- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Geography & Travel
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts

- Introduction

Historical motives
Philosophical and social perspectives.

mixed economy
mixed economy , in economics , a market system of resource allocation, commerce, and trade in which free markets coexist with government intervention. A mixed economy may emerge when a government intervenes to disrupt free markets by introducing state-owned enterprises (such as public health or education systems), regulations, subsidies , tariffs , and tax policies. Alternatively, a mixed economy can emerge when a socialist government makes exceptions to the rule of state ownership to capture economic benefits from private ownership and free market incentives. A combination of free market principles of private contracting and socialist principles of state ownership or planning is common to all mixed economies.
In addition to taking a variety of forms, mixed economies have come about from a variety of motives and historical causes. The British Corn Laws of the early 1800s, for example, were government interventions in the free market to protect native agricultural interests by limiting imports. The laws encouraged foreign protectionist responses and resulted in higher food and labour costs at home, which in turn led to an invigorated laissez-faire and free trade movement. However, at roughly the same time, abuses of factory workers led to government intervention to reform labour conditions for women and children.
In developed Western economies between the late 1800s and early 1900s, most political economists and governments believed that social prosperity progressed best in economic systems composed of free markets, in which social and monetary order was protected by the actions of governmental and banking institutions. This belief was profoundly shaken, however, by the system’s twin catastrophic failures that came to be known as the Great Depression (1929–39)—failing first to prevent the global economic collapse and then failing to recover communities from the horrendous human tragedies of unemployment and poverty wrought by the collapse. Between 1933 and 1939 the New Deal , a series of interventionist legislation and government programs in the United States , was championed by Pres. Franklin D. Roosevelt to head off social unrest caused by widespread unemployment during the Great Depression. In the mid-20th century many people agreed that the Great Depression arose from fundamental flaws in the free market theory of equilibrating supply and demand and that this meant that the free market alone would be incapable of recovering from another global economic downturn.
In developed Western economies, the historical development of the mixed economy is the evolutionary change of the free market concept as it adapted to avoid the risks of widespread social unrest and potential revolutionary socialist or Marxist change. Social democratic programs that arose in continental Europe in the 20th century created coalitions of business interests with major social groups to improve social welfare without jettisoning private property and the market economy. This mixed economic approach included economic planning , high tariffs, guarantees of group rights, and social welfare programs .
Mixed economies also arose in many countries that formerly had centrally planned and socialist economies. The mixed economies in modern China and Russia, for example, evolved from communist systems that were too inefficient to compete in the modern global economy. The social experience of the Chinese and Russian people during that process was a profound testament to the personal difficulties and turmoil that people endure when a country makes a transition to a mixed economy.
As the historical examples suggest, mixed economies have public, private, legislative, judicial, and regulatory components. There is not a single ideal, standard, or typical set of economic features, and the mix may vary from country to country. Components in the mix may include government subsidies, fees, taxes, set-aside programs and regulations, state-owned enterprises, mandatory social security , or national health programs.
Many economists and political philosophers have argued in favour of government action to enforce the ordinary rules of law in economic matters. For example, Scottish social philosopher and political economist Adam Smith , and later Austrian-born British economist Friedrich A. Hayek , noted the important role of government in assisting the functioning of markets by preventing violence and fraud , protecting property and public safety, enforcing contracts, and providing public infrastructure and utilities that would otherwise be unprofitable. In a mixed economy, however, there is a presumption that government must go beyond this limited role to improve distributive justice in society. Smith wrote that such intervention violated the ethical principle that indicates that economic efficiency is the best long-term path to social progress. Hayek also objected to such government intervention because he believed it to be economically inefficient, though even more important in his view was the inevitable tendency for the mixed economy to be politically abusive of individual liberty .
Despite those philosophical and moral objections, almost all modern economic systems in the world today are mixed economies. While the globalization of the world economy limits government intervention in free trade, governments still retain mechanisms for social welfare exceptions to the free market rule. At times, politicians have attempted to invoke such exceptions for reasons of parochial interest or political expediency.
Public policy-making in mixed economies frequently must balance the concern for individual liberty with the need for a fair, equitable, and just society. Balancing those concerns with integrity and procedural justice requires the participation of diverse social segments as stakeholders in an ongoing and dynamic search for a fair and appropriate economic system . For that reason, the success of the mixed economy depends on the integrity of governmental and social support for ethical principles of compassion, empathy, and respect for individual and minority rights. Without such support, the mixed economy can turn into a system of coercive government manipulated by powerful stakeholders.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- US & World Economies
- Economic Theory
What Is a Mixed Economy?
Mixed Economies Explained
Definition and Examples of Mixed Economies
How mixed economies work, advantages of a mixed economy, disadvantages of a mixed economy.
The Balance / Adriana Sanchez
A mixed economy is a system that combines characteristics of market, command, and traditional economies. It benefits from the advantages of all three while also experiencing some of the disadvantages.
A mixed economy combines the advantages and disadvantages of three different types of economies: market, command, and traditional economies. It's the most flexible system.
The United States Constitution guided America towards a mixed economy. The Fifth Amendment protects ownership of private property. It also limits government interference in business operations. That promotes the innovation that's a hallmark of a market economy.
At the same time, the Constitution encourages the government to promote general welfare. That creates the ability to use aspects of a command economy if it's for the overall good of the people.
The First Amendment protects the rights of groups to practice their religious beliefs. That allows communities, like the Amish in Pennsylvania, to retain their traditional economies.
Most of the world's major economies are now mixed economies.
Globalization makes it difficult for command or traditional economies to avoid becoming a mixed economy. One reason is that most countries' leaders realize that their people are best served through international trade.
According to the theory of comparative advantage , a country prospers when it exports what it does best and imports what another country does best. That's why many countries import oil from Saudi Arabia, clothing from China, and tequila from Mexico.
Another reason is that the free market is the basis for the global economy. No single government controls it. World organizations have implemented some regulations and agreements, but there is no world government with the power to create a global command economy.
To understand how mixed economies work, it's important to first understand how each of the three types of economies it combines—market, command, and traditional economies—works.
Characteristics of Market Economies
A market economy has six defining characteristics. The U.S. has all six characteristics of a market economy.
- The law protects ownership of private property.
- Everyone is free to live, work, produce, buy and sell whatever they choose (as long as it's legal).
- Self-interest drives the buying and selling of goods and services, including employment. Sellers want the highest price, and buyers want the best value for their money.
- The law protects competition.
- Prices are allowed to float along with supply and demand.
- The primary role of government is to make sure that everyone has free access to a free market. Congress passes regulations to make sure no one is manipulating the market. The First Amendment of the U.S. Constitution protects the free press. That ensures equal access to information for everyone.
Characteristics of Command Economies
Many aspects of the U.S. economy follow the characteristics of a command economy .
- There is an annual federal budget that outlines the government's priorities and takes the place of a central plan.
- Congress guides the allocation of resources. Taxes discourage some activities while subsidies encourage others.
- Government spending follows the country's priorities. For example, U.S. military spending increased after the 9/11 attacks.
- The government owns a monopoly in important national industries. These include NASA , the interstate highway system, and defense.
- The federal government uses regulations to support economic priorities, such as agriculture.
Characteristics of Traditional Economies
The U.S. is moving further away from a traditional economy , but tradition still guides many economic policies.
A traditional economy relies on agriculture, hunting, and fishing. American traditions support the family farm. That has led to millions in agricultural subsidies. This is despite the predominance of a few global agribusinesses.
Laws and treaties also protect the fishing industry. Hunting is no longer needed as a primary source of food for most Americans, but tradition still supports it. Laws and permits protect the right to hunt.
Characteristics of Mixed Economies
A mixed economy has three of the following characteristics of a market economy. First, it protects private property. Second, it allows the free market and the laws of supply and demand to determine prices. Third, it is driven by the motivation of the self-interest of individuals.
Most mixed economies have some characteristics of a command economy in strategic areas. It allows the federal government to safeguard its people and its market. The government has a large role in the military , international trade, and national transportation.
The government’s role in other areas depends on the priorities of the citizens. In some, the government creates a central plan that guides the economy. Other mixed economies allow the government to own key industries. These include aerospace, energy production, and even banking.
The government may also manage health care, welfare, and retirement programs.
Most mixed economies retain characteristics of a traditional economy, but those traditions don't guide how the economy functions. The traditions are so ingrained that the people aren’t even aware of them. For example, they still fund royal families. Others invest in hunting and fishing.
A mixed economy has the advantages of a market economy. First, it distributes goods and services to where they are most needed. It allows prices to measure supply and demand.
Second, it rewards the most efficient producers with the highest profit. That means customers get the best value for their dollar. Third, it encourages innovation to meet customer needs more creatively, cheaply, or efficiently.
Fourth, it automatically allocates capital to the most innovative and efficient producers. They, in turn, can invest the capital in more businesses like them.
A mixed economy also minimizes the disadvantages of a market economy. A market economy could neglect areas like defense, technology, and aerospace. A larger governmental role allows fast mobilization to these priority areas.
The expanded government role also makes sure less competitive members receive care. That overcomes one of the disadvantages of a pure market economy which only rewards those who are most competitive or innovative. Those who can't compete remain at risk.
A mixed economy can also take on all the disadvantages of the other types of economies. It just depends on which characteristics the mixed economy emphasizes.
For example, if the market has too much freedom, it can leave the less competitive members of society without any government support.
Central planning of government industries also creates problems. The defense industry could become a government-subsidized monopoly or oligarchy system. That could increase the country's debt, slowing down economic growth in the long run.
Successful businesses can lobby the government for more subsidies and tax breaks. The government could protect the free market so much that it doesn’t regulate enough. For example, businesses that were too big to fail could be bailed out by the government if they started going bankrupt.
Key Takeaways
- A mixed economy combines the advantages and disadvantages of three different types of economies: market, command, and traditional economies.
- To understand how a mixed economy works, it's important to first understand each of the three types of economies it combines.
- Most countries have a mixed economy these days as a result of globalization.
National Archives. " The Bill of Rights: A Transcription ,"
National Archives. " The Constitution of the United States: A Transcription ,"
Econlib. “ Comparative Advantage ,”
Paul A. Samuelson. “ Economics ,” Page 11.
Navajocode. “ 7 Predominant Advantages and Disadvantages of a Traditional Economy .”
Paul A. Samuelson. “ Economics ,” Page 30.
Paul A. Samuelson. “ Economics ,” Page 691.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/MenatWork-6a1203608f1649e0a2fc742e087a066e.jpeg)
Mixed Economic System
An economic system that combines the elements of both a market economy and a planned economy
What is a Mixed Economic System?
The mixed economic system is defined as an economic system that combines the elements of a market economy and the elements of a planned economy. It is a synthesis of socialism and capitalism , which contains both private enterprises and public enterprises. Most modern economies implement a mixed economic system.
A mixed economic system brings the advantages of free markets and also government intervention. However, there are also concerns about the sustainability and efficiency of a mixed economic system.
- A mixed economic system synthesizes the elements of a market economy and the elements of a command economy.
- In a mixed economic system, free markets co-exist with government intervention, and private enterprises co-exist with public enterprises.
- The advantages of a mixed economy include efficient production and allocation of resources, as well as improvement of social welfare.
How Does the Mixed Economic System Work
A mixed economic system takes on both the characteristics of a market economy and a planned economy. In the market economy, private enterprises are free to set up businesses and make profits. The market ( supply and demand ) determines the prices of goods and services, as well as the allocation of resources.
In a command economy, on the other side, the government regulates the market or owns the key industries. Production and sales of goods are determined by the government. Cuba and North Korea are some of the few countries with a command economy.
In a mixed economic system, the private sector and public sector co-exist. There is a certain level of economic freedom so that the private sector can decide the use of capital and seek profits. It simultaneously allows the government to intervene in some economic activities and industries. Through providing public goods and collecting taxes, the government can create more social welfare.
The United States follows a mixed economic system. Most of the industries in the U.S. are dominated by private enterprises with a certain level of government intervention, such as agricultural subsidies and financial regulations.
Some essential industries, such as national defense, public transportation, and package delivery, are partially publicly owned. The mixed economic system is the most common and practical system in modern society. A pure command economy or market economy only exists theoretically.
Benefits of a Mixed Economic System
Combining the features of a market economy and a command economy, a mixed economic system carries advantages from both sides
1. Efficient allocation of resources
Resources are allocated efficiently to where they are needed the most in the private sector. Hence, customers’ needs can be better met.
2. Incentives for innovation and production efficiency
In a free market with competition, the enterprises that can produce more efficiently are rewarded with higher profits. Companies are thus motivated to allocate capital to achieve innovation and efficiency of production. Customers can receive the best value for what they paid for.
3. Government support
The public sector in a mixed economy alleviates the disadvantages of a free market. Private companies might neglect some industries that are essential or bring social welfare because of their low profitability. In a mixed economy, government intervention can support these key industries, such as education, defense, and aerospace, through subsidies or ownership.
The government also takes care of the less competitive companies and disadvantaged individuals. For example, tax is an effective tool to reduce inequality by redistributing incomes. The government can also implement health care, retirement, and other programs to improve the welfare of the general society.
Drawbacks of a Mixed Economic System
It is difficult to determine what elements of free markets and government intervention a mixed economic system should contain. It varies among different societies at different periods without a fixed standard.
1. Lack of government support
If the economy is given too much freedom, disadvantaged groups will not receive sufficient support from the government. If the economy sees excessive government intervention, enterprises will be disincentivized to produce efficiently. It is crucial for a mixed economy to find a balance.
2. Undue influence from private enterprises
As private enterprises and government intervention are combined in the same system, large corporations may seek to lobby the government. They may influence legislation or activities to benefit themselves.
Government intervention also leads to moral hazards . Private enterprises, especially the large ones, might take more risks since they know they are too big to fail. The government will bail them out if they fall into economic crises.
Criticisms of the Mixed Economic System
There are many criticisms of mixed economic systems. The Austrian school of economics questions the sustainability of a mixed economy. It states that any government intervention will lead to unintended consequences that require further intervention.
For example, price controls can cause shortages in supply, and the government needs to take extra actions to stimulate production. Therefore, a mixed economy is unstable and tends toward socialism.
Another criticism is from the Public Choice economists. They suggest that the interaction of the markets, government policymakers, and economic interest groups will drive the policy away from the public interest. The interested groups will take away some resources from productive activities and use them to influence economic policy for their own benefits.
Additional Resources
Thank you for reading CFI’s guide to Mixed Economic System. To keep advancing your career, the additional CFI resources below will be useful:
- Laissez-faire
- Monetarist Theory
- Neoclassical Economics
- Socialism vs. Capitalism
- See all economics resources
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in

What Is a Mixed Economy?

Written by True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
Reviewed by subject matter experts.
Updated on June 08, 2023
Are You Retirement Ready?
Table of contents.
A mixed economy is one that contains aspects of market capitalism (a free-market system), socialism (government control over the means of production, including state ownership of all or almost all property), and a combination of the two.
The most common form in which this takes place is allowing private citizens to own some, but not all, forms of property. Most economies in the world today are considered to be 'mixed'.
It can be said that each country's economy is unique with its own different combinations, however, countries with strong market economies tend to have high levels of personal freedom while socialist states focus on equality within society.
Countries often try to find a balance between these two systems with varying degrees of success depending on how they choose to implement them.
Mixed Economy vs. Free Market Capitalism
The most significant difference between a mixed economy and free market capitalism is that the government plays a role in a mixed economy.
In a pure free market capitalist system, the government does not interfere in the workings of the market, but in a mixed economy, the government intervenes to ensure that some essentials are available to everyone, such as healthcare, education, and public transportation.
Another key difference is that in a mixed economy, private enterprise is allowed to flourish, while under pure capitalism, it would be banned.
Mixed economies also have higher levels of social welfare spending which provide benefits to citizens, whereas capitalist systems only offer limited social welfare programs or none at all.
Pros of a Mixed Economy
There are pros to mixed economies just as there are for any other type of economy.
The benefits of a mixed economy include:
Economic Stability
Firstly, it leads to more economic stability as there are multiple sources of revenue and fewer points of failure.
It encourages innovation and creativity as businesses compete with each other to become more productive and efficient.
Reduces Social Inequality
It helps to reduce social inequality as citizens have access to a variety of social services provided by the government.
Increased Efficiency
It leads to increased efficiency as different sectors of the economy are better able to adapt to changing circumstances.
Encourages Private Enterprise and Entrepreneurship
A mixed economy allows for private enterprise and entrepreneurship to flourish, as citizens are able to start their own businesses and compete in a free market.
Cons of a Mixed Economy
There are also cons to mixed economies, which include:
Lack of Social Mobility
One issue is that there can be a lack of social mobility as those who are born into wealthy families have an advantage over those who are not.
Inefficient Government
Another issue is that the government can often be inefficient and corrupt, with money being wasted on unnecessary projects. Social unrest may occur when the wealth gap between different social classes becomes too large.
Abuse of Power
There is also the risk that those with power or influence will abuse it, which can lead to corruption within government institutions.
Corruption and Cronyism
When there is a mixed economy, corruption and cronyism can be more difficult to regulate as the government's policies may overlap with each other.
Favoring Special Interests
Lastly, it can also favor special interest groups who have close ties with members of the government.
Living in a Mixed Economy Country
Mixed economies vary from country to country, so it can be difficult to make generalizations. However, there are some things you can look out for.
Countries with mixed economies usually have a higher level of economic freedom than those with socialist economies, and private enterprise is encouraged.
There tends to be a higher level of regulation in mixed economies than in pure capitalist or socialist systems, and the government plays a more active role in the economy. In most cases, there is a mix of public and private ownership of property and resources.
Mixed Economies Around the World
It is difficult to give exact figures for the number of countries that have mixed economies as there are so many different types and degrees of the mixture.
Examples of Countries With Mixed Economies
Although there are not very many pure socialist or capitalist countries left in the world, you can still find examples of both such as North Korea (socialist) and Luxembourg (capitalist). However, here is a list of some countries with mixed economies:
Brazil is considered to be a 'developing country' by economists but it has always had a more market-based approach than most other developing nations. It has a high level of economic freedom and a mixed economy with a large state sector.
It also has the largest foreign reserves in the developing world, which is usually seen as a sign of economic security.
The Chinese government controls large sectors of its economy including major industries such as steel production and energy generation. However, it also has a very strong private sector with low regulation compared to other socialist countries.
There is often much debate about whether or not China can be considered a truly communist nation given that capitalism plays such an important role in the country's economy today.
As one of the most influential economies in Europe, Germany has transformed over time from having a strong socialist sector to more of a mixed economy with both public and private ownership.
The Indian economy was originally based on socialism when it became independent back in 1947. However, since 1991 when reforms were implemented by Prime Minister Narasimha Rao there has been much greater economic freedom in the country, resulting in increased economic growth and sustainable development.
Today India is considered to have a mixed economy that includes a mixture of private enterprise and state-owned services.
United Kingdom
The UK has also been transitioning from a socialist to a mixed economy in recent decades.
Key industries such as energy production and railways are now owned and operated by the private sector, but the government continues to play an important role in other areas such as healthcare and education.
United States
Although often considered to be a capitalist nation, the United States actually has a mixed economy with both public and private ownership.
The largest sector of the economy is made up of private businesses, but there are also many large public companies such as Walmart, General Electric, and Coca Cola.
Additionally, social programs such as Medicare and Medicaid are provided by the government which helps to ensure that all citizens have access to basic healthcare.
A mixed economy is one where there is a mix of public and private ownership of property and resources.
They can be found all over the world in both developed and developing countries.
There are pros and cons to living in a mixed economy, but in general, it can be said that they offer more stability and security than either pure capitalist or socialist economies.
Mixed Economy FAQs
What is a mixed economy, what are the pros and cons of living in a mixed economy, how do i know if i live in a mixed economy.
It is difficult to say definitively whether or not you live in a mixed economy as there are so many different types and degrees of the mixture. However, if you have a mixture of public and private ownership in your country, then it is likely that you reside in a mixed economy.
Why are there so many different types of economies in the world?
There are many different reasons why there are so many different types of economies in the world. Some of the most common reasons include geography, history, culture, and political system.
What are some examples of countries with mixed economies?
China, Germany, India, the United Kingdom, and the United States are all examples of countries with mixed economies.
About the Author
True Tamplin, BSc, CEPF®
True Tamplin is a published author, public speaker, CEO of UpDigital, and founder of Finance Strategists.
True is a Certified Educator in Personal Finance (CEPF®), author of The Handy Financial Ratios Guide , a member of the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing, contributes to his financial education site, Finance Strategists, and has spoken to various financial communities such as the CFA Institute, as well as university students like his Alma mater, Biola University , where he received a bachelor of science in business and data analytics.
To learn more about True, visit his personal website or view his author profiles on Amazon , Nasdaq and Forbes .
Related Topics
- Command Economy
- Cost-Push Inflation
- Demand-Pull Inflation
- Economic Outlook
- Free Market Economy
- GDP Per Capita
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Gross National Product (GNP)
- Hyperinflation
- Inferior Goods
- Knowledge Economy
- Liquidity Constraints
- Macro Environment
- Mixed Economy
- Monopolistic Competition
- Operation Twist
- Perfect Competition
- Producer Price Index (PPI)
- Purchase Annual Percentage Rate (APR)
- Real Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- Trade Deficit
- What Does the 80/20 Rule Mean?
- Wholesale Price Index (WPI)
Ask a Financial Professional Any Question
Discover wealth management solutions near you, our recommended advisors.

Claudia Valladares
WHY WE RECOMMEND:
Fee-Only Financial Advisor Show explanation
Bilingual in english / spanish, founder of wisedollarmom.com, quoted in gobanking rates, yahoo finance & forbes.
IDEAL CLIENTS:
Retirees, Immigrants & Sudden Wealth / Inheritance
Retirement Planning, Personal finance, Goals-based Planning & Community Impact

Taylor Kovar, CFP®
Certified financial planner™, 3x investopedia top 100 advisor, author of the 5 money personalities & keynote speaker.
Business Owners, Executives & Medical Professionals
Strategic Planning, Alternative Investments, Stock Options & Wealth Preservation
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. If you continue to use this site we will assume that you are happy with it.
Fact Checked
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
Our team of reviewers are established professionals with decades of experience in areas of personal finance and hold many advanced degrees and certifications.
They regularly contribute to top tier financial publications, such as The Wall Street Journal, U.S. News & World Report, Reuters, Morning Star, Yahoo Finance, Bloomberg, Marketwatch, Investopedia, TheStreet.com, Motley Fool, CNBC, and many others.
This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year.
We follow strict ethical journalism practices, which includes presenting unbiased information and citing reliable, attributed resources.
Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.
Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications. Our work has been directly cited by organizations including Entrepreneur, Business Insider, Investopedia, Forbes, CNBC, and many others.
Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs.
How It Works
Step 1 of 3, ask any financial question.
Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Your information is kept secure and not shared unless you specify.

Step 2 of 3
Our team will connect you with a vetted, trusted professional.
Someone on our team will connect you with a financial professional in our network holding the correct designation and expertise.

Step 3 of 3
Get your questions answered and book a free call if necessary.
A financial professional will offer guidance based on the information provided and offer a no-obligation call to better understand your situation.

Where Should We Send Your Answer?

Just a Few More Details
We need just a bit more info from you to direct your question to the right person.
Tell Us More About Yourself
Is there any other context you can provide.
Pro tip: Professionals are more likely to answer questions when background and context is given. The more details you provide, the faster and more thorough reply you'll receive.
What is your age?
Are you married, do you own your home.
- Owned outright
- Owned with a mortgage
Do you have any children under 18?
- Yes, 3 or more
What is the approximate value of your cash savings and other investments?
- $50k - $250k
- $250k - $1m
Pro tip: A portfolio often becomes more complicated when it has more investable assets. Please answer this question to help us connect you with the right professional.
Would you prefer to work with a financial professional remotely or in-person?
- I would prefer remote (video call, etc.)
- I would prefer in-person
- I don't mind, either are fine
What's your zip code?
- I'm not in the U.S.
Submit to get your question answered.
A financial professional will be in touch to help you shortly.

Part 1: Tell Us More About Yourself
Do you own a business, which activity is most important to you during retirement.
- Giving back / charity
- Spending time with family and friends
- Pursuing hobbies
Part 2: Your Current Nest Egg
Part 3: confidence going into retirement, how comfortable are you with investing.
- Very comfortable
- Somewhat comfortable
- Not comfortable at all
How confident are you in your long term financial plan?
- Very confident
- Somewhat confident
- Not confident / I don't have a plan
What is your risk tolerance?
How much are you saving for retirement each month.
- None currently
- Minimal: $50 - $200
- Steady Saver: $200 - $500
- Serious Planner: $500 - $1,000
- Aggressive Saver: $1,000+
How much will you need each month during retirement?
- Bare Necessities: $1,500 - $2,500
- Moderate Comfort: $2,500 - $3,500
- Comfortable Lifestyle: $3,500 - $5,500
- Affluent Living: $5,500 - $8,000
- Luxury Lifestyle: $8,000+
Part 4: Getting Your Retirement Ready
What is your current financial priority.
- Getting out of debt
- Growing my wealth
- Protecting my wealth
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Which of these is most important for your financial advisor to have.
- Tax planning expertise
- Investment management expertise
- Estate planning expertise
- None of the above
Where should we send your answer?
Submit to get your retirement-readiness report., get in touch with, great the financial professional will get back to you soon., where should we send the downloadable file, great hit “submit” and an advisor will send you the guide shortly., create a free account and ask any financial question, learn at your own pace with our free courses.
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals.

Get Started
To ensure one vote per person, please include the following info, great thank you for voting., get in touch with an advisor, submit your info below and someone will get back to you shortly..

- Books, Journals, Papers
- Guides & How To’s
- Life Around The World
- Research Methods
- Functionalism
- Postmodernism
- Social Constructionism
- Structuralism
- Symbolic Interactionism
- Sociology Theorists
- General Sociology
- Social Policy
- Social Work
- Sociology of Crime & Deviance
- Sociology of Art
- Sociology of Dance
- Sociology of Food
- Sociology of Sport
- Sociology of Disability
- Sociology of Economics
- Sociology of Education
- Sociology of Emotion
- Sociology of Family & Relationships
- Sociology of Gender
- Sociology of Health
- Sociology of Identity
- Sociology of Ideology
- Sociology of Inequalities
- Sociology of Knowledge
- Sociology of Language
- Sociology of Law
- Sociology of Anime
- Sociology of Film
- Sociology of Gaming
- Sociology of Literature
- Sociology of Music
- Sociology of TV
- Sociology of Migration
- Sociology of Nature & Environment
- Sociology of Politics
- Sociology of Power
- Sociology of Race & Ethnicity
- Sociology of Religion
- Sociology of Sexuality
- Sociology of Social Movements
- Sociology of Technology
- Sociology of the Life Course
- Sociology of Violence & Conflict
- Sociology of Work
- Sociology of Travel & Tourism
- Urban Sociology
- Privacy Policy
- Terms & Conditions
What is a Mixed Economy?

Table of Contents
Defining features of a mixed economy, theoretical foundations.
- Historical Context
- Sociological Implications
- Challenges and Criticisms
- Essay Suggestions
- Research Suggestions
- Further Reading
A mixed economy represents a hybrid economic system combining elements of both capitalism and socialism. This framework incorporates private and public enterprises, seeking to balance the benefits of market freedom and government intervention. From a sociological perspective, the mixed economy can be analyzed through the lenses of economic sociology, social stratification, political sociology, and the sociology of organizations. This essay outlines the defining features of a mixed economy, its theoretical foundations, historical context, and its implications for society.
A mixed economy blends private and public ownership of property and businesses. It allows the market to operate freely within certain sectors while the government intervenes in others to correct market failures, redistribute resources, and provide public goods. Key characteristics include:
- Coexistence of Sectors : In a mixed economy, both private and public sectors exist and function simultaneously. Private businesses operate for profit , driven by market forces, while public enterprises and services are managed by the state to meet collective needs.
- Regulation and Deregulation : The government plays a regulatory role to ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and prevent monopolies. Conversely, deregulation in specific sectors can promote efficiency and innovation.
- Social Welfare Programs : A mixed economy often includes extensive social welfare programs, such as healthcare, education , and social security, funded by taxes and designed to reduce inequality and provide a safety net for the vulnerable.
- Market and Planning : Economic planning by the government complements market mechanisms. Planning is used to address long-term social and economic goals, such as infrastructure development, environmental sustainability, and economic stability.
The mixed economy concept draws from various economic and sociological theories:
Membership Required
You must be a member to access this content.
View Membership Levels
Mr Edwards has a PhD in sociology and 10 years of experience in sociological knowledge
Related Articles

Laissez-Faire Economics: An Outline and Explanation
Laissez-faire economics is a concept rooted in classical liberalism, advocating minimal governmental intervention in economic affairs. The term, derived from...

Jean Piaget’s Theory of Cognitive Development: The Concrete Operational Stage
The concept of the "Concrete Operational Stage" originates from Jean Piaget's theory of cognitive development, a comprehensive framework that explains...

Effort Bargaining in Sociology: An Analytical Overview

Egocentrism in Sociology

Mick Lynch: An analysis
Get the latest sociology.
Would you be interested in enrolling in courses from Easy Sociology?
Recommended

Understanding the Concept of Equality of Outcome in Sociology

The Role of Media in Primary Socialisation
24 hour trending.

Media Framing: An Introduction
The symbolic interactionist view of education: a detailed outline and explanation, pierre bourdieu’s symbolic violence: an outline and explanation, the work and contributions of emile durkheim in sociology, the role and functions of the education system: exploring its relationship to the economy and class structure.
Easy Sociology makes sociology as easy as possible. Our aim is to make sociology accessible for everybody. © 2023 Easy Sociology
© 2023 Easy Sociology

16 Mixed Economy Advantages and Disadvantages
Mixed economies are systems which combine elements of free market systems with command economy structures. You will have private enterprises working with public entities, mixing elements of capitalism and socialism together to produce results. This system is such an effective method of economic growth and consistency that most governments in the world today, including the United States, support its use.
The typical mixed economy preserves the individual and corporate right to own property. It will reserve the right of the government to interfere in the market economy when necessary to create specific outcomes or meet societal goals.
These are the significant advantages and disadvantages of a mixed economy to evaluate when looking at this specific system.
List of the Advantages of a Mixed Economy
1. It provides capital through the promotion of innovation. Mixed economies promote the value of organizations which are the most efficient. The only way to reach this status is to invest in research and development. Innovation is highly prized in this economy type because its consumers demand the best at all times. When an organization solves pain points for their customer, the additional capital they receive gets reinvested into the overall society to solve more issues.
2. It permits spending in systems that a pure capitalist economy would neglect. Mixed economies allow for private ownership because the view is that the state is less capable of creating profits than the individual. At the same time, however, the government also recognizes that there is a duty to the infrastructure, social needs, and financial safety nets required for a society to survive. Pure capitalism would not offer food stamps, unemployment, or even highway building because each person or company would serve their needs first at all times.
3. It provides goods or services whenever they’re required. The advantages of a free-market economy are found in the mixed economy from the perspective of distribution. When goods or services become necessary in specific regions, this structure ensures that people and organizations get what they require. Supply and demand are measured frequently with a mixed economy, which creates pricing mechanisms based on scarcity. Companies can then predict how each item will fare to create new efficiencies for each market segment.
4. It protects the general wellbeing of the general population. The mixed economy approach doesn’t support the concept that anyone can do anything at any time. It won’t support the concept that the bare minimum is the only requirement to meet either. Governments interfere with unsafe products hit the market, when pricing mechanisms are unfair, or when monopolies seek to create an unfair advantage in the corporate/consumer relationship. This structure allows the government to inform consumers that products are unsafe to use without calling for specific restrictions on corporate entities unless illegal actions occur.
5. It provides an equal level of economic control within society. Consumers, corporations, and governments all offer checks and balances to each other within the confines of the mixed economy. The private sector receives responsibility for the production of goods and services, while the average is given the task of being a consumer. Governments provide the service of protection, safety, and oversight of the overall market, along with the infrastructure necessary that permits economic activities in the first place.
6. It improves production levels and overall efficiency rates. Mixed economies encourage competition at all levels. They encourage disruptors of any size to enter their industry because that inspires more innovation. Consumers will always shop for the best possible product to meet their needs, even if that means being disloyal to brands they’ve used for years.
35% of the revenues for the average company will come from new customers. 80% of consumers say that they’re willing to pay more for a better customer experience. Companies focus on improvements also because a 2% shift in customer retention for them can lower costs by up to 10%.
7. It provides more opportunities for companies to grow. Companies earn to their full potential when an innovative and ethical approach to business opportunities are taken. When organizations grow through success, their employees enjoy in it as well. The mixed economy allows everyone to pursue legal business ventures without highly-restrictive government oversights. This structure makes it possible for workers to find jobs they want, businesses to find opportunities they want, and then both contribute to the government to provide for the greater wellbeing of everyone involved.
8. It still defines the role of government within the society. A mixed economy doesn’t permit the government to take full control of private enterprise. It also provides a specific role for state-backed enterprises to function while maintaining private elements to it. There are currently 26 different government-owned companies in the U.S. operating right now, including Amtrak, Farm Credit System Insurance Corporation, and North Dakota Mill and Elevator. Public utilities are another example of this structure. Even though these corporations are owned by the government, they follow the free market practices which private companies are bound to in their operations.
9. It helps to create more jobs. The structure of the mixed economy allows for private corporations to build revenue streams that support direct employment opportunities. Individuals can form their own businesses in this economy too, working as an independent contractor, freelancer, or owner. When the economy grows, the size of government increases too, creating public-sector jobs which contribute spending at the local level.
10. It creates a layer of protection for the most vulnerable. Without a mixed economy in place, societies would focus on productivity instead of need. Individuals with disabilities would be cast aside unless they could offer contributions to the general good. If you lost your job, then too bad – you’re on your own until you can find another one. The role of the government in this structure creates a safety net which protects the most vulnerable. People don’t get rich off of government benefits. They get the basics of what they must have to survive.
List of the Disadvantages of a Mixed Economy
1. It creates private businesses which could disrupt the economy. The free market system works toward a monopoly whenever it can. That process occurs because the role of an organization is to maintain its power however it can once it’s achieved. That is why government intervention stops monopolizing efforts. A monopoly creates new pricing structures due to the guaranteed requirement that customers use their goods or services.
A mixed economy still allows companies to become too big. Numerous bailouts were offered during the 2007-2009 global recession years to “prop up” the companies which would create a strong negative influence in personal finances. There must be debt controls in place, then correctly regulated by the government, for a mixed economy to be prosperous.
2. It creates higher levels of debt. Governments require funding, just as corporations and individuals need income to exist. If the state becomes involved with specific enterprises through subsidies or backing, then the presence of a de facto monopoly occurs, even if the legal definition is not met. One example of this issue involves Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac.
Fannie Mae was chartered by the government in 1938 to ensure a supply of mortgage funds was available throughout the country. It operates today as a shareholder company with a congressional charter. Freddie Mac followed a similar path in 1980, but as a private company, to do the same thing. These enterprises ensure households access debt products if they want them.
3. It triggers poverty if managed incorrectly. The mixed economy works when all three entities provide checks and balances for one another. If one element receives a greater share of the pie, then someone else receives less of it. The imbalance continues unless specific corrections are made to restore its balance.
This issue affects the United States in profound ways. The wealthiest 1% of Americans own 40% of the country’s wealth. That’s the highest share since at least 1962. Middle Class wages saw their first bump in meaningful value in 2018 since the 1980s. Less than 40% of households are classified as being in the Middle Class as well, which is one of the lowest rates of any developed country.
4. It does not guarantee that the state will avoid interference. Think about how the government works in the United States. The average person is governed under at least four different tiers of management. They have local regulations and laws to follow, then county statutes, state laws, and then federal requirements. That means four different entities attempt to offer checks and balances to individual and corporate activities. They can all act together or work separately.
The recent surge in cannabis access legislation at the state level is an excellent example of this issue. There are currently 10 states which have legalized recreational marijuana use in the United States, along with the District of Columbia. Some counties may decide to prohibit recreational use. Some local governments have passed moratoriums to prevent businesses from locating there to sell these products. Then there’s the federal government, which still classifies the drug as a Schedule I, making it illegal to possess at the national level.
5. It can become subject to the ideas of special interest groups. The 2016 presidential cycle in the United States was one of the most expensive in history. Hillary Clinton received more than $10 million in donations from six different groups, including Soros Fund Management, Saban Capital Group, and Renaissance Technologies. Paloma Partners contributed $21.6 million to her campaign.
The same issue occurred with Donald Trump’s campaign, with McMahon Ventures, the Walt Disney Company, and GH Palmer and Associates donating more than $5 million on behalf of the candidate. Renaissance Technologies also donated more than $10 million to Trump’s campaign, as they did to Clinton’s effort. The reason why these contributions occur is to influence governmental policies as they relate to the private business world.
6. It offers higher tax rates than other economy types. The mixed economy offers numerous benefits, but it also offers high tax rates. Governments are funded through taxation and the revenues (if any) earned from their private or chartered companies. Individuals and corporations are taxed at various, often progressive levels based on the amount of income received.
According to World Atlas, all of the top 10 highest income tax rates in the world are found in Europe, with Belgium leading the way at 40.7%. The United States ranks 16th on the list, with an average rate of 26%.
These mixed economy advantages and disadvantages seek to create harmony between the state and private enterprise. Most nations create checks and balances which allow companies to grow, wealth to be earned, and social services offered to those who require them. Some governments may attempt to legislate a more significant chunk of the available economics, while others might interfere with corporate or individual decisions. The success or failure of this economy type depends on all three groups protecting, supporting, and challenging each other all the time.

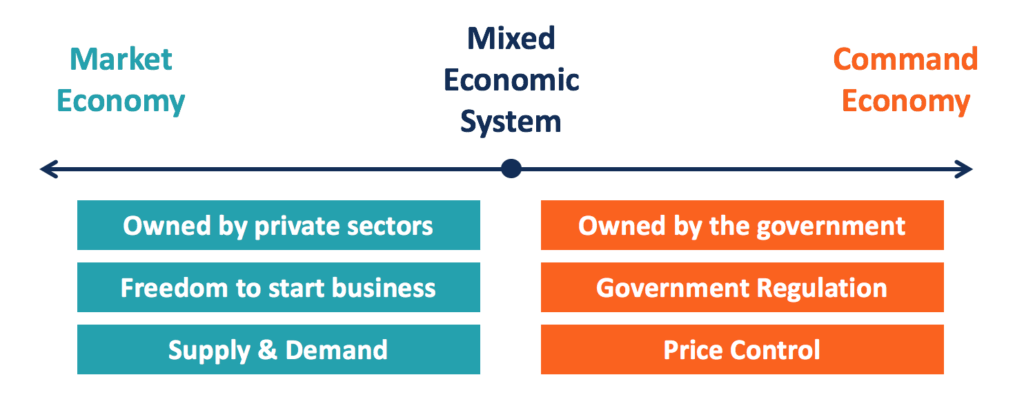
Mixed economy
- Definition – A mixed economy means that part of the economy is left to the free market, and part of it is managed by the government.
- Mixed economies start from the basis of allowing private enterprise to run most businesses.
- Then the governments intervene in certain areas of the economy, such as providing public services (health, education, waste management) and the regulation or private business (e.g. legal right to private property, and abuse of monopoly power)
- In reality, most economies are mixed, with varying degrees of state intervention.
Features of mixed economies
- Individuals are able to set up business and make a profit. However, usually progressive taxes and means-tested benefits to reduce inequality and provide a safety net.
- Prices are determined by market forces ‘invisible hand’. But, the government may regulate some goods. For example, placing a higher tax on cigarettes to discourage use.
- Most businesses are privately owned. However, the government may own or be involved in regulating natural monopolies, e.g. tap water, electricity, gas.
- Businesses are free to decide what to produce and price to pay, but there are government regulations on the environment, labour markets and abuse of monopoly power – limiting pollution
- An economy largely driven by private investment and enterprise, but government can intervene to reduce fluctuations in the economic cycle. For example, reduce inflation or boost economic growth (fiscal policy)
Examples of mixed economies
Share of government spending as a % of GDP
- Iceland (57%)
- Sweden (52%)
- France (52.8%)
- United Kingdom (47.3%)
- United States (38.9%)
- Russia (34.1%)
- India – (27%)
- China – (20%)
- Hong Kong (18.6%)
- More at – list of government spending as a % of GDP
All the above economies are mixed. The government manages a section of the economy, and private firms and individuals operate the rest.
There are different degrees of state intervention. European economies such as Sweden and France have a generous level of social security spending; in western Europe, education and healthcare are free at the point of use. However, in the US, government spending as a share of GDP is lower, but health care has to be paid for.
As economies develop, the government often take a higher share of total spending. Developed countries, such as in Western Europe, often choose to provide state welfare support, and greater government regulation of business and the environment. Developing economies, such as Cameroon and Uganda have government sector which spends less than 20% of GDP
Advantages of mixed economies
- Incentives to be efficient . Most business and industry can be managed by private firms. Private firms tend to be more efficient than government-controlled firms because they have a profit incentive to cut costs and be innovative.
- Limits government interference . Mixed economies can reduce the amount of government regulation and intervention prevalent in a command economy.
- Regulation on the abuse of monopoly power, e.g. prevent mergers, prevent excessively high prices.
- Taxation and regulation of goods with negative externalities, e.g. pollution,
- Subsidy or state support for goods and services which tend to be under-consumed in a free market. This can include public goods, like police and national defence, and merit goods like education and healthcare.
- A degree of equality. A mixed economy can create greater equality and provide a ‘safety net’ to prevent people from living in absolute poverty. At the same time, a mixed economy can enable people to enjoy the financial rewards of hard work and entrepreneurship.
- Macroeconomic stability . Governments can pursue policies to provide macroeconomic stability, e.g. expansionary fiscal policy in times of a recession.
- Even libertarians who dislike government intervention believe there needs to be legal support for private property and government provision of law and order.
Disadvantages of mixed economies
- How much should the government intervene? Can be difficult to know how much governments should intervene, e.g. discretionary fiscal policy may create alternative problems such as government borrowing.
- Too much inequality? Mixed economies are criticised by socialists for allowing too much market forces, leading to inequality and an inefficient allocation of resources.
- Government failure . Mixed economies are criticised by free-market economists for allowing too much government intervention. Libertarians argue that governments make very poor managers of the economy, invariably being influenced by political and short-term factors.
- In reality, it depends on how a mixed economy is managed. Even the most ardent free-market economists will agree we need a degree of government intervention – if only to protect private property. For example, Adam Smith in ‘Wealth of Nations’ argued governments needed to prevent the exploitation of monopoly power.
- Very few economists would argue that the government should try and intervene in all areas of the economy. Private business and financial incentives play an important role in a well-functioning economy – even if the desire is to promote greater redistribution.
- Command economy
- Free market economy
24/7 writing help on your phone
To install StudyMoose App tap and then “Add to Home Screen”
Understanding Mixed Economies: Features, Pros, and Cons
Save to my list
Remove from my list

Advantages of A Mixed Economy
Disadvantages of a mixed economy, introduction to economic systems, differentiate between free market economy and mixed economy.
Understanding Mixed Economies: Features, Pros, and Cons. (2016, Jun 02). Retrieved from https://studymoose.com/mixed-economic-system-essay
"Understanding Mixed Economies: Features, Pros, and Cons." StudyMoose , 2 Jun 2016, https://studymoose.com/mixed-economic-system-essay
StudyMoose. (2016). Understanding Mixed Economies: Features, Pros, and Cons . [Online]. Available at: https://studymoose.com/mixed-economic-system-essay [Accessed: 27 Aug. 2024]
"Understanding Mixed Economies: Features, Pros, and Cons." StudyMoose, Jun 02, 2016. Accessed August 27, 2024. https://studymoose.com/mixed-economic-system-essay
"Understanding Mixed Economies: Features, Pros, and Cons," StudyMoose , 02-Jun-2016. [Online]. Available: https://studymoose.com/mixed-economic-system-essay. [Accessed: 27-Aug-2024]
StudyMoose. (2016). Understanding Mixed Economies: Features, Pros, and Cons . [Online]. Available at: https://studymoose.com/mixed-economic-system-essay [Accessed: 27-Aug-2024]
- The Dynamics of Mixed Economies: An In-Depth Exploration Pages: 3 (673 words)
- Research design: Qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods approaches Pages: 10 (2919 words)
- Narrative Essay. A Day of Mixed Happiness and Sadness Pages: 2 (560 words)
- Rational Comprehensive, Incremental, and Mixed Scanning Theories Pages: 2 (569 words)
- Mixed Branding Strategies: Unveiling Opportunities and Challenges Pages: 2 (577 words)
- Single Sex schools and Mixed Schools Pages: 2 (566 words)
- The Advantages of Mixed-Sex Schools as an Education System Pages: 11 (3255 words)
- Popular culture is sending mixed messages Pages: 3 (825 words)
- Exploring Economic Systems: Tradition, Capitalism, Socialism, Mixed Pages: 4 (1120 words)
- A trip of mixed emotions towards becoming an adult in Marigold by Eugenia W. Collier Pages: 5 (1307 words)

👋 Hi! I’m your smart assistant Amy!
Don’t know where to start? Type your requirements and I’ll connect you to an academic expert within 3 minutes.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- The Government's Role
Elements of Our Mixed Economy
Financial policies, other types of economic systems, strength of the u.s. economy, global impact of the u.s. economy, the bottom line, is the united states a market economy or a mixed economy.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/picture-53893-1440688982-5bfc2a88c9e77c005143c705.png)
Amanda Bellucco-Chatham is an editor, writer, and fact-checker with years of experience researching personal finance topics. Specialties include general financial planning, career development, lending, retirement, tax preparation, and credit.
- Economics Defined with Types, Indicators, and Systems
- Economy Definition
- History of Economics
- Is Economics a Science?
- Understanding Finance vs. Economics
- Macroeconomics
- Microeconomics
- Four Economic Concepts
- Law of Supply and Demand
- Demand-Side Economics
- Supply-Side Economics
- Market Economy
- Command Economy
- Economic Value
- Keynesian Economics
- Social Economics
- Economic Indicator
- Top 10 US Economic Indicators
- Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
- What Is GDP and Why Is It So Important?
- Consumer Spending
- Retail Sales
- The Top 25 Economies in the World
- Examples of Free Market Economies
- Is the US a Market Economy or a Mixed Economy? CURRENT ARTICLE
- Primary Drivers of the Chinese Economy
- How India Makes Its Money
- European Union (EU)
- The German Economic Miracle
- The Economy of the United Kingdom
- How the North Korean Economy Works
The United States has a mixed economy. Its economic system functions with characteristics of both capitalism and socialism.
A mixed economic system protects some private property and allows a level of economic freedom in the use of capital. But governments also intervene in economic activities for the public good and to achieve social aims.
Key Takeaways
- The U.S. has a mixed economy which exhibits characteristics of both capitalism and socialism .
- A mixed economy embraces the free market when it comes to capital use, but it also involves government intervention for the public good.
- The U.S. government controls part of the economy with restrictions and licensing requirements in areas such as education, roads, hospital care, and postal delivery.
- The federal government provides a limited welfare state to reduce the effects of extreme poverty.
- The government also intervenes through the Federal Reserve, by adjusting the costs of borrowing money.
The U.S. Government's Role in the Mixed Economy
The U.S. government has always played a role in the economic affairs of the nation. Over the course of the nation's history, many services began to come under the influence or direct control of the public sector.
During some periods, however, the nation had more of a true free-market economy, where the private sector was largely unrestricted in its economic activity.
Free Market Economy vs. Mixed Economy
Free Market Economy
A "true" or "absolute" free market economy requires that all property be owned by private individuals and all goods and services be privately provided.
Prices are allowed to fluctuate based on supply and demand, and all transactions are voluntary, not compelled, or restricted by the government. This system is also referred to as " pure capitalism " or " laissez-faire capitalism ."
Mixed Economy
Conversely, a mixed economy has elements of both free markets and economic intervention by the government. Many private transactions are allowed but only under conditions aligned with the government's goals.
There are several different ways market economies are changed in a mixed economy. Governments might place restrictions on voluntary transactions, such as licensing or regulatory requirements.
Governments might also own public property or provide public services and use tax policies or subsidies to change the price signals in the market.
The U.S. government keeps partial control over the economy with regulatory restrictions, such as licensing or banning certain activities.
The U.S. government controls or partially controls many goods or services, such as education, courts, roads, hospital care, and postal delivery. It also provides subsidies to agricultural producers, oil companies, financial companies, and utility firms.
Controlling What People Buy and Sell
For example, private individuals cannot legally provide or purchase certain types of goods, such as cocaine, haggis, raw milk (in some states), and most types of flavored cigarettes. Other products face heavy taxation to discourage their use.
Business Registration and Licensing
In the U.S., private businesses need to register with government agencies, and many types of professionals can only operate with government-approved licenses, including funeral attendants, auctioneers, private investigators, makeup artists, hairstylists, real estate agents , and financial advisers.
Approval of Foods and Medicines
Nearly every type of business and every form of economic exchange is affected by government policy in the U.S. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) must approve consumable foods and medicines before they can be sold and requires that producers provide very specific disclaimers.
Advertising
Businesses can only advertise their goods and services if they comply with the Federal Trade Commission (FTC) . The hiring, compensating, and firing of employees must comply with the Fair Labor Standards Act (FLSA) , the Employee Retirement Income Security Act (ERISA), and many other regulations from agencies such as the Department of Labor (DOL).
The success of the mixed economy in the U.S. is underscored by the nation's standard of living compared to other countries and its global economic strength.
The U.S. government also plays a role in the economy via financial policies that can influence inflation and business production. The Federal Reserve is charged with controlling monetary policy, which has to do with the quantity, velocity, and availability of the circulating money supply. Congress and the executive branch handle fiscal policy , which focuses on government revenue and spending.
Expansionary monetary policy aims to inject liquidity, stimulate lending and spending, and discourage savings. Contractionary policy is supposed to reduce aggregate demand, encourage savings, slow down the rate of inflation, or burst asset bubbles. While expansionary policy is analogous to pushing on the gas pedal, contractionary policy is like stepping on the brakes.
An economy encompasses all of the activities related to the production, consumption, and trade of goods and services in an entity. Economic systems can be categorized into three main types : traditional economies, command economies, and market economies.
- Traditional: A traditional economy is based on goods, services, and work, all of which rely on customs, history, and time-honored beliefs. Tradition guides economic decisions such as production and distribution. Societies with traditional economies depend on agriculture, fishing, hunting, gathering, or some combination of them, and there is very little division of labor or specialization. The traditional economy is very basic and the most ancient of the four types.
- Command: In a command economy , a central governmental authority controls the economic structure and dictates the levels of production and the prices that may be charged for goods and services. It's also known as a planned system and is common in communist societies.
- Market: A market economy is based on the concept of free markets. There is very little government interference and control over resources. Any economic decision and the pricing of goods and services are guided by the interactions of a country's individual citizens and businesses as well as the relationship between supply and demand.
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. economy regained strength at a faster rate than other world economies. By March 2023, U.S. GDP was over 5% higher than the pre-pandemic level. Employment was particularly strong, with unemployment falling to record lows in early 2023. At the same time, several other leading global economies had not yet returned to their pre-pandemic levels of output.
However, there were some causes for concern. Consumer prices rose steadily as the pandemic progressed despite repeated interventions by the Federal Reserve. Inflation had risen 5% as of March 2023, meaning that real wages fell about 1.6% from the year prior.
For the year up to February 2024, real average hourly earnings increased 1.1 percent. This positive change, in combination with the reduction of the average workweek by 0.6 percent, brought about a 0.5-percent increase in real average weekly earnings in this year-over-year period.
As of September 2023, the federal government employed more than two million civilians.
Government interventions can also affect the global economy, due to the outsized influence of the U.S. on world markets. A classic example of this is the importance of the Federal Reserve in international financial markets.
Because the dollar is one of the default currencies in international transactions, a sudden change in U.S. monetary or fiscal policy can cause ripples throughout the world economy.
The U.S. also accounts for a large share of global GDP and stock market capitalization. As a result, many regional economies tend to sync with U.S. economic cycles. Global recessions tend to co-occur with severe recessions in the U.S. economy. Although this relationship does not necessarily imply causation, it does indicate a central U.S. role in the world economy.
How Does the Federal Reserve Affect the Economy?
In the United States, the federal reserve intervenes in economic activity by buying and selling debt. This affects the cost of lending money, thereby encouraging or discouraging more economic activity by businesses and borrowing by consumers.
Does the U.S. Have a Welfare State?
The United States has a limited welfare state that is intended to reduce the effects of extreme poverty. Examples of related programs include the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) , commonly known as food stamps, and Medicaid, which provides health care assistance to those with limited incomes .
Government subsidies—that is, financial contributions granted to private companies to help them keep the price of a commodity or service low—also play a role in the support of those in need.
Does the U.S. Have State-Owned Enterprises?
The federal government has several government-sponsored enterprises that generate revenue, although that is not their primary purpose. Freddie Mac and Fannie Mae lend money for residential mortgages, thereby facilitating homeownership among people who might not otherwise qualify for a loan. The United States Postal Service also generates revenue from its business activities, although the amount typically is less than its expenses .
While U.S. politicians tend to be highly committed to free market values, the government regularly intervenes in the nation's economic affairs. Thus, the U.S. has a mixed economy. In fact, the public sector has an enormous impact on the American economy.
By providing public goods and services such as education, military protection, federal highways, and national parks, the U.S. government impacts the U.S. economy. These goods and services are paid for with tax revenue, which highlights another role of government: redistribution of income.
Public sector employment is also a way of reducing unemployment in the short term, and it can create demand in other sectors of the economy.
Food and Drug Administration. " What does FDA do? "
Federal Trade Commission. " Advertising and Marketing ."
Department of Labor. " Summary of the Major Laws of the Department of Labor ."
Federal Reserve. " About the Fed ."
U.S. Department of Commerce. " News: Unemployment Is at Its Lowest Level in 54 Years ."
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Consumer Price Index News Release: Consumer Price Index—March 2023 ."
Bureau of Labor Statistics. " Real Earnings Summary ."
Congressional Research Service. " Current Federal Civilian Employment by State and Congressional District ."
Center for Economic Policy Research. " Understanding the Global Role of the U.S. Economy ."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1960812009-45f7b53505b640d293dc008901ea0a48.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
From Mixed Economy to Free Market Economy Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
At present the global economy is shifting towards a free market economy. But in order to appreciate the significance of this change it is important to understand the evolution from a centrally controlled economy to a free market economy.
In modern times, the common feature of many Western governments is a mixed economy. In this structure the government does not control a major part of the resources. However, the government reserves the right to control critical sectors of the economy. The rationale for this design is based on efficiency. Nevertheless, there is a pronounced shift to a free market economy as the world discovers the problems inherent in a mixed economy.
Examples of a mixed economy can be found in many parts of the world and the list includes most countries in Western Europe, in the American continent as well as major countries in Asia. Those who advocated the use of a mixed economy made the argument that it will result in “low unemployment, low poverty, steady economic growth, and an equitable distribution of wealth by means of the most effective policies” (Wild 35).
However, there are inherent flaws to this economic structure. One of the problems associated with this feature is extensive government ownership of resources. As a result there is little incentive for efficiency and accountability. The proposed solution is to transform a mixed economy into something that resembles a free market economy. The process requires a transition and one of which, is a move towards privatization.
Privatization is the process of selling government-owned resources (Wild 35). The intended consequence of this action is to free the government from the demands of managing the day-to-day operations of government owned companies and other related agencies. At the same time it eliminates the practice of appointing managers for the sake of political considerations rather than his or her ability to properly manage a firm.
A free market economy must be founded on the principle of Laissez-Faire economics, meaning the capacity to allow industries to operate with little interference from the government. The end result will create free choice, free enterprise, and price flexibility. There are requirements that must be fulfilled in order to achieve these three things. First, there must be anti-trust laws to promote fair competition. Secondly, the government must respect property rights. Thirdly, there must be a stable fiscal and monetary environment. Fourthly, there must be political stability. Finally, there must be economic freedom.
In the beginning of the modern period, most of the governments in the Western hemisphere subscribed to the idea of a mixed economy. But in recent times, many government leaders and business leaders argue the inefficiency of a mixed economy. The better alternative is a free market economy.
But in order for a free market economy to prosper a process of transition must first occur. The first stage requires privatization of economic resources and the transfer of the same to private entities. There is also the need to build on the idea that there must be minimal interference from the government.
Furthermore, the government must aspire to achieve free choice, free enterprise and price flexibility. These three main goals can only be achieved if the government establish anti-trust laws and respect property rights. In addition the government must labor to provide a stable fiscal and monetary environment as well as political stability and economic freedom.
Works Cited
Wild, John. International Business: The Challenge of Globalization . New Jersey: Prentice Hall, 2010. Print.
- Understanding Recession and Expansion: Economic Impact on Businesses
- Paul Krugman: How Did Economists Get It So Wrong?
- Walmart and Antitrust Regulations
- Blue Cross and Blue Shield Antitrust Case
- Antitrust Charges Against Johnson & Johnson
- Unemployment in Saudi Arabia
- Effects of Increasing Interest Rates in Africa
- Australia's Economy and Major Events
- Islamic Business
- Major Reasons for Food Prices Increase
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, April 25). From Mixed Economy to Free Market Economy. https://ivypanda.com/essays/from-mixed-economy-to-free-market-economy/
"From Mixed Economy to Free Market Economy." IvyPanda , 25 Apr. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/from-mixed-economy-to-free-market-economy/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'From Mixed Economy to Free Market Economy'. 25 April.
IvyPanda . 2020. "From Mixed Economy to Free Market Economy." April 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/from-mixed-economy-to-free-market-economy/.
1. IvyPanda . "From Mixed Economy to Free Market Economy." April 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/from-mixed-economy-to-free-market-economy/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "From Mixed Economy to Free Market Economy." April 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/from-mixed-economy-to-free-market-economy/.

Mixed Economy Definition, Examples, Features, Merits & Demerits
In a mixed economy, the means of production are owned & controlled by both state & private individuals or entities. Read all about Mixed Economy Examples, Features, Merits & Demerits for UPSC Exam.

Table of Contents
Mixed Economy
A mixed economy is an economic system that combines elements of both a free market economy and a command economy. In a mixed economy, the government and private sector both play important roles in economic decision-making.
In a mixed economy, the government regulates certain industries and provides public goods and services such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. At the same time, private individuals and businesses are allowed to own property, make profits, and engage in market transactions.
Read about: India’s GDP Growth Rate
Mixed Economy Features
Some of the key features of a Mixed Economy include:
| 1. | Private Property | Individuals and businesses are allowed to own property and assets and to make decisions about how to use them. |
| 2. | Free Market | Markets are allowed to operate relatively freely, with supply and demand determining prices and quantities. |
| 3. | Government Regulation | The government regulates certain industries and economic activities to ensure fair competition, protect consumers, and promote public welfare. |
| 4. | Public Goods and Services | The government provides certain public goods and services, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure, that are considered essential for the common good but might not be profitable for private businesses to provide. |
| 5. | Taxation and Redistribution | The government uses taxation and other policies to redistribute wealth and income, reduce inequality, and promote social welfare. |
| 6. | Mixed Ownership | Some industries and businesses are owned and operated by the government, while others are privately owned and operated. |
| 7. | Economic Planning | The government may engage in some level of economic planning to guide investment and development in certain sectors, although this is typically less extensive than in a command economy. |
| 8. | Entrepreneurship | Private individuals and businesses are allowed to innovate, take risks, and create new products, services, and industries. |
Read about: Capitalist Economy
Mixed Economy in India
India is often cited as an example of a mixed economy, where both the government and private sector play important roles in economic decision-making.
In India, the government has historically had a significant presence in the economy, with state-owned enterprises and public sector undertakings operating in a wide range of industries, including transportation, energy, and telecommunications. The government has also been involved in economic planning, with a focus on promoting social welfare and reducing inequality.
At the same time, India has also undergone significant economic liberalization in recent decades, with a move towards more market-oriented policies and an emphasis on private sector development. This has included measures such as deregulation, privatization, and foreign investment liberalization.
Today, the Indian economy is characterized by a mix of public and private ownership, with both domestic and foreign companies operating in a wide range of sectors. The government still plays a significant role in certain industries, such as banking and insurance, and provides public goods and services such as education and healthcare
Read about: Macroeconomics and Microeconomics
Mixed Economy Examples
There are many examples of countries with mixed economies, where both the government and the private sector play important roles in economic decision-making. Here are some examples:
- Canada is often cited as a classic example of a mixed economy, with a mix of private and public ownership in various industries, significant government intervention in certain sectors such as healthcare and education, and a commitment to social welfare programs.
- Germany is known for its social market economy, which combines a strong emphasis on private enterprise and market competition with government regulation and support for social welfare programs such as healthcare and pensions.
- Japan has a highly developed mixed economy, with a strong emphasis on private enterprise and innovation, significant government intervention in certain industries such as transportation and energy, and a commitment to social welfare programs.
- Sweden is often cited as a model for the Nordic model of social democracy, which combines a strong welfare state with a highly competitive private sector and an emphasis on innovation and entrepreneurship.
- The United Kingdom has a mixed economy that combines elements of both capitalism and socialism. The government plays an important role in providing public goods and services such as healthcare and education, while also encouraging private enterprise and market competition.
Read about: GDP of Indian States
Mixed Economy Merits
Mixed economies have several strengths, which make them a popular economic model around the world. Some of the key strengths of mixed economies include:
- Flexibility: Mixed economies allow for a high degree of flexibility, as they combine the advantages of both private enterprise and government intervention. This enables them to respond effectively to changing economic conditions and social needs.
- Innovation: Mixed economies can promote innovation and entrepreneurship, as they provide a supportive environment for private enterprise and competition, while also investing in public goods and services that support innovation and growth.
- Stability: Mixed economies can provide a stable economic environment, as they combine market mechanisms with government intervention to mitigate the risks and uncertainties of the business cycle.
- Social Welfare: Mixed economies can provide a high level of social welfare, as they combine market mechanisms with government programs to ensure that basic needs are met for all members of society.
- Balanced Growth: Mixed economies can promote balanced economic growth, as they combine private enterprise with government intervention to ensure that growth is sustainable and equitable and that benefits are shared widely across society.
Mixed Economy Demerits
While mixed economies have several strengths, they also face several challenges. Some of the key challenges of mixed economies include:
- Balancing Private Enterprise and Government Intervention: One of the biggest challenges of mixed economies is striking the right balance between private enterprise and government intervention. Too much government intervention can stifle private enterprise and innovation, while too little intervention can lead to market failures and inequality.
- Political Pressure: Mixed economies are subject to political pressures, as government policies are often influenced by political considerations rather than purely economic ones. This can lead to inefficiencies and distortions in the economy.
- Coordination: Mixed economies require effective coordination between government agencies, private enterprises, and other stakeholders to ensure that economic policies and programs are implemented effectively. This can be challenging, particularly in large and complex economies.
- Bureaucracy: Government intervention in mixed economies can lead to bureaucratic inefficiencies, as government agencies may become overly complex and bureaucratic in their operations.
- Fiscal Sustainability: Mixed economies require significant public investment in infrastructure, social welfare programs, and other public goods and services. This can lead to fiscal challenges, particularly if public spending is not matched by tax revenues.
Read about: Unemployment Rate in India
Difference Between Capitalist, Socialist and Mixed Economy
Some of the key points of difference include:
| 1. | Ownership of means of production | Privately owned | Publicly owned | Mix of private and public ownership |
| 2. | Role of market forces | Central | Minimal | Important |
| 3. | Role of government | Limited | Extensive | Regulates and provides public goods/services |
| 4. | Economic inequality | High | Low | Moderate |
| 5. | Competition | Encouraged | Discouraged | Encouraged with regulation |
| 6. | Social services | Private or none | Provided by the state | Provided by both private and public sectors |
| 7. | Economic planning | Limited | Extensive | Limited, focused on specific areas |
| 8. | Examples | United States | Cuba, North Korea | Canada, Japan, Germany |
Read about: Socialist Economy
Mixed Economy UPSC
Mixed Economy is an important topic for the UPSC exam as it is included in the UPSC Syllabus for both the Preliminary and Mains exams under the Economics section. Understanding the features, strengths, and challenges of mixed economies is essential for aspirants preparing for the UPSC exam. StudyIQ UPSC Online Coaching and UPSC Mock Test cover this topic comprehensively, which can help aspirants to prepare for the exam effectively.
Sharing is caring!
Mixed Economy FAQs
What is mixed economy with example.
A mixed economy combines elements of capitalism and socialism. Examples include the United States, Canada, and Germany.
What is mixed economy in India?
India has a mixed economy where private and public sectors coexist, and the government invests in public goods and services.
What are the 3 mixed economies?
The three types of mixed economies are market-oriented, welfare-oriented, and state-directed.
What are the 4 types of mixed economy?
The four types of mixed economies are state-guided market economies, state-directed economies, liberalized economies, and social market economies.
I, Sakshi Gupta, am a content writer to empower students aiming for UPSC, PSC, and other competitive exams. My objective is to provide clear, concise, and informative content that caters to your exam preparation needs. I strive to make my content not only informative but also engaging, keeping you motivated throughout your journey!

Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Trending Event
- KPSC KAS Question Paper 2024
- KPSC KAS Answer Key 2024
- SSC CGL Tier 1 Admit Card 2024
- TNPSC Group 4 Result 2024

Recent Posts

- UPSC Online Coaching
- UPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Prelims Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Mains Syllabus 2024
- UPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPSC Age Limit 2024
- UPSC Calendar 2025
- UPSC Syllabus in Hindi
- UPSC Full Form
- UPPSC Exam 2024
- UPPSC Calendar
- UPPSC Syllabus 2024
- UPPSC Exam Pattern 2024
- UPPSC Application Form 2024
- UPPSC Eligibility Criteria 2024
- UPPSC Admit card 2024
- UPPSC Salary And Posts
- UPPSC Cut Off
- UPPSC Previous Year Paper
BPSC Exam 2024
- BPSC 70th Notification
- BPSC 69th Exam Analysis
- BPSC Admit Card
- BPSC Syllabus
- BPSC Exam Pattern
- BPSC Cut Off
- BPSC Question Papers
SSC CGL 2024
- SSC CGL Exam 2024
- SSC CGL Syllabus 2024
- SSC CGL Cut off
- SSC CGL Apply Online
- SSC CGL Salary
- SSC CGL Previous Year Question Paper
- SSC CGL Admit Card 2024
- SSC MTS 2024
- SSC MTS Apply Online 2024
- SSC MTS Syllabus 2024
- SSC MTS Salary 2024
- SSC MTS Eligibility Criteria 2024
- SSC MTS Previous Year Paper
SSC Stenographer 2024
- SSC Stenographer Notification 2024
- SSC Stenographer Apply Online 2024
- SSC Stenographer Syllabus 2024
- SSC Stenographer Salary 2024
- SSC Stenographer Eligibility Criteria 2024
SSC GD Constable 2025
- SSC GD Salary 2025
- SSC GD Constable Syllabus 2025
- SSC GD Eligibility Criteria 2025
IMPORTANT EXAMS

- Terms & Conditions
- Return & Refund Policy
- Privacy Policy
- EssayBasics.com
- Pay For Essay
- Write My Essay
- Homework Writing Help
- Essay Editing Service
- Thesis Writing Help
- Write My College Essay
- Do My Essay
- Term Paper Writing Service
- Coursework Writing Service
- Write My Research Paper
- Assignment Writing Help
- Essay Writing Help
- Call Now! (USA) Login Order now
- EssayBasics.com Call Now! (USA) Order now
- Writing Guides
What Are The Advantages And Disadvantages Of A Mixed Economy? (Essay Sample)
For any socioeconomic setup, there exist distinct economies. For example, there were the traditional economies which mostly focused on barter trade, market economies, which were more about currency, and the command economy. There is however, a new version known as a mixed economy. This is one that combines all the three economies, that is, the traditional, market as well as command economies. A mixed economy is aimed at taking advantage of all the three types of economies, harnessing these advantages into one set of economic system. Just like the three distinct types of economies, a mixed economy has various advantages as well as disadvantages as will be discussed shortly.
Table of Contents
Advantages of a Mixed Economy
A mixed economy protects private property of individuals, entities or corporations. This ensures that there is safety of investments for businesspeople. It also provides for the development and maturity of a free market. A major advantage of this is that it allows for the laws of supply and demand to take root, thereby enabling the market to adjust itself automatically based on the market forces. The good thing about this is that there is no market dictation of prices by any business entity, since there is market liberalism. Goods and services can be distributed in areas where they are deemed essential and required.
Secondly, a mixed economy usually pays back the best producers in the market setup with the highest returns. This is to simply imply that the biggest profits go to the most efficient player in the market. Efficiency to a large extent translates to quality. Therefore, consumers in a mixed economy have the privilege of enjoying the best quality products, since the market players will be in a competition to produce the best possible quality of products. This brings another advantage for the market, since it encourages not only innovation, but also creativity by these players. In the end, they strive to produce quality products but at the lowest prices possible, which is good news for the consumer.
Finally, a mixed economy incorporates a level playing field for both the private enterprises as well as the government. This ensures that the capitalist and socialist aspects of these two respectively, can merge into one productive system. In essence, the government intervenes to ensure that there is a balanced mode of economic growth within such an economy, while also ensuring that not only do these businesses make profits, but also give some of it back to the society through corporate social responsibility. In the end, it is a win-win scenario for both the market players and the people.
Disadvantages of a Mixed Economy
Much of the disadvantages of a mixed economy emanate from the impact of the government on its running. First, since the government is more focused on the welfare of the society more than the economy itself, there is bound to be a less than maximum use of the available resources. This is because the government in most cases will focus its efforts in channeling more resources towards the improvement of the society’s welfare, than towards products and services that improve the economy as a whole. Secondly, private businesses encounter a lot of challenges as a result of the influence of the government through bureaucratic processes or even favoritism, which is usually a mainstay in such an economic system.
Finally, a mixed economy usually results in the concentration and accumulation of wealth in the hands of just a handful of people therein, instead of the entire society. This translates to suppression of the general interests of the people in favor of these few who have control of the markets and hence the economy. Soon, unethical practices can easily set in, as the people also try to muscle their control over such an economy.

- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Guest Essay
The China Hangover Is Here

By Michael Beckley
Mr. Beckley is the author of “Danger Zone: The Coming Conflict With China.”
In the 2000s, former President Hugo Chávez of Venezuela bet his country’s economic future on a rising China, securing tens of billions of dollars in investments and loans-for-oil deals. It paid off at first. China voraciously consumed Venezuelan oil and financed infrastructure projects, such as a high-speed railway and power plants.
The 2010s brought a reckoning. Oil prices fell, and growth in Chinese oil demand slowed along with its economy. Venezuela’s oil export revenues plummeted, to $22 billion in 2016 from more than $73 billion in 2011. Misrule by Mr. Chávez and his handpicked successor, Nicolás Maduro, and myriad other domestic problems already had Venezuela on the brink; the gamble on China helped push it over the edge. In 2014, Venezuela’s economy collapsed. People scavenged for food in garbage dumps, hospitals were short of essential medicines and crime surged. Since then, nearly eight million people have fled the country. China largely cut Venezuela off from new credit and loans , leaving behind a slew of unfinished projects .
Venezuela’s over-dependence on China was an early warning that the world ignored. Dozens of other countries that rode China’s rise are now at serious risk of financial distress and debt default as the Chinese economy stagnates. Yet China refuses to offer meaningful foreign debt relief and is doubling down at home on its protectionist trade practices when it should be undertaking reforms to free up and restart its economy, the world’s second-largest and a crucial engine of global growth.
That is the flip side of China’s “miracle.” After the 2008 global financial crisis, the world needed an economic savior, and China filled that role. Starting in 2008, it pumped $29 trillion into its economy over nine years — equivalent to about one-third of global G.D.P. — to keep it going. The positive ripple effects were felt worldwide: From 2008 to 2021 China accounted for more than 40 percent of global growth . Developing countries eagerly attached themselves to what seemed like an unstoppable economic juggernaut, and China became the top trading partner for most of the world’s nations. Like Venezuela, many discovered that the booming Chinese economy was a lucrative new market for their commodity exports, and they leaned heavily into that, allowing other sectors of their economies to languish.
China also lent more than $1 trillion abroad, largely for infrastructure projects to be built by Chinese companies under its Belt and Road Initiative. Over the past two decades, one in three infrastructure projects in Africa was built by Chinese entities. The long-term debt risks for fragile developing economies were often ignored.
Chinese lending has slowed to a trickle
Annual foreign lending
$90 billion
$87 billion
Source: Boston University Global Development Policy Center
China’s economic growth has slowed sharply over the last few decades
China has consistently reported higher economic growth than outside sources estimate. While The Conference Board in recent years estimated numbers close to China’s, Rhodium Group estimated much smaller growth.
15% annual growth of G.D.P.
Reported by China
Estimated by
The Conference Board
Estimated by Rhodium Group
Sources: National Bureau of Statistics of China; The Conference Board; Rhodium Group
China is a major trading partner across the world
Share of total trade with China
10 percent or less
more than 10 percent
No recent data availabe
No recent data available
More than 10 percent
Source: United Nations Comtrade
Note: Trade data as of 2023. For countries where 2023 data is not available, the most recent year is used. Trade figures are reported annually from each nation and may still be incomplete.
China has been one of the world’s largest lenders to emerging markets
Aggregate external public debt owed by developing and emerging markets
$400 billion
International
Monetary Fund
Sources: Horn et al. (2021) “ China's Overseas Lending ,” Journal of International Economics; World Bank; Paris Club; International Monetary Fund
Note: Chart shows debt owed by developing and emerging markets included in the World Bank International Debt Statistics. Data on public debt owed to China is incomplete after 2017.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
We've detected unusual activity from your computer network
To continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot.
Why did this happen?
Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy .
For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below.
Stock market today: Dow closes at a record even as losses for Big Tech pull S&P 500 and Nasdaq lower
The Dow Jones Industrial Average closed at a record high on Wall Street, even as losses for Big Tech companies pulled the S&P 500 and the Nasdaq composite lower
The Dow Jones Industrial Average climbed to an all-time high, even as big tech companies weighed on the broader market, leading U.S. stock indexes to a mixed finish on Wall Street.
The S & P 500 fell 0.3% Monday, remaining within 0.9% of its record set in July. The Nasdaq composite fell 0.9%, pulled down by several technology companies that tend to tip the market because of their big values. Nvidia lost 2.2%, Microsoft fell 0.8%, Amazon dropped 0.9%, Meta Platforms slid 1.3% and Tesla lost 3.2%.
The Dow rose 0.2%, to 41,240, eclipsing its previous high set in mid-July. The average is less influenced by big tech, with only Apple and Microsoft among the most valuable “Magnificent Seven” stocks in the index. That helped limit the impact of the big tech decliners.
The price of U.S. crude oil jumped 3.5% after Israel and the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah traded heavy fire on Sunday, triggering potential supply worries.
Bond yields held relatively steady. The yield on the 10-year Treasury rose to 3.82% from 3.80% late Friday.
The stock market is coming off a two-week winning streak that’s helped keep the S & P 500 and Dow within striking distance of notching new highs. Monday’s mixed market finish came at the start of a week featuring another full slate of corporate earnings and the government’s latest inflation reading.
Monday started off with a surprisingly good report showing that orders for long-lasting goods from U.S. factories, including cars, jumped 9.9% in July. An update on consumer confidence is on tap for Tuesday and the U.S. will provide a revised estimate on Thursday of economic growth during the second quarter.
Semiconductor company Nvidia reports its latest financial results on Wednesday. It has been a big beneficiary of Wall Street’s mania around artificial intelligence , becoming one of the stock market’s most massive companies , with a total value topping $3 trillion. The stock is up more than 155% for the year.
Shares in other chipmakers also fell. Broadcom lost 4.1%, Advanced Micro Devices dropped 3.2% and Lam Research slid 3.4%.
All told, the S & P 500 fell 17.77 points to 5,616.84. The Dow rose 65.44 points to 41,240.52, and the Nasdaq dropped 152.03 points to close at 17,725.76.
Others companies reporting quarterly results this week include Kohl’s, Chewy, Salesforce and Dollar General.
The key report for investors this week will come on Friday, when the the government serves up its latest data on inflation with the PCE, or personal consumption and expenditures report, for July. It is the Federal Reserve's preferred measure of inflation.
Fed Chair Jerome Powell strongly signaled on Friday that the central bank is planning to start cutting its benchmark interest rate, which currently stands at a two-decade high. The Fed raised interest rates in order to tame inflation back to its target of 2%. The final push to the target has been elusive.
Inflation has been steadily easing and economists polled by FactSet expect the latest PCE data to show a 2.6% inflation reading. The PCE was as high as 7.1% in the middle of 2022.
The Fed has been trying to tame inflation by slowing economic growth, but not by so much that it causes a recession. The dynamics of its concerns have shifted.
“Recent commentary coming out of conversations with Fed officials shows they care more about the risk of the economy slowing,” said Nathan Thooft, chief investment officer and senior portfolio manager at Manulife Investment Management.
Traders are forecasting a rate cut to come at the Fed's meeting in September. They expect the central bank to trim its main interest rate by at least 1 percentage point by the end of the year, according to data from CME Group.
Popular Reads

Jury deliberating fate of ex-politician accused of killing Las Vegas investigative reporter
- Aug 26, 12:10 AM

Stock market today: Dow Jones Industrial Average inches up to another record high in mixed trading
- Aug 27, 12:18 AM

Russia unleashes massive missile and drone barrage on targets throughout Ukraine
- Aug 26, 2:49 AM
Trudeau says Canada is imposing a 100% tariff on imports of Chinese-made electric vehicles
- Aug 26, 8:31 AM
Alaska governor declares disaster following landslide in Ketchikan
- Aug 26, 12:44 AM
ABC News Live
24/7 coverage of breaking news and live events

IMAGES
COMMENTS
A mixed economy may emerge when a government intervenes to disrupt free markets by introducing state-owned enterprises (such as public health or education systems), regulations, subsidies, tariffs, and tax policies. Alternatively, a mixed economy can emerge when a socialist government makes exceptions to the rule of state ownership to capture ...
Mixed Economic System: A mixed economic system is an economic system that features characteristics of both capitalism and socialism. A mixed economic system protects private property and allows a ...
A mixed economy combines the advantages and disadvantages of three different types of economies: market, command, and traditional economies. To understand how a mixed economy works, it's important to first understand each of the three types of economies it combines. Most countries have a mixed economy these days as a result of globalization.
A mixed economic system takes on both the characteristics of a market economy and a planned economy. In the market economy, private enterprises are free to set up businesses and make profits. The market ( supply and demand) determines the prices of goods and services, as well as the allocation of resources. In a command economy, on the other ...
A mixed economy is one that contains aspects of market capitalism (a free-market system), socialism (government control over the means of production, including state ownership of all or almost all property), and a combination of the two. The most common form in which this takes place is allowing private citizens to own some, but not all, forms ...
A mixed economy represents a hybrid economic system combining elements of both capitalism and socialism. This framework incorporates private and public enterprises, seeking to balance the benefits of market freedom and government intervention. From a sociological perspective, the mixed economy can be analyzed through the lenses of economic ...
A mixed economy is an economic system that accepts both private businesses and nationalized government services, like public utilities, safety, military, welfare, and education. A mixed economy also promotes some form of regulation to protect the public, the environment, or the interests of the state. This is in contrast to a laissez faire capitalist economy which seeks to abolish or privatize ...
1. It provides capital through the promotion of innovation. Mixed economies promote the value of organizations which are the most efficient. The only way to reach this status is to invest in research and development. Innovation is highly prized in this economy type because its consumers demand the best at all times.
Pros and Cons of a Mixed Economic System. Advantages. Allows capitalism and socialism to coexist. Allows government to internalize positive and negative externalities. Allows for correction of ...
See why leading organizations rely on MasterClass for learning & development. A mixed economy relies on free enterprise to drive a country's financial markets. At the same time, the government dictates federal fiscal and social policy to prevent economic inefficiency and provide general welfare for a country's citizens.
Mixed economies have clearly, and for many decades, publicly accepted the responsibility of establishing at least a minimal level of economic and physical security for their populations. Public funds, in substantial quantity, are devoted to financial transfers and so- cial services that form such a security web.
Definition - A mixed economy means that part of the economy is left to the free market, and part of it is managed by the government.; Mixed economies start from the basis of allowing private enterprise to run most businesses. Then the governments intervene in certain areas of the economy, such as providing public services (health, education, waste management) and the regulation or private ...
A mixed economy is an economic system in which both the private sector and state direct the economy, reflecting characteristics of both market economies and planned economies. Most mixed economies can be described as market economies with strong regulatory oversight and governmental provision of public goods. Some mixed economies also feature a ...
2.1 Mixed Economy. Mixed economic system is a unique economic system in which independent producers produce goods and services and the government to control and monitor manufacturers and the prices are so affordable to the public. Maintained to ensure the welfare of the people's purchasing power and manufacturer to produce products based on ...
The U.S. has a mixed economy which exhibits characteristics of both capitalism and socialism. ... These include white papers, government data, original reporting, and interviews with industry ...
Nevertheless, there is a pronounced shift to a free market economy as the world discovers the problems inherent in a mixed economy. Examples of a mixed economy can be found in many parts of the world and the list includes most countries in Western Europe, in the American continent as well as major countries in Asia.
Open Document. Mixed Economy. A mixed economy is an economic system that incorporates aspects of more than one economic system. This usually means an economy that contains both privately-owned and state-owned enterprises or that combines elements of capitalism and socialism, or a mix of market economy and planned economy characteristics.
The most know economy is a mixed economy. Economies have to decide how much or how little they want from each economy. They have to take from traditional, market, and command economies, in order to make mixed economy. In order to make this decision they have to answer many questions. They have to look at what more people in the economy want and ...
A mixed economy is an economic system that combines elements of both a free market economy and a command economy. In a mixed economy, the government and private sector both play important roles in economic decision-making. In a mixed economy, the government regulates certain industries and provides public goods and services such as education ...
In the imperfect mixed economy, then, people and companies who evade taxes, who violate the law, who implement schemes to circumvent government interventions, may even have the moral high ground. They may be justified to do illegal stuff. And they may be justified to capture regulation or even fight for new regulation that favours their industry.
Here are some essay topics that cover both capitalism and socialism: 1. Compare and contrast the fundamental principles of capitalism and socialism. 2. Analyze the impact of capitalism on income inequality and social mobility. 3. Critically examine the role of government regulation in a capitalist economy. 4.
A mixed economy protects private property of individuals, entities or corporations. This ensures that there is safety of investments for businesspeople. It also provides for the development and maturity of a free market. A major advantage of this is that it allows for the laws of supply and demand to take root, thereby enabling the market to ...
Essay On Mixed Economy. A country with a mixed economy is one in which the government adopts characteristics of both capitalism and socialism. In a mixed economic system, the nation allows for a level of economic freedom in the use of capital, but also permits the government to intervene in economic activities in order to achieve a particular ...
Analysis Of The United Kingdoms Mixed Economy Economics Essay. The United Kingdom has a mixed economy based on the Capitalist system on free trade and global economic, despite its limits being established by the Government. 'A Capitalist economic system is one characterised by free markets and the absence of government intervention in the ...
The United States is less directly exposed; manufactured exports to China make up less than 1 percent of America's G.D.P. But the glut of Chinese products such as electrical vehicles and solar ...
This is Washington Edition, the newsletter about money, power and politics in the nation's capital. Today, real economy correspondent Jarrell Dillard looks at the intersection of consumer ...
Stock indices finished today's trading session mixed amid the release of new economic data. The Nasdaq 100 and the S&P 500 fell 1.04% and 0.32%, respectively. Meanwhile ...
Stock indices finished today's trading session mixed amid the release of new economic data. The Nasdaq 100 (NDX) and the S&P 500 (SPX) fell 1.04% and 0.32%, respectively. Meanwhile, the Dow ...
This paper examines the impact of China's economic deceleration on Singapore, highlighting how the deepening trade integration and China's pivotal role in Global Value Chains (GVCs) amplify these spillover effects. Utilizing multi-region input-output tables, empirical estimates, and the IMF's Global Integrated Monetary and Fiscal model, it identifies significant sectoral and aggregate impacts ...
Asian stocks are mixed after U.S. stocks rallied close to their records on the expectation the Federal Reserve will start cutting interest rates soon to help the economy HONG KONG -- Asian stocks ...