R&D Project Management: key elements and best practices

R&D project management is one of the most complex tasks you may encounter as a Project Manager. While in more ‘traditional’ projects, so to say, the objectives to be achieved and well-defined schedules, budgets and resources are clear from the initial stages of the project, this rarely happens with this type of project.
R&D projects rarely have such a rigid structure, but rather live in uncertainty throughout the project life cycle. Changing market needs, new opportunities to be exploited, constant adjustments in product development and resource allocation. There are so many changing circumstances in this type of projects and so many interests involved that in the end many of them fail because they end up losing focus on what is most important in this type of initiatives:
- Alignment with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- To meet users’ and customers’ needs .
Do you currently manage R&D and new product development projects ? Would you like to know what are the key elements and best practices to take the management of this type of projects to the highest level? If so, read on.
TABLE OF CONTENTS

What is R&D project management?
- Understanding the R&D project environment.
- Customer involvement.
- Requirements Management.
- Resource Management across multiple projects.
- Communications Management.
- Work with business objectives always in mind.
- Manage your resources wisely.
- Use Phase Gates Process across the entire portfolio.
- Documentation of all the knowledge bases of the project.
- Keep stakeholders informed.
- Use a SaaS PPM software.
- Managing your R&D projects with Triskell Software.
Project management consists of a set of frameworks and processes for planning and managing the different phases of a project. This is, broadly speaking, a classic definition of what is nowadays understood as Project Management in which you, as Project Manager , plan, prioritize and supervise the different operations and tasks to be carried out to complete the project within the agreed deadlines and budgets, optimizing to the maximum issues such as resource management or project costs.
However, can this traditional view of project management be applied, for example, to the research and development of new products or services? Is it possible in this type of projects to work with well-defined objectives, requirements, deadlines and budgets from the beginning, as it is the case with the projects you normally manage in your organization?
If there is one thing that defines R&D projects is their high degree of uncertaintyr
The answer is NO. If there is one thing that defines R&D projects, it is their high degree of uncertainty. Think about it for a moment. Most of these projects consist of researching and developing entirely new products that address a specific user need for which there is nothing available on the market.</p<
These are projects that, if well-executed, can give companies a great competitive advantage. But its management is complex, as the definition of the following aspects may change throughout the project life cycle:
- Needs: in R&D projects, the research phase plays a fundamental role in identifying possible market opportunities and unmet customer needs. However, what happens if these needs change during the course of the project? How can you effectively manage new product development projects in an environment where customer demands change with such volatility?
- Requirements: while in more traditional projects the requirements are already fully defined in the planning phase, this is rarely the case with R&D projects. There are many factors, both internal and external, that can force these requirements to be reviewed and modified: changing customer needs, lack of resources or funds, lack of knowledge of certain technologies, etc.
- Objectives: R&D projects have the greatest importance for the companies, hence their prioritization is the highest possible. However, what happens if the strategic objectives change? What if the market opportunity disappears and the company focuses on new goals? This aspect plays a fundamental role in R&D project management.
- Delivery dates: giving realistic dates for completing a new product development project is practically a pipe dream. The outcomes of an R&D project are usually uncertain, hence the difficulty of establishing delivery dates for this type of initiative. On the other hand, the evolution of needs and requirements throughout the project life cycle may also cause changes in the agreed end-of-project dates.
Provide dates for completing a new product development project is a pipe dream
Key elements of R&D project management
Due to all these constraints, the research and development of a new product brings with it governance and management challenges that, although they may have similarities to those you have to deal with in your day-to-day project management, have their own peculiarities.
For efficient R&D project management, it is necessary to know which are its key elements. Understanding these differentiating elements will enable you to better manage all the issues you will encounter throughout the project life cycle, and will increase the success rate of the research and development projects you manage. These key aspects are as follows:
We will now analyze each of them.
1. Understanding the R&D project environment
It is important to know in detail the environment in which R&D projects are planned and developed, as it is one of the most turbulent and volatile environments that you will encounter as a project manager. You will face governance and management challenges that will be difficult to respond to immediately due to the complexity and uncertainty surrounding these new product development projects. Some outstanding examples:
- Set targets in new product development initiatives that require technology that, in most cases, has not yet been discovered.
- Develop a detailed project timeline, with milestones and key dates, when many of the R&D project requirements are yet to be verified once product development begins.
- Not having certain skills or roles in the organization to carry out the project while the organization’s executives require you to complete the project within certain deadlines.
- Coordinate with the Marketing department to introduce the product to the market at the right time before it ceases to be an opportunity for the business.
Knowing how to manage an environment in which executives, teams and external partners can influence the development of the project will be the biggest challenge you will face as an R&D project manager.
2. Customer involvement
Customer involvement in the development of new products is key. Their feedback will not only allow you to develop products that are easy to use and maintain, but also to identify improvements in aspects such as usability, product performance and satisfaction of consumer needs . Feedback that, if used wisely, will help to achieve greater market penetration of the products and, therefore, more profits for the company.
Customer feedback will allow identifying improvements in the usability of the product and the satisfaction of the consumer’s needs
It is recommended to involve the customer in several of the phases of the R&D project life cycle, such as:
- List of project requirements. A feedback with the client at this point will help to identify the pain points and problems that the client wants to solve, and from there do the relevant market research before project initiation.
- Testing and validation of the product prototype , in order to identify possible improvements and errors to be corrected for the final version of the product.
- Evaluations of the final product to establish whether the product has met the customer’s needs and possible improvements for future versions of the product.
3. Requirements Management
The active involvement of the client in the development of R&D projects means that the management of the requirements of this type of initiative has some peculiarities compared to other types of projects. While it is normal to have clear project requirements in the early stages of a project, this is not the case when it comes to new product development.
The requirements for this type of project tend to evolve over time. And the lack of agility and flexibility of organizations to adapt to this type of circumstances, very common in R&D projects, causes many of them to fail. An efficient management of these requirements and a clear communication of any changes in them will be critical to manage key aspects of these projects such as resource management, capacity planning or project budgets.
Project stakeholders should not lose focus on the strategic objectives
Therefore, when managing project requirements, it is essential that all project stakeholders (project managers, development teams, external partners, executives , etc.) never lose focus on the strategic objectives and overall purpose of the R&D project.
4. Resource Management across multiple projects
Most R&D projects are large-scale, involving the allocation of multiple organizational resources to perform the various tasks of the project throughout its life cycle.
If we add to this what we have already mentioned in the previous point regarding the complexity of managing the requirements of an R&D project, you will now understand the importance of resource management and capacity planning for this type of initiatives.
- Capacity planning will help you estimate the resources you will need to allocate to each of the project areas and tasks throughout the project life cycle, taking into account the evolution of the project requirements and the priority of the project for the organization.
- On the other hand, with efficient resource management , you will know at any time how many resources need to be allocated to the project and the efforts that need to be dedicated to it. Here it will be important to list the skills and competencies of each of the members of the company in order to detect strengths and weaknesses and, depending on the project requirements, to seek or not those resources outside the organization.
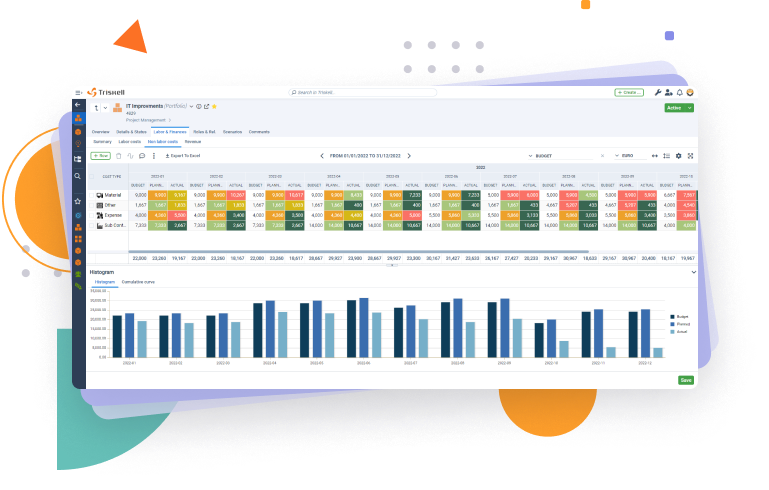
See the Triskell platform in action in a personal demo
5. Communications Management
When managing R&D projects, it is essential to have a communications plan in place that establishes the following:
- The periodicity with which we will inform the different project stakeholders about the evolution of the project.
- Main communication channels (reports, alerts, email, discussion forums, etc.).
- How and where will be documented all information relating to all such communications.
You must put in place a project communications plan for efficient project management
Considering how quickly requirements can change and, above all, the uncertainty that always surrounds R&D projects, having a clear understanding of how all project changes will be communicated is essential for efficient project management.
Best Practices for R&D project management
Now that you know the key elements that differentiate R&D project management, it is important that you implement a series of best practices to increase the probability of success in the development of new products. Some of them will be familiar to you because you are probably already putting them into practice in other types of projects, but in R&D and new product development are especially relevant. They are the following:
1. Work with business objectives always in mind.
When managing R&D projects, it is essential that all parties involved never lose focus on the strategic objectives of the organization. Hence, if there are changes in factors such as priority, requirements, budget or project deadlines, you can make decisions aligned with the vision and mission of the organization.
Having processes and tools in place that allow you to plan What-if scenario simulations will be critical to managing budgets, costs and other factors will be key to the efficient management of your new product development projects.
2. Manage your resources wisely
Dealing with all the workload involved in new product development is one of the biggest challenges any project manager has to face, especially when it comes to resource management. If it is already complex to plan the allocation and management of resources in any type of project, program or portfolio, this becomes even more complicated when you enter the R&D field.
Again, the uncertainty surrounding these initiatives is the cause of this. Depending on the type of R&D project you may have tighter schedules, while in others you may not have any deadlines for each of the project milestones.
You should plan in advance the resources you will need for the project
What-if scenario simulations are essential to keep project objectives and requirements aligned at any time. But also, with the strategic vision of the organization, they become even more relevant for resource management. It is key to the process to be able to plan in advance the resources you will need for the project based on how the priority, requirements and deadlines of the project evolve.
3. Use Phase Gate Process across the entire portfolio
R&D project management requires the implementation of rigorous control processes to review the progress of the project and make the corresponding adjustments when necessary. There is no point in devoting resources, money and time to a new product that, once finished, does not meet the needs of customers and markets because we have not been exhaustive when it comes to periodically reviewing what has been done.
Therefore, the Phase-Gate methodology is best suited to the R&D project environment. This methodology mainly consists of implementing a review process for each of the phases of the project (ideation, scope, business case, development, testing and launch), in which, after having analyzed the progress made and identifying possible improvements to be implemented, one of the following decisions is taken:
- Move the project to the next phase.
- Stop it to carry out the pertinent improvements.
- Cancel it because it is no longer profitable for the organization.
You can learn more about the Phase-Gate Process in the following post.

A comprehensive guide of Phase Gate Process for R&D projects
4. documentation of all the knowledge bases of the project.
In an R&D project, the documentation process takes on special relevance, more than in any other type of project. Not only the progress made should be documented, but also any changes that may have occurred in the project (new requirements, budget and resources adjustments, updated deadlines, etc.) and the reasons why these changes have been made.
All communications with project stakeholders (minutes, e-mails, reports, presentations, etc.) shall also be recorded.
All changes to the project and the reasons behind them should be documented
All this documentation will serve as a knowledge base not only for the current project, but will also serve as a repository for future R&D projects to be managed and as a source of learning from past successes and mistakes.
5. Keep stakeholders informed
Due to the importance of R&D projects and new product development for organizations, communication with stakeholders must be regular and smooth.
From the initial stages of the project, you should establish a frequency with which to communicate with them. These are communications that will go beyond reporting on the progress of the project, since you must agree with them on aspects such as:
- Project requirements.
- Project objectives.
- Budgets and costs.
- Resource allocation and recruitment.
- Collaborations with external partners.
- Testing and validation of the prototype.
- Project cancellation.
- Changes in requirements or project delivery dates.
As indicated in the previous point, all communications with stakeholders must be documented for proper monitoring of the project’s progress.
6. Use a SaaS PPM software
If you think that by filling in spreadsheets you will be able to manage your R&D projects, get that idea out of your head because this type of project is much more complex than any other you manage in your organization. A traditional project management tool is also not enough to cover many of the governance and management challenges involved in new product development, as these tools do not efficiently cover issues such as planning and strategic alignment.
A PPM software is the best option to take R&D project management to the next level. With a PPM tool you will be able to:
- Prioritize your projects by aligning them with the organization’s strategic objectives.
- Plan capacity and resource management based on these strategic objectives.
- Perform What-if scenario analysis in advance.
- Keep all stakeholders informed with fully customizable alerts and notification systems.
- Create reports and dashboards to monitor the progress of the project and inform the organization’s executives about its status in real-time.
Managing your R&D project portfolio with Triskell Software
The Triskell platform is the PPM software with strategy execution management functionalities that will allow you to successfully address all the challenges and difficulties you will encounter when managing your R&D projects. Thanks to its flexibility and ability to integrate with different tools (e.g. ERP software, Jira or Microsoft Project) you will be able to plan, monitor and manage all aspects of your R&D projects.
Here are some of Triskell’s features that will help you to achieve excellence in R&D project management:
- Roadmaps with which to plan the project and to visualize the different tasks to be completed throughout its life cycle.
- Workflows to organize project activities.
- Stage reviews to decide whether to go ahead with the project or to make the appropriate modifications.
- Cost control to monitor all expenses derived from your R&D projects.
- Budget management to keep under control the budget allocated to your projects.
- Resource management to allocate resources and monitor their use in your organization for the R&D projects you manage.
- Ideas management to undertake on new R&D projects or improve the requirements of existing ones.
- What-if Scenario analysis to plan in advance the organization’s capacity for possible changes of course.
- Integration with ERP software and other project management and execution tools such as Microsoft Project or Jira .
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get stories like this in your inbox
Request a demo of Triskell Software
If you would like to learn more about how Triskell can help you manage your organization’s R&D projects, request a demo below.
FAQs about R&D projects
What are the biggest challenges of managing r&d projects.
The biggest challenges of managing R&D projects stem from their inherent uncertainty. Unlike traditional projects with well-defined goals and deliverables, R&D projects often involve exploration and discovery. This makes it difficult to predict timelines, costs, and even the final outcome. Additionally, R&D projects often require flexibility and adaptation as new information or challenges arise.
How can I ensure my R&D project aligns with business objectives?
Ensuring your R&D project aligns with business objectives requires constant focus and communication. Here are some key steps:
- Clearly define the business objectives the R&D project aims to support.
- Regularly assess the project’s progress against these objectives.
- Maintain open communication with stakeholders to ensure everyone is informed and aligned.
- Be prepared to adapt the project if necessary to better serve the overall business goals.
What are Phase Gates and how do they benefit R&D project management?
Phase Gates are decision points implemented throughout the R&D project lifecycle. At each Phase Gate, a project team evaluates progress against pre-defined criteria. This evaluation determines whether the project moves forward to the next phase, requires replanning, or needs to be terminated.
Phase Gates benefit R&D project management by:
- Ensuring projects stay on track and avoid wasting resources on dead ends.
- Providing opportunities to make course corrections based on new information.
- Promoting better communication and collaboration among stakeholders.
What are some best practices for documenting knowledge gained during R&D projects?
Capturing and documenting learnings throughout an R&D project is crucial for future success. Here are some best practices:
- Maintain detailed project documentation , including project goals, milestones, and decisions made.
- Encourage team members to record their findings and observations throughout the project.
- Hold regular debriefing sessions to discuss lessons learned and areas for improvement.
- Develop a knowledge management system to store and share R&D project learnings across the organization.
Related Content

PMO success factors: how to make an extraordinary PMO
Unlock PMO success with these game-changing factors! Discover proven strategies for Project Management Office triumph.

Why the CIO needs a PMO approach
Unlock business success: discover why the CIO must embrace a PMO approach! to elevate efficiency and boost productivity.

Lean Budgeting for Agile Portfolios: A Comprehensive Guide
Lean Budgeting: the financial revolution for Agile portfolios. Discover how to streamline project financing and optimize value delivery.
- Strategic Planning
- Project & Program Management
- IT Portfolio Management software
- Innovation and Product Development
- Transformation Program
- Resource and Capacity Planning
- Idea and Demand Management
- Project Financial Management
- Build your own Solution
- Triskell Platform Overview
- Key Features
- News & Events
- Become a partner
- E-Books & White Papers
- Case Studies
- Product Demos
© 2024 Triskell Software. All Rights Reserved.
Legal Notice
Privacy Policy
Cookies policy
Quality Management and Information Security System Policy

We use technologies such as cookies to store and/or access device information. We do this to improve the browsing experience and to display (non-) personalized advertisements. Consenting to these technologies will allow us to process data such as browsing behavior or unique ID's on this site. Not consenting, or withdrawing consent, may adversely affect certain features and functions.

Triskell Software, named a Representative Vendor - 2024 Market Guide for Enterprise Agile Planning Tools
Triskell Software has been named a Representative Vendor in 2024 Gartner® Market Guide for Enterprise Agile Planning Tools. Discover how Triskell can assist companies to manage strategies, investments, and outcomes efficiently.
Breadcrumbs Section. Click here to navigate to respective pages.

Project Management for Research and Development
DOI link for Project Management for Research and Development
Get Citation
Today's leading organizations recognize the importance of research and development (R&D) to maintain and grow market share. If companies want to survive into the future, they must accelerate their R&D-to-market cycles or find themselves behind the competition.Project Management for Research and Development: Guiding Innovation for Positive R
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Chapter 1 | 50 pages, project management approaches, chapter 2 | 62 pages, project management as an enabler, chapter 3 | 54 pages, bounding the creative spaces, chapter 4 | 76 pages, measuring success, chapter 5 | 60 pages, building blocks to success, chapter 6 | 68 pages, overcoming obstacles, chapter 7 | 54 pages, facilitating the creative team, chapter 8 | 14 pages, process steps for the r&d project.
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Taylor & Francis Online
- Taylor & Francis Group
- Students/Researchers
- Librarians/Institutions
Connect with us
Registered in England & Wales No. 3099067 5 Howick Place | London | SW1P 1WG © 2024 Informa UK Limited
American Society for Microbiology
Project management tips for researchers.
Jan. 23, 2019
Project Monitoring and Control
Project closing.
- Undergraduate Student
- Graduate Student
- Management Skills
- Professional Development
Author: Caleb McKinney, Ph.D.

The 2024 Clinical Virology Symposium Registration Now Open!
Discover asm membership, get published in an asm journal.

- Contact AIChE
- Communities
- Learning & Careers
- Publications
- Careers at AIChE
- Equity, Diversity, Inclusion
- Young Professionals
- Operating councils
- Local Sections
Other Sites & Tools
Technical groups, follow aiche, project management for research and development.
Managing projects in R & D is different—and uniquely challenging. Learn the principles, skills and tools essential to your success.
In 60 minutes, you’ll learn the three most important keys to successful project management, as well as how to more effectively work with people, set priorities, and apply project management basics. Whether you’re managing projects now or will be in the future, you’ll gain an entirely new perspective on the meaning of the word “communication” that will help you create more effective and fulfilling interpersonal relations. This webinar also introduces useful tools for developing effective R & D project objectives that ensure you achieve your desired results.
Take a look at your agenda:
- The importance of people and effective teams
- Communication: A paradigm shift in interpersonal relations
- How to develop effective and clear objectives
- Project management basics
Eldon Larsen
Webinar content is available with the kind permission of the author(s) solely for the purpose of furthering AIChE’s & IChemE’s mission to educate, inform and improve the practice of professional chemical engineering. The content reflects the views, opinions, and recommendations of the presenters. AIChE does not warrant or represent, expressly or by implication, the correctness or accuracy of the content of the information presented. All other uses are forbidden without the express consent of the author(s). For permission to re-use, please contact [email protected] . Attendee contact information, including email addresses, will be shared with AIChE and IChemE, with the option to unsubscribe from future communications.
- AIChE Member Credits - 1
- AIChE Pro Members - $76.00
- AIChE Graduate Student Members - Free
- AIChE Undergraduate Student Members - Free
- AIChE Explorer Members - $109.00
- Non-Members - $109.00
- Source: AIChE
- Language: English
- Skill Level: Intermediate
- Duration: 1 hour
Explore More Areas of Advancement

AIChE Practice+ provides learners with opportunities to work on real-world challenges through industry internships and competitions.

With AIChE Career Discovery ® , we'll help you to identify aptitudes and skills you’ll need in order to achieve your full potential at various career stages.

AIChE Credential validates your proficiency with potential employers in areas such as process intensification, safety, sustainability and others.
Get full access to Project Management for Research and Development and 60K+ other titles, with a free 10-day trial of O'Reilly.
There are also live events, courses curated by job role, and more.
Project Management for Research and Development
Read it now on the O’Reilly learning platform with a 10-day free trial.
O’Reilly members get unlimited access to books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from O’Reilly and nearly 200 top publishers.
Book description
Today’s leading organizations recognize the importance of research and development (R&D) to maintain and grow market share. If companies want to survive into the future, they must accelerate their R&D-to-market cycles or find themselves behind the competition. Project Management for Research and Development: Guiding Innovation for Positive R&D Outcomes explains how to apply proven project management methods to obtain positive outcomes in R&D and innovation projects. It addresses the specific factors companies must consider when using project management to scope, define, and manage R&D projects. It also offers best practices and case studies that illustrate actual applications of theory. This book details methods to help readers optimize results in R&D through the use of structured processes derived from the project management field and other complementary disciplines. Each chapter includes diagrams, surveys, checklists, and question-answer forms to guide readers in determining where their activity falls along a project spectrum and to help them structure their own R&D project. The methods presented in this book can easily be applied to innovation projects and creative endeavors. As there are limited sources of information on how to utilize project management methodology effectively in these types of projects, this book is an ideal resource for anyone looking to add structure and proven methods to enable R&D, innovation, and other creative activities.
Table of contents
- Front Cover (1/2)
- Front Cover (2/2)
- Contents (1/3)
- Contents (2/3)
- Contents (3/3)
- List of Figures
- List of Tables
- Acknowledgments
- About the Author
- Introduction
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (1/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (2/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (3/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (4/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (5/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (6/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (7/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (8/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (9/10)
- Chapter 1: Project Management Approaches (10/10)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (1/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (2/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (3/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (4/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (5/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (6/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (7/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (8/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (9/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (10/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (11/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (12/13)
- Chapter 2: Project Management as an Enabler (13/13)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (1/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (2/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (3/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (4/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (5/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (6/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (7/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (8/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (9/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (10/11)
- Chapter 3: Bounding the Creative Spaces (11/11)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (1/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (2/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (3/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (4/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (5/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (6/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (7/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (8/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (9/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (10/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (11/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (12/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (13/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (14/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (15/16)
- Chapter 4: Measuring Success (16/16)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (1/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (2/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (3/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (4/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (5/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (6/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (7/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (8/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (9/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (10/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (11/12)
- Chapter 5: Building Blocks to Success (12/12)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (1/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (2/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (3/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (4/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (5/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (6/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (7/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (8/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (9/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (10/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (11/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (12/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (13/14)
- Chapter 6: Overcoming Obstacles (14/14)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (1/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (2/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (3/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (4/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (5/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (6/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (7/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (8/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (9/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (10/11)
- Chapter 7: Facilitating the Creative Team (11/11)
- Chapter 8: Process Steps for the R&D Project (1/3)
- Chapter 8: Process Steps for the R&D Project (2/3)
- Chapter 8: Process Steps for the R&D Project (3/3)
- Appendix A (1/3)
- Appendix A (2/3)
- Appendix A (3/3)
- Bibliography
Product information
- Title: Project Management for Research and Development
- Author(s): Lory Mitchell Wingate
- Release date: August 2014
- Publisher(s): Auerbach Publications
- ISBN: 9781466596306
You might also like
Project management, planning and control, 7th edition.
by Albert Lester
Project Management, Planning and Control, Managing Engineering, Construction and Manufacturing Projects to PMI, APM and BSI …
The Principles of Project Management (SitePoint: Project Management)
by Meri Williams
A full color guide for anyone who finds themselves responsible for executing projects and needs some …
Mastering Project Time Management, Cost Control, and Quality Management: Proven Methods for Controlling the Three Elements that Define Project Deliverables
by Randal Wilson
Mastering Project Time Management, Cost Control, and Quality Management gives managers powerful insights and tools for …
Effective Project Management
by Garth G.F. Ward
A practical and accessible guide to managing a successful project Effective Project Management is based around …
Don’t leave empty-handed
Get Mark Richards’s Software Architecture Patterns ebook to better understand how to design components—and how they should interact.
It’s yours, free.

Check it out now on O’Reilly
Dive in for free with a 10-day trial of the O’Reilly learning platform—then explore all the other resources our members count on to build skills and solve problems every day.


1st Edition
Project Management for Research and Development Guiding Innovation for Positive R&D Outcomes
- Taylor & Francis eBooks (Institutional Purchase) Opens in new tab or window
Description
Today’s leading organizations recognize the importance of research and development (R&D) to maintain and grow market share. If companies want to survive into the future, they must accelerate their R&D-to-market cycles or find themselves behind the competition. Project Management for Research and Development: Guiding Innovation for Positive R&D Outcomes explains how to apply proven project management methods to obtain positive outcomes in R&D and innovation projects. It addresses the specific factors companies must consider when using project management to scope, define, and manage R&D projects. It also offers best practices and case studies that illustrate actual applications of theory. This book details methods to help readers optimize results in R&D through the use of structured processes derived from the project management field and other complementary disciplines. Each chapter includes diagrams, surveys, checklists, and question-answer forms to guide readers in determining where their activity falls along a project spectrum and to help them structure their own R&D project. The methods presented in this book can easily be applied to innovation projects and creative endeavors. As there are limited sources of information on how to utilize project management methodology effectively in these types of projects, this book is an ideal resource for anyone looking to add structure and proven methods to enable R&D, innovation, and other creative activities.
Table of Contents
Lory Mitchell Wingate has achieved notable success in program and project management within policy research, aerospace engineering, production and support, and scientific research organizations. With over 25 years of experience in both for-profit and non-profit companies, Wingate possesses detailed knowledge and expertise in project management and has developed a strong method for combining the best practices from several disciplines into a winning formula for the management of research and development. She has an MBA in information technology management, and is a Certified Project Management Professional (PMP ® ). Wingate’s area of expertise is in project management, program management, and systems engineering, and she actively pursues opportunities to present training workshops and materials associated with her areas of expertise.
About VitalSource eBooks
VitalSource is a leading provider of eBooks.
- Access your materials anywhere, at anytime.
- Customer preferences like text size, font type, page color and more.
- Take annotations in line as you read.
Multiple eBook Copies
This eBook is already in your shopping cart. If you would like to replace it with a different purchasing option please remove the current eBook option from your cart.
Book Preview

The country you have selected will result in the following:
- Product pricing will be adjusted to match the corresponding currency.
- The title Perception will be removed from your cart because it is not available in this region.
- News & Highlights
- Publications and Documents
- Education in C/T Science
- Browse Our Courses
- C/T Research Academy
- K12 Investigator Training
- Harvard Catalyst On-Demand
- Translational Innovator
- SMART IRB Reliance Request
- Biostatistics Consulting
- Regulatory Support
- Pilot Funding
- Informatics Program
- Community Engagement
- Diversity Inclusion
- Research Enrollment and Diversity
- Harvard Catalyst Profiles

Project Management Strategies for Research Team Members
Webinar series on the principles of project management
For more information:
- Understand the foundational principles of project management.
- Explore how project management principles and strategies can influence your work with colleagues and stakeholders on various projects.
Managing projects is a detailed and systematic process. Yet, the applications of this process vary across disciplines and teams. This webinar series will introduce how to troubleshoot, forecast, and problem solve using project management in various contexts while considering how these elements impact the work of teams. Each of the four independent sessions will be led by David Vincenti, PMP, a certified project management professional. This series will identify the principles of project management and how to apply templates and skills to your work and experiences in team settings. The last session will feature a panel of guest speakers who utilize successful project management strategies in their respective roles and professions. Those without official training in this area will gain skills and confidence in project management during this series.
Boundary-Crossing Skills for Research Careers
This session explores approaches to developing a broad range of competencies integral to establishing and maintaining a successful research career. The series delves into the following competencies: team science, mentorship, project management, communication, leadership, and funding research. For more information and to access other resources and webinars in the series, please visit Boundary-Crossing Skills for Research Careers.
Meet the Presenter

Vincenti has presented to academic and professional audiences on project management, professional development, and other topics, and has been recognized for his work with career planning for early-career technical professionals. He holds degrees in materials engineering and technology management from Stevens Institute of Technology.
Meet the Panelists
Sarita Patil, MD: Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School and Assistant Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital
Jane Shim, BA : Clinical Research Coordinator, Food Allergy Center, Massachusetts General Hospital
Neal Smith, MSc : Senior Computational Biologist, Center for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases, Massachusetts General Hospital
Yamini Virkud, MD, MA, MPH : Pediatric Allergist/Immunologist and Assistant Professor, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Session dates
Session 1: Defining the Work November 1, 2022 | 12:00pm ET This session introduces basic project management principles. You will learn the definition of a project, how to manage project scope, and how to draft the baseline of a project while considering how projects can be connected.
Session 2: Creating the Plan November 3, 2022 | 12:00pm ET In this session, you will learn to apply project planning terms and understand how to break a project into manageable parts, sequence tasks, and manage time while considering how these components affect your work and the work of your team members.
Session 3: Finalizing the Plan November 8, 2022 | 12:00pm ET In this session, you will explore project management principles further by calculating risks, managing a process, reviewing a project plan, and forecasting the execution and completion of a project while considering how these elements impact your work and the work of your team members.
Session 4: Panel Discussion November 10, 2022 | 12:00pm ET This culminating session features a panel discussion with four successful project management practitioners. The panelists will share their experiences in their respective roles and professions, and discuss how they engage in project management work within team settings.
Time commitment
50-minute sessions on Zoom
This series is designed for team members in the clinical and translational (c/t ) workforce who are familiar with project management but have no formal training. Attendees are welcome to attend on their own or with their team members.
We believe that the research community is strengthened by understanding how a number of factors including gender identity, sexual orientation, race and ethnicity, socioeconomic status, culture, religion, national origin, language, disability, and age shape the environment in which we live and work, affect each of our personal identities, and impacts all areas of human health.
Eligibility
There are no eligibility requirements. Prior session attendees have included: PhD, MD, postdocs, junior faculty, and medical students.
Registration is currently closed. Please check back for future opportunities.
Related Courses
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
What does a Research And Development Project Manager do?
It is the responsibility of a research and development manager to research, plan, and implement new protocols and programs into their organization. Research and development managers supervise research and the development of new knowledge-based products. They create research programs that incorporate existing developments for product improvement. To become a research and development manager, one needs research experience, skills in research and development projects, and work experience in the industry.
- Responsibilities
- Skills And Traits
- Comparisions
- Types of Research And Development Project Manager

Research and development project manager responsibilities
A research and development project manager's pivotal responsibilities include managing overall software strategy, developing standard operating procedures, and coordinating the work of developers and technical writers. They also administer project management principles, remediate design history files, and lead software, electronics, and electrical functions for product research. As Professor Donald Yeung from the University of Maryland - College Park noted, "I believe the courses students take along with their GPA in these courses is one level of demonstration." This reflects the importance of technical skills in their role.
Resume snippets often highlight these responsibilities. For instance, "managed overall software strategy across product lines to have effective software feature that differentiates from competition" and "developed, worked from, and managed Gantt charts" are common inclusions. Additionally, "created mobile web application for internal product lifecycle management tool" and "led the chemical & engineering support of the R&D group" further underscore the breadth of their duties.
Here are examples of responsibilities from real research and development project manager resumes:
- Manage Linux/Apache server configuration for company version control and bug tracking, creating PHP/MySQL database on server for product specification library.
- Prepare, organize, and review paperwork for lot release in accordance with FDA, USP, and ISO standards.
- Comply with MFi, ISO 13485 and partner with FitLinxx (CSAFE), Netpulse (NetpulseOne) and LiveStrong.
- Select the PLC, HMI and instrument requirements for projects.
- Develop scope and estimate for PLC applications and DCS expansions.
- Image creation of AutoCAD workstations-Roll out new versions-configure AutoCAD standards.
- Purify water system, hvac, compress air, others).
- Train and certify as an internal auditor for ISO 9002 and ISO 14000.
- Respond to FDA inquiries regarding medical device reports with preparation of appropriate trending data and details of corrective action plans.
- Perform QA system testing ensuring acceptable product performance.
- Lead in the characterization of proprietary biomarkers and their development into molecular diagnostics while following cGLP guidelines.
Research and development project manager skills and personality traits
We calculated that 15 % of Research And Development Project Managers are proficient in R , Project Management , and Product Development . They’re also known for soft skills such as Detail oriented , Math skills , and Analytical skills .
We break down the percentage of Research And Development Project Managers that have these skills listed on their resume here:
Helped win the company's largest R &D Federal contract at DHS (CanScan - Domestic Nuclear Detection Office).
Administered project management principles and procedures for various aspects of a six-phase new product development process.
Participated in innovation sessions, generating ideas / concepts; addressing unmet consumer needs and driving future product development.
Fracture and stress analysis testing on implantable medical devices using BOSE Electroforce 3200 load frame and Wintest Software
Oversee design, development and construction of proprietary tooling that enabled enhancing product portfolio.
Managed collaborative, inter-company R&D projects for new manufacturing technologies including water jet machining and factory network protocols.
Common skills that a research and development project manager uses to do their job include "r," "project management," and "product development." You can find details on the most important research and development project manager responsibilities below.
Math skills. Many research and development project manager duties rely on math skills. "architectural and engineering managers use calculus and other mathematics to develop new products and processes.," so a research and development project manager will need this skill often in their role. This resume example is just one of many ways research and development project manager responsibilities rely on math skills: "direct corporate qualitative and quantitative market research programs key accomplishments:. "
Analytical skills. Another skill that relates to the job responsibilities of research and development project managers is analytical skills. This skill is critical to many everyday research and development project manager duties, as "architectural and engineering managers evaluate information to solve problems." This example from a resume shows how this skill is used: "responded to fda inquiries regarding medical device reports with preparation of appropriate trending data and details of corrective action plans. "
Communication skills. For certain research and development project manager responsibilities to be completed, the job requires competence in "communication skills." The day-to-day duties of a research and development project manager rely on this skill, as "architectural and engineering managers must effectively convey information and expectations related to projects." For example, this snippet was taken directly from a resume about how this skill applies to what research and development project managers do: "identified, developed, and implemented process improvements that improved communications and efficiencies. "
Organizational skills. Another crucial skill for a research and development project manager to carry out their responsibilities is "organizational skills." A big part of what research and development project managers relies on this skill, since "architectural and engineering managers keep track of many workers, schedules, and budgets simultaneously." How this skill relates to research and development project manager duties can be seen in an example from a research and development project manager resume snippet: "identify best-in-class industry product development partners, establish business relationships, and negotiate development contracts to enhance organizational and portfolio excellence. "
See the full list of research and development project manager skills
The three companies that hire the most research and development project managers are:
- Thermo Fisher Scientific 17 research and development project managers jobs
- Johnson & Johnson 6 research and development project managers jobs
- Biogen 3 research and development project managers jobs
Choose from 10+ customizable research and development project manager resume templates

Compare different research and development project managers
Research and development project manager vs. engineering supervisor.
An engineering supervisor is responsible for monitoring the engineering operations of an organization, developing strategic processes and techniques to improve staff's performance, and facilitating training and programs to maximize productivity. Engineering supervisors evaluate technology procedures and reports to identify and design new opportunities that would generate more resources for revenues and profits. They also meet with clients and handle their business requirements and specifications, informing them of other services that the company offers. An engineering supervisor resolves project complaints and implements business plans to achieve high-quality deliverables.
There are some key differences in the responsibilities of each position. For example, research and development project manager responsibilities require skills like "medical devices," "portfolio," "d project," and "development projects." Meanwhile a typical engineering supervisor has skills in areas such as "hvac," "plumbing," "preventive maintenance," and "customer service." This difference in skills reveals the differences in what each career does.
Research and development project manager vs. Engineering operations manager
Engineering Operations Managers are responsible for managing mechanical or electrical repair and maintenance activities. Their duties include supervising the facility's daily operations, directing engineers, contractors, and subcontractors in executing a project, forecasting maintenance, and operation costs, preparing an annual budget, and leading strategic sourcing initiatives. Other duties include training staff, working with the human resource team to plan development initiatives, and processing payment applications, orders, invoices, and change requests. An Engineering Operations Manager also conducts procedures for contract bidding of maintenance activities. They are essential in facilitating communication between teams in engineering and operations.
Each career also uses different skills, according to real research and development project manager resumes. While research and development project manager responsibilities can utilize skills like "medical devices," "portfolio," "d project," and "development projects," engineering operations managers use skills like "engineering operations," "linux," "hvac," and "plumbing."
Research and development project manager vs. Vice president of engineering
A Vice President Of Engineering manages all aspects of the company's engineering product development activities. They are responsible for strategic planning, production designing, quality assurance, and problem resolution.
Some important key differences between the two careers include a few of the skills necessary to fulfill the responsibilities of each. Some examples from research and development project manager resumes include skills like "medical devices," "portfolio," "d project," and "development projects," whereas a vice president of engineering is more likely to list skills in "architecture," "cloud," "infrastructure," and "java. "
Research and development project manager vs. Manufacturing engineering manager
Manufacturing engineering managers manage manufacturing process development and enforcement. The managers maintain the proper functionality of a product and the efficiency of cost. They ensure the cohesive work between manufacturing departments and the engineering team. Their main responsibility is to design and operate integrated systems for economically competitive and high-quality products. They need to have skills in teamwork, technical knowledge, information technology, and commercial awareness. It is also necessary for them to have strong leadership skills .
Types of research and development project manager
- Project Manager
- Engineering Manager
- Project Engineering Manager
- Engineering Director
- Design Manager
- Engineering Supervisor
Updated June 25, 2024
Editorial Staff
The Zippia Research Team has spent countless hours reviewing resumes, job postings, and government data to determine what goes into getting a job in each phase of life. Professional writers and data scientists comprise the Zippia Research Team.
What Similar Roles Do
- What a Design Engineering Manager Does
- What a Design Manager Does
- What an Engineering Director Does
- What an Engineering Manager Does
- What an Engineering Operations Manager Does
- What an Engineering Program Manager Does
- What an Engineering Supervisor Does
- What an Engineering/Maintenance Manager Does
- What a Manufacturing Engineering Manager Does
- What a Process Engineering Manager Does
- What a Product Development Manager Does
- What a Product Engineering Manager Does
- What a Project Engineering Manager Does
- What a Project Manager Does
- What a Research And Development Director Does
Research And Development Project Manager Related Careers
- Design Engineering Manager
- Engineering Operations Manager
- Engineering Program Manager
- Engineering/Maintenance Manager
- Manufacturing Engineering Manager
- Process Engineering Manager
- Product Development Manager
- Product Engineering Manager
- Research And Development Director
Research And Development Project Manager Related Jobs
Resume for related jobs.
- Design Manager Resume
- Engineering Director Resume
- Engineering Manager Resume
- Engineering Program Manager Resume
- Engineering Supervisor Resume
- Engineering/Maintenance Manager Resume
- Manufacturing Engineering Manager Resume
- Product Development Manager Resume
- Project Engineering Manager Resume
- Project Manager Resume
- Research And Development Director Resume
- Research And Development Engineer Resume
- Research And Development Manager Resume
- Senior Engineering Manager Resume
- Senior Project Manager Resume
- Zippia Careers
- Executive Management Industry
- Research And Development Project Manager
- What Does A Research And Development Project Manager Do
Browse executive management jobs
Research and Development Manager Skills
Learn about the skills that will be most essential for Research and Development Managers in 2024.
Getting Started as a Research and Development Manager
- What is a Research and Development Manager
- How To Become
- Certifications
- Tools & Software
- LinkedIn Guide
- Interview Questions
- Work-Life Balance
- Professional Goals
- Resume Examples
- Cover Letter Examples
What Skills Does a Research and Development Manager Need?
Find the important skills for any job.

Types of Skills for Research and Development Managers
Innovative mindset and problem-solving, technical and scientific knowledge, strategic planning and execution, data analysis and critical thinking, leadership and team management, top hard skills for research and development managers.
- Strategic Thinking and Visioning
- Creative Problem-Solving
- Collaborative Leadership
- Effective Communication
- Adaptability and Flexibility
- Emotional Intelligence
- Conflict Resolution and Negotiation
- Team Building and Motivation
- Risk Management and Decision Making
- Time Management and Prioritization
Top Soft Skills for Research and Development Managers
- Scientific Research Methodology
- Data Analytics and Statistical Analysis
- Technical Product Knowledge
- Prototyping and CAD Software Proficiency
- Intellectual Property Management
- Experiment Design and Execution
Regulatory Compliance and Quality Assurance
- Project Management Tools and Techniques
- Resource Allocation and Budget Management
- Advanced Material Science
Most Important Research and Development Manager Skills in 2024
Innovation management and foresight, cross-disciplinary collaboration, project management proficiency, intellectual property knowledge, resourcefulness and budgeting acumen, strategic talent development, environmental and social governance (esg) integration.

Show the Right Skills in Every Application
Research and development manager skills by experience level, important skills for entry-level research and development managers, important skills for mid-level research and development managers, important skills for senior research and development managers, most underrated skills for research and development managers, 1. intellectual curiosity, 2. conflict resolution, 3. resourcefulness, how to demonstrate your skills as a research and development manager in 2024, how you can upskill as a research and development manager.
- Immerse in Emerging Technologies: Keep abreast of cutting-edge technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and biotechnology that can revolutionize R&D processes.
- Advance Your Project Management Skills: Pursue advanced training in project management methodologies, such as Scrum or Kanban, to optimize R&D project workflows and outcomes.
- Strengthen Data Analysis Competencies: Enhance your ability to interpret complex data by learning advanced data analytics tools and techniques, which are essential for informed decision-making in R&D.
- Expand Your Scientific Knowledge Base: Regularly attend webinars, subscribe to relevant journals, and take specialized courses to stay updated on the latest scientific discoveries and trends.
- Develop Strategic Thinking: Engage in workshops or courses that focus on strategic planning and foresight to better align R&D initiatives with long-term business goals.
- Enhance Leadership and Team Management: Invest in leadership development programs to cultivate skills that foster innovation, collaboration, and resilience within your R&D team.
- Build a Culture of Continuous Learning: Create an environment that encourages knowledge sharing and continuous learning among your team members to spur collective growth.
- Network with Industry Innovators: Actively participate in industry associations and innovation clusters to exchange ideas and collaborate with other R&D leaders.
- Embrace Regulatory Knowledge: Stay informed about global and local regulatory changes that impact R&D activities to ensure compliance and mitigate risks.
- Focus on Intellectual Property (IP) Management: Understand the nuances of IP rights and patent laws to protect your organization's innovations and leverage them strategically.
Skill FAQs for Research and Development Managers
What are the emerging skills for research and development managers today, how can research and development managers effectivley develop their soft skills, how important is technical expertise for research and development managers.
Research and Development Manager Education

More Skills for Related Roles
Steering innovative product journeys from ideation to successful market launches
Leading technical teams, driving innovation and ensuring project success in engineering
Leading tech innovation, driving team performance for efficient engineering solutions
Driving tech innovation, leading strategic IT decisions, shaping the future of business
Driving tech projects from conception to completion, ensuring efficiency and quality
Start Your Research and Development Manager Career with Teal
Research and Development Project Definition and Portfolio Management
- First Online: 22 June 2022
Cite this chapter

- Olivier L. de Weck 2
3689 Accesses
1 Citations
Ultimately, technology progresses through individual steps which are the results of specific research and development (R&D) projects. In this chapter, we first describe what kinds of R&D projects exist, and how to plan and successfully execute them. We then consider how multiple projects together – as a set – constitute an R&D portfolio. Portfolios can be defined with the help of targets set by technology roadmaps. Given a fixed total R&D budget, it is also possible to optimize the composition of an R&D portfolio by balancing expected return and risk. We give an example of what an R&D portfolio might look like, by considering the portfolio of a major technology firm.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Subscribe and save.
- Get 10 units per month
- Download Article/Chapter or eBook
- 1 Unit = 1 Article or 1 Chapter
- Cancel anytime
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
The distinction between R&D and R&T is unique to some countries in Europe such as France and Germany, whereas in the United States the term R&D is used throughout. One of the subtleties is that government funding for R&T (projects at TRL 6 or earlier) is generally acceptable, whereas government funding for product and service development (R&D after TRL 6) is generally considered a government subsidy and potentially subject to adverse WTO rulings.
We focus on the “value” generated by technology in Ch. 17. In simple terms, we can think of investing some amount of money in order to improve one (or more) FOM’s by some amount, ∆FOM/∆$, and this improvement in FOM should then later return a positive multiple in terms of enhanced revenues or cost savings, ∆$/∆FOM. The product of these two terms can be interpreted as a ROI of the technology investment.
This happened to the Mars Science Laboratory (MSL) mission which carried the Curiosity rover to the surface of Mars and whose original launch date slipped from 2009 to 2011, in part due to technical challenges with cryogenic actuators.
Source: https://www.airbus.com/innovation/future-technology/autonomy.html
For example, it is usually much more expensive to raise the TRL level of a technology from TRL 5 to 6, compared to raising it from TRL 3 to 4. This is because as technology maturity progresses, the fidelity and complexity of equipment, test procedures, and (simulated or actual) use cases becomes much higher, requiring more time, effort, and money.
The scaled agile framework (SAFe) claims to be able to integrate several projects into a coherent whole at the enterprise level, see: https://www.scaledagileframework.com/
One subtlety of the basic EVM calculations is that it does not capture the interdependencies shown on the critical path diagram (e.g., Fig. 16.5 ), and therefore, the schedule performance in terms of SPI can be different than the schedule tracked in terms of the critical path.
This assumes that the remainder of the project will be executed at the same level of cost efficiency as the project exhibited up until “Time Now.”
A more Machiavellian perspective on overoptimism is that project proponents deliberately low ball project estimates in terms of cost and schedule such that the project is more likely to gain approval and get started. This assumes that, once underway, project leaders will be able to secure additional resources and time as project sponsors will want to see the project succeed, rather than face its cancellation.
An example of such a type of project is the Airbus E-Fan X project wherein the goal was to develop and demonstrate in flight a 2 [MW] class electric propulsion system. The project was set up as an allied partnership between Airbus, Siemens, and Rolls Royce. Note that the project was prematurely stopped due to budget cuts related to the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020.
This is a disguised name to protect the confidentiality of the actual company.
The work in this section is credited to Dr. Kaushik Sinha , mainly done during 2017–2018.
A fundamental assumption for φ min is that even a small investment in a technology may yield value, for example, partnering on an R&D project with external organizations, doing in-depth technology scouting (Ch. 14), modeling and simulation, etc. R&D investments in a technology are usually not “all or nothing” propositions. However, there may be a minimum level of investment needed to “unlock” any value at all.
The details of the individual technologies are not important here, we simply want to illustrate the overall principle of R&D portfolio optimization.
Most technology-based companies, including financial departments led by CFOs, use deterministic planning to allocate resources and are uncomfortable using probabilities or statistical analysis of any sort. This is somewhat surprising, since statistical-based risk analysis is the very basis of financial markets.
Garvey P.R., “Probability Methods for Cost Uncertainty Analysis: A Systems Engineering Perspective”, CRC Press (2000), ISBN-10: 0824789660.
Google Scholar
Georgiopoulos P., Fellini R., Sasena M. and Papalambros P., “Optimal design decisions in product portfolio valuation”, DETC2002/DAC-34097, Montreal, 2002
Legge Jr RS, Lozano PC. Electrospray propulsion based on emitters microfabricated in porous metals. Journal of Propulsion and Power. 2011 Mar;27(2):485-95.
Markowitz, Harry. "Portfolio selection." The Journal of Finance , 7, no. 1 (1952): 77-91.
Pennings E. and Sereno L., “Evaluating pharmaceutical R&D under technical and economic uncertainty”, Volume 212, Issue 2, Pages 374-385, European Journal of Operational Research, 2011
Sega R., de Weck O.L, et al., “Controlling Cost Growth of NASA Earth and Space Science Missions” By Committee on Cost Growth in NASA Earth and Space Science Missions, National Research Council (NRC) of the National Academy of Sciences,ISBN-13: 978-0-309-15737, Washington D.C., July 2010
Shishko R. , Ebbeler D. H. , and Fox G., “NASA Technology Assessment Using Real Options Valuation”, Systems Engineering , Vol. 7, No. 1, 2004
Sinha K., de Weck O., “Empirical Validation of Structural Complexity Metric and Complexity Management for Engineering Systems”, Systems Engineering , 19(3), pp. 193-206, May 2016
Wheelwright, S.C. and Clark, K. B., 1992, “Creating Project Plans to Focus Product Development,” Harvard Business Review, 70(2), pp. 70-82.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, USA
Olivier L. de Weck
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar

Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2022 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this chapter
de Weck, O.L. (2022). Research and Development Project Definition and Portfolio Management. In: Technology Roadmapping and Development . Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88346-1_16
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-88346-1_16
Published : 22 June 2022
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-88345-4
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-88346-1
eBook Packages : Engineering Engineering (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
3 Ways to Successfully Manage Large-Scale R&D Projects
- Travis Kimmel

Navigate even the most complex projects with confidence and resilience.
Managing extended R&D projects comes with its unique challenges, with even the popular agile method struggling in such contexts. Drawing from a recent significant build at Lattice, an HR software startup, three key factors emerge as essential for success in managing large projects. First, securing executive commitment ensures risk acceptance and a flexible budgeting approach. Second, setting expectations, especially in R&D, calls for transparent communication regarding delivery timelines, and fostering a culture centered on learning and adaptability. Lastly, true leadership and project success hinge on owning the outcome, promoting bold decision-making and ensuring teams focus on tasks without fear of blame. By integrating these principles, organizations can navigate even the most complex projects with confidence and resilience.
In project management, challenges tend to grow as projects — especially those centered on research and development — extend over time. It becomes harder to manage deadlines and allocate resources over lengthy horizons. The most popular method for managing projects flexibly, known as agile , struggles when applied to extended ventures. This is mainly because long-running innovative endeavors, such as skunkworks, often lack regular feedback from end-users, which is essential for the agile approach.
- TK Travis Kimmel is the General Manager of Lattice HRIS. He was previously co-founder and CEO of GitPrime, a Colorado-based software company founded in 2015 and acquired by Pluralsight in 2019.
Partner Center
Research & Development World
Five simple ways to improve project management processes for your R&D team
By Heather Hall | June 28, 2022
By William Malsam, Director of Content, ProjectManager

William Malsam, ProjectManager
Research and development (R&D) teams understand the constant pressure to develop products that are simultaneously high-quality, innovative and impactful. As a larger volume of R&D teams work from different locations and try to find success regardless of their work style or individual role, it’s becoming increasingly difficult to manage project processes that yield success.
Simply improving the way in which you manage your R&D processes can keep quality and speed top of mind both internally for R&D teams and across the organization as a whole. By consistently implementing the following five project management processes, research and development teams in any vertical can build new products faster while meeting the necessary quality standards.
- Always start with a project plan
Through a detailed and thorough project plan, R&D teams can lay the foundation for a successful and collaborative project. What is the targeted final product and what are the steps necessary to get there? A project plan helps align team members and lay the project infrastructure.
As successful R&D projects always start with an ironed-out plan, the project planning stage is arguably the most important step in the project as a whole. It pinpoints the project’s goals, risks, deadlines and helps the team understand what’s expected of them. As a singular R&D project could take place over a period of years, it’s important to lay the framework that will set your team up for long-term success.
Plans exist on formal documents that outline the who, what, where, why and how of the project. Here are the documents associated with the project planning phase:
- Project charter is a general project overview that outlines the constraints, project stakeholders and reasoning behind why a product is being developed.
- Statement of work defines the scope, schedule, deliverables, milestones and tasks.
- Work breakdown structure divides the project into different phases, subprojects and deliverables that accumulate into the final product.
- Project plan contains four sections including scope management, quality management, risk assessment, stakeholder management and more.
Thankfully, project planning software makes it seamless to produce the above documents and keeps manufacturing teams on track throughout the project. For example, pre-built product development templates make it easy to carry the project through the conception, design, prototyping, pre-production and marketing phases effortlessly. Spend less time building workflows and more time focusing on the overarching product strategy.
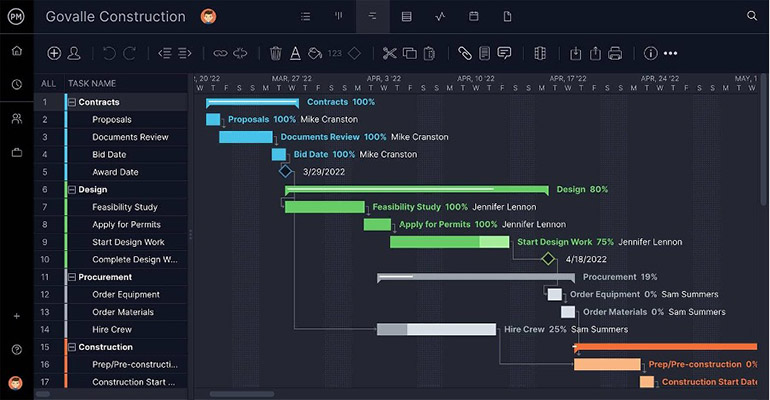
Online Gantt charts visualize your project timeline and progress, making it easy to keep track of details such as product and market research, task duration, dependencies and a project baseline with associated costs, to name a few. Regardless of whether your R&D team prefers agile or waterfall to drive the innovation process, they’ll have easy access to the cloud-based tools they need to find success in this hybrid work landscape.
- Ensure your team is on the same page
Aligning with your team on goals, progress and task breakdowns allows you to focus less on the nitty gritty details and more on a clear, overarching roadmap of how to execute the project. Communication plans, clearly defined roles with RACI (responsible, accountable, consulted and informed) charts and kickoff meetings are integral to ensuring individual roles are on the same page.
Not only do individuals within the same R&D team need to be aligned on project objectives, but teams must communicate cross-functionally to marry the product’s design and functionality. Many road bumps encountered by today’s R&D organizations stem from organizational systems that don’t align with the product and minimal transparency between groups.
For example, let’s say you’re responsible for developing a product that helps vehicles check blind spots. To develop further advances to current blind spot monitors, R&D teams require coordination with electrical systems, brake systems and steering systems. With a traditional project management approach, this coordination may not come until the final testing stage when it is too late.
To avoid this problem, R&D teams can continuously refer to project-level reports and dashboards for shareable project data. For example, project management software offers hybrid R&D teams a suite of collaborative tools such as reporting, dashboards and multiple project views to outpace competitors. The more time that R&D organizations have to focus on how they can deliver overarching goals to their customers, the less time they’ll spend tracking down specific metrics or communicating key details with other departments.
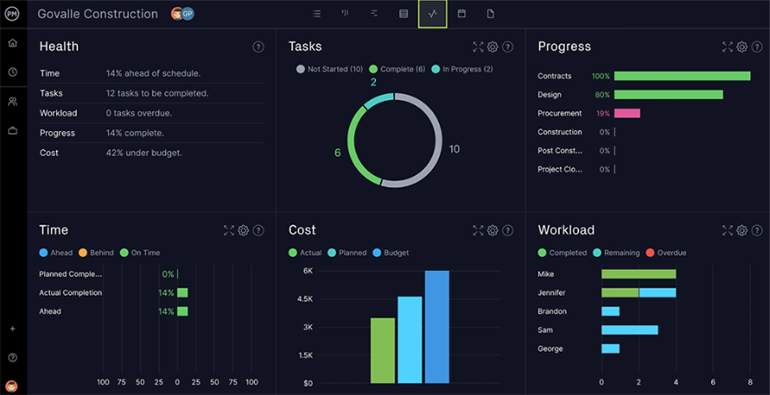
- Declutter your virtual workspace
As many projects must toe the line between project management and R&D work, teams can declutter their workspace to drive productivity and maintain quality. The sheer speed associated with producing a new product is becoming faster than ever, making it hard to keep track of one project at a time let alone a slew of incoming product requests.
Moreover, different team members naturally gravitate towards different tools, software, email chains, file sharing methods, etc. Simply tracking down the right information or collaborating with another manufacturing site can be troublesome and time-consuming.
Organization is key in keeping track of details and ensuring nothing slips through the cracks. Centralizing the workspace and using a singular tool to house all files, project plans and varied details yields more productivity with less confusion.
For example, find a tool that offers Gantt charts to create project-level tasks, allocate working hours, set a status and even include task priority levels. If the project manager needs to add a last-minute task for budget approval for the VP of R&D, they can simply locate the project and tag him or her accordingly.
Many software options offer both Gantt charts and Kanban boards in one. For R&D teams that gravitate toward a more visual workflow, they can utilize the Kanban board to see how the product development process is coming along. Kanban boards are particularly helpful to pinpoint project slip, making it easier for project or engineering managers to see when budgets trickle into the red to take immediate action. By streamlining the workflow into predictable and easy-to-navigate formats, the project management process becomes a well-oiled machine.
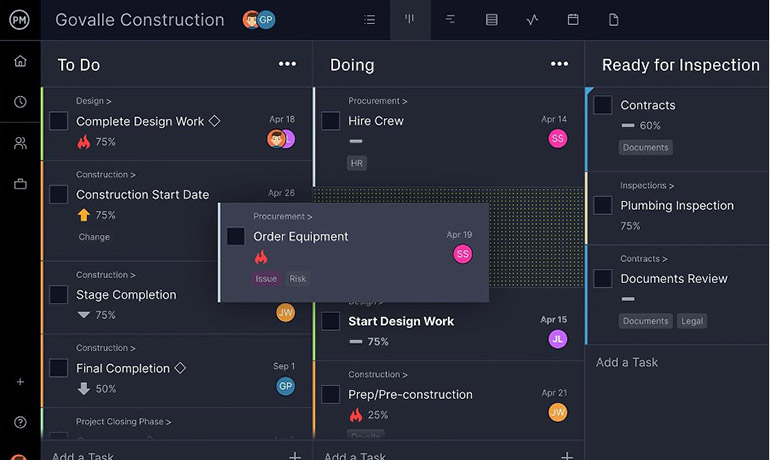
- Create custom workflows & automation
Without a method of streamlining workflows and processes, R&D teams may struggle to deliver quality, timely products. Sticky notes, one-off emails with task requests or sending a siloed Slack message simply don’t cut it anymore. With such a chaotic way to communicate and track down project details, important work and messaging undoubtedly slips through the cracks.
Enter automation. This doesn’t need to be robots or high-tech solutions. Rather, establish an agreed-upon workflow and take advantage of automated tasks to significantly reduce busywork and prioritize project quality. R&D projects are undoubtedly complex in nature, and it can take the project manager a significant amount of time to set up the project. Multiply this same front-end work across projects and innovation pace screeches to a halt. Even if you don’t have software, you can still create workflows using calendars and task reminders.
Consider the role of VPs, directors, or managers within R&D organizations and how they oversee quality efforts. Streamlined workflows make it easy to determine what tasks need to be approved by which role. Let’s say you need an operations manager to approve the resources within a given project; why not set up a workflow on a Kanban board that guides the task to your manager when the task is completed? Clearly defining responsibilities can help teams maintain both speed and quality.
- Don’t forget to create a roadmap
Long-term roadmaps, whether you’re forecasting budgets or capacity planning, allows R&D leaders to balance workloads and maximize resources. There is huge value in seeing a project through to completion, but it’s always a good idea to be prepared for what’s around the corner.
To balance your team’s workload, you need to know what’s on their plate. Regularly keeping in touch with your team allows you to better understand the types of projects they’re taking on and what their workload is like. This helps avoid the all-too-common issue of some team members sitting idly waiting for more tasks while some are overworked. Balancing workloads gives you the confidence needed to accept or reject incoming project requests and gives you insight into skill gaps that could round out your team.
If you’re a Manager of Engineering working from a different location than your team, you lose the opportunity to chat with them as you pop over to their desk or pass them on their way to lunch. To compensate for this lack of visibility, make sure to check in with your team regularly and create a system that clearly communicates workloads and resource fluctuations.
Better projects are around the corner
Navigating modern R&D projects is significantly easier when you have a project plan, your team is on the same page, and you have access to the right tools to streamline your work. For a higher-tech solution that wraps all these offerings into one, consider project management software to help your team deliver projects on time and under budget.
William leads the content team at ProjectManager , delivering the best project management content in the industry. With more than five years of experience at ProjectManager, William is tuned into the latest trends in project management, and how software can solve critical problems affecting productivity, collaboration and deliverability. William is based in Austin, and is a graduate of Univ. of Texas, Austin. He can be reached at [email protected]
Tell Us What You Think! Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Articles Read More >

R&D World announces 2024 R&D 100 Professional Award Winners
Ai-assisted gymnastics judging is here.

How charge density waves could pave the way to faster, more efficient electronic devices

OpenAI unveils SearchGPT test version; Tesla’s humanoid robot to debut in 2025
Search r&d world.
- R&D World Home
- Environment
- Life Science
- Material Science
- R&D Management
- 3D Printing
- A.I./Robotics
- Battery Technology
- Regulations/Standards
- Nanotechnology
- HPC/Supercomputing
- Informatics
- Semiconductors
- R&D Market Pulse
- Winner Archive
- R&D 100 Awards
- Digital Issues
- Global Funding Forecast
- R&D Index
Research project management support
Learn about project management services designed to support successful outcomes for principal investigators.
Greetings from the Project Management Office in the Research & Innovation Division. Our team is here to support Principal Investigators throughout the entire lifecycle of their research awards and grants. So, what is a project manager? Well, a project manager is someone who uses their skills and expertise in project management methodology to directly support the planning, tracking and execution of a project. Within the University of Nevada, Reno, this means becoming a member of the project team and supporting the PI by strategizing for success, drafting project management documentation and providing award-related administrative expertise.
The Project Management Office is designed to support research efforts from all across campus, any college, school or department, that would benefit from more organized, cohesive and streamlined project execution. Support will be tailored to each project’s unique needs, but can include strategic planning, meeting facilitation and moderation, liaising with the sponsor and subawardees, assistance with amendments, timeline, milestone and deliverable tracking and annual reporting support. A project manager is also happy to assist with specific aspects of proposal development, such as the incorporation of project management or risk mitigation plans.
During the execution of your award, your project manager will work seamlessly with the Sponsored Projects office and your departmental support to ensure compliance. The goal of the PMO is to help PIs achieve success on their projects by alleviating project management and administrative burdens and by steering the team through strategic conversations to ensure success. Your success is our success!
Want to learn more about how project management can impact your research? Visit the project management services webpage for resources and to request assistance .
About the author
Erica Hall has worked in program and project management for more than five years and is a certified Project Management Professional (PMP). Prior to joining the University of Nevada, Reno, Erica worked at the Nevada Department of Public Safety as a program manager and later at both Tesla and Sierra Nevada Corporation in operations support and project management roles.

By: Erica Hall Senior Project Manager, Research & Innovation
Unexpected Pack Pride
Journalism student Ashton Despain reflects on his decision to attend the University of Nevada, Reno

Trent at the Olympics
Journalism student Lexi Trent expands on her experience at the 2024 Paris Olympics

UPD-NC Officers Careers
Looking for inspiration, King, a recent graduate and intern with UPDNC, asked three individuals how they decided on a career in law enforcement

Daniel Jones TEDx Talk
Associate Professor of Management in the College of Business Daniel Jones reflects on his TEDx Reno talk

Editor's Picks

University of Nevada, Reno signs agreements with two universities in Italy

Reflecting on Steve Alford’s Olympic triumph: a gold medal journey
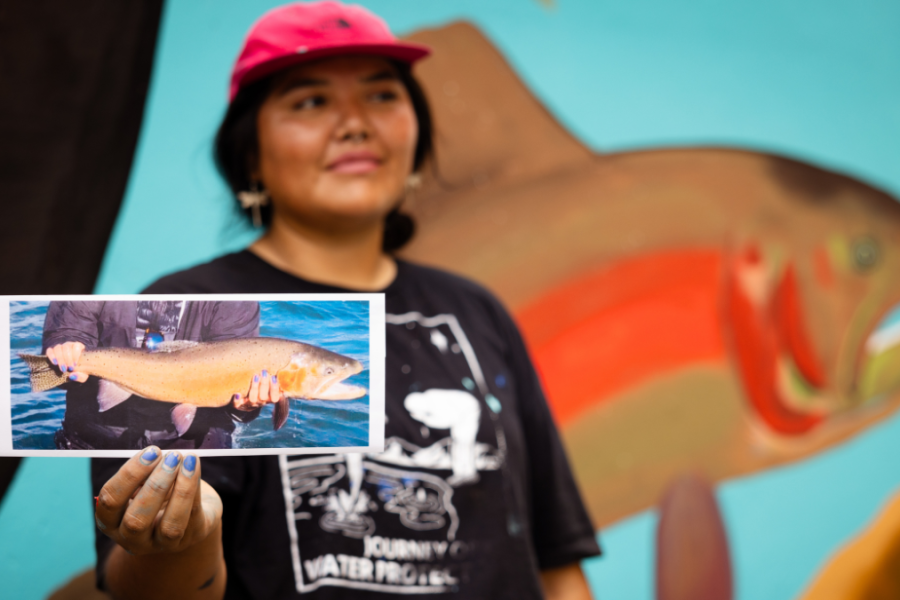

Representation matters

Faces of the Pack: Jennifer Pearson
Nevada Today
Research published in PNAS proposes a new model that predicts river tributary length and spacing
The work may improve scientists’ ability to route water, sediment, and nutrients through river networks

Lactation/quiet room opens in Thompson Building inside the suite of Gender, Race, and Identity
The newest addition provides a private space near the Quad on campus

Moving closer to “one protein, one drug”
Chemistry professor works on compound that could be used to treat diseases from cancer to hepatitis B

NSF CAREER Award recipient Mark Lescroart studies mechanisms of attention
$700,000 research project funded to explore neurological disorders and everyday tasks; ‘Perception depends on the goal’

UNR Med celebrates the arrival of the M.D. Class of 2028
71 future doctors honored in inspiring White Coat Ceremony

University of Nevada, Reno School of Music welcomes Maureen Yuen
Yuen, a violinist and researcher, joins the school’s faculty

Kickoff to Kindergarten fair returns to prepare young children for school
Extension hosts school readiness pre-k event with community partners

NSF CAREER Award recipient Li Ke incorporates data science into middle school science curricula
Li Ke is the first in education to receive this prestigious award in Northern Nevada

From Concept to Completion: The Role of Project Management in Engineering

In the dynamic field of engineering, project management plays a vital role in bringing ideas to life efficiently. It ensures smooth processes, optimal use of resources, and on-time project completion from conception to final product.
Understanding the role of project management in engineering is essential for engineering professionals aiming to succeed in today's competitive environment.
Understanding Project Management in Engineering
In engineering, project management is necessary to turn ideas into accomplishments while maintaining quality and safety. It helps ensure that projects are executed efficiently, on schedule, and within budget. Project management not only coordinates the detailed logistics of engineering projects but also aligns strategic goals with practical operations.
In engineering, project management principles are fundamental to structuring and executing complex initiatives. These principles help in defining project scope, allocating resources carefully, and managing risks proactively. Project management ensures that each project phase progresses smoothly with a focus on reaching set goals.
Key Components of Engineering Project Management
Several key components of engineering project management are essential for successful project execution. These components ensure that projects are delivered efficiently, on schedule, within budget, and with the highest standards of quality and safety.
Scope and resource planning ensures foresight and accuracy in meeting project demands.
Risk management helps to anticipate and handle potential challenges by creating strategies to maintain project timelines and expected outcomes.
Quality control helps to maintain excellent standards and assures that project outcomes meet or exceed expectations.
Coordination and communication with team members and stakeholders helps manage complexities and achieve shared project goals.
The Role of an Engineering Project Manager
The role of an engineering project manager is instrumental in ensuring the successful execution of complex engineering projects. They foster collaboration within the team, assign tasks proficiently, and resolve any project-related issues that arise. Key skills for effective engineering project management include leadership, problem-solving, risk management, and communication. These skills empower project managers to navigate challenges, optimize resource allocation, and maintain stakeholder satisfaction throughout the project.
Engineering Manager vs. Project Manager: What’s the Difference?
For those balancing work and family responsibilities, pursuing an online master's in engineering offers valuable flexibility. Designed to accommodate busy schedules, online programs feature asynchronous courses, allowing you to study at your own pace.
Application of new-found engineering knowledge in real-time
Although both roles require leadership and supervision, there are clear distinctions between an engineering manager and a project manager .
Engineering managers concentrate on strategic planning and growth within engineering departments, overseeing technical aspects and long-term goals.
Project managers are more hands-on in managing individual projects, emphasizing detailed planning, coordination, and timely completion. To effectively carry out their responsibilities, engineering managers must possess project management skills.
The Value of Project Management for Engineers
Engineers must understand the skills required for project management. This empowers them to efficiently handle complex projects by utilizing resources such as materials, time, and manpower.
Mastering project management improves communication, fostering better team collaboration and reducing misunderstandings. Additionally, it enables engineers to proactively identify and address potential risks early on. Excellent time management ensures projects stay on track and meet deadlines effectively.
Pathways to Becoming a Project Manager in Engineering
Becoming a project manager in engineering requires a mix of education and experience. With a background in engineering, aspiring project managers often pursue advanced degrees like a master's in engineering management or project management. These programs enhance technical skills and develop leadership abilities essential for managing engineering projects. Pursuing a master’s degree provides a deeper understanding of project planning, budgeting, and risk assessment.
Practical experience is also valuable, giving hands-on exposure to real project situations. Engineers aiming to be project managers benefit from roles involving project coordination, team leadership, and decision-making. This experience enhances problem-solving skills and improves communication abilities, both of which are important for effectively managing project teams and meeting stakeholder expectations.
Degrees in Engineering Management vs. Project Management
Engineering management or project management? While both degrees target future project managers, they vary in their focus and coursework. A master's in engineering management stresses combining technical skills with business knowledge, training graduates for leadership positions within engineering departments.
A master's in engineering management concentrates on project planning, implementation, and oversight across different industries. This provides graduates with adaptable skills suitable for project management roles outside engineering-specific environments.
Choosing between these options relies on career objectives and preferred specialization. Both degrees offer pathways to achieving fulfilling careers in project management.
Enhance Your Project Management Skills at Vanderbilt
Vanderbilt University School of Engineering offers a comprehensive online master’s in engineering management . The curriculum integrates theoretical knowledge with practical applications, giving you the tools needed to navigate complex engineering projects effectively.
Download our free guide to jumpstart your engineering leadership career and learn how Vanderbilt’s program will prepare you to excel in diverse engineering management roles.
Take the next step toward a rewarding career in engineering management today.

Subscribe to the Blog
← All Posts
Media Inquiries
615-322-6397 Email
Latest Stories
[annual symposium] project management in construction management, construction project engineer vs. project manager: differences & similarities, civil engineers need a construction management degree — here’s why, keep reading.

Explore Stories by Topic
- Construction Management
- Engineering Research
- Surgery and Intervention
- Engineering Online
- Computer Science
- Cyber-physical Systems
- Engineering Management
- Risk, Reliability and Resilience
- Engineering Careers
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Research and Development?
- Understanding R&D
- Types of R&D
- Pros and Cons
- Considerations
- R&D vs. Applied Research
- R&D Tax Credits
The Bottom Line
- Business Essentials
What Is Research and Development (R&D)?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/wk_headshot_aug_2018_02__william_kenton-5bfc261446e0fb005118afc9.jpg)
Investopedia / Ellen Lindner
Research and development (R&D) is the series of activities that companies undertake to innovate. R&D is often the first stage in the development process that results in market research product development, and product testing.
Key Takeaways
- Research and development represents the activities companies undertake to innovate and introduce new products and services or to improve their existing offerings.
- R&D allows a company to stay ahead of its competition by catering to new wants or needs in the market.
- Companies in different sectors and industries conduct R&D—pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, and technology companies generally spend the most.
- R&D is often a broad approach to exploratory advancement, while applied research is more geared towards researching a more narrow scope.
- The accounting for treatment for R&D costs can materially impact a company's income statement and balance sheet.
Understanding Research and Development (R&D)
The concept of research and development is widely linked to innovation both in the corporate and government sectors. R&D allows a company to stay ahead of its competition. Without an R&D program, a company may not survive on its own and may have to rely on other ways to innovate such as engaging in mergers and acquisitions (M&A) or partnerships. Through R&D, companies can design new products and improve their existing offerings.
R&D is distinct from most operational activities performed by a corporation. The research and/or development is typically not performed with the expectation of immediate profit. Instead, it is expected to contribute to the long-term profitability of a company. R&D may often allow companies to secure intellectual property, including patents , copyrights, and trademarks as discoveries are made and products created.
Companies that set up and employ departments dedicated entirely to R&D commit substantial capital to the effort. They must estimate the risk-adjusted return on their R&D expenditures, which inevitably involves risk of capital. That's because there is no immediate payoff, and the return on investment (ROI) is uncertain. As more money is invested in R&D, the level of capital risk increases. Other companies may choose to outsource their R&D for a variety of reasons including size and cost.
Companies across all sectors and industries undergo R&D activities. Corporations experience growth through these improvements and the development of new goods and services. Pharmaceuticals, semiconductors , and software/technology companies tend to spend the most on R&D. In Europe, R&D is known as research and technical or technological development.
Many small and mid-sized businesses may choose to outsource their R&D efforts because they don't have the right staff in-house to meet their needs.
Types of Research and Development (R&D)
There are several different types of R&D that exist in the corporate world and within government. The type used depends entirely on the entity undertaking it and the results can differ.
Basic Research
There are business incubators and accelerators, where corporations invest in startups and provide funding assistance and guidance to entrepreneurs in the hope that innovations will result that they can use to their benefit.
M&As and partnerships are also forms of R&D as companies join forces to take advantage of other companies' institutional knowledge and talent.
Applied Research
One R&D model is a department staffed primarily by engineers who develop new products —a task that typically involves extensive research. There is no specific goal or application in mind with this model. Instead, the research is done for the sake of research.
Development Research
This model involves a department composed of industrial scientists or researchers, all of who are tasked with applied research in technical, scientific, or industrial fields. This model facilitates the development of future products or the improvement of current products and/or operating procedures.
The largest companies may also be the ones that drive the most R&D spend. For example, Amazon has reported $1.147 billion of research and development value on its 2023 annual report.
Advantages and Disadvantages of R&D
There are several key benefits to research and development. It facilitates innovation, allowing companies to improve existing products and services or by letting them develop new ones to bring to the market.
Because R&D also is a key component of innovation, it requires a greater degree of skill from employees who take part. This allows companies to expand their talent pool, which often comes with special skill sets.
The advantages go beyond corporations. Consumers stand to benefit from R&D because it gives them better, high-quality products and services as well as a wider range of options. Corporations can, therefore, rely on consumers to remain loyal to their brands. It also helps drive productivity and economic growth.
Disadvantages
One of the major drawbacks to R&D is the cost. First, there is the financial expense as it requires a significant investment of cash upfront. This can include setting up a separate R&D department, hiring talent, and product and service testing, among others.
Innovation doesn't happen overnight so there is also a time factor to consider. This means that it takes a lot of time to bring products and services to market from conception to production to delivery.
Because it does take time to go from concept to product, companies stand the risk of being at the mercy of changing market trends . So what they thought may be a great seller at one time may reach the market too late and not fly off the shelves once it's ready.
Facilitates innovation
Improved or new products and services
Expands knowledge and talent pool
Increased consumer choice and brand loyalty
Economic driver
Financial investment
Shifting market trends
R&D Accounting
R&D may be beneficial to a company's bottom line, but it is considered an expense . After all, companies spend substantial amounts on research and trying to develop new products and services. As such, these expenses are often reported for accounting purposes on the income statement and do not carry long-term value.
There are certain situations where R&D costs are capitalized and reported on the balance sheet. Some examples include but are not limited to:
- Materials, fixed assets, or other assets have alternative future uses with an estimable value and useful life.
- Software that can be converted or applied elsewhere in the company to have a useful life beyond a specific single R&D project.
- Indirect costs or overhead expenses allocated between projects.
- R&D purchased from a third party that is accompanied by intangible value. That intangible asset may be recorded as a separate balance sheet asset.
R&D Considerations
Before taking on the task of research and development, it's important for companies and governments to consider some of the key factors associated with it. Some of the most notable considerations are:
- Objectives and Outcome: One of the most important factors to consider is the intended goals of the R&D project. Is it to innovate and fill a need for certain products that aren't being sold? Or is it to make improvements on existing ones? Whatever the reason, it's always important to note that there should be some flexibility as things can change over time.
- Timing: R&D requires a lot of time. This involves reviewing the market to see where there may be a lack of certain products and services or finding ways to improve on those that are already on the shelves.
- Cost: R&D costs a great deal of money, especially when it comes to the upfront costs. And there may be higher costs associated with the conception and production of new products rather than updating existing ones.
- Risks: As with any venture, R&D does come with risks. R&D doesn't come with any guarantees, no matter the time and money that goes into it. This means that companies and governments may sacrifice their ROI if the end product isn't successful.
Research and Development vs. Applied Research
Basic research is aimed at a fuller, more complete understanding of the fundamental aspects of a concept or phenomenon. This understanding is generally the first step in R&D. These activities provide a basis of information without directed applications toward products, policies, or operational processes .
Applied research entails the activities used to gain knowledge with a specific goal in mind. The activities may be to determine and develop new products, policies, or operational processes. While basic research is time-consuming, applied research is painstaking and more costly because of its detailed and complex nature.
R&D Tax Credits
The IRS offers a R&D tax credit to encourage innovation and significantly reduction their tax liability. The credit calls for specific types of spend such as product development, process improvement, and software creation.
Enacted under Section 41 of the Internal Revenue Code, this credit encourages innovation by providing a dollar-for-dollar reduction in tax obligations. The eligibility criteria, expanded by the Protecting Americans from Tax Hikes (PATH) Act of 2015, now encompass a broader spectrum of businesses. The credit tens to benefit small-to-midsize enterprises.
To claim R&D tax credits, businesses must document their qualifying expenses and complete IRS Form 6765 (Credit for Increasing Research Activities). The credit, typically ranging from 6% to 8% of annual qualifying expenses, offers businesses a direct offset against federal income tax liabilities. Additionally, businesses can claim up to $250,000 per year against their payroll taxes.
Example of Research and Development (R&D)
One of the more innovative companies of this millennium is Apple Inc. As part of its annual reporting, it has the following to say about its research and development spend:
In 2023, Apple reported having spent $29.915 billion. This is 8% of their annual total net sales. Note that Apple's R&D spend was reported to be higher than the company's selling, general and administrative costs (of $24.932 billion).
Note that the company doesn't go into length about what exactly the R&D spend is for. According to the notes, the company's year-over-year growth was "driven primarily by increases in headcount-related expenses". However, this does not explain the underlying basis carried from prior years (i.e. materials, patents, etc.).
Research and development refers to the systematic process of investigating, experimenting, and innovating to create new products, processes, or technologies. It encompasses activities such as scientific research, technological development, and experimentation conducted to achieve specific objectives to bring new items to market.
What Types of Activities Can Be Found in Research and Development?
Research and development activities focus on the innovation of new products or services in a company. Among the primary purposes of R&D activities is for a company to remain competitive as it produces products that advance and elevate its current product line. Since R&D typically operates on a longer-term horizon, its activities are not anticipated to generate immediate returns. However, in time, R&D projects may lead to patents, trademarks, or breakthrough discoveries with lasting benefits to the company.
Why Is Research and Development Important?
Given the rapid rate of technological advancement, R&D is important for companies to stay competitive. Specifically, R&D allows companies to create products that are difficult for their competitors to replicate. Meanwhile, R&D efforts can lead to improved productivity that helps increase margins, further creating an edge in outpacing competitors. From a broader perspective, R&D can allow a company to stay ahead of the curve, anticipating customer demands or trends.
There are many things companies can do in order to advance in their industries and the overall market. Research and development is just one way they can set themselves apart from their competition. It opens up the potential for innovation and increasing sales. However, it does come with some drawbacks—the most obvious being the financial cost and the time it takes to innovate.
Amazon. " 2023 Annual Report ."
Internal Revenue Service. " Research Credit ."
Internal Revenue Service. " About Form 6765, Credit for Increasing Research Activities ."
Apple. " 2023 Annual Report ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/research_pharma-5bfc322b46e0fb0051bf11a0.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy

- About Expand
- FAQs Expand
- Announcements Expand
- Training Materials Expand
- Documents Expand
- Live Charts Expand
- Contact Expand
- Live Data Dashboard Expand

The NOAA Research and Development (R&D) Database (NRDD) is a secure, web-based enterprise tool to house project management data for all R&D conducted by NOAA and its partnerships.
NOAA monitors its research and development portfolio through the NRDD, an online repository that serves as a single access point for information on research and development (R&D) projects conducted by NOAA and NOAA-funded external partners. To date, over 5,000 NOAA R&D project records are contained in the database. View the live project dashboard for the most recent information.
Benefits of NRDD
NRDD was designed to provide the following functions, information and analyses:
- Share information to improve communication, collaboration, coordination, planning, and integration across NOAA and decrease project redundancy;
- Identify, track, and facilitate R&D transition projects;
- Strengthen the linkages between strategy and execution across Line/Staff Offices;
- Provide corporate performance reporting (as mandated in the reports for Government Performance and Results Act (GPRA), Annual Performance Plan (APP), Annual Operating Plan (AOP), and other ad-hoc requests);
- Plan and track execution and evaluation of progress towards NOAA goals;
- Track and align project funds with source(s) of funding;
- Capture trends in R&D investments;
- Enable awareness for characterizing and balancing NOAA’s R&D portfolio.
Inappropriate uses of NRDD data
It is important to understand NRDD's intended purpose and limitations. Misuse or misinterpretation of NRDD data may have unintended consequences for NOAA.
NRDD data are limited by incomplete data entry and participation across NOAA. Line Office participation in the NRDD can vary and requirements for data fields have changed over time. See the NRDD Fields List for more information on which data fields are currently required and historical changes to mandatory fields. Please take these limitations (both level of Line Office participation and changes in field requirements over time) into account when using NRDD data.
NRDD does not represent an organization’s full portfolio. NRDD only contains research and development (R&D) projects. Therefore, any activities being funded or conducted by NOAA that do not fall under R&D will not be entered in NRDD: this includes maintenance of observing/monitoring systems (or other data-generating systems) that are in operations, administrative or other support activities, etc. Furthermore, the primary NOAA funder is responsible for NRDD project data entry. As such, if an organization is partnering on a project that has not been entered by the primary funder, this activity would not be accounted for within NRDD.
NRDD projects are not meant to represent a standard unit of measure. An R&D project, as defined by NRDD, must consist of a defined endpoint, objective, and final deliverable; a single active Readiness Level; designated NOAA monies or resources; and a defined timeline. However, there are no criteria related to the size or cost of a project. Therefore, comparing portfolios by the number of projects can be misleading because projects may vary widely in size, resources, and level of effort.
NRDD is not a budget tracking tool. While NRDD collects some resource information including total annual planned project cost, supporting internal and external grants, full time employee (FTE) hours, shiptime hours, and HPC hours, these data are estimates and not meant to track or justify budget allocations to NOAA organizations. Resource information within NRDD is intended to provide context for estimating the size of, and general investment in, a given R&D project.
NRDD History & Authority
In September 2016, the NOAA Science Council voted unanimously to implement a R&D database (then called the Project Data Management System), and former NOAA Chief Scientist Richard Spinrad signed a Memorandum requiring NOAA-wide participation. The database has since been endorsed by the Acting Chief Scientist and current Science Council Chair Craig McLean. NRDD is overseen by the NOAA Research and Development Enterprise Committee (RDEC) of the NOAA Science Council.
The need for a R&D tracking tool is mentioned in multiple NOAA Administrative Orders (NAOs), including NAO 216-105B Policy on Research and Development Transitions and its Handbook , as well as NAO 216-115B Research and Development in NOAA . NRDD is detailed in the Handbook for NAO 216-115B.
Please contact [email protected] with any questions.
Copyright 2023 by NOAA
NOAA Privacy Statement | Web Accessibility Statement | Disclaimer for External Links | NOAA | U.S. Department of Commerce | NOAA Research | USA.gov | FOIA
TechRepublic
Account information.

Share with Your Friends
What Is Project Management?
Your email has been sent

| Benefits of product management | Challenges of project management |
|---|---|
Project management helps teams track and organize their work within a project to achieve its goals. This process involves the application of various skills, tools and techniques, and the coordination of team members to meet project demands. Below, we explore the requirements of project management, its various types, and ways you can implement the process into your team’s workflow.
What is project management?
Project management is the process of planning, overseeing and executing a project to achieve its goals and objectives within the set budget and timeline. There are several roles and methods of project management, each designed to meet the specific project’s needs and improve efficiency. To make this process proceed more smoothly, project managers will often use tools or software to keep track of tasks and communicate with team members.
While project management has its fair share of challenges, the benefits are well worth it. Effective project management keeps a project on time and budget, with the flexibility to make adjustments and changes as needed.
Types of project management styles
There are several methodologies used in project management, each providing a different approach to cater to projects of varying scale and complexity.
The waterfall project management model takes a linear, strategic approach to projects. This straightforward style breaks a project down into sequential phases; each phase is only allowed to begin when the previous one has been entirely completed. This project management style is primarily used for well-defined projects that don’t require significant changes once they’ve started.
Agile project management allows teams to take an iterative, flexible approach to a project. This project management methodology encourages collaboration and feedback. Project managers typically use this style to break down projects into smaller, more manageable tasks. It’s great for projects that require adaptability as requirements change and evolve.
Scrum is a version of the agile project management methodology. This approach places a further emphasis on incremental work. In scrum project management, team members focus on sprints, which are short iterations wherein team members deliver small pieces of the project efficiently and quickly.
Kanban is another project management methodology under the agile framework. The kanban style emphasizes a visual system, where cards and boards are used to manage work and better illustrate the responsibilities of team members. This is a valuable methodology for projects that require a steady flow of deliverables.
The lean project management methodology focuses on efficiency. It operates on a cycle that is designed to raise productivity and reduce waste, which includes not only physical waste but also intangibles such as time and effort. This methodology is often combined with agile to improve workflows.
Often used in manufacturing, the Six Sigma project management style emphasizes continuous improvement. Through statistical models, project managers can reduce errors in work and improve efficiency.
Project management roles
To effectively execute a project across multiple teams or departments, there are various project management roles that must be filled. These roles range from the project managers themselves to team members.
Project sponsor
The project sponsor provides necessary resources, such as funding, personnel or materials for a project. This person may be an employee at your company or an outside client. The project sponsor is typically responsible for final approval on deliverables.
Stakeholders
Stakeholders are those who have a vested interest in the project. They typically give information or instructions and ensure the project meets its intended goals and expectations.
Project manager
The project manager works closely with sponsors and stakeholders. Their primary goal is to oversee the project’s development and ensure things are completed on time and within budget. Project managers determine which project management methodology should be used, oversee day-to-day activities, set milestones and identify resources needed for the project.
Team members
Team members work on individual tasks within a project. Their responsibilities vary based on the project methodology and its requirements. Team members typically report to either a team leader or the project manager and complete deliverables within a specific timeframe.
Project management phases
The process of managing projects follows a life cycle, which consists of different phases from the inception of the project up until its completion. These stages can be further divided based on needs or complexity.
Initiation is the first phase in project management. During this stage, the project team discusses the purpose of the project as well as general objectives and goals. It is during initiation that overall project feasibility may be debated.
The planning stage is when the project is defined in greater detail. The scope, specific objectives, deliverables, milestones and resources needed are identified during this phase. It’s also when the project manager determines which methodology will be used to achieve the desired outcome.
The project plan is put into action during the execution phase. Active collaboration is an integral part of this stage, as the team works toward moving the project to completion. Throughout this phase, the project manager tracks and monitors progress and identifies how to resolve issues.
Monitoring is the phase in which project managers track things at a high level — whether the project is progressing as planned, on time and within budget. Monitoring also requires managers to plan ahead and try to prevent any bottlenecks or disruptions as best as possible.
The final phase of project management involves handing over deliverables. These deliverables are then reviewed and approved by major stakeholders. Project closure serves as an opportunity for the team to wrap up loose ends and resolve issues that arise during the review process.
Project management software
To make project management easier and more efficient, many teams make use of project management software . At present, there is a wide variety of software solutions available. Some of these solutions are best suited for specific project management styles, while others can be customized to meet unique project needs.
Having the right software is critical to maintaining transparent communication and collaboration throughout the project life cycle.
Subscribe to the Project Management Insider Newsletter
Subscribe to Project Management Insider for best practices, reviews and resources. From project scheduling software to project planning apps, stay up to date with the latest in project management tools. Delivered Wednesdays
- The Best Simple Project Management Software
- The Best Project Management Certifications
- Telephone Interview Cheat Sheet: Project Manager
- Best Software for Businesses and End Users

Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.

Department Research Administrator
- Madison, Wisconsin
- COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING/ADMINISTRATION
- Sponsored Programs, Grants, and Contracts
- Partially Remote
- Staff-Full Time
- Opening at: Aug 19 2024 at 16:45 CDT
- Closing at: Sep 2 2024 at 23:55 CDT
Job Summary:
We are seeking a Department Research that provides proposal and award management support. Core duties of this role include proposal development, award setup, project management and closeout. Additionally, this position will work with Principal Investigators (PIs), Key Personnel and research staff to develop non-technical and budgetary proposal documents, ensuring accuracy and compliance with sponsor, state and university requirements, administrative management of awards, and closeout/reporting. A successful candidate in this role will be skilled in time management, attention to detail, and collaborative work, as well as have the ability to adapt to varied workflows and department culture. This position is part of the College of Engineering Research Services Team and reports directly to the Assistant Dean for Research Administration. The College of Engineering has 8 academic departments and over 30 centers that annually submit over 600 proposals resulting in approximately $103 million in awards and close to $120 million in research expenditures.
Responsibilities:
- 15% Executes research administration operational policies and procedures including financial, administrative, staffing, and compliance on behalf of a unit
- 15% Reviews and approves programmatic transactions spanning the life-cycle of sponsored projects to ensure compliance with institutional and/or sponsor policies and procedures
- 10% Serves as a key resource to leadership and staff in the unit as well as a liaison to partners and stakeholders
- 50% Executes activities related to proposal submission, contract negotiation, and/or award setup on behalf of a unit
- 5% Executes activities related to financial compliance, audit, or reporting on behalf of a unit
- 5% Provides training to faculty, staff, and/or administrators within the unit regarding policy, procedure, and/or execution of sponsored project administration
Institutional Statement on Diversity:
Diversity is a source of strength, creativity, and innovation for UW-Madison. We value the contributions of each person and respect the profound ways their identity, culture, background, experience, status, abilities, and opinion enrich the university community. We commit ourselves to the pursuit of excellence in teaching, research, outreach, and diversity as inextricably linked goals. The University of Wisconsin-Madison fulfills its public mission by creating a welcoming and inclusive community for people from every background - people who as students, faculty, and staff serve Wisconsin and the world. For more information on diversity and inclusion on campus, please visit: Diversity and Inclusion
Required Bachelor's Degree
Qualifications:
Required qualifications: - 1 year required in grant management/research administration at a university or research organization - Experience in cloud-based grant administration or financial computer systems. - Experience in Microsoft Suite or Google Suite Preferred qualifications: - 2 years of experience in grant management/research administration at a university or research organization - Experience applying fiscal and administrative rules, regulations and procedures for administering sponsored projects. - Demonstrated track record of working collaboratively with multiple groups/stakeholders. - Excellent organizational skills and attention to detail with a demonstrated ability to simultaneously execute multiple tasks while responding to multiple demands. - Demonstrated ability to work independently to solve problems. - Excellent oral and written communication skills.
Full Time: 100% This position may require some work to be performed in-person, onsite, at a designated campus work location. Some work may be performed remotely, at an offsite, non-campus work location. The anticipated schedule would be working 2 days on site with 3 days remote per week.
Appointment Type, Duration:
Ongoing/Renewable
Minimum $72,000 ANNUAL (12 months) Depending on Qualifications Employees in this position can expect to receive benefits such as generous vacation, holidays, and paid time off; competitive insurances and savings accounts; retirement benefits. Benefits information can be found at ( https://hr.wisc.edu/benefits/ )
How to Apply:
Please click on the "Apply Now" button to start the application process. Applicants will be asked to upload a resume and cover letter outlining relevant qualifications and experience as it pertains to the required and preferred qualifications outlined in this job posting.
Tamara Kuhn Martin [email protected] 608-265-0504 Relay Access (WTRS): 7-1-1. See RELAY_SERVICE for further information.
Official Title:
Multi-fun Res Admin Mgr(SC016)
Department(s):
A19-COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING/RESEARCH ADMIN
Employment Class:
Academic Staff-Renewable
Job Number:
The university of wisconsin-madison is an equal opportunity and affirmative action employer..
You will be redirected to the application to launch your career momentarily. Thank you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Applicant Tutorial
Disability Accommodations
Pay Transparency Policy Statement
Refer a Friend
You've sent this job to a friend!
Website feedback, questions or accessibility issues: [email protected] .
Learn more about accessibility at UW–Madison .
© 2016–2024 Board of Regents of the University of Wisconsin System • Privacy Statement
Before You Go..
Would you like to sign-up for job alerts.
Thank you for subscribing to UW–Madison job alerts!

IMAGES
COMMENTS
The application of basic project management principles, as outlined in the example of a tailored controls matrix (Table 1), to research and development activities provides a level of rigor governed by risk elements to sufficiently plan and manage the work to achieve the desired requirements and deliverables.
One of the most difficult and complex of organizational initiatives to manage is the research and development (R&D) project. This article examines an approach to managing R&D projects, an approach that focuses on resolving the challenges commonly encountered while working in this environment. In doing so, it describes the nature of the R&D environment and the problems faced by R&D project ...
Learn how to manage R&D projects effectively in a volatile and uncertain environment. Discover the key aspects of R&D project portfolio management, such as customer involvement, requirements management, resource management and communications management.
Learn how to manage your research projects with various tools and software. Find recommendations for grant writing, data management, risk assessment, communications and more.
Today's leading organizations recognize the importance of research and development (R&D) to maintain and grow market share. If companies want to survive into the future, they must accelerate their R&D-to-market cycles or find themselves behind the competition.Project Management for Research and Development: Guiding Innovation for Positive R.
Project management is also a key transferable skill that you can utilize within academia or the broader workforce. Lets review five stages of a typical project management life cycle and how you might apply these fundamentals to your own research projects. Initiation During the initiation stage, you determine the scope and feasibility of a project.
In the field of pharmaceutical research and development (R&D), project management has not yet been embraced with as much enthusiasm as in other fields. Part of the reason is due to the unique nature of pharmaceutical R&D, and part is because most project managers come up through the company ranks and lack formal project management training. This article discusses a number of issues facing ...
Here are ten best practices that will help you with your R&D project: Read the industry trade presses. There is an abundance of vendor and technology information in technology and business trade ...
Project Management for Research and Development. Managing projects in R & D is different—and uniquely challenging. Learn the principles, skills and tools essential to your success. In 60 minutes, you'll learn the three most important keys to successful project management, as well as how to more effectively work with people, set priorities ...
Title: Project Management for Research and Development. Author (s): Lory Mitchell Wingate. Release date: August 2014. Publisher (s): Auerbach Publications. ISBN: 9781466596306. Today's leading organizations recognize the importance of research and development (R&D) to maintain and grow market share. If companies want to survive into the ...
Jerzy KISIELNICKI. Warsaw University of Technology, Faculty of Management, Poland. e-mail: j.kisielnick [email protected]. Abstract: Implementation of R&D projects determines whether the organization ...
Today's leading organizations recognize the importance of research and development (R&D) to maintain and grow market share. If companies want to survive into the future, they must accelerate their R&D-to-market cycles or find themselves behind the competition.Project Management for Research and Development: Guiding Innovation for Positive R&D Outcomes explains how to apply proven project ...
In this session, you will explore project management principles further by calculating risks, managing a process, reviewing a project plan, and forecasting the execution and completion of a project while considering how these elements impact your work and the work of your team members. Session 4: Panel Discussion. November 10, 2022 | 12:00pm ET.
We break down the percentage of Research And Development Project Managers that have these skills listed on their resume here:. R, 15%. Helped win the company's largest R &D Federal contract at DHS (CanScan - Domestic Nuclear Detection Office). Project Management, 15%. Administered project management principles and procedures for various aspects of a six-phase new product development process.
In the dynamic field of research and development (R&D), managers play a pivotal role in steering innovative projects and fostering an environment where new ideas can flourish. As we progress into 2024, the skill set required for R&D Managers continues to evolve, blending a mix of scientific expertise, project management, and strategic leadership.
Abstract. Ultimately, technology progresses through individual steps which are the results of specific research and development (R&D) projects. In this chapter, we first describe what kinds of R&D projects exist, and how to plan and successfully execute them. We then consider how multiple projects together - as a set - constitute an R&D ...
In project management, challenges tend to grow as projects — especially those centered on research and development — extend over time. It becomes harder to manage deadlines and allocate ...
Research and development (R&D) teams understand the constant pressure to develop products that are simultaneously high-quality, innovative and impactful. ... William leads the content team at ProjectManager, delivering the best project management content in the industry. With more than five years of experience at ProjectManager, William is ...
Management of research and development projects in small technical services companies. Project Management Journal, 28 (1), 19-24. In today's economic climate, the small technical services company faces the dilemma of providing qualified and current technical personnel to support customer requirements while keeping prices down and still ...
Greetings from the Project Management Office in the Research & Innovation Division. Our team is here to support Principal Investigators throughout the entire lifecycle of their research awards and grants. So, what is a project manager? Well, a project manager is someone who uses their skills and ...
To effectively carry out their responsibilities, engineering managers must possess project management skills. The Value of Project Management for Engineers. Engineers must understand the skills required for project management. This empowers them to efficiently handle complex projects by utilizing resources such as materials, time, and manpower.
The first and foremost step towards the successful orchestration of R&D projects is recognizing change and uncertainty as an integral part of the management process. The research and development environment is volatile and dynamic, and without understanding this specificity, it will be rather challenging to manage it.
Research And Development - R&D: Research and development (R&D) refers to the investigative activities a business conducts to improve existing products and procedures or to lead to the development ...
Introduction. This paper offers a series of models designed to aid in the evaluation and control of an individual research and development project. The project under consideration is as-. sumed to involve costs incurred over a period [0, T] and a return earned at T (or dis-. counted to T) when the project is completed.
The NOAA Research and Development (R&D) Database (NRDD) is a secure, web-based enterprise tool to house project management data for all R&D conducted by NOAA and its partnerships. NOAA monitors its research and development portfolio through the NRDD, an online repository that serves as a single access point for information on research and ...
Research and development centers potentially are one of a university's strongest instrumentalities for obtaining grants and contracts, producing knowledge, generating new and useful products, and delivering research-based ... project management and evaluation; and especially fugitive materials that are germane to the center's work A center ...
Learn what project management is and how it helps plan, execute and complete projects efficiently. Discover key principles, methodologies and tools that ensure successful project outcomes.
Job Summary: We are seeking a Department Research that provides proposal and award management support. Core duties of this role include proposal development, award setup, project management and closeout. Additionally, this position will work with Principal Investigators (PIs), Key Personnel and research staff to develop non-technical and budgetary proposal documents, ensuring accuracy and ...
Project management is said to have lost its relevance for innovation initiatives because it overemphasizes planning and control over flexibility, leading to approaches that are poorly adapted to high-uncertainty endeavors (Lenfle & Loch, 2010). In response, the concepts of targeted flexibility (Lenfle & Loch, 2010) and adaptive project management (Shenhar & Dvir, 2007) have been proposed.
The Department of Surgery is seeking applicants for a Clinical Research Coordinator 3, Non-Licensed. A Clinical Research Coordinator 3, Non-Licensed (CRC-3, NL), holds a pivotal role in the clinical research field, performing a broad spectrum of duties with minimal supervision. This position demands an advanced understanding of clinical research procedures, Good Clinical Practices (GCP), and ...