
Effect sizes and confidence intervals
For each hypothesis test performed, you should present confidence intervals and estimates of effect sizes .
Confidence intervals are useful for showing the variability around point estimates. They should be included whenever you report population parameter estimates.
Effect sizes indicate how impactful the outcomes of a study are. But since they are estimates, it’s recommended that you also provide confidence intervals of effect sizes.
Subgroup or exploratory analyses
Briefly report the results of any other planned or exploratory analyses you performed. These may include subgroup analyses as well.
Subgroup analyses come with a high chance of false positive results, because performing a large number of comparison or correlation tests increases the chances of finding significant results.
If you find significant results in these analyses, make sure to appropriately report them as exploratory (rather than confirmatory) results to avoid overstating their importance.
While these analyses can be reported in less detail in the main text, you can provide the full analyses in supplementary materials.
Scribbr Citation Checker New
The AI-powered Citation Checker helps you avoid common mistakes such as:
- Missing commas and periods
- Incorrect usage of “et al.”
- Ampersands (&) in narrative citations
- Missing reference entries
To effectively present numbers, use a mix of text, tables , and figures where appropriate:
- To present three or fewer numbers, try a sentence ,
- To present between 4 and 20 numbers, try a table ,
- To present more than 20 numbers, try a figure .
Since these are general guidelines, use your own judgment and feedback from others for effective presentation of numbers.
Tables and figures should be numbered and have titles, along with relevant notes. Make sure to present data only once throughout the paper and refer to any tables and figures in the text.
Formatting statistics and numbers
It’s important to follow capitalization , italicization, and abbreviation rules when referring to statistics in your paper. There are specific format guidelines for reporting statistics in APA , as well as general rules about writing numbers .
If you are unsure of how to present specific symbols, look up the detailed APA guidelines or other papers in your field.
It’s important to provide a complete picture of your data analyses and outcomes in a concise way. For that reason, raw data and any interpretations of your results are not included in the results section.
It’s rarely appropriate to include raw data in your results section. Instead, you should always save the raw data securely and make them available and accessible to any other researchers who request them.
Making scientific research available to others is a key part of academic integrity and open science.
Interpretation or discussion of results
This belongs in your discussion section. Your results section is where you objectively report all relevant findings and leave them open for interpretation by readers.
While you should state whether the findings of statistical tests lend support to your hypotheses, refrain from forming conclusions to your research questions in the results section.
Explanation of how statistics tests work
For the sake of concise writing, you can safely assume that readers of your paper have professional knowledge of how statistical inferences work.
In an APA results section , you should generally report the following:
- Participant flow and recruitment period.
- Missing data and any adverse events.
- Descriptive statistics about your samples.
- Inferential statistics , including confidence intervals and effect sizes.
- Results of any subgroup or exploratory analyses, if applicable.
According to the APA guidelines, you should report enough detail on inferential statistics so that your readers understand your analyses.
- the test statistic value
- the degrees of freedom
- the exact p value (unless it is less than 0.001)
- the magnitude and direction of the effect
You should also present confidence intervals and estimates of effect sizes where relevant.
In APA style, statistics can be presented in the main text or as tables or figures . To decide how to present numbers, you can follow APA guidelines:
- To present three or fewer numbers, try a sentence,
- To present between 4 and 20 numbers, try a table,
- To present more than 20 numbers, try a figure.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2024, January 17). Reporting Research Results in APA Style | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/results-section/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, how to write an apa methods section, how to format tables and figures in apa style, reporting statistics in apa style | guidelines & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!

Sample articles
Qualitative psychology ®.
- Recommendations for Designing and Reviewing Qualitative Research in Psychology: Promoting Methodological Integrity (PDF, 166KB) February 2017 by Heidi M. Levitt, Sue L. Motulsky, Fredrick J. Wertz, Susan L. Morrow, and Joseph G. Ponterotto
- Racial Microaggression Experiences and Coping Strategies of Black Women in Corporate Leadership (PDF, 132KB) August 2015 by Aisha M. B. Holder, Margo A. Jackson, and Joseph G. Ponterotto
- The Lived Experience of Homeless Youth: A Narrative Approach (PDF, 109KB) February 2015 by Erin E. Toolis and Phillip L. Hammack
- Lifetime Activism, Marginality, and Psychology: Narratives of Lifelong Feminist Activists Committed to Social Change (PDF, 93KB) August 2014 by Anjali Dutt and Shelly Grabe
- Qualitative Inquiry in the History of Psychology (PDF, 82KB) February 2014 by Frederick J. Wertz
More About this Journal
- Qualitative Psychology
- Pricing and subscription info
- Special section proposal guidelines
- Special sections
- Call for articles: Methodological Retrospectives
Contact Journals
A study of the effect of viewing online health popular science information on users' willingness to change health behaviors – based on the psychological distance perspective
- Published: 05 September 2024
Cite this article

- Jingfang Liu 1 &
- Shiqi Wang 1
Along with increased health awareness and the advent of the information age, online health popular science information (OHPSI) has received more attention. However, it is unknown how the lots of online health information influences users to change unhealthy behavioral habits. Therefore, based on the psychological distance perspective, our research investigated the effect of viewing online health information on users' willingness to change their health behaviors in the future. In addition, this study also introduced the protection motivation theory to further investigate the mediating effect of protection motivation in the mechanisms of psychological distance in online health information. The data of the study were obtained by the research method of questionnaire survey and the proposed hypotheses were validated using Smartpls software. 87.28% of the respondents in this study's survey sample were aged 18–40 years old, and people in this age group have higher pressure from study and work, and live a fast-paced life with less free time, which makes them more likely to pay attention to OHPSI to improve their health. Therefore, the age group of the sample of this study is in line with the research purpose of this paper, which is conducive to enhancing the authenticity and reliability of the conclusions of this study. The conclusions of the study showed that the temporal, social, hypothetical and experiential distances in psychological distance can positively influence users' self-protection motivation. And protection motivation has a positive effect on users' willingness to change health behaviors. In addition, protection motivation can completely mediate the influence of psychological distance on users' willingness to change health behaviors after viewing online health information. The research not only expands the scope of application of construal level theory and protection motivation theory, but also has significant impact for creators of OHPSI and public health departments.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Explore related subjects
- Artificial Intelligence
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as privacy and ethical restrictions.
Abbreviations
- Online health popular science information
- Construal level theory
Protection motivation theory
Temporal distance
Social distance
Hypothetical distance
Experiential distance
- Protection motivation
Willingness to change health behaviors
Partial least squares
Composite reliability
Average variance extracted
Akhtar, N., Siddiqi, U. I., & Islam, T. (2023). Do perceived threats to psychological distance influence tourists' reactance and online Airbnb booking intentions during COVID-19? Kybernetes . https://doi.org/10.1108/k-03-2023-0508
Bar-Anan, Y., Liberman, N., & Trope, Y. (2006). The association between psychological distance and construal level: Evidence from an implicit association test. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 135 (4), 609–622. https://doi.org/10.1037/0096-3445.135.4.609
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Blauza, S., Heuckmann, B., Kremer, K., & Buessing, A. G. (2023). Psychological distance towards COVID-19: Geographical and hypothetical distance predict attitudes and mediate knowledge [Article]. Current Psychology, 42 (10), 8632–8643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02415-x
Boss, S. R., Galletta, D. F., Lowry, P. B., Moody, G. D., & Polak, P. (2015a). What do systems users have to fear? Using fear appeals to engender threats and fear that motivate protective security behaviors. MIS Quarterly, 39 (4), 837–864.
Article Google Scholar
Boss, S. R., Galletta, D. F., Lowry, P. B., Moody, G. D., & Polak, P. (2015b). What do systems users have to fear? Using fear appeals to engender threats and fear that motivate protective security behaviors. MIS Quarterly, 39 (4), 837-U461. https://doi.org/10.25300/misq/2015/39.4.5
Brust, M., Gebhardt, W. A., van der Voorde, N. A. E., Numans, M. E., & Kiefte-de Jong, J. C. (2022). The development and validation of scales to measure the presence of a teachable moment following a cardiovascular disease event. Preventive Medicine Reports, 28 , 101876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmedr.2022.101876
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Bujnowska-Fedak, M. M., & Wegierek, P. (2020). The impact of online health information on patient health behaviours and making decisions concerning health. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 17 (3), 880. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17030880
Chen, F., Dai, S., Zhu, Y., & Xu, H. (2019). Will concerns for ski tourism promote pro-environmental behaviour? An implication of protection motivation theory. International Journal of Tourism Research, 22 (3), 303–313. https://doi.org/10.1002/jtr.2336
Chen, X. (2023). Online health communities influence people's health behaviors in the context of COVID-19. Plos One, 18 (4). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0282368
Choi, J., Nelson, D., & Almanza, B. (2018). Food safety risk for restaurant management: Use of restaurant health inspection report to predict consumers’ behavioral intention. Journal of Risk Research, 22 (11), 1443–1457. https://doi.org/10.1080/13669877.2018.1501590
Diviani, N., van den Putte, B., Giani, S., & van Weert, J. C. M. (2015). Low health literacy and evaluation of online health information: A systematic review of the literature. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 17 (5), e112. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.4018
Dong, W., Lei, X., & Liu, Y. (2022). The mediating role of patients’ trust between web-based health information seeking and patients’ uncertainty in China: Cross-sectional web-based survey. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 24 (3), e25275. https://doi.org/10.2196/25275
Farooq, A., Laato, S., Islam, A., & Isoaho, J. (2021). Understanding the impact of information sources on COVID-19 related preventive measures in Finland. Technology in Society, 65 , 101573. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techsoc.2021.101573
Fiedler, K. (2007). Construal level theory as an integrative framework for behavioral decision-making research and consumer psychology. Journal of Consumer Psychology, 17 (2), 101–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1057-7408(07)70015-3
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (1981). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research, 18 (1), 39–50.
Gefen, D., & Straub, D. (2005). A practical guide to factorial validity using PLS-Graph: Tutorial and annotated example. Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 16 (1), 5.
Google Scholar
Hair, J. F., Sarstedt, M., Ringle, C. M., & Mena, J. A. (2012). An assessment of the use of partial least squares structural equation modeling in marketing research. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 40 (3), 414–433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-011-0261-6
Hale, T. M. (2013). Is there such a thing as an online health lifestyle?: Examining the relationship between social status, Internet access, and health behaviors. Information Communication & Society, 16 (4), 501–518. https://doi.org/10.1080/1369118x.2013.777759
Han, D., Duhachek, A., & Agrawal, N. (2016). Coping and construal level matching drives health message effectiveness via response efficacy or self-efficacy enhancement. Journal of Consumer Research, 43 (3), 429–447.
Hodges, P. W., Hall, L., Setchell, J., French, S., Kasza, J., Bennell, K., Hunter, D., Vicenzino, B., Crofts, S., & Dickson, C. (2021). Effect of a consumer-focused website for low back pain on health literacy, treatment choices, and clinical outcomes: Randomized controlled trial. Journal of Medical Internet Research, 23 (6), e27860.
Jones, C., Hine, D. W., & Marks, A. D. (2017). The future is now: Reducing psychological distance to increase public engagement with climate change. Risk Analysis, 37 (2), 331–341. https://doi.org/10.1111/risa.12601
Kim, S., & Jin, Y. (2020). Organizational threat appraisal by publics: The effects of perceived temporal distance on health crisis outcomes. International Journal of Communication, 14 , 4075–4095. <Go to ISI>://WOS:000616658300105
Kim, D. H., & Song, D. (2019). Can brand experience shorten consumers’ psychological distance toward the brand? The effect of brand experience on consumers’ construallevel. Journal of Brand Management, 26 (3), 255–267. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41262-018-0134-0
Lahiri, A., Jha, S. S., Chakraborty, A., Dobe, M., & Dey, A. (2021). Role of threat and coping appraisal in protection motivation for adoption of preventive behavior during COVID-19 pandemic. Frontiers in Public Health, 9 , 678566. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.678566
Li, Y. F., Song, Y. Y., Zhao, W., Guo, X. T., Ju, X. F., & Vogel, D. (2019). Exploring the role of online health community information in patients’ decisions to switch from online to offline medical services. International Journal of Medical Informatics, 130 , 103951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2019.08.011
Liberman, N., & Trope, Y. (1998). The role of feasibility and desirability considerations in near and distant future decisions: A test of temporal construal theory. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 75 (1), 5–18. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-3514.75.1.5
Liu, F., Fang, M., Cai, L., Su, M., & Wang, X. (2021). Consumer motivations for adopting omnichannel retailing: A safety-driven perspective in the context of COVID-19. Frontiers in Public Health, 9 , 708199. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2021.708199
Mao, Y., Chen, H., Wang, Y., Chen, S., Gao, J., Dai, J., Jia, Y., Xiao, Q., Zheng, P., & Fu, H. (2021). How can the uptake of preventive behaviour during the COVID-19 outbreak be improved? An online survey of 4827 Chinese residents. BMJ Open, 11 (2), e042954. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2020-042954
Massara, F., & Severino, F. (2013). Psychological distance in the heritage experience. Annals of Tourism Research, 42 , 108–129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2013.01.005
Negrone, A. J., Caldwell, P. H., & Scott, K. M. (2023). COVID-19 and Dr. Google: Parents’ changing experience using online health information about their children’s health during the pandemic. Journal of Paediatrics and Child Health, 59 (3), 512–518. https://doi.org/10.1111/jpc.16339
Rogers, R. W. (1975). A protection motivation theory of fear appeals and attitude change1. The Journal of Psychology, 91 (1), 93–114.
Shanshan, S., Chenhui, D., & Lijuan, L. (2022). Metaphor and board writing matter: The mediating roles of psychological distance and immersion in video lectures [Article]. Computers & Education, 191 , 104630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2022.104630
Shin, M., Kim, Y., & Park, S. (2020). Effect of psychological distance on intention in self-affirmation theory. Psychological Reports, 123 (6), 2101–2124. https://doi.org/10.1177/0033294119856547
Soroya, S. H., Nazir, M., & Faiola, A. (2022). Impact of health-related internet use on disease management behavior of chronic patients: Mediating role of perceived credibility of online information. Information Development . https://doi.org/10.1177/02666669221144622
Sousa, P., Martinho, R., Reis, C. I., Dias, S. S., Gaspar, P. J. S., Dixe, M. D., Luis, L. S., & Ferreira, R. (2020). Controlled trial of an mHealth intervention to promote healthy behaviours in adolescence (TeenPower): Effectiveness analysis. Journal of Advanced Nursing, 76 (4), 1057–1068. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.14301
Spence, A., Poortinga, W., & Pidgeon, N. (2012). The psychological distance of climate change. Risk Analysis, 32 (6), 957–972. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1539-6924.2011.01695.x
Wang, S., Hurlstone, M. J., Leviston, Z., Walker, I., & Lawrence, C. (2019b). Climate change from a distance: An analysis of construal level and psychological distance from climate change. Frontiers in Psychology, 10 , 230. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.00230
Wang, X., Duan, X., Li, S., & Bu, T. (2022). Effects of message framing, psychological distance, and risk perception on exercise attitude in Chinese adolescents. Frontiers in Pediatrics, 10 , 991419. https://doi.org/10.3389/fped.2022.991419
Wang, J., Liu-Lastres, B., Ritchie, B. W., & Mills, D. J. (2019a). Travellers' self-protections against health risks: An application of the full protection motivation theory. Annals of Tourism Research, 78 . https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annals.2019.102743
Weiss, K., & Konig, L. M. (2023). Does the medium matter? Comparing the effectiveness of videos, podcasts and online articles in nutrition communication. Applied Psychology-Health and Well Being, 15 (2), 669–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/aphw.12404
White, A. E., Johnson, K. A., & Kwan, V. S. Y. (2014). Four ways to infect me: Spatial, temporal, social, and probability distance influence evaluations of disease threat. Social Cognition, 32 (3), 239–255. https://doi.org/10.1521/soco.2014.32.3.239
Yan, J., Wei, J., Zhao, D., Vinnikova, A., Li, L., & Wang, S. (2018). Communicating online diet-nutrition information and influencing health behavioral intention: The role of risk perceptions, problem recognition, and situational motivation. Journal of Health Communication, 23 (7), 624–633. https://doi.org/10.1080/10810730.2018.1500657
Zhang, J., Xie, C., Lin, Z., & Huang, S. (2023). Effects of risk messages on tourists’ travel intention: Does distance matter? Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 55 , 169–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhtm.2023.03.020
Zhao, S., Ye, B., Wang, W., & Zeng, Y. (2022). The intolerance of uncertainty and “untact” buying behavior: The mediating role of the perceived risk of COVID-19 variants and protection motivation. Frontiers in Psychology, 13 , 807331. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.807331
Zhonglin, W., & Baojuan, Y. (2014). Analyses of mediating effects: The development of methods and models. Advances in Psychological Science, 22 (5), 731–745. https://doi.org/10.3724/sp.J.1042.2014.00731
Zhou, P., Zhao, Y., Xiao, S., & Zhao, K. (2022). The impact of online health community engagement on lifestyle changes: A serially mediated model. Frontiers in Public Health, 10 . https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.987331
Zhou, J. J., & Fan, T. T. (2019). Understanding the factors influencing patient e-health literacy in Online Health Communities (OHCs): A social cognitive theory perspective. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16 (14), 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16142455
Zhu, Z., Zhao, Y., & Wang, J. (2022). The impact of destination online review content characteristics on travel intention: Experiments based on psychological distance perspectives. Aslib Journal of Information Management . https://doi.org/10.1108/ajim-06-2022-0293
Zou, X., Chen, Q., Zhang, Y. Y., & Evans, R. (2023). Predicting COVID-19 vaccination intentions: The roles of threat appraisal, coping appraisal, subjective norms, and negative affect. BMC Public Health, 23 (1), 230. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-023-15169-x
Download references
This research received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Management, Shanghai University, Shanghai, 201800, China
Jingfang Liu & Shiqi Wang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Conceptualization, J.L. and S.W.; methodology, J.L. and S.W.; software, S.W.; validation, S.W.; formal analysis and S.W.; investigation, S.W.; resources, S.W.; data curation, S.W.; writing—original draft preparation, S.W.; writing—review and editing, S.W.; visualization, S.W. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Shiqi Wang .
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval.
This project received ethical approval from the Ethics Committee of Shanghai University, with ethics approval number ECSHU 2023–072.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Liu, J., Wang, S. A study of the effect of viewing online health popular science information on users' willingness to change health behaviors – based on the psychological distance perspective. Curr Psychol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06582-5
Download citation
Accepted : 15 August 2024
Published : 05 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06582-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Willingness to change health behavior
- Psychological distance
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
APA Sample Paper: Experimental Psychology - Purdue OWL® - Purdue University. Writing in Psychology: Experimental Report Writing. Rhetorical Considerations and Style in Psychology Writing. Writing the Experimental Report: Overview, Introductions, and Literature Reviews. Writing the Experimental Report: Methods, Results, and Discussion.
Recently published articles from subdisciplines of psychology covered by more than 90 APA Journals™ publications. For additional free resources (such as article summaries, podcasts, and more), please visit the Highlights in Psychological Research page.
B.S. Research Paper Example (Literature Review) This is an example of a research paper that was written in fulfillment of the B.S. research paper requirement. It uses APA style for all aspects except the cover sheet (this page; the cover sheet is required by the department). It describes research that the author investigated while taking the PSYC 199 course.
B.S. Research Paper Example (Empirical Research Paper) This is an example of a research paper that was written in fulfillment of the B.S. research paper requirement. It uses APA style for all aspects except the cover sheet (this page; the cover sheet is required by the department). It describes research that the author was involved in while taking the PSYC 199 course.
Guide to Writing a Research Report for Psychology Included in this guide are suggestions for formatting and writing each component of a research report as well as tips for writing in a style appropriate for Psychology papers. Remember, it is always best to check with your department-approved writing book and your professor if you have any questions or concerns.
Sample One-Experiment Paper (continued) emotional detection than young adults, or older adults could show a greater facilitation than. young adults only for the detection of positive information. The results lent some support to the. first two alternatives, but no evidence was found to support the third alternative.
Here we consider each of these sections in detail, including what information it contains, how that information is formatted and organized, and tips for writing each section. At the end of this section is a sample APA-style research report that illustrates many of these principles.
Series Foreword Why are you reading this book? Perhaps you have recently been assigned to write a research paper in an undergraduate course. Maybe you are considering graduate school in one of the behavioral, health, or social sci-ence disciplines, such as psychology, public health, nursing, or medicine, and know that having a strong research background gives you a major advantage in getting ...
Many psychology students dislike writing a research paper, their aversion driven by anxiety over various aspects of the process. This primer for undergraduates explains how to write a clear, compelling, well-organized research paper. From picking a promising topic, to finding and digesting the pertinent literature, to developing a thesis, to outlining and presenting ideas, to editing for ...
This primer for undergraduates explains how to write a clear, compelling, well-organized research paper, with tips and illustrated examples for each step of the process.
Remember to follow APA format as you write your paper and include in-text citations for any materials you reference. Make sure to cite any information in the body of your paper in your reference section at the end of your document. Writing a psychology research paper can be intimidating at first, but breaking the process into a series of ...
Research Paper Structure Whether you are writing a B.S. Degree Research Paper or completing a research report for a Psychology course, it is highly likely that you will need to organize your research paper in accordance with American Psychological Association (APA) guidelines. Here we discuss the structure of research papers according to APA style.
The methods section of a research paper describes the procedures, participants, and materials used in an experiment. Learn more about how to write a method section.
Common Types of Psychology Papers Research psychologists engage in a variety of kinds of writing, including grant proposals, research applications and renewals, review articles, research articles, and textbooks.
These sample papers formatted in seventh edition APA Style show the format that authors should use to submit a manuscript for publication in a professional journal and that students should use to submit a paper to an instructor for a course assignment.
If you need to write a paper in your psychology class, there are several psychology research topics to consider. Here are 50+ topics of psychology research.
vard Writing Project.Writing for psychology incorporates many of the organizational elements you learned. in Expository Writing. In Expos, you were taught general academic guidelines for formulating a thesis, providing a motive for the thesis, supporting this thesis with convincing evidence, and anticipating o.
4 Undergraduate Writing in Psychology. Before you can jump in and do any type of scientific writing, careful plan-ning needs to occur, and this is the central topic of Chapter 2. The development of a clear topic and research question (or thesis statement) is essential to laying the foundation on which your scientific writing will be built.
APA Sample Paper Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here.
This sample psychology research paper features: 6000 words (approx. 20 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 32 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help.
The methods section of an APA style paper is where you report in detail how you performed your study. Research papers in the social and natural sciences often follow APA style. This article focuses on reporting quantitative research methods.
The results section of a quantitative research paper is where you summarize your data and report the findings of any relevant statistical analyses. The APA manual provides rigorous guidelines for what to report in quantitative research papers in the fields of psychology, education, and other social sciences.
Qualitative Psychology ® Recommendations for Designing and Reviewing Qualitative Research in Psychology: Promoting Methodological Integrity (PDF, 166KB) February 2017 by Heidi M. Levitt, Sue L. Motulsky, Fredrick J. Wertz, Susan L. Morrow, and Joseph G. Ponterotto
The data of the study were obtained by the research method of questionnaire survey and the proposed hypotheses were validated using Smartpls software. 87.28% of the respondents in this study's survey sample were aged 18-40 years old, and people in this age group have higher pressure from study and work, and live a fast-paced life with less ...